MICRON MT28F400B5WG-8T, MT28F400B5CG-8TET, MT28F004B5WG-8T, MT28F004B5WG-8TET, MT28F400B5CG-8T Datasheet
...
PRODUCTS AND SPECIFICATIONS DISCUSSED HEREIN ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE BY MICRON WITHOUT NOTICE.
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
1
4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
FLASH MEMORY
MT28F004B5
MT28F400B5
5V Only, Dual Supply (Smart 5)
0.18µm Process Technology
FEATURES
• Seven erase blocks:
16KB/8K-word boot block (protected)
Two 8KB/4K-word parameter blocks
Four main memory blocks
• Smart 5 technology (B5):
5V ±10% V
CC
5V ±10% VPP application/production
programming
1
• Advanced 0.18µm CMOS floating-gate process
• Compatible with 0.3µm Smart 5 device
• Address access time: 80ns
• 100,000 ERASE cycles
• Industry-standard pinouts
• Inputs and outputs are fully TTL-compatible
• Automated write and erase algorithm
• Two-cycle WRITE/ERASE sequence
• Byte- or word-wide READ and WRITE
(MT28F400B5, 256K x 16/512K x 8)
•Byte-wide READ and WRITE only
(MT28F004B5, 512K x 8)
• TSOP and SOP packaging options
Notes: 1. This generation of devices does not support 12V VPP
compatibility production programming; however, 5V
V
PP application production programming can be used
with no loss of performance.
2. Contact factory for availability.
Part Number Example:
MT28F400B5WG-8 T
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MT28F004B5 (x8) and MT28F400B5 (x16, x8)
are nonvolatile, electrically block-erasable (Flash),
programmable, read-only memories containing
4,194,304 bits organized as 262,144 words (16 bits) or
524,288 bytes (8 bits). Writing or erasing the device is
done with a 5V V
PP voltage, while all operations are
performed with a 5V V
CC. Due to process technology
advances, 5V V
PP is optimal for application and pro-
duction programming. These devices are fabricated
with Micron’s advanced 0.18µm CMOS floating-gate
process.
The MT28F004B5 and MT28F400B5 are organized
into seven separately erasable blocks. To ensure that
critical firmware is protected from accidental erasure
or overwrite, the devices feature a hardware-protected
boot block. Writing or erasing the boot block requires
either applying a super-voltage to the RP# pin or driving WP# HIGH in addition to executing the normal
write or erase sequences. This block may be used to
store code implemented in low-level system recovery.
The remaining blocks vary in density and are written
and erased with no additional security measures.
Please refer to Micron’s Web site (www.micron.com/
flash) for the latest data sheet.
OPTIONS MARKING
• Timing
80ns access -8
• Configurations
512K x 8 MT28F004B5
256K x 16/512K x 8 MT28F400B5
• Boot Block Starting Word Address
Top (3FFFFh) T
Bottom (00000h) B
•Operating Temperature Range
Commercial (0ºC to +70ºC) None
Extended (-40ºC to +85ºC) ET
•Packages
MT28F400B5
Plastic 44-pin SOP (600 mil) SG
2
Plastic 48-pin TSOP Type I WG
MT28F004B5
Plastic 40-pin TSOP Type I VG
40-Pin TSOP Type I
44-Pin SOP
2
48-Pin TSOP Type I
4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
2
Pin Assignment (Top View)
48-Pin TSOP Type I
Order Number and Part Marking
MT28F400B5WG-8 B
MT28F400B5WG-8 T
MT28F400B5WG-8 BET
MT28F400B5WG-8 TET
44-PIN SOP
1
Order Number and Part Marking
MT28F400B5SG-8 B
MT28F400B5SG-8 T
MT28F400B5SG-8 BET
MT28F400B5SG-8 TET
40-Pin TSOP Type I
Order Number and Part Marking
MT28F004B5VG-8 B
MT28F004B5VG-8 T
MT28F004B5VG-8 BET
MT28F004B5VG-8 TET
Notes: 1. Contact factory for availability.
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
NC
NC
WE#
RP#
V
PP
WP#
NC
NC
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A16
BYTE#
V
SS
DQ15/(A-1)
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
OE#
V
SS
CE#
A0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
VPP
WP#
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
CE#
V
SS
OE#
DQ0
DQ8
DQ1
DQ9
DQ2
DQ10
DQ3
DQ11
RP#
WE#
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
BYTE#
V
SS
DQ15/(A-1)
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A9
A8
WE#
RP#
V
PP
WP#
A18
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A17
V
SS
NC
NC
A10
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
V
CC
V
CC
NC
DQ3
DQ2
DQ1
DQ0
OE#
V
SS
CE#
A0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
3
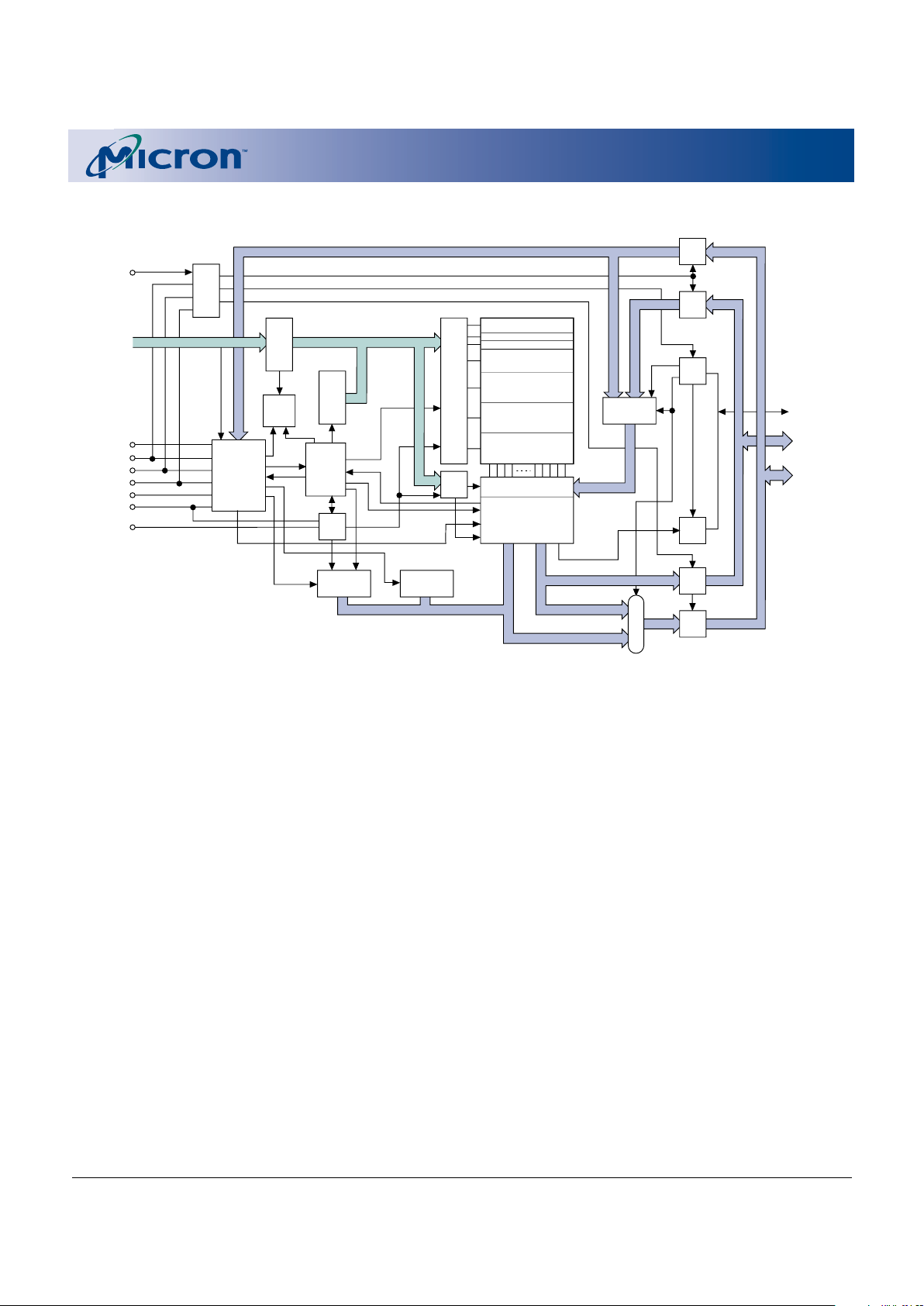
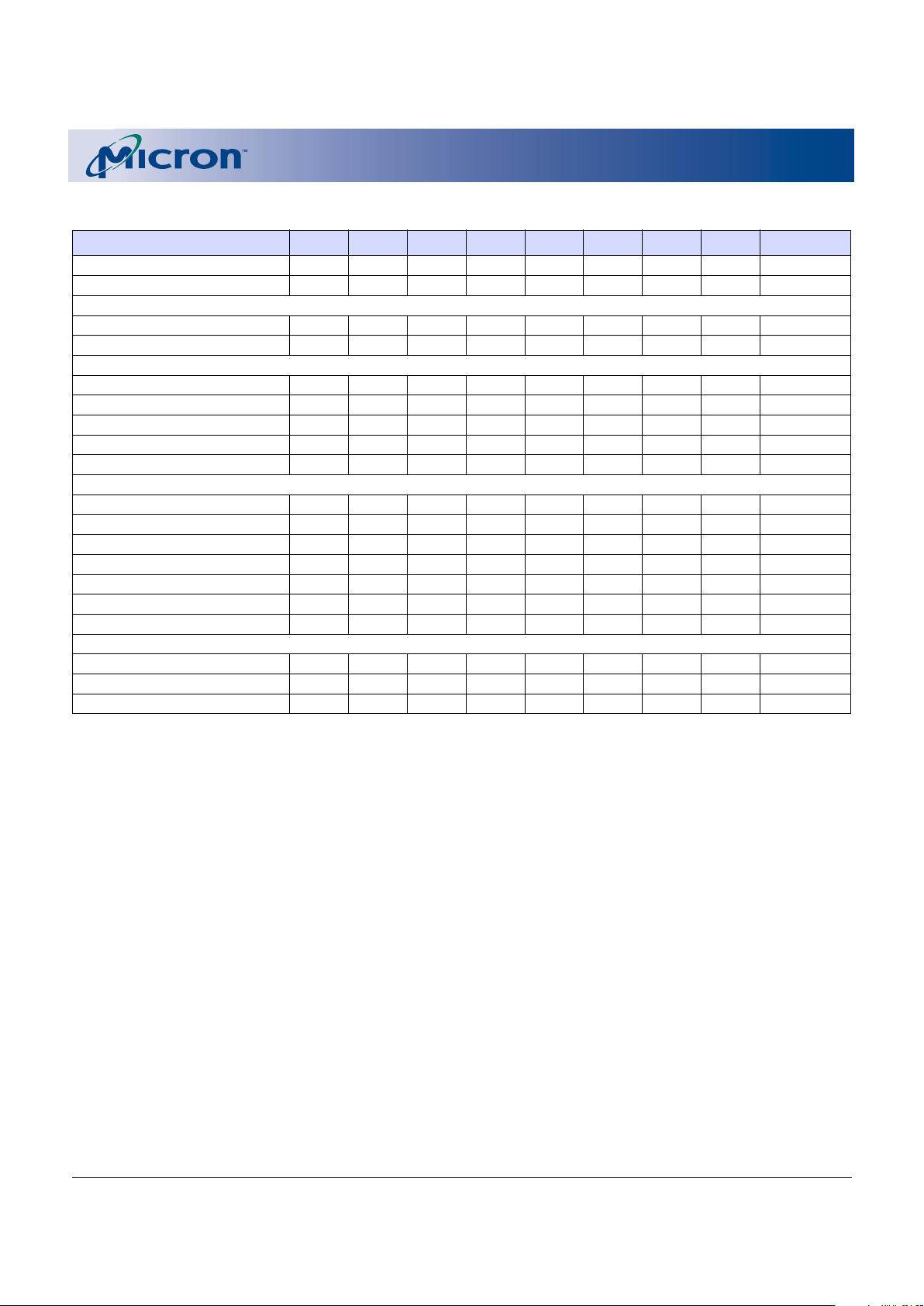
Functional Block Diagram
Notes: 1. Does not apply to MT28F004B5.
16KB Boot Block
8KB Parameter Block
8KB Parameter Block
96KB Main Block
128KB Main Block
128KB Main Block
Y - Select Gates
Sense Amplifiers
Write/Erase-Bit
Compare and Verify
Addr.
Buffer/
Latch
Power
(Current)
Control
Addr.
Counter
Command
Execution
Logic
I/O
Control
Logic
V
PP
Switch/
Pump
Status
Register
Identification
Register
Y -
Decoder
128KB Main Block
X - Decoder/Block Erase Control
Output
Buffer
Input
Buffer
State
Machine
BYTE#
1
A
0–A17/(18)
CE#
OE#
WE#
RP#
V
PP
DQ15/(A - 1)
1
MUX
DQ15
8
8
7
DQ8–DQ14
1
DQ0–DQ7
16
8
18 (19)
7
A-1
9
(10)
9
8
Output
Buffer
Output
Buffer
Input
Buffer
Input
Buffer
Input Data
Latch/Mux
7
A9
VCC
WP#
4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
4
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
44-PIN SOP
NUMBERS
40-PIN
TSOP
NUMBERS
48-PIN
TSOP
NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
43 9 11 WE# Input
Write Enable: Determines if a given cycle is a WRITE cycle.
If WE# is LOW, the cycle is either a WRITE to the command
execution logic (CEL) or to the memory array.
2 12 14 WP# Input
Write Protect: Unlocks the boot block when HIGH if VPP =
5V and RP# = V
IH during a WRITE or ERASE. Does not affect
WRITE or ERASE operation on other blocks.
12 22 26 CE# Input
Chip Enable: Activates the device when LOW. When CE# is
HIGH, the device is disabled and goes into standby power
mode.
44 10 12 RP# Input
Reset/Power-Down: When LOW, RP# clears the status
register, sets the internal state machine (ISM) to the array
read mode and places the device in deep power-down
mode. All inputs, including CE#, are “Don’t Care,” and all
outputs are High-Z. RP# unlocks the boot block and
overrides the condition of WP# when at V
HH, and must be
held at V
IH during all other modes of operation.
14 24 28 OE# Input
Output Enable: Enables data output buffers when LOW.
When OE# is HIGH, the output buffers are disabled.
33 – 47 BYTE# Input
Byte Enable: If BYTE# = HIGH, the upper byte is active
through DQ8–DQ15. If BYTE# = LOW, DQ8–DQ14 are
High-Z, and all data is accessed through DQ0–DQ7. DQ15/
(A-1) becomes the least significant address input.
11, 10, 9, 8,
7, 6, 5, 4,
42, 41, 40,
39, 38, 37,
36, 35, 34, 3
21, 20, 19,
18, 17,
16,15, 14, 8,
7, 36, 6, 5,
4, 3, 2, 1,
40, 13
25, 24, 23,
22, 21, 20,
19, 18, 8, 7,
6, 5, 4, 3, 2,
1, 48, 17
A0–A17/
(A18)
Input
Address Inputs: Select a unique, 16-bit word or 8-bit byte.
The Q15/(A-1) input becomes the lowest order address
when BYTE# = LOW (MT28F400B5) to allow for a selection
of an 8-bit byte from the 524,288 available.
31 – 45 DQ15
(A-1)
Input/
Output
Data I/O: MSB of data when BYTE# = HIGH. Address Input:
LSB of address input when BYTE# = LOW during READ or
WRITE operation.
15, 17, 19,
21, 24, 26,
28, 30
25-28, 32-35 29, 31, 33,
35, 38, 40,
42, 44
DQ0–DQ7 Input/
Output
Data I/Os: Data output pins during any READ operation or
data input pins during a WRITE. These pins are used to
input commands to the CEL.
16, 18, 20,
22, 25, 27,
29
– 30, 32, 34,
36, 39, 41,
43
DQ8–
DQ14
Input/
Output
Data I/Os: Data output pins during any READ operation or
data input pins during a WRITE when BYTE# = HIGH. These
pins are High-Z when BYTE# is LOW.
11113V
PP Supply
Write/Erase Supply Voltage: From a WRITE or ERASE
CONFIRM until completion of the WRITE or ERASE, VPP
must be at V
PPH (5V). VPP = “Don’t Care” during all other
operations.
23 30, 31 37 V
CC Supply
Power Supply: +5V ±10%.
13, 32 23, 39 27, 46 V
SS Supply
Ground.
– 29, 37, 38 9, 10, 15, 16 NC –
No Connect: These pins may be driven or left unconnected.
4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
5
Notes: 1. L = VIL (LOW), H = VIH (HIGH), X = VIL or VIH (“Don’t Care”).
2. V
PPH = 5V.
3. Operation must be preceded by ERASE SETUP command.
4. Operation must be preceded by WRITE SETUP command.
5. The READ ARRAY command must be issued before reading the array after writing or erasing.
6. When WP# = V
IH, RP# may be at VIH or VHH.
7. A1–A8, A10–A17 = V
IL.
8. Value reflects DQ8–DQ15.
TRUTH TABLE (MT28F400B5)
1
FUNCTION RP# CE# OE# WE# WP# BYTE# A0 A9 VPP
DQ0–
DQ7
DQ8–
DQ14
DQ15/
A - 1
Standby
H H X X X X X X X High-Z High-Z High-Z
Reset
L X X X X X X X X High-Z High-Z High-Z
READ
READ (word mode)
H L L H X H X X X Data-Out Data-Out Data-Out
READ (byte mode)
H L L H X L X X X Data-Out High-Z A-1
Output Disable
H L H H X X X X X High-Z High-Z High-Z
WRITE/ERASE (EXCEPT BOOT BLOCK)
2
ERASE SETUP
HLHLX X XXX 20h X X
ERASE CONFIRM
3
HLHLX X XXVPPH D0h X X
WRITE SETUP
H L H L X X X X X 10h/40h X X
WRITE (word mode)
4
HLHLX H XXVPPH Data-In Data-In Data-In
WRITE (byte mode)
4
HLHLX L XXVPPH Data-In X A-1
READ ARRAY
5
HLHLX X XXX FFh X X
WRITE/ERASE (BOOT BLOCK)
2
ERASE SETUP
HLHLX X XXX 20h X X
ERASE CONFIRM
3
VHH LHLXXXXVPPH D0h X X
ERASE CONFIRM
3, 6
HLHLH X XXVPPH D0h X X
WRITE SETUP
H L H L X X X X X 10h/40h X X
WRITE (word mode)
4
VHH LHLX H XXVPPH Data-In Data-In Data-In
WRITE (word mode)
4, 6
HLHLH H XXVPPH Data-In Data-In Data-In
WRITE (byte mode)
4
VHH LHLX L XXVPPH Data-In X A-1
WRITE (byte mode)
4, 6
HLHLH L XXVPPH Data-In X A-1
READ ARRAY
5
HLHLX X XXX FFh X X
DEVICE IDENTIFICATION
7
Manufacturer
Compatibility (word
mode)
8
HLLHX H LVID X 89hX 00h –
Manufacturer
Compatibility (byte
mode)
HLLHX L LV
ID X 89h High-Z X
Device (word mode, top
boot)
8
HLLHX H HVID X 70h 44h –
Device (byte mode, top
boot)
HLLHX L HV
ID X 70h High-Z X
Device (word mode,
bottom boot)
8
HLLHX H HVID X 71h 44h –
Device (byte mode,
bottom boot)
HLLHX L HV
ID X 71h High-Z X
4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
6
Notes: 1. L = VIL, H = VIH, X = VIL or VIH.
2. V
PPH = 5V.
3. Operation must be preceded by ERASE SETUP command.
4. Operation must be preceded by WRITE SETUP command.
5. The READ ARRAY command must be issued before reading the array after writing or erasing.
6. When WP# = V
IH, RP# may be at VIH or VHH.
7. A1–A8, A10–A18 = V
IL.
TRUTH TABLE (MT28F004B5)
1
FUNCTION RP# CE# OE# WE# WP# A0 A9 VPP DQ0–DQ7
Standby
HHXXXXXX High-Z
RESET
LXXXXXXX High-Z
READ
READ
HL LHXXXX Data-Out
Output Disable
HLHHXXXX High-Z
WRITE/ERASE (EXCEPT BOOT BLOCK)2
ERASE SETUP
HLHLXXXX 20h
ERASE CONFIRM
3
HLHLXXXVPPH D0h
WRITE SETUP
HLHLXXXX 10h/40h
WRITE
4
HLHLXXXVPPH Data-In
READ ARRAY
5
HLHLXXXX FFh
WRITE/ERASE (BOOT BLOCK)
2
ERASE SETUP
HLHLXXXX 20h
ERASE CONFIRM
3
VHH LHLXXXVPPH D0h
ERASE CONFIRM
3, 6
HLHLHXXVPPH D0h
WRITE SETUP
HLHLXXXX 10h/40h
WRITE
4
VHH LHLXXXVPPH Data-In
WRITE
4, 6
HLHLHXXVPPH Data-In
READ ARRAY
5
HLHLXXXX FFh
DEVICE IDENTIFICATION
7
Manufacturer Compatibility
HLLHXLV
ID X 89h
Device (top boot)
HLLHXHV
ID X 78h
Device (bottom boot)
HLLHXHV
ID X 79h

4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
7
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The MT28F004B5 and MT28F400B5 Flash memories incorporate a number of features ideally suited for
system firmware. The memory array is segmented into
individual erase blocks. Each block may be erased
without affecting data stored in other blocks. These
memory blocks are read, written and erased with commands to the command execution logic (CEL). The
CEL controls the operation of the internal state
machine (ISM), which completely controls all WRITE,
BLOCK ERASE, and VERIFY operations. The ISM protects each memory location from over-erasure and
optimizes each memory location for maximum data
retention. In addition, the ISM greatly simplifies the
control necessary for writing the device in-system or in
an external programmer.
The Functional Description provides detailed information on the operation of the MT28F004B5 and
MT28F400B5 and is organized into these sections:
•Overview
• Memory Architecture
• Output (READ) operations
•Input Operations
• Command Set
•ISM Status Register
• Command Execution
• Error Handling
•WRITE/ERASE Cycle Endurance
•Power Usage
•Power-Up
OVERVIEW
Smart 5 Technology (B5)
Smart 5 technology allows maximum flexibility for
in-system READ, WRITE and ERASE operations. For
5V-only systems, WRITE and ERASE operations may be
executed with a V
PP voltage of 5V. Due to process tech-
nology advances, 5V V
PP is optimal for application and
production programming.
Seven Independently Erasable
Memory Blocks
The MT28F004B5 and MT28F400B5 are organized
into seven independently erasable memory blocks that
allow portions of the memory to be erased without
affecting the rest of the memory data. A special boot
block is hardware-protected against inadvertent erasure or writing by requiring either a super-voltage on
the RP# pin or driving the WP# pin HIGH. One of these
two conditions must exist, along with the V
PP voltage
(5V) on the V
PP pin, before a WRITE or ERASE will be
performed on the boot block. The remaining blocks
require that only the V
PP voltage be present on the VPP
pin before writing or erasing.
Hardware-Protected Boot
This block of the memory array can be erased or
written only when the RP# pin is taken to V
HH or when
the WP# pin is brought HIGH. This provides additional
security for the core firmware during in-system firmware updates should an unintentional power fluctuation or system reset occur. The MT28F004B5 and
MT28F400B5 are available with the boot block starting
at the bottom of the address space (“B” suffix) or the
top of the address space (“T” suffix).
Selectable Bus Size (MT28F400B5 only)
The MT28F400B5 allows selection of an 8-bit (512K
x 8) or 16-bit (256K x 16) data bus for reading and writing the memory. The BYTE# pin is used to select the
bus width. In the x16 configuration, control data is
read or written only on the lower eight bits (DQ0–
DQ7).
Data written to the memory array utilizes all active
data pins for the selected configuration. When the x8
configuration is selected, data is written in byte form;
when the x16 configuration is selected, data is written
in word form.
Internal State Machine (ISM)
Block erase and byte/word write timing are simplified with an ISM that controls all erase and write algorithms in the memory array. The ISM ensures
protection against overerasure and optimizes write
margin to each cell.
During WRITE operations, the ISM automatically
increments and monitors WRITE attempts, verifies
write margin on each memory cell and updates the
ISM status register. When BLOCK ERASE is performed,
the ISM automatically overwrites the entire addressed
block (eliminates overerasure), increments and monitors ERASE attempts, and sets bits in the ISM status
register.
ISM Status Register
The ISM status register enables an external processor to monitor the status of the ISM during WRITE and
ERASE operations. Two bits of the 8-bit status register
are set and cleared entirely by the ISM. These bits indicate whether the ISM is busy with a WRITE or ERASE
task and when an ERASE has been suspended. Addi-

4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
8
tional error information is set in three other bits: V
PP
status, write status, and erase status.
Command Execution Logic (CEL)
The CEL receives and interprets commands to the
device. These commands control the operation of the
ISM and the read path (i.e., memory array, ID register
or status register). Commands may be issued to the
CEL while the ISM is active. However, there are restrictions on what commands are allowed in this condition.
See the Command Execution section for more detail.
Deep Power-down Mode
To allow for maximum power conservation, the
MT28F004B5 and MT28F400B5 feature a very low current, deep power-down mode. To enter this mode, the
RP# pin is taken to V
SS ±0.2V. In this mode, the current
draw is a maximum of 20µA at 5V V
CC. Entering deep
power-down also clears the status register and sets the
ISM to the read array mode.
MEMORY ARCHITECTURE
The MT28F004B5 and MT28F400B5 memory array
architecture is designed to allow sections to be erased
without disturbing the rest of the array. The array is
divided into seven addressable blocks that vary in size
and are independently erasable. When blocks rather
than the entire array are erased, total device endurance is enhanced, as is system flexibility. Only the
ERASE function is block-oriented. All READ and
WRITE operations are done on a random-access basis.
The boot block is protected from unintentional
ERASE or WRITE operations with a hardware protection circuit that requires a super-voltage be applied to
RP# or that the WP# pin be driven HIGH before erasure
is commenced. The boot block is intended for the core
firmware required for basic system functionality. The
remaining six blocks do not require that either of these
two conditions be met before WRITE or ERASE operations.
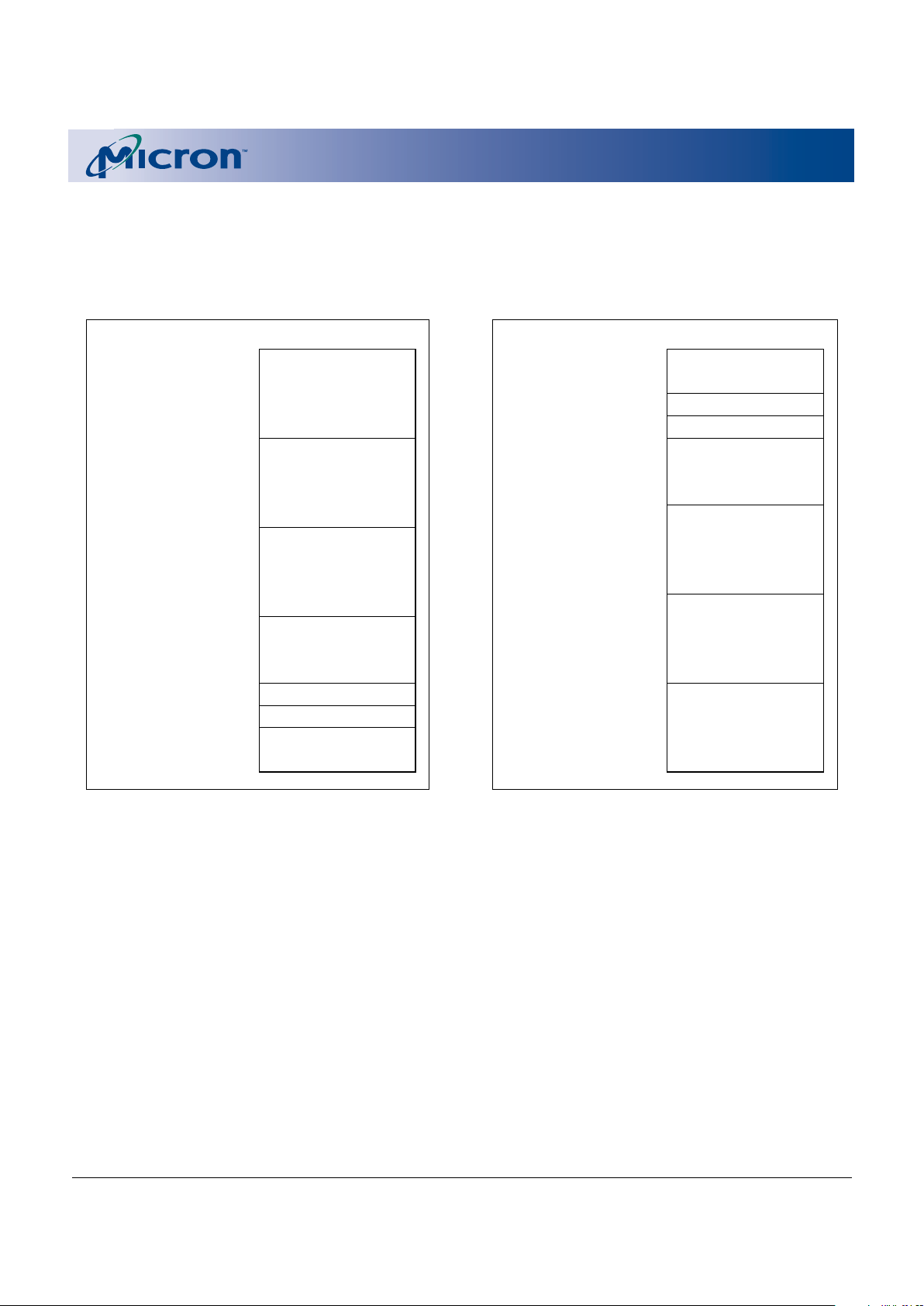
Boot Block
The hardware-protected boot block provides extra
security for the most sensitive portions of the firmware. This 16KB block may only be erased or written
when the RP# pin is at the specified boot block unlock
voltage (V
HH) or when the WP# pin is VIH. During a
WRITE or ERASE of the boot block, the RP# pin must
be held at V
HH or the WP# pin held HIGH until the
ERASE or WRITE is completed. The V
PP pin must be at
V
PPH (5V) when the boot block is written to or erased.
The MT28F004B5 and MT28F400B5 are available in
two configurations and top or bottom boot block. The
top boot block version supports processors of the x86
variety. The bottom boot block version is intended for
680X0 and RISC applications. Figure 1 illustrates the
memory address maps associated with these two versions.
Parameter Blocks
The two 8KB parameter blocks store less sensitive
and more frequently changing system parameters and
also may store configuration or diagnostic coding.
These blocks are enabled for erasure when the V
PP pin
is at V
PPH. No super-voltage unlock or WP# control is
required.
Main Memory Blocks
The four remaining blocks are general-purpose
memory blocks and do not require a super-voltage on
RP# or WP# control to be erased or written. These
blocks are intended for code storage, ROM-resident
applications or operating systems that require in-system update capability.
4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
9
Figure 1
Memory Address Maps
Bottom Boot
MT28F004B5/400B5xx-xxB
Top Bo ot
MT28F004B5/400B5xx-xxT
3FFFFh
30000h
2FFFFh
20000h
1FFFFh
10000h
0FFFFh
04000h
03FFFh
03000h
02FFFh
02000h
01FFFh
00000h
128KB Main Block
128KB Main Block
128KB Main Block
96KB Main Block
8KB Parameter Block
8KB Parameter Block
16KB Boot Block
WORD ADDRESS
7FFFFh
60000h
5FFFFh
40000h
3FFFFh
20000h
1FFFFh
08000h
07FFFh
06000h
05FFFh
04000h
03FFFh
00000h
BYTE ADDRESS
3FFFFh
3E000h
3DFFFh
3D000h
3CFFFh
3C000h
3BFFFh
30000h
2FFFFh
20000h
1FFFFh
10000h
0FFFFh
00000h
16KB Boot Block
8KB Parameter Block
8KB Parameter Block
96KB Main Block
128KB Main Block
128KB Main Block
128KB Main Block
WORD ADDRESS
7FFFFh
7C000h
7BFFFh
7A000h
79FFFh
78000h
77FFFh
60000h
5FFFFh
40000h
3FFFFh
20000h
1FFFFh
00000h
BYTE ADDRESS

4Mb
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK FLASH MEMORY
4Mb Smart 5 Boot Block Flash Memory ©2002, Micron Technology Inc.
MT28F004B5_3.fm - Rev. 3, Pub. 8/2002
10
OUTPUT (READ) OPERATIONS
The MT28F004B5 and MT28F400B5 feature three
different types of READS. Depending on the current
mode of the device, a READ operation produces data
from the memory array, status register or device identification register. In each of these three cases, the
WE#, CE# and OE# inputs are controlled in a similar
manner. Moving between modes to perform a specific
read is described in the Command Execution section.
Memory Array
To read the memory array, WE# must be HIGH, and
OE# and CE# must be LOW. Valid data is output on the
DQ pins when these conditions have been met and a
valid address is given. Valid data remains on the DQ
pins until the address changes, or until OE# or CE#
goes HIGH, whichever occurs first. The DQ pins continue to output new data after each address transition
as long as OE# and CE# remain LOW.
The MT28F400B5 features selectable bus widths.
When the memory array is accessed as a 256K x 16,
BYTE# is HIGH, and data will be output on DQ0–
DQ15. To access the memory array as a 512K x 8,
BYTE# must be LOW, DQ8–DQ14 are High-Z, and all
data is output on DQ0–DQ7. The DQ15/(A - 1) pin
becomes the lowest order address input so that
524,288 locations can be read.
After power-up or RESET, the device is automatically in the array read mode. All commands and their
operations are described in the Command Set and
Command Execution sections.
Status Register
Performing a READ of the status register requires
the same input sequencing as a READ of the array
except that the address inputs are “Don’t Care.” The
status register contents are always output on DQ0–
DQ7, regardless of the condition of BYTE# on the
MT28F400B5. DQ8–DQ15 are LOW when BYTE# is
HIGH, and DQ8–DQ14 are High-Z when BYTE# is
LOW. Data from the status register is latched on the
falling edge of OE# or CE#, whichever occurs last. If the
contents of the status register change during a READ of
the status register, either OE# or CE# may be toggled
while the other is held LOW to update the output.
Following a WRITE or ERASE, the device automatically enters the status register read mode. In addition,
a READ during a WRITE or ERASE produces the status
register contents on DQ0–DQ7. When the device is in
the erase suspend mode, a READ operation produces
the status register contents until another command is
issued, while in certain other modes, READ STATUS
REGISTER may be given to return to the status register
read mode. All commands and their operations are
described in the Command Set and Command Execution sections.
Identification Registers
A READ of the two 8-bit device identification registers requires the same input sequencing as a READ of
the array. WE# must be HIGH, and OE# and CE# must
be LOW. However, ID register data is output only on
DQ0–DQ7, regardless of the condition of BYTE# on the
MT28F400B5. A0 is used to decode between the two
bytes of the device ID register; all other address inputs
are “Don’t Care.” When A0 is LOW, the manufacturer
compatibility ID is output, and when A0 is HIGH, the
device ID is output. DQ8–DQ15 are High-Z when
BYTE# is LOW. When BYTE# is HIGH, DQ8–DQ15 are
00h when the manufacturer compatibility ID is read
and 44h when the device ID is read.
To get to the identification register read mode,
READ IDENTIFICATION may be issued while the
device is in certain other modes. In addition, the identification register read mode can be reached by applying a super-voltage (V
ID) to the A9 pin. Using this
method, the ID register can be read while the device is
in any mode. When A9 is returned to V
IL or VIH, the
device returns to the previous mode.
INPUT OPERATIONS
The DQ pins are used either to input data to the
array or to input a command to the CEL. A command
input issues an 8-bit command to the CEL to control
the mode of operation of the device. A WRITE is used
to input data to the memory array. The following section describes both types of inputs. More information
describing how to use the two types of inputs to write
or erase the device is provided in the Command Execution section.
Commands
To perform a command input, OE# must be HIGH,
and CE# and WE# must be LOW. Addresses are “Don’t
Care” but must be held stable, except during an ERASE
CONFIRM (described in a later section). The 8-bit
command is input on DQ0–DQ7, while DQ8–DQ15 are
“Don’t Care” on the MT28F400B5. The command is
latched on the rising edge of CE# (CE#-controlled) or
WE# (WE#-controlled), whichever occurs first. The
condition of BYTE# on the MT28F400B5 has no effect
on a command input.
 Loading...
Loading...