MICRON MT28F320A18FF-70TET, MT28F320A18FF-70BET, MT28F320A18FF-70T, MT28F320A18FF-70B Datasheet
‡
PRODUCTS AND SPECIFICATIONS DISCUSSED HEREIN ARE FOR EVALUATION AND REFERENCE PURPOSES ONLY AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE BY
MICRON WITHOUT NOTICE. PRODUCTS ARE ONLY WARRANTED BY MICRON TO MEET MICRON’S PRODUCTION DATA SHEET SPECIFICATIONS.
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
1
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
‡
FLASH MEMORY
MT28F320A18
Low Voltage, Extended Temperature
0.15µm Process Technology
FEATURES
• 32Mb block architecture
Seventy-one erasable blocks:
Eight 4K-word parameter blocks
Sixty-three 32K-word main memory blocks
•V
CC, VCCQ, VPP voltages*
1.65V (MIN), 1.95V (MAX) V
CC, VCCQ
0.9V (MIN), 1.95V (MAX) V
PP (in-system
PROGRAM/ERASE)
12V ±5% (HV) V
PP tolerant (factory programming
compatibility)
• Random access time: 70ns @ 1.65V V
CC
• Low power consumption (VCC = 1.8V)
Asynchronous Read < 18mA
Write/Erase < 40mA (MAX)
Standby < 50µA (MAX)
Automatic power saving feature (APS)
• Enhanced write and erase suspend options
ERASE-SUSPEND-to-READ
PROGRAM-SUSPEND-to-READ
ERASE-SUSPEND-to-PROGRAM
• Dual 64-bit chip protection registers for security
purposes
• Cross-compatible command support
Extended command set
Common flash interface
• PROGRAM/ERASE cycle
100,000 WRITE/ERASE cycles per block
(V
PP = VPP1)
*An extended voltage range of 1.65V–2.20V for Vcc and VccQ,
and 0.9V–2.20V for Vpp is available upon request. A voltage
range of 1.42V–1.60V for VccQ is also available upon request.
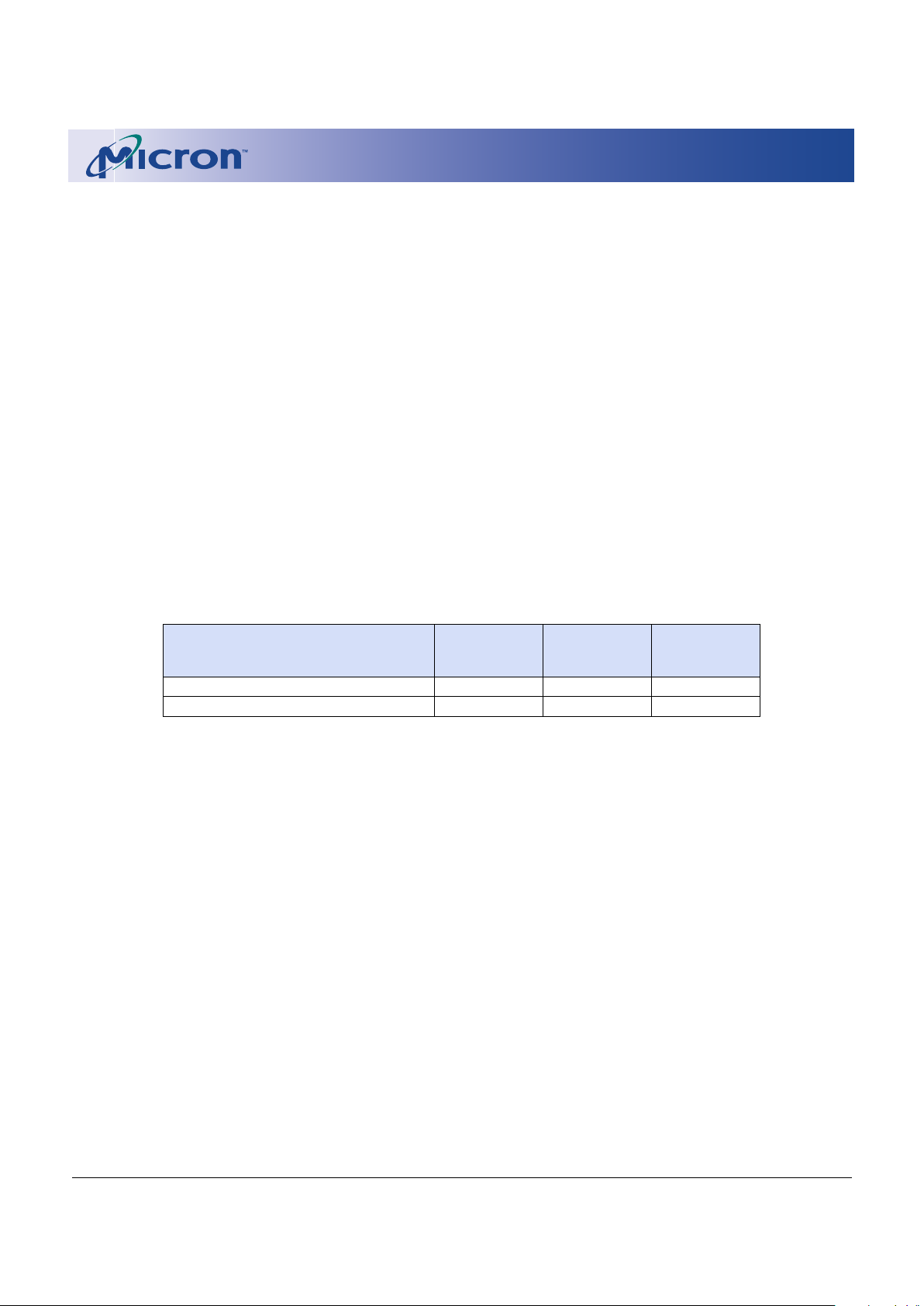
Ball Assignment
48-Ball FBGA
Note: See page 6 for Ball Description table.
See page 36 for mechanical drawing.
Part Number Example:
MT28F320A18FF-70 TET
OPTIONS MARKING
• Timing
70ns access -70
• Configurations
2 Meg x 16 MT28F320A18
• Boot Block Configuration
To p T
Bottom B
•Package
48-ball FBGA (6 x 8 ball grid) FF
• Temperature Range
Extended (-40ºC to +85ºC) ET
A
B
C
D
E
F
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Top View
(Ball Down)
A13
A14
A15
A16
V
CCQ
V
SS
A19
A17
A6
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
WP#
A18
A20
DQ2
DQ3
V
CC
A8
WE#
A9
DQ5
DQ6
DQ13
A4
A2
A1
A0
V
SS
OE#
A7
A5
A3
CE#
DQ0
DQ1
A11
A10
A12
DQ14
DQ15
DQ7
V
PP
RP#
DQ11
DQ12
DQ4
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MT28F320A18 is a nonvolatile electrically
block-erasable (Flash) memory containing eight 4Kword parameter blocks and sixty-three 32K-word main
blocks.
The MT28F320A18 allows soft protection for blocks,
as read only, by configuring soft protection registers
with dedicated command sequences. For security purposes, a 128-bit chip protection register is provided.
The embedded WORD WRITE and BLOCK ERASE
functions are fully automated by an on-chip write state
machine (WSM). An on-chip status register can be
used to monitor the WSM status and to determine the
progress of the PROGRAM/ERASE task.
The ERASE/PROGRAM SUSPEND functionality
allows compatibility with existing EEPROM emulation
software packages.
The device is manufactured using 0.15µm process
technology.
Please refer to Micron’s Web site (www.micron.com/
flash) for the latest data sheet.
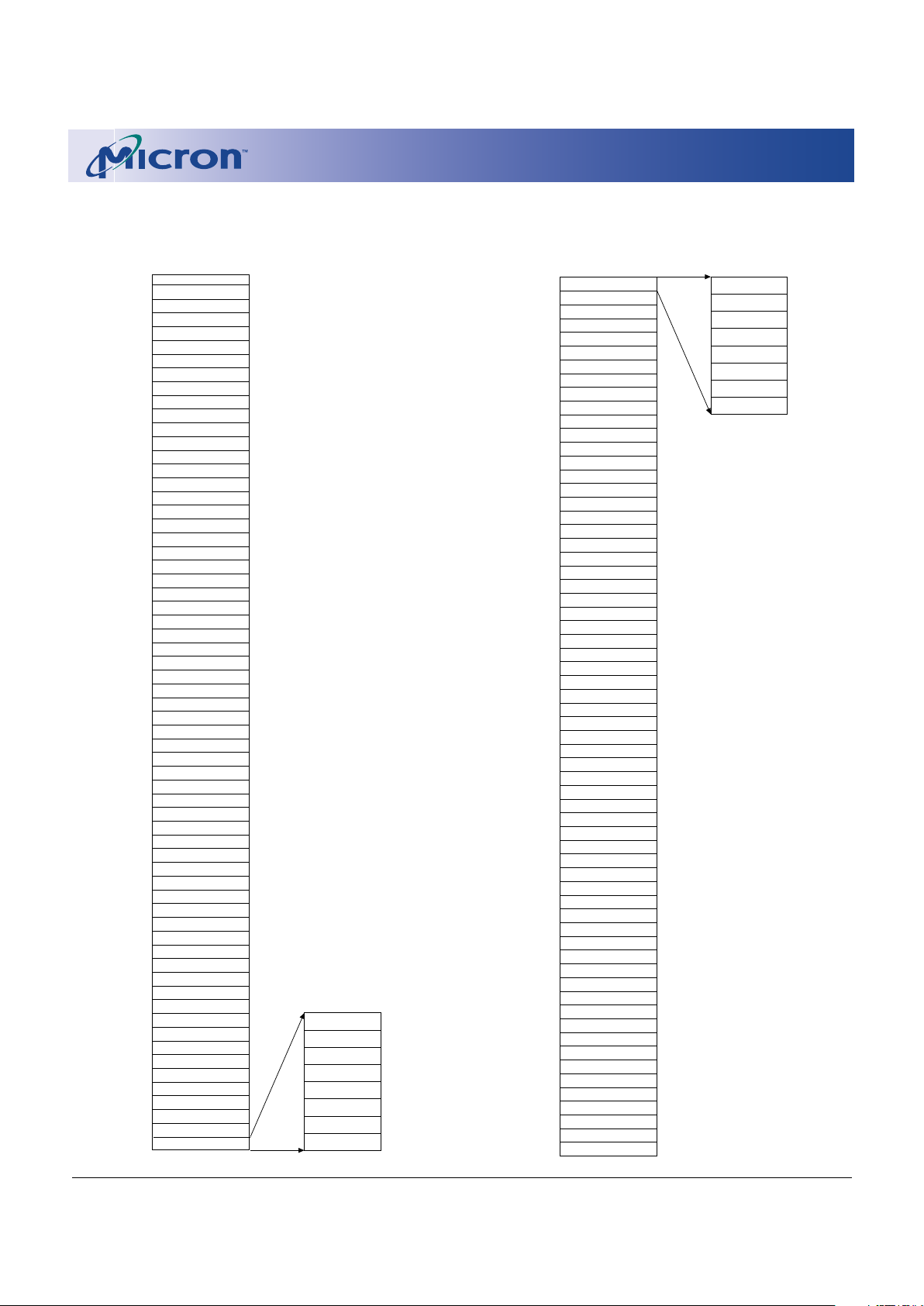
ARCHITECTURE AND MEMORY
ORGANIZATION
The MT28F320A18 contains eight 4K-word parame-
ter blocks and sixty-three 32K-word main blocks.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the bottom and top
memory organizations for the 32Mb device.
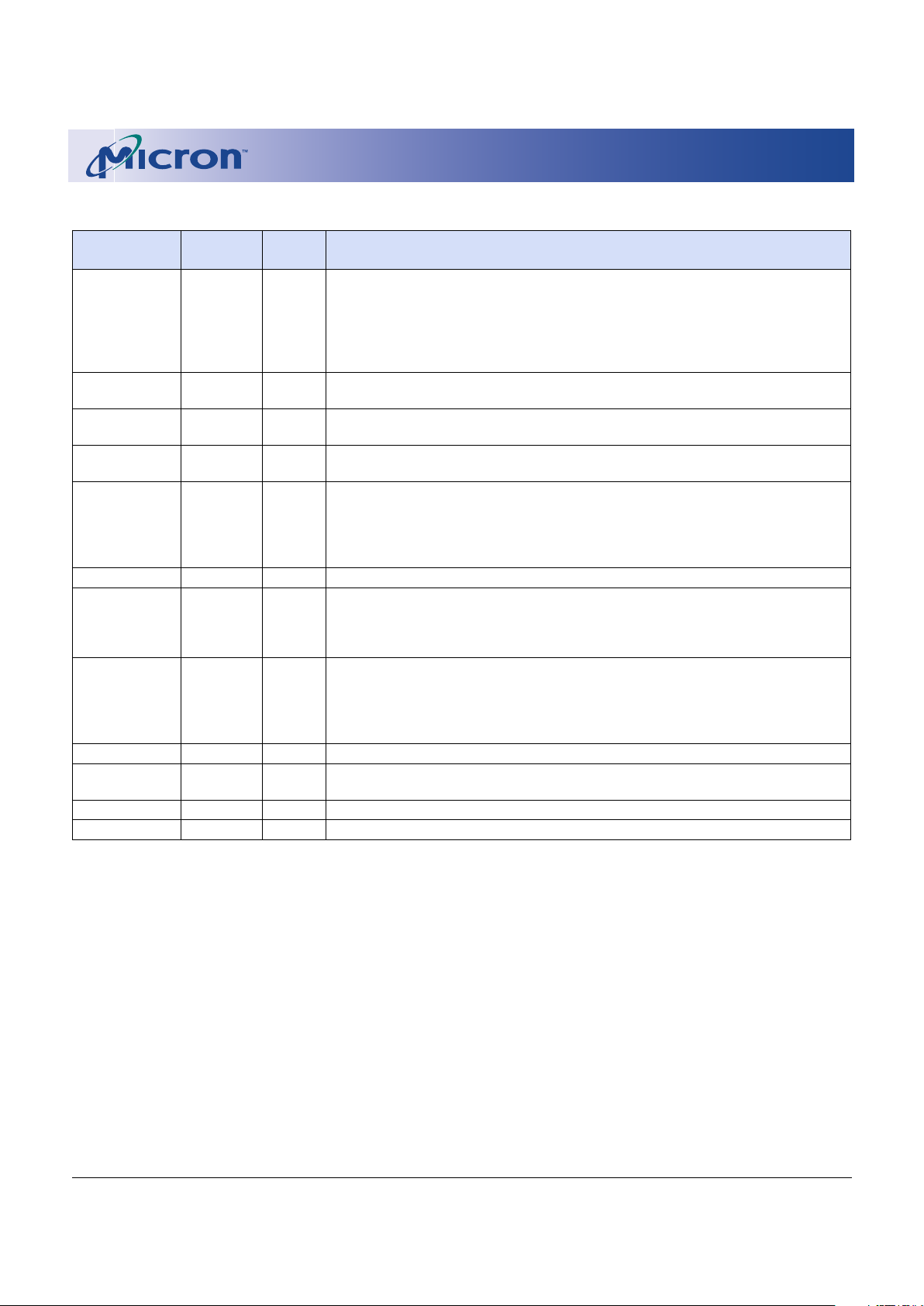
DEVICE MARKING
Due to the size of the package, Micron’s standard
part number is not printed on the top of each device.
Instead, an abbreviated device mark comprised of a
five-digit alphanumeric code is used. The abbreviated
device marks are cross referenced to Micron part numbers in Table 1.
Table 1: Cross Reference for Abbreviated Device Marks
PART NUMBER
PRODUCT
MARKING
SAMPLE
MARKING
MECHANICAL
SAMPLE
MARKING
MT28F320A18FF-70 BET
FW722 FX722 FY722
MT28F320A18FF-70 TET
FW723 FX723 FY723
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
3
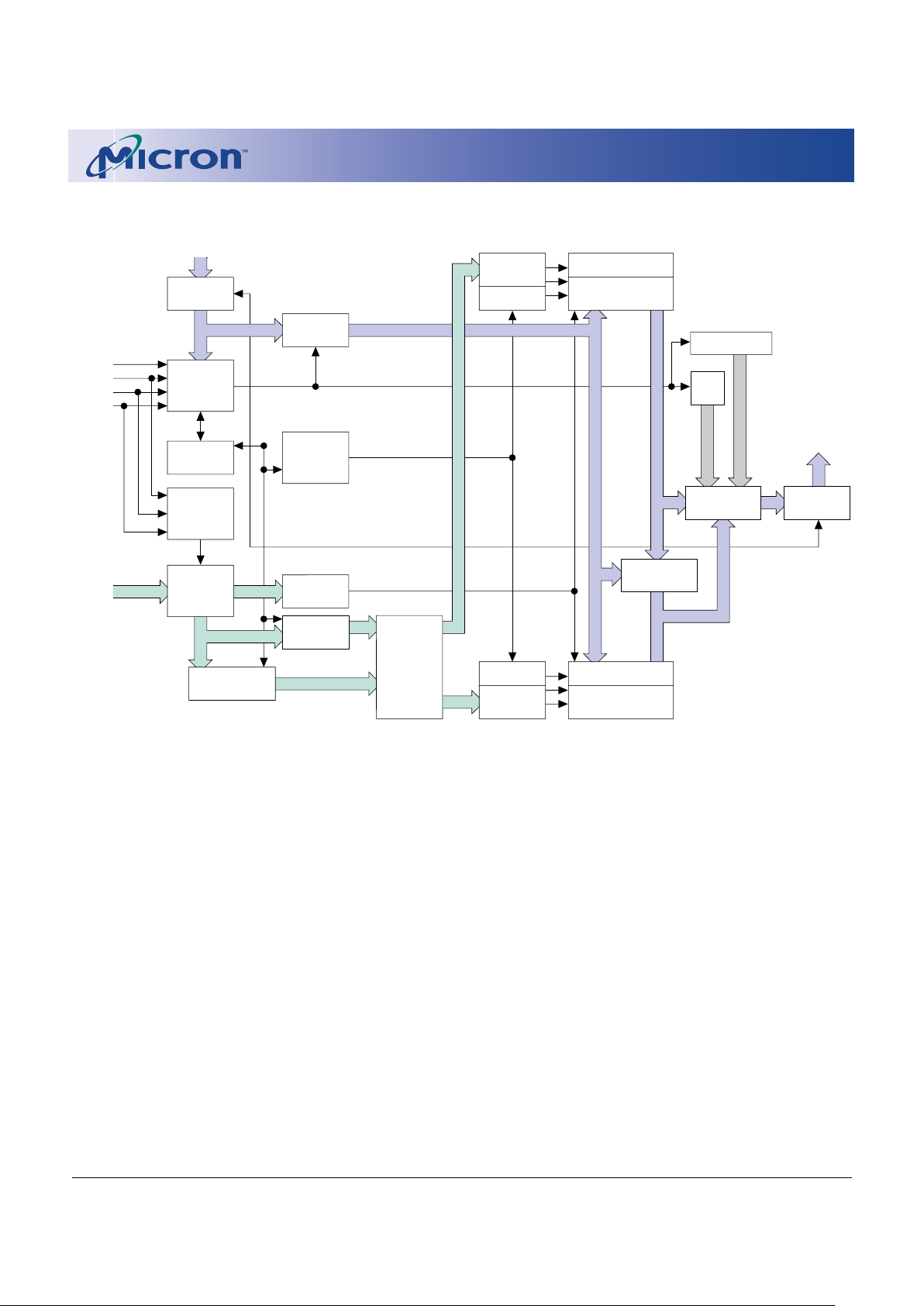
Functional Block Diagram
Address
Input
Buffer
X DEC
Y/Z DEC
Data Input
Buffer
Output
Multiplexer
Data
Comparator
Address
CNT WSM
Output
Buffer
Status
Reg.
WSM
Program/
Erase Change
Pump Voltage
Switch
Address Latch
DQ0–DQ15
DQ0–DQ15
CSM
RP#
CE#
WE#
OE#
I/O Logic
A0–A20
Data
Register
Bank a Blocks
Bank b Blocks
Y/Z Gating/Sensing
Y/Z Gating/Sensing
ID Reg.
APS
Control
X DEC
Y/Z DEC
Address
Multiplexer
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
4
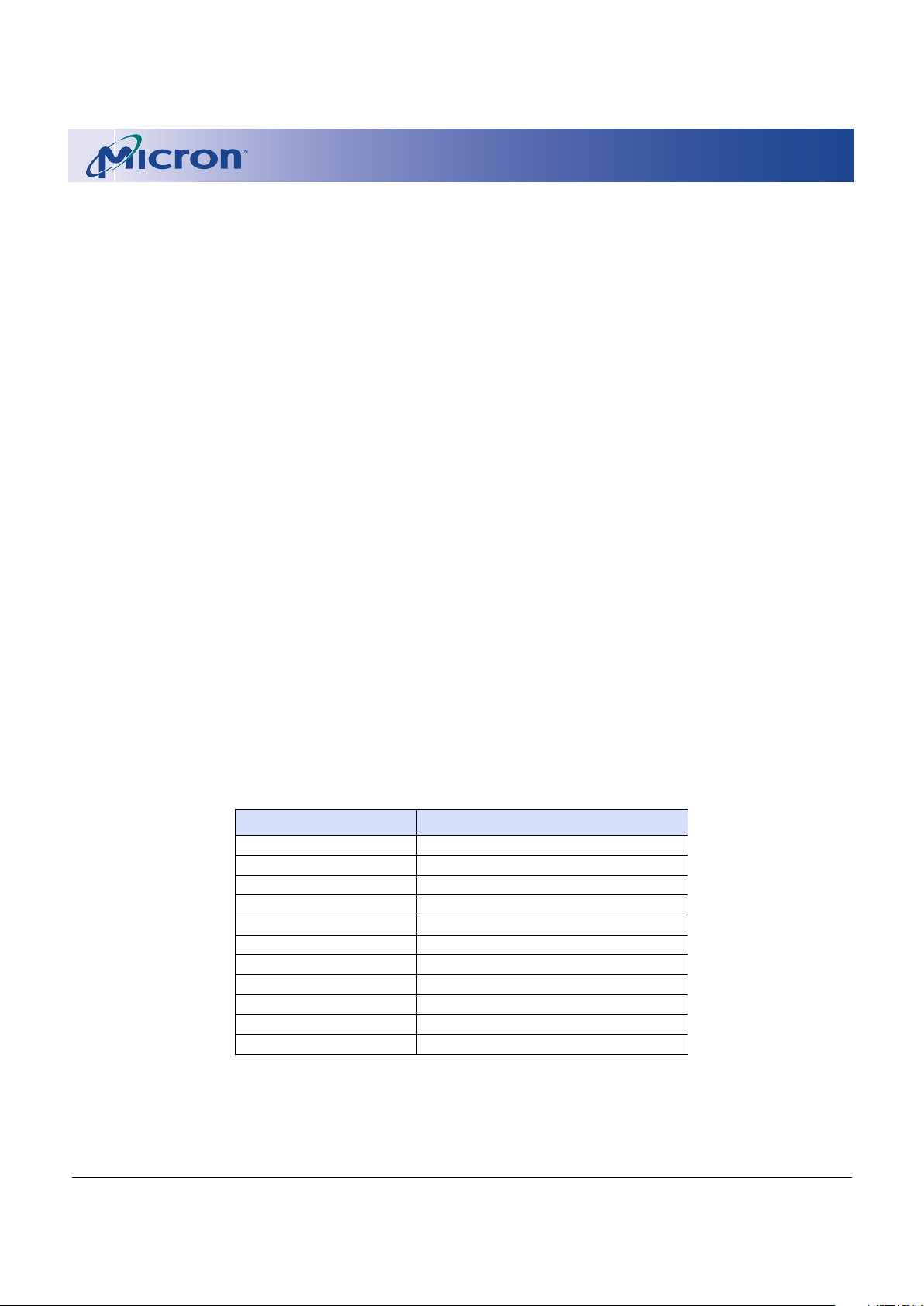
PART NUMBERING INFORMATION
Micron’s low-power devices are available with sev-
eral different combinations of features (see Figure 1).
Valid combinations of features and their corresponding part numbers are listed in Table 2.
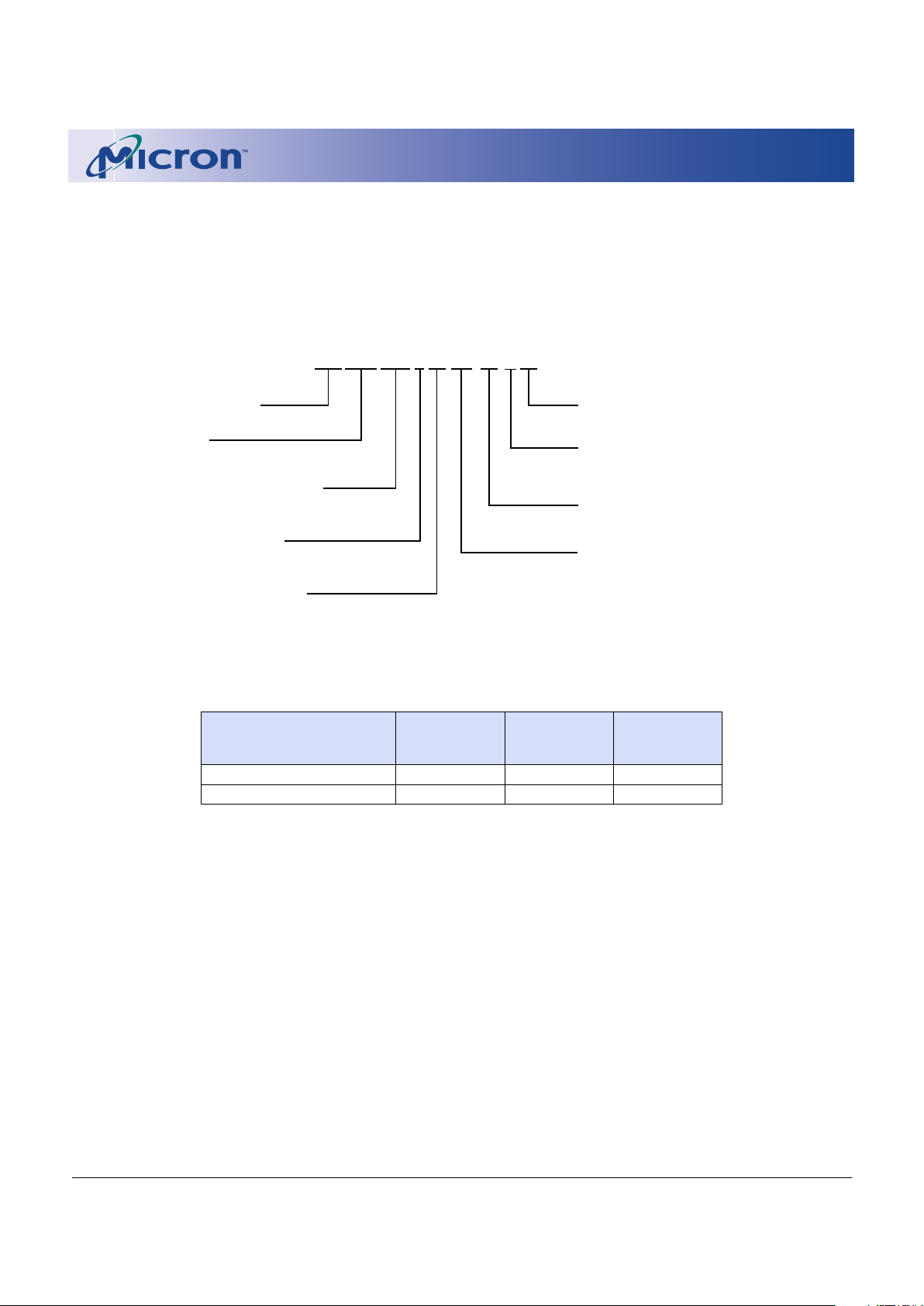
Figure 1: Part Number Chart
MT 28F 320 A18 FF -70 T ET
Micron Technology
Flash Family
28F = Dual-Supply Flash
Density/Organization/Banks
320 = 32Mb (2,048K x 16)
Access Time
-70 = 70ns
Read Mode Operation
A = Asynchronous
Package Code
FF = 48-ball FBGA (8 x 6 grid)
Operating Temperature Range
ET = Extended (-40ºC to +85ºC)
Boot Block Starting Address
B = Bottom boot
T = Top boot
Operating Voltage Range
18 = 1.65V–1.95V
Table 2: Valid Part Number Combinations
PART NUMBER
ACCESS
TIME (ns)
BOOT BLOCK
STARTING
ADDRESS
OPERATING
TEM P ER AT UR E
RANGE
MT28F320A18FF-70 BET
70 Bottom -40ºC to +85ºC
MT28F320A18FF-70 TET
70 Top -40ºC to +85ºC
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
5
Figure 2: 32Mb Bottom Boot Block
Memory Address Map
Figure 3: 32Mb Top Boot Block
Memory Address Map
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Blocks
8 x 4K-Word Blocks
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
1FFFFFh
1F8000h
1F7FFFh
1F0000h
1EFFFFh
1E8000h
1E7FFFh
1E0000h
1DFFFFh
1D8000h
1D7FFFh
1D0000h
1CFFFFh
1C8000h
1C7FFFh
1C0000h
1BFFFFh
1B8000h
1B7FFFh
1B0000h
1AFFFFh
1A8000h
1A7FFFh
1A0000h
19FFFFh
198000h
197FFFh
190000h
18FFFFh
188000h
187FFFh
180000h
17FFFFh
178000h
177FFFh
170000h
16FFFFh
168000h
167FFFh
160000h
15FFFFh
158000h
157FFFh
150000h
14FFFFh
148000h
147FFFh
140000h
13FFFFh
138000h
137FFFh
130000h
12FFFFh
128000h
127FFFh
120000h
11FFFFh
118000h
117FFFh
110000h
10FFFFh
108000h
107FFFh
100000h
0FFFFFh
0F8000h
0F7FFFh
0F0000h
0EFFFFh
0E8000h
0E7FFFh
0E0000h
0DFFFFh
0D8000h
0D7FFFh
0D0000h
0CFFFFh
0C8000h
0C7FFFh
0C0000h
0BFFFFh
0B8000h
0B7FFFh
0B0000h
0AFFFFh
0A8000h
0A7FFFh
0A0000h
09FFFFh
098000h
097FFFh
090000h
08FFFFh
088000h
087FFFh
080000h
07FFFFh
078000h
077FFFh
070000h
06FFFFh
068000h
067FFFh
060000h
05FFFFh
058000h
057FFFh
050000h
04FFFFh
048000h
047FFFh
040000h
03FFFFh
038000h
037FFFh
030000h
02FFFFh
028000h
027FFFh
020000h
01FFFFh
018000h
017FFFh
010000h
00FFFFh
008000h
007FFFh
000000h
ADDRESS RANGE
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
Parameter
Blocks
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
007FFFh
007000h
006FFFh
006000h
005FFFh
005000h
004FFFh
004000h
003FFFh
003000h
002FFFh
002000h
001FFFh
001000h
000FFFh
000000h
8 x 4K-Word Blocks
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
32K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
4K-Word Block
Parameter
Blocks
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1FFFFFh
1FF000h
1FEFFFh
1FE000h
1FDFFFh
1FD000h
1FCFFFh
1FC000h
1FBFFFh
1FB000h
1FAFFFh
1FA000h
1F9FFFh
1F9000h
1F8FFFh
1F8000h
ADDRESS RANGE
1F8000h
1F0000h
1E8000h
1E0000h
1D8000h
1D0000h
1C8000h
1C0000h
1B8000h
1B0000h
1A8000h
1A0000h
198000h
190000h
188000h
180000h
178000h
170000h
168000h
160000h
158000h
150000h
148000h
140000h
138000h
130000h
128000h
120000h
118000h
110000h
108000h
100000h
0F8000h
0F0000h
0E8000h
0E0000h
0D8000h
0D0000h
0C8000h
0C0000h
0B8000h
0B0000h
0A8000h
0A0000h
098000h
090000h
088000h
080000h
078000h
070000h
068000h
060000h
058000h
050000h
048000h
040000h
038000h
030000h
028000h
020000h
018000h
010000h
008000h
000000h
1FFFFFh
1F7FFFh
1EFFFFh
1E7FFFh
1DFFFFh
1D7FFFh
1CFFFFh
1C7FFFh
1BFFFFh
1B7FFFh
1AFFFFh
1A7FFFh
19FFFFh
197FFFh
18FFFFh
187FFFh
17FFFFh
177FFFh
16FFFFh
167FFFh
15FFFFh
157FFFh
14FFFFh
147FFFh
13FFFFh
137FFFh
12FFFFh
127FFFh
11FFFFh
117FFFh
10FFFFh
107FFFh
0FFFFFh
0F7FFFh
0EFFFFh
0E7FFFh
0DFFFFh
0D7FFFh
0CFFFFh
0C7FFFh
0BFFFFh
0B7FFFh
0AFFFFh
0A7FFFh
09FFFFh
097FFFh
08FFFFh
087FFFh
07FFFFh
077FFFh
06FFFFh
067FFFh
05FFFFh
057FFFh
04FFFFh
047FFFh
03FFFFh
037FFFh
02FFFFh
027FFFh
01FFFFh
017FFFh
00FFFFh
007FFFh
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
6
BALL DESCRIPTIONS
48-BALL FBGA
NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
D8, C8, B8, A8,
C7, B7, A7, C6,
B6, A6, C5, B5,
C3, A3, C2, B2,
A2, D1, C1, B1,
A1
A0–A20 Input
Address Inputs: Inputs for the address during READ and WRITE operations.
Addresses are internally latched during WRITE and ERASE cycles.
D7 CE# Input
Chip Enable: Activates the device when LOW. When CE# is HIGH, the device is
disabled and goes into standby power mode.
F8 OE# Input
Output Enable: Enables the outputs buffer when LOW. When OE# is HIGH, the
output buffers are disabled.
B3 WE# Input
Write Enable: Determines if a given cycle is a WRITE cycle. If WE# is LOW, the cycle
is either a WRITE to the command state machine (CSM) or to the memory array.
B4 RP# Input
Reset: When RP# is a logic LOW, the device is in reset mode, which drives the
outputs to High-Z and resets the write state machine (WSM). When RP# is at logic
HIGH, the device is in standard operation. When RP# transitions from logic LOW
to logic HIGH, the device resets all blocks to locked and defaults to the read array
mode.
A5 WP# Input
Write Protect: Controls the lock down function of the flexible locking feature.
E7, F7, D5, E5,
F4, D3, E3, F2,
D6, E6, F6, D4,
E4, F3, D2, E2
DQ0–DQ15 Input/
Output
Data Inputs/Outputs: Inputs array data on the second CE# and WE# cycle during
PROGRAM command. Inputs commands to the command user interface when CE#
and WE# are active.
A4 V
PP Supply
Block Erase and Program Power Supply: [V
PP1 = 0.9V–1.95V or VPP2 = 11.4V–
12.6V]. A valid voltage on this contact allows block erase or data programming.
Memory contents cannot be altered when V
PP ≤ VPPLK. Block erase and program
at invalid V
PP voltages should not be attempted. It provides factory programming
compatibility when driven to 11.4V–12.6V
F5 V
CC Supply
Device Power Supply: [1.65V–1.95V] Supplies power for device operation.
E1 V
CCQ Supply
I/O Power Supply: [1.65V–1.95V] Supplies power for input/output buffers. This
input should be tied directly to VCC.
E8, F1 V
SS Supply
Do not float any ground ball.
C4 NC –
Internally not connected.
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
7
COMMAND STATE MACHINE
Commands are issued to the command state
machine (CSM) using standard microprocessor write
timings. The CSM acts as an interface between external microprocessors and the internal write state
machine (WSM). The available commands are listed in
Table 3, their definitions are given in Table 4 and their
descriptions in Table 5. Program and erase algorithms
are automated by an on-chip WSM. Table 6 shows the
CSM transition states.
Once a valid PROGRAM/ERASE command is
entered, the WSM executes the appropriate algorithm,
which generates the necessary timing signals to control the device internally and accomplish the
requested operation. A command is valid only if the
exact sequence of WRITE cycles is completed. After the
WSM completes its task, the WSM status bit (SR7) (see
Table 8) is set to a logic HIGH level (1), allowing the
CSM to respond to the full command set again.
OPERATIONS
Device operations are selected by entering a standard JEDEC 8-bit command code with conventional
microprocessor timings into an on-chip CSM through
I/Os DQ0–DQ7. The number of bus cycles required to
activate a command is typically one or two. The first
operation is always a WRITE. Control signals CE# and
WE# must be at a logic LOW level ( V
IL), and OE# and
RP# must be at logic HIGH (V
IH). The second opera-
tion, when needed, can be a WRITE or a READ
depending upon the command. During a READ operation, control signals CE# and OE# must be at a logic
LOW level (Vil), and WE# and RP# must be at logic
HIGH (V
IH).
Table 7 illustrates the bus operations for all the
modes: write, read, reset, standby, and output disable.
When the device is powered up, internal reset circuitry initializes the chip to a read array mode of operation. Changing the mode of operation requires that a
command code be entered into the CSM. An on-chip
status register is available. The status register allows
the monitoring of the progress of various operations
that can take place on a memory. The status register is
interrogated by entering a READ STATUS REGISTER
command onto the CSM (cycle 1) and reading the register data on I/Os DQ0–DQ7 (cycle 2). Status register
bits SR0–SR7 correspond to DQ0–DQ7 (see Table 8).
Command Definition
Once a specific command code has been entered,
the WSM executes an internal algorithm, generating
the necessary timing signals to program, erase, and
verify data. See Table 4 for the CSM command definitions and data for each of the bus cycles.
Table 3: Command State Machine Codes For
Device Mode Selection
COMMAND DQ0–DQ7 CODE ON DEVICE MODE
40h/10h
Program setup/alternate program setup
20h
Block erase setup
50h
Clear status register
60h
Protection configuration setup
70h
Read status register
90h
Read protection configuration register
98h
Read query
B0h
Program/erase suspend
C0h
Protection register program/lock
D0h
Program/erase resume – erase confirm
FFh
Read array

2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
8
STATUS REGISTER
The status register allows the user to determine
whether the state of a PROGRAM/ERASE operation is
pending or complete. The status register is monitored
by toggling OE# and CE# by reading the resulting status code on I/Os DQ0–DQ7. The high-order I/Os
(DQ8–DQ15) are set to 00h internally, so only the loworder I/Os (DQ0–DQ7) need to be interpreted.
Register data is updated and latched on the falling
edge of OE# or CE#, whichever occurs last. Latching
the data prevents errors from occurring if the register
input changes during a status register read.
The status register provides the internal state of the
WSM to the external microprocessor. During periods
when the WSM is active, the status register can be
polled to determine the WSM status. Table 8 defines
the status register bits.
After monitoring the status register during a PROGRAM/ERASE operation, the data appearing on DQ0–
DQ7 remains as status register data until a new command is issued to the CSM. To return the device to
other modes of operation, a new command must be
issued to the CSM.
COMMAND STATE MACHINE
OPERATIONS
The CSM decodes instructions for read array, read
protection configuration register, read query, read status register, clear status register, program, erase, erase
suspend, erase resume, erase confirm, program setup,
alternate program setup, program suspend, program
resume, lock block, unlock block and lock down block,
chip protection register program, and chip protection
register lock. The 8-bit command code is input to the
device on DQ0–DQ7 (see Table 3 for CSM codes and
Table 4 for command definitions). During a PROGRAM
or ERASE cycle, the CSM informs the WSM that a PROGRAM or ERASE cycle has been requested. During a
PROGRAM cycle, the WSM controls the program
sequences and the CSM responds to a PROGRAM SUSPEND command only. During an ERASE cycle, the
CSM responds to an ERASE SUSPEND command only.
When the WSM has completed its task, the WSM status
bit (SR7) is set to a logic HIGH level and the CSM
responds to the full command set. The CSM stays in
the current command state until the microprocessor
issues another command.
The WSM successfully initiates an ERASE or PRO-
GRAM operation only when V
PP is within its correct
voltage range.
CLEAR STATUS REGISTER
The internal circuitry can set, but not clear, the
block lock status bit (SR1), the V
PP status bit (SR3), the
program status bit (SR4), and the erase status bit (SR5)
of the status register. The CLEAR STATUS REGISTER
command (50h) allows the external microprocessor to
clear these status bits and synchronize to the internal
operations. When the status bits are cleared, a READ
ARRAY command (FFh) must be issued before data
can be read from the memory array, or a READ STATUS
REGISTER command (70h) must be issued to read status.
READ OPERATIONS
The following READ operations are available: READ
ARRAY, READ PROTECTION CONFIGURATION REGISTER, READ QUERY and READ STATUS REGISTER.
Read Array
The array is read by entering the command code
FFh on DQ0–DQ7. Control signals CE# and OE# must
be at a logic LOW level (V
IL), and WE# and RP# must be
at logic HIGH level (V
IH) to read data from the array.
Data is available on DQ0–DQ15. Any valid address
within any of the blocks selects that address and allows
data to be read from that address. Upon initial powerup or device reset, the device defaults to the read array
mode.
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
9
Read Chip Protection Configuration
Register
The chip identification mode outputs four types of
information: the manufacturer/device identifier, the
block locking status, the protection register content,
and protection register lock. Two bus cycles are
required for this operation: the chip identification data
is read by entering the command code 90h on DQ0–
DQ7 and the identification code address on the
address lines.
Control signals CE# and OE# must be at a logic LOW
level (V
IL), and WE# and RP# must be at a logic HIGH
level (V
IH) to read data from the protection configura-
tion register. Data is available on DQ0–DQ15. To return
to read array mode, write the read array command
code FFh on DQ0–DQ7. See Table 10 for further
details.
WA: Word address of memory location to be written, or read
IA: Identification code address
BA: Address within the block
ID: Identification code data
SRD: Data read from the status register
QA: Query code address
QD: Query code data
WD: Data to be written at the location WA
PA: Protection register address
LPA: Lock protection register address
AD: Array data
PD: Protection register data
X: “Don’t Care”
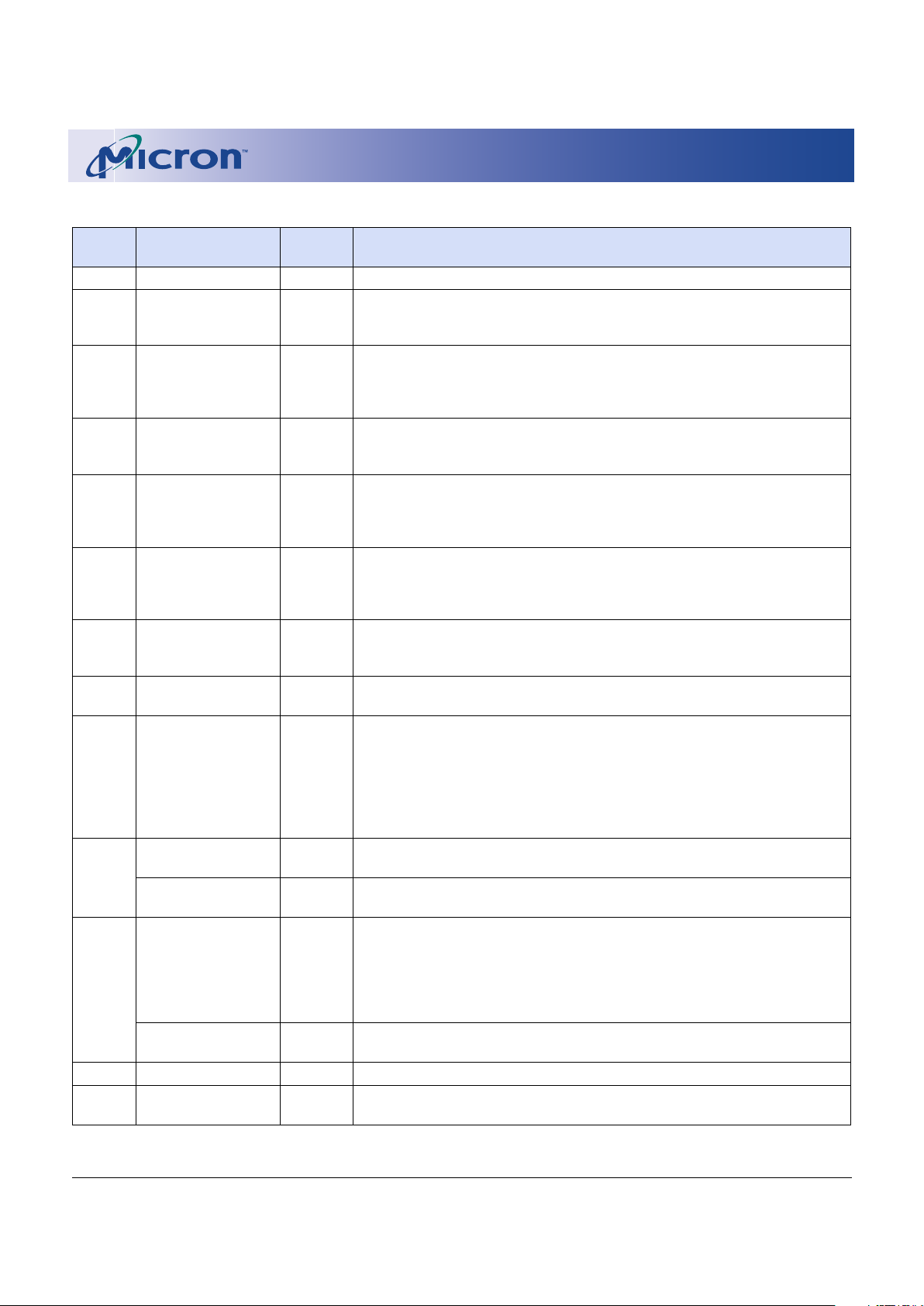
Table 4: Command Definitions
COMMAND
FIRST BUS CYCLE SECOND BUS CYCLE
OPERATION ADDRESS DATA OPERATION ADDRESS DATA
READ ARRAY
WRITE X FFh READ WA AD
READ PROTECTION
CONFIGURATION REGISTER
WRITE X 90h READ IA ID
READ STATUS REGISTER
WRITE X 70h READ – SRD
CLEAR STATUS REGISTER
WRITE X 50h – – –
READ QUERY
WRITE X 98h READ QA QD
BLOCK ERASE SETUP
WRITE X 20h WRITE BA D0h
PROGRAM SETUP/ALTERNATE
PROGRAM SETUP
WRITE X 40h/10h WRITE WA WD
PROGRAM/ERASE SUSPEND
WRITEXB0h–––
PROGRAM/ERASE RESUME –
ERASE CONFIRM
WRITEXD0h–––
LOCK BLOCK
WRITE X 60h WRITE BA 01h
UNLOCK BLOCK
WRITE X 60h WRITE BA D0h
LOCK DOWN BLOCK
WRITE X 60h WRITE BA 2Fh
PROTECTION REGISTER PROGRAM
SETUP
WRITE X C0h WRITE PA PD
PROTECTION REGISTER LOCK
WRITE X C0h WRITE LPA FFFDh
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
10
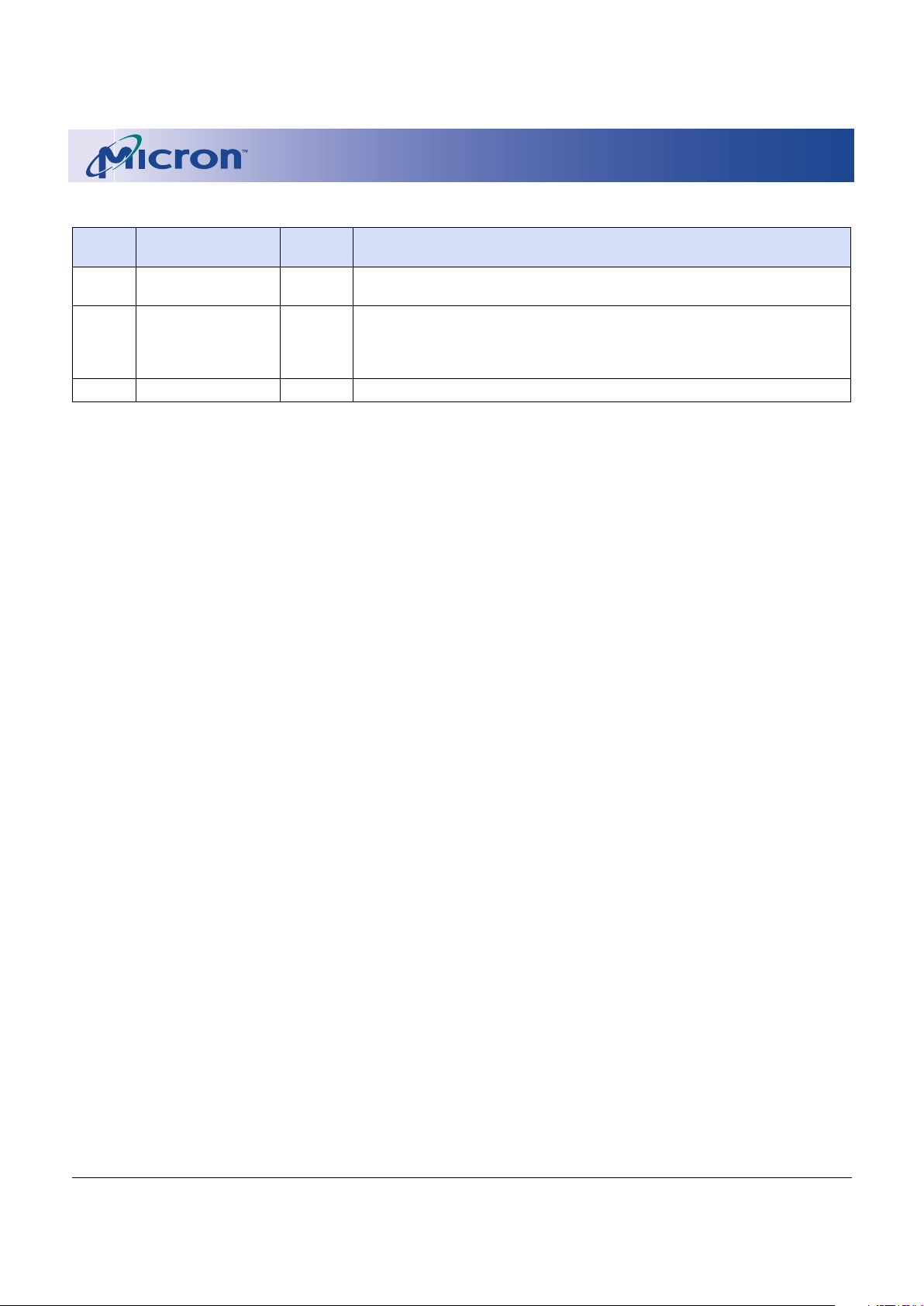
Table 5: Command Descriptions
CODE DEVICE MODE
BUS
CYCLE DESCRIPTION
10h
Alt. Program Setup
First
Operates the same as a PROGRAM SETUP command.
20h
Erase Setup
First
Prepares the CSM for an ERASE CONFIRM command. If the next command is
not an ERASE CONFIRM command, the command will be ignored, and the
device will go to read status mode and wait for another command.
40h
Program Setup
First
A two-cycle command: The first cycle prepares for a PROGRAM operation, the
second cycle latches addresses and data and initiates the WSM to execute the
program algorithm. The Flash device outputs status register data on the
falling edge of OE# or CE#, whichever occurs first.
50h
Clear Status Register
First
The WSM can set the block lock status (SR1), V
PP Status (SR3), program status
(SR4),and erase status (SR5) bits in the status register to “1,” but it cannot
clear them to “0.” Issuing this command clears those bits to “0.”
60h
Protection
Configuration Setup
First
Prepares the CSM for changes to the block locking status. If the next
command is not BLOCK UNLOCK, BLOCK LOCK, or BLOCK LOCK DOWN, then
the CSM will set both the program and erase status register bits to indicate a
command sequence error.
70h
Read Status Register
First
Places the device into read status register mode. Reading the device will
output the contents of the status register for the addressed bank. The device
will automatically enter this mode for the addressed bank after a PROGRAM
or ERASE operation has been initiated.
90h
Read Protection
Configuration
Register
First
Puts the device into the read protection configuration register mode so that
reading the device will output the manufacturer/device codes, block lock
status, protection register, or protection register lock.
98h
Read Query
First
Puts the device into the read query mode so that reading the device will
output common flash interface information.
B0h
Program/Erase
Suspend
First
Suspends the currently executing PROGRAM/ERASE operation. The status
register will indicate when the operation has been successfully suspended by
setting either the program suspend (SR2) or erase suspend (SR6) and the
WSM status bit (SR7) to a “1” (ready). The WSM will continue to idle in the
suspend state, regardless of the state of all input control pins except RP#,
which will immediately shut down the WSM and the remainder of the chip if
RP# is driven to V
IL.
C0h
Program Device
Protection Register
First
Writes a specific code into the device protection register.
Lock Device
Protection Register
First
Locks the device protection register; data can no longer be changed.
D0h
Erase Confirm
Second
If the previous command was an ERASE SETUP command, then the CSM will
close the address and data latches, and it will begin erasing the block
indicated on the address pins. During programming/erase, the device will
respond only to the READ STATUS REGISTER, PROGRAM/ERASE SUSPEND
commands and will output status register data on the falling edge of OE# or
CE#, whichever occurs last.
Program/Erase
Resume
First
If a program or erase operation was previously suspended, this command will
resume the operation.
FFh
Read Array
First
During the read array mode, array data will be output on the data bus.
01h
Lock Block
Second
If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP, the CSM
will latch the address and lock the block indicated on the address bus.
2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
11
2Fh
Lock Down
Second
If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP, the CSM
will latch the address and lock down the block indicated on the address bus.
D0h
Unlock Block
Second
If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP, the CSM
will latch the address and unlock the block indicated on the address bus. If
the block had been previously set to lock down, this operation will have no
effect.
00h
Invalid/Reserved Unassigned command that should not be used.
Table 5: Command Descriptions (continued)
CODE DEVICE MODE
BUS
CYCLE DESCRIPTION

2 MEG x 16
1.8V ENHANCED+ BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
PRELIMINARY
2 Meg x 16, 1.8V Enhanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F320A18_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 9/2002
12
Read Query
The read query mode outputs common flash interface (CFI) data when the device is read (see Table 12).
Two bus cycles are required for this operation. It is possible to access the query by writing the read query
command code 98h on DQ0–DQ7. Control signals CE#
and OE# must be at a logic LOW level (V
IL), and WE#
and RP# must be at logic HIGH level (V
IH) to read data
from the query. The CFI data structure contains information such as block size, density, command set, and
electrical specifications. To return to read array mode,
write the read array command code FFh on DQ0–DQ7.
Read Status Register
The status register is read by entering the command
code 70h on DQ0–DQ7. Two bus cycles are required for
this operation: one to enter the command code and a
second to read the status register. In a READ cycle, the
register data is updated on the falling edge of OE# or
CE#, whichever occurs last.
PROGRAMMING OPERATIONS
There are two CSM commands for programming:
PROGRAM SETUP and ALTERNATE PROGRAM SETUP
(see Table 3).
After the desired command code is entered (10h or
40h command code on DQ0–DQ7), the WSM takes
over and correctly sequences the device to complete
the PROGRAM operation. The WRITE operation may
be monitored through the status register (see the Status Register section). During this time, the CSM will
only respond to a PROGRAM SUSPEND command
until the PROGRAM operation has been completed,
after which time all commands to the CSM become
valid again. The PROGRAM operation can be suspended by issuing a PROGRAM SUSPEND command
(B0h). Once the WSM reaches the suspend state, it
allows the CSM to respond only to READ ARRAY, READ
STATUS REGISTER, READ PROTECTION CONFIGURATION, READ QUERY, and PROGRAM RESUME. During the PROGRAM SUSPEND operation, array data
should be read from an address other than the one
being programmed. To resume the PROGRAM operation, a PROGRAM RESUME command (D0h) must be
issued to cause the CSM to clear the suspend state previously set (see Figure 4 for programming operation
and Figure 5 for program suspend and program
resume).
During programming, V
PP must remain in the
appropriate V
PP voltage range as shown in the Recom-
mended Operating Conditions table.
ERASE OPERATIONS
An ERASE operation must be used to initialize all
bits in an array block to “1”. After BLOCK ERASE CONFIRM is issued, the CSM responds only to an ERASE
SUSPEND command until the WSM completes its task.
Block erasure inside the memory array sets all bits
within the address block to logic "1". Erase is accomplished only by blocks; data at single address locations
within the array cannot be erased individually. The
block to be erased is selected by using any valid
address within that block. Block erasure is initiated by
a command sequence to the CSM: BLOCK ERASE
SETUP (20h) followed by BLOCK ERASE CONFIRM
(D0h) (see Figure 6). A two-command erase sequence
protects against accidental erasure of memory contents.
When the BLOCK ERASE CONFIRM command is
complete, the WSM automatically executes a sequence
of events to complete the block erasure. During this
sequence, the block is programmed with logic "0",
data is verified, all bits in the block are erased, and
finally verification is performed to ensure that all bits
are correctly erased. Monitoring the ERASE operation
is possible through the status register (see the Status
Register section).
During the execution of an ERASE operation the
ERASE SUSPEND command (B0h) can be entered to
direct the WSM to suspend the ERASE operation. Once
the WSM has reached the suspend state, it allows the
CSM to respond only to the READ ARRAY, READ STATUS REGISTER, READ QUERY, READ CHIP PROTECTION CONFIGURATION, PROGRAM SETUP,
PROGRAM/ERASE RESUME and LOCK SETUP (see
the Block Locking section). During the ERASE SUSPEND operation, array data must be read from a block
other than the one being erased. To resume the ERASE
operation, an ERASE RESUME command (D0h) must
be issued to cause the CSM to clear the suspend state
previously set (see Figure 7). It is also possible that an
ERASE can be suspended and a write to another block
can be initiated. After the completion of a write, an
erase can be resumed by writing an ERASE RESUME
command.
 Loading...
Loading...