MICRON MT28C6428P20FM-85T, MT28C6428P20FM-85TET, MT28C6428P20FM-85B, MT28C6428P20FM-80T, MT28C6428P18FM-85TET Datasheet
...
1
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
‡
‡
PRODUCTS AND SPECIFICATIONS DISCUSSED HEREIN ARE FOR EVALUATION AND REFERENCE PURPOSES ONLY AND ARE
SUBJECT TO CHANGE BY MICRON WITHOUT NOTICE. PRODUCTS ARE ONLY WARRANTED BY MICRON TO MEET MICRON’S
PRODUCTION DATA SHEET SPECIFICATIONS.
FLASH AND SRAM
COMBO MEMORY
MT28C6428P20
MT28C6428P18
Low Voltage, Extended Temperature
0.18µm Process Technology
FEATURES
• Flexible dual-bank architecture
• Support for true concurrent operations with no
latency:
Read bank b during program bank a and vice versa
Read bank b during erase bank a and vice versa
• Organization: 4,096K x 16 (Flash)
512K x 16 (SRAM)
• Basic configuration:
Flash
Bank a (16Mb Flash for data storage)
– Eight 4K-word parameter blocks
– Thirty-one 32K-word blocks
Bank b (48Mb Flash for program storage)
– Ninety-six 32K-word main blocks
SRAM
8Mb SRAM for data storage
– 512K-words
• F_VCC, VCCQ, F_VPP, S_VCC voltages
MT28C6428P20
1.80V (MIN)/2.20V (MAX) F_VCC read voltage
1.80V (MIN)/2.20V (MAX) S_VCC read voltage
1.80V (MIN)/2.20V (MAX) VCCQ
MT28C6428P18
1.70V (MIN)/1.90V (MAX) F_VCC read voltage
1.70V (MIN)/1.90V (MAX) S_VCC read voltage
1.70V (MIN)/1.90V (MAX) VCCQ
MT28C6428P20/P18
1.80V (TYP) F_VPP (in-system PROGRAM/ERASE)
1.0V (MIN) S_VCC (SRAM data retention)
12V ±5% (HV) F_VPP (in-house programming and
accelerated programming algorithm [APA]
activation)
• Asynchronous access time
Flash access time: 80ns @ 1.80V F_VCC
SRAM access time: 80ns @ 1.80V S_VCC
• Page Mode read access
Interpage read access: 80ns @ 1.80V F_VCC
Intrapage read access: 30ns @ 1.80V F_VCC
• Low power consumption
• Enhanced suspend options
ERASE-SUSPEND-to-READ within same bank
PROGRAM-SUSPEND-to-READ within same bank
ERASE-SUSPEND-to-PROGRAM within same bank
• Read/Write SRAM during program/erase of Flash
• Dual 64-bit chip protection registers for security
purposes
• PROGRAM/ERASE cycles
100,000 WRITE/ERASE cycles per block
• Cross-compatible command set support
Extended command set
Common flash interface (CFI) compliant
OPTIONS MARKING
• Timing
80ns -80
85ns -85
• Boot Block Configuration
Top T
Bottom B
• Operating Voltage Range
F_VCC = 1.70V–1.90V 18
F_VCC = 1.80V–2.20V 20
• Operating Temperature Range
Commercial (0oC to +70oC) None
Extended (-40oC to +85oC) ET
• Package
67-ball FBGA (8 x 8 grid) FM
Part Number Example:
MT28C6428P20FM-80 BET
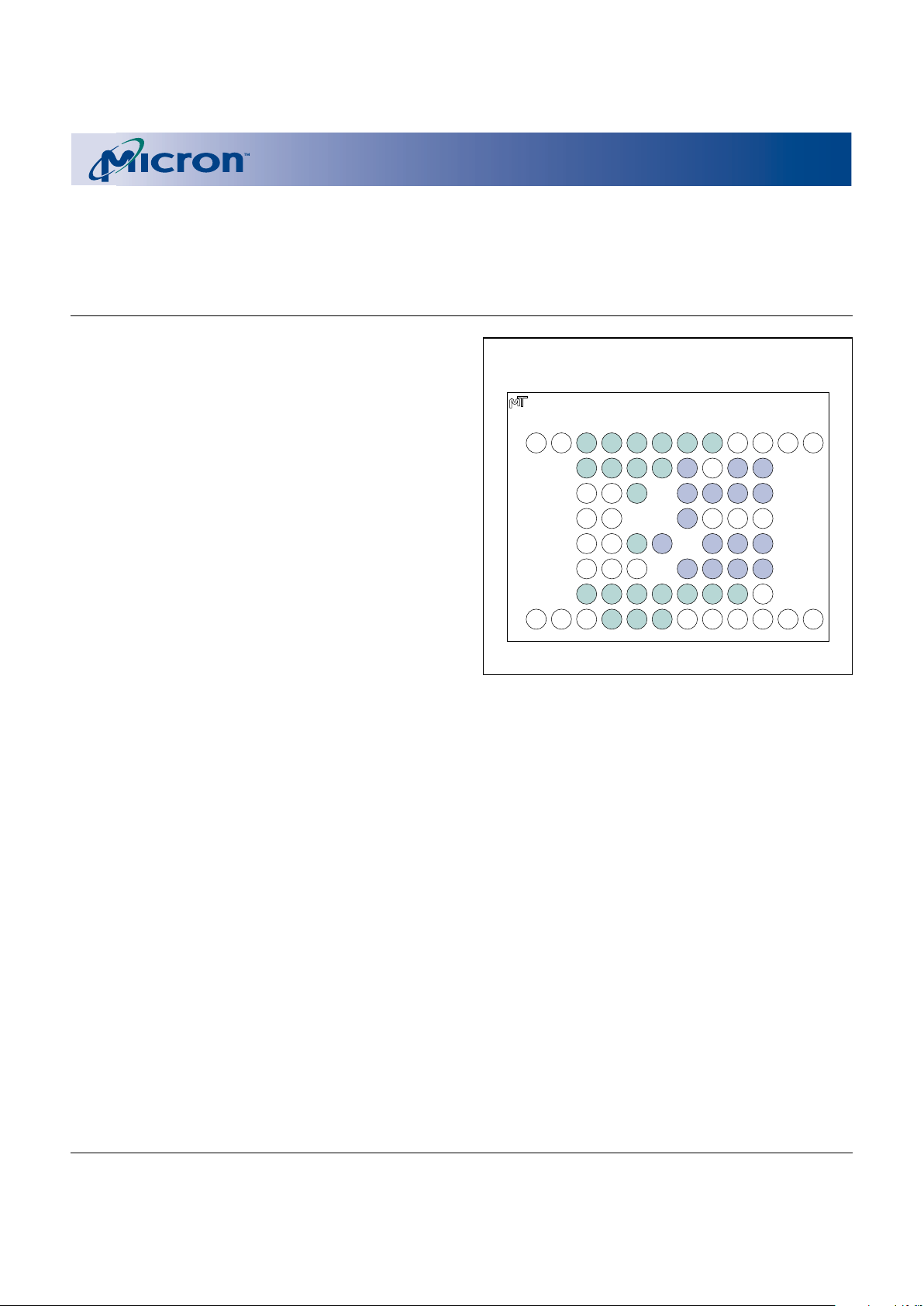
BALL ASSIGNMENT
67-Ball FBGA (Top View)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Top View
(Ball Down)
NC
NC
A14
A9
DQ11
A6
A0
A15
A10
A21
A19
S_OE#
A7
A4
A20
A16
F_WE#
V
SS
F_WP#
S_LB#
A18
F_V
CC
A12
S_WE#
DQ6
S_CE2
DQ10
DQ8
A2
F_V
SS
F_V
SS
DQ14
DQ4
S_V
CC
DQ2
DQ0
A1
F_OE#
V
cc
Q
DQ7
DQ5
F_V
CC
DQ3
DQ1
S_CE1#
NCNCNCNCNC
A13
DQ15
DQ13
DQ12
DQ9
A3
F_CE#
NC
NC
A11
A8
NC
F_RP#
F_V
PP
S_UB#
A17
A5
2
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
Table 1
Cross Reference for Abbreviated Device Marks
PRODUCT SAMPLE MECHANICAL
PART NUMBER MARKING MARKING SAMPLE MARKING
MT28C6428P20FM-80 BET FW454 FX454 FY454
MT28C6428P20FM-80 TET FW453 FX453 FY453
MT28C6428P18FM-85 BET FW455 FX455 FY455
MT28C6428P18FM-85 TET FW452 FX452 FY452
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MT28C6428P20 and MT28C6428P18 combination Flash and SRAM memory devices provide a compact, low-power solution for systems where PCB real
estate is at a premium. The dual-bank Flash devices
are high-performance, high-density, nonvolatile
memory with a revolutionary architecture that can significantly improve system performance.
This new architecture features:
• A two-memory-bank configuration supporting
dual-bank operation;
• A high-performance bus interface providing a fast
page data transfer; and
• A conventional asynchronous bus interface.
The devices also provide soft protection for blocks
by configuring soft protection registers with dedicated
command sequences. For security purposes, dual 64bit chip protection registers are provided.
The embedded WORD WRITE and BLOCK ERASE
functions are fully automated by an on-chip write state
machine (WSM). The WSM simplifies these operations
and relieves the system processor of secondary tasks.
An on-chip status register, one for each bank, can be
used to monitor the WSM status to determine the
progress of a PROGRAM/ERASE command.
The erase/program suspend functionality allows
compatibility with existing EEPROM emulation software packages.
The devices take advantage of a dedicated power
source for the Flash memory (F_VCC) and a dedicated
power source for the SRAM (S_VCC), both at 1.70V–2.20V
for optimized power consumption and improved noise
immunity. A dedicated I/O power supply (VCCQ) is provided with an extended range (1.70V–2.20V), to allow a
direct interface to most common logic controllers and
to ensure improved noise immunity. The separate
S_VCC pin for the SRAM provides data retention capability when required. The data retention S_VCC is speci-
fied as low as 1.0V. The MT28C6428P20 and
MT28C6428P18 devices support two F_VPP voltage
ranges, an in-circuit voltage of 0.9V–2.2V and a production compatibility voltage of 12V ±5%. The 12V ±5%
F_VPP2 is supported for a maximum of 100 cycles and 10
cumulative hours.
The MT28C6428P20 and MT28C6428P18 contain
an asynchronous 8Mb SRAM organized as 512K-words
by 16 bits. The devices are fabricated using an advanced CMOS process and high-speed/ultra-lowpower circuit technology, and then are packaged in a
67-ball FBGA package with 0.80mm pitch.
ARCHITECTURE AND MEMORY
ORGANIZATION
The Flash devices contain two separate banks of
memory (bank a and bank b) for simultaneous READ
and WRITE operations, which are available in the following bank segmentation configuration:
• Bank a comprises one-fourth of the memory and
contains 8 x 4K-word parameter blocks, while the
remainder of bank a is split into 31 x 32K-word
blocks.
• Bank b represents three-fourths of the memory, is
equally sectored, and contains 96 x 32K-word
blocks.
Figures 2 and 3 show the bottom and top memory
organizations.
DEVICE MARKING
Due to the size of the package, Micron’s standard
part number is not printed on the top of each device.
Instead, an abbreviated device mark comprised of a
five-digit alphanumeric code is used. The abbreviated
device marks are cross referenced to Micron part numbers in Table 1.
3
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
PART NUMBERING INFORMATION
Micron’s low-power devices are available with sev-
eral different combinations of features (see Figure 1).
Table 2
Valid Part Number Combinations
1
BOOT BLOCK OPERATING
ACCESS STARTING TEMPERATURE
PART NUMBER TIME (ns) ADDRESS RANGE
MT28C6428P20FM-80 BET 80 Bottom -40oC to +85oC
MT28C6428P20FM-80 TET 80 Top -40oC to +85oC
MT28C6428P18FM-85 BET 85 Bottom -40oC to +85oC
MT28C6428P18FM-85 TET 85 Top -40
o
C to +85oC
NOTE: 1. For part number combinations not listed in this table, please contact
your Micron representative.
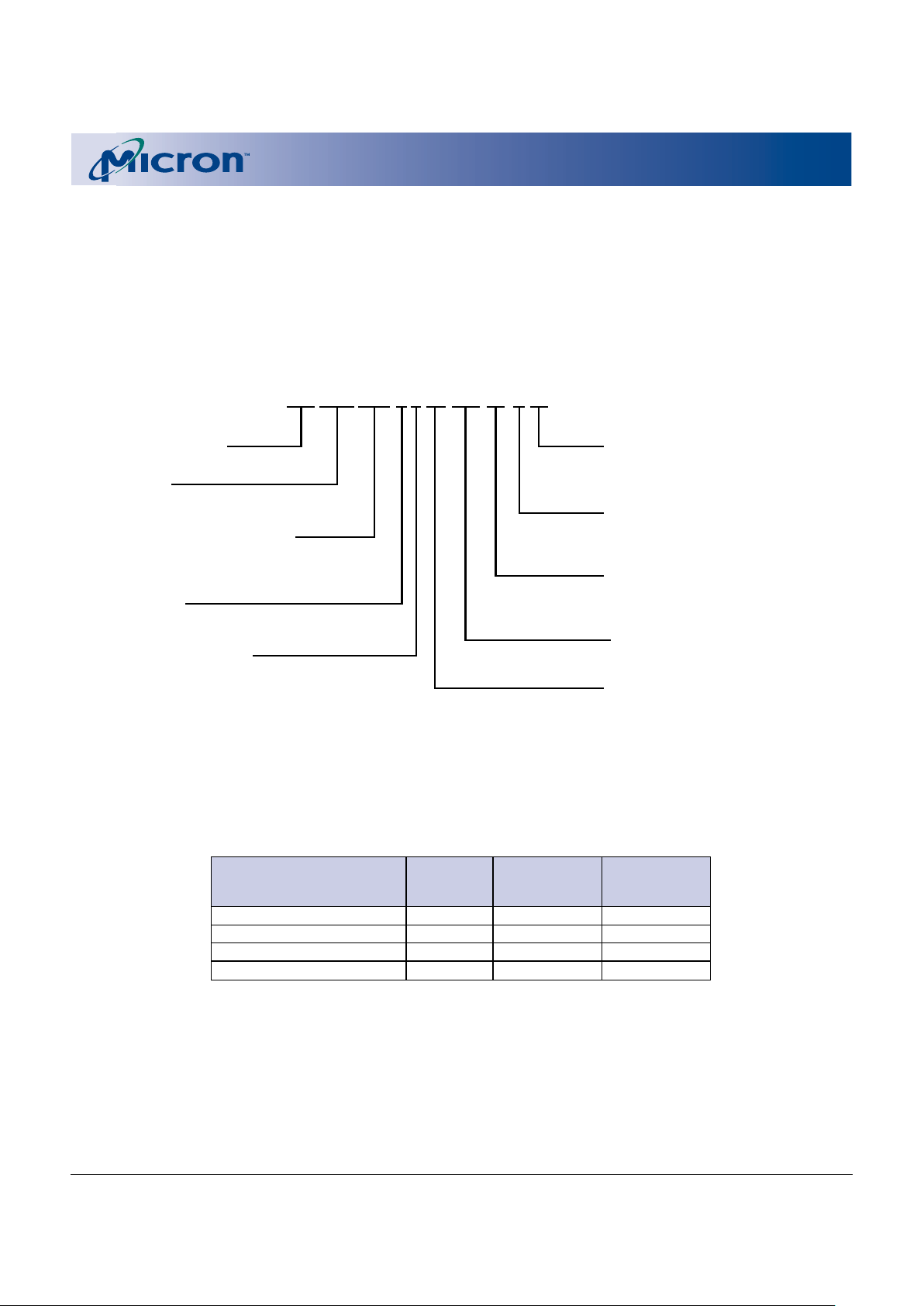
Figure 1
Part Number Chart
Valid combinations of features and their corresponding part numbers are listed in Table 2.
MT 28C 642 8 P 20 FM-80 T ET
Micron Technology
Flash Family
28C = Dual-Supply Flash/SRAM Combo
Density/Organization/Banks
642 = 64Mb (4,096K x 16)
bank a = 1/4; bank b = 3/4
SRAM Density
8 = 8Mb SRAM (512K x 16)
Access Time
-80 = 80ns
-85 = 85ns
Read Mode Operation
P = Asynchronous/Page Read
Package Code
FM = 67-ball FBGA (8 x 8 grid)
Operating Temperature Range
None = Commercial (0ºC to +70ºC)
ET = Extended (-40ºC to +85ºC)
Boot Block Starting Address
B = Bottom boot
T = Top boot
Operating Voltage Range
20 = 1.80V–2.20V V
CC
18 = 1.70V–1.90V
4
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
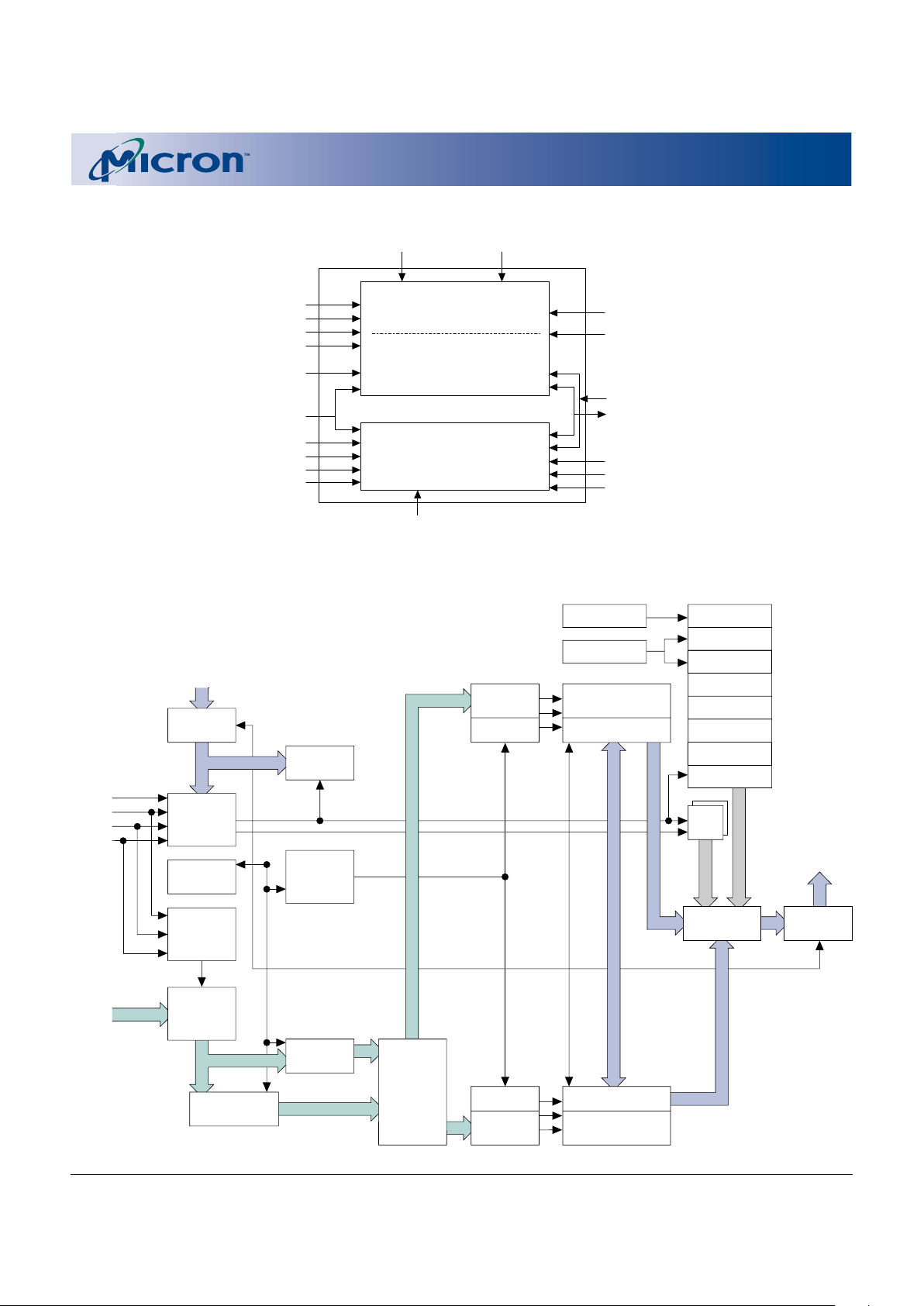
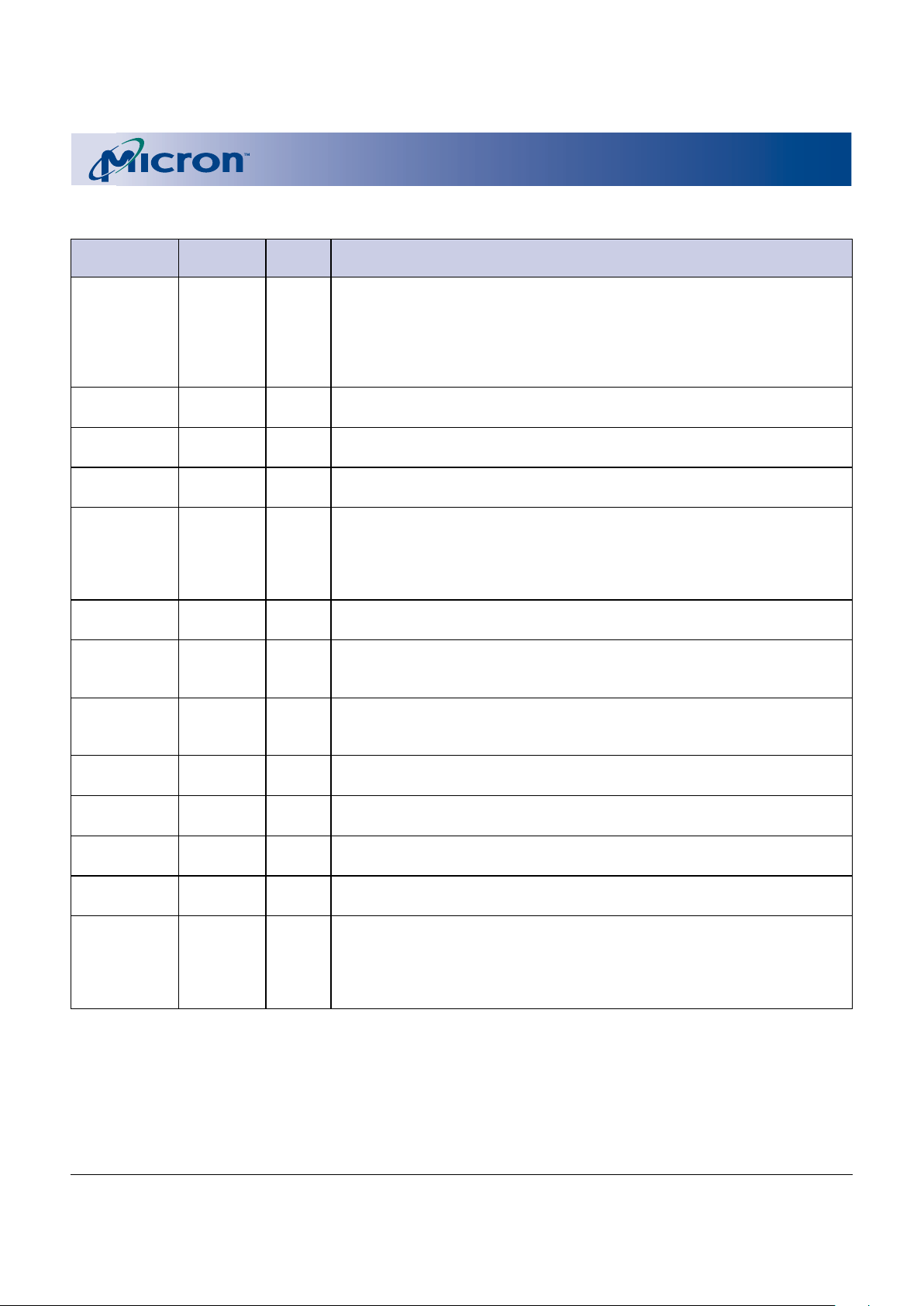
BLOCK DIAGRAM
F_V
PP
S_OE#
S_CE2
S_CE1#
S_WE#
DQ0
–
DQ15
A19
–
A20
A0
–
A18
F_RP#
F_CE#
F_OE#
F_WE#
F_V
CC
F_WP#
F_
V
SS
FLASH
SRAM
S_
V
SS
S_UB#
S_LB#
4,096K x 16
512K x 16
Bank a
Bank b
S_V
CC
VCCQ
FLASH FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Address
Input
Buffer
X DEC
Y/Z DEC
Data Input
Buffer
Output
Multiplexer
Address
CNT/WSM
Output
Buffer
Status
Reg.
WSM
Program/
Erase
Pump Voltage
Generators
Address Latch
DQ0-DQ15
DQ0–DQ15
CSM
F_RST#
F_CE#
X DEC
Y/Z DEC
F_WE#
F_OE#
I/O Logic
A0–A21
Address
Multiplexer
Bank 2 Blocks
Y/Z Gating/Sensing
Data
Register
Bank 1 Blocks
Y/Z Gating/Sensing
ID Reg.
RCR
Block Lock
Device ID
Manufacturer’s ID
OTP
Query
PR Lock
Query/OTP
PR Lock
5
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
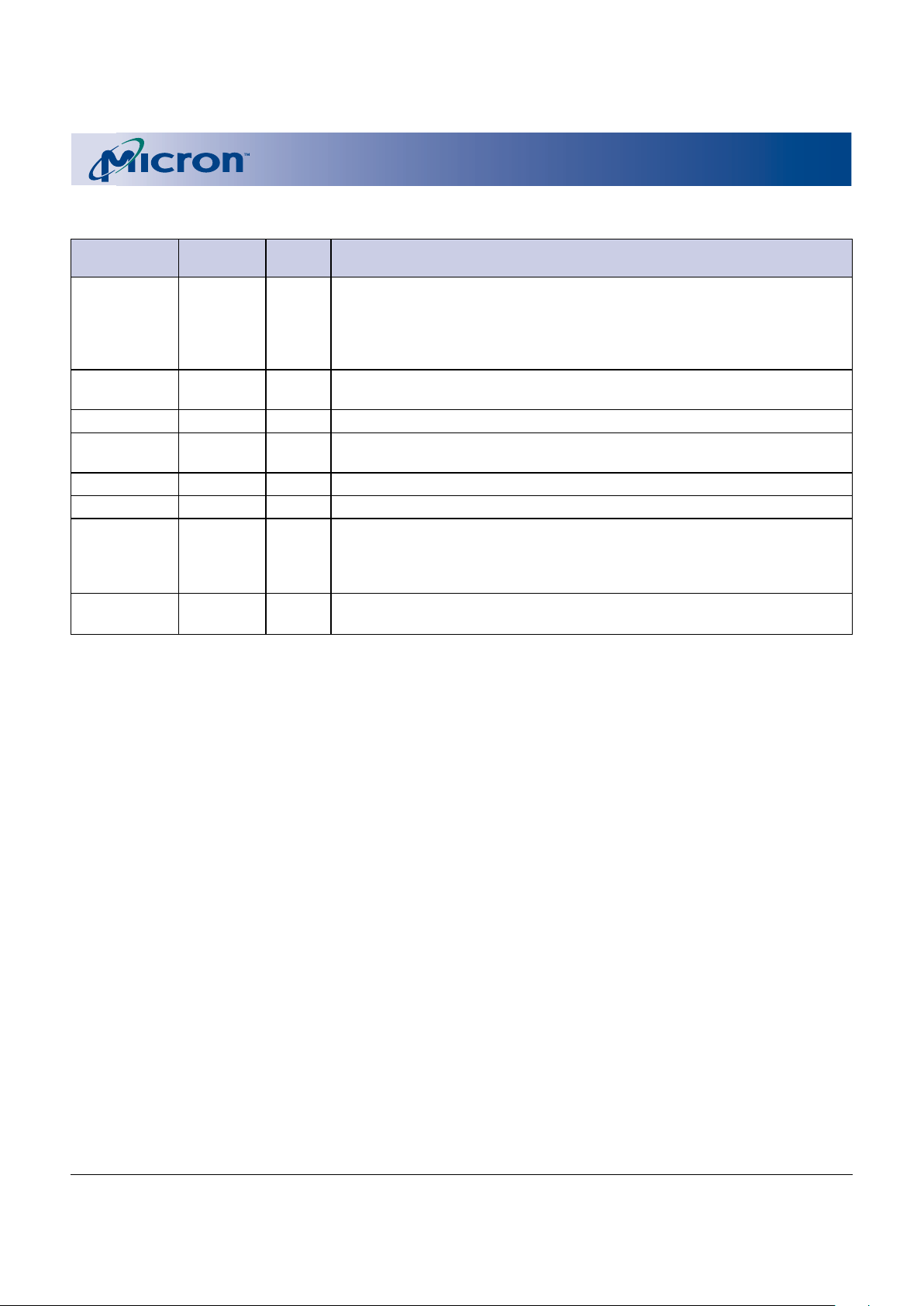
BALL DESCRIPTIONS
67-BALL FBGA
NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
H6, G9, G8, G7, A0–A21 Input Address Inputs: Inputs for the addresses during READ and WRITE
H5, H4, G6, G5, operations. Addresses are internally latched during READ and WRITE
B4, B6, B5, A4, cycles. Flash: A0–A21; SRAM: A0–A18.
A8, A7, A6, A5,
B3, G4, G3, E5,
A3, C5
H7 F_CE# Input Flash Chip Enable: Activates the device when LOW. When CE# is HIGH,
the device is disabled and goes into standby power mode.
H9 F_OE# Input Flash Output Enable: Enables Flash output buffers when LOW. When
F_OE# is HIGH, the output buffers are disabled.
C3 F_WE# Input Flash Write Enable: Determines if a given cycle is a Flash WRITE cycle.
F_WE# is active LOW.
D4 F_RP# Input Reset. When F_RP# is a logic LOW, the device is in reset, which drives
the outputs to High-Z and resets the WSM. When F_RP# is a logic HIGH,
the device is in standard operation. When F_RP# transitions from logic
LOW to logic HIGH, the device resets all blocks to locked and defaults to
the read array mode.
E3 F_WP# Input Flash Write Protect. Controls the lock down function of the flexible
locking feature.
G10 S_CE1# Input SRAM Chip Enable1: Activates the SRAM when it is LOW. HIGH level
deselects the SRAM and reduces the power consumption to standby
levels.
D8 S_CE2 Input SRAM Chip Enable2: Activates the SRAM when it is HIGH. LOW level
deselects the SRAM and reduces the power consumption to standby
levels.
F5 S_OE# Input SRAM Output Enable: Enables SRAM output buffers when LOW. When
S_OE# is HIGH, the output buffers are disabled.
B8 S_WE# Input SRAM Write Enable: Determines if a given cycle is an SRAM WRITE cycle.
S_WE# is active LOW.
F3 S_LB# Input SRAM Lower Byte: When LOW, it selects the SRAM address lower byte
(DQ0–DQ7).
F4 S_UB# Input SRAM Upper Byte: When LOW, it selects the SRAM address upper byte
(DQ8–DQ15).
F9, F10, E9, DQ0–DQ15 Input/ Data Inputs/Outputs: Input array data on the second CE# and WE#
E10, C9, C10, Output cycle during PROGRAM command. Input commands to the command
C8, B10, F8, user interface when CE# and WE# are active. Output data when CE#
F7, E8, E6, D7, and OE# are active.
C7, B9, B7
(continued on next page)
6
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
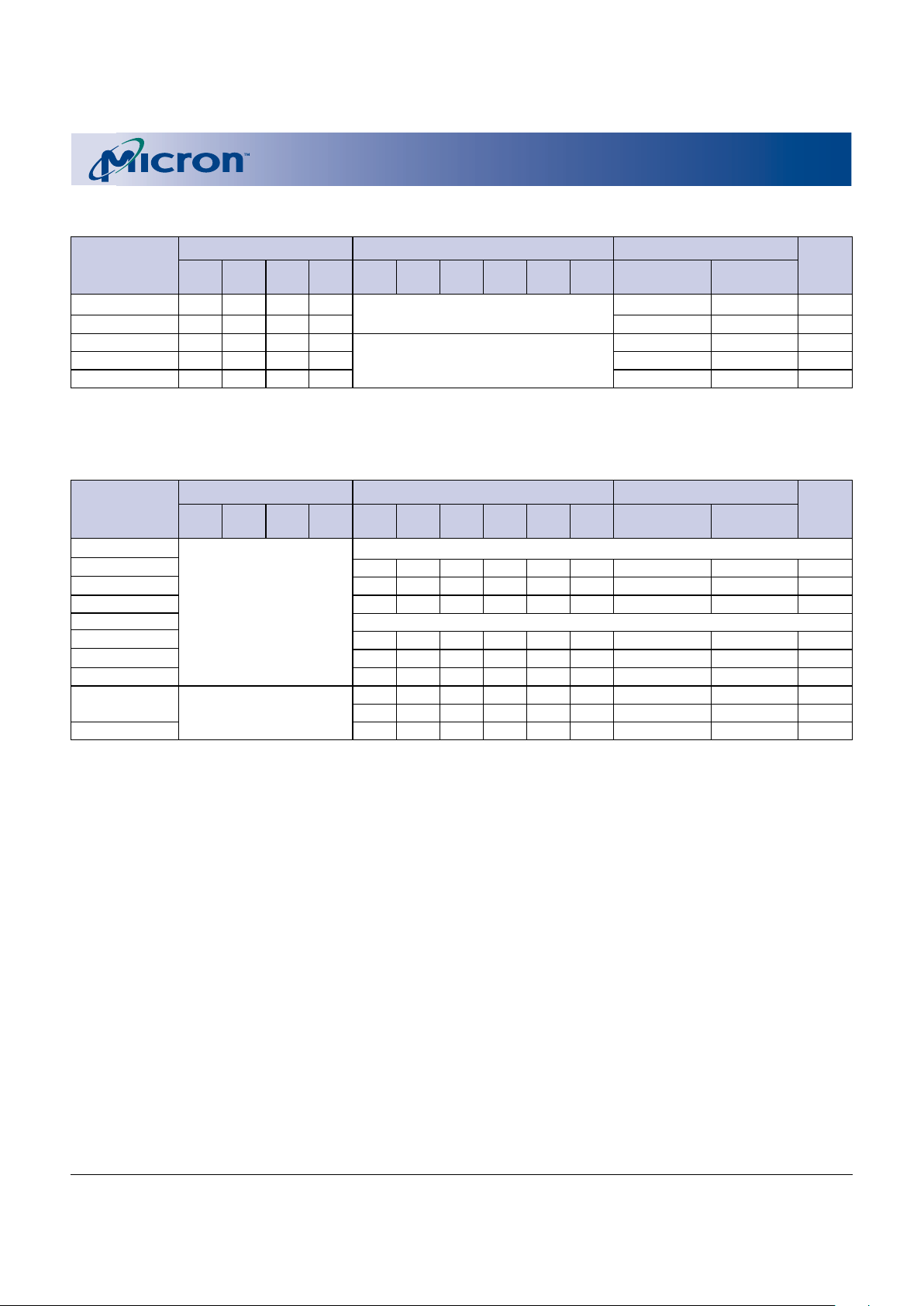
BALL DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
67-BALL FBGA
NUMBERS SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
E4 F_VPP Input/ Flash Program/Erase Power Supply: [0.9V–2.2V or 11.4V–12.6V].
Supply Operates as input at logic levels to control complete device protection.
Provides backward compatibility for factory programming when driven
to 11.4V–12.6V. A lower F_V
PP voltage range (0.0V–2.2V) is available.
Contact factory for more information.
D10, H3 F_V
CC Supply Flash Power Supply: [1.70V–1.90V or 1.80V–2.20V]. Supplies power for
device operation.
A9, H8 F_VSS Supply Flash Specific Ground: Do not float any ground ball.
D9 S_VCC Supply SRAM Power Supply: [1.70V–1.90V or 1.80V–2.20V]. Supplies power for
device operation.
D3 S_VSS Supply SRAM Specific Ground: Do not float any ground ball.
A10 VCCQ Supply I/O Power Supply: [1.70–1.90V or 1.80V–2.20V].
A1, A2, A11, NC – No Connect: Lead is not internally connected; it may be driven or
A12, C4, H1, floated.
H2, H10, H11,
H12
C6, D5, D6, – – Contact balls not mounted; corresponding position on PCB can be used
E7, F6 to reduce routing complexity.
7
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
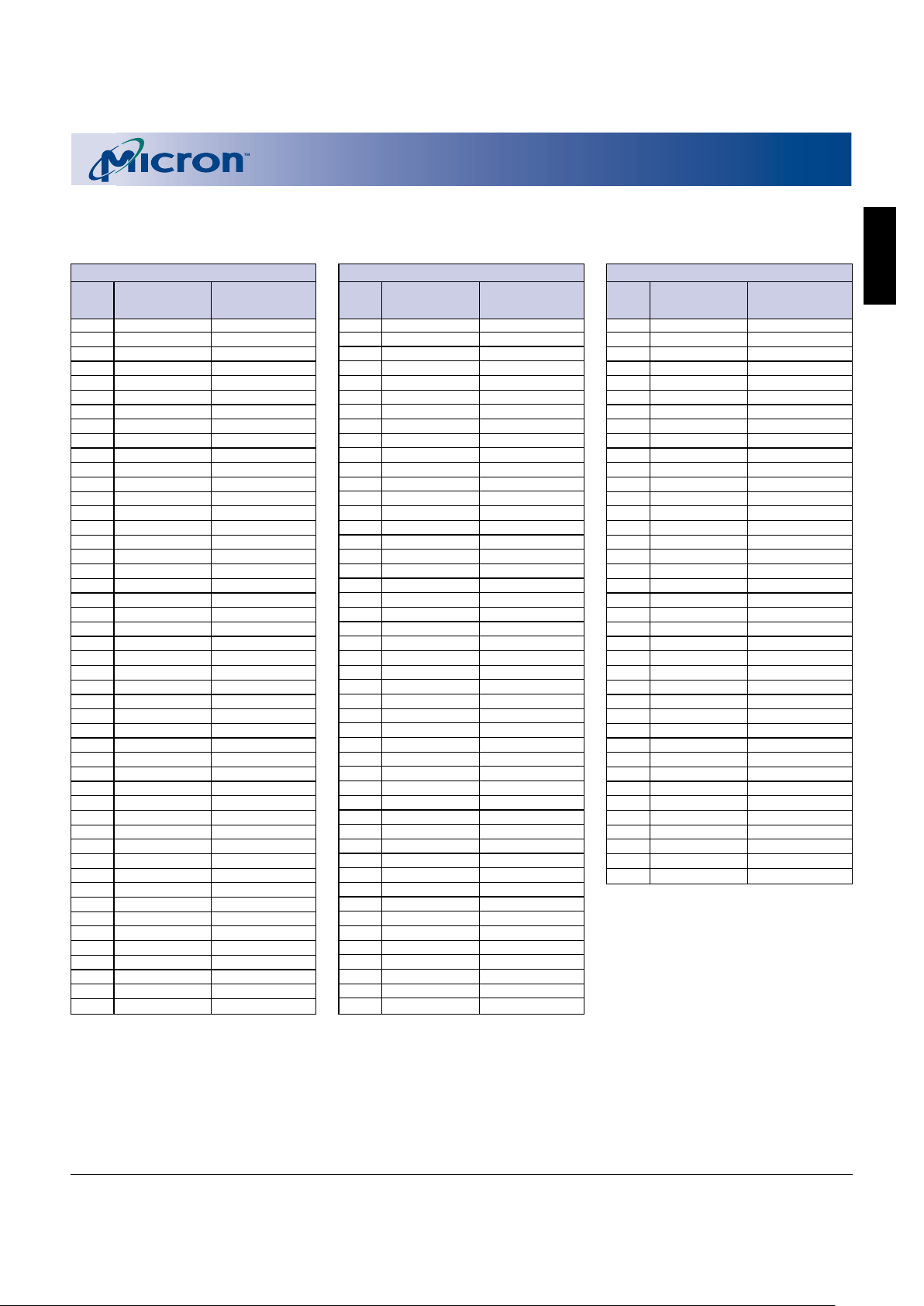
NOTE: 1. Two devices may not drive the memory bus at the same time.
2. Allowable Flash read modes include read array, read query, read configuration, and read status.
3. Outputs are dependent on a separate device controlling bus outputs.
4. Modes of the Flash and SRAM can be interleaved so that while one is disabled, the other controls outputs.
5. SRAM is enabled and/or disabled with the logical function: S_CE1# or S_CE2.
6. Simultaneous operations can exist, as long as the operations are interleaved such that only one device attempts to
control the bus outputs at a time.
7. Data output on lower byte only; upper byte High-Z.
8. Data output on upper byte only; lower byte High-Z.
9. Data input on lower byte only.
10. Data input on upper byte only.
TRUTH TABLE – FLASH
FLASH SIGNALS SRAM SIGNALS MEMORY OUPUT
MODES
F_RP# F_CE# F_OE# F_WE# S_CE1# S_CE2 S_OE# S_WE# S_UB# S_LB#
MEMORY DQ0–DQ15 NOTES
BUS CONTROL
Read H L L H SR AM mu st be H ig h- Z Flash DOUT 1, 2, 3
Write H L H L Flash DIN 1
Standby H H X X Other High-Z 4
Output Disable H L H H SRAM any mode allowable Other High-Z 4, 5
Reset L X X X Other High-Z 4, 6
TRUTH TABLE – SRAM
FLASH SIGNALS SRAM SIGNALS MEMORY OUPUT
MODES
F_RP# F_CE# F_OE# F_WE# S_CE1# S_CE2 S_OE# S_WE# S_UB# S_LB#
MEMORY DQ0–DQ15 NOTES
BUS CONTROL
Read
DQ0–DQ15 L H L H L L SRAM DOUT 1, 3
DQ0–DQ7 L H L H H L SRAM DOUT LB 7
DQ8–DQ15 Flash must be High-Z L H L H L H SRAM DOUT UB 8
Write
DQ0–DQ15 L H H L L L SRAM DIN 1, 3
DQ0–DQ7 L H H L H L SRAM DIN LB 9
DQ8–DQ15 L H H L L H SRAM DIN UB 10
Standby H X X X X X Other High-Z 4
Flash any mode allowable X L X X X X Other High-Z 4
Output Disable L H X X X X Other High-Z 4
FLASH
8
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
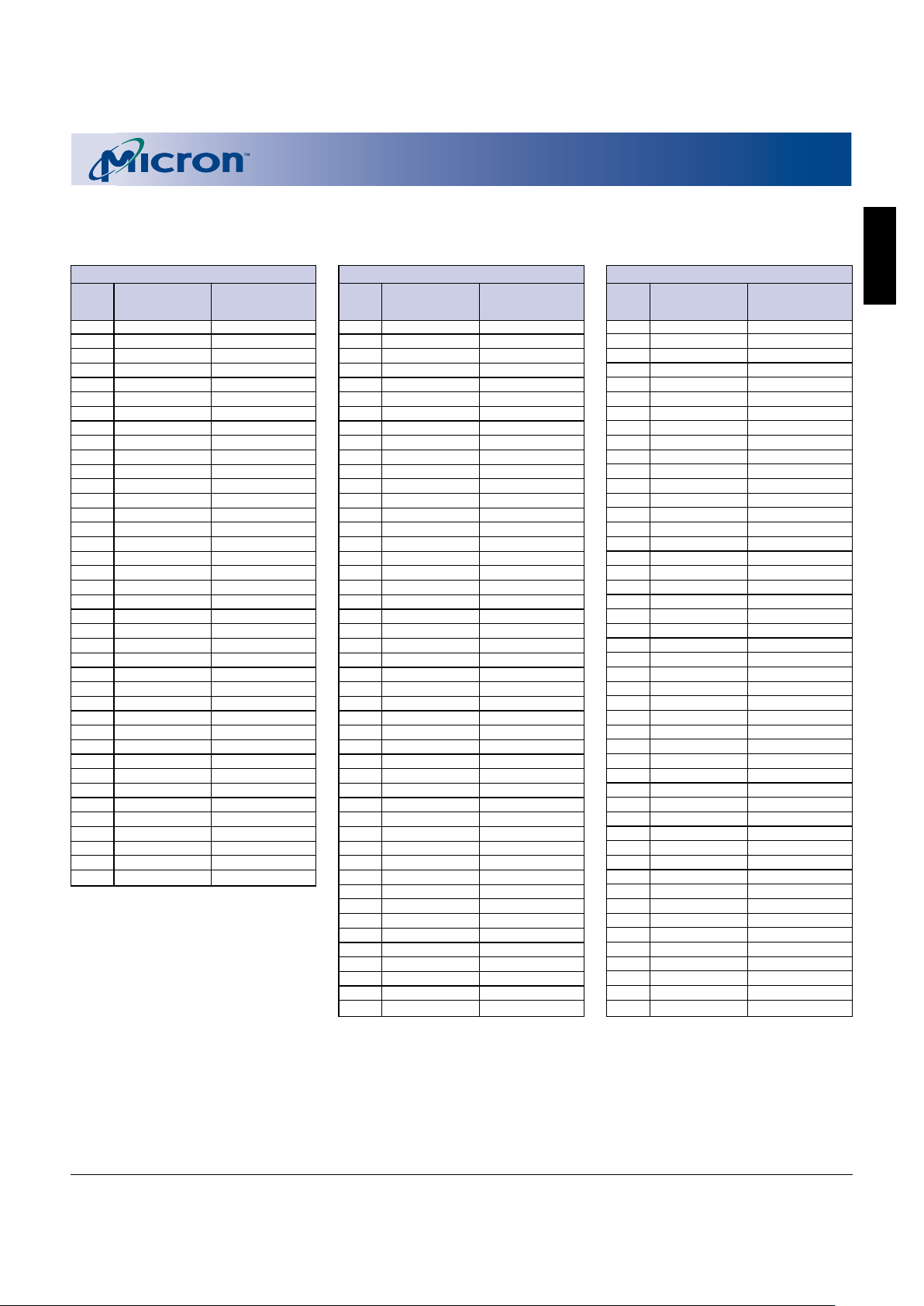
Figure 2
Bottom Boot Block Device
Bank a = 16Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/ (x16)
K-words)
38 64/32 0F8000h–0FFFFFh
37 64/32 0F0000h–0F7FFFh
36 64/32 0E8000h–0EFFFFh
35 64/32 0E0000h–0E7FFFh
34 64/32 0D8000h–0DFFFFh
33 64/32 0D0000h–0D7FFFh
32 64/32 0C8000h–0CFFFFh
31 64/32 0C0000h–0C7FFFh
30 64/32 0B8000h–0BFFFFh
29 64/32 0B0000h–0B7FFFh
28 64/32 0A8000h–0AFFFFh
27 64/32 0A0000h–0A7FFFh
26 64/32 098000h–097FFFh
25 64/32 090000h–097FFFh
24 64/32 088000h–087FFFh
23 64/32 080000h–087FFFh
22 64/32 078000h–07FFFFh
21 64/32 070000h–077FFFh
20 64/32 068000h–067FFFh
19 64/32 060000h–067FFFh
18 64/32 058000h–05FFFFh
17 64/32 050000h–057FFFh
16 64/32 048000h–04FFFFh
15 64/32 040000h–047FFFh
14 64/32 038000h–03FFFFh
13 64/32 030000h–037FFFh
12 64/32 028000h–02FFFFh
11 64/32 020000h–027FFFh
10 64/32 018000h–01FFFFh
9 64/32 010000h–017FFFh
8 64/32 008000h–00FFFFh
7 8/4 007000h–007FFFh
6 8/4 006000h–006FFFh
5 8/4 005000h–005FFFh
4 8/4 004000h–004FFFh
3 8/4 003000h–003FFFh
2 8/4 002000h–002FFFh
1 8/4 001000h–001FFFh
0 8/4 000000h–000FFFh
Bank b = 48Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/ (x16)
K-words)
134 64/32 3F8000h–3FFFFFh
133 64/32 3F0000h–3F7FFFh
132 64/32 3E8000h–3EFFFFh
131 64/32 3E0000h–3E7FFFh
130 64/32 3D8000h–3DFFFFh
129 64/32 3D0000h–3D7FFFh
128 64/32 3C8000h–3CFFFFh
127 64/32 3C0000h–3C7FFFh
126 64/32 3B8000h–3BFFFFh
125 64/32 3B0000h–3B7FFFh
124 64/32 3A8000h–3AFFFFh
123 64/32 3A0000h–3A7FFFh
122 64/32 398000h–39FFFFh
121 64/32 390000h–397FFFh
120 64/32 388000h–38FFFFh
119 64/32 380000h–387FFFh
118 64/32 378000h–37FFFFh
117 64/32 370000h–377FFFh
116 64/32 368000h–36FFFFh
115 64/32 360000h–367FFFh
114 64/32 358000h–35FFFFh
113 64/32 350000h–357FFFh
112 64/32 348000h–34FFFFh
111 64/32 340000h–347FFFh
110 64/32 338000h–33FFFFh
109 64/32 330000h–337FFFh
108 64/32 328000h–32FFFFh
107 64/32 320000h–327FFFh
106 64/32 318000h–31FFFFh
105 64/32 310000h–317FFFh
104 64/32 308000h–30FFFFh
103 64/32 300000h–307FFFh
102 64/32 2F8000h–2FFFFFh
101 64/32 2F0000h–2F7FFFh
100 64/32 2E8000h–2EFFFFh
99 64/32 2E0000h–2E7FFFh
98 64/32 2D8000h–2DFFFFh
97 64/32 2D0000h–2D7FFFh
96 64/32 2C8000h–2CFFFFh
95 64/32 2C0000h–2C7FFFh
94 64/32 2B8000h–2BFFFFh
93 64/32 2B0000h–2B7FFFh
92 64/32 2A8000h–2AFFFFh
91 64/32 2A0000h–2A7FFFh
90 64/32 298000h–29FFFFh
89 64/32 290000h–297FFFh
88 64/32 288000h–28FFFFh
87 64/32 280000h–287FFFh
Bank b = 48Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/ (x16)
K-words)
86 64/32 278000H–27FFFFh
85 64/32 270000h–277FFFh
84 64/32 268000h–26FFFFh
83 64/32 260000h–267FFFh
82 64/32 258000h–25FFFFh
81 64/32 250000h–257FFFh
80 64/32 248000h–24FFFFh
79 64/32 240000h–247FFFh
78 64/32 238000h–23FFFFh
77 64/32 230000h–237FFFh
76 64/32 228000h–22FFFFh
75 64/32 220000h–227FFFh
74 64/32 218000h–21FFFFh
73 64/32 210000h–217FFFh
72 64/32 208000h–20FFFFh
71 64/32 200000h–207FFFh
70 64/32 1F8000h–1FFFFFh
69 64/32 1F0000h–1F7FFFh
68 64/32 1E8000h–1EFFFFh
67 64/32 1E0000h–1E7FFFh
66 64/32 1D8000h–1DFFFFh
65 64/32 1D0000h–1D7FFFh
64 64/32 1C8000h–1CFFFFh
63 64/32 1C0000h–1C7FFFh
62 64/32 1B8000h–1BFFFFh
61 64/32 1B0000h–1B7FFFh
60 64/32 1A8000h–1AFFFFh
59 64/32 1A0000h–1A7FFFh
58 64/32 198000h–19FFFFh
57 64/32 190000h–197FFFh
56 64/32 188000h–18FFFFh
55 64/32 180000h–187FFFh
54 64/32 178000h–17FFFFh
53 64/32 170000h–177FFFh
52 64/32 168000h–16FFFFh
51 64/32 160000h–167FFFh
50 64/32 158000h–15FFFFh
49 64/32 150000h–157FFFh
48 64/32 148000h–14FFFFh
47 64/32 140000h–147FFFh
46 64/32 138000h–13FFFFh
45 64/32 130000h–137FFFh
44 64/32 128000h–12FFFFh
43 64/32 120000h–127FFFh
42 64/32 118000h–11FFFFh
41 64/32 110000h–117FFFh
40 64/32 108000h–10FFFFh
39 64/32 100000h–107FFFh
FLASH
9
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
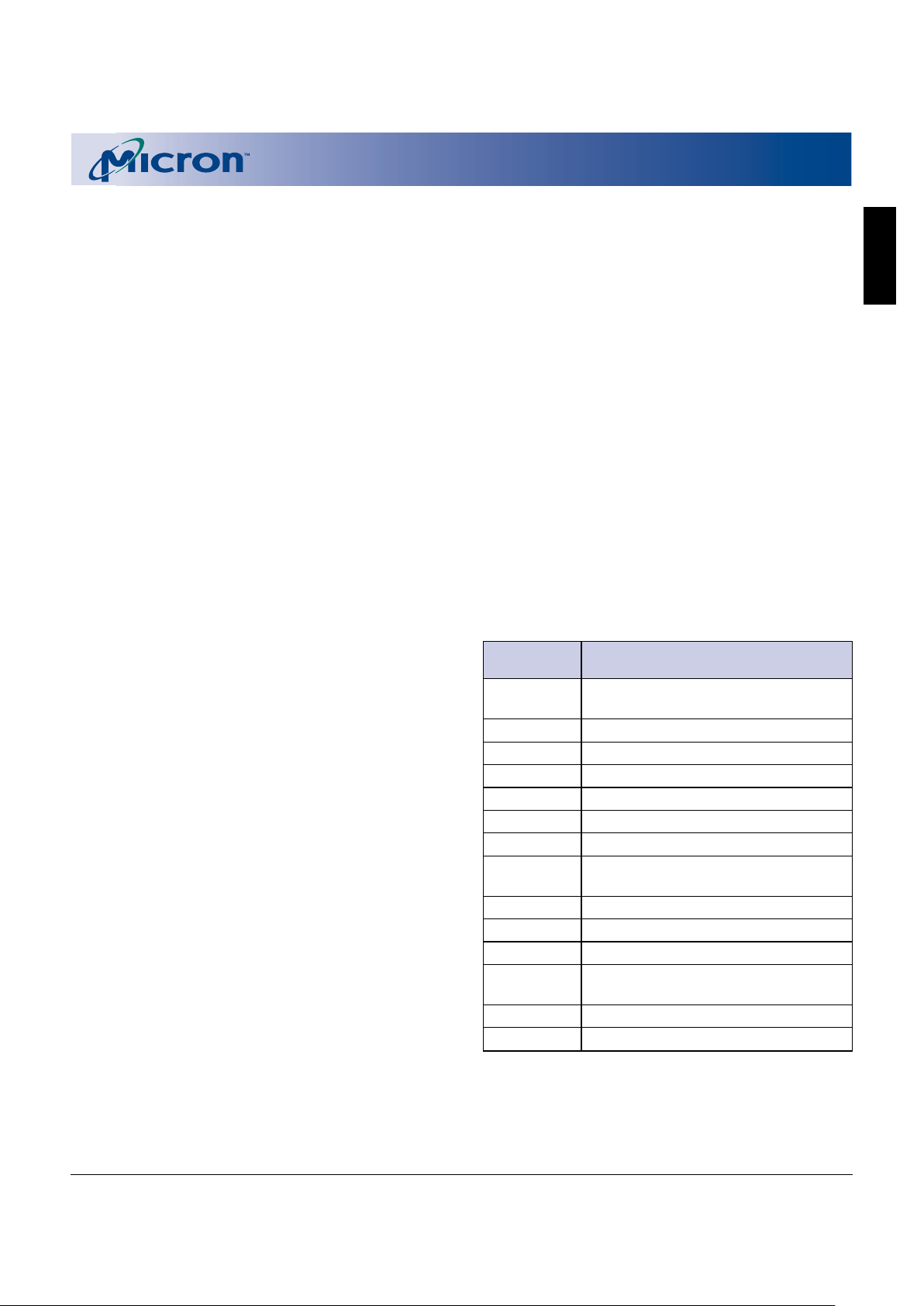
Figure 3
Top Boot Block Device
Bank a = 16Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/ (x16)
K-words)
134 8/4 3FF000h–3FFFFFh
133 8/4 3FE000h–3FEFFFh
132 8/4 3FD000h–3FDFFFh
131 8/4 3FC000h–3FCFFFh
130 8/4 3FB000h–3FBFFFh
129 8/4 3FA000h–3FAFFFh
128 8/4 3F9000h–3F9FFFh
127 8/4 3F8000h–3F8FFFh
126 64/32 3F0000h–3F7FFFh
125 64/32 3E8000h–3EFFFFh
124 64/32 3E0000h–3E7FFFh
123 64/32 3D8000h–3DFFFFh
122 64/32 3D0000h–3D7FFFh
121 64/32 3C8000h–3CFFFFh
120 64/32 3C0000h–3C7FFFh
119 64/32 3B8000h–3BFFFFh
118 64/32 3B0000h–3B7FFFh
117 64/32 3A8000h–3AFFFFh
116 64/32 3A0000h–3A7FFFh
115 64/32 398000h–39FFFFh
114 64/32 390000h–397FFFh
113 64/32 388000h–38FFFFh
112 64/32 380000h–387FFFh
111 64/32 378000h–37FFFFh
110 64/32 370000h–377FFFh
109 64/32 368000h–36FFFFh
108 64/32 360000h–367FFFh
107 64/32 358000h–35FFFFh
106 64/32 350000h–357FFFh
105 64/32 348000h–34FFFFh
104 64/32 340000h–347FFFh
103 64/32 338000h–33FFFFh
102 64/32 330000h–337FFFh
101 64/32 328000h–32FFFFh
100 64/32 320000h–327FFFh
99 64/32 318000h–31FFFFh
98 64/32 310000h–317FFFh
97 64/32 308000h–30FFFFh
96 64/32 300000h–307FFFh
Bank b = 48Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/ (x16)
K-words)
95 64/32 2F8000h–2FFFFFh
94 64/32 2F0000h–2F7FFFh
93 64/32 2E8000h–2EFFFFh
92 64/32 2E0000h–2E7FFFh
91 64/32 2D8000h–2DFFFFh
90 64/32 2D0000h–2D7FFFh
89 64/32 2C8000h–2CFFFFh
88 64/32 2C0000h–2C7FFFh
87 64/32 2B8000h–2BFFFFh
86 64/32 2B0000h–2B7FFFh
85 64/32 2A8000h–2AFFFFh
84 64/32 2A0000h–2A7FFFh
83 64/32 298000h–29FFFFh
82 64/32 290000h–297FFFh
81 64/32 288000h–28FFFFh
80 64/32 280000h–287FFFh
79 64/32 278000h–27FFFFh
78 64/32 270000h–277FFFh
77 64/32 268000h–26FFFFh
76 64/32 260000h–267FFFh
75 64/32 258000h–25FFFFh
74 64/32 250000h–257FFFh
73 64/32 248000h–24FFFFh
72 64/32 240000h–247FFFh
71 64/32 238000h–23FFFFh
70 64/32 230000h–237FFFh
69 64/32 228000h–22FFFFh
68 64/32 220000h–227FFFh
67 64/32 218000h–21FFFFh
66 64/32 210000h–217FFFh
65 64/32 208000h–20FFFFh
64 64/32 200000h–207FFFh
63 64/32 1F8000h–1FFFFFh
62 64/32 1F0000h–1F7FFFh
61 64/32 1E8000h–1EFFFFh
60 64/32 1E0000h–1E7FFFh
59 64/32 1D8000h–1DFFFFh
58 64/32 1D0000h–1D7FFFh
57 64/32 1C8000h–1CFFFFh
56 64/32 1C0000h–1C7FFFh
55 64/32 1B8000h–1BFFFFh
54 64/32 1B0000h–1B7FFFh
53 64/32 1A8000h–1AFFFFh
52 64/32 1A0000h–1A7FFFh
51 64/32 198000h–19FFFFh
50 64/32 190000h–197FFFh
49 64/32 188000h–18FFFFh
48 64/32 180000h–187FFFh
Bank b = 48Mb
Block Block Size Address Range
(K-bytes/ (x16)
K-words)
47 64/32 178000h–17FFFFh
46 64/32 170000h–177FFFh
45 64/32 168000h–16FFFFh
44 64/32 160000h–167FFFh
43 64/32 158000h–15FFFFh
42 64/32 150000h–157FFFh
41 64/32 148000h–14FFFFh
40 64/32 140000h–147FFFh
39 64/32 138000h–13FFFFh
38 64/32 130000h–137FFFh
37 64/32 128000h–12FFFFh
36 64/32 120000h–127FFFh
35 64/32 118000h–11FFFFh
34 64/32 110000h–117FFFh
33 64/32 108000h–10FFFFh
32 64/32 100000h–107FFFh
31 64/32 0F8000h–0FFFFFh
30 64/32 0F0000h–0F7FFFh
29 64/32 0E8000h–0EFFFFh
28 64/32 0E0000h–0E7FFFh
27 64/32 0D8000h–0DFFFFh
26 64/32 0D0000h–0D7FFFh
25 64/32 0C8000h–0CFFFFh
24 64/32 0C0000h–0C7FFFh
23 64/32 0B8000h–0BFFFFh
22 64/32 0B0000h–0B7FFFh
21 64/32 0A8000h–0AFFFFh
20 64/32 0A0000h–0A7FFFh
19 64/32 098000h–09FFFFh
18 64/32 090000h–097FFFh
17 64/32 088000h–08FFFFh
16 64/32 080000h–087FFFh
15 64/32 078000h–07FFFFh
14 64/32 070000h–077FFFh
13 64/32 068000h–06FFFFh
12 64/32 060000h–067FFFh
11 64/32 058000h–05FFFFh
10 64/32 050000h–057FFFh
9 64/32 048000h–04FFFFh
8 64/32 040000h–047FFFh
7 64/32 038000h–03FFFFh
6 64/32 030000h–037FFFh
5 64/32 028000h–02FFFFh
4 64/32 020000h–027FFFh
3 64/32 018000h–01FFFFh
2 64/32 010000h–017FFFh
1 64/32 008000h–00FFFFh
0 64/32 000000h–007FFFh
FLASH
10
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
FLASH MEMORY OPERATING MODES
COMMAND STATE MACHINE
Commands are issued to the command state machine (CSM) using standard microprocessor write timings. The CSM acts as an interface between external
microprocessors and the internal write state machine
(WSM). The available commands are listed in Table 3,
their definitions are given in Table 4 and their descriptions in Table 5. Program and erase algorithms are automated by the on-chip WSM. Table 7 shows the CSM
transition states.
Once a valid PROGRAM/ERASE command is entered, the WSM executes the appropriate algorithm,
which generates the necessary timing signals to control the device internally. A command is valid only if the
exact sequence of WRITEs is completed. After the WSM
completes its task, the write state machine status
(WSMS) bit (SR7) (see Table 8) is set to a logic HIGH
level (VIH), allowing the CSM to respond to the full command set again.
OPERATIONS
Device operations are selected by entering a standard JEDEC 8-bit command code with conventional
microprocessor timings into an on-chip CSM through
I/Os DQ0–DQ7. The number of bus cycles required to
activate a command is typically one or two. The first
operation is always a WRITE. Control signals F_CE#
and F_WE# must be at a logic LOW level (VIL), and F_OE#
and F_RP# must be at logic HIGH (VIH). The second
operation, when needed, can be a WRITE or a READ
depending upon the command. During a READ operation, control signals F_CE# and F_OE# must be at a
logic LOW level (VIL), and F_WE# and F_RP# must be at
logic HIGH (VIH).
Table 7 illustrates the bus operations for all the
modes: write, read, reset, standby, and output disable.
When the device is powered up, internal reset circuitry initializes the chip to a read array mode of operation. Changing the mode of operation requires that a
command code be entered into the CSM. For each one
of the two Flash memory partitions, an on-chip status
register is available. These two registers allow the monitoring of the progress of various operations that can
take place on a memory bank. One of the two status
registers is interrogated by entering a READ STATUS
REGISTER command onto the CSM (cycle 1), specifying an address within the memory partition boundary,
and reading the register data on I/O pins DQ0–DQ7
(cycle 2). Status register bits SR0-SR7 correspond to
DQ0–DQ7 (see Table 8).
COMMAND DEFINITION
Once a specific command code has been entered,
the WSM executes an internal algorithm, generating
the necessary timing signals to program, erase, and
verify data. See Table 4 for the CSM command definitions and data for each of the bus cycles.
STATUS REGISTER
The status register allows the user to determine
whether the state of a PROGRAM/ERASE operation is
pending or complete. The status register is monitored
by toggling F_OE# and F_CE# and reading the resulting status code on I/Os DQ0–DQ7. The high-order I/Os
(DQ8–DQ15) are set to 00h internally, so only the loworder I/Os (DQ0–DQ7) need to be interpreted. Address
lines select the status register pertinent to the selected
memory partition.
Table 3
Command State Machine Codes For
Device Mode Selection
COMMAND
DQ0–DQ7 CODE ON DEVICE MODE
10h Accelerated Programming Algorithm
(APA)
20h Block erase setup
40h Program setup
50h Clear status register
60h Protection configuration setup
60h Enable/disable deep power-down
70h Read status register
90h Read protection configuration
register
98h Read query
B0h Program/erase suspend
C0h Protection register program/lock
D0h Program/erase resume – erase
confirm
D1h Check block erase confirm
FFh Read array
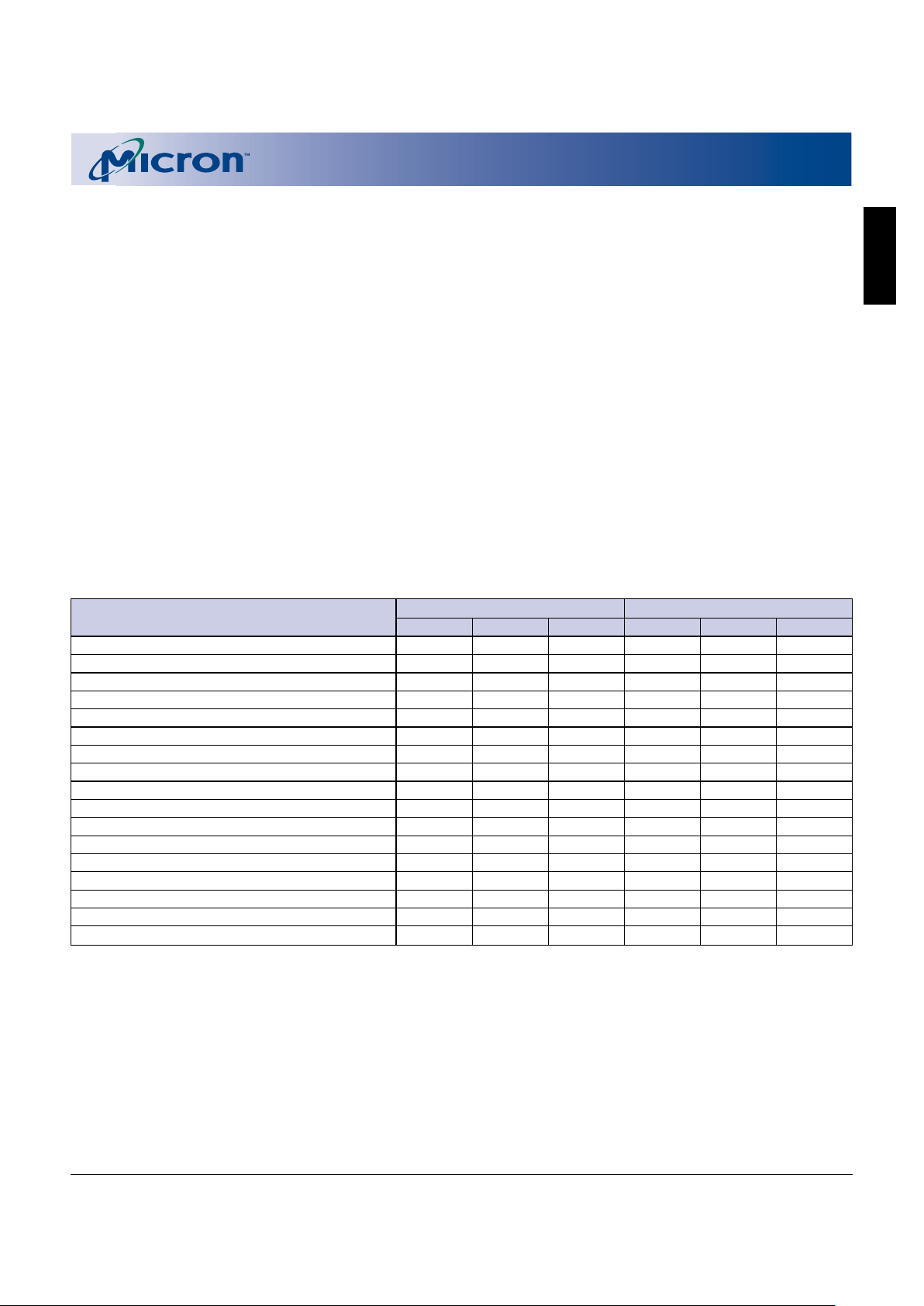
FLASH
11
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
Register data is updated and latched on the falling
edge of F_OE# or F_CE#, whichever occurs last. The
latest falling edge of either of these two signals updates the latch within a given READ cycle. Latching the
data prevents errors from occurring if the register input
changes during a status register read.
The status register provides the internal state of the
WSM to the external microprocessor. During periods
when the WSM is active, the status register can be polled
to determine the WSM status. Table 8 defines the status register bits.
After monitoring the status register during a
PROGRAM/ERASE operation, the data appearing on
DQ0–DQ7 remains as status register data until a new
command is issued to the CSM. To return the device to
other modes of operation, a new command must be
issued to the CSM.
COMMAND STATE MACHINE OPERATIONS
The CSM decodes instructions for the commands
listed in Table 3. The 8-bit command code is input to
the device on DQ0–DQ7 (see Table 4 for command
definitions). During a PROGRAM or ERASE cycle, the
CSM informs the WSM that a PROGRAM or ERASE cycle
has been requested.
During a PROGRAM cycle, the WSM controls the
program sequences and the CSM responds to a PROGRAM SUSPEND command only.
During an ERASE cycle, the CSM responds to an
ERASE SUSPEND command only. When the WSM has
completed its task, the WSMS bit (SR7) is set to a logic
HIGH level and the CSM responds to the full command
set. The CSM stays in the current command state until
the microprocessor issues another command.
The WSM successfully initiates an ERASE or PROGRAM operation only when F_VPP is within its correct
voltage range.
Table 4
Command Definitions
FIRST BUS CYCLE SECOND BUS CYCLE
COMMAND OPERATION ADDRESS1DATA OPERATION ADDRESS1DATA
1
READ ARRAY WRITE WA FFh
READ PROTECTION CONFIGURATION REGISTER WRITE IA 90h READ I A ID
READ STATUS REGISTER WRITE BA 70h READ X SRD
CLEAR STATUS REGISTER WRITE BA 50h
READ QUERY WRITE QA 98h READ QA QD
BLOCK ERASE SETUP WRITE BA 20h WRITE BA D0h
PROGRAM SETUP WRITE WA 40h WRITE WA WD
ACCELERATED PROGRAMMING ALGORITHM (APA) WRITE WA 10h WRITE WA WD
PROGRAM/ERASE SUSPEND WRITE BA B0h
PROGRAM/ERASE RESUME – ERASE CONFIRM WRITE BA D0h
LOCK BLOCK WRITE BA 60h WRITE BA 01h
UNLOCK BLOCK WRITE BA 60h WRITE BA D0h
LOCK DOWN BLOCK WRITE BA 60h WRITE BA 2Fh
CHECK BLOCK ERASE WRITE BA 20h WRITE BA D1h
PROTECTION REGISTER PROGRAM WRITE PA C0h WRITE PA PD
PROTECTION REGISTER LOCK WRITE LPA C0h WRITE LPA FFFDh
ENABLE/DISABLE DEEP POWER-DOWN WRITE DPW 60h WRITE DPW 03h
NOTE: 1. BA: Address within the block
DPW: BBCFh = Disable deep power-down
BBDFh = Enable deep power-down
IA: Identification code address
ID: Identification code data
LPA: Lock protection register address
PA: Protection register address
PD: Data to be written at location PA
QA: Query code address
QD: Query code data
SRD: Data read from the status register
WA: Word address of memory location to be written, or read
WD: Data to be written at the location WA
X: “Don’t Care”
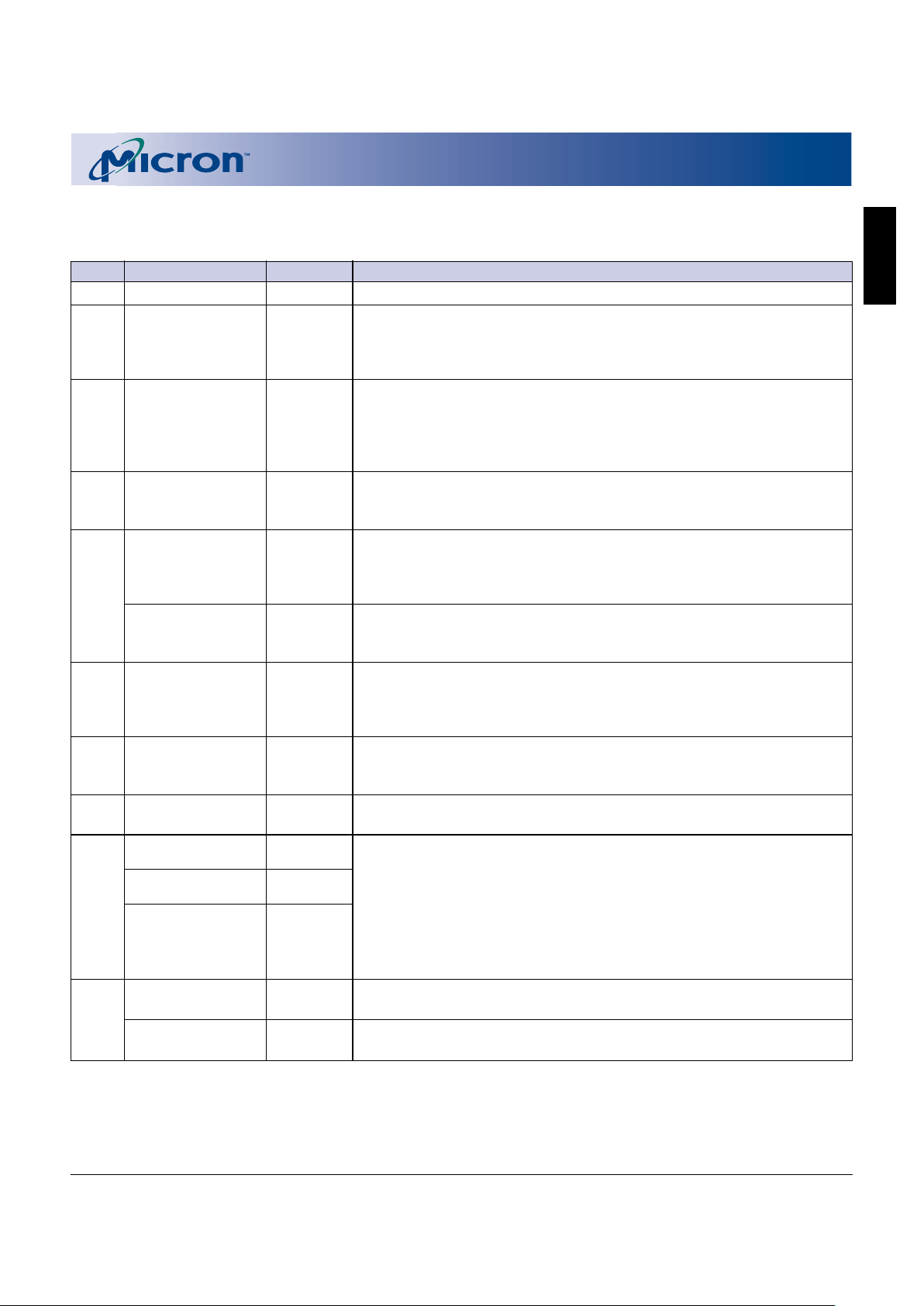
FLASH
12
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
Table 5
Command Descriptions
CODE DEVICE MODE BUS CYCLE DESCRIPTION
10h APA First Prepares for an accelerated program operation.
20h Erase Setup First Prepares the CSM for the ERASE command. If the next command is
not a CHECK BLOCK ERASE OR ERASE CONFIRM command, the
command will be ignored, and the device will go to read status
mode and wait for another command.
40h Program Setup First A two-cycle command: The first cycle prepares for a PROGRAM
operation, the second cycle latches addresses and data and initiates
the WSM to execute the program algorithm. The Flash outputs status
register data on the falling edge of F_OE# or F_CE#, whichever
occurs first.
50h Clear Status First The WSM can set the program status (SR4), and erase status (SR5) bits
Register in the status register to “1,” but it cannot clear them to “0.” Issuing
this command clears those bits to “0.”
60h Protection First Prepares the CSM for changes to the block locking status. If the next
Configuration command is not BLOCK UNLOCK, BLOCK LOCK or BLOCK LOCK
Setup DOWN, the command will be ignored, and the device will go to read
status mode.
Set Read First Puts the device into the set read configuration mode so that it will be
Configuration possible to set the option bits related to burst read mode.
Register
70h Read Status First Places the device into read status register mode. Reading the device
Register outputs the contents of the status register for the addressed bank.
The device automatically enters this mode for the addressed bank
after a PROGRAM or ERASE operation has been initiated.
90h Read Protection First Puts the device into the read protection configuration mode so that
Configuration reading the device outputs the manufacturer/device codes or block
lock status.
98h Read Query First Puts the device into the read query mode so that reading the device
outputs common Flash interface information.
B0h Program Suspend First Suspends the currently executing PROGRAM/ERASE/CHECK BLOCK
ERASE operation. The status register indicates when the operation
Erase Suspend First has been successfully suspended by setting either the program
suspend (SR2) or erase suspend (SR6) and the WSMS bit (SR7) to a
Check Block First “1” (ready). The WSM continues to idle in the suspend state,
Erase Suspend regardless of the state of all input control pins except F_RP#, which
immediately shuts down the WSM and the remainder of the chip if
F_RP# is driven to VIL.
C0h Program Device First Writes a specific code into the device protection register.
Protection Register
Lock Device First Locks the device protection register; data can no longer be changed.
Protection Register
(continued on the next page)
FLASH
13
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
Table 5
Command Descriptions (continued)
CODE DEVICE MODE BUS CYCLE DESCRIPTION
D0h Erase Confirm Second If the previous command was an ERASE SETUP command, then the
CSM closes the address and data latches, and it begins erasing the
block indicated on the address pins. During programming/erase, the
device responds only to the READ STATUS REGISTER, PROGRAM
SUSPEND, or ERASE SUSPEND commands and outputs status register
data on the falling edge of F_OE# or F_CE#, whichever occurs last.
Program/Erase/ First If a PROGRAM, ERASE or CHECK BLOCK ERASE operation was
Check Block Erase previously suspended, this command resumes the operation.
Resume
FFh Read Array First During the array mode, array data is output on the data bus.
01h Lock Block Second If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP,
the CSM latches the address and locks the block indicated on the
address bus.
2Fh Lock Down Second If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP,
the CSM latches the address and locks down the block indicated on
the address bus.
D0h Unlock Block Second If the previous command was PROTECTION CONFIGURATION SETUP,
the CSM latches the address and unlocks the block indicated on the
address bus. If the block had been previously set to lock down, this
operation has no effect.
00h Invalid/Reserved Unassigned command that should not be used.
D1h Check Block Second If the previous command was ERASE SETUP command, the CSM
Erase Confirm closes the address latches and checks that the block is completely
erased.

FLASH
14
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
CLEAR STATUS REGISTER
The internal circuitry can set, but not clear, the block
lock status bit (SR1), the F_VPP status bit (SR3), the
program status bit (SR4), and the erase status bit (SR5)
of the status register. The CLEAR STATUS REGISTER
command (50h) allows the external microprocessor to
clear these status bits and synchronize to the internal
operations. When the status bits are cleared, the device returns to the read array mode.
READ OPERATIONS
The following READ operations are available: READ
ARRAY, READ PROTECTION CONFIGURATION REGISTER, READ QUERY and READ STATUS REGISTER.
READ ARRAY
The array is read by entering the command code
FFh on DQ0–DQ7. Control signals F_CE# and F_OE#
must be at a logic LOW level (VIL), and F_WE# and F_RP#
must be at a logic HIGH level (VIH) to read data from the
array. Data is available on DQ0–DQ15. Any valid address within any of the blocks selects that address and
allows data to be read from that address. Upon initial
power-up or device reset, the device defaults to the
read array mode.
READ CHIP PROTECTION IDENTIFICATION DATA
The chip identification mode outputs three types
of information: the manufacturer/device identifier, the
block locking status, and the protection register. Two
bus cycles are required for this operation: the chip identification data is read by entering the command code
90h on DQ0–DQ7 to the bank containing address 00h
and the identification code address on the address
lines. Control signals F_CE# and F_OE# must be at a
logic LOW level (VIL), and F_WE# and F_RP# must be at
a logic HIGH level (VIH) to read data from the protection
configuration register. Data is available on DQ0–DQ15.
After data is read from protection configuration register, the READ ARRAY command, FFh, must be issued to
the bank containing address 00h prior to issuing other
commands. See Table 10 for further details.
READ QUERY
The read query mode outputs common flash interface (CFI) data when the device is read (see Table 12).
Two bus cycles are required for this operation. It is
possible to access the query by writing the read query
command code 98h on DQ0–DQ7 to the bank containing address 0h. Control signals F_CE# and F_OE# must
be at a logic LOW level (VIL), and F_WE# and F_RP#
must be at a logic HIGH level (VIH) to read data from the
query. The CFI data structure contains information
such as block size, density, command set, and electrical specifications. To return to read array mode, write
the read array command code FFh on DQ0–DQ7.
READ STATUS REGISTER
The status register is read by entering the command
code 70h on DQ0–DQ7. Two bus cycles are required for
this operation: one to enter the command code and a
second to read the status register. In a READ cycle, the
address is latched and register data is updated on the
falling edge of F_OE# or F_CE#, whichever occurs last.
Register data is updated and latched on the falling
edge of F_OE# or F_CE#, whichever occurs last.
FLASH
15
4 Meg x 16 Asynchronous/Page Flash 512K x 16 SRAM Combo Memory Micron Technology, Inc., reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT28C6428P20_3.p65 – Rev. 3, Pub. 7/02 ©2002, Micron Technology, Inc.
4 MEG x 16 ASYNCHRONOUS/PAGE FLASH
512K x 16 SRAM COMBO MEMORY
ADVANCE
Table 6
Command State Machine Transition Table
)noititraptneserpehtfoetatstxendna(noititraptneserpehtottupnidnammoC
tneserpehtfoetatstneserP
noititrap
etatstneserP
rehtoehtfo
noititrap
hF2
kcoL
nwod
mrifnoc
h10
kcoL
mrifnoc
h0C
PTO
putes
h06
kcolnU/kcoL
nwodkcoL/
h89
daeR
yreuq
h09
daeR
ecived
DI
h05
raelC
sutats
retsiger
h07
daeR
sutats
h0B
margorP
esarE/
dnepsus
h0D
,mrifnocEB
,emuserE/P
mrifnocBLU
h02
esarE
putes
h04/h01
/APA
margorP
putes
hFF
daeR
yarra
7RS
ataD
nehw
daer
etatSedoM
yarradaeR
kcoL
daeR
yreuq
daeR
DI
daeR
yarra
daeR
sutats
yarradaeR
1yarrAyarrA
daeR
1puteS
2ysuB
yarradaeR
PTO
putes
yarradaeR
esarE
putes
margorP
putes
daeR
yarra
3eldI
yarradaeR
yarradaeR 4
esarE
dnepsus
yarradaeR5
.gorP
dnepsus
yarradaeR
kcoL
daeR
yreuq
daeR
DI
daeR
yarra
daeR
sutats
yarradaeR
1IFCyreuQ
6puteS
7ysuB
yarradaeR
PTO
putes
yarradaeR
esarE
putes
margorP
putes
daeR
yarra
8eldI
yarradaeR
yarradaeR 9
esarE
dnepsus
yarradaeR01
.gorP
dnepsus
yarradaeR
kcoL
daeR
yreuq
daeR
DI
daeR
yarra
daeR
sutats
yarradaeR
1DI
eciveD
DI
11puteS
21ysuB
yarradaeR
PTO
putes
yarradaeR
esarE
putes
margorP
putes
daeR
yarra
31eldI
yarradaeR
yarradaeR 41
esarE
dnepsus
yarradaeR51
.gorP
dnepsus
yarradaeR
kcoL
daeR
yreuq
daeR
DI
daeR
yarra
daeR
sutats
yarradaeR
1sutatSsutatS
61puteS
71ysuB
yarradaeR
PTO
putes
yarradaeR
esarE
putes
margorP
putes
daeR
yarra
81eldI
yarradaeR
yarradaeR 91
esarE
dnepsus
yarradaeR02
.gorP
dnepsus
ysubretsigernoitcetorP 1sutatSputeS
P
r
o
t
e
c
t
i
o
n
r
e
g
i
s
t
e
r
12eldI
ysubretsigernoitcetorP 0sutatSysuB22eldI
yarradaeRkcoL
daeR
yreuq
daeR
DI
daeR
yarra
daeR
sutats
yarradaeR1sutatSenoD
32puteS
42ysuB
yarradaeR
PTO
putes
kcoL
daeR
yreuq
daeR
DI
daeR
yarra
daeR
sutats
yarradaeR
esarE
putes
margorP
putes
daeR
yarra
1sutatSenoD
52eldI
yarradaeR
yarradaeR 62
esarE
dnepsus
yarradaeR72
.gorP
dnepsus
(continued on next page)
 Loading...
Loading...