Micron MTFDHAL1T6TCU, MTFDHAL1T9TCT, MTFDHAL3T2TCU, MTFDHAL3T8TCT, MTFDHAL6T4TCU User Manual
...Page 1

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
9200 NVMe SSDs
MTFDHAL1T6TCU, MTFDHAL1T9TCT, MTFDHAL3T2TCU,
MTFDHAL3T8TCT, MTFDHAL6T4TCU, MTFDHAL7T6TCT,
MTFDHAL8TATCW, MTFDHAL11TATCW
Features
Features
• Micron® 3D NAND Flash
• PCIe® Gen3: U.2 ×4
•
NVMe™ 1.2
• Capacity
– 9200 ECO: 11.0TB, 8.0TB
– 9200 PRO: 1.92TB, 3.84TB, 7.68TB
– 9200 MAX: 1.6TB, 3.2TB, 6.4TB
• Endurance (total bytes written)
– 1.6TB: Up to 8.8PB
– 1.92TB: Up to 3.5PB
– 3.2TB: Up to 17.5PB
– 3.84TB: Up to 7.0PB
– 6.4TB: Up to 35.1PB
– 7.68TB: Up to 14.0PB
– 8.0TB: Up to 11.7PB
– 11.0TB: Up to 16.1PB
• 512 and 4096 byte sector sizes
• Power: <5W idle, 25W power limited, or unlimited
• Surprise insertion/surprise removal (SISR) and
hot-plug capable
• Power-backed cache
• Steady state performance
form factor)
– Sequential 128KB read: 2.85–3.15 GB/s
– Sequential 128KB write: 1.9–2.3 GB/s
– Random 4KB read: 700K–770K IOPS
– Random 4KB write: 130K–280K IOPS
• Latency to media performance, typical (QD = 1)
– READ: 92–150µs3, WRITE: 21µs
• Reliability
– MTTF: 2 million hours
– Field-upgradable firmware
– UBER: <1 sector per 1017 bits read
• SMBus for drive management
• End-to-end data path protection
• SMART command set support
• Cryptographic erase
• FlexPro (flexible over provisioning)
1
1
1, 2
(varies by capacity and
4
5
• Temperature
6
– 0°C to 80°C SMART temperature
– 0°C to 35°C ambient for U.2
– Temperature protection
• Mechanical/electrical
– U.2: 69.85 × 15.00 × 100.5mm, 12V (–6%/+8%)
• Shock
– U.2: 1500g @ 0.5ms
• Vibration: 3.1 G
5–800Hz @ 30 min/axis
RMS
Controller Features
• NVMe controller
– Number of queues: 128 SQ/CQ pairs
– Weighted round robin with urgent arbitration
• Interrupt coalescing
• NVMe command set attributes
– Completion queue entry size: 16 bytes
– Submission queue entry size: 64 bytes
• 4KB Atomic operations
Notes:
1. User capacity: 1GB = 1 billion bytes;
1TB = 1 trillion bytes;
1PB = 1 peta bytes.
2. Steady state as defined by SNIA Solid State
Storage Performance Test Specification Enterprise v1.1.
3. READ latency varies by capacity.
4. Based on population statistics that are not
relevant to individual units and a T
60°C.
5. 4K sector size support only.
6. Operating temperature is the drive case
temperature as measured by the SMART
temperature. See air flow recommendations.
CASE
of
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
Products and specifications discussed herein are subject to change by Micron without notice.
1
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2
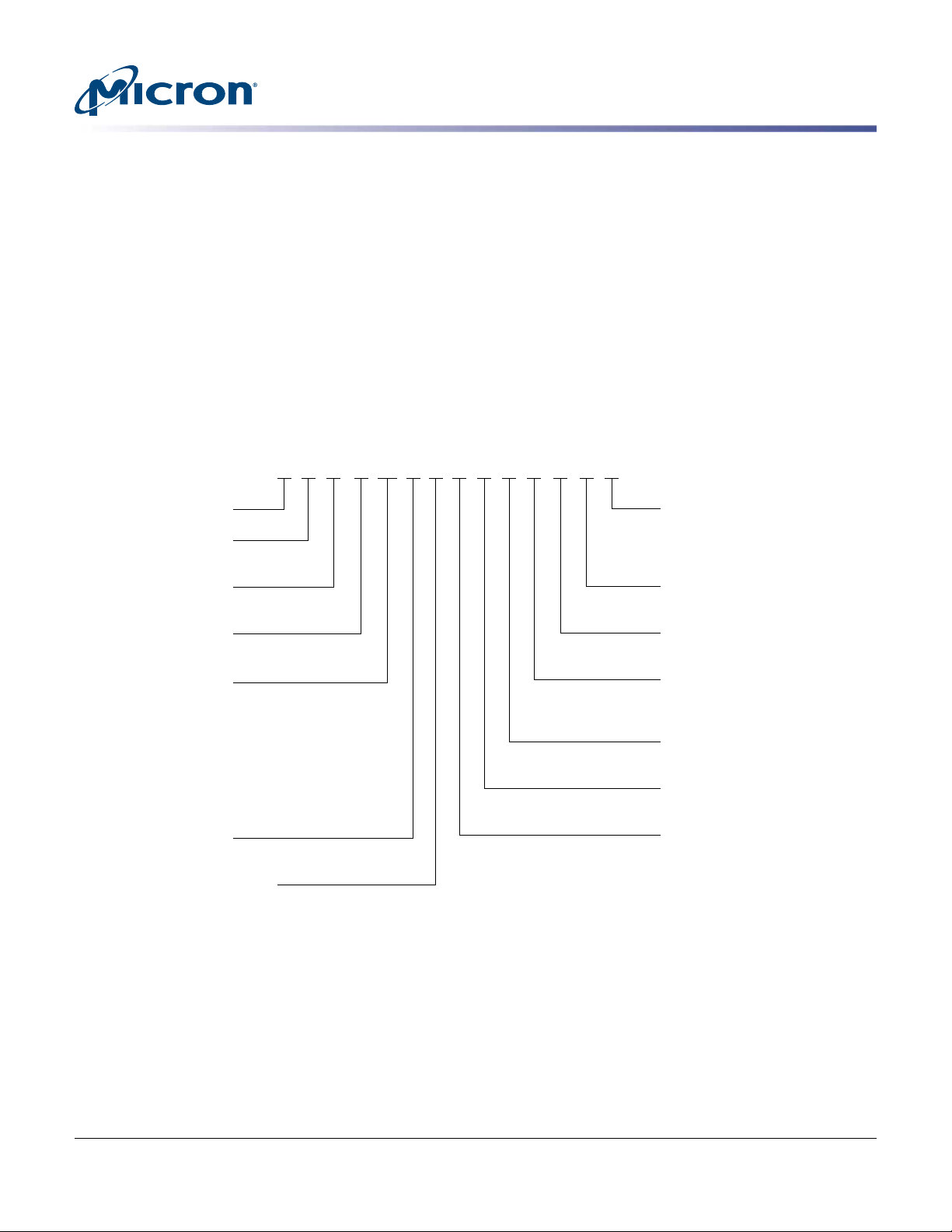
FD H 1T6 T
Micron Technology
Product Family
FD = Flash drive
Drive Interface
H = PCIe Gen3
Drive Form Factor
AL = 2.5-inch, 15mm
Device Capacity
1T6 = 1.6TB
1T9 = 1.92TB
3T2 = 3.2TB
3T8 = 3.84TB
6T4 = 6.4TB
7T6 = 7.68TB
8T0 = 8.0TB
11T0 = 11.0TB
NAND Flash Type
T = TLC
Flash Drive Product Family
CU = 9200 MAX
CT = 9200 PRO
CW = 9200 ECO
Production Status
Blank = Production
ES = Engineering sample
MS = Mechanical sample
Customer Designator
YY = Standard
Additional Features
AB = Standard
Extended Firmware Features
Z = Standard
8 = VPD/SMBUS on by default
Sector Size
1 = 512 Bytes
NAND Component
AR = 384Gb, TLC, x16, 1.8V (3D)
BOM Production
1 = First generation
AL CU 1 Z AB ESAR 1 YY
MT
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Features
Native Drivers
• Microsoft Windows Server® 2016
• Red Hat® Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.5+
• CentOS® 6.5+
• SUSE® Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4, 12+
• Ubuntu® 12.04.03+, 14.04+
Custom Drivers
• Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2, Hyper-V (recommended)
• RHEL 6.1-6.4
• CentOS 6.1-6.4
• SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1-SP3
• VMware® 5.5, 6.0+
Part Numbering Information
The Micron® 9200 SSD is available in different configurations and capacities. Visit www.micron.com for a list of
valid part numbers.
Figure 1: Part Number Chart
Warranty: Contact your Micron sales representative for further information regarding the product, including product warranties.
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
2
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

General Description
The Micron 9200® NVMe SSD Series is Micron's flagship performance product line.
These products utilize a Gen3 PCIe interface, the innovative Non-Volatile Memory Express protocol and Micron's own high-speed NAND to provide high throughput and
IOPS, very low latency, and consistent quality of service. The 9200 product line has Micron's FlexPro™ firmware architecture which allows you to actively tune capacity to optimize drive performance and endurance and is available in high capacities up to 11
TBs. Reliability assurance measures include cyclic redundancy checks (CRC), end-toend data path protection, capacitor-backed power loss protection and Micron's extensive validation, quality and reliability testing. It features thermal monitoring and protection, SMART attributes for status polling and SMBus for out-of-band management.
The Micron 9200 has three endurance classes: the PRO for read-centric use at roughly 1
drive writes per day (DWPD); and the MAX for mixed-use workloads at about 3 DWPD;
and the ECO for less than 1 DWPD. The PRO version comes in 1.92TB, 3.84TB, and
7.68TB capacities, while the MAX is sized at 1.6TB, 3.2TB, 6.4TB, and the ECO in 8.0TB
and 11.0TB.
Logical Block Address Configuration
The number of logical block addresses (LBAs) reported by the device ensures sufficient
storage space for the specified capacity.
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
General Description
Table 1: LBA Count in Accordance with IDEMA LBA1-03
Capacity 512-Byte Sector LBA Count 4KB Sector LBA Count
1.6TB 3,125,627,568 390,703,446
1.92TB 3,750,748,848 468,843,606
3.2TB 6,251,233,968 781,404,246
3.84TB 7,501,476,528 937,684,566
6.4TB 12,502,446,768 1,562,805,846
7.68TB 15,002,931,888 1,875,366,486
8.0TB 15,628,053,168 1,953,506,646
11.0TB 21,488,565,168 2,686,070,646
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
3
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Performance
Table 2: Drive Performance
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Performance
9200 ECO
(TB)
9200 PRO
(TB)
9200 MAX
(TB)
Specification
Sequential read
3.15 3.15 2.85 3.15 3.15 2.85 3.15 3.15 GB/s
(128KB I/O size)
Sequential write
2.3 2.25 1.9 2.3 2.3 1.9 2.3 2.3
(128KB I/O size)
Random read
740K 770K 700K 770K 750K 700K 770K 770K IOPS
(4KB I/O size)
Random write
135K 130K 185K 170K 160K 255K 280K 270K
(4KB I/O size)
Mixed 70/30 read/write
320K 330K 325K 355K 355K 370K 445K 450K
(4KB I/O size)
Notes:
1. Performance specifications shown are with power limiting off. See Electrical Characteristics section for more details.
2. The stated specifications are preliminary.
3. Performance is steady state as defined by SNIA Solid State Storage Performance Test
Specification Enterprise v1.1.
4. Performance may vary up to 10% over life of drive.
Table 3: Latency
Specification Queue Depth = 1 Unit
READ latency (TYP) 1.6TB–3.84TB 92 µs
READ latency (TYP) 6.4TB–8TB 101
READ latency (TYP) 11TB 105
WRITE latency (TYP) all capacities 21
Unit8.0 11.0 1.92 3.84 7.68 1.6 3.2 6.4
Note:
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
1. Quality of service is measured using random 4KB workloads, QD = 1 at steady state.
4
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 5

Functional Description
Mean Time to Failure
The mean time to failure (MTTF) for the device can be calculated based on the component reliability data using the methods referenced in the Telcordia SR-322 reliability
prediction procedures for electronic equipment and measured during reliability demonstration test.
Table 4: MTTF
Endurance
SSD endurance is dependent on many factors, including: usage conditions applied to
the drive, drive performance and capacity, formatted sector size, error correction codes
(ECCs) in use, internal NAND PROGRAM/ERASE cycles, write amplification factor,
wear-leveling efficiency of the drive, over-provisioning ratio, valid user data on the
drive, drive temperature, NAND process parameters, and data retention time.
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Functional Description
Capacity MTTF (Operating Hours)
All 2.0 million
The device is designed to operate under a wide variety of conditions, while delivering
the maximum performance possible and meeting enterprise market demands.
While actual endurance varies depending on conditions, the drive lifetime can be estimated based on capacity, assumed fixed-use models, ECC, and formatted sector size.
Lifetime estimates for the device are shown in the following tables in total bytes written.
Table 5: Total Bytes Written
Model Capacity (TB) Total Bytes Written (PB)
9200 ECO
9200 PRO
9200 MAX
Note:
1. Values shown are based on system modeling.
8.0 11.7
11.0 16.1
1.92 3.5
3.84 7.0
7.68 14.0
1.6 8.8
3.2 17.5
6.4 35.1
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
5
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 6

Data Retention
Wear Leveling
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Functional Description
Data retention refers to the capability of the SSD media (that is, NAND flash) to retain
programmed data. The three primary factors that affect data retention are:
• Power-on/power-off state: Data retention generally improves when the SSD is in use
(that is, not shelved in a power-off state).
• Temperature: Data retention decreases as the temperature increases.
• Number of PROGRAM/ERASE cycles on the media: When the SSD ships from the factory, it is typically able to retain user data for up to 5 years in a powered-off state.
Data retention is guaranteed for three months at 40ºC (MAX), which assumes worstcase power and media wear (the SSD remains in a powered-off state and has reached
end of life).
The device uses sophisticated wear-leveling algorithms to maximize endurance by distributing PROGRAM/ERASE cycles uniformly across all blocks in the array. Both static
and dynamic wear leveling are utilized to optimize the drive’s lifespan.
Both types of wear leveling aim to distribute “hot” data away from blocks that have experienced relatively heavy wear. Static wear leveling accomplishes this by moving data
that has not been modified for an extended period of time out of blocks that have seen
few PROGRAM/ERASE cycles and into more heavily worn blocks. This frees up fresher
blocks for new data while reducing expected wear on tired blocks. Dynamic wear leveling, by contrast, acts on in-flight data to ensure it is preferentially written to the leastworn free blocks rather than those closer to the end of their rated life. These techniques
are used together within the controller to optimally balance the wear profile of the
NAND array.
Firmware Update Capability
The SSD supports firmware updates as defined by the NVMe specification. When a
download operation completes, an ACTIVATE command must be issued.
Power Loss Subsystem and Rebuild
The SSD supports an unexpected power loss with a power-backed write cache. No user
data is lost during an unexpected power loss. When power is subsequently restored, the
SSD returns to a ready state within a maximum of 120 seconds.
Boot
The 9200 is not intended to be a bootable device. Boot functionality is not validated by
Micron, and any use in this manner is done at the user's own risk. Please visit Mi-
cron.com to find other SSD products that are recommended for boot.
SMBus Sideband Management
If the system management bus (SMBus) is configured to be enabled, the SSD uses the
SMBus interface for presenting product data, monitoring drive health, checking drive
status before power-up, and error posting.
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
6
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 7
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Functional Description
Protocol supported: Enterprise SSD Form Factor interface with its accompanying vital
product data (VPD) definition.
Management data and vital product data may be accessed at fixed addresses with
+3.3V
at this fixed address when the drive is fully powered up.
Table 6: Out of Band Management Details
Out of Band Protocol SMBUS Address
Enterprise SSD Form Factor 0x53 0xA6 Vital product data (VPD)
NVMe Management Interface 1.0 0x6A 0xD4 Subsystem management data (SMD)
prior to powering up the drive completely. This data continues to be available
AUX
Alternate Address
(due to bit shift) Data
Notes:
1. SMBUS addresses will appear at an alternate address in certain tools due the inclusion of
direction bit in the SMBUS spec.
2. Out of band management is disabled by default.
Table 7: Vital Product Data (VPD) Structure
Address #Bytes Function Value Byte Offset Description
0x53
(7bit)
3 Class code 02h 0 Device type and programming interface
08h 1
01h 2
2 ID 44h 3 PCI-SIG vendor ID (0x1344 is assigned to
13h 4
Micron)
20 Varies 5–24 Serial number
40 Varies 25–64 Model number
1 PCIe port0 capabilities 03h 65 Maximum link speed
1 04h/08h 66 Maximum link width (04h if U.2, 08h if
HHHL)
1 PCIe port1 capabilities 00h 67 Maximum link speed
1 00h 68 Maximum link width
1 Initial power requirements 08h 69 12V Power rail initial power requirement
(W)
2 Reserved 0 70–71 –
1 Maximum power require-
ments
24h 72 12V power rail maximum power require-
ment (W)
2 Reserved 0 73–74 –
2 Capability list pointer 4Dh 75 16b address offset pointers to start of ca-
00h 76
pability list, see Capability List Pointer table
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
7
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 8

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Functional Description
Table 8: Capability List Pointer
Address #Bytes Value Byte Offset R/W Description
0x004D 2 A5h 0 RO PCI-SIG vendor specific capability
00h 1
2 00h 2 RO Pointer to next capability
00h 3
2 44h 4 RO PCI-SIG vendor ID (0x1344 is assigned to
13h 5
2 0000h 6–7 RO Reserved
2 Varies 8 RO Temperature value (Celsius), little-endian
Varies 9 RO
Micron)
format. For example, byte[8:9] = 29h 00h
indicates the temperature is 41°C
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
8
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 9

Electrical Characteristics
Stresses greater than those listed may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a
stress rating only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
reliability.
Table 9: Power Consumption
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Electrical Characteristics
Specification
Active reads
(Maximum RMS)
Active writes
(Maximum RMS)
128K sequential reads
(Average RMS)
128K sequential writes
(Average RMS)
4K random reads
(Average RMS)
4K random writes
(Average RMS)
Mixed 70/30 read/write
(Average RMS)
Notes:
1. Average power consumption.
2. 25W power limiting by VU command.
Table 10: Operating Voltage
9200 ECO
(TB)
9200 PRO
(TB)
25
25
9200 MAX
(TB)
2
2
19 21 17 19 19 17 19 19
20 20 18 20 20 18 20 20
17 17 16 16 17 16 16 17
20 21 18 21 20 18 20 21
19 20 17 20 18 16 20 17
Unit8.0 11.0 1.92 3.84 7.68 1.6 3.2 6.4
W
Electrical Characteristic Value
12V power rail Operating voltage 12Vdc (±8%)
MAX/MIN rise time 10–100ms
MAX/MIN fall time <5s
Inrush current (typical peak) 3.0A
MAX average current (RMS) 2.5A
3.3V
power rail Operating voltage 3.3V (–8% to 8%)
AUX
MAX/MIN rise time 50ms/1ms
MAX/MIN fall time 5s/1ms
MAX average current 20mA
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
9
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 10

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Electrical Characteristics
Environmental Conditions
Table 11: Temperature and Airflow
Temperature and Airflow 2.5" U.2 Notes
Operating temperature (as indicated by the SMART temperature attribute)
Operating ambient temperature Ambient: 0°C to 35°C;
Operating airflow 450 LFM at 25°C ambient 3, 4
Storage temperature –40°C to 85°C 5
Humidity 25% to 95% noncondensing
0°C to 85°C 1
2
Case: 0°C to 70°C
Notes:
1. If SMART temperature exceeds 75°C (SMART composite), write performance will be
throttled.
2. Temperature of air impinging on the SSD.
3. Airflow must flow along the length of the drive parallel to and through any cooling
fins.
4. Airflow is measured upstream of the drive before any acceleration as the air goes
around the drive.
5. Contact Micron for additional information.
Table 12: Shock and Vibration
Shock and Vibration 2.5" U.2
Shock (nonoperational) 1500G at 0.5ms half-sine
Vibration (nonoperational) 3.1 G
Note:
1. Shock and vibration ratings refer to the ability to withstand stress events only. Prolonged or repeated exposure to conditions listed or greater stresses may result in permanent damage to the device. Functional operation of the device under these conditions is not implied. See warranty for more information.
5–800Hz at 30 min/axis
RMS
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
10
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 11

Supported Commands
NVMe Admin Command Set
The 9200 supports the following mandatory NVMe admin commands, as described in
the NVMe 1.2 specification:
• Delete I/O submission queue
• Create I/O submission queue
• Get log page
• Delete I/O completion queue
• Create I/O completion queue
• Identify
• Abort
• Set features
• Get features
• Asynchronous event request
The following optional NVMe admin commands are also supported:
• Firmware activate
• Firmware image download
• Format NVM
• Security Send
• Security Receive
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Supported Commands
NVMe I/O Command Set
The 9200 supports the following mandatory NVMe I/O commands, as described in the
NVMe 1.2 specification:
• Write
• Read
• Flush
The following optional NVMe I/O commands are also supported:
• Dataset management
• Deallocate
Log Pages
The Get Log Page command can be used to retrieve the following logs:
• 01h - Error information
• 02h - SMART / health information
• 03h - Firmware slot information
• CAh - Vendor Unique SMART
• 05h - Command Effects Log
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
11
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 12

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Supported Commands
SMART and Health Information
The SSD supports SMART/Health log information as defined in the NVMe specification
as well as extended health information. These logs persist through power cycles and reflect lifetime data.
Table 13: SMART/Health Information (Log Identifier 02h)
Bytes Name Description
0 Critical warning Indicates critical warnings for the state of the controller. Each bit corre-
sponds to a critical warning type; multiple bits may be set. If a bit is
cleared to 0, the critical warning does not apply. Critical warnings may
result in an asynchronous event notification to the host.
• Bit 00: If set to 1, the available spare space has fallen below the
threshold.
• Bit 01: If set to 1, the temperature has exceeded a critical threshold.
• Bit 02: If set to 1, the device reliability has been degraded due to significant media-related errors or any internal error that degrades device reliability.
• Bit 03: If set to 1, the media has been placed in read-only mode.
• Bit 04: If set to 1, the volatile memory backup device has failed. This
field is only valid if the controller has a volatile memory backup solution.
• Bits 07:05 Reserved
2:1 Temperature Contains the temperature of the overall device (controller and NVM in-
cluded) in units of Kelvin. If it exceeds the temperature threshold, an
asynchronous event may be issued to the host. For the 9100, the value
reported is the maximum temperature measured on either the board
or controller.
3 Available spare Contains a normalized percentage (0–100%) of the remaining available
spare capacity, beginning at 100% and decreasing.
4 Available spare threshold When the available spare falls below the threshold indicated in this
field, an asynchronous event may be issued to the host. The value is indicated as a normalized percentage (0–100%). Threshold is set to 5%.
5 Percentage used Contains a vendor-specific estimate of the percentage of the device life
used based on the actual device usage and the manufacturer's prediction of device life.
A value of 100 indicates that the estimated endurance of the device
has been consumed, but may not indicate a device failure.
Refer to the JEDEC JESD218 standard for SSD device life and endurance
measurement techniques.
31:6 Reserved Reserved
47:32 Data units read Contains the number of 512-byte data units the host has read from the
controller; this value does not include metadata. This value is reported
in thousands (that is, a value of 1 corresponds to 1000 units of 512
bytes read) and is rounded up. When the LBA size is a value other than
512 bytes, the controller shall convert the amount of data read to 512byte units.
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
12
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 13

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Supported Commands
Table 13: SMART/Health Information (Log Identifier 02h) (Continued)
Bytes Name Description
63:48 Data units written Contains the number of 512-byte data units the host has written to the
controller; this value does not include metadata. This value is reported
in thousands (that is, a value of 1 corresponds to 1000 units of 512
bytes written) and is rounded up. When the LBA size is a value other
than 512 bytes, the controller shall convert the amount of data written
to 512-byte units. For the NVM command set, logical blocks written as
part of write operations shall be included in this value. Write uncorrectable commands shall not impact this value.
79:64 Host read commands Contains the number of read commands issued to the controller.
95:80 Host write commands Contains the number of write commands issued to the controller. For
the NVM command set, this is the number of write commands.
111:96 Controller busy time Contains the amount of time the controller is busy with I/O commands.
The controller is busy when there is a command outstanding to an I/O
queue (specifically, a command was issued via an I/O submission queue
tail doorbell write and the corresponding completion queue entry has
not been posted yet to the associated I/O completion queue.) This value is reported in minutes.
127:112 Power cycles Contains the number of power cycles.
143:128 Power on hours Contains the number of power-on hours. This does not include time
that the controller was powered and in a low-power state condition.
159:144 Unsafe shutdowns Contains the number of unsafe shutdowns. This count is incremented
when a shutdown notification (CC.SHN) is not received prior to loss of
power.
175:160 Media errors Contains the number of occurrences where the controller detected an
unrecovered data integrity error. Errors such as uncorrectable ECC, CRC
checksum failure, or LBA tag mismatch are included in this field.
191:176 Number of error info log entries Contains the number of error information log entries over the life of
the controller.
511:192 Reserved Reserved
Vendor Unique SMART
In addition to the standard SMART log, the 9200 provides the following details in a vendor unique log:
Table 14: Vendor Unique SMART Attributes (Log Identifier CAh)
Bytes Name Description
0:1 F9 - NAND_writes_1GiB Raw value reports the number of writes to NAND in 1 GiB increments.
3:4 Normalized value
5:11 Current raw value
12:13 FA - NAND_reads_1GiB Raw value reports the number of reads to NAND in 1 GiB increments.
15:16 Normalized value
17:23 Current raw value
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
13
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 14

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Supported Commands
Table 14: Vendor Unique SMART Attributes (Log Identifier CAh) (Continued)
Bytes Name Description
24:25 EA - Thermal throttle status Raw value indicates throttle status and total throttling time.
27:28 Normalized value
29:35 Current raw value
36:37 E7 - Temperature Raw value reports the maximum and minimum temperature in Kelvin
39:40 Normalized value
41:47 Current raw value
48:49 E8 - Power consumption Raw value reports the maximum and minimum average power con-
51:52 Normalized value
53:59 Current raw value
60:61 AF - Power loss protection Normalized value reports the power loss protection status. 100 indi-
63:64 Normalized value
65:71 Current raw value
Byte 0: If set to 1, throttling is active; if set to 0, throttling is not active
Bytes 1–4: Total throttling time in minutes since power on
Bytes 5: Reserved
over the lifetime of the device.
Byte 0–1: The maximum temperature sampled from the temperature
sensor
Bytes 2–3: The minimum temperature sampled from the temperature
sensor
Bytes 4–5: The current temperature sampled from the temperature sensor
sumption in watts.
Bytes 0–1: The maximum power consumption
Bytes 2–3: The minimum power consumption
Bytes 4–5: The average power consumption
cates protection was successful. 0 indicates protection failed. A power
loss failure indicator will persist until a Format NVM command is executed.
Get/Set Features
The following features can be configured or retrieved using NVMe SET FEATURES and
GET FEATURES commands:
• 02h – Power management (Commands are accepted but values are not returned. A
custom power governor feature is utilized for power management.)
• 04h – Temperature threshold
• 05h – Set error recovery
• 07h – Number of queues (Maximum supported is 128 for both submission and completion queues.)
• 08h – Interrupt coalescing
• 09h – Interrupt vector configuration
• 0Bh – Asynchronous event configuration
• D4h – Device initiated thermal
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
14
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 15

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Interface Connectors
Interface Connectors
The host interface connector conforms to the PCIe Electromechanical Specification.
A mechanical indent is used to separate the PCIe power pins from the differential signal
contacts. The pins are numbered below in ascending order from left to right. Side B refers to component side. Side A refers to the solder side.
U.2 Pin Assignments
The U.2 2.5" form factor follows the SFF-8639 specification and supports built-in latching.
Table 15: PCIe Interface Connector Pin Assignments (U.2 Form Factor)
Pin Name Description Pin Name Description
S1 GND Ground E7 REFCLK0+ PCIe REFCLK 0 p
S2 DNC E8 REFCLK0- PCIe REFCLK 0 p
S3 DNC E9 GND Ground
S4 GND Ground E10 PETp0 PCIe TX Lane 0 p
S5 DNC E11 PETn0 PCIe TX Lane 0 n
S6 DNC E12 GND Ground
S7 GND Ground E13 PERn0 PCIe RX Lane 0 n
E1 REFCLK1+ DNC E14 PERp0 PCIe RX Lane 0 p
E2 REFCLK1- DNC E15 GND Ground
E3 3.3Vaux 3.3V auxiliary power E16 RSVD Reserved
E4 PERST1# DNC S8 GND Ground
E5 PERST0# PCIe Fundamental Reset S9 DNC
E6 RSVD Reserved S10 DNC
P1 DNC S11 GND Ground
P2 DNC S12 DNC
P3 DNC S13 DNC
P4 IfDet_N Interface detect S14 GND Ground
P5 GND Ground S15 RSVD Reserved
P6 GND Ground S16 GND Ground
P7 DNC S17 PETp1 PCIe TX Lane 1 p
P8 DNC S18 PETn1 PCIe TX Lane 1 n
P9 DNC S19 GND Ground
P10 PRSNT_N Presence detect S20 PERn1 PCIe RX Lane 1 n
P11 Activity Activity signal from the drive S21 PERp1 PCIe RX Lane 1 p
P12 Hot-Plug Ground S22 GND Ground
P13 +12V_pre 12V power S23 PETp2 PCIe TX Lane 2 p
P14 +12V 12V power S24 PETn2 PCIe TX Lane 2 n
P15 +12V 12V power S25 GND Ground
S26 PERn2 PCIe RX Lane 2 n
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
15
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 16

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Interface Connectors
Table 15: PCIe Interface Connector Pin Assignments (U.2 Form Factor) (Continued)
Pin Name Description Pin Name Description
S27 PERp2 PCIe RX Lane 2 p
S28 GND Ground
E17 PETp3 PCIe TX Lane 3 p
E18 PETn3 PCIe TX Lane 3 n
E19 GND Ground
E20 PERn3 PCIe RX Lane 3 n
E21 PERp3 PCIe RX Lane 3 p
E22 GND Ground
E23 SMCLK SMBus clock
E24 SMDAT SMBus data
E25 DualPortEn_N Dual port enable
Notes:
1. PRSNT_N is open and IfDet_N is grounded to indicate PCIe support.
2. DualPortEn_N pin should be left un-connected or un-driven by the system to enable single port operation with all 4 lanes. If this pin is asserted (driven low) by the system, the
SSD will function as PCIe x2 lane only.
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
16
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 17

PCIe Header
Byte
offset
31 0
Device ID = 5192h
Vendor ID = 1344h
00h
Status Command
04h
Class code = 010802h Revision ID = 0
08h
BIST Header type = 00h Master latency timer Cache line size
0Ch
Subsystem vendor ID = 1344h
2Ch
~
~
~
~
1.6TB U.2 SSID = 2D00h,
3.2TB U.2 SSID = 4A00h,
6.4TB U.2 SSID = 5A00h
Byte
offset
31 0
Device ID = 5191h
Vendor ID = 1344h
00h
Status Command
04h
Class code = 010802h Revision ID = 0
08h
BIST Header type = 00h Master latency timer Cache line size
0Ch
Subsystem vendor ID = 1344h
2Ch
~
~
~
~
1.92TB SSID = 2D00h
3.84TB SSID = 4A00h
7.68TB SSID = 5A00h
Figure 2: 9200 MAX PCIe Header
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
PCIe Header
Figure 3: 9200 PRO PCIe Header
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
17
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 18

Figure 4: 9200 ECO PCIe Header
Byte
offset
31 0
Device ID = 5190h
Vendor ID = 1344h
00h
Status Command
04h
Class code = 010802h Revision ID = 0
08h
BIST Header type = 00h Master latency timer Cache line size
0Ch
Subsystem vendor ID = 1344h
2Ch
~
~
~
~
8.0TB SSID = 5C00h,
11.0TB SSID = 5F00h
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
PCIe Header
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
18
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 19

Physical Configuration
69.85 ±0.25 61.72
14.80
+0
-0.5
Y X
A
A
See Detail B
Detail B
0.50
3.00
0.30
Detail C
See Detail C
Section A–A
M3 THD
4 PL
MIN 2.5
full THD
6in-bl MAX torque
0.5
S
X Y Z
Z
90.60
14.00
100.20
MAX
14.00
M3 THD
4 PL
MIN 3
full THD
6in-bl MAX torque
0.5
S
X Y Z
90.60
3.50 ±0.38
Micron's 9200 conforms to PCI Express CEM and SFF-8639 specifications.
Figure 5: U.2 (2.5") Nominal Dimensions
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Physical Configuration
Note:
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
19
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
1. Length does not include 0.3 connector protrusion.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 20

Compliance
FCC Rules
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Compliance
The device complies with the following specifications:
• CE (Europe): EN 55022 Class B, EN 55024, RoHS
• UL: UL-60950-1, 2nd Edition
• BSMI (Taiwan): Approval to CNS 13438 Class B
• RCM (Australia, New Zealand): AS/NZS CISPR22 Class B
• KCC RRL (Korea): Approval to KN32 Class B, KN 35
• W.E.E.E.: Compliance with EU WEEE directive 2012/19/EC. Additional obligations
may apply to customers who place these products in the markets where WEEE is enforced.
• TUV (Germany): Approval to IEC60950/EN60950
• V
(Japan): 2015-04 Class B, CISPR22
CCI
• IC (Canada): ICES-003 Class B, CISPR22 Class B
• This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
• Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
References
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
• PCI Express CEM Specification V2.0
• PCI Express Specification V3.0
• SFF-8639
• IDEMA Specification
• Telcordia SR-322 Procedures
• NVM Express Specification revision 1.2
20
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 21

Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Appendix A
Appendix A
Identify Data Structures
Table 16: Identify Controller Data Structure
Identify
Controller
Data
Structure
Bytes DS
1
1:0 F 0x1344 M PCI vendor ID (VID) Contains the company vendor identifier that
3:2 F 0x1344 M PCI subsystem vendor ID
23:4 V varies M Serial number (SN) Contains the serial number for the NVM sub-
63:24 V varies M Model number (MN) Contains the model number for the NVM
71:64 V varies M Firmware revision (FR) Contains the currently active firmware revi-
72 F 0x1 M Recommended arbitration
75:73 F 0x75-0xA0-0x00 M IEEE OUI identifier (IEEE) Contains the organization unique identifier
76 X 0x0 O Controller multi-path I/O and
77 F 0x20 M Maximum data transfer size
79:78 F 0x1 M Controller ID (CNTLID) This field contains the controller ID of the
83:80 F 0x00010200 M Version (VER) This field indicates the version of the NVM
95:92 V 0x1 M Optional asynchronous events
239:96 – – – – Reserved
Default
Value M/O2Feature Name Description
is assigned by the PCI SIG.
Contains the company vendor identifier that
(SSVID)
is assigned by the PCI SIG for the subsystem.
system.
subsystem.
sion for the NVM subsystem.
This is the recommended arbitration burst
burst (RAB)
size.
(OUI) for the controller vendor.
This field specifies multi-path I/O and namenamespace sharing capabilities (CMIC)
space sharing capabilities of the controller
and NVM subsystem.
Supports MDTS of 128K.
(MDTS)
controller whose status is reported in this da-
ta structure.
express specification 1.2 that the controller
implementation supports.
This field indicates the optional asynchrosupported (OAES)
nous events supported by the controller.
Notes:
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
1. DS = Data structure; F = Fixed; V = Variable; X = Both
2. M/O = Mandatory/Optional
21
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 22

Table 17: Identify Namespace Data Structure
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Appendix A
Bytes DS
512 F 0x55 M Submission queue entry size
513 F 0x44 M Completion queue entry size
1
Value M/O2Feature Name Description
Required and maximum submission queue
(SQES)
entry size is 32 bytes
Required and maximum submission queue
(CQES)
entry size is 16 bytes
515:514 – – – – Reserved
519:516 F 0x1 M Number of namespaces (NN) Supports up to 32 namespaces
Default
521:520 F 0x14 M Optional NVM command sup-
port (ONCS)
523:522 F 0x0 M Fused operation support
Supports dataset management and write un-
correctable optional NVMe commands
Fused commands not supported
(FUSES)
524 F 0x4 M Format NVM attributes (FNA) Secure/Crypto erase not supported
525 F 0x1 M Volatile write cache (VWC) Volatile write cache is present
527:526 F 0x0 M Atomic write unit normal
(AWUN)
529:528 F 0x0 M Atomic write unit power fail
(AWUPF)
Atomic write size for controller during nor-
mal equals to 4K bytes
Indicates the atomic write size for the con-
troller during a power fail condition equals
512 bytes
530 X 0x0 M NVM vendor specific com-
Not supported
mand configuration (NVSCC)
531 – – – – Reserved
533:532 F 0x0 M Atomic compare and write
Not supported
unit (ACWU)
535:534 – – – – Reserved
539:536 F 0x0 O SGL support (SGLS) Not supported
703:540 – – – – Reserved
I/O command set attributes
2047:704 – – – – Reserved
Notes:
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
1. DS = Data structure; F = Fixed; V = Variable; X = Both
2. M/O = Mandatory/Optional
22
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 23

Revision History
Rev. E – 10/17
Rev. D – 8/17
Micron 9200 NVMe SSDs
Revision History
• Removed HHHL through the data sheet
• Updated Drive Performance table and Latency table in Performance
• Updated Power Consumption table
• Corrected PCIe header information
• Updated Drive Performance table, Latency table, and Quality of Service table in Performance section
• Updated Out of Band Management Details table in SMBus Sideband Management:
Added NVMe Management Interface 1.0
• Updated Power Consumption table in Electrical Characteristics: Changed Idle power
specification
• Updated Temperature and Airflow table in Environmental Conditions: Changed Operating ambient temperature specification and Operating airflow specification
• Updated Shock and Vibration table
Rev. C – 7/17
• Updated Part Number Chart
• Updated formatting
Rev. B – 1/17
• Updated figure 1
• Updated formatting
Rev. A – 10/16
• Initial release
8000 S. Federal Way, P.O. Box 6, Boise, ID 83707-0006, Tel: 208-368-4000
www.micron.com/products/support Sales inquiries: 800-932-4992
Micron and the Micron logo are trademarks of Micron Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This data sheet contains minimum and maximum limits specified over the power supply and temperature range set forth herein.
Although considered final, these specifications are subject to change, as further product development and data characterization some-
times occur.
CCMTD-731836775-10493
9200_u2_nvme_pcie_ssd.pdf - Rev. E 10/17 EN
23
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2016 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...