
M
user,s guide.
Microsoft® Broadband Networking
Wireless Base Station| MN-500
Important
Do not plug a phone jack (RJ-11) into any Ethernet (RJ-45) port on your base station. Doing so may damage the device.
You must use twisted pair cables with RJ-45 connectors that conform to FCC standards in the device’s Ethernet ports.
Important
Ne branchez pas une ligne téléphonique dans aucuns des port de réseau (RJ45).
Caution
For use with UL Listed, CSA and GS approved personal computers.
Only use AC Adapter provided with the unit, Part number FA-4A030-1
Not intended for use in machinery, medical or industrial applications.
Do not use onboard an aircraft or in hazardous locations such as gas stations or other explosive environment.
For indoor use only.
Do not touch or re-orient the antenna while the device is transmitting.
Device should be located at least 20 cm (8 inches) away from any human body in order to meet FCC exposure limits.
Exposure time should be limited if the distance is less.
Avertissement
N’utilisez qu’avec des composantes homologuées UL, CSA ou TUV.
N’utilisez qu’avec le bloc d’alimentation fourni avec cet appareil No de modèle FA-4A030-1
Ne pas utiliser ce dispositif dans une application industrielle ou médicale.
Ne pas utiliser dans un avion ou en présence de vapeur explosive (station = service).
N’utiliser qu’à l’intérieur.
Ne touchez pas à l’antenne lorsque l’appareil est en fonction
Ce dispositif doit être à plus de 20 cm (8 pouces) de toute personne.
Information in this document, including URL and other Internet Web site references, is subject to change without notice.
Unless otherwise noted, the example companies, organizations, products, domain names, e-mail addresses, logos, people,
places and events depicted herein are fictitious, and no association with any real company, organization, product, domain
name, e-mail address, logo, person, place or event is intended or should be inferred. Complying with all applicable copyright
laws is the responsibility of the user. Without limiting the rights under copyright, no part of this document may be reproduced,
stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise), or for any purpose, without the express written permission of Microsoft Corporation.
Microsoft may have patents, patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights covering subject
matter in this document. Except as expressly provided in any written license agreement from Microsoft, the furnishing of this
document does not give you any license to these patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property.
© 2002 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Microsoft, Windows and Xbox are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States
and/or other countries.
The names of actual companies and products mentioned herein may be the trademarks of their respective owners.

contents.
1 | Introduction ................................................................................................... 1
Base Station Indicators and Controls ................................................ 3
Resetting the Base Station ................................................................. 3
Restoring Base Station Factory Settings ........................................... 4
Placing and Positioning the Base Station ......................................... 4
Understanding Wireless Connections .................................................... 5
Recommendations for Best Wireless Performance ......................... 5
Adjusting the Antennas ........................................................................ 5
Wireless Range Table ........................................................................... 6
Understanding Wireless Security (WEP) ............................................ 6
Understanding Ethernet Connections ................................................... 6
Ethernet Cables, Phone Cables, and Connections ........................... 7
Straight-Through and Crossover Ethernet Cables ............................. 7
2 | Planning .......................................................................................................... 9
Determining Your Network Settings ..................................................... 14
3 | Setup ............................................................................................................ 15
Typical Setup Steps................................................................................ 16
Step 1: Install the software ............................................................... 16
Step 2: Connect the base station to the computer ........................ 17
Step 3: Configure the base station and network ............................ 18
Step 4: Test your network .................................................................. 18
Other Setup Methods ............................................................................ 19
If You Have a Non-Ethernet Modem ................................................. 19
Using the Base Station as a Wireless Access Point Only ............... 19
If You Have No Ethernet Computers ................................................. 20
Connecting the Base Station Wirelessly .......................................... 20
Replacing Existing Networks ................................................................ 22
Connecting Existing Networks .............................................................. 22
Connecting Ethernet Networks to the Base Station ....................... 23
Connecting HomePNA or HomeRF Networks .................................. 23
Connecting Existing Wireless Networks ........................................... 23
If Your Computers Are on a Domain ................................................. 24
Setting Up the Base Station on a Windows 2000 Computer ........... 24
Setting Up the Base Station on a Non-Windows Computer .............. 24

Adding to Your Network ......................................................................... 24
Adding Wireless Computers to Your Network .................................. 25
Adding Ethernet Computers to Your Network.................................. 25
Adding Non-Computer Devices to Your Network ............................. 25
If You Connected the Hardware First ................................................... 26
If You Do Not Want to Use the Setup Wizard ...................................... 26
4 | Networking .................................................................................................. 27
Logging on to Your Network .................................................................. 27
Allowing Access to an Internet Connection ......................................... 28
Allowing Access to Files and Folders ................................................... 28
Allowing Access to Printers ................................................................... 31
About Sharing Other Peripheral Devices ............................................. 32
About Reading E-Mail Messages on a Network ................................. 32
Playing Games on a Network and the Internet................................... 32
Connecting to Other Wireless Networks .............................................. 33
5 | Monitor......................................................................................................... 35
View the Status of Your Computer ....................................................... 36
View the Status of Your Network Connection ..................................... 36
View the Status of Your Internet Connection ...................................... 36
View the Status of Other Network Devices ......................................... 36
View and Change Network Settings ..................................................... 37
Update Software, Drivers, and Firmware ............................................ 37
Secure Your Network ............................................................................. 38
Protect Your Network from Hackers ................................................. 38
Protect Your Network from Computer Viruses ................................. 39
Protect Your Network from Unauthorized Access ........................... 39
6 | Configure ..................................................................................................... 41
Opening the Base Station Management Tool ................................. 42
Logging Off .......................................................................................... 42
Navigating the Base Station Management Tool ............................. 42
Configuring the Base Station ............................................................ 44
Configuring Network Computers ....................................................... 45
Using the Base Station As a Bridge .................................................. 46
Home Page ............................................................................................. 47
Wide Area Network ............................................................................. 47
Local Area Network ............................................................................ 48
DHCP Client List .................................................................................. 49
Base Station Information ................................................................... 49
ii Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Management Settings ........................................................................... 50
Reset the Base Station ...................................................................... 50
Restore Factory Default Settings ...................................................... 50
Back Up Base Station Settings ......................................................... 51
Restore Base Station Settings from a Backup................................ 52
Upgrade Base Station Firmware ....................................................... 53
Establish Base Station Time Zone ................................................... 54
Synchronize Time to Internet Time Server ....................................... 54
Change the Base Station Password ................................................. 55
Local Area Network Settings ................................................................ 56
IP Address and Subnet Mask ............................................................ 56
DHCP Server ........................................................................................ 57
Wide Area Network Settings ................................................................. 57
Dynamic Internet Connection ............................................................ 58
MAC Addresses ................................................................................... 58
Static Internet Connection ................................................................. 59
PPPoE Internet Connection ............................................................... 59
Disabled Connection .......................................................................... 60
Wireless Settings ................................................................................... 60
Wireless Network Name (SSID) ........................................................ 61
Wireless Channel ................................................................................ 61
Data Rate ............................................................................................ 61
Security Settings .................................................................................... 62
Wireless Security (WEP) ..................................................................... 62
Firewall Settings .................................................................................. 63
Network Mode ..................................................................................... 64
Port Forwarding .................................................................................. 65
Virtual Demilitarized Zone ................................................................. 68
MAC Filtering ....................................................................................... 69
Client Filtering ..................................................................................... 71
Base Station Log ................................................................................ 72
7 | Troubleshooting ......................................................................................... 73
Software .................................................................................................. 73
Hardware ................................................................................................. 75
Networks ................................................................................................. 76
Internet Connections ............................................................................. 78
Contents iii

Reference .................................................................................................... 79
Technical Support .................................................................................. 79
Regulatory Information .......................................................................... 80
Limited Warranty .................................................................................... 81
Technical Specifications........................................................................ 83
System Requirements ........................................................................... 84
Glossary ....................................................................................................... 85
iv Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Note
The Setup Wizard guides you
through the process of
connecting and configuring
your base station. Install the
software and then follow the
steps in the wizard to connect
your new base station.
introduction.
The Microsoft Broadband
Networking Wireless Base Station
Congratulations on the purchase of your Microsoft® Broadband
Networking Wireless Base Station! The base station allows you to
share an Internet connection, files, printers, and other devices
among all the computers on a wireless network. Your box contains:
Setup CD-ROM
Install This First!
Wireless
Base Station
Base Station Stand
(Detachable)
Blank Floppy
Disk
Power Supply
The Microsoft Wireless Base Station can support over 200
simultaneous wired and wireless connections. You can use this
flexibility to choose the best type of network connection for each of
your networked devices. For a discussion of connection options,
see Chapter 2.
The typical network configuration is for the base station to serve
as the central access point for your wireless network and share
your broadband Internet connection with all the computers on the
network. For setup instructions, see Chapter 3.
The base station includes a firewall and network address
translation (NAT), which provide security for your broadband
Internet connection. This is especially important when an “alwayson” broadband Internet connection is shared among computers on
a home or small office network. With the base station installed,
intruders from the Internet cannot access the computers or files
on your network.
Even with the base station installed, however, your wireless
network is vulnerable to eavesdropping by other wireless networks,
and your system can be attacked by computer viruses. To protect
your network, establish a wireless security (also known as Wired
Equivalent Privacy, or WEP) key during setup, use an antivirus
program to protect against computer viruses, and follow basic
security rules such as setting strong passwords and not opening
unknown attachments.
Blue Ethernet
Cable
User’s Guide and
Start Here Guide
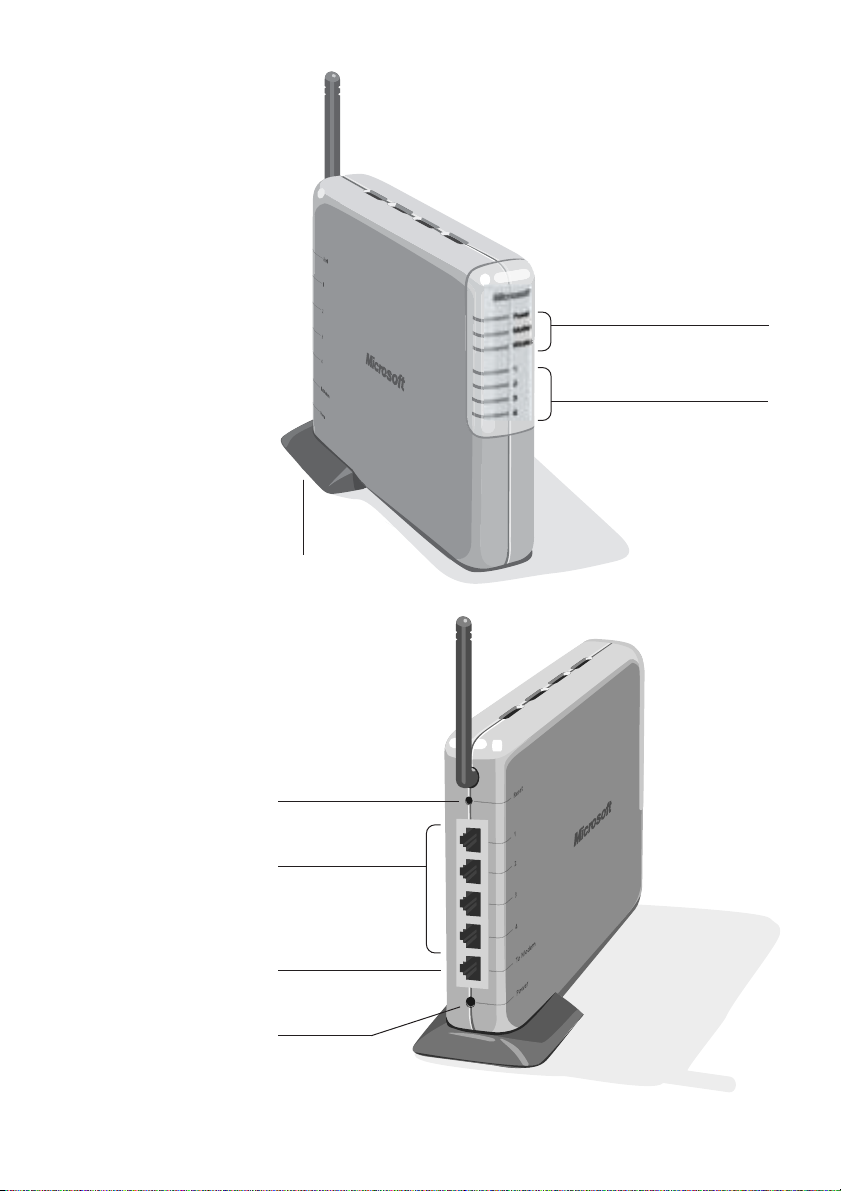
Antenna
Optional
Stand
Base Station
(Front View)
Indicator lights, which
display Power, Modem and
Wireless status
Indicator lights, which
display Ethernet port status
and correspond to the
Ethernet ports on the back
of the base station
Reset Button
Ethernet ports 1-4,
which correspond to
the status indicator
lights on the front
of the base station
To Modem port, which
connects to your modem
with an Ethernet cable
Power Port
Base Station
(Back View)
2 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide
Base Station Indicators and Controls
The preceding diagram shows the location of all ports, jacks,
controls, and indicator lights on the base station.
The base station contains two antennas, one internal and one
external. The external antenna is adjustable for best wireless
reception.
The front of the base station has seven green (and labeled)
indicator lights. After the base station is connected, these lights
will be on, off, or blinking, indicating the following states.
Light On Off Blinking
Important
Do not hold down the reset
button for more than five
seconds, unless you want to
erase all of your base station
settings and return them to
the factory defaults.
Power Receiving power Not receiving power Green or orange during
reset and restore
Modem Modem connected Modem off or Data being sent
and on not connected or received on modem
Wireless Radio enabled Radio disabled Wireless data being
status sent or received
Ethernet Ethernet device Ethernet device Data being sent or
status (4) connected and on off or not connected received over Ethernet
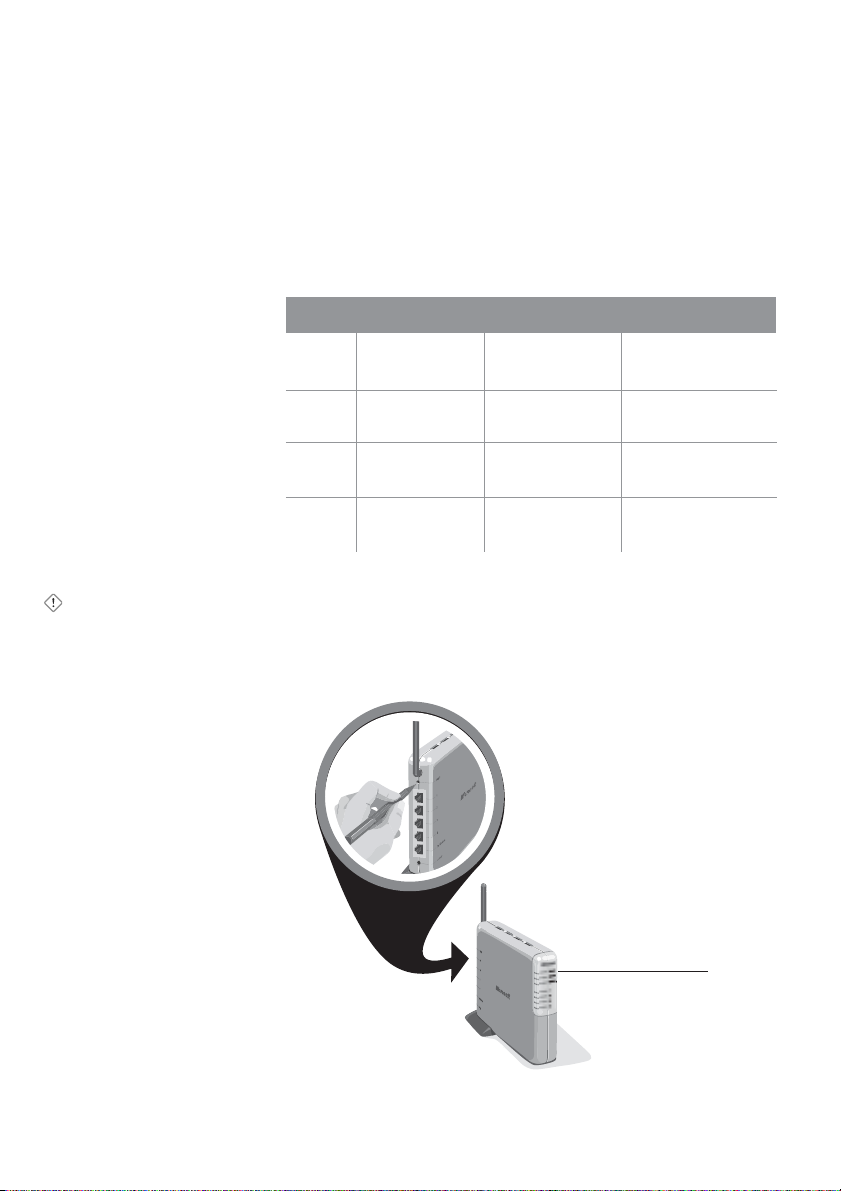
Resetting the Base Station
To reset the base station to correct temporary connectivity
problems, use a pointed object to briefly press and release the
reset button on the back of the base station, as shown in the
following illustration.
Resetting or Restoring the Base Station
Power Indicator
Light
Chapter 1: Introduction 3

Observe the power indicator light, and release the button as soon
as the light turns from green to orange. The light will return to
green when the reset is complete. Do not unplug the base station
during a reset.
Restoring Base Station Factory Settings
To return the base station to its factory default settings (for
example, if you forget your base station password), you can use the
reset button on the back of the base station to clear all base
station settings, restore the default settings, and reset the base
station.
To restore the base station factory settings
1. Use a pointed object to press the reset button on the back of
the base station, while observing the power indicator light. Hold
the button down until the light starts to blink green and orange,
about five seconds.
2. Release the button and wait for the light to turn solid orange
and then green, which can take up to 60 seconds.
Do not unplug the base station during a restore.
Placing and Positioning the Base Station
You can place the base station vertically in the provided stand, as
shown in the following diagram, or horizontally without the stand.
You can also rotate the base station to obtain the best wireless
performance.
Attaching the Base Station Stand
The Microsoft Wireless Base Station must be physically connected
to a power outlet and to your broadband modem, so the base
station should be placed near these.
To place the base station and adjust its antenna for the best
wireless performance, see “Recommendations for Best Wireless
Performance” in this chapter.
4 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Understanding Wireless Connections
Your base station uses a wireless protocol called IEEE 802.11b,
or Wi-Fi (wireless-fidelity), which works by radio transmission.
Although wireless transmission speed is usually faster than
broadband connection speed, it is slower than Ethernet.
Wi-Fi radio waves travel in all directions, and can transmit through
walls and floors. Wireless transmission can theoretically cover up
to 1,000 square feet and occur at speeds of up to 11 megabits per
second (Mbps), but actual network range and data throughput rate
will be less, depending on several factors.
Important
Do not rely on radio
transmission limitations to
secure your network. Enable
wireless security (WEP) to
protect your network from
unwanted access. For more
information, see
“Understanding Wireless
Security (WEP)” in this chapter.
Recommendations for Best Wireless Performance
The following information will help you achieve the best wireless
range, coverage, and transmission rate from your wireless devices:
• You should place the base station near the center of your
intended wireless network area. This will also minimize the
possibility of eavesdropping by neighboring wireless networks.
• Radio signals can travel farther outside of buildings, and the
best performance is when wireless components are in direct
line of sight to one another.
• Putting wireless components in high places helps avoid obstacles
and provides better coverage to upper stories of buildings.
• Building construction such as metal framing, UV window film,
metallic paint, and concrete or masonry walls and floors will
reduce radio signal strength. Try to avoid putting wireless
components next to walls, fireplaces, or other large, solid
objects; or next to large metal objects such as computer cases,
monitors, and appliances.
• Wireless signal range, speed, and strength can be affected by
interference from neighboring wireless networks and devices.
Electro-magnetic devices such as televisions, radios,
microwave ovens, and cordless phones, especially those with
frequencies in the 2.4 GHz range, may also interfere with
wireless transmission.
• Standing or sitting too close to wireless equipment can also
affect radio signal quality.
Adjusting the Antennas
You can adjust the wireless antennas for the best radio reception.
Start with the antenna pointing straight up, and adjust the antenna
if wireless reception is poor. Certain areas, such as directly below
the antenna, get relatively poor reception. Pointing the antenna
toward another wireless component does not improve reception.
The antennas should not be placed next to large pieces of metal,
because this can cause interference.
Chapter 1: Introduction 5
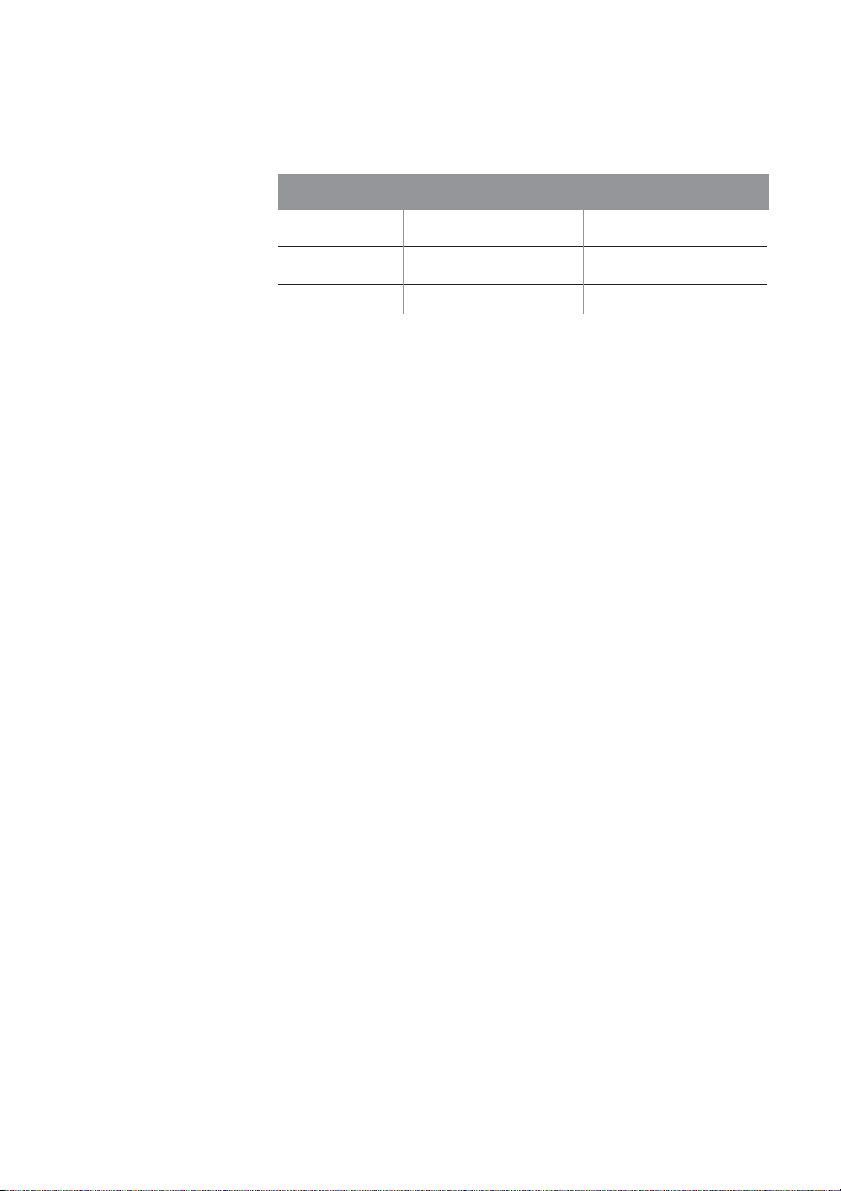
Wireless Range Table
The following table shows the interaction between wireless
coverage area and transmission speed for Microsoft wireless
components under typical installation circumstances.
Data Rate Open Environment Closed Environment
11 Mbps up to 900 feet up to 160 feet
5.5 Mbps up to 1300 feet up to 200 feet
2 or 1 Mbps up to 1500 feet up to 300 feet
Understanding Wireless Security (WEP)
Anyone within wireless range who knows your wireless network
name will be able to access the network and any data that is being
transmitted over it, unless you enable wireless security. Microsoft
wireless components use wireless security called Wireless
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) to prevent unauthorized users from
accessing your network. A network key—called a WEP key—
encrypts, or codes, data so that it is readable only by other
computers that have the key. The WEP key is stored on each
networked computer, so that data can be encrypted and decrypted
as it is transmitted over the network.
It is recommended that you enable WEP during base station setup.
You can simply choose to enable WEP security and allow the Setup
Wizard to assign your network a WEP key, or you can set your own
WEP key and choose other advanced options. For more information
about WEP and security, see “Securing Your Network” in Chapter 5
and “Security Settings” in Chapter 6.
Understanding Ethernet Connections
In most cases, the Microsoft Wireless Base Station uses Ethernet
to connect to your broadband modem and at least one computer.
You can also connect up to three additional Ethernet devices, such
as the Microsoft Broadband Networking 10/100 Ethernet PCI
Adapter and the Microsoft Broadband Networking 10/100
Ethernet 5-Port Switch, to the Microsoft Wireless Base Station. By
using hubs or switches, you can connect many more Ethernet
devices to your base station.
Ethernet is the most common and one of the fastest wired network
protocols, with connection speeds of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or
higher. Although power outlets, fluorescent lights, power supplies,
and coiled or overlong cables can interfere with Ethernet
transmission, interference is seldom a problem in Ethernet
networks.
To connect to your base station through Ethernet, a computer or
other device must have an Ethernet network interface card, which
provides an external port for an Ethernet cable.
6 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide
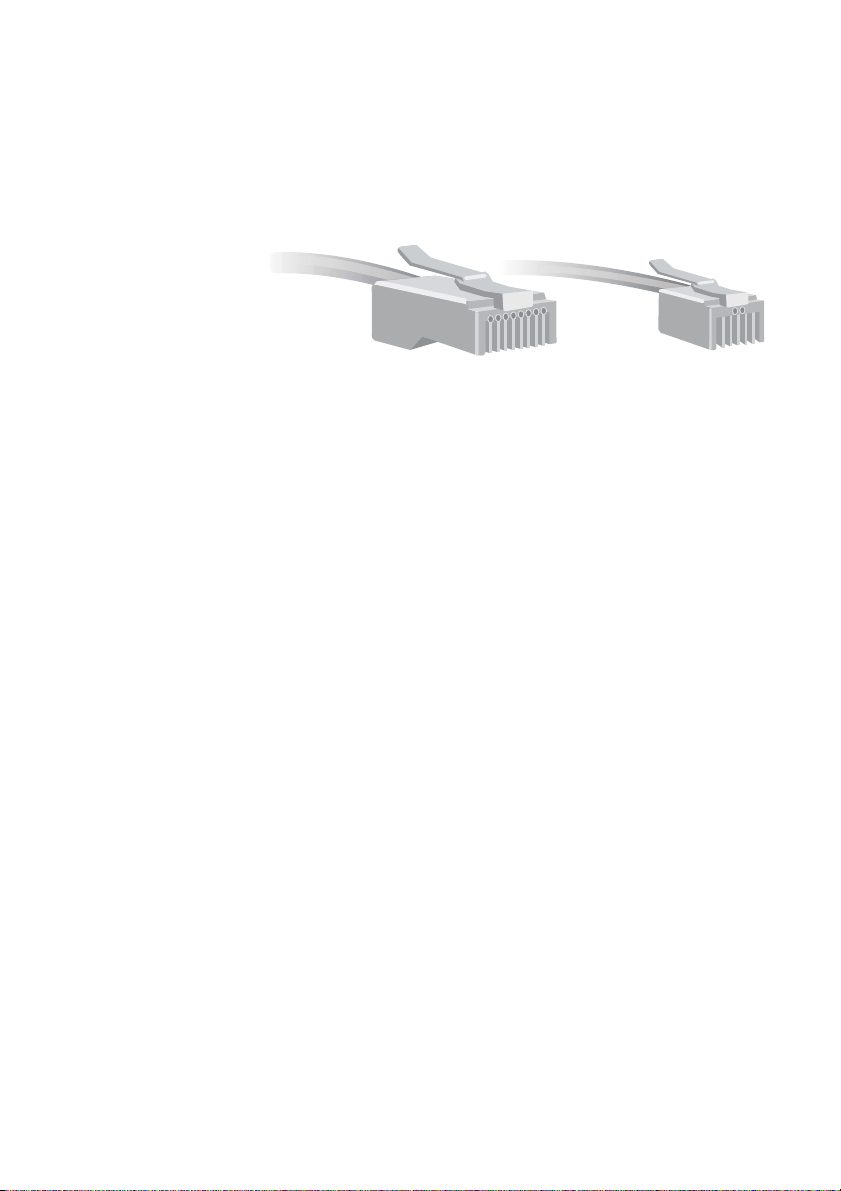
Ethernet Cables, Phone Cables, and Connections
Ethernet ports and cables resemble telephone connections and
lines, but are thicker and wider. To determine whether a cable is an
Ethernet or phone cable, look at the end and count the number of
wires or contacts in the connector. Ethernet (RJ-45) connectors
have eight contacts, whereas standard phone line (RJ-11)
connectors have four, as shown in the following diagram.
RJ-45 Ethernet
(8 wires)
RJ-11 Telephone
(4 or 6 wires)
Use only Ethernet cables to connect to your base station. Plugging
a phone jack into the base station could damage the base station.
Straight-Through and Crossover Ethernet Cables
Data is sent and received through specific wires in Ethernet cables.
Depending on the arrangement of the send and receive wires
within the cable, Ethernet cables may be the straight-through type
or the crossover type.
Most broadband modems are connected to computers through
Ethernet, and they may use straight-through or crossover cables.
To connect the modem to the base station, it is important to use
the original cable that came with your modem, or the same type.
To connect computers to the base station, you should
use straight-through Ethernet cables. If the blue cable provided in
your kit is not long enough for your needs, you can use any
straight-through cable.
Chapter 1: Introduction 7

To determine which type of Ethernet cable you have, inspect the
cable ends. The following diagram shows the arrangement of wires
in each type of cable.
Both ends of a
Straight-Through
Ethernet Cable
Crossover
Ethernet Cable
straight-through
cable have the
same arrangement
of colored wires.
In a crossover cable,
the arrangement of
the colored wires
changes between
the two ends.
8 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide
2
planning.
Wireless Base Station Setup
Options
The easiest and fastest way to set up your Microsoft® Broadband
Networking Wireless Base Station is to follow the setup
instructions in the Start Here guide or the “Typical Setup Steps”
in Chapter 3 of this manual.
Set up the base station on the computer that is now connected to
your broadband modem, by running the Setup Wizard and
connecting your base station when the wizard prompts you to do so.
Set up the base station before you install any wireless network
adapters on other computers,
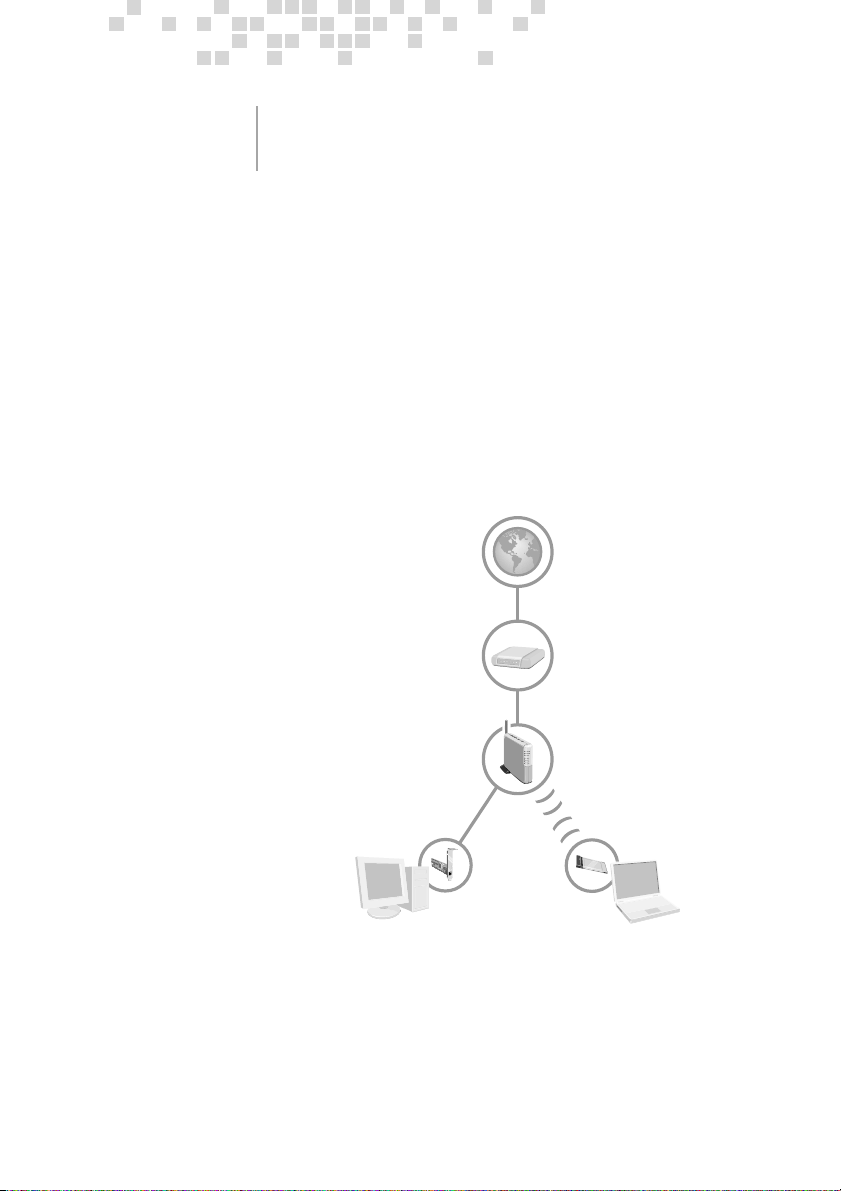
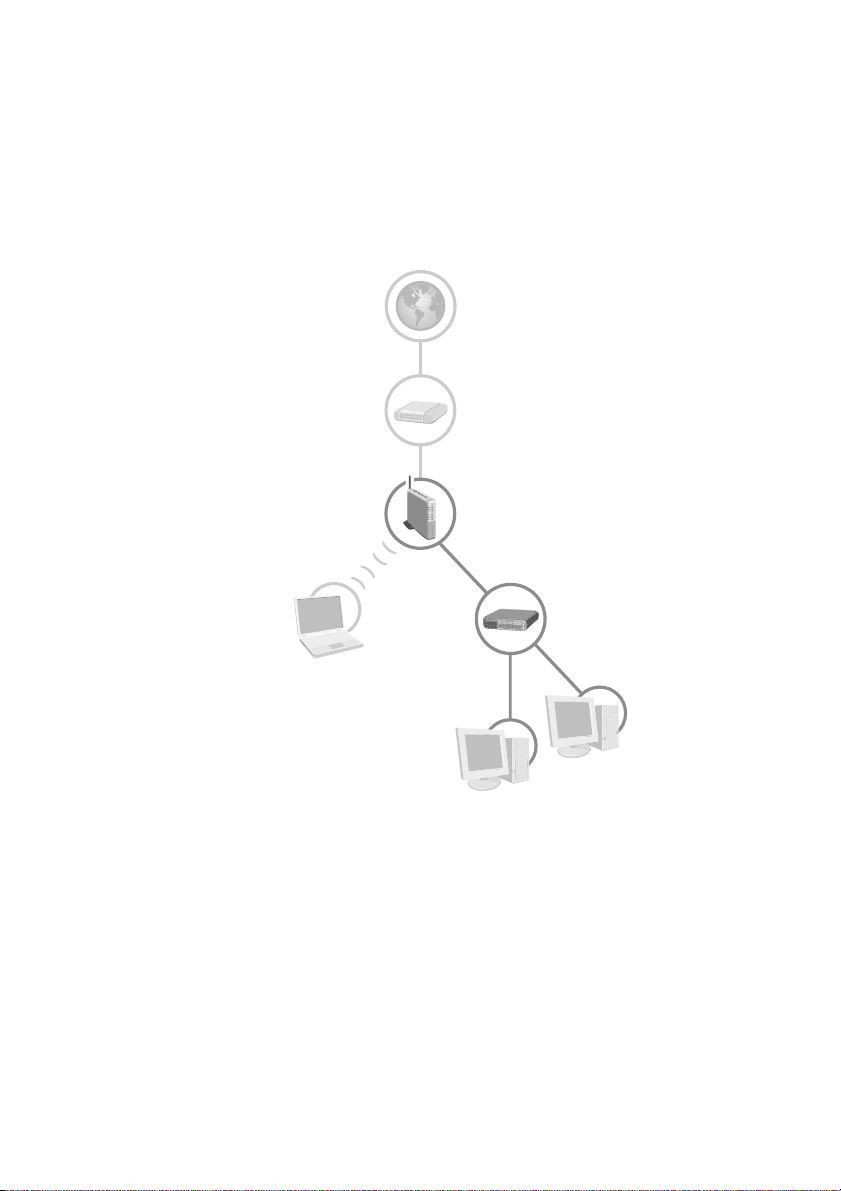
Your finished network setup may resemble the following diagram.
Typical Setup
First Computer
One computer, and your broadband modem, connect to the base
station with Ethernet cables. Other computers can make wired or
wireless connections to the base station.
Active Internet Connection
Broadband Modem
(DSL or Cable)
Wireless Base Station
Second Computer
Note
You cannot set up the base
station on a Windows 2000
computer by using the Setup
Wizard. You can use a
different computer to set up
the base station, you can use
the Base Station Management
Tool to set up the base station
on the Windows 2000
computer, or you can set up a
network by installing wireless
adapters only.
Note
If you are not sure which types
of connections your computer
or modem has, see Chapter 1.
You can use this setup method on a computer that is running
Microsoft Windows
®
XP, Windows Millennium Edition, Windows 98
SE, or Windows 98, and is not currently networked. The computer
must have a working broadband Internet connection and must
connect directly to your broadband modem with an Ethernet cable.
If you have a different computer configuration, or want a different
setup method, look through this chapter for the description that
best matches your situation.
My modem doesn’t connect to my computer through Ethernet.
• If your modem connects through USB but also has an Ethernet
connection, you can switch to the Ethernet port. For
instructions, see page 19.
• If your modem has no Ethernet connection, you have three
choices:
• You can obtain a new modem that has an Ethernet
connection.
• You can set up a network by using wireless adapters only and
no base station. For information, see the documentation that
came with your adapter.
• You may be able to set up the base station as a wireless
access point only, as shown in the following diagram. For
more information, see page 19.
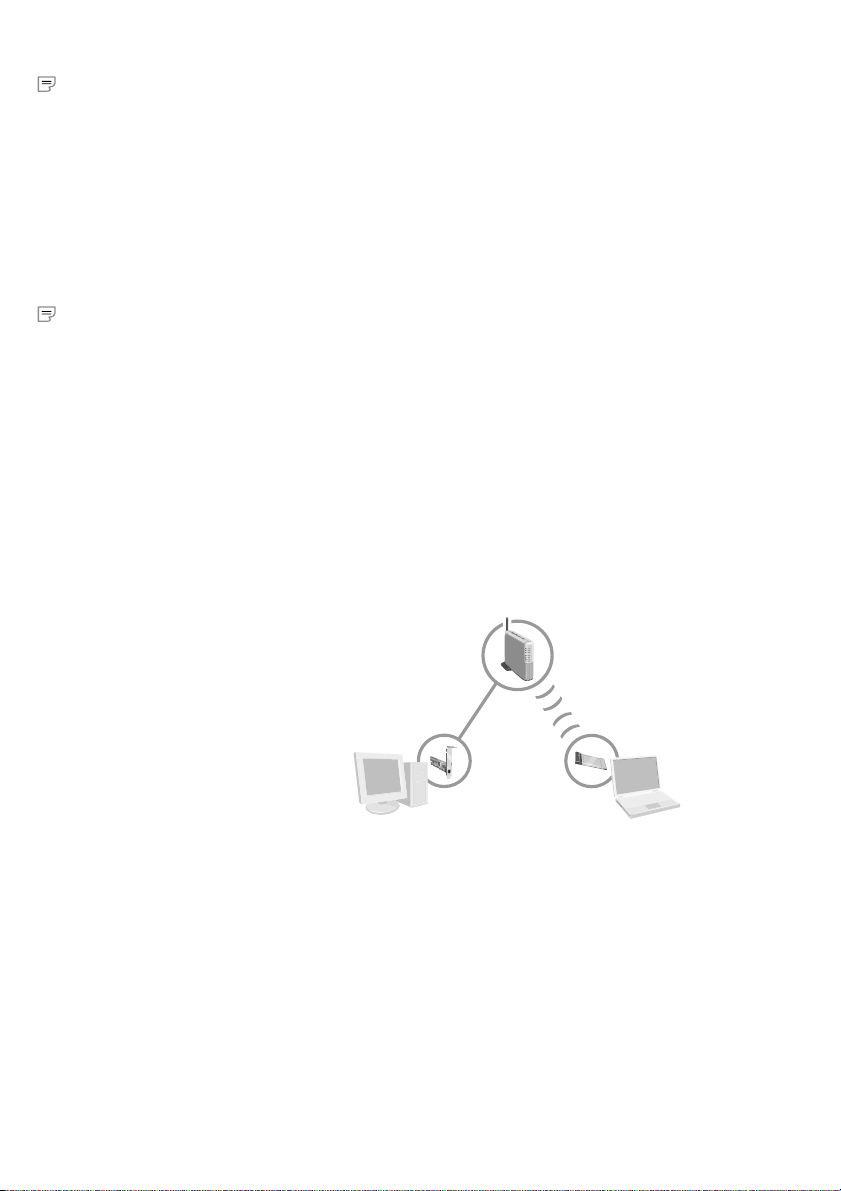
Wireless Base Station
First Computer*
Ethernet or Wireless
Adapter
*To connect the base station, the first computer requires an installed Ethernet
adapter (shown), or wireless adapter.
I don’t have a working Internet connection, or I don’t want to
share my Internet connection through my base station.
The Setup Wizard cannot configure the base station automatically
if your computer does not have an active Internet connection. It is
highly recommended that you establish a working broadband
Internet connection before you set up the base station.
10 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide
Second Computer
Wireless Notebook
Adapter shown
If you have a broadband Internet connection, but it is not working
during setup or the Setup Wizard cannot access your Internet
settings, you can enter the settings manually. For instructions, see
Chapter 6, or specific procedures in Chapter 3 that require this.
The base station was designed to share a broadband Internet
connection over a wireless network. If you want to set up a wireless
network without sharing an Internet connection through the base
station, it is recommended that you set up a network by using
wireless adapters only and no base station. For instructions, see
your adapter documentation.
None of my computers have Ethernet connections.
By using wireless adapters, you can connect all your computers to
the base station wirelessly, as shown in the following diagram. For
instructions, see page 20.
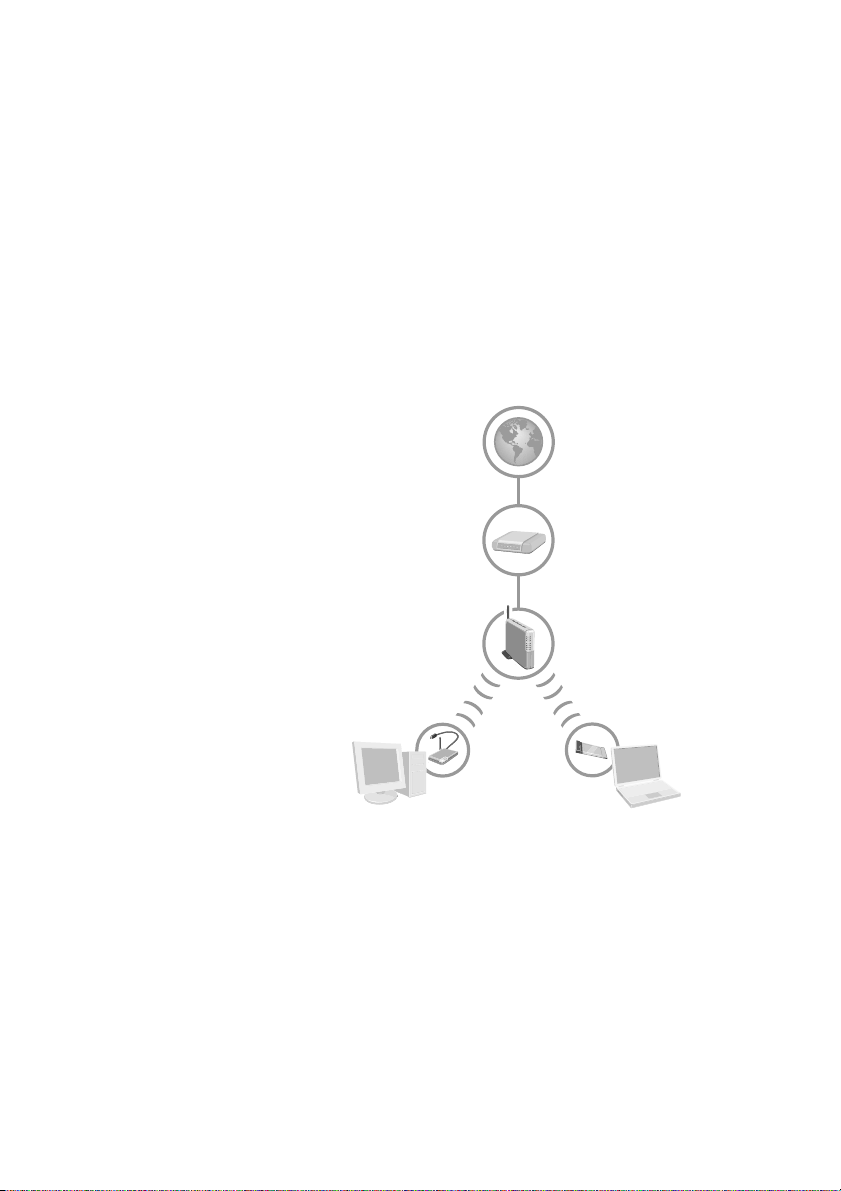
Active Internet Connection
Broadband Modem
(DSL or Cable)
Wireless Base Station
First Computer
Wireless USB
Adapter shown
Second Computer
Wireless Notebook
Adapter Shown
I want all my computers to connect to the base station
wirelessly.
You can switch a computer to a wireless connection to the base
station after first using it to set up the base station with a wired
connection. For instructions, see page 21.
Chapter 2: Planning 11
I want to replace my existing base station, router, or gateway
with the Microsoft Wireless Base Station.
For instructions, see page 22. Do not disconnect your existing base
station until you are instructed to do so during setup.
I want to add my existing network to the base station.
• The following diagram shows how you can add an Ethernet hub
or switch to the base station. For instructions, see page 23.
Active Internet Connection
Broadband Modem
(DSL or Cable)
Wireless Base Station
Ethernet Hub
or Switch
• To connect HomePNA or HomeRF networks, see page 23.
• To connect existing wireless networks, see page 23.
One or more of my computers is on a domain.
To set up computers that are already on a domain, see page 24.
I want to install the base station on a computer that is running
Microsoft WIndows 2000.
You cannot set up the base station on a Windows 2000 computer
by using the Setup Wizard. For setup options, see page 24.
12 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide
Existing Ethernet
Network

I want to install the base station on Macintosh or other
computers that are not running Windows.
For base station setup instructions, see page 24 and Chapter 6.
I want to add more computers or other devices to my base
station.
• To add computers that have wireless adapters, see page 25.
• To add computers that have Ethernet adapters, see page 25.
• To add non-computer devices, see page 25.
I am not sure whether to use wired or wireless connections to
add devices to my base station.
Consider the following factors:
• Speed. If connection speed between your network components
is very important, you may want to use Ethernet connections.
• Convenience. Wireless connections don’t require cabling or
opening your computer cases, but connecting existing networks
to the base station through Ethernet may be more convenient.
• Range and coverage. An environment that contains many
physical barriers or interference factors may not be ideal for
wireless networking.
• Mobility. Mobility may be relatively unimportant for a desktop
computer, but is much more useful for a laptop, notebook, or
other portable computer.
• Security. Because of the unrestricted nature of their
transmission, wireless networks have inherent security issues.
However, the base station’s built-in firewall and NAT provide
security, and you can also use WEP encryption.
I don’t want to use the Setup Wizard.
To set up the base station by using the Base Station Management
Tool, see Chapter 6.
I connected the base station before running the Setup Wizard.
For setup options, see page 26.
Chapter 2: Planning 13

Determining Your Network Settings
If your system matches the configuration described on page 10
and you are using the typical setup method, the Setup Wizard can
detect your settings automatically and use them to set up your
network. However, if your system configuration or chosen setup
option requires you to enter your settings manually, the following
instructions will help you locate them. You can record this
information on the inside back cover of this User’s Guide for future
reference.
To determine your workgroup name in Windows XP or
Windows 2000
1. Click Start, then click Control Panel, and then double-click
System.
2. For Windows XP, click the Computer Name tab.
For Windows 2000, click the Network Identification tab.
To determine your workgroup name in Windows 98
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click Network, and then double-click Locating your
network workgroup.
To determine your Internet settings
Your Internet settings may include such information as dynamic or
static IP address, username, password, primary and secondary
DNS, and default gateway. To determine these:
• Use your modem’s utility program if you have one.
• Call your Internet service provider or locate the documentation
they sent you when you signed up for DSL or cable service.
• Before starting setup or disconnecting your modem, you can
use the Windows Network or Network Connections control panel
to determine the settings. For more information, see Windows
Help.
To determine your wireless network settings
• If you are adding to a Microsoft wireless network, use the
Broadband Network Utility to determine your wireless network
name, channel, and WEP security key (if set).
• If you have a non-Microsoft wireless network, use your network
utility program to determine the settings.
14 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide
3
Important
Run the Setup Wizard before
connecting your base station.
If you connected your base
station before installing the
software, or if you do not want
to use the Setup Wizard, see
“If You Connected the
Hardware First” and “If You Do
Not Want to Use the Setup
Wizard” in this chapter.
setup.
Installing, Connecting, and
Configuring Your Wireless Base
Station
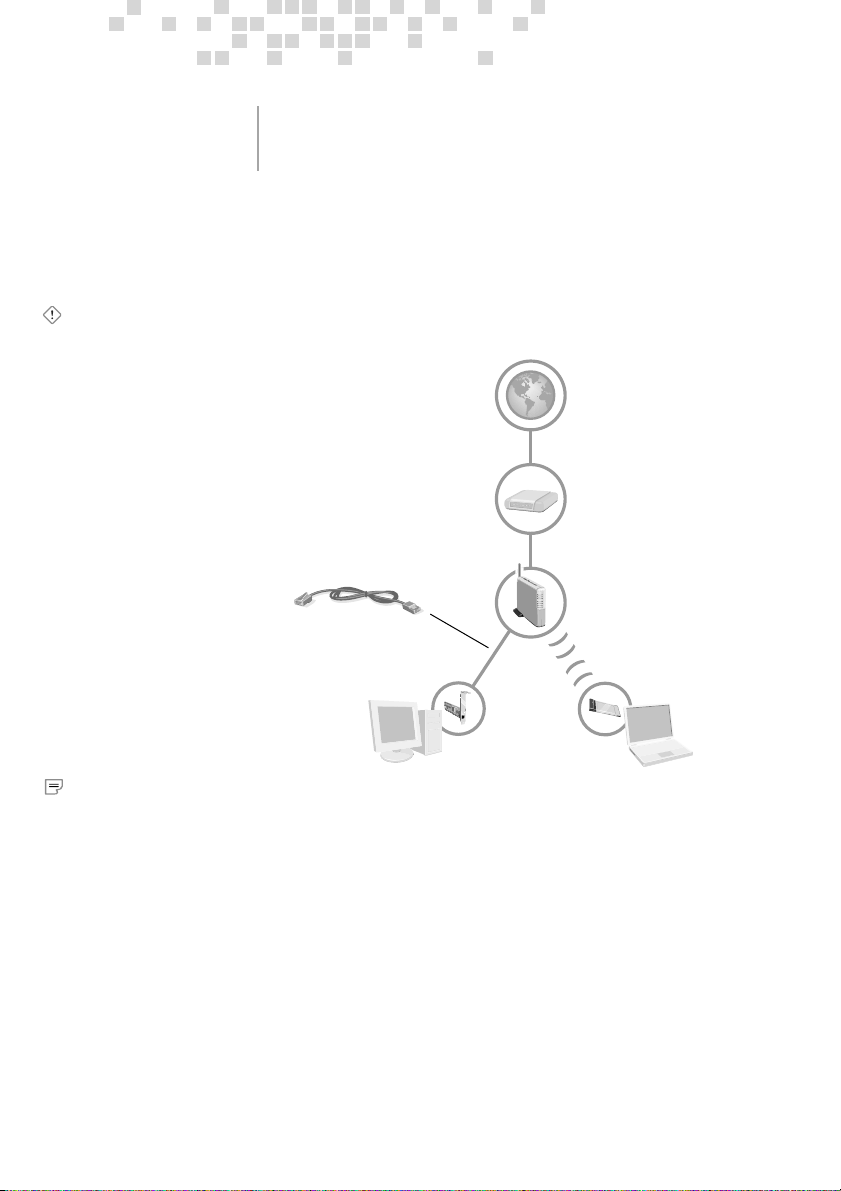
The typical connection method for the base station resembles the
following diagram.
Active Internet Connection
Ethernet Connection
Easy setup: Use the blue
Ethernet cable to connect
the base station to your
first computer.
You can change this to a
wireless connection later.
Broadband Modem
(DSL or Cable)
Wireless Base Station
Note
You cannot set up the base
station on a Microsoft
Windows 2000 computer by
using the Setup Wizard. You
can use a different computer
to set up the base station, you
can use the Base Station
Management Tool to set up
the base station on the
Windows 2000 computer, or
you can set up a network by
installing wireless adapters
only.
First Computer*
Installing the software on
this computer configures
the base station.
*In this setup method, the first computer requires an installed Ethernet adapter to
connect the base station, as shown here.
One computer, and your broadband modem, connect to the base
station with Ethernet cables. Other computers can make a wireless
or wired connections to the base station.
You can use this setup method for a Microsoft
Windows Me, Windows 2000, Windows 98 SE, or Windows 98
based computer that is connected directly to a DSL or cable
modem with an Ethernet cable. The computer must have a working
Internet connection and must not be connected to any other
computers or networks.
Second Computer
Installing the software on
this computer configures
the adapter.
®
Windows® XP,

Important
If you have an existing
network, do not use the typical
setup steps. See Chapter 2 to
locate the correct setup
method. Do not disconnect
your existing network until you
are instructed to do so.
Do not use this setup method if your computers do not match the
above configuration, or if they are already connected to a network.
See Chapter 2 to choose an alternate setup method.
It is important to follow the setup steps in the exact order given.
Install the software first, and then connect the base station. This
takes advantage of the software’s ability to detect your current
Internet and system settings and use them to configure your
wireless network.
Set up the Microsoft Wireless Base Station before you set up other
devices on your wireless network.
Note
During setup, you may be
prompted to restart your
computer or insert your
Windows Setup CD-ROM. You
may also need to specify the
location of the needed setup
files on the Windows Setup
CD-ROM by typing D:\win98.
Substitute the drive letter of
your CD-ROM drive.
Note
If you have questions or
problems during setup, click
the Help button on each setup
page for more information. If
you need to start setup over,
choose the Repair option.
Typical Setup Steps
Step 1: Install the software
1. Take the following items to the computer that is now directly
connected by an Ethernet cable to your cable or DSL modem:
• The Microsoft Broadband Networking Setup CD-ROM
• The Microsoft Wireless Base Station
• The blue Ethernet cable that came with your base station
• The AC power supply
• The blank floppy disk from your kit
• These installation instructions
2. Before you proceed with setup, check the following:
• Are you a member of the Administrator group?
On computers running Windows 2000 or Windows XP, you
must be a member of the Administrator group to set up a
network. If you cannot run setup, click Log Off from the Start
menu, press CTRL+ALT+DELETE, and then log on with an
administrator’s name and password.
• Are you running any firewall or Internet connection sharing
software?
Disable any firewall or Internet connection sharing software
on your computers. Your base station will replace these
functions, and the Setup Wizard cannot proceed if they are
enabled.
• Do you have a Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Internet connection or a static Internet Protocol (IP) address?
16 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

With these types of Internet connections, the Setup Wizard
will prompt you to enter information—for a PPPoE connection,
your user name, password, and service name; for a static IP
address, the IP, subnet, and ISP gateway addresses. If you
know you have one of these types of connections, gather this
information beforehand. For information about how to
determine your Internet settings, see “Determining Your
Network Settings” in Chapter 2.
3. To install the software, insert the setup CD-ROM into the
CD-ROM drive. If the Setup Wizard does not start automatically
after a few seconds, open My Computer, double-click the
CD-ROM icon, and then double-click Setup or Setup.exe. The
Welcome screen should appear.
4. In the Setup Wizard, choose to set up the base station, and
then proceed through the Setup Wizard.
Note
Leave your computer and
modem on while you connect
your base station.
Important
The modem must use its
original Ethernet cable or one
of the same type to connect to
the base station. For more
information, see “StraightThrough and Crossover
Ethernet Cables” in Chapter 1.
Note
If the blue Ethernet cable is
too short for your needs, you
can use any straight-through
Ethernet cable to connect your
computer to the base station.
For more information about
Ethernet cables, see
“Understanding Ethernet
Connections” in Chapter 1.
Step 2: Connect the base station to the computer
1. When the Setup Wizard instructs you to connect your base
station, position the base station close to your modem and
computer, and near the center of your intended network area. If
you want to position the base station vertically, attach the
included stand. For more information about placing and
positioning your base station, see Chapter 1.
2. Unplug your modem cable from the Ethernet port on the back of
your computer. Leave the other end of the cable plugged in to
the modem. Plug the cable into the port labeled To Modem on
the back of the base station. The base station is now connected
to your modem.
3. Plug one end of the blue Ethernet cable that came with your
base station into the Ethernet port labeled 1 on the back of the
base station and plug the other end into the Ethernet port on
the back of your computer.
4. Plug one end of the power supply that came with your base
station into the Power port on the back of the base station, and
plug the other end into an electrical outlet. The power indicator
light on the front of the base station should illuminate.
5. Return to the Setup Wizard and click Next.
Chapter 3: Setup 17
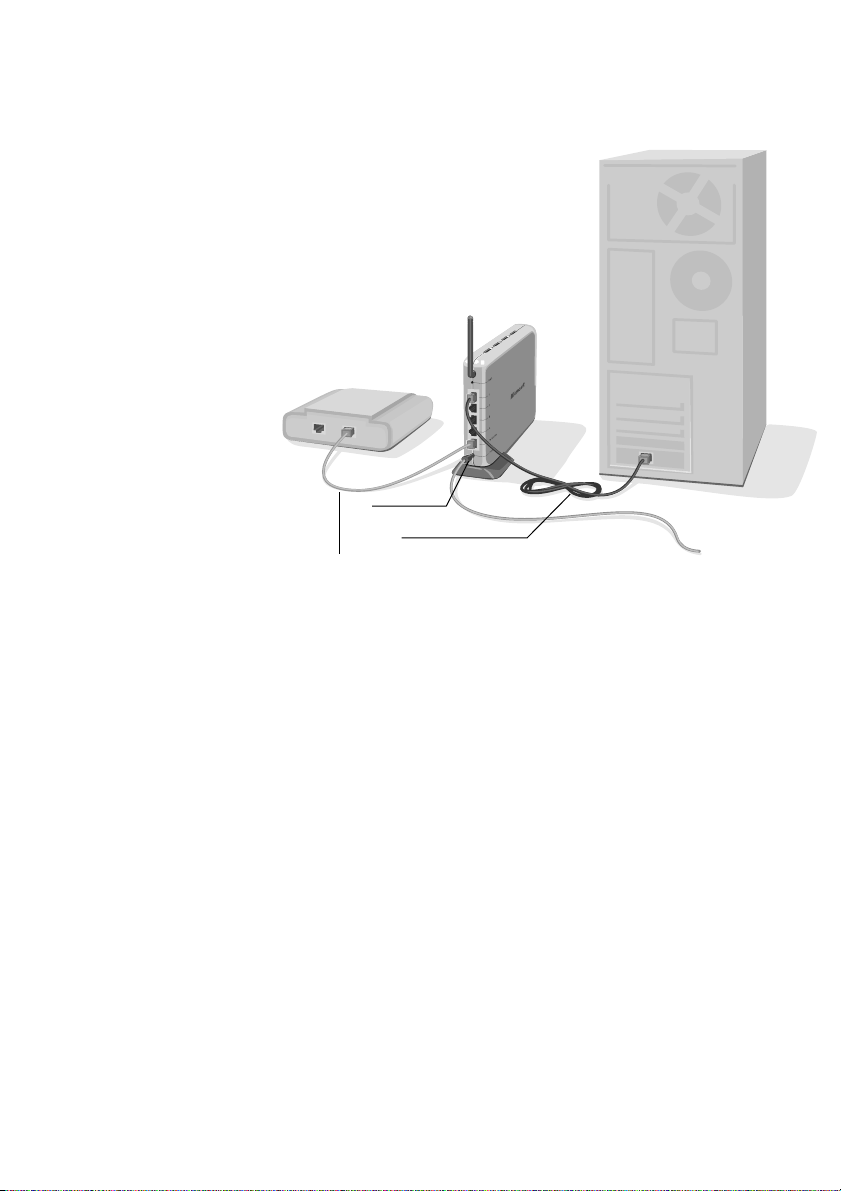
Your base station setup should now resemble the following
diagram.
First Computer
Wireless
Base Station
Existing
Broadband
Modem
Existing
Ethernet
Cable
Power Port
Blue Ethernet Cable
(included in box)
To Powe r
Supply
Step 3: Configure the base station and network
1. Continue to follow the Setup instructions to establish your
wireless network settings:
• You will be given an opportunity to enable wireless security
(WEP). It is recommended that you choose to enable WEP.
For more information, click Help on the WEP security page, or
see Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 of this manual.
• When you are asked, you can save your network settings to a
floppy disk for use in subsequent setups. A blank floppy disk
is provided for this. If you don’t choose to save to a disk, you
will be given a list of network settings to print or write down.
2. Click Finish to exit Setup.
3. Remove the Setup CD-ROM from the CD-ROM drive and the
floppy disk (if used) from the floppy disk drive. You can use the
same CD-ROM and floppy disk to set up additional computers.
Step 4: Test your network
1. View the status of your network in the Broadband Network
Utility. Ensure that you can see your base station and the
computer that is connected to it in the utility’s status screen.
18 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

2. If your broadband Internet connection is being shared through
your wireless network, open your Web browser and try accessing
a Web site such as www.microsoft.com. If your network is
working properly, you will be able to access the Internet from
the computer you just set up.
Other Setup Methods
In addition to the typical method, there are other ways to set up
your base station, depending on your computer and network
characteristics and the results you want. See Chapter 2 for help in
choosing your base station setup method and finding the
appropriate setup instructions.
If You Have a Non-Ethernet Modem
The Microsoft Wireless Base Station is designed specifically for
use with an external, broadband Ethernet modem. If you have a
modem with both USB and Ethernet connections, you must use the
Ethernet connection to connect to the base station.
To change your USB modem to an Ethernet connection
1. Before running setup, replace the USB cable between your
modem and computer with the Ethernet cable that came with
your modem. If you do not have this cable, see your modem
documentation or contact your Internet service provider to
determine whether you need to obtain a straight-through or
crossover Ethernet cable for the modem. Ensure that your
Internet connection is working through the Ethernet cable
before you start setup.
2. If your system matches the requirements for the typical setup
method, you can now follow the “Typical Setup Steps” in this
chapter.
If your modem does not have an Ethernet connection, you have
three choices:
• You can obtain a new modem that has an Ethernet connection.
• You can set up a network with wireless adapters only and no
base station. For information, see your adapter documentation.
• You may be able to set up the base station as a wireless access
point only. See the following section.
Using the Base Station as a Wireless Access Point Only
The base station is designed to work with an external Ethernet
modem. If you do not have one, you will not be able to run the
Setup Wizard or share your Internet connection through the base
station. If you do not want to share your Internet connection
through the base station, and you are comfortable with configuring
your base station through the Base Station Management Tool, you
can use the base station as an access point for your wireless
network only.
Chapter 3: Setup 19

To set up the base station as a wireless access point only
1. Plug one end of the blue Ethernet cable that came with your
base station into the Ethernet port labeled 1 on the back of the
base station and plug the other end into the Ethernet port on
the back of your computer.
2. Plug one end of the power supply that came with your base
station into the Power port on the back of the base station, and
plug the other end into an electrical outlet.
3. Use a pointed object to press the reset button on the back of
the base station, while observing the power indicator light. Hold
the button down until the light starts to blink green and orange,
about five seconds.
4. Release the button and wait for the light to turn solid orange
and then green, which can take up to 60 seconds.
5. Configure the base station through the Base Station
Management Tool. See Chapter 6 for instructions.
To set up the base station as a wireless access point if none of
your computers have Ethernet ports
1. Attach a wireless adapter to your computer by following the
instructions in your adapter documentation.
2. Follow steps 2 through 5 in the preceding procedure to connect
and configure the base station.
You should then be able to connect to your base station through
the wireless adapter. Although you may be able to share your
Internet connection through the networked computer, this is not
supported through Microsoft Wireless Setup. If you use a computer
that is running Windows XP to share your Internet connection, be
sure to enable Windows Internet Connection Sharing and Internet
Connection Firewall on that computer.
If You Have No Ethernet Computers
If none of your computers have available Ethernet ports, but they
do have available USB or PC Card connections, you can connect all
of your computers to the base station wirelessly, as described in
the following section. You will need to purchase wireless adapters
to configure your base station this way.
Connecting the Base Station Wirelessly
You can connect all of your computers to the base station
wirelessly if none of the computers have Ethernet connections, if
they cannot be located near the modem and base station, or if you
want all of them to be mobile.
You will need to purchase a wireless adapter for each computer
that you want to connect to the base station.
20 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Important
Setting up the base station
through a wireless adapter is
not recommended, because
your wireless and Internet
settings are vulnerable to
wireless eavesdropper during
setup. If possible, set up the
base station through a wired
connection and then switch to
a wireless connection.
Important
Get your Internet connection
settings before you disconnect
your computer from your
modem.
If you have a computer with an Ethernet connection, the
recommended method for connecting to the base station wirelessly
is to first set up and configure the base station through a wired
connection, and then change the computer to a wireless
connection. That way, you can set up the base station automatically
through the Setup Wizard and use these settings to set up the
wireless connection. The wired setup method is also more secure.
To connect a computer to the base station wirelessly if it was
originally set up with a wired connection
1. Complete the “Typical Setup Steps.” Ensure that your Internet
connection and network are operating correctly through the
wired connections.
2. Remove the blue Ethernet cable between the base station and
the computer that you want to set up wirelessly. Leave the
modem connected to the base station.
3. Install a wireless adapter on the computer according to the
instructions in your adapter documentation. If it is a MIcrosoft
adapter, run the Setup Wizard first.
If none of your computers have Ethernet connections, you can set
up the base station wirelessly from the beginning. You will install a
wireless adapter on the computer that was originally connected to
the modem, and configure the base station through this adapter.
The modem must still connect to the base station through
Ethernet, so if you had a USB modem connection, you must switch
to the Ethernet connection for connecting to the base station.
To configure the base station wirelessly from the beginning
1. Before you start setup or disconnect your modem, get your
Internet settings. For instructions, see “Determining Your
Network Settings” in Chapter 2. For most Internet connections,
you will need your Internet host name. For static IP connections,
you will need your MAC address and IP addresses; and for
PPPoE connections, your user name, password, and service
name. You must enter these settings during setup.
2. After recording your Internet settings, disconnect your modem
from your computer. If your modem previously used a USB cable,
replace the USB cable with an Ethernet cable by following the
instructions under “If You Have a Non-Ethernet Modem” in this
chapter.
3. On the computer that was connected to your broadband modem,
follow the “Typical Setup Steps” in this chapter. Choose to set up
the base station.
Because your modem has now been disconnected from your
computer, the Setup Wizard will alert you that it cannot detect
your Internet connection. Choose to proceed with setup. Later in
setup, you will be able to enter the Internet settings you saved in
step 1 of this procedure.
Chapter 3: Setup 21

Important
You cannot configure the base
station through a nonMicrosoft wireless adapter.
4. In Step 2.1 of the “Typical Setup Steps,” when the Setup Wizard
directs you to connect your base station, connect the Ethernet
cable from your modem to the To Modem port of the base
station, and connect AC power to the base station as instructed.
Your modem is now connected to the base station. Do not
connect your computer to the base station.
5. Continue to follow the Setup Wizard. During the wizard, choose
the type of wireless adapter you are going to install.
6. When the Setup Wizard directs you to connect your adapter,
connect a Microsoft Wireless USB Adapter or Microsoft Wireless
Notebook Adapter to your computer as instructed in the adapter
documentation.
7. When you are prompted, enter the Internet settings you
recorded in step 1 of this procedure.
Important
If you are replacing an existing
network, do not disconnect
any devices on your existing
network until the Setup Wizard
directs you to connect your
base station.
Note
You can leave your computers,
modem, and base station on
while you replace or add
existing networks.
Replacing Existing Networks
If any of your computers are currently connected to a network, you
can remove the computers from the network and connect each of
them to your Microsoft Wireless Base Station by following the
“Typical Setup Steps” in this chapter.
If your computers were disconnected from a base station, router,
or gateway, the Setup Wizard will not be able to access your
Internet or network settings after the existing base station is
removed. Therefore, you should obtain your Internet settings before
disconnecting the existing base station. For instructions, see
“Determining Your Network Settings” in Chapter 2.
For most Internet connections, you will need your Internet host
name. For static IP connections, you will need your MAC address
and IP addresses; and for PPPoE connections, your user name,
password, and service name. You must enter these during setup to
reestablish your Internet connection.
Connecting Existing Networks
You can connect several types of existing networks to the base
station, as explained in the sections that follow. If you are
connecting an existing network to the Microsoft Wireless Base
Station, disable any Internet connection sharing or firewall
software on the network before you start setting up the base
station. The base station replaces this software.
If your existing network contains a router, gateway, or base station,
the existing router may conflict with the Microsoft Wireless Base
Station. If you experience problems with your Internet connection
or with certain programs after adding the Microsoft base station to
an existing wired or wireless router, you may need to disable
network address translation (NAT) on one of the routers. For more
information, see “Network Address Translation” in Chapter 6.
22 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Note
You can leave your computers,
modem, and base station on
while you replace or add
existing networks.
Note
Some Uplink ports on hubs
have directional switches.
If your base station is not
detected after being
connected to the Uplink
port of your hub, move the
directional switch to the
opposite position and try your
connection again.
Connecting Ethernet Networks to the Base Station
If your computers are networked directly together through
crossover Ethernet cables or through direct parallel, serial, or USB
connections, disconnect them and use non-crossover Ethernet
cables (including the provided blue cable) or wireless adapters to
connect each computer to the base station.
To connect your existing Ethernet hub or switch to the base
station
1. Choose one of the computers on the network to set up first, and
follow the “Typical Setup Steps” in this chapter.
2. In Step 2.1 of the “Typical Setup Steps,” when the Setup Wizard
prompts you to connect your base station, unplug your modem
cable from the Ethernet hub or switch. Leave the cable plugged
in to the modem.
3. Plug the modem cable into the To Modem port on the back of
the base station.
4. Plug one end of the blue Ethernet cable into the Ethernet port
labeled 1 on the back of the base station.
5. Plug the other end of the cable into the Uplink port on your hub.
An alternate connection method is to use a crossover Ethernet
cable to connect the base station to an Ethernet port, rather than
the Uplink port, on the hub.
Connecting HomePNA or HomeRF Networks
You can connect a HomePNA network to your Microsoft Wireless
Base Station by using a HomePNA-to-Ethernet adapter. For more
information, see your HomePNA network documentation or contact
the manufacturer.
Microsoft wireless components are not compatible with HomeRF
technology. To access computers on an existing HomeRF network,
disconnect the computers from the HomeRF network and connect
them to the Microsoft Wireless Base Station by using Ethernet
adapters or Wi-Fi compatible wireless adapters.
Connecting Existing Wireless Networks
You can connect an existing Wi-Fi compatible wireless network to
your Microsoft Wireless Base Station. Ensure that the existing base
station and adapters use the same wireless network name,
channel, and WEP key, if enabled, as your Microsoft Wireless Base
Station. If the routing function of the existing base station, router,
or gateway conflicts with the router on the Microsoft Wireless Base
Station, you may need to disable network address translation (NAT)
on one of the routers. For more information, see “Network Address
Translation” in Chapter 6.
Chapter 3: Setup 23

If Your Computers Are on a Domain
If any of the computers that you want to network are already
members of a domain—for example, if you have a laptop that is on
a domain at work, and you want to connect it to your home
wireless network—the Setup Wizard will detect this and skip the
file-sharing and printer-sharing sections of setup. You will not be
able to share files and printers with other computers on the
wireless network, but you will be able to access your computer’s
domain when you return to work.
It is possible to switch to a workgroup after setup, to access files
on your wireless network. However, you will then have to switch
back to the domain to access your work network. For more
information, see your Broadband Network Utility Help.
Setting Up the Base Station on a Windows 2000
Computer
You cannot use the Setup Wizard to set up the base station on a
computer that is running Windows 2000. Your options are to
• Use a different computer to set up the base station.
• Use the Base Station Management Tool to set up the base
station. See Chapter 6 for instructions.
• Set up a network by installing wireless adapters only. See your
adapter documentation for instructions.
Setting Up the Base Station on a Non-Windows
Computer
You will not be able to use the Setup Wizard to set up the base
station on a Macintosh or other computer that is not running
Windows. You can connect the base station to your broadband
modem and to an Ethernet port on the computer as shown in the
“Typical Setup Steps.” To configure the base station, you can use
the Base Station Management Tool. See Chapter 6 for instructions.
Adding to Your Network
The base station can support over 200 simultaneous wired and
wireless connections. You can add even more Ethernet devices by
connecting Ethernet hubs or switches to the base station. For more
information on connecting hubs or switches, see “Connecting
Ethernet Networks to the Base Station” in this chapter.
The following sections discuss adding wireless computers, wired
computers, and other devices to your network. If you are not sure
whether to use a wired or a wireless connection for adding devices
to your network, see Chapter 2.
24 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Adding Wireless Computers to Your Network
To connect wireless computers to your network, follow the steps in
your adapter documentation. The Microsoft Wireless Base Station
works with Microsoft or non-Microsoft Wi-Fi compliant wireless
adapters.
The base station will automatically detect a wireless computer,
provided that the computer has the correct network settings. The
adapter must use the same wireless network name (SSID), wireless
channel, and wireless security (WEP) key (if used) as the rest of
your wireless network. To share files and printers, the computer
must also use the same workgroup name as the other computers
on the network.
To determine your wireless network settings, refer to the Broadband
Network Utility. Enter these settings into your adapter’s setup
program if necessary.
Adding Ethernet Computers to Your Network
A computer can be added to the base station through an Ethernet
connection if it has an IEEE 802.3-compliant Ethernet adapter card
such as the Microsoft Broadband Networking 10/100 Ethernet PCI
Adapter, an available Ethernet port, and a straight-through Ethernet
cable to connect the computer to the base station. You can connect
up to four Ethernet computers to the base station, and you can add
even more Ethernet devices by connecting Ethernet hubs or
switches, such as a Microsoft Broadband Networking 10/100
Ethernet 5-Port Switch. To connect Ethernet hubs or switches to the
base station, see “Connecting Ethernet Networks to the Base
Station” in this chapter.
To connect an Ethernet computer to the base station, run the Setup
Wizard, choosing to add an adapter to the network and selecting
your type of Ethernet adapter. When Setup prompts you to do so,
connect the Ethernet cable from your computer to one of the
numbered Ethernet ports on the back of the base station.
Note
To determine whether your
Ethernet device needs a
straight-through or crossover
Ethernet cable to connect to
the base station, refer to the
documentation for your device.
Adding Non-Computer Devices to Your Network
You can connect non-computer devices, such as Microsoft Xbox
video game systems or wireless network print servers, to the base
station. A non-computer device can be added to the network if it
has an IEEE 802.3-compliant Ethernet adapter or an IEEE
802.11b-compliant wireless network adapter.
To connect an Ethernet device to the base station, run the Setup
Wizard, choosing to add an adapter to the network and selecting
your type of Ethernet adapter. When Setup prompts you to do so,
connect the Ethernet cable from your device to one of the
numbered Ethernet ports on the back of the base station.
Chapter 3: Setup 25
TM

To connect a wireless device to the base station, refer to the
documentation for your device. You will need to configure the
device to use your existing network’s wireless network name,
channel, and WEP security key if set.
If You Connected the Hardware First
If you connected the base station before installing the software,
the Setup Wizard may not be able to access the Internet to copy
configuration settings. It is recommended that you disconnect the
base station, reconnect your modem and computer in their original
configuration, ensure that your Internet connection is working, and
then rerun the Setup Wizard.
If You Do Not Want to Use the Setup Wizard
If you do not want to use the Setup Wizard to set up your base
station, you can enter your Internet settings and configure the base
station in the Base Station Management Tool. For more
information, see Chapter 6.
26 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

4
Note
The information in this chapter
provides general guidance for
basic networking tasks.
Microsoft Windows
provides more specific and
detailed instructions for the
procedures described in this
section. To open Windows
Help, click Start, and then
click Help (or Help and
Support in Microsoft
Windows XP).
Help
networking.
Using Your Network
After setting up your wireless network, you can perform common
networking tasks, such as making printers and files available to
other computers, and playing multiplayer games.
This chapter provides information about:
• Logging on to your network.
• Allowing access to an Internet connection.
• Allowing access to files and folders.
• Allowing access to printers.
• Sharing other peripheral devices.
• Reading e-mail messages on your network.
• Playing games on your network and on the Internet.
• Connecting to other wireless networks.
Logging on to Your Network
After starting your computer, you must always log on to your
network to access shared files, printers, and other resources.
®
If you have Microsoft
Microsoft Windows Millennium Edition, do not click Cancel during
the logon process, even if you decide to leave your password blank.
Type your user name, type your password (or leave it blank), and
then click OK.
Windows® 98, Microsoft Windows 98 SE, or
Do Not
Click Cancel

If you are already in the process of using Windows, and you haven’t
yet logged on to your network, you can log off and then log back on.
To log off and log back on to your network
1. Click Start.
2. Click Log Off. (Or, in Microsoft Windows 2000, click Shut Down,
make sure “Log Off” appears in the drop-down box, and then
click OK.)
3. Log on to your network.
After you log on to your network, you can perform certain network
functions, such as opening shared files from Windows Explorer.
Important
Before you proceed, please
check with your Internet
service provider about its
policy regarding Internet
sharing.
Note
If you have Microsoft
Windows 2000 or Microsoft
Windows XP, you will need to
have sufficient privileges (or
be the network administrator)
in order to share folders with
others. For more information,
look up “administrator” in
Windows Help.
Allowing Access to an Internet Connection
Before you installed the Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless
Base Station, one of your computers was already connected to the
Internet through a broadband connection. Now that you’ve
installed the base station, the other computers on your network
can share that original Internet connection. You can now use any of
your networked computers to access the Internet the way you
usually do.
Note that the rate that you are able to send and receive data over
the Internet is highly dependent on many factors. Adding another
user to your Internet connection typically reduces the speed of
data transfer, but you are unlikely to notice the difference.
To access the Internet from each computer on a network
1. Make sure that you have a Web browser (such as Microsoft
Internet Explorer) installed on each computer that is connected
to your network.
2. On any of the networked computers, open the Web browser.
3. Search for the Web site you want, or enter the address in the
Address bar.
Allowing Access to Files and Folders
The information in this section provides general guidance for a few
basic file-sharing tasks. For more detailed instructions and
information about sharing files and folders, see Windows Help. To
access Windows Help, click Start, and then click Help (or Help and
Support in Windows XP).
To make it easy to share files and folders, all of your networked
computers should be in the same workgroup. For more
information, look up “workgroup” in Windows Help.
Sharing files and folders is a two-step process. You will need to:
1. Make the files and folders available to the network.
28 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

2. Use Windows (Network Neighborhood, My Network Places, or
Windows Explorer) to access the shared files and folders.
To make your files and folders available to the network
While setting up your broadband network, you may have chosen to
share all of your files and folders with the network. If you decide
that you only want to share some of your files and folders with the
network, you can use Microsoft Windows
to specify which files and
folders to share.
You can share an entire drive with the network, or you can share
specific folders. Let’s say that you store photographs of your
children in a folder named “Kids” on your computer, and you want
to make the photographs available to your network. In this case,
you would share the Kids folder, and not share the other folders on
your computer.
Only the computer users on your network will have access to the
files you share. At times, you may want to prevent users, such as
your children or your roommates, from accessing particular folders
and the files they contain. If you want to increase the security of
your shared files, you can assign permissions and passwords to
your files and folders. For more information, look up “permission”
and “access control” in Windows Help. (In Microsoft Windows
Millennium Edition, look up “controlling access.”)
Although you can share files, printers, and other devices on your
network, you cannot share software products such as Microsoft
Word or Microsoft Excel. Each computer on the network must have
those programs installed, and then you can share the files that you
create within those programs.
For a computer’s files and folders to be available to the network,
the computer must be turned on and logged into the network. Also,
if the computer is turned on but in sleep mode, it will not be
accessible from the network. For more information, look up “power
options” in Windows XP Help, or “power management” in Windows
Me, Windows 2000, and Microsoft Windows 98 Help.
To access and organize your files
Windows Explorer displays the hierarchical structure of files,
folders, and drives on your computer. Using Windows Explorer, you
can copy, move, rename, and search for files and folders. For
example, you can open a folder that contains a file that you want to
copy or move, and then drag the file to another folder or drive.
To open Windows Explorer, click Start, point to All Programs (or
Programs, depending on your version of Windows), point to
Accessories, and then click Windows Explorer. (In some versions
of Windows, you can skip the Accessories step.)
For more information about using Windows Explorer, see Windows
Help.
Chapter 4: Networking 29

You can use My Network Places (or Network Neighborhood, in
Windows 2000 and Windows 98) to view and access all of the
shared files and folders on your network.
My Network Places presents a view of the network similar to the
view of your computer presented by Windows Explorer. Use My
Network Places when you:
• Want to see all the resources available on the network.
• Already know where the resource that you want is located.
• Want to copy files and folders from one network location to
another.
To open My Network Places, click Start, and then click My Network
Places.
To open Network Neighborhood (in Windows 2000 and
Windows 98), double-click Network Neighborhood on your
desktop.
To open a file stored on another computer on the network
In order to complete this procedure, you must have on your local
computer the type of program (such as Microsoft Word or Microsoft
Excel) that was used to create the type of file you’re trying to open.
For example, if you want to open an .xls file, you must already have
Microsoft Excel installed on the computer from which you’re
opening the file.
1. Open My Network Places or Network Neighborhood.
2. Double-click the name of the computer that has the file that you
want to open.
3. Locate the file that you want to open.
4. Double-click the file.
To copy a file from your computer to another place on the
network
1. Open Windows Explorer, My Network Places, or Network
Neighborhood. Your computer and the other computer to which
you want to copy a file will appear in the same window.
2. On your computer (which is often represented by drive letter C:),
locate the file that you want to copy to another computer on the
network.
3. Click to highlight the file.
4. On the Edit menu, click Copy.
30 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

5. Click the destination folder on the other computer (which is
usually represented by a drive letter other than C:). You may
need to scroll through the window to find the folder you want.
6. On the Edit menu, click Paste.
Note
Some printer drivers are not
designed for sharing printers.
For more information, see the
documentation that came with
your printer.
Allowing Access to Printers
Using Windows, you can print documents on a printer that is
attached to another computer on your network.
The following procedures provide general guidance for a few basic
printer-sharing tasks. For complete instructions and information
about sharing printers, see Windows Help.
Note that there is a difference between a “network printer” and a
local printer that you share with your network. A network printer is
connected directly to a network, rather than being attached to a
particular computer. The type of printer that you are likely to use
with the Broadband Network Utility is a local printer that is
attached to a specific computer and can be shared with the other
computers on your network.
Before you can use a printer that is attached to another computer
on your network, you will need to do the following:
• Make the printer available to the network (this is also known as
sharing a printer).
• Install the printer drivers on each networked computer that will
use the shared printer.
• Run the Add Printer Wizard on each computer that you want to
print from.
The procedures for sharing a printer, installing drivers, and running
the Add Printer Wizard differ depending on your version of
Windows. For more detailed instructions, look up “sharing printers”
in Windows Help.
Note
The computer that is
connected to the printer must
be turned on in order for the
other computers on the
network to use the printer.
To print to a shared printer that is attached to another computer
on the network
1. Open the document that you want to print, such as a document
in Microsoft Word).
2. On the File menu, click Print.
3. In the Print dialog box, select the shared printer from the list of
printers.
4. Click OK.
For more detailed instructions, look up “printers” in Windows Help.
Chapter 4: Networking 31

About Sharing Other Peripheral Devices
In addition to most printers, you can share storage devices—such
as hard drives, CD-ROM drives, and Zip drives—on your network.
Storage devices that are not assigned a drive letter (such as tape
drives) cannot be shared. Tape backups of your computer must be
done from the computer that is attached to the tape drive.
Scanners, Web cameras, and CD-ROM burners cannot be shared
with other computers on your network.
About Reading E-Mail Messages on a Network
You can access your e-mail messages from each networked
computer the same way that you would access your e-mail
messages without a network (assuming that you have an Internet
connection). Open your e-mail program, or, if you have a Webbased e-mail account, sign in to your account through your Web
browser.
Keep in mind the following: If you download e-mail messages from
your e-mail account to one computer, those messages will not be
accessible from the other computers on your network. Likewise, if
you share an account with another person, and he or she
downloads mail from the shared account to one computer on the
network, you will not see that mail when you access the account
from another computer.
To illustrate this point, let’s say you share a postal mailbox at your
home with your spouse. If you come home first and take the letters
out of the mailbox, they will no longer be inside the mailbox when
your spouse comes home later and checks for mail.
If you want your e-mail messages to remain available to all users of
your network at any time, you should not download the messages
to one computer. (However, you should delete old messages from
your e-mail account on a regular basis, so that you don’t exceed
the storage space given to you by your e-mail provider.)
Playing Games on a Network and the Internet
Many of the most popular games now have multiplayer capability,
allowing two or more players to compete by using a local network.
With network-enabled games, you can use your networked
computers to play games with friends and family members.
Most games come with documentation that explains all you need
to know to configure your network for multiplayer gaming. However,
the following check list might help you prepare for playing games
over the network:
• If you have purchased a multiplayer game, be sure to install it
on each computer on the network that will be used for playing
games.
32 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

• Make sure that the network protocols necessary to run the
games that you want are installed on each computer. For more
information, see the documentation that came with your games.
• If you are playing a Web-based game, you may also be required
to pay user fees or download game files to your computer. Be
sure to follow the directions provided on the game’s Web site.
• If you experience problems connecting to a Web-based game,
you may need to configure the base station to work with the
ports that your game uses. For more information, see “Port
Forwarding” in Chapter 6.
For information about playing games on the Web, and for other
game-related information, see the following Web site:
http://www.microsoft.com/broadbandnetworking/.
Connecting to Other Wireless Networks
Many places, such as offices, hotels, and airports, provide wireless
networks that you can access from a portable computer while
you’re away from your own home or office.
If your operating system is Windows XP and you have a Microsoft
Broadband Networking Wireless USB Adapter or Microsoft
Broadband Networking Wireless Notebook Adapter, you can
connect to other wireless networks, assuming that you have the
necessary permissions and passwords for those networks.
If you do not have Windows XP, you can use the Broadband
Network Utility to connect to other wireless networks. For more
information, see “View and Change Network Settings” in Chapter 5.
For example, if you are traveling and have brought your laptop
computer for a flight (with the Microsoft Wireless Notebook
Adapter), you can automatically switch to the airport’s wireless
network.
Note
While connecting to another
wireless network, you may
need to switch between a
workgroup and a domain. For
more information about this
task, see “Switching Between
Workgroup and Domain” in the
Broadband Network Utility
Help.
To connect to an available wireless network
1. In the Windows notification area (the area on the taskbar to the
right of the taskbar buttons), right-click the Wireless Network
Connection icon, and then click View Available Wireless
Networks.
Wireless Network
Connection Icon
2. In Connect to Wireless Network, under Available Networks,
click the wireless network that you want to connect to.
Chapter 4: Networking 33

3. If wireless security (also known as Wired Equivalent Privacy, or
WEP) is enabled on the network you are joining, type the key in
the Network Key field. (A network administrator, or the person
who set up the local-area network, should have the key that you
need for this field.)
4. Click Connect.
5. To configure additional wireless network connection settings, or
if you are having difficulty making a connection to the wireless
network that you selected, click Advanced, and then configure
the settings on the Wireless Networks tab.
34 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

5
monitor.
The Broadband Network Utility
The Broadband Network Utility is automatically installed on your
computer when you install the Setup software. Use it to check the
status of your network or change network settings. The Broadband
Network Utility also shows the devices currently connected on your
network.
This chapter describes how to:
• View computer, network connection, and Internet connection
status.
• View and change network settings.
• Update network software, drivers, and firmware.
• Secure your network.
Note
The information displayed
in the main window of the
Broadband Network Utility
may vary depending on your
network configuration.
Your Computer Status
Your Network Status
Your Internet
Connection Status
To open the Broadband Network Utility
• Click Start, point to Programs, and then click Broadband
Network Utility.
-or-
• Double-click the Broadband Network Utility icon
notification area of your desktop.
Status of all computers and
devices in your workgroup
in the

The following sections describe how to interpret status information
about your network and perform common tasks by using the
Broadband Network Utility.
If you requre more information on the status settings provided in
the Broadband Network Utility, see Broadband Network Utility Help.
To open Broadband Network Utility Help
1. Open the Broadband Network Utility.
2. On the Help menu, click Microsoft Broadband Network Utility
Help.
View the Status of Your Computer
This area of the Broadband Network Utility displays information
about the computer that you are currently using. If there is a
problem with your computer, on the Help menu of the Broadband
Network Utility, click Microsoft Broadband Network Utility Help.
In the left pane of the Help window, double-click Troubleshooting,
and then click the topic that you want.
Note
If you set up an ad hoc
network, Network Connection
Status will not be displayed in
the Broadband Network Utility.
View the Status of Your Network Connection
This area of the Broadband Network Utility displays information
about your network, such as the workgroup name.
You can also view information about the status of your network
connection by resting the pointer on the Broadband Network
Utility icon
or tray.
in the Windows notification area of your taskbar
View the Status of Your Internet Connection
This area of the Broadband Network Utility indicates whether you
are currently connected to the Internet.
View the Status of Other Network Devices
This area of the Broadband Network Utility displays information
about all the computers in your workgroup and other devices
connected to your network.
To refresh the network device list
• Right-click the icon for the active devices in the network device
list, and then click Refresh list.
To remove an inactive device from the network device list
• Right-click the dimmed icon for the device, and then click
Remove device.
36 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

View and Change Network Settings
You can view network settings from the Broadband Network Utility.
On computers running Windows 2000 or Windows XP, you must be
logged in as an administrator to change network settings.
To view network settings
• On the Tools menu, click Computer Settings.
There are three types of settings that you can view and change
from the Computer Settings dialog box:
• Adapter settings. These are the settings that you see when you
first open the Computer Settings dialog box. On the Adapter
tab, you can change the adapter that you are currently using.
You can also view the IP address for your computer and local
network and the default gateway IP address.
• Wireless settings. On the Wireless tab, you can view or change
the network name (SSID), wireless channel, and data rate. You
can also change these settings from the Base Station
Management Tool. To learn more about these settings, see
“Wireless Settings” in Chapter 6.
• Encryption settings. On the Encryption tab, you can turn
wireless security (WEP) on or off, change the encryption
strength, and create or change your WEP keys. You can also
change these settings from the Base Station Management Tool.
To learn more about these settings, see “Wireless Security
(WEP)” in Chapter 6.
Update Software, Drivers, and Firmware
Occasionally, Microsoft may provide upgrades to the Broadband
Network Utility software, network drivers, or firmware on the
Microsoft Broadband Networking Web site. When an upgrade is
available, you will automatically be notified. After you log on to a
networked computer, a message will appear in the notification area
of your desktop with a link to the Microsoft Broadband Networking
Web site.
You can also check for upgrades on the Web site from the
Broadband Network Utility.
To upgrade network software, drivers, or firmware
1. Open the Broadband Network Utility.
2. On the Help menu, click Update.
3. Follow the instructions on the Microsoft Broadband Networking
Web site to download the most current software, drivers, or
firmware.
Chapter 5: Monitor 37

Secure Your Network
This section provides some general information about how to
protect your network from security threats.
The single most important step that you can take to secure your
network is to install the Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless
Base Station. The base station provides an important security layer
between your network computers and the Internet. However, even
with the base station installed, your wireless network is still
vulnerable to viruses and eavesdropping. To minimize risks to your
network security, follow these suggestions:
• Enable wireless security (WEP) when you run the Setup Wizard.
• Install an antivirus software program and do not open unknown
e-mail attachments.
• Create strong passwords.
Some security mechanisms, such as network address translation
(NAT) and firewall settings, are activated on the Microsoft Wireless
Base Station by default. You can customize these security settings
from the Base Station Management Tool. For information about
the Base Station Management Tool, see Chapter 6.
Protect Your Network from Hackers
The Microsoft Wireless Base Station provides a firewall and NAT to
secure your system from hacker attacks.
A firewall is a barrier that helps protect your network from outside
intruders. Like an actual firewall built to prevent fire from
spreading between adjoining buildings, computer firewalls help
prevent the spread of unauthorized communication between an
individual computer or group of networked computers and the
Internet.
The firewall specifies what information can be communicated from
the computers on your network to the Internet, and from the
Internet to the computers on your network. You may discover,
however, that you may not be able to transmit data from some
programs across the firewall. If this is the case, you can use the
Base Station Management Tool to configure the base station to
transmit the data that you require.
Network address translation hides the IP addresses of the
computers on a network from the Internet so that only the base
station’s IP address is visible. Hiding network IP addresses
provides another layer of protection against hackers trying to
access the computers on your network.
For more information about NAT and firewall settings, see
“Security Settings” in Chapter 6.
38 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Protect Your Network from Computer Viruses
Setting up a network by using the Broadband Networking Wireless
Base Station and adapters cannot protect against viruses.
To avoid having a problem with viruses on your network, follow
these suggestions:
• Install an antivirus program on each computer on your network
and use it regularly to check your computers for viruses.
Remember to update the antivirus program on a regular basis.
• Learn the common signs of viruses: unusual messages that
appear on your screen, decreased system performance, missing
data, and inability to access your hard drive. If you notice any of
these problems on your computer, run your antivirus program
immediately to minimize the chances of losing data.
• Educate yourself about how viruses are commonly spread so
that you do not spread one yourself:
• Do not load a program from an untrusted source onto one of
your network computers.
• Never open attachments to e-mail messages that you are not
expecting.
• Use your antivirus software to scan all floppy disks before
copying or opening files from them, or before starting your
computer from them.
Protect Your Network from Unauthorized Access
Because wireless networks use radio signals, it is possible for
other wireless network devices outside your immediate area to pick
up the signals and either connect to your network or capture the
network traffic. To help prevent unauthorized connections or the
possibility of eavesdroppers listening in on your network traffic, do
the following:
• Position your base station away from windows and toward the
center of your home. This decreases the strength of the signal
outside your home.
• Enable 128-bit wireless security (WEP) on your network when
you run the Setup Wizard. Encryption scrambles the data so
that it is decipherable only with the information necessary to
decrypt it. If you did not enable wireless security when you ran
the Setup Wizard, you can do so from the Broadband Network
Utility or from the Base Station Management Tool. For more
information, see “Wireless Security (WEP)” of Chapter 6.
• Use media access control (MAC) filtering. You can use MAC
filtering to grant or deny users the ability to connect to your
network based on the MAC addresses of the adapters they are
using. For information about MAC filtering, see “MAC Filtering”
in Chapter 6.
Chapter 5: Monitor 39

40 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

6
configure.
Customizing the Base Station
The Base Station Management Tool is a Web-based utility that you
can use to manage network settings and customize security
options on the Microsoft
Station.
You can select many base station settings when you run the Setup
Wizard. However, if you want to change a setting, such as your
base station password, or if you have special network requirements
(for example, if you want to establish a Web server on your
network), you can use the Base Station Management Tool to
configure the necessary settings.
If you do not run the Setup Wizard when you set up your network,
you must use the Base Station Management Tool to configure your
network settings.
This chapter explains how to perform the following tasks:
• Open the Base Station Management Tool and view the current
configuration of your base station.
• Configure the base station with the settings provided by your
Internet service provider (ISP) so that your networked
computers can connect to the Internet.
• Manage network time settings, base station password, and
firmware upgrades.
• Create a backup file of the base station settings.
• Change the wireless channel and wireless network name (also
known as Service Set Identifier, or SSID) for your network.
• Customize security features, such as firewall settings, media
access control (MAC) filtering, and wireless security (also known
as Wired Equivalent Privacy, or WEP) settings.
• Change the base station configuration from routing mode to
bridging mode.
• Limit access to the Internet or to particular applications on one
or more of your networked computers by setting up client
filtering.
• Set up the network to allow unrestricted access to the Internet
from one computer by establishing a virtual demilitarized zone
(DMZ).
• Configure port forwarding to run applications with special
network requirements.
®
Broadband Networking Wireless Base

Opening the Base Station Management Tool
You can open the Base Station Management Tool from the
Microsoft Broadband Network Utility or open it directly from a Web
browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5 or later, or Netscape
Navigator 4.7 or later. To use the Base Station Management Tool,
you must have a Java-enabled browser installed on your computer.
To open the Base Station Management Tool
1. In the Broadband Network Utility, on the Tools menu, click Base
Station Management Tool.
-orOpen your Web browser, and then type the IP address of the
base station in the address field. By default, this address is
http://192.168.2.1. However, you can change this address in
the Base Station Management Tool.
2. To log on, type the base station password that you created when
you ran the Setup Wizard. The base station password is case
sensitive. If you did not run the Setup Wizard, use the default
base station password of admin.
If you do not remember the base station password that you set
when you ran the Setup Wizard, you will need to restore the factory
default settings on the base station and use the default base
station password of admin. When you restore the original settings,
you lose your ISP settings and must reconfigure these settings
from the Wide Area Network page in the Base Station
Management Tool.
For information about restoring factory default settings by using
the Reset button on the base station, see “Resetting the Base
Station” in Chapter 1.
Logging Off
It is important to log off the Base Station Management Tool after
you have finished using it. Logging off protects the configuration of
your base station so that unauthorized users cannot access and
change your settings. Logging off also ensures that you can open
the Base Station Management Tool from another computer if you
need to. The Base Station Management Tool cannot be opened
simultaneously on two different networked computers.
To log off the Base Station Management Tool, on any page of the
Base Station Management Tool, click Log Off.
Navigating the Base Station Management Tool
After you log on, the Home page of the Base Station Management
Tool opens. You can use the menu in the left pane to navigate to
the other pages of the Base Station Management Tool.
42 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

The following table lists the menu items in the Base Station
Management Tool and the tasks that you can perform on each page.
Menu item Tasks
Home View current network settings and activity.
Management Reset the base station, back up and restore base station
Local Area Network Enable the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Wide Area Network Specify and configure the type of Internet connection
Wireless Set up or modify the connection between your base
settings, upgrade firmware, establish time settings, and
change the base station password. For more
information, see “Management Settings” in this chapter.
server on your base station and set the IP address range
and lease time. For more information, see “Local Network
Settings” in this chapter.
that your base station uses. For more information, see
“Wide Area Network Settings” in this chapter.
station and the wireless computers on your network. For
more information, see “Wireless Settings” in this chapter.
Chapter 6: Configure 43

continued
Menu item Tasks
Security Configure a variety of specialized security functions,
including:
• Firewall
• Wireless security (WEP)
• Port forwarding, including vir tual servers and special
applications
• Client filtering
• MAC filtering
You can also view the base station log from the Security section.
For more information, see “Security Settings” in this chapter.
If you need help at any time, click the Help button available on
each page of the Base Station Management Tool.
Configuring the Base Station
Typically, when you run the Setup Wizard, you establish the settings
required for your base station to connect to the Internet. If you
completed the Setup Wizard, you only need to use the Base Station
Management Tool when you want to modify your network settings.
You must use the Base Station Management Tool to establish the
initial settings if any of the following are true:
• You did not run the Setup Wizard when you connected your
network hardware and installed the network software.
• You are trying to configure the base station from a computer
running Microsoft Windows
running Windows (for example, a Macintosh).
• You want to set the base station to bridging mode to extend the
capabilities of an existing network.
If any of these situations apply to you, you must initially configure
the base station from the Base Station Management Tool.
®
2000 or from a computer not
To configure the base station from the Base Station
Management Tool
1. Connect the base station to a computer. For information about
how to do this, see Chapter 3.
2. Configure the TCP/IP properties of each computer that you want
to connect to your network. For information about how to do
this, see “Configuring Network Computers” in this chapter.
3. On the computer connected to the base station, open your Web
browser, and then type 192.168.2.1 in the address field.
4. In the logon box, type your password. The default password is
admin.
44 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

5. On the Management menu, click Change Password, and then
create a new base station password.
6. Click Wide Area Network. On the Wide Area Network page,
select the type of Internet connection you have, and then enter
the settings provided by your ISP. If you do not know the type of
Internet connection you have, contact your ISP for assistance.
7. On the Security menu, click Wireless Security, and then create
your wireless security settings. For information about wireless
security settings, see “Wireless Security (WEP)” in this chapter.
8. Turn on your broadband modem, and then check the status of
the Broadband Connection on the Home page of the Base
Station Management Tool. If the status is Disconnected, click
Renew or Connect. If the status is still Disconnected, confirm
the ISP settings with your ISP, and then try to configure the base
station again.
Configuring Network Computers
When you manually configure the base station, you must configure
the TCP/IP properties of each computer that you connect to your
network.
Before you configure the TCP/IP properties for each computer, you
should establish the computer name and the workgroup name on
each computer. Each computer name must be unique, while the
workgroup name should be the same for all computers in the
workgroup.
The procedure for establishing the computer and workgroup names
on a computer varies depending on which version of Windows you
are using. For information about how to establish these names,
consult Windows Help or Broadband Network Utility Help.
To configure the TCP/IP properties of a computer running
Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows Me
1. Click Start, point to Settings, and then click Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Network icon.
3. In the Configuration dialog box, select the TCP/IP protocol line
that is associated with your network adapter.
4. Click the Properties button, click the IP Address tab, and then
select Obtain an IP address automatically.
5. Click the Gateway tab and make sure that all fields are empty,
and then click OK. When the Network Properties dialog box
appears, click OK again.
6. If you are prompted to supply the original Windows installation
files, insert your Windows CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive, and
then browse to the location of your CD-ROM drive.
7. When you are prompted to restart your computer, click OK.
Chapter 6: Configure 45

To configure the TCP/IP properties of a computer running
Windows XP
1. Click Start, click Control Panel, and then double-click Network
Connections.
2. Double-click the icon for the connection you want to configure,
and then in the Connection Status dialog box, click Properties.
3. On the General tab, under This connection uses the following
items, click Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click
Properties.
4. Click Obtain IP address automatically, and then click Obtain
DNS server address automatically.
5. Click OK to close the TCP/IP Properties dialog box, and then
click OK to close the Connection Properties dialog box.
Caution
When you configure the base
station as a bridge, the Base
Station Management Tool is
no longer available.
Using the Base Station As a Bridge
If you already have a functioning network in your home or office,
you can use the base station to expand network connectivity, for
example, by adding wireless functionality to a wired network. This
is called bridging because the base station acts as a bridge
between two networks or segments of a network.
Before you change the base station to bridging mode, make sure
that the following conditions are true:
• A device on your network, such as your modem, is providing
router capabilities, or a device on your network is providing a
Network Address Translation (NAT) service.
• There is an existing DHCP server on your network.
• All devices on your network use static (fixed) IP addresses.
To configure the base station as a bridge
1. Connect the base station to a computer on your network. For
information about how to do this, see Chapter 3.
2. On the computer connected to the base station, open your Web
browser, and then type 192.168.2.1 in the address field.
3. At the logon prompt, type your password. The default password
is admin.
4. On the Management menu, click Change Password, and then
create a new base station password.
5. On the Security menu, click Wireless Settings, and then create
your wireless security settings. For information about wireless
security settings, see “Wireless Security (WEP)” in this chapter.
6. On the Security menu, click Network Mode.
46 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

7. Select the Bridging Mode check box, and then click Yes to
confirm your selection. When you switch from routing mode to
bridging mode, the base station resets. While the reset is in
progress, the power light on the base station blinks and then
turns orange. When the light is solid green, the reset is
complete.
8. After the reset is complete, turn off the computer and the base
station. Remove the cable from the base station Ethernet port
and insert it into the To Modem port. Leave the other end of the
cable connected to the Ethernet port of the computer.
9. Turn on the base station and restart your computer.
Home Page
You can view current base station and Internet connection settings
from the Home page of the Base Station Management Tool. The
following sections describe these settings.
Wide Area Network
The wide area network settings provide a summary of the Internet
settings provided by your ISP. The settings that appear will vary
depending on whether your ISP account provides a static (fixed) IP
address, a dynamic Internet connection, or a Point-to-Point
Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) connection. If your Internet
connection is disabled, the WAN settings will be unavailable.
The following table describes the WAN settings and how to modify
them.
Setting Description Notes
Broadband Appears as If the Base Station Management Tool
connection Connecting, shows that your broadband connection is
WAN IP Shows the IP This is the external (public) IP address
address address provided that connects your network to the
Connected, disconnected when you expect it to be
Disconnecting, or connected, try clicking Release and then
Disconnected. Renew to change the base station IP
address. If you have a PPPoE connection,
try clicking Disconnect and then
Connect. You can also try resetting the
base station and your broadband
modem. If you complete these steps and
the Broadband Connection is still
disconnected, contact your ISP for
assistance.
by your ISP. Internet.
If your ISP provides you an IP address
dynamically (by using a DHCP server),
this address may change periodically. You
can click the Release button and then the
Renew button to get a new IP address.
Chapter 6: Configure 47

continuedcontinuedcontinued
Setting Description Notes
Releasing your IP address is a good idea
if you are having trouble accessing the
Internet and you have determined that
the computer is not the source of the
problem. If renewing the IP address does
not resolve the problem, contact your ISP
for assistance.
Subnet mask Your ISP If you are using a static Internet
Default The IP address that The gateway setting is automatically
gateway the base station generated when you have a dynamic or
Primary Your ISP provides In some cases, these settings may be
Domain Name the DNS automatically filled in. Otherwise, you
System (DNS) addresses. can enter them on the Wide Area
and Secondary Network page of the Base Station
DNS Management Tool.
establishes the connection, you can change the subnet
WAN subnet mask. mask for your wide area network, but you
should use the subnet mask provided by
your ISP. The subnet mask does not
appear when you are using a PPPoE
Internet connection.
uses to send data PPPoE connection. If you have a static
from your network (fixed) IP address, your ISP should
to the Internet. provide the gateway setting, and you can
enter the setting on the Wide Area
Network page of the Base Station
Management Tool. If you have a dynamic
connection and your Gateway setting is
blank, you should click Release and then
Renew.
Local Area Network
The Local Area Network settings relate to your local network—that
is, how the base station is configured in relation to the devices on
your network.
The following table describes the LAN settings and how to modify
them.
Setting Description Notes
Local IP address The default IP You can change the local IP address
Subnet mask The subnet mask for You cannot change the subnet mask
48 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide
address of your base on the Local Area Network page of
station is the Base Station Management
192.168.2.1. Tool, but this is not recommended.
your local network is of your LAN.
255.255.255.0.

continuedcontinuedcontinued
Setting Description Notes
DHCP server Appears as Enabled You can change this setting on the
Firewall Appears as Enabled You can change this setting in the
or Disabled. Local Area Network page of the
Base Station Management Tool.
or Disabled. Security section of the Base Station
Management Tool.
DHCP Client List
When a DHCP server is enabled on a network, each device (also
called a client, which can be a desktop computer, notebook
computer, or another connected device) leases an IP address for a
specified period of time. The DHCP client list shows all the clients
that have an active lease on an IP address and the IP address and
MAC address of each client. The list includes any device with an
active lease, even if that device is no longer actively connected to
the network. A client is removed from the DHCP client list when its
lease has expired. The network can support up to 253 clients at
one time.
You can specify the IP address lease time from the Local Area
Network page of the Base Station Management Tool. For
information about how to do this, see “Local Network Settings” in
this chapter.
The DHCP client list is relevant to your network only if you have the
DHCP server enabled on the base station. For information about
how to enable or disable the DHCP server, see “DHCP Server” in
this chapter.
Base Station Information
You can view current network status in the Base Station
Management Tool, under Network Information. The following table
describes this network information.
Setting Description Notes
Runtime code These settings show When you check for firmware
version and the version numbers upgrades at www.microsoft.com/
Boot code of your firmware. broadbandnetworking, you should
version download the version on the Web only
LAN MAC This is the MAC For information about MAC
address address of the base addresses, see “MAC Addresses”
station. in this chapter.
MAC address This is the MAC For information about MAC
address that your ISP addresses, see “MAC Addresses”
sees. in this chapter.
if it is later than this version.
Chapter 6: Configure 49

continuedcontinuedcontinued
Setting Description Notes
Note
You can also reset the base
station by using the reset
button on the physical device.
For information about how to
perform a hardware reset, see
Chapter 1.
Serial number This is the serial If you need to call Product Suppor t
number of your base Ser vices for assistance, you may
station. need to provide the serial number.
Management Settings
When you want to change the settings related to the management
of your base station (for example, resetting the base station,
backing up or restoring settings, establishing time settings, or
changing the password), use the Management menu in the Base
Station Management Tool. The following sections describe how to
perform management-related tasks.
Reset the Base Station
You can reset the base station when you experience any of the
following problems:
• You have DHCP enabled on the base station, but the base
station is not assigning IP addresses.
• The computers on the network are no longer able to connect to
the Internet.
• The base station is not performing as expected.
When you reset the base station, you are forcing it to reinitialize
and restart all of its functions. The base station settings will not
change when you reset the base station.
To reset the base station
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Management.
2. On the Management menu, click Reset.
3. On the Reset Base Station page, click Reset. While the reset is
in progress, the power light on the base station blinks and then
turns orange. When the light is solid green, the reset is
complete.
If you want to open the Base Station Management Tool after the
reset is complete, type your base station password on the Logon
page. Do not attempt to log on until the reset is complete and the
power light on the base station is solid green.
Restore Factory Default Settings
You can restore the base station to its factory default settings if
absolutely necessary. When you restore factory default settings,
you clear any special base station configurations that you have
established. You will need to reconfigure your base station settings
or restore these settings from a backup file.
50 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

You should restore the original factory default settings only under
the following circumstances:
• You are experiencing serious problems with your base station,
and resetting the base station does not fix the problem.
• You cannot remember your base station password.
If you cannot remember your base station password, you will not
be able to open the Base Station Management Tool. In this
situation, you must restore the factory default settings from the
base station, and then use the default password admin to log on
to the Base Station Management Tool.
To restore factory default settings
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Management.
2. On the Management menu, click Back Up and Restore.
3. Under Restore Factory Default Settings, click Restore Factory
Default Settings. While the original factory default settings are
being restored, the power light on the base station blinks and
then turns orange. When the light is solid green, the settings
have been restored.
If you want to open the Base Station Management Tool after the
settings are restored, type admin as the password on the Logon
page. Do not try to log on to the base station until the settings are
restored and the base station power light is solid green.
After you restore the factory default settings, you should navigate
to each page of the Base Station Management Tool and
reestablish the network settings you need, or restore the base
station settings by using a backup file. For information about
creating a backup file of your settings, see the following section.
Be sure to establish your unique base station password as soon as
possible after restoring the factory default settings to prevent
unauthorized users from logging on. For information about
changing the base station password, see “Change the Base Station
Password” in this chapter.
Back Up Base Station Settings
You can create a backup file of all your base station settings from
the Base Station Management Tool. The backup file can include
settings that you established when you completed the Setup
Wizard and the settings that you modified from the Base Station
Management Tool.
It is a good idea to create a backup file after you have the base
station set up and operating normally. If for some reason the base
station malfunctions, you can restore the factory default settings to
the base station, and then use the backup file to reconfigure your
base station and resume normal operations.
Chapter 6: Configure 51

It is recommended that you back up settings whenever you change
settings, such as your base station password.
To back up base station settings
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Management.
2. On the Management menu, click Back Up and Restore.
3. Click Back Up Settings.
4. If you receive a message asking you whether to open or save
the file, click Save.
5. Type a name for the file that contains your base station settings
(or use the default name Config.bin), browse to the folder or
disk where you want to save the file, and then click Save.
Restore Base Station Settings from a Backup
If you have created a backup file of your base station settings, you
can restore settings from the backup file at any time. This
capability is particularly useful if the base station malfunctions and
you must restore the factory default settings. Instead of manually
reconfiguring each of your network settings from the Base Station
Management Tool, you can restore all of your saved settings from
the backup file.
To restore base station settings from a backup file
1. On the computer where you saved the backup file of your base
station settings, open the Base Station Management Tool.
2. Type the current base station password. If you have just
restored the factory default settings to the base station, the
password will be admin.
3. On the Management menu, click Back Up and Restore.
4. Under Restore Base Station Settings from a Backup, type the
path and name of the backup settings file, or click Browse to
search for the file that contains your network settings.
5. Click Restore Settings. While the settings are being restored,
the power light on the base station blinks and then turns
orange. When the light is solid green, the settings have been
restored.
If you want to open the Base Station Management Tool after the
settings are restored, type your base station password on the
Logon page. Do not attempt to log on until the settings are
restored and the power light on the base station is solid green.
52 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

Upgrade Base Station Firmware
Firmware is the term used to describe the programs stored in the
flash memory of hardware devices such as the Broadband
Networking Wireless Base Station. The firmware defines the
functionality of your base station. Occasionally, Microsoft may
provide upgrades to the firmware to improve the performance of
your base station. You can upgrade the firmware from the Base
Station Management Tool.
You can perform a firmware upgrade from any of your network
computers, but it is recommended that you use a computer with a
wired (Ethernet) connection to the base station.
During an upgrade, all users connected to the network will lose
network functionality.
To upgrade the base station firmware
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Management.
2. On the Management menu, click Firmware Upgrade.
3. Follow the directions on the screen to upgrade your firmware.
While the firmware is being programmed into your base station,
the power light on the base station blinks and then turns
orange. When the light is solid green, the update is complete. If
the upgrade fails, the power light will continue to blink slowly
until you successfully upgrade the firmware. In this situation,
you can try to upgrade the firmware again, or you can reset the
base station.
If you want to open the Base Station Management Tool after a
successful firmware update, type your base station password on
the Logon page. Do not attempt to log on until the firmware
upgrade is complete and the power light on the base station is
solid green.
Certain programs do not allow pop-up windows from Web browsers.
If you have one of these programs installed on your computer, you
may experience problems when you click the Microsoft Broadband
Networking Web site link on the Upgrade Firmware page. If you
do experience problems, you can open the Microsoft Broadband
Networking site by typing
http://www.microsoft.com/broadbandnetworking/
in the address field of your Web browser and browsing to the
update page, or by turning off the software that prevents pop-up
windows.
For information about how to upgrade network software and
drivers from the Broadband Network Utility, see Broadband
Network Utility Help.
Chapter 6: Configure 53

Establish Base Station Time Zone
The base station uses the date and time for client filtering and to
time stamp entries to the base station log.
The base station system clock is set to the Pacific time zone by
default. You can change the base station time zone from the Base
Station Management Tool.
To change the base station time zone
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Management.
2. On the Management menu, click Set Time.
3. Under Base Station Time Zone, in the drop-down list box, click
the time zone you want.
4. Select the Adjust automatically for daylight saving time check
box if you want the base station to adjust for daylight-saving
time.
5. If you selected the Adjust automatically for daylight saving
time check box, type the date that you want daylight-saving time
to start and the date that you want daylight-saving time to end.
You must update these dates each year to correspond with
daylight-saving time.
6. Click Update Time Settings to ensure that the changes that you
made are saved.
Synchronize Time to Internet Time Server
The base station automatically attempts to synchronize with one of
a set of Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) servers when it is
connected to the Internet. If you want to synchronize the base
station to a specific SNTP server, you can do so from the Base
Station Management Tool. Before you can set the SNTP server, you
must identify the IP address for the server that you want to use.
To locate an SNTP server
1. Open your Web browser, and go to your favorite search engine
(for example, http://www.msn.com).
2. Type Time synchronization on the Internet as a search term.
3. Review the search results, and browse to the SNTP server site
that you want to use.
4. Write down the IP address for the SNTP server that you have
accessed.
To synchronize the base station with an SNTP server
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Management.
54 Microsof t Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

2. On the Management menu, click Time Settings.
3. Under Synchronize Time to Internet Time Server, type the IP
address for the specific SNTP server that you want to use, and
then click Add.
4. Repeat step 3 for any additional backup SNTP servers that you
want to specify.
Change the Base Station Password
Access to the Base Station Management Tool is password
protected so that only users who know the base station password
can change your network configuration. If you ran the Setup
Wizard, you were prompted to establish a password. This is your
base station password. If you did not run the Setup Wizard, your
default password is admin. You can change the base station
password from the Base Station Management Tool.
It is a good idea to change your password every two to three
months, or more frequently if you are concerned that an
unauthorized person has administrative access to the base
station.
If at any point you restore the factory default settings for the base
station, the default password admin is also restored. You can use
this password to access the base station, and then create a new
password at the earliest opportunity.
When you change your base station password, be sure to update
your backup file.
To change the base station password
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Management.
2. On the Management menu, click Change Password.
3. In the Current password box, type your current password
4. In the New password box, type in a new password. The base
station password can contain 3–16 alphanumeric characters
and is case sensitive.
5. In the Retype new password box, retype the new password. Do
not use the Copy and Paste commands to add the new
password to the Retype new password box. If you did not type
your password correctly in the New Password box, you will not
know what your password is when you paste it into the Retype
new password box.
6. If you want, in the Log out inactive user in box, type a time
interval. After the specified time interval elapses without
activity, you will need to log on to the Base Station Management
Tool again in order to view or change settings.
7. To save the new password, click Apply.
Chapter 6: Configure 55

Be sure to store your password in a safe place. If you forget or
misplace your password and cannot log on to the Base Station
Management Tool, you can restore the base station to the factory
default settings from the physical device, and then use the default
password admin to open the Base Station Management Tool. For
more information about restoring factory default settings on the
base station, see “Resetting the Base Station” in Chapter 1.
Note
If you set the Broadband
Networking Wireless Base
Station to bridging mode, the
settings on the Local Area
Network page in the Base
Station Management Tool will
be unavailable.
Local Area Network Settings
You can configure settings for your local network on the Local Area
Network page of the Base Station Management Tool. This
configuration includes the following:
• Changing the IP address of your base station and viewing the
subnet mask assigned to your local network.
• Enabling or disabling a DHCP server on the base station.
• Setting the IP address range and lease time for the DHCP
server.
• Entering the local domain name for the DHCP server if
necessary.
Before you configure your local network, take some time to learn
about the options available. The following sections describe each
of the local area network settings.
IP Address and Subnet Mask
The default IP address of your local network is 192.168.2.1. This
address is reserved for private local networks; it is not visible to
the Internet.
You do not need to change the IP address unless you have a
specific reason to do so—for example, if your modem IP address
overlaps with the base station IP address. If you want to change
the IP address of your base station, be sure to change it to another
nonroutable (private) IP address.
The IP addresses assigned to the computers on your local network
by the DHCP server are derived from the base station IP address. If
you change the base station IP address, the DHCP IP address
range will also change.
The subnet mask for your local network is 255.255.255.0. You
cannot change the subnet mask assigned to your local network.
To modify the base station IP address
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click Local
Area Network.
2. Type a new IP address for the base station.
3. To save the changes, click Apply.
56 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

DHCP Server
The base station DHCP server allocates IP addresses to the
computers on your local network from a specific range of IP
addresses. Each time a computer on your network requests an IP
address, it receives one within the specified IP address range.
Typically, the DHCP server will assign the same IP address to a
client computer each time the client logs on to the network.
The base station provides a default IP address range for the DHCP
server to use. If you want, you can select a specified IP address
range when you enable the DHCP server.
To enable the DHCP server on the base station
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click Local
Area Network.
2. If it is not already selected, select the Enabled check box to
enable the DHCP server on the base station.
3. If you do not want to use the IP address pool specified by the
DHCP server, type a starting IP address and an ending IP
address for the pool. Do not include the base station IP address
in the IP address pool. For example, if you are using the default
base station IP address (192.168.2.1), the address range must
be between 192.168.2.2 and 192.168.2.254.
4. Select a lease time for the assigned IP addresses. The default
time is two hours.
5. Type a local domain name if your ISP provided one for you.
6. To save your changes, click Apply.
Wide Area Network Settings
The WAN settings on your network depend on your ISP account.
ISPs provide broadband customers with one of three different
types of Internet connections:
• Dynamic
• Static
• PPPoE
The Setup Wizard helps you configure your Internet connection. If
you did not run the Setup Wizard, the Broadband Networking
Wireless Base Station selects a dynamic connection by default. If
you have a static Internet connection or a PPPoE connection, you
can change the WAN setting from the Wide Area Network page of
the Base Station Management Tool.
You also have the option to disable your network Internet
connection, if necessary. The following sections describe each type
of Internet connection and how to configure your base station for
that option.
Chapter 6: Configure 57

Dynamic Internet Connection
If your ISP provides a DHCP server, you should select a dynamic
Internet connection for the WAN. This connection enables your ISP
to assign the IP address to your base station dynamically based on
the IP addresses available in the ISP’s subnet.
When you select a dynamic Internet connection, you may be
required to enter the host name and the DNS addresses, if your ISP
provided this information.
To establish a dynamic Internet connection
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click Wide
Area Network.
2. Under Internet Connection Type, click Dynamic.
3. Specify a host name if your ISP provided one to you.
4. Specify a MAC address, and click Clone MAC Address, if
necessary. For information about this option, see the following
section.
5. Specify the DNS primary and secondary addresses, if your ISP
provided you with this information and it has not been obtained
automatically.
6. To save the WAN settings, click Connect.
MAC Addresses
A MAC address is a unique numerical identifier for a hardware
device, such as a base station or adapter. Your base station has
two MAC addresses, one for the local area network and one for the
wide area network. Each network adapter that you use also has a
MAC address that is assigned at the time of manufacture and
printed on the label.
Some ISPs record the MAC address of the adapter that you use
when you first connect to the Internet. Depending on your ISP
account, you may experience problems if you later use the base
station’s default MAC address to connect to the Internet.
One way to avoid this problem is to clone the MAC address of the
adapter installed in the computer where you initially connected to
the Internet. When you clone the adapter MAC address, it replaces
the base station WAN MAC address, so each device on the network,
including the base station, appears to have that MAC address.
To clone a MAC address
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click Wide
Area Network.
58 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

2. In the MAC address box, type the MAC address of the adapter
installed in the computer that is connected to your base station.
The MAC address appears on the label on the underside of your
adapter.
3. Click Clone MAC address.
It is a good idea to record the MAC address of the adapter that you
clone, so that if you lose your settings or no longer have the
adapter, you do not lose your ability to connect to the Internet.
Static Internet Connection
If your ISP account provides a static (fixed) IP address, you should
configure the WAN settings on your base station for a static
Internet connection.
To establish a static Internet connection
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click Wide
Area Network.
2. Under Internet Connection Type, click Static.
3. Under Static Connection, type the information provided by your
ISP, including the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway IP
address, and DNS addresses (if provided).
4. To save the WAN settings, click Apply.
PPPoE Internet Connection
If your ISP uses a PPPoE connection, you should configure the WAN
settings on your base station for a PPPoE connection.
A PPPoE Internet connection functions like a dial-up connection in
that your user name and password are passed to the ISP for
authentication to establish an Internet connection. This interaction
happens automatically when the base station is turned on.
Unlike a dial-up connection, a PPPoE Internet connection is
persistent unless any of the following occurs: you disable the
connection; the base station is turned off or loses power; or you
specify a maximum idle time, and this time elapses.
To establish a PPPoE Internet connection
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click Wide
Area Network.
2. Under Internet Connection Type, click PPPoE.
3. Under Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE), type your
user name and password.
4. Type a service name if your ISP supplied it.
Chapter 6: Configure 59

5. Type a maximum idle time, if your ISP instructs you to. You will
be disconnected from the Internet if the time that you specify
elapses without activity.
6. Type the DNS primary and secondary addresses, if your ISP
provided you with this information.
7. To save the WAN settings, click Apply.
Disabled Connection
You can disable your Internet connection at any time. You may
want to disable your Internet connection in the following situations:
• You suspect that an unauthorized individual is accessing your
network.
• You want to limit your children’s access to the Internet.
• You want to limit the exposure of your local network to the WAN.
Disabling your Internet connection does not affect your Internet
connection settings in any way. When you reestablish your
connection, your original settings are intact.
To disable the Internet connection
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click Wide
Area Network.
2. Under Internet Connection Type, click Disabled.
3. To disable your Internet connection, click Apply.
Wireless Settings
You can enable or disable wireless access from the Wireless page
of the Base Station Management Tool. When you enable wireless
access, you must establish the following base station settings:
• Wireless network name (SSID)
• Wireless channel
• Data rate
It is likely that you already established the wireless network name
(SSID) and wireless channel when you ran the Setup Wizard. If you
did not run the Setup Wizard, or if for some reason you want to
modify these settings, you must update the wireless network name
(SSID) and wireless channel on all the devices that connect
wirelessly to your network. For information about how to update the
wireless network name and wireless channel on specific devices,
see the Broadband Network Utility Help.
When you enable wireless access on your network, you should also
enable wireless security (WEP). For more information about
wireless security, see “Wireless Security (WEP)” in this chapter.
60 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

Wireless Network Name (SSID)
The wireless network name, also known as the Service Set
Identifier (SSID), identifies your network. Because the network
name is broadcast by the base station, any user of a wireless
device that supports the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers (IEEE) 802.11b standard could attempt to join your
wireless network, if that device is in range.
To prevent users of unauthorized wireless clients from joining your
wireless network, enable wireless security (WEP). For information
about wireless security (WEP), see “Wireless Security (WEP)” in this
chapter.
If you know the MAC addresses of all the wireless clients that you
want to access your network, you can use MAC filtering to prevent
unauthorized access. For information about MAC filtering, see
“MAC Filtering” in this chapter.
Wireless Channel
The wireless channel is a path through which signals flow to and
from your network. If you are having difficulty sending or receiving
information on a wireless client, try changing the wireless channel.
Be sure that each wireless device uses the same wireless channel
as the base station.
Data Rate
The data rate indicates the speed at which wireless data can be
transmitted across the network. Typically, you will want to leave the
data rate at the default setting of Automatic, which enables the
maximum data transfer speed. You may want to decrease the data
rate, however, if any of the following are true:
• You are using a device that requires a slower bandwidth for data
transfer.
• You want to conserve bandwidth on your network.
• You are experiencing problems maintaining a connection with a
wireless device.
To enable wireless access
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Wireless.
2. Select the Enable wireless access check box.
3. If you want to change the wireless channel, click a number in
the Wireless channel number drop-down list box.
4. If you want to change the network name, type a new network
name in the Wireless network name (SSID) box. The network
name is case sensitive and cannot exceed 32 characters.
Chapter 6: Configure 61

5. If you want to decrease the data rate from Automatic, click one
of the other options available in the Data rate drop-down list
box.
6. To apply these settings, click Apply.
Security Settings
The Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station is configured to
protect your network from the most common hacker attacks and
other security risks. If necessary, you can change the default base
station settings or establish special services from the Security
section of the Base Station Management Tool.
The following sections describe the security features of the base
station and how to customize them.
Be aware that changing security settings may affect whether the
computers on your LAN are able to connect to the LAN and
Internet. You should not change the default security settings unless
you are absolutely clear about your objective in doing so.
Wireless Security (WEP)
The Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station uses wireless
security (WEP) to prevent unauthorized users from accessing data
that is being transmitted over the network. From the Base Station
Management Tool, you can:
• Enable wireless encryption.
• Change the network key or modify the encryption settings that
you established in the Setup Wizard.
• Disable wireless encryption.
When data is encrypted, it is rendered unreadable by a network
key—called a WEP key—before being transmitted between wireless
nodes. The data is readable only by computers that have the
network key to decrypt the data.
The WEP key that you establish is stored with all of your network
settings on each networked computer so that data can be
encrypted and decrypted as it is transmitted over the network. If
you change the WEP key that the base station uses, you must
ensure that each computer on your wireless network uses the
same WEP key so that it can communicate with the base station.
For information about how to change the WEP key on each
computer, see the Broadband Network Utility Help.
When you enable wireless encryption, you can choose between 64bit or 128-bit encryption. The number defines the strength of the
data encryption. The higher the number, the more difficult the data
is to decrypt.
62 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

After you select the wireless encryption strength, you can type the
WEP keys. For 64-bit encryption, you can type up to four WEP keys,
each of which consists of ten hexadecimal digits. For 128-bit
encryption, you must type one WEP key that consists of 26
hexadecimal digits. A hexadecimal digit is a number or letter in the
range 0–9 or A–F.
Although encryption may slow down the speed at which data is
transmitting, you will not observe any noticeable changes to
network behavior as a result of data encryption and decryption.
To enable wireless security
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Wireless Security.
3. Click Enable wireless security.
4. In the Encryption strength drop-down list box, click 128-bit or
leave the default setting of 64-bit.
5. If you selected 128-bit encryption, in the first Key box, type an
encryption key. If you selected 64-bit encryption, you can type
up to four WEP keys in the Key boxes.
6. If you selected 64-bit encryption, in the Key index drop-down list
box, click a key index. The key index number indicates which of
the four WEP keys will be enabled on the network.
7. To enable the wireless encryption, click Apply.
8. Update the WEP keys stored on each wireless device on your
network.
You can update wireless encryption settings for each network
device from the Broadband Network Utility. If you are using a nonMicrosoft adapter, use the software installed with that adapter to
update wireless encryption settings.
Note
If you set the Broadband
Networking Wireless Base
Station to bridging mode, the
firewall settings in the Base
Station Management Tool will
be unavailable.
Firewall Settings
The Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station provides a
firewall to protect your network against malicious transmissions.
Just as the name implies, a firewall acts as a barrier or buffer zone
between your local network and the Internet. It checks data
packets being transmitted to your network and discards any
suspicious data.
The firewall is enabled by default, but you can choose to disable it
from the Base Station Management Tool. Do not disable the
firewall unless you have a good reason to do so.
To change the firewall settings
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
Chapter 6: Configure 63

2. On the Security menu, click Firewall Settings.
3. To enable the firewall, select the Enable the integrated firewall
check box.
-orTo disable the firewall, clear the Enable the integrated firewall
check box.
4. To save your changes, click Apply.
Block Ping Commands
You can configure the firewall to discard network ping commands.
A ping command is like a short conversation between a device on
the WAN and your base station. When a device on the WAN sends
a ping command, the base station responds.
When you block ping commands, you are telling the base station
not to respond to a ping initiated from the WAN. This security
mechanism hides your network from hackers who may be pinging
random IP addresses to see where they get a response. A response
verifies your network location, and a hacker can then use this
information to send malicious communications to your network.
In general, it is a good idea to discard ping commands sent from
the WAN. The only circumstances in which blocking ping
commands may present a problem are:
• When your ISP needs to ping your network to ensure that the
connection is still valid.
• When you or another person needs to check your Internet
connection from an external network. For example, you may
want to do this to make sure that you can access your Web
server.
• When you are playing games on the Internet, and other players
need to verify your network location and connection speed.
To block ping commands
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Firewall Settings.
3. Select the Discard pings check box.
4. To save your changes, click Apply.
Network Mode
You have the option to use the base station for routing services or
as a bridge between two networks. The Broadband Networking
Wireless Base Station is set to routing mode by default.
64 Microsof t Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

When you change the base station to bridging mode, you disable
network address translation (NAT), which is an important feature of
your network. When NAT is enabled, you can use the single IP
address supplied by your ISP to connect multiple computers to the
Internet. Ordinarily, if you wanted to connect multiple computers,
you would need to arrange additional addresses (for example, by
purchasing additional accounts). NAT enables multiple clients to
share a single connection to the Internet.
If you choose to use the base station as a bridge between two
networks or segments of a network, make sure that another device
on your network (such as a base station, gateway, or router) is
providing NAT service. If you do not have a NAT service on your
network, you should lease an IP address for each computer on your
network. Be aware that each of these IP addresses will be exposed
to the Internet.
To change the base station network mode
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Network Mode.
3. Select the Bridging Mode check box.
4. To save your changes, click Apply.
Note
If you set the Broadband
Networking Wireless Base
Station to bridging mode, the
port forwarding settings in
the Base Station Management
Tool will be unavailable.
Note
Port forwarding involves the
configuration of data ports.
Do not confuse the data
ports, which are logical
programmatic elements, with
physical ports, such as the
Ethernet port on your base
station.
Port Forwarding
You can configure the ports on your base station to establish
virtual servers or run applications with special network
requirements on your network. This is called port forwarding. To
understand how port forwarding works, you must first understand
ports and their role in data transmission.
About Ports
Information passes from the Internet to computers on your network
across ports. In any network communication, there is an outbound
(destination) port and an inbound (source) port. These ports are
used in conjunction with the source and destination IP addresses
to establish a connection between two networked computers.
There are many different types of data transmitted across a
network, and certain types of data must pass out of certain ports.
The data type is recognized by the protocol, or rules, that it follows.
For example, the e-mail messages that you send may follow one
type of protocol, whereas the games that you play may follow
another protocol. Typically, the data protocol determines the ports
to which the data is passed.
The Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station opens the ports
for certain applications automatically when a client on your local
network transmits data to the WAN.
Chapter 6: Configure 65

This enables transmission of some of the more common data sent
to and from the Internet, such as e-mail messages and Web
browser data.
To run applications with special network requirements or to
establish a virtual server, however, you may need to change the
port configuration on the base station. You can configure, or
forward, ports from the Base Station Management Tool.
Application-Triggered Port Forwarding
Some applications, such as Internet games and videoconferencing,
require multiple ports for data transmission. File Transfer Protocol
(FTP) data, for example, is sent from your computer to one port
and returns to another port. These multiple port transmissions may
cause problems when the base station is set to routing mode so
that NAT is enabled on your base station, because the NAT service
anticipates that data sent to one port will return to the same port.
The Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station has already
been configured to accommodate some common application
protocols that require multiple ports, including FTP, Simple Mail
Transfer Protocol (SMTP), and Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3).
To configure port forwarding for other applications that require
multiple ports, you must specify the outbound (destination) port to
which data following a particular protocol will be sent, and the
inbound (source) port or ports to which related data will return.
Essentially, you are telling the base station how to direct traffic
across the networks.
The inbound ports that you specify will open only when data is sent
to the corresponding outbound port. These ports will close again
after a certain amount of time has elapsed with no data sent to
the inbound port. You can set ranges of ports, multiple ports, and
combinations of single and multiple ports for the inbound ports.
You can configure the base station to accommodate up to 20
applications. To identify the protocol that an application uses and
the ports to which the data should be sent, consult the
documentation for that application.
To establish application-triggered port forwarding
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Port Forwarding, and then click
Set up application-triggered port forwarding.
3. In the available Description box, type a description of the
application that you want to enable.
4. In the Outbound port box, type the number of the outbound
port. The outbound port should be one number between 0 and
65535. To determine which port the application uses, consult
the documentation for the application.
66 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

5. In the Trigger type drop-down list box, click the trigger type. The
trigger type should be specified in the documentation for the
application.
6. In the Inbound port(s) box, type the inbound port. The inbound
port can be a single port or a comma-separated list of ports or
port ranges. For example, you could type 4-25, or 243, or 10,
24-50, 74. You are limited to 256 characters.
7. In the Public type drop-down list box, click the public type. The
public type should be specified in the documentation for the
application.
8. Select the Enable check box.
9. To save the changes you have made, click Apply, or to delete
the changes, click Cancel.
If an application does not function correctly after you enable
multiple ports, check the documentation for the application to
verify that you are enabling the correct ports to open. If you have
set the correct ports to open and the application still does not
function properly, you may need to establish a DMZ on one of the
client computers on your network to run the application. For
information about establishing a DMZ, see “Virtual Demilitarized
Zone” in this chapter.
Persistent Port Forwarding
When you host a server on your network—for example, a Web or
FTP server—you must configure the base station to perform
persistent port forwarding.
Persistent port forwarding is similar to application-triggered port
forwarding in that you are opening inbound ports to allow particular
types of data or data requests to be sent from the Internet to one
of the networked computers. The difference is that you are opening
these inbound ports permanently, rather than configuring them to
open only when there is data sent to an outbound port. In addition,
you are directing the data sent to that port to a particular computer
on your local network.
For example, if you set up a Web server on one of the computers
on your network, you must direct unsolicited requests sent to
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) Port 80, which handles
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) or Web data, to that computer.
An unsolicited request is any data communication that is not
initiated by a computer on your local network.
Although not required, it is recommended that you have a static
(fixed) IP address to host any type of server on your network.
To establish persistent port forwarding, you will need the following
information:
Chapter 6: Configure 67

• The IP address of the server computer on your local network. To
determine the IP address assigned to the computer that you will
use as a server, check the DHCP client list on the Home page of
the Base Station Management Tool.
• The inbound and private port numbers and protocol that
correspond to the type of data that your server handles.
Some of the common TCP inbound ports include:
• HTTP Port 80
• FTP Port 21
• Telnet Port 23
• POP3 Port 110
To configure persistent port forwarding
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Port Forwarding, and then click
Set up persistent port forwarding.
3. In the Description box, type a description of the server field.
(This step is optional.)
4. In the Inbound port box, type the inbound port to which data
packets sent from the Internet to the server will be passed. The
inbound port can be a single port or a comma-separated list of
ports or port ranges. For example, you could type 4-25, or 243,
or 10, 24-50, 74. You are limited to 256 characters.
5. In the Type box, select the protocol (UDP or TCP) for the port.
6. In the Private IP address box, type the private IP address of the
client computer that is hosting the server.
7. In the Private port boxes, type the private port on the server
that the data will be sent to. To identify the private port number,
consult the documentation for your server software.
8. To save the changes you have made, click Apply, or to delete
the changes, click Cancel.
Note
If you set the Broadband
Networking Wireless Base
Station to bridging mode, the
virtual demilitarized zone
settings in the Base Station
Management Tool will be
unavailable.
Virtual Demilitarized Zone
In certain situations, you may want to set up a virtual demilitarized
zone (DMZ) on one of the clients on your network. When you
establish a DMZ, you essentially open all inbound ports and direct
the base station to forward certain inbound data packets (those
that are not in response to a transmission initiated by a LAN client
and not handled through application-triggered or persistent port
forwarding) to a particular computer on your LAN. This computer
becomes the DMZ host.
68 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

A DMZ host is useful for experimenting with new games on the
Internet or for setting up a server on your network before you know
which ports to open for that server. A DMZ, however, should be
used only in very specific and finite situations. The computer that
hosts the DMZ is fully exposed to the Internet, and is thus
susceptible to malicious attacks and unauthorized access.
Because the computer is a virtual DMZ behind the base station, as
opposed to a real DMZ out on the Internet, it has access to the
other computers on your LAN. If a hacker were to upload a virus to
the virtual DMZ, the virus could spread to all the computers on
your network.
Because the virtual DMZ that you establish is behind the base
station NAT, the IP address for the DMZ is not public. This means
that the DMZ can resolve most, but not all, connection problems.
To establish a virtual DMZ
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Virtual DMZ (Demilitarized Zone).
3. Select the Enable check box.
4. In the text box, type the IP address assigned to the computer
that will host the virtual DMZ. To determine the IP address, see
the DHCP client list on the Home page of the Base Station
Management Tool.
5. To save the changes you have made, click Apply, or to delete
the changes, click Cancel.
Note
If you set the Broadband
Networking Wireless Base
Station to bridging mode, the
MAC filtering settings in the
Base Station Management tool
will be unavailable.
MAC Filtering
You can increase the security on your network by using MAC
filtering. MAC filtering enables you to control access to network
resources, including your Internet connection and shared files and
printers. You can configure the base station to permit or deny a
client access to network resources based on the MAC address of
the adapter that the client uses.
If you want to use MAC filtering, the first step is to enable the type
or types of MAC address control that you want. The two types of
MAC address control are connection control and association
control.
Connection Control
You can use connection control to control which wired and wireless
clients will be able to connect to the base station and have access
to the Internet and all network resources.
When a wired client cannot connect to the base station, it can
communicate with other clients on the wired local network, but it
cannot:
Chapter 6: Configure 69

• Connect to the Internet.
• Communicate with wireless clients on the network.
When a wireless client is denied association control, it cannot
connect to the base station, so connection control is irrelevant. For
information about using MAC filtering to control the access of
wireless clients, see “Association Control.”
To enable connection control
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click MAC Filtering.
3. Select the Enable connection control check box.
4. If you do not want unspecified clients to connect to the base
station, in the drop-down list box, click Deny. In this case, any
client whose MAC address is not listed in the MAC Address table
will not be able to connect to the base station or access the
Internet.
5. If you clicked Deny in step 4, in the MAC Address table, specify
the MAC address of any clients that you want to connect to the
base station, and then select the Allow Connection check box.
6. To save your changes, click Apply.
When you enable connection control, be sure you do not prohibit
your own computer from connecting to the base station. If you deny
unspecified MAC addresses from connecting, type the MAC
address of your adapter into the MAC Address table and select the
connection control check box.
If you do block your own access to the base station, you must
restore the factory default settings by using the reset button on the
physical device, and then reconfigure the base station. For
information about how to do this, see “Resetting the Base Station”
in Chapter 1.
Association Control
You can use association control to control which wireless clients
can establish a wireless link with the base station. Association
control is not applicable to wired clients.
When a wireless client is allowed to associate with the wireless
network and connect to the base station, it has full access to the
Internet and network resources.
When a wireless client is allowed to associate with the wireless
network, but not connect to the base station, it can communicate
with other clients on the wireless network, but it cannot
communicate with wired clients on the network or connect to the
Internet.
70 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

When a wireless client is not allowed to associate with the wireless
network, it cannot:
• Connect to the base station.
• Communicate with any wired or wireless clients on the network.
• Connect to the Internet.
To enable association control
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click MAC Filtering.
3. Select the Enable association control check box.
4. If you do not want unspecified wireless clients to establish a
wireless link with the base station, in the drop-down list box,
click Deny. In this case, any wireless client whose MAC address
is not listed in the MAC Address table will not be able to
associate with the base station, access the Internet, or
communicate with clients on the network.
5. If you clicked Deny in step 4, in the MAC Address table, specify
the MAC address of any wireless clients that you want to
connect to the base station, and then select the Allow
Association check box.
6. To save your changes, click Apply.
For more information about MAC filtering options, see the
Broadband Network Utility Help.
Note
If you set the Broadband
Networking Wireless Base
Station to bridging mode, the
client filtering settings in the
Base Station Management
Tool will be unavailable.
Client Filtering
You can use client filtering to control the Internet access of each
client on your network. This feature is particularly useful if, for
example, you want to restrict the time that your children spend
surfing the Web.
To configure client filtering, you must have the following
information:
• The private IP address assigned to the client computer. To
determine the IP address assigned to the client computer,
check the DHCP client list on the Home page of the Base
Station Management Tool.
• The ports for the type of application data to which you want to
control access.
For example, if you want to control Web browsing, you specify TCP
Port 80 on client 192.168.2.XX.
It is recommended that you assign static IP addresses to each of
the client devices whose access to the Internet you want to control.
Chapter 6: Configure 71

To enable client filtering
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Client Filtering.
3. In the appropriate box, type the IP address of the client device
whose access to the Internet you want to control.
4. In the Outbound port(s) boxes, type the outbound port protocol
and port number for the data that you want to control.
5. In the appropriate boxes, specify the date and time range when
you want to block access to this data. If you want to filter access
on a particular day, for example, every Sunday, enter the same
time and the same date for the start and end period. If you want
to block access all the time, click Always.
6. Select the Block check box, and then click Apply to apply the
client filtering.
Base Station Log
You can access the base station log for your network from the
Security section of the Base Station Management Tool. This log
records general base station activity and time stamps each log file
entry. If you have any concerns about unusual activity on your
network, review the base station log.
The base station log can maintain up to 256 lines of data. When
the base station log reaches maximum capacity, the base station
deletes the oldest log entries.
To view the base station log
1. Open the Base Station Management Tool, and then click
Security.
2. On the Security menu, click Base Station Log.
72 Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station User’s Guide

7
troubleshooting.
Basic Troubleshooting
This chapter will help you solve the most common installation and
setup problems that you may have with the Microsoft
Networking Wireless Base Station. Issues are covered for the
following areas:
• Software
• Hardware
• Networks
• Internet connections
If the problem you are experiencing is not covered in this chapter,
you can find more troubleshooting information in Broadband
Network Utility Help, or on the Microsoft Broadband Networking
Web site at http://www.microsoft.com/broadbandnetworking/.
Software
This section will help you solve the most common installation and
setup problems for the Microsoft Wireless Base Station software.
®
Broadband
Note
For computers that are
running Microsoft
Windows 2000 or Microsoft
Windows XP, you must be
logged on as an administrator
to perform installations. If you
do not have administrative
rights, see Windows Help.
I’m having problems running the Broadband Network Utility
Setup Wizard.
• Verify that your desktop or notebook computer conforms with
the minimum system requirements for a Microsoft Wireless
Base Station.
During a typical installation, the Broadband Network Utility is
automatically installed when you set up your network; however,
if you do not have the minimum system requirements, the
software may not install fully or at all. If you are using a
computer that is running Microsoft Windows
Broadband Network Utility must be installed for WEP support.
If WEP is not supported on one of the computers, then the
network and other devices on the network cannot communicate
with the computer that does not support WEP.
• Turn off any virus detection software.
• Make sure that you are installing the software before installing
the hardware.
®
2000, the

I’m having problems running an online application.
• This might be due to the firewall feature of the base station. To
configure the base station to allow specific applications to
function through the firewall, see Chapter 6.
I’m getting an error message during installation or setup.
Follow the instructions in the error message screen to try to solve
the problem. The following table contains more information about
the error messages that can appear, including possible causes and
solutions for the errors. Click Help on the error message screen for
more information.
Error message Details
Setup was unable to detect For a wired connection, make sure that the
your base station cable connections are not loose, the correct
type of Ethernet cable (straight-through versus
crossover) is being used, cables are
connected to the correct ports, and the
base station is receiving power.
For a wireless connection, make sure that your
broadband modem is connected to the base
station To Modem port through an Ethernet
cable, the base station power adapter is
securely connected to an electrical outlet,
there is no interference from other devices,
and that the network settings are correct.
If none of the above fix the problem, tr y
restoring the base station to factory defaults
by pressing the Reset button for at least 5
seconds. For more details about restoring the
base station to factory defaults, see
Chapter 1.
Action: Click Help on the error message
screen.
Setup was unable to detect Make sure that the cable connections are not
your network adapter loose, that cards are properly seated, and that
74 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide
the adapter is receiving power and is
connected to a USB port.
If none of the above fix the problem, tr y
connecting the adapter to another USB
port or seating the PC Card in another slot if
available.
Action: Click Help on the error message
screen.

continued
Error message Details
Setup was unable to detect a Make sure your broadband modem is turned
connection to the Internet on and working.
Action: Click Help on the error message
screen.
Hardware
This section will help you solve the most common installation and
setup problems for the Microsoft Wireless Base Station.
My computer is not detecting my base station.
• Make sure that both the base station and the computer that it
is connected to with a wired connection are powered, and that a
link light is illuminated on each device. For more information
about the indicator lights on the base station, see Chapter 1.
• Make sure that the correct ends or the correct cables in your
network are securely fastened to the correct ports.
For more information about the indicator lights on the base
station, see Chapter 3.
Check all of the following connections: power cables, cables
between the base station and computers, and cables between
the base station and the modem.
Incomplete or incorrect connections prevent devices from
communicating with each other and therefore generate
problems in your network. By checking the physical connections,
you can determine if the problem is associated with network
settings.
Ethernet cables look very similar to standard residential
telephone cables. However, Ethernet cables have a wider and
thicker connector (RJ-45) on the end than residential telephone
connectors (RJ-11). Although a standard residential telephone
connector can be inserted into an Ethernet port, the port will
not function and the cable may damage your Ethernet device.
My broadband modem has a built-in router that conflicts with
my Microsoft Wireless Base Station.
• Turn off Network Address Translation (NAT) on the modem.
If you have more than one component that is running NAT on
your network, some of your applications may not connect to the
Internet, some features in certain applications may not work,
and some components may appear as unavailable in the
Broadband Network Utility. For instructions for turning off NAT
on your modem, see the documentation for your modem.
Chapter 7: Troubleshooting 75

• Enable bridging mode in the base station.
For more information about bridging mode and how to enable it,
see Chapter 6.
Networks
This section will help you solve the most common installation and
setup problems for a Microsoft Wireless Base Station on a
network.
I get all the way through setup and it says it was successful, but
some network tasks do not work.
• If you cannot access the Internet, open the Broadband Network
Utility and check the status of the connection between the base
station and the modem. For more troubleshooting information
about this problem, see Broadband Network Utility Help.
• If you cannot access files or folders that have been made
available to the network, make sure that you are logged on to
your computer and the network, and that the files or folders
have been made available to you. For more information about
making files and folders available to the network and how to
verify access privileges, see Chapter 4. For more
troubleshooting information about this problem, see Broadband
Network Utility Help.
• If you cannot print to a network printer, make sure that the
printer has been made available to the network. For more
information about making a printer available to the network and
verifying network availability of a printer, see Chapter 4. For
more troubleshooting information about this problem, see
Broadband Network Utility Help.
• If you cannot use your e-mail application the same way as you
did before installing the base station and the Broadband
Network Utility, make sure that your POP3 and news settings in
your e-mail application are correct.
In your e-mail application, verify that you are using a full Internet
designation, such as pop3.email.msn.com, for your mail client
rather than a local designation, such as mail. For more
information about obtaining a full Internet designation for your
ISP, see the ISP documentation. For more troubleshooting
information about this problem, see Broadband Network Utility
Help.
My network isn’t working.
• Verify that the base station is plugged into a power source.
• Verify that the correct cables and cards are securely fastened to
the correct ports.
76 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

• Verify that you have the correct network settings.
Incorrect network settings will inhibit networked computers
from communicating properly. For example, a computer may try
to detect a network by using the wrong name or by using a
different communication protocol than all of the other
computers on the network. You can view and modify network
settings in the Broadband Network Utility.
My wireless network connection works occasionally.
• Verify that your computer is within the recommended range of
the base station and that there is no interference from other
wireless devices.
Signals that are transmitted between the base station and a
wireless adapter or PC Card are affected by interference from
other wireless devices—including 2.4 GHz cordless phones,
microwave ovens, and neighboring wireless networks. Move the
other devices as needed, and refrain from using them while you
are using the network. Alternatively, you can move the network.
To minimize interference from another wireless network, try
changing channels. For more information about changing your
network channel, see Chapter 6.
• Verify that other devices on your network that may be running
NAT and/or DHCP servers have NAT and DHCP servers
disabled.
Devices such as your modem may have NAT and/or Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers running at the same
time as the base station. If this is the case, the devices will
interfere with each other and cause intermittent failures. For
instructions for disabling NAT and DHCP servers on the other
device, see the documentation for the other device.
My computer is within the recommended range of the base
station; however, it can’t detect the network.
• Verify that physical barriers and other forms of interference are
limited.
Physical barriers between the computer and the base station,
and interference from microwave ovens and other wireless
devices—including 2.4 GHz cordless phones and neighboring
wireless networks—affect the signals that are transmitted
between the base station and a wireless adapter or PC Card. If
this occurs, move your network components closer to the base
station.
Chapter 7: Troubleshooting 77

Internet Connections
This section will help you solve the most common installation and
setup problems for sharing an Internet connection.
My computer can’t find the Internet.
• Check the IP address in network settings on another computer
in the network.
The IP address is available in the Broadband Network Utility.
If your computer can’t find the Internet, it may be looking for the
wrong IP address. Although the IP address may have been
correct previously, if you changed ISPs, then all of the IP
addresses in your network changed as well. See the
documentation that you received from your ISP for the correct IP
address.
• If you are using Microsoft Internet Explorer, verify that the
Internet Explorer proxy setting is turned off.
For more information about the Internet Explorer proxy setting,
see Internet Explorer Help.
• Check the status of the connection to the base station and to
the Internet in the Broadband Network Utility.
If you are still unable to resolve the problem, see Broadband
Network Utility Help.
My shared Internet connection is slow.
• Verify that your computer is within the recommended range of
the base station. For more information about the recommended
range, see Chapter 1.
Factors that affect shared Internet connection speed:
• The number of computers that are sharing the connection
• The range between your computer and the base station
• Interference from other wireless devices
78 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

reference.
Visit Us on the Web
Please visit our Web site at http://www.microsoft.com/
broadbandnetworking/.
Click Help in the Broadband Network Utility
Click Help in the Microsoft® Broadband Network Utility for detailed
troubleshooting information.
Technical Support
Product Name: Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless
Base Station
Support Info http://support.microsoft.com/directory/
Online: productsupportoption.asp.
In Canada, visit
http://www.microsoft.ca/support/.
Online Support: Work with a Microsoft Support Professional
over the Internet. Submit your issue online:
http://support.microsoft.com/directory/
onlinesr.asp.
Phone Support: Toll-free support for U.S. customers:
(800) 936-3900. For customers in Canada:
(800) 668-7975. These numbers are only for
support of Microsoft Broadband Networking
products. Please do not use these phone
numbers for support of other Microsoft products.
TTY Users: Microsoft text telephone (TTY/TDD) services are
available at (425) 635-4948 in Washington
state or (800) 892-5234 in the U.S. Call
(905) 568-9641 in Canada.
Worldwide: The support terms listed here are available in the
United States only.
Support outside the United States may vary.
Please visit http://support.microsoft.com/
default.aspx?scid=/international.aspx?
for regional contact details.
Conditions: Microsoft’s support services are subject to
then-current prices, terms, and conditions,
which are subject to change without notice.

Regulatory Information
United States Radio and TV Interference Regulations
This device complies with Part 15 of the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
The Microsoft hardware device(s) that accompanies this software can radiate radio frequency (RF) energy. If not installed
and used in strict accordance with the instructions given in the printed documentation and Online User’s Guide, the device
may cause harmful interference with other radio-communications devices (for example AM/FM radios, televisions, baby
monitors, cordless phones, etc.). Any cable that is connected to the device must be a shielded cable that is properly
grounded. There is, however, no guarantee that RF interference will not occur in a particular installation.
Your Microsoft hardware device has been tested, and it complies with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance
with the specifications in Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful RF interference in a residential installation.
To determine if your hardware device is causing interference to other radio-communications devices, disconnect the device
from your computer. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the device. If the interference continues after you
disconnect the hardware device, turn the computer off and then on again. If the interference stopped when the computer
was off, check to see if one of the input/output (I/O) devices or one of the computer’s internal accessory boards is causing
the problem. Disconnect the I/O devices one at a time and see if the interference stops.
If this hardware device does cause interference, try the following measures to correct it:
• Relocate the antenna of the other radio-communications device (for example AM/FM Radios, televisions, baby monitors,
cordless phones, etc) until the interference stops.
• Move the hardware device farther away from the radio or TV, or move it to one side or the other of the radio or TV.
• Plug the computer into a different power outlet so that the hardware device and radio or TV are on different circuits
controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.
• If necessary, ask your computer dealer or an experienced radio-TV technician for more suggestions. You may find helpful
information in the booklet “The Interference Handbook” (1995), published by the FCC. The booklet is available from the
FCC at 1-888-CALL FCC or at http://www.fcc.gov/cib/Publications/tvibook.html.
Note
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by Microsoft could void the user’s authority to operate this device.
For use with UL Listed and GS approved personal computers.
Not intended for use in machinery or industrial applications.
Tested to comply with FCC standards. For home and office use.
Model Number: MN-100, MN-110, MN-120, MN-130, MN-150, MN-500, MN-510, MN-520.
In addition, the following models have been approved under FCC certification rather than under the FCC Declaration of
Conformity Process:
MN-500, FCC ID: HEDACC300568;
MN-510, FCC ID: HEDACCWN330168;
MN-520, FCC ID: HEDACC3501D68
Microsoft Corporation
One Microsoft Way
Redmond, WA 98052-6399.
(800) 426-9400 (United States)
(800) 933-4750 (Canada)
Canadian Radiocommunication Regulations
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003
The term ‘’IC:‘’ before the certification/registration number only signifies that the Industry Canada technical specifications
were met.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme aux normes NMB-003 du Canada.
L’expression «IC:» avant le numéro d’homologation/enregistrement signifie seulement que les spécifications techniques
d’Industrie Canada ont été respectées.
80 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Limited Warranty
PLEASE READ THIS MANUFACTURER’S GUARANTEE CAREFULLY TO UNDERSTAND YOUR RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS
MANUFACTURER’S GUARANTEE AND LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
NOTE: The following guarantee is not restricted to any territory and does not affect any statutory rights that you may have.
The term “Hardware Device” means the enclosed Microsoft Hardware Device. This Manufacturer’s Guarantee does not cover
your data, or any separate software, whether or not packaged or included with the Hardware Device.
MICROSOFT GUARANTEE. Microsoft guarantees (this “Guarantee”) that on the day you receive the Hardware Device and for
the next two (2) years thereafter (a) the Hardware Device will be substantially free from defects in materials and
workmanship, and (b) any support services provided by Microsoft will be substantially as described in applicable written
materials provided to you by Microsoft, and Microsoft support engineers will use reasonable efforts, care and skill to solve
any problem issues. In the event that the Hardware Device fails to comply with this Guarantee, Microsoft shall either, at
Microsoft’s option, (a) repair or replace the Hardware Device or (b) return the price you paid for the Hardware Device (if any),
provided that you return the Hardware Device to Microsoft with a copy of your receipt of purchase. You may exercise this
remedy without charge, except that you are responsible for any expenses you may incur. This Guarantee is void if failure of
the Hardware Device results from any accident, abuse or misapplication. Any replacement Hardware Device shall be
guaranteed for the remainder of the original Guarantee period or thirty (30) days, whichever is longer. Microsoft shall not be
liable for any loss or damage that you could have reasonably avoided, for example, by backing up your software and files
regularly.
EXCLUSION OF ALL OTHER TERMS. YOU AGREE THAT THIS GUARANTEE IS YOUR SOLE GUARANTEE IN RELATION TO THE
HARDWARE DEVICE AND ANY SUPPORT SERVICES. MICROSOFT AND ITS SUPPLIERS MAKE NO OTHER GUARANTEES OR
WARRANTIES WITH RESPECT TO THE HARDWARE DEVICE, THE SUPPORT SERVICES AND ANY PRODUCT MANUAL(S) OR
OTHER WRITTEN MATERIALS THAT ACCOMPANY THE HARDWARE DEVICE. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY
APPLICABLE LAW AND SUBJECT TO THIS GUARANTEE, MICROSOFT AND ITS SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES,
CONDITIONS AND OTHER TERMS, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED (WHETHER BY STATUTE, COMMON LAW, COLLATERALLY
OR OTHERWISE), INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY (IF ANY) IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY, SATISFACTORY QUALITY AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, LACK OF VIRUSES, LACK OF
NEGLIGENCE, LACK OF WORKMANLIKE EFFORT, TITLE, AUTHORITY, OR NONINFRINGEMENT WITH RESPECT TO THE
HARDWARE DEVICE, THE SUPPORT SERVICES AND THE PRODUCT MANUAL(S) OR OTHER WRITTEN MATERIALS THAT
ACCOMPANY THE HARDWARE DEVICE. ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES THAT ARE NOT DEEMED EXCLUDED ARE LIMITED TO
THE ORIGINAL GUARANTEE PERIOD OR TO THE SHORTEST PERIOD PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, WHICHEVER IS
GREATER.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW AND EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
THIS GUARANTEE, MICROSOFT AND ITS SUPPLIERS SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
(INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, DAMAGES FOR
LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF BUSINESS INFORMATION OR OTHER PECUNIARY
LOSS, FOR PERSONAL INJURY OR FOR FAILURE TO MEET ANY DUTY INCLUDING GOOD FAITH OR REASONABLE CARE, OR
FOR NEGLIGENCE) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE HARDWARE DEVICE, EVEN IF MICROSOFT HAS
BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN ANY CASE MICROSOFT’S ENTIRE LIABILITY UNDER ANY
PROVISION OF THIS AGREEMENT SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE AMOUNT ACTUALLY PAID BY YOU FOR THE HARDWARE
DEVICE. THESE LIMITATIONS DO NOT APPLY TO ANY LIABILITIES THAT CANNOT BE EXCLUDED OR LIMITED BY
APPLICABLE LAWS. THE FOREGOING LIMITATIONS, EXCLUSIONS AND DISCLAIMERS SHALL APPLY TO THE MAXIMUM
EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, EVEN IF ANY REMEDY FAILS ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
REGISTRATION. You need not return the registration card for this Guarantee to be effective.
BENEFICIARY. To the extent allowed by applicable law, this Guarantee is only made to you, the first user of the Hardware
Device, and there are no third party beneficiaries of this Guarantee. It is not intended for and does not apply to anyone else
(except as required by law).
GOVERNING LAW. If you acquired the Hardware Device in the United States of America, the laws of the State of Washington,
U.S.A., apply to this agreement. If you acquired this Hardware Device in the European Union, Iceland, Norway or Switzerland
then local laws apply. If you acquired this product in Canada, except where expressly prohibited by local laws, the laws in
force in the Province of Ontario, Canada apply to this agreement and each of the parties hereto irrevocably attorns to the
jurisdiction of the courts of the Province of Ontario and further agrees to commence any litigation which may arise hereunder
in the courts located in the Judicial District of York, Province of Ontario.
If you acquired this Hardware Device outside of the countries listed above, then local laws may apply.
QUESTIONS. Should you have any questions concerning this agreement, or if you desire to contact Microsoft for any reason,
please use the address information enclosed in this Hardware Device to contact the Microsoft subsidiary serving your
country, or visit Microsoft on the World Wide Web at http://www.microsoft.com/.
Reference 81

Limited Warranty Continued
VEUILLEZ VOUS ASSURER QU’APRÈS UNE LECTURE ATTENTIVE VOUS AYEZ BIEN COMPRIS L’ENSEMBLE DES DROITS ET
LIMITATIONS EXPOSÉES DANS CETTE GARANTIE DU FABRICANT
GARANTIE ET EXCLUSION DE RESPONSABILITÉ DU FABRICANT
REMARQUE : La garantie ci-dessous n’est pas limitée à un territoire particulier, et n’influence en aucune manière les droits
légaux dont vous disposez.
« Dispositif matériel » désigne le dispositif matériel Microsoft ci-inclus. Cette Garantie du Fabricant ne s’applique pas à vos
données ou aux logiciels séparés, qu’ils soient ou non emballés ou inclus avec le Dispositif matériel.
GARANTIE MICROSOFT. Microsoft garantit (la « Garantie ») que pour une période de 2 ans à compter de la date de
réception : (a) le Dispositif matériel sera, pour l’essentiel, exempt de vices matériels et de fabrication ; et (b) tout service
d’assistance fourni par Microsoft sera, pour l’essentiel, conforme à la documentation imprimée applicable fournie par
Microsoft, et les ingénieurs du service technique de Microsoft feront des efforts raisonnables pour résoudre toute difficulté
technique. Dans l’éventualité où le Dispositif matériel manque d’être conforme aux stipulations de la présente Garantie,
Microsoft pourra, au choix de Microsoft, (a) réparer ou remplacer le Dispositif matériel ; ou (b) rembourser le prix que vous
avez payé pour le Dispositif matériel (le cas échéant), à condition que le Dispositif matériel soit retourné à Microsoft avec
une copie de votre reçu. Vous êtes libre d’exercer ce recours sans frais, à l’exception que vous êtes seul responsable des
dépenses que vous encourrez. Cette Garantie est nulle si le défaut du Dispositif matériel est causé par un accident, un
traitement abusif ou une mauvaise application. Tout Dispositif matériel de remplacement sera garanti pour le reste de la
période de garantie initiale ou pour trente (30) jours, selon la plus longue de ces périodes. Microsoft n’est en aucun cas
responsable des pertes et dommages que vous auriez pu raisonnablement éviter en sauvegardant régulièrement vos
logiciels et vos données, par exemple.
EXCLUSION DE TOUTES AUTRES CONDITIONS. VOUS RECONNAISSEZ QUE LA GARANTIE CI-DESSUS EST VOTRE SEUL
RECOURS EN CE QUI CONCERNE LE DISPOSITIF MATÉRIEL ET LES SERVICES D’ASSISTANCE. MICROSOFT ET SES
FOURNISSEURS NE FONT AUCUNE AUTRE GARANTIE QUANT AU DISPOSITIF MATÉRIEL, AUX SERVICES D’ASSISTANCE ET AUX
MANUELS DE PRODUIT OU TOUTE AUTRE DOCUMENTATION IMPRIMÉE ACCOMPAGNANT LE DISPOSITIF MATÉRIEL. DANS
TOUTE LA MESURE PERMISE PAR LA RÉGLEMENTATION APPLICABLE ET CONFORMÉMENT À LA GARANTIE, MICROSOFT ET
SES FOURNISSEURS EXCLUENT TOUTE GARANTIE ET AUTRES CONDITIONS, EXPRESSES OU IMPLICITES (PAR
JURISPRUDENCE, DROIT COUTUMIER, SECONDAIRE OU AUTRE), Y COMPRIS, DE MANIÈRE NON LIMITATIVE, TOUTE GARANTIE
IMPLICITE DE QUALITÉ, D’ADÉQUATION À UN USAGE PARTICULIER, D’ABSENCE DE VIRUS, DE NÉGLIGENCE ET DE DÉFAUT DE
FABRICATION, DE TITRE, D’AUTORITÉ OU D’ABSENCE DE CONTREFAÇON EN CE QUI CONCERNE LE DISPOSITIF MATÉRIEL, LES
SERVICES D’ASSISTANCE, LES MANUELS DE PRODUIT ET AUTRES DOCUMENTS IMPRIMÉS ACCOMPAGNANT LE DISPOSITIF
MATÉRIEL. TOUTE GARANTIE IMPLICITE QUI N’EST PAS EXCLUE EST LIMITÉE À LA PÉRIODE DE GARANTIE D’ORIGINE OU À
LA PLUS COURTE PÉRIODE PERMISE PAR LA RÉGLEMENTATION APPLICABLE, SI CELLE-CI EST PLUS LONGUE.
EXCLUSION DE RESPONSABILITÉ. DANS TOUTE LA MESURE PERMISE PAR LA RÉGLEMENTATION APPLICABLE ET SAUF
STIPULATION CONTRAIRE DANS CETTE GARANTIE, MICROSOFT OU SES FOURNISSEURS NE POURRONT EN AUCUN CAS
ÊTRE TENUS RESPONSABLES DE TOUT DOMMAGE DE QUELQUE NATURE QUE CE SOIT (NOTAMMENT ET DE MANIÈRE
NON LIMITATIVE LES DOMMAGES SPÉCIAUX, ACCESSOIRES, INCIDENTS OU INDIRECTS POUR PERTES DE BÉNÉFICES,
INTERRUPTIONS D’ACTIVITÉ, PERTES D’INFORMATIONS OU AUTRES PERTES PÉCUNIAIRES, POUR PRÉJUDICES
CORPORELS OU MANQUEMENT À TOUTE OBLIGATION (NOTAMMENT L’OBLIGATION DE BONNE FOI ET DE DILIGENCE), OU
POUR DES ACTES DE NÉGLIGENCE, RÉSULTANT DE L’UTILISATION OU DE L’IMPOSSIBILITÉ D’UTILISER LE DISPOSITIF
MATÉRIEL, MÊME SI MICROSOFT OU UN QUELCONQUE FOURNISSEUR A ÉTÉ PRÉVENU DE L’ÉVENTUALITÉ DE TELS
DOMMAGES. EN TOUT ÉTAT DE CAUSE, LA RESPONSABILITÉ TOTALE DE MICROSOFT AU TITRE DE TOUTE STIPULATION
DU PRÉSENT CONTRAT NE SAURAIT EXCÉDER LE MONTANT QUE VOUS AVEZ EFFECTIVEMENT PAYÉ POUR LE DISPOSITIF
MATÉRIEL. CES LIMITATIONS NE S’APPLIQUENT À AUCUNE OBLIGATION QUI NE PEUT ÊTRE EXCLUSE OU LIMITÉE PAR
LES LOIS EN VIGUEUR. LES PRÉSENTES LIMITATIONS ET EXCLUSIONS DEMEURERONT APPLICABLES DANS TOUTE LA
MESURE PERMISE PAR LA RÉGLEMENTATION EN VIGUEUR, QUAND BIEN MÊME UN QUELCONQUE RECOURS NE
PRODUIRAIT PAS D’EFFET.
ENREGISTREMENT. Il n’est pas nécessaire de renvoyer la carte d’enregistrement pour faire valoir la présente Garantie.
BÉNÉFICIAIRE. Dans la mesure permise par la réglementation applicable, la présente Garantie s’applique uniquement à
vous, le premier utilisateur du Dispositif matériel, et aucun tiers ne peut devenir le bénéficiaire de cette Garantie. La
Garantie n’est pas destinée et ne s’applique pas à d’autres personnes que vous (à moins que cela ne soit requis par la loi).
DROIT APPLICABLE. Si vous avez acquis le Dispositif matériel aux États-Unis, ce CLUF est régi par les lois de l’État de
Washington, États-Unis d’Amérique. Si le Dispositif matériel a été acquis en Union Européenne, en Islande, en Norvège ou en
Suisse, le droit local pourra, le cas échéant, s’appliquer. Si vous avez acquis le Dispositif matériel au Canada, les lois en
vigueur de la province d’Ontario, Canada, s’appliqueront à ce contrat et chacune des parties aux présentes accepte les
tribunaux de la province d’Ontario, et accepte d’entamer tout litige lié aux présentes dans les tribunaux situés dans le
District juridique de York, province d’Ontario.
Si vous avez acquis le Dispositif matériel en dehors des pays énoncés ci-dessus, le droit local pourra, le cas échéant,
s’appliquer.
QUESTIONS. Pour toute question relative à ce contrat, ou si vous souhaitez contacter Microsoft pour toute autre raison,
veuillez vous reporter à l’adresse fournie dans la documentation accompagnant ce Dispositif matériel pour contacter la
filiale Microsoft desservant votre pays, ou consulter le site Internet de Microsoft à http://www.microsoft.com/.
82 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

Technical Specifications
Base Station
Standards IEEE 802.11b, Wi-Fi compliant, TCP/IP, NAT, DHCP, UDP, FTP, PPPoE, PPTP,
Ports LAN: • Four 10/100 Mbps Switched Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 ports
Data Rate 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps with Auto-fallback support
Modulation CCK, DBPSK, DQPSK
Range Data Rate Open Environment Closed Environment
Frequency Range ISM Band (2.400 to 2.4835 GHz)
Channels 1-11 United States, Canada
Wireless Security (WEP) Off, 64-bit, and 128-bit
Indicators LAN (1-4): Link/Activity LED for each port
Transmit Power Greater than +15 dBm; Less than +20 dBm
Operating Temperature 0 to 40 deg C
Storage Temperature -20 to 60 deg C
Humidity 10 to 95 percent non-condensing
Emissions FCC Part 15 Class B; Canada RSS-210
Safety UL
Physical Dimensions 1.2" x 5.3" x 6.8" (30.5 x 134.6 x 172.7 mm)
Weight 10.55 oz (299 g) without power supply
L2TP, HTTP, DNS, IPSec/VPN Pass through
• RJ-45 Connectors
• UTP/STP CAT 3 or better cabling required for 10-BaseT operation
• UTP/STP CAT 5 or better required for 100-BaseTX operation
WAN: • One 10 Mbps Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 port
• RJ-45 Connector
• UTP/STP CAT 3 or better cabling required for 10-BaseT operation
11 Mbps up to 900 feet up to 160 feet
5.5 Mbps up to 1300 feet up to 200 feet
2.0 or 1 Mbps up to 1500 feet up to 300 feet
Please see the Microsoft Broadband Networking Web site for the latest
data: www.microsoft.com/broadbandnetworking/.
Approved for use only in the United States and Canada.
To Modem: Link/Activity LED
Wireless: Status LED including Activity indication
Power: Power/Reset Dual Color LED
Reference 83

System Requirements
To use the Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station:
• Computer with a network adapter to configure Base Station
• External broadband (cable, DSL, or other) modem with Ethernet port (not compatible with
dial-up modems)
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or Netscape Navigator 4.7 or later to view and use Base
Station HTML configuration screens
• Available 120V AC power outlet
Additional requirements for using the Microsoft Broadband Networking Setup Wizard and
Microsoft Broadband Network Utility:
• Personal computer with processor running Microsoft Windows 98, Windows 98 SE, Windows
Millennium Edition (Windows Me), Windows 2000* Professional, Windows XP Professional, or
Windows XP Home Edition operating system
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or later; setup will install Internet Explorer 6.0 browser
components if needed, but will not displace your primary browser
• 28 MB of available hard-disk space if you already have Internet Explorer 5.5 or 6.0;
132 MB of available hard-disk space if you are installing Internet Explorer for the first time
• 4x or faster CD-ROM drive
• VGA or higher resolution monitor
*Setup features and functionality are limited on Windows 2000
Recommended:
• Personal computer with Ethernet network adapter for easiest Base Station setup
• Microsoft Mouse or compatible pointing device
• 3.5" high-density disk drive
Not all ISPs allow you to share a broadband connection. Please check with your ISP.
84 Microsof t Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

glossary.
This glossary contains common terms for wired and wireless
networking.
100Base-T Also known as “Fast Ethernet,” an Ethernet cable standard with a
data transfer rate of up to 100 Mbps.
10Base-T An older Ethernet cable standard with a data transfer rate of up to
10 Mbps.
802.11, 802.11b A family of IEEE-defined specifications for wireless networks.
Includes the 802.11b standard, which supports high-speed (up to
11 Mbps) wireless data transmission. Microsoft
Networking wireless products comply with the 802.11b standard.
802.3 The IEEE-defined specification that describes the characteristics of
Ethernet connections.
access point See wireless access point.
ad hoc network A solely wireless computer-to-computer network. Unlike an
infrastructure network, an ad hoc network does not include a
central base station, router, or gateway.
adapter See network adapter.
base station A device (also known as a router or gateway) that acts as a central
point for networked devices, receives transmitted messages, and
forwards them. Microsoft Broadband Networking base stations can
link many computers on a single network, and can share a secure
Internet connection with wired and wireless devices.
®
Broadband
broadband connection A high-speed connection, typically 256 Kbps or faster. Broadband
services include cable modems and DSL.
broadband modem A device that enables a broadband connection to access the
Internet. The two most common types of broadband modems are
cable modems, which rely upon cable television infrastructure, and
DSL modems, which rely upon telephone lines operating at DSL
speeds.
cable modem See broadband modem.
CAT 5 cable Abbreviation for “Category 5 cable.” A type of Ethernet cable that
has a maximum data rate of 100 Mbps.
client Any computer or program that connects to, or requests the
services of, another computer or program on a network. For a local
area network or the Internet, a client is a computer that uses
shared network resources provided by a server.

client/server network A network of two or more computers that rely upon a central server
to mediate the connections or provide additional system
resources. This dependence upon a server differentiates a client/
server network from a peer-to-peer network.
computer name A name that uniquely identifies a computer on the network so that
all its shared resources can be accessed by other computers on
the network. One computer’s name cannot be the same as any
other computer or domain name on the network.
crossover cable See Ethernet cable.
DHCP Acronym for “Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.” A TCP/IP
protocol that automatically assigns temporary IP addresses to
computers on a local area network. Microsoft Broadband
Networking base stations support the use of DHCP which,
combined with ICS, allows you to share one Internet connection
with multiple computers on a network.
dial-up connection An Internet connection of limited duration that uses a public
telephone network rather than a dedicated circuit or some other
type of private network. The Microsoft Broadband Networking
hardware does not support the use of a dial-up connection to the
Internet.
DNS Acronym for “Domain Name System.” A data query service chiefly
used on the Internet for translating host names into Internet
addresses. The DNS database maps DNS domain names to IP
addresses, so that users can locate computers and services
through user-friendly names.
domain In a networked computer environment, a collection of computers
that share a common domain database and security policy. A
domain is administered as a unit with common rules and
procedures, and each domain has a unique name.
driver Within a networking context, mediates communication between a
computer and a network adapter installed on that computer.
DSL Acronym for “Digital Subscriber Line.” A constant, high-speed
digital connection to the Internet that uses standard copper
telephone wires.
DSL modem See broadband modem.
duplex A mode of connection; full-duplex transmission allows for the
simultaneous transfer of information between the sender and the
receiver. Half-duplex transmission only allows for the transfer of
information in one direction at a time.
dynamic IP address The IP address assigned (using the DHCP protocol) to a device that
requires it. A dynamic IP address can also be assigned to a router
by an ISP.
86 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

encryption The process of encoding data to prevent unauthorized access,
especially during transmission. Microsoft wireless hardware relies
upon encryption to ensure that data transmissions cannot be
accessed by users outside the network. Also see WEP.
Ethernet A networking standard that uses cables to provide network access.
Ethernet cable A type of cable that facilitates network communications.
firewall A security system that protects a network from external threats,
such as hacker attacks, originating outside the network. A
hardware firewall is a connection routing device with specific data
checking settings, that protects all of the devices connected to it.
The Microsoft Broadband Networking Base Station includes a
hardware firewall. A software firewall resides on a single computer,
protecting that computer from external threats. See Microsoft
Windows
®
XP Help for more information about the Internet
Connection software firewall.
firmware Sof tware information stored in non-volatile memory on a device.
gateway See base station.
gateway address The IP address used when making a connection outside your
immediate network.
host name The DNS name of a device on a network, used to simplify the
process of locating computers on a network.
hub A device with multiple ports that serves as a central connection
point for communication lines from all devices on a network. When
data arrives at one port, it is copied to the other ports.
ICS Acronym for “Internet Connection Sharing.” A software feature in
Microsoft Windows that allows computers on a network to access
online services through a single Internet connection. Microsoft
Broadband Networking hardware replaces software ICS.
infrastructure network A network configuration in which wireless devices connect to a
wireless access point (such as a base station) instead of
connecting to each other directly.
Internet domain See domain.
IP address Acronym for “Internet Protocol” address. IP is the protocol within
TCP/IP that is used to send data between computers over the
Internet. An IP address is an assigned number used to identify a
computer that is connected to a network through TCP/IP. An IP
address consists of four numbers (each of which can be no greater
than 255) separated by periods, such as 192.168.1.1.
ISP Acronym for “Internet Service Provider.” A company that provides
individuals or companies access to the Internet.
Glossary 87

LAN Acronym for “local area network.” A group of computers and other
devices dispersed over a relatively limited area (for example, a
building) and connected by a communications link that enables
any device to interact with any other on the network.
MAC address Acronym for “media access control” address. The address that is
used for communication between network adapters on the same
subnet. Each network adapter is manufactured with its own unique
MAC address.
Mbps Abbreviation of “megabits per second.” A unit of bandwidth
measurement that defines the speed at which information can be
transferred through a network or Ethernet cable. One megabyte is
roughly equivalent to eight megabits.
modem A device that facilitates the transmission and reception of
information between computers.
NAT Acronym for “network address translation.” The process of
converting between IP addresses used within a private network
and Internet IP addresses. NAT enables all of the computers on a
network to share one IP address. The Microsoft Broadband
Networking Base Station supports NAT, which provides an extra
layer of network security by masking the actual IP addresses of the
computers using a base station.
network A collection of two or more computers that are connected to each
other through wired or wireless means. These computers can share
access to the Internet and the use of files, printers, and other
equipment.
network adapter Also known as a “network interface card” (NIC). An expansion card
or other device used to provide network access to a computer,
printer, or other device.
PC Card A peripheral that adds memory, mass storage, modem capability,
or other networking services to portable computers.
peer-to-peer network A network of two or more computers that communicate without
using a central server. This lack of reliance upon a server
differentiates a peer-to-peer network from a client/server network.
Plug and Play A set of specifications that allows a computer to automatically
detect and configure various peripheral devices, such as monitors,
modems, and printers.
port A physical connection through which data is transferred between a
computer and other devices (such as a printer, monitor, or
modem), a network, or another computer. Also, a software channel
for network communications.
88 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide

PPPoE Acronym for “Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet.” A specification
for connecting users on an Ethernet network to the Internet using a
broadband connection (typically through a DSL modem). Microsoft
Broadband Networking hardware supports PPPoE for connections
that require it.
protocol A set of rules that computers use to communicate with each other
over a network.
RJ-11 connector An attachment used to join a telephone line to a device such as a
modem.
RJ-45 connector An attachment found on the ends of all Ethernet cables.
router See base station.
server A computer that provides shared resources, such as storage space
or processing power, to network users.
shared folder A folder on a computer that has been made available for other
people to use on a network.
shared printer A printer connected to a computer that has been made available
for other people to use on a network.
sharing To make the resources associated with one computer available to
users of other computers on a network.
SSID Acronym for “Service Set Identifier,” also known as a “wireless
network name.” An SSID value uniquely identifies your network and
is case sensitive.
static IP address A permanent Internet address of a computer (assigned by an ISP).
straight-through cable See Ethernet cable.
subnet A distinct network that forms part of a larger computer network.
Subnets are connected through routers and can use a shared
network address to connect to the Internet.
subnet mask Determines whether two computers on a network can
communicate with each other directly. Similar in form to an IP
address and typically provided by an ISP. An example of a subnet
mask value is 255.255.0.0.
switch A central device that functions similarly to a hub, forwarding
packets to specific ports rather than broadcasting every packet to
every port. A switch is more efficient when used within a high
volume network.
TCP/IP Acronym for “Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol.” A
networking protocol that allows computers to communicate across
interconnected networks and the Internet. Every computer on the
Internet communicates using TCP/IP.
Glossary 89

USB Acronym for “universal serial bus.” A hardware standard for easily
connecting peripherals to a computer system.
USB adapter A device that connects to a USB port; the Microsoft Broadband
Networking Wireless USB Adapter is a type of USB adapter.
USB connector The end of the USB cable that is plugged into a USB port.
USB port A rectangular slot in a computer into which a USB connector is
inserted.
WAN Acronym for “wide area network.” A geographically widespread
network that might include many linked local area networks
(LANs).
WEP Acronym for “Wired Equivalent Privacy,” also known as “Wireless
Security.” A wireless network encryption mechanism that protects
data transmitted over wireless networks. If you are operating a
wireless network, it is strongly recommended that you enable WEP.
Wi-Fi A commonly used term to mean the wireless 802.11b standard.
wireless access point A device that exchanges data between wireless computers or
between wireless computers and wired computers on a network.
wireless network name See SSID.
WLAN Acronym for “wireless local area network.” A network that
exclusively relies upon wireless technology for the device
connections.
workgroup A group of users working on a common project and sharing
computer files, typically over a LAN. A user who has a home
network that is not being controlled by a domain controller can be
a member of a workgroup.
90 Microsoft Broadband Networking Wireless Base Station User’s Guide


0702 Part No. X08-84133

My Network Settings
Use this page to record your network settings.
Workgroup or domain name:
Base Station password:
Wireless Settings
Record the information used to configure a computer for wireless access to your network here.
All computers accessing your network with a wireless connection need to use the same
wireless settings.
Wireless network name (SSID):
Wireless security (WEP) key:
Wireless channel (ad-hoc networks only):
Wide Area Network (WAN) Settings
Complete this section only if your network has a base station (gateway or router). You can
obtain this information from your Internet service provider (ISP). Your ISP may not require
all of the settings listed below.
Dynamic IP (DHCP) Settings
Complete this section only if your ISP uses a DHCP connection.
Host name (optional):
Adapter MAC address (optional):
Static IP Address Settings
Complete this section only if your ISP has assigned you a specific IP address.
Static IP address:
Subnet mask:
IP gateway address:
Primary DNS server:
Secondary DNS server:
PPPoE Settings
Complete this section only if your ISP uses PPPoE with your DSL connection.
User name:
Password:
Service name (optional):

M
www.microsoft.com/broadbandnetworking0702 Part No. X08-84133
 Loading...
Loading...