Page 1

4 10/100/1000TX plus 1 MINI GBIC
Web Managed Switch
User Manual
MS453510M
Page 2

CE Mark Warning
This is a Class-A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause
radio interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate
measures.
Page 3

Content
CE Mark Warning ................................................................................................. 2
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................... 1
Features ............................................................................................................... 1
Software Feature .................................................................................................. 2
Package Contents ................................................................................................ 3
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION ............................................................ 4
Physical dimension .............................................................................................. 4
Front Panel ........................................................................................................... 4
Rear Panel ........................................................................................................... 5
LED Indicators ...................................................................................................... 5
Desktop Installation .............................................................................................. 7
Attaching Rubber Feet .................................................................................. 7
Power On ............................................................................................................. 7
NETWORK APPLICATION ............................................................... 8
Small Workgroup .................................................................................................. 8
Segment Bridge ................................................................................................... 8
WEB-BASED MANAGEMENT ....................................................... 10
About Web-based Management ......................................................................... 10
System Login ..................................................................................................... 10
System Configuration ......................................................................................... 11
Port Configuration .............................................................................................. 13
Statistics-1 (Overview) ....................................................................................... 14
Statistics-2 (Detailed) ......................................................................................... 15
VLAN Setting ...................................................................................................... 15
VLAN Port Setting ....................................................................................... 16
Port Trunk .......................................................................................................... 17
LACP Setting ...................................................................................................... 18
LACP Status ....................................................................................................... 19
Page 4

Spanning Tree ................................................................................................... 20
RSTP System Configuration ....................................................................... 20
RSTP Port Configuration ............................................................................ 22
Spanning Tree Status ........................................................................................ 22
802.1X Configuration ......................................................................................... 23
Parameters Configuration ........................................................................... 24
QoS Setting ....................................................................................................... 25
System Restart .................................................................................................. 28
Factory Default .................................................................................................. 28
Firmware Upload ............................................................................................... 28
Configuration Upload/Download ........................................................................ 29
TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................... 31
Incorrect connections ......................................................................................... 31
Faulty or loose cables ......................................................................... 31
Non-standard cables ........................................................................... 31
Improper Network Topologies ............................................................. 32
Diagnosing LED Indicators ................................................................................ 32
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION ....................................................... 33
APPENDIX ...................................................................................... 36
10 /100BASE-TX Pin outs ................................................................................. 36
10/100Base-TX Cable Schematic ...................................................................... 36
10/100/1000Base-TX Pin outs ........................................................................... 37
10/100/1000Base-TX Cable Schematic ............................................................. 38
Page 5

Introduction
The 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch is a multi-port
Switch that can be used to build high-performance switched workgroup networks.
The Switch is targeted at workgroup or department.
The 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch features a
“store-and-forward “ switching scheme that offers low latency for high-speed
networking and allows the switch to auto-learn and store source address in a
8K-entry MAC address table.
The 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch has 4 auto-sensing
10/100/1000 Base-TX RJ-45 ports plus one MINI GBIC slot that enables
extended distance connection.
Features
Conforms to IEEE 802.3, 802.3u, 802.3ab, 802.3x and 802.1x
Store-and-Forward switching architecture
Web Management
Auto-MDIX on all ports
10Gbps back-plane
N-Way Auto-Negotiation
Supports Port Based VLAN
Supports Class of Service
Supports STP (Spanning Tree Protocol)
Supports Port Trunk
Back pressure with half duplex (10/100Mbps)
Flow control with full duplex (10/100/1000Mbps)
Web Firmware upgrade
1
Page 6
One default button for system default
The trunk group up to 2 and maximum trunk port
Port Based VLAN
Port based
8K MAC address table
112Kbytes memory buffer
True non-blocking switching
8K Jumbo Frame supported
Software Feature
Management
Firmware update
System default
Port Trunk
VLAN
Web Management
Web UI firmware update
Default IP: 192.168.16.1
Gateway: 192.168.16.254
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
IEEE802.3ad port trunk with link aggregation
control protocol (LACP)
member up to 2 ports.
VLAN ID up to 5
VLAN group up to 5
DHCP
Quality of Service
Class of Service
2
DHCP client feature
Tag based
IPv4 ToS
Per port supports 4 priority queues
Page 7
IEEE802.1w rapid spanning tree and compatible
Spanning Tree
with IEEE 802.1d
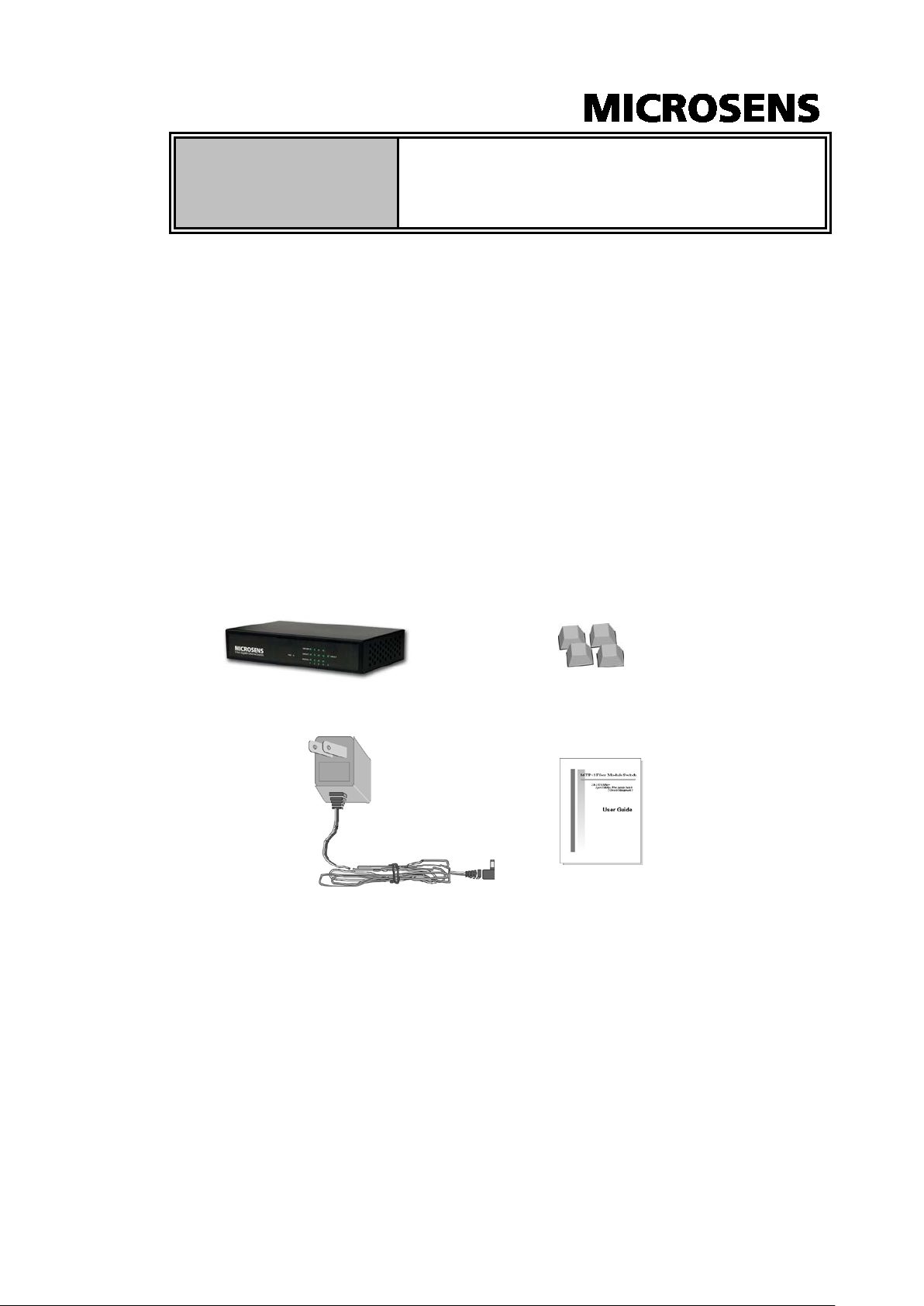
Package Contents
Unpack the contents of the 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed
Switch and verify them against the checklist below:
4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch
DC Power Cord
Four Rubber Pads
User Manual
4 10/100/1000 plus 1 Mini-GBIC Four Rubber Pads
Web Managed Switch
DC Power Adapter
Package Contents
User Manual
Compare the contents of your 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed
Switch package with the standard checklist above. If any item is missing or
damaged, please contact your local dealer for exchanging.
3
Page 8

Hardware Description
This section mainly describes the hardware of the 4 10/100/1000T plus 1
Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch, and gives a physical and functional overview
on certain switch.
Physical dimension
The 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch physical dimension
is
165 x 100 x 32.5 mm
(W x D x H).
Front Panel
The Front Panel of the 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch
consists of LED Indicators and a reset button. Please refer to LED Indicator
section for LED description.
Reset button:
back to the default settings. Press the button more than 5 seconds, and then
the switch will restart and set all configurations back to the default settings.
4
It provides an easy way for user to reset the configuration
Page 9

Rear Panel
The rear panel consists of the 4 10/100/1000Base-TX RJ-45 port, one Mini G BIC
slot, and DC Power Jack as shown in the figure below. The switch will wor k with
DC in the range of 12V/0.8A.
The Rear Panel of 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch
RJ-45 Ports (Auto MDI/MDIX):
10Base-T, 100Base-TX or 1000Base-T connections.
In general,
means connecting to a workstation or PC. Therefore,
would allow connecting to another Switch or workstation without changing
non-crossover or crossover cabling.
Mini GBIC slot:
with a variety of different transmitter and receiver types, allowing users to
select the appropriate transceiver for each link to provide the required
optical reach over the available optical fiber type.
indicator—LNK/ACT—for Mini-GBIC port on the front panel.
LED Indicators
4x 10/100/1000 N-way auto-sensing for
means connecting to another Hub or Switch while
MDI
Auto MDI/MDIX
The appropriate replaceable Mini-GBIC port is
There is one LED
MDIX
available
The LED Indicators display the real-time information of systematic operation
status. Please see definition of the LED indicators as follows.
5
Page 10
No Power inputs or Power cord
The port is operating at the speed of
The port is operation at the speed of
In 10Mbps mode or no device
The port is well connected with the
The port is in processing of receiving
The port is operating in Full-duplex
Collision of Packets occurs in the
Half-duplex mode or no device
The port is well connected with the
receiving
LED Status Color Description
On Green Power On
Power
Off --
disconnected
On Green
1000Mbps.
100/1000
LNK /ACT
FDX /COL
On Yellow
100Mbps.
Off --
attached
On Green
device.
Blinks Green
or transmitting data.
Off -- No device attached.
On Yellow
mode.
Blinks Yellow
port.
Off --
On Green
LNK /ACT
Blinks Green
(MINI GBIC)
Off --
6
attached.
device.
The port is in processing of
or transmitting data.
No data transmitted or no device
connected
The Definition of LED Indicators
Page 11

Desktop Installation
Set the switch on a sufficiently large flat space with a power outlet nearby. The
surface where you put the switch should be clean, smooth, level and sturdy.
Make sure there is enough clearance around the switch to allow att achment of
cables, power cord and allow air circulation.
Attaching Rubber Feet
A. Make sure mounting surface on the bottom of the switch is grease and dust
free.
B. Remove adhesive backing from your Rubber Pads.
C. Apply the Rubber Feet to each corner on the bottom of the switch. These
footpads can prevent the switch from shock/vibration.
Power On
Connect the power adaptor to the power jack on the rear panel of the switch. The
other side of power adaptor is connected to the power outlet . The external power
supply in the switch works with DC power in 12V/0.8A. Please check with the
power indicator on the front panel to see if power is properly supplied.
7
Page 12
Network Application
This section provides user a few samples of network topology in witch the switch
is used. In general, the 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch
is designed as a segment switch. That is, with its address table (8000 MAC
address) and high performance, it is ideal for interconnecting networking
segments.
PC, workstations, and servers can communicate each other by directly
connecting with 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch. The
switch automatically learns nodes address, which are subsequently used to filter
and forward all traffic based on the destination address.
By using Uplink port, the switch can connect with another switch or hub to
interconnect other small-switched workgroups to form a larger switc hed network.
Meanwhile, you can also use fiber ports to connect switches. The distance
between two switches via fiber cable depends on the type of fiber transceiver.
Small Workgroup
The 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switc h can be used as a
standalone switch to which personal computers, server, printer server, are
directly connected to form small workgroup.
Segment Bridge
For enterprise networks where large data broadcasts are constantly processed,
this switch is an ideal solution for department users to connect to the corporate
backbone.
8
Page 13

Two 4 10/100/1000T + 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switches with PCs, print
server, and local server attached, are both connected to the core s witch. All the
devices in this network can communicate with each other through the 4
10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch. Connecting servers to the
4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch allows users accessing
the data on server. By using fiber ports to connect switches, the distance
between two switches depends on the type of fiber transceiver.
9
Page 14

Web-Based Management
This section introduces the function of the 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web
Managed Switch configuration.
About Web-based Management
On the CPU board of the switch there is an embedded HTML web site residing in
flash memory, which offers advanced management features and allow users to
manage the switch from anywhere on the network through a standard browser
such as Microsoft Internet Explorer.
The Web-Based Management supports Internet Explorer 6.0. And, it is applied
with Java Applets for reducing n etwork ban dwidth con sumption, enhance access
speed and present an easy viewing screen.
System Login
The default value list as below:
IP Address:
Subnet Mask:
Default Gateway:
Password:
192.168.16.1
root
255.255.255.0
192.168.16.254
1. Launch the Internet Explorer.
2. Key in “http://” + “IP Address” of the 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web
Managed Switch, and then press “
3. Login screen will appear right after.
10
Enter
”.
Page 15

Apply
4. Key in the default password as “
5. Click
, and then configuration is ready to be set up.
root
”.
Main Interface
System Configuration
Displays system parameters information listed as below, and the other
parameters of system can be configured as well.
MAC Address: Displays the unique hardware address assigned by
manufacturer (default).
S/W Version: Displays the Software Version of Kernel.
H/W Version: Displays the Hardware Version of the switch.
Active IP Address: Displays the current IP Address.
Active Subnet Mask: Displays the current IP Subnet Mask.
Active Gateway: Displays the current Gateway.
DHCP Server: Displays the DHCP Server IP Address when DHCP check
box is enabled.
Lease Time Left: Displays DHCP lease time. After 50% of the lease time
11
Page 16

has passed, the client/switch will attempt to renew the lease with the original
DHCP server that it obtained the lease from using a DHCPREQUEST
message. Any time the client/switch boots and the lease is 50% or more
passed, the client/switch will attempt to renew the lease. At 87.5% of the
lease completion, the client/switch will attempt to contact any DHCP server
for a new lease.
System Configuration Interface
DHCP Enable:
Fallback IP Address:
12
Tick the check box to enable DHCP Client Function.
Assign the fallback IP address for DHCP IP assigning
Page 17

Apply
Refresh
failure (The default IP is 192.168.16.1).
Fallback Subnet Mask:
Fallback Gateway:
192.168.16.254).
TFTP Server Enabled:
function.
Management VLAN (1 ~ 4095):
and 4095. It is used for Remote Management Security; in fact, it gives the
port permission t o access the switch only when the port’s VLAN group ID is
equal to the Management VLAN ID.
Name:
Password:
Inactivity Timeout:
10 and 10000 seconds.
And then, click
Assign the name of the switch.
Web GUI login password. The default password is
Assign the switch IP Subnet Mask.
Assign the switch Gateway (The default value is
Tick this check box to enable the TFTP server
Assign a number of VLAN group between 1
root.
Set the timeout period for security in number between
to have the configuration take effect.
Or, click
to reset the configuration before applying.
Port Configuration
Specify the negotiation mode, enable flow control, and set maximum frame size
in the range between 1518 and 9600 for each port.
Link:
100FDX, 100HDX, 10FDX, and 10 HDX. The system will automatically
detect link speed.
Mode:
Flow control:
Duplex mode.
“Down” means “No Link”. Link speed status includes: 1000FDX,
Specify the speed, full-duplex or half-duplex mode of t he ports.
Set Flow Control Function as “enable” or “disable” in Full
MaxFrame (1522 ~ 9600):
received on the port.
Set the Maximum Frame Size in bytes for frames
13
Page 18

Apply
Refresh
Clear
Refresh
Click
Or, click
to have the configuration take effect.
to reset the configuration before Applying.
Port Configuration interface
Statistics-1 (Overview)
The following information provides the current port statistic information.
Press
new setting information shown as below.
button to clean all counts, and then click
to get the
Statistics Overview interface
14
Page 19

Clear
Refresh
Apply
Statistics-2 (Detailed)
The following information provides statistics detail information on each port, and
the user can simply click the port to view the statistics information.
Press
new setting information as below.
button to clean all counts, and then click
VLAN Setting
to get the
Statistics Detail interface
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical network grouping that limits the broadcast
domain, which would allow users to isolate network traffic, and therefore only the
members of the VLAN will receive traffic from the members of the same VLAN.
Basically, creating a VLAN from a switch is logically equivalent to reconnecting a
group of network devices to another Layer 2 switch. However, all the network
devices are still plugged into the same switch physically.
Assign the VLAN ID in number between 1 and 4095.
Group the members of VLAN by ticking the check box.
Click
Tick all check boxes by clicking ‘
’.
all
to bring up the configuration interface as below.
add all
’ or remove all ticks by clicking ‘
clear
15
Page 20

VLAN Po r t Set ting
There are 16 VLAN entries per page among 16 pages. To search the
specified VLAN, please type in the VLAN ID in the empty field beside the
label of ‘
Quick Search Vlan Entry, Vlan ID:
’ and then press ‘Search’.
VLAN Port Setting
Click
the VID Setting.
16
VLAN Setting interface
to bring up the configuration interface for adjusting
PVID:
Awareness:
Enter the Port VLAN ID.
Enable the awareness so that ports will strip the VLAN tag from
received frames and insert the tag (contains PVI D) into transmitted frames.
Page 21

Apply
Refresh
Disable the awareness so that ports will not strip the tag from received
frames or insert the tag in transmitted frames.
Frame Type:
Set the outgoing frame.
Tag: Outgoing fram es with VLAN-Tagged.
All: All type of frames.
Click
Or, click
to have the configuration take effect.
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
VLAN Port Setting interface
Port Trunk
Port trunk allows multiple links to be bundled together and act as a single
physical link for increased throughput. It provides load balancing, and
redundancy of links in a switched inter-network. Actually, the link does not have
an inherent total bandwidth equal to the sum of its component physical links.
Traffic in a trunk is distributed across an individual link within the trunk in a
deterministic method that called a hash algorithm. Traffic pattern on the network
17
Page 22

Apply
Refresh
should be considered carefully before applying it. When a proper hash algorithm
is used, traffic is kind of randomly decided to be transmitted across either link
within the trunk and load balancing will be seen.
Select the group members. Normal means the port is not the trunk member.
Click
Or, click
to have the configuration take effect.
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
Port Trunk interface
LACP Setting
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is a computer networking term
and is part of IEEE specification 802.3ad that allows bundling several physical
ports t ogether to form a single logical channel. LACP allows a n etwork switch to
negotiate an automatic bundle by sending LACP packets to the peer . LACP is a
protocol implementation in OSI layer 2 which controls through which physical
links the traffic will be routed.
Protocol Enable:
Key Value (auto | 1 - 255):
potentially can be aggregated together.
18
Tick the check box to enable LACP protocol of the port.
The LACP key determines which ports
Page 23

Apply
Refresh
Click
Or, click
to have the configuration take effect.
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
LACP Setting interface
LACP Status
When the LACP aggregator has been set up, the LACP status information will
display as below.
19
Page 24

LACP Status interface
Spanning Tree
The Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) is an evolution of the Spanning Tr ee
Protocol and provides for faster spanning tree convergence after a topology
change. The system also supports STP and the system will aut omatically detect
the connected device that is running STP or RSTP protocol.
RSTP System Configuration
System Priority:
lowest value has the highest priority and is selected as the root. If the value
has being changed, user has to reboot the switch. The value must be
multiple of 4096 according to the protocol standard rule.
A value used to identify the root bridge. The bridge with the
20
Page 25

Hello Time (1-10):
The scale of 1 ~ 10 sec will be set as a period of time that
how often the switch broadcasts hello messages to other switches.
Max Age (6-40):
The number of seconds (from 6 ~ 40) which determines the
amount of time that protocol information received on a port is stored by the
switch.
Forward Delay Time (4-30):
The number of seconds (from 4 ~ 30) which
determines how long each of the listening and learning states will last before
the port begins forwarding.
Force version:
Select the RSTP default protocol. ‘Normal’ means RSTP
protocol. ‘Compatible’ means it’s compatible with STP protocol.
RSTP Configuration interface
21
Page 26

Apply
Refresh
Refresh
RSTP Port Configuration
Protocol Enable:
Edge:
forwarding state and is not part of the STP topology unless BPDUs are seen
on the port. To configure the port as an edge port, tick the check box.
Path Cost:
bridge at the specified port. Enter a number 1 through 200,000,000
Click
Or, click
An edge port is a port connected to a non-switch device. It is kept in a
The cost of the path to the other bridge from this transmitting
Enable or disable the RSTP protocol for the port.
to have the configuration take effect.
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
Spanning Tree Status
Click
to get the newest configuration information. The Rapid
Spanning Tree Protocol information will display as below.
RSTP Status interface
22
Page 27

Apply
802.1X Configuration
IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE standard for port-based Network Access Control; it is
part of the IEEE 802 (802.1) group of protocols. It provides authentication to
devices attached to a LAN port, establishing a point-to-point connection or
preventing access from that port if authentication fails. IEEE 802.1X is avai lable
on certain network switches, and can be configured to authenticate hosts which
are equipped with supplicant software, denying unauthorized access to the
network at the data link layer.
Mode:
RADIUS IP:
RADIUS UDP Port:
to the specified Radius Server
RADIUS Secret:
with the specified radius server. This key must match the encryption key
used on the Radius Server
Admin State:
Disable or enable IEEE 802.1x authentication.
Set the Radius Server IP address.
Set the UDP destination port for authentication requests
Set an encryption key for authenticating usage sessions
Select the state of port.
Force Authorized:
authorized state.
Force Unauthorized:
unauthorized state.
Auto:
accordance with the outcome of an authentication exchange between
the Supplicant and the authentication server
The specified port is set to the authorized or unauthorized state in
The specified port is required to be held in the
The specified port is required to be held in the
Re-authenticate:
Force Reinitialize:
Statistics:
Re-authenticate All:
Force reinitialize All:
Click
Click to view each port statistic.
Restart authentication process for the port.
Restart authentication process for the port.
Restart authentication process for all the port.
Restart authentication process for all the port
to have the configuration take effect.
23
Page 28

Refresh
Apply
Or, click
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
802.1X Configuration interface
Parameters Configuration
You can configure this page to enable client re-authentication and how often it
occurs.
Reauthentication Enable:
Reauthentication Period (1~3600 seconds):
second between re-authentication attempts.
EAP Timeout (1~255 seconds):
supplicant response to an EAP request.
Click
to have the configuration take effect.
Enable the re-authentication mode.
Set the period of time in
Set the period of time the switch waits for a
24
Page 29

Refresh
Apply
Refresh
Or, click
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
QoS Setting
Configure QoS mode, port priority, TOS and COS priority setting.
Mode:
Port Priority:
Click
Or, click
Specify the QoS mode—port, DSCP, or vlantag.
Select the priority level—low, normal, medium, or high.
to have the configuration take effect.
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
25
Page 30

DSCP Mapping
Apply
Refresh
Click
Click
Or, click
QoS Configuration interface
to enter DSCP priority configuration interface.
DSCP [0- 63]:
The system provides 0 ~ 63 TOS priority level. Wh en the
IP packet is received, the system will check the DSCP level value in the
IP packet. For example, port 1 is set as DSCP mode and DSCP level 25
is set as high. When the packet is received via port 1, the system will
check the DSCP value of the received IP packet. If the DSCP value of
the received IP packet is 25 (priority = high), and then the packet priority
will have the highest priority.
Priority:
Select the priority level—high, medium, low, or normal
to have the configuration take effect.
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
26
Page 31

VLAN tag M apping
Apply
Refresh
QoS DSCP Mapping interface
After having set mode as ‘vlantag’, click
tag priority configuration interface.
Set the VLAN tag priority level from 0 ~ 7 for each port.
Click
Press
to have the configuration take effect.
to refresh the configuration to view the newest state.
to enter VLAN
QoS VLAN Tag Priority Mapping interface
27
Page 32

Yes
Yes
Browse...
System Restart
Reboot the switch in software reset.
Click
to restart the system.
System Restart interface
Factory Default
Reset the switch to default configuration.
Click
to reset all the configurations to factory default value.
Factory Default interface
Firmware Upload
The system provides the Web GUI firmware upgrade function which allows users
to upgrade the switch firmware.
Click
28
to locate the firmware.
Page 33

Upload
Browse
Upload
Yes
And t hen, press
to update the firmware.
Software Upload interface
Configuration Upload/Download
The system provides the Web GUI configuration file transfer function which would
allow user to backup and restore the switch configuration.
Click
And then, press
to locate the file.
to upload the file.
Configuration Upload interface
And then, press
to update the loaded file.
29
Page 34

Download
For restoring the configuration, press
to restore the file.
Configuration Download interface
30
Page 35

Troubleshooting
This section is intended to help users to solve the most common problems on the
4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web Managed Switch.
Incorrect connections
The switch port can auto detect straight or crossover cable when the switch link
with other Ethernet device. For the RJ-45 connector should use c orrect UTP or
STP cable, 10/100Mbps port use 2 pairs twisted cable and Gigabit 1000T port
use 4 pairs twisted cable. If the RJ-45 connector is not correctly pinned on right
position then the link will fail. For fiber connection, please notice that fiber cable
mode and fiber module should match.
Faulty or loose cables
Look for loose or obviously faulty connections. If they appear to be OK, make
sure the connections are snug. If that does not correct the problem, try a different
cable.
Non-standard cables
Non-standard and miss-wired cables may cause numerous network collisions
and other network problem, and can seriously impair network performance. A
category-5 cable tester is a recommended tool for every 100Base-T network
installation.
RJ-45 ports:
cable for RJ-45 connections: 100Ω Category 3, 4 or 5 cable for 10Mbps
Use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shielded twisted-pair (STP)
31
Page 36

connections or 100Ω Cat egory 5 cable for 100Mbps connections. Also be sure
that the length of any twisted-pair connection does not exceed 100 meters (328
feet). Gigabit port should use cat-5e or above cable for 1000Mbps connections.
The length does not exceed 100 meters.
Improper Network Topologies
It is important to make sure that users have a valid n etwork topology. Common
topology faults include excessive cable length and too many repeaters (hubs)
between end nodes. In addition, users should m ake sure that network topology
contains no data path loops. Between any two ends nodes, there should be only
one active cabling path at any time. Data path loops will cause broadcast st orms
that will severely impact network performance.
Diagnosing LED Indicators
To assist in identifying problems, the switch can be easily monitored through
panel indicators which describe common problems the user may encounter and
where the user can find possible solutions.
If the power indicator does not turn on when the power cord is plugged in, the
user may have a problem with power outlet, or power cord. However, if the switch
powers off after running for a while check for loose power connections, power
losses or surges at power outlet. If the problem still cannot be resolved, contact
the local dealer for assistance.
32
Page 37

IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet
Protocol
CSMA/CD
Technology
Store-and-Forward switching architecture
duplex/
Technical Specification
This section provides the specifications of 4 10/100/1000T plus 1 Mini-GBIC Web
Managed Switch.
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
IEEE 802.3ab 1000Base-T
IEEE 802.3z Gigabit Fiber
IEEE 802.3x Flow Control and Back-pressure
Standard
Transfer Rate
IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
IEEE 802.3ad Port trunk with LACP
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service
IEEE 802.1x user authentication
IEEE802.1Q VLAN Tagging
14,880pps for 10Mbps
148,800pps for 100Mbps
1,488,000pps for 1000Mbps
LED Indicators
Per RJ-45 port:
Collision
Per MINI GBIC:
Per unit:
Power
33
100/1000, Link/Activity, Full
Link/Activity
Page 38

10BASE-T: 2-pair UTP/STP Cat. 3, 4, 5 cable
Gigabit copper: 4 x RJ-45 with Auto-MDIX
Power
Operating
Network Cable
Connector
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm (100m)
100BASE-TX: 2-pair UTP/STP CAT. 5 cable
EIA/TIA-568 100-ohm (100m)
Gigabit Copper: 4 pair UTP/STP CAT. 5e cable
EIA/TIA 568 100-ohm (100M)
MINI GBIC: 1 x MINI GBIC socket (3.3v)
Back-plane
MAC address
Memory Buffer
Jumbo packet
Dimensions
Power Supply
10Gbps
8K
112Kbytes
Supports 8Kbytes Jumbo Frame
165 x 100 x 32.5 mm (W x D x H)
External power DC 12V/0.8A
Consumption
5.1 Watt (maximum)
(DC)
0oC to 45oC (32℉ to 113℉)
Temperature
34
Page 39

Operating
10% to 90% (Non-condensing)
Humidity
EMI
CE
35
Page 40

Pin Number
Assignment
1
Tx+
2
Tx-
3
Rx+
6
Rx-
1
Receive Data plus (RD+)
Transmit Data plus (TD+)
2
Receive Data minus (RD-)
Transmit Data minus (TD-)
3
Transmit Data plus (TD+)
Receive Data plus (RD+)
6
Transmit Data minus (TD-)
Receive Data minus (RD-)
Appendix
10 /100BASE-TX Pin outs
With10/100BASE-TX cable, pins 1 and 2 are used for transmitting data, and pins
3 and 6 for receiving data.
RJ-45 Pin Assignments
[NOTE]
wire pair.
The table below shows the 10 / 100BASE-TX MDI and MDI-X port pin outs.
“+” and “-” signs r epresent the polarity of the wires that make up each
Pin MDI-X Signal Name MDI Signal Name
10/100Base-TX Cable Schematic
The following two figures show the 10/100Base-TX cable schematic.
36
Page 41

Straight-through cable schematic
Cross over cable schematic
10/100/1000Base-TX Pin outs
The following figure shows the 10/100/1000 Ethernet RJ-45 pin outs.
37
Page 42

10/100/1000Base-TX Cable Schematic
Straight through cables schematic
Cross over cables schematic
38
 Loading...
Loading...