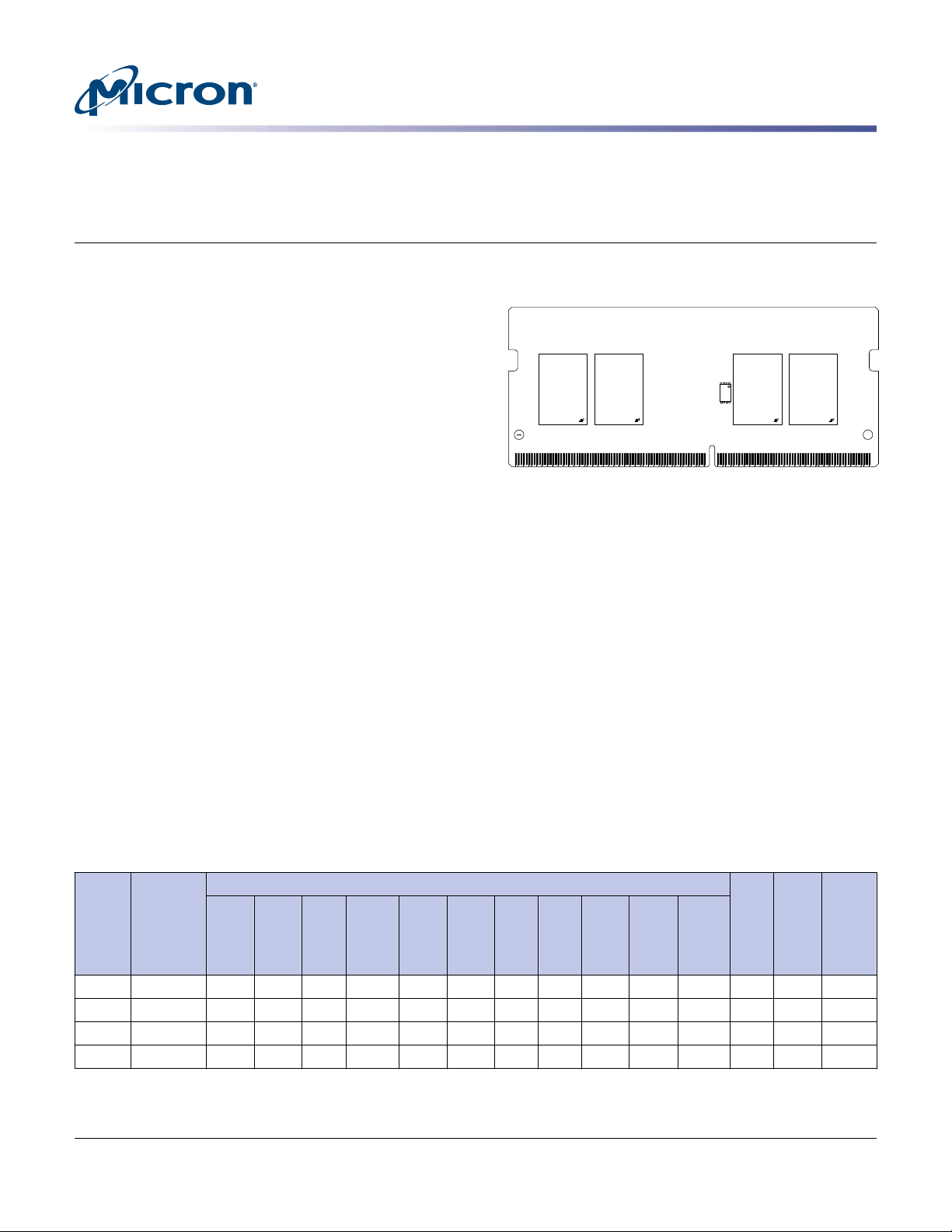
DDR4 SDRAM SODIMM
Module Height: 30mm (1.181in)
MTA8ATF1G64HZ – 8GB
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Features
Features
• DDR4 functionality and operations supported as
defined in the component data sheet
• 260-pin, small-outline dual in-line memory module
(SODIMM)
• Fast data transfer rates: PC4-2666, PC4-2400, or
PC4-2133
• 8GB (1 Gig x 64)
• VDD = 1.20V (NOM)
• VPP = 2.5V (NOM)
• V
• Nominal and dynamic on-die termination (ODT) for
data, strobe, and mask signals
• Low-power auto self refresh (LPASR)
• Data bus inversion (DBI) for data bus
• On-die V
• Single-rank
• On-board I2C serial presence-detect (SPD) EEPROM
• 16 internal banks; 4 groups of 4 banks each
• Fixed burst chop (BC) of 4 and burst length (BL) of 8
via the mode register set (MRS)
• Selectable BC4 or BL8 on-the-fly (OTF)
• Gold edge contacts
• Halogen-free
• Fly-by topology
• Terminated control command and address bus
= 2.5V (NOM)
DDSPD
generation and calibration
REFDQ
Figure 1: 260-Pin SODIMM (MO-310 R/C A1)
Options Marking
• Operating temperature
– Commercial (0°C ≤ T
• Package
– 260-pin DIMM (halogen-free) Z
• Frequency/CAS latency
– 0.75ns @ CL = 19 (DDR4-2666) -2G6
– 0.83ns @ CL = 17 (DDR4-2400) -2G3
– 0.93ns @ CL = 15 (DDR4-2133) -2G1
≤ 95°C) None
OPER
Table 1: Key Timing Parameters
Industry
Speed
Grade
-2G6 PC4-2666 2666 2666 2400 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 – 1333 – 14.16 14.16 46.16
-2G4 PC4-2400 – 2400 2400 2400 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 – 1333 13.32 13.32 45.32
-2G3 PC4-2400 – 2400 2400 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 1333 – 14.16 14.16 46.16
-2G1 PC4-2133 – – – 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 – 1333 13.5 13.5 46.5
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
Nomen-
clature
Products and specifications discussed herein are subject to change by Micron without notice.
Data Rate (MT/s)
CL =
20,
CL =19CL =18CL =17CL =16CL =15CL =14CL =13CL =12CL =11CL =
10 CL = 9
1
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
t
RCD
(ns)
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
t
RP
(ns)
t
RC
(ns)
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Table 2: Addressing
Parameter 8GB
Row address 64K A[15:0]
Column address 1K A[9:0]
Device bank group address 4 BG[1:0]
Device bank address per group 4 BA[1:0]
Device configuration 8Gb (1 Gig x 8), 16 banks
Module rank address CS0_n
Table 3: Part Numbers and Timing Parameters – 8GB Modules
Base device: MT40A1G8,1 8Gb DDR4 SDRAM
Part Number
2
Density Configuration
MTA8ATF1G64HZ-2G6__ 8GB 1 Gig x 64 21.3 GB/s 0.75ns/2666 MT/s 19-19-19
MTA8ATF1G64HZ-2G3__ 8GB 1 Gig x 64 19.2 GB/s 0.83ns/2400 MT/s 17-17-17
MTA8ATF1G64HZ-2G1__ 8GB 1 Gig x 64 17.0 GB/s 0.93ns/2133 MT/s 15-15-15
Module
Module
Bandwidth
Memory Clock/
Data Rate
Clock Cycles
(CL-tRCD-tRP)
Features
Notes:
1. The data sheet for the base device can be found on micron.com.
2. All part numbers end with a two-place code (not shown) that designates component and PCB revisions.
Consult factory for current revision codes. Example: MTA8ATF1G64HZ-2G3B1.
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
2
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Pin Assignments
Pin Assignments
The pin assignment table below is a comprehensive list of all possible pin assignments
for DDR4 SODIMM modules. See Functional Block Diagram for pins specific to this
module.
Table 4: Pin Assignments
260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM Front 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM Back
Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol
1 V
3 DQ5 69 V
5 V
7 DQ1 73 V
9 V
11 DQS0_c 77 V
13 DQS0_t 79 DQ30 145 BA1 211 DQ52 14 V
15 V
17 DQ7 83 DQ26 149 CS0_n 215 DQ49 18 V
19 V
21 DQ3 87 CB5/NC 153 V
23 V
25 DQ13 91 CB1/NC 157 CS1_n/NC223 V
67 DQ29 133 A1 199 DM5_n/
SS
DBI5_n
135 V
SS
71 DQ25 137 CK0_t 203 DQ46 6 V
SS
139 CK0_c 205 V
SS
SS
75 DM3_n/
141 V
201 V
DD
207 DQ42 10 V
DD
SS
SS
DBI3_n
143 PARITY 209 V
SS
81 V
SS
85 V
SS
SS
SS
147 V
DD
151 WE_n/
213 V
217 V
SS
SS
SS
A14
219 DQS6_c 22 V
DD
89 V
SS
155 ODT0 221 DQS6_t 24 DQ12 90 V
SS
SS
2 V
4 DQ4 70 DQ24 136 V
SS
SS
68 V
72 V
134 EVENT_n,NF200 DQS5_t
SS
DD
138 CK1_t/NF 204 DQ47
SS
202 V
8 DQ0 74 DQS3_c 140 CK1_c/NF 206 V
SS
12 DM0_n/
76 DQS3_t 142 V
78 V
144 A0 210 V
SS
DD
208 DQ43
DBI0_n
80 DQ31 146 A10/AP 212 DQ53
SS
16 DQ6 82 V
84 DQ27 150 BA0 216 DQ48
SS
20 DQ2 86 V
SS
SS
148 V
DD
152 RAS_n/
214 V
218 V
A16
88 CB4/NC 154 V
SS
DD
220 DM6_n/
DBI6_n
SS
156 CAS_n/
222 V
A15
26 V
92 CB0/NC 158 A13 224 DQ54
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
27 V
29 DQ9 95 DQS8_c 161 ODT1/NC227
31 V
33 DM1_n/
93 V
SS
97 DQS8_t 163 V
SS
99 V
159 V
SS
165 C1, CS3_n,NC231 V
SS
DD
DD
225 DQ55 28 DQ8 94 V
V
SS
30 V
229 DQ51 32 DQS1_c 98 V
SS
34 DQS1_t 100 CB6/NC 166 SA2 232 DQ60
DBI_n
35 V
37 DQ15 103 V
39 V
41 DQ10 107 V
43 V
101 CB2/NC 167 V
SS
SS
105 CB3/NC 171 V
SS
SS
109 CKE0 175 V
SS
233 DQ61 36 V
SS
169 DQ37 235 V
237 DQ56 40 V
SS
173 DQ33 239 V
241 DM7_n/
SS
SS
SS
38 DQ14 104 CB7/NC 170 DQ36 236 DQ57
42 DQ11 108 RESET_n 174 DQ32 240 DQS7_c
44 V
DBI7_n
45 DQ21 111 V
47 V
113 BG1 179 DQS4_t 245 DQ62 48 V
SS
49 DQ17 115 BG0 181 V
51 V
SS
117 V
53 DQS2_c 119 A12 185 V
177 DQS4_c 243 V
DD
247 V
SS
183 DQ38 249 DQ58 52 V
DD
251 V
SS
SS
SS
SS
46 DQ20 112 V
50 DQ16 116 ALERT_n 182 DQ39 248 V
54 DM2_n/
55 DQS2_t 121 A9 187 DQ34 253 SCL 56 V
57 V
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
SS
123 V
DD
189 V
255 V
SS
DDSPD
58 DQ22 124 V
3
SS
96 DM8_n/
SS
DBI_n/NC
SS
102 V
SS
106 V
SS
110 CKE1/NC176 V
SS
SS
SS
DD
160 V
162 C0/
CS2_n/NC
164 V
REFCA
168 V
172 V
178 DM4_n/
DD
SS
SS
SS
226 V
228 DQ50
230 V
234 V
238 V
242 DQS7_t
244 V
DBI4_n
114 ACT_n 180 V
SS
118 V
SS
DD
184 V
SS
SS
246 DQ63
250 DQ59
120 A11 186 DQ35 252 V
DBI2_n
122 A7 188 V
SS
190 DQ45 256 SA0
DD
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
SS
254 SDA
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
SS
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Pin Assignments
Table 4: Pin Assignments (Continued)
260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM Front 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM Back
Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol
59 DQ23 125 A8 191 DQ44 257 V
61 V
63 DQ19 129 V
65 V
127 A6 193 V
SS
DD
131 A3 197 V
SS
259 V
SS
195 DQ40 – – 64 V
SS
– – 66 DQ28 132 A2 198 DQS5_c – –
PP
PP
60 V
126 A5 192 V
SS
SS
258 V
62 DQ18 128 A4 194 DQ41 260 SA1
SS
130 V
DD
196 V
SS
– –
TT
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
4
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Pin Descriptions
Pin Descriptions
The pin description table below is a comprehensive list of all possible pins for DDR4
modules. All pins listed may not be supported on this module. See Functional Block Diagram for pins specific to this module.
Table 5: Pin Descriptions
Symbol Type Description
Ax Input Address inputs: Provide the row address for ACTIVATE commands and the column address for
A10/AP Input Auto precharge: A10 is sampled during READ and WRITE commands to determine whether an
A12/BC_n Input Burst chop: A12/BC_n is sampled during READ and WRITE commands to determine if burst
ACT_n Input Command input: ACT_n defines the ACTIVATE command being entered along with CS_n. The
BAx Input Bank address inputs: Define the bank (with a bank group) to which an ACTIVATE, READ,
BGx Input Bank group address inputs: Define the bank group to which a REFRESH, ACTIVATE, READ,
C0, C1, C2
(RDIMM/LRDIMM on-
ly)
CKx_t
CKx_c
CKEx Input Clock enable: CKE HIGH activates and CKE LOW deactivates the internal clock signals, device
CSx_n Input Chip select: All commands are masked when CS_n is registered HIGH. CS_n provides external
Input Chip ID: These inputs are used only when devices are stacked; that is, 2H, 4H, and 8H stacks for
Input Clock: Differential clock inputs. All address, command, and control input signals are sampled
READ/WRITE commands in order to select one location out of the memory array in the respective bank (A10/AP, A12/BC_n, WE_n/A14, CAS_n/A15, and RAS_n/A16 have additional functions;
see individual entries in this table). The address inputs also provide the op-code during the
MODE REGISTER SET command. A17 is only defined for x4 SDRAM.
auto precharge should be performed on the accessed bank after a READ or WRITE operation
(HIGH = auto precharge; LOW = no auto precharge). A10 is sampled during a PRECHARGE command to determine whether the precharge applies to one bank (A10 LOW) or all banks (A10
HIGH). If only one bank is to be precharged, the bank is selected by the bank group and bank
addresses.
chop (on-the-fly) will be performed (HIGH = no burst chop; LOW = burst- chopped). See Command Truth Table in the DDR4 component data sheet.
input into RAS_n/A16, CAS_n/A15, and WE_n/A14 are considered as row address A16, A15, and
A14. See Command Truth Table.
WRITE, or PRECHARGE command is being applied. Also determine which mode register is to be
accessed during a MODE REGISTER SET command.
WRITE, or PRECHARGE command is being applied. Also determine which mode register is to be
accessed during a MODE REGISTER SET command. BG[1:0] are used in the x4 and x8 configurations. x16-based SDRAM only has BG0.
x4 and x8 configurations using through-silicon vias (TSVs). These pins are not used in the x16
configuration. Some DDR4 modules support a traditional DDP package, which uses CS1_n,
CKE1, and ODT1 to control the second die. All other stack configurations, such as a 4H or 8H,
are assumed to be single-load (master/slave) type configurations where C0, C1, and C2 are used
as chip ID selects in conjunction with a single CS_n, CKE, and ODT. Chip ID is considered part of
the command code.
on the crossing of the positive edge of CK_t and the negative edge of CK_c.
input buffers, and output drivers. Taking CKE LOW provides PRECHARGE POWER-DOWN and
SELF REFRESH operations (all banks idle), or active power-down (row active in any bank). CKE is
asynchronous for self refresh exit. After V
tialization sequence, it must be maintained during all operations (including SELF REFRESH). CKE
must be maintained HIGH throughout read and write accesses. Input buffers (excluding CK_t,
CK_c, ODT, RESET_n, and CKE) are disabled during power-down. Input buffers (excluding CKE
and RESET#) are disabled during self refresh.
rank selection on systems with multiple ranks. CS_n is considered part of the command code
(CS2_n and CS3_n are not used on UDIMMs).
has become stable during the power-on and ini-
REFCA
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
5
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Pin Descriptions
Table 5: Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Symbol Type Description
ODTx Input On-die termination: ODT (registered HIGH) enables termination resistance internal to the
PARITY Input Parity for command and address: This function can be enabled or disabled via the mode
RAS_n/A16
Input Command inputs: RAS_n/A16, CAS_n/A15, and WE_n/A14 (along with CS_n) define the com-
CAS_n/A15
WE_n/A14
RESET_n CMOS Input Active LOW asynchronous reset: Reset is active when RESET_n is LOW and inactive when RE-
SAx Input
SCL Input
DQx, CBx I/O Data input/output and check bit input/output: Bidirectional data bus. DQ represents
DM_n/DBI_n/
I/O Input data mask and data bus inversion: DM_n is an input mask signal for write data. Input
TDQS_t (DMU_n,
DBIU_n), (DML_n/
DBIl_n)
SDA I/O Serial Data: Bidirectional signal used to transfer data in or out of the EEPROM or EEPROM/TS
DQS_t
I/O Data strobe: Output with read data, input with write data. Edge-aligned with read data, cen-
DQS_c
DQSU_t
DQSU_c
DQSL_t
DQSL_c
ALERT_n Output Alert output: Possesses functions such as CRC error flag and command and address parity error
EVENT_n Output Temperature event: The EVENT_n pin is asserted by the temperature sensor when critical tem-
DDR4 SDRAM. When enabled, ODT (RTT) is applied only to each DQ, DQS_t, DQS_c, DM_n/
DBI_n/TDQS_t, and TDQS_c signal for x4 and x8 configurations (when the TDQS function is enabled via the mode register). For the x16 configuration, RTT is applied to each DQ, DQSU_t,
DQSU_c, DQSL_t, DQSL_c, UDM_n, and LDM_n signal. The ODT pin will be ignored if the mode
registers are programmed to disable RTT.
register. When enabled in MR5, the DRAM calculates parity with ACT_n, RAS_n/A16, CAS_n/A15,
WE_n/A14, BG[1:0], BA[1:0], A[16:0]. Input parity should be maintained at the rising edge of the
clock and at the same time as command and address with CS_n LOW.
mand and/or address being entered and have multiple functions. For example, for activation
with ACT_n LOW, these are addresses like A16, A15, and A14, but for a non-activation command with ACT_n HIGH, these are command pins for READ, WRITE, and other commands defined in Command Truth Table.
SET_n is HIGH. RESET_n must be HIGH during normal operation.
Serial address inputs: Used to configure the temperature sensor/SPD EEPROM address range
on the I2C bus.
Serial clock for temperature sensor/SPD EEPROM: Used to synchronize communication to
and from the temperature sensor/SPD EEPROM on the I2C bus.
DQ[3:0], DQ[7:0], and DQ[15:0] for the x4, x8, and x16 configurations, respectively. If cyclic redundancy checksum (CRC) is enabled via the mode register, the CRC code is added at the end of
the data burst. Any one or all of DQ0, DQ1, DQ2, or DQ3 may be used for monitoring of internal V
level during test via mode register setting MR[4] A[4] = HIGH; training times change
REF
when enabled.
data is masked when DM_n is sampled LOW coincident with that input data during a write access. DM_n is sampled on both edges of DQS. DM is multiplexed with the DBI function by the
mode register A10, A11, and A12 settings in MR5. For a x8 device, the function of DM or TDQS
is enabled by the mode register A11 setting in MR1. DBI_n is an input/output identifying
whether to store/output the true or inverted data. If DBI_n is LOW, the data will be stored/
output after inversion inside the DDR4 device and not inverted if DBI_n is HIGH. TDQS is only
supported in x8 SDRAM configurations (TDQS is not valid for UDIMMs).
combo device.
tered-aligned with write data. For x16 configurations, DQSL corresponds to the data on
DQ[7:0], and DQSU corresponds to the data on DQ[15:8]. For the x4 and x8 configurations, DQS
corresponds to the data on DQ[3:0] and DQ[7:0], respectively. DDR4 SDRAM supports a differential data strobe only and does not support a single-ended data strobe.
flag as output signal. If a CRC error occurs, ALERT_n goes LOW for the period time interval and
returns HIGH. If an error occurs during a command address parity check, ALERT_n goes LOW until the on-going DRAM internal recovery transaction is complete. During connectivity test mode,
this pin functions as an input. Use of this signal is system-dependent. If not connected as signal,
ALERT_n pin must be connected to VDD on DIMMs.
perature thresholds have been exceeded. This pin has no function (NF) on modules without
temperature sensors.
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
6
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Table 5: Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Symbol Type Description
TDQS_t
TDQS_c
(x8 DRAM-based
RDIMM only)
V
DD
V
PP
V
REFCA
V
SS
V
TT
V
DDSPD
RFU – Reserved for future use.
NC – No connect: No internal electrical connection is present.
NF – No function: May have internal connection present, but has no function.
Output Termination data strobe: When enabled via the mode register, the DRAM device enables the
same RTT termination resistance on TDQS_t and TDQS_c that is applied to DQS_t and DQS_c.
When the TDQS function is disabled via the mode register, the DM/TDQS_t pin provides the data mask (DM) function, and the TDQS_c pin is not used. The TDQS function must be disabled in
the mode register for both the x4 and x16 configurations. The DM function is supported only in
x8 and x16 configurations. DM, DBI, and TDQS are a shared pin and are enabled/disabled by
mode register settings. For more information about TDQS, see the DDR4 DRAM component data sheet (TDQS_t and TDQS_c are not valid for UDIMMs).
Supply Module power supply: 1.2V (TYP).
Supply DRAM activating power supply: 2.5V –0.125V / +0.250V.
Supply Reference voltage for control, command, and address pins.
Supply Ground.
Supply Power supply for termination of address, command, and control VDD/2.
Supply Power supply used to power the I2C bus for SPD.
Pin Descriptions
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
7
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

DQ Map
Table 6: Component-to-Module DQ Map
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
DQ Map
Component
Reference
Number
Component
DQ Module DQ
Module Pin
Number
Component
Reference
Number
Component
DQ Module DQ
U1 0 3 21 U2 0 19 63
1 0 8 1 17 49
2 2 20 2 18 62
3 1 7 3 16 50
4 6 16 4 22 58
5 4 4 5 21 45
6 7 17 6 23 59
7 5 3 7 20 46
U4 0 38 183 U5 0 55 225
1 36 170 1 52 211
2 39 182 2 54 224
3 37 169 3 53 212
4 35 186 4 50 228
5 32 174 5 49 215
6 34 187 6 51 229
7 33 173 7 48 216
U6 0 56 237 U7 0 40 195
1 58 249 1 42 207
2 57 236 2 41 194
3 59 250 3 43 208
4 61 233 4 44 191
5 62 245 5 47 204
6 60 232 6 45 190
7 63 246 7 46 203
U8 0 29 67 U9 0 12 24
1 30 79 1 15 37
2 28 66 2 13 25
3 31 80 3 14 38
4 24 70 4 9 29
5 26 83 5 10 41
6 25 71 6 8 28
7 27 84 7 11 42
Module Pin
Number
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
8
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

Functional Block Diagram
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
U1
DQ32
DQ33
DQ34
DQ35
DQ36
DQ37
DQ38
DQ39
U4
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
U9
DQ40
DQ41
DQ42
DQ43
DQ44
DQ45
DQ46
DQ47
U7
DQ16
DQ17
DQ18
DQ19
DQ20
DQ21
DQ22
DQ23
U2
DQ48
DQ49
DQ50
DQ51
DQ52
DQ53
DQ54
DQ55
U5
DQ24
DQ25
DQ26
DQ27
DQ28
DQ29
DQ30
DQ31
U8
DQ56
DQ57
DQ58
DQ59
DQ60
DQ61
DQ62
DQ63
U6
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
DQ
ZQ
CS0_n
Rank 0
CK0_t
CK0_c
Vref CA
Vss
DDR4 SDRAM
DDR4 SDRAM
Vdd
Vddspd
SPD EEPROM
Vtt
DDR4 SDRAM
DDR4 SDRAM
Vpp
Clock, control, command, and address line terminations:
Vss
Vss
Vss
Vss
Vss
Vss
Vss
Vss
A0
SPD EEPROM
A1 A2
SA0
SDA
SCL
EVT
U3
Control, command, and
address termination
DDR4
SDRAM
VTT
CK0_t
CK0_c
DDR4
SDRAM
VDD
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DQS0_t
DQS0_c
DBI0_n/DM0_n
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DM_n/ CS_n DQS_t DQS_c
DBI_n
DQS1_t
DQS1_c
DBI1_n/DM1_n
DQS2_t
DQS2_c
DBI2_n/DM2_n
DQS3_t
DQS3_c
DBI3_n/DM3_n
DQS4_t
DQS4_c
DBI4_n/DM4_n
DQS6_t
DQS6_c
DBI6_n/DM6_n
DQS7_t
DQS7_c
DBI7_n/DM7_n
BA[1:0]
BG[1:0]
ACT_n
A[13:0]
RAS_n/A16
CAS_n/A15
WE_n/A14
CKE0
ODT0
RESET
PAR_IN
ALERT_CONN
BA[1:0]: DDR4 SDRAM
BG[1:0]: DDR4 SDRAM
ACT_n: DDR4 SDRAM
A[13:0]: DDR4 SDRAM
RAS_n/A16: DDR4 SDRAM
CAS_n/A15: DDR4 SDRAM
WE_n/A14: DDR4 SDRAM
CKE0: Rank 0
ODT0: Rank 0
RESET_n: DDR4 SDRAM
PAR: DDR4 SDRAM
ALERT_DRAM: DDR4 SDRAM
CS0_n, BA[1:0], BG[1:0],
ACT_n, A[13:0], RAS_n/A16,
CAS_n/A15, WE_n/A14,
CKE0, ODT0
DQS5_t
DQS5_c
DBI5_n/DM5_n
Vss
Vss
SA1
CK1_t
CK1_c
Figure 2: Functional Block Diagram
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Functional Block Diagram
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
Note:
1. The ZQ ball on each DDR4 component is connected to an external 240Ω ±1% resistor
that is tied to ground. It is used for the calibration of the component’s ODT and output
driver.
9
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

General Description
High-speed DDR4 SDRAM modules use DDR4 SDRAM devices with two or four internal
memory bank groups. DDR4 SDRAM modules utilizing 4- and 8-bit-wide DDR4 SDRAM
devices have four internal bank groups consisting of four memory banks each, providing a total of 16 banks. 16-bit-wide DDR4 SDRAM devices have two internal bank
groups consisting of four memory banks each, providing a total of eight banks. DDR4
SDRAM modules benefit from DDR4 SDRAM's use of an 8n-prefetch architecture with
an interface designed to transfer two data words per clock cycle at the I/O pins. A single
READ or WRITE operation for the DDR4 SDRAM effectively consists of a single 8n-bitwide, four-clock data transfer at the internal DRAM core and eight corresponding n-bitwide, one-half-clock-cycle data transfers at the I/O pins.
DDR4 modules use two sets of differential signals: DQS_t and DQS_c to capture data
and CK_t and CK_c to capture commands, addresses, and control signals. Differential
clocks and data strobes ensure exceptional noise immunity for these signals and provide precise crossing points to capture input signals.
Fly-By Topology
DDR4 modules use faster clock speeds than earlier DDR technologies, making signal
quality more important than ever. For improved signal quality, the clock, control, command, and address buses have been routed in a fly-by topology, where each clock, control, command, and address pin on each DRAM is connected to a single trace and terminated (rather than a tree structure, where the termination is off the module near the
connector). Inherent to fly-by topology, the timing skew between the clock and DQS signals can be easily accounted for by using the write-leveling feature of DDR4.
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
General Description
Module Manufacturing Location
Micron Technology manufactures modules at sites world-wide. Customers may receive
modules from any of the following manufacturing locations:
Table 7: DRAM Module Manufacturing Locations
Manufacturing Site Location Country of Origin Specified on Label
Boise, USA USA
Aguadilla, Puerto Rico Puerto Rico
Xian, China China
Singapore Singapore
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
10
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

Address Mapping to DRAM
Address Mirroring
To achieve optimum routing of the address bus on DDR4 multi rank modules, the address bus will be wired as shown in the table below, or mirrored. For quad rank modules, ranks 1 and 3 are mirrored and ranks 0 and 2 are non-mirrored. Highlighted address pins have no secondary functions allowing for normal operation when crosswired. Data is still read from the same address it was written. However, Load Mode operations require a specific address. This requires the controller to accommodate for a
rank that is "mirrored." Systems may reference DDR4 SPD to determine if the module
has mirroring implemented or not. See the JEDEC DDR4 SPD specification for more details.
Table 8: Address Mirroring
Edge Connector Pin DRAM Pin, Non-mirrored DRAM Pin, Mirrored
A0 A0 A0
A1 A1 A1
A2 A2 A2
A3 A3 A4
A4 A4 A3
A5 A5 A6
A6 A6 A5
A7 A7 A8
A8 A8 A7
A9 A9 A9
A10 A10 A10
A11 A11 A13
A13 A13 A11
A12 A12 A12
A14 A14 A14
A15 A15 A15
A16 A16 A16
A17 A17 A17
BA0 BA0 BA1
BA1 BA1 BA0
BG0 BG0 BG1
BG1 BG1 BG0
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Address Mapping to DRAM
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
11
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

SPD EEPROM Operation
DDR4 SDRAM modules incorporate serial presence detect (SPD). The SPD data is stored in a 512-byte JEDEC JC-42.4-compliant EEPROM that is segregated into four 128byte, write-protectable blocks. The SPD content is aligned with these blocks as shown in
the table below.
Block Range Description
0 0–127 000h–07Fh Configuration and DRAM parameters
1 128–255 080h–0FFh Module-specific parameters
2 256–319 100h–13Fh Reserved; all bytes coded as 00h
320–383 140h–17Fh Manufacturing information
3 384–511 180h–1FFh End-user programmable
The first 384 bytes are programmed by Micron to comply with JEDEC standard JC-45,
"Appendix X: Serial Presence Detect (SPD) for DDR4 SDRAM Modules." The remaining
128 bytes of storage are available for use by the customer.
The EEPROM resides on a two-wire I2C serial interface and is not integrated with the
memory bus in any way. It operates as a slave device in the I2C bus protocol, with all
operations synchronized by the serial clock. Transfer rates of up to 1 MHz are achievable at 2.5V (NOM).
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
SPD EEPROM Operation
Micron implements reversible software write protection on DDR4 SDRAM-based modules. This prevents the lower 384 bytes (bytes 0–383) from being inadvertently programmed or corrupted. The upper 128 bytes remain available for customer use and unprotected.
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
12
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Electrical Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Stresses greater than those listed may cause permanent damage to the module. This is a
stress rating only, and functional operation of the module at these or any other conditions outside those indicated in each device's data sheet is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may adversely affect reliability.
Table 9: Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Notes
V
V
DDQ
V
VIN, V
Table 10: Operating Conditions
Symbol Parameter Min Nom Max Units Notes
V
V
V
REFCA(DC)
I
VTT
V
I
I/O
I
OZpd
I
OZpu
I
VREFCAVREFCA
VDD supply voltage relative to V
DD
V
supply voltage relative to V
DDQ
Voltage on VPP pin relative to V
PP
Voltage on any pin relative to V
OUT
DD
VDD supply voltage 1.14 1.2 1.26 V 1
DRAM activating power supply 2.375 2.5 2.75 V 2
PP
Input reference voltage command/
address bus
Termination reference current from V
Termination reference voltage (DC) –
TT
command/address bus
I
Input leakage current; any input excluding ZQ;
I
0V < VIN < 1.1V
DQ leakage; 0V < Vin < V
I
Input leakage current; ZQ –3.0 – 3.0 µA 5, 6
I
Output leakage current; V
Output leakage current; V
disabled; ODT is disabled with ODT input HIGH
leakage; V
tialized)
SS
SS
SS
SS
DD
= VDD; DQ is disabled – – 5.0 µA
OUT
=VSS; DQ and ODT are
OUT
= VDD/2 (after DRAM is ini-
REFCA
–0.4 1.5 V 1
–0.4 1.5 V 1
–0.4 3.0 V 2
–0.4 1.5 V
0.49 × V
TT
–750 – 750 mA
0.49 × VDD 20mV
0.5 × V
DD
DD
0.5 × VDD0.51 × VDD +
0.51 × V
20mV
DD
V 3
V 4
–2.0 – 2.0 µA 5
–4.0 – 4.0 µA 5
– – 5.0 µA
–2.0 – 2.0 µA 5
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
Notes:
1. V
tracks with VDD; V
DDQ
and VDD are tied together.
DDQ
2. VPP must be greater than or equal to VDD at all times.
3. V
must not be greater than 0.6 x VDD. When VDD is less than 500mV, V
REFCA
may be
REF
less than or equal to 300mV.
4. VTT termination voltages in excess of the specification limit adversely affect the voltage
margins of command and address signals and reduce timing margins.
5. Multiply by the number of DRAM die on the module.
6. Tied to ground. Not connected to edge connector.
13
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Electrical Specifications
Table 11: Thermal Characteristics
Symbol Parameter/Condition Value Units Notes
T
C
T
C
T
OPER
T
OPER
T
STG
RH
STG
NA Change Rate of Storage Temperature 20 °C/hour
Commercial operating case temperature 0 to 85 °C 1, 2, 3
>85 to 95 °C 1, 2, 3, 4
Normal operating temperature range 0 to 85 °C 5, 7
Extended temperature operating range (optional) >85 to 95 °C 5, 7
Non-operating storage temperature –55 to 100 °C 6
Non-operating Storage Relative Humidity (non-condensing) 5 to 95 %
Notes:
1. Maximum operating case temperature; TC is measured in the center of the package.
2. A thermal solution must be designed to ensure the DRAM device does not exceed the
maximum TC during operation.
3. Device functionality is not guaranteed if the DRAM device exceeds the maximum TC during operation.
4. If TC exceeds 85°C, the DRAM must be refreshed externally at 2X refresh, which is a 3.9µs
interval refresh rate.
5. The refresh rate must double when 85°C < T
OPER
≤ 95°C.
6. Storage temperature is defined as the temperature of the top/center of the DRAM and
does not reflect the storage temperatures of shipping trays.
7. For additional information, refer to technical note TN-00-08: "Thermal Applications"
available at micron.com.
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
14
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
DRAM Operating Conditions
DRAM Operating Conditions
Recommended AC operating conditions are given in the DDR4 component data sheets.
Component specifications are available at micron.com. Module speed grades correlate
with component speed grades, as shown below.
Table 12: Module and Component Speed Grades
DDR4 components may exceed the listed module speed grades; module may not be available in all listed speed grades
Module Speed Grade Component Speed Grade
-2G6 -075
-2G4 -083E
-2G3 -083
-2G1 -093E
-1G9 -107E
Design Considerations
Simulations
Micron memory modules are designed to optimize signal integrity through carefully designed terminations, controlled board impedances, routing topologies, trace length
matching, and decoupling. However, good signal integrity starts at the system level. Micron encourages designers to simulate the signal characteristics of the system's memory bus to ensure adequate signal integrity of the entire memory system.
Power
Operating voltages are specified at the edge connector of the module, not at the DRAM.
Designers must account for any system voltage drops at anticipated power levels to ensure the required supply voltage is maintained.
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
15
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
IDD Specifications
IDD Specifications
Table 13: DDR4 IDD Specifications and Conditions – 8GB (Die Revision A)
Values are for the MT40A1G8 DDR4 SDRAM only and are computed from values specified in the 8Gb (1 Gig x 8) component data sheet
Parameter Symbol 2666 2400 2133 Units
One bank ACTIVATE-PRECHARGE current I
One bank ACTIVATE-PRECHARGE, Word Line Boost, IPP current I
One bank ACTIVATE-READ-PRECHARGE current I
Precharge standby current I
Precharge standby ODT current I
Precharge power-down current I
Precharge quiet standby current I
Active standby current I
Active standby IPP current I
Active power-down current I
Burst read current I
Burst read I
current I
DDQ
Burst write current I
Burst refresh current (1x REF) I
Burst refresh IPP current (1x REF) I
Self refresh current: Normal temperature range (0°C to 85°C) I
Self refresh current: Extended temperature range (0°C to 95°C) I
Self refresh current: Reduced temperature range (0°C to 45°C) I
Auto self refresh current (25°C) I
Auto self refresh current (45°C) I
Auto self refresh current (75°C) I
Bank interleave read current I
Bank interleave read IPP current I
Maximum power-down current I
DD0
PP0
DD1
DD2N
DD2NT
DD2P
DD2Q
DD3N
PP3N
DD3P
DD4R
DDQ4R
DD4W
DD5B
PP5B
DD6N
DD6E
DD6R
DD6A
DD6A
DD6A
DD7
PP7
DD8
520 480 440 mA
24 24 24 mA
640 600 560 mA
440 400 360 mA
520 480 440 mA
280 240 200 mA
400 360 360 mA
480 440 440 mA
24 24 24 mA
320 320 280 mA
1400 1280 1200 mA
560 520 480 mA
1400 1200 1200 mA
1800 1800 1800 mA
240 240 240 mA
240 240 240 mA
280 280 280 mA
200 200 200 mA
160 160 160 mA
200 200 200 mA
280 280 280 mA
1720 1640 1600 mA
120 120 120 mA
160 160 160 mA
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
16
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
IDD Specifications
Table 14: DDR4 IDD Specifications and Conditions – 8GB (Die Revision B)
Values are for the MT40A1G8 DDR4 SDRAM only and are computed from values specified in the 8Gb (1 Gig x 8) component data sheet
Parameter Symbol 2666 2400 2133 Units
One bank ACTIVATE-PRECHARGE current I
One bank ACTIVATE-PRECHARGE, Word Line Boost, IPP current I
One bank ACTIVATE-READ-PRECHARGE current I
Precharge standby current I
Precharge standby ODT current I
Precharge power-down current I
Precharge quiet standby current I
Active standby current I
Active standby IPP current I
Active power-down current I
Burst read current I
Burst read I
current I
DDQ
Burst write current I
Burst refresh current (1x REF) I
Burst refresh IPP current (1x REF) I
Self refresh current: Normal temperature range (0°C to 85°C) I
Self refresh current: Extended temperature range (0°C to 95°C) I
Self refresh current: Reduced temperature range (0°C to 45°C) I
Auto self refresh current (25°C) I
Auto self refresh current (45°C) I
Auto self refresh current (75°C) I
Bank interleave read current I
Bank interleave read IPP current I
Maximum power-down current I
DD0
PP0
DD1
DD2N
DD2NT
DD2P
DD2Q
DD3N
PP3N
DD3P
DD4R
DDQ4R
DD4W
DD5B
PP5B
DD6N
DD6E
DD6R
DD6A
DD6A
DD6A
DD7
PP7
DD8
408 384 360 mA
24 24 24 mA
504 480 456 mA
280 272 264 mA
400 400 360 mA
200 200 200 mA
240 240 240 mA
368 344 320 mA
24 24 24 mA
312 296 280 mA
1160 1080 1000 mA
560 560 480 mA
1048 984 920 mA
2000 2000 2000 mA
224 224 224 mA
240 240 240 mA
280 280 280 mA
160 160 160 mA
64 64 64 mA
160 160 160 mA
240 240 240 mA
1440 1400 1360 mA
120 120 120 mA
200 200 200 mA
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
17
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
SPD EEPROM Operating Conditions
SPD EEPROM Operating Conditions
For the latest SPD data, refer to Micron's SPD page: micron.com/spd.
Table 15: SPD EEPROM DC Operating Conditions
Parameter/Condition Symbol Min Nom Max Units
Supply voltage V
Input low voltage: logic 0; all inputs V
Input high voltage: logic 1; all inputs V
Output low voltage: 3mA sink current V
Input leakage current: (SCL, SDA) VIN = V
Output leakage current: V
OUT
= V
DDSPD
> 2V V
DDSPD
or V
DDSPD
or V
SSSPD
SSSPD
, SDA in High-Z I
DDSPD
IL
IH
OL
I
LI
LO
– 2.5 – V
–0.5 – V
DDSPD
×
0.3
V
DDSPD
0.7
×
– V
DDSPD
0.5
+
– – 0.4 V
– – ±5 µA
– – ±5 µA
V
V
Notes:
1. Table is provided as a general reference. Consult JEDEC JC-42.4 EE1004 and TSE2004 device specifications for complete details.
2. All voltages referenced to V
DDSPD
.
Table 16: SPD EEPROM AC Operating Conditions
Parameter/Condition Symbol Min Max Units
Clock frequency
Clock pulse width HIGH time
Clock pulse width LOW time
Detect clock LOW timeout
SDA rise time
SDA fall time
Data-in setup time
Data-in hold time
Data out hold time
Start condition setup time
Start condition hold time
Stop condition setup time
Time the bus must be free before a new transition can start
Write time
Warm power cycle time off
Time from power on to first command
t
SCL 10 1000 kHz
t
HIGH 260 – ns
t
LOW 500 – ns
t
TIMEOUT 25 35 ms
t
R – 120 ns
t
F – 120 ns
t
SU:DAT 50 – ns
t
HD:DI 0 – ns
t
HD:DAT 0 350 ns
t
SU:STA 260 – ns
t
HD:STA 260 – ns
t
SU:STO 260 – ns
t
BUF 500 – ns
t
W – 5 ms
t
POFF 1 – ms
t
INIT 10 – ms
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
Note:
1. Table is provided as a general reference. Consult JEDEC JC-42.4 EE1004 and TSE2004 device specifications for complete details.
18
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

Module Dimensions
3.7 (0.145)
MAX
PIN 1
20.0 (0.787)
TYP
1.8 (0.071)
(2X)
0.5 (0.019)
TYP
0.35 (0.014)
TYP
.65 (0.025) R0
(4X)
PIN 259
PIN 260
PIN 2
Front view
2.0 (0.079)
TYP
6.0 (0.236)
TYP
65.6 (2.58)
TYP
2.55 (0.10)
TYP
30.13 (1.186)
29.87 (1.176)
Back view
1.3 (0.051)
1.1 (0.043)
28.5 (1.12)
TYP
35.5 (1.4)
TYP
2.5 (0.98)
TYP
4.0 (0.157)
TYP
38.3 (1.51)
TYP
0.6 (0.24) x 45° (4X)
1.0 (0.039)
TYP
1.75 (0.07)
TYP (2X)
0.25 (0.1) x 45° (2X)
18.0 (0.71)
TYP
4.0 (0.157) TYP (2X)
69.73 (2.745)
69.47 (2.735)
U1
U2
U3
U4
U5
U6 U7
U8 U9
Figure 3: 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
8GB (x64, SR) 260-Pin DDR4 SODIMM
Module Dimensions
Although considered final, these specifications are subject to change, as further product development and data characterization some-
PDF: 09005aef8621b8d2
atf8c1gx64hz.pdf – Rev. E 4/16 EN
Notes:
1. All dimensions are in millimeters (inches); MAX/MIN or typical (TYP) where noted.
2. The dimensional diagram is for reference only.
8000 S. Federal Way, P.O. Box 6, Boise, ID 83707-0006, Tel: 208-368-4000
www.micron.com/products/support Sales inquiries: 800-932-4992
Micron and the Micron logo are trademarks of Micron Technology, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This data sheet contains minimum and maximum limits specified over the power supply and temperature range set forth herein.
times occur.
19
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...