Micronas Intermetall HAL710SF-K, HAL710SF-E Datasheet
HAL710
Hall-Effect Sensor
with Direction Detection
Edition Feb. 20, 2001
6251-478-1AI
ADVANCE INFORMATION
MICRONAS
MICRONAS

HAL710 ADVANCE INFORMATION
Contents
Page Section Title
3 1. Introduction
3 1.1. Features
3 1.2. Applications
4 1.3. Marking Code
4 1.3.1. Special Marking of Prototype Parts
4 1.4. Operating Junction Temperature Range
4 1.5. Hall Sensor Package Codes
4 1.6. Solderability
5 2. Functional Description
7 3. Specifications
7 3.1. Outline Dimensions
7 3.2. Dimensions of Sensitive Areas
7 3.3. Positions of Sensitive Areas
8 3.4. Absolute Maximum Ratings
8 3.5. Recommended Operating Conditions
9 3.6. Electrical Characteristics
10 3.7. Magnetic Characteristics
10 3.7.1. Magnetic Thresholds
10 3.7.2. Matching B
10 3.7.3. Hysteresis Matching
and B
S1
S2
11 4. Application Notes
11 4.1. Ambient Temperature
11 4.2. Extended Operating Conditions
11 4.3. Signal Delay
11 4.4. Test Mode Activation
11 4.5. Start-up Behavior
12 4.6. EMC and ESD
12 5. Data Sheet History
2 Micronas

ADVANCE INFORMATION HAL710
Hall-Effect Sensor with Direction Detection
1. Introduction
The HAL 710 is a monolithic integrated Hall-effect sensor manufactured in CMOS technology with two independent Hall plates S1 and S2 spaced 2.35 mm apart.
The device has two open-drain outputs:
The ’Count Output’ operates like a single latched Hall
switch according to the magnetic field present at Hall
plate S1 (see Fig. 3–3).
The ‘Direction Output’ indicates the direction of a linear
or rotating movement of magnetic objects.
In combination with an active target providing a
sequence of alternating magnetic north and south
poles, the sensor forms a system generating the signals required to control position, speed, and direction
of the target movement.
The internal circuitry evaluates the direction of the
movement and updates the ‘Direction Output’ at every
edge of the ‘Count Signal’ (rising and falling). The
Direction Output is high if the target moves from Hall
plate S1 to Hall plate S2. It is low if the target first
passes plate S2 and later plate S1. The state of the
Direction Output only changes at a rising or falling
edge of the Count Output.
1.1. Features
– generation of ‘Count Signals’ and ‘Direction Signals’
– delay of the ‘Count Signals’ with respect to the
‘Direction Signal’ of 1 µs minimum
– switching type latching
– low sensitivity
–typical B
–typical B
: 14.9 mT at room temperature
ON
: −14.9 mT at room temperature
OFF
– temperature coefficient of −2000 ppm/K in all mag-
netic characteristics
– switching offset compensation at typically 150 kHz
– operation from 3.8 V to 24 V supply voltage
– operation with static magnetic fields and dynamic
magnetic fields up to 10 kHz
– overvoltage protection at all pins
– reverse-voltage protection at V
DD
-pin
– robustness of magnetic characteristics against
mechanical stress
– short-circuit protected open-drain outputs by ther-
mal shut down
– constant switching points over a wide supply voltage
range
– EMC corresponding to DIN 40839
The design ensures a setup time for the Direction Output with respect to the corresponding Count Signal
edge of 1/2 clock periods (1 µs minimum).
The device includes temperature compensation and
active offset compensation. These features provide
excellent stability and matching of the switching points
in the presence of mechanical stress over the whole
temperature and supply voltage range. This is required
by systems determining the direction from the comparison of two transducer signals.
The sensor is designed for industrial and automotive
applications and operates with supply voltages from
3.8 V to 24 V in the ambient temperature range from
−40 °C up to 125 °C.
The HAL 710 is available in the SMD package
SOT-89B.
1.2. Applications
The HAL 710 is the optimal sensor for position-control
applications with direction detection and alternating
magnetic signals such as:
– multipole magnet applications,
– rotating speed and direction measurement,
position tracking (active targets), and
– window lifters.
Micronas 3
HAL710 ADVANCE INFORMATION
HALXXXPA-T
Temperature Range: K, or E
Package: SF for SOT-89B
Type: 710
Example: HAL 710SF-K
→ Type: 710
→ Package: SOT-89B
→ Temperature Range: T
J
= −40 °C to +140 °C
1.3. Marking Code
All Hall sensors have a marking on the package surface (branded side). This marking includes the name
of the sensor and the temperature range.
Type Temperature Range
K E
HAL710 710K 710E
1.3.1. Special Marking of Prototype Parts
Prototype parts are coded with an underscore beneath
the temperature range letter on each IC. They may be
used for lab experiments and design-ins but are not
intended to be used for qualification test or as production parts.
1.4. Operating Junction Temperature Range
1.6. Solderability
All packages: according to IEC68-2-58
During soldering, reflow processing and manual
reworking, a component bod y temperature of 260 °C
should not be exceeded.
Components stored in the original packaging should
provide a shelf life of at least 12 months, starting from
the date code prin ted on the labels, even in environments as extreme as 40 °C and 90% relative humidity.
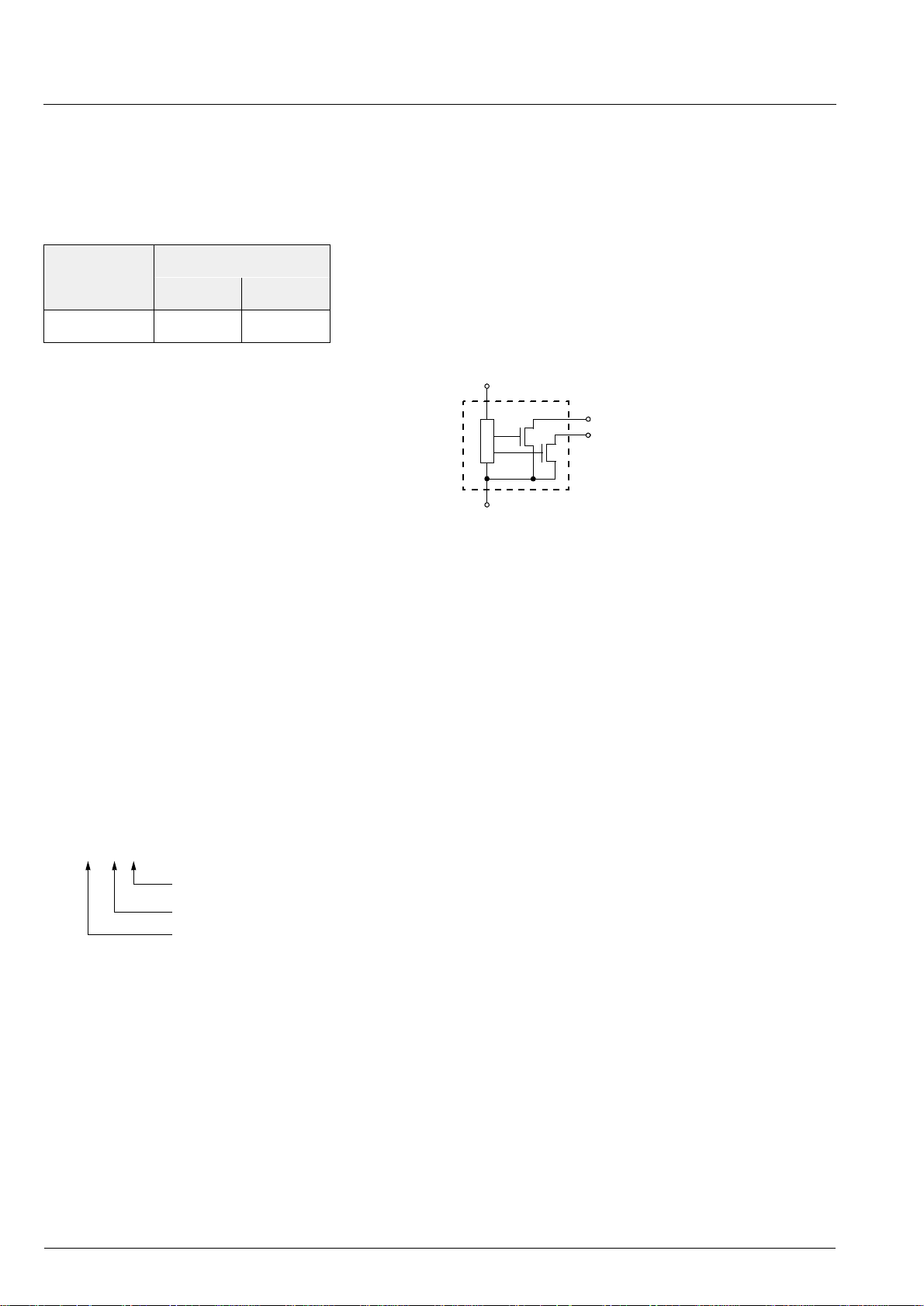
V
1
DD
3 Count Output
2 Direction Output
4GND
Fig. 1–1: Pin configuration
The Hall sensors from Micronas are specified to the
chip temperature (junction temperature T
= −40 °C to +140 °C
K: T
J
= −40 °C to +100 °C
E: T
J
The relationship between ambient temperature (T
).
J
A
and junction temperature is explained in Section 4.1.
on page 11.
1.5. Hall Sensor Package Codes
)
Hall sensors are available in a wide variety of packaging quantities. For more detailed information, please
refer to the brochure: “Ordering Codes for Hall Sensors”.
4 Micronas
 Loading...
Loading...