Micron MTA18ASF2G72AZ – 16GB User Manual
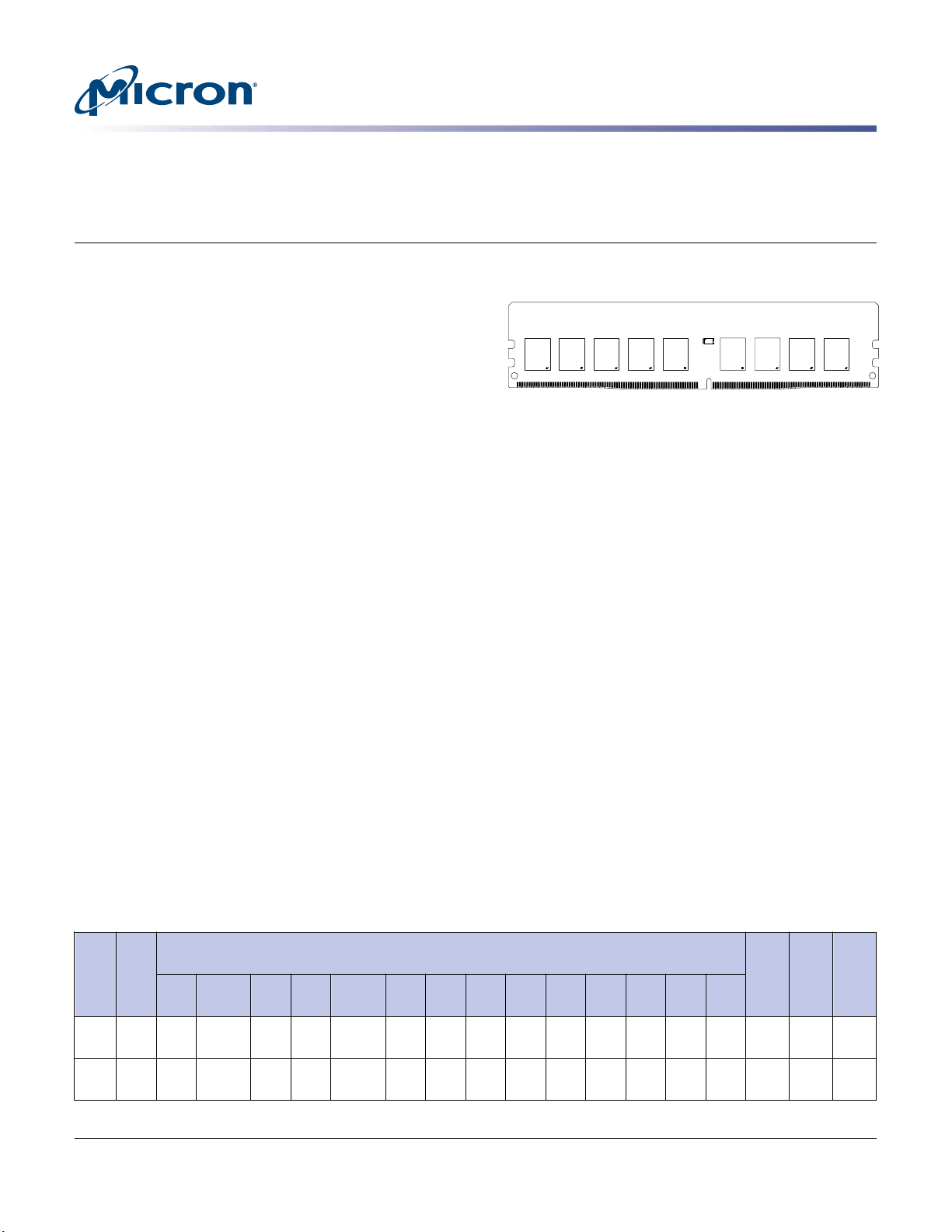
Module height: 31.25mm (1.23in)
16GB (x72, ECC, DR) 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM
DDR4 SDRAM UDIMM
MTA18ASF2G72AZ – 16GB
Features
Features
• DDR4 functionality and operations supported as
defined in the component data sheet
• 288-pin, unbuffered dual in-line memory module
(UDIMM)
• Fast data transfer rates: PC4-3200, PC4-2666, or
PC4-2400
• 16GB (2 Gig x 72)
• VDD = 1.20V (NOM)
• VPP = 2.5V (NOM)
• V
• Supports ECC error detection and correction
• Nominal and dynamic on-die termination (ODT) for
data, strobe, and mask signals
• Low-power auto self refresh (LPASR)
• Data bus inversion (DBI) for data bus
• On-die V
• Dual-rank
• On-board I2C temperature sensor with integrated
serial presence-detect (SPD) EEPROM
• 4 internal device bank groups with 4 banks per
group produce 16 device banks
• Fixed burst chop (BC) of 4 and burst length (BL) of 8
via the mode register set (MRS)
• Selectable BC4 or BL8 on-the-fly (OTF)
• Gold edge contacts
• Halogen-free
• Fly-by topology
• Terminated control, command, and address bus
= 2.5V (NOM)
DDSPD
generation and calibration
REFDQ
Figure 1: 288-Pin UDIMM (MO-309, R/C-E1)
Options Marking
• Operating temperature
– Commercial
(0°C ≤ T
OPER
≤ 95°C)
• Package
– 288-pin DIMM (halogen-free) Z
• Frequency/CAS latency
– 0.625ns @ CL = 22 (DDR4-3200) -3G2
– 0.75ns @ CL = 19 (DDR4-2666) -2G6
– 0.83ns @ CL = 17 (DDR4-2400) -2G3
None
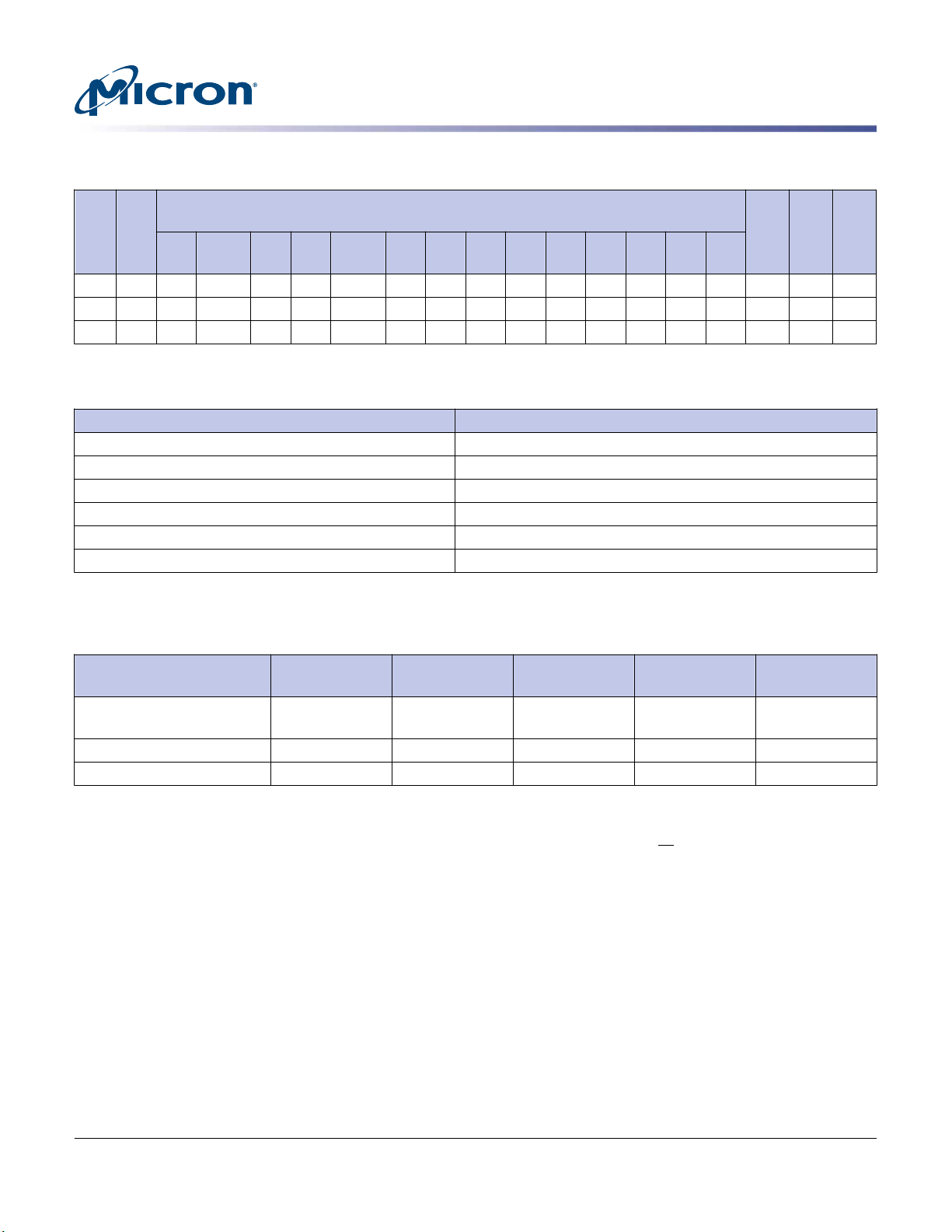
Table 1: Key Timing Parameters
PC4-
Grade
Speed
-3G2 3200 3200 3200/–2666 2666 2400 2400 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 1333 – 13.75 13.75 45.75
-2G9 2933 – 2933/
PDF: CCMTD-1725822587-9907
asf18c2gx72az.pdf – Rev. E 11/17 EN
Data Rate (MT/s)
CL =
t
22/
21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
2666 2666 2400 2400 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 1333 – 14.32 14.32 46.32
2933
1
Products and specifications discussed herein are subject to change by Micron without notice.
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
RCD
(ns)
t
RP
(ns)
t
RC
(ns)24
16GB (x72, ECC, DR) 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM
Features
Table 1: Key Timing Parameters (Continued)
Data Rate (MT/s)
CL =
t
Grade
Speed
PC4-
22/
21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
-2G6 2666 – – 2666 2666 2400 2400 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 1333 – 14.16 14.16 46.16
-2G3 2400 – – – – 2400 2400 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 1333 – 14.16 14.16 46.16
-2G1 2133 – – – – – – 2133 2133 1866 1866 1600 1600 1333 1333 13.5 13.5 46.5
Table 2: Addressing
Parameter 16GB
Row address 64K A[15:0]
Column address 1K A[9:0]
Device bank group address 4 BG[1:0]
Device bank address per group 4 BA[1:0]
Device configuration 8Gb (1 Gig x 8), 16 banks
Module rank address 2 CS_n[1:0]
RCD
(ns)
t
RP
(ns)
t
RC
(ns)24
Table 3: Part Numbers and Timing Parameters – 16GB Modules
Base device: MT40A1G8,1 8Gb DDR4 SDRAM
Part Number
MTA18ASF2G72AZ-3G2__
2
Density Configuration
16GB 2 Gig x 72 25.6 GB/s 0.625ns/3200
MTA18ASF2G72AZ-2G6__ 16GB 2 Gig x 72 21.3 GB/s 0.75ns/2666 MT/s 19-19-19
MTA18ASF2G72AZ-2G3__ 16GB 2 Gig x 72 19.2 GB/s 0.83ns/2400 MT/s 17-17-17
Module
Notes:
1. The data sheet for the base device can be found at micron.com.
2. All part numbers end with a two-place code (not shown) that designates component and PCB revisions.
Consult factory for current revision codes. Example: MTA18ASF2G72AZ-3G2E1.
Module
Bandwidth
Memory Clock/
Data Rate
MT/s
Clock Cycles
(CL-tRCD-tRP)
22-22-22
PDF: CCMTD-1725822587-9907
asf18c2gx72az.pdf – Rev. E 11/17 EN
2
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.

16GB (x72, ECC, DR) 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM
Features
Important Notes and Warnings
Micron Technology, Inc. ("Micron") reserves the right to make changes to information published in this document,
including without limitation specifications and product descriptions. This document supersedes and replaces all
information supplied prior to the publication hereof. You may not rely on any information set forth in this document if you obtain the product described herein from any unauthorized distributor or other source not authorized
by Micron.
Automotive Applications. Products are not designed or intended for use in automotive applications unless specifically designated by Micron as automotive-grade by their respective data sheets. Distributor and customer/distributor shall assume the sole risk and liability for and shall indemnify and hold Micron harmless against all claims,
costs, damages, and expenses and reasonable attorneys' fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of
product liability, personal injury, death, or property damage resulting directly or indirectly from any use of nonautomotive-grade products in automotive applications. Customer/distributor shall ensure that the terms and conditions of sale between customer/distributor and any customer of distributor/customer (1) state that Micron
products are not designed or intended for use in automotive applications unless specifically designated by Micron
as automotive-grade by their respective data sheets and (2) require such customer of distributor/customer to indemnify and hold Micron harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses and reasonable attorneys'
fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of product liability, personal injury, death, or property damage
resulting from any use of non-automotive-grade products in automotive applications.
Critical Applications. Products are not authorized for use in applications in which failure of the Micron component could result, directly or indirectly in death, personal injury, or severe property or environmental damage
("Critical Applications"). Customer must protect against death, personal injury, and severe property and environmental damage by incorporating safety design measures into customer's applications to ensure that failure of the
Micron component will not result in such harms. Should customer or distributor purchase, use, or sell any Micron
component for any critical application, customer and distributor shall indemnify and hold harmless Micron and
its subsidiaries, subcontractors, and affiliates and the directors, officers, and employees of each against all claims,
costs, damages, and expenses and reasonable attorneys' fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of
product liability, personal injury, or death arising in any way out of such critical application, whether or not Micron or its subsidiaries, subcontractors, or affiliates were negligent in the design, manufacture, or warning of the
Micron product.
Customer Responsibility. Customers are responsible for the design, manufacture, and operation of their systems,
applications, and products using Micron products. ALL SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS HAVE INHERENT FAILURE RATES AND LIMITED USEFUL LIVES. IT IS THE CUSTOMER'S SOLE RESPONSIBILITY TO DETERMINE
WHETHER THE MICRON PRODUCT IS SUITABLE AND FIT FOR THE CUSTOMER'S SYSTEM, APPLICATION, OR
PRODUCT. Customers must ensure that adequate design, manufacturing, and operating safeguards are included
in customer's applications and products to eliminate the risk that personal injury, death, or severe property or environmental damages will result from failure of any semiconductor component.
Limited Warranty. In no event shall Micron be liable for any indirect, incidental, punitive, special or consequential
damages (including without limitation lost profits, lost savings, business interruption, costs related to the removal
or replacement of any products or rework charges) whether or not such damages are based on tort, warranty,
breach of contract or other legal theory, unless explicitly stated in a written agreement executed by Micron's duly
authorized representative.
PDF: CCMTD-1725822587-9907
asf18c2gx72az.pdf – Rev. E 11/17 EN
3
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
16GB (x72, ECC, DR) 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM
Pin Assignments
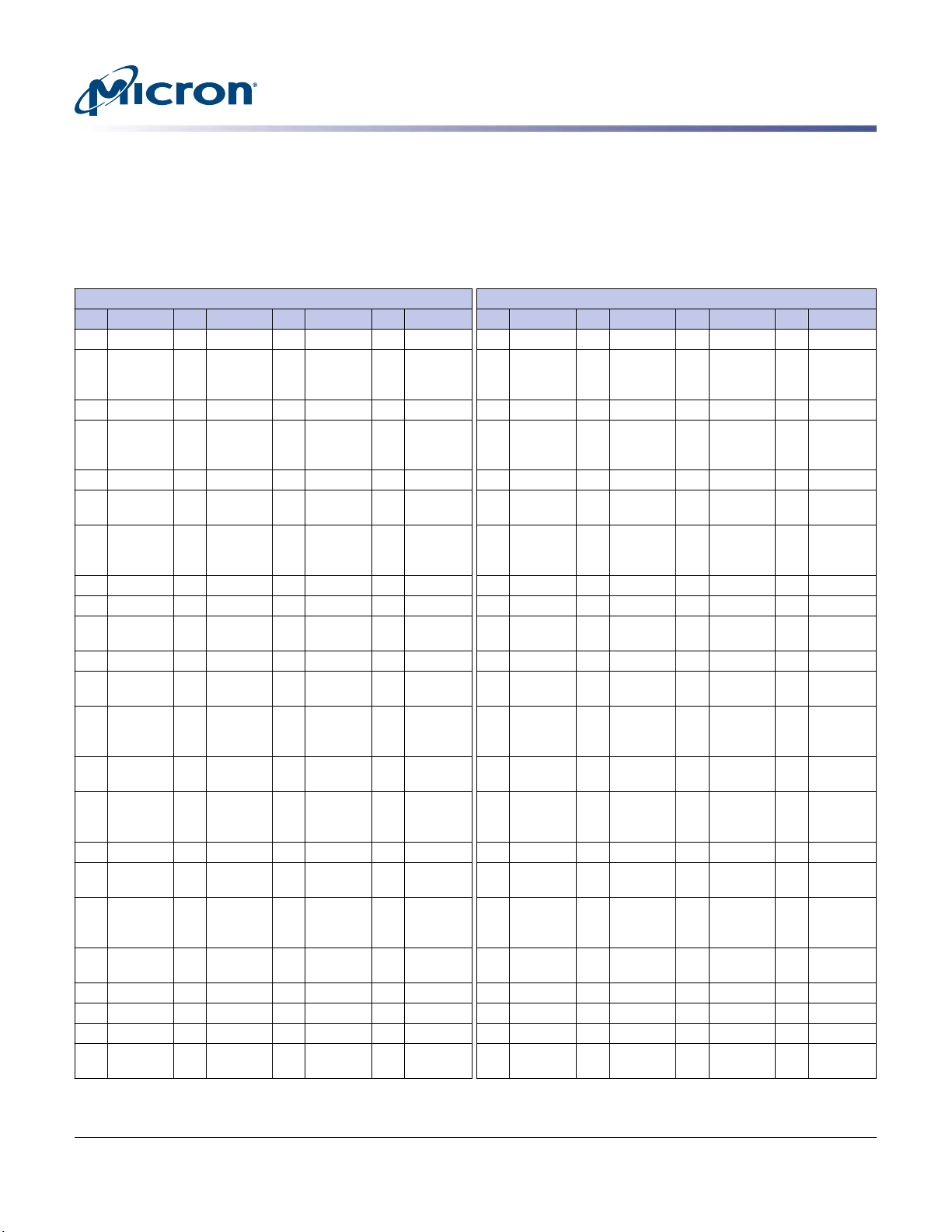
Pin Assignments
The pin assignment table below is a comprehensive list of all possible pin assignments
for DDR4 UDIMM modules. See Functional Block Diagram for pins specific to this
module.
Table 4: Pin Assignments
288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM Front 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM Back
Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol
1 NC 37 V
2 V
38 DQ24 74 CK0_t 110 DM5_n/
SS
3 DQ4 39 V
4 V
SS
40 DM3_n/
DBI3_n,
NC
5 DQ0 41 NC 77 V
6 V
42 V
SS
73 V
SS
DD
109 V
SS
DBI5_n,
NC
75 CK0_c 111 NC 147 V
SS
76 V
78 EVENT_n,NF114 V
SS
112 V
DD
113 DQ46 149 V
TT
SS
SS
145 NC 181 DQ29 217 V
146 V
REFCA
148 DQ5 184 V
182 V
183 DQ25 219 CK1_c 255 DQS5_c
SS
185 DQS3_c 221 V
SS
218 CK1_t 254 V
SS
220 V
SS
DD
DD
TT
253 DQ41
SS
256 DQS5_t
257 V
SS
150 DQ1 186 DQS3_t 222 PARITY 258 DQ47
7 DM0_n/
43 DQ30 79 A0 115 DQ42 151 V
DBI0_n,
NC
8 NC 44 V
9 V
45 DQ26 81 BA0 117 DQ52 153 DQS0_t 189 V
SS
10 DQ6 46 V
11 V
47 CB4/ NC 83 V
SS
12 DQ2 48 V
13 V
49 CB0/ NC 85 V
SS
14 DQ12 50 V
15 V
SS
51 DM8_n/
80 V
SS
82 RAS_n/
SS
84 CS0_n 120 V
SS
86 CAS_n/
SS
87 ODT0 123 V
DBI8_n,
NC
16 DQ8 52 NC 88 V
17 V
18 DMI_n/
DBI1_n,
NC
19 NC 55 V
SS
53 V
SS
54 CB6/
DBI8_n,
NC
SS
89 CS1_n,NC125 V
90 V
91 ODT1,NC127 V
DD
A16
DD
DD
A15
DD
DD
187 V
SS
116 V
118 V
152 DQS0_c 188 DQ31 224 BA1 260 DQ43
SS
SS
154 V
190 DQ27 226 V
SS
119 DQ48 155 DQ7 191 V
SS
121 DM6_n/
156 V
157 DQ3 193 V
192 CB5, NC 228 WE_n/
SS
DBI6_n,
NC
122 NC 158 V
159 DQ13 195 V
SS
124 DQ54 160 V
161 DQ9 197 DQS8_t 233 V
SS
126 DQ50 162 V
163 DQS1_c 199 CB7, NC 235 NC 271 DQ51
SS
194 CB1, NC 230 NC 266 DQS6_c
SS
196 DQS8_c 232 A13 268 V
SS
198 V
SS
223 V
SS
225 A10_AP 261 V
SS
227 NC 263 V
SS
DD
DD
A14
229 V
SS
231 V
SS
234 NC 270 V
SS
DD
DD
DD
259 V
SS
SS
262 DQ53
SS
264 DQ49
265 V
SS
267 DQS6_t
SS
269 DQ55
SS
20 V
56 CB2/ NC 92 V
SS
21 DQ14 57 V
22 V
58 RESET_n 94 V
SS
23 DQ10 59 V
PDF: CCMTD-1725822587-9907
asf18c2gx72az.pdf – Rev. E 11/17 EN
93 NC 129 V
SS
95 DQ36 131 V
DD
128 DQ60 164 DQS1_t 200 V
DD
165 V
SS
130 DQ56 166 DQ15 202 V
SS
167 V
SS
4
SS
SS
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
SS
236 V
DD
272 V
SS
201 CB3, NC 237 NC 273 DQ61
238 SA2 274 V
SS
203 CKE1,NC239 V
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
SS
275 DQ57
SS
16GB (x72, ECC, DR) 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM
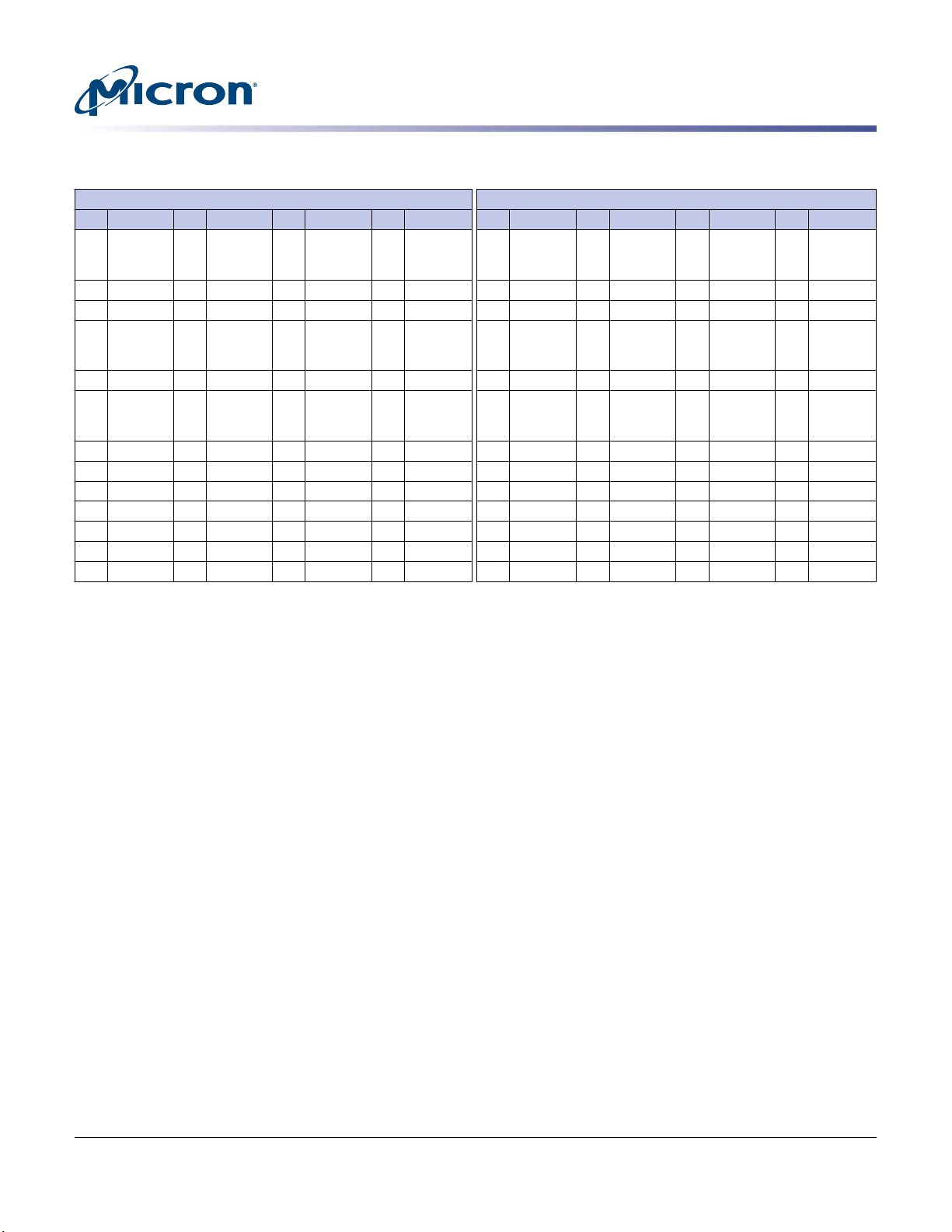
Pin Assignments
Table 4: Pin Assignments (Continued)
288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM Front 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM Back
Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol Pin Symbol
24 V
25 DQ20 61 V
26 V
27 DQ16 63 BG0 99 DM4_n/
28 V
29 DM2_n/
DBI2_n,
NC
30 NC 66 A9 102 DQ38 138 V
31 V
32 DQ22 68 A8 104 DQ34 140 SA1 176 V
33 V
34 DQ18 70 V
35 V
36 DQ28 72 A1 108 DQ40 144 NC 180 V
60 CKE0 96 V
SS
DD
62 ACT_n 98 V
SS
64 V
SS
DD
65 A12/BC_n 101 V
67 V
SS
69 A6 105 V
SS
71 A3 107 V
SS
DD
DD
SS
132 DM7_n/
168 DQ11 204 V
DBI7_n,
NC
97 DQ32 133 NC 169 V
SS
134 V
170 DQ21 206 V
SS
135 DQ62 171 V
DBI4_n,
NC
100 NC 136 V
137 DQ58 173 V
SS
103 V
139 SA0 175 DQS2_t 211 A7 247 DQ39 283 V
SS
141 SCL 177 DQ23 213 A5 249 DQ35 285 SDA
SS
106 DQ44 142 V
143 V
SS
172 DQ17 208 ALERT_n 244 DQS4_c 280 DQ63
SS
174 DQS2_c 210 A11 246 V
SS
178 V
PP
179 DQ19 215 V
PP
DD
205 NC 241 V
SS
DD
207 BG1 243 V
SS
209 V
SS
212 V
SS
214 A4 250 V
SS
216 A2 252 V
SS
DD
DD
DD
240 DQ37 276 V
277 DQS7_c
SS
SS
242 DQ33 278 DQS7_t
279 V
SS
245 DQS4_t 281 V
282 DQ59
SS
248 V
SS
SS
284 V
286 V
251 DQ45 287 V
288 V
SS
SS
SS
SS
DDSPD
PP
PP
PP
PDF: CCMTD-1725822587-9907
asf18c2gx72az.pdf – Rev. E 11/17 EN
5
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
16GB (x72, ECC, DR) 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM
Pin Descriptions
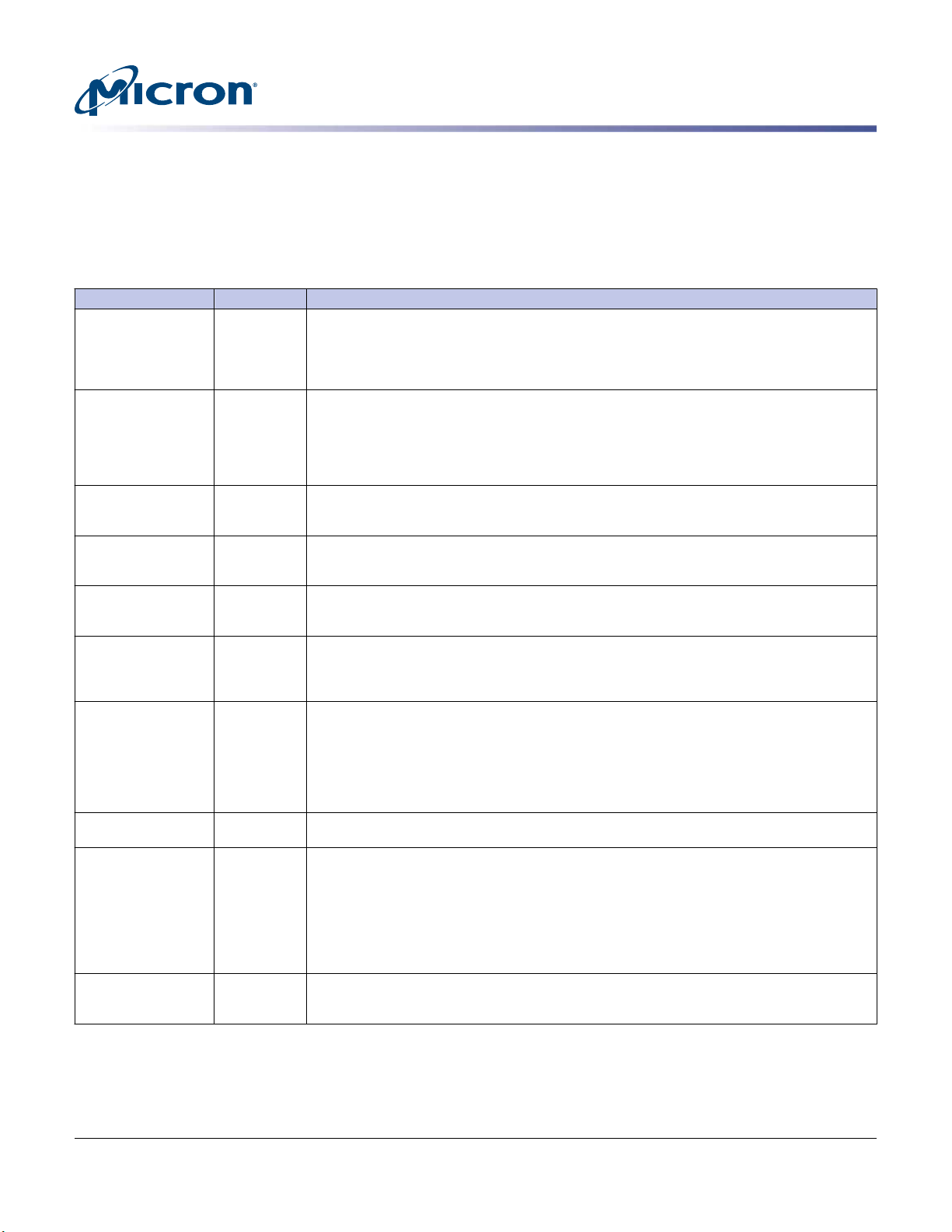
Pin Descriptions
The pin description table below is a comprehensive list of all possible pins for DDR4
modules. All pins listed may not be supported on this module. See Functional Block Diagram for pins specific to this module.
Table 5: Pin Descriptions
Symbol Type Description
Ax Input Address inputs: Provide the row address for ACTIVATE commands and the column address for
A10/AP Input Auto precharge: A10 is sampled during READ and WRITE commands to determine whether an
A12/BC_n Input Burst chop: A12/BC_n is sampled during READ and WRITE commands to determine if burst
ACT_n Input Command input: ACT_n defines the ACTIVATE command being entered along with CS_n. The
BAx Input Bank address inputs: Define the bank (with a bank group) to which an ACTIVATE, READ,
BGx Input Bank group address inputs: Define the bank group to which a REFRESH, ACTIVATE, READ,
C0, C1, C2
(RDIMM/LRDIMM on-
ly)
CKx_t
CKx_c
CKEx Input Clock enable: CKE HIGH activates and CKE LOW deactivates the internal clock signals, device
CSx_n Input Chip select: All commands are masked when CS_n is registered HIGH. CS_n provides external
Input Chip ID: These inputs are used only when devices are stacked; that is, 2H, 4H, and 8H stacks for
Input Clock: Differential clock inputs. All address, command, and control input signals are sampled
READ/WRITE commands in order to select one location out of the memory array in the respective bank (A10/AP, A12/BC_n, WE_n/A14, CAS_n/A15, and RAS_n/A16 have additional functions;
see individual entries in this table). The address inputs also provide the op-code during the
MODE REGISTER SET command. A17 is only defined for x4 SDRAM.
auto precharge should be performed on the accessed bank after a READ or WRITE operation
(HIGH = auto precharge; LOW = no auto precharge). A10 is sampled during a PRECHARGE command to determine whether the precharge applies to one bank (A10 LOW) or all banks (A10
HIGH). If only one bank is to be precharged, the bank is selected by the bank group and bank
addresses.
chop (on-the-fly) will be performed (HIGH = no burst chop; LOW = burst chopped). See Command Truth Table in the DDR4 component data sheet.
input into RAS_n/A16, CAS_n/A15, and WE_n/A14 are considered as row address A16, A15, and
A14. See Command Truth Table.
WRITE, or PRECHARGE command is being applied. Also determine which mode register is to be
accessed during a MODE REGISTER SET command.
WRITE, or PRECHARGE command is being applied. Also determine which mode register is to be
accessed during a MODE REGISTER SET command. BG[1:0] are used in the x4 and x8 configurations. x16-based SDRAM only has BG0.
x4 and x8 configurations using through-silicon vias (TSVs). These pins are not used in the x16
configuration. Some DDR4 modules support a traditional DDP package, which uses CS1_n,
CKE1, and ODT1 to control the second die. All other stack configurations, such as a 4H or 8H,
are assumed to be single-load (master/slave) type configurations where C0, C1, and C2 are used
as chip ID selects in conjunction with a single CS_n, CKE, and ODT. Chip ID is considered part of
the command code.
on the crossing of the positive edge of CK_t and the negative edge of CK_c.
input buffers, and output drivers. Taking CKE LOW provides PRECHARGE POWER-DOWN and
SELF REFRESH operations (all banks idle), or active power-down (row active in any bank). CKE is
asynchronous for self refresh exit. After V
tialization sequence, it must be maintained during all operations (including SELF REFRESH). CKE
must be maintained HIGH throughout read and write accesses. Input buffers (excluding CK_t,
CK_c, ODT, RESET_n, and CKE) are disabled during power-down. Input buffers (excluding CKE
and RESET_n) are disabled during self refresh.
rank selection on systems with multiple ranks. CS_n is considered part of the command code
(CS2_n and CS3_n are not used on UDIMMs).
has become stable during the power-on and ini-
REFCA
PDF: CCMTD-1725822587-9907
asf18c2gx72az.pdf – Rev. E 11/17 EN
6
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
16GB (x72, ECC, DR) 288-Pin DDR4 UDIMM
Pin Descriptions
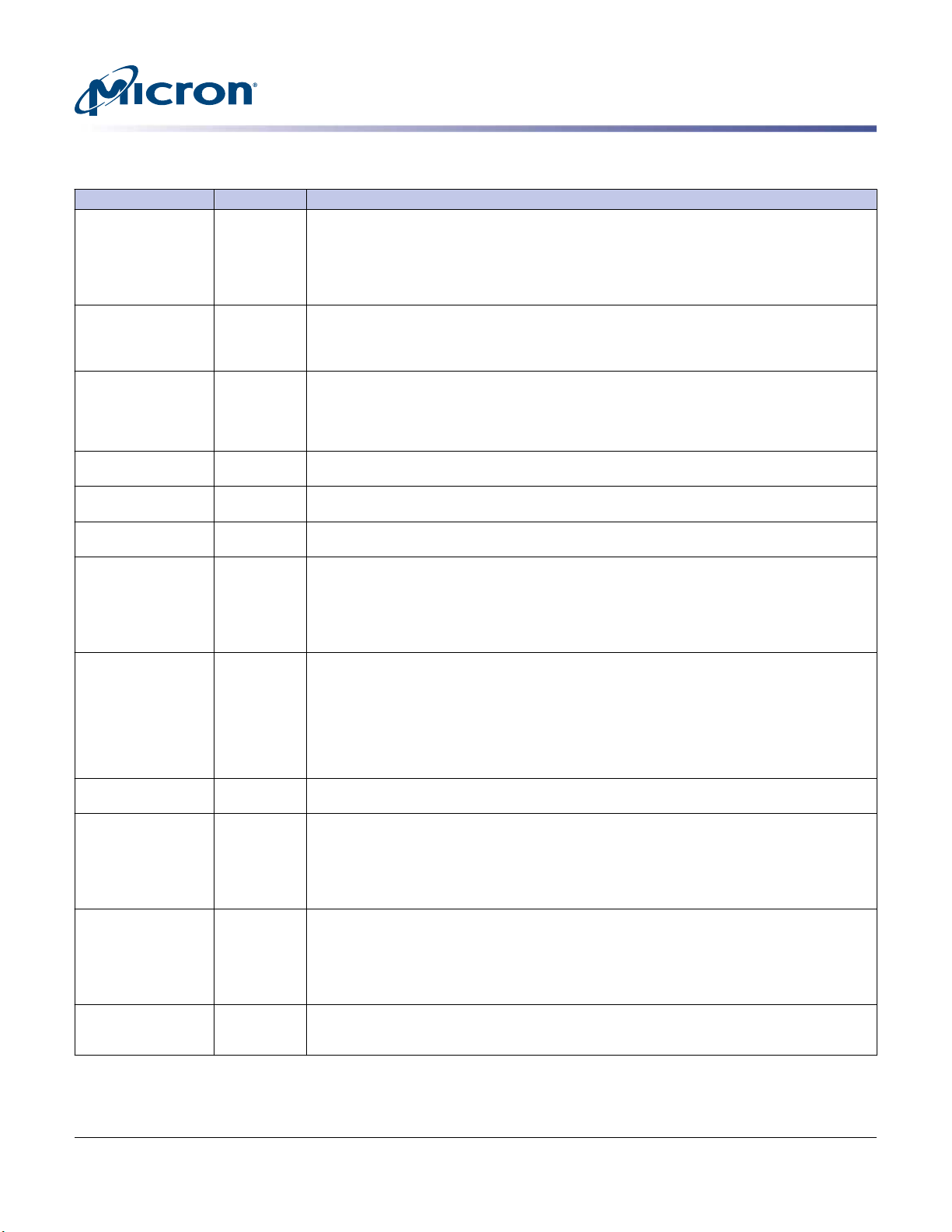
Table 5: Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Symbol Type Description
ODTx Input On-die termination: ODT (registered HIGH) enables termination resistance internal to the
PARITY Input Parity for command and address: This function can be enabled or disabled via the mode
RAS_n/A16
Input Command inputs: RAS_n/A16, CAS_n/A15, and WE_n/A14 (along with CS_n) define the com-
CAS_n/A15
WE_n/A14
RESET_n CMOS Input Active LOW asynchronous reset: Reset is active when RESET_n is LOW and inactive when RE-
SAx Input
SCL Input
DQx, CBx I/O Data input/output and check bit input/output: Bidirectional data bus. DQ represents
DM_n/DBI_n/
I/O Input data mask and data bus inversion: DM_n is an input mask signal for write data. Input
TDQS_t (DMU_n,
DBIU_n), (DML_n/
DBIl_n)
SDA I/O Serial Data: Bidirectional signal used to transfer data in or out of the EEPROM or EEPROM/TS
DQS_t
I/O Data strobe: Output with read data, input with write data. Edge-aligned with read data, cen-
DQS_c
DQSU_t
DQSU_c
DQSL_t
DQSL_c
ALERT_n Output Alert output: Possesses functions such as CRC error flag and command and address parity error
EVENT_n Output Temperature event: The EVENT_n pin is asserted by the temperature sensor when critical tem-
DDR4 SDRAM. When enabled, ODT (RTT) is applied only to each DQ, DQS_t, DQS_c, DM_n/
DBI_n/TDQS_t, and TDQS_c signal for x4 and x8 configurations (when the TDQS function is enabled via the mode register). For the x16 configuration, RTT is applied to each DQ, DQSU_t,
DQSU_c, DQSL_t, DQSL_c, UDM_n, and LDM_n signal. The ODT pin will be ignored if the mode
registers are programmed to disable RTT.
register. When enabled in MR5, the DRAM calculates parity with ACT_n, RAS_n/A16, CAS_n/A15,
WE_n/A14, BG[1:0], BA[1:0], A[16:0]. Input parity should be maintained at the rising edge of the
clock and at the same time as command and address with CS_n LOW.
mand and/or address being entered and have multiple functions. For example, for activation
with ACT_n LOW, these are addresses like A16, A15, and A14, but for a non-activation command with ACT_n HIGH, these are command pins for READ, WRITE, and other commands defined in Command Truth Table.
SET_n is HIGH. RESET_n must be HIGH during normal operation.
Serial address inputs: Used to configure the temperature sensor/SPD EEPROM address range
on the I2C bus.
Serial clock for temperature sensor/SPD EEPROM: Used to synchronize communication to
and from the temperature sensor/SPD EEPROM on the I2C bus.
DQ[3:0], DQ[7:0], and DQ[15:0] for the x4, x8, and x16 configurations, respectively. If cyclic redundancy checksum (CRC) is enabled via the mode register, the CRC code is added at the end of
the data burst. Any one or all of DQ0, DQ1, DQ2, or DQ3 may be used for monitoring of internal V
level during test via mode register setting MR[4] A[4] = HIGH; training times change
REF
when enabled.
data is masked when DM_n is sampled LOW coincident with that input data during a write access. DM_n is sampled on both edges of DQS. DM is multiplexed with the DBI function by the
mode register A10, A11, and A12 settings in MR5. For a x8 device, the function of DM or TDQS
is enabled by the mode register A11 setting in MR1. DBI_n is an input/output identifying
whether to store/output the true or inverted data. If DBI_n is LOW, the data will be stored/
output after inversion inside the DDR4 device and not inverted if DBI_n is HIGH. TDQS is only
supported in x8 SDRAM configurations (TDQS is not valid for UDIMMs).
combo device.
tered-aligned with write data. For x16 configurations, DQSL corresponds to the data on
DQ[7:0], and DQSU corresponds to the data on DQ[15:8]. For the x4 and x8 configurations, DQS
corresponds to the data on DQ[3:0] and DQ[7:0], respectively. DDR4 SDRAM supports a differential data strobe only and does not support a single-ended data strobe.
flag as output signal. If a CRC error occurs, ALERT_n goes LOW for the period time interval and
returns HIGH. If an error occurs during a command address parity check, ALERT_n goes LOW until the on-going DRAM internal recovery transaction is complete. During connectivity test mode,
this pin functions as an input. Use of this signal is system-dependent. If not connected as signal,
ALERT_n pin must be connected to VDD on DIMMs.
perature thresholds have been exceeded. This pin has no function (NF) on modules without
temperature sensors.
PDF: CCMTD-1725822587-9907
asf18c2gx72az.pdf – Rev. E 11/17 EN
7
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2015 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...