Micronas Intermetall SDA9410-B13 Datasheet

PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET
SDA 9410-B13
DAEDALUS
Display Processor and
Scan Rate Converter
using Embedded DRAM
Technology Units
Edition March 2, 2001
6251-553-1PD

SDA 9410 - B13
Revision History: 2000-05 (V 1.0)
Previous Versions: 1998-08-01
Changes to the previous issue Version 00, Edition 08.98, are marked with a change
bar
We Listen to Your Comments
Any information within this document that you feel is wrong, unclear or missing at all?
Your feedback will help us to continuously improve the quality of this document.
Please send your proposal (including a reference to this document) to:
docservice@micronas.com
Micronas 2

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
4 Pin Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Pin Diagram: P-MQFP-100 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
5 System description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
5.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
5.2 Input sync controller (ISCM/ISCS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
5.3 Input format conversion (IFCM/IFCS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
5.4 Input signal processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
5.4.1 Adjustable delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
5.4.2 Vertical and horizontal compression (VHCOMM/VHCOMS) . . . . . . . . . .32
5.4.3 Noise reduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
5.4.4 Noise measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
5.4.5 Letter box detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
5.5 Clock concept . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
5.6 Application modes and memory concept . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
5.6.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
5.6.2 Configuration controlling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
5.6.3 SRC mode configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
5.6.4 SSC and MUP mode configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
5.6.5 Configuration switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
5.6.6 Joint line free display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
5.6.7 Master slave switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
5.6.8 Refresh and still picture mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
5.6.9 Memory management and animation controlling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
5.7 Output sync controller (OSCM/S) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
5.7.1 HOUT generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
5.7.2 VOUT generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
5.7.3 Switching from H-and-V-freerunning to H-and-V-locked mode . . . . . . . .83
5.7.4 Operation mode generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
5.8 Motion estimation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
5.9 Motion compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
5.10 Global motion, film mode and phase detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
5.11 Vertical expansion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
5.12 Display processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
5.12.1 Peaking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
5.12.2 Digital luminance transition improvement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
5.12.3 Digital colour transition improvement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .113
5.12.4 Insertion facilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
5.12.5 Coarse delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
3 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
5.12.6 Digital-to-Analog conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
5.13 I²C Bus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
5.13.1 I²C Bus slave address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
5.13.2 I²C Bus format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
5.13.3 I²C Bus commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
5.13.4 Detailed description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
6 Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .170
6.1 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
6.2 Operating range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
6.3 Characteristics (Under operating range conditions) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .173
7 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
8 Wave forms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
8.1 I²C Bus timing START/STOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
8.2 I²C Bus timing DATA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .176
8.3 Timing diagram clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
8.4 Clock circuit diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .177
9 Package Outlines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .178
4 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Figure 1 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Figure 2 Block diagram 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Figure 3 Pin configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Figure 4 Principles of SRC mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Figure 5 Principles of SSC mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Figure 6 Principles of MUP mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Figure 7 Input I²C Bus parameter. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Figure 8 Field detection and VINM delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Figure 9 Explanation of 656 format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Figure 10 SYNCENM/SYNCENS signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Figure 11 Input timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Figure 12 Block diagram of input processing blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Figure 13 Block diagram of VHCOMM/VHCOMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Figure 14 Principles of panorama mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
Figure 15 Block diagram of noise reduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Figure 16 Block diagram of motion detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Figure 17 LUT for motion detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Figure 18 Example of noise measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Figure 19 Principle of letter box detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Figure 20 Block diagram of letter box detection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
Figure 21 Histogram and line type decision . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Figure 22 Visibility of letter box detection I²C Bus parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Figure 23 Clock concept of SDA 9410 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Figure 24 Application for SDA 9410 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Figure 25 Supported data formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Figure 26 Switching from SRC-PIP mode to SSC mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Figure 27 Changing picture sizes to get a double window display. . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Figure 28 Completing the operations to a master slave exchange . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Figure 29 Example for animation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Figure 30 Equation of the position of the left upper picture corner . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Figure 31 Explanation of memory management I . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Figure 32 Explanation of memory management II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Figure 33 Explanation of memory management III . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Figure 34 Block diagram of OSCM/S . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Figure 35 Output I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Figure 36 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Figure 37 Ingenious configurations of the HOUT and VOUT generator . . . . . . . .80
Figure 38 VOUT generation depending on I²C Bus parameter RMODE . . . . . . . .82
Figure 39 Explanation of field and display line-scanning pattern . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Figure 40 Explanation of operation mode timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .85
Figure 41 Principle of block matching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
Figure 42 Block diagram of motion estimation and compensation. . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Figure 43 Block diagram of motion estimation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
5 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Figure 44 Relative positions of the spatial predictors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Figure 45 Timing of 100 Hz scan rate conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Figure 46 Principles of motion compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Figure 47 Principles of motion compensation for the b field (FILSEL=0). . . . . . .101
Figure 48 Output sequence generation: Camera mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 49 Output sequence generation: PAL film mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Figure 50 Output sequence generation: NTSC film mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Figure 51 Calculation of maximum VPAN value . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Figure 52 Block diagram of display processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Figure 53 Block diagram peaking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Figure 54 Principles of DCTI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Figure 55 Application for SDA 9410. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
6 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Table 1 Pin definitions and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 2 Input signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 3 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 4 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 5 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 6 Input read I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 7 Input signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 8 Input data formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 9 Input sync formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 10 DELM/DELS I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 11 Examples of vertical filter adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 12 Conversion table between dezV and DEZVM / DEZVS. . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 13 Input write I²C Bus parameter YPEAKM/YPEAKS/CPEAKM/CPEAKS 35
Table 14 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 15 Examples of horizontal filter adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 16 Conversion table between dezH and DEZHM/DEZMS . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 17 Input write I²C Bus parameter CHFILM/CHFILS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 18 Filter I²C Bus parameter in case of PANAON=1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 19 I²C Bus parameter PANAST in case of PANAON=1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 20 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 21 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 22 I²C Bus parameter TNRVAY/C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 23 I²C Bus parameter TNRHOY/C and TNRKOY/C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 24 I²C Bus parameter TNRCLY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 25 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 26 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 27 Input read I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 28 Line Type Decision of LBD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 29 Evaluation of the reliability signal RELY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 30 Correction of “start/end-line decision filter” block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 31 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 32 Input read I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 33 Input signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 34 Output signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 35 Clock concept switching matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 36 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 37 Definition of MEMOP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 38 Definition of CHRFORM/CHRFORS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Table 39 Definition of ORGMEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Table 40 Definition of ORGMEMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Table 41 Definition of VERRESM/VERRESS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 42 Programmable data configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 43 Applications of different data configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
7 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Table 44 Maximum picture sizes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 45 Definition of MEMWRS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 46 Definition of MEMWRM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 47 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 48 Definition of WRFLDM/WRFLDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 49 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 50 Definition of ORGMEMM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 51 Definition of ORGMEMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 52 Definition of MEMRDM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 53 Definition of MEMRDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 54 Definition of MEMWRM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 55 Definition of MEMWRS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 56 Switching from SRC PIP mode to SSC mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Table 57 Changing the picture sizes to double window format. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 58 Performing a master slave exchange . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 59 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 60 Output read I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 61 Supported data formats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Table 62 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Table 63 Output read I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Table 64 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Table 65 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Table 66 Input write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Table 67 Output signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Table 68 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Table 69 Output write I²C Bus parameter INTMODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Table 70 Output write I²C Bus parameter INTMODE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Table 71 Static operation modes (only valid for ADOPMOM=0, RMODE=0) . . . 86
Table 72 Static operation modes (only valid for ADOPMOM=0, RMODE=1) . . . 87
Table 73 Special combinations of STOPMOM and ADOPMOM . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Table 74 Display line-scanning pattern sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Table 75 Static operation modes slave. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Table 76 Adaptive operation modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Table 77 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Table 78 Key I²C Bus parameters of the 3-D RS motion estimation. . . . . . . . . . 96
Table 79 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Table 80 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Table 81 Principles of global motion and film mode detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Table 82 Definition of scmin/scmax depending on SFMINTH/SFMAXTH . . . . 105
Table 83 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Table 84 Output read I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Table 85 Output write I²C Bus parameter VERINT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Table 86 Examples of reachable expansion factors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
8 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Table 87 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Table 88 Output signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Table 89 Conversion table BCOF/HCOF to gain_bp/gain_hp . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Table 90 Output write I²C Bus parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Table 91 I²C Bus parameter THRESY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Table 92 I²C Bus parameter THRESY_UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Table 93 I²C Bus parameter ASCENTLTI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Table 94 Output write I²C Bus parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Table 95 I²C Bus parameter THRESC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Table 96 I²C Bus parameter ASCENTCTI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Table 97 Output write I²C Bus parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Table 98 Output write I²C Bus parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Table 99 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Table 100 Output write I²C Bus parameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
9 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
BLANK PAGE
10 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Introduction
1 Introduction
The SDA 9410 is a new component of the Micronas MEGAVISION® IC set, which
enables the system to reduce large area and line flickering of interlaced TV standards.
The scan rate conversion to 100/120 Hz interlaced or 50/60 Hz progressive scan is
motion vector based. For the 100/120 Hz (50/60 Hz) conversion the SDA 9410 really
calculates 100/120 Hz (50/60 Hz) fields with continuous motion phases to avoid double
contour effects in the motion display. In the special case of movie sources, which have
a non-continuous motion phase, the SDA 9410 generates at the output an appropriate
sequence with a continuous motion phase („True Motion“).
Due to the frame based signal processing, the noise reduction has been greatly
improved. Furthermore different motion detectors for luminance and chrominance have
been implemented. For automatic controlling of the noise reduction parameters a noise
measurement algorithm is included, which measures the noise level in the picture or in
the blanking period. In addition a spatial noise reduction is implemented, which reduces
the noise even in the case of motion.
The SDA 9410 has two input channels, which can be used for different features like
Picture-in-Picture (maximum approximately 1/9 picture) and “Double-window/Splitscreen”. The two input signals can be scaled horizontally and vertically with variable
factors. Panorama modes will be supported.
Besides that an algorithm for the detection of letter box pictures is included. The SDA
9410 delivers the start and the end line of the active picture part of the input signal to an
external µC.
the full screen
Picture sharpness can be greatly improved by a LTI (luminance transition improvement)
or/and peaking and a CTI (colour transition improvement) algorithm. The resolution of
the output signals is 9 bit. The SDA 9410 has analog output signals.
The µC calculates the zoom factors for displaying the active picture part on
and sends this values back to the SDA 9410.
11 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Features
2Features
• Different application modes
- SRC mode:
- High performance scan rate converter
- High performance scan rate converter plus high resolution frame based joint-linefree Picture-in-Picture (maximum approximately 1/9 picture)
- SSC mode:
- Split screen applications with two signal sources (e.g. double window)
- MUP mode:
- Multipicture display mode (e.g. tuner scan)
• 8 bit amplitude resolution of each input channel
- Two input channels
- Input frequency up to 27 MHz
- ITU-R 656 data format (8 wires data only and additional sync information or 8 wires
including sync information)
- 4:2:2 luminance and chrominance parallel (2x8 wires)
• Two different representations of input chrominance data
- 2’s complement code
- Positive dual code
• Two flexible input sync controllers
• Vertical peaking of the input signal
• Flexible scaling of the input signal
- Flexible digital vertical compression of the input signal
(1.0, ... [2 line resolution] ... , 1/32)
- Flexible horizontal compression and expansion of the input signal
(2.0, ... [4 pixel resolution] ... ,1.0 , ... [4 pixel resolution] ... , 1/32)
- Panorama mode (programmable characteristic)
• Noise reduction
- Motion adaptive spatial and temporal noise reduction (3D-NR)
- Temporal noise reduction for luminance and chrominance, frame based or field
based
- Different motion detectors for luminance and chrominance or identical
- Flexible programming of the temporal noise reduction parameters
- Automatic measurement of the noise level (5 bit value, readable by I²C-bus)
• 3-D motion estimation
- High performance motion estimation based on block matching algorithm
- Film mode detector (PAL and NTSC), Global motion flag (readable by I²C bus)
• Automatic detection of letter box formats (readable by I²C bus)
• TV mode detection by counting line numbers (PAL, NTSC, readable by I²C bus)
• Embedded memory
- 6 Mbit embedded DRAM core for field memories
- 1,1 Mbit embedded DRAM core for line memories, vector memory, block-to-line
12 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Features
converter
- 36 kbit SRAM for block matching, line-to-block converter
• Flexible clock and synchronization concept
- Decoupling of the input and output clock system possible
• Scan rate conversion
- Motion compensated 100/120 Hz interlaced scan conversion (Micronas VDU)
- Motion compensated 50/60 Hz progressive scan conversion (Micronas VDU)
- Simple interlaced modes: ABAB, AABB, AAAA, BBBB
- Simple progressive modes: AB, AA*, B*B
- True Motion: 50 Hz motion resolution even for 25 Hz PAL film sources
60 Hz motion resolution even for 30 Hz NTSC film sources
- Large area and line flicker reduction
• Flexible digital vertical expansion of the output signal (1.0, ... [1/64] ... , 2.0)
• Sharpness improvement
- Digital colour transition improvement (DCTI)
- Digital luminance transition improvement (DLTI)
- Peaking (luminance only)
• Flexible output sync controller
- Flexible positioning of the two output channels in all application modes
- Flexible height and width of the two output pictures
- Flexible programming of the output sync raster
• Signal manipulations
- Still frame or field
- Insertion of coloured background
- Insertion of a selection border
- Adjustable delay between Y and UV signal (+4,...[1]...,-3 input pixels) at the input
side
- Adjustable delay between Y and UV signal (+3,...[0.5]...,- 4 output pixels) at the
output side
• Three D/A converters
- 9 bit amplitude resolution for Y, -(R-Y), -(B-Y) output
- 60 MHz maximal clock frequency
- Two-fold oversampling
- Simplification of external analog post filtering and differential analog outputs
• I²C-bus control (400 kHz)
• P-MQFP-100 package
• 3.3 V ± 5% supply voltage
13 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
3 Block diagram
HINM
VINM
SYNCENM
CLKM
YINM
UVINM
YINS
UVINS
CLKS
HINS
VINS
SYNCENS
clock
doubling
PLLM
conversion
conversion
clock
doubling
PLLS
ISCM
Input sync controller Master
LM
Line memory
ISCS
VHCOMM
Vertical and
horizontal
compression/
expansion
VHCOMS
Vertical and
horizontal
compression/
expansion
LM
Line memory
IFCM
Input
format
IFCS
Input
format
Input sync controller Slave
TSNR
Temporal,
spatial
noise
reduction
RESETTEST
LBD
Letter
box
detection
ED
eDRAM
+
Buffer
+
Voltage
control
+
Test-
controller
MC
Memory
Controller
VM
Vector
memory
ME
motion
estimation
LM
Line
memory
SRCM
Scan rate
conversion
Master
Vertical
expansion
SRCS
X2
clock
doubling
PLLD
M
U
X
X1/CLKD
OSCM/S
Output sync
controller
Master
DLTI
DCTI
Peaking
Block diagram
OFC
4:4:4
8:8:8
Framing
Delay
SDA
DAC
DAC
DAC
I²C
SCL
CLKOUT
INTERLACED
HOUT
VOUT
BLANK
YO
UO
VO
bd9410
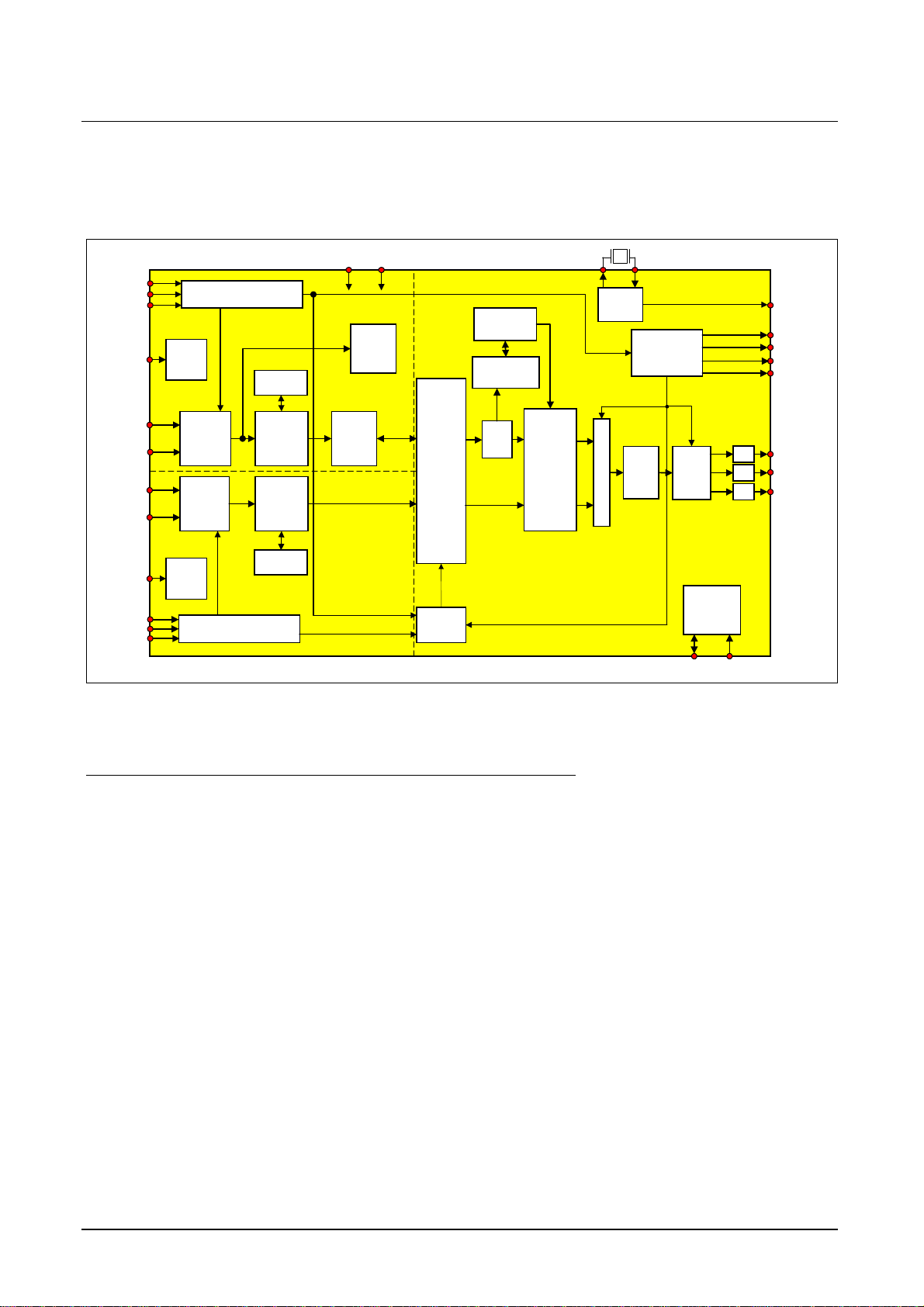
Figure 1 Block diagram
The SDA 9410 contains the blocks, which will be briefly described below:
ISCM/S - Flexible input sync controller
IFCM/S - Input format conversion, Adjustable delay
VHCOMM/S - Vertical and horizontal compression, horizontal expansion, panorama mode (only M)
TSNR - Temporal and spatial noise reduction, noise measurement
LBD - Letter box detection
ME - Motion estimation, Film mode and phase detection
MC - Memory controller
OSCM/S - Flexible output sync controller
OFC - Output format conversion, 4:4:4, 8:8:8 interpolation, Adjustable delay
SRCM/S - Scan rate conversion, vertical expansion
MUX - Combination of the two output channels
DLTI/DCTI/Peaking - Luminance and chrominance transition improvement, luminance peaking
2
I
C - I²C bus interface
PLLM/S/D - PLL for frequency doubling
LM - Line memory core, VM - Vector memory core
ED - eDRAM core
14 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
INPUT PROCESSING MASTER
YINM
UVINM
YINS
UVINS
HINM
VINM
HINS
VINS
VERTICAL AND
HORIZONTAL
COMPRE SSION /
HORIZONTAL
EXPANSION
VERT. PEAKING
INPUT PROCESSING
SLAVE
VERTICAL AND
HORIZONTAL
COMPRE SSION /
HORIZONTAL
EXPANSION
VERT. PEAKING
INPUT SYNC
CONTROLLE R
3D
SPATIO
TEMP ORA L
NOISE
REDUCTION
LETTE R
BOX
DETECTION
eDRAM
MAIN
MEMORY
MEMORY
CONTROLLE R
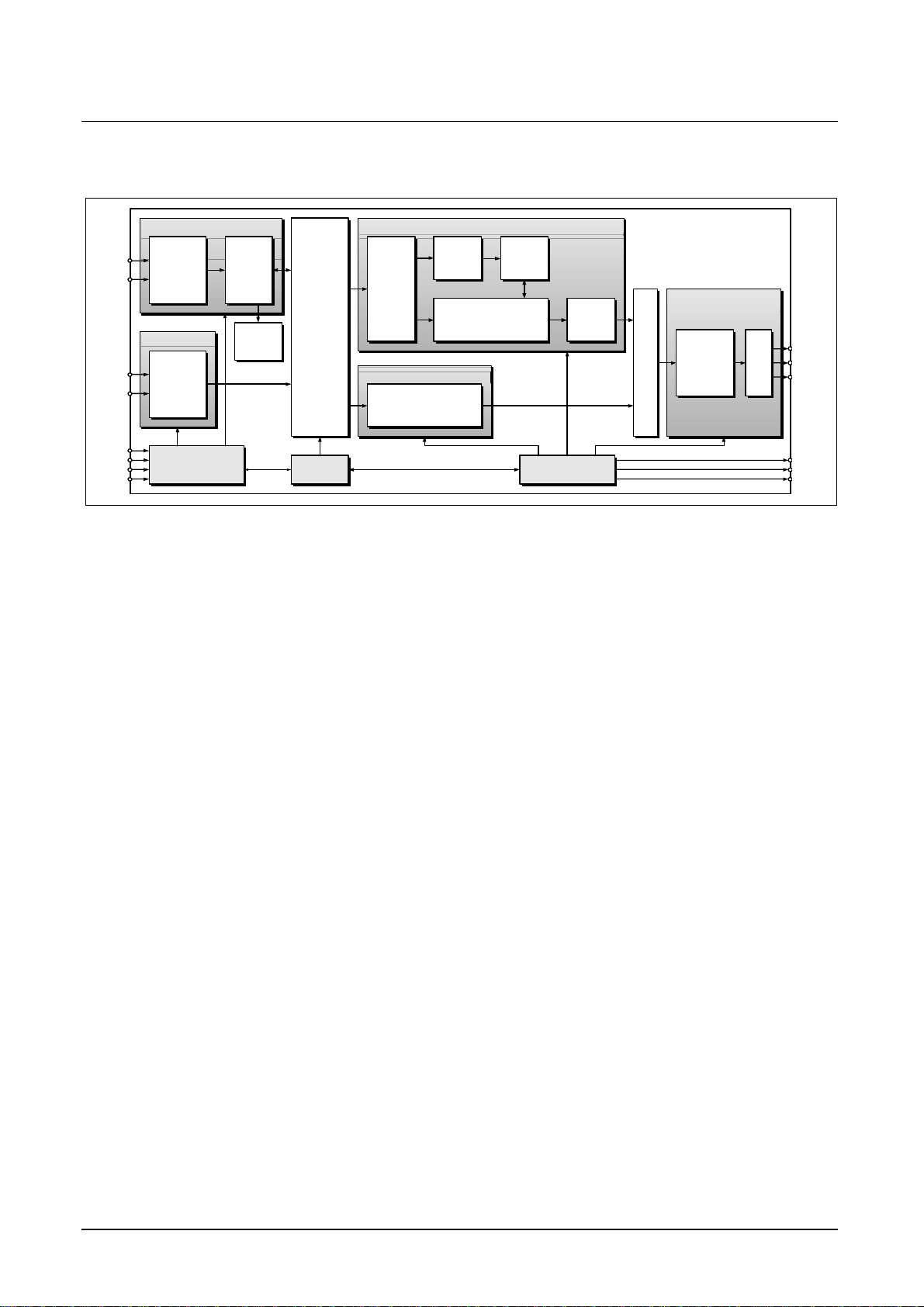
Figure 2 Block diagram 2
LINE TO
BLOCK
CONVERSION
OUTPUT PROCESSING SLAVE
SCAN RA TE CONVERS ION
MOTION
ES TIMA TION
FILM MODE
DETECTION
SCAN RATE CONVERSION
VERTICAL ZOOM
OUTPUT PROCESSING MASTER
eDRAM
VECTOR
MEMORY
BLOCK TO
LINE
CONVERSION
OUTPUT SY NC
CONTROLLE R
MUX
Block diagram
DISPLAY PROCESSING
DLTI
DCTI
PEAKING
8:8:8
INTERPOLATION
TRIP LE
DAC
Y0
U0
V0
HOUT
VOUT
BLANK
15 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
4 Pin Description
Pin Diagram: P-MQFP-100
(top view)
VDDL4
SYNCENS
VSSL4
YINS6
YINS7
RESET
TES T
IUQ_O
IU_O
VDDU
IYQ_O
IY_O
VDDY
IVQ_O
IV_O
VDDV
VSSA4
RREF_I
UREF_I
VDDA5
VSSA5
VDDA1
VSSA1
VDDP7
VSSP8
VINS
HINS
VSSP1
VDDP1
80
81
85
90
95
100
15
YINS3
VDDL1
VDDP2
VSSP2
YINS5
YINS4
VSSE1
VDDE1
DAEDALUS
SDA 9410
Pin Description
UVI NS6
UVI NS7
VSSP3
CLKS
VSSA2
VDDA2
YINS0
YINS1
YINS2
VDDP3
251510 20
UVI NS3
UVI NS4
UVI NS5
515560657075
50
UVI NS2
UVI NS1
UVI NS0
YINM7
YINM6
45
YINM5
YINM4
VSSP4
YINM3
YINM2
40
YINM1
YINM0
UVI NM7
UVI NM6
VDDP4
35
UVI NM5
UVI NM4
UVI NM3
UVI NM2
31
UVI NM1
30
X2
VOUT
HOUT
CLKOUT
X1/CLKD
IN TER LACED
VDDL3
VSSL3
BLANK
VDDL2
VDDP6
VSSP7
VSSL2
VSSL9
VDDE2
VSSL8
CLKM
VSSP6
VSSA3
VSSL7
VDDA3
VDDP5
VSSL6
SCL
SDA
VINM
HI NM
VSSP5
UVI NM0
SYNCENM
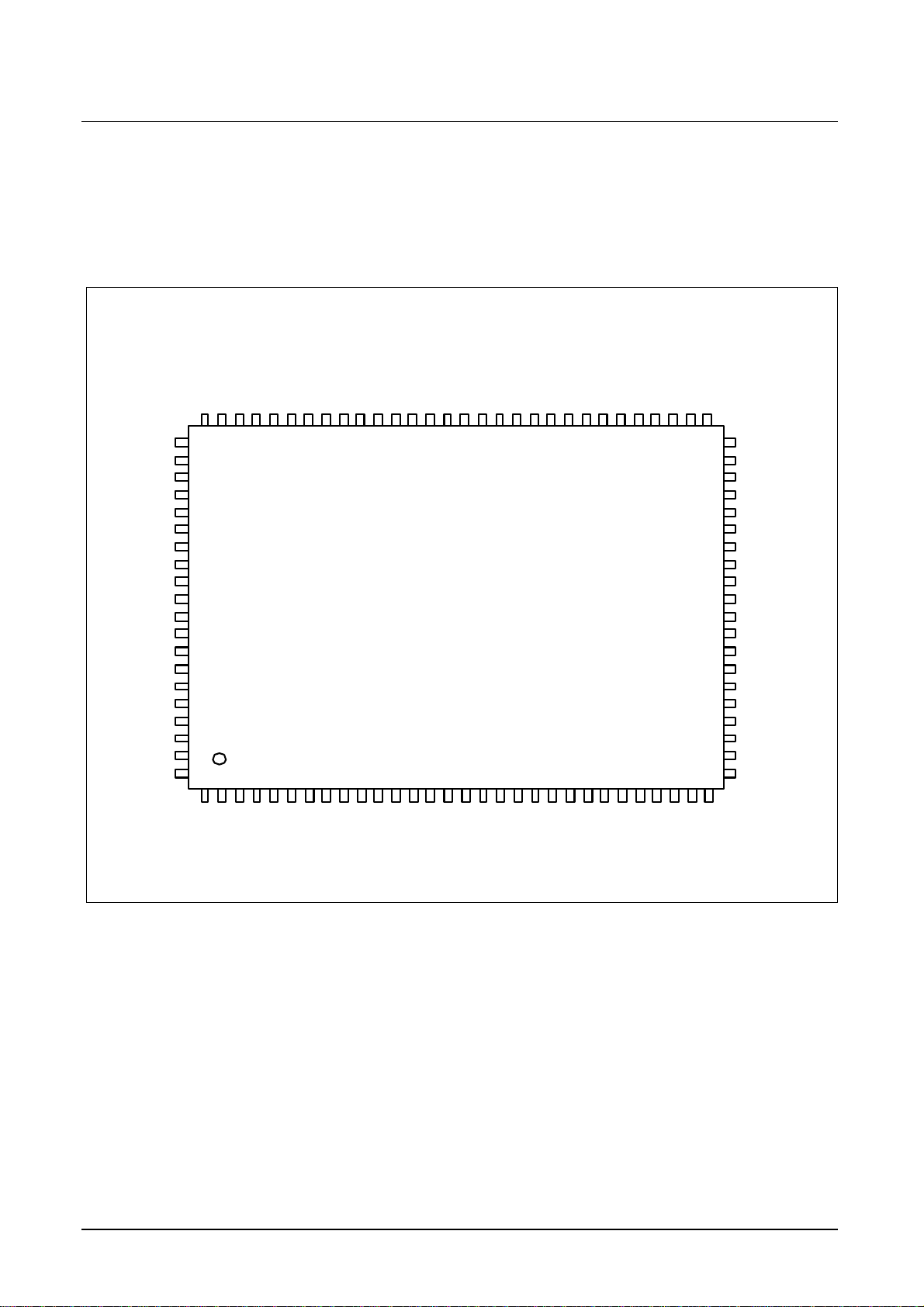
Figure 3 Pin configuration
16 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Pin Description
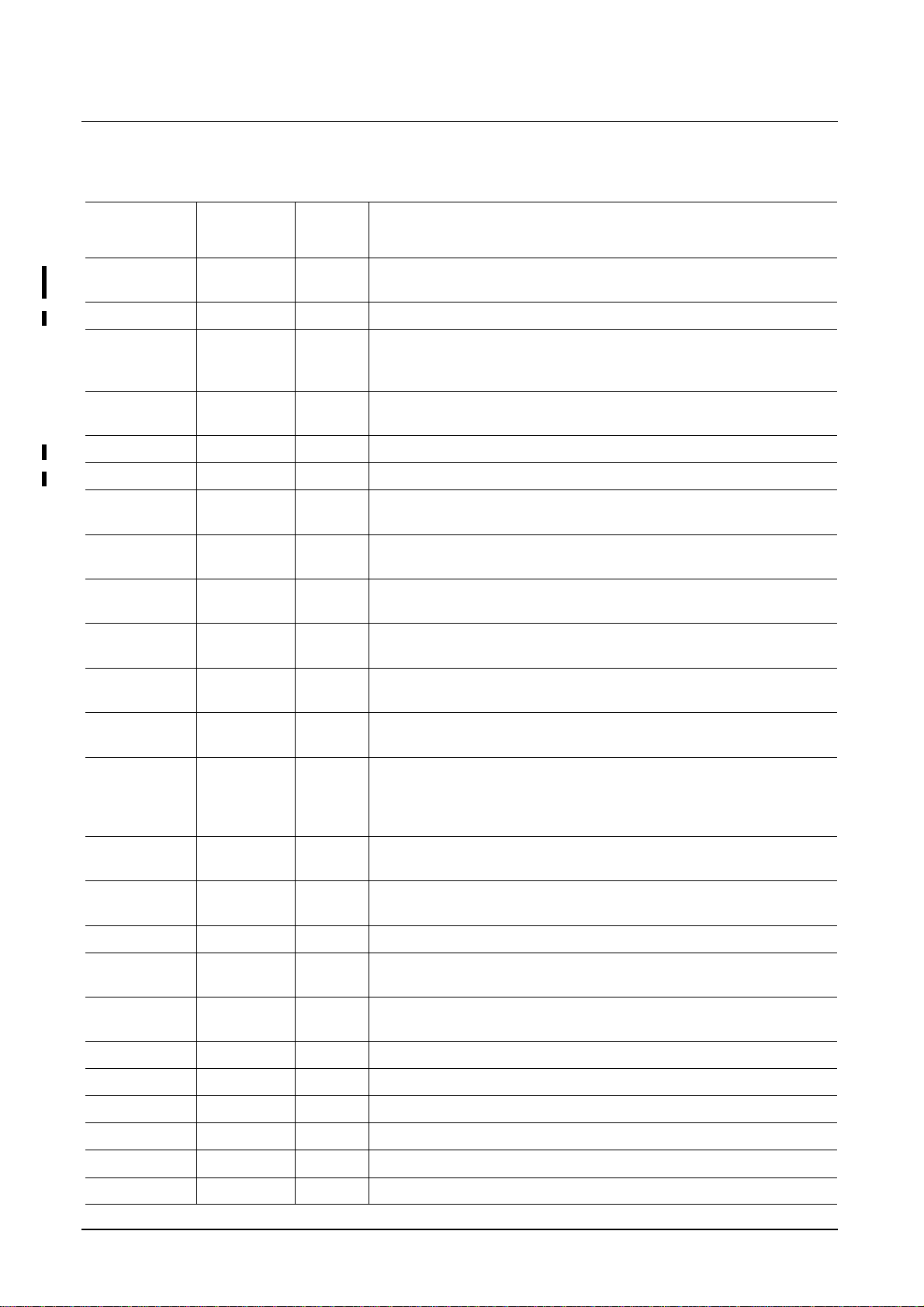
Table 1 Pin definitions and functions
Symbol Pin
Num.
VSSLx *) 8,13,15,16,
22,23,75
VDDLx 9,12, 68,74 S Supply voltage for digital logic parts ( V
VSSPx 10,17,29,43,
57, 70, 79,
100
VDDPx 11,21,36,54,
69, 80,99
VSSE1 67 S Supply voltage for embedded DRAM ( V
VDDEx 14,66 S Supply voltage for embedded DRAM ( V
VSSAx 19,59,92,96, 98S Supply voltage for analog PLL and for analog parts DAC ( V
VDDAx 20,60, 95,97 S Supply voltage for analog PLL and for analog parts DAC
YINM 0...7 39,...,42;
44,...,47
Input
Function
Outp.
S Supply voltage for digital logic parts ( VSS = 0 V )
= 3.3 V )
DD
S Supply voltage for pads ( V
S Supply voltage for pads ( V
( V
= 3.3 V )
DD
I/TTL Data input Y master channel
= 0 V )
SS
= 3.3 V )
DD
= 0 V )
SS
= 3.3 V )
DD
= 0 V )
SS
UVINM 0...7 30,...,35;
37; 38
YINS 0...7 61,...,65;
71,...,73
UVINS 0...7 48,..,53;
55;56
RESET 81 I/TTL System reset. The RESET input is low active. In order to ensure
HINM 27 I/TTL
VINM 26 I/TTL
SYNCENM 28 I/TTL Synchronization enable input master channel
HINS 77 I/TTL
VINS 78 I/TTL
SYNCENS 76 I/TTL Synchronization enable input slave channel
SDA 24 IO I
SCL 25 I I
I/TTL PD Data input UV master channel
I/TTL PD Data input Y slave channel
I/TTL PD Data input UV slave channel
correct operation a "Power On Reset" must be performed. The
RESET pulse must have a minimum duration of two clock periods of
the master (CLKM) and slave clock (CLKS), respectively.
H-Sync input master channel
PD
V-Sync input master channel
PD
H-Sync input slave channel
PD
V-Sync input slave channel
PD
2
C-Bus data line
2
C-Bus clock line
BLANK 7 O/TTL Blanking signal
VOUT 5 O/TTL V-Sync output
HOUT 4 O/TTL H-Sync output
17 Micronas
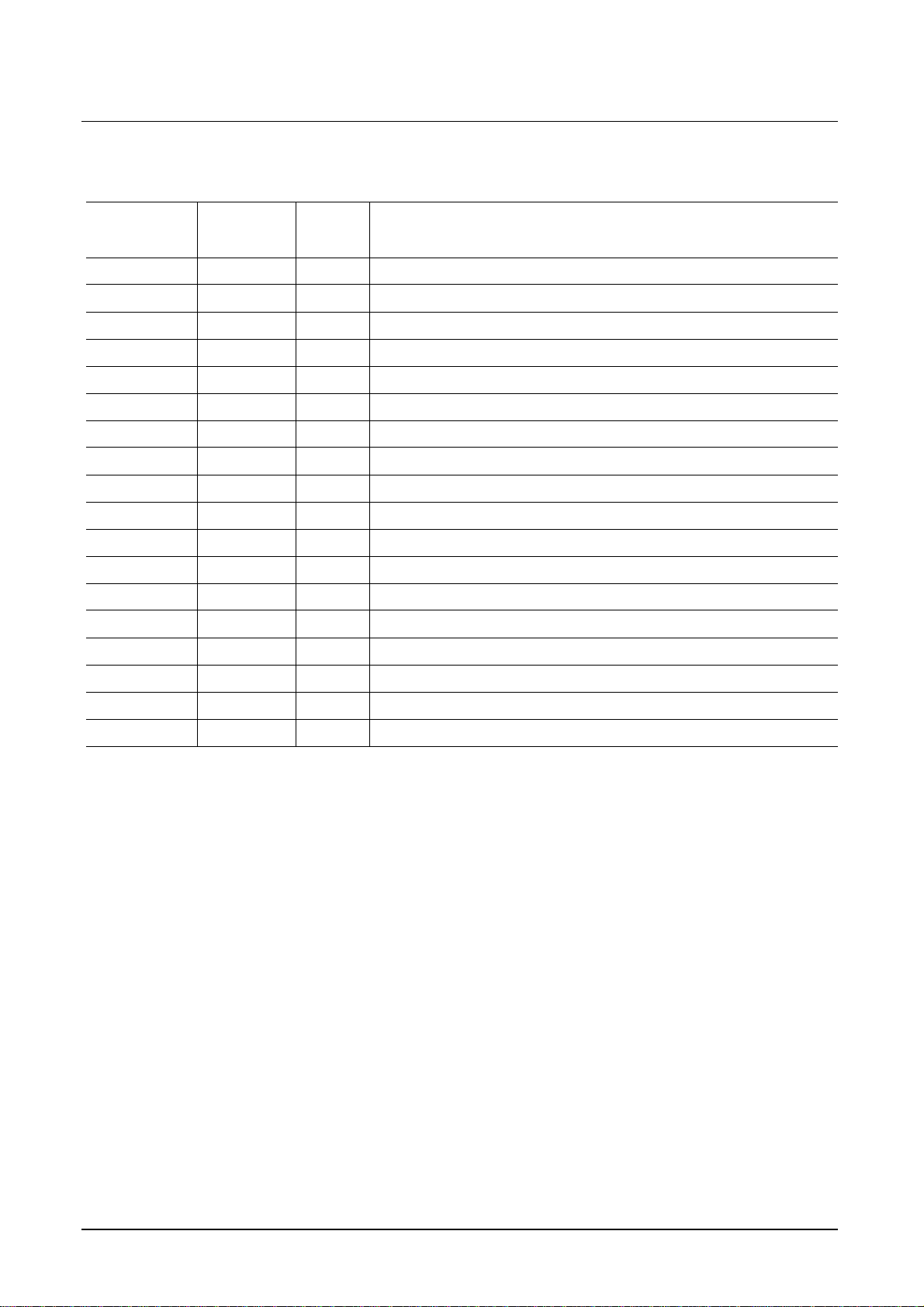
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Table 1 Pin definitions and functions (continued)
Symbol Pin
Num.
INTERLACED 6 O/TTL Interlace signal for AC coupled vertical deflection
CLKM 18 I/TTL System clock master channel
CLKS 58 I/TTL System clock slave channel
X1 / CLKD 2 I/TTL Crystal connection / System clock display channel
X2 1 O/ANA Crystal connection
CLK-OUT 3 O/TTL System clock output
TEST 82 I/TTL Test input, connect to V
IY_O 87 O/ANA Analog luminance output Y
IYQ_O 86 O/ANA Differential analog Y output, connect to V
VDDY 88 S Supply voltage for analog parts DAC ( V
IU_O 84 O/ANA Analog luminance output U
IUQ_O 83 O/ANA Differential analog U output, connect to V
VDDU 85 S Supply voltage for analog parts DAC ( V
IV_O 90 O/ANA Analog luminance output V
Input
Outp.
Function
for normal operation
SS
DD
DD
for normal operation
SS
= 3.3 V )
for normal operation
SS
= 3.3 V )
Pin Description
IVQ_O 89 O/ANA Differential analog V output, connect to V
VDDV 91 S Supply voltage for analog parts DAC ( V
UREF_I 94 I/ANA Analog reference voltage for DACs
RREF_I 93 Reference resistor for DACs
for normal operation
SS
= 3.3 V )
DD
S: supply, I: input, O: output, TTL: digital (TTL)
ANA: analog
PD: pull down (switched on or off depending on I²C bus parameter FORMATM,
FORMATS or SLAVECON)
*) x - placeholder for number
18 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Introduction
5 System description
5.1 Introduction
The SDA 9410 is the first single-chip Micronas MEGAVISION® feature box including
scan rate conversion and the necessary field memories, a second input channel for split
screen applications like picture-and-picture and digital-to-analog converters. The SDA
9410 has three application modes: the SRC (Scan Rate Conversion) mode, the SSC
(Split SCreen) mode and the MUP (MUlti Picture) mode.
The two input channels of the SDA 9410 are not equivalent. One input channel is always
the so called “master” channel and one input channel is always the so called “slave”
channel. Both channels are combined of the output side of the SDA 9410 in the “MUX”
block. The master channel is always the "synchronization" master of both channels.
In the SRC mode the SDA 9410 can be used as a high performance scan rate converter.
Scan rate conversion is done by a motion compensated algorithm known as Micronas
VDU (Vector Driven Up conversion). In addition a high resolution frame based joint-linefree picture-and-picture (maximum approximately 1/9 picture) can be displayed. The
figure below shows an example of the SRC mode.
Figure 4 Principles of SRC mode
19 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Introduction
For this usage the 6 Mbit eDRAM core is separated in two luminance fields and two
chrominance fields (either 4:2:0 or 4:1:1) and a memory area for luminance and
chrominance fields (4:1:1) [maximum circa 1/9 picture] for picture-in-picture applications.
The vector based scan rate conversion is possible for the master channel only.
For the SSC mode the 6 Mbit eDRAM core is split in two 3 Mbit areas, which are able to
contain a maximum of two luminance fields and two chrominance fields (either 4:2:0 or
4:1:1). The figure below shows different applications (“Double window”, “Zoom-in-zoom-
out”). In this case only a simple scan rate conversion (e.g. field doubling for interlaced
conversion: AABB) for both output channels is possible.
Figure 5 Principles of SSC mode
20 Micronas

SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Introduction
The MUP mode allows the combination of one life picture and a configuration of still
pictures. The figure below shows an application. In this case only a simple scan rate
conversion (e.g. field doubling for interlaced conversion: AABB or AAAA) is possible.
Figure 6 Principles of MUP mode
The behaviour of the master and the slave channel does not differ in general. Therefore
for further description of the master and the slave channel the figures are also valid for
both unless it is pointed out.
21 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Input sync controller (ISCM/ISCS)
5.2 Input sync controller (ISCM/ISCS)
Signals Pin number Description
HINM 27 horizontal synchronization signal (polarity programmable, I²C Bus
parameter 11h HINPOLM, default: high active)
VINM 26 vertical synchronization signal (polarity programmable, I²C Bus
parameter 11h VINPOLM, default: high active)
SYNCENM 28 enable signal for HINM and VINM signal, low active ("Input format
conversion (IFCM/IFCS)" on page 26)
HINS 77 horizontal synchronization signal (polarity programmable, I²C Bus
parameter 33h HINPOLS, default: high active)
VINS 78 vertical synchronization signal (polarity programmable, I²C Bus
parameter 33h VINPOLS, default: high active)
SYNCENS 76 enable signal for HINS and VINS signal, low active ("Input format
conversion (IFCM/IFCS)" on page 26)
Table 2 Input signals
The input sync controller derives framing signals from the H- and V-Sync for the input
data processing. The framing signals depend on different I²C Bus parameters and mark
the active picture area.
HINM
pixels per line
VINM
lines
per
field
NAPIPPHM+PD)*
(NAPIPDLM*4 +
CLKM
(APPLIPM*8)*CLKM
PD - Processing Delay
NALIPM + PD
(ALPFIPM*2)
inpar01
Figure 7 Input I²C Bus parameter
The distance between the incoming H-syncs in system clocks of CLKM/CLKS must be
even.
22 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
I²C Bus parameter
[Default value]
NALIPM
[20]
NALIPS
[20]
ALPFIPM
[144]
ALPFIPS
[144]
NAPLIPM
NAPIPDLM
[0]
NAPIPPHM
[0]
NAPLIPS
NAPIPDLS
[0]
NAPIPPHS
[0]
Input sync controller (ISCM/ISCS)
Sub address Description
12h Not Active Line InPut Master defines the number of lines from
the V-Sync to the first active line of the field
34h Not Active Line InPut Slave defines the number of lines from
the V-Sync to the first active line of the field
10h Active Lines Per Field InPut Master defines the number of
active lines
32h Active Lines Per Field InPut Slave defines the number of active
lines
03h, 0Ch Not Active Pixels Per Line InPut Master defines the number of
pixels from the H-Sync to the first active pixel of the line. The
number of pixels is a combination of NAPIPDLM and
NAPIPPHM.
2Dh, 2Eh Not Active Pixels Per Line InPut defines the number of pixels
from the H-Sync to the first active pixel of the line. The number
of pixels is a combination of NAPIPDLS and NAPIPPHS.
APPLIPM
[180]
APPLIPS
[180]
0Fh Active Pixels Per Line InPut Master defines the number of
active pixels
31h Active Pixels Per Line InPut Slave defines the number of active
pixels
Table 3 Input write I²C Bus parameter
Inside of the SDA 9410 a field detection block is necessary for the detection of an odd
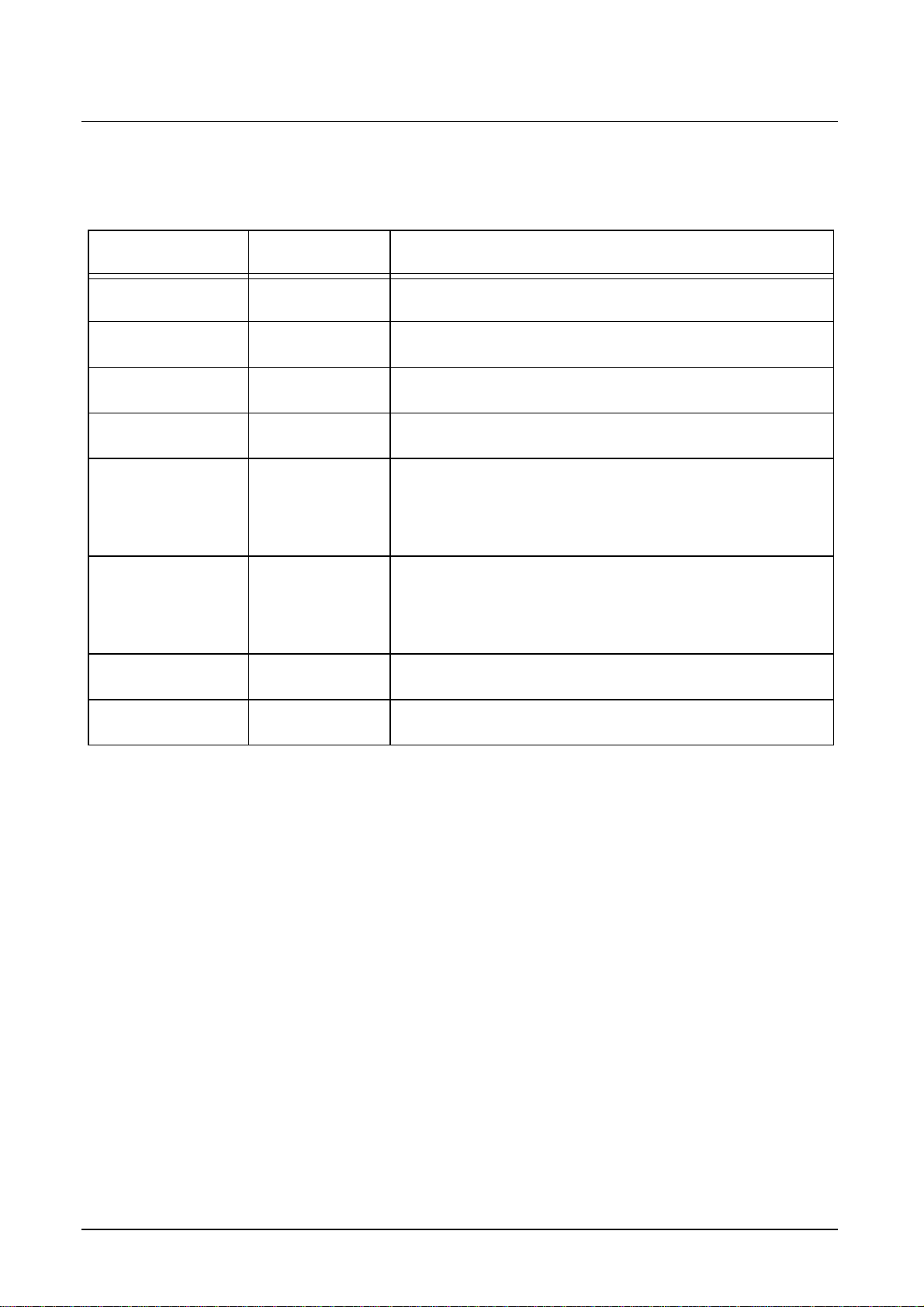
(A) or even (B) field. Therefore the incoming H-Sync H1 (delayed HINM/HINS signal,
delay depends on NAPIPDLM/NAPIPDLS and NAPIPPHM/NAPIPPHS) is doubled (H2
signal). Depending on the phase position of the rising edge of the VINM/VINS signal an
A (rising edge between H1 and H2) or B (rising edge between H2 and H1) field is
detected. For proper operation of the field detection block, the VINM/VINS must be
delayed depending on the delay of the HINM/HINS signal (H1). The figure below
explains the field detection process and the functionality of the VINDELM/VINDELS I²C
Bus parameter (inside the SDA 9410 the delayed VINM/VINS signal is called Vd and the
detected field signal is called Ffd).
23 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
CLKM
H1
H2
VINM
Vd
Ffd
VINM
Vd
(VINDELM * 128 + 1) *
Tclkm
x
(VINDELM * 128 + 1) *
x
Figure 8 Field detection and VINM delay
Input sync controller (ISCM/ISCS)
Field 1(A)
Tclkm
Field 2(B)Ffd
I²C Bus parameter
[Default value]
VINDELM
[0]
VINDELS
[0]
FIEINVM
1 : Field A=1
[0]: Field A=0
FIEINVS
1 : Field A=1
[0]: Field A=0
VCRMODEM
[1]: on
0 : off
VCRMODES
[1]: on
0 : off
Sub address Description
11h Delay of the incoming V-Sync VINM (must be adjusted
depending on the delay of the HINM signal)
33h Delay of the incoming V-Sync VINS (must be adjusted
depending on the delay of the HINS signal)
0Bh Inversion of the internal field polarity master
2Dh Inversion of the internal field polarity slave
0Bh In case of non standard interlaced signals (VCR, Play-
Stations) a filtering of the internal field signal has to be done
(should also be used for normal TV signals)
2Dh In case of non standard interlaced signals (VCR, Play-
Stations) a filtering of the internal field signal has to be done
(should also be used for normal TV signals)
Table 4 Input write I²C Bus parameter
In case of non-standard signals the field order is indeterminate (e.g. AAA... , BBB... ,
AAABAAAB..., etc.). Therefore a special filtering algorithm is implemented, which can be
switched on by the I²C Bus parameter VCRMODEM/VCRMODES. It is recommended to
set the I²C Bus parameter VCRMODEM=1. In other case (VCRMODEM=0) an additional
24 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Input sync controller (ISCM/ISCS)
internal signal VTSEQM is generated. This signal level is high (VTSEQM=1), if at least
the last to fields were identical. Due to the fixed storage places of the fields in the internal
memory block, this information is necessary for the scan rate conversion processing
("Output sync controller (OSCM/S)" on page 77, it is recommended in case of
VCRMODEM=0 to choose an adaptive operation mode).
The OPDELM I²C Bus parameter is used to adjust the outgoing V-Sync VOUT in relation
to the incoming delayed V-Sync VINM. In case of SSC and MUP mode the
recommended default value should not be changed.
I²C Bus parameter
[Default value]
OPDELM
[170]
Sub address Description
1Bh Delay (in number of lines) of the internal V-Sync (delayed
VINM) to the outgoing V-Sync (VOUT)
Table 5 Input write I²C Bus parameter
The internal line counter is used to determine the information about the standard of the
incoming signal.
I²C Bus parameter Sub address Description
TVMODEM 7Bh TV standard of the incoming signal master:
1: NTSC
0: PAL
TVMODES 7Dh TV standard of the incoming signal slave:
1: NTSC
0: PAL
Table 6 Input read I²C Bus parameter
25 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Input format conversion (IFCM/IFCS)
5.3 Input format conversion (IFCM/IFCS)
Signals Pin number Description
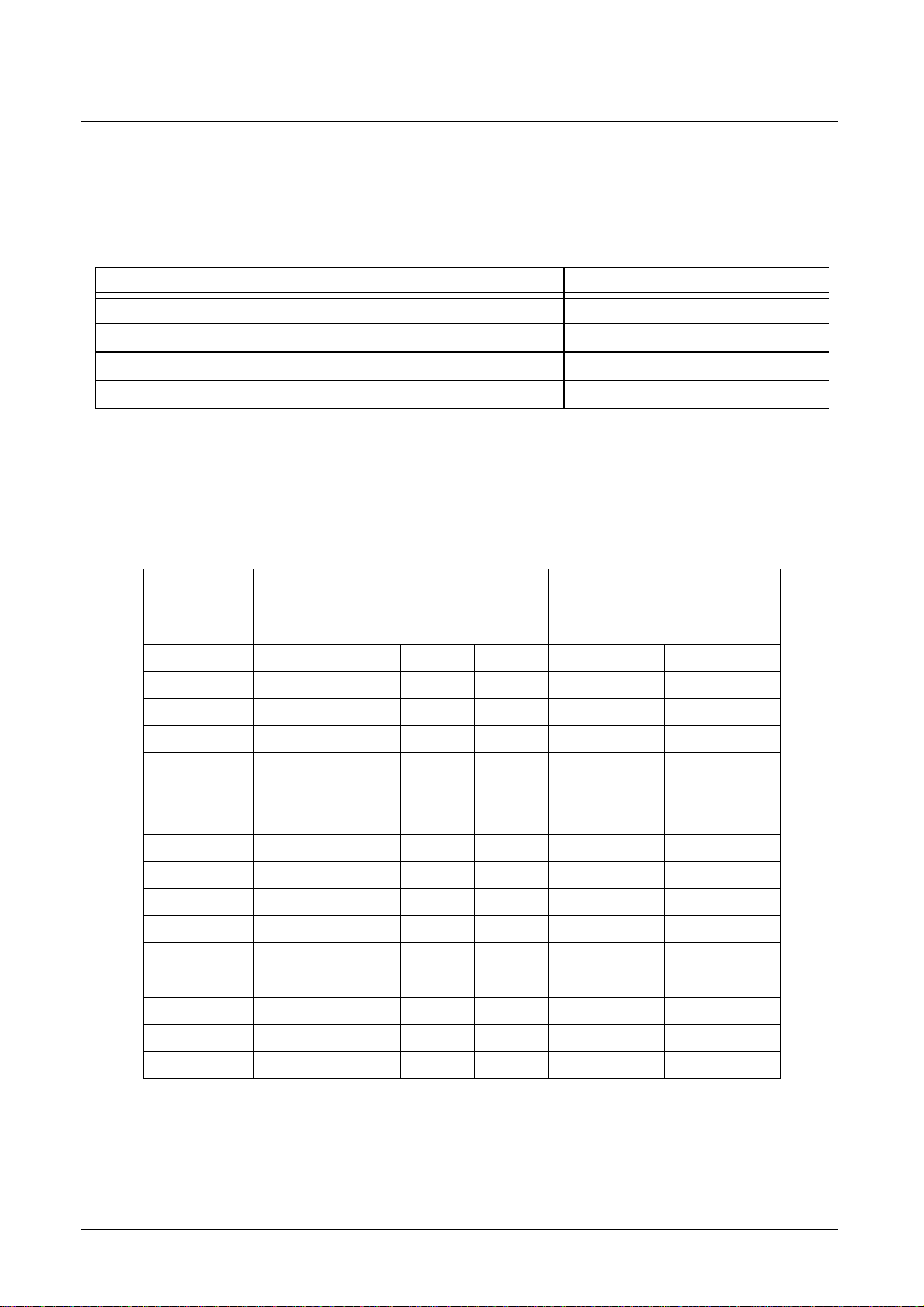
YINM0...7 39,40,41,42,44,45,46,47 luminance input master
UVINM0...7 30,31,32,33,34,35,37.38 chrominance input master
YINS0...7 61,62,63,64,65,71,72,73 luminance input slave
UVINS0...7 48,49,50,51,52,53,55,56 chrominance input slave
Table 7 Input signals
The SDA 9410 accepts at the input side the sample frequency relations
of Y : (B-Y) : (R-Y): 4:2:2 and CCIR 656.
Data
Pin
CCIR 656
FORMATM = 1X
FORMATM = 01
4:2:2 Parallel
FORMATM = 00
YINM7 U
YINM6 U
YINM5 U
YINM4 U
YINM3 U
YINM2 U
YINM1 U
YINM0 U
07
06
05
04
03
02
01
00
Y
07
Y
06
Y
05
Y
04
Y
03
Y
02
Y
01
Y
00
V
07
V
06
V
05
V
04
V
03
V
02
V
01
V
00
Y
17
Y
16
Y
15
Y
14
Y
13
Y
12
Y
11
Y
10
UVINM7 U
UVINM6 U
UVINM5 U
UVINM4 U
UVINM3 U
UVINM2 U
UVINM1 U
UVINM0 U
Y
07
Y
06
Y
05
Y
04
Y
03
Y
02
Y
01
Y
00
07
06
05
04
03
02
01
00
Y
17
Y
16
Y
15
Y
14
Y
13
Y
12
Y
11
Y
10
V
07
V
06
V
05
V
04
V
03
V
02
V
01
V
00
Table 8 Input data formats
X
: X: signal component a: sample number b: bit number
ab
26 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Input format conversion (IFCM/IFCS)
In case of CCIR 656 three modes are supported (FORMATM/FORMATS=11 means full
CCIR 656 support, including H-, V-Sync and Field signal, FORMATM/FORMATS=01
means only data processing, H- and V-Sync have to be added separately according
PAL/NTSC norm, FORMATM/FORMATS=10 means only data processing, H- and Vsync have to be added separately according CCIR656-PAL/NTSC norm). The
representation of the samples of the chrominance signal is programmable as positive
dual code (unsigned, I²C Bus parameter TWOINM/TWOINS=0) or two's complement
code (TWOINM/TWOINS=1, "I²C Bus" on page 117, I²C Bus parameter 0Bh,2Dh).
Inside the SDA 9410 all algorithms assume positive dual code.
FORMATM/
FORMATS
00 PAL/NTSCPAL/NTSC4:2:2 4:2:2
01 (CCIR 656 only
data)
10 CCIR 656 CCIR 656 CCIR 656 x
HINS/HINS VINM/VINS YINM/YINS UVINM/UVINS
PAL/NTSC PAL/NTSC CCIR 656 x
11 (full CCIR 656) x x CCIR 656 x
Table 9 Input sync formats
The amplitude resolution for each input signal component is 8 bit, the maximum clock
frequency is 27 MHz. Consequently the SDA 9410 is dedicated for application in high
quality digital video systems.
27 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Input format conversion (IFCM/IFCS)
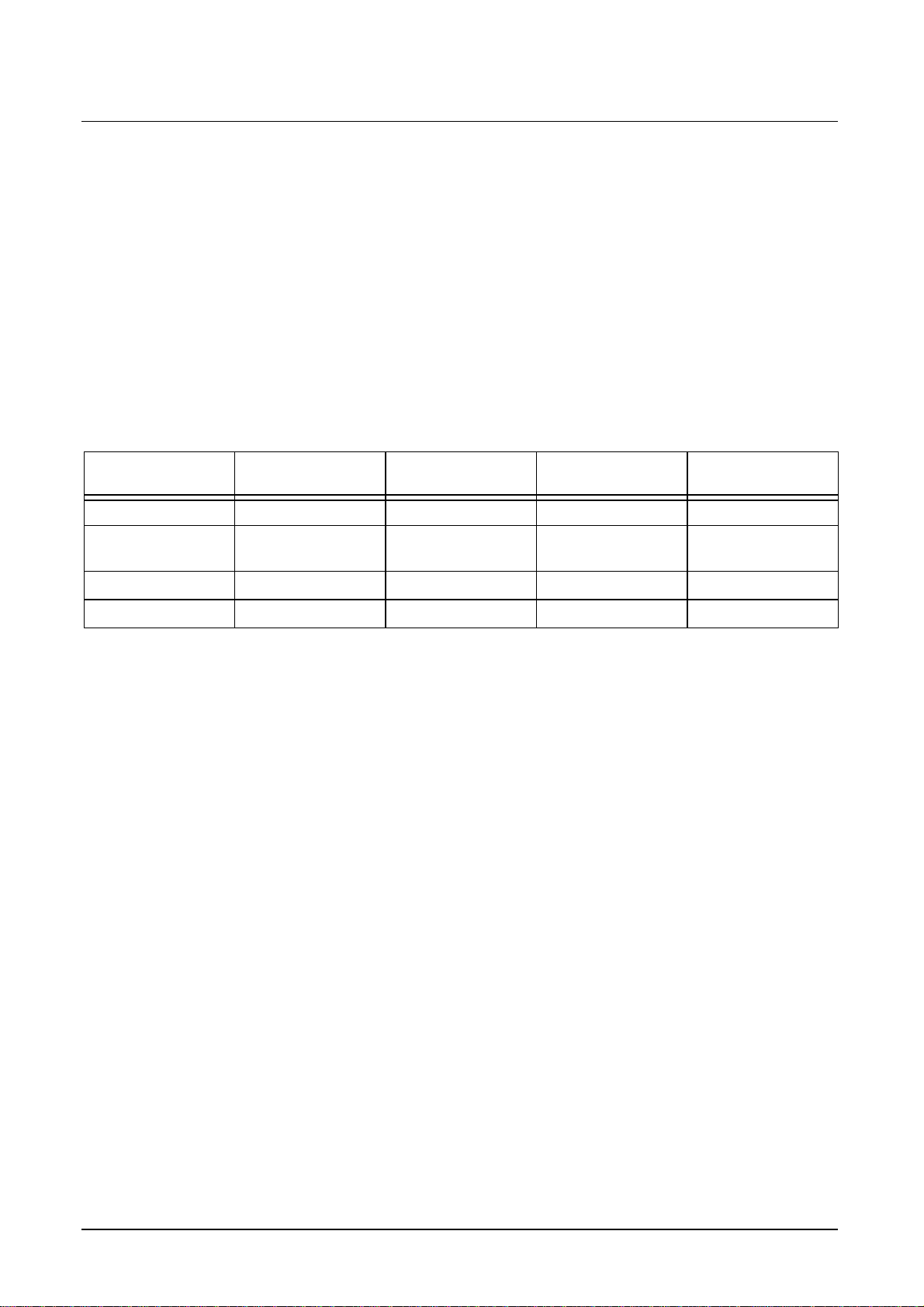
The Figure 9 shows the generation of the internal H- and V-syncs in case of full CCIR
656 mode. The H656 sync is generated after the EAV. The V656 and F656 signals
change synchronously with the EAV timing reference code.
CLK1 (27 MHz)
CCIR 656 interface
YIN
CLK1 (27 MHz)
YIN
H656
V656
(e.g.)
F656
(e.g.)
SAVEAV
288 Tclk1(PAL)
276 Tclk1(NTSC)
1728 Tclk1(PAL)
1716 Tclk1(NTSC)
x
EAV x x EAVx xSAV x
u0 y0 v0 y1 u2 y3
EAV
EAV
11111111 00000000 00000000 1FV1P3P2P1P
MSB LSB
SAV
11111111 00000000 00000000 1FV0P3P2P1P
0
0
F = 0 during field 1(A)
F = 1 during field 2(B)
V = 0 elsewhere
V = 1 during field blanking
Figure 9 Explanation of 656 format
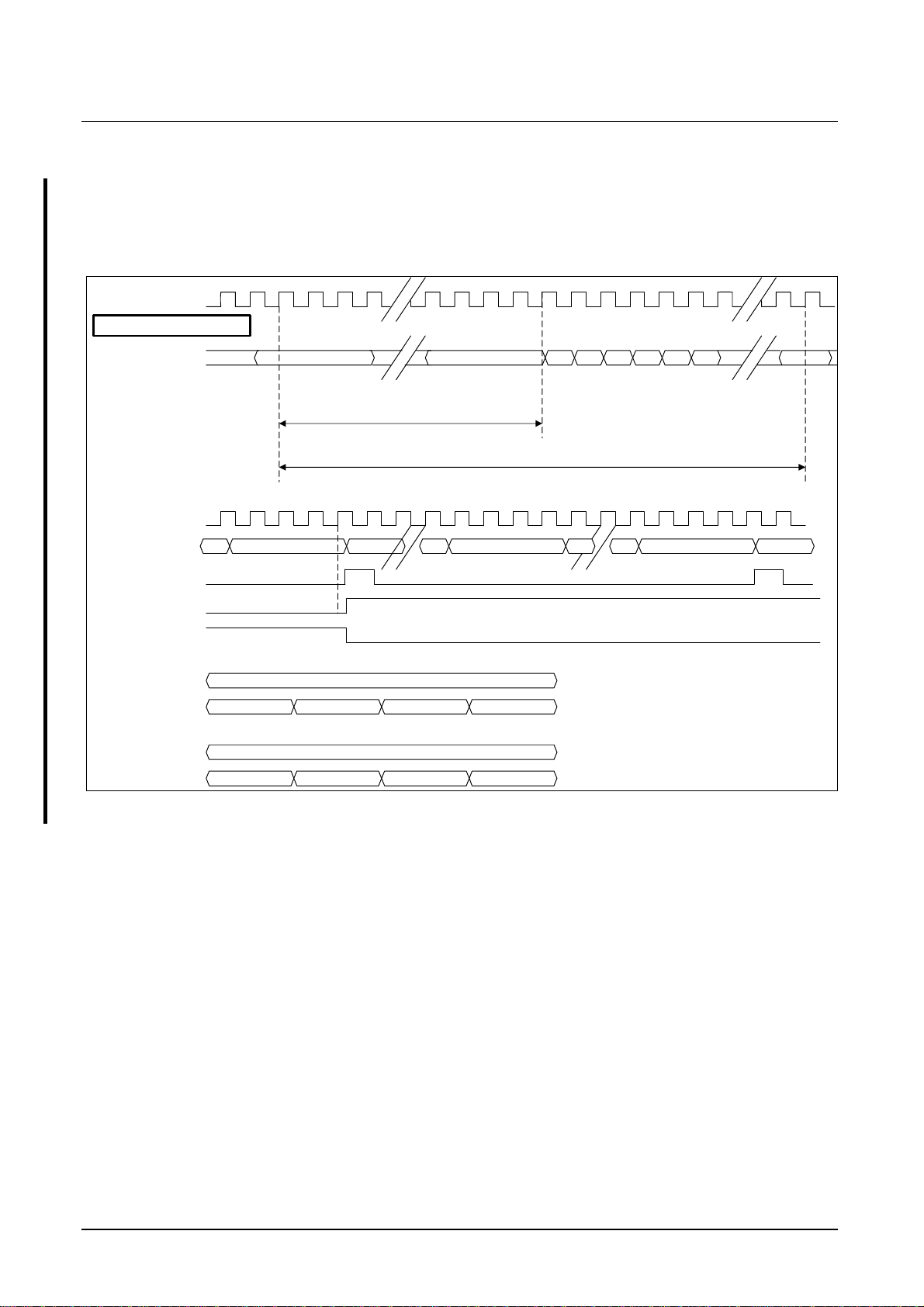
The Figure 10 explains the functionality of the SYNCENM/SYNCENS signal. The SDA
9410 needs the SYNCENM/SYNCENS (synchronization enable) signal, which is used to
gate the YINM/YINS, UVINM/UVINS as well as the HINM/HINS and the VINM/VINS
signal. This is implemented for frontends which are working with 13.5 MHz and a large
output delay time for YINM/YINS, UVINM/UVINS, HINM/HINS and VINM/VINS (e.g.
Micronas VPC32XX, output delay: 35 ns). For this application the half system clock
CLKM/CLKS (13.5 MHz) from the frontend should be provided at this pin. In case the
frontend is working at 27.0 MHz with sync signals having delay times smaller than 25 ns,
this input can be set to low level (SYNCENM/SYNCENS=
V
) (e.g. Micronas SDA 9206,
SS
output delay: 25 ns). Thus the signals YINM/YINS, UVINM/UVINS, HINM/HINS and
VINM/VINS are sampled with the CLKM/CLKS system clock when the SYNCENM/
SYNCENS input is low.
The Figure 10 shows the gated inputs signals YINMen, UVINMen, HINMen and
VINMen.
28 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
SYNCENM
YINM
UVINM
YINMen
UVINMen
HINM/VINM
HINMen/VINMen
CLKM
x
x
y0 y1 y2 y3
u0 v0 u2 v2
x
x
y0 y1 y2 y3
u0 v0 u2 v2
Input format conversion (IFCM/IFCS)
Figure 10 SYNCENM/SYNCENS signal
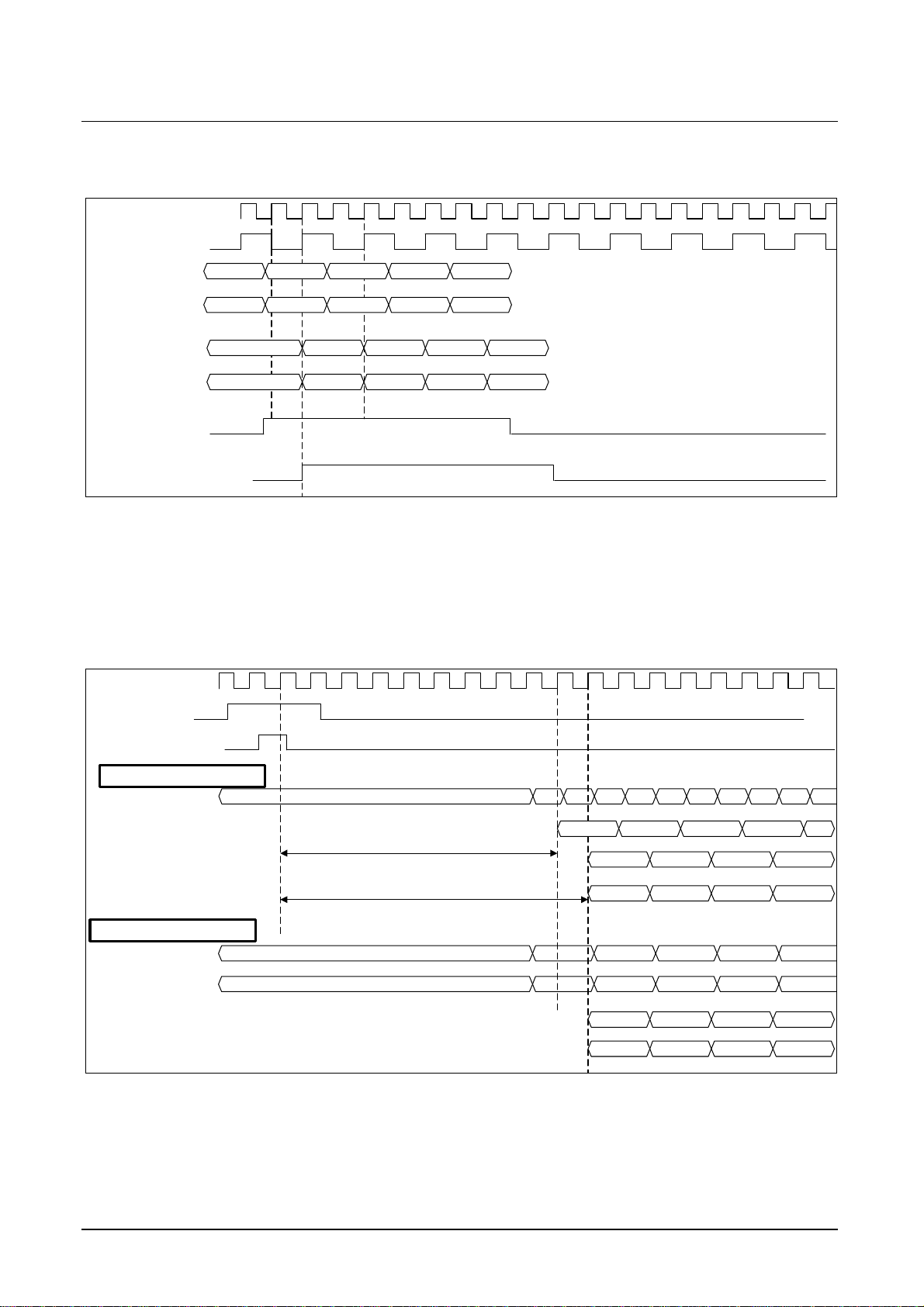
The Figure 11 shows the input timing and the functionality of the NAPIPDLM/NAPIPDLS
and NAPIPPHM/NAPIPPHS I²C Bus parameter in case of CCIR 656 and 4:2:2 parallel
data input format for one example. The signals HINMint, YINMint and UVMint are the
internal available sampled input signals.
CLKM
HINM
HINMint
CCIR 656 interface
YINM
(NAPIPDLM* 4 + NAPIPPHM + 7) * Tclkm
=(0 * 4 + 2 + 7) * Tclkm = 9 Tclkm (e.g.)
YINMint
UVINMint
4:2:2 interface
YINM
UVINM
YINMint
UVINMint
(NAPIPDLM* 4 + NAPIPPHM + 7) * Tclkm
=(0 * 4 + 3 + 7) * Tclkm = 10 Tclkm (e.g.)
Figure 11 Input timing
u0 y0 v0 y1 u2 y2 v2 y3xxx
y0 y1 y2 y3xxx
u0 v0 u2 v2xxx
u0 v0
y0
u0 v0 u2 v2
y0 y1 y3 y4
u0 v0 u2 v2
u2
y1
u4 y4
v2
u4
y2
y3
y4
u4
29 Micronas
SDA9410 Preliminary Data Sheet
Input signal processing
5.4 Input signal processing
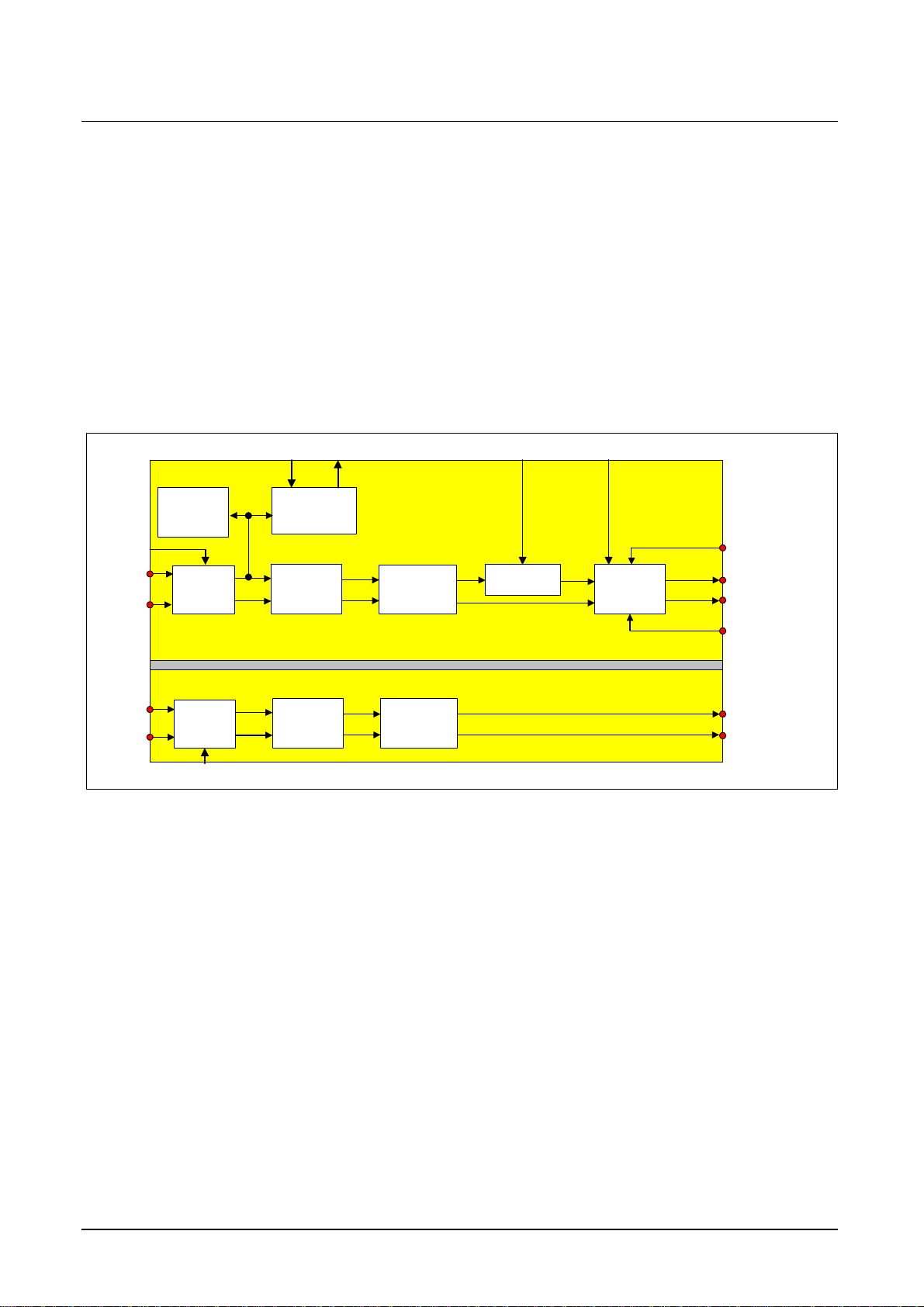
The Figure 12 shows a detailed block diagram of the input processing blocks. The input
signal can be vertically and horizontally compressed or horizontally expanded by a large
number of factors. Furthermore the input signal can be processed by different noise
reduction algorithms to reduce the noise in the signal. The noise measurement block
determines the noise level of the input signal. The letter box detection block finds the
start and end line of letter box pictures. The information can be used by a µC to calculate
zooming factors and to control the IC for resizing the picture for a full screen display on
16:9 tubes.
DELM
YINM
UVINM
Letter
box
detection
Delay
-3/+4
NMLINE, NMALG NOISEME
Noise
measurement
Line
memories
MASTER
Vertical and
horizontal
compression/
expansion
SNRON
Spatial noise
reduction
NRON
Temporal
reduction
noise
YM from Memory
YM to Memory
CM to Memory
CM from Memory
YINS
UVINS
Delay
-3/+4
DELS
Line
memories
SLAVE
Vertical and
horizontal
compression/
expansion
bdldr01
YS to Memory
CS to Memory
Figure 12 Block diagram of input processing blocks
The different blocks and the corresponding I²C Bus parameters will be described now in
more detail.
30 Micronas
 Loading...
Loading...