Page 1

User’s Manual
VoIP FXO Gateway
Model No.: SP5052A/S, SP5054A/S
http://www.micronet.info
Page 2

Table of Contents
1. WEB CONFIGURA TION............................................................................................. 3
STEP 1. USE WEB BROSWER TO CONNECT GATEWAY ..................................................... 3
STEP 2. INPUT THE LOGIN NAME AND PASSWORD............................................................. 3
STEP 3. START TO CONFIGURE....................................................................................... 4
1.1 NETWORK INTERFACE............................................................................................ 4
1.2 SIP CONFIG.......................................................................................................... 6
1.3 SECURITY CONFIG................................................................................................. 8
1.4 LINE CONFIGURATION............................................................................................ 8
1.5 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION....................................................................................... 9
1.6 VOICE SETTING (FOR ADVANCED USER)............................................................... 10
1.7 TONE SETTING.....................................................................................................11
1.8 PHONE BOOK...................................................................................................... 12
1.9 PREFIX CONFIGURATION...................................................................................... 14
1.10 ROUTING TABLE .................................................................................................. 16
1.11 FXO PASSWORD................................................................................................. 18
1.12 IP PACKET TOS................................................................................................... 18
1.13 PASSWORD ......................................................................................................... 19
1.14 ROM UPGRADE .................................................................................................. 20
1.15 FLASH CLEAN...................................................................................................... 20
1.16 COMMIT DATA...................................................................................................... 21
1.17 REBOOT SYSTEM................................................................................................. 21
2. COMMAND LISTS..................................................................................................... 22
2.1 [HELP]................................................................................................................. 25
2.2 [QUIT] ................................................................................................................. 26
2.3 [DEBUG].............................................................................................................. 26
2.4 [REBOOT]............................................................................................................ 27
2.5 [FLASH]............................................................................................................... 27
2.6 [COMMIT]............................................................................................................. 27
2.7 [IFADDR].............................................................................................................. 28
2.8 [TIME] ................................................................................................................. 29
2.9 [PING] ................................................................................................................. 29
2.10 [SYSCONF].......................................................................................................... 30
2.11 [SIP].................................................................................................................... 32
2.12 [SECURITY].......................................................................................................... 33
1
Page 3

2.13
[LINE].................................................................................................................. 34
2.14 [ROUTE] .............................................................................................................. 35
2.15 [PREFIX].............................................................................................................. 37
2.16 [PAUSE]............................................................................................................... 38
2.17 [PBOOK].............................................................................................................. 39
2.18 [VOICE] ............................................................................................................... 41
2.19 [TONE] ................................................................................................................ 44
2.20 [FXOPWD]............................................................................................................ 44
2.21 [RECORD]............................................................................................................ 45
2.22 [TOS]................................................................................................................... 53
2.23 [PT]..................................................................................................................... 53
2.24 [ROM].................................................................................................................. 54
2.25 [PASSWD]............................................................................................................ 55
2.26 [AUTH]................................................................................................................. 56
2.27 [SETMAC] ............................................................................................................ 56
2
Page 4
1. Web configuration
The initial version for HTTPD web management interface provides user to
configure easily rather than command operating method through RS-232 /
TELNET.
The configuration function and step is similar with the way through
command line. Basically this version is not the finalized version for web
interface. Please refer to the manual for more information. Below provide a
simple user guide for user to configure via web interface. Next version for
HTTPD web management will not like the command format, but friendly
interface.
Step 1. Use Web Broswer to Connect Gateway
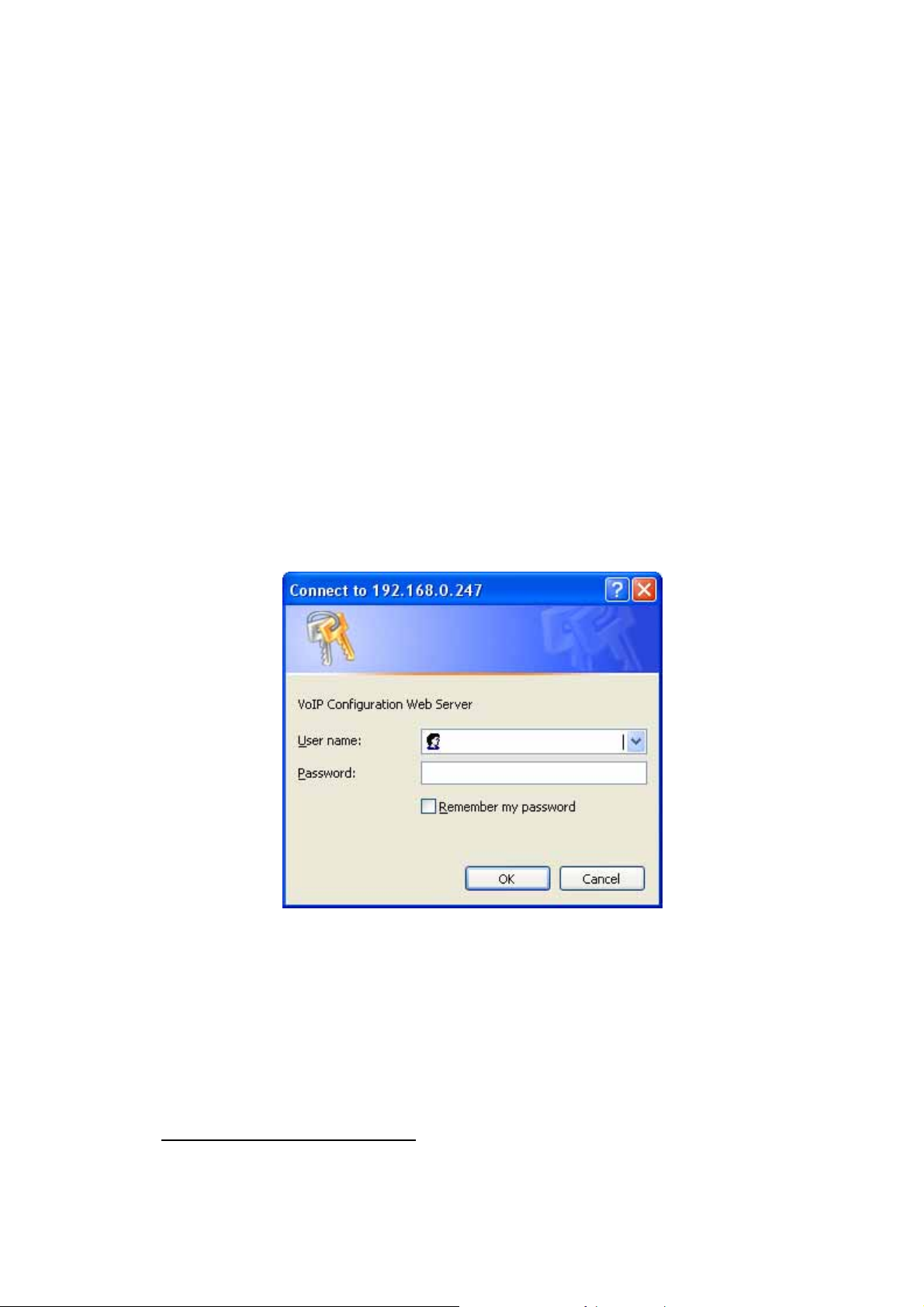
Step 2. Input the login name and password
Login name: root / administrator
Password: None (just press Enter in default value)
The web interface main screen
3
Page 5
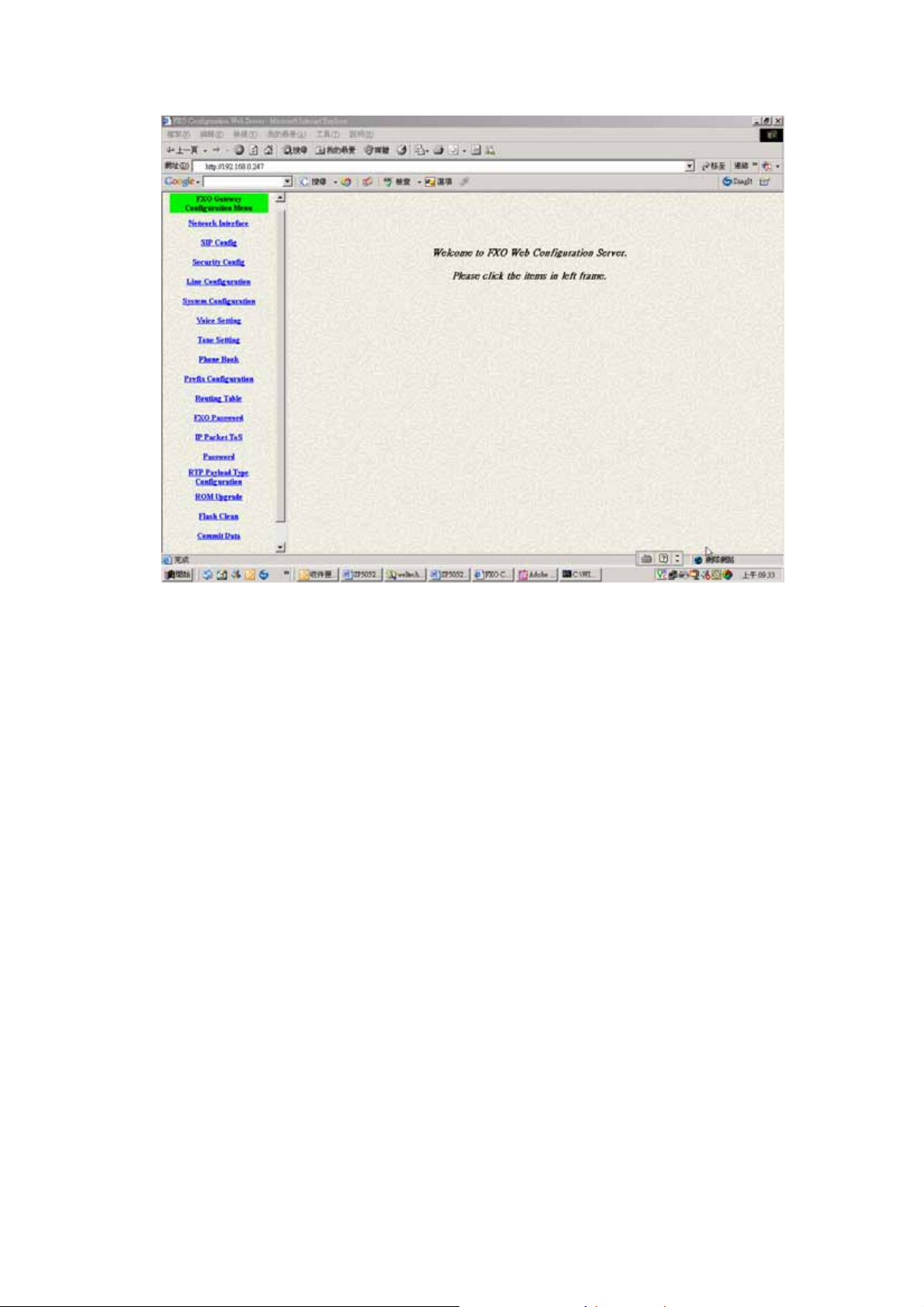
Step 3. Start to Configure
Most of all commands displayed in console / telnet are transfer to web
interface. The most important commands are Network Interface, SIP Config
and Reboot System. The method is as the same as command mode.
1.1 Network Interface
Users have to configure the Network configurations in this page. This
gateway will be work while it is connecting with the internet network. Please
get more info from the following descriptions. (See figure 3.1)
4
Page 6

Parameter Description:
z IP Address: Define the ip address for your networking if it is the fixed
ip. Please get this info from your ISP.
z Subnet Mask: Define the mask address for your networking. Please
get this info from your ISP.
z Default Routing Gateway: Define the default gateway for your
networking. Please get this info from your ISP.
z IP Mode: To configure the fixed or dynamic ip address for this unit.
Please configure to PPPoE if the ADSL is using the PPPoE type.
z HTTP Port: To configure the HTTP port for access this unit from the
remote side.
z DNS primary: To configure the first ip address for the DNS server.
z DNS secondary: To configure the second ip address for the DNS
server.
z SNTP: Enable the SNTP server registering function if user wants to
get the correct time from the Command Line Interface.
z SNTP Server Address: Enter the correct ip address of the SNTP
server or get the incorrect time from the Command Line Interface.
z GMT: Configuring the time area for the time display in the Command
Line Interface.
z PPPoE User Name: To configure the user name for the PPPoE
connection.
z PPPoE Password: To configure the password for the PPPoE
5
Page 7
connection.
z PPPoE IP Address: In the PPPoE mode, this table will show the ip
address that this unit gets from the ISP.
z PPPoE Destination: In the PPPoE mode, this table will show the
default gateway address that this unit gets from the ISP.
z PPPoE DNS primary: In the PPPoE mode, this table will show the
DNS ip address that this unit gets from the ISP.
z After Remote Host Disconnection: This unit will reboot and
re-connect to the ISP
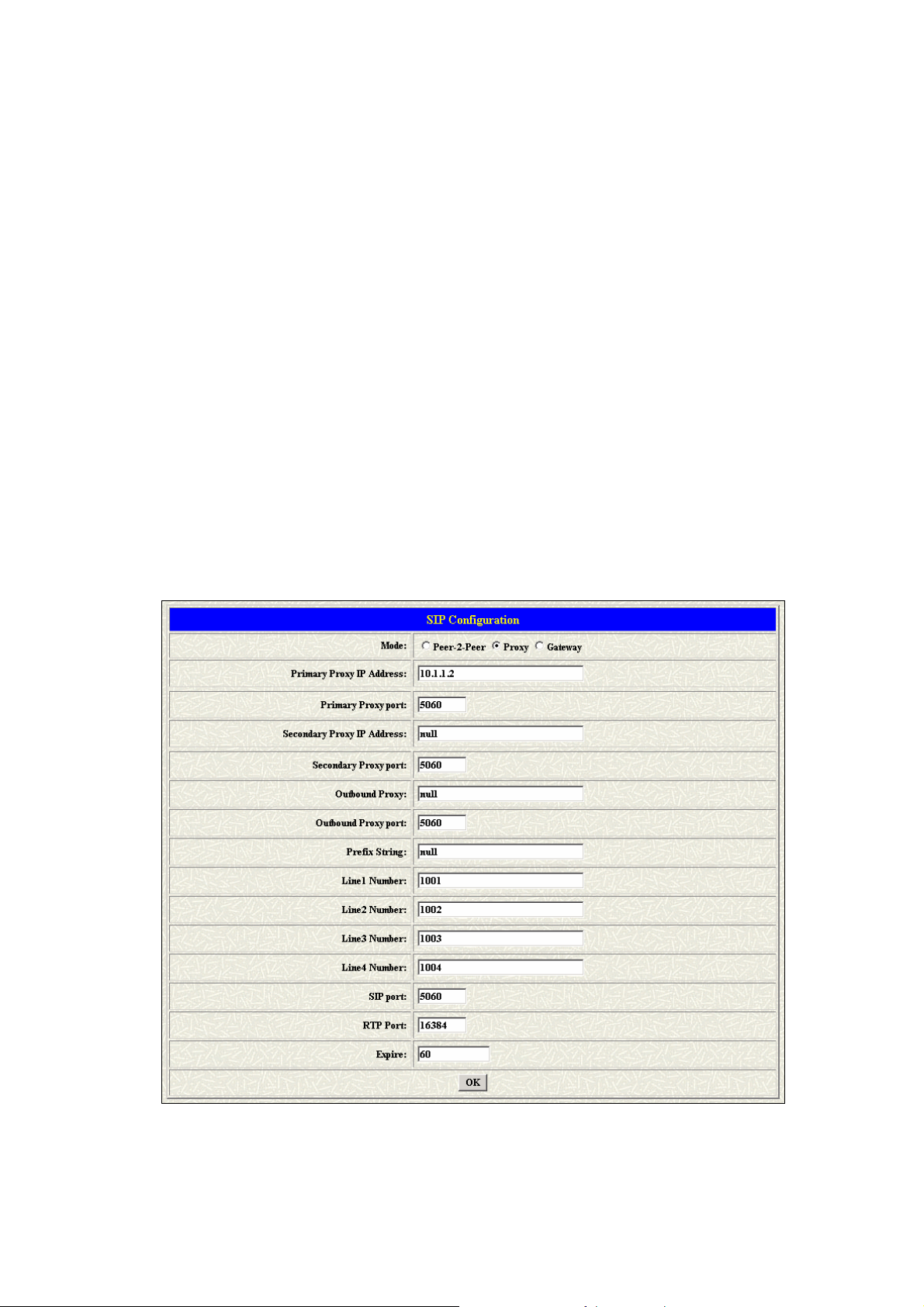
1.2 SIP Config
This WEB page will help user to configure the information about the dial
mode, GK information and some TCP/IP port for the communication.
Please get more info about this configuration from the below detail
descriptions. (See figure 3.5)
Parameter Description:
z Mode – Pick up the calling mode for this gateway.
6
Page 8

z Peer-2-Peer: It only supports the peer-to-peer mode and
users have to define the phone book for this mode.
z Proxy: Users have to register on the Proxy if users picked up
this option.
z Gateway: Only user line1 has to register on the Proxy, then
the line1, line2, line3 and line4 join in the same hunting group
automatically.
z Primary Proxy IP Address: Enter the proxy ip if users pick up the
proxy mode.
z Primary Proxy port: Set Proxy port for SP5050 series to send
message, default value is 5060, if there is no special request of
Proxy server, please don’t change this value.
z Secondary Proxy IP Address: Set secondary Proxy IP Address or
URL address (Domain Name Server must be configured. Please
refer to Network Interface). When SP5050 series fail to register to
primary Proxy, it will try to register to secondary Proxy, when it fails
again, it will retry to register to Primary Proxy.
z Secondary Proxy port: Set the secondary proxy port for every SIP
message, default value is 5060.
z Outbound Proxy: This version could support the outbound proxy.
Users could define the ip address or domain name in this table.
z Outbound Proxy port: Set outbound Proxy port for SP5050 series to
send message, default value is 5060, if there is no special request of
Proxy server, please don’t change this value.
z Prefix String: Users could define this if the registration name was a
phonetic alphabet not the numbers.
z Line 1 Number: The phone number of the Line 1.
z Line 2 Number: The phone number of the Line 2.
z Line 3 Number: The phone number of the Line 3.
z Line 4 Number: The phone number of the Line 4.
z SIP port: Users could change the sip port of this unit for the
registration.
z RTP port: Users could change the beginning RTP ports in this table.
z Expire: Users could change the expire time for the register message
sending.
7
Page 9
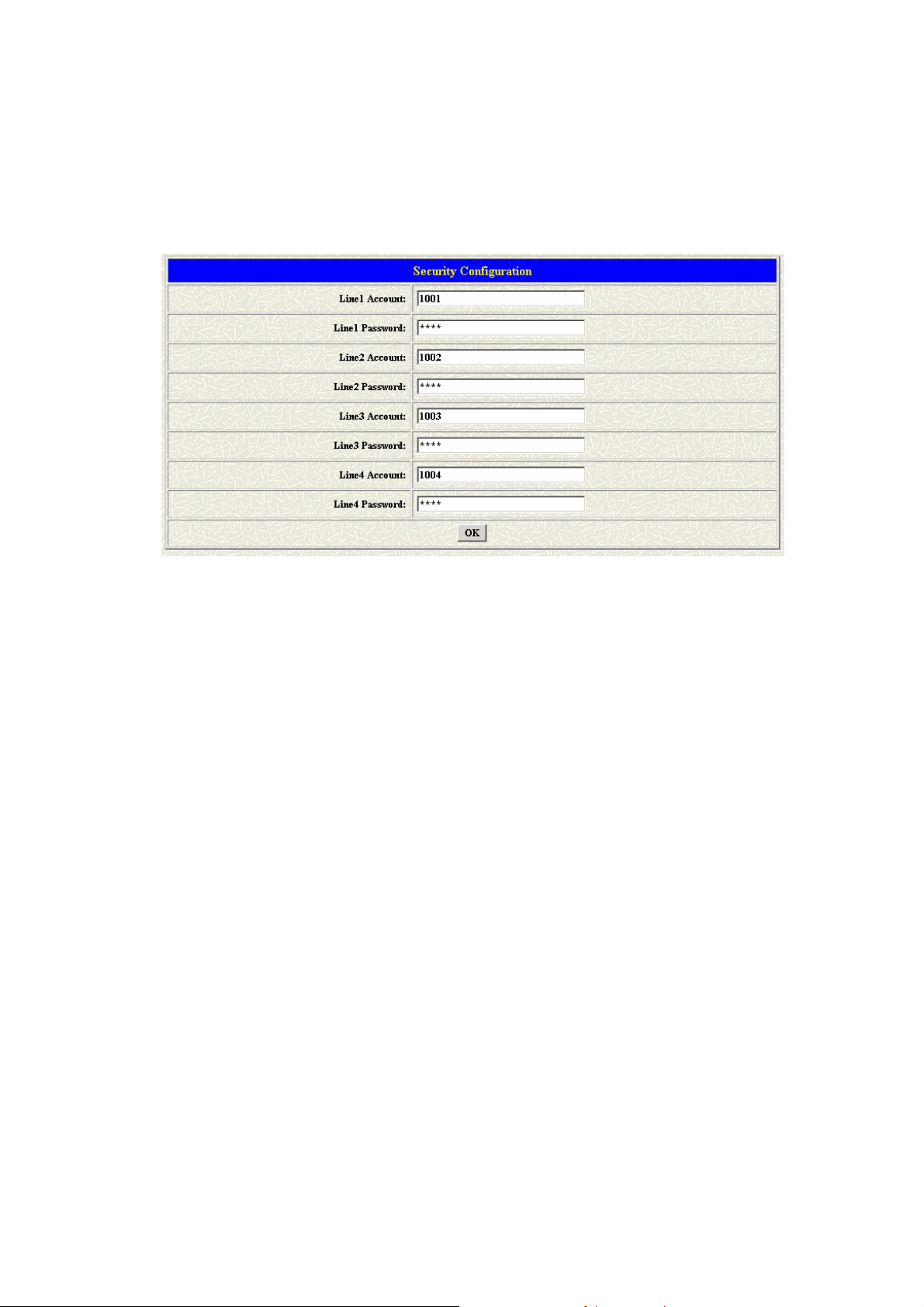
1.3 Security Config
Some proxy will include the security policy. The endpoint may need the
user account and password for the registration. If these are necessary,
users could put the correct account and password in the correct table.
Parameter Description:
z Line 1 Account: The user name for the line 1 account.
z Line 1 Password: The password for the line 1 account.
z Line 2 Account: The user name for the line 2 account.
z Line 2 Password: The password for the line 2 account.
z Line 3 Account: The user name for the line 3 account.
z Line 3 Password: The password for the line 3 account.
z Line 4 Account: The user name for the line 4 account.
z Line 4 Password: The password for the line 4 account.
Note: These configuration settings are provided by Service Provider.
1.4 Line Configuration
The Line configuration will show the status of the registrations and the ports.
It includes the hunt group, hotline, and no answer forward configuration.
Press the Line configuration button to enter configuration table.
8
Page 10
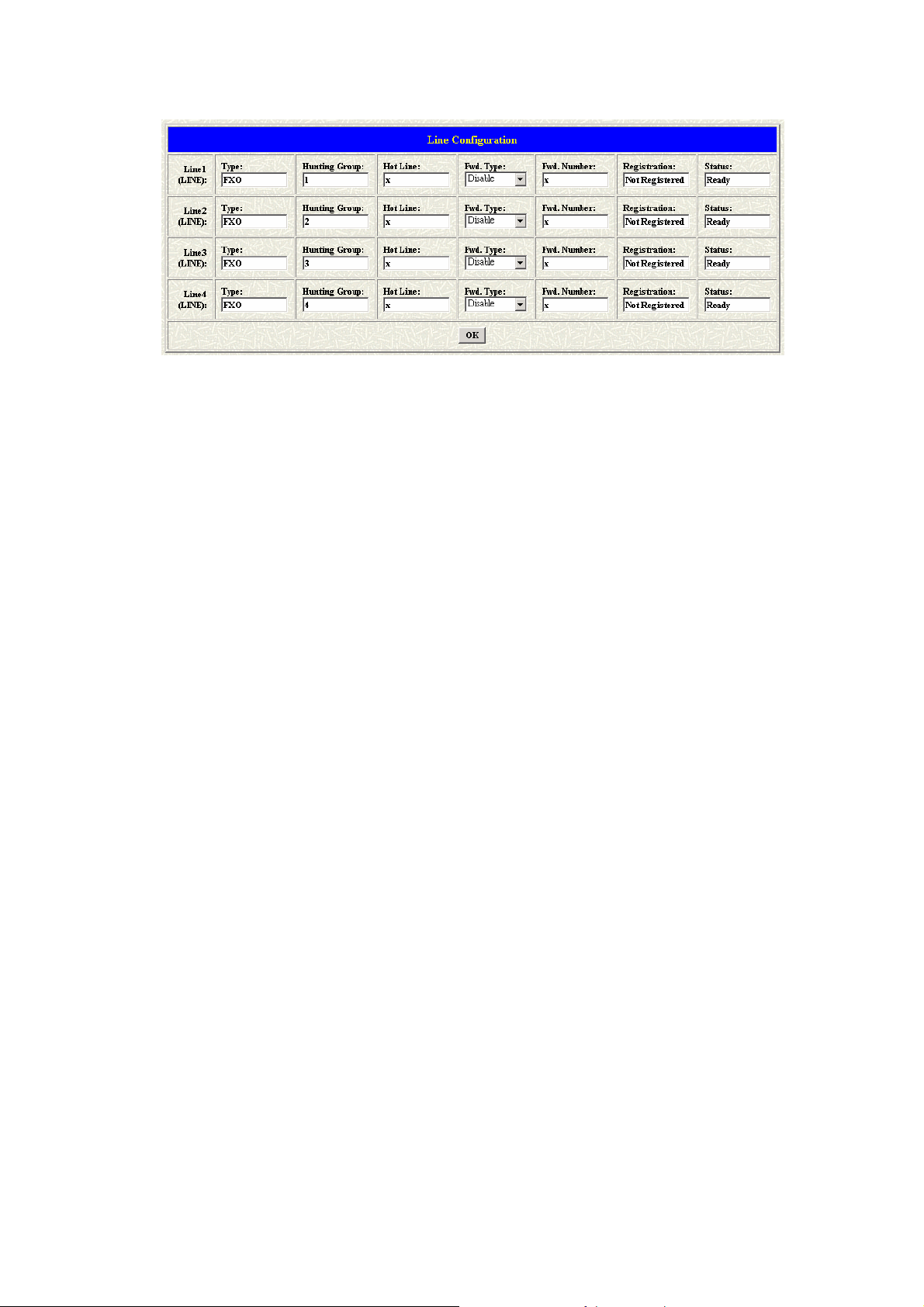
Parameter Description:
z Type: Show the type of this port. There are only one types of this
gateway. (SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S will show the FXS and FXO type.
It can not be changed.)
z Hunting Group: Define the group number of this port. When the port
is busy, the call could be transferred to another port in the same
group.
z Hotline: Enable or Disable the hotline mode. The hotline mode will
be enabled if you enter the hotline number. The default setting is
disabled.
z Fwd. Type: Forward the call to IP. Forward type: 0: disable, 1:
uncondition, 2:busy
z Fwd. Number: destination number to which the call is forwarded
z Registration: To show the gateway registered on the Proxy Server or
not.
z Status: To show the port is busy or ready.
1.5 System Configuration
There are some parameters in the system configurations, please get more
detail as following.
9
Page 11

Parameter Description:
z Keypad Type: Select different DTMF Keypad Type
z In-Band: The DTMF signal sending by RTP.
z RFC2833: RTP Payload for DTMF Digits
z INFO: The DTMF signal sending by SIP INFO.
z Inter Digit Time: Set the DTMF inter-digit time (second). Parameter
defines the maximum amount of time between digits. If a digit is not
followed by another within this time limit, then digit collection is
terminated.
z Ring Time: It for the ring detection from the PSTN. The ring detection
will be failed if users configure it too long.
z Ring Before Answer: Decide how many rings the gateway will pick
up the call from FXO ports.
z Flash time: Set the detective flash range in ms.
z End of Dial: Press # key after numbers dialed.
1.6 Voice Setting (For Advanced User)
Users could configure the voice codec or gain level in this web page.
Please get more detail info from the following description.
10
Page 12
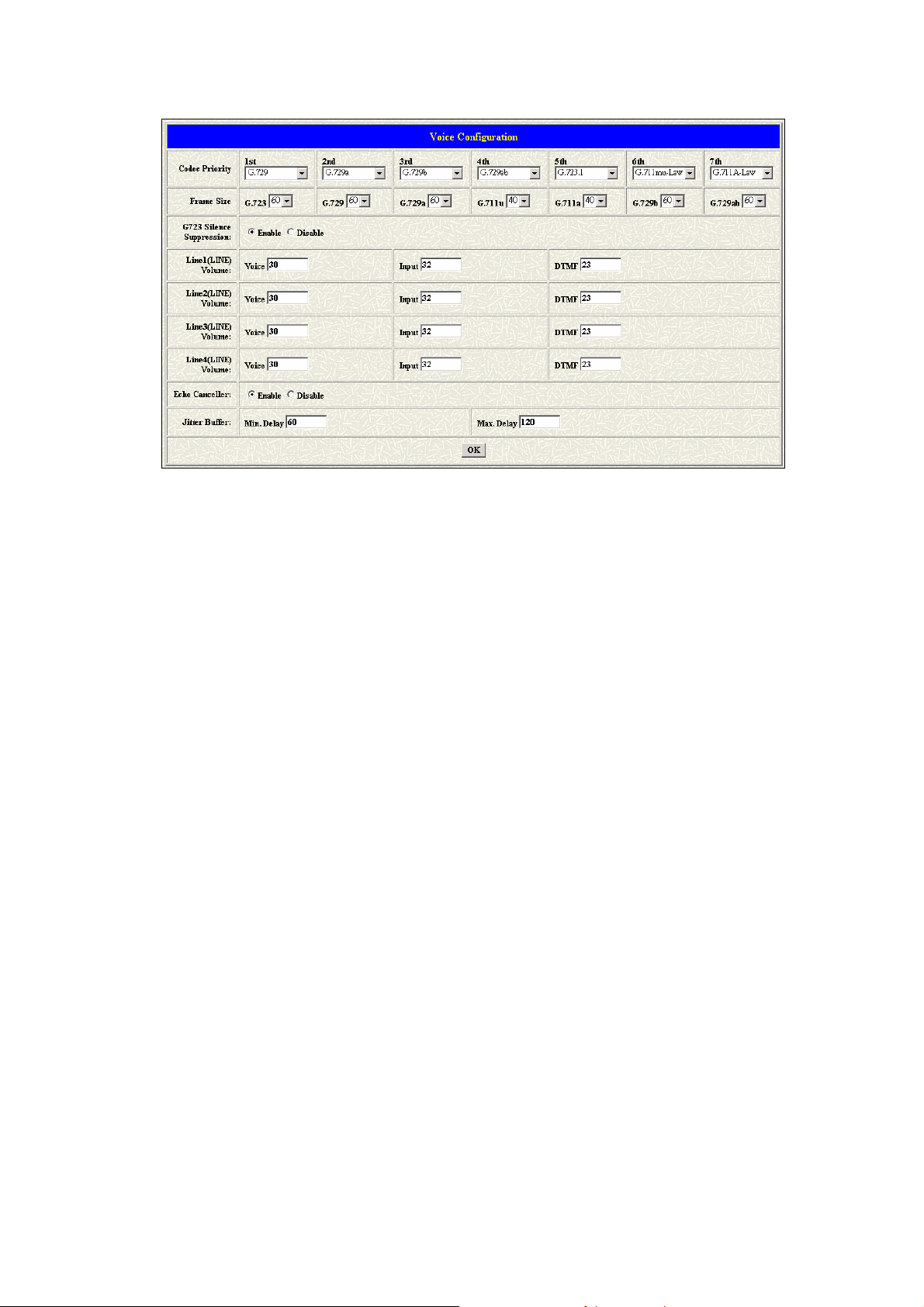
Parameter Description:
z Codec Priority: This could help users configure the codec priority for
using.
z Frame Size: To configure the packet size for the codec that users
want.
z G.723 Silence Suppression: To enable the VAD and CNG function
for the G.723 codec.
z Volume: Adjust the volume in “Voice” (sending out); “Input”
(receiving); “ DTMF” (DTMF sending out). Please Noted the value is
limited.
z Echo Cancel: To enable or disable the echo cancellation function.
z Jitter Buffer: TO configure the Min or Max delay for the Jitter Buffer.
The min is from 0ms and the max is 150ms.
Note: A large jitter buffer causes increase in the delay and decreases the
packet loss. A small jitter buffer decreases the delay but increases the
packet loss. The size of the jitter buffer depends on the condition of the
network, which varies with time. Typically the packet loss should be less
than 10% for a good quality of speech.
1.7 Tone Setting
The Tone Setting is for the Tone detecting. The call will be dropped if the
pattern of the tone from PSTN side is as same as the pattern in the
disconnect tone table. The same result for the Ring Back Tone. User could
11
Page 13
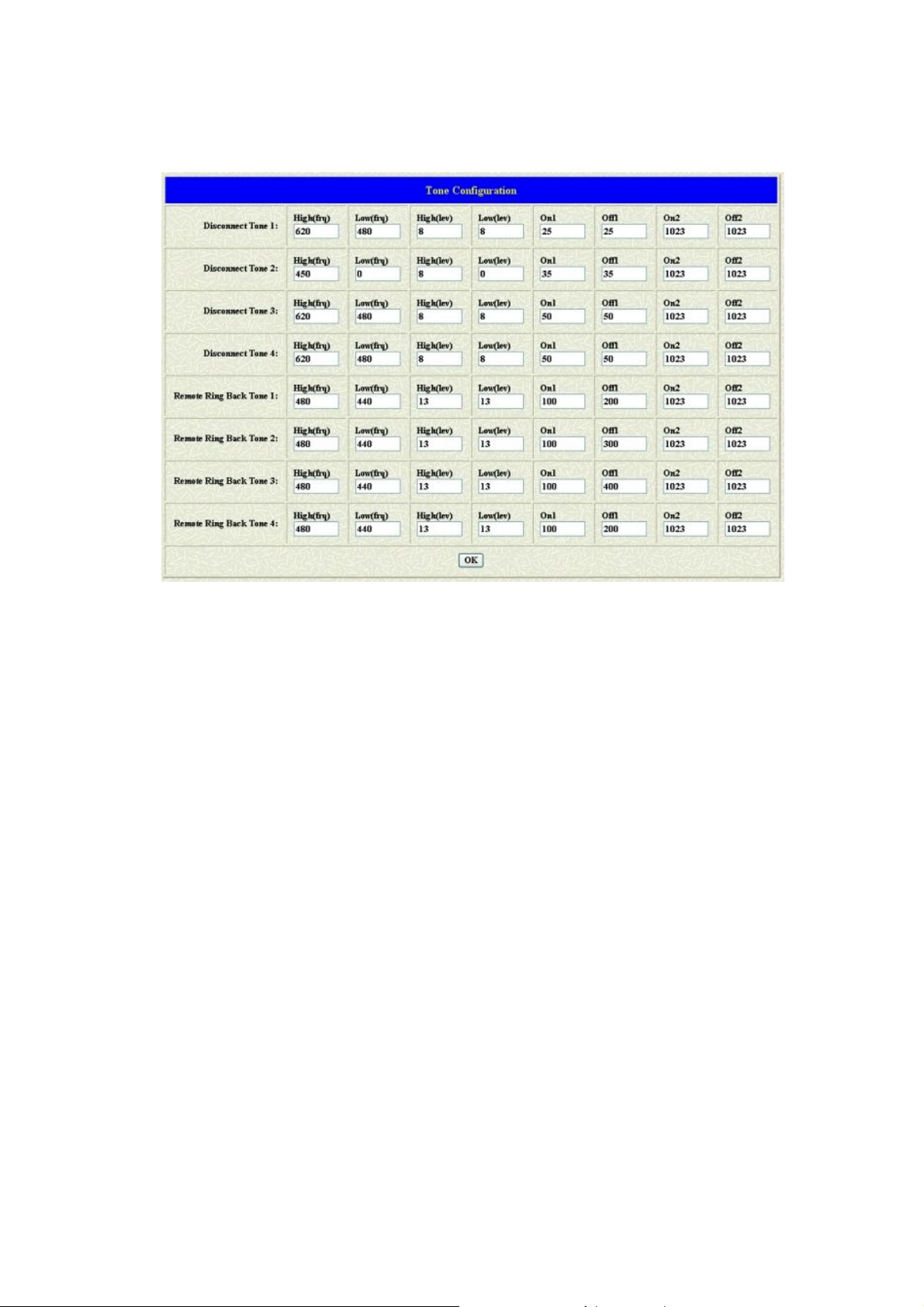
define the pattern of the disconnect tone if the disconnect tone from PSTN
side is not the standard tone.
Parameter Description:
z Disconnect Tone 1 – 4: To configure the frequency, level gain and
on/off time for the busy tone from PSTN or PABX side. The busy
tone supports 4 tables.
z Remote Ring Back Tone: To configure the frequency, level gain and
on/off time for the ring tone from PSTN side. The gateway won’t
connect the calls if the ring tone value is incorrect.
1.8 Phone Book
The Phone Book configuration is only support the gateway in Peer-to-Peer
mode. Please refer the chapter 2 about the Peer-to-Peer mode.
12
Page 14

Parameter Description:
z Index: The list number of the Phone Book.
z Name: The name for this contact number.
z E164: The dialing number for the calling side.
z IP Address: The destination IP address for this phone number.
z Port: The call signal port of the destination.
z Drop: Support the drop function. Enable is for enable this drop
function; Disable is for disable this drop function. The Drop Prefix will
drop the E164 number, which you had configured in the E164 table.
z Insert: Support the insert digits function.
Note:
z It will be the drop function if user enable the Drop Prefix function
and put nothing into the Insert Prefix table.
z It will be the insert function if user disable the Drop Prefix function
and put the digits into the Insert Prefix table.
z It will be the replace function if user enable the Drop Prefix
function and put the digits into the Insert Prefix table.
13
Page 15
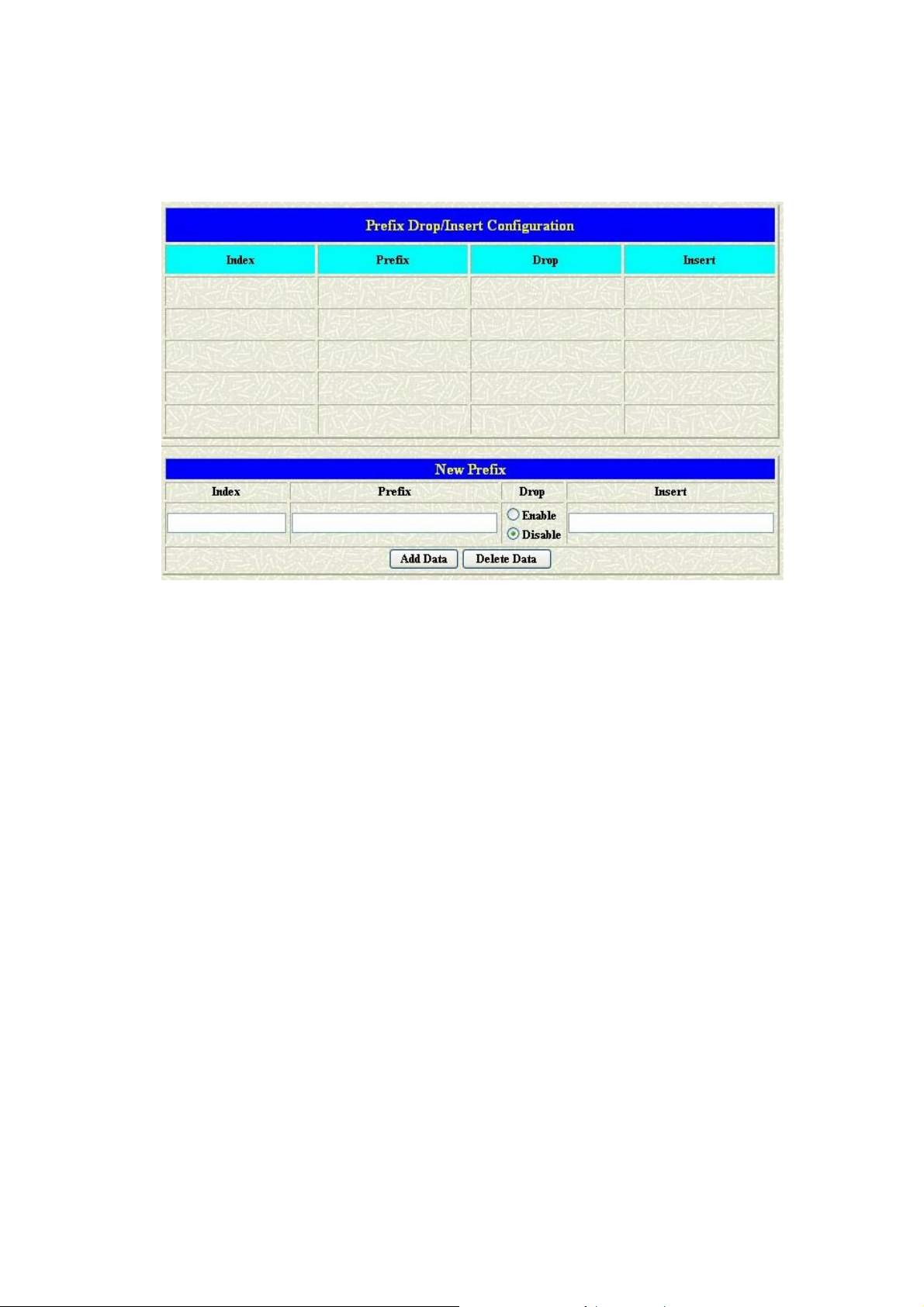
1.9 Prefix Configuration
The Prefix function is using the drop and inserts function.
Parameter Description:
z Index: The list number of the Phone Book
z Prefix: The prefix number of the whole num bers that could be into
this gateway
z Drop: The drop function. Enable this function by the Enable button;
Disable this function by the Disable button
z Insert: The insert function. Users could enter the digits that you want
to insert in this number
z Add Data: Press this button if users fill the entire information table
above
z Delete Date: If users want to delete the record from the table, enter
the index number first and press this button. The record will be
deleted
This function is just like the Phone Book configuration. But it will make the
drop and insert function in the GK routed mode. All the numbers into this
gateway will check out the prefix table first and find out the destination in
the Routing Table.
There is an example about the configuration, please follow up these steps.
14
Page 16
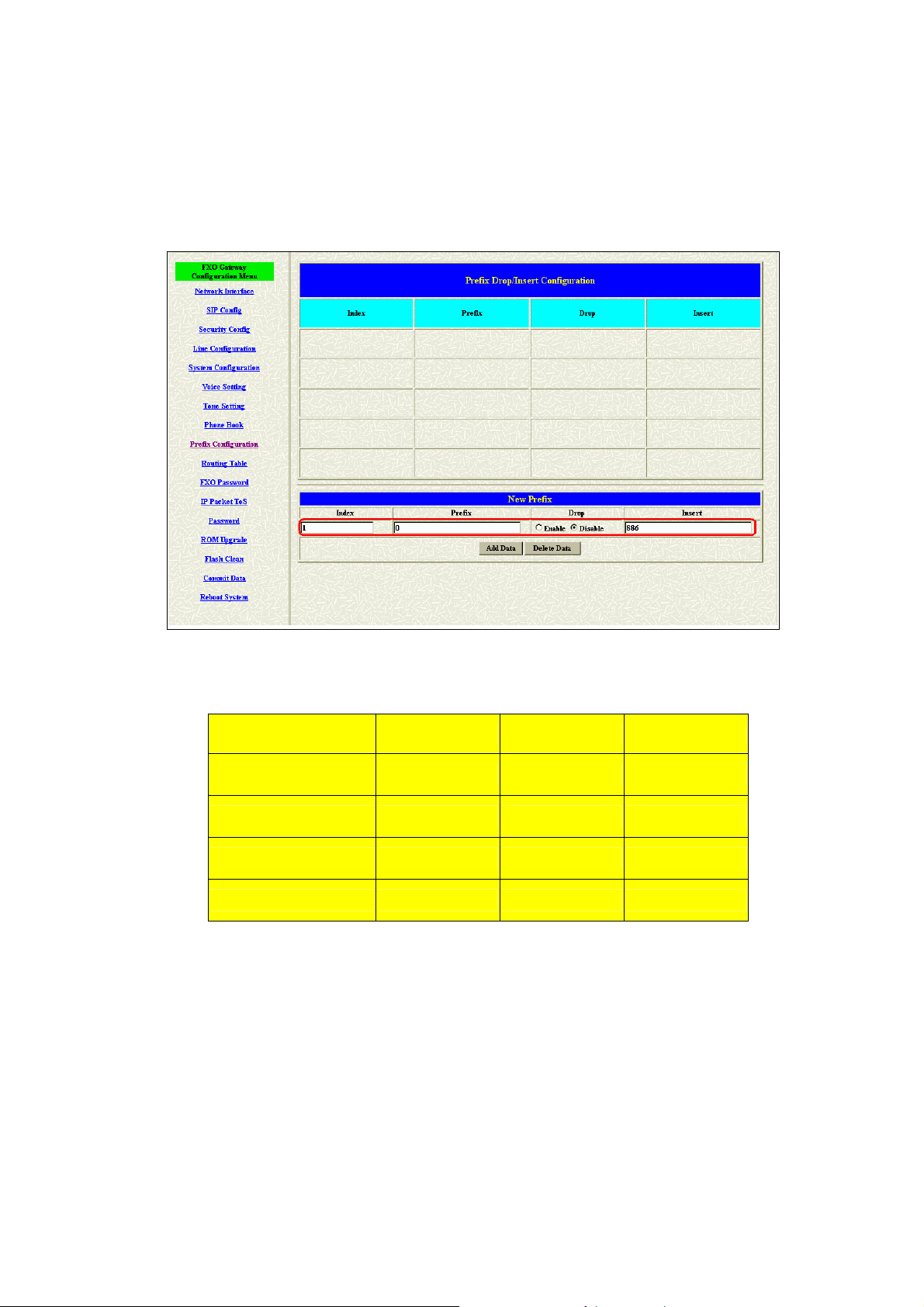
1. Press the Prefix Configuration button to enter the configuration table.
2. Enter the index number. Put the prefix numbers you will dial in the
prefix table, enable (disable) the drop function and enter the numbers
you want to insert.
The usage is as same as the drop, insert function of the Phone Book.
Input (Prefix) Drop Insert Output
100 Disable X 100
200 Disable 0 0200
300 Enable X X
400 Enable 500 500
3. Press the Prefix Configuration button to reload the configuration table
15
Page 17
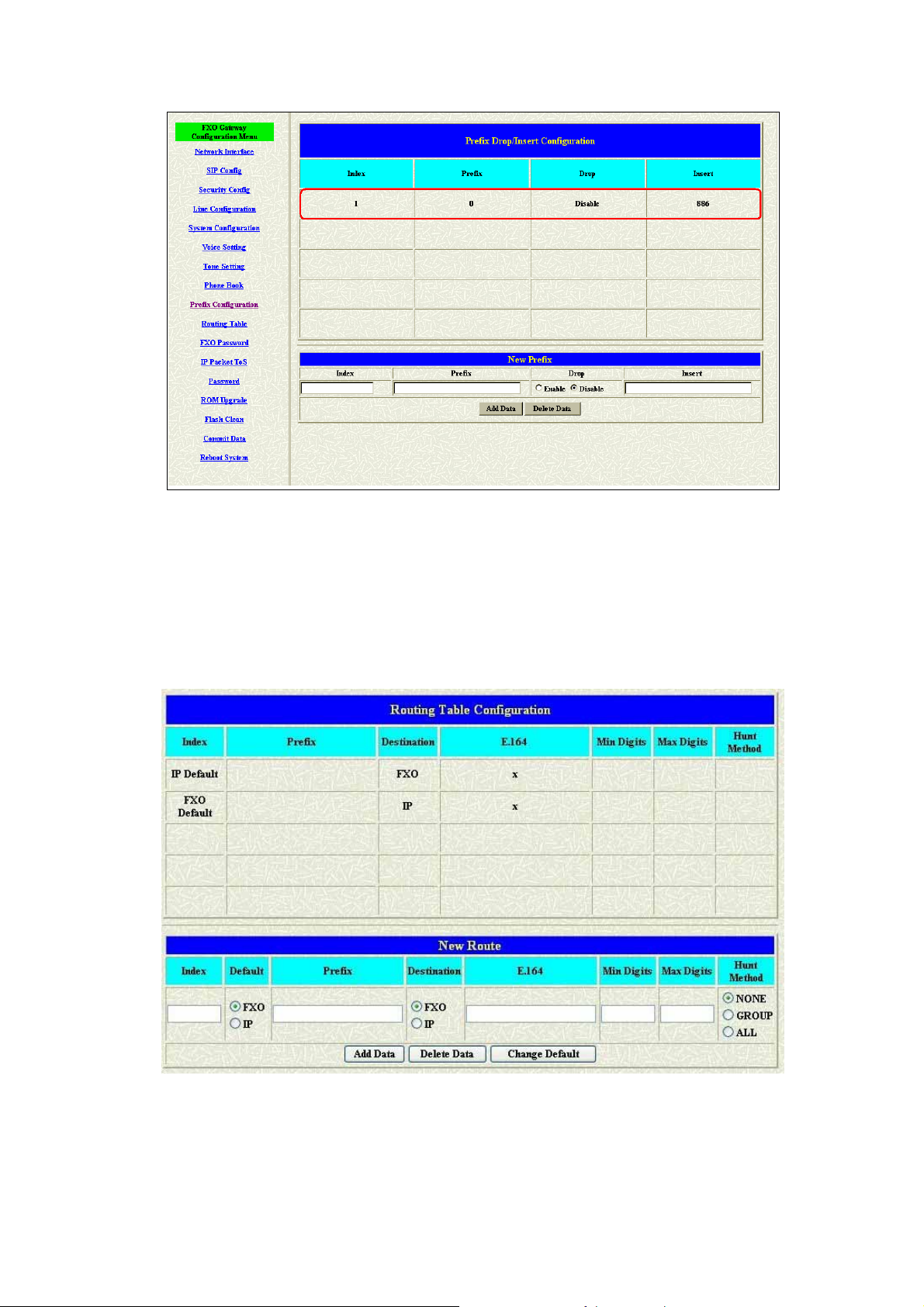
4. Please Commit it and Reboot the system if the configuration is
finished.
1.10 Routing Table
Parameter Description:
z Index: Define the number of this data.
z Prefix: Define the number you dial. You could just define the first
16
Page 18
digit of the numbers
z Destination: Define the destination of this rule. There are three
directions of the destination.
z E164: Define a right E164 number of the destination you want.
z Min Digits: The minima digits you dial.
z Max Digits: The maxima digits you dial.
z Hunt Method – Enable the Hunt Group function and pick up the hunt
type.
z None – Disable this function
z Group – The call will search other ports to be the destination
with the same group if the origin destination is busy.
z All – The call will search other ports to be the destination with
the same type if the origin destination is busy.
The min and max digits are the range for the number you dial. For example:
The min number of digits is 1 and max number of digits is 10. The call will
follow this routing if the number I dial is between 1 and 10 digits. If I dial
over 10 digits, this call will follow the default routing.
Routing Table is a rule to define the destination of the calls you make. You
could define the rules by the number you dial or by the ports. The Routing
Table button will show you the configuration table.
In fact, there are two directions of the incoming calls (from IP or FXO side).
The explanation of the default routing is as below:
Incoming calls
location
Destination Explanation
The destination will be the FXO port
IP (Default) FXO
when the calls from the IP side without
any define rules.
The destination will be the IP side when
FXO (Default) IP
the calls from the FXO port without any
define rules.
The most important usage is for the one-stage-dialing function. For the
one-stage-dialing function under the Proxy mode, users have to make sure
about that the Proxy could support some kind of the function just like the
routing.
17
Page 19

1.11 FXO Password
You will get the IVR if you make calls from PSTN side. The IVR will ask you
the password you set, and you could make other calls to IP side if the
password you type is correct. Please press the FXO Password button to
configure the password
Note:
This function is only for the calls from the PSTN side. It’s not ready for the
IP side as so far.
1.12 IP Packet ToS
The Type of Service needs worked with the network router supported. The
router will check all the packets if it supports the TOS function. There is a
field in the packet for the TOS value. This WEB is for users to configure
18
Page 20

these values to make the packets with the correct values for the TOS
service from the gateway.
According to the RFC 1349 document, the TOS value as following:
1000 – minimize delay
0100 – maximize throughput
0010 – maximize reliability
0001 – minimize monetary cost
0000 – normal service
These values are the Binary format. Please change to the Decimal and put
these values in to the correct table.
1.13 Password
There are two accounts for login to access or change the configurations.
One is “root”, another is “administrator”. Users could define the password
for these two login account. The account “root” could make all the
configurations back to the default setting, but the account “administrator”
couldn’t. This is the difference between these two accounts.
Users could define the password for the accounts in this page.
19
Page 21

1.14 ROM Upgrade
User could update the firmware just by the web configuration interface.
There are two types for the upgrading procedure. One is using the TFTP
server; another is using the FTP server.
Parameter Description:
z TFTP Server IP Address: Set TFTP server IP address
z Target File name: Set file name prepared to upgrade
z Method: Select download method as TFTP or FTP
z FTP Server IP Address: Set FTP server IP address
z FTP Login: Set FTP login name and password
z Target File Type: Select which sector of Gateways to upgrade
1.15 Flash Clean
Press CLEAN will clean all configurations of Gateways and reset to factory
default value.
The password of the account and the networking configuration couldn’t be
back to the default setting by this command.
20
Page 22

1.16 Commit Data
Press COMMIT when any configuration has been changed before reboot
1.17 Reboot System
After commit configuration, user has to REBOOT device to be able run the
configurations properly.
21
Page 23

2. Command list
Command Line user interface is provided via out-of-band console access
and telnet.
Console Access
y Launch the HyperTerminal program, then the following windows pop-up
on the screen. (START – Program files – Accessories –
Communication – HyperTerminal)
y Define a name such as ‘SP5052A’ for this new connection.
y After pressing OK button, the next window popping up is necessary to
connect choose COM Port.
22
Page 24

Note:
Make sure the gateway serial cable is connected to correct COM port
as the terminal selected, try the different port if failed.
y Configure the COM Port Properties as following:
(1) Bits per second: 9600
(2) Flow control: None
Press ‘OK’ button, and start configuring Gateway.
y Power on the gateway, the message shows while booting. About 40
seconds for complete boot-up.
23
Page 25

Telnet
Please set your PC with IP address (10.1.1.x), mask (255.255.0.0), and
default gateway (10.1.1.254). Click on START Æ RUN Æ telnet 10.1.1.3.
Then, login with username (root) and password (no password).
24
Page 26

2.1 [help]
Type help or man or ? to list all the available command.
--------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ ?
help help/man/? [command]
quit quit/exit/close
debug show debug message
reboot reboot local machine
flash clean configuration from flash rom
commit commit flash rom data
ifaddr internet address manipulation
time show current time
ping test that a remote host is reachable
sysconf System information manipulation
sip sip information manipulation
security Security information manipulation
line Line information manipulation
route Routing information manipulation
pause FXO Pause information manipulation
prefix Prefix drop/insert information manipulation
pbook Phone book information manipulation
voice Voice information manipulation
tone Setup of disconnect tone and remote ring back tone
fxopwd Setup of FXO password
record Record voice for greeting and ask pin code
tos IP Packet ToS (Type of Service)values
pt DSP payload type configuration and information
rom ROM file update
passwd Password setting information and configuration
auth Set configuration items for "administrator" user.
usage: help [command]
---------------------------------------------------------------
25
Page 27

2.2 [quit]
Type quit will quit the Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway
configuration mode. And turn back to login prompt.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ quit
Disconnecting...
login:
---------------------------------------------------------------
Note: It is recommended that type the “quit” command before you leave the
console. If so, Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway will ask
password again when next user connects to console port.
2.3 [debug]
Open debug message will show up specific information while Micronet
SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway is in operation. After executing the
debug command, it should execute command debug -open as well. One
example is demonstrated below.
Debug message information and configuration
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ debug
Debug message information and configuration
Usage:
debug [-add type1 [[type2]...]] | -open | -close | -status
-status Display the enabled debug flags.
-add Add debug flag.
-delete Remove specified debug flag.
-open Start to show debug messages.
-close Stop showing debug messages.
Example:
debug -add sip fsm
debug -add vp
debug -open
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameters Usage:
-status Display the enabled debug flags.
-add Add debug flag.
26
Page 28

- sip: sip related information
- vp : voice related information
-delete Remove specified debug flag.
-open Start to show debug messages.
-close Stop showing debug messages.
2.4 [reboot]
After commit command, type reboot to reload Micronet SP5052A/S /
SP5054A/S Gateway in new configuration.
2.5 [flash]
This command will clean the configuration stored in the flash rom and
reboot Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway in factory default
setting.
---------------------------------------------------------------
Flash memory information and configuration
Usage:
flash -clean
Note:
This command will clean the configuration stored in
the flash and reboot it.
---------------------------------------------------------------
Warning: Once users execute flash -clean, all the configurations of
Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway will be cleaned. This can only
be executed by user who log in with root.
2.6 [commit]
Save changes after configuring the Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S
Gateway.
27
Page 29

---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ commit
This may take a few seconds, please wait....
Commit to flash memory ok!
usr/config$
---------------------------------------------------------------
Note: Users should use commit to save modified value, or they will not be
activated after system reboot.
2.7 [ifaddr]
Configure and display Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway network
information.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ ifaddr
LAN information and configuration
Usage:
ifaddr [-print]|[-mode used]|[-sntp mode [server][-cmcenter ipaddress]]
ifaddr [-ip ipaddress][-mask subnetmask][-gate defaultgateway]
ifaddr [-dns index [dns server address]][-reboot on/off]
ifaddr [-id username][-pwd password][-http http port][-autodns used]
-print Display LAN information and configuration.
-ip Specify ip address.
-mask Set Internet subnet mask.
-gate Specify default gateway ip address
-mode Set ip client service(0=FIX IP, 1=DHCP, 2=PPPoE).
-sntp Set SNTP server mode and specify IP address.
-autodns Specify the way to obtain DNS Server (0:Manual/1:Auto).
-dns Specify IP address of DNS Server.
-timezone Set local timezone.
-ipsharing Specify usage of an IP sharing device and specify IP
address.
-id Connection user name for PPPoE.
-pwd Connection password for PPPoE.
-reboot Reboot after remote host disconnection.
-echo PPPoE Echo Request (0=disable, 1=enable).
Note:
28
Page 30

SNTP mode (0=no update, 1=specify server IP, 2=broadcast mode).
Example:
ifaddr -ip 210.59.163.202 -mask 255.255.255.0 -gate 210.59.163.254
ifaddr -mode 1
ifaddr -sntp 1 210.59.163.254
ifaddr -autodns 1
ifaddr -dns 1 168.95.1.1
ifaddr -ipsharing 1 210.59.163.254
---------------------------------------------------------------
2.8 [time]
When SNTP function of Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway is
enabled and SNTP server can be found as well, type time command to
show current network time.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ time
Current time is WED JUL 14 16:00:00 2004
---------------------------------------------------------------
2.9 [ping]
Use ping to test whether a specific IP is reachable or not.
Responsed
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ ping www.yahoo.com
PING www.yahoo.com (66.94.230.46): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 66.94.230.46: icmp_seq=0. time=195. ms
64 bytes from 66.94.230.46: icmp_seq=1. time=195. ms
64 bytes from 66.94.230.46: icmp_seq=2. time=195. ms
64 bytes from 66.94.230.46: icmp_seq=3. time=195. ms
----www.yahoo.com PING Statistics----
4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip (ms) min/avg/max = 195/195/195
29
Page 31

---------------------------------------------------------------
No Responsed
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ ping 192.168.0.20
PING 192.168.0.20: 56 data bytes
no answer from 192.168.0.20
---------------------------------------------------------------
2.10 [sysconf]
This command displays the system information and configuration.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ sysconf
sysconf [-idtime digit][-keypad dtmf]
[-rba digit][-eod digit][-bl digit]
[-localrbt digit]
[-ring on_time off_time]
sysconf -print
-print Display system overall information and configuration.
-idtime Inter-Digits time.(1~10 sec)
-keypad Select DTMF type: 0=In-band,
1=RFC2833.
-callerid CallerId Type .(Caller type, 0: none, 1: FSK, 2: ETSI)
- dtrmfstart DTMF CallerID Start Symbol
-dtmaend DTMF CallerID End Symbol
-ring The ring time for ring detection.(Uint:ms)
-delay The FXO dial DTMF delay.(1~9)(Uint:s)
-rba the number of ring times before answer.(1~5)
-eod End of dial.(Enable:1 / Disable:0)
-connect Auto connect time.(0=Disable, for 1~65535 sec)
-onhook Auto ON-HOOK if detect reverse.(Enable:1 / Disable:0)
-billing Billing.(0=none, 1=reverse, 2=billing tone)
-Int
General IVR in FXO.(Enable:1 / Disable:0)
-silence Silence Detection.(0=Disable, 1=Enable)
-ivr General IVR in FXO.(Enable:1 / Disable:0)
30
Page 32

-flashtime Flash time setting.(1-200, 1->10ms)
Example: sysconf -ring 500
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Usages:
-idtime set the duration (in second) of two pressed digits in dial mode
as timed out. If after the duration user hasn’t pressed next
number, it will dial out all number pressed. (1-10 seconds)
-keypad keypad type when relay DTMF signal.
0 Æ In-Band
1 Æ RFC2833.
1. number (instead of Line number of FXO Line)+ PSTN
number to make a call to PSTN side connected with FXO
Line.
2. After gateway-prefix-drop function is enabled, user must
remember to re-configure line number of FXS Line,
because line number of FXS Line must remove prefix
number. For example, origin line number of FXS line is
1001, prefix is 100, since prefix number will be drop, once
gateway has incoming call 1001, after drop gateway prefix
100, it will search line number “1”. So line number must be
set as “1”.
-callerid Support FSK and ETSI caller ID function. After the first ring
destination site, device will send line number as caller ID to
called site. It only supports on Hotline mode.
-ring ring time for ring detection (in ms). When Gateway has
incoming call from PSTN side to FXO port, Gateway will
determine it is a ring but not noise only if it is longer than this
ring time.
Note: In Taiwan, the ring time of PSTN usually is 1000ms, so if user set
ring time longer that 1000ms, FXO port may not be able to pick up the call
from PSTN side.
-delay When FXO port has an incoming call from IP side and signal
connection is established, it will wait the dial tone from PSTN
or PBX. But sometimes the dial tone from PBX is too late so
some errors will occur. Now user can use this command to
31
Page 33

change the time waiting for dial tone.
-rba set how many rings the gateway will answer the call
(1 ~ 5 rings)
-eod End of dial.(Enable:1 / Disable:0)
-connect The unit will send the connect message to the IP side
automatically. This function just supports the
one-stage-dialing function.
2.11 [sip]
This command is to configure SIP related parameters.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ sip
SIP stack information and configuration
Usage:
sip [-mode pxmode]
sip [-px address] [-px2 address] [-outpx address]
sip [-pxport number] [-px2port number] [-outpxport number]
[-expire t1] [-prefix prefixstring] [-line number]
sip -print
-print Display SIP stack information and configuration.
-mode Configure as Peer-to-Peer mode:0/Proxy mode:1/Gatway:2.
-px Primary Proxy server address. (IPv4 address or dns
name)
-px2 Secondary Proxy server address. (IPv4 address or dns
name)
-pxport Proxy server port. (the port of proxy)
-px2port Secondary Proxy server port. (the port of Secondary
proxy)
-outpx OutBound Proxy server address. (IPv4 address or dns
name)
-outpxport OutBound Proxy server port. (the port of OutBound
proxy)
-prefix Specify prefix string, use it when UserID contains
Alphabets (if UserID uses numerals, specify as null)
-line1 Line 1 is E.164 number of L1.
32
Page 34

-line2 Line 2 is E.164 number of L2.
-line3 Line 3 is E.164 number of L3.
-line4 Line 4 is E.164 number of L4.
-pbsearch Search phone book 0: off/1: on.
-expire The relative time after which the message expires (0 ~
(2^31-1))
-port SIP local UDP port number (1~65534), Default: 5060
-rtp RTP port number (1~65534), Default: 16384
-lmedia Late Media 0:off/1:on.
-cidchange CID Change in From Header 0:off/1:on.
-busy busy response message, Default: 486
Example:
sip -px 210.59.163.171 -line1 70 -line2 71
---------------------------------------------------------------
2.12 [security]
This command is to configure proxy related parameters. Proxy provides a
simple security function.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ security
Secuirty information and configuration
Usage:
security [-name username] [-password password]
security -print
-print Display system account information and configuration.
-line Specify which line number you want to set the account.
-name Specify user name.
-password Specify password.
Example:
security -line 1 -name kkk -password 12345
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameters Usage:
-print print current proxy related information and configurations.
-line specify which line to be configured.
-name to specify proxy user name.
-password to specify proxy user password.
33
Page 35

2.13 [line]
Configure the Hotline, Hunt and No Answer Forward
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ line
Gateway line information and configuration
Usage:
line -config number [hunt number][hotline number]
line -print Gateway line information.
hunt Hunting group.
hotline Hot line configuration.
fwdtype forward type.
To IP:
0:disable
1:un condition
2:busy
forward forward.
Example:
line -config 1 hunt 1 hotline 1003 forward1002
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Usages:
-print print out all current settings of line
-config determine which line to configure
-hunt set hunting group flag of each line.
User can assign different hunt group number represent
different hunt group. For example, if user assigns FXS TEL1
as hunt group 1, and FXS TEL2 as hunt group 2, they will be
determined as 2 different groups. On the other hand, if user
assigns FXS TEL1 as hunt group 1, and FXS TEL2 as hunt
group 1 too, when having incoming call to FXS TEL1, which is
busy, this call will be route to FXS Line2. Note: FXO Lines
and FXS TELs are treated as 2 different groups, so even they
are in the same hunt group, call will only be routed to the
same FXS or FXO Lines.
-hotline set hotline table.
The Hotline Mode is applied to the gateway will automatically
dial out a phone number. In the other hand, user will hear ring
back tone or dial tone immediately depended on
configurations of destination device.
34
Page 36

Example : Call out from FXO Line
Proxy Mode Usage: Set gateway under proxy mode. Create a Hotline
table with “line ” command. ---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ line - config 1 hotline 1001
---------------------------------------------------------------
In this example means: if user picks up phone set of FXO Line1, gateway
will automatically dial out “1001”.
P2P Mode Usage: Set gateway under P2P mode. Create phone book table
with “pbook ” command. Create a Hotline table with “line ” command.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ pbook - add name micronet ip 10.1.1.1 e164 1001
usr/config$ line - config 1 hotline 1001
---------------------------------------------------------------
In this example means: if user dials into FXO Line1, gateway will
automatically dial out IP address of “1001”.
2.14 [route]
Routing table for your calls
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ route
Routing table information and configuration
Usage:
route -add [prefix number][dst number][e164 number]
[min number][max number][hunt number]
route -delete index
route -modify index [prefix number][dst number][e164 number]
[min number][max number][hunt number]
route -ip [dst number][e164 number]
route -fxo [dst number][e164 number]
route -print Routing table information.
prefix The prefix of dialed number.
dst Destination port(FXO:1/IP:2).
e164 Destination e164 number(when destination is FXO).
min Min digits.(0 ~ 255)
max Max digits.(0 ~ 255)
hunt Hunt method for busy forward
35
Page 37

(NONE:0/GROUP:1/ALL:2).
Example:
route -add prefix 100 dst 1 e164 1001 min 1 max 3 hunt 1
route -ip dst 1 e164 1001
route -fxo dst 2 e164 x
route -modify 1 prefix 100 dst 2 e164 1001 min 1 max 3 hunt 1
route -delete 1
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Usages:
-print print out all routing table information
-add add a routing rule in routing table. User can add less than 50
rules. (route –add prefix "prefix number "dst" destination port
type "e164" e.164 number of port "min" minimum digits
needed "max" maximum digits can't be exceeded")
-delete delete a routing rule in routing table (route –delete "index of
routing rule")
-modify modify a routing rule in routing table. (route –modify "index of
routing rule" prefix “prefix number "dst"destination port type
"e164" e.164 number of port "min" minimum digits needed
"max" maximum digits can't be exceeded")
-ip create routing table for incoming call from IP side. (route –ip
dst “destination port type” e164 "e.164 number of port")
-fxo create routing table for incoming call from FXO Lines.
(route –fxo dst “destination port type” e164 "e.164 number of
port")
prefix prefix of dialed number
dst destination port, 1 means FXO Lines
2 means IP side
x means no determinate number.
e164 destination e.164 number.
min minimum digits needed.
max maximum digits needed.
hunt set hunt method for busy forward.
0 means no hunting,
1 means hunting method follows the rule of [line],
2 means hunting method is to hunt between all ports in the
same type.
36
Page 38

Note: 1. When destination is IP side, e.164 number doesn't need to
determine.
2. If user doesn’t want to determine a specific port to route, e.164
number must set as "x".
2.15 [prefix]
For drop or insert digits
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ prefix
Prefix drop/insert information and configuration
Usage:
prefix -add [prefix number][drop number][insert digits]
prefix -delete index
prefix -modify index [prefix number][drop number][insert number]
prefix -print Prefix drop/insert information.
prefix The prefix of dialed number.
drop Drop prefix(Enable:1/Disable:0).
insert Insert digits.
Example:
prefix -add prefix 100 drop 1 insert 2000
prefix -add prefix 100 drop 1
prefix -add prefix 100 drop 0 insert 200
prefix -delete 1
prefix -modify 1 prefix 100 drop 0 insert 300
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Usages:
-add add a rule to drop or insert prefix digits of incoming
call.(prefix –add prefix “prefix number” drop 0/1 insert “insert
number”)
-delete delete a rule to drop or insert prefix digits of incoming call.
(prefix –delete prefix “prefix number”)
-modify modify a rule to drop or insert prefix digits of incoming call.
(prefix –modify prefix “prefix number” drop 0/1 insert “insert
number”)
prefix set which prefix number to implement prefix rule.
drop enable or disable drop function. If this function is enabled,
37
Page 39

Gateway will drop prefix number on incoming call.
insert set which digit to insert on incoming call.
2.16 [pause]
Pause function allows users define a prefix for FXO, it usually apply to
one-stage-dialing. For example, the FXO port is connect to a PBX, when an
incoming call from IP side, users will hear a dial tone from PBX. If they want
to dial to a PSTN, they must press a special code and wait 1~2 seconds for
the PSTN dial tone. But in one-stage-dialing application, the FXO will not
wait for the dial tone and it will dial immediately. Now user can define a
special prefix, so if FXO detect the prefix, it will wait a moment then keep
dialing.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ pause
Prefix drop/insert information and configuration
Usage:
pause -add [prefix number][delay number]
pause -delete index
pause -modify index [prefix number][drop number][insert number]
pause -print Prefix drop/insert information.
prefix The prefix of dialed number.
delay delay time(second).
Example:
pause -add prefix 100 delay 1
pause -delete 1
pause -modify 1 prefix 101 delay 0
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Usages:
-add add a new record to pause function. When adding a
record, users have to specify prefix and delay seconds to
complete the command.
-delete delete a record to pause function.
-print print out current contents of Pause function.
38
Page 40

2.17 [pbook]
Phone Book function allows users to define their own numbers, which
mapping to real IP address. It is effective only in peer-to-peer mode. When
adding a record to Phone Book, users do not have to reboot the machine,
and the record will be effective immediately.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ pbook
Phone book information and configuration
Usage:
pbook [-add [name string][e164 number][ip address]
[drop digit][insert number]]
[-modify number [name string][e164 number][ip address]
[drop digit][insert number]]
[-delete number]
pbook -print
-print Display phone book information and configuration.
-add Add new phone book record)
-delete Delete phone book record
-modify Modify phone book record.
name : 1 ~ 10 characters.
e164 : 1 ~ 10 digits.
ip : IP adress.
drop : 0:Disable/1:Enable.
insert : 1 ~ 10 digits.
Example:
pbook -add name test e164 1234 ip 192.168.1.10 drop 1 insert 5678
pbook -delete 1
pbook -modify 1 name test e164 5678 ip 192.168.1.10 drop 0
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Usages:
-print print out current contents of Phone Book. Users can also add
index number, from 1 to 100, to the parameter to show specific
phone number.
Note: <index number> means the sequence number in phone book. If
users do request a specific index number in phone book, Micronet
SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway will give each record a automatic
sequence number as index.
39
Page 41

-add add a new record to phone book. When adding a record, users
have to specify name, ip, and e164 number to complete the
command.
-search search a record in phone book. The searching criteria can be
name, ip, or e164.
-delete delete a specific record. “pbook –delete 3” means delete index 3
record.
-insert add a new record and force to assign a specific index number for
it.
-modify modify an existing record. When using this command, users have
to specify the record’s index number, and then make the change.
Phonebook Rules:
To meet the requirements of communicating with trunk Gateway or
other applications, Phonebook has following characteristics to be
noticed.
When the destination side is a terminal, for ex: IP Phone or soft
phone, e164 number stands for exact destination phone number.
When the destination side is a Gateway, for ex: T1/E1 Gateway,
e164 phone number stands only for Gateway prefix. That is to say,
users have to continue to dial destination number, following the
prefix number. A example is as below:
A Æ Micronet FXO Gateway
In Phonebook, there’s a record:
Index Name IP E164
1 B_Gateway 192.168.1.2 0
B Æ E1 trunk Gateway, which connects to PSTN with E1 PRI.
If users want to make a call to PSTN number “82265699”, they
have to pickup one of the phone connected to Micronet FXO
Gateway, and then dial “082265699”. After receiving the complete
dialed number, Micronet FXO Gateway will search for its Phone
Book, find “0” as matched prefix, and then dial out to B’s IP
address directly with destination e.164 (phone number)
40
Page 42

“82265699”. Pleased be noted that “0” is eliminated from Micronet
FXO Gateway itself.
Note:
1. Because of above characteristics, users have to take care of
the number plan very well to avoid the numbering conflict. If
users already defined “0” for specific trunk Gateway, other
terminal started with “0” shall be avoided, or the number will
be routed to the trunk Gateway defined “0”.
2. If user wants to set 2 sets of similar e164 such as 123 and
1234, please be careful configure 123 first, or it may cause
problem when user dial 1234, Micronet FXO Gateway may
dials out IP address of 123.
3.
(1) If called party is FXO product, please set e164 of pbook as
e.164 of called party, and remember to set sysconf –drule
in_drop “e.164”(refer to 5.12.)in called party.
(2) If called party is FXS product, please set e164 of pbook as
prefix of called party, when dialing to different line of FXS
product, please dial line number.
2.18 [voice]
The voice command is associated with the audio setting information. There
are four voice codecs supported by Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S
Gateway.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ voice
Voice codec setting information and configuration
Usage:
voice [-send [G723 ms] [G729 ms] [G729A ms] [G729B ms] [G729AB ms] [G711U ms]
[G711A ms] ]
[-volume line [voice level] [input level] [dtmf level]]
41
Page 43

[-nscng [G711U used1] [G711A used2] [G723 used3]]
[-echo used] [-mindelay t1] [-maxdelay t2] [-optfactor f]
voice -print
voice -priority [G723] [G729] [G729A] [G729B] [G729AB] [G711U] [G711A]
-print Display voice codec information and configuration.
-send Specify sending packet size.
G.723 (30/60/90 ms)
G.729 (20/40/60 ms)
G.729A (20/40/60 ms)
G.729B (20/40/60 ms)
G.729AB (20/40/60 ms)
G.711U (20/40/60 ms)
G.711A (20/40/60 ms)
-priority Priority preference of installed codecs.
G.723
G.729
G.729A
G.729B
G.729AB
G.711U
G.711A
-volume Specify the following levels:
voice volume (0~63, default: 30),
input gain (0~63, default: 30),
dtmf volume (0~31, default: 23),
-nscng No sound compression and CNG. (G.723.1 only, On=1, Off=0).
-echo Setting of echo canceller. (On=1, Off=0, per port basis).
-mindelay Setting of jitter buffer min delay. (0~150, default: 90).
-maxdelay Setting of jitter buffer max delay. (0~150, default: 150).
Example:
voice -send g723 60 g729 60 g729a 60 g729b 60 g729ab 60 g711u 60 g711a 60
voice -volume 1 voice 20 input 32 dtmf 27
voice -echo 1 1
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameters Usage:
-print print current voice information and configurations.
-send to define packet size for each codec. 20/40/60ms means to
send a voice packet per 20/40/60 milliseconds. The smaller
the packet size, the shorter the time delay. If network is in
42
Page 44

good condition, smaller sending packet size is
recommended. In this parameter, 20/40/60ms is applicable
to G.711u/a law, and G.729a codec, while 30/60ms is
applicable to G.723.1 codec.
-priority codec priority while negotiating with other sip device. This
parameter determines the listed sequence in TCS message.
The codec listed in left side has the highest priority when
both parties determining final codec.
-volume There are three adjustable value.
z voice volume stands for volume, which can be heard
from Micronet SP5052A/S / SP5054A/S Gateway
side;
z input gain stands for volume, which the opposite
party hears. The maximum number is 35. If the
number is over 35, the echo may be happened. Once
you increase input gain, the voice volume from PSTN
to IP side is increased too.
z dtmf volume stands for DTMF volume/level, which
sends to its own Line1 or Line2.
-nscng silence suppression and comfort noise generation setting (1
= ON; 0 = OFF). It is applicable to G. 723 codec only. An
example is demonstrated below:
--------------------------------------------------------------usr/config$ voice -nscng g723 1
---------------------------------------------------------------
-mindelay the minimum jitter buffer size. (Default value= 90 ms)
-maxdelay the minimum jitter buffer size. (Default value= 150
ms)
--------------------------------------------------------------usr/config$ voice -mindelay 90 -maxdelay 150 -optfacor 7
---------------------------------------------------------------
-echo activate each canceller (1 = ON; 0 = OFF).
Note: be sure to know well the application before you change
voice parameters because this might cause incompatibility.
43
Page 45

2.19 [tone]
Disconnecting and Ring Back tone configuration
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ tone
Disconnect tone and remote ring back tone configuration
Usage:
tone [num][freqHi ][freqLo ][freqHiLev][freqLoLev]
[Tone1ON][Tone1OFF][Tone2ON ][Tone2OFF ]]
tone -print Display tone configuration.
[num] Tone index(1~4:Disconnect tone / 5~8:Remote ring back
tone).
Example:
tone -print
tone 1 620 480 8 8 50 50 1023 1023
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameters Usage :
tone x 1 - 4 is disconnect tone, 5 - 8 is remote ring back tone.
2.20 [fxopwd]
Call restriction from FXO port
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ fxopwd
FXO password information and configuration
Usage:
fxopwd -add [passwd number]
fxopwd -delete index
fxopwd -modify index [passwd number]
44
Page 46

fxopwd -print FXO password information.
passwd The password.
Example:
fxopwd -add passwd 1234
fxopwd -delete 1
fxopwd -modify 1 passwd 1234
---------------------------------------------------------------
Caller will be asked PIN number to pass the call through the gateway from
FXO port to IP side when fxopwd set
2.21 [record]
Record your own Greeting, Asking PIN and analyze Disconnect tone
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ record
Record greeting voice and ask pin code voice, tone analize.
Usage:
record -greeting filename
-askpin filename
-tone
Example:
record -greeting greeting.100
record -askpin askpin.100
record -tone
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameters Usage :
-greeting record greeting file. User must assign a file name for
greeting, once record is finished, file recorded will be
display in rom –print.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--
usr/config$ record -greeting greeting.test
Please off hook the LINE 1 and press (N) for the next step...
n
Press (R) to start record...
r
45
Page 47

Press (S) to stop record...
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
.....................................................s..............................................
....................................................................................................
Press (P) to play the voice or (W) to write to flash or (Q) to quit...
p
w
Please wait a moment...
Write flash ok...
Boot Rom : boot.104
Application Rom : 4fxo.118a
DSP App : 48302ce3.140
DSP Kernel : 48302ck.140
DSP Test Code : 483cbit.bin
Greetings : greeting.test
Ask Pin : askpin.102
q
usr/config$
-askpin record askpin file. User must assign a file name for askpin
file, once record is finished, file recorded will be display in
rom –print.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--
usr/config$ record -askpin askpin.test
Please off hook the LINE 1 and press (N) for the next step...
n
Press (R) to start record...
r
46
Page 48

Press (S) to stop record...
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
..........................................................................s.........................
....................................................................................................
..........................
Press (P) to play the voice or (W) to write to flash or (Q) to quit...
p
w
Please wait a moment...
Write flash ok...
Boot Rom : boot.104
Application Rom : 4fxo.118a
DSP App : 48302ce3.140
DSP Kernel : 48302ck.140
DSP Test Code : 483cbit.bin
Greetings : test.100
Ask Pin : askpin.test
q
usr/config$
-tone analyze tone frequency. Gateway can analyze tone
frequency as users provide tone in FXO Line1.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--
usr/config$ record –tone
usr/config$ record -tone
Press (R) to start record...
r
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
47
Page 49

....................................................................................................
..........
Analizing!! Please wait a moment...
Frequency 1 : 620
Frequency 2 : 474
0.25sec on 0.25sec off
usr/config$
-greeting record the greeting file
-askpin record the askpin file
-tone analyze the tone from PSTN or PABX
The Procedures of recording the disconnect tone
Micronet FXO/FXSO Gateway in the latest version use the "record -tone"
command to analyze the disconnect tone. Please prepare connection as
the figure shown.
Note: Please connect extension (or PSTN) line to the second FXO port (L2)
of FXO gateway that takes charge of tone detection. For FXS/FXO gateway,
however, the first FXO port (LINE1) is in charge.
Procedure:
(1). Prepare Telnet or Console connection, and login the system.
(2). Place command "record -tone", and press "r"...
(3). Make a call from handset (Ext.8509) to the Ext.8401 into the FXO port.
(4). After greeting tone, hang up the call from Ext.8509
(5). Press R key and Enter to start analysis
48
Page 50

6). According to the result, enter the Freq. into Tone table.
command:
usr/config$ tone 1 480 620 1 1 25 25 1023 1023
【Example-1】
(Make a call from PSTN to FXO port)
usr/config$ record -tone
Press (R) to start record...
(Please make sure that you are already finish the steps 2 ~ 7)
r (Press “Enter” button after you key in “R”)
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
............
Analizing!! Please wait a moment...
(You coule hang up the call from PSTN if you get this message)
Frequency 1 : 481
Frequency 3 : 621
0.25sec on 0.25sec off
tone 4 481 621 8 8 25 25 1023 1023
49
Page 51

(Put this value in to the tone table)
tone –print
Disconnect tone 1 paramter
Frequency high : 620
frequency low : 480
frequency high level : 8
frequency low level : 8
Tone1 on : 25
Tone1 off : 25
Tone2 on : 1023
Tone2 off : 1023
Disconnect tone 2 paramter
Frequency high : 450
frequency low : 0
frequency high level : 8
frequency low level : 0
Tone1 on : 35
Tone1 off : 35
Tone2 on : 1023
Tone2 off : 1023
Disconnect tone 3 paramter
Frequency high : 620
frequency low : 480
frequency high level : 8
frequency low level : 8
Tone1 on : 50
Tone1 off : 50
Tone2 on : 1023
Tone2 off : 1023
Disconnect tone 4 paramter
Frequency high : 621
frequency low : 481
frequency high level : 8
frequency low level : 8
Tone1 on : 25
Tone1 off : 25
Tone2 on : 50
50
Page 52

Tone2 off : 50
(Confirm the values is correct or not)
(Key in the commit and reboot command if you finish the procedures as
above)
【Example-2】
(Make a call into FXO port)
usr/config$ record -tone
Press (R) to start record...
(Please make sure that you are already finish the steps 2 ~ 7)
r (Press “Enter” button after you key in “R”)
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
....................................................................................................
............
Analizing!! Please wait a moment...
(You could hang up the call from PSTN if you get this message)
Frequency 1 : 473
Frequency 2 (2623) is more than 1000, please ignore it.
0. 25sec on 0.25sec off
tone 4 473 473 8 8 25 25 1023 1023
(Please configure the high and low frequency as the same value if you just
get a singal frequency)
tone –print
Disconnect tone 1 paramter
Frequency high : 620
frequency low : 480
frequency high level : 8
51
Page 53

frequency low level : 8
Tone1 on : 25
Tone1 off : 25
Tone2 on : 1023
Tone2 off : 1023
Disconnect tone 2 paramter
Frequency high : 450
frequency low : 0
frequency high level : 8
frequency low level : 0
Tone1 on : 35
Tone1 off : 35
Tone2 on : 1023
Tone2 off : 1023
Disconnect tone 3 paramter
Frequency high : 620
frequency low : 480
frequency high level : 8
frequency low level : 8
Tone1 on : 50
Tone1 off : 50
Tone2 on : 1023
Tone2 off : 1023
Disconnect tone 4 paramter
Frequency high : 473
frequency low : 473
frequency high level : 8
frequency low level : 8
Tone1 on : 25
Tone1 off : 25
Tone2 on : 50
Tone2 off : 50
(Confirm the values is correct or not)
(Key in the commit and reboot command if you finish the procedures as
above)
52
Page 54

2.22 [tos]
TOS service allows users to achieve QoS on IP network.
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ tos
IP Packet ToS(type of Service)/Differentiated Service configuration
Usage:
tos [-rtptype dscp]
tos [-sigtype dscp]
tos -print
[-rtpreliab mode]
tos -print
Example:
tos -rtptype 7 -sigtype 0
---------------------------------------------------------------
In QoS, a modification of the type of service byte. Six bits of this byte are
being reallocated for use as the DSCP field, where each DSCP specifies a
particular per-hop behavior that is applied to a packet. Support for DSCP
still is lacking in some network equipment, please refer to RFC 2474
DSCP : Differentiated Services Code Point
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
P X CC M PT Sequence Number
Ver
Timestamp
SSRC
CSRC
[0..15] :::
Note:
1. The value of rtptype and sigtype is from 0 to 63.
2. Users should be aware that TOS is effective only when network
devices (for ex: router, switch.. etc.) support TOS.
2.23 [pt]
RTP Payload Type Configuration
---------------------------------------------------------------
53
Page 55

usr/config$ pt
RTP payload type configuration and information
Usage:
pt -print Display the RTP payload type information
-rfc2833 Configurate the DTMF RFC2833 payload type
-dtmf Configurate the DTMF payload type
-fax Configurate the FAX payload type
Example:
pt -rft2833 96 -fax 101
---------------------------------------------------------------
The RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) Payload Type
Idea for use the Payload Type:
z Selective Retransmission :
Priority bit indicates the importance of the payload
Only important packets are retransmitted
z Multiple Retransmission Attempts :
New SNHP value assigned for each transmission of a high priority
packet. Client is able to detect a failure in a high priority
(re)transmission
For more informations, please refer to your network administrator
2.24 [rom]
Firmware Information and Upgrade command
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ rom
ROM files updating commands
Usage:
rom [-print][-app][-boot][-dsptest][-dspcore][-dspapp][-greet][-askpin]
-s TFTP/FTP server ip -f filename
rom -print
-print show versions of rom files. (optional)
-app update main application code(optional)
-boot update main boot code(optional)
-boot2m update 2M code(optional)
-dsptest update DSP testing code(optional)
54
Page 56

-dspcore update DSP kernel code(optional)
-dspapp update DSP application code(optional)
-greeting update greeting voice file(optional)
-askpin update ask pin code voice file(optional)
-s IP address of TFTP/FTP server (mandatory)
-f file name(mandatory)
-method download via TFTP/FTP (TFTP: mode=0, FTP: mode=1)
-ftp specify username and password for FTP
Note:
This command can run select one option in 'app', 'boot',
, 'dsptest', 'dspcore', and 'dspapp'.
Example:
rom -method 1
rom -ftp vwusr vwusr
rom -app -s 192.168.4.101 -f app.bin
---------------------------------------------------------------
Parameter Usages:
-print show versions of all rom files
-app application ROM file
-boot boot ROM file
-boot2m contains application and boot ROM files together
-s to specify TFTP server’s IP address when upgrading ROM files.
-f to specify the target file name, which will replace the old one.
-method to decide using TFTP or FTP as file transfer server.
“0” is for TFTP and “1” is for FTP.
-ftp if users choose FTP in above item, it is necessary to specify
pre-defined username and password when upgrading files.
2.25 [passwd]
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ passwd
Password setting information and configuration
Usage:
passwd -set Loginname Password
passwd -clean
Note:
55
Page 57

1. Loginname can be only 'root' or 'administrator'
2. passwd -clean will clear all passwd stored in flash,
please use it with care.
Example:
passwd -set root Your_Passwd_Setting
2.26 [auth]
---------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ auth
Root control what command administrator can use.
Usage:
auth -print Display auth switch configuration.
Use item name to do config name (0=Disable, 1=Enabled).
Example: auth -ifaddr 1
2.27 [setmac]
To set mac address please key in command setmac:(when key in MAC
address ,press enter each time after key in two characters). Please get the
MAC address from the bottom of your FXO VOIP units.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
usr/config$ setmac
- enter mac address (xxxxxxxxxxxx):
0001a8002baa
- the mac address is 00 01 a8 00 2b aa
- if mac address is correct,please press 'y' to
setup configuration,else press 'n' to continue
y
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
56
 Loading...
Loading...