Page 1

.......
Page 2
Page 2
Page 3

Notices
Copyright
Copyright © 2015 Microsemi
All rights reserved.
Due to continued product development this information may change without notice. If you
find any errors in the documentation, please report them to us in writing. Microsemi doesnot
warrant that this document is error-free.
LimitedProductWarranty
Hardware and embedded software – Depending on the product, for a period of one, or two
years from date of shipment by Microsemi, Microsemi warrants that all Products shall be free
from defects in design, material, and workmanship; shall conform to and perform in accordance with Microsemi's published specifications, if any; shall be free and clear of any liens and
encumbrances; and shall have good and valid title. This warranty will survive inspection,
acceptance, and payment by Buyer. Microsemi does not warrant that the operation of such
Products will be uninterrupted or error free. This warranty does not cover failurescaused by
acts of God, electrical or environmental conditions; abuse, negligence, accident, loss or damage in transit; or improper site preparation.
This warranty shall be null and void in the event (i) Buyer or any third party attemptsrepair of
the goods without Microsemi’s advance written authorization, or (ii) defects are the result of
improper or inadequate maintenanceby Buyer or third party; (iii) of damage to said goods by
Buyer or third party-supplied software, interfacing or supplies; (iv) of improper use (including
termination of non-certified third party equipment on Microsemi’s proprietary interfaces and
operation outside of the product's specifications) by Buyer or third party; or (v) the goods are
shipped to any country other than that originallyspecifiedin the Buyer's purchase order.
Goodsnot meeting the foregoing warranty will be repaired or replaced, at Microsemi’s
option, upon return to Microsemi’s factory freight prepaid; provided, however that Buyer has
first obtained a return materials authorization number ("RMA Number") from Microsemi
authorizing such return. The RMA Number shall be placed on the exterior packaging of all
returns. Microsemi will pay shippingcosts to return repaired or replacement goods to Buyer.
Microsemi reservesthe right to disallow a warranty claim following an inspection of returned
product. When a warranty claim is questioned or disallowed, Microsemi will contact Buyer by
telephone or in writing to resolve the problem.
LimitationofLiability
The remedies provided herein are the Buyer’s sole and exclusive remedies. In no event or circumstanceswill Microsemi be liable to Buyer for indirect, special, incidental or consequential
damages, including without limitation, loss of revenues or profits, business interruption costs,
lossof data or software restoration, or damages relating to Buyer’s procurement of substitute products or services. Except for liability for personal injury or property damage arising
from Microsemi’s negligence or willful misconduct, in no event will Microsemi’s total
3
Page 4

cumulative liability in connection with any order hereunder or Microsemi’s Goods, from all
causes of action of any kind, including tort, contract, negligence, strict liability and breach of
warranty, exceed the total amount paid by Buyer hereunder. SOME JURISDICTIONS DO
NOT ALLOW CERTAIN LIMITATIONS OR EXCLUSIONS OF LIABILITY, SO THE
ABOVE LIMITATIONS OR EXCLUSIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO ALL BUYERS.
ContactInformation
Microsemi
Frequency and Time Division
3870 N. 1st Street
San Jose, CA 95134
Telephone: +1 (408) 428-7907
For Sales, Technical Support, and Return MaterialsAuthorization, please See "Microsemi
Customer Assistance" on page 5
RevisionHistory
Revision Date Description
B August 2007 made corrections, moved and consolidated topics.
C October 2010 Added VDC Power and Telecommunications topics.
D August 2011 Added models 1520R-350i and 1520R-350i-RB.
D1 March 2013 Added TACACS+ user authentication, and support for extended
character set in Radius andTACACS+ login.
E Not released.
F November 2013 Added IPv6 content.
F1 May 2015 Changed description of downloads for software updates.
4
Page 5

MicrosemiCustomerAssistance
To find the Microsemi representative closest to your location, please visit Microsemi Worldwide Saleshttp://www.microsemi.com/sales-contacts/0online.
To reach a Microsemi Customer Assistance Center, call one of the following numbers:
n Worldwide Main Number: 1-408-428-7907
n US Toll-free Number: 1-888-367-7966
n Europe, Middle East & Africa: 49 700 32886435
5
Page 6
Page 7

Table of Contents
.
Notices 3
Copyright 3
Limited Product Warranty 3
Limitation of Liability 3
Contact Information 4
Revision History 4
Microsemi Customer Assistance 5
Table of Contents 7
S300, S350 and S350i Quick Start Guide 13
Configuring the SyncServer 13
Status LEDs 15
Halting the SyncServer 15
Product Overview 17
Comparison by Model 18
Web Interface 21
Login 23
Properties of User Names and Passwords 23
STATUS - General 24
STATUS - Network 25
STATUS - Timing 26
STATUS - GPS 26
WARNING: GPS Position and Altitude 28
STATUS - NTP 28
NTP Daemon Status 28
STATUS - PTP 31
PTP Daemon Status 31
STATUS - Alarms 32
NETWORK - Ethernet 32
NETWORK - SNMP 35
NETWORK - SNMP Traps 37
NETWORK - Ping 37
NTP - Sysinfo 39
NTP Daemon Status 39
NTP - Assoc 42
NTP - Config 43
7
Page 8

NTP - MD5 Keys 47
NTP - Autokey 48
NTP - Autokey Client 49
NTP - Prefs 50
PTP Option and Time Interval Test 51
Time Interval Test 52
PTP and NTP Performance 52
PTP Management Messages 52
How to Activate the PTP Option 53
PTP - Master 54
IEEE 1588-2008 Annex J Recommended Default Settings 58
PTP - Slaves 58
PTP - Performance 59
Charting PTPPerformance 60
PTP - Save-Restore 60
To Save Configuration Settings to a File 60
To Restore Configuration Settings from a File 61
TIMING - Time Zone 61
TIMING - HW Clock 61
TIMING - Holdover 63
TIMING - Sysplex 64
TIMING -Time Interval 67
REFERENCES - GPS 70
GPS Position and Operating Mode 70
REFERENCES - Timecode 71
REFERENCES - Modem 72
RESTART button 75
REFERENCES - LF Radio 75
SYSTEM - General 76
SYSTEM - Upgrade 77
SYSTEM - Factory Reset 77
Factory Default Settings 78
SYSTEM - Options 82
ADMIN - Web 82
ADMIN - Users 84
ADMIN - Alarms 85
Alarm Descriptions 86
Factory Default Settings for Alarms 89
ADMIN - Logs Config 90
ADMIN - Relays 92
ADMIN - RADIUS 93
ADMIN - TACACS+ 94
SERVICES - Startup 95
SERVICES - HTTP 96
SERVICES - SSH 97
SERVICES - Email 97
8
Page 9

LOGS 97
WIZARDS - 1st Setup 99
WIZARDS - NTP 99
WIZARDS - SNMP 99
WIZARDS - Backup 99
WIZARDS - Restore 100
WIZARDS - Upgrade 100
Keypad/Display Interface 101
TIME Button 101
STATUS Button 102
MENU Button 104
Command Line Interface 107
Specifications 111
Front Panel 112
USB Ports 112
Console RS-232 Port 112
Status LEDs 113
Keypad/Display 113
Rear Panel 114
Radio (LF Radio Module) 114
Modem 114
Power and Alarm Relays 114
Network Ports 115
Sysplex Out 116
10MHz In 117
10MHz Out 117
1PPS In 117
1PPS Out 118
IRIG In (Timecode In) 118
IRIG Out (Timecode Out) 119
IRIG Control Function Bits 120
GPS Receiver 121
Chassis Grounding Screw 122
WARNING: Grounding 122
VDC Power Supply 122
WARNING: VDC Power 123
VAC Power Supply 123
CAUTION: VAC Power 123
Power Switch 123
Physical 124
Environmental 124
9
Page 10

Shock and Vibration 124
Accuracy & Stability - Timing Performance 124
GPS Antenna 125
Timing Holdover 126
Network Protocols 126
NTP 127
CE/WEEE/RoHS Conformance 127
Safety Standards 128
EMC Standards 129
VCCI Compliance Information 129
Listing of Memory Devices 129
Reliability 130
Maintainability 130
Web Interface 131
Software 131
Failure Detection and Reporting 131
Warnings and Cautions 131
WARNING: Grounding 131
WARNING: VDC Power 132
WARNING: GPS Antenna 132
WARNING: GPS Position and Altitude 133
WARNING: Removing Power 133
CAUTION: VAC Power 133
CAUTION: DHCP Not Available 134
CAUTION: Stopping the SyncServer 134
CAUTION: Lithium Battery 134
Tasks 135
Installation Guide 136
Unpacking 136
Rack Mounting 137
Grounding the SyncServer 137
WARNING: Grounding 137
Connecting VAC Power 137
CAUTION: VAC Power 138
Electrical Installations in Norway and Sweden 138
Connecting VDC Power 138
WARNING: VDC Power 139
Telecommunications (Modem) Interfaces 139
Using GPS 140
WARNING: GPS Antenna 140
Selecting a Site for the Antenna 141
Installing the GPS Antenna 142
Operating in "Window Mode" 143
Verifyingthe GPS Installation 145
GPS Cable Configurations/Options 145
10
Page 11

Configuring LAN1 148
CAUTION: DHCP Not Available 149
Logging in to the Web Interface 149
Using the 1st Setup Wizard 149
Configuring the Network Ports 149
Adding Server Associations 150
Using the Other Input References 150
Troubleshooting 151
Passwords 151
Alarms and Notification 151
NTP Clients 151
Upgrading System Software 152
Web Interface 154
Using NTP 154
Adding Server Associations 154
Adding Peer Associations 155
Verifying Server and Peer Associations 155
Adding Broadcast Associations 156
Adding Multicast Associations 157
Configuring NTP Clients 158
Using the Modem for Dial-up Time Service 159
Working with Generic NTP Devices 160
Using NTP Authentication 160
Using MD5 Keys on a SyncServer 161
Using MD5 Keys on a Generic NTP device 162
Using Autokey 163
Enabling Secure Login 164
Recovering a Password 164
Halting the SyncServer 165
CAUTION: Stopping the SyncServer 165
Backing Up/Restoring Configurations 165
Creating a Backup File 166
Restoring from a Backup File 167
Transferring Configurations 167
Restoring the Factory Default Configuration 167
WARNING: Removing Power 169
Removing the Top Cover 169
Replacing the Battery 169
CAUTION: Lithium Battery 169
Using LF Radio 170
Introduction 170
Unpacking 171
Connecting and Finding a Signal 171
Configuring the SyncServer 173
Troubleshooting Antenna Locations 173
Mounting Outdoors 173
Additional Resources 173
11
Page 12

Microsemi Worldwide Sales 173
Using Redundant Ethernet Ports 174
About Redundant Ethernet Ports 174
Configuring Redundant Ethernet Ports 174
Verifying Redundancy 174
Restoring Redundant Ethernet Ports 175
Managing Users 175
Changing the Password 175
Enabling Password Recovery 175
Creating a New User 176
Deleting a Current User 176
Estimating Worst Case Time Error when GPS is Unavailable 176
Setting the Time Manually 177
Distributing GPS Time 178
Distributing Non-UTC Time 180
Configuring SNMP 181
SNMP MIB 182
Glossary 195
Command Line 195
GPS 195
Hardware Clock 196
Input References 196
Leap Indicator 197
NTP Associations 197
NTP Daemon 198
NTP Packet 198
PING 201
PTP (Precision Time Protocol 202
Stratum 202
Synchronizing NTP association 202
UTC 202
Operational Configuration 203
Index 205
12
Page 13

Configuringthe SyncServer
S300, S350 and S350i Quick Start Guide
In this section
Configuring the SyncServer 13
Status LEDs 15
Halting the SyncServer 15
This topic guides the user on how to:
n Configure a SyncServer that stillhas its original factory configuration.
n Read the status LEDs on the front panel.
n Shut the SyncServer down correctly.
For more information about the featuresand tasksdescribed here, consult the following sections in the main User Guide:
n Web Interface (on page 21)
n Keypad/Display Interface (on page 101)
n Specifications (on page 111)
n Tasks (on page 135)
For your convenience, cross referencesin this QuickStart Guide provide the page numbers
of topics in the main User Guide.
Configuring the SyncServer
Recommended Tasks
GPS antennas not rated for 12 VDC power may be damaged if connected to the SyncServer.
1. Mount the standard L1 GPS antenna (supplied) in a locationthat offers good visibilityof
GPS satellites, such as a rooftop or outdoor antenna mast with wide open views of the
skyand horizon. Avoidobstructions and sources of Radio FrequencyInterference.
Observe building codes and regulations. Also see Using GPS (on page 140) and
WARNING: GPS Antenna (on page 132).
a. Note: For the SyncServer 350i, which doesn't have a GPS receiver, connect an
IRIG signal to the IRIG In connector on the rear panel and skip references to GPS and
antennas in the rest of this procedure.
2. On the rear panel:
n
Connect the GPS antenna cable (supplied) to the GPS Ant connector.
n
Connect LAN1 and any of the other network ports to the network.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 13
Page 14

S300, S350 and S350i Quick Start Guide
n Consult Warnings and Cautions (on page 131) for safety informationregarding
grounding and power.
n Connect the power and turn the power switch on.
3. Using the front panel keypad:
n
Configure LAN1 with a staticIP address using the MENU button and 1) LAN1.
n
View the LAN1 IP address by pressing the STATUS button repeatedly until the
LAN1 STATUS screen is shown.
4.
Go to the SyncServer Login page by entering the LAN1 IP addressas the URL in Internet
Explorer.
5. Log in. The user name is "admin". The password is "symmetricom".
6.
Configure the SyncServer using WIZARDS - 1st Setup. Select the following options:
n "Configure Password Recovery" (Ask the IT department for the IP address of the
SMTP server).
n "Send test mail when finished"
n "Set Local Time Zone"
7.
Configure the remaining network ports using NETWORK - Ethernet.
n Assignstatic IP addresses.
n Protect LAN1 and the other ports from unauthorized IP addresses or address
ranges using the Allowed Access feature.
8. Configure the NTP clients on your network with the IP address(es) of the SyncServer's
network ports.
The SyncServer is providing synchronized time to the network when the SYNC LED (front
panel) is orange or green.
Optional Tasks
In the web interface:
n Connect any other Input References to the rear panel and configure them usingthe
pages under the REFERENCES section.
n
Use the NTP – Config page to synchronize the SyncServer with any other NTP servers.
n
Use WIZARDS - SNMP to set up alarm notification by SNMP.
n
Use SERVICES - Email to set up alarm notification by email.
n
When the SyncServer is completelyconfigured, use WIZARDS - Backup to save a backup
file of the configuration to a safe location. Write the location of the backup file on this printed document and store it in a location that is easy to find.
Page 14..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 15
Status LEDs
The four tricolor LEDs provide the following status information:
Red Orange Green Dark
Sync
Network
NTP
Alarm
SyncServer is
not synchronized
to a
reference.
NTP Stratum 16.
Link failure on the
LAN1.
>7000 NTP packets persecond.
Major Alarm. Minor Alarm. No Current/Enabled Alarms. Power off.
Also see Stratum (on page 202).
SyncServer is synchronized to a remote
NTP server.
NTP Stratum 2-15.
Link failure on the LAN2,
LAN3, or LANGBE.
> 5000 packets per
second.
SyncServer is synchronized to
an Input Reference or the
modem1.
NTP Stratum 1.
All configured ports operational. Power off.
NTP activity within the last
second.
Status LEDs
Power off.
No NTP
activity in
the last
second.
Halting the SyncServer
Microsemi recommends shutting the operating systemdown before removing the power.
Using the keypad/display interface:
1.
Press the MENU button.
2.
Select 3) Sys Control.
3.
Select 2) Shutdown.
4.
Press the ENTER button.
5. When the displayshows "SystemStopped - OK to Turn Power Off Now!" turn the power
off.
Or, using the web interface:
1.
Go to the SERVICES - Startup page.
2.
Select Halt and clickthe APPLY button.
3. Wait approximately30 seconds before removing power.
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a modem.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 15
Page 16
Page 17

Product Overview
The SyncServer Network Time Server offers the following protocolsfor synchronizing equipment over a network:
n NTP
n PTP Grand Master (option)
n SNTP
n Time (TCP and UDP versions)
n Daytime (TCP and UDP versions)
n Sysplex Output (dedicated port)
These protocols are capable of synchronizing computers, servers, and networking equipment on an enterprise-scale network to within milliseconds of officialUTC time. This degree
of synchronization is desirable for precise time-stamping of events and data correlation.
Key Features
n Ultra High-Bandwidth NTP Time Server
n Stratum 1 Operation via GPS* Satellites
n Gigabit Ethernet port plus 3 additionalIndependent 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Ports
n Internal Dial-up Modem* for Time Reference Redundancy
n Independent Time References: GPS, Timecodes, 1PPS, 10MHz
n VersatileTiming Outputs: IRIG A/B/E/G/NASA36/XR3/2137 AM or DCLS, 1PPS,
10MHz, Sysplex
n Stratum 2 Operation via NTP Servers
n RADIUS, NTPv4 Autokey, MD5 Authentication
n TACACS+Authentication
n Secure Web-Based Management
n SSH, SSL, SCP, SNMP, Custom MIB, HTTPS, Telnet, and More
n IPv6 and IPv4 Compatible
n Nanosecond Time Accuracy to UTC
n Alarm Relays
n Rubidium & OCXO Oscillator Upgrades
n Upgrade to Radio Broadcast Time Sync
n IEEE 1588 / PTP Grandmaster Option
n Time Interval Measurement Option
* Note, the S350i SyncServer does not feature a GPS receiver, or modem.
Key Benefits
n Synchronize Hundreds of Thousands of Client, Server & WorkstationClocks
n Very Reliable and Secure Source of Time for Your Network
n Multiple NTP Ports for Easy Network Configuration and Adaptation
n ExtremelyAccurateTime Source for Network Synchronization
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 17
Page 18
Product Overview
n EnhancedNetwork & SecurityFeatures
n User Prioritized Reference Selection between, GPS, Timecode, 1PPS and 10MHz
n Access MultipleTime Sources for Reliable and Secure Time
n Intuitive Web Interface for Easy Control & Maintenance
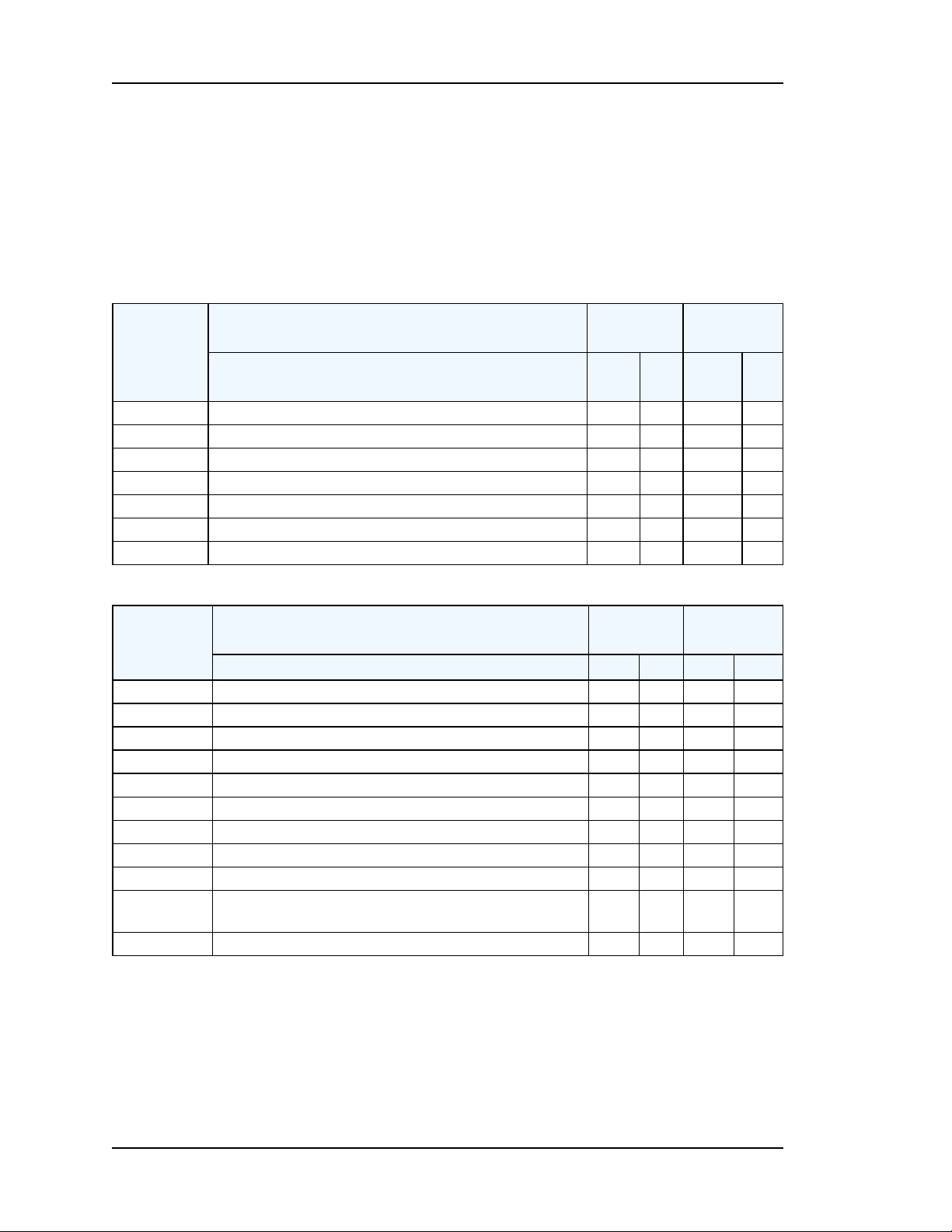
Comparison by Model
Time
Protocols
Time
References
(inputs)
SyncServer Model Comparison
Enterprise
Class
Advanced
Feature S200 S300 S250
NTP Server (v2, v3, v4) Y
NTP Broadcast Server/Client Y
NTP Peering/Client Y
NTP Multicast Server/Client Y
IEEE 1588 PTP Grandmaster (optional)
SNTP, Time, Daytime Y
NTP performance, requests/second 3200
SyncServer Model Comparison
Enterprise
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y Y
Y
7000
Advanced
Class
Feature S200 S300 S250 S350
GPS (12 channel) Y
NTP Peering Y
Dial-upinternal modem (ACTS, JJY, ITU-R TF583.4)
Low Frequency Radio (WWVB, JJY, DCF77) (optional)
10MHz input Y
1PPS input Y
IRIG B AM Input Y
IRIG A/B/E/G/NASA36/XR2/2137 inputs (AM & DCLS)
Time Interval Measurement & Charting (S350
PTPOption)
Reference priority, user configurable
Y
Y
Y Y**
Y Y**
Timing
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
3200
Timing
Y*
Y
S35-
0
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
7000
Y*
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
* The S250i and 350i models use a timecodeinput instead of GPS as their primary Input
Reference.
** The SyncServer S350i does not include a low frequencyradio, or modem.
Page 18..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 19
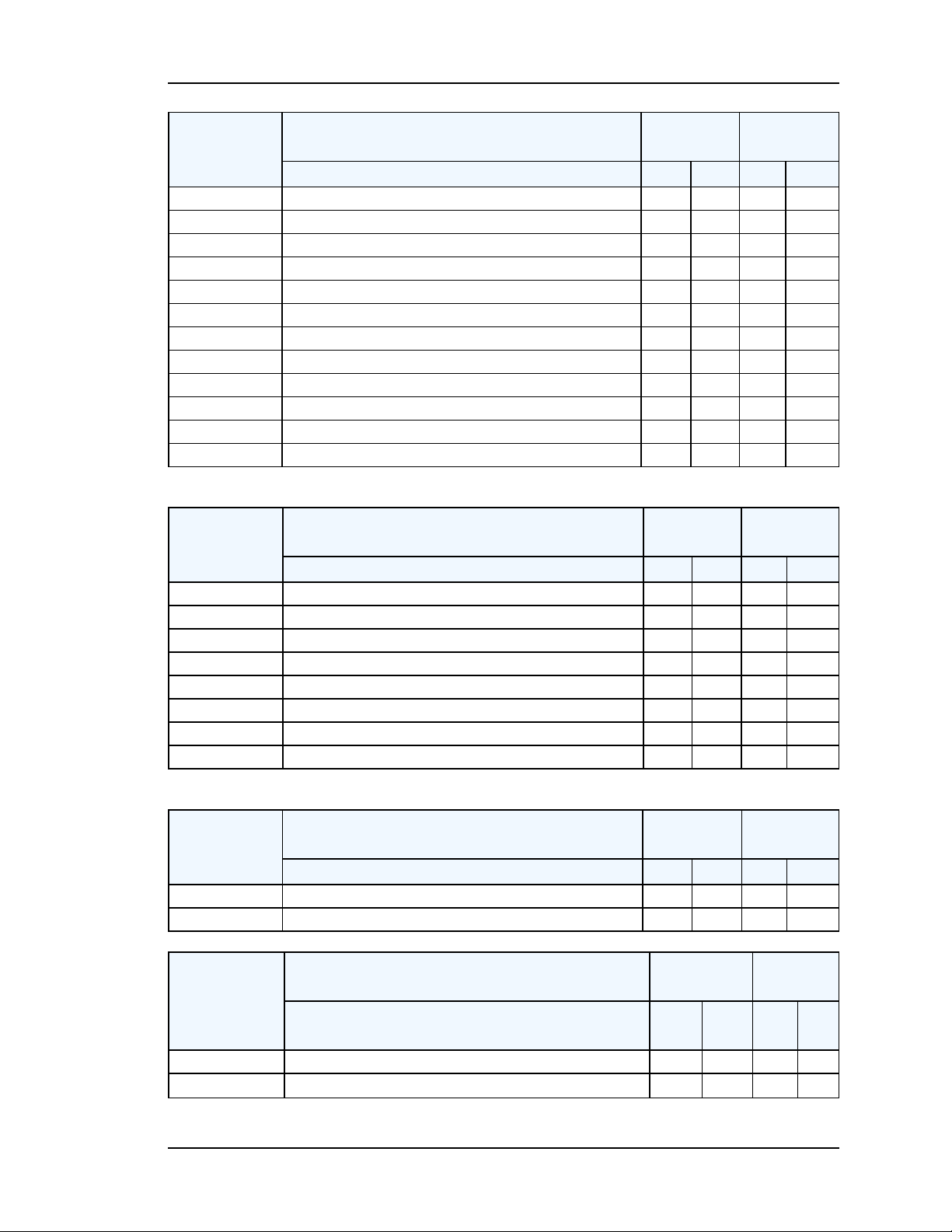
Comparison by Model
Network
Security
Protocols
User Inter-
face
SyncServer Model Comparison
Enterprise
Feature S200 S300 S250 S350
HTTP/HTTPS/SSL Y
Telnet (w/disablefcn.) Y
SNMP V1, V2c, V3 with Custom MIB II Y
DHCP (w/disable can.) Y
SSH/SCP (w/disable fcn.) Y
IPv6 and IPv4/IPv6 Y
MD5 for NTP Y
NTP v4 Autokey (Server and Client)
RADIUS Authenticated login
TACACS+ Authenticated login
1000Base-T equipped port (Gigabit)
Total number of Ethernet ports 3
SyncServer Model Comparison
Enterprise
Feature S200 S300 S250 S350
Web Interface Y
Vacuum fluorescent display/multi-line Y
Numeric keypad Y
LED’s: Sync, Network, Alarm, NTP Y
USB Y
RS-232Console Port Y
Alarm relays
Keypadlockout
Class
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y Y
Y Y
Y Y
Y Y
4
Class
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y Y
Y Y
Advanced
Timing
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
3
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
4
Advanced
Timing
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Oscillator
SyncServer Model Comparison
Enterprise
Class
Feature S200 S300 S250 S350
Timing
Outputs
OCXO upgrade Y
Rubidium upgrade Y
SyncServer Model Comparison
Enterprise
Y
Y
Class
Feature S200 S300 S250
Timing accuracy +/-50 ns Y
Sysplex output (dedicatedport) Y
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 19
Y
Y
Advanced
Timing
Y
Y
Y
Y
Advanced
Timing
S35-
0
Y
Y
Y
Y
Page 20
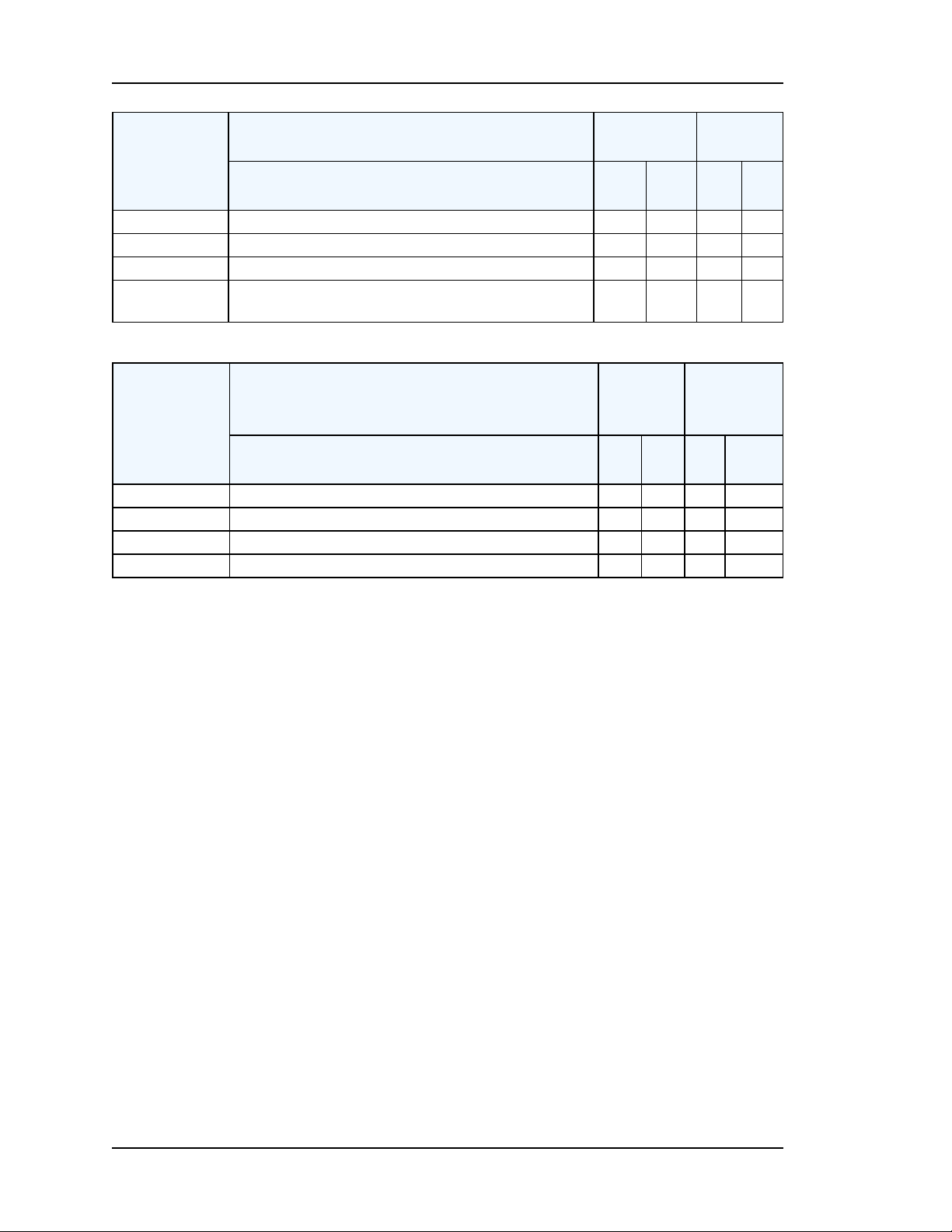
Product Overview
Timing
Outputs
Misc.
SyncServer Model Comparison
Enterprise
Class
Advanced
Timing
Feature S200 S300 S250
1PPS output Y
10MHz output Y
IRIG B AM output Y
IRIG A/B/E/G/NASA36/XR2/2137 outputs (AM &
DCLS)
SyncServer Model Comparison
Feature S200 S300
General server status logs Y
Autocheck for firmwareupgrades Y
Email alerts Y
Serve NTP in UTC or GPS Timescale
Enter-
prise
Class
Advanced
Timing
S25-
0
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y Y*
S35-
0
Y
Y
Y
Y
S350
Y
Y
Y
* The 350i model uses a timecode input instead of GPS as its primary Input Reference.
Page 20..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 21

Web Interface
This section providesa topic for each page in the web interface, with an explanation of each
field, notes, and links to related topics.
This section contains
Login 23
Properties of User Names and Passwords 23
STATUS - General 24
STATUS - Network 25
STATUS - Timing 26
STATUS - GPS 26
WARNING: GPS Position and Altitude 28
STATUS - NTP 28
NTP Daemon Status 28
STATUS - PTP 31
PTP Daemon Status 31
STATUS - Alarms 32
NETWORK - Ethernet 32
NETWORK - SNMP 35
NETWORK - SNMP Traps 37
NETWORK - Ping 37
NTP - Sysinfo 39
NTP Daemon Status 39
NTP - Assoc 42
NTP - Config 43
NTP - MD5 Keys 47
NTP - Autokey 48
NTP - Autokey Client 49
NTP - Prefs 50
PTP Option and Time Interval Test 51
Time Interval Test 52
PTP and NTP Performance 52
PTP Management Messages 52
How to Activatethe PTP Option 53
PTP - Master 54
IEEE 1588-2008 Annex J Recommended Default Settings 58
PTP - Slaves 58
PTP - Performance 59
Charting PTPPerformance 60
PTP - Save-Restore 60
To Save Configuration Settings to a File 60
To Restore Configuration Settings from a File 61
TIMING - Time Zone 61
TIMING - HW Clock 61
TIMING - Holdover 63
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 21
Page 22

Web Interface
TIMING - Sysplex 64
TIMING -Time Interval 67
REFERENCES - GPS 70
GPS Position and Operating Mode 70
REFERENCES - Timecode 71
REFERENCES - Modem 72
RESTART button 75
REFERENCES - LF Radio 75
SYSTEM - General 76
SYSTEM - Upgrade 77
SYSTEM - Factory Reset 77
Factory Default Settings 78
SYSTEM - Options 82
ADMIN - Web 82
ADMIN - Users 84
ADMIN - Alarms 85
Alarm Descriptions 86
Factory Default Settings for Alarms 89
ADMIN - Logs Config 90
ADMIN - Relays 92
ADMIN - RADIUS 93
ADMIN - TACACS+ 94
SERVICES - Startup 95
SERVICES - HTTP 96
SERVICES - SSH 97
SERVICES - Email 97
LOGS 97
WIZARDS - 1st Setup 99
WIZARDS - NTP 99
WIZARDS - SNMP 99
WIZARDS - Backup 99
WIZARDS - Restore 100
WIZARDS - Upgrade 100
Page 22..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 23

Login
Login
Use the Login page to:
n Log in to the Sync Server's web interface.
n Recover lost passwords.
n View system status.
The Login page includes the following elements:
n
Username: Enter the username here. (Factorydefault: "admin")
n
Password: Enter the corresponding password here. (Factory default: "symmetricom")
n
Secure: Opens an encrypted web session (HTTPS, port 443). For this feature to be available, the user must enable it by usingthe SERVICES - HTTP page.
n
Recover Password: Prompts the user to answer a password recovery question. If the user
answers correctly, the Sync Server resets the password to a random string and emailsit
to the user's email address. For this feature to be available, the user must enable it using
the ADMIN - Users or WIZARDS - 1st Setup pages.
Use the ADMIN - Web (on page 82) page to configure the status information on the Login page.
Also see Logging in to the Web Interface (on page 149) and Recovering a Password
(on page 164).
PropertiesofUserNames andPasswords
Usernames
Quantity & Length
There is an upper limit of 32 individual users, each username has a maximum of 32 characters in length.
Character set (Charset)
Each username is limited to the following printable ASCII characters:
n Upper case letters {A-Z}
n Lower case letters {a-z}
n Numbers {0-9}
n Period {.}
n Dash {-}
n Underscore {_}
n Plus {+}
Usernamesmay NOT contain any of the following:
n Standard ASCII keyboard characters not described above, i.e. ! @ # $% ^ & * () = {} [] |
\ ; : ' " < > ? , /
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 23
Page 24

Web Interface
n Grave accent {`}
n Tilde {~}
n Whitespace characters (space, tab, linefeed, carriage-return, formfeed, vertical-tab etc.)
n Non-ASCII characters
n Non-printablecharacters
Passwords
Length
The password can have a maximum of 64 characters in length.
Character set (Charset)
Passwords must contain, at minimum, either a mix of upper and lowercase letters, or a mix of
letters and numbers.
Passwords are limited to the followingprintable ASCII characters:
n Upper case letters {A-Z}
n Lower case letters {a-z}
n Numbers {0-9}
n Tilde {~}
n Most standard ASCII keyboard symbols, i.e. ! @ # $% ^ & * () _ - = {} [] | : ; " < > , . ? /
Passwords may NOT be all-lowercase, all-uppercase, all-numeric, or match the username.
They additionallymay NOT containany of the following:
n Single-quote / apostrophe {'}
n Grave accent {`}
n Plus {+}
n Backslash {\}
n Whitespace characters (space, tab, linefeed, carriage-return, formfeed, vertical-tab etc.)
n Non-ASCII characters
n Non-printablecharacters
STATUS - General
Overall System Information
n
Hostname: The network hostname of the SyncServer, which can be configured on the
SYSTEM - General web page.
n
Model: The model number of the SyncServer.
n
Serial Number: The unique serial number of the SyncServer.
n
Local Time: The local time, determined by the time zone setting on the TIMING - Time Zone
web page.
n
Release Version: The system release version.
Page 24..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 25
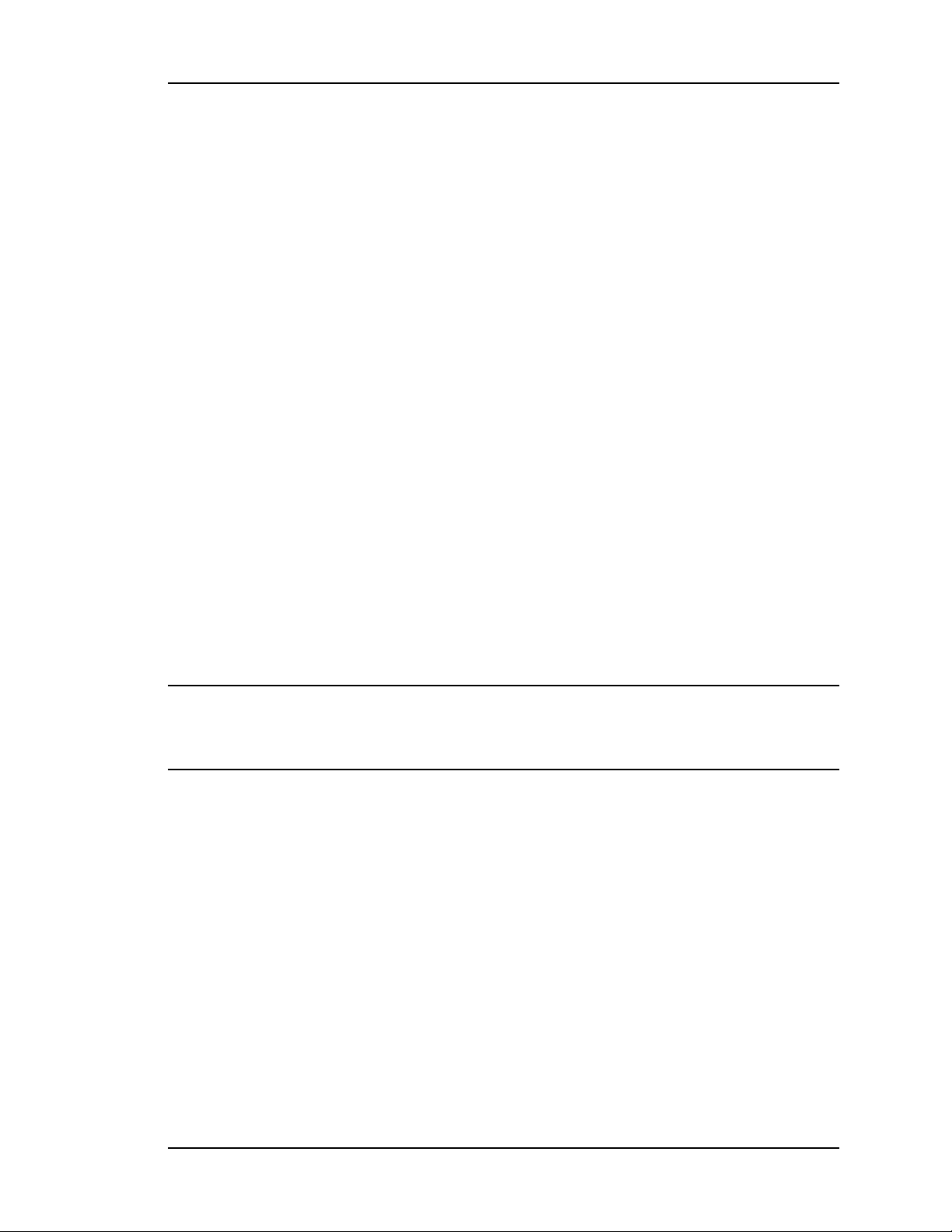
STATUS - Network
n
Software Version: The software version.
n
Hardware Clock Version: The version of the software on the Hardware Clock.
n
Up Time: The time elapsed since the operating system started.
n
Load Average: A figure of merit for the operating system “load” for the previous 1, 5, and
15 minutes (left to right).
n
Memory Used (Mbyte): The amount of memory occupied by the system.
n
Memory Free (Mbyte): The amount of free memory remaining.
n
Flash: The type of compact flash card installed.
n
CPU Vendor: The CPU vendor/manufacturer.
n
Model: The CPU model.
n
Number: The CPU number.
STATUS - Network
Network Status for each of the SyncServer's network ports:
n
The name of the Port.
n
The following Address information for each network port:
n
mac: The MAC Address.
n
v4: The IPv4 Address, if used.
n
v6 link: The IPv6 Address, if used.
n
The State of the physical network port device (not of the connection). An "Up Arrow"
meansit is "running". A "Down Arrow" means it is "not running".
Management Port DNS Servers: Both user-entered and DHCP-assignedDNS Server
addresses that are available from the LAN1 port.
The SyncServer requires at least one valid DNS server to resolve domain names, which
may be used in NTP associations, and SMTP gateways (email). Without a DNS server, any
function that uses a DNS name instead of an IP address may be affected. These can include
NTP, password recovery, and email notification of alarms.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 25
Page 26

Web Interface
STATUS - Timing
Hardware Clock Status
Current Sync Source: The Input Reference currently used by the Hardware Clock. Consult the
TIMING - HW Clock topic for more information.
Hardware Clock Time: The time according to the Hardware Clock.
Hardware Clock Status: "Locked" means the Hardware Clockis synchronized to one of its ref-
erences, or to the internal oscillator in "Holdover". "Unlocked" means the Hardware Clock
doesn't have an Input Referenceand the Holdover period has expired. Also see TIMING -
HW Clock (on page 61) and TIMING - Holdover (on page 63).
Oscillator Type: The type of the oscillator installed in the Hardware Clockfor operation and holdover.
For each of the following Input Status lines, "Locked"means that the reference is valid and
can be selected by the Hardware Clock. "Unlocked" meansthe reference is not valid, and is
therefore not available for use by the Hardware Clock. Also see TIMING - HW Clock (on
page 61) to arrange the priorityof the Input References.
Some of these references are optionsor are only available in specific SyncServer models.
(Consult Product Overview (on page 17) for more information about featuresand models):
n *GPS Input Status (note, the 350i SyncServer does not have a GPS receiver)
n Timecode Input Status
n 1PPS Input Status
n 10MHz Input Status
n LFR Input Status
* The SyncServer S350i does not have a GPS receiver.
Leap Warning: The state of the Leap Indicator (on page 197) as reported by the current input
reference.
STATUS - GPS
GPS Receiver Operation
This page displays the status of the GPS Receiver.
Receiver Description: "GPS" indicatesthe presenceof a 12-channel GPS receiver.
Receiver Status:
1
n Receiver Down: The Hardware Clock can't communicate with the receiver.
n Unknown Mode: An undefined mode of the GPS receiver.
n Acquiring Signal: The receiver is attempting to track a GPS signal.
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
Page 26..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 27

STATUS - GPS
n Bad Geometry: The geometry of the tracked satellitesis unsatisfactory for a position solu-
tion.
n Propagate Mode: A position estimation mode used in highly dynamic environments.
n 2d Solution: The receiver is able to perform position fixes for latitude and longitude but
does not have enough satellites for altitude.
n 3d Solution: The receiver is now able to perform position fixes for latitude, longitude and
altitude.
n Position Hold: Positionfixes are no longer attempted, and the surveyed or user-entered
position is used.
n Time Valid: The receiver has valid timinginformation from GPS satellites (including GPS-
UTC Offset and Leap Indicator). If the GPS receiver and antenna are set up correctly, the
receiver status should eventuallyreach and remain in this state.
Mode:
n Survey: The receiver is surveying and averaging its position. When it has finished sur-
veying, the receiver switches to Position Hold mode. Survey mode and PositionHold
mode are appropriate for static applications, such as a typicalserver room environment.
This is the default mode when the SyncServer starts.
n Dynamic: The GPS receiver surveys continuously to determine its position and doesn't
switch to another mode. This mode must be initiated by a user, and is appropriatefor
mobile applications such as ships, land vehicles, and aircraft. The degree of accuracy this
mode offers is fine for NTP time over networks, but is less than optimal for the timing outputs available on some SyncServer models.
n Position Hold: The GPS receiver has completed Survey mode and switched to this
mode, or the user has manuallyentered a positionand "forced"it into this mode. The
accuracy and stability of the SyncServer's timing outputs are optimalwhen the receiver
has its exact position and is in this mode.
Antenna Cable Delay (nS):
The user-configured value (on the REFERENCES - GPS page) to compensate for GPS signal
propagation from the antenna along the length of the cable to the receiver.
Antenna Status:
The GPS receiver supplies power to the GPS antenna through the antenna cable. It also
monitors the current to that circuit to detect open or short circuits.
n Good: The current to the GPS antenna and cable is normal.
n Open:The current is too low. The GPS antenna or cableis probably disconnected or
broken. Some splitters may cause this condition as well.
n Short: The current is too high. The GPS antenna or cable probably has a short circuit.
Position: The latitude and longitude of the GPS antenna in degrees, minutes, and fractional
seconds. Referenced to WGS-84.
Altitude: The altitude of the antenna in meters. Referenced to WGS-84.
Satellites: The list of GPS satellites visible to the receiver:
n Sat Number: The GPS satellite's Satellite Vehicle (SV) number, a unique identification
number
n Signal: The relative strengthof the GPS signal (dBW = decibels relative to 1 Watt).
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 27
Page 28

Web Interface
n Status: "Current" means that the receiver is usingthe GPS signal in its timing solution.
"Tracked" means the receiver is trackingthe signal, but isn't using it in the timingsolution.
WARNING:GPSPositionandAltitude
GPS position and altitude are for timingpurposes only. They are not intendedfor navigation
or other critical applications.
AVERTISSEMENT : La position et l'altitude de GPS sont seulement pour la synchronization. Ellesne sont pas prévues pour la navigation ou d'autres situations critiques
(situations de la vie-ou-mort).
STATUS - NTP
NTPDaemonStatus
This page displays the status of the NTP daemon. Many of the fieldsbelow are based on the
NTP Packet (on page 198). Also see http://www.ntp.org.
system peer: The IP address of the clocksource. The sourceis selected by the NTP daemon that is most likely to provide the best timing information based on: stratum, distance, dispersion and confidence interval. The system peer identified as "SYMM_TE(0)" is the local
SyncServer Hardware Clock. Also see Hardware Clock (on page 196).
system peer mode: The relationship of the SyncServer to a system peer, usually a "client".
Depending the configuration, the mode can be:
n Client: A host operating in this mode sends periodic messages regardlessof the reach-
ability state or stratum of its peer. By operating in this mode the host, usually a LAN workstation, announcesits willingnessto be synchronized by, but not to synchronize the peer.
n Symmetric Active: A host operating in this mode sends periodic messages regardless
of the reachabilitystate or stratum of its peer. By operating in this mode the host
announces its willingness to synchronize and be synchronized by the peer.
n Symmetric Passive: This type of association is ordinarilycreated upon arrivalof a mes-
sage from a peer operating in the symmetricactive mode and persists onlyas long as the
peer is reachable and operating at a stratum level less than or equal to the host; otherwise, the association is dissolved. However, the association will always persist until at
least one message has been sent in reply. By operating in this mode the host announces
its willingness to synchronize and be synchronized by the peer.
A host operatingin client mode (a workstation, for example) occasionally sendsan NTP message to a host operating in server mode (the SyncServer), perhaps right after rebooting and
at periodic intervals thereafter. The server responds by simply interchanging addresses and
ports, filling in the required time information and returningthe message to the client. Servers
need retain no state information between client requests, while clientsare free to manage
the intervalsbetween sending NTP messages to suit local conditions.
In the symmetric modes, the client/server distinction (almost) disappears. Symmetric passive
mode is intendedfor use by time servers operating near the root nodes (lowest stratum) of
the synchronization subnet and with a relativelylarge number of peers on an intermittent
Page 28..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 29
STATUS - NTP
basis. In this mode the identity of the peer need not be known in advance, since the association with its state variables is created only when an NTP message arrives. Furthermore,
the state storage can be reused when the peer becomes unreachable or is operating at a
higher stratum level and thus ineligible as a synchronization source.
Symmetric active mode is intendedfor use by time servers operating near the end nodes
(highest stratum) of the synchronization subnet. Reliable time service can usuallybe maintained with two peers at the next lower stratum level and one peer at the same stratum level,
so the rate of ongoing polls is usually not significant, even when connectivity is lost and error
messages are being returned for every poll.
leap indicator (LI):
The Leap Indicator (LI) is a two-bit binary number in the NTP packet header that provides
the following information:
n Advance warning that a leap second adjustment will be made to the UTC timescale at the
end of the current day. Leap secondsare events mandated by the world time authority
(BIPM) in order to synchronize the UTC time scale with the earth's rotation.
n Whether the NTP daemon is synchronized to a timing reference. The settings on the
NTP - Prefs (on page 50) page affect LI behavior.
LI Value Meaning
00 0 No warning.
01 1 Leapsecondinsertion: Last minute of the day has 61 seconds.
10 2 Leapseconddeletion: Last minute of the day has 59 seconds.
11 3 Alarm condition (Not synchronized)
When the SyncServer or NTP daemon is started or restarted, the leap indicator is set to "11",
the alarm condition. This alarm condition makes it possible for NTP clients to recognizethat
an NTP server (the SyncServer) is present, but that it has yet to validate its time from its time
sources. Once the SyncServer finds a valid source of time and sets its clock, it sets the leap
indicator to an appropriate value. The NTP Leap Change Alarm on the ADMIN - Alarms
page can be configured to generate an alarm and send notificationseach time the leap indicator changes state.
stratum:
This is an eight-bit integer that indicates the position of an NTP node within an NTP timing
hierarchy. It is calculated by adding 1 to the stratum of the NTP system peer.
For the SyncServer, the stratum valuesare defined as follows:
Stratum Definition
0 Hardware Clock when locked.
1 Primary server
2-15 Secondary server
16-255 Unsynchronized, unreachable.
For example, the SyncServer is:
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 29
Page 30

Web Interface
n stratum 1 when the Hardware Clock (stratum0) is synchronized to an input reference, in
holdover mode, or in freerun mode.
n stratum 2 through 15 when it is synchronized to a remote NTP server.
n stratum 16 when it is unsynchronized, indicating that it is searchingfor a valid source of
timing information.
The settingson the NTP - Prefs (on page 50) page affect stratum behavior.
precision: This is a signed integer indicating the precision of the selected peer clock, in
seconds to the nearest power of two. A typicalvalue is -18 for a Hardware Clock where the
uppermost 18 bits of the time stamp fractional component have value, indicating a precision
in the microsecond range.
root distance (also root delay): This is a measure of the total round trip delay to the root of
the synchronization tree. A typical value for a SyncServer operatingat stratum 1 would be 0
since the SyncServer is a root of the synchronization tree For other stratum levels, an appropriate valueis displayed. Depending on clock skew and dispersion, this value could be positive or negative.
root dispersion: This is a signed fixed-point number indicating the maximum error relative
to the primary reference source at the root of the synchronization subnet, in seconds. Only
positive values greater than zero are possible.
reference ID: This is a four-byte field used to identifythe reference clock source. At initialization, while the stratum is 16, this field shows the progression of the NTP clock PLL. The
field will start with a value of INIT (may be displayed as 73.78.73.84, the ASCII decimalvalues). Once a peer has been selected, the clock may be stepped, in which case the reference
ID field will change to STEP (or 83.84.69.80). Once the PLL is locked, the stratum will be
updatedand the reference ID will identify the selected peer. In the case of a SyncServer
operating at stratum 1, the reference ID will displaythe sourcefor the local timing reference
(e.g., GPS1, IRIG, FREE). In the case where the selected peer is another NTP server, the
reference ID will display the IP addressof the server or a hash unique to the association
between the SyncServer and the remote server.
reference time (also reference timestamp): The time when the SyncServer last received
an update from the selected peer. Represented using time stamp format in local time. If the
local clock has never been synchronized, the valueis zero. A time stamp of zero corresponds
to a local time of Thu, Feb 7 2036 6:28:16.000. This value is typically updatedevery16
seconds for a locally attached hardware reference (e.g., GPS, IRIG) and in an interval of 641024 seconds for a readily accessible remote NTP server.
system flags: These flagsdefine the configured behavior NTP daemon running on the SyncServer. The definitionof the variablesis provided.
n kernel: The NTP daemon is enabled for the precision-time kernelsupport for the ntp_adj-
time() system call.
n monitor: The NTP daemon is enabled its monitoring facility.
n ntp: Enables the server to adjust its local clockby means of NTP.
n stats: The NTP daemon is enabled itsstatistics facility.
n auth: The NTP daemonis enabled itsauthentication facility.
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
Page 30..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 31

STATUS - PTP
jitter: Jitter (also called timing jitter) refers to short-term variations in frequency with componentsgreater than 10 Hz.
stability: Stability refers to how well the SyncServer can maintain a constant frequency over
time. It is usually affected by aging, environment changes, etc. The value is expressed units
of parts per million (ppm).
broadcastdelay: The broadcast and multicast modes require a special calibration to determine the network delaybetween the local and remote servers. Typically, this is done automaticallyby the initialprotocol exchanges between the client and server. This is the
broadcast or multicast delay reported by the NTP daemon. The value is always set to 0.004
seconds on the SyncServer.
authdelay: When NTP authentication is enabled and performed on outgoing NTP packets,
this adds a trivial amount of fixed delay that can be removed based on the authdelay value.
This valueis always set to zero on the SyncServer.
STATUS - PTP
This page will only appear if the IEEE-1588 2008 PTP option has been activated.
See "How to Activate the PTP Option" on page 53
From this page, the statusof a list of PTP system parameters of the PTPDaemon can be
viewed.
See "PTP - Master" on page 54
PTPDaemonStatus
Field Example of Field Value
Clock ID 00:a0:69:ff:fe:01:6e:8d
PTP Slaves Tracked "0"
PTP Version "2"
Clock Class "6" (Synchronized)
Clock Accuracy "21" (Within 100 ns)
Time Source "20" (GPS)
Current UTC Offset "34 sec"
UTC Valid True or False
Leap 59 Trueor False
Leap 61 Trueor False
Time Traceable True or False
Frequency Traceable True or False
Transport Protocol The choices for the Transport Protocol are:
1
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 31
Page 32

Web Interface
Field Example of Field Value
l IPv4/UDP – this is Default
l 802.3
Sync Interval "1 pkt/1 sec"
Delay Mechanism "E2E"
ITT "1"
E2E Delay Interval "1 pkt/1 sec"
P2P Delay Interval "1 pkt/1 sec"
Priority 1 "128"
Priority 2 "128"
Domain Number "0"
Announce Transmit Interval "2 sec"
Announce Timeout Multiplier "3"
STATUS - Alarms
Current Major or Minor Alarms
Alarms with Severityset to:
n Major are displayed in red text.
n Minor are displayed in orange text.
n Notify are not displayed.
Alarms can be configured using the ADMIN - Alarms page.
For each listing:
Time: The local date and time at which the alarm was raised.
Severity: The severityof the alarm event (Major/Minor).
Name: The name of the alarm, from the list of alarmson the ADMIN - Alarms page.
NETWORK - Ethernet
Use this page to get status and configure Ethernet LAN port network settings, including DNS
servers.
Ethernet Port Configuration
Edit the network port configuration and view network port status.
EDIT: Clicking thisbuttonopensa dialog box for configuring the network port.
Pending Changes: A check mark indicates that settings have changed, reminding the user
to clickthe APPLY button.
Port: The name of the network port.
Page 32..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 33

NETWORK - Ethernet
IP Address: The port's MAC, IPv4, and/or IPv6 network addresses.
Usage: These icons summarize information about the port:
n
(Checkmark): The user has changed the configuration, but hasn't clickedthe APPLY
button at the bottom of the page yet.
n
(Management Port): This network port is configured as the management port (web
interface, SNMP, email, DNS).
n
(Up Arrow): The physical network port is enabled and functioning (does not indicate a
valid physical connection or configuration).
n
n (Question Mark): Status unknown - usually when there are pendingchanges.
n
n
(DHCP): The network configuration is automaticvia DHCP
(Number "6"): Uses IPv6
(Letter "B"): Configured for bonding with another port in a redundant pair.
DNS Servers
The DNS Server fieldsdisplay the IP addresses of Domain Name Service (DNS) servers.
The SyncServer requires a valid DNS server address to resolve domain names. If a DNS
server isn't provided, NTP associations (NTP - Config) and the SMTP Gateway
(SERVICES - Email) must be specifiedusing an IP address. DNS messages are only communicated through LAN1 port. The specified DNS servers must be reachable from the LAN1
port.
n Management Port User DNS Servers: Manuallyenter one or more DNS Server IP
addresses here, if not supplied by DHCP.
n Management Port DHCP DNS Servers (Read Only): If LAN1 has DHCP enabled,
and DHCP is configured to supply DNS server addresses, displaysthe DNS server IP
addresses supplied by DHCP. These values are not user-editable.
Note: If the SMTP Gateway (which supportsPassword Recovery and Email Notification of
Alarms) and NTP associations are addressed using domain names, a valid DNS server
addressmust be supplied to the SyncServer.
Network Port Configuration
To edit the settings for a network port, click the corresponding EDIT button on the
NETWORK - Ethernet page. This opens a dialog box titled with the name of the port followed by "Configuration".
To apply configuration changes, clickAPPLY buttons on both this configuration window and
later on the NETWORK - Ethernet page.
Connection Mode:
n Static: A user must configure the network port manually.
n DHCP: A DHCP server will automatically configure the network port when changes are
applied. Not available for IPv6.
n Disabled: This disablesthe network port.
Note: If the Connection Mode is DHCP and the lease expiresor the SyncServer reboots, a
DHCP server could assign a new IP addressto the SyncServer’s network port. If this occurs
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 33
Page 34

Web Interface
with the LAN1 port, use the STATUS button on the front panel to obtain the new IP address.
Furthermore, if it occurs to a network port servicing NTP requests, NTP clients will no longer
be able to get a response from that port. In that case, the NTP clientswould have to use an
alternateNTP source or become unsynchronized. For this reason, Microsemi recommends
using static IP addresses, only using DHCP for convenience during temporary installations.
IP Version:
n IPv4: The port uses IPv4 exclusively. (Static or DHCP)
n IPv6: The port uses IPv6 exclusively. The user must enter a static IPv6 address.
IP Address: The port's IPv4 address (e.g., "192.168.0.100") or IPv6 address(es) with
scope (e.g., fe80::2a0:6dff:fe00:10).
Mask: The port's IPv4 subnet mask (e.g., "255.255.255.0"). With IPv6, the mask is the
length of the prefix.defined in CIDR format (Classless Inter Domain Routing). Typically, the
IPv6 mask is 64.
Note: The SyncServer does not support masks on IPv6 gateway entry. While the user interface will accept/display a user entered mask, such as “/64” for the IPv6 gateway, the underlying software checks for the entered mask and removes it, before sending the unmasked
IPv6 gateway address down to the lower level Linux system components to configure the network interface.
Gateway: The port's IPv4 or IPv6 gateway (e.g., "192.168.0.1"). This is an optional configuration parameter.
Management: Reserved for future use.
Redundant: Bonds LAN3 to LAN2 as virtual device with a single network address.
n Active: The Active port handles network traffic. LAN2 is "Active" by default.
n Backup: The Backup port handles network traffic if the connection to the Active port fails.
LAN3 is the "Backup" port by default.
If the connection to LAN2 fails, LAN2 becomesbackup and LAN3 becomesactive. After
repairing the connection, the user can manuallyreconfigure LAN2 as the Active port:
1. In the "LAN2 Configuration" window, select the "Redundant" checkbox, select "Active",
and then clickthe APPLY button.
2. On the NETWORK - Ethernet page, click the APPLY button.
To release a redundant bond, deselect the "Redundant" checkboxand applythe changes. If
the bond doesn't release, reboot the SyncServer.
Allowed Access: Restricts the LAN port to access by specified IP addresses or address
ranges. If the user leavesthis field blank, the LAN port acceptsconnections from any IP
address. Allowed Accessapplies to all forms of network traffic, including NTP and HTTP connections. Reconfiguring the IP address of the LAN port erases the Allowed Access list.
The user can specify addressranges by setting the IP addressfollowed by the mask prefix
length, as described RFC 1518 and RFC 1519 for Classless Inter-domain Routing. The
mask prefix length specifies the number of masked bits starting from the left-most pos-
ition. For example, to allow access from the network representedby 192.168.0.0,
Page 34..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 35

NETWORK - SNMP
255.255.0.0, the user would enter 192.168.0.0/16. In other words, the first 16 bits of the
address, 192.168, are masked bits representing the network address The remaining bits are
host addresswhich is set to 0.
Note: When configuring Allowed Access, take care to avoidblocking DNS, HTTP, NTP,
RADIUS, SMTP, SNMP, and SSH traffic.
Speed/Duplex: Sets the network port speed automatically(Auto), to 10 or 100. Sets the
transmission to Full or Half duplex. User must exercise caution when changingspeed and
duplexsettings on any of the SyncServer ports. Speed and duplex settings on a network port
are negotiated with its network link partner. Depending on the settings of the port’s linkpartner, the requested settingsmaynot be actuallytaken. Sometimes the network link between
the port and its link partner may be lost due to changing of the speed and duplexsettings.
Microsemi recommends usingthe Auto setting.
Side Effects
Applying changes to the Ethernet port configuration restarts the NTP and xinetd daemons
(services). During that time:
n The NTP daemon, NTP stratum, web interface are temporarily unavailable.
n The Status LEDs, NTP stratum, and Alarms change states.
Attach Cables to IPv6 Configured Ports
The NTP daemonrescans all interface ports every five minutes.
If a cable is not attached to an IPv6 configured port when the network settings are applied,
the NTP daemon will not be able to bind to that IPv6 port. If a cable is attached later to the
IPv6 configuredport, up to five minutescan pass before the next rescan. At the time of the
next rescan, the NTP daemon would then be able to bind the port, and respond to NTP packets.
The solutionto this behavior is to have the cable connected to the SyncServer IPv6 configured port before applyingthe network settings.
NETWORK - SNMP
This page provides configuration of basic SNMP settings and the creation of SNMPv3 users.
Basic Configuration
Establish the identity and community membership of the device.
sysLocation: Identify the location of the SyncServer (e.g. Server Room A, Company Divi-
sion B, etc). Used by network management consoles.
sysName: Provide the SyncServer with a unique name. (This is distinct and separatefrom
"hostname" on the SYSTEM - General and STATUS - General pages.) Used by network
management consoles.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 35
Page 36

Web Interface
sysContact: The name of the individual responsible for the SyncServer. Used by network
management consoles.
Read Community: The SNMP read community string. The string must be providedfor
SNMP v1/v2c GETS/WALKS to gain access.
Write Community: The SNMP write community string.
Note: At this time, the SyncServer does not support any writable SNMP variables.
V3 Users
SNMP user names are separate and distinct from the access control list usernames used to
log in to the SyncServer's user interfaces. SNMP user names are used by the network management software.
This is the list of SNMP v3 users. To delete a user, select the checkbox for a user name and
click the DELETE button. When prompted, enter the passphrase specified when the user
was created. The SNMP admin user cannot be deleted.
(Using SNMP v3 requires an SNMP v3 user on the recipient systems' SNMP v3-capable
agent/client)
User Name: Name of v3 User.
Mode: Currently only rouser (read-onlyuser) mode is supported.
Level: Shows the Min Priv level of the user (see Min Priv, below):
n auth: Authentication
n noauth: No Authentication
n priv: Auth and Privacy
n blank: default level for admin
Add v3 User
To create an SNMPv3 user, complete the form and click the SAVE button.
Name: Alphanumeric user name, with no spaces or specialcharacters.
Auth Phrase: Create a unique authentication passphrase for the user. It must be at least
eight characters long.
Auth Crypt: The authentication type, MD5 or SHA1. It uses the Auth Phrase as its key
when calculating the message hash.
Priv Phrase: Creates a unique encryption passphrase for messagesexchangedbetween
the network management software and the SyncServer. It must be at least eight characters
long.
Min Priv: Establishesthe minimum authentication level required for the user. One of the following must be selected:
n Authentication (Auth): Auth Phrase is always required
n Auth and Privacy(Priv): Auth and Priv Phrase are always required
Page 36..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 37

NETWORK - SNMP Traps
NETWORK - SNMP Traps
Use this page to configure, add, or delete SNMP trap recipients. The page is divided into two
sections. The first section displaysthe current recipients. The second section provides a form
for adding recipients or modifying existing recipients. The first section only displays basic
information for each recipient.
Trap Recipients
Destination: The IP address to which traps are to be sent.
Ver: The SNMP version (v1, v2c or v3).
(Send as Inform): If trap is to be sent as inform, ‘inform’is written, otherwise is blank.
User/Community: For SNMPv1/v2c traps, an optional community. For SNMPv3 traps, a
required SNMP v3 user on the recipient system. (Using SNMP v3 requires an SNMP v3
user on the recipient systems' SNMP v3-capable agent/client)
Add/Edit Trap Recipient
IP Address: The IP address to which traps are to be sent.
The SNMP version: v1, v2c, or v3.
User/Community: For SNMPv1/v2c traps, an optional community. For SNMPv3 traps, a
required SNMP v3 user on the recipient system.
Send as Inform: Sends an INFORM-PDU, otherwise a TRAP-PDU or TRAP2-PDU is sent.
Auth Phrase: For SNMPv3 traps, an optional Auth Phrase.
The hash algorithm used for the Auth Phrase: MD5 or SHA1.
Priv Phrase: For SNMPv3 traps, an optionalPriv Phrase.
To edit a trap recipient, select the checkbox of a specific recipient and click the EDIT button.
Edit the values displayed in Add/Edit Trap Recipient and click the SAVE button. Similarly,
use the DELETE button to remove trap recipients from the list.
NETWORK - Ping
Network Ping Test
Use this page to PING a network node from one of the SyncServer's network ports. This feature can be used to test and troubleshoot network connectivity issues.
To use PING:
1. Select the network port from which to send the PING packets. (See "Ping 6 Command"
on page 38
2.
For IPv6 networks, select Ping 6.
3.
Enter the IP address of the host and click the APPLY button. Ping Output displays the results
five seconds after clicking apply.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 37
Page 38

Web Interface
Ping 6 Command
The SyncServer software executes the following command when pinging an IPv6 address.
ping6 -c 5 -w 5 -I <eth dev> ipv6address
-c 5 sends 5 ping requests.
-w 5 times out after 5 secondsregardless of the target is reachable or not.
ipv6address is the target address(Customer inputsthis address in the SyncServer entry
box)
-I <eth dev> specifies the interface which corresponds to the drop down choice:
LAN1 – “-I eth0”
LAN2 – “-I eth1”
LAN3 – “-I eth2”
LANG – “-I eth3”.
The drop down choice of the interface, suggeststhat it correspondsto where the ping6
packet will be sent from. This is not entirely correct.
For example, the “-I eth0” only means to set the source IP address in the ping packet to that
of the eth0, it does not specify which interface it actually will always use to send out the packets. The interface the ping6 uses to send out the packetsis entirely determined by the Linux
kernel routingtable.
If the target Ipv6address is a link-local IPv6 address, the -I <eth dev> must also be a linklocal address as specified in the way that SyncServer port was configured.
For example:
ping6 -c 5 -w 5 -I <LAN1> ipv6address
If the ipv6address is a link-local address, then the LAN1 specified from the SyncServer
drop down menu on the ping page must also be configured with a link-local address. If it is
configured that way then the ping packet will be sent out that LAN1 port.
If the ipv6address address is a global address, then the -I <eth dev> information is ignored
and the Linux kernel routing table decides which port to send the ping packet out of. This is
how it is possible to specify a globaladdress to send a ping6 to, but not have the packet exit
the specified LAN port. It is because either the LAN port did not have a global address specified, or if it did, the Linux kernel chose not to send the packet out that port, but rather
another LAN port that had a global address assigned.
Page 38..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 39

NTP - Sysinfo
NTP - Sysinfo
NTPDaemonStatus
This page displays the status of the NTP daemon. Many of the fieldsbelow are based on the
NTP Packet (on page 198). Also see http://www.ntp.org.
system peer: The IP address of the clocksource. The sourceis selected by the NTP daemon that is most likely to provide the best timing information based on: stratum, distance, dispersion and confidence interval. The system peer identified as "SYMM_TE(0)" is the local
SyncServer Hardware Clock. Also see Hardware Clock (on page 196).
system peer mode: The relationship of the SyncServer to a system peer, usually a "client".
Depending the configuration, the mode can be:
n Client: A host operating in this mode sends periodic messages regardlessof the reach-
ability state or stratum of its peer. By operating in this mode the host, usually a LAN workstation, announcesits willingnessto be synchronized by, but not to synchronize the peer.
n Symmetric Active: A host operating in this mode sends periodic messages regardless
of the reachabilitystate or stratum of its peer. By operating in this mode the host
announces its willingness to synchronize and be synchronized by the peer.
n Symmetric Passive: This type of association is ordinarilycreated upon arrivalof a mes-
sage from a peer operating in the symmetricactive mode and persists onlyas long as the
peer is reachable and operating at a stratum level less than or equal to the host; otherwise, the association is dissolved. However, the association will always persist until at
least one message has been sent in reply. By operating in this mode the host announces
its willingness to synchronize and be synchronized by the peer.
A host operatingin client mode (a workstation, for example) occasionally sendsan NTP message to a host operating in server mode (the SyncServer), perhaps right after rebooting and
at periodic intervals thereafter. The server responds by simply interchanging addresses and
ports, filling in the required time information and returningthe message to the client. Servers
need retain no state information between client requests, while clientsare free to manage
the intervalsbetween sending NTP messages to suit local conditions.
In the symmetric modes, the client/server distinction (almost) disappears. Symmetric passive
mode is intendedfor use by time servers operating near the root nodes (lowest stratum) of
the synchronization subnet and with a relativelylarge number of peers on an intermittent
basis. In this mode the identity of the peer need not be known in advance, since the association with its state variables is created only when an NTP message arrives. Furthermore,
the state storage can be reused when the peer becomes unreachable or is operating at a
higher stratum level and thus ineligible as a synchronization source.
Symmetric active mode is intendedfor use by time servers operating near the end nodes
(highest stratum) of the synchronization subnet. Reliable time service can usuallybe maintained with two peers at the next lower stratum level and one peer at the same stratum level,
so the rate of ongoing polls is usually not significant, even when connectivity is lost and error
messages are being returned for every poll.
leap indicator (LI):
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 39
Page 40

Web Interface
The Leap Indicator (LI) is a two-bit binary number in the NTP packet header that provides
the following information:
n Advance warning that a leap second adjustment will be made to the UTC timescale at the
end of the current day. Leap secondsare events mandated by the world time authority
(BIPM) in order to synchronize the UTC time scale with the earth's rotation.
n Whether the NTP daemon is synchronized to a timing reference. The settings on the
NTP - Prefs (on page 50) page affect LI behavior.
LI Value Meaning
00 0 No warning.
01 1 Leapsecondinsertion: Last minute of the day has 61 seconds.
10 2 Leapseconddeletion: Last minute of the day has 59 seconds.
11 3 Alarm condition (Not synchronized)
When the SyncServer or NTP daemon is started or restarted, the leap indicator is set to "11",
the alarm condition. This alarm condition makes it possible for NTP clients to recognizethat
an NTP server (the SyncServer) is present, but that it has yet to validate its time from its time
sources. Once the SyncServer finds a valid source of time and sets its clock, it sets the leap
indicator to an appropriate value. The NTP Leap Change Alarm on the ADMIN - Alarms
page can be configured to generate an alarm and send notificationseach time the leap indicator changes state.
stratum:
This is an eight-bit integer that indicates the position of an NTP node within an NTP timing
hierarchy. It is calculated by adding 1 to the stratum of the NTP system peer.
For the SyncServer, the stratum valuesare defined as follows:
Stratum Definition
0 Hardware Clock when locked.
1 Primary server
2-15 Secondary server
16-255 Unsynchronized, unreachable.
For example, the SyncServer is:
n stratum 1 when the Hardware Clock (stratum0) is synchronized to an input reference, in
holdover mode, or in freerun mode.
n stratum 2 through 15 when it is synchronized to a remote NTP server.
n stratum 16 when it is unsynchronized, indicating that it is searchingfor a valid source of
timing information.
The settingson the NTP - Prefs (on page 50) page affect stratum behavior.
precision: This is a signed integer indicating the precision of the selected peer clock, in
seconds to the nearest power of two. A typicalvalue is -18 for a Hardware Clock where the
Page 40..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 41

NTP - Sysinfo
uppermost 18 bits of the time stamp fractional component have value, indicating a precision
in the microsecond range.
root distance (also root delay): This is a measure of the total round trip delay to the root of
the synchronization tree. A typical value for a SyncServer operatingat stratum 1 would be 0
since the SyncServer is a root of the synchronization tree For other stratum levels, an appropriate valueis displayed. Depending on clock skew and dispersion, this value could be positive or negative.
root dispersion: This is a signed fixed-point number indicating the maximum error relative
to the primary reference source at the root of the synchronization subnet, in seconds. Only
positive values greater than zero are possible.
reference ID: This is a four-byte field used to identifythe reference clock source. At initialization, while the stratum is 16, this field shows the progression of the NTP clock PLL. The
field will start with a value of INIT (may be displayed as 73.78.73.84, the ASCII decimalvalues). Once a peer has been selected, the clock may be stepped, in which case the reference
ID field will change to STEP (or 83.84.69.80). Once the PLL is locked, the stratum will be
updatedand the reference ID will identify the selected peer. In the case of a SyncServer
operating at stratum 1, the reference ID will displaythe sourcefor the local timing reference
(e.g., GPS1, IRIG, FREE). In the case where the selected peer is another NTP server, the
reference ID will display the IP addressof the server or a hash unique to the association
between the SyncServer and the remote server.
reference time (also reference timestamp): The time when the SyncServer last received
an update from the selected peer. Represented using time stamp format in local time. If the
local clock has never been synchronized, the valueis zero. A time stamp of zero corresponds
to a local time of Thu, Feb 7 2036 6:28:16.000. This value is typically updatedevery16
seconds for a locally attached hardware reference (e.g., GPS, IRIG) and in an interval of 641024 seconds for a readily accessible remote NTP server.
system flags: These flagsdefine the configured behavior NTP daemon running on the SyncServer. The definitionof the variablesis provided.
n kernel: The NTP daemon is enabled for the precision-time kernelsupport for the ntp_adj-
time() system call.
n monitor: The NTP daemon is enabled its monitoring facility.
n ntp: Enables the server to adjust its local clockby means of NTP.
n stats: The NTP daemon is enabled itsstatistics facility.
n auth: The NTP daemonis enabled itsauthentication facility.
jitter: Jitter (also called timing jitter) refers to short-term variations in frequency with componentsgreater than 10 Hz.
stability: Stability refers to how well the SyncServer can maintain a constant frequency over
time. It is usually affected by aging, environment changes, etc. The value is expressed units
of parts per million (ppm).
broadcastdelay: The broadcast and multicast modes require a special calibration to determine the network delaybetween the local and remote servers. Typically, this is done
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 41
Page 42

Web Interface
automatically by the initial protocol exchangesbetween the client and server. This is the
broadcast or multicast delay reported by the NTP daemon. The value is always set to 0.004
seconds on the SyncServer.
authdelay: When NTP authentication is enabled and performed on outgoing NTP packets,
this adds a trivial amount of fixed delay that can be removed based on the authdelay value.
This valueis always set to zero on the SyncServer.
RESTART Button
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
NTP - Assoc
Use this page to view the status of NTP associations listed on the NTP - Config page.
Also see NTP Associations (on page 197) in the Glossary.
NTP Associations
NTP associationswith non-validIP addresses and domainnames are not shown. (If a
known good domain name does not appear on this list, there may be a problem with the
DNS server configuration on the NETWORK - Ethernet page, or with the DNS service itself.)
Remote: The domain name or IP address of the remote end of the NTP association. “Hardware Clock” is the SyncServer's Hardware Clock. In the case of a remote NTP connection,
this will be the IP address of the remote end.
The character in the left margin indicates the mode in which this peer entry is operating:
n * (asterisk) the association with which the NTP daemon is synchronizing (the system
peer on NTP - Sysinfo), marked "synchronizing".
n + (plus) indicates the SyncServer is symmetric active mode.
n - (minus) indicatesthe SyncServer is symmetric passive mode.
n = (equal) means the SyncServer is in client mode, marked "being polled".
n ^ (caret) indicates that the SyncServer is broadcasting to the remote node, marked
"broadcasting to".
n ~ (tilde) denotes that the remote node is broadcasting to the SyncServer.
Local: The IP address of the SyncServer network port at the local end of the NTP association. For the Hardware Clock it is "127.0.0.1", the IP addressof the loopbackport.
St: The stratum level of the remote clock in the NTP hierarchy. Lower values are given more
emphasis. For the local Hardware Clock, stratum 0 is a special value that indicates the Hardware Clock it is synchronized by a "timing root" reference such as GPS1. Valuesin the range
of 1 through 15 indicate the number of steps the remote NTP connection is from its timing
root. Stratum 16 is a special value that indicates that the remote connection is not
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
Page 42..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 43

NTP - Config
synchronized. The stratum reported by the SyncServer is incrementedby one from its synchronizing peer. For example, while synchronized to the Hardware Clock(Stratum 0), the
stratum of the SyncServer is one (Stratum 1).
Poll: The length of the interval(in seconds) with which the SyncServer polls the remote
server, usually startingat 64 seconds and gradually increasing to 1024 seconds. Valid values
range from 16 to 65535, increasing by powers of 2. The polling interval for the Hardware
Clock is fixed at 16 seconds. The user-configured Minimum and Maximum Poll Interval settings on the NTP - Config page limit this interval.
Reach: This is an 8-bit shift register that keeps track of the last 8 attemptsto reach the remote
end of the association. New bits are added to the rightmost end of the register (1 for reached
or 0 for unreached) and old bits "fall off" the left hand side. The shift register is represented in
octal. For example, by converting "377" from octal to binary, one gets "11111111", indicating
8 successful polls. For a sequence of eight successful polling attempts on a new association,
the octal value of Reach increasesas follows: 1, 3, 7, 17, 37, 77, 177, 377. If the value isn't
one of those just shown, there may be a problem pollingthe remote end of the association. If
the value remainsat 0, or decreasesto 0, the association is becoming unreachable.The
reach valuestays 0 if the SyncServer is a broadcast or multicast server.
Delay: The total delay, in seconds, of the round trip to the remote end of the NTP association.
For example, a value of "0.07817" equalsapproximately 78 milliseconds. The Delay for the
Hardware Clock is "0". For most NTP associations, typical valuesrange from tens to hundreds of milliseconds. The NTP daemon's clockselection algorithm givespreference to
lower Delay values.
Offset: The time offset between the SyncServer and the remote server, in seconds, of the last
poll. The NTP daemon's clock selectionalgorithm givespreference to lower Offset values.
The Offset for the Hardware Clock is usually in the microsecond range. For external NTP
associations, the offset is affected by the time base of the remote node and the characteristics of the network path, with values typically in the 1 - 10 millisecond range.
Disp: Dispersion representsthe maximum error of the SyncServer relative to the NTP association. There are two components in dispersion, those determined by the peer relative to the
primary reference source of standard time and those measured by the SyncServer relative
to the peer. They provide not only precision measurements of offset and delay, but also definitive maximum error bounds, so that the SyncServer can determine not only the time, but the
quality of the time as well.
RESTART Button
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
NTP - Config
Use this page to create, edit, or delete NTP associations.
Note: The SyncServer S350i does not include either a modem or GPS receiver.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 43
Page 44

Web Interface
Also see Configuring NTP for more information.
Current NTP Associations
To edit or delete an association, select it using the checkbox and then click the EDIT or
DELETE button below. If the user selects EDIT, the details for that association are displayed
under Add/Edit NTP Association for the user to edit. Use the SAVE button to save the
changes and the RESTART button to make any changes take effect.
The list of Current NTP Associationsalwaysincludesthe Hardware Clock, which:
n Cannot be deleted or edited.
n Is configured as a preferred server ("server 127.127.45.0 prefer # pseudoaddressfor the
timing engine" in ntp.conf).
n Is displayed at the top of the list.
Additionally, the factory default configuration includesthree Stratum 1 NTP servers operated
by Microsemi on the Internet.
The user should consider adding NTP servers available on the local network to the list of Current NTP Associations.
Add/Edit NTP Association
Use Add/Edit NTP Association to edit existing associations or to add new ones. The SyncServer can have multiple associations, each with a different Role.
In the followingexplanations, the term "SyncServer" means "the local NTP daemon on the
SyncServer".
Role
n
Server:
n Addressing: Use with IPv4 classA, B and C addresses.
n Description: Createsa persistent association between the SyncServer (client)
and an NTP node (server). The client synchronizes with the server if the client's
clock selection algorithm selects this server as the best clock. Typical server associations include: the hardware clock, the factory default NTP servers, and servers
added by the user. Also see system peer mode: client under NTP Daemon
Status (on page 28).
n Typical Usage: The user creates a Server associationto designate an NTP node
that has an NTP Stratum better or equal to that of the SyncServer (client). Often,
the NTP server is another Stratum 1 server with a GPS reference that is outside
the user's administrative jurisdiction. The NTP servers operated by Microsemi
that are part of the factory default configuration are an example of this.
n
Peer:
n Addressing: Use with IPv4 classA, B and C addresses.
n Description: Createsa persistent symmetric-active association between the Syn-
cServer (peer1) with an NTP node (peer2). For the NTP node running in symmetric passive mode, there is nothing needs to be done on the NTP node.
However, the NTP node can be configured in symmetric active mode too. When
Page 44..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 45

n
Broadcast:
NTP - Config
configured, the two nodes can synchronize with each other in a varietyof failure
scenarios, suchas lossof GPS and Internet connectivity. See system peer mode:
symmetric-active under NTP Daemon Status (on page 28).
n Typical Usage: The user configuresNTP associations on two NTP nodes that
point to the each other. The two nodes are usually of equal stratum and have independent references, such as two separate GPS installations or two separate network paths to NTP servers on the Internet. In the event of a reference failure, the
peers can synchronize to the node that has the best remaining reference.
n Addressing: Use an IPv4 broadcast address of the localsubnet. To broadcast
NTP messages on a subnet, if the local interface IP address were 192.168.61.58
and the mask were 255.255.255.0, the broadcast addresscould be
192.168.61.255.
n Description: Createsa broadcast server association. When configured with a
broadcast address (e.g., 192.168.61.255), the association broadcasts NTP messagesfrom the network interface with the matching IP address(e.g.,
192.168.61.58). Broadcast messages go out to all nodes on the subnet, and are
usually blocked by routers from reachingadjacent subnets. Consult with the network administrator to select a correctly-scoped address and Time to live value.
n This type of association requires authentication on both the server and the clients.
See Using NTP Authentication (on page 160).
n Typical Usage: Broadcast associations to reduce network traffic with a large num-
ber of NTP clients.
n Broadcast Client:
n Addressing: The user does not specifyan address with this setting.
n Description: Createsan association that listens for NTP broadcast messages on
all of the network interfaces. Upon receiving the first broadcast message, the
broadcast client association initiates a brief exchange with the server to calibrate
the propagation delay. Afterwards, the broadcast client associationlistens to and
gets the time from the broadcast server messages. This type of association
requiresauthentication on both the server and the clients. See Using NTP
Authentication (on page 160).
n Typical Usage: Broadcast client associations can get authenticated time on net-
works that have a broadcast server.
n Multicast Server: Create a Broadcast association with members of a multicast group.
The multicast address is a class D address starting from 224.0.0.1. (The IANA assigned
224.0.1.1 to be the NTP multicast address.) However, user can choose any class D
addressthat is not used on the local network by other protocols. Routers can be configured to transmit multicast messages to adjacent subnets.
n
Multicast Client:
n Addressing: Use the same IPv4 class D multicast address as the Multicast Server
(potentially 224.0.1.1).
n Description: Createsan association that listens for NTP multicast messages on all
of the network interfaces. Upon receiving the first message, the multicast client
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 45
Page 46

Web Interface
association initiates a brief exchange with the server to calibrate the propagation
delay. Afterwards, the multicast client association listensto and gets the time from
the server messages. This type of association requires authentication on both the
server and the clients. See Using NTP Authentication (on page 160).
n Typical Usage: Multicast client associations can get authenticated time on net-
works that have a multicast server.
Note: When authentication is configured, the same authentication scheme is available for all
NTP associationsand over all network interfaces.
Prefer: The NTP daemon will synchronize with an association marked prefer over an equi-
valent association that is not.
Address: The IP address or DNS name of the NTP association.
(If present, configure the Modem phone number using the REFERENCES - Modem page.)
Port: (FactoryDefault = "Default") With the default setting, the NTP daemon automatically
detects and uses a valid network port to communicate with configured NTP server(s).
Depending on the IP routing infrastructure, this is typically LAN1. The user can override this
by selecting a specificnetwork port. If so, the addressmust be specified using an IP address
instead of a DNS name. The Port settingis onlyavailable for Server, Peer, Broadcast, and
Multicast associations.
Burst
n
Burst: When the server is reachable, send a burst of eight packets instead of the usual
one. The packet spacing is about two seconds. This is designed to improve timekeeping
quality for server associations. This settingshould only be used in agreement with the
administrator of the remote NTP device as the traffic load may be onerous.
n
iBurst: When the server is unreachable, send a burst of eight packets instead of the usual
one. As long as the server is unreachable, the packet spacing is about 16s to allow a
modem call to complete. Once the server is reachable, the packet spacing is about two
seconds. This is designed to speed the initialsynchronization acquisition with the server
command.
Version: Specifies the version number to be used for outgoing NTP packets. Versions1-4 are
the choices, with version 4 the default.
Minimum / Maximum Poll Interval: These options specify the minimum and maximum poll inter-
valsfor NTP messages, in seconds to the power of two. The maximum poll interval defaults
to 10 (1,024 s), but can be increased to an upper limit of 17 (36.4 h). The minimum poll interval defaults to 6 (64 s), but can be decreased to a lower limit of 4 (16 s).
MD5 Key: Use this field to authenticate NTP messagesto and from the SyncServer for this
specific association. When enabled, the NTP packet header includes authentication fields
encrypted using either the MD5 key number (1 to 16) or autokey. Prior to selecting either
option, the user must configure the NTP - MD5 Keys, NTP - Autokey, or NTP - Autokey Client
pages.
Note: MD5 and Autokeycannot be used on the SyncServer concurrently. Configuring one
method erasesthe keys or certificates of the other.
Page 46..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 47

NTP - MD5 Keys
Time to Live: This option is used only with broadcast association. It specifiesthe time-to-live
on broadcast server. Consult with the network administrator to specify a correct value. If this
field is left blank, the value of TTL defaultsto 127.
RESTART Button
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
NTP - MD5 Keys
Use this page to generate or manipulate keysgenerated using the RSA Message Digest 5
(MD5) algorithm authentication method. MD5 Keys are used to authenticate (not encrypt)
NTP messages sent or received by the SyncServer, using a cryptochecksum.
Also see Using MD5 Keys on a SyncServer (on page 161).
Note: MD5 and Autokeycannot be used on the SyncServer concurrently. Configuring one
method erasesthe keys or certificates of the other.
NTP MD5 Security Keys
Use this page to manage MD5 keysas follows:
n View and copy the current keys.
n Upload a file containing keysfrom a local PC drive to the SyncServer.
n Download the SyncServer's current key file to a localPC drive.
Generate: This button generates new random MD5 keys, immediately replacing any previous
MD5 keys and erasing Autokey certificates and keys.
Current Keys: This window displays the current list of keys.
The first line gives the SyncServer's hostname and the NTP time stamp of when the keys
were created. The second lineshows the local time and date the keyswere generated.
Each row of key information providesthe followinginformation:
n The key number, 1 through 16
n The key type, "MD5".
n The key, an ASCII string containing only displayable characters. As an example, the ran-
dom key generator may produce "\jdh.u$r;x"y:upH"
n A comment that identifiesthe key type. For example: "# MD5 key"
Upload Keys: Use this text field, with the BROWSE button, to enter the file path of the keys file.
Then clickthe UPLOAD button to load the keys to the SyncServer.
Download Keys: Press the Save As… button to save the Current Keys to your PC as a file.
After keys are generated, the user can select Key and a key number in the MD5 key field on
the NTP - Config page.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 47
Page 48

Web Interface
Note: Disregard the "Unable to Open Key File" message while the Current Keys field is
empty.
RESTART Button
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
NTP - Autokey
Use this page to:
n Enable autokey authentication.
n Generate and download autokey keyfiles and certificates.
n Create peer, broadcast, and multicast associations that are configured for autokey.
Also see Using NTP Authentication (on page 160).
Note: MD5 and Autokeycannot be used on the SyncServer concurrently. Configuring one
method erasesthe keys or certificates of the other.
Configuration of SyncServer as Autokey Server
Key Generation/Deletion
Identity Scheme: Select the scheme to be used on the SyncServer and the client.
n
PC: Private Certificate
n
IFF: Identification Friend or Foe
n
GQ: Guillow-Quisquate
Note: The PC scheme does not have a group key file. The user installs the IFF and GQ
group key file on the Autokey client.
Server Password: Enter an alphanumeric string to serve as an autokey password. Cryptographically, a string of random ASCII characters would be the strongest password. This is
equivalent to the "crypto pw <server-password>" line in ntp.conf on a generic NTP device.
Client Password: When the IFF IdentityScheme is selected, enter a client password to be
used by all of the Autokey clients associated with this server. When configuring the Autokey
client, the user enters the client password on the NTP - Autokey Client page.
Use the GENERATE button to create the key file and/or certificate file. After the keys and/or
certificateshave been generated, Auto (autokey) becomes availablein the MD5 Keys menu
on the NTP - Config page. Use this field to apply autokey authentication to NTP associations.
Use the DELETE button to clear previous keys and certificates. This is a required step before
generating new ones.
Key File Download
Page 48..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 49

NTP - Autokey Client
After using the GENERATE button, select the individualkeyor certificatefiles and click SAVE
AS to download them to a secure location.
For the PC scheme, save both the server host key and certificatefiles to a secure location
and install them on the Autokey clients. For the IFF and GQ schemes, save the group key file
to a secure location and installit on the Autokey clients.
After downloading the keys, click the RESTART button to make the key(s) active on the NTP
server.
Note: NTP Autokeysare not active until the user clicks RESTART.
Also see: Using Autokey (on page 163)
RESTART Button
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
See"RESTARTBu tton"onpage 49
NTP - Autokey Client
Use this page to manage (add or remove) Autokey keysfor NTP associations where the SyncServer is an NTP client.
Note: MD5 and Autokeycannot be used on the SyncServer concurrently. Configuring one
method erasesthe keys or certificates of the other.
Configuration of SyncServer as Autokey Client
Removal of Existing Client Relationship
To remove keys, select the checkbox of the key(s), and click the DELETE button. Existing keys
are identified by their Scheme and Filename. ClickRESTART to completethe removalprocess.
Upon completing the removalprocess, the SyncServer will not be able to authenticate NTP
packets from NTP servers that use those keys.
NTP Autokeys are not fullyremoved until the user clicks RESTART.
Addition of New Client Relationship
To add keys, use the following fields as described.
Select the Identity Scheme of the key.
n
For PC and GQ identity schemes, enter the Server Password, the same password used
while generating the keysor certificates on the Autokey server (using the NTP - Autokey
page).
n
For the PC scheme, use BROWSE to locate the Server Host Key File and Server Certificate
File at a secure location. For IFF and GQ, use BROWSE to locate the group key file from a
secure location.
Enter the Server Password, if needed.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 49
Page 50

Web Interface
Use INSTALL to upload the key and/or certificate files to the SyncServer.
After uploading the keys, click the RESTART button to make the key(s) active on the Syn-
cServer.
Upon making the added keys active, the SyncServer will be able to authenticate NTP pack-
ets from NTP servers that use those keys.
Newly added NTP Autokeysare not active until the user clicksRESTART.
RESTART Button
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
NTP - Prefs
The settingson this page determine whether the NTP daemon, once synchronized, can
report an unsynchronized state.
Note: Microsemirecommendskeeping the default Standard NTP Rules setting below. The
Override Behavior setting is mostlya "compatibility" setting for custom systems built around
legacy TrueTime GPS clocks such as the NTS-200.
Note: The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
Out of the three following stagesof operation, the NTP - Prefs settings onlyapply during the
Loss of All References stage:
1. Startup: Upon starting, before synchronizingwith any NTP associations, the NTP dae-
mon reports to potential NTP clients that it is unsynchronized by settingleap indicator to
11 and stratum to 16.
2. Typical Operation: After synchronizing to an NTP association the NTP daemon usesleap
indicator and stratum normally. Leap indicator reports whether a leap event is pending
(usually 00 - no alarm). Stratum reports the stratum of the NTP daemon relative to the
system peer (usually 1 through 3).
3. Loss of All References: If the NTP daemon cannot get the time from any association:
n
With Standard NTP Rules (Factory Default) The stratum and leap indicator remain
the same as they were in the Typical Operation stage. The system peer remains
the unchanged, but the reference time stamp isn't updated and the reach statistic
gradually decreases to zero.
n
With Override Behavior, if the estimated time error exceeds the Time Error Limit on
the TIMING - Holdover page, stratum reports 16 and leap indicator reports 11, as
they did during in the Startup stage.
After Loss of All References, if the NTP daemon synchronizes with an NTP association
again, it resumesTypical Operation.
Comments:
Page 50..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 51

PTP Option and Time Interval Test
n Given a pool of NTP associations from which to choose, an NTP client typically syn-
chronizes with the best one, and does not require Override Behavior to eliminate poor
associations.
n Given a lack of NTP associations from which to choose, an NTP client may reject a Syn-
cServer with better timing accuracy and stability than itself, if Override Behavior is
enabled.
n The SyncServer's NTP daemon can get time from a server, peer, broadcastclient, and
multicastclient associations.
n Also see NTP Daemon Status (on page 28), TIMING - HW Clock (on page 61),
TIMING - Holdover (on page 63), Leap Indicator (on page 197), and Stratum (on
page 202).
RESTART Button
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
PTP Option and Time Interval Test
The precision time protocol (PTP) option allows the user to configure the S300 Series SyncServer into a IEEE 1588-2008 Grandmaster. This hardware based PTP option is only supported on LAN2 of the S300 and S350 SyncServers. The Time Interval Measurement is
included as part of the PTP option on the S350 only.
When the PTPoption is not activatedon a S300/S350 SyncServer, the PTP button (fourth
from top) of the web interface will be grayed out. If PTP was not factory installed, See "How
to Activate the PTP Option" on page 53.
Oncethe PTPoption is activated on a S300/S350 SyncServer, the PTP button on the web
interface will become active. In addition to the PTP option button, upon activation, several
other web pages will become available. Four pages associated with the PTPbutton will
enableyou to:
n Set up PTP configuration parameters See "PTP - Master" on page 54
n Save and restore PTP configuration parameters See "PTP - Save-Restore" on
page 60
n Monitor slave activity See "PTP - Slaves" on page 58
n Collect measurement data and view PTPperformance over the network by run-
ning charts. See "PTP - Performance" on page 59
In addition to the pages associated with the PTP button, the following pageswill allow further
monitoring and control of the PTPoption:
n The status of the PTPDaemon can be monitored at STATUS> PTP See
"STATUS - PTP" on page 31
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 51
Page 52

Web Interface
n In addition to existing alarms, alarms relevant to PTP are trapped at Admin >
Alarms See "ADMIN - Alarms" on page 85
n PTPsettingsfor Daemon current state and startup can be found at Services >
Startup See "SERVICES - Startup" on page 95
Time Interval Test
The Time Interval Test feature is provided along with the PTP option in the S350.
Details of the Time IntervalTest feature can be seen at TIMING > Time Interval
See "TIMING -Time Interval" on page 67
PTP and NTP Performance
The PTP daemon has the highest priority. When the PTP daemon is on it will adversely
affect the number of NTP requests the SyncServer can process.
n With PTP turned on, the amount of NTP packets the SyncServer can handle is
reducedto half or greater, dependingon amount of PTP traffic.
n PTPMessageCapacity is 4000 delay_requests per second.
n NTP vs PTPCapacity: PTP is a higher priority than NTP.
PTP delay_request messages/second NTP Requests/second
10 3500
3000 2000
4000 1100
n The PTP daemon can process up to 6000 delay_reqests per second. However,
any amount over 4000 results in Web UI being unresponsive.
n If the PTP Slave NIC rate is1000BASE-T, this will result a delay of 3 micro-
seconds at the slave. It is important to note that the LAN2 port only works as
100BASE-TX, a slave that operates at a 1000BASE-T will have an issue, this
can be resolved by reducing the slaves connection speed to 100BASE-TX. See
the user manual for your slavedevice to determine how this can be done.
PTP Management Messages
Management Message Name Actions Supported
NULL_MANAGEMENT GET, COMMAND supported (no op)
CLOCK_DESCRIPTION GET supported
USER_DESCRIPTION GET supported
SAVE_IN_NON_VOLATILE_STORAGE COMMAND supported
RESET_NON_VOLATILE_STORAGE COMMAND supported
INITIALIZE COMMAND supported
FAULT_LOG NOT SUPPORTED
Page 52..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 53

PTP and NTP Performance
Management Message Name Actions Supported
FAULT_LOG_RESET NOT SUPPORTED
DEFAULT_DATA_SET GET supported
CURRENT_DATA_SET GET supported
PARENT_DATA_SET GET supported
TIME_PROPERTIES_DATA_SET GET supported
PORT_DATA_SET GET supported
PRIORITY1 GET supported
PRIORITY2 GET supported
DOMAIN GET supported
SLAVE_ONLY GET supported
LOG_ANNOUNCE_INTERVAL GET supported
ANNOUNCE_RECEIPT_TIMEOUT GET supported
LOG_SYNC_INTERVAL GET supported
VERSION_NUMBER GET supported
ENABLE_PORT COMMAND supported
DISABLE_PORT COMMAND supported
TIME GET supported
CLOCK_ACCURACY GET supported
UTC_PROPERTIES GET supported
TRACEABILITY_PROPERTIES GET supported
TIMESCALE_PROPERTIES GET supported
UNICAST_NEGOTIATION_ENABLE NOT SUPPORTED
PATH_TRACE_LIST NOT SUPPORTED
PATH_TRACE_ENABLE NOT SUPPORTED
GRANDMASTER_CLUSTER_TABLE NOT SUPPORTED
UNICAST_MASTER_TABLE NOT SUPPORTED
UNICAST_MASTER_MAX_TABLE_SIZE NOT SUPPORTED
ACCEPTABLE_MASTER_TABLE NOT SUPPORTED
ACCEPTABLE_MASTER_TABLE_ENABLED NOT SUPPORTED
ACCEPTABLE_MASTER_MAX_TABLE_SIZE NOT SUPPORTED
ALTERNATE_MASTER NOT SUPPORTED
ALTERNATE_TIME_OFFSET_ENABLE NOT SUPPORTED
ALTERNATE_TIME_OFFSET_NAME NOT SUPPORTED
ALTERNATE_TIME_OFFSET_MAX_KEY NOT SUPPORTED
ALTERNATE_TIME_OFFSET_PROPERTIES NOT SUPPORTED
DELAY_MECHANISM GET supported
LOG_MIN_PDELAY_REQ_INTERVAL GET supported
How to Activate the PTP Option
PTPin the 300 Series SyncServer can be activated at the time of purchase or at a later date.
This section describes PTPactivation after the SyncServer has left Microsemi.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 53
Page 54

Web Interface
A PTPoption key is required to activate the PTP option in the S300 series SyncServer by following this process:
1. Log into your SyncServer, See "Logging in to the Web Interface" on page 149
2. Identify your SyncServer serial number on the followingweb page, SYSTEM >
Options. The SyncServer Serial Number is shown on the left, towards the top of this
web page.
3. Contact Microsemi sales at www.microsemi.com/sales-contacts/0 to purchase a PTP
option key.
4. Enter the PTPoption key in the Option Key text box of this web page.
5. Clickthe Apply button at the bottom left of the web page to activate the PTP option.
6. Once the SyncServer has accepted the Option Key, the PTP Grand Master option will
show up on the right side under "Installed Options."
7. Go to NETWORK > Ethernet page and enable LAN2 interface (preferably Static
address).
8. Go to the SERVICES >Startup page and make sure the PTP daemonis turned on
and set to auto.
9. Go to the PTP > Master page and change the settingsas desired.
PTP - Master
Note: PTP is only supported on LAN2 of the 300 Series SyncServer
This page is used to set up parameters associated with the IEEE-1588 2008 PTP Grand-
master Configuration.
The following is a list of these configuration parameters:
Transport Protocol
Select from:
l UDP
l 802.3
Sync Interval
The Sync Interval is used to specify the mean time interval between successive Sync messages(the syncInterval) when transmitted as multicast messages.
The configurable range is 2-6to 2+6(2-6to 2+6, is 1 second/64-packets to 64-packets/second).
Default is 20, which is 1 packet/second
Page 54..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 55

PTP - Master
Select from :
l 64pkt/1 sec
l 32 pkt/1 sec
l 16 pkt/1 sec
l 8 pkt/1 sec
l 4 pkt/1 sec
l 2 pkt/1 sec
l 1 pkt/1 sec
l 1 pkt/2 sec
l 1 pkt/4 sec
l 1 pkt/8 sec
l 1 pkt/16 sec
l 1 pkt/32 sec
l 1 pkt/64 sec
Note: The IEEE 1588-2008 requires the delay_request setting to be = or less than the sync
interval. Bear this in mind as this Web UI does not enforce this.
Delay Mechanism
The choices for the Delay Mechanismare:
l E2E (End to End)
l P2P (Peer to Peer)
Packet TTL
(Time to live - TTL)
In this text box you can set the number of router hops up to 256 hops.
The TTL range is 1 to 256, if you enter 0 or >256 a message stating that the value of TTL is
out of range will appear.
Note: 1588 multicast packets typically operate at a TTL of 1, changing this valuemayaffect
the qualityof your network timing.
E2E Delay Interval
The end-to-end E2E DelayInterval controls the number of request packets from the slaves
connected to this unit. See "Sync Interval" on page 54
When the E2E selection is made at the Delay Mechanism (see above), the following selections are available:
l 64pkt/1 sec
l 32 pkt/1 sec
l 16 pkt/1 sec
l 8 pkt/1 sec
l 4 pkt/1 sec
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 55
Page 56

Web Interface
l 2 pkt/1 sec
l 1 pkt/1 sec
l 1 pkt/2 sec
l 1 pkt/4 sec
l 1 pkt/8 sec
l 1 pkt/16 sec
l 1 pkt/32 sec
l 1 pkt/64 sec
P2P Delay Interval
The peer-to-peer P2P Delay Intervalcontrols the number of request packets from the slaves
connected to this unit. See "Sync Interval" on page 54
When the P2P selection is made at the Delay Mechanism (see above), the following selections are available:
l 64pkt/1 sec
l 32 pkt/1 sec
l 16 pkt/1 sec
l 8 pkt/1 sec
l 4 pkt/1 sec
l 2 pkt/1 sec
l 1 pkt/1 sec
l 1 pkt/2 sec
l 1 pkt/4 sec
l 1 pkt/8 sec
l 1 pkt/16 sec
l 1 pkt/32 sec
l 1 pkt/64 sec
Page 56..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 57

PTP - Master
Priority 1
The priority field affectsthe result of the Best Master Clock Algorithm. The lower number in
this field will win the BMC calculation. The initialization value of priority1 is specified in a PTP
profile. Choicesare:
l 0 – 255
l Default is 128
Priority 2
The priority field affectsthe result of the Best Master Clock Algorithm. The lower number in
this field will win the BMC calculation. The initialization value of priority2 is specified in a PTP
profile. Choicesare:
l 0 – 255
l Default is 128
Domain Number
A domainconsistsof one or more PTP devices communicating with each other as defined by
the protocol. A domain defines the scope of PTP message communication, state, operations, data sets, and timescale. PTP devices may participate in multiple domains; however,
unless otherwise specified in the standard, the operation of the protocol and the timescale in
different domains is independent.
The configurable range is 0 – 255
l Default is 0
Mean Announce Message Transmit Interval
This is the Announce Interval specified in IEEE 1588-2008 and is specified as the mean time
interval between successive Announce messages.
Selections available:
l 1 sec
l 2 sec
l 4 sec
l 8 sec
l 16 sec
l 32 sec
l 64 sec
l Default is 2 seconds
Announce Receipt Timeout Multiplier
The value of Announce ReceiptTimeout is an integral multiple of the announceInterval (see
section 7.7.3.1 of IEEE 1588-2008).
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 57
Page 58

Web Interface
l The configurable range is 2 to 10 (2
l Default is 3
2
to 210).
Return to IEEE 1588-2008 Annex J Recommended Default Settings check box
If you are not sure what selections to make, click on this button to get the standard settings.
Any slave should support theses settings as these settingsmeet the specification.
IEEE 1588-2008 Annex J Recommended Default Settings
Transport Protocol UDP
Sync Interval 1 pkt/1 sec
Delay Mechanism E2E
Packet TTL 1
E2E Delay Interval 1 pkt/1 sec
P2P Delay Interval 1 pkt/1 sec
Priority 1 128
Priority 2 128
Domain Number 0
Mean Announce Message Transmit Interval 2 sec
Announce Receipt Timeout Multiplier 3
PTP - Slaves
This page will show all the slaves associated with this SyncServer, both activeand inactive
within the last 14 days. It shows when each slave was last accessed. The range of access
recording is from within 10 minutesto 14 days.
This page has a text box to log the slaves. The number of slaves tracked is shown below the
text box. For each slave, there are three parameters monitored:
n Address shows the IPaddress of the slave (xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx)
n Last Access shows the date and time of the last access, (MM-DD-YYYY HH:MM).
Page 58..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 59

PTP - Performance
n Activity shows an activity messagein red text if the slave is inactive, or in blue text if
the slave is active. An exampleof an active message would be "Active within the last
10 minutes"in blue text.
Below the text box logging the slavesare three options to clear slaves from the SyncServer
monitoring list:
n Remove ALL Slaves
n Remove ALL SlavesNot accessed for 1 Day
n Remove ALL SlavesNot accessed for 7 Days
After making one of these three selections, click the APPLY button to activate the selection,
or click the CANCEL button to abort the process.
Note: Slaves inactive for 14 days will be automatically removed
PTP - Performance
This page will provide insights into SyncServer PTP Grandmaster operations.
It is set up as a running log, in 15 Minute Performance Intervals for up to 4 days. For each
loggedinterval, you can see the start time in 15 minutesincrements, showing:
n How many delay requestswere generated.
n How many Sync Messages were sent.
n How full is the queue.
l For example, if the PTPslave activity is increasing, then the PTPpacket
queuescan start filling up. When the number starts to grow from 0%, this is an
indication that the SyncServer is processing packets, the network is busy, and
requests are sitting in the queue. If the queue percentage reaches 100%, the
queue will be flushed.
An example of the PTP Performance Logged in 15 Minute Intervals
Delay Requests Sync Messages Resets
Interval Start Time Count Queue Count Queue Daemon Queues
09-05-2010 07:15 1372 0% 899 0% 0 0
09-05-2010 07:30 1481 0% 893 0% 0 0
09-05-2010 07:45 1367 0% 897 0% 0 0
09-05-2010 08:00 1355 0% 896 0% 0 0
09-05-2010 08:15 1355 0% 897 0% 0 0
09-05-2010 08:30 1373 0% 896 0% 0 0
Click the RESET button to reset the performance log.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 59
Page 60

Web Interface
Charting PTPPerformance
The PTP Performance chart is handy to show how your network traffic is occurring dynamically. For example, the cause of a spike at traffic occurring at a certain time each day could
be investigated, improving the network performance.
To Create a Chart
Click the CHART button to view a chart of the PTPpacket performance. After several
seconds, a chart will appear. The chart will show the selected data set. Delay data sets have
a red chart line, and sync data sets have a black or blue chart line. Both data sets are drawn
against a timeline of the 15 minute intervals.
To view different data sets, click the Data Set button. Available selections are:
l E2E Packets
l P2P Packets
l E2E Packet Errors
l P2P Packet Errors
l E2E Queues
l P2P Queues
l Daemon Resets
PTP - Save-Restore
Use this page to Save or Restore PTP Grandmaster Configuration settings.
The current PTP Configuration is displayed, reflecting values set up on the PTPMaster web
page. An example of settings is:
Transport Protocol UDP Priority 1 128
Sync Interval 1 pkt/1 sec Priority 2 128
Delay Mechanism E2E Domain Number 0
Packet TTL 1 Mean Announce MessageTransmit Interval 2 sec
E2E Delay Interval 1 pkt/1 sec Announce Receipt Timeout Multiplier 3
P2P Delay Interval 1 pkt/1 sec
To Save Configuration Settings to a File
Click the Save As... button.
Page 60..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 61

TIMING - Time Zone
To Restore Configuration Settings from a File
1. Clickthe Browse... button.
2. Navigate to the file that contains the configuration settingsto be restored.
3. Clickthe UPLOAD button
TIMING - Time Zone
Local Time Zone
This setting affects:
n
The time shown on the SyncServer front panel display when the user presses the TIME
button. Also see TIME Button (on page 101).
n The time output by the IRIG out connector if the Output Type is set to Local on the
REFERENCES - Timecode page. Also see REFERENCES - Timecode (on page 71).
The Time Zone setting does not affect NTP or any of the other timing outputs.
To set the time zone, select a profile from the list of Time Zones and click the APPLY button.
Each profile contains the offset from UTC to the time zone, plusany rules for daylight saving
time or summer time adjustments.
The Time Zones are alphabetically organized as follows:
n Most Time Zones are sorted by continent and city name.
n Some Time Zones are sorted by country and city name.
n Some Time Zones are sorted by acronym (e.g., UTC, EST).
n Some islands are sorted by ocean (e.g., Atlantic, Pacific, Indian) or national affiliation.
Current shows the time zone in effect and the localtimeat the moment the page was generated.
TIMING - HW Clock
Hardware Clock Configuration
Managethe referenceslisted under Clock Source Priorities as follows:
n
Enable or disable the reference using the checkboxesunder Enable. Checking the box
enables the reference, clearing it disables the reference.
n
Change the priority of the reference by highlighting it and then using the Up/Down Arrow
buttonsmove it up or down in priority.
n
Restore the default priority and availability settings by clicking the DEFAULTS button.
n Each reference shows its default priority. For example, "GPS [Default 1]".
note: The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
Microsemi recommends usingthe default priorities.
The Forced Timing Source setting affects all timingoutputs and displays:
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 61
Page 62

Web Interface
n
Auto: The SyncServer automatically synchronizes with a Hardware Clock Input Reference , or a synchronizing NTP association.
n
Free Run: The user sets the time on the SyncServer by entering the UTC date and time
under UTC Time. The SyncServer uses its internal oscillator to keep time. This setting overrides the Hardware Clock's Input References. However, a synchronizing NTP association can override the FreeRun setting:
n If the user intends to use UTC time, Microsemi recommends keeping the current
NTP configuration.
n If the user intends to distribute non-UTC time, Microsemi recommends changing
the current NTP configuration by deleting all synchronizing NTP associations.
See Setting the Time Manually (on page 177) and Distributing Non-UTC
Time (on page 180).
Microsemi recommends usingthe Auto setting.
Also see Hardware Clock (on page 196).
IMPORTANT: If the user is preparing to switch from Free Run to Auto and the time is more
than 1000 seconds off UTC time, manually set it within1000 seconds of UTC time before
switching to Auto.
Note: On the Sysplex Timer output, if the user sets Forced Timing Source to Free Run, the
Sysplex Flywheel Quality Character in effect at that moment remainsin effect thereafter.
Also see TIMING - Sysplex (on page 64).
Ignore UTC Corrections from GPS Reference
When the Hardware Clock is lockedto the GPS receiver, the GPS receiver passes GPS
time and a GPS-UTC offset to the Hardware Clock.
When Ignore UTC Corrections from GPS Reference setting is:
n Unselected, the Hardware Clock uses the GPS-UTC offset and passesUTC time to the
NTP daemon. (Recommended) (FactoryDefault)
n Selected, the Hardware Clock ignores the GPS-UTC offset and passes GPS time to the
NTP daemon.
To use this setting, consult Distributing GPS Time (on page 178).
This setting has no effect when the Hardware Clockis locked to non-GPS references.
WARNING: The Free Run and Ignore UTC Corrections from GPS Reference settings can
have serious effects upon timing networks and systems that expect UTC time. These settings
should only be used by knowledgeable and authorized persons under carefully controlled conditions.
Use the APPLY button to apply changes to the configuration.
Page 62..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 63

TIMING - Holdover
TIMING - Holdover
Overview
The SyncServer uses holdover to continueoperating as a stratum 1 NTP server/peer for a
period of time if the Input References become unavailable.
For example: A SyncServer in a downtown office buildinggets time from GPS1. Surrounding
skyscrapers occasionally block signals from the GPS satellitesas they move acrossthe sky,
causing "gaps" that last several hours. The SyncServer uses holdover to continue operating
as a stratum 1 NTP server during these gaps.
The factory default settings are appropriate for most situations. However, the user should
consider extending holdover to cover the longest anticipated "gap" if more than one of the following conditions is true:
n The SyncServer is the only NTP server available to the NTP clients.
n The SyncServer only has one Hardware Clock Input Reference (e.g., GPS, Timecode).
n
The Hardware Clockis the only NTP association listed on the NTP - Assoc page.
n Restoring an Input Reference would take longer than the holdover period in days.
Please note the Holdover settings on this page also affect NTP if Override Behavior is selec-
ted on the NTP - Prefs page.
Also see Stratum (on page 202).
The Settings
The user can simply set the number of days Holdover lasts, or specify a Time Error Limit. Set-
ting either field generatesan equivalent value in the other field.
About Time Error: When no Input Referencesare available, the oscillator drifts away from
the correct time, accumulatingtime error. The type of oscillator affects how quickly time error
grows. The SyncServer keepsan ongoingestimate of the time error. Holdover ends when
the estimated time error is equal to or greater than the user-configured Time Error Limit.
The Oscillator Type affects the rate at which the oscillator accumulatestimeerror when no
Input References are available.
n
TCXO – The standard temperature-compensated oscillator.
n
OCXO – The optional oven-compensated oscillator is more stable and offers better holdover performance than the TCXO.
n
Rubidium – The optional rubidium oscillator has the best stability and holdover performance.
Several methodsare available for the user to adjust Holdover or Time Error Limit:
n
Entering a value for Holdover Limit or Time Error Limit and clickthe SET button.
n Slidingthe green verticalbar on the Holdover graph left or right.
n
Slidingthe one of the black spheresunder Holdover Limit or Time Error Limit left or right.
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 63
Page 64

Web Interface
In Depth
Before entering holdover:
n The Hardware Clockis synchronized to one of the Input References and reports Stratum
0 to the NTP daemon.
n The NTP daemonis synchronized to the Hardware Clock"reference clock" and reports
Stratum 1 to the network.
The Hardware Clockentersholdover when the Input Reference becomes unavailable and
no other Input References are available.
While in holdover:
n The Hardware Clockuses the internaloscillator to keep time (flywheeling).
n The NTP daemon(Stratum 1) remainssynchronized to the Hardware Clock (Stratum 0,
Reference = the name of the last Input Reference).
n The SyncServer estimates the time error (difference) between the oscillator-based Hard-
ware Clock time and UTC.
n If two or more synchronizing NTP associations are available and the Hardware Clock
accumulates too much time error, the NTP daemon "drops" the Hardware Clockand syn-
chronizes with the best association, with a corresponding adjustment to its Stratum.
The Hardware Clockleaves holdover when one of the following occurs:
n An Input Reference becomes available again. (As a result, the NTP daemon returns to
Stratum 1 operation.)
n The estimated time error exceedsthe user-configurable Time Error Limit.
If the estimated time error exceeds the user-configurable Time Error Limit:
n The Hardware Clockreports to the NTP daemon that it is unsynchronized (Stratum 16).
n If one or more synchronizing NTP associations are available, the NTP daemon syn-
chronizes with the best one, with a corresponding change to its stratum.
n If no synchronizing NTP associations are available, the NTP daemon's behavior is
determined by the settings on the NTP - Prefs page. See NTP - Prefs (on page 50).
n With the S300 and S350, the Hardware Clock synchronizes to the NTP daemon.
n With the S200, S250, and S250i, the Hardware Clock "flywheels" on the internal oscil-
lator until an Input Reference becomes available again.
TIMING - Sysplex
The Sysplex Timer port outputs serial time stringsfor IBM mainframe Sysplex systems. The
Sysplex Timer provides a common time reference acrossall the members of an IBM Sysplex. The Sysplex Timer is a key component when systemson multiple CPCs share access
to the same data.
See Sysplex Out (on page 116) for specifications and more information on the format of the
Sysplex output string.
Sysplex Output Configuration
The Sysplex Out port located on the rear panel outputs the time of day once per second.
Page 64..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 65

TIMING - Sysplex
Autostart:
n
Yes: The Sysplex Out connector automatically outputsthe time of day after systemstar-
tup. The user cannot stop or restart the output by entering the "C" or "R" commands.
n No: The user starts or stops the Sysplex output by sending the following characters to the
Sysplex Out connector:
n "C" or "c" to start the output.
n "R" or "r" to stop the output.
Parity: (Odd, None, Even) The parity settingof the Sysplex Out port (should match that of the
receiving device).
Flywheel Quality Character:
The user can set the Flywheel QualityCharacter to:
n "" (space)
n "X"
n
"F" (for Flywheel Quality Character)
About Sysplex and the Hardware Clock
To achieve the highest levels of precision and accuracy, the Sysplex Timer port gets its time
directly from the Hardware Clock. The Hardware Clocksynchronizes with the highest priority Input Reference (e.g. GPS1, Timecode).
With the S300 and S350, if the Input References become unavailable, and Holdover expires,
the Hardware Clocksynchronizes to the time the NTP daemongets from other synchronizing NTP associations(if any are present). The default configuration includes three
NTP servers on the Internet. If no synchronizing NTP associations are present, the Hardware Clock is unsynchronized and uses the internal oscillator to keep time.
In the S200, S250, and S250i, if the Input References become unavailable, and Holdover
expires, the Hardware Clock is unsynchronized and uses the internal oscillator to keep time.
The time quality character at the end of the Sysplex output string reflects the synchronization
state of the Hardware Clock. The user can select the time qualitycharacter used after holdover expiresand the hardware clockis:
n Synchronized to the NTP daemon, or
n Using the internal oscillator to keep time.
This setting is called the Flywheel Quality Character.
About the Flywheel Quality Character
The time quality character at the end of the Sysplex output string has three states:
n The first state is "X", time is invalid. The Hardware Clockhas not yet synchronized to an
Input Reference.
n The second state is "" (space), time is valid. Hardware Clock has synchronized to an
Input Reference, or is in Holdover.
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 65
Page 66

Web Interface
n The third state is "F", the Flywheel QualityCharacter. The Hardware Clock has no Input
Referencesand Holdover has expired. (On the SyncServer S300 and S350, if a syn-
chronizing NTP association is present, the Hardware Clockis synchronized to the NTP
daemon.)
The time quality character can progress through a number of states:
1. After the user starts the SyncServer, the Sysplex port starts outputting a time string. Ini-
tially, the time quality character is "X" (time invalid).
2. When the Hardware Clock locks to an Input Reference, the time quality character
becomes "" (time valid).
3. If the Hardware Clock losesall Input References and enters Holdover, the time quality
character remains "" (time valid).
4. If Holdover expires, the time qualitycharacter becomesthe Flywheel Quality Character,
determined by the user.
5. If an Input Reference becomes available again, the Hardware Clock synchronizes with it
and the time quality character becomes "" (time valid) again.
Usuallythere is a short delaybetween the Hardware Clockchanging state and the time qual-
ity character changing.
Here are some potential guidelinesfor configuring the Flywheel Quality Character (FQC):
n The user sets the FQC to " " if one or more of the following are true:
n The S300 or S350 is configuredwith two or more synchronizingNTP associations
and the user is satisfied with using time from other NTP associations.
n The SyncServer oscillator type has superior time keeping properties compared to
the receiving equipment. This is usually the case since most computer equipment
usesuncompensated quartz oscillators.
n The user sets the FQC to "F" if the receiving equipment can handle "F" as a time quality
character in some way that is useful and distinct from the "" or "X" time quality char-
acters.
n The user sets the FQC to "X" so that the receiving equipment to handlestimefrom NTP
or the Hardware Clock internal oscillator as "X" (time invalid).
Troubleshooting: If the time quality character remains "X" (time invalid) even though Input
Referencesare connected to the SyncServer.
n Verify that the physical connectionto the input connector is validand that there are no
cable breaks or short circuits.
n
On the TIMING - HW Clock page, verifythat the Input Referenceis Enabled and that Forced
Timing Source is set to Auto.
n
For Timecode, on the REFERENCES - Timecode page, check that the Timecode Input set-
ting matches the input signal type.
n For GPS, wait for the GPS receiver to complete the GPS acquisition process and
achieve "locked" status. Also see Operating in "Window Mode" (on page 143).
Also see TIMING - Holdover (on page 63) and TIMING - HW Clock (on page 61).
Note: If the user sets Forced Timing Source on the TIMING - HW Clock page to Free Run, the
Flywheel Quality Character in effect at that moment remains in effect thereafter.
Page 66..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 67

TIMING -Time Interval
TIMING -Time Interval
You can use the Time Interval only if you have purchased the PTP option. See "How to Activate the PTP Option" on page 53
Time Interval is only availableon S350 Syncservers with the PTPoption enabled.
The time interval is measuredfrom the 1PPS in and compared to the top of second of the
internalhardware HW Clock. This means that you cannot use the 1PPS input as a reference
sourceand measure Time Intervalat the same time. The Web UI will not prevent you from
doing this, but the user should disable the 1PPS in on the TIMING > HWClock page when
making a Time Interval measurement.
From the TIMING, Time Interval page, press the CHART button to access the charting
applet.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 67
Page 68

Web Interface
Please Note: It takes a few moments for the charting applet to open in a separate browser
window on the host computer. After the charting applet is open, you have access to several
options to customize the graph to your liking.
Pressingthe Graph pull down menu in the upper left of the applet allows you to select
among the following chart types to view the Time Interval Measurement data:
l Line
l Scatter
l Column
l Histogram
From the Graph pull down menu, you can also select between a Dynamic or Static view of
your data. If you are currently running a measurement and would like to view the data as it is
being processed, select the Dynamic view.
From the Data pull down menu, you can view data from the:
l Last 5 minutes
l Last 15 Minutes
l Last Hour
l All Data
l Custom Data Range…
Page 68..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 69

TIMING -Time Interval
You can also set up the Histogramchart from the Data menu or Reload Data from the database to the chart.
After a test has completed, you can zoom in on portions of the data set by selecting the Cus-
tom Data Range… and changing the Start Date to Display or Stop Date to Display.
You can configure the way the Histogram chart is displayed using the Histogram Setup…
selection in the Data menu. When the Dynamic Scale checkbox is selected, the Histogram
chart sets the first peak of the data in the center and automatically sets the x-axisvalues
appropriately for an equal Section Size. If this value does not work for your data, uncheck
the Dynamic Scale and manually select valuesfor Start, End and Section Size.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 69
Page 70

Web Interface
If none of the provided charts meets the needs of your data set, please use the Save AS...
function provided on the TIMING, Time Interval page to export your data to the tool of your
choice for further analysis.
REFERENCES - GPS
GPSPositionandOperatingMode
Note: The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
This page can be used to view or set the GPS receiver's Position and Mode, as well as the
GPS Antenna Cable Delay. Note that the SyncServer model 350i does not have a GPS
receiver.
Status: Indicates whether the GPS receiver is a valid reference (locked) or not (unlocked).
Current Position: The GPS antenna position in Latitude and Longitude by degrees, minutes,
and seconds, and the cardinal points of the compass followed by the altitude in Meters.
These values can be permanently set when the GPS Mode is set to Position Hold.
Mode:
n
Survey: In this mode, the receiver surveys and averages its position before switching to
Position Hold mode. Use this setting for stationary applications, such as server rooms.
This is the default setting.
n
Dynamic: In this mode, the receiver continuously updates its position. Use this setting if
the position of the SyncServer could change occasionally or continuously, such as
vehicles, aircraft, and ships. This setting provideslower timing precision and accuracy
than the Survey and PositionHold modes.
n
Position Hold: In this mode, the receiver calculatesthe time based on a fixed position that
has been providedby Survey Mode or entered by the user. Use this setting if GPS vis-
ibility is poor and the receiver has difficulty establishing its positionusing Survey mode
after one day. The accuracy of the user-entered position affects the accuracy of the tim-
ing solution from the GPS reference. Also see Operating in "Window Mode" (on page
143).
Antenna Cable Delay:
Use this setting to achieve the highest timing precision and accuracy on the timing outputs
suchas IRIG Out or 1PPS Out. This settinghas a negligible effect on NTP synchronization
because the scale of the adjustment (nanoseconds) is not significant compared to millisecond latencies on typical networks.
The Antenna Cable Delay advances the Hardware Clock slightly to cancel out the signal
delay caused by the length of the GPS antenna cable.
To calculate the adjustment, select the signal propagation rate for the appropriate cabletype
from the table below and multiplyit by the length of the cable.
Type Rate per foot Rate per meter
RG-58 1.4 nS/foot 4.59 nS/meter
RG-59 1.24 nS/foot 4.06 nS/meter
Page 70..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 71

REFERENCES - Timecode
For example, the standard 50 foot RG-59 antenna cable x 1.24 nS/foot = 62 nS of Antenna
Cable Delay.
Or, using meters, the standard 15.24 meter RG-59 antenna cable x 4.06 nS/meter = 62 nS
of Antenna Cable Delay.
Note: Use the Cable Delay setting on the REFERENCES - Timecode page to compensate for
the length of the Timecode Output cable. Avoid usingAntenna Cable Delay for that purpose.
REFERENCES - Timecode
Use this page to configure the timecode input and output on the SyncServer.
Also see IRIG In (Timecode In) (on page 118) and IRIG Out (Timecode Out) (on page
119).
Timecode Configuration
Status: Reports "locked" when the Timecode Input signaland configuration are both valid.
Otherwiseit reports "unlocked".
Configure the Timecode Input setting to match the input signal on the IRIG In connector.
n If the Timecode Input is marked "without YR", and there are no other Input References or
synchronizing NTP associations(the default NTP servers on NTP - Assoc page), verify
that the time SyncServer includesthe correct year. If needed, manuallyset the year. See
in Setting the Time Manually (on page 177).
Note: IRIG B 1344 provides a Leap Indicator warning during the minutepreceding a leap
second insertion/deletion. If a leap second adjustment occurs while the SyncServer is synchronized to IRIG B 1344 *, NTP clients that don't poll the SyncServer during this oneminutewarning period may be off by approximately one seconduntil they synchronize to the
new time. If the Maximum Poll Interval of the NTP clients is sufficientlyshorter than one
minute(e.g., 16 or 32 seconds), this scenario is less likely to occur.
*The "SyncServer is locked to IRIG B 1344" when Hardware Clock locked to the 1344 timecode input and the Hardware Clock is the "synchronizing" NTP association for the NTP daemon.
Timecode Output
Use the Timecode Output to configure the signal type on the IRIG Out connector.
The Cable Delay and Output Type settings onlyapply to the Timecode Output.
Cable Delay (nS): Compensatesfor delays caused by the length of the cable on the IRIG Out
connector. Use the table below to calculate the Cable Delay by selecting the signal propagation rate for the type of cable and multiplying it by the length of the cable.
Type Rate per foot Rate per meter
RG-58 1.4 nS/foot 4.59 nS/meter
RG-59 1.24 nS/foot 4.06 nS/meter
For example, a 50 foot length of RG-59 cable x 1.24 nS/foot = 62 nS of Cable Delay.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 71
Page 72

Web Interface
Or, using metric units, a 15.24 meter length of RG-59 cable x 4.06 nS/meter = 62 nS of
Cable Delay.
Output Type: Set the time scale used for the Timecode Output.
n
UTC: Coordinated UniversalTime. This is the factory default setting.
n
Local: The local time, as configured on the TIMING - Time Zone page.
Note: The timecode output can also be affectedby the Ignore UTC Corrections from GPS
Reference setting on the TIMING - HW Clock page. Also see TIMING - HW Clock (on page
61). Note that the SyncServer model 350i does not have a GPS receiver.
References
Please consult the Range Commander's Council document 200-04 - IRIG Serial Time Code
Formats (TTG) on the product information CD and at https://ws-
mrc2vger.wsmr.army.mil/rcc/manuals/200-04/TT-45.pdf for definitions of the following timecodes:
n IRIG A
n IRIG B
n IRIG E
n IRIG G
n NASA 36
n XR3/2137
Timecode glossary:
n
AM: Amplitude Modulated
n
B 1344: Standard IRIG-B with information encoded in the control bits per the IEEE 1344
standard. These include year, daylight savingtime, Leap Indicator, time quality, and parity information.
n
BCD: Binary Coded Decimal encoding of hours, minutes, seconds, and daysof year
(hh:mm:ss:ddd)
n
CF: Control Function (elements - varioususes depending on the implementation)
n
DC: TTL Levels
n
DCLS: Direct Current Level Shift (width coded)
n
Hz: Hertz
n
kHz: Kilohertz
n
Legacy TrueTime: Standard IRIG-B with four time-quality bits and a lock indicator encoded
in the control bits
n
SBS: Straight Binary Second encoding of seconds in the day
n
YR: Year
REFERENCES - Modem
note: The SyncServer S350i does not include a modem.
Use the REFERENCES - Modem page to create an NTP server association for the modem on
the NTP - Config page. The modem association operates as a backup reference, getting the
time from an automated dial-up time service if more accurate NTP associationsaren't
Page 72..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 73

REFERENCES - Modem
available (e.g., if the hardware clock or other server associations became unreachable).
While the SyncServer's NTP daemon is synchronized to the modem association (system
peer = modem), the Sync LED on the front panel is green and the SyncServer operates as a
stratum 1 NTP server.
The REFERENCES - Modem page provides the telephone numbers of several established time
services. The user can edit or replace these with the number of any compatible dial-uptime
service (same protocols, time code, and time scale). Microsemi recommendsthat users outside the United States, Japan, and Germany determinewhether a localtimekeeping authority offers a compatible dial-up time service.
After the modem association has been created, the user can influence how often the modem
calls the time service by modifying the Minimum Poll Interval (default 00:02:08, in hh/mm/ss format) and Maximum Poll Interval (default 18:12:16, in hh/mm/ss format) on the NTP
- Config page. The intervalbetween calls starts out close to the Minimum Poll Interval and
gradually increasesto the Maximum Poll Interval over a day or so. Decreasing the Max-
imum Poll Interval improves timing accuracy, but also increases the frequency of phone calls.
Note: All communication and service chargesare the responsibility of the user.
The user can determine the highest acceptable value for the Maximum Poll Interval by multiplying it with the estimated drift rate of the oscillator (given on the TIMING - Holdover page).
For example, on a SyncServer equipped with a TCXO oscillator, the default Maximum Poll
Interval, 18:12:16, translates into approximately 0.76 days or approximately 14 ms of drift
between synchronizations. This value may be acceptable for network timing applications, but
should be considered if more precise timing is required, particularly from the timingoutputs
from the rear panel.
Note: The settingson the TIMING - Holdover page do not applyto the modem association, they
only applyto the Hardware Clock Input References.
Modem Configuration
Dial Configuration:
n
Tone Dial (ATDT): (FactoryDefault) Configures the modem for "touch tone" dialing, common throughout the world.
n
Pulse Dial (ATDP): Configures the modem for pulse "rotary telephone" dialing, still used in
selected regions of the world.
n
None (User Dial Command): Makes AT commands available in the Dial-Up Time Reference
Phone Number(s) fields. Phone numbers must be preceded by a valid AT command. Some
potentiallyuseful AT modem commands for getting an outside line from a PBX system:
n AT X0 establishesblind dialing and dials0, commonin Japan.
n AT X9 establishesblind dialing and dials9, commonin USA.
Note: Leave a space between T and X in the preceding commands.
Modem Pre-Test
The user can test a number by entering a number in the Test Number field and clicking the
TEST MODEM button. If successful, "Modem Connected to Test Number" appears in small text
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 73
Page 74

Web Interface
to the right of the CANCEL button. If the user does not supplya phone number, this feature
verifies the operation of the modem. Testing a number does not synchronize the NTP daemon to the service.
Preconfigured Phone Numbers
Selecting one of the service providers does two things:
n Enters phone numbers for the dial-up time service in the Dial-Up Time Reference Phone
Number(s) field(s).
n Sets the protocols, time code, and time scale the modem will use to decode the dial-up
time service.
Select one of the following services:
n
ACTS: NIST Automated Computer Time Service (ACTS) in the United States. See
http://tf.nist.gov/service/acts.htm.
n
Disable Echo Delay: ACTS measures the echo delay to calibrate for the propagation delay of the telephone circuit and equipment in order to achieve accuraciesof
approximately 1 or 2 milliseconds. Selecting Disable Echo Delay disables this feature for ACTS, resulting in lower accuracies.
n
USNO: An ACTS-likeservice provided by the US Naval Observatory in the United States.
Does not provide delay compensation.
n
JJY: NICT Dial-up standard time service (Telephone JJY) in Japan. See http://jjy.n-
ict.go.jp/time/teljjy/teljjy_p1-e.html.
n
ITU-R: Selecting ITU-R generates the phone number for PTB’s telephone time service in
Germany. If needed, please consult the list of other ITU-R service providers below.
Dial-Up Time Reference Phone Number(s)
Selecting an item under Preconfigured Phone Numbers populatesthese fields. The user can
also enter phone numbers directly. Use a "." (period) character to insert a pause.
Note: Review this list to ensure that the nearest service, or the service with the lowest
charges, is at the top of the list.
Comments
The services and numbers listed below are subject to change. Please consult with your local
time-keeping authority for the latest information.
Note: Some ITU-R services chargefees. All tolls and fees are the responsibility of the customer.
ITU-R services: Services that comply with the ITU-R Recommendation (ITU-R TF583.4)
are now available from the primary timing centres of: Austria, Belgium, Germany, Italy, The
Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, and the
United Kingdom.
This is a partial list of those services:
n
Germany: Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB)'s timecode service. +49 5 31 51
20 38. http://www.ptb.de/en/org/4/44/_index.htm
Page 74..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 75

REFERENCES - LF Radio
n
United Kingdom: National Physical Laboratory (NPL)'s TRUETIME service. +44 0891 516
333. http://www.npl.co.uk/npl/ctm/truetime.html
n
Italy: Istituto Elettrotecnico Nazionale"Galileo Ferrais" (IEN)'s CTD service. +39 166 11
46 15. http://www.ien.it/ar96/tf.htm
n
Switzerland: Swiss Federal Office of Metrology 's timecodeservice. +41 031 323 32 25.
http://www.metas.ch/en/labors/official-time/modem/index.html
n
Sweden: SP Swedish National Testing and Research Institute 's timecode service. +46 33
41 57 83 http://www-v2.sp.se/metrology/timefreq/eng/timesynch_modem.htm
n
Netherlands: SwindenLaboratorium (VSL). 09 00 61 71 81 9. http://nmi.nl/tijd_service-
663.pagina?lg=en
RESTARTbutton
After changing the NTP configuration, click the RESTART button to put the new configuration
into effect. While the NTP daemonrestarts, its servicesare temporarily unavailable, and it
generatesthe following alarm events: NTP Stratum Change, NTP System Peer Change,
NTP Leap Change.
REFERENCES - LF Radio
The Low Frequency (LF) Radio is an optional Input Reference for the SyncServer S300 and
S350 models. The LF radio option operates as an Input Reference.
note: The S350i SyncServer does not include the Low frequency radio.
Also see Using LF Radio (on page 170).
Low Frequency Radio Configuration
Installed Radio Option: Specify the format of the radio time service for decoding:
n Not Installed (Default): disablesthe LF radio module.
n WWVB (60 kHz)
n DCF77 (77.5 kHz)
n JJY (40 kHz or 60 kHz) The customer specifies the frequencyat the time the LF Radio
option is purchased.
Select Not Installed:
n If the LF radio option isn't present.
The 72 hour Reachability Chart shows a series of color-coded vertical bars:
n Green - Time was decoded.
n Red - Time was not decoded.
The height (y-axis) of the bars indicates a figure of merit. For example, the taller the green
bar, the better the signal and the more often the signal was decoded during the 15-minute
interval.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 75
Page 76

Web Interface
When choosing a location for the LF Antenna module, seek the one with the shortest red
bars during the day, and the tallest green bars at night.
Each tick-mark along the bottom of the graph representsan hour, with extended tick marks
for 6 and 24-hour periods.
Each green or red vertical bar represents a 15-minuteinterval, with four bars per hour. The
most recent data is displayed on the right, and the data moves from right to left.
SYSTEM - General
Use this page to manage:
n The network Hostname for the SyncServer.
n Automatically check for software upgrades.
Hostname: (Default: "SyncServer") The hostname identifiesthe SyncServer on the network
and is also an important element of NTP autokey authentication. When operating multiple
SyncServerson a network domain, or when using NTP autokey, replacethe hostname with
a unique descriptive string composed of alphanumeric characters with no spaces or special
characters. The field has been programmed to reject invalid characters.
Software Update Availability Check: (Default: Enabled) When enabled, the SyncServer checks
a file on the Symmetricomweb site for software upgrades shortlyafter noon, local time,
Mondaythrough Friday, as determined by the Local Time Zone setting on the TIMING - Time
Zone page. If the software Release and Revision on upgradeS300.txt are more recent than
that of the software on the SyncServer, the SyncServer displays a notice on the STATUS -
General page, and generates a System Upgrade Alarm on the ADMIN - Alarms page.
In order for the Software Update Availability Check to function, LAN1 must have:
n Firewall access to the Internet (port 80)
n A valid DNS server
To manuallycheck if an upgrade is available, or if network conditions prevent Software
Update Availability Check from checking automatically, compare http://up-
date.symmetricom.com/upgradeS300.txt with the STATUS - General page.
For example, compare "Version=1.10" and "Last Checkpoint: 1.103" on upgradeS300.txt
with "Release Version1.10 Build 1.103" on the STATUS - General page. Sincethe values are
the same, no upgrade is available.
Note: The default configuration of the System Upgrade Alarm on the ADMIN - Alarms page is
"Severity= Minor", "Send SNMP trap", "Write to log", and "Send email notification" when
upgradesbecome available. SNMP and alarm email must be configured correctly to function.
The user can also contact Microsemi Customer Assistance (on page 5) for information
about upgrades.
Page 76..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 77

SYSTEM - Upgrade
SYSTEM - Upgrade
Use this page to upgrade the SyncServer's software. This can be done using the web interface to upload the new software from workstation, or using the keypad/displayinterface to
uploadthe new software from a USB flash memory device connected to one of the SyncServer's USB ports. Please consult Upgrading System Software (on page 152) before
upgrading the software.
Note: Please avoid decompressing the *.tar upgrade file prior to upgrading the SyncServer.
The SyncServer will not installsoftware from an upgrade file that has been modified or
decompressed and recompressed. If needed, pleasedownload a new software file from
Microsemi.
Upload Upgrade Package to SyncServer
BROWSE button: Choose an upgrade file that's accessible from your workstation, such as a
network drive or Desktop.
UPLOAD button: Upload the upgrade file to the SyncServer.
Manage Files in SyncServer
Current Files: This window displays upgrade files and an upgrade history file.
Optional Parameters: This field can be used to supplyoptional installationparameters, if
required. This field is not required for normal operation.
INSTALL button: To install the upgrade file, select the file and click the INSTALL button.
VIEW button: To see the upgrade history, select the upgradehist.txt file and click the VIEW but-
ton.
DELETE button: To delete a file, select the file and click the DELETE button. It may be neces-
sary to upload a file before the upgradehist.txt file can be selected and deleted.
SYSTEM - Factory Reset
Use this page to reset the SyncServer to its original factory default configuration.
Before resetting the factory defaults, the user may want to back up the current configuration
if they intend to use it again in the future.
To reset the factory defaults, select Reset to Factory Defaults and click the APPLY but-
ton. This clears *ALL* of the current settingson the SyncServer, restores the original factory
default configuration, and rebootsthe SyncServer.
After restarting, the user may need to configure LAN1 before reconnecting to the web interface. The default usernameand password (admin, symmetricom).
A partial list of the defaults restored by this operation:
n Network port settings
n NTP Associations
n Hostname
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 77
Page 78

Web Interface
n All settingsdefined on the ADMIN pages (Web, Users, Alarms, Logs Config), including
the username and password settings.
n All services are reset to their default modesof operation.
n Hardware Clock settings, including forced mode, Time Zone, Position and Time Error
Limit, IRIG Input and Output, etc.
n All cryptographic materials (NTP keys, sshd keys, SNMP users and communities)
deleted.
n Logs are erased.
Also see Backing Up/Restoring Configurations (on page 165), Configuring LAN1 (on
page 148), and Logging in to the Web Interface (on page 149).
FactoryDefaultSettings
Note: The S350i SyncServer does not include a GPS receiver,LFradio, or modem.
NETWORK – Ethernet
For LAN1:
Connection Mode: Static
IP Version: IPv4
IP Address: 192.168.0.100
Mask255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.0.100
Redundant: 000.000.000.000
Allowed Access: Null
Speed/Duplex: Auto
For LANGBE, LAN2, LAN3:
Connection Mode: Disabled
IP Version: None
IP Address: None
Mask: None
Gateway: None
Redundant: None
Allowed Access: None
Speed/Duplex: None
Mgmt Port User DNS Servers: Null
NETWORK – SNMP
sysLocation: unknown
sysName: SyncServer
sysContact: admin@localhost
Read Communitysymmpublic
Write Communitysymmprivate
User Name: admin
Page 78..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 79

Mode: rouser
Level: Null
NETWORK – SNMP Traps
Destination: None
Ver: None
(Inform): None
User/Community: None
NTP – Config
For HW Clock:
Checkbox: Grayed
Role: Server
Prefer*
IP Address: Hardware Clock
Poll Min: Null
Poll Max: Null
Key: Null
Burst: Null
For 69.25.96.11, 69.25.96.12, and 69.25.96.14:
Checkbox: Active
Role: Server
Prefer: Null
IP Address: 69.25.96.11, 69.25.96.12, and 69.25.96.14
Poll Min: Null
Poll Max: Null
Key: Null
Bursti: Burst
SYSTEM - Factory Reset
NTP – MD5 Keys, Autokey, Autokey Client
All null.
NTP – Prefs
Leap Indicator Bits/StratumFollow Standard NTP rules (Default)
TIMING – Timezone
Time Zones: UTC
TIMING – HW Clock
Clock Source PrioritiesGPS, Timecode, WWVB, 1PPS, 10MHz, T1E1
Enable: All enabled
Forced Timing Source: Auto
Ignore GPS - UTC Correction: Disabled
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 79
Page 80

Web Interface
TIMING – Holdover
Time Error Limit: 1 ms
TIMING – Sysplex
Autostart: No
Parity: Odd
Flywheel Quality Character: X
REFERENCES – GPS
ModeSurvey
Latitude: 0 degrees, 0 minutes, 0 seconds, North
Longitude: 0 degrees, 0 minutes, 0 seconds, East
Altitude: 0 Meters
Antenna Cable Delay: 0
REFERENCES – IRIG-B
Timecode Input: B 1344 AM
Timecode Output: B 1344 AM
Output Type: UTC
Cable Delay: 0
REFERENCES – Modem
Dial Configuration: Tone Dial (ATDT)
Preconfigured Phone Numbers: None
Dial-Up Time Reference Phone Number(s): None
REFERENCES – LF Radio
Installed Radio Option: WWVB (60 kHz)
SYSTEM – General
Hostname: SyncServer
Check for software Upgrades: Checked
ADMIN – Web
For Login Page Configuration:
Appearance Graphic (login page with configurable system information)
Title: Null
Time, Hostname, LED's: Checked
NTP Status: Checked
Hardware Clock Status: Checked
GPS Receiver Status and Satellite Count: Checked
Highest Severity Alarm: Checked
Page 80..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 81

SYSTEM - Factory Reset
Version Info, Uptime: Checked
IP Addresses for all configured LAN ports: Checked
For Configuration Settings:
Warn when Navigating without saving changes: Checked
Update the configuration backup file when configuration changes are applied: Checked
Send Browser hint to not Auto Complete Passwords: Not checked
ADMIN – Users
Username: admin
Password: symmetricom
See also: Properties of User Names and Passwords (on page 23)
ADMIN – Alarms
Under the ADMIN - Alarms topic, see Factory Default Settings for Alarms (on page 89).
ADMIN – Logs Config
auth.log: Notice
daemon.log: Notice
kern.log: Notice
syslog: Notice
messages: Debug, Info, Notice, Warning
Remote Log System: Null
ADMIN – Relays
Alarm Relay: Off (no activation on any alarm)
System Restart Delay: 60 minutes
ADMIN – RADIUS
RADIUS Authentication: Disabled
ADMIN – TACACS+
TACACS+ Authentication: Disabled
SERVICES – Startup
Web Server: On, Auto
NTP: On, Auto
SNMP: On, Auto
SSH: On, Auto
Sysplex: On, Auto
Time: On, Auto
Time-UDP: On, Auto
Daytime: On, Auto
Telnet: Off
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 81
Page 82

Web Interface
System Control: Run
SERVICES – HTTP
Security: Standard (Port 80) Only
SERVICES – SSH
Protocol: SSH-1 & SSH-2
Log Level: INFO
Server Key Bits: 768
Key Regeneration: 3600 Seconds
SERVICES – Email
SMTP Gateway: Null
User1-10: Null
SYSTEM - Options
Use this page to installavailable options.
See "How to Activate the PTP Option" on page 53 to install the PTP option
This page gives:
l The SyncServer serial number for use in obtaining the option key.
l A text box for entering the option key.
l Two text boxes showing both the available options and installed options.
l Buttons to apply the available options or cancel the process.
ADMIN - Web
Use this page to:
n Configure the appearance and information displayed on the login page.
n Modifythe behavior of the web interface.
Login Page Configuration
The settingsin this section configure the Login page to:
n Displaystatus information. This is convenient for monitoring status without logging in, par-
ticularly if LAN1 is on a privateadministrative network.
n Remove status and information that identifiesthe SyncServer from the login page. This
makesit more difficult for unauthorized users to recognize the SyncServer via its web
interface.
The login page choices are:
Page 82..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 83

ADMIN - Web
n
Plain: Login page does not contain any identifyingtext or graphics.
n
Graphic: Login page contains identifying text, graphics, and user-selected status information.
The configurable systeminformation includes the following choices:
n
Title: A user-determined text string at the top of the login page.
n
Time, Hostname and LEDs: The localtime, the hostname, and the status LEDs.
n
NTP Status: The NTP Stratum and Reference ID.
n
Hardware Clock Status: The current Sync Source and whether the Hardware Clock is
locked.
n
GPS1Receiver Status and the Satellite Count: GPS receiver is providing timing information
and the number of satellites visible.
n
Highest Severity Alarm: The name of the most recent and most severe pending alarm.
n
Version Information and Uptime: The model number, software version, and uptime since the
unit was started.
n
IP Addresses for all Configured LAN Ports: The MAC, IPv4, and IPv6 addresses of the LAN
ports.
Save Configuration Settings
Beyond the login page, the user can determine the behavior of the web pages.
Warn when Navigating without saving Changes: (Enabled by default)
n When this feature is enabled, the SyncServer sends warnings messages if the user
makessettings changes and navigatesaway from the page without clicking the APPLY
button. This reducesthe possibility of accidentally losingunsaved changes.
n When this feature is disabled, the SyncServer suppresses these warning messages.
Save Configuration Changes when Submitted: (Enabled by default)
n When this feature is enabled, the SyncServer updates the configuration backup file in
non-volatile memory when the user applies or saveschanges to the configuration. This
may slow the web interface's response time, but ensuresthat the current configuration is
backed up and will be restored if the SyncServer is rebooted.
n When this feature is disabled, the SyncServer does not update the backup file when the
user applies or saveschanges to the configuration. This may improve the web interface's
response time to applied changes but leavesthe backup file unchanged. This option can
be useful for keeping a "known good configuration"available while trying out experimental configurations. If the experimental configurations aren't satisfactory, use the
WIZARDS - Restore page to restore the known good configuration. Once the desired configuration is reached, manually save the configuration backup file to non-volatile memory
using the WIZARDS - Backup page.
Send Browser hint to not Auto Complete Passwords: (Disabled by default)
n Enabling this setting enhances security. It prompts browsers to suppress the "auto-com-
plete"and "remember password" features. This makes it more difficult for unauthorized
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 83
Page 84

Web Interface
users to gain accessto the SyncServer from an authorized user's workstationor by
exploiting stored browser settings.
ADMIN - Users
Use this page to:
n Add a new user
n Set a new password
n Enable and configure password recovery
n Send a test email for password recovery
For information about creating and deleting users, or changing passwords and enabling
password recovery, see Managing Users (on page 175).
Note: All users have complete administrative privileges.
User Creation, Deletion and Password Maintenance
User: Select New User to create a new username or select a current username from the list
to change its settings.
Delete Selected User: To delete a current username, select this box and click the APPLY but-
ton. The web interface preventsthe last remaining username from being deleted.
New Username: When User is set to New User, enter the username to create. See also: Prop-
erties of User Names and Passwords (on page 23)
Old Password: When User is set to a current username, enter the corresponding password to
authenticate changes being made elsewhere on this page.
New Password: To change the password, enter a new password with six or more characters,
including lower and upper case letters, or letters and at least one number. See also: Prop-
erties of User Names and Passwords (on page 23)
Retype New Password: Confirm the spelling of the password by entering it one more time.
Password Recovery: Select this checkbox to enable password recovery from the Login page.
With password recovery enabled, the user can reset the password from the Login page by
correctly answering the password recovery question. The SyncServer then sends an email
message containing a new automatically generated password to the email address supplied
on the ADMIN - Users page. After logging in, the user can reset the password to a known
value.
Note: The SyncServer does not providea method for recovering forgotten usernames. If all
usernames have been forgotten, restore the factory configuration using the hardware
jumper. See Restoring the Factory Default Configuration (on page 167).
Recovery Question: Select one of the standard recovery questions, or create a custom question.
Answer: Enter the answer to the recoveryquestion. Case sensitive.
Email Address: The emailaddress to which the password recovery message is sent.
Page 84..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 85

ADMIN - Alarms
SMTP Gateway: The email server that forwards the password recovery message (e.g., smtp.domainname.com). The SyncServer must have a validSMTP Gateway addresses for
password recovery to work. If LAN1 is unableto reach a DNS server, the SMTP gateway
must be entered as an IP address, not as a DNS name. If needed, contact a network administrator to obtain this information.
Send Test Email: Select this option to verify that password recovery by email is configured correctlyand works.
Note: Once applied, recovery question, answer, and email address data do not remain visible
on the page. The SMTP Gateway entered here is also used for email notification of alarms.
However, email addressesfor alarm notification are entered on the SERVICES - Email page.
Email notification of alarms is configured on the ADMIN - Alarms page.
ADMIN - Alarms
Alarm Configuration and Notification
Use this page to view alarm status and to perform the following tasks:
n ConfiguringAlarm Severity (ALARM LED color).
n Manually clearing alarms.
n ConfiguringAlarms to clear automatically after 15 minutes.
n Configuringnotification by SNMP traps and email messages.
n Logging of alarms, notification events.
The Alarm LED at the top left corner of the web interface and on the front panel indicates the
highest severity alarm on the ADMIN - Alarms page:
n Red: Alarm with severity = Major.
n Orange: Alarm with severity = Minor.
n Green: Alarm with severity = Notification, or no alarms.
Alarm Configuration and Notification
Name: Describesthe system event that causes the alarm. Also see Alarm Descriptions (on
page 86).
State: A graphic LED indicating the alarm state and severity at the time the page was gen-
erated:
n Grey LED: Severity is set to Notify.
n Green LED: Severity is Major or Minor, and there is no alarm.
n Orange LED: Severity is set to Minor, and there is an alarm.
n Red LED: Severity is set to Major, and the alarm there is an alarm.
Note: To check the current state, clickthe refresh icon (rotating arrows) at the lower right
corner of the page.
Clear Now: This checkbox is only available during an alarm. To clear the alarm, select the
Clear Now checkbox and clickthe APPLY button. Doing so returns the alarm to a "No
Alarm" state.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 85
Page 86

Web Interface
Auto Clear: Automatically clears the alarm after 15 minutes, regardlessof the condition that
caused it.
Severity: Determines the Alarm LED response to an alarm and sets the "Level:" in the SNMP
trap, email message, and log entry.
n Notify: Does not raise an alarm (No change to Alarm LED color).
n Minor: Raises a minor system alarm (Alarm LED = Orange).
n Major: Raises a major system alarm (Alarm LED = Red).
Note: If enabled, Send Trap, Write Log, and Send Email operate in response to alarms,
regardless of Severity.
Send Trap: Sends an SNMP trap when the alarm occurs and ends. SNMP must be configured correctly on the NETWORK - SNMP and NETWORK – SNMP Traps pages for this to work.
Write Log: Generatesa log entry in syslog when the alarm occurs and ends. The log can be
viewed from the LOGS - syslog page.
Send Email: Generates a descriptiveentry in an email message when the alarm occurs and
ends. The SyncServer compiles the entries over a 5-minute period and sends emailmessagesat five-minute intervals, so an email alert may contain more than 1 alarm. For Send
Email to work, the SERVICES - Email page must be configured with a valid SMTP Gateway
and email address. If the SMTP gateway is a DNS name, LAN1 on NETWORK - Ethernet must
be configuredwith a valid DNS server address.
Note: When Clear Now and Auto Clear are used to clear an alarm, Send Trap, Write Log,
and Send Email do not generate notification messages or log entries.
AlarmDescriptions
Note: Alarm indicators for optional features or equipment appear when the related option is
present and enabled.
Note: The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
NTP System Peer Change Alarm: The SyncServer's current NTP synchronization peer has
changed.
NTP Stratum Change Alarm: The NTP Stratum level has degraded. For example, the NTP
Stratum has gone from 1 to 2.
NTP Leap Change Alarm: The SyncServer raises this alarm when the leap indicator changes
state. See STATUS - NTP (on page 28).
This change of state has two potential causes: The first is that the SyncServer was reconfigured, causing the NTP daemonto be restarted. More rarely, this can occur when the SyncServer is within 24 hours of a leap second adjustment.
System Network Alarm: Alarms if a configured port has no connection (network link). Clears if
all configured ports have connections.
System Upgrade Alarm: The SyncServer checksfor software upgradesand raises this alarm if
a software upgrade is available. Microsemi recommends leaving this alarm enabled.
Page 86..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 87

ADMIN - Alarms
Microsemi recommends enabling Send Trap and/or Send Email for this alarm on the ADMIN -
Alarms page.
Note: In order to detect upgrades, the SyncServer must be correctly configured with a DNS
server and must have http accessto the Internet through port 80. This feature is enabled by
default, but can be disabled on the SYSTEM - General page.
System Config Change Alarm: Generatesan alarm if the systemconfiguration has been
changed. If the Auto Clear is not selected, this alarm will remain pending until cleared by the
administrator.
System Health Alarm: The web interface has been unableto automatically save user configuration changesto the backup file. The user might need to perform a manual backup using
the WIZARDS - Backup page.
System Up/Down Alarm: Reserved for future use.
System Authentication Alarm: The SyncServer detected a failed login attempt on the web inter-
face.
Timing No Source Alarm: The Hardware Clock doesnot have a valid timing reference.
Timing GPS Source Alarm: (Displayed on GPS-equipped SyncServersonly) The GPS time ref-
erence is not providingvalid timing information. This may be caused by:
n An insufficient number of visible GPS satellites.
n The GPS satellite signalsmay be blocked from reaching the antenna, or are too weak to
be detected by the receiver.
n The GPS antenna cable may be disconnected, broken, shorted, or too long.
Timing Timecode Source Alarm: The Hardware Clock is not detecting a valid input signal on the
IRIG In connector.
Timing PPS Source Alarm: The Hardware Clock is not detecting a valid input signal on the
1PPS In connector.
Timing 10MHz Source Alarm: The Hardware Clock is not detecting a valid input signal on the
10MHz In connector.
Timing GPS Antenna Short Alarm: (Displayed on GPS-equipped SyncServers only) The GPS
receiver detects an overcurrent condition on the GPS antenna cable. The likely cause is a
short circuit.
Timing GPS Antenna Open Alarm: (Displayedon GPS-equipped SyncServers only) The GPS
receiver detects too little current in the power supplied to the GPS antenna. The likely cause
is a disconnected or broken GPS antenna cable. A GPS splitter may also cause this condition.
Timing Oscillator DAC Range Alarm: The SyncServer is applying the maximumor minimum
DAC value to steer the oscillator. If this recurs frequentlyor over a sustained period of time,
there may be a problem with the oscillator.
Timing Rubidium Lock Alarm: The optional Rubidium oscillator, if installed, has not stabilized its
frequency output. After power up, this alarm may be raised for up to several minutesuntil the
Rubidium warms up and stabilizesitsfrequency output.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 87
Page 88

Web Interface
Timing Oscillator Unlock Alarm: The Hardware Clock's oscillator frequency is not locked to the
reference source.
Timing Source Change: The Hardware Clock has switched timing references.
Timing Source Change Lower Accuracy Input: The Hardware Clockhas switchedto a lower-pri-
ority timingsource.
Timing PLL Unlock Alarm: The Hardware Clock oscillator's PLL unlocked.
Timing Time Quality 1e-6 Alarm: The Hardware Clock's estimated time error has exceeded 1e-
6 seconds(1 microsecond).
Timing Time Quality 1e-5 Alarm: The Hardware Clock's estimated time error has exceeded 1e-
5 seconds(10 microseconds).
Timing Time Quality 1e-4 Alarm: The Hardware Clock's estimated time error has exceeded 1e-
4 seconds(100 microseconds).
Timing Time Quality 1e-3 Alarm: The Hardware Clock's estimated time error has exceeded 1e-
3 seconds(1 millisecond).
Timing Leap Event Alarm: The leap indicator from the Hardware Clock's GPS or IRIG 1344 tim-
ing references, indicates that a leap event is pending. The pending event can be a Leap
Second Insertion, Leap Second Deletion, or Clear Alarm, which indicatesthat the alarm has
passed. See STATUS - Timing (on page 26) for more information.
Note: IRIG-1344 onlyprovides a Leap Indicator warning during the last minute of the day of
the event. In this case, while the SyncServer will propagate that information via NTP, NTP clients may not query the SyncServer in time to be warned of the leap secondadjustment.
LAN1 Link Alarm: A network connection is not available on LAN1. Note that if LAN1 is down,
SNMP and Email notification do not work and the web interface is not available.
Note: The Network LED indicates the statusof the "LAN* Link Alarms". Please consult
Status LEDs (on page 15).
LAN2 Link Alarm: LAN2 has lost its network connection.
LAN3 Link Alarm: LAN3 has lost its network connection.
LANG Link Alarm: LANGbE has lost its network connection.
Timing NTP Daemon Alarm: The NTP Daemon is no longer a valid source of timing to the Hard-
ware Clock.
Timing <LF Radio> Source Alarm: The LF Radio module cannot be decodedby the Hardware
Clock. The values for <LF Radio> can be WWVB, DCF77, and JJY.
System RADIUS Server Alarm: This alarm is raised when the system failed to create firewall
rules to allow RADIUS packets. Without the proper firewall rules, RADIUS server(s) cannot
provide authentication service.
System Reset Default Config Alarm: Typically, during a reboot, the SyncServer applies the current configuration. This alarm is raised when the system failed to initialize itself to the current
configuration and it automaticallyrestoreditself to the default configuration. The circumstancesare usually caused by missing or corrupted current configuration.
Page 88..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 89

ADMIN - Alarms
PTP Leap 59: Leap second deletion is pending. The last minute of the day will have 59
seconds.
PTP Leap 61: Leap second insertion is pending. The last minute of the day will have 61
seconds.
PTP Clock Accuracy: The system is not locked to a reference source and is not within the holdover specifications. The PTP ClockClass is 52.
PTP Queue Reset: A PTP queue has filled up and was flushed.
PTP Daemon Reinit: The PTP daemon was overloaded and reinitialized.
FactoryDefaultSettingsforAlarms
Name
NTP System Peer Change Notify
NTP Stratum Change
NTP Leap Change
System Network
System Upgrade
System Config Change Notify
System Health
System Up/Down
System Authentication
Timing No Source
Timing GPS1Source
Timing Timecode Source
Timing PPS Source
Timing 10MHz Source
Timing GPS AntennaShort
Timing GPS AntennaOpen
Timing Oscillator DAC Range Notify
Timing Rubidium Lock Notify
Timing Oscillator Unlock Notify
Timing Source Change Notify
Timing Source Lower Accuracy Input Notify
Timing PLL Unlock
Timing Quality 1e-6
Auto
Clear
Severity
Y Major Y Y Y
Y
Y
Notify
Notify
Minor Y Y Y
Y Major Y Y Y
Y Minor Y Y Y
Y
Notify
Y Major Y Y Y
Y Major Y Y Y
Y
Y
Y
Notify
Notify
Notify
Y Major Y Y Y
Y Major Y Y Y
Y
Y
Notify
Notify
Send
Trap
Write
Log
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Send
Email
Timing Quality 1e-5
Timing Quality 1e-4
Timing Quality 1e-3
1
The SyncServer S350i does not include a GPS receiver.
Y
Y
Y
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 89
Notify
Notify
Notify
Y
Y
Y
Page 90

Web Interface
Name
Timing Leap Event
LAN1 Link
LAN2 Link
LAN3 Link
LANG Link
Timing NTP Daemon
Timing DCF77 Source
System RADIUS Server
System Reset Default Config
PTP Leap 59
PTP Leap 61
PTP Clock Accuracy
PTP Queue Reset Major
PTP Daemon Reinit Major Y
Auto
Clear
Y
Severity
Notify
Y Major Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Notify
Notify
Notify
Notify
Notify
Notify
Major Y
Y
Y
Y
Notify
Notify
Notify
Send
Trap
Write
Log
ADMIN - Logs Config
Send
Email
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
System Log Configuration
Use this page to configure the SyncServers logging subsystem. The SyncServer uses klogd
and syslogd, the standard logging facilities. What is logged and where it is logged is based on
the options selected in this page. A default set of options is preconfigured that should provide
a level of detail sufficient for the majority of applications. Each entry is broken down into facility and priority, where facility is the part of the system such as the kernel or the application
daemons and priority indicates the severity of the message. The priority ranges from
"Emerg", which represents onlyverysignificant events like kernel panics to "Debug", where
even debug messages are logged. Messages are generally logged to different filesto allow
easier parsing. The messages file is unique however in that its default configuration captures
all messages flowing through the logging daemons. But, due to the high volume of traffic, it is
cleared at each power cycle or reboot.
Note: Most users should leave the logs configured in the default manner unless directed to
make changes by Microsemi technical support.
Log Types
syslog: syslog holds messages about system level events. Examples of system events are
privilege changes(e.g., sudo) and messages about regularly schedulesevents such as cron.
auth.log: The authentication log contains entries regarding authentication events from login or
PAM (PluggableAuthentication Module).
kern.log: The kernel log containsentries submittedby the kernel. Examplesof kernel events
are network errors or hardware changes.
Page 90..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 91

ADMIN - Logs Config
daemon.log: The daemon log contains entriessubmitted by the daemon processes that
provide the services in the SyncServer. Examples of daemon log entries are NTP changes,
SNMP events, and xinetd events.
messages: The messages file is something of a catchallfile. By selecting variouspriorities, it
is possible to capture large amounts of data regarding system operation. However, the
volume of data becomesimpractical to manage quickly. As such, this file is cleared at each
power cycle or reboot.
events: The eventslog is not configurable. This log is maintainedoutside syslogd and contains configuration and event data related to operations performed in the web interface.
Log Priorities
In the caseof kernel, syslog, auth and daemon logs, the priority specified will cause all messagesgreater than or equal to the selected priority to be logged. The prioritiesare defined in
ascending order.
In the caseof the messageslog, only the selected priorities are logged. As such, up to four
prioritylevels are supported.
Debug: This priority levelcaptures debug output from applications designed to produce this
type of output. This level generatesa large volume of traffic and is not recommended unless
it is done under the direction of technical support personnel. An example may be a signal
handler called.
Info: This level captures informationaloutput. This level typically provides information regarding successful operations. An example may be a successful file save or a normal application
startup.
Notice: This levelcaptures transactional information. An example of this couldbe a network
connection or login.
Warning: This level captures information that is not expected by the application or system.
This couldbe something the system is not configured to handle. An example might be a malformed network packet or a drive change caused by inserting a thumb drive into a USB slot.
Err (deprecated): The use of this level is deprecated.
Crit: This levelcaptures critical information. This data can often be used to debug the failure
of a system or application under abnormal conditions. An example of this may be a memory
error.
Alert: This level capturesinformation about which the administrator should be made aware.
An example of this could be a failed login attempt.
Emerg: This level captures messages of the highest priority. These are typically last resort
messages before an abnormal exit of the calling application or the system itself. An example
of this would be a hardware error or memory exhausted message.
Remote Log System
It is possibleto send a copy of all messages to a remote system runningsyslogd. This allows
centralized management of alarm messages. As the system logs are written to a RAM based
volume, messages may be lost if the system is rebooted or power cycled or experiences an
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 91
Page 92

Web Interface
unexpected failure. They may also be overwritten if memory is low. Microsemi recommends
rotating log files, if needed. Specifying the DNS name or IP address of a remote server will
configure the SyncServer to send a copy of each message received by the syslog and kernel
log daemonsto the remote address, if it is reachable. The remote server can then be configured to filter the messages using its configuration file.
A complete definition of how Syslog is configured may be obtained by consulting the standard syslog.conf man pages that are widely available on the Internet.
ADMIN - Relays
The SyncServer S300/S350 has two alarm output relays located on the rear panel, Power
and Alarm.
Also see Power and Alarm Relays (on page 114).
Relays Configuration
Loss of Power Alarm Relay
Power: This relay de-energizeswhen the SyncServer loses power. Its behavior cannot be
configured.
Minor/Major Alarm Relay
The user can configure the conditions that de-energize the Alarm relay:
n
Any Major Alarm: Alarms with Severity = Major.
n
Any Major or Minor Alarm: Alarms with Severity = Major or Minor.
n
Off (no relay activation on any alarm): The relay is remains energized except when the SyncServer losespower or is rebooted.
The following pages/actions may de-energize the Alarm relay:
n
SERVICES - Startup: Using Halt or Reboot.
n
NETWORK - Ethernet: Applying changes to the network configuration.
n
All NTP - * pages: Using RESTART on any of the NTP-related pages.
n
SYSTEM - Upgrade: Upgrading the firmware.
n
SYSTEM - Factory Reset: Resetting the configuration to factory defaults.
n
Using the following WIZARDS: 1st Setup, NTP, Restore, Upgrade.
For more information on major/minor alarm states, see ADMIN - Alarms (on page 85).
System Restart Delay (Minutes)
Use this setting to prevent the Alarm relay from de-energizing for a user-configured period of
time after the SyncServer starts or restarts. The delaycan be set to allow enough time for
unwanted alarm conditions to clear. The factory default setting is 60 minutes. The range is 1
to 99 minutes. This setting only affects the Alarm relay. It does not affect other aspects of
alarm operation.
Page 92..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 93

ADMIN - RADIUS
ADMIN - RADIUS
RADIUS authentication provides a method for users to log into a varietyof RADIUS-enabled
devices usinga centrally managed username and password. The SyncServer implements
RADIUS in accordancewith portions of RFC 2865 and RFC 2866.
RADIUS authentication on the SyncServer is designed to inter-operate with standard compliant RADIUS servers:
n When RADIUS is enabled and configured a user can log in to the SyncServer using a
RADIUS username and password.
n
The SyncServer contactseach RADIUS server listed on the ADMIN - RADIUS page until it
receives authentication from a RADIUS server.
n If RADIUS authentication fails due to AUTHINFO_UNAVAIL reason (in other words,
server is not available), the SyncServer attempts to authenticate the user against its own
access control list.
The LAN1 port must have access to the authenticating RADIUS servers.
Extended Character Set for RADIUS logins
The following character set is available for RADIUS logins:
~!@#$%^&*()_+|\=-'{}[]:"';<>?/.,
RADIUS Configuration
For each server, set the following values:
RADIUS Server IPv4 Address: The RADIUS server's IPv4 address.
Secret Key: The authentication key shared by the RADIUS server and the SyncServer.
Timeout: The number of seconds to wait for authenticationfrom the RADIUS server before
disconnecting and trying the next one.
Enable RADIUS Authentication: Makes RADIUS and then standard SyncServer authentication
available.
Disable RADIUS Authentication: Makes RADIUS authentication unavailable. Only standard
SyncServer authentication is available.
Note: The RADIUS and TACACS+ authentication is exclusive. When RADIUS authentication is enabled, the TACACS+ authentication is automatically disabled. Vice versa, when
TACACS+ authentication is enabled, the RADIUS authentication is disabled. When the SyncServer is started, power on or reboot, if the software detects that both RADIUS and
TACACS+ authentication are enabled, the TACACS+ authentication will be disabled and
only RADIUS authentication is left enabled.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 93
Page 94

Web Interface
ADMIN - TACACS+
TACACS+ (TerminalAccess Controller Access-ControlSystem Plus) is an access control
network protocol for routers, network access servers and other networked computing
devices.
Unlike RADIUS and the predecessors of TACACS+ (TACACS and XTACACS),
TACACS+ provides separate authentication, authorization and accounting services. Like
RADIUS, TACACS and XTACACS, TACACS+ is an open, publicly documented protocol.
TACACS+ uses the TCP protocol and encrypts the entire packet (except the header).
TACACS+ authentication on the SyncServer is designed to inter-operate with standard compliant TACACS+ servers:
n When TACACS+ is enabled and configured a user can log in to the SyncServer using a
TACACS+ username and password.
n
The SyncServer contactsthe TACACS+ server listedon the ADMIN - TACACS+ page until
it receivesauthentication from a TACACS+ server.
n If TACACS+ authentication failsdue to AUTHINFO_UNAVAIL reason (in other words,
server is not available), the SyncServer attempts to authenticate the user against its own
access control list.
The LAN1 port must have access to the authenticating TACACS+ servers.
Extended Character Set for TACACS+ logins
The following character set is available for TACACS+ logins:
~!@#$%^&*()_+|\=-'{}[]:"';<>?/.,
TACACS+ Configuration
For each server, set the following values:
TACACS+ Server IPv4 Address: The TACACS+ server's IPv4 address.
Secret Key: The authentication key shared by the TACACS+ server and the SyncServer.
Enable TACACS+ Authentication: Makes TACACS+ and then standard SyncServer authen-
tication available.
Disable TACACS+ Authentication: Makes TACACS+ authentication unavailable. Only standard
SyncServer authentication is available.
Note: The RADIUS and TACACS+ authentication is exclusive. When RADIUS authentication is enabled, the TACACS+ authentication is automatically disabled. Vice versa, when
TACACS+ authentication is enabled, the RADIUS authentication is disabled. When the SyncServer is started, power on or reboot, if the software detects that both RADIUS and
Page 94..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 95

SERVICES - Startup
TACACS+ authentication are enabled, the TACACS+ authentication will be disabled and
only RADIUS authentication is left enabled.
SERVICES - Startup
Daemon Current State and Startup
The SyncServer uses a number services that operate continuously to support its functions.
Use this page to:
n View the current state of the servicesand to turn them on or off.
n Enable or disable services from starting automatically when the SyncServer is started.
n Run, Reboot, or Halt the SyncServer's operating servicesand operating system.
Daemon
A list of the user controllable daemons supported by the SyncServer:
Web Server (HTTPD): Provides the SyncServer's web interface. If Auto Startup is deselected
and the SyncServer reboots, the web interface will not be available.
To start the web server after it has been stopped, open a command line session through the
Console RS-232 port located on the front panel or, if available, through a Telnet session with
LAN1 port. Once logged in, restart the web server by typing "HTTP on".
NTP: Network Time Protocol daemon. Supports all NTP functions.
PTP: Precision Time Protocol daemon. Supportsall PTP functions.
SNMP: Simple Network Management Protocol daemon. Respondsto SNMP requests and
sendsSNMP traps.
SSH: Secure Shell daemon. Provides an encryptedchannel for command line sessions with
the SyncServer through the LAN1 port.
Sysplex: Sysplextiming information on the Sysplex Timer-Out connector.
Time: Time Protocolrequests per RFC 868 over TCP.
Time - UDP: Time Protocol requestsper RFC 868 over UDP.
Daytime: Daytime Protocol per RFC 867 over TCP.
Daytime - UDP: Daytime Protocol per RFC 867 over UDP.
Telnet: Telnet protocol service for remote access to the command line interface on LAN1.
Current State/Startup
Shows the current state of the service. To change the state, select the desired state and click
the APPLY button.
On: The service is running.
Off: The service is stopped.
Auto: When selected, the servicestartsautomatically when the SyncServer reboots.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 95
Page 96

Web Interface
Note: Services that cannot be directly turned off display grayedout On and Off radio buttons.
These services can only be controlled by selectingor deselecting Auto Startup. Applying the
change will then stop or start the service as appropriate.
System Control
Run: The SyncServer continues to operate normally. This is the default setting.
Reboot: Reboots the SyncServer. During this process, the browser displays "This browser
will attempt to reconnect..." When the SyncServer finishesrebooting, the browser displays
the login screen (provided DHCP hasn't changed the IP address).
Halt: Halts the operating system after about 15 seconds, typically. While the SyncServer is
halting, the web interface displays "Halting System - This browser session cannot continue..." and the front panel displaystates "Shutting down. Please wait...". Wait at least 15
seconds, and shut the power switch off.
SERVICES - HTTP
Web Server Configuration
The SyncServer's web interface allows both standard and secure (encrypted) network
access. Standard access is provided by default. To use encrypted access, a secure certificate must be created. The SyncServer can only use self-signed certificates.
Creating a new certificate overrides previously created certificates. The certificate values
used are not significant to the SyncServer. They are provided to any user using the certificate. All of the fields must contain values.
When a certificate has been created, the Secure log in option appears on the loginpage. The
entire session uses the selected communication method.
Security
Standard (Port 80) Only: The web interface is available using a standard non-encrypted http
connection. This is the factory default configuration.
Secure (Port 443) and Standard (Port 80): The web interface is available using either type of con-
nection.
Secure (Port 443) Only: The web interface is available using an SSL-encrypted connection.
Note: To connect to Port 443, the URL in the browser must begin with "https".
Certificate Info:
Common Name: SyncServer's hostname, as entered on the SYSTEM - General page. The
default factory configuration is "SyncServer".
Bits: Number of RSA Key Bits, 1024 or 2056 bits. The default factory configuration is "1024".
Days to Expiration: The number of days before the certificate expires.
ISO Country Code: The Two-Character International Country Code.
State: The state where the SyncServer is located.
Page 96..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 97

SERVICES - SSH
Locality: The localitywhere the SyncServer is located.
Organization: The organization or companythe SyncServer belongs to.
Organizational Unit: The organizationalunit or division that uses or is responsible for the Syn-
cServer.
Email Address: The email address of the administrator responsible for the SyncServer.
SERVICES - SSH
SSH Security Configuration
After setting the other optionson this page, select Regenerate SSH Secure Keys and click the
APPLY button to generate a new set of SSH secure keys. This step is required before the
user can log in to LAN1 using SSH.
Protocol: Sets the protocol to SSH-1 & SSH-2, SSH-1 Only, or SSH-2 Only.
Allowed Users: List user names that are allowed SSH access.
Denied Users: List user names to excludefrom SSH access.
Note: Use a space character between user names. This list supports the ? wild card as a substitute for an individual character, and the * wild card as a substitute for the rest of a word.
For example, Allowed Users = Bird* would let Bird1 and Birddog log in. Allowed Users =
Bird? would let Bird1 log in, but not Birddog.
Log Level: The level of verbosity level for logging ssh messages. Can be set to QUIET,
FATAL, ERROR, INFO, VERBOSE, or DEBUG.
Server Key Bits: The number of bits to use when generating the keys. Can be set to 512, 768,
1024, or 2048.
Key Regeneration: The interval, in seconds, with which to regeneratekeys.
SERVICES - Email
SMTP Gateway and Alarm Email Recipients
This page establishesthe SMTP gateway and emailaddresses used by the SyncServer for
emailnotification of alarms and password recovery emails. This page must be configured correctlyfor "Send Email" notification on the ADMIN - Alarms page to work.
SMTP Gateway: Enter the DNS name or IP address of a SMTP server that's reachable
from LAN1.
User 1-10: Enter the email address of the individuals who should receive email notifications
of alarms.
LOGS
System Event Log
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 97
Page 98

Web Interface
The Logs page provides access to system activity and messages that are generatedby the
various subsystems in the SyncServer. The logs are separated by function. The logging
behavior can be configured using the ADMIN - Logs Config page. Each of the logs records a
seriesof time-stamped events.
In the caseof the system, auth, daemon, kern and messages logs, the entries take the standard form definedby the syslog daemon. These entries are:
date time system facility message: Here "system" is the hostname that generated the message. The "facility" is a component of the system generating the message. This could be anything likethe kernel itself, system daemons and even applications. Finally, there is the text of
the message itself. Here are two messageson the system SyncServer. One is from daemon.log and the other from the kernel:
Sep 19 19:20:26 SyncServer ntpd[3577]: ntpd 4.2.0b@1.1396-o Tue Aug 9
01:05:42 UTC 2005 (7)
Sep 10 00:06:18 SyncServer kernel: Jida-Driver installed
In the caseof the event log, the entries take the form of:
Date time user source description
Here "user" is the user logged into the web interface, "source" is the IP address of the remote
system using the web interface and "description" provides information regarding the nature
of the event. Here is a message showing a successful remote login along with the user id and
IP addressof the contact.
10/01/2005 22:36:28 admin 192.168.7.16 Successful login
Events: The events log is not configurable. This log is maintained outside syslogd and contains configuration and event data related to operations performed in the web interface.
syslog: syslog holds messages about system level events. Examples of system events are
privilege changes(e.g., sudo) and messages about regularly schedulesevents such as cron.
auth.log: The authentication log contains entries regarding authentication events from login or
PAM (PluggableAuthentication Module).
daemon.log: The daemon log contains entriessubmitted by the daemon processes that
provide the services in the SyncServer. Examples of daemon log entries are NTP changes,
SNMP events, and xinetd events.
kern.log: The kernel log containsentries submittedby the kernel. Examplesof kernel events
are network errors or hardware changes.
messages: The messages file is something of a catchallfile. By selecting variouspriorities, it
is possible to capture large amounts of data regarding system operation. However, the
volume of data becomesimpractical to manage quickly. As such, this file is cleared at each
power cycle or reboot.
Every 20 minutes, if no new messages were logged, the Syslog daemon logs a -- MARK -message to indicate that it is alive and well.
Page 98..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
Page 99

WIZARDS - 1st Setup
WIZARDS - 1st Setup
Microsemi strongly recommends using the 1st Setup to perform the initial configuration of the
SyncServer, which includes:
n Setting a new password.
n ConfiguringPassword Recovery (optional).
n Configuringthe IP address, hostname, and DNS for LAN1 (erases network settings for
all other network ports.
n Setting the local time zone (optional).
Also see:
n For STEP 1: Password Setup and STEP 1A: Password Recovery, also see ADMIN -
Users (on page 84).
n For STEP 2: LAN1 IP Address, Hostname and DNS Servers, also see NETWORK -
Ethernet (on page 32).
n For STEP 2A: Local Time Zone, also see TIMING - Time Zone (on page 61).
WIZARDS - NTP
Microsemi recommends usingthiswizard to perform an initial NTP configuration of up to 5
server associations.
To modify an existing NTP configuration, use the NTP - Config page instead.
Note: This Wizard deletes all NTP associations that are not server associations.
Also see: NTP - Config (on page 43) and NTP - MD5 Keys (on page 47).
WIZARDS - SNMP
Use the SNMP wizard to add or change the following SNMP v1/v2c settings:
n Set SysLocation, SysContact and SysName
n Set the Read and Write Community Strings
n Add up to four v1/v2cTrap Destinations
Advanced SNMP configuration (e.g., SNMP v3) is performed on the NETWORK - SNMP and
NETWORK - Traps pages. Upon completing the Wizard, the new SNMP settingsreplace the
previous ones and the SNMP daemon restarts.
See also NETWORK - SNMP (on page 35) and NETWORK - SNMP Traps (on page 37).
WIZARDS - Backup
The Backup wizard guides the operator through saving the SyncServer’s current configuration to nonvolatilememory in the SyncServer, and optionally transfers the backup configuration to a remote location. The backup file can be used to:
n 'Clone' the configuration to other SyncServerswith the same Software Version.
n Restore the SyncServer's configuration if it is lost or becomesunusable.
997-01520-02 Rev. F1.......................................................................... Page 99
Page 100

Web Interface
WIZARDS - Restore
Use the WIZARDS - Restore page to restore a saved configuration from a backup file, or to
restore the factory default configuration.
Reset to Factory Defaults: Returns the SyncServer to its original factory configuration, removing ALL user-entered and operational information including password, IP addressing, GPS
position, and time zone. See SYSTEM - Factory Reset (on page 77).
Restore Last Backup from SyncServer: Restores the configuration as it was when the user created the most recent backup configuration file. The backup file is located in the SyncServer’s
nonvolatile memory.
Restore From USB flash drive: Restores the configuration from a backup file located on a USB
drive attached either of the USB ports on the front panel.
Restore backup from workstation hard-drive or network directory: Restores the configuration
from any backup file located on localor network drive accessible to the browser.
Note: Resetting or restoring the configuration reboots the SyncServer. If LAN1 is configured
to use DHCP, the DHCP server may assign a new IP address to LAN1. If needed, use the
front panel STATUS button to view the new IP address on the LAN1 STATUS screen.
WIZARDS - Upgrade
Use WIZARDS - Upgrade to update the SyncServer software.
SyncServer upgrade packages are available at http://www.microsemi.com/ftdsupport
and then following the links from the Support menu.
Users are required to register in order to download software. Some export restrictionsmay
apply.
To upgrade the software, download the upgrade package file to:
n A file area that is accessible to the web browser.
n To a USB flash drive, or to an area where it can be copied to a USB flash drive.
Then use WIZARDS - Upgrade to copy the upgrade file to the SyncServer and perform the
upgrade.
Note: The SyncServer automatically decompresses the software upgrade ".tar" file. Please
do not decompressthe ".tar" file prior to upgrading the SyncServer.
Page 100..........................................................................997-01520-02 Rev. F1
 Loading...
Loading...