Page 1

DN120 DeviceNet
Gateway
User’s Manual
DN120
PN 84-210010 Rev A
Page 2

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 – OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................... 4
CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLATION ............................................................................................................................. 5
M
OUNTING
IRING
W
DeviceNet Interface............................................................................................................................................. 6
Serial Channel Interface ..................................................................................................................................... 6
Wiring Examples................................................................................................................................................. 7
CHAPTER 3 – THEORY OF OPERATION........................................................................................................... 8
G
ATEWAY OPERATION
DeviceNet Object Model ..................................................................................................................................... 8
DeviceNet Interface............................................................................................................................................. 9
Serial Channel Interface ................................................................................................................................... 10
............................................................................................................................................................... 5
..................................................................................................................................................................... 6
............................................................................................................................................. 8
Asynchronous Serial Communication .............................................................................................................................11
Status Information ...........................................................................................................................................................11
Receiving Messages ........................................................................................................................................................12
Stream Mode ..............................................................................................................................................................12
Block Mode................................................................................................................................................................12
Returning Received Data............................................................................................................................................13
Padding Message Data ...............................................................................................................................................13
Re-sending Received Data .........................................................................................................................................14
Transmitting Messages....................................................................................................................................................15
Synchronization...............................................................................................................................................................15
Receive Sequence Number.........................................................................................................................................15
Transmit Sequence Number .......................................................................................................................................15
Synchronous Handshake Protocol..............................................................................................................................16
CHAPTER 4 – GATEWAY CONFIGURATION.................................................................................................18
C
ONFIGURE DEVICENET INTERFACE
....................................................................................................................... 18
DeviceNet Baud Rate Switch............................................................................................................................. 18
MAC ID Switches.............................................................................................................................................. 18
Serial Channel Baud Rate / Option Switch ....................................................................................................... 19
OWER UP GATEWAY
P
............................................................................................................................................. 19
DeviceNet Status LEDs ..................................................................................................................................... 19
Serial Channel Status LEDs.............................................................................................................................. 20
Register EDS File.............................................................................................................................................. 20
ONFIGURE SERIAL CHANNEL
C
ONFIGURE DEVICENET MASTER SCAN LIST
C
................................................................................................................................21
......................................................................................................... 26
Poll Consume Size............................................................................................................................................. 26
Poll Produce Size..............................................................................................................................................26
CHAPTER 5 – DEVICENET SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................27
D
EVICENET MESSAGE TYPES
EVICENET CLASS SERVICES
D
EVICENET OBJECT CLASSES
D
................................................................................................................................. 27
................................................................................................................................. 27
................................................................................................................................. 27
IDENTITY OBJECT ............................................................................................................................................. 28
ROUTER OBJECT................................................................................................................................................ 29
DEVICENET OBJECT.......................................................................................................................................... 30
ASSEMBLY OBJECT........................................................................................................................................... 31
CONNECTION OBJECT ...................................................................................................................................... 32
SERIAL STREAM OBJECT................................................................................................................................. 34
CHAPTER 6 – RSNETWORX CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE....................................................................36
ONFIGURE DEVICENET INTERFACE
C
Microscan Systems, Inc.
....................................................................................................................... 37
2
Page 3

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
C
ONNECT
ONFIGURE SERIAL CHANNEL
C
ONFIGURE DEVICENET MASTER SCAN LIST
C
CHAPTER 7 – CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES................................................................................................ 59
E
XAMPLE
XAMPLE
E
XAMPLE
E
XAMPLE
E
XAMPLE
E
CHAPTER 8 – TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................................................. 68
& R
EGISTER
EDS F
ILE
........................................................................................................................... 37
................................................................................................................................45
......................................................................................................... 52
1 – R
ECEIVING FIXED-LENGTH DATA
.................................................................................................... 59
Barcode Scanner...............................................................................................................................................59
DN120 Gateway................................................................................................................................................ 59
2 – R
ECEIVING PRE-DELIMITED DATA
................................................................................................... 61
Barcode Scanner...............................................................................................................................................61
DN120 Gateway................................................................................................................................................ 61
3 – R
ECEIVING POST-DELIMITED DATA
................................................................................................. 63
Barcode Scanner...............................................................................................................................................63
DN120 Gateway................................................................................................................................................ 63
4 – T
RANSMITTING FIXED-LENGTH DATA
.............................................................................................. 65
Bar Code Scanner ............................................................................................................................................. 65
DN120 Gateway................................................................................................................................................ 65
5 – T
RANSMITTING VARIABLE-LENGTH DATA
....................................................................................... 67
Bar Code Scanner ............................................................................................................................................. 67
DN120 Gateway................................................................................................................................................ 67
APPENDIX A – PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS..................................................................................................69
D
EVICENET INTERFACE
ERIAL CHANNEL
S
NVIRONMENTAL
E
.......................................................................................................................................... 69
................................................................................................................................................... 69
................................................................................................................................................... 69
APPENDIX B – DEVICENET TEMPLATE.........................................................................................................70
APPENDIX C – ASCII CHARACTER CODES.................................................................................................... 71
Microscan Systems, Inc.
3
Page 4

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
(
)
(
)
y
y
M
y
Chapter 1 – Overview
This document describes how to install, configure, and operate the DN120 series of serial to
DeviceNet gateways. The following products are covered in this user manual:
Part Number Serial Channel
DN120 RS232 full duplex
The DN120 gateways allow you to easily interface a wide variety of serial devices to any
DeviceNet industrial control network. Each gateway contains the feature-packed D.I.P.
DeviceNet core. Standard DN120 products are tightly packaged and sealed in a rugged
industrial case. Board-level and customized gateways are also available upon request.
Serial Status LEDs
Serial Baud Rate
Switch
Rotar
DeviceNet MAC ID
Switches
Rotar
DeviceNet Status LEDs
(NET, MOD)
(RX, TX)
DeviceNet Baud Rate
Switch
Rotar
DN120
Isolated Serial Channel
male DB9 connector
Product Features
• 500V isolated serial channel
• RS232 with RTS/CTS flow control
• XON/XOFF software flow control
• 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 bps serial data rates
• Configurable parity
• 64 byte transmit and receive FIFO buffers
• Powered from DeviceNet 24VDC
• Loss-of-ground protection circuitry
• DeviceNet slave mode supports POLL and EXPLICIT messages
• Rotary switches set DeviceNet baud rate and MAC ID
• Rotary switch sets serial data rate
• 4 bi-color status LEDs
• Encapsulated circuit board in compact industrial case
ounting Holes
DeviceNet Channel
male 5-pin micro connector
Microscan Systems, Inc.
4
Page 5
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
A
Chapter 2 – Installation
This chapter describes how to install and connect the DN120 gateway to a DeviceNet network
and your serial device.
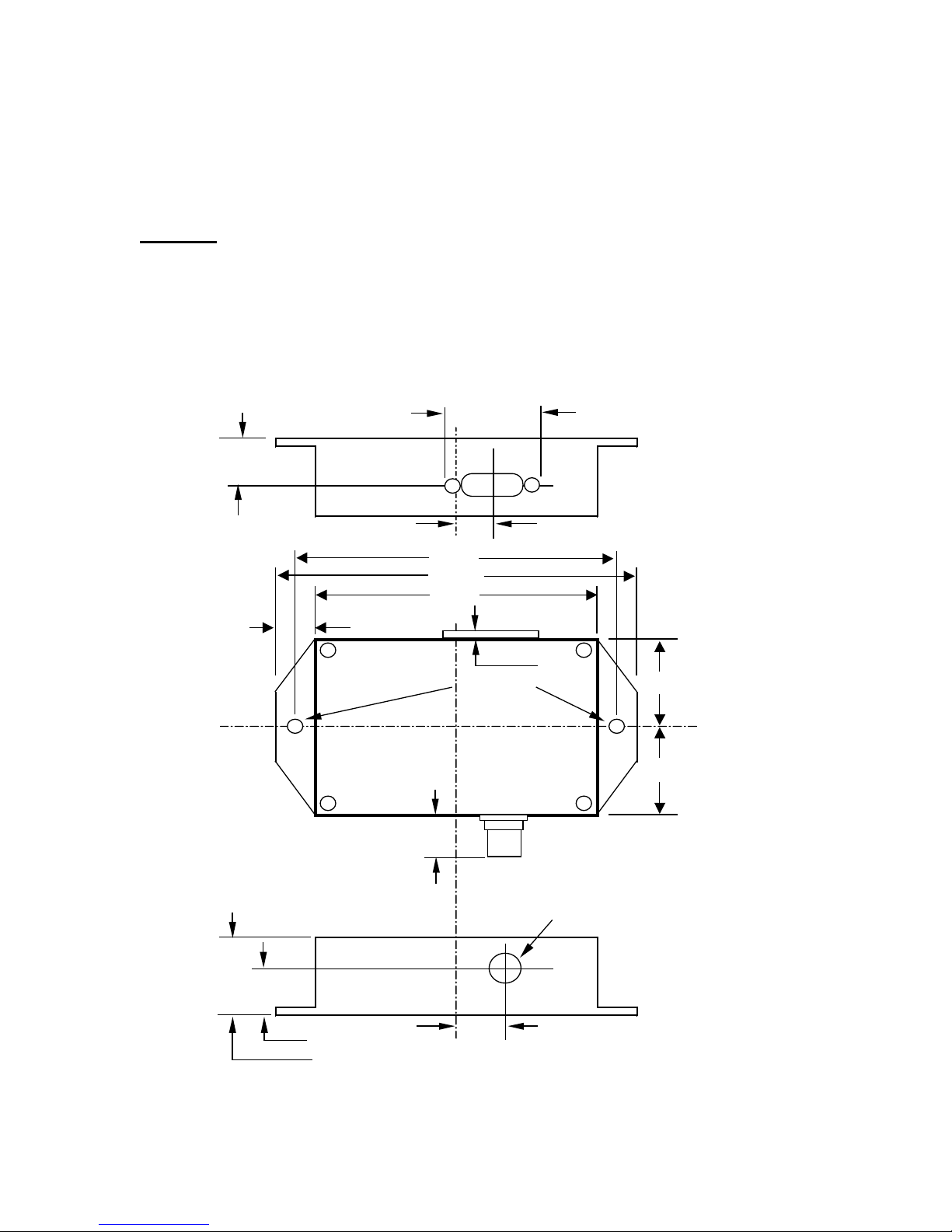
Mounting
Mount on a horizontal or vertical surface. While the RTV encapsulation protects its circuitry,
the DN120 serial channel connector is not rated for NEMA4 / IP65 environments. Mount the
gateway in a suitable location or enclosure for your application. The gateway will generate up to
1.4W of heat, so provide sufficient clearance and airflow to maintain 0°C to 70°C operating
temperature range. Use two screws (not provided) in the 0.19 inch mounting holes shown below
to fasten the DN120 to the mounting surface.
1.25
ll dimensions
are inches
0.65 0.45
3.80
4.30
3.30
0.50
0.12
Mtg. Ho les 1.225
(2) 0.19 DIA.
0.725
0.625 DIA. On Case Wall
1.225
Microscan Systems, Inc.
0.70
0.542
1.10
5
Page 6

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
_
Wiring
The DN120 requires two connections – one to the DeviceNet network (male 5-pin micro
connector) and one to the target serial device (male DB9 connector). Follow all applicable
electrical codes in your area when mounting and wiring any electrical device.
All power is received from the DeviceNet network. The DN120 draws up to 50mA from the
24VDC power supply. Select your DeviceNet cables and power supply so that it can provide
sufficient current for all networked devices at their peak operating power.
DeviceNet Interface
Male 5-Pin Micro Connector
V+
V-
PIN SIGNAL COLOR DESCRIPTION
1 DRAIN NONE Cable shield or drain wire.
2 V+ RED DeviceNet 24VDC(+) power.
3 V- BLACK DeviceNet 24VDC(-) power.
4 CAN_H WHITE Communication signal.
5 CAN_L BLUE Communication signal.
Serial Channel Interface
Male DB9 Serial Connector
1
23
6
78
DN120 (RS232)
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 NC No Connect. Do not connect any wires to NC pins.
2 RXD Receive Data. RS232 input signal.
3 TXD Transmit Data. RS232 output signal.
4 NC No Connect.
5 GND Ground. Common for RS232 signals.
6 NC No Connect.
7 RTS Request To Send. RS232 output signal.
8 CTS Clear To Send. RS232 input signal.
9 NC No Connect.
4
DRAIN
CAN_L
CAN
5
9
H
Microscan Systems, Inc.
6
Page 7
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
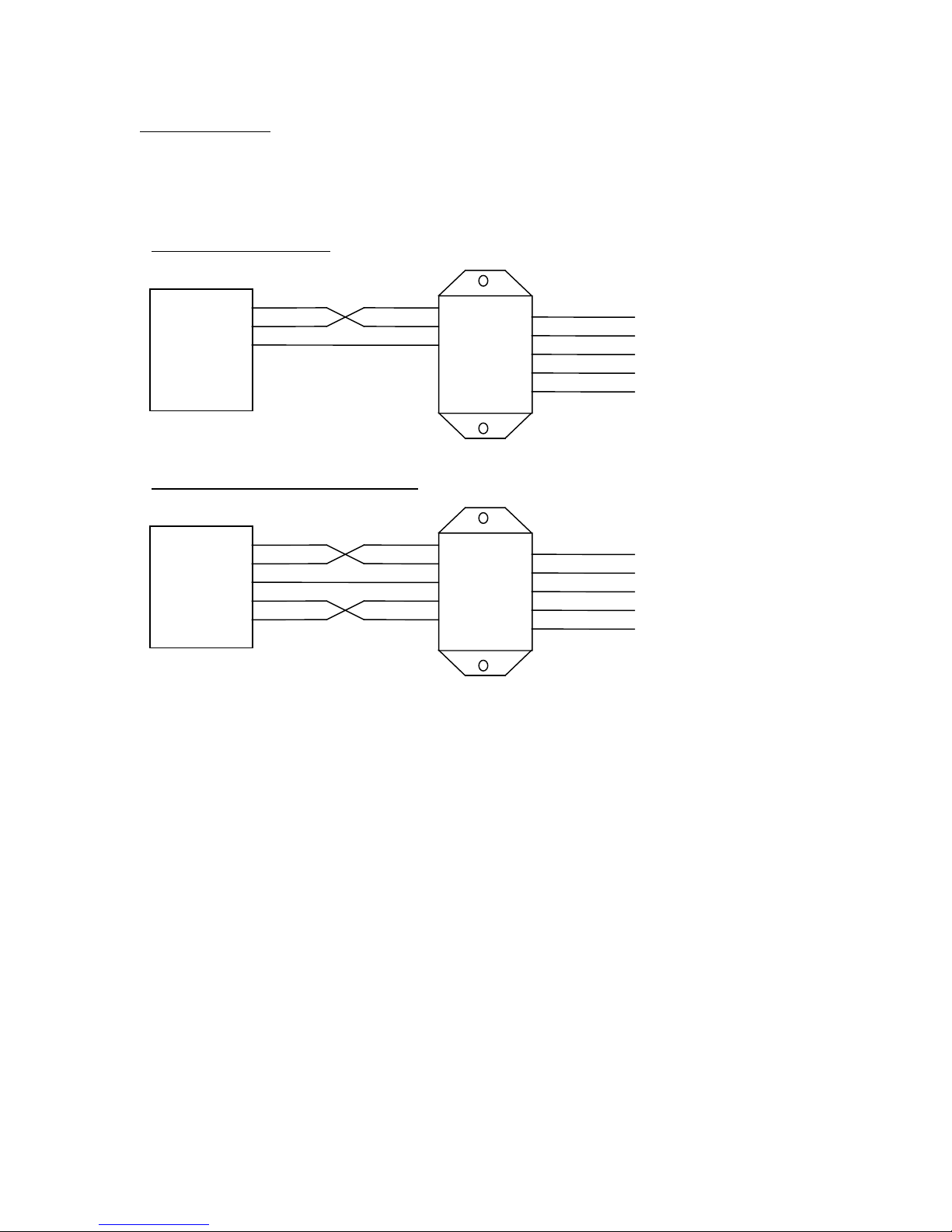
Wiring Examples
The following are typical DN120 gateway wiring configurations. Your RS232 or RS422/485
interface may vary. Refer to your device’s documentation for the required data and control
signals.
Simple RS232 Interface
2
RS232
Serial
Device
RXD
3
TXD
5
GND
RXD
TXD
GND
2
3
5
DN120
1
2
3
4
5
DRAIN
VDC+
VDC-
CAN H
CAN L
RS232 Interface, HW Flow Control
RS232
Serial
Device
2
RXD
3
TXD
5
GND
RTS
7
CTS
8
RXD
TXD
GND
RTS
CTS
2
3
5
7
8
DN120
1
2
3
4
5
DRAIN
VDC+
VDC-
CAN H
CAN L
Microscan Systems, Inc.
7
Page 8
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
M
R
l
Chapter 3 – Theory of Operation
This chapter describes how the DN120 gateway operates. You should have a working
knowledge of DeviceNet and asynchronous serial communications before continuing. The Open
DeviceNet Vendors Association (www.odva.com) is a good source for general DeviceNet
information. Refer to your serial device documentation for its protocol information.
Gateway Operation
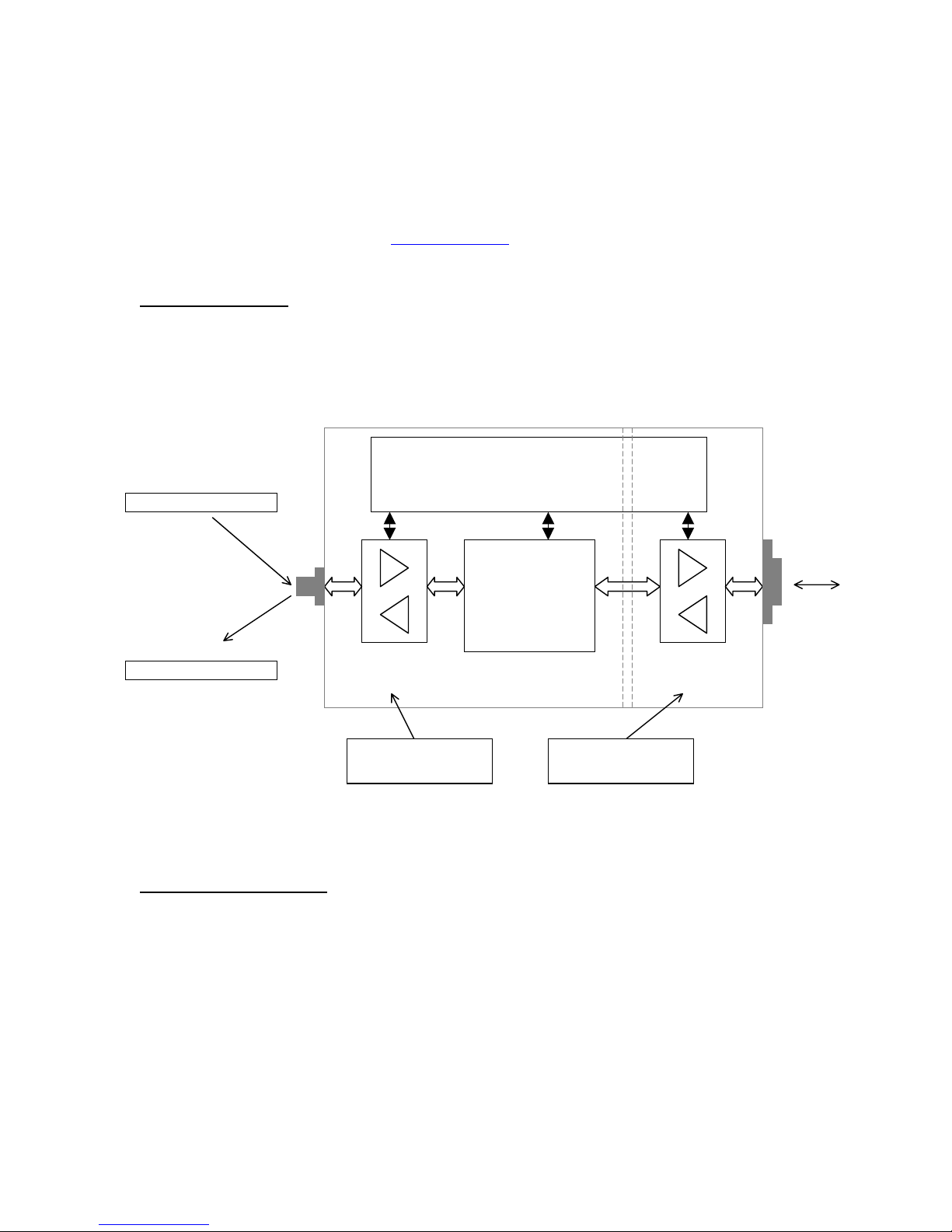
The DN120 gateway receives asynchronous serial messages over its serial channel and returns
the received bytes as input data to the DeviceNet master. The gateway transmits bytes sent as
output data from the DeviceNet master out its serial channel. The following diagram shows the
major gateway components.
DC:DC Power Conversion
• 24VDC DeviceNet power input
DeviceNet Poll Command
output data
• VDC for Core & DeviceNet channel
• isolated VDC for serial channel
5-pin male
micro connector
DeviceNet Poll Response
input data
DeviceNet Channel
• 24VDC power
• communications
DeviceNet Object
or Rotary Switches
Configures the DeviceNet
interface baud rate and
AC ID address.
Gateway Core
• microcontroller
• RAM
• Flash ROM
Serial Channel
• communications
• flow control
Serial Stream Object
Configures the serial channel.
eceives and transmits seria
messages. Controls optional
synchronization.
Male DB9
connector
serial
messages
DeviceNet Object Model
The DeviceNet Specification defines an Object Model that consists of Objects and Attributes.
An Object is a predefined software process, and an Object Attribute is a data value used or
generated by that process. An Object Instance is one occurrence of an Object, operating on its
unique set of Attribute values. The DN120 gateway has six different Object Classes, or types.
Five are standard objects defined by the DeviceNet Specification (Identity, Router, DeviceNet,
Assembly, Connection). One is a device-specific object defined for the DN120 gateway (Serial
Stream). The Serial Stream Object configures and controls the serial channel. It receives and
packages serial data into DeviceNet input bytes, and transmits DeviceNet output bytes as serial
data. Chapter 5 contains detailed information on each DeviceNet object class, instance, and their
associated attributes.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
8
Page 9
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
DeviceNet Interface
The DN120 gateway operates as a DeviceNet slave. It supports Explicit Messages and Polled
I/O Messages of the predefined master/slave connection set. The Explicit Unconnected Message
Manager (UCMM) is not supported.
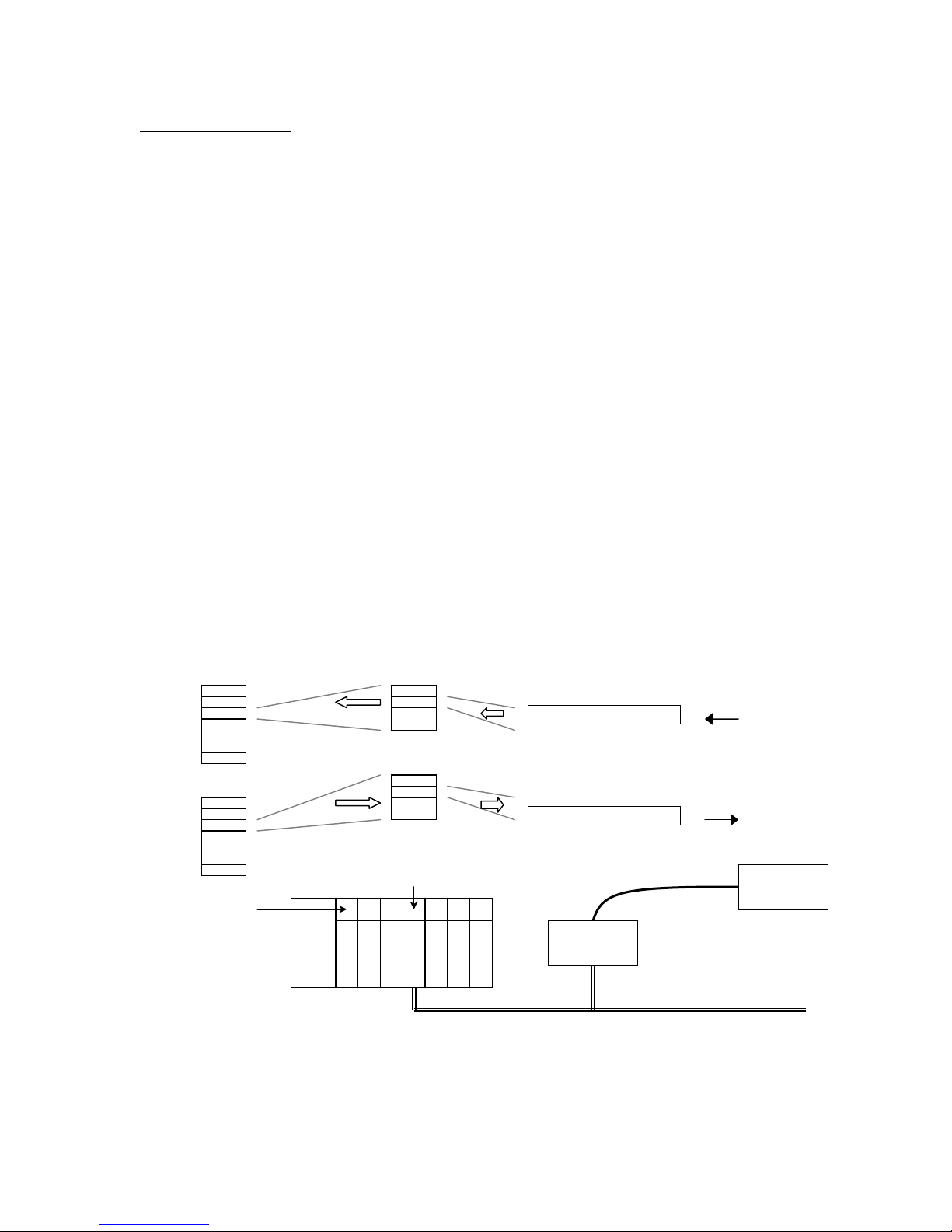
There are four independent processes operating in a DN120 gateway application. The first
process is the exchange of input and output data between the user application program and the
DeviceNet master. The second process is the exchange of input and output data between the
gateway and DeviceNet master, using Polled I/O messaging. The third process is receiving serial
messages and converting it to input data. The fourth process is converting output data and
transmitting it as serial messages.
The DeviceNet Polled I/O Message process consists of the DeviceNet master sending output data
to the DN120 in the form of a Poll Command message, and the DN120 returning input data to
the DeviceNet master in a Poll Response message. The output and input data bytes are typically
mapped into data files inside the DeviceNet master. These data files are exchanged with the user
application program. The application processes the received input data from the gateway and
writes new output data to the DeviceNet master, which sends them to the gateway.
The Polled I/O data exchange typically occurs at a faster rate than the serial transmit and receive
operation, because the DeviceNet baud rate is much greater than the serial channel baud rate.
The DN120 has transmit and receive buffers to handle the slower serial processes. The gateway
also provides synchronization features to ensure delivery of received messages to the application
program, and transmission of application messages out the serial channel.
DeviceNet Poll Response
input data
DeviceNet Poll Command
output data
DeviceNet
Master
Application
Program
DN120
Gateway
Receive
Message Packet
Transmit
Message Packet
Serial
Device
Microscan Systems, Inc.
9
Page 10
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
The DN120 configuration defines the number of output bytes in a Poll Command message, and
the number of input bytes in a Poll Response message. Each Poll Command and Poll Response
message can contain up to 2 overhead bytes for DN120 status and data synchronization
information. The remaining bytes contain output data to be transmitted out the serial channel, or
input data received by the serial channel.
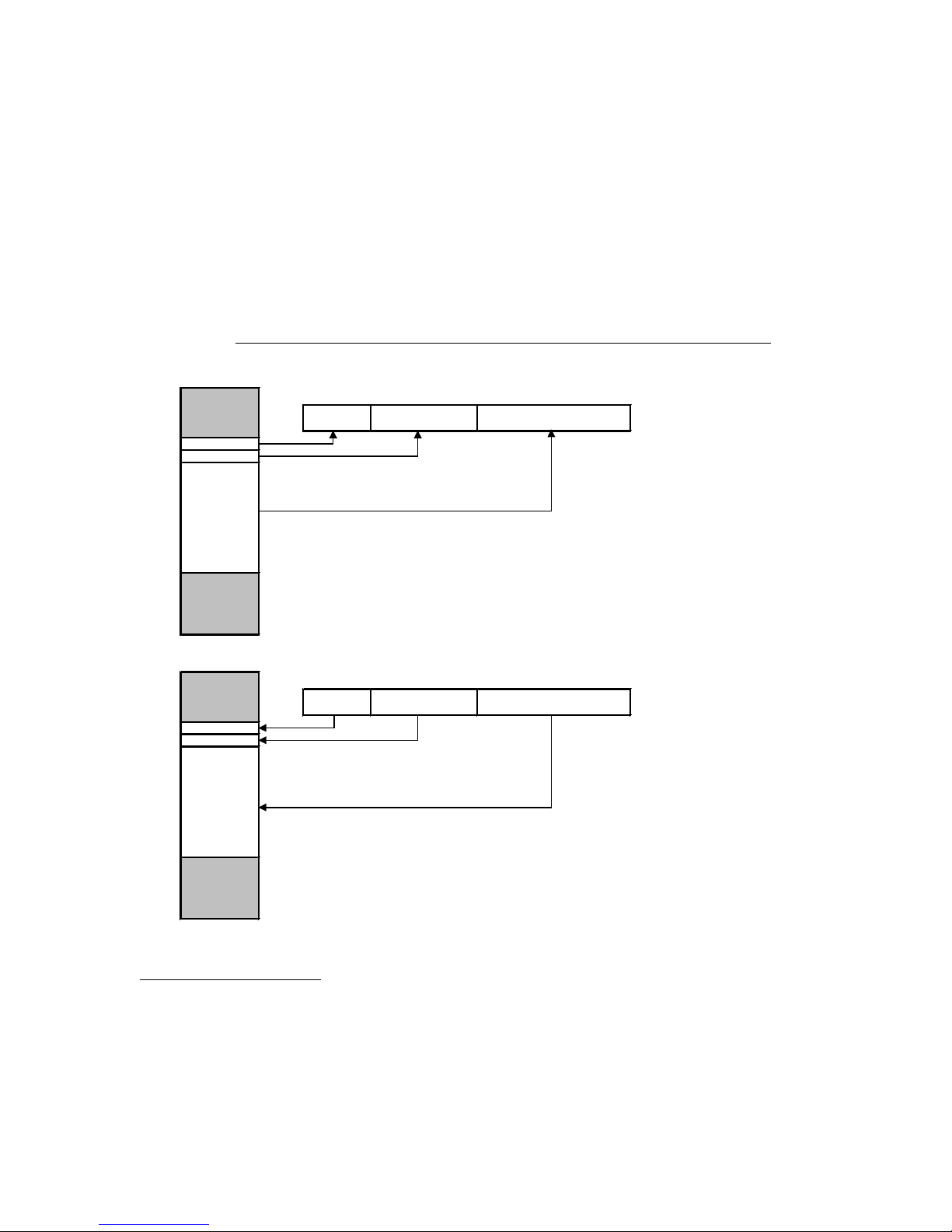
The following diagram shows how the input and output bytes map into the Poll Response and
Poll Command messages. The gateway supports a maximum of 67 output bytes in a Poll
Command message, and a maximum of 67 input bytes in a Poll Response message.
DeviceNet Master Mapping of DeviceNet Poll Command and Poll Response Data
DeviceNet Master Outputs DeviceNet Poll Command Message Data
Status Clear
output bytes
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output byte
output bytes
DeviceNet Master Inputs DeviceNet Poll Response Message Data
input bytes
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input byte
input bytes
(if enabled)
Status
(if enabled)
TX Sequence Number (if
enabled)
RX Sequence Nu mber (if
enabled)
Other Output Bytes
(1-65 bytes)
Other Input Bytes
(1-65 bytes)
Serial Channel Interface
The DN120 serial channel consists of an asynchronous serial transmitter and receiver. The serial
interface is configured and controlled by the Serial Stream Object. The Serial Stream Object
attributes configure the serial channel baud rate, parity, and flow control. This configuration
applies to both the serial transmitter and receiver. The DN120 gateway has separate 64-byte
serial transmit and receive FIFO buffers, allowing full duplex operation when supported by the
physical layer media.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
10
Page 11

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Asynchronous Serial Communication
Devices communicating on an asynchronous serial link exchange information one bit at a time.
Each bit is transmitted for a specific period of time, defined by the baud rate. Devices use
internal timing circuitry to generate the baud rate. There is no clocking signal between devices
to synchronize the serial data flow, hence the term asynchronous serial communications.
Serial data bits are organized into bytes. When a data byte is asynchronously transmitted, it is
preceded by a start bit, followed by the data bits, an optional parity bit, and one or more stop bits.
There can be a variable transmission delay between successive data bytes, since each byte is
framed by its own start and stop bits. The receiver starts saving bits after is receives a valid start
bit (0), and stops when it receives the expected number of stop bits (1). The data byte’s leastsignificant bit is transmitted first (data bit 0), and the most-significant bit is last (data bit N).
[ start bit ] [ data bit 0 ] [ data bit 1 ] … [ data bit N ] [ optional parity bit ] [ stop bit(s) ]
The parity bit detects single-bit errors in the transmission. The parity bit is calculated and
inserted by the transmitter. The receiver calculates the parity of an incoming byte, and compares
it to the parity bit sent by the transmitter. If the two bit values do not match, then at least one
serial bit value was corrupted during transmission.
Flow control enables the receiving device to regulate the rate of incoming data. Hardware flow
control uses RTS/CTS signals between the devices to control the rate of transmission. Software
flow control uses serial characters XON/OFF to control the rate. CTS Detect Mode uses the
CTS signal to enable serial communications. Flow control helps prevent data loss, if the
receiving device cannot store incoming data fast enough, or if its Receive Buffer is full and
cannot accept more data until existing data is processed.
The DN120 supports baud rates from 300 to 19200 bits per second. It supports 8 data bits with
no parity, 7 data bits with parity, and 1 stop bit. The DN120 model supports RTS/CTS,
XON/XOFF, and CTS Detect Mode flow control options.
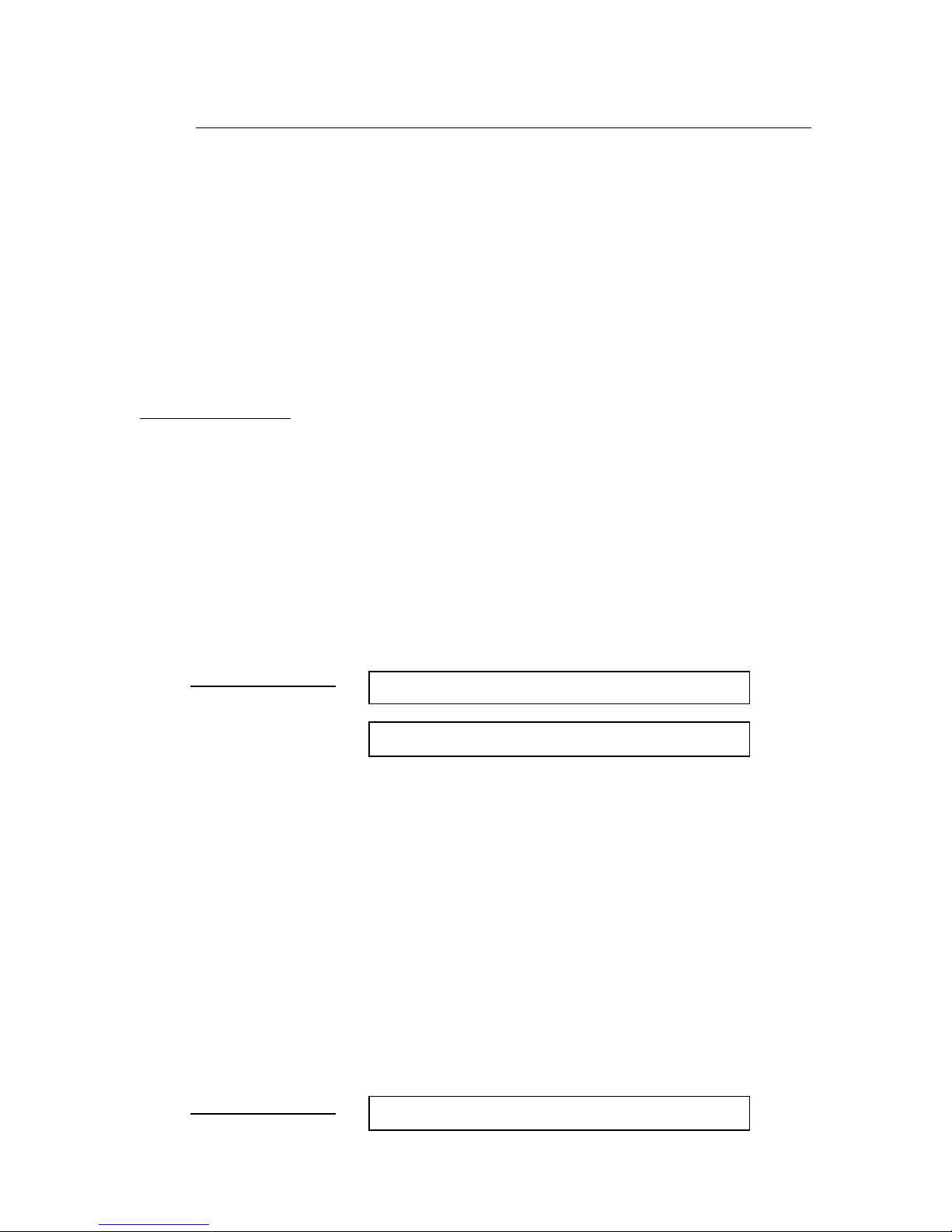
Status Information
The gateway can be configured to return serial channel status information in the Poll Response
message, and receive error-clearing commands in the Poll Command message. When enabled,
the Status byte is returned as an input byte, and the Status Clear byte is received as an output
byte. These bytes contain 8 status bits, defined below. Each bit represents either an error or
state condition for the serial transmitter and receiver. Clearing the associated error bit in the
Status Clear output byte will reset Receive Parity Error, Receive Buffer Overflow, Framing
Error, and Transmit Buffer Overflow error conditions.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
Status / Status Clear Bytes
11
Page 12
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
M
Bit Status (1st input byte) Status Clear (1st output byte)
0 Transmit Channel Blocked not used
1 Transmit Buffer Empty not used
2 Receive Parity Error Set = 0 to clear Receive Parity Error condition
3 Receive Buffer Empty not used
4 Receive Buffer Overflow Set = 0 to clear Receive Buffer Overflow condition
5 Framing Error Set = 0 to clear Framing Error condition
6 Transmit Buffer Overflow Set = 0 to clear Transmit Buffer Overflow condition
7 CTS Signal State (1 = asserted) not used
A user application can use the Transmit Buffer Empty and Receive Buffer Empty status bits to
monitor the transmitter and receiver states. However, the DN120 gateway also has three data
synchronization features (Receive Sequence Number, Transmit Sequence Number, Handshake
Protocol) that an application can use to better monitor the serial operations.
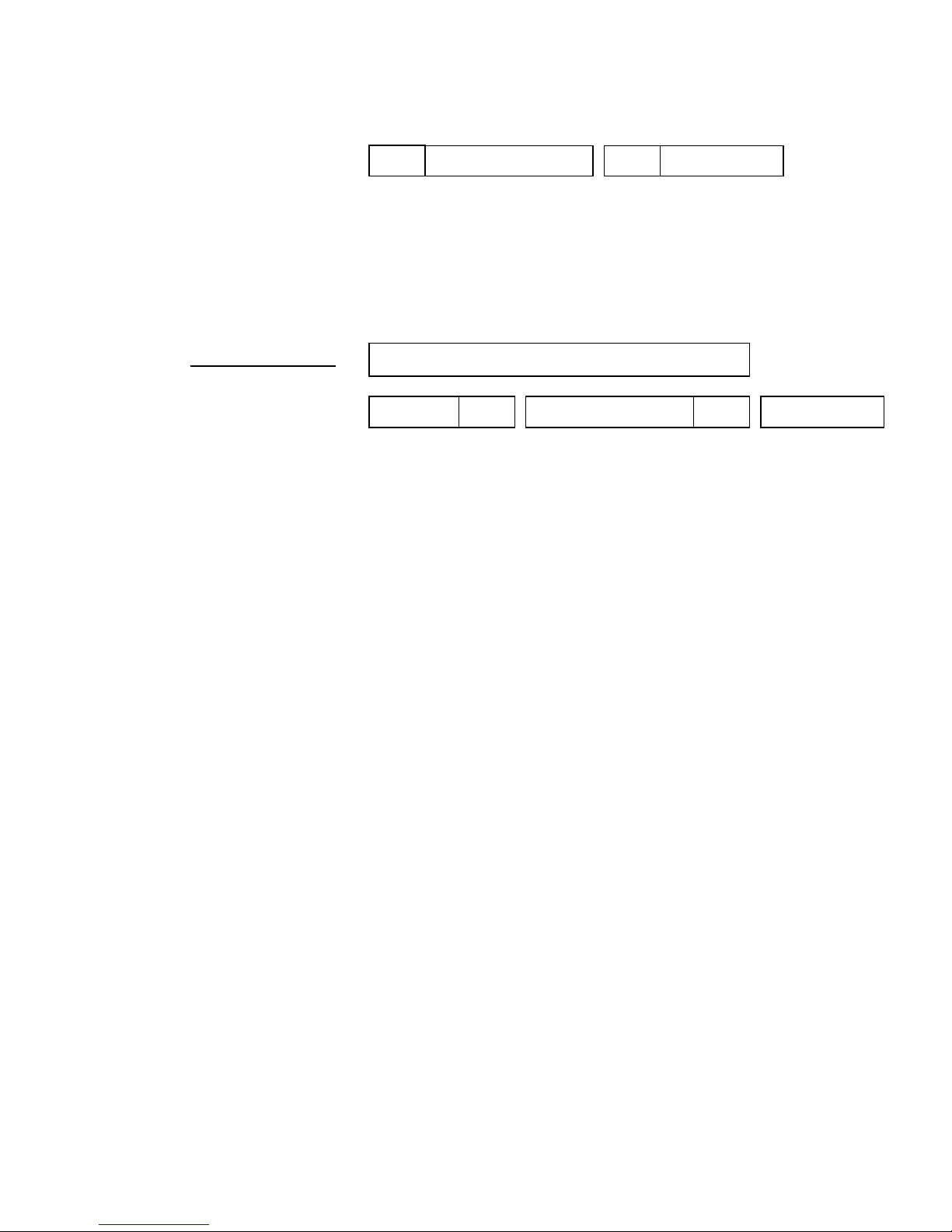
Receiving Messages
The DN120 gateway has two modes for receiving serial data: Stream Mode and Block Mode.
Stream Mode is best suited for applications with fixed-length serial messages, but it can also be
used to capture any stream of serial data. Block Mode is intended for both fixed and variable-
length message applications, where a Delimiter byte denotes the beginning or end of a message.
Stream Mode
Stream Mode saves all received message bytes in the Receive Buffer. There is no defined
beginning or end to the message stream. The only limitation is the gateway must send bytes
from the Receive Buffer to the DeviceNet master (Poll Response message) faster than it saves
new message bytes in the Receive Buffer, or the 64-byte buffer may eventually overflow.
Incoming data stream
Stream Mode
0x45 0x62 0x02 0x31 0x32 0x32 0x42 0x45 0x02 0x42 0x43 0x44 …
0x45 0x62 0x02 0x31 0x32 0x32 0x42 0x45 0x02 0x42 0x43 0x44 …
essage Bytes
Block Mode
Block Mode uses a configurable Delimiter byte to signal the start or end of a new message
packet. The Delimiter cannot be used in any other part of the message, or it would be incorrectly
interpreted as the start or end of a message. The gateway can be configured to save the Delimiter
byte in the Receive Buffer, or discard it. In Block Mode, the gateway does not return any new
message data to the DeviceNet master until the entire serial message has been received.
The Pre-Delimiter Block Mode configuration expects the Delimiter at the start of a message.
When a Delimiter byte is received, the gateway saves all subsequent bytes in the Receive Buffer
until another Delimiter is received (signaling the start of another message), or until the Maximum
Receive Size number of bytes has been saved. All bytes received after the Maximum Receive
Size and before the next Delimiter are discarded. In this mode, the maximum number of bytes in
a single message is defined by the Maximum Receive Size attribute.
Incoming data stream
Microscan Systems, Inc.
0x45 0x62 0x02 0x31 0x32 0x32 0x42 0x45 0x02 0x42 0x43 0x44 …
12
Page 13
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
D
M
D
r
M
D
r
M
D
r
M
D
D
r
M
Pre-Delimiter Mode
0x02 0x31 0x32 0x32 0x42 0x45
0x02 0x42 0x43 0x44 …
elimiter = 0x02
elimite
essage Bytes
elimite
essage Bytes
The Post-Delimiter Block Mode configuration expects the Delimiter at the end of a message.
The gateway saves all received bytes in the Receive Buffer until a Delimiter is received. In this
mode, the maximum number of bytes in a single message is limited by the Receive Buffer size
(64 bytes), not the Maximum Receive Size attribute.
Incoming data stream
Post-Delimiter Mode
elimiter = 0x02
0x45 0x62 0x02 0x31 0x32 0x32 0x42 0x45 0x02 0x42 0x43 0x44 …
0x45 0x62
essage Bytes
0x02
elimite
0x31 0x32 0x32f 0x42 0x45
essage Bytes
0x02
elimite
0x42 0x43 0x44 …
essage Bytes
Returning Received Data
When the gateway receives a Poll Command message, it removes some or all of the bytes
currently in the Receive Buffer and returns them as input bytes in a Poll Response message.
The Maximum Receive Size attribute defines the maximum number of bytes that can be returned
in a single Poll Response message. If the Receive Buffer contains more bytes than can fit into
one Poll Response message, the remaining bytes are returned in subsequent Poll Response
messages. RX Message is the string of valid message bytes returned in a single Poll Response
message. The RX Message byte string can be formatted as either a Short_String (byte array with
st
1
byte = length) or a Byte Array (no length byte). The number of bytes in an RX Message string
can be less than or equal to the Maximum Receive Size, but never larger. When the number is
less, the remaining Poll Response input bytes are either padded or undefined.
In Stream Mode, the gateway will always try to fill Poll Response message with bytes from the
Receive Buffer. The only time the RX Message size is less than the Maximum Receive Size is
when there are no more bytes in the Receive Buffer.
In Block Mode, the gateway will not return any data in a Poll Response message unless it has a
complete serial message saved in the Receive Buffer. If the message sizes are small, the gateway
may have several messages saved in the Receive Buffer, depending upon how fast the DeviceNet
master polls the gateway for data. The messages are returned one at a time in a Poll Response
message, regardless of their size. If the message is large, then it is returned in multiple Poll
Response messages.
Padding Message Data
Microscan Systems, Inc.
13
Page 14

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
R
r
B
P
R
R
R
If the number of RX Message bytes currently in the Receive Buffer is less than the Maximum
Receive Size number, then the remaining input bytes are undefined. The gateway can optionally
fill the unused input bytes with a Pad character. The Pad characters can be added at the
beginning or end of the message.
oll Response Message Data
Status
1. The are enough message bytes in Receive
uffer to fill Poll Response.
2. The are not enough message bytes in
eceive Buffer to fill Poll Response. Unused
input bytes are undefined.
3. The are not enough message bytes in
eceive Buffer to fill Poll Response. Pad bytes
are added after message bytes.
4. The are not enough message bytes in
eceive Buffer to fill Poll Response. Pad bytes
are added before message bytes.
eceive Sequence Numbe
other input bytes
RX Message bytes
RX Message bytes undefined
RX Message bytes
Pad Bytes
RX Message Bytes
Pad Bytes
If configured for Pre-Delimiter Block Mode and the Delimiter byte is saved, the Pad characters
are added either after the last valid message byte (right justification) or before the Delimiter byte
(left justification).
If configured for Post-Delimiter Block Mode and the Delimiter byte is saved, the Pad characters
are added either before the first valid message byte (left justification), or after the last valid
message byte but before the Delimiter byte (right justification).
Re-sending Received Data
The DN120 gateway can be configured to return received message bytes only once in a Poll
Response message, and return no data (null value) in subsequent Poll Response messages until
new message bytes are received. For the Short_String data type, a null value consists of the
length byte = 0. For the Byte Array data type, a null value consists of no data.
The gateway can also be configured to always return received message bytes in a Poll Response
message. If no new bytes in the Receive Buffer, then the last received bytes are returned. If new
bytes are in the Receive Buffer, then they are returned. The gateway provides Receive Sequence
Number or Handshake Protocol synchronization options to indicate whether the returned bytes
represent old or new data.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
14
Page 15

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
P
Transmitting Messages
The Serial Stream Object receives output bytes (TX Message) from the DeviceNet master in a
Poll Command message. It saves the output bytes in the Transmit Buffer, to be transmitted when
the serial channel is available. The maximum number of bytes that can be sent in one Poll
Command message is defined by the Maximum Transmit Size attribute. The Transmit Buffer can
hold up to 64 bytes. Because the DeviceNet Polled I/O data exchange may occur many times
faster than the transmission of serial data, the application may need to synchronize the transmit
data exchange with the gateway.
The number of output bytes in the Poll Command message is fixed. The Status Clear and
Transmit Sequence Number bytes are always sent, if enabled. The remaining number of bytes in
the Poll Command is defined by the Maximum Transmit Size attribute. If the number of TX
Message bytes sent is less than the Maximum Transmit Size number, then the remaining output
bytes are undefined. The gateway uses the Short_String length to determine the valid number of
bytes to transmit. If Byte Array format is used, all the bytes are transmitted.
oll Command Message Data
Status Clear Transmit Sequence Number other output bytes
1. TX Message bytes fill Poll Command
message.
2. TX Message is smaller than Poll Command
message. Unused output bytes are undefined.
TX Message bytes
TX Message bytes undefined
Synchronization
To ensure that no information is lost between the gateway’s serial channel and the user
application program, the DN120 has three synchronization options: Receive Sequence Number,
Transmit Sequence Number, and Handshake Protocol.
Receive Sequence Number
When enabled, the gateway returns a Receive Sequence Number input byte in the DeviceNet Poll
Response message. The 8-bit Receive Sequence Number is incremented by the gateway
whenever it returns new data in the input bytes. The user application uses the Receive Sequence
Number to signal the receipt of new message data. Valid numbers are 0-255.
Transmit Sequence Number
When enabled, the gateway receives a Transmit Sequence Number output byte in the DeviceNet
Poll Command message. The gateway will not send the TX Message bytes out the serial channel
unless the 8-bit Transmit Sequence Number is different than the last received value. Valid
numbers are 0-255.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
15
Page 16
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
R
D
t
N
Synchronous Handshake Protocol
The gateway can be configured with a more robust transmit and receive synchronization process.
The Handshake protocol requires the user application to acknowledge the receipt of new RX
Message input bytes. The protocol also requires the gateway to acknowledge the transmission of
the last TX Message output bytes. When enabled, both the Receive Sequence Number input byte
and Transmit Sequence Number output byte are used. They are segmented into four 4-bit
numbers, shown below. Valid numbers are 1 to 15, with 0 reserved to reset the gateway’s
numbers.
Transmit Sequence Number byte
Receive Acknowledge Number Transmit Request Number
Bits 4-7 (upper nibble) Bits 0-3 (lower nibble)
eceive Sequence Number byte
Receive Request Number Transmit Acknowledge Number
Bits 4-7 (upper nibble) Bits 0-3 (lower nibble)
The Receive Request Number is incremented by the gateway when it returns new RX Message
input bytes in the Poll Response Message. The gateway will increment from 15 to 1, skipping 0.
The user application acknowledges receipt of this RX Message by setting the Receive
Acknowledge Number equal to the Receive Request Number. The updated Receive Acknowledge
Number is sent back to the gateway in the next Poll Command Message. When the Receive
Acknowledge Number equals the Receive Request Number, the gateway can return the next set of
RX Message. If the user application sends 0 as the Receive Acknowledge Number, the gateway
resets its Receive Request Number to 0.
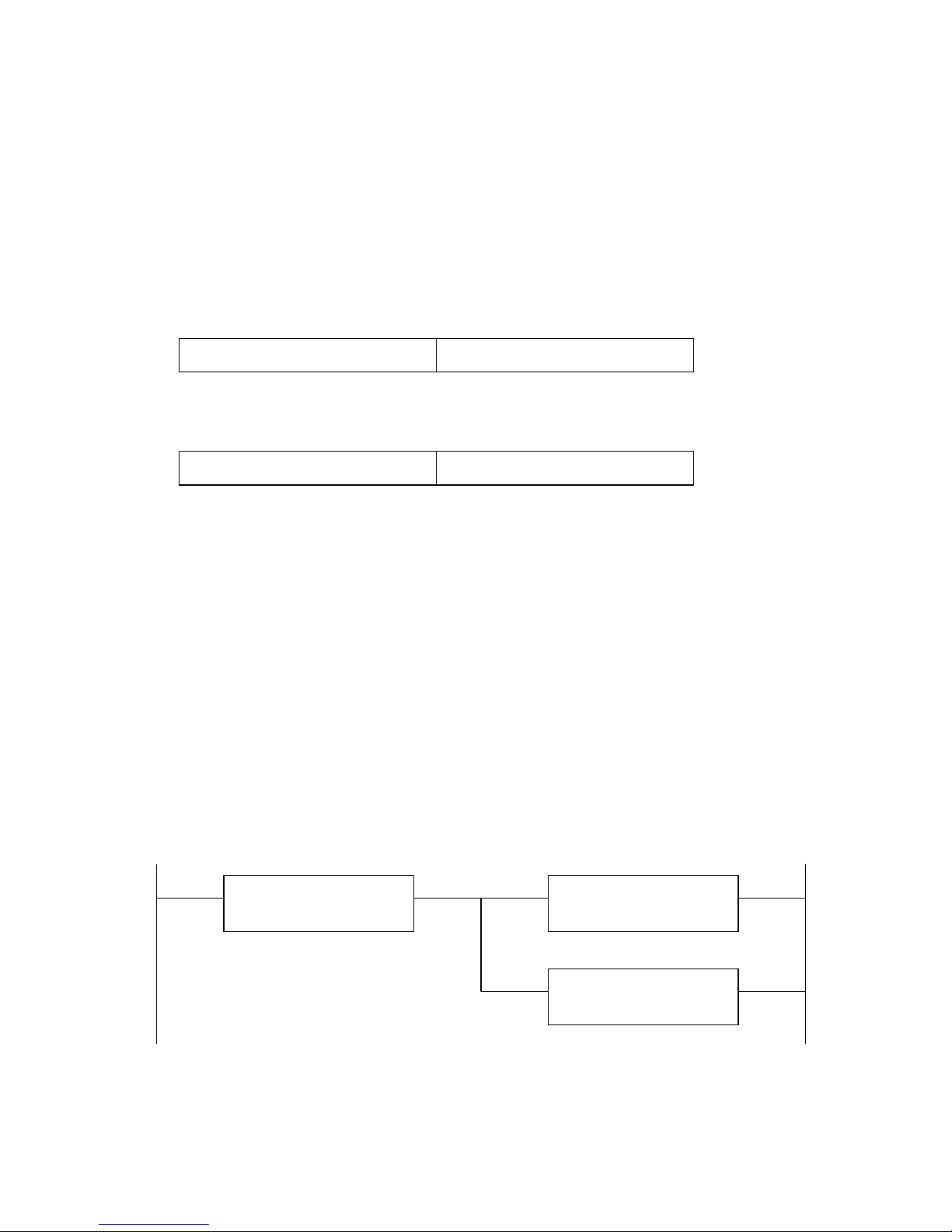
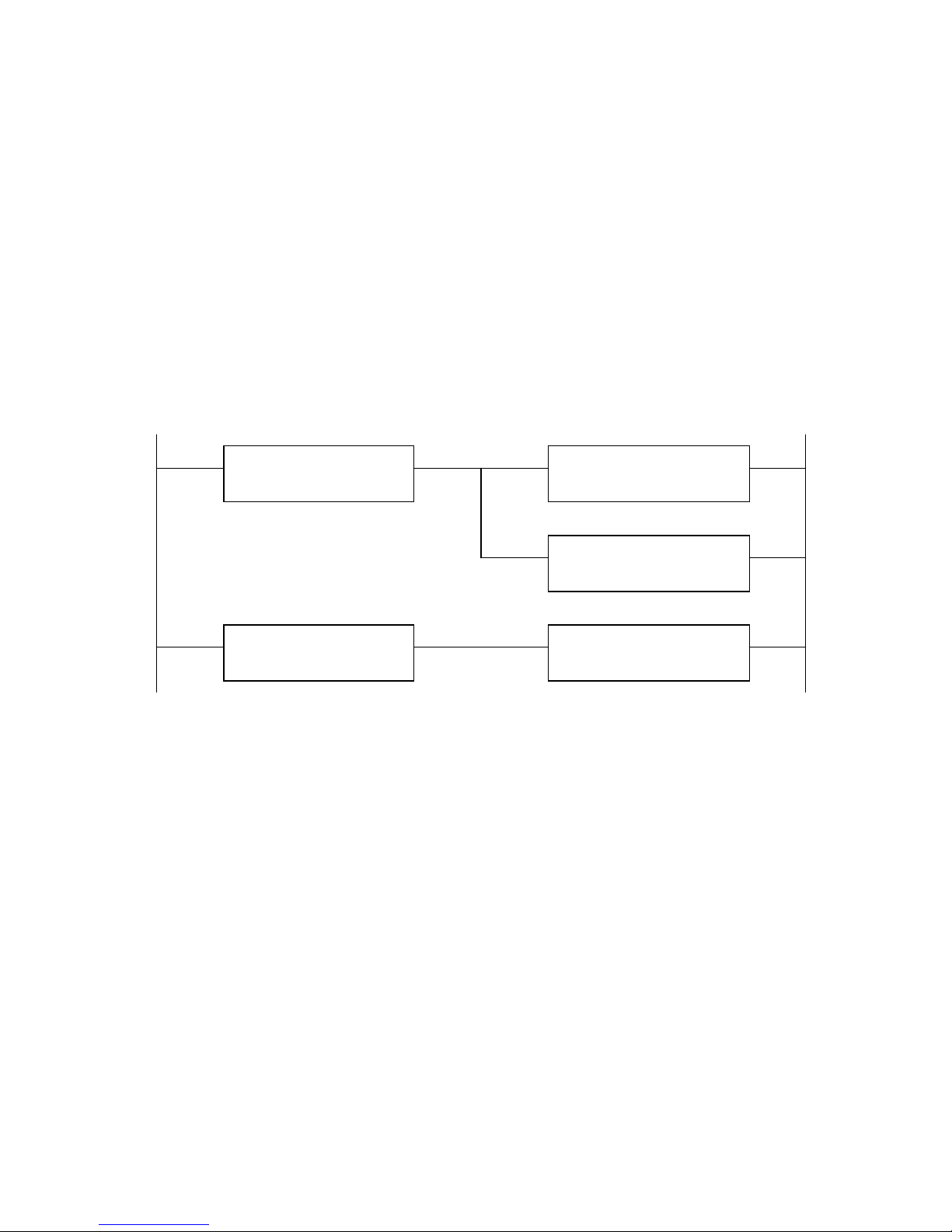
The following ladder-logic rung shows how the user application program can monitor the
gateway’s Receive Request Number (RX Rqst Num), save the new RX Message bytes, and set
Receive Acknowledge Number (RX Ack Num) equal to Receive Request Number (RX Rqst
Num).
id gateway increment the RX Rqs
um, indicating new data?
Compare Function:
RX Rqst Num <> RX Ack Num
Copy Function:
<byte array> = RX Message
Copy Function:
RX Ack Num = RX Rqst Num
Microscan Systems, Inc.
16
Page 17
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
D
I
I
The Transmit Request Number is incremented by the user application when it sends new TX
Message output bytes in the Poll Command Message. After the gateway transmits these TX
Message bytes, it sets the Transmit Acknowledge Number equal to the Transmit Request Number,
acknowledging the transmission. The updated Transmit Acknowledge Number is returned in the
next Poll Response Message. If the user application sends 0 as the Transmit Request Number,
the gateway ignores the TX Message output bytes and resets its Transmit Acknowledge Number
to 0.
The following ladder-logic rungs show how the user application program writes a new TX
Message value, increments the Transmit Request Number (TX Rqst Num), and waits for the
Transmit Acknowledge Number (TX Ack Num) to equal the Transmit Request Number (TX Rqst
Num). Note the application must wrap the Transmit Request Number from 15 to 1.
id gateway finish (acknowledge)
transmitting the last message?
Compare Function:
TX Ack Num == TX Rqst Num
Write next output bytes to transmit.
Copy Function:
TX Message = <byte array>
f TX Rqst Number greater than 15,
then reset number to 1 (1-15 range)
Compare Function:
TX Rqst Num == 16
ncrement TX Rqst Num (new data)
Addition Function:
TX Rqst Num = TX Rqst Num + 1
Write Function:
TX Rqst Num = 1
Microscan Systems, Inc.
17
Page 18
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Chapter 4 – Gateway Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure and operate the DN120 gateway. You configure the
gateway by reading and writing attribute values over its DeviceNet interface. There are a variety
of DeviceNet configuration tools available. Simple configuration tools use GET_ATTRIBUTE
and SET_ATTRIBUTE explicit message commands to read and write attribute values,
addressing each attribute by its Object, Instance, and Attribute numbers. This information is
contained in Chapter 5. More sophisticated configuration tools use EDS files to simplify
attribute configuration. You can configure the gateway using pull-down menus, buttons, and
data entry fields from the gateway’s Electronic Data sheet (EDS) file. Chapter 6 contains a
configuration example using the Rockwell Software RSNetworx program.
Configure DeviceNet Interface
Set the DeviceNet Baud Rate and MAC ID Address using the rotary switches. Configure
switches before connecting to the DeviceNet network. There is either a small triangular
indicator or white indicator on the switch. Use a small screwdriver to align that indicator with
the desired setting. Remove the DN120 cover if necessary to access the rotary switches.
DeviceNet Baud Rate Switch
Valid settings are 125K, 250K, 500K, or PGM. When PGM is selected, the DN120 uses the
baud rate saved in its retentive memory. A valid baud rate must be stored before the PGM
selection can be used. The baud rate is stored from the previous DN120 power cycle. It can also
be set over the network (DeviceNet Object Baud Rate attribute).
POSITION SETTING POSITION SETTING
0 125 Kbps 5 invalid
1 250 Kbps 6 invalid
2 500 Kbps 7 invalid
3 invalid 8 invalid
4invalid 9PGM
MAC ID Switches
The two MAC ID switches represent decimal numbers from 00 to 99. The LSB switch selects
the Ones digit and the MSB switch selects the Tens digit. Valid MAC IDs are 00 to 63. Setting
a MAC ID address greater than 63 forces the gateway to use the MAC ID saved in retentive
memory. A valid MAC ID must first be stored before this feature can be used. The MAC ID is
stored from the previous DN120 power cycle. It can also be set over the network (DeviceNet
Object MAC ID attribute).
MSB LSB Address MSB LSB Address
0 0 to 9 00 to 09 6 4 to 9 stored address
1 0 to 9 10 to 19 7 0 to 3 stored address
2 0 to 9 20 to 29 8 0 to 9 stored address
3 0 to 9 30 to 39 9 0 to 9 stored address
4 0 to 9 40 to 49
5 0 to 9 50 to 59
6 0 to 3 60 to 63
Microscan Systems, Inc.
18
Page 19

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Serial Channel Baud Rate / Option Switch
The DN120 gateway has a rotary switch for the serial channel. This switch has different
functions for the DN120 models.
The DN120 model uses the rotary switch to select the RS232 channel baud rate. Valid settings
are 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 bits per second, and PRG (table below). When
PRG is selected, the DN120 uses the Baud Rate attribute in the Serial Stream Object. A valid
baud rate must be written over DeviceNet to this attribute.
POSITION SETTING POSITION SETTING
0 9600 bps 5 300 bps
1 4800 bps 6 19200 bps
2 2400 bps 7 invalid
3 1200 bps 8 invalid
4 600 bps 9 PRG
Power Up Gateway
Connect the gateway to a DeviceNet network to power up the gateway.
DeviceNet Status LEDs
The DN120 gateway has two bi-color status LEDs (NET and MOD) that indicate operational
status. During power-up, the LEDs cycle through a sequence of alternating red and green. After
power-up, the NET LED should be flashing green (or solid green if allocated to a DeviceNet
master) and the MOD LED should be solid green. If this does not occur, disconnect from
DeviceNet and verify all the switch settings. See Chapter 8 for additional troubleshooting topics.
State DeviceNet Status LED (NET)
Off No power.
Flashing Red Configuration error. Check DeviceNet switch settings.
Solid Red Unrecoverable error.
Flashing Green Device not allocated to a DeviceNet master.
Solid Green Normal runtime, device allocated as a slave.
State Module Status LED (MOD)
Off No power.
Flashing Red Configuration error. Check object attribute settings.
Solid Red Unrecoverable error.
Flashing Green Not defined.
Solid Green Normal Operation.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
19
Page 20

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Serial Channel Status LEDs
The gateway has two bi-color LEDs to indicate serial channel activity. The TX LED flashes
green when a packet is being transmitted. The RX LED flashes green when a packet is being
received. A fault is indicated by solid red. After power-up, both LEDs should be off.
State Transmit Status LED (TX)
Off No data being transmitted
Flashing Red Not defined
Solid Red Transmit error (parity or overrun error)
Flashing Green Data being transmitted
Solid Green Not defined
State Receive Status LED (RX)
Off No data being received
Flashing Red Not defined
Solid Red Receive error (parity or overrun error)
Flashing Green Data being received
Solid Green Not defined
Register EDS File
If using a DeviceNet configuration tool that supports Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) files, you
should now register the gateway’s EDS file with the software. The latest EDS file versions can
be downloaded from www.mksinst.com. Select the EDS file that matches your gateway’s part
number and firmware version. Follow your configuration tool instructions to register EDS file.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
20
Page 21

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Configure Serial Channel
The Serial Stream Object attributes control the DN120 serial channel. These settings apply to all
serial transmit and receive operations. Before you can set or change any gateway configuration
settings, make sure the gateway is not in the DeviceNet master scanlist.
Serial Stream Object Instance Attributes (Class Code 64)
Number Name Data Type Value
3 Receive Data Short_String
or
Byte Array
4 Transmit Data Short_String
or
Byte Array
5 Status USINT Bit 0 – Transmit Channel Blocked
6 Baud Rate USINT 0 = 9600 bps 4 = 600 bps
7 Parity USINT 0 = no parity 5 = mark (force to 1)
8 Data Size USINT Read-only. 7 bits if parity enabled, 8 bits if no parity.
9 Stop Bits USINT Read-only. Fixed at 1 bit.
10 Flow Control USINT 0 = none 2 = CTS / RTS
11 Receive Count USINT Number of bytes in Receive Buffer. Any write clears buffer.
12 Transmit Count USINT Number of bytes in Transmit Buffer. Any write clears buffer.
13 Maximum Receive Size USINT Defines the maximum #bytes returned by RX Message read.
14 Data Format USINT Bit 0 – String Format (0 = Short_String, 1 = Byte Array)
15 Block Mode USINT Bit 0 – Pre/Post Delimiter (0 = pre-delimiter, 1 = post-delimiter)
16 Delimiter USINT Delimiter byte value
17 Pad Character CHAR Pad byte value
18 Maximum Transmit Size USINT Defines the maximum # bytes that can be transmitted.
19 Idle String Short_String 1-16 byte string transmitted when gateway receives a null Poll
Received message data. Returned in Poll Response Message.
Message data to transmit. Received in Poll Command Message.
Bit 1 – Transmit Buffer Empty
Bit 2 – Receive Parity Error (set = 0 to clear)
Bit 3 – Receive Buffer Empty
Bit 4 – Receive Buffer Overflow Error (set = 0 to clear)
Bit 5 – Framing Error (set = 0 to clear)
Bit 6 – Transmit Buffer Overflow Error (set = 0 to clear)
Bit 7 – CTS Signal State (1 = asserted)
1 = 4800 bps 5 = 300 bps
2 = 2400 bps 6 = 19200 bps
3 = 1200 bps
1 = even parity 6 = space (force to 0)
2 = odd parity
1 = XON / XOFF 4 = CTS Detect Mode
Bit 1 – Strip Parity Bits (0 = retain, 1 = strip)
Bit 2 – Pad Justification (0 = left justify, 1 = right justify)
Bit 3 – Pad Received Message (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 1 – Strip Delimiter (0 = keep delimiter, 1 = strip delimiter)
Bit 2 – Delimiter Enable (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 3 – Enable Receive Sequence Number (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 4 – Enable Transmit Sequence Number (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 5 – Re-send (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 6 – Synchronization (0 = no, 1 = handshake protocol)
(no input bytes). Short_String length = 0 for no Idle String.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
21
Page 22

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
R
r
D
D
R
D
D
20 Fault String Short_String 1-16 byte string transmitted when gateway’s Polled I/O
connection times out. Short_String length = 0 for no Fault String.
21 Status Enable USINT Set to any nonzero value to enable Status input byte.
22 Status Clear Enable USINT Set to any nonzero value to enable Status Clear output byte.
23 Four Wire USINT NA
24 Option Switch USINT NA
Receive Data – Data from the last valid message packet. Receive Data includes the Status and
Receive Sequence Number bytes if enabled, and the RX Message bytes. The RX Message format
is either Short_String or Byte Array, defined by Data Format attribute. If no message data is
available, the RX Message will be a null packet or Short_String with length = 0. Receive Data is
returned in the DeviceNet Poll Response Message.
eceive Data
Status
eceive Sequence Numbe
ata Format =
xxxxxxx0
Short_String data bytes Byte Array data bytesLength
RX Message
ata Format =
xxxxxxx1
Transmit Data – Data to transmit out the serial channel by the gateway. Transmit Data includes
the Status Clear and Transmit Sequence Number bytes if enabled, and the TX Message bytes.
Format is either Short_String or Byte Array, defined by Data Format attribute. Transmit Data is
typically received in the DeviceNet Poll Command Message. Reading Transmit Data returns the
last byte in the Transmit Buffer.
Transmit Data
Status Clear Transmit Sequence Number TX Message
ata Format =
xxxxxxx0
Short_String data bytes Byte Array data bytesLength
ata Format =
xxxxxxx1
Status – Contains bit-mapped serial channel status and error bits for transmit and receive
operations. Clearing the bits indicated will clear the error condition.
Baud Rate – Sets the serial channel’s data or baud rate. Enter number from 1-6 to select
corresponding baud rate value. For DN120, the RS232 Baud Rate switch must be set to PRG
before this attribute can be used to set the baud rate.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
22
Page 23

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Parity – Selects the parity type used in the serial byte.
Data Size – Read-only attribute indicates number of data bits in one serial byte. This number
does not include start, parity, or stop bits. If parity is enabled, 7 data bits are used. If no parity, 8
data bits are used.
Stop Bits – Read-only attribute indicates number of stop bits in one serial byte. Fixed at 1.
Flow Control – Selects the method of flow control used across the serial interface.
NONE means there is no flow control over the serial data exchange. The transmitting device can
overflow the receiving device’s buffer.
XON/XOFF is a software flow control option. Receiving device sends an XOFF character to the
transmitting device when its buffer is full, stopping further transmission. It sends an XON
character when it can again receive data. The XOFF and XON characters are not saved as
message data.
CTS/RTS is an RS232 hardware flow control option, available only on the DN120 gateway. The
RTS is an output and CTS is an input signal. The gateway keeps RTS active (low) when it can
receive data. It only transmits data when CTS is active (low).
CTS Detect Mode is an RS232 hardware flow control option, available only on the DN120
gateway. When CTS is asserted, the DN120 serial channel can transmit and receive. When CTS
is not asserted, the DN120 serial channel is disabled and Receive Buffer cleared.
Receive Count – Number of bytes currently available in the Receive Buffer. Writing any value
to this attribute will clear the Receive Buffer.
Transmit Count – Number of bytes currently in the Transmit Buffer. Writing any value to this
attribute will clear the Transmit Buffer.
Maximum Receive Size – Defines the maximum number of data bytes to be returned when the
Receive Buffer is read using either an Explicit Message or a Poll Response Message.
Data Format – Control byte that defines the format of the TX Message and RX Message bytes
transferred across DeviceNet.
Bit 3 selects whether the RX Message bytes are padded with the Pad bytes. Set this bit = 1 to
enable. If there are not enough message bytes in the Receive Buffer to fill up the RX Message
input bytes, then Pad characters are added at either the beginning or end of the message bytes.
Bit 2 selects whether Pad bytes are added at the beginning of the message (0 = left justify) or at
the end of the message (1 = right justify). This bit is used only if the Pad option is enabled.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
23
Page 24

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Bit 1 defines whether the gateway saves the parity bit in received message bytes (set = 0), or if
the gateway forces the parity bit to 0 in received message bytes (set = 1). This is typically used
when receiving 7-bit ASCII data.
Bit 0 defines String Format for TX Message and RX Message byte strings. Set to 0 for
Short_String format, and 1 for Byte Array format. Short_String defines the first byte as an
explicit length byte, containing the number of bytes that follow. Byte Array has an implied
length, derived from the Maximum Receive Size attribute.
Block Mode – Control byte that defines the serial receive mode, synchronization mode, and re-
send message option.
Bit 6 enables the Handshake Protocol synchronization option. When enabled, the Receive
Sequence Number byte is added to Receive Data input bytes, and the Transmit Sequence Number
byte is added to the Transmit Data output bytes.
Bit 5 enables the re-send message option. When enabled, the gateway continuously returns RX
Message data in the Poll Response message. If no new data has been received, then the last data
bytes are returned.
Bit 4 enables the Transmit Sequence Number synchronization option. When enabled, the
Transmit Sequence Number byte is added to the Transmit Data output bytes.
Bit 3 enables the Receive Sequence Number synchronization option. When enabled, the Receive
Sequence Number byte is added to the Receive Data output bytes.
Bit 2 selects the serial receive mode. Set = 0 for Stream Mode, and set = 1 for Block Mode.
Bit 1 selects whether the Delimiter is saved in the Receive Buffer (set = 0), or it is discarded (set
= 1). This bit is only used when Block Mode is enabled.
Bit 0 selects Pre-Delimiter Mode (set = 0) or Post-Delimiter Mode (set = 1). This bit is only
used when Block Mode is enabled.
Delimiter – Byte value used to indicate the start of a new message (Pre-Delimiter Mode), or the
end of a received message (Post-Delimiter Mode). This attribute is only used in Block Mode.
Pad Character – Byte value used to pad the RX Message bytes.
Maximum Transmit Size – Defines the maximum size of TX Message output bytes, or the
maximum number of data bytes to be transmitted across the RS232 channel from one Poll
Command message.
Idle String – Defines the byte string that is transmitted when the gateway receives a null Poll (no
input bytes, or a Short_String value with length = 0). Enter the byte string in Short_String data
Microscan Systems, Inc.
24
Page 25

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
format, with 1st byte = string length. Set the length byte to 0 if you don’t want to transmit an Idle
String. The Idle String can be from 0 to 16 bytes long, not counting Short_String length byte.
Example Idle String is [ 0x01 0x41 ], where string length is 1 and data byte is 0x41 (‘A’). You
must use the RSNetworx Class Instance Editor (Set Attribute Single command) to write a
Short_String attribute value.
Fault String – Defines the byte string that is transmitted when the gateway’s connection to the
DeviceNet master times out. Enter the byte string in Short_String data format, with 1
st
byte =
string length. Set the length byte to 0 if you don’t want to transmit a Fault String. The Fault
String can be from 0 to 16 bytes long, not counting Short_String length byte.
Example Fault String is [ 0x02 0x42 0x43 ], where string length is 2 and data bytes are 0x42
(‘B’) and 0x43 (‘C’). You must use the RSNetworx Class Instance Editor (Set Attribute
Single command) to write a Short_String attribute value.
Status Enable – Write any nonzero value to include the Status byte in Receive Data input bytes.
Status Clear Enable – Write any nonzero value to include the Status Clear byte in Transmit
Data output bytes.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
25
Page 26

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Configure DeviceNet Master Scan List
You must calculate the number of input and output bytes required by your DN120 configuration
before you can add the gateway to the DeviceNet master scanlist. You need to configure the
DeviceNet master to send the specific number of output bytes in its Poll Command Message, and
receive the specific number of input bytes in the gateway’s Poll Response Message. Once the
input and output bytes are mapped in the DeviceNet master, the user application program will be
able to read and write data values to the input and output bytes.
Poll Consume Size
The Poll Consume Size is the size (in bytes) of the Poll Command Message data field that is sent
by the DeviceNet master to the DN120.
Poll Command data:
[Status Clear byte][Transmit Sequence Number byte][Short_String length byte][TX data bytes (0-64)]
The first 3 bytes are present if enabled. The following equation is used to calculate the DN120
Poll Consume Size. Only include the overhead bytes that are enabled.
Status Clear byte 1
Transmit Sequence Number byte 1
Short_String length byte 1
+ Maximum Transmit Size ____
Poll Consume Size ____
Poll Produce Size
The Poll Produce Size is the size (in bytes) of the Poll Response Message data field that is sent
from the DN120 to the DeviceNet master.
Poll Response data:
[Status byte][Receive Sequence Number byte][Short_String length byte][RX data bytes (0-64)]
The first 3 bytes are present if enabled. The following equation is used to calculate the DN120
Poll Produce Size. Only include the overhead bytes that are enabled.
Status byte 1
Receive Sequence Number byte 1
Short_String length byte 1
+ Maximum Receive Size ____
Poll Produce Size ____
Microscan Systems, Inc.
26
Page 27

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Chapter 5 – DeviceNet Specifications
This chapter describes the DN120 gateway DeviceNet specifications.
DeviceNet Message Types
The DN120 is a Group 2 Slave Device that supports the following message types.
CAN IDENTIFIER GROUP 2 MESSAGE TYPE
10xxxxxx111 Duplicate MAC ID Check Message
10xxxxxx110 Unconnected Explicit Request Message
10xxxxxx101 Master I/O Poll Command Message
10xxxxxx100 Master Explicit Request Message
xxxxxx = DN120 MAC ID
DeviceNet Class Services
The DN120 is a Group 2 Slave Device that supports the following class services and instance
services.
SERVICE CODE SERVICE NAME
05 (0x05) Reset
14 (0x0E) Get Attribute Single
16 (0x10) Set Attribute Single
75 (0x4B) Allocate Group 2 Identifier Set
76 (0x4C) Release Group 2 Identifier Set
DeviceNet Object Classes
The DN120 device supports the following DeviceNet object classes.
CLASS CODE OBJECT TYPE
01 (0x01) Identity
02 (0x02) Router
03 (0x03) DeviceNet
04 (0x04) Assembly
05 (0x05) Connection
64 (0x40) Serial Stream Object
Microscan Systems, Inc.
27
Page 28

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
IDENTITY OBJECT
The Identity Object is required on all DeviceNet devices. It provides product identification and
general information.
Identity Object Class Code 01 (0x01)
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 1
2 Get Max Object Instance UINT 1
6 Get Max Class Identifier UINT 7
7 Get Max Instance Attribute UINT 7
Instance
Attribute
1 Get Vendor UINT 59 = D.I.P. Products
2 Get Product Type UINT 12 = Communications
3 Get Product Code UINT 1
4 Get Revision STRUCT of
5 Get Device Status WORD Bit 0 = owned (0 available, 1 allocated)
6 Get Serial Number UDINT Unique serial number for every device
7 Get Product Name STRUCT of
Access Name Type Value
Access Name Type Value
Major Revision USINT 4
Minor Revision USINT 0
Bit 2 = configured (0 no, 1 yes)
Bit 4-7 = vendor specific (0)
Bit 8 = minor configuration fault
Bit 9 = minor device fault
Bit 10 = major configuration fault
Bit 11 = major device fault
Bit 1, 3, 12-15 = reserved (0)
Length USINT 6
Name STRING [6]
Common Services
Service Code Class Instance Service Name
05 (0x05) No Yes Reset
14 (0x0E) Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single
Microscan Systems, Inc.
28
Page 29

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
ROUTER OBJECT
The Message Router Object provides a messaging connection point through which a Client may
address a service to any object class or instance residing in the DN120 device.
Router Object Class Code 02 (0x02)
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 1
6 Get Max Class Identifier UINT 7
7 Get Max Instance Attribute UINT 2
Instance
Attribute
2 Get Number of Connections UINT 2
Access Name Type Value
Access Name Type Value
Common Services
Service Code Class Instance Service Name
14 (0x0E) Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single
Microscan Systems, Inc.
29
Page 30

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
DEVICENET OBJECT
The DeviceNet Object contains information about the DN120 DeviceNet interface configuration.
DeviceNet Object Class Code 03 (0x03)
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 2
Instance
Attribute
1 Get/Set MAC ID USINT Settable only if MAC ID switches > 63.
2 Get/Set Baud Rate USINT Settable only if Baud switch > 2. Valid
3 Get/Set Bus Off Interrupt BOOL 0 = hold CAN in OFF state (default)
4 Get/Set Bus Off Counter USINT Writing this attribute forces counter value
5 Get Allocation Information STRUCT of
Access Name Type Value
Access Name Type Value
Valid numbers are 0 to 63. Returns last
value set or switch value.
settings are 0 = 125K, 1 = 250K, 2 = 500K.
Returns last value set or switch value.
1 = reset CAN
to zero.
Choice Byte BYTE bit 0 = explicit msg, set to 1 to allocate
bit 1 = polled IO, set to 1 to allocate
bit 2 = strobed IO, not supported
bits 3-7 = reserved, set to 0
Master Node Address USINT Allocated to this DeviceNet master
Common Services
Service Code Class Instance Service Name
14 (0x0E) Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single
16 (0x10) No Yes Set_Attribute_Single
75 (0x4B) No Yes Allocate Master/Slave
76 (0x4C) No Yes Release Master/Slave
Microscan Systems, Inc.
30
Page 31

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
ASSEMBLY OBJECT
The Assembly Object instances bind attributes of multiple objects to allow data to or from each
object to be sent or received over a single connection.
Assembly Object Class Code 04 (0x04)
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 2
2 Get Max Class ID UINT 2
Instance
Attribute
3 Get Data Stream note 1 Instance 1 for input data stream.
Access Name Type Value
Access Name Type Value
Instance 2 for output data stream.
Common Services
Service Code Class Instance Service Name
14 (0x0E) Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single
16 (0x10) No Yes Set_Attribute_Single
Instance 1 Input Data Stream and Instance 2 Output Data Stream are structured as either an array of
bytes or as a Short_String consisting of a single byte length field and N data bytes. The Input Data
Stream is the data returned in the Poll Response Message. The Output Data Stream is the data
returned in the Poll Command Message. See Chapter 3 for a complete description of the Poll
Format.
Poll Response:
[Status byte][Receive Sequence Number byte][Short_String Length byte][RX data bytes]
Poll Command:
[Status Clear byte][Transmit Sequence Number byte][Short_String Length byte][TX data bytes]
Microscan Systems, Inc.
31
Page 32

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
CONNECTION OBJECT
The Connection Object instances manage the characteristics of each communication connection.
The DN120 is a Group 2 Only Slave device that supports 1 Explicit Message Connection (Instance
1) and 1 Poll Message Connection (Instance 2).
Connection Object Class Code 05 (0x05)
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 1
Instance
Attribute
1 Get State USINT 0 = non-existent
2 Get Instance Type USINT 0 = Explicit Message
3 Get Transport Class Trigger USINT 0x83 for Explicit Message
4 Get Production Connection UINT Explicit Message:
5 Get Consumed Connection UINT Explicit Message:
6 Get Initial Communication
7 Get Production Size UINT 67 for Explicit Message
8 Get Consumed Size UINT 71 for Explicit Message
9 Get/Set Expected Packet Rate UINT Default 2500 msec
12 Get/Set Timeout Action USINT 0 = Timeout (Explicit Message default)
13 Get Production Path Length USINT 0 for Explicit Message
14 Get Production Path STRUCT of Null for Explicit Message
15 Get Consumed Path Length USINT 0 for Explicit Message
Access Name Type Value
Access Name Type Value
1 = configuring
2 = established
3 = timed out
1 = I/O Message
0x82 for I/O Message
10xxxxxx011 = produced connection id
I/O Message:
01111xxxxxx = produced connection id
10xxxxxx100 = consumed connection id
I/O Message:
10xxxxxx101 = consumed connection id
USINT 0x21 for Explicit Message
Characteristics
Log. Seg., Class USINT 0x20
Class Number USINT 0x04
Log. Seg., Instance USINT 0x24
Instance Number USINT 0x01
Log. Seg., Attribute USINT 0x30
Attribute Number USINT 0x03
0x01 for I/O Message
See Stream Object for I/O Message
See Stream Object for I/O Message
1 = Auto Delete
2 = Auto Reset (I/O Message default)
6 for I/O Message
STRUCT for I/O Message
6 for I/O Message
Microscan Systems, Inc.
32
Page 33

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
16 Get Consumed Path STRUCT of Null for Explicit Message
STRUCT for I/O Message
Log. Seg., Class USINT 0x20
Class Number USINT 0x04
Log. Seg., Instance USINT 0x24
Instance Number USINT 0x02
Log. Seg., Attribute USINT 0x30
Attribute Number USINT 0x03
17 Get Production Inhibit UINT 0
Common Services
Service Code Class Instance Service Name
05 (0x05) Yes Yes Reset
14 (0x0E) Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single
16 (0x10) No Yes Set_Attribute_Single
Microscan Systems, Inc.
33
Page 34

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
SERIAL STREAM OBJECT
The Serial Stream Object configures the DN120 serial channel.
Serial Stream Object Class Code 64 (0x40)
Class
Attribute
1 Get Revision UINT 1
2 Get Max Object Instance UINT 1
6 Get Max Class Identifier UINT 7
7 Get Max Instance Attribute UINT 22
Instance
Attribute
3 Get Receive Data Data Format Received message data. Returned in Poll Response
4 Get/Set Transmit Data Data Format Message data to transmit. Received in Poll
5 Get/Set Status USINT Bit 0 – Transmit Channel Blocked
6 Get/Set Baud Rate USINT 0 = 9600 bps 4 = 600 bps
7 Get/Set Parity USINT 0 = no parity 5 = mark (force to 1)
8 Get Data Size USINT 7 (parity enabled) or 8 (no parity)
9GetStop Bits USINT1
10 Get/Set Flow Control USINT 0 = none 2 = CTS / RTS
11 Get/Set Receive Count USINT Number of bytes in Receive Buffer. Write to clear.
12 Get/Set Transmit Count USINT Number of bytes in Transmit Buffer. Write to clear
13 Get/Set Maximum Receive Size USINT Maximum # bytes returned by Receive Buffer read.
14 Get/Set Data Format USINT Bit 0 – String Format (0 = Short_String, 1 = Array)
15 Get/Set Block Mode USINT Bit 0 – Pre/Post Delimiter (0 = Pre-, 1 = Post-)
16 Get/Set Delimiter USINT Delimiter byte value
17 Get/Set Pad Character CHAR Pad byte value
18 Get/Set Maximum Transmit Size USINT Defines maximum # bytes that can be transmitted.
Access Name Type Value
Access Name Type Value
Command.
Bit 1 – Transmit Buffer Empty
Bit 2 – Receive Parity Error (0 to clear)
Bit 3 – Receive Buffer Empty
Bit 4 – Receive Buffer Overflow Error (0 to clear)
Bit 5 – Framing Error (0 to clear)
Bit 6 – Transmit Buffer Overflow Error (0 to clear)
Bit 7 – CTS Signal State (1 = asserted)
1 = 4800 bps 5 = 300 bps
2 = 2400 bps 6 = 19200 bps
3 = 1200 bps
1 = even parity 6 = space (force to 0)
2 = odd parity
1 = XON / XOFF 4 = CTS Detect Mode
Bit 1 – Strip Parity Bits (0 = retain, 1 = strip)
Bit 2 – Pad Justification (0 = left, 1 = right)
Bit 3 – Pad Received Message (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 1 – Strip Delimiter (0 = keep, 1 = strip)
Bit 2 – Delimiter Enable (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 3 – Enable Receive Sequence Number
Bit 4 – Enable Transmit Sequence Number
Bit 5 – Re-send (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Bit 6 – Synchronization (0 = no, 1 = yes)
Microscan Systems, Inc.
34
Page 35

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
19 Get/Set Idle String Short_String Byte string transmitted when gateway receives null
Poll (no input bytes). Length = 0 for no Idle String.
20 Get/Set Fault String Short_String Byte string transmitted when gateway’s Polled I/O
connection times out. Length=0 for no Fault String
21 Get/Set Status Enable USINT Nonzero value enables Status input byte.
22 Get/Set Status Clear Enable USINT Nonzero value enables Status Clear output byte.
Common Services
Service Code Class Instance Service Name
05 (0x05) No Yes Reset
14 (0x0E) Yes Yes Get_Attribute_Single
16 (0x10) No Yes Set_Attribute_Single
Microscan Systems, Inc.
35
Page 36

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
g
p
y
(
)
)
)
)
(
)
gh (
)
p
,
p
,
g
p
(
)
Chapter 6 – RSNetworx Configuration Example
This chapter shows how to set up configure a DN120 gateway using the Rockwell Software
RSNetworx software and your gateway’s Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) file. The system
configuration uses an Allen-Bradley 1770-KFD DeviceNet adapter (MAC ID 62) to connect the
PC running RSNetworx to the DeviceNet network. A SLC500 system with a 1747-SDN
DeviceNet Scanner (MAC ID 00) is the DeviceNet master. DN120 gateway has MAC ID 03.
120VAC
Input
NL
Fuse 1A Fuse 6A
To PC RS232 25
Pin Serial Interface
For Used with
RSLo
To PC RS232 9
Serial Interface For
Used with RSLinx
& RSNetWorx Prog.
24VDC Power Supply
120VAC 24VDC
GND
ic Prog.
in
120/240VAC
Neutral
GND
+
--
PC Interface
RS232-PLC
RS232 serial
communication
PC Interface Mod.
RS232-DeviceNet
.Slot 2
24vdc output
1747-P1
Module
1747-PIC
1770-KFD
Slot 0
SLC502
PLC CPUFuse 3A
1747-L524
DeviceNet
Scanner
1747-SDN
Comm. Comm.
Slot 1
8 pt. Input
module
1746-IV8
DeviceNet network
Pin
1
3
to pin 5 DeviceNet connector
to pin 1 DeviceNet connector
DIP790 Device
Net Dist. Board
5
Slot 3Power Su
8 pt.Output
module
1746-OB8
PS to DeviceNet Dist.
Color Descri
black
clear
red BUS+
tion
BUS- (0vdc
Shield (Drain)
24vdc
9
in DIN RS232 Serial
Interface to Barcode
Scanner
Reader
h Scale or etc .
Wei
RS232 Pin Layout
Pin Pin Pin
Func. Func.
27
RXD
38
TXD
53
GND
Pin 1,4,6,9 are unused
Figure 1. DN120 Integrated with Allen Bradley SLC500
Microscan Systems, Inc.
RTS
CTS
DeviceNet
Module
Gatewa
DN120
RS232-DeviceNet
DeviceNet
Male Connector
43
5
12
Terminal Connector
Pin
Color
1
black
2
3
4
5
blue
clear
white
red
data low (CAN L
data high (CAN H)
DeviceNet Connector
Color Description
1
clear
2
red
black
4
5
data hi
white
blue data low
Description
BUS-
V-
shield (Drain
V+ (BUS+)
shield (Drain)
V+ (BUS+)
V- (BUS-)
CAN H
CAN L
36
Page 37

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Configure DeviceNet Interface
Follow instructions in Chapter 4 to set the gateway’s rotary switches to 125Kbps baud rate and
MAC ID to 03. Set the RS232 Baud Rate switch to PRG mode. Connect the gateway to the
DeviceNet network to power it up. During power-up, the NET and MOD LEDs cycle through a
sequence of alternating red and green. After power-up, the NET LED should be flashing green
and the MOD LED should be solid green.
Connect & Register EDS File
1) Start up the RSNetworx program. Select the Online operation from the Network menu.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
37
Page 38

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
2) The following text box should pop up, showing the networks connected to your computer.
3) Click on the 1770-KFD-1 + to show all connected DeviceNet devices. The gateway is at
MAC ID 03, verifying its DeviceNet connection. It is an Unrecognized Device until the
gateway’s EDS file is registered with RSNetworx.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
38
Page 39

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
4) Click Cancel to close Browse for network window. Select the EDS Wizard… operation from
the Tools menu. Click Next> to continue.
5) Select the Register an EDS file(s) option and click Next>.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
39
Page 40

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
6) Select Register a single file option. Browse for your gateway’s EDS file. You can download
the latest EDS and ICON files from the www.microscan.com website. Click Next> when
you have the correct path and EDS file name in the Named: box.
7) The next screen shows the RSNetworx installation test results. Click View file… to view the
actual EDS file text. Click Next> to continue.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
40
Page 41

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
8) The next screen allows you to customize the gateway’s icon for RSNetworx. Click on
Change icon…
9) The Change Icon screen pops up. Click Browse to enter path for DN120 icon file. You can
download the icon file from www.microscan.com.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
41
Page 42

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
10) Enter the path to DN120 icon file in the File name: box. Click Open to continue.
11) The DN120 icon should have changed to the proper icon. Click Next to continue.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
42
Page 43

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
12) The final step is to finish EDS file registration. Click Next> to complete the registration
process. Click Finish to close the EDS Wizard window.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
43
Page 44

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
13) Repeat steps 1, 2, and 3 to browse the DeviceNet network. RSNetworx should now
recognize the device at MAC ID 03 as a DN120 gateway, and display the DN120 icon. Click
Cancel when finished.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
44
Page 45

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Configure Serial Channel
Once the gateway is connected to DeviceNet and communicating with RSNetworx, you can
configure its serial channel. Make sure the gateway is not in the DeviceNet master scanlist
before changing any attribute values.
The Serial Stream Object attributes control the gateway’s serial channel transmit and receive
operations. The following steps show how to configure the Serial Stream Object attributes using
the RSNetworx program.
1) Select the Online operation from the Network menu. Select the DeviceNet adapter (1770-
KFD-1 in this example) and click OK.
2) RSNetworx prompts you to upload the network configuration. Click OK to continue.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
45
Page 46

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
3) RSNetworx displays the following text box while it uploads the network configuration.
4) The following screen displays the online nodes.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
46
Page 47

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
5) Left-click on the DN120 icon to select it. Right-click and select Properties from the pop-up
menu. You can also double-click on the DN120 icon to open its properties box.
6) RSNetworx displaces the following text box while is reads DN120 EDS file.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
47
Page 48

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
7) The DN120 Properties Box is displayed.
8) Select the Parameters tab. You will be prompted for the parameters source. Select the
Upload button to upload DN120 parameters from the actual device. All the DN120
parameters are now shown in the Properties window.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
48
Page 49

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
9) You may now edit the Serial Stream Object attributes in this window
Note that the Idle String and Fault String attributes are not listed. These attributes use
Short_String data type, which is not supported by RSNetworx EDS File interface.
10) Use the Class Instance Editor to configure Short_String attributes.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
49
Page 50

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
11) Select the Set_Attribute_Single service code to write an attribute value, and the
Get_Attribute_Single service code to read an attribute value. Check Values in decimal box
to enter class, instance, attribute, and data values in decimal.
The Idle String address is Class 64, Instance 1, Attribute Number 19. The Fault String
address is Class 64, Instance 1, Attribute Number 20. Enter the Short_String data as length
byte, then data bytes. Example is [0x01 0x02] for a single byte string 0x02 (ASCII STX).
12) Enter the remaining Serial Stream Object attributes in the Parameters Box window.
Status – Click on … to open selection box. Shows current status and error information. Click
on any errors to clear check. Press OK to continue.
Baud Rate – Click on arrow to the right of the current value to select from pull-down menu.
Parity – Click on arrow to the right of the current value to select from pull-down menu.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
50
Page 51

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Data Size – Read-only value, set to 8 if no parity selected and 7 if party selected.
Stop Bit – Read-only value, always set to 1.
Flow Control – Click on arrow to the right of the current value to select from pull-down menu.
Receive Count – Read-only value.
Transmit Count – Read-only value.
Maximum Receive Size – Click on current value and enter desired number in decimal.
Maximum Transmit – Click on current value and enter desired number in decimal.
Data Format – Click on …
to open selection box. Click on check box to select the desired
option. The Delimiter Mode uses bits 0, 1, 2, 3 of the byte. Ignore bits 4 through 7.
Block Mode – Click on … to open up selection box. Click on check box to set or clear the
desired bit. The Serial Status byte uses bits 0 through 6. Ignore bit 7.
Receive Delimiter – Click on current value and enter number in decimal.
Pad Char – Click on current value and enter number in decimal.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
51
Page 52

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Configure DeviceNet Master Scan list
After all the object instances have been configured, the DeviceNet master can be configured to
poll the gateway.
1) Before using the RSNetworx to map the gateway’s Polled I/O connection to 1747-SDN
DeviceNet master scanner, you must calculate the Poll Produce Size & Poll Consume Size.
Chapter 4 describes how to calculate these values.
2) Double click on the 1747-SDN icon to open its Properties box. You can also left click on
the icon to select it, right click for the pop-up menu, and select Properties.
3) Select the Scan list tab. RSNetworx prompts you for the Scanner Configuration. Click
Upload to upload current 1747-SDN configuration from the node. RSNetworx displays the
upload progress.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
52
Page 53
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
4) The next window shows the Available Devices: that can be added to the 1747-SDN Scanlist.
5) Select the Automap on Add checkbox if you want RSNetworx to automatically map the
DN120 input and output bytes into the 1747-SDN memory.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
53
Page 54

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
6) Select the DN120 under Available Devices: and click the > button to transfer to Scanlist.
7) RSNetworx warns that the DN120 does not contain any I/O data. Click OK to continue.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
54
Page 55

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
8) Click on the Edit I/O Parameters button. Use the ∧ and ∨ buttons to set Rx Size: to the
calculated Poll Consume Size value and the Tx Size: to the calculated Poll Produce Size
value. Click Apply to update I/O parameters.
9) RSNetworx prompts to Automap the new input and output data bytes. Select Yes to
automap. If you select No, then you must manually map the I/O bytes in the memory tables.
10) RSNetworx prompts if you want to download the changes to the 1747-SDN. Click Yes.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
55
Page 56

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
11) Select the Input tab to view the automapped DN120 input bytes.
12) Click the Advanced… button to view current input mapping detail. Change the mapping to
suit your application. Click Apply Mapping button after you make changes. Click Yes at the
RSNetworx prompt to download any changes to the 1747-SDN. Click Close to continue.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
56
Page 57

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
13) Select the Output tab to view the automapped DN120 output bytes.
14) Click the Advanced… button to view current input mapping detail. Change the mapping to
suit your application. Click Apply Mapping button after you make changes. Click Yes at the
RSNetworx prompt to download any changes to the 1747-SDN. Click Close to continue.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
57
Page 58

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Microscan Systems, Inc.
58
Page 59
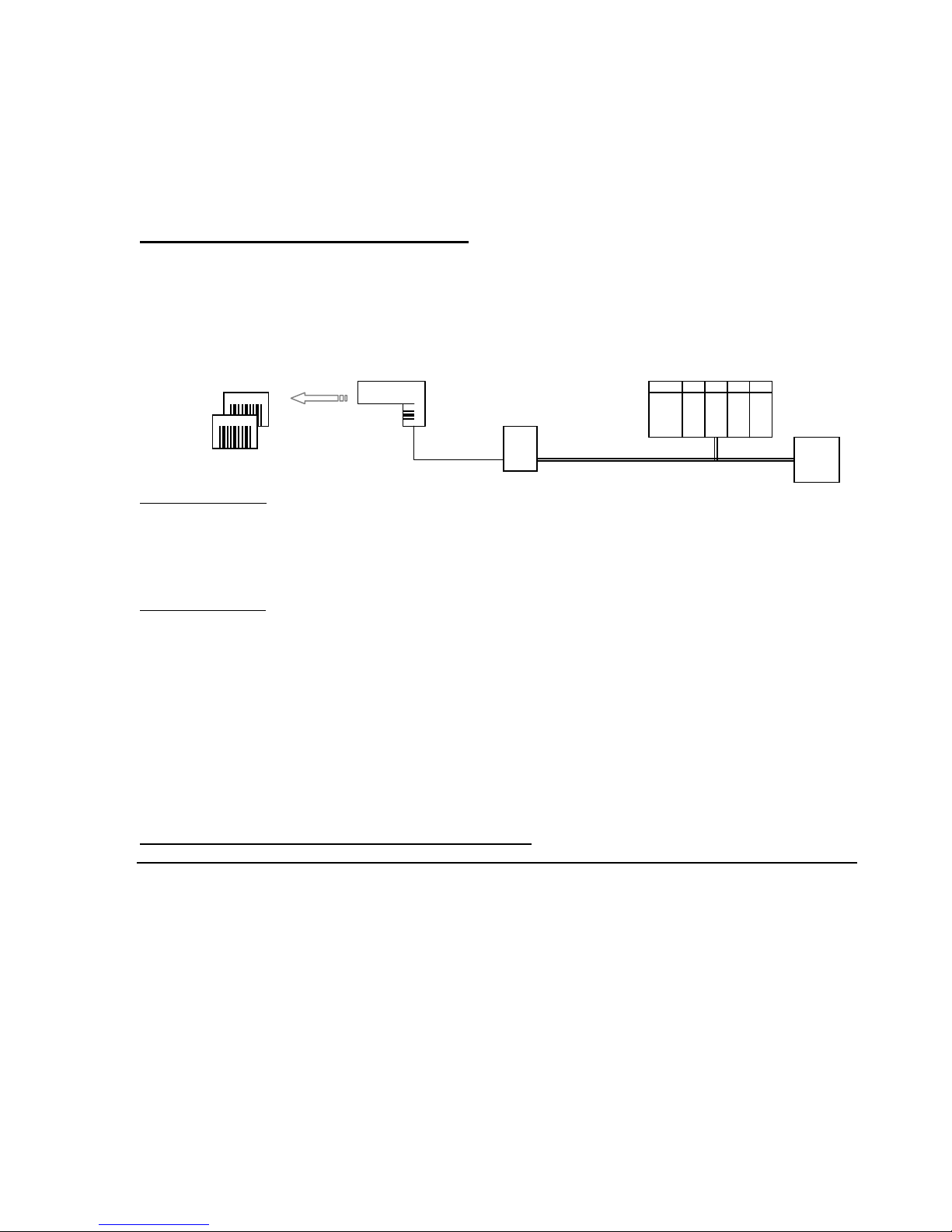
DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Chapter 7 – Configuration Examples
This chapter contains four example gateway configurations.
Example 1 – Receiving Fixed-Length Data
Read UPC labels into a PLC using a serial barcode scanner, a DN120 gateway, and a DeviceNet
scanner (master). The barcode scanner RS232 channel is connected to a DN120 serial channel.
The DN120 DeviceNet channel is connected to the PLC DeviceNet scanner. The DeviceNet
network is powered by an external 24VDC power supply.
PLC & DeviceNet Scanner
CDN066
Gateway
DeviceNet network
Barcode Scanner
The barcode scanner’s RS232 channel is set for 9600 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
When it reads a UPC label, it transmits a 5-byte serial message, which consists of the 5 ASCII
characters printed on the UPC label.
Power
Supply
DN120 Gateway
The receive mode will be Stream Mode, since there is no defined Delimiter for the start of a
message or the end of a message. All received data bytes will be returned as DeviceNet input
bytes. The Maximum Receive Size is 5, because the Barcode Scanner messages have a fixed
length of 5 bytes. The data bytes will be returned as a Short_String. The gateway will only
return the data bytes once in a Poll Response Message.
The Serial Stream Object can now be configured. The following shows the Serial Stream Object
attribute settings for this application. The 3rd column lists the address string if using
Set_Attribute_Single commands to write the attribute values.
Serial Stream Object Configuration (Class Code 64 or 0x40)
Attribute Data Class / Instance / Attribute / Data Description
6. Baud Rate 0 0x40 0x01 0x06 0x00 0 = 9600 bps
7. Parity 0 0x40 0x01 0x07 0x00 0 = no parity
10. Flow Control 2 0x40 0x01 0x0A 0x02 2 = CTS / RTS
13. Max Receive Size 5 0x40 0x01 0x0D 0x05 Fixed message size of 5 bytes
14. Data Format 00000001 0x40 0x01 0x0E 0x01 String Format = Short_String
15. Block Mode 00000000 0x40 0x01 0x0F 0x00
The gateway will return 6 bytes of Receive Data, because the Maximum Receive Size is set to 5
and the data format is Short String (add 1 for length byte). The Status and Receive Sequence
Number bytes are not enabled. The Poll Produce Size can now be calculated for this DN120
configuration.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
59
Page 60

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Status byte 0
Receive Sequence Number byte 0
Short_String length byte 1
+ Maximum Receive Size 5
Poll Produce Size 6
The format of the Poll Response Message input bytes is as follows:
[ Short_String length ] [ Short_String data ]
1 byte 5 bytes
The gateway always returns 6 input bytes in the Poll Response Message, even if a new barcode
message has not been received. The gateway will return new message data only once, and return
a null data string if there is no new message data. The application should check the Short_String
length byte to determine if a new message is being returned. A length of 5 indicates valid data
bytes (new message data). A length of 0 indicates no valid data bytes (no new message).
The Barcode Scanner sends the following 5-byte serial message when it reads a UPC label
printed with ‘12345’ (ASCII numbers).
0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x35
The gateway generates the following Poll Response Message in response to the first Poll
Command Message after its receives the Barcode message. The Short_String length is 5, since 5
bytes were received.
0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x350x05
The gateway generates the following Poll Response Message in response to subsequent Poll
Command Messages, until it receives another Barcode message. The Short_String length is 0,
indicating a null data string. The 5 data bytes are undefined.
XX XX XX XX XX0x00
Microscan Systems, Inc.
60
Page 61

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Example 2 – Receiving Pre-Delimited Data
Same configuration as Example 1.
Barcode Scanner
The barcode scanner’s RS232 channel is set for 9600 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
When it reads a UPC label, it transmits following ASCII message format. The message always
begins with the ASCII STX start-of-text (0x02) character. The barcode data will consist of a
variable number of 1 to 14 ASCII characters, depending upon the UPC label being scanned. It
will not transmit a 0x02 in the barcode data field.
[ STX ] [ ASCII barcode data ]
DN120 Gateway
The receive mode will be Pre-Delimiter Mode, because the barcode messages always begin with
the same character. The Delimiter is 0x02 (STX). The Maximum Receive Size is 15, because the
largest message contains 1 STX byte and 14 ASCII bytes. The received bytes will be returned as
a Short_String. An ASCII NUL Pad character (0x00) will be added at the end of the message if
needed. The gateway will always return the data bytes in the Poll Response Message. The
Receive Sequence Number will be used to indicate when a new message is returned.
The Serial Stream Object can now be configured. The following shows the Serial Stream Object
attribute settings for this application. The 3rd column lists the address string if using
Set_Attribute_Single commands to write the attribute values.
Serial Stream Object Configuration (Class Code 64 or 0x40)
Attribute Data Class / Instance / Attribute / Data Description
6. Baud Rate 0 0x40 0x01 0x06 0x00 0 = 9600 bps
7. Parity 0 0x40 0x01 0x07 0x00 0 = no parity
10. Flow Control 2 0x40 0x01 0x0A 0x02 2 = CTS / RTS
13. Max Receive Size 15 0x40 0x01 0x0D 0x0F Receive messages up to 15 bytes
14. Data Format 00001101 0x40 0x01 0x0E 0x0D Pad receive message
15. Block Mode 00101101 0x40 0x01 0x0F 0x2D Re-send = enabled
16. Delimiter STX 0x40 0x01 0x10 0x02 0x02 = ASCII STX character
17. Pad Character NUL 0x40 0x01 0x11 0x00 0x00 = ASCII NUL character
Pad justification = right (end of msg)
String Format = Short_String
Receive Sequence Number = enabled
Delimiter = enabled
Pre-Delimiter
The gateway will return up to 16 bytes of Receive Data, because the Maximum Receive Size is
set to 15 and the data format is Short String (add 1 for length byte). The Status byte is not
enabled. The Receive Sequence Number byte is enabled. The Poll Produce Size can now be
calculated for this DN120 configuration.
Status byte 0
Receive Sequence Number byte 1
Short_String length byte 1
+ Maximum Receive Size 15
Poll Produce Size 17
Microscan Systems, Inc.
61
Page 62

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
The format of the Poll Response Message input bytes is as follows:
[ Receive Sequence Number ] [ Short_String length ] [ Short_String data ] [ Pad bytes ]
1 byte 1 byte 0-15 bytes
The gateway always returns 17 input bytes in the Poll Response Message, even if the scanned
barcode data contains fewer bytes. The application should check the Short_String length byte to
determine the number of valid data bytes being returned in a particular Poll Response Message.
The remaining input bytes have undefined values.
The gateway will always return the last received Short_String data in its Poll Response Message.
The gateway increments the Receive Sequence Number when new Short_String data is returned.
The application can use the Receive Sequence Number to determine if the Short_String data is
new or old information.
The Barcode Scanner sends the following 8-byte serial message when it reads a UPC label
printed with ‘1234567’ (ASCII numbers).
0x02 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x35 0x36 0x37
The gateway generates the following Poll Response Message. The Receive Sequence Number is
1, since this is the first message received from the Barcode Scanner. The Short_String length is
8, since 8 bytes were received. 7 Pad characters are added at the end of the message.
0x02 0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x35 0x36 0x370x01 0x08 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
Microscan Systems, Inc.
62
Page 63

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Example 3 – Receiving Post-Delimited Data
Same configuration as Example 1.
Barcode Scanner
The barcode scanner’s RS232 channel is set for 9600 bps, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit.
When it reads a UPC label, it transmits following ASCII message format. The message always
begins ends with the ASCII ETX end-of-text (0x03) character. The barcode data will consist of
a variable number of 1 to 14 ASCII characters, depending upon the UPC label being scanned. It
will not transmit a 0x03 in the barcode data field.
[ ASCII barcode data ] [ ETX ]
DN120 Gateway
The receive mode will be Post-Delimiter Mode, because the barcode messages always end with
the same character. The Delimiter is 0x03 (ETX), and will not be included in the receive data.
The Maximum Receive Size is 15, because the largest message contains 14 ASCII bytes and 1
ETX byte. The received bytes will be returned a Short String. The gateway will only return new
data bytes once in the Poll Response Message. The Status byte will be enabled.
The Serial Stream Object can now be configured. The following shows the Serial Stream Object
attribute settings for this application. The 3rd column lists the address string if using
Set_Attribute_Single commands to write the attribute values.
Serial Stream Object Configuration (Class Code 64 or 0x40)
Attribute Data Class / Instance / Attribute / Data Description
6. Baud Rate 0 0x40 0x01 0x06 0x00 0 = 9600 bps
7. Parity 0 0x40 0x01 0x07 0x00 0 = no parity
10. Flow Control 2 0x40 0x01 0x0A 0x02 2 = CTS / RTS
13. Max Receive Size 15 0x40 0x01 0x0D 0x0F Receive messages up to 15 bytes
14. Data Format 00000001 0x40 0x01 0x0E 0x01 String Format = Byte Array
15. Block Mode 00000110 0x40 0x01 0x0F 0x06 Delimiter = enabled
16. Delimiter ETX 0x40 0x01 0x10 0x03 0x03 = ASCII ETX character
Strip Delimiter enabled
Post-Delimiter
The gateway will return up to 16 bytes of Receive Data, because the Maximum Receive Size is
set to 15 and the data format is Short String (add 1 for length byte). The Status byte is enabled.
The Receive Sequence Number byte is not enabled. The Poll Produce Size can now be
calculated for this DN120 configuration.
Status byte 1
Receive Sequence Number byte 0
Short_String length byte 1
+ Maximum Receive Size 15
Poll Produce Size 17
Microscan Systems, Inc.
63
Page 64

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
The format of the Poll Response Message input bytes is as follows:
[ Status ] [ Short_String length ] [ Short_String data ] [ undefined bytes ]
1 byte 1 byte 0-15 bytes
The gateway always returns 16 input bytes in the Poll Response Message, even if the scanned
barcode data contains fewer bytes, or if a new barcode message has not been received. The
gateway returns new message data only once, and returns a null data string if there is no new
message data. The application should use the Short_String length byte to determine if a new
message is being returned. A length greater than zero indicates the number of valid data bytes
(new message data). A length of 0 indicates no valid data bytes (no new message).
The Barcode Scanner sends the following 6-byte serial message when it reads a UPC label
printed with ‘12345’ (ASCII numbers).
0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x35 0x03
The gateway generates the following Poll Response Message in response to the first Poll
Command Message after its receives the Barcode message. The Status Byte is 0x0A, indicating
no transmit or receive errors, an empty Transmit Buffer, and an empty Receive Buffer. The
Delimiter is stripped, so the Short_String length is 5. There are 5 valid data bytes, and the
remaining 10 input bytes are undefined.
0x31 0x32 0x33 0x34 0x350x0A 0x05 XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX
The gateway generates the following Poll Response Message in response to subsequent Poll
Command Messages, until it receives another Barcode message. The Short_String length is 0,
indicating a null data string. The 15 other input bytes are undefined.
0x0A 0x00 XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX XX
Microscan Systems, Inc.
64
Page 65

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Example 4 – Transmitting Fixed-Length Data
Print an ASCII string from a PLC to a bar code scanner, using a DN120 gateway and a
DeviceNet scanner (master). The text message string is always 25 characters long, including any
ASCII control characters. The bar code scanner RS232 channel is connected to a DN120 serial
channel. The DN120 DeviceNet channel is connected to the PLC DeviceNet scanner. The
DeviceNet network is powered by an external 24VDC power supply.
PLC & DeviceNet Scanner
DN120
Gateway
DeviceNet network
Power
Supply
Bar Code Scanner
The bar code scanner’s RS232 channel is set for 9600 bps, 7 data bits, even parity, and 1 stop bit.
DN120 Gateway
The DN120 serial channel is configured to transmit this RS232 message format. A string format
will be Byte Array, since the message size is fixed. Transmit Sequence Numbers will be used to
signal a new message to transmit. The Maximum Transmit Size is 25, which is the number of
message bytes. The Serial Stream Object attributes are shown below for this application. The
3rd column lists the address string if using Set_Attribute_Single commands to write the attribute
values.
Serial Stream Object Configuration (Class Code 64 or 0x40)
Attribute Data Class / Instance / Attribute / Data Description
6. Baud Rate 5 0x40 0x01 0x06 0x05 5 = 300 bps
7. Parity 1 0x40 0x01 0x07 0x01 1 = Even parity
10. Flow Control 1 0x40 0x01 0x0A 0x01 1 = XON / XOFF
14. Data Format 00000000 0x40 0x01 0x0E 0x00 String Format = Byte Array
15. Block Mode 00010000 0x40 0x01 0x0F 0x10 Transmit Sequence Number enabled
18. Max Transmit Size 25 0x40 0x01 0x12 0x19 Fixed message size of 25 bytes
The gateway will transmit 25 output bytes received in a Poll Command Message. The Status
Clear byte is not enabled. The Transmit Sequence Number is enabled. The Length Byte is not
enabled (Byte Array format). The Poll Consume Size can now be calculated for this DN120
configuration.
Status Clear byte 0
Transmit Sequence Number byte 1
Short_String length byte 0
+ Maximum Receive Size 25
Poll Produce Size 26
Microscan Systems, Inc.
65
Page 66

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
The format of the Poll Command Message output bytes is as follows:
[ Transmit Sequence Number ] [ message data ]
1 byte 25 bytes
The gateway always receives 26 output bytes in the Poll Command Message. It will not transmit
a new serial message until the Transmit Sequence Number received in the Poll Command is
different than the number received in a previous Poll Command. The application should
increment the Transmit Sequence Number when it sends new output byte values in the Poll
Command Message, to enable the transmission of the new message.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
66
Page 67

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Example 5 – Transmitting Variable-Length Data
Same configuration as Example 4, except the text message string can be from 1 to 25 characters
long, including ASCII control characters.
Bar Code Scanner
The bar code scanner’s RS232 channel is set for 9600 bps, 7 data bits, even parity, and 1 stop bit.
DN120 Gateway
The DN120 serial channel is configured to transmit this RS232 message format. A string format
will be Short_String, since the message size is variable. The Maximum Transmit Size is 25,
since the largest text message contains 25 characters. The Serial Stream Object attributes are
shown below for this application. The 3rd column lists the address string if using
Set_Attribute_Single commands to write the attribute values.
Serial Stream Object Configuration (Class Code 64 or 0x40)
Attribute Data Class / Instance / Attribute / Data Description
6. Baud Rate 5 0x40 0x01 0x06 0x05 5 = 300 bps
7. Parity 1 0x40 0x01 0x07 0x01 1 = Even parity
10. Flow Control 1 0x40 0x01 0x0A 0x01 1 = XON / XOFF
14. Data Format 00000001 0x40 0x01 0x0E 0x01 String Format = Short_String
15. Block Mode 00000000 0x40 0x01 0x0F 0x00 Transmit Sequence Number disabled
18. Max Transmit Size 25 0x40 0x01 0x12 0x19 Fixed message size of 25 bytes
The gateway will transmit the output bytes received in a Poll Command Message. The Status
Clear byte is not enabled. The Transmit Sequence Number is not enabled. The Length Byte is
enabled (Short_String format). The Poll Consume Size can now be calculated for this DN120
configuration.
Status Clear byte 0
Transmit Sequence Number byte 0
Short_String length byte 1
+ Maximum Receive Size 25
Poll Produce Size 26
The format of the Poll Command Message output bytes is as follows:
[ Short_String length ] [ message data ]
1 byte 25 bytes
The gateway always receives 26 output bytes in the Poll Command Message, regardless of the
variable length messages. The gateway uses the Short_String length byte to determine the valid
number of message bytes in the Poll Command Message. It will only transmit the valid message
bytes. All remaining output bytes are ignored. If the gateway receives a Poll Command
Message with Short_String length = 0, no output bytes are transmitted. The application can send
variable-length Short_Strings to be transmitted, and send Null Data (length = 0) when there is no
message to transmit.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
67
Page 68

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Chapter 8 – Troubleshooting
Problem Possible Cause
DeviceNet Configuration Program
does not recognize Gateway.
DeviceNet Configuration Program
does not recognize Gateway after
loading EDS file.
• Register Gateway EDS file with Configuration Program.
• Check Major and Minor Revisions for Gateway and EDS file, to see if you have
correct EDS file for your Gateway's firmware version.
Gateway does not appear on
DeviceNet network.
After setting Gateway MAC ID,
DeviceNet Master does not
recognize Gateway.
NET LED is flashing red.
NET LED is solid red.
NET LED is off.
MOD LED is flashing or solid red.
RX LED does not flash green when
data is sent to the Gateway.
• Check wiring and cable connections.
• Check DeviceNet power supply voltage.
• Make sure Gateway baud rate matches network baud rate.
• Verify Gateway baud rate is set from rotary switches or retentive memory value.
• Make sure Gateway MAC ID is not used by another device.
• Disconnect Gateway from network before changing MAC ID.
• Make sure Gateway MAC ID is not used by another device.
• Verify Gateway MAC ID is set from rotary switches or retentive memory value.
• Verify DeviceNet baud rate.
• Gateway is removed from DeviceNet Master scanlist or network. Power cycle
Gateway to reset.
• Make sure Gateway MAC ID is not used by another device. Possible DeviceNet
network failure.
• Check wiring and cable connections.
• Check DeviceNet power supply voltage.
• Make sure Gateway baud rate matches network baud rate.
• Verify Gateway baud rate is set from rotary switches or retentive memory value.
• Gateway has failed. Cycle power to reset. Replace Gateway if necessary.
• If Sync enabled, make sure Receive Request Number and Receive Acknowledge
Number are equal. Application must acknowledge last received message before
gateway will receive the next message.
• Verify data is being received in Receive Data.
• Verify source device is transmitting data to Gateway.
• Make sure hardware flow control signals are properly connected.
RX LED is solid red after Gateway
receives data.
TX LED is solid red after receiving
data from DeviceNet Master.
TX LED does not flash green when
Gateway should be transmitting
data.
1747-SDN Scanner displays error
code 77.
Microscan Systems, Inc.
• Check Status byte for any Receiver errors. Reset Gateway or clear Status error
bits if necessary.
• Make sure parity is set to match transmitting device settings.
• Check Status byte for Transmitter errors. Reset Gateway or clear Status error
bits if necessary.
• Make sure parity is set to match receiving device settings.
• If Transmit Sequence Number enabled, make sure number is being incremented
by the application. Gateway will not transmit new data unless the Transmit
Sequence Number is changed.
• Verify data is being saved in Transmit Data.
• Gateway Poll Produce Size and/or Poll Consume Size value do not 1747-SDN
Poll Rx/Tx settings.
68
Page 69

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Appendix A – Product Specifications
DeviceNet Interface
Power Requirements: 11 - 28 Vdc @ 50 mA
Loss of Ground: Yes
Reverse Polarity: -30 Vdc
Signal Levels: ISO11898
Serial Channel
Isolation: 500 Volts
ESD Protection: +/- 10 kV
Overload Protection: +/- 30 Volts
Short Circuit: Indefinite
RS232 Output Levels: +/- 7.9 Volts (unloaded, typical)
Environmental
Operating Temperature: 0o C to 70o C
Storage Temperature: -25o C to 85o C
Size (inches): 3.25 x 2.37 x 1.08
Mounting (inches) 0.5 tabs, 3/16 diameter mounting holes
PCB Encapsulation: RTV Silicon Compound
Microscan Systems, Inc.
69
Page 70

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Appendix B – DeviceNet Template
Class InstanceAttribute Default Setting Unit Comments
Microscan Systems, Inc.
70
Page 71

DN120 DeviceNet Gateway User’s Manual
Appendix C – ASCII Character Codes
Non-Printable Characters Printable Characters
Hex Dec Char Name Kybd Hex Dec Char Hex Dec Char Hex Dec Char
0x00 0 NUL Null Ctrl @ 0x20 32 Space 0x40 64 @ 0x60 96 `
0x01 1 SOH Start of heading Ctrl A 0x21 33 ! 0x41 65 A 0x61 97 a
0x02 2 STX Start of text Ctrl B 0x22 34 " 0x42 66 B 0x62 98 b
0x03 3 ETX End of text Ctrl C 0x23 35 # 0x43 67 C 0x63 99 c
0x04 4 EOT End of transmit Ctrl D 0x24 36 $ 0x44 68 D 0x64 100 d
0x05 5 ENQ Enquiry Ctrl E 0x25 37 % 0x45 69 E 0x65 101 e
0x06 6 ACK Acknowledge Ctrl F 0x26 38 & 0x46 70 F 0x66 102 f
0x07 7 BEL Bell Ctrl G 0x27 39 ' 0x47 71 G 0x67 103 g
0x08 8 BS Backspace Ctrl H 0x28 40 ( 0x48 72 H 0x68 104 h
0x09 9 HT Horizontal tab Ctrl I 0x29 41 ) 0x49 73 I 0x69 105 i
0x0A 10 LF Line feed Ctrl J 0x2A 42 * 0x4A 74 J 0x6A 106 j
0x0B 11 VT Vertical tab Ctrl K 0x2B 43 + 0x4B 75 K 0x6B 107 k
0x0C 12 FF Form feed Ctrl L 0x2C 44 , 0x4C 76 L 0x6C 108 l
0x0D 13 CR Carriage return Ctrl M 0x2D 45 - 0x4D 77 M 0x6D 109 m
0x0E 14 SO Shift out Ctrl N 0x2E 46 . 0x4E 78 N 0x6E 110 n
0x0F 15 SI Shift in Ctrl O 0x2F 47 / 0x4F 79 O 0x6F 111 o
0x10 16 DLE Data line escape Ctrl P 0x30 48 0 0x50 80 P 0x70 112 p
0x11 17 DC1 Device control 1 Ctrl Q 0x31 49 1 0x51 81 Q 0x71 113 q
0x12 18 DC2 Device control 2 Ctrl R 0x32 50 2 0x52 82 R 0x72 114 r
0x13 19 DC3 Device control 3 Ctrl S 0x33 51 3 0x53 83 S 0x73 115 s
0x14 20 DC4 Device control 4 Ctrl T 0x34 52 4 0x54 84 T 0x74 116 t
0x15 21 NAK Negative acknowledge Ctrl U 0x35 53 5 0x55 85 U 0x75 117 u
0x16 22 SYN Synchronous idle Ctrl V 0x36 53 6 0x56 86 V 0x76 118 v
0x17 23 ETB End of transmit block Ctrl W 0x37 55 7 0x57 87 W 0x77 119 w
0x18 24 CAN Cancel Ctrl X 0x38 56 8 0x58 88 X 0x78 120 x
0x19 25 EM End of medium Ctrl Y 0x39 57 9 0x59 89 Y 0x79 121 y
0x1A 26 SUB Substitute Ctrl Z 0x3A 58 : 0x5A 90 Z 0x7A 122 z
0x1B 27 ESC Escape Ctrl [ 0x3B 59 ; 0x5B 91 [ 0x7B 123 {
0x1C 28 FS File separator Ctrl \ 0x3C 60 < 0x5C 92 \ 0x7C 124 |
0x1D 29 GS Group separator Ctrl ] 0x3D 61 = 0x5D 93 ] 0x7D 125 }
0x1E 30 RS Record separator Ctrl ^ 0x3E 62 > 0x5E 94 ^ 0x7E 126 ~
0x1F 31 US Unit separator Ctrl _ 0x3F 63 ? 0x5F 95 _ 0x7F 127 DEL
Microscan Systems, Inc.
71
 Loading...
Loading...