MICRON MT28F640J3RG-15ET, MT28F640J3RG-12, MT28F640J3RG-12ET, MT28F640J3RG-15, MT28F640J3FS-15ET Datasheet
...
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
Q-FLASHTM MEMORY
FEATURES
• x8/x16 organization
• One hundred twenty-eight 128KB erase blocks
(128Mb)
Sixty-four 128KB erase blocks (64Mb)
Thirty-two 128KB erase blocks (32Mb)
•VCC, VCCQ, and VPEN voltages:
2.7V to 3.6V VCC operation
2.7V to 3.6V or 4.5V to 5.5V* VCCQ operation
2.7V to 3.6V, or 5V VPEN application programming
• Interface Asynchronous Page Mode Reads:
150ns/25ns read access time (128Mb)
120ns/25ns read access time (64Mb)
110ns/25ns read access time (32Mb)
• Enhanced data protection feature with VPEN = VSS
Flexible sector locking
Sector erase/program lockout during power
transition
• Security OTP block feature
Permanent block locking (Contact factory for
availability)
• Industry-standard pinout
• Inputs and outputs are fully TTL-compatible
• Common Flash Interface (CFI) and Scalable
Command Set
• Automatic write and erase algorithm
• 4.7µs-per-byte effective programming time using
write buffer
• 128-bit protection register
64-bit unique device identifier
64-bit user-programmable OTP cells
• 100,000 ERASE cycles per block
• Automatic suspend options:
Block Erase Suspend-to-Read
Block Erase Suspend-to-Program
Program Suspend-to-Read
NOTE: MT28F128J3, and MT28F320J3 are preliminary status.
MT28F640J3 is production status.
OPTIONS MARKING
• Timing
150ns (128Mb) -15
120ns (64Mb) -12
110ns (32Mb) -11
• Operating Temperature Range
Commercial Temperature (0ºC to +85ºC) None
Extended Temperature (-40ºC to +85ºC) ET
‡
MT28F128J3‡, MT28F640J3,
MT28F320J3
56-Pin TSOP Type I
•VCCQ Option*
2.7V–3.6V None
4.5V–5.5V F
• Packages
56-pin TSOP Type I RG
64-ball FBGA (1.0mm pitch) FS
MT28F640J3RG-12 ET
*Contact factory for availability of the MT28F320J3 and
MT28F640J3.
‡
64-Ball FBGA
Part Number Example:
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02
‡
PRODUCTS AND SPECIFICATIONS DISCUSSED HEREIN ARE FOR EVALUATION AND REFERENCE PURPOSES ONLY AND ARE
SUBJECT TO CHANGE BY MICRON WITHOUT NOTICE. PRODUCTS ARE ONLY WARRANTED BY MICRON TO MEET MICRON’S
PRODUCTION DATA SHEET SPECIFICATIONS.
1

GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MT28F128J3 is a nonvolatile, electrically blockerasable (Flash), programmable memory containing
134,217,728 bits organized as 16,777,218 bytes (8 bits)
or 8,388,608 words (16 bits). This 128Mb device is organized as one hundred twenty-eight 128KB erase blocks.
The MT28F640J3 contains 67,108,864 bits organized
as 8,388,608 bytes (8 bits) or 4,194,304 words (16 bits).
This 64Mb device is organized as sixty-four 128KB erase
blocks.
Similarly, the MT28F320J3 contains 33,554,432 bits
organized as 4,194,304 bytes (8 bits) or 2,097,152 words
(16 bits). This 32Mb device is organized as thirty-two
128KB erase blocks.
These three devices feature in-system block locking. They also have common flash interface (CFI) that
permits software algorithms to be used for entire families of devices. The software is device-independent,
JEDEC ID-independent with forward and backward
compatibility.
Additionally, the scalable command set (SCS) allows a single, simple software driver in all host systems
to work with all SCS-compliant Flash memory devices.
The SCS provides the fastest system/device data transfer rates and minimizes the device and system-level
implementation costs.
To optimize the processor-memory interface, the
device accommodates VPEN, which is switchable during
block erase, program, or lock bit configuration, or
hardwired to VCC, depending on the application. VPEN is
treated as an input pin to enable erasing, programming, and block locking. When VPEN is lower than the
VCC lockout voltage (VLKO), all program functions are
disabled. Block erase suspend mode enables the user
to stop block erase to read data from or program data to
any other blocks. Similarly, program suspend mode
enables the user to suspend programming to read data
or execute code from any unsuspended blocks.
VPEN serves as an input with 2.7V, 3.3V, or 5V for
application programming. VPEN in this Q-Flash family
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
can provide data protection when connected to ground.
This pin also enables program or erase lockout during
power transition.
Micron’s even-sectored Q-Flash devices offer individual block locking that can lock and unlock a block
using the sector lock bits command sequence.
Status (STS) is a logic signal output that gives an
additional indicator of the internal state machine (ISM)
activity by providing a hardware signal of both status
and status masking. This status indicator minimizes
central processing unit (CPU) overhead and system
power consumption. In the default mode, STS acts as
an RY/BY# pin. When LOW, STS indicates that the ISM
is performing a block erase, program, or lock bit configuration. When HIGH, STS indicates that the ISM is
ready for a new command.
Three chip enable (CE) pins are used for enabling and
disabling the device by activating the device’s control
logic, input buffer, decoders, and sense amplifiers.
BYTE# enables selecting x8 or x16 READs/WRITEs
to the device. BYTE# at logic LOW selects an 8-bit mode
with address A0 selecting between the low byte
and the high byte. BYTE# at logic HIGH enables 16-bit
operation.
RP# is used to reset the device. When the device is
disabled and RP# is at VCC, the standby mode is enabled. A reset time (tRWH) is required after RP#
switches HIGH until outputs are valid. Likewise, the
device has a wake time (tRS) from RP# HIGH until
WRITEs to the command user interface (CUI) are recognized. When RP# is at GND, it provides write protection, resets the ISM, and clears the status register.
A variant of the MT28F320J3 also supports the new
security block lock feature for additional code security.
This feature provides an OTP function for locking the
top two blocks, the bottom two blocks, or the entire
device. (Contact factory for availability.)
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2
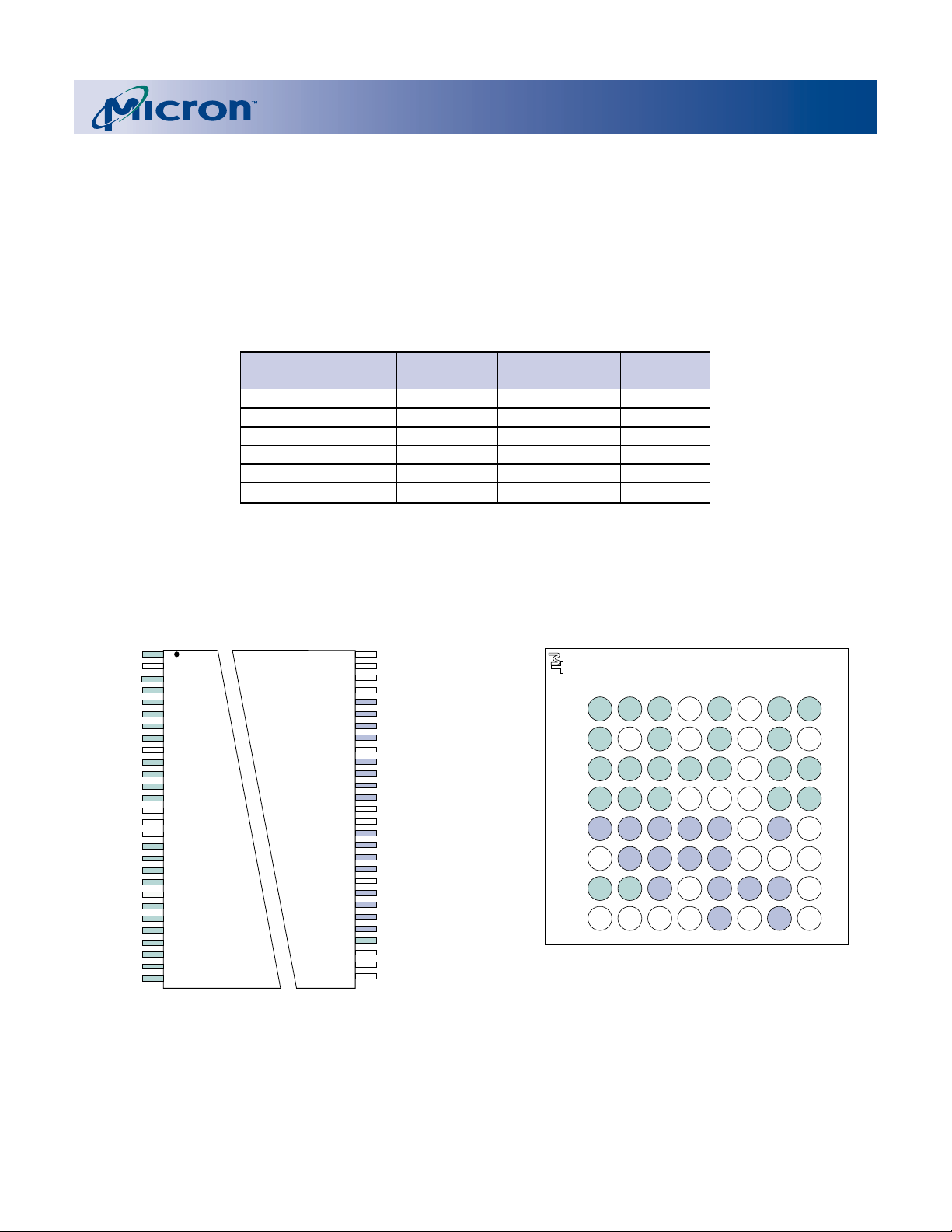
DEVICE MARKING
Due to the size of the package, Micron’s standard
part number is not printed on the top of each device.
Instead, an abbreviated device mark comprised of a
Cross Reference for Abbreviated Device Marks
PRODUCT ENGINEERING QUALIFIED
PART NUMBER MARKING SAMPLE SAMPLE
MT28F320J3FS-11 FW201 FX201 FQ201
MT28F320J3FS-11 ET FW207 FX207 FQ207
MT28F640J3FS-12 FW202 FX202 FQ202
MT28F640J3FS-12 ET FW209 FX209 FQ209
MT28F128J3FS-15 FW203 FX203 FQ203
MT28F128J3FS-15 ET FW501 FX501 FQ501
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
five-digit alphanumeric code is used. The abbreviated
device marks are cross referenced to Micron part numbers in Table 1.
Table 1
A22
CE1
A21
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
V
A15
A14
A13
A12
CE0
V
PEN
RP#
A11
A10
A9
A8
V
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
PIN /BALL ASSIGNMENT (Top View)
56-Pin TSOP Type I
56
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CC
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
SS
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
NC
55
WE#
54
OE#
53
STS
52
DQ15
51
DQ7
50
DQ14
49
DQ6
48
V
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
SS
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
Q
V
SS
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
V
CC
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
A0
BYTE#
A23
CE2
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
64-Ball FBGA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
A1
A2
A3
A4
DQ8
BYTE#
A23
CE2
DQ1
DQ0
DNU
A6
A8
V
A9
SS
A10
A7
A11
A5
DQ9
DQ10
DQ2
A0
V
CC
A13
V
PEN
A14
CE0
A15
A12
DNU
RP#
DQ4
DQ3
DQ12
DQ11
DQ5
V
CC
Q
DQ13
V
SS
Top View
(Ball Down)
V
DNU
DNU
DNU
DNU
DNU
DQ6
V
CC
A18
A19
A20
A16
DQ15
DNU
DQ14
DQ7
SS
A22
CE1
A21
A17
STS
OE#
WE#
NC
NOTE: 1. A22 only exists on the 64Mb and 128Mb devices. On the 32Mb, this pin/ball is a no connect (NC).
2. A23 only exists on the 128Mb device. On the 32Mb and 64Mb, this pin/ball is a no connect (NC).
3. The # symbol indicates signal is active LOW.
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
3
A0–A23
I/O
Control
Logic
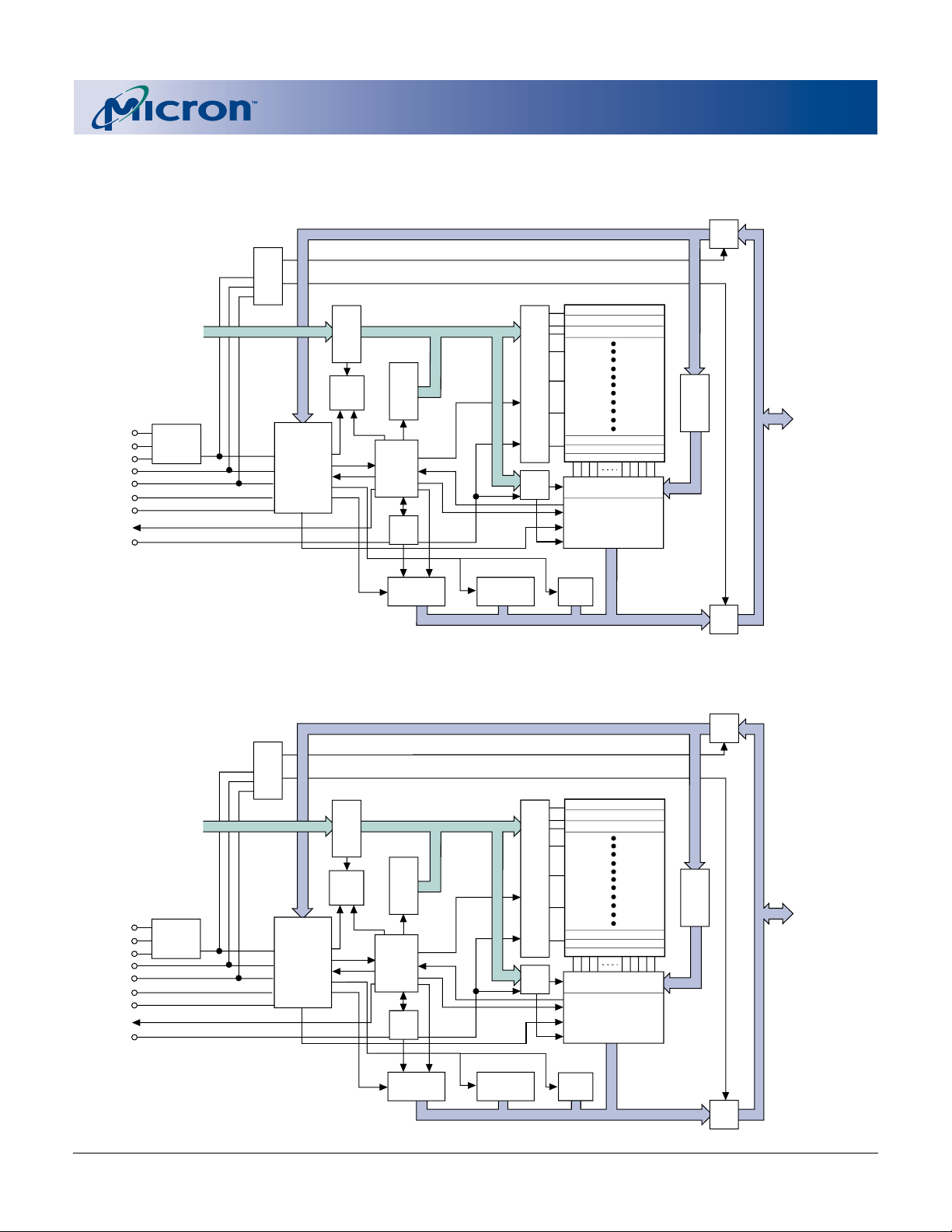
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
(128Mb)
Addr.
Buffer/
Latch
128KB Memory Block (0)
128KB Memory Block (1)
X - Decoder/Block Erase Control
128KB Memory Block (2)
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
Input
Buffer
CE0
CE1
CE2
OE#
WE#
RP#
V
STS
V
Power
(Current)
Control
Addr.
Counter
Write
Buffer
DQ0–DQ15
CE Logic
CC
PEN
Command
Execution
Logic
State
Machine
Switch/
Pump
PP
V
Status
Register
Identification
Register
Decoder
128KB Memory Block (125)
128KB Memory Block (126)
128KB Memory Block (127)
Y -
Query
Y - Select Gates
Sense Amplifiers
Write/Erase-Bit
Compare and Verify
Output
Buffer
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
(64Mb)
Input
Buffer
I/O
Control
Logic
128KB Memory Block (0)
128KB Memory Block (1)
X - Decoder/Block Erase Control
128KB Memory Block (2)
A0–A22
Addr.
Buffer/
Latch
Power
(Current)
Control
Addr.
Counter
Write
Buffer
DQ0–DQ15
CE0
CE1
CE2
OE#
WE#
RP#
V
CC
STS
V
PEN
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
CE Logic
Command
Execution
Logic
State
Machine
Switch/
Pump
PP
V
Status
Register
Identification
4
Decoder
Register
Y -
Query
128KB Memory Block (61)
128KB Memory Block (62)
128KB Memory Block (63)
Y - Select Gates
Sense Amplifiers
Write/Erase-Bit
Compare and Verify
Output
Buffer
A0–A21
I/O
Control
Logic
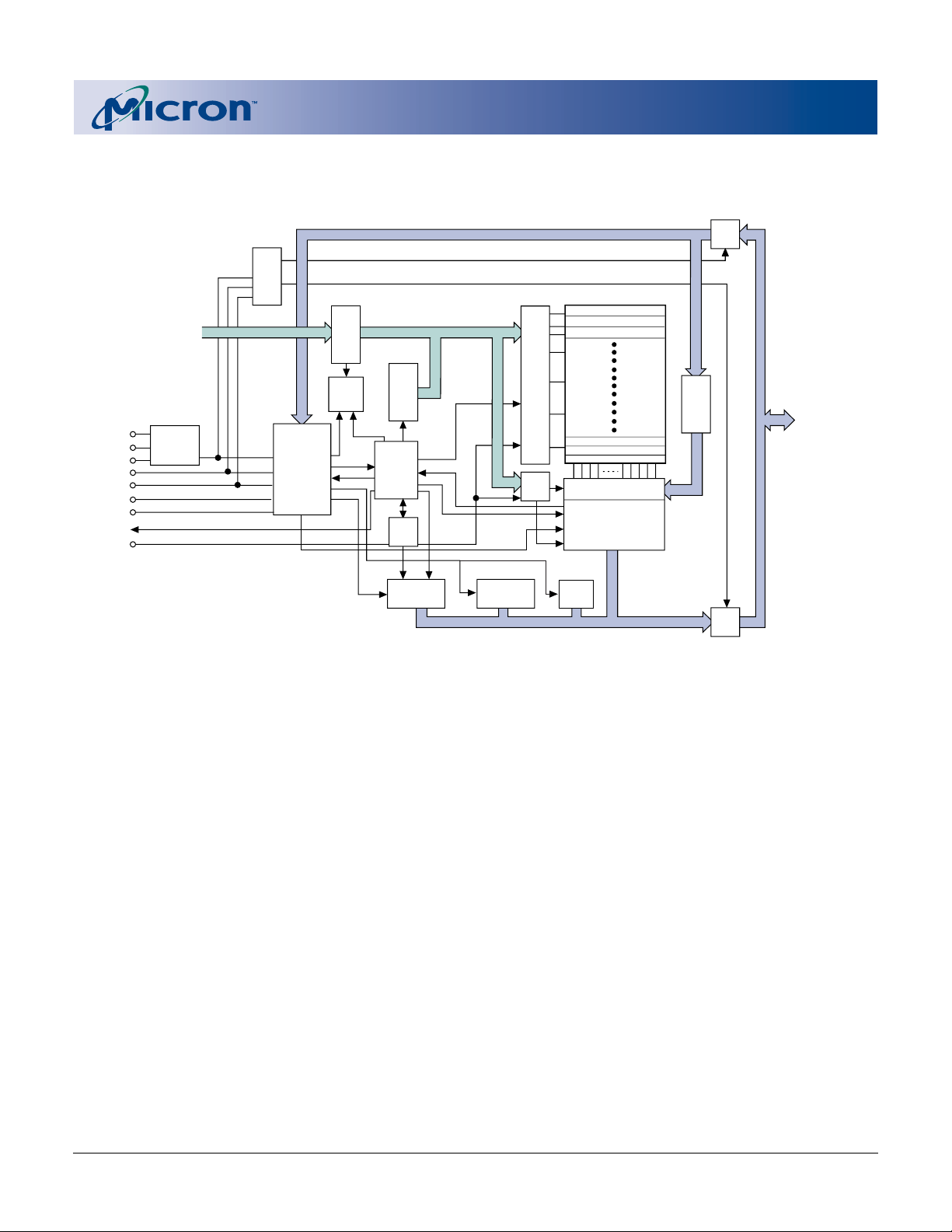
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
(32Mb)
Addr.
Buffer/
Latch
128KB Memory Block (0)
128KB Memory Block (1)
X - Decoder/Block Erase Control
128KB Memory Block (2)
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
Input
Buffer
CE0
CE1
CE2
OE#
WE#
RP#
V
STS
V
Power
(Current)
Control
Addr.
Counter
Write
Buffer
DQ0–DQ15
Y -
Query
128KB Memory Block (29)
128KB Memory Block (30)
128KB Memory Block (31)
Y - Select Gates
Sense Amplifiers
Write/Erase-Bit
Compare and Verify
Output
Buffer
CE Logic
CC
PEN
Command
Execution
Logic
State
Machine
Switch/
Pump
PP
V
Status
Register
Identification
Register
Decoder
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
5
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
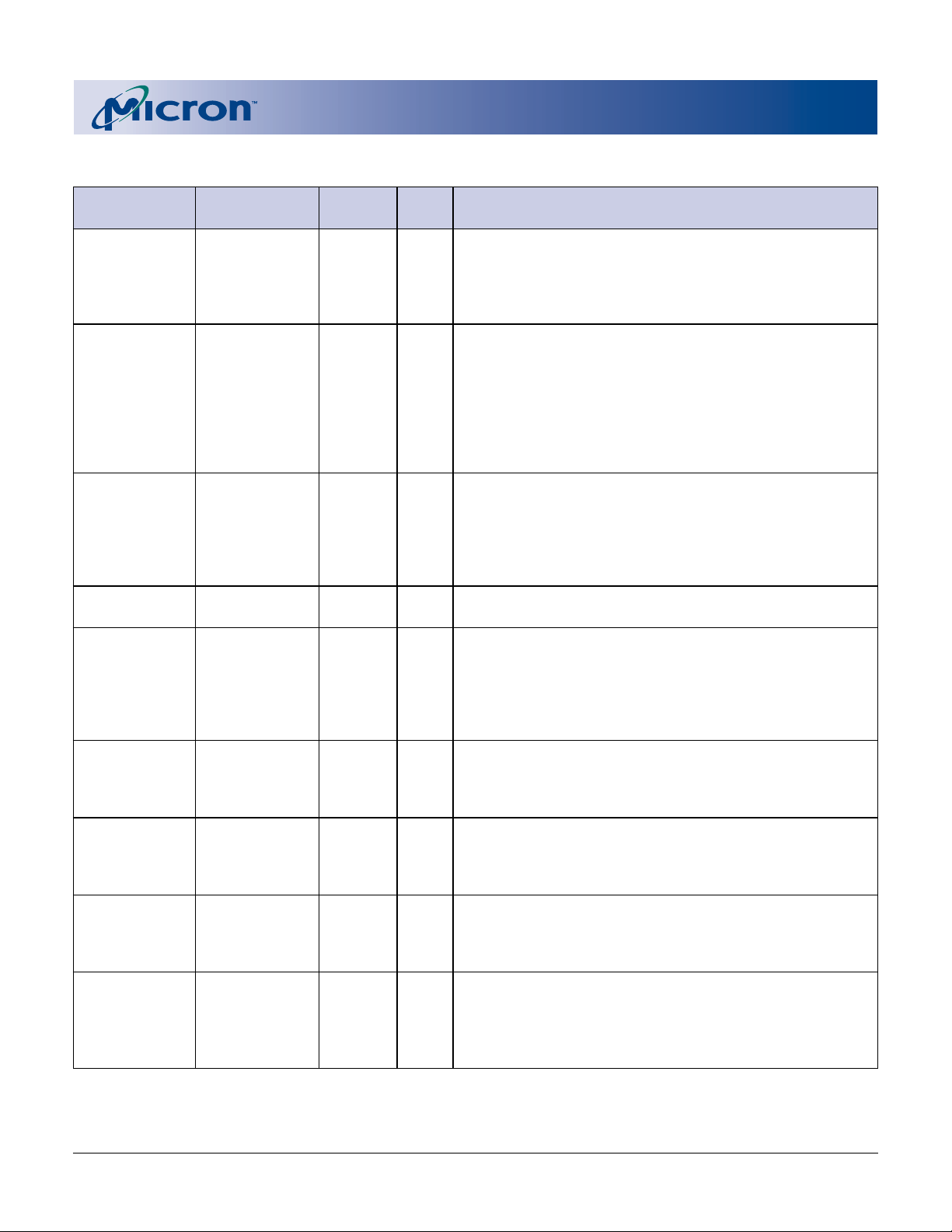
PIN/BALL DESCRIPTIONS
56-PIN TSOP 64-BALL FBGA
NUMBERS NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
55 G8 WE# Input Write Enable: Determines if a given cycle is a WRITE
cycle. If WE# is LOW, the cycle is either a WRITE to the
command execution logic (CEL) or to the memory array.
Addresses and data are latched on the rising edge of the
WE# pulse.
14, 2, 29 B4, B8, H1 CE0, CE1, Input Chip Enable: Three CE pins enable the use of multiple
CE2 Flash devices in the system without requiring additional
logic. The device can be configured to use a single CE
signal by tying CE1 and CE2 to ground and then using
CE0 as CE. Device selection occurs with the first edge of
CE0, CE1, or CE2 (CEx) that enables the device. Device
deselection occurs with the first edge of CEx that
disables the device (see Table 2).
16 D4 RP# Input Reset/Power-Down: When LOW, RP# clears the status
register, sets the ISM to the array read mode, and places
the device in deep power-down mode. All inputs,
including CEx, are “Don’t Care,” and all outputs are
High-Z. RP# must be held at VIH during all other modes
of operation.
54 F8 OE# Input Output Enables: Enables data ouput buffers when LOW.
When OE# is HIGH, the output buffers are disabled.
32, 28, 27, G2, A1, B1, C1, A0–A21/ Input Address inputs during READ and WRITE operations. A0 is
26, 25, 24, 23, D1, D2, A2, C2, (A22) only used in x8 mode. A22 (pin 1, ball A8) is only
22, 20, 19, 18, A3, B3, C3, D3, (A23) available on the 64Mb and 128Mb devices. A23 (pin 30,
17, 13, 12, 11, C4, A5, B5, C5, ball G1) is only available on the 128Mb device.
10, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, D7, D8, A7, B7,
3, 1, 30 C7, C8, A8, G1
31 F1 BYTE# Input BYTE# LOW places the device in the x8 mode. BYTE#
HIGH places the device in the x16 mode and turns off
the A0 input buffer. Address A1 becomes the lowest
order address in x16 mode.
15 A4 V
33, 35, 38, 40, F2, E2, G3, E4, DQ0– Input/ Data I/O: Data output pins during any READ operation
44, 46, 49, 51, E5, G5, G6, H7, DQ15 Output or data input pins during a WRITE. DQ8–DQ15 are not
34, 36, 39, 41, E1, E3, F3, F4, used in byte mode.
45, 47, 50, 52 F5, H5, G7, E7
53 E8 STS Output Status: Indicates the status of the ISM. When configured
PEN
Input Necessary voltage for erasing blocks, programming data,
or configuring lock bits. Typically, V
VCC. When V
PEN
≤ V
PENLK
, this pin enables hardware write
PEN
is connected to
protect.
in level mode, default mode it acts as an RY/BY# pin.
When configured in its pulse mode, it can pulse to
indicate program and/or erase completion. Tie STS to
VCCQ through a pull-up resistor.
(continued on next page)
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
6
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
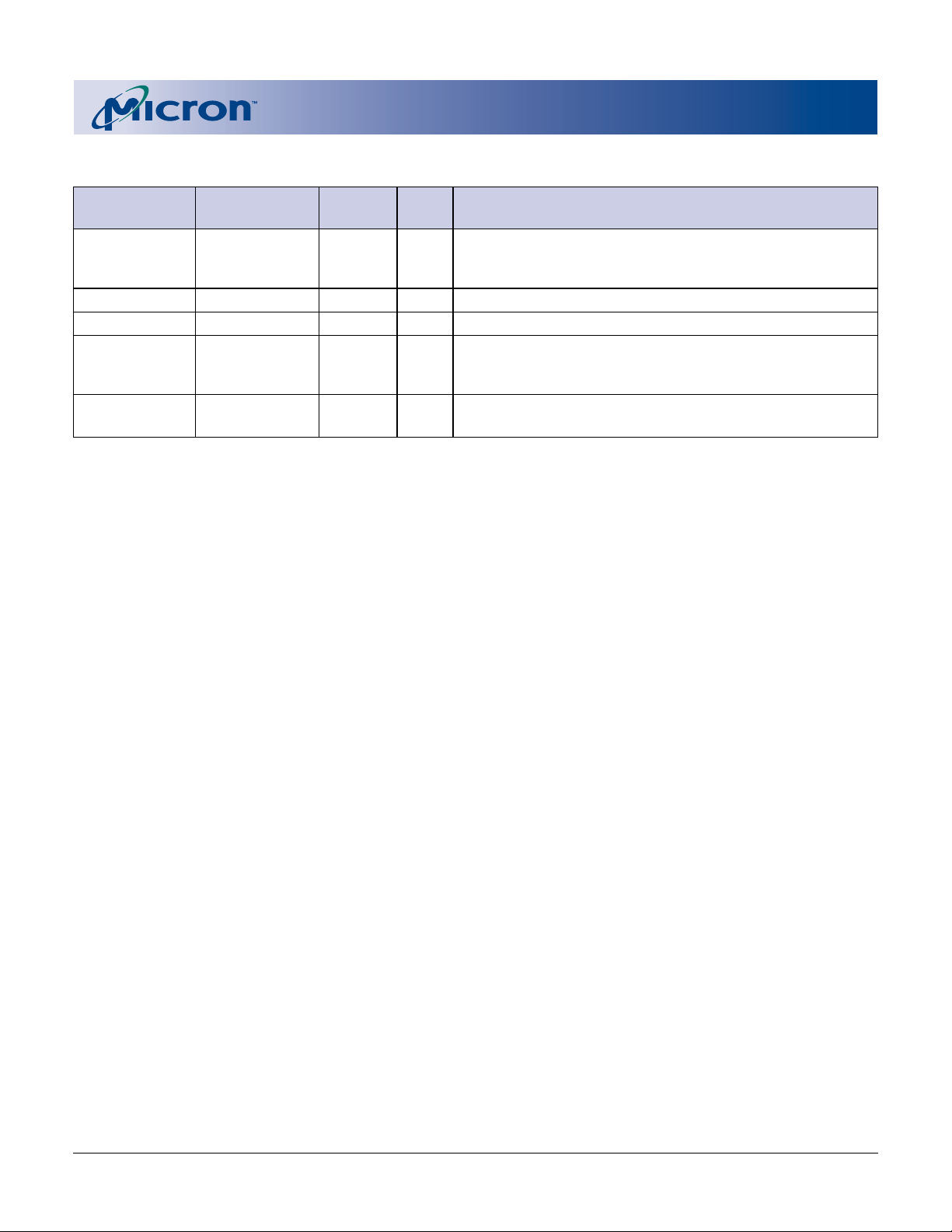
PIN/BALL DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
56-PIN TSOP 64-BALL FBGA
NUMBERS NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
43 G4 VCCQ Supply VCCQ controls the output voltages. To obtain output
voltage compatible with system data bus voltages,
connect VCCQ to the system supply voltage.
9, 37 H3, A6 VCC Supply Power Supply: 2.7V to 3.6V.
21, 42, 48 B2, H4, H6 VSS Supply Ground.
56 H8 NC – No Connect: These may be driven or left unconnected.
Pin 1 and ball A8 are NCs on the 32Mb device. Pin 30
and ball G1 are NCs on the 32Mb and 64Mb devices.
– B6, C6, D5, D6, DNU – Do Not Use: Must float to minimize noise.
E6, F6, F7, H2
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
7
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
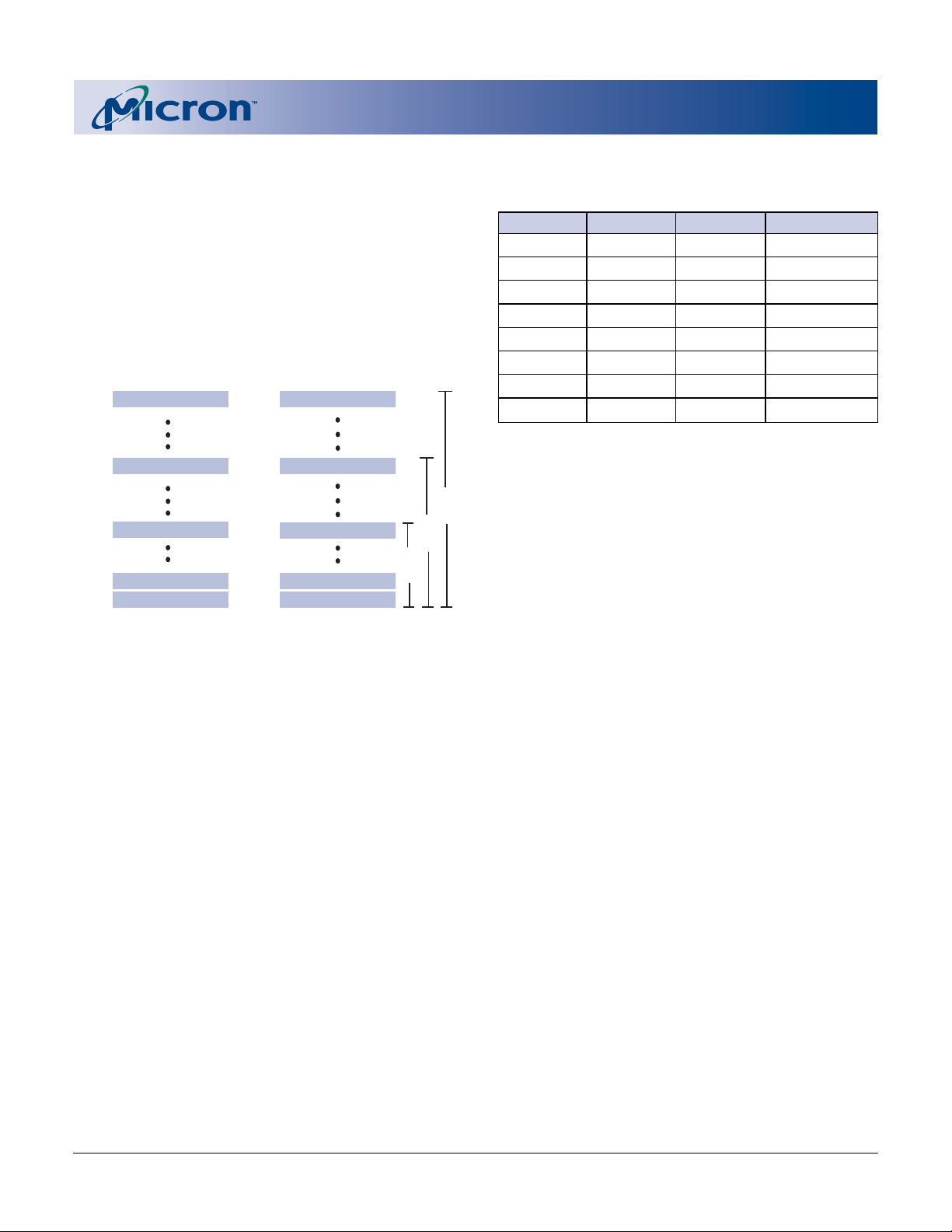
MEMORY ARCHITECTURE
The MT28F128J3, MT28F640J3, and MT28F320J3
memory array architecture is divided into one hundred twenty-eight, sixty-four, or thirty-two 128KB
blocks, respectively (see Figure 1). The internal architecture allows greater flexibility when updating data
because individual code portions can be updated independently of the rest of the code.
Figure 1
Memory Map
FFFFFFh
FE0000h
7FFFFFh
7E0000h
3FFFFFh
3E0000h
03FFFFh
020000h
01FFFFh
000000h
128KB Block 127
128KB Block 63
128KB Block 31
128KB Block 1
128KB Block 0
A0–A23: 128Mb
A0–A22: 64Mb
A0–A21: 32Mb
Byte-Wide (x8) Mode Word-Wide (x16) Mode
7FFFFFh
7F0000h
3FFFFFh
3F0000h
1FFFFFh
1F0000h
01FFFFh
010000h
00FFFFh
000000h
64K-Word Block 127
64K-Word Block 63
64K-Word Block 31
64K-Word Block 1
64K-Word Block 0
A1–A23: 128Mb
A1–A22: 64Mb
A1–A21: 32Mb
64Mb
b
32M
128Mb
Table 2
Chip Enable Truth Table
CE2 CE1 CE0 DEVICE
VIL VIL VIL Enabled
VIL VIL VIH Disabled
VIL VIH VIL Disabled
VIL VIH VIH Disabled
VIH VIL VIL Enabled
VIH VIL VIH Enabled
VIH VIH VIL Enabled
VIH VIH VIH Disabled
NOTE: For single-chip applications, CE2 and CE1 can be
connected to GND.
high-speed page buffer. A0–A2 select data in the page
buffer. Asynchronous page mode, with a page size of
four words or eight bytes, is supported with no additional commands required.
OUTPUT DISABLE
The device outputs are disabled with OE# at a logic
HIGH level (VIH). Output pins DQ0–DQ15 are placed in
High-Z.
BUS OPERATION
All bus cycles to and from the Flash memory must
conform to the standard microprocessor bus cycles.
The local CPU reads and writes Flash memory insystem.
READ
Information can be read from any block, query, identifier codes, or status register, regardless of the VPEN
voltage. The device automatically resets to read array
mode upon initial device power-up or after exit from
reset/power-down mode. To access other read mode
commands (READ ARRAY, READ QUERY, READ IDENTIFIER CODES, or READ STATUS REGISTER), these
commands should be issued to the CUI. Six control
pins dictate the data flow in and out of the device: CE0,
CE1, CE2, OE#, WE#, and RP#. In system designs using
multiple Q-Flash devices, CE0, CE1, and CE2 (CEx)
select the memory device (see Table 2). To drive data
out of the device and onto the I/O bus, OE# must be
active and WE# must be inactive (VIH).
When reading information in read array mode, the
device defaults to asynchronous page mode, thus providing a high data transfer rate for memory subsystems.
In this state, data is internally read and stored in a
STANDBY
CE0, CE1, and CE2 can disable the device (see
Table 2) and place it in standby mode, which substantially reduces device power consumption. DQ0–DQ15
outputs are placed in High-Z, independent of OE#. If
deselected during block erase, program, or lock bit configuration, the ISM continues functioning and consuming active power until the operation completes.
RESET/POWER-DOWN
RP# puts the device into the reset/power-down
mode when set to VIL.
During read, RP# LOW deselects the memory, places
output drivers in High-Z, and turns off internal circuitry. RP# must be held LOW for a minimum of tPLPH.
t
RWH is required after return from reset mode until
initial memory access outputs are valid. After this wakeup interval, normal operation is restored. The command execution logic (CEL) is reset to the read array
mode and the status register is set to 80h.
During block erase, program, or lock bit configuration, RP# LOW aborts the operation. In default mode,
STS transitions LOW and remains LOW for a maximum
time of tPLPH + tPHRH, until the RESET operation is
complete. Any memory content changes are no longer
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
8
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Reserved for Future
Implementation
Manufacturer Code
Device Code
010000h
00FFFFh
000004h
000003h
000002h
000001h
000000h
Reserved for Future
Implementation
Reserved for Future
Implementation
Reserved for Future
Implementation
Block 63
Block 0
3FFFFFh
3F0003h
3F0002h
3F0000h
3EFFFFh
1EFFFFh
1F0003h
1F0002h
1F0000h
01FFFFh
010003h
010002h
32Mb
64Mb
128Mb
Block 63 Lock Configuration
Block 0 Lock Configuration
Reserved for Future
Implementation
(Blocks 32 through 62)
Reserved for Future
Implementation
7FFFFFh
7F0003h
7F0002h
7F0000h
7EFFFFh
Block 127 Lock Configuration
Reserved for Future
Implementation
Block 31
Reserved for Future
Implementation
(Blocks 2 through 30)
Block 1
Reserved for Future
Implementation
Block 1 Lock Configuration
Block 127
Block 31 Lock Configuration
(Blocks 64 through 126)
Q-FLASH MEMORY
valid; the data may be partially corrupted after a program or partially changed after an erase or lock bit
configuration. After RP# goes to logic HIGH (VIH), and
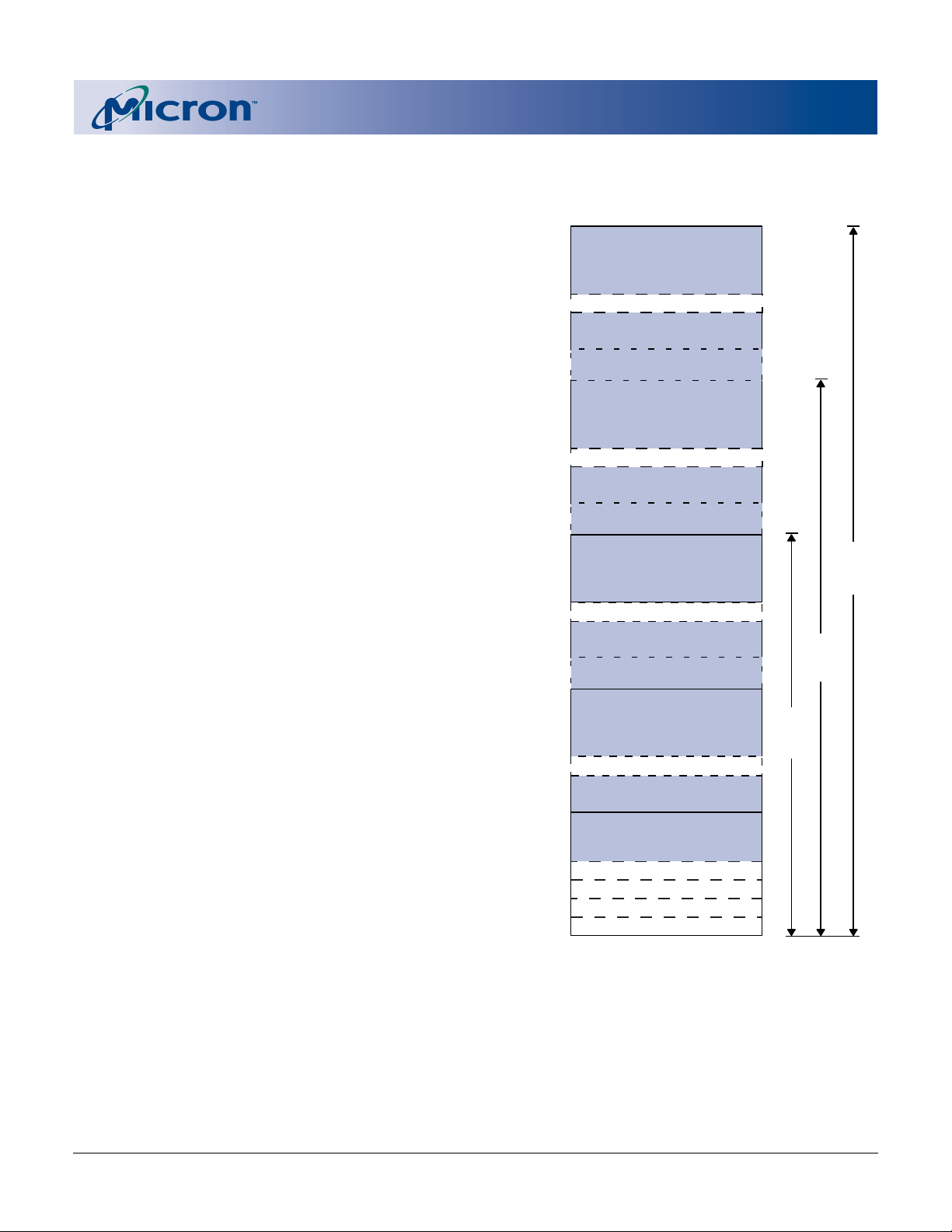
Device Identifier Code Memory Map
Figure 2
after tRS, another command can be written.
It is important to assert RP# during system reset.
After coming out of reset, the system expects to read
from the Flash memory. During block erase, program,
or lock bit configuration mode, automated Flash memories provide status information when accessed. When
a CPU reset occurs with no Flash memory reset, proper
initialization may not occur because the Flash memory
may be providing status information instead of array
data. Micron Flash memories allow proper initialization following a system reset through the use of the RP#
input. RP# should be controlled by the same RESET#
signal that resets the system CPU.
READ QUERY
The READ QUERY operation produces block status
information, CFI ID string, system interface information, device geometry information, and extended query
information.
READ IDENTIFIER CODES
The READ IDENTIFIER CODES operation produces
the manufacturer code, device code, and the block lock
configuration codes for each block (see Figure 2). The
block lock configuration codes identify locked and unlocked blocks.
WRITE
Writing commands to the CEL allows reading of device data, query, identifier codes, and reading and clearing of the status register. In addition, when VPEN = VPENH,
block erasure, program, and lock bit configuration can
also be performed.
The BLOCK ERASE command requires suitable command data and an address within the block. The BYTE/
WORD PROGRAM command requires the command
and address of the location to be written to. The CLEAR
BLOCK LOCK BITS command requires the command
and any address within the device. SET BLOCK LOCK
BITS command requires the command and the block to
be locked. The CEL does not occupy an addressable
memory location. It is written to when the device is
enabled and WE# is LOW. The address and data needed
to execute a command are latched on the rising edge of
WE# or the first edge of CEx that disables the device
(see Table 2). Standard microprocessor write timings
are used.
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
NOTE: When obtaining these identifier codes, A0 is not used
in either x8 or x16 modes. Data is always given on the
LOW byte in x16 mode (upper byte contains 00h).
9
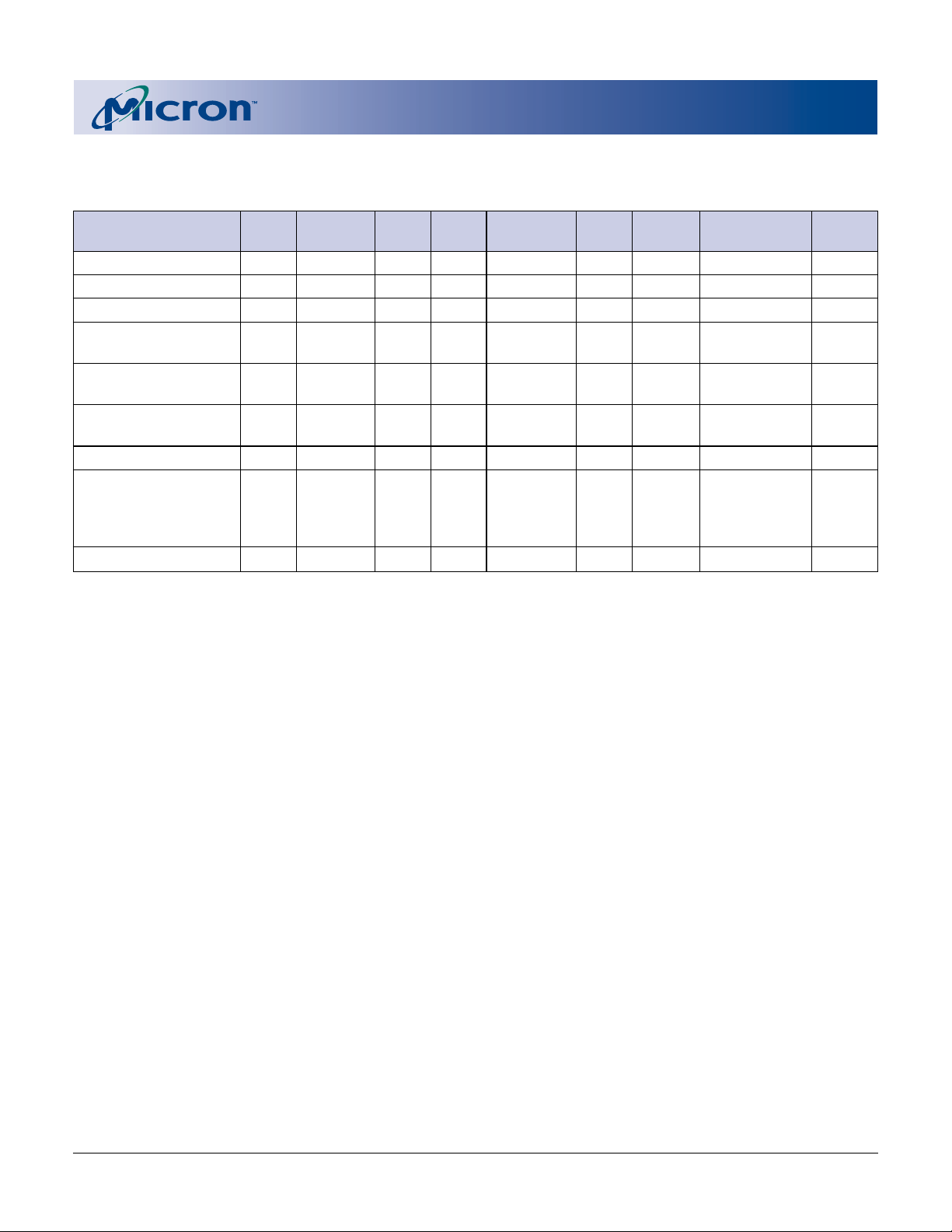
Table 3
Bus Operations
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
CE0, CE1, STS DEFAULT
MODE RP# CE2
1
OE#2WE#2ADDRESS VPEN DQ
Read Array VIH Enabled VIL VIH XXDOUT High-Z
3
MODE NOTES
4
5, 6, 7
Output Disable VIH Enabled VIH VIH X X High-Z X
Standby VIH Disabled X X X X High-Z X
Reset/Power-Down VIL X X X X X High-Z High-Z
4
Mode
Read Identifier Codes VIH Enabled VIL VIH See X Note 8 High-Z
4
Figure 2
Read Query VIH Enabled VIL VIH See X Note 9 High-Z
4
Table 7
Read Status (ISM off) VIH Enabled VIL VIH XXDOUT
Read Status (ISM on) VIH Enabled VIL VIH XX
DQ7 DOUT
DQ15–DQ8 High-Z
DQ6–DQ0 High-Z
Write VIH Enabled VIH VIL XVPENH DIN X 7, 10, 11
NOTE: 1. See Table 2 for valid CE configurations.
2. OE# and WE# should never be enabled simultaneously.
3. DQ refers to DQ0–DQ7 if BYTE# is LOW and DQ0–DQ15 if BYTE# is HIGH.
4. High-Z is VOH with an external pull-up resistor.
5. Refer to DC Characteristics. When VPEN ≤ VPENLK, memory contents can be read, but not altered.
6. X can be VIL or VIH for control and address pins, and VPENLK or VPENH for VPEN. See DC Characteristics for VPENLK and
VPENH voltages.
7. In default mode, STS is VOL when the ISM is executing internal block erase, program, or lock bit configuration
algorithms. It is VOH when the ISM is not busy, in block erase suspend mode (with programming inactive), program
suspend mode, or reset/power-down mode.
8. See Read Identifier Codes section for read identifier code data.
9. See Read Query Mode Command section for read query data.
10. Command writes involving block erase, program, or lock bit configuration are reliably executed when VPEN = VPENH and
VCC is within specification.
11. Refer to Table 4 for valid DIN during a WRITE operation.
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
10
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
COMMAND DEFINITIONS
When the VPEN voltage is less than VPPLK, only READ
operations from the status register, query, identifier
codes, or blocks are enabled. Placing VPENH on VPEN enables BLOCK ERASE, PROGRAM, and LOCK BIT CON-
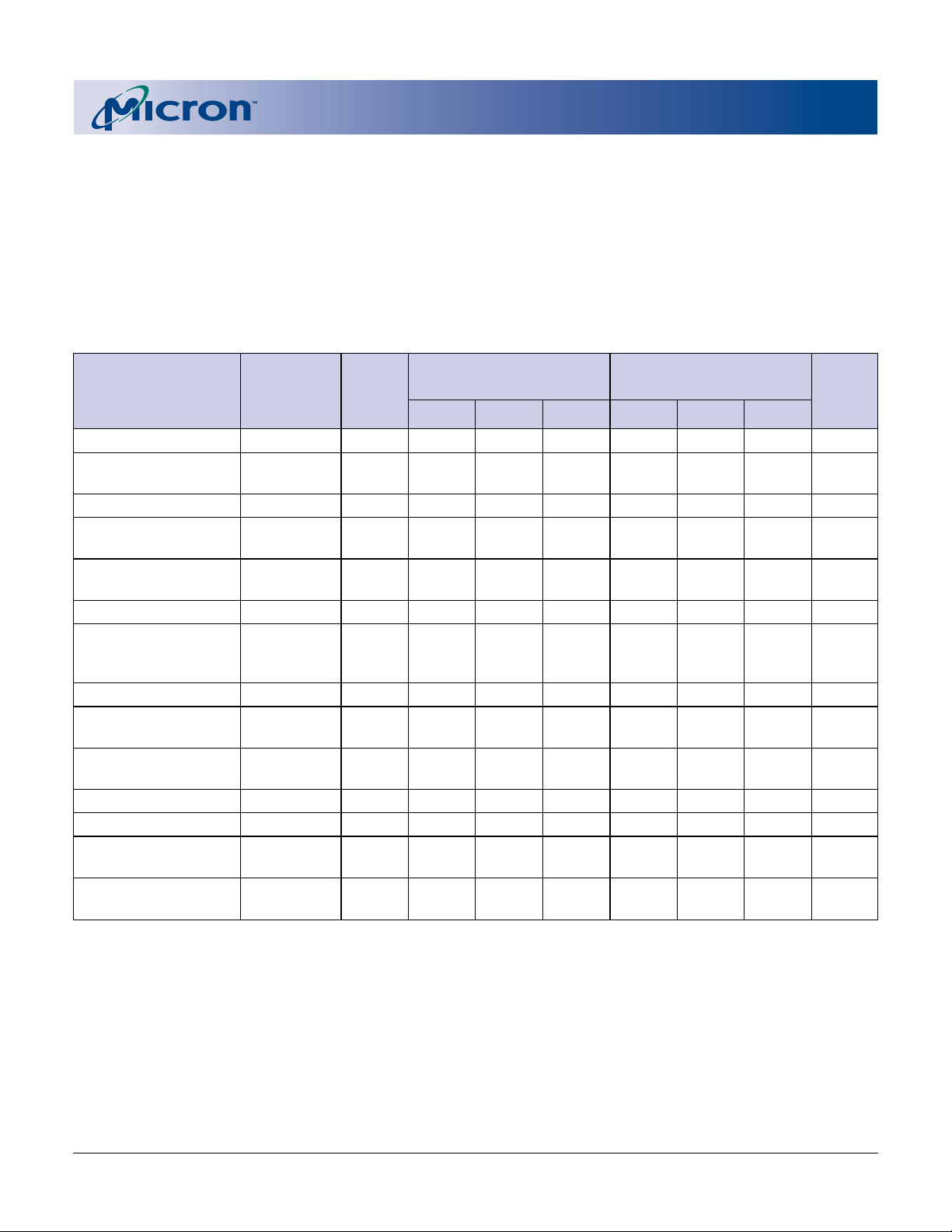
Table 4
Micron Q-Flash Memory Command Set Definitions
COMMAND SCALABLE BUS
OR BASIC CYCLES FIRST BUS CYCLE SECOND BUS CYCLE
COMMAND REQ’D
READ ARRAY SCS/BCS 1 WRITE X FFh
READ IDENTIFIER SCS/BCS 2 WRITE X 90h READ IA ID 7
CODES
READ QUERY SCS 2 WRITE X 98h READ QA QD
READ STATUS SCS/BCS 2 WRITE X 70h READ X SRD 8
REGISTER
CLEAR STATUS SCS/BCS 1 WRITE X 50h
REGISTER
WRITE TO BUFFER SCS/BCS > 2 WRITE BA E8h WRITE BA N 9, 10, 11
WORD/BYTE SCS/BCS 2 WRITE X 40h WRITE PA PD 12, 13
PROGRAM or
BLOCK ERASE SCS/BCS 2 WRITE BA 20h WRITE BA D0h 11, 12
BLOCK ERASE, SCS/BCS 1 WRITE X B0h 12, 14
PROGRAM SUSPEND
BLOCK ERASE, SCS/BCS 1 WRITE X D0h 12
PROGRAM RESUME
CONFIGURATION SCS 2 WRITE X B8h WRITE X C C
SET BLOCK LOCK BITS S CS 2 WRITE X 60h WRITE BA 01h
CLEAR BLOCK SCS 2 WRITE X 60h WRITE X D0h 15
LOCK BITS
PROTECTION 2 WRITE X C0h WRITE PA PD
PROGRAM
SET
2
OPER3ADDR4DATA
FIGURATION operations. Device operations are selected by writing specific commands into the CEL, as
seen in Table 4.
1
10h
5, 6
OPER3ADDR4DATA
5, 6
NOTES*
*Notes appear on the next page.
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
11

128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
NOTE: 1. Commands other than those shown in Table 4 are reserved for future device implementations and should not be used.
2. The SCS is also referred to as the extended command set.
3. Bus operations are defined in Table 3.
4. X = Any valid address within the device
BA = Address within the block
IA = Identifier code address; see Figure 2 and Table 15
QA = Query data base address
PA = Address of memory location to be programmed
5. ID = Data read from identifier codes
QD = Data read from query data base
SRD = Data read from status register; see Table 16 for a description of the status register bits
PD = Data to be programmed at location PA; data is latched on the rising edge of WE#
CC = Configuration code
6. The upper byte of the data bus (DQ8–DQ15) during command WRITEs is a “Don’t Care” in x16 operation.
7. Following the READ IDENTIFIER CODES command, READ operations access manufacturer, device, and block lock codes.
See Block Status Register section for read identifier code data.
8. If the ISM is running, only DQ7 is valid; DQ15–DQ8 and DQ6–DQ0 float, which places them in High-Z.
9. After the WRITE-to-BUFFER command is issued, check the XSR to make sure a buffer is available for writing.
10. The number of bytes/words to be written to the write buffer = n + 1, where n = byte/word count argument. Count
ranges on this device for byte mode are n = 00h to n = 1Fh and for word mode, n = 0000h to n = 000Fh. The third and
consecutive bus cycles, as determined by n, are for writing data into the write buffer. The CONFIRM command (D0h) is
expected after exactly n + 1 WRITE cycles; any other command at that point in the sequence aborts the WRITE-toBUFFER operation. Please see Figure 4, WRITE-to-BUFFER Flowchart, for additional information.
11. The WRITE-to-BUFFER or ERASE operation does not begin until a CONFIRM command (D0h) is issued.
12. Attempts to issue a block erase or program to a locked block while RP# = VIH will fail.
13. Either 40h or 10h is recognized by the ISM as the byte/word program setup.
14. Program suspend can be issued after either the WRITE-to-BUFFER or WORD/BYTE PROGRAM operation is initiated.
15. The CLEAR BLOCK LOCK BITS operation simultaneously clears all block lock bits.
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
12
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
READ ARRAY COMMAND
The device defaults to read array mode upon initial
device power-up and after exiting reset/power-down
mode. The read configuration register defaults to asynchronous read page mode. Until another command is
written, the READ ARRAY command also causes the
device to enter read array mode. When the ISM has
started a block erase, program, or lock bit configuration, the device does not recognize the READ ARRAY
command until the ISM completes its operation, unless the ISM is suspended via an ERASE or PROGRAM
SUSPEND command. The READ ARRAY command
functions independently of the VPEN voltage.
READ QUERY MODE COMMAND
This section is related to the definition of the data
structure or “data base” returned by the CFI QUERY
command. System software should retain this structure to gain critical information such as block size,
density, x8/x16, and electrical specifications. When
this information has been obtained, the software
knows which command sets to use to enable Flash
writes or block erases, and otherwise control the Flash
component.
QUERY STRUCTURE OUTPUT
The query “data base” enables system software to
obtain information about controlling the Flash component. The device’s CFI-compliant interface allows the
host system to access query data. Query data are always located on the lowest-order data outputs (DQ0–
DQ7) only. The numerical offset value is the address
relative to the maximum bus width supported by the
device. On this family of devices, the query table device starting address is a 10h, which is a word address
for x16 devices.
For a x16 organization, the first two bytes of the
query structure, “Q” and “R” in ASCII, appear on the
low byte at word addresses 10h and 11h. This CFIcompliant device outputs 00h data on upper bytes,
thus making the device output ASCII “Q” on the LOW
byte (DQ7–DQ0) and 00h on the HIGH byte (DQ15–
DQ8). At query addresses containing two or more bytes
of information, the least significant data byte is located
at the lower address, and the most significant data
byte is located at the higher address. This is summarized in Table 5. A more detailed example is provided in
Table 6.
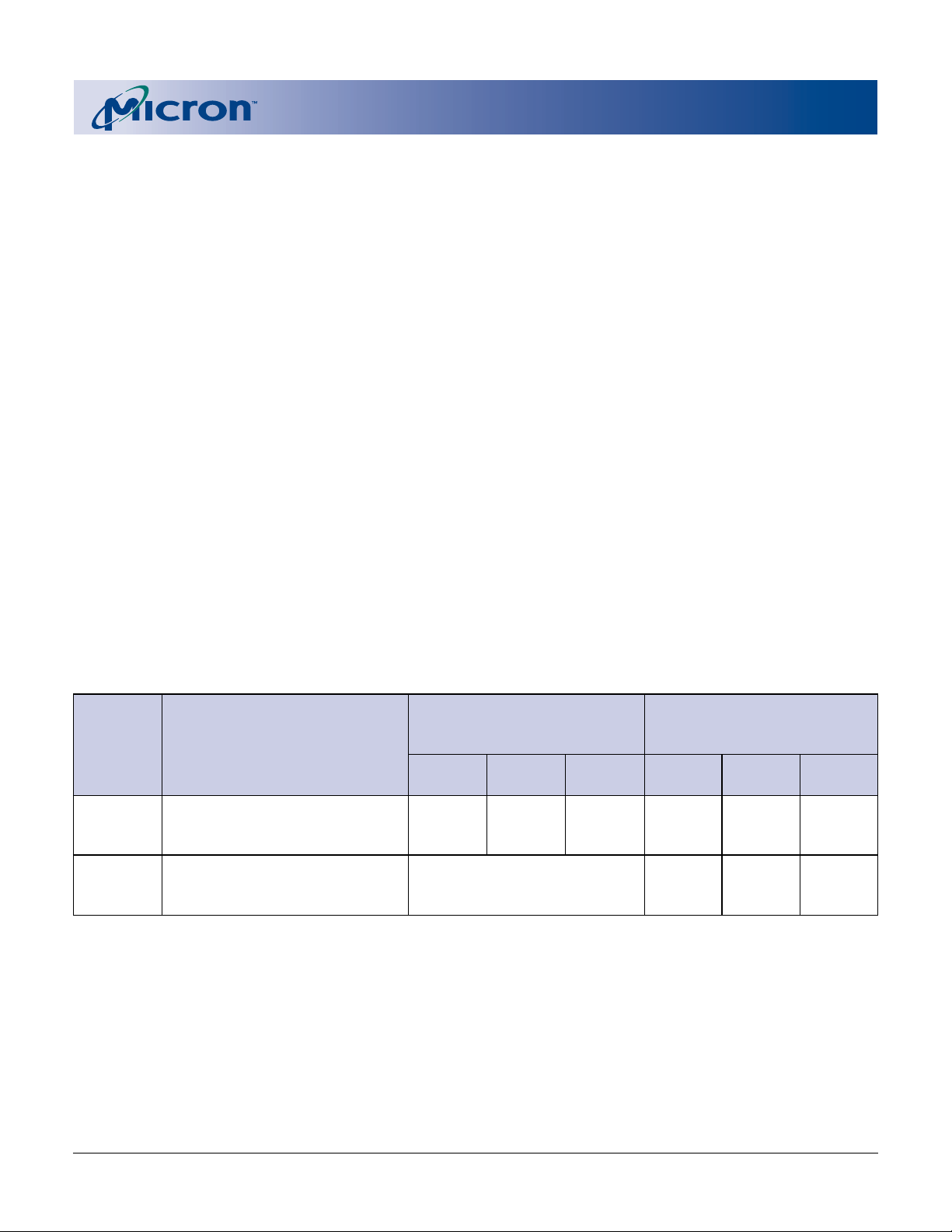
Table 5
Summary of Query Structure Output as a Function of Device and Mode
QUERY DATA WITH
MAXIMUM DEVICE BUS QUERY DATA WITH BYTE
DEVICE QUERY START LOCATION IN WIDTH ADDRESSING ADDRESSING
TYPE/ MAXIMUM DEVICE BUS HEX HEX ASCII HEX HEX ASCII
MODE WIDTH ADDRESSES OFFSET CODE VALUE OFFSET CODE VALUE
x16 device 10h 10 0051 Q 20 51 Q
x16 mode 11 0052 R 21 00 Null
12 0059 Y 22 52 R
x16 device 20 51 Q
x8 mode N/A
NOTE: 1. The system must drive the lowest-order addresses to access all the device’s array data when the device is configured in
x8 mode. Therefore, word addressing where these lower addresses are not toggled by the system is “Not Applicable”
for x8-configured devices.
1
N/A
1
21 51 Q
22 52 R
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
13
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
QUERY STRUCTURE OVERVIEW
The QUERY command makes the Flash component
display the CFI query structure or data base. The structure subsections and address locations are outlined in
Table 7.
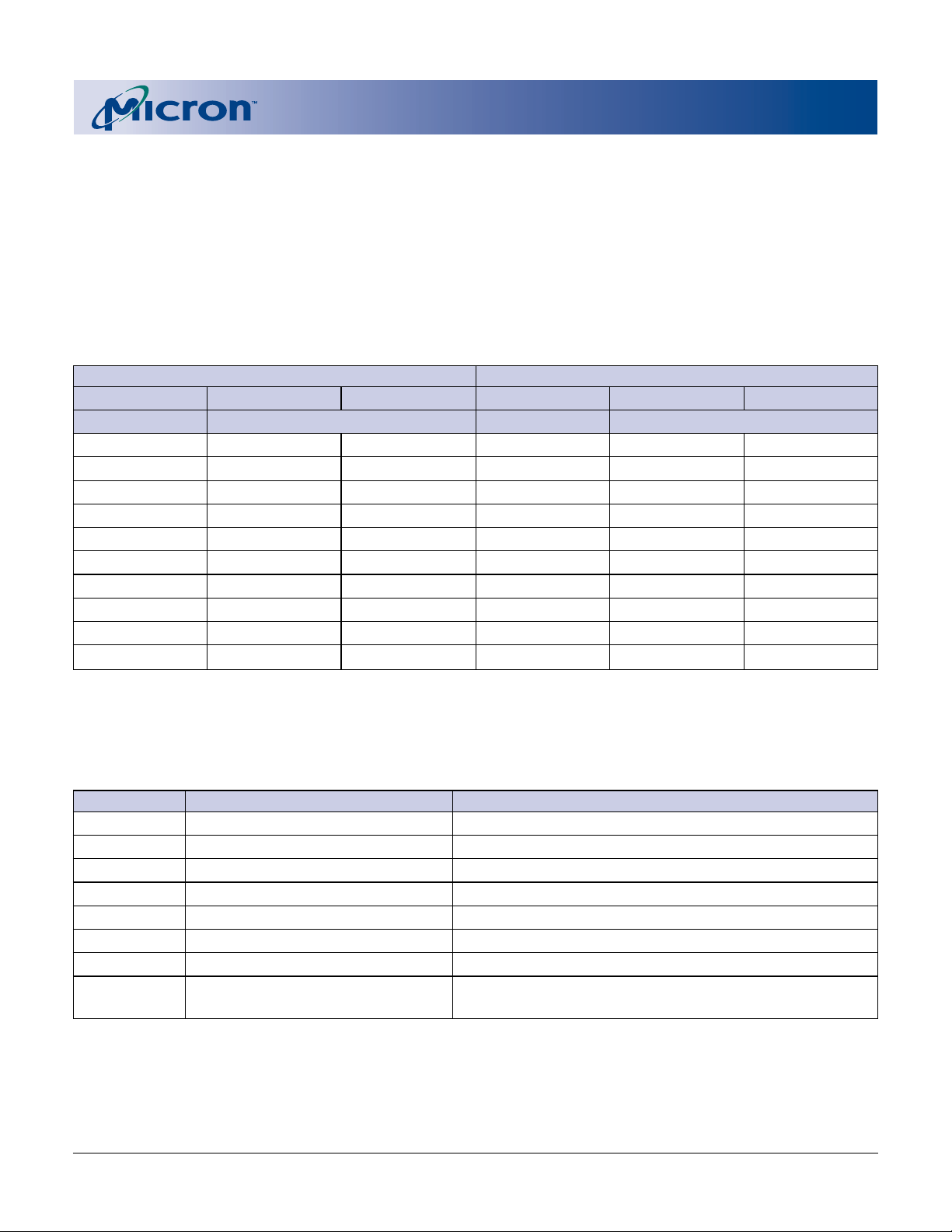
Table 6
Example of Query Structure Output of a x16- and x8-Capable Device
WORD ADDRESSING BYTE ADDRESSING
OFFSET HEX CODE VALUE OFFSET HEX CODE VALUE
A16–A1 DQ15–DQ0 A7–A0 DQ7–DQ0
0010h 0051 Q 20h 51 Q
0011h 0052 R 21h 51 Q
0012h 0059 Y 22h 52 R
0013h P_ID LO PrVendor 23h 52 R
0014h P_ID HI ID # 24h 59 Y
0015h P LO PrVendor 25h 59 Y
0016h P HI TblAdr 26h P_ID LO PrVendor
0017h A_ID LO AltVendor 27h P_ID LO PrVendor
0018h A_ID HI ID # 28h P_ID HI ID #
... ... ... ... ... ...
Table 7
Query Structure
OFFSET SUBSECTION NAME DESCRIPTION
00h Manufacturer compatibility code
01h Device code
(BA+2)h
04–0Fh Reserved Reserved for vendor-specific information
10h CFI Query Identification String Reserved for vendor-specific information
1Bh System Interface Information Command set ID and vendor data offset
27h Device Geometry Definition Flash device layout
3
P
NOTE: 1. Refer to the Query Structure Output section and offset 28h for the detailed definition of offset address as a function
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
2
of device bus width and mode.
2. BA = Block address beginning location (i.e., 020000h is block two’s beginning location when the block size is 64K-word).
3. Offset 15 defines “P,” which points to the Primary Extended Query Table.
Block Status Register Block-specific information
Primary Extended Query Table Vendor-defined additional information specific to the
primary vendor algorithm
14
1
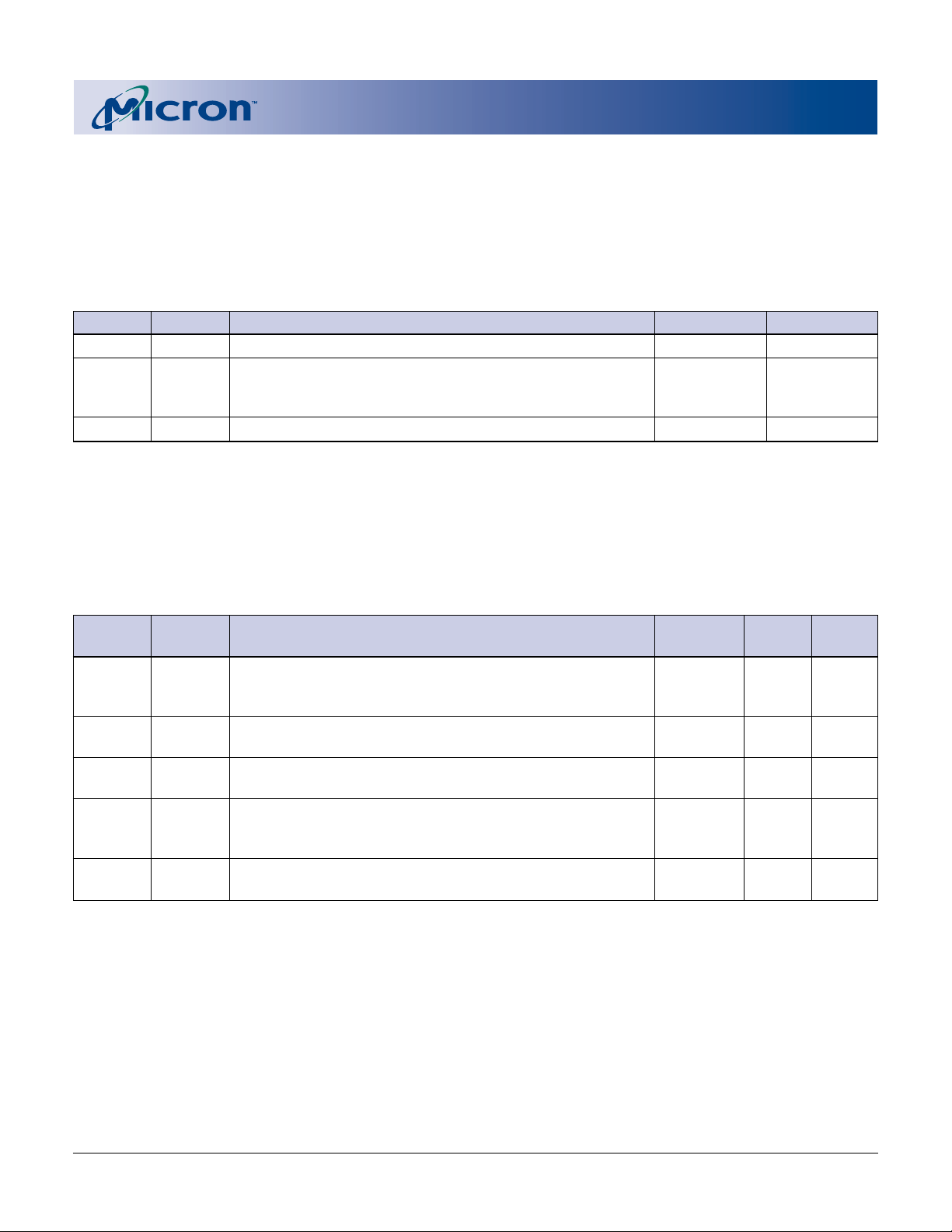
CFI QUERY IDENTIFICATION STRING
The CFI query identification string verifies whether
the component supports the CFI specification. Addi-
Table 8
Block Status Register
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
tionally, it indicates the specification version and supported vendor-specified command set(s).
OFFSET LENGTH DESCRIPTION ADDRESS
(BA+2)h
NOTE: 1. BA = The beginning location of a block address (i.e., 010000h is block one’s (64K-word) beginning location in word
1
mode).
1 Block Lock Status Register (BA+2)h 00 or 01
BSR0 Block Lock Status
0 = Unlocked (BA+2)h (bit 0) 0 or 1
1 = Locked
BSR1–7 Reserved for Future Use (BA+2)h (bit 2–7) 0
1
VALUE
Table 9
CFI Identification
OFFSET LENGTH DESCRIPTION ADDRESS HEX VALUE
CODE
10h 3 Query-unique ASCII string “QRY” 10h 51 Q
11h 52 R
12h 59 Y
13h 2 Primary vendor command set and control interface ID 13h 01
code. 16-bit ID code for vendor-specified algorithms 14h 00
15h 2 Extended query table primary algorithm address 15h 31
16h 00
17h 2 Alternate vendor command set and control interface ID 17h 00
code; 0000h means no second vendor-specified 18h 00
algorithm exists
19h 2 Secondary algorithm extended query table address; 19h 00
0000h means none exists 1Ah 00
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
15
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb
Q-FLASH MEMORY
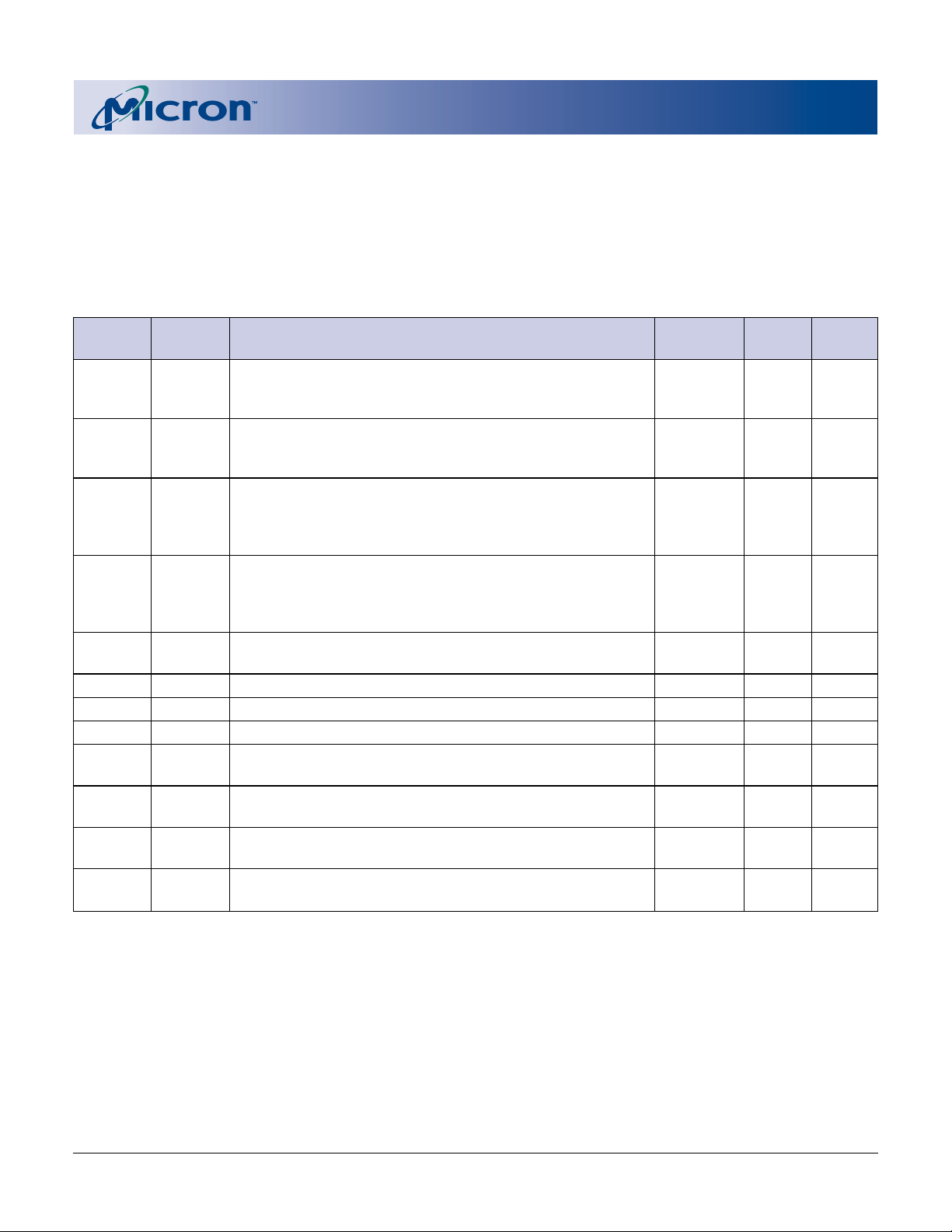
SYSTEM INTERFACE INFORMATION
Table 10 provides useful information about optimizing system interface software.
Table 10
System Interface Information
OFFSET LENGTH DESCRIPTION ADDRESS HEX VALUE
CODE
1Bh 1 V
1Ch 1 VCC logic supply maximum program/erase voltage
1Dh 1 VPP [programming] supply minimum program/erase
1Eh 1 VPP [programming] supply maximum program/erase
1Fh 1 “n” such that typical single word program 1Fh 07 128µs
20h 1 “n” such that typical max. buffer write timeout = 2n µs 20h 07 128µs
21h 1 “n” such that typical block erase timeout = 2n ms 21h 0A 1s
22h 1 “n” such that typical full chip erase timeout = 2n ms 22h 00 N/A
23h 1 “n” such that maximum word program timeout = 2
24h 1 “n” such that maximum buffer write timeout = 2
25h 1 “n” such that maximum block erase timeout = 2
26h 1 “n” such that maximum chip erase timeout = 2
CC logic supply minimum program/erase voltage
Bits 0–3 BCD 100mV 1Bh 27 2.7V
Bits 4–7 BCD volts
Bits 0–3 BCD 100mV 1Ch 36 3.6V
Bits 4–7 BCD volts
voltage
Bits 0–3 BCD 100mV 1Dh 00 0.0V
Bits 4–7 Hex volts
voltage
Bits 0–3 BCD 100mV 1Eh 00 0.0V
Bits 4–7 Hex volts
timeout = 2n µs
n
23h 04 2ms
times typical
n
24h 04 2ms
times typical
n
25h 04 16s
times typical
n
26h 00 N/A
times typical
128Mb, 64Mb, 32Mb Q-Flash Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28F640J3_7.p65 – Rev. 6, Pub. 8/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
16
 Loading...
Loading...