Page 1
Read the instructions carefully before using this device.
Prieš naudodamiesi prietaisu perskaitykite instrukciją.
Pirms šīs ierīces izmantošanas uzmanīgi izlasiet instrukcijas.
Enne seadme kasutust lugege hoolikalt juhiseid.
Перед использованием прибора внимательно прочтите данное руководство.
Lue ohjeet huolellisesti ennen kuin käytät laitetta.
Europe / Middle-East / Africa
Microlife AG
Espenstrasse 139
9443 Widnau / Switzerland
Tel. +41 / 71 727 70 30
Fax +41 / 71 727 70 39
Email admin@microlife.ch
www.microlife.com
Asia
Microlife Corporation.
9F, 431, RuiGang Road, NeiHu
Taipei, 11492, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel. 886 2 8797-1288
Fax.886 2 8797-1283
Email service@microlife.com.tw
www.microlife.com
North / Central / South America
Microlife USA, Inc.
1617 Gulf to Bay Blvd., 2nd Floor Ste A
Clearwater, FL 33755 / USA
Tel. +1 727 442 5353
Fax +1 727 442 5377
Email msa@microlifeusa.com
www.microlife.com
IB AG1-20 N-V6 0813
Page 2

Microlife BP AG1-20
Aneroid Blood Pressure Kit
EN
Instruction Manual (1-11)
Aneroidinis kraujospūdžio matavimo komplektas
LT
Naudojimo instrukcija
Aneroīda asinsspiediena mērierīces komplekts
LV
Instrukcija
(24-35)
Aneroidne vererõhu mõõtmise komplekt
EE
Kasutusjuhend
Механический прибор для
RU
измерения артериального давления
Руководство по пользованию
FI
Aneroid verenpainemittari pakkaus
Käyttöohjeet
(36-47)
(62-73)
(12-23)
(48-61)
Page 3

Aneroid Blood Pressure Kit
Instruction Manual
Page 4

Table of contents
1. Introduction
1.1. Features
1.2. Important information about self-measurement
2. Important information on the subject of blood pressure and its measurement
2.1. How does high/low blood pressure arise?
2.2. Which values are normal?
2.3. What can be done, if regular high/low values are obtained?
3. The various components of the blood pressure kit
4. Carrying out a measurement
4.1. Before the measurement
4.2. Common sources of error
4.3. Fitting the cuff
4.4. Measuring procedure
4.4.1. Putting the chest piece under the cuff
4.4.2. Inflating the cuff
4.4.3. Systolic blood pressure reading
4.4.4. Diastolic blood pressure reading
4.4.5. Recording your readings
5. Malfunction / Troubleshooting
6. Care and maintenance, recalibration
7. Guarantee
8. Reference to standards
9. www.microlife.com
10. Technical specifications
EN
1
Page 5

1. Introduction
1.1. Features
The aneroid blood pressure kit is a non-automated, mechanical blood pressure measuring device
for use on the upper arm.
It offers proven reliability and superior performance at an economical price. With the advanced
non-stop pin mechanism and ergonomic bulb with complete valves, the aneroid blood pressure
kit ensures you a precise and consistent measurement. Nevertheless, its durable nylon cuff,
high-grade bearing and aneroid bellow provide consistent operation. The entire unit stores in a
zippered Nylon bag for easy portability.
Before using, please read through this instruction manual carefully and then keep it in a safe
place. For further questions on the subject of blood pressure and its measurement, please
contact your doctor.
Attention!
1.2. Important information about self-measurement
• Donotforget:self-measurement means control, not diagnosis or treatment. Unusual
values must always be discussed with your doctor. Under no circumstances should you alter
the dosages of any drugs prescribed by your doctor.
2. Important information on the subject of blood pressure and its measurement
2.1. How does high/low blood pressure arise?
The level of blood pressure is determined in a part of the brain, the so-called circulatory centre,
and adapted to the respective situation by way of feedback via the nervous system. To adjust the
blood pressure, the strength and frequency of the heart (Pulse), as well as the width of circulatory
blood vessels is altered. The latter is effected by way of fine muscles in the blood-vessel walls.
Thelevelofarterialbloodpressurechangesperiodicallyduringtheheartactivity:Duringthe
«blood ejection» (Systole) the value is maximal (systolic blood pressure value), at the end of
the heart’s «rest period» (Diastole) minimal (diastolic blood pressure value). The blood pressure
values must lie within certain normal ranges in order to prevent particular diseases.
2
Page 6
2.2 Which values are normal?
Blood pressure is too high if at rest, the diastolic pressure is above 90 mmHg and/or the systolic
blood pressure is over 140 mmHg. In this case, please consult your doctor immediately. Longterm values at this level endanger your health due to the associated advancing damage to the
blood vessels in your body.
With blood pressure values that are too low, i.e. systolic values under 100 mmHg and/or diastolic
values under 60 mmHg, likewise, please consult your doctor.
Even with normal blood pressure values, a regular self-check with your blood pressure monitor is recommended. In this way you can detect possible changes in your values early and react appropriately.
If you are undergoing medical treatment to control your blood pressure, please keep a record of
the level of your blood pressure by carrying out regular self-measurements at specific times of
the day. Show these values to your doctor. Never use the results of your measurements to
alter independently the drug doses prescribed by your doctor.
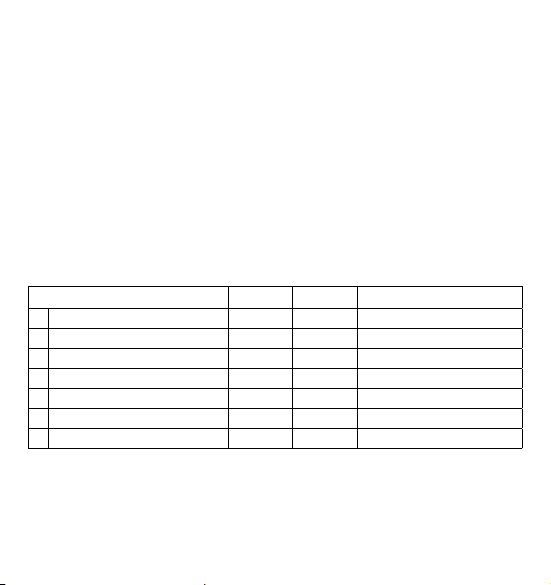
Tableforclassifyingbloodpressurevalues(unitsmmHg)accordingtoWorldHealthOrganization:
Range Systolic Diastolic Recommendation
blood pressure too low
1. blood pressure optimum
2. blood pressure normal
3. blood pressure slightly high
4. blood pressure too high
5. blood pressure far too high
6. blood pressure dangerously high
< 100 < 60
100 - 120 60 - 80
120 - 130 80 - 85
130 - 140 85 - 90
140 - 160 90 - 100
160 - 180 100 - 110
≥ 180 ≥ 110
Consult your doctor
Self-check
Self-check
Consult your doctor
Seek medical advice
Seek medical advice
Urgently seek medical advice!
☞ Further information
• Ifyourvaluesaremostlystandardunderrestingconditionsbutexceptionallyhighundercon
ditions of physical or psychological stress, it is possible that you are suffering from so-called
«labile hypertension». Please consult your doctor if you suspect that this might be the case.
• Correctlymeasureddiastolicbloodpressurevaluesabove120mmHgrequireimmediate
medical treatment.
3
Page 7

2.3. What can be done, if regular increased/low values are obtained?
a) Please consult your doctor.
b) Increased blood pressure values (various forms of hypertension) are associated long- and
medium term with considerable risks to health. This concerns the arterial blood vessels of
your body, which are endangered due to constriction caused by deposits in the vessel walls
(Arteriosclerosis). A deficient supply of blood to important organs (heart, brain, muscles) can
be the result. Furthermore, with long-term continuously increased blood pressure values, the
heart will become structurally damaged.
c) There are many different causes of the appearance of high blood pressure. We differentiate
between the common primary (essential) hypertension, and secondary hypertension. The
latter group can be ascribed to specific organic malfunctions. Please consult your doctor for
information about the possible origins of your own increased blood pressure values.
d) There are measures which you can take, not only for reducing a medically established high
bloodpressure,butalsoforprevention.Thesemeasuresarepartofyourgeneralwayoflife:
A) Eating habits
• Striveforanormalweightcorrespondingtoyourage.Reduceoverweight!
• Avoidexcessiveconsumptionofcommonsalt.
• Avoidfattyfoods.
B) Previous illnesses
Followconsistentlyanymedicalinstructionsfortreatingpreviousillnesssuchas:
• Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus)
• Fat metabolism disorder
• Gout
C) Habits
• Giveupsmokingcompletely
• Drinkonlymoderateamountsofalcohol
• Restrictyourcaffeineconsumption(Coffee)
D) Physical constitution
• Afterapreliminarymedicalexamination,doregularsport.
• Choosesportswhichrequirestaminaandavoidthosewhichrequirestrength.
4
Page 8

• Avoidreachingthelimitofyourperformance.
• Withpreviousillnessesand/oranageofover40years,pleaseconsultyourdoctorbefore
beginning your sporting activities. He will advise you regarding the type and extent of types
of sport that are possible for you.
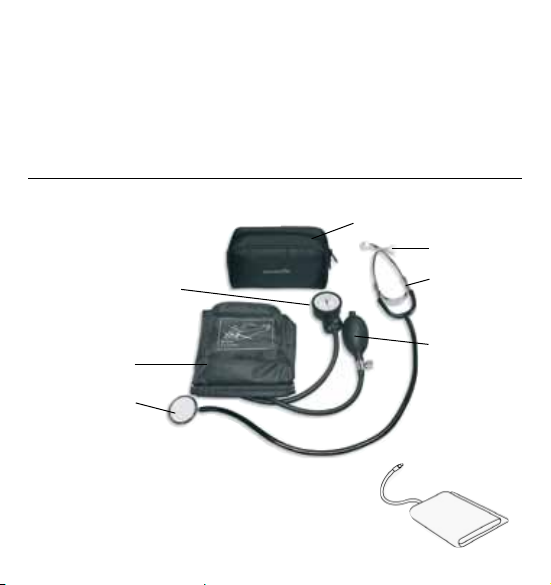
3. The various components of the Aneroid Blood Pressure Kit
TheillustrationshowstheBPAG120,consistingof:
a) Measuring unit:
Manometer
Soft bag
Ear piece
Stethoscope
Cuff
Bulb & Valves
Chest piece
b) Cuff:
Type AC-1M, for arm circumference 22 - 32 cm or
Type AC-1L, for arm circumference 32 - 42 cm
(available as special accessory)
4. Carrying out a measurement
4.1. Before the measurement
• Avoideating,smokingaswellasallformsofexertiondirectlybeforethemeasurement.
5
Page 9
All these factors influence the measurement result. Try and find time to relax by sitting in
an armchair in a quite atmosphere for about ten minutes before the measurement.
• Removeanygarmentthatfitscloselytoyourupperarm.
• Measurealwaysonthesamearm(normallyleft).
• Attempttocarryoutthemeasurementsregularlyatthesametimeofday,sincetheblood
pressure changes during the course of the day.
4.2. Common sources of error
Note: Comparable blood pressure measurements always require the same conditions! These are
normally always quiet conditions.
• Alleffortsbythepatienttosupportthearmcanincreasethebloodpressure.Makesureyou
are in a comfortable, relaxed position and do not activate any of the muscles in the measurement arm during the measurement. Use a cushion for support if necessary.
• Ifthearmarteryliesconsiderablylower(higher)thantheheart,anerroneouslyhigher(lower)
blood pressure will be measured! (Each 15 cm difference in height results in a measurement
error of 10 mmHg!)
• Cuffsthataretoonarrowortooshortresultinfalsemeasurementvalues.Selectingthecorrect
cuff is of extraordinary importance. The cuff size is dependent upon the circumference of the arm
(measured in the centre). The permissible range is printed on the cuff. If this is not suitable for
your use, please contact your dealer. Note: Only use clinically approved Original-Cuffs!
• Aloosecufforasidewaysprotrudingairpocketcausesfalsemeasurementvalues.
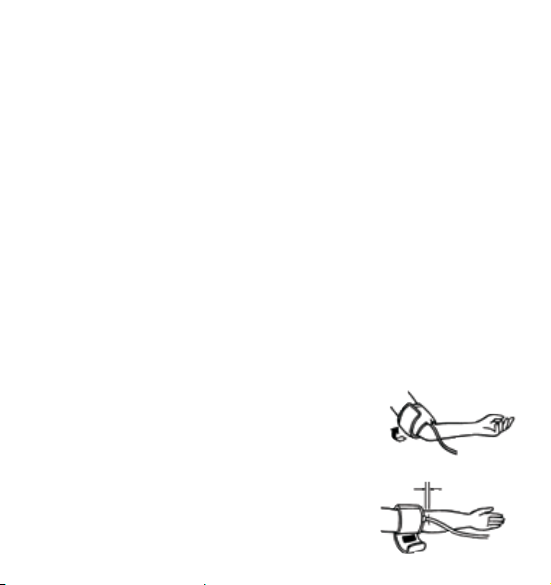
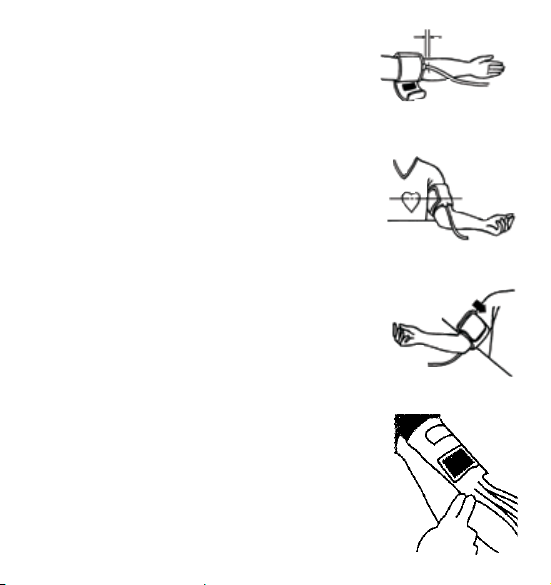
4.3. Fitting the cuff
a) Push the cuff over the left upper arm so that the tube
points in the direction of the lower arm.
b) Lay the cuff on the arm as illustrated. Make certain
that the lower edge of the cuff lies approximately
2 to 3 cm above the elbow and that the rubber tube
leaves the cuff on the inner side of the arm.
2 - 3 cm
Important! The mark (ca. 3 cm long bar) must lie
exactly over the artery which runs down the inner
side of the arm.
6
tube
Page 10
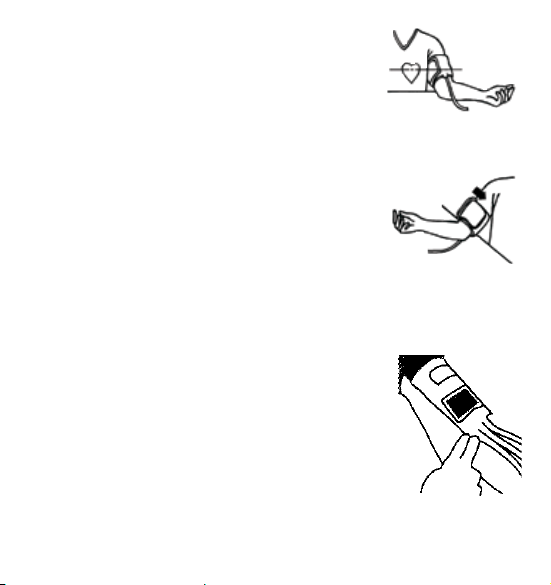
c) Tighten the free end of the cuff and close the cuff
with the closer.
d) There must be no free space between the arm and
the cuff as this would influence the result. Clothing
must not restrict the arm. Any piece of clothing which
does (e.g. a pullover) must be taken off.
e) Secure the cuff with the closer in such a way that it lies
comfortably and is not too tight. Lay the arm on the table
(palm upwards) so that the cuff is at the same height as
the heart. Make sure that the tube is not kinked.
f) Remain seated quietly for 2 minutes before you begin
the measurement.
Comment:
If it is not possible to fit the cuff to the left arm, it can also be
placed on the right one. However all measurements should be
made using the same arm.
4.4. Measuring procedure
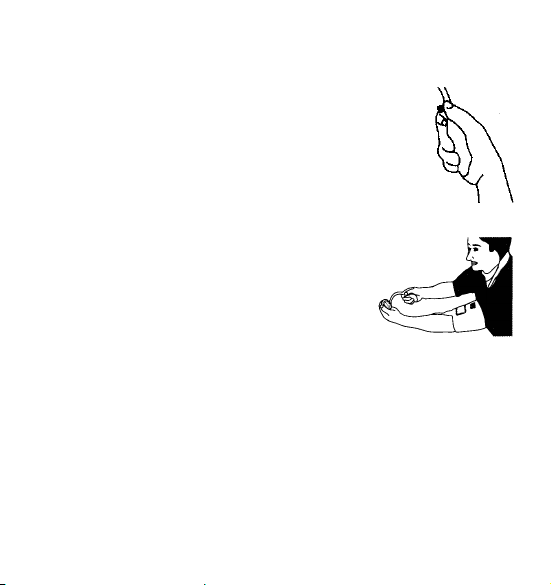
4.4.1. Put the chest piece under the cuff
The chest piece shall not be placed ON or INTO the cuff, it shall be
placed either under the cuff, or 1 - 2 cm below it. The chest piece
is then placed correctly , when the Korrot koff’s sound appears
strongest (‘loudest’). Make sure the chest piece is in contact with
skin and above the brachial artery. Wear the binaural (ear pieces)
properly to check the Korotkoff’s sound during measurement.
Before using the stethoscope, be sure there is no crack on the
diaphragm, ear pieces, and tubing. Any improper setup or damage
of the stethoscope will cause distorted sound or poor sound
transmission to make inaccurate reading.
7
Page 11
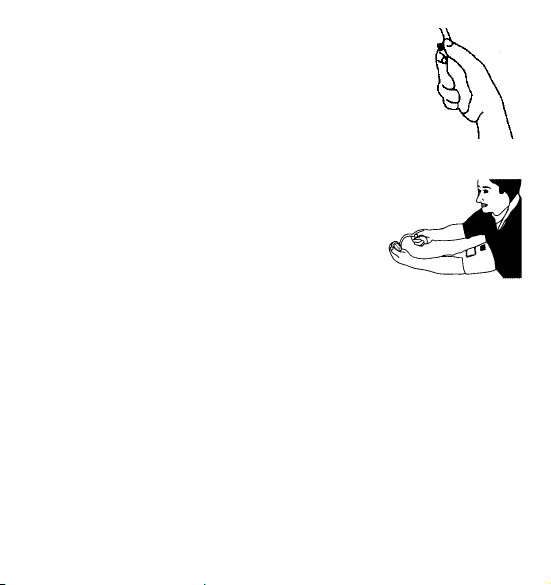
4.4.2. Inflating the cuff
Close the air valve on the bulb by turning the screw clock wise.
Do not over-tighten. Squeeze the inflation bulb with the hand at
a steady rate until the pointer on the gauge is 30 mmHg above
your normal systolic pressure value. If you are not sure the
value, inflate to 200 mmHg first.
4.4.3. Systolic blood pressure reading
Slowly open air valve by turning screw counter clockwise and hold
stethoscope chest piece over brachial artery. Proper de flation rate is
essential for an accurate reading, so you should practice and master
a recommended defla tion rate of 2 - 3 mmHg per second or a drop
of 1 - 2 marks on the pressure gauge each heartbeat. You should not
keep the cuff inflated any longer than necessary. As the cuff begins
to deflate, you must listen care fully with the stethos cope. Note the
reading on the gauge as soon as you hear a faint, rhythmic tapping or
thumping sounds. This is the systolic blood pressure reading. Listen
care fully and familiarize yourself with pulse (Korotkoff’s) sound.
4.4.4. Diastolic blood pressure reading
Allow the pressure to continue dropping at the same deflation rate. When your diastolic blood
pressure value reached, the thumping sound stops. Deflate the cuff valve completely. Remove
the cuff from arm and stethoscope from ears.
4.4.5. Record your readings
Repeat the measurement at least two times. Do not forget to record your readings and the time
of the day measurement is made immediately after you finish measuring. A suitable time is first
thing in the morning, or just before evening meals. Remember that your physician is the only
person qualified to analyze your blood pressure.
☞ Further information
Measurements should not occur soon after each other, since otherwise, the results will be falsified. Wait
therefore for several minutes in a relaxed position, sitting or lying, before you repeat a measurement.
8
Page 12
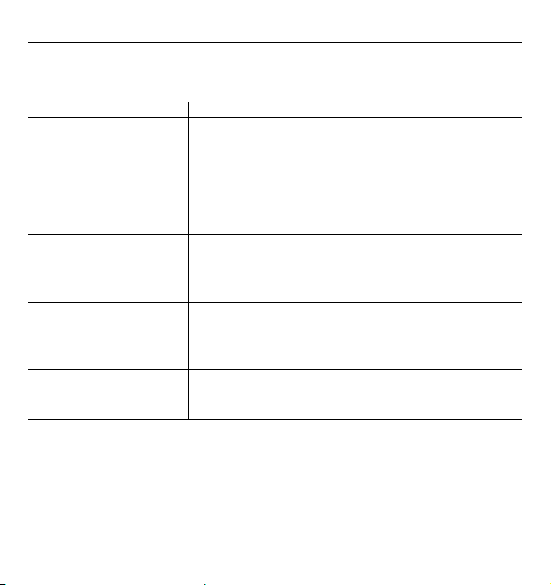
5. Malfunction / Troubleshooting
If problems occur when using the device, the following points should be checked and if
necessary,thecorrespondingmeasuresaretobetaken:
Malfunction
The sound transmission is
poor, distorted or there is
extraneous noise.
The pressure does not rise
although the bulb is pumping.
The deflation rate can not be
set to 2-3 mmHg/ sec. by
adjusting the air release valve.
Pointer is not at 0 +/- 3 mmHg
at rest.
☞ Further information
The level of blood pressure is subject to fluctuations even with healthy people. Important thereby
is, that comparable measurements always require the same conditions (rest condition)!
If, in spite of observing all these factors, the fluctuations are more than 15 mmHg, and/or you
hear irregular pulses on several occasions, please consult your doctor.
You must consult your specialist dealer or chemist if there are technical problems with the blood
pressure instrument. Never attempt to repair the instrument yourself!
Any unauthorised opening of the instrument invalidates all guarantee claims!
Remedy
1. Check the ear pieces if they are plugged or cracked. If not,
make sure they do not fit poorly as worn.
2. Check the tube if it is broken or twisted.
3. Check the bell and diaphragm of chest piece if there is any crack.
4. Make sure the chest piece is in proper contact with skin and
over brachial artery during measuring. Clean or replace any
defective parts if found to avoid inaccurate reading.
1. Make sure that the valve is closed.
2. Make sure the cuff is properly connected to bulb and manometer.
3. Check if the cuff, tube and bulb is leaky. Replace the defective
parts if any.
•Disassemblethevalvefrombulbtocheckifthereisany
blockage in the airway of the valve. Clean the blockage and
try again. If it still does not work, replace it to avoid inaccurate
reading.
1. Make sure that the valve is open for zero check.
2. If still more than 3 mmHg deviation, contact your dealer to
recalibrate the manometer.
9
Page 13

6. Care and maintenance, recalibration
With proper care and maintenance, this blood pressure measuring device will provide years of
satisfactoryservice.Followthegeneralrulesbelow:
•Donotdrop.
•Neverinflatebeyond300mmHg.
•Donotexposethedevicetoeitherextremetemparatures,humidity,ordirectsunlight.
•Nevercontactthecufffabricwithasharpinstrument,sincethiscouldcausedamage.
•Alwaysdeflatecuffcompletelybeforestorage.
•Donotdismantlemanometerunderanycircumstance.
•Storethewholedeviceinstoragebagprovided,tokeepallthepartsclean.
•Storagetemperaturecondition:20- +70 °C at a relative air humidity of 85 % (non-condensing).
•Wipe off the manometer and bulb with a damp cloth. Sterilization is not necessary, since the parts
of manometer should not come into direct contact with the patient‘s body during measurement.
•Removethebladderfirst,andwipethecloser,bladderandtubeswithadampcloth.Thecuffcan
be washed with soap and cold water. But do rinse the cuff with clear water and keep it air dry.
Periodical recalibration
Sensitive measuring devices must from time to time be checked for accuracy. We therefore
recommend a periodical inspection of the static pressure display every 2 years.
Your specialist dealer would be pleased to provide more extensive information about this.
7. Guarantee
This blood pressure monitor is guaranteed for 2 years from date of purchase. This guarantee
includes the instrument and the cuff. The guarantee does not apply to damage caused by
improper handling, accidents, not following the operating instructions or alterations made to the
instrument by third parties.
The guarantee is only valid upon presentation of the guarantee card filled out by the dealer.
Nameandcompanyaddressoftheresponsibledealer:
10
Page 14

8. Reference to standards
Device standard: Device corresponds to the requirements of the
EN 1060-1/-2
ANSI / AAMI SP09
This device complies with the requirements of the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC.
9. www.microlife.com
Detailed user information about our products as well as services can be found at www.microlife.com
10. Technical specifications
Weight: 450 g
Size: 175 x 70 x 103 mm
Storage temperature: -20 °C to +70 °C; 85 % relative humidity maximum
Operation temperature: 0 - 46 °C
Measuring range: 0 - 300 mmHg
Measuring resolution: 2 mmHg
Accuracy: within ±3 mmHg in 18 - 33 °C;
within ±6 mmHg in 34 - 46 °C
Inflation source: a volume of at least 200cc to a pressure of 300 mmHg in 4 - 10 sec.
Pressure reduction rate: 2 - 3 mmHg/sec.
Air leakage: < ± 4 mmHg/min
Hysteresis error: within 0 - 4 mmHg
Accessories: 1. M-cuff (adult size with arm circumference of 22 - 32 cm) with
inlaid bladder
2. bulb and valve
3. stethoscope
4. soft bag
Technical alterations reserved.
11
Page 15

Aneroidinis kraujospūdžio matavimo komplektas
Naudojimo instrukcija
12
Page 16

Turinys
1. Įvadas
1.1. Prietaiso savybės
1.2. Svarbi informacija apie savarankišką kraujospūdžio matavimą
2. Svarbi informacija apie kraujospūdį ir jo matavimą
2.1. Kaip atsiranda aukštas / žemas kraujospūdis?
2.2. Koks kraujospūdis laikytinas normaliu?
2.3. Ką daryti, jei kraujospūdis nuolat per aukštas ar per žemas?
3. Kraujospūdžio matuoklio sudėtinės dalys
4. Matavimas
4.1. Prieš matuojant
4.2. Dažniausios klaidos
4.3. Manžetės uždėjimas
4.4. Matavimo procedūra
4.4.1. Stetoskopo galvutės pridėjimas
4.4.2. Manžetės pripūtimas
4.4.3. Sistolinio kraujospūdžio parodymai
4.4.4. Diastolinio kraujospūdžio parodymai
4.4.5. Žymėkitės kraujospūdžio parodymus
5. Galimi gedimai ir jų šalinimas
6. Prietaiso priežiūra ir eksploatacija, kalibravimas
7. Garantija
8. Standartų nuorodos
9. www.microlife.lt
10. Techninės specifikacijos
LT
13
Page 17

1. Įvadas
1.1. Prietaiso savybės
Aneroidinis kraujospūdžio matavimo komplektas - neautomatinis kraujospūdžio matavimui
ant žasto skirtas prietaisas. Tai išbandytas ir patikimas matavimo prietaisas už patrauklią
kainą. Šiuolaikiško adatinio nepertraukiamo veikimo mechanizmo ir ergonomiško balionėlio
su vožtuvais dėka prietaisas užtikriną tikslų ir darnų matavimą. Kokybiška, dėvėjimuisi atspari
manžetė bei aneroidinis manometras užtikrina ilgą prietaiso tarnavimo laiką. Komplektas
laikomas nailoniniame dėkle su užtrauktuku ir yra patogus nešiotis.
Prieš pradėdami naudotis prietaisu, įdėmiai perskaitykite šią instrukciją, o vėliau laikykite ją
saugioje vietoje. Jei turite papildomų klausimų, susijusių su kraujospūdžiu ir jo matavimu,
kreipkitės į gydytoją.
DĖMESIO!
1.2. Svarbi informacija apie savarankišką kraujospūdžio matavimą.
•
Nepamirškite – savarankiškas kraujospūdžio matavimas reiškia kontrolę, bet ne
diagnozę ar gydymą. Gavę neįprastus matavimo duomenis, būtinai konsultuokitės su
gydytoju. Jokiu būdu nekeiskite gydytojo paskirtų vaistų ar jų dozių.
2. Svarbi informacija apie kraujospūdį ir jo matavimą
2.1. Kaip atsiranda aukštas/žemas kraujospūdis?
Kraujospūdį reguliuoja smegenyse esantis cirkuliacinis centras, nerviniu keliu reaguojantis į
aplinkos veiksnius . Koreguojant kraujospūdį, kinta širdies susitraukimų stiprumas ir dažnis
(pulsas) bei cirkuliacinių kraujagyslių spindis. Pastarasis kinta dėl plonųjų raumenų skaidulų,
esančių kraujagyslių sienelėse. Arterinis kraujospūdis keičiasi periodiškai: širdžiai susitraukiant
(sistolė) sistolinis kraujospūdis būna aukščiausias, o širdžiai «atsipalaiduojant» (diastolė) –
diastolinis kraujospūdis žemiausias.
14
Page 18
Koks kraujospūdis laikytinas normaliu?
2.2
Kraujospūdis yra aukštas, jei ilsintis diastolinis kraujospūdis viršija 90 mmHg ir/arba
sistolinis kraujospūdis aukštesnis nei 140 mmHg. Tokiu atveju nedelsiant kreipkitės į
gydytoją. Ilgalaikis nurodyto lygio kraujospūdis pavojingas Jūsų sveikatai, nes yra susijęs su
progresuojančiais kraujagyslių pažeidimais.
Į gydytoją kreipkitės ir tada, kai kraujospūdis per žemas (sistolinis kraujospūdis yra žemesnis
nei 100 mmHg ir/arba diastolinis – žemesnis nei 60 mmHg). Net ir esant normaliam
kraujospūdžiui patartina reguliariai jį matuoti. Tai padeda laiku pastebėti kraujospūdžio
pakitimus ir tinkamai į juos reaguoti.
Jei Jūs gydomas nuo hipotenzijos ar hipertenzijos, kas dieną tuo pačiu metu matuokite ir
registruokite kraujospūdį. Matavimo duomenis parodykite gydytojui.
Niekada savarankiškai nekeiskite gydytojo paskirtų vaistų dozių remdamiesi savo
matavimų rezultatais.
Kraujospūdžio klasifikacija pagal PSO (mmHg):
Zona Sistolinis
kraujospūdis
Kraujospūdis per žemas
Optimalus kraujospūdis
1.
Normalus kraujospūdis
2.
Šiek tiek padidėjęs
3.
kraujospūdis
Per aukštas kraujospūdis
4.
Labai smarkiai padidėjęs
5.
kraujospūdis
Pavojingai padidėjęs
6.
kraujospūdis
< 100 < 60
100 - 120 60 - 80
120 - 130 80 - 85
130 - 140 85 - 90
140 - 160 90 - 100
160 - 180 100 - 110
≥ 180 ≥ 110
Diastolinis
kraujospūdis
Rekomendacijos
Pasitarkite su gydytoju
Savarankiškai matuokitės
kraujospūdį
Savarankiškai matuokitės
kraujospūdį
Pasitarkite su gydytoju
Kreipkitės į gydytoją
Kreipkitės į gydytoją
Skubiai kreipkitės į gydytoją!
15
Page 19

☞
Papildoma informacija
•
Jei Jūsų kraujospūdis normalus kai ilsitės, tačiau fizinio ar fiziologinio streso sąlygomis smarkiai
padidėja – Jūs tikriausiai sergate «labilia hipertenzija». Jei įtariate, kad tai yra kraujospūdžio
pokyčių priežastis, kreipkitės į gydytoją.
•
Jei teisingai atlikus matavimus diastolinis kraujospūdis yra didesnis nei 120 mmHg,
nedelsiant būtinas medicininis gydymas.
2.3.
Ką daryti, jei kraujospūdis nuolat per aukštas ar per žemas?
a) Pirmiausia kreipkitės į gydytoją
b) Ilgalaikis ar vidutinės trukmės kraujospūdžio padidėjimas (įvairios hipertenzijos formos)
yra pavojingas sveikatai. Tai kelia pavojų Jūsų kraujagyslėms, susiaurėjusioms dėl
aterosklerozės. Rezultatas – sumažėjęs gyvybiškai svarbių organų (širdies, smegenų,
raumenų) aprūpinimas krauju. Be to, ilgalaikis nuolatinis kraujospūdžio padidėjimas
pakeičia anatominę širdies struktūrą.
c) Yra daug kraujospūdžio padidėjimo priežasčių. Hipertenzija gali būti įprastinė pirminė arba
antrinė. Pastaroji gali būti priskirta prie tam tikrų organų veiklos sutrikimų. Norint sužinoti
galimas Jūsų padidėjusio kraujospūdžio priežastis,būtina konsultuotis su gydytoju.
d) Mediciniškai nustačius padidėjusį kraujospūdį, o taip pat ir padidėjimo profilaktikai galima
imtis tam tikrų priemonių, kurios, beje, yra Jūsų gyvenimo dalis:
A)
Valgymo įpročiai
•
Siekite normalaus, Jūsų amžių atitinkančio svorio. Sumažinkite antsvorį!
•
Nevartokite daug druskos!
•
Venkite riebaus maisto!
B)
Persirgtos ligos
Nuosekliai laikykitės gydytojų nurodymų kitoms ligoms (diabetui, podagrai, riebalų medabolizmo
sutrikimams) gydyti.
C) Įpročiai
•
Nerūkykite!
•
Saikingai vartokite alkoholį!
•
Mažiau gerkite kavos!
16
Page 20
D) Fizinė parengtis
•
Po preliminarios medicininės apžiūros reguliariai sportuokite.
•
Pasirinkite sporto šaką, kuriai reikalinga ištvermė, o ne fizinė jėga.
•
Žinokite savo galimybes, nepervarkite.
•
Jei sergate anksčiau minėtomis ligomis ir/arba Jums yra daugiau nei 40 metų, prieš
pradėdami sportuoti pasitarkite su gydytoju.
3. Kraujospūdžio matuoklio sudėtinės dalys
Paveikslėlyje pavaizduotas kraujospūdžio matuoklis BP AG1-20, kurį sudaro:
a)
Matavimo blokas:
Manometras
Manžetė
Stetoskopo galvutė
b)
Manžetė:
Tipas AC-1M žastui, kurio apimtis 22 - 32 cm
arba
Tipas AC-1L žastui, kurio apimtis 32 - 42 cm (galima įsigyti papildomai)
Dėtuvė
Ausinės
Stetoskopas
Balionėlis ir
vožtuvai
17
Page 21
4.
Matavimas
4.1.
Prieš matuojant
•
Prieš pat matavimą nevalgykite, nerūkykite, o taip pat venkite bet kokios įtampos. Šie
faktoriai veikia matavimo rezultatus. Prieš atlikdami matavimą atsipalaiduokite. Apie
10 minučių pasėdėkite fotelyje tylioje aplinkoje.
•
Nusivilkite prie žasto priglundančius drabužius.
•
Visada matuokite ant tos pačios rankos (dažniausiai ant kairės).
•
Matavimus stenkitės atlikti reguliariai, tuo pačiu paros metu, nes kraujospūdis kinta
dienos bėgyje.
4.2.
Dažniausios klaidos
Pastaba: Kraujospūdžio matavimui yra būtinos vienodos sąlygos, pageidautina
ramybės būsena!
Kraujospūdį gali padidinti bet kokios pastangos paremiant ranką. Įsitikinkite, kad sėdite
patogiai ir atsipalaidavę. Matavimo metu neįtempkite jokių matuojamos rankos raumenų.
Jei reikia, atramai panaudokite pagalvėlę.
•
Jei žasto arterija bus gerokai žemiau (aukščiau) širdies, gausite klaidingą didesnį (mažesnį)
kraujospūdį! (15 cm aukščio skirtumas sąlygoja 10 mmHg matavimo paklaidą!)
•
Klaidingus matavimų rezultatus sąlygoja per siauros ir per trumpos manžetės. Labai svarbu
pasirinkti reikiamo dydžio manžetę. Jos dydis priklauso nuo žasto apimties (matuojama per
žasto vidurį). Ant manžetės yra pažymėtas tinkamas žasto apimties intervalas. Jei manžetė
Jums netinka, kreipkitės į prekybos įstaigą. Pastaba: Naudokite tik kliniškai patvirtintas
originalias manžetes.
•
Neteisingus matavimo rezultatus sąlygoja laisvai uždėta manžetė arba iš šonų išsikišanti
oro kišenė.
4.3.
Manžetės uždėjimas
a) Manžetę užmaukite ant kairiojo žasto, kad guminis
vamzdelis eitų dilbio link.
b) Ant kairiojo žasto užvyniotą manžetę pasukite taip,
kaip pavaizduota paveikslėlyje. Užtikrinkite, kad
18
Page 22
apatinis manžetės kraštas būtų 2 - 3 cm aukščiau
alkūnės, o guminis vamzdelis eitų vidine dilbio
puse. Dėmesio! Balta 3 cm ilgio juostelė turi būti
tiksliai virš arterijos, einančios vidine dilbio puse.
c) Užsekite manžetę.
d) Tarp žasto ir manžetės neturi būti jokio tarpo,
nes tai paveiks matavimų rezultatus. Rankos
neturi veržti drabužiai. Būtina nusivilkti bet kokius
veržiančius drabužius, (pvz., megztinį).
e) Manžetė turi būti širdies lygmenyje. Pasistenkite
manžetės neužveržti pernelyg stipriai. Laikykite
ranką ant stalo delnu į viršų. Patikrinkite, ar
vamzdelis neperspaustas.
f) Prieš pradėdami matavimą, 2 minutes ramiai pasėdėkite.
Komentaras:
Jei neįmanoma manžetės uždėti ant kairės rankos, ją
galima uždėti ir ant dešinės. Tačiau visus matavimus
būtina atlikti ant tos pačios rankos.
4.4.
Matavimo procedūra
4.4.1.
Stetoskopo galvutės pridėjimas
Stetoskopo galvutės negalima dėti ANT manžetės ar Į man žetę.
Galvutę reikia pakišti po manžete arba priglausti 1 - 2 cm žemiau
manžetės krašto. Stetoskopo padėtis gera yra tada, kai
Korotkovo signalai (dunksniai) girdimi garsiausiai. Įsitikin kite,
kad stetoskopo galvutė prigludusi prie odos ir yra ties žasto
arterija. Gerai įsidėkite stetoskopo ausines, kad matuodami
kraujospūdį gerai girdėtumėte signalus. Prieš naudodamiesi
stetoskopu patikrinkite, ar netrūkus membrana, ausinės ar
2 - 3 cm
vamzdelis
19
Page 23
žarnelė. Jei stetoskopas netinkamai uždėtas ar pažeistas, bus
girdimas iškreiptas signalas arba dėl prasto garso perdavimo
bus gauti netikslūs parodymai.
4.4.2.
Manžetės pripūtimas
Uždarykite guminės kriaušės oro vožtuvą pasukdami varžtą
laikrodžio rodyklės kryptimi. Neperveržkite. Pastoviu ritmu
spaudykite guminę kriaušę, kol matavimo prietaiso rodyklė
bus 30 mmHg virš jūsų įprasto sistolinio kraujospūdžio
parodymo. Jei nesate tikri dėl parodymo, pirmiausia
pripūskite iki 200 mmHg lygmens.
4.4.3.
Sistolinio kraujospūdžio parodymai
Lėtai atidarinėkite oro vožtuvą pasukdami varžtą prieš laikrodžio
rodyklę ir laikydami stetoskopo galvutę ant žasto arterijos. Norint
gauti tikslius parodymus, labai svarbu teisingai išleidinėti orą,
todėl jums reikėtų pasitreniruoti ir išmokti išleidinėti orą rekomen duojamu 2 - 3 mmHg per sekundę greičiu arba taip, kad su
kiekvienu širdies dūžiu spaudimo parodymai kristų po vieną ar
dvi padalas. Nereikia laikyti pripūstos manžetės ilgiau nei būtina.
Kai iš manžetės leidžiamas oras, įdėmiai klausykite stetoskopu.
Kai tik išgirsite silpną ritmišką dunksnojimą ar duslius garsus, pasižiūrėkite į matavimo prietaiso
parodymus. Tai sistolinio kraujo spaudimo parodymai. Įdėmiai paklausykite ir įsiklausykite į
Ko rot kovo signalus.
4.4.4.
Diastolinio kraujo spaudimo parodymai
Leiskite spaudimui kristi tuo pačiu greičiu. Kai pasiekiama jūsų diastolinio spaudimo reikšmė,
dingsta dunksniai. Visiškai išleiskite orą pro vožtuvą. Nusiimkite stetoskopą ir manžetę.
4.4.5.
Užrašykite savo parodymus
Spaudimą matuokite bent du kartus. Baigę matavimą nepamirškite užsirašyti parodymų ir
matavimo datos bei laiko. Kraujospūdį geriausia matuotis atsikėlus ryte arba prieš vakarienę.
Nepamirškite, kad tik jūsų gydytojas yra tinkamai kvalifikuotas analizuoti jūsų kraujospūdį.
20
Page 24

☞
Papildoma informacija
Atlikus vieną matavimą, negalima tuoj pat vykdyti antro, nes gausite klaidingus rezultatus. Prieš
pradėdami pakartotinį matavimą, keletą minučių atsipalaiduokite, pasėdėkite arba pagulėkite.
5.
Galimi gedimai ir jų šalinimas
Jei naudojant prietaisą iškyla sunkumų, reikia patikrinti toliau išvardintus punktus ir, jei reikia,
imtis atitinkamų priemonių:
Sutrikimas
Prastai perduodamas garsas,
jis iškraipytas arba yra trukdžių.
Slėgis nekyla net ir intensyviai
pumpuojant orą į manžetę.
Negalima nustatyti 2 - 3 mmHg/s
oro išleidimo greičio reguliuojant
oro vožtuvą
.
Nenaudojant rodyklė nestovi ties
0 +/- 3 mmHg padala
Priemonės
1.
Patikrinkite, ar įkištos ir neįtrūkusios ausinės. Jei ne,
patikrinkite, ar jos nesusidėvėjusios.
2.
Patikrinkite, ar neįtrūkusi arba nesusisukusi žarnelė.
3
. Patikrinkite, ar neįtrūkus stetoskopo galvutė arba
membrana.
4
. Patikrinkite, ar galvutė gerai prigludus prie odos ir ar
ji yra ties žasto arterijos. Jei reikia, nuvalykite arba
pakeiskite pažeistas dalis, kad jos netrukdytų gauti
teisingus rezultatus.
1.
Patikrinkite, ar uždarytas vožtuvas.
2
. Patikrinkite, ar manžetė gerai pritvirtinta prie guminės
kriaušės ir manometro.
3
. Patikrinkite, ar manžetė, guminė kriaušė ir žarnelė
neleidžia oro.
•
Atjunkite vožtuvą nuo guminės kriaušės ir patikrinkite, ar
vožtuvo kanaluose nėra jokių kliūčių. Pašalinkite kliūtis ir
pamėginkite dar kartą. Jei vožtuvas neveikia, pakeiskite jį.
1.
Patikrinkite, ar atidarytas vožtuvas nuliniams
parodymams.
2
. Jei nukrypimas daugiau kaip 3 mmHg, kreipkitės į
vietinį atstovą dėl prietaiso kalibravimo.
21
Page 25

☞
Svarbi informacija
Svyruoja net ir sveikų žmonių kraujospūdis. Todėl svarbu, kad palyginami duomenys būtų atlikti
vienodomis sąlygomis (ramybės sąlygomis)! Jei laikantis visų reikalavimų rezultatų skirtumai
viršija 15 mmHg ir/arba kelis kartus išgirstate nepastovaus pulso garsus, prašome konsultuotis
su gydytoju. Atsiradus techninėms kraujospūdžio matuoklio problemoms, privalote konsultuotis
su pardavimo specialistu arba vaistininku. Niekada nesistenkite prietaisą taisyti patys!
Bet koks neįgaliotas prietaiso atidarymas panaikina visus garantinius įsipareigojimus!
6.
Prietaiso priežiūra ir eksploatacija. Kalibravimas.
Tinkamai prižiūrimas ir eksploatuojamas prietaisas tarnaus ilgus metus. Laikykitės šių taisyklių:
•
Prietaiso nemėtykite.
•
Nepumpuokite oro daugiau nei iki 300 mmHg.
•
Saugokite įrenginį nuo ekstremalių temperatūrų, drėgmės, dulkių ir tiesioginės saulės šviesos.
•
Venkite manžetės kontakto su aštriais daiktais.
•
Pasinaudoję prietaisu pilnai išleiskite orą iš manžetės.
•
Prietaisą saugokite specialioje dėtuvėje – tai apsaugos jį nuo nešvarumų.
•
Saugojimo temperatūra -20 °C - +70 °C, santykinė drėgmė 85 %.
•
Prietaisą valykite minkštu, sausu audiniu. Sterilizacija nebūtina, nes manometras neturi
tiesioginio sąlyčio su žmogaus kūnu.
•
Manžetę skalbkite tik prieš tai iš jos išėmę oro pūslę. Oro pūslę valykite drėgna šluoste.
Manžetę skalbkite šaltame vandenyje su muilu, po to ją perskalaudami ir išdžiovindami ore.
Periodinis kalibravimas
Kartais būtina patikrinti jautrių matavimo įrenginių tikslumą. Remiantis tuo, mes rekomenduojame kas 2 metus atlikti periodišką statinio spaudimo parodymų patikrinimą. Jūsų platinimo
specialistas su malonumu apie tai pateiks išsamesnę informaciją.
7.
Garantija
Nuo pirkimo datos kraujospūdžio matuokliui suteikiama dviejų metų garantija. Ši garantija
galioja ir prietaisui, ir manžetei. Garantija negalioja pažeidimams, kuriuos sukėlė neteisingas
22
Page 26

naudojimas, avarijos, darbo instrukcijų nesilaikymas arba trečių asmenų atlikti prietaiso
pakeitimai. Garantija galioja tik pateikus platintojo užpildytą garantijos kortelę.
8.
Standartų nuorodos
Prietaiso standartas: Prietaisas atitinka šiuos reikalavimus:
EN 1060-1/-2; ANSI / AAMI SP09
Šis prietaisas atitinka Medicinos prietaisų Direktyvos 93/42/EEB reiklavimus.
9.
www.microlife.lt
Detali informacija apie mūsų prietaisus bei paslaugas pateikiama tinklapyje www.microlife.lt
10.
Techninės specifikacijos
Masė: 450 g
Dydis
:
Sugojimo temperatūra: -20 °C - +70 °C; 85% maksimali santykinė drėgmė
Darbinė temperatūra
Matuojamas intervalas: nuo 0 - 300 mmHg
Matavimo padala
Tikslumas
Oro įpūtimo šaltinis: min. 200cc tūris iki 300 mmHg slėgio per 4 - 10 sek.
Slėgio kritimo tempas
Oro išleidimas
Histerezės klaida
Priedai
2. Guminė kraušė ir vožtuvas
3. Stetoskopas
4. Dėtuvė
Galimi techniniai pakeitimai.
:
: ±
: <±
:
:
175 x 70 x 103 mm
:
0 - 46 °C
2 mmHg
3 mmHg nuo 18 - 33 °C ir
±
6 mmHg nuo 34 - 46 °C
:
2 - 3 mmHg
4 mmHg/min
Tarp 0 - 4 mmHg
1. Manžetė, skirta žastui, kurio apimtis 22 - 32 cm
23
Page 27

Aneroīda asinsspiediena mērierīces komplekts
Instrukcija
24
Page 28

Satura rādītājs
1.
Ievads
1.1.
Apraksts
1.2.
Svarīga informācija par patstāvīgu mērīšanu
2.
Svarīga informācija par asins spiedienu un tā mērīšanu
2.1.
Kā rodas augsts/zems asinsspiediens?
2.2.
Kādi ir normāli rādītāji?
2.3.
Kas darāms, kad tiek iegūti augsti/zemi rādītāji?
3.
Dažādas asinsspiediena mērītāja komplekta sastāvdaļas
4.
Mērījumu veikšana
4.1.
Pirms mērīšanas
4.2.
Visbiežākie kļūmju avoti
4.3.
Manšetes uzvilkšana
4.4.
Mērīšanas procedūra
4.4.1.
4.4.2.
4.4.3.
4.4.4.
4.4.5.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Stetoskopa galviņas novietošana zem manšetes
Manšetes piepūšana
Sistoliskā asinsspiediena rādījums
Diastoliskā asinsspiediena rādījums
Jūsu rādījumu ierakstīšana
Bojājums/Bojājumu noteikšana un novēršana
Kopšana un uzglabāšana, atkārtota kalibrēšana
Garantija
Atsauce uz standartiem
www.microlife.lv
Tehniskās specifikācijas
LV
25
Page 29

1.
Ievads
1.1.
Apraksts
Aneroīda asinsspiediena mērītāja komplekts ir neautomātiska, mehāniska asins mērīšanas
ierīce, kas domāta rokas augšdaļai.
Tā sniedz pārbaudītu ticamību un lielisku darbību par taupīgu cenu. Pateicoties uzlabotajam
nepārtrauktajam adatas mehānismam un ergonomiskam gumijas bumbierim ar vārstiem,
aneroīda asinsspiediena mērītājs nodrošina precīzu un saskaņotu mērīšanu. Bez tam, izturīgā
neilona manšete, augstas kvalitātes balsts un aneroīda mērinstruments nodrošina saskaņotu
darbību. Visa ierīce tiek uzglabāta neilona somiņā ar rāvējslēdzēju, lai to būtu vieglāk pārnēsāt.
Pirms lietošanas uzmanīgi izlasiet šo lietošanas pamācību un saglabājiet to. Ja rodas papildus
jautājumi attiecībā uz asinsspiedienu un tā mērīšanu, griezieties ar tiem pie sava ārsta.
Uzmanību!
1.2.
Svarīga informācija par patstāvīgu mērīšanu
•
Neaizmirstiet: patstāvīga mērīšana tiek veikta kontrolei, nevis diagnozes uzstādīšanai
vai pašārstēšanās nolūkā. Nestandarta rādītājus vienmēr ir jāapspriež ar savu ārstu.
Nekādā gadījumā nemainiet ārsta izrakstīto medikamentu devu.
2.
Svarīga informācija par asins spiedienu un tā mērīšanu
2.1.
Kā rodas augsts/zems asinsspiediens?
Asinsspiediena līmenis tiek noteikts vienā smadzeņu daļā, tā saucamajā asinsrites centrā, un
tiek pielāgots attiecīgajai situācijai, nosūtot nervu sistēmai atbildes signālus. Lai noregulētu
asinsspiedienu, tiek mainīts sirdspukstu (pulsa) stiprums un biežums, kā arī cirkulācijas
asinsvadu platums. Pēdējo ietekmē ar asinsvadu sieniņās esošo sīko muskuļu palīdzību.
Arteriālā asinsspiediena līmenis sirdsdarbības laikā periodiski mainās: «asins izmetes»
(sistole) rādītājs ir maksimāli liels (sistoliskā asinsspiediena rādītājs), sirds «miera stāvoklī»
(diastole) – minimālais (diastoliskā asinsspiediena rādītājs). Asinsspiedienu rādītājiem ir jābūt
noteikta normāla diapazona ietvaros, tas ir nepieciešams noteiktu slimību novēršanai.
26
Page 30

Kādi ir normāli rādītāji?
2.2.
Asinsspiediens ir pārāk augsts, ja miera stāvoklī diastoliskais asinsspiediens ir virs 90 mmHg
un/vai sistoliskais asinsspiediens pārsniedz 140 mmHg. Šajā gadījumā ilgstoši nemainīgi rādītāji
apdraud Jūsu veselību, jo tas izraisa progresējošus asinsvadu bojājumus Jūsu organismā.
Ar asinsspiediena rādītājiem, kas ir pārāk zemi, t.i. sistoliskais rādītājs ir zemāks par 100 mmHg un/
vai diastoliskais rādītājs ir zem 60 mmHg, tāpat ir jākonsultējas ar ārstu. Pat ar normāliem asinsspiediena rādītājiem ir ieteicams veikt regulāras pārbaudes, izmantojot asinsspiediena mērītāju.
Ja Jūs izejat medicīnisko ārstēšanu, lai kontrolētu Jūsu asinsspiedienu, reģistrējiet
asinsspiediena līmeni, veicot regulārus mērījumus noteiktā diennakts laikā. Parādiet šos
rādītājus savam ārstam. Nekad neizmantojiet mērījumu rezultātus, lai patstāvīgi mainītu
Jūsu ārsta izrakstīto medikamentu devas.
Asinsspiediena rādītāju (vienība – mmHg) klasifikācija atbilstoši Pasaules Veselības organizācijai:
Amplitūda Sistoliskais Diastoliskais Ieteikums
pazemināts asinsspiediens
optimāls asinsspiediens
1.
normāls asinsspiediens
2.
nedaudz paaugstināts
3.
< 100 < 60
100 - 120 60 - 80
120 - 130 80 - 85
130 - 140 85 - 90
Konsultējieties ar ārstu!
Veiciet pašpārbaudi!
Veiciet pašpārbaudi!
Konsultējieties ar ārstu!
asinsspiediens
paaugstināts asinsspiediens
4.
ļoti paaugstināts
5.
140 - 160 90 - 100
160 - 180 100 - 110
Meklējiet medicīnisku palīdzību!
Meklējiet medicīnisku palīdzību!
asinsspiediens
asinsspiediens
6.
≥ 180 ≥ 110
bīstami augsts
☞
Papildus informācija
•
Ja Jūsu rādītāji miera stāvoklī pārsvarā ir standarta, bet īpaši augsti fiziska vai
Nekavējoties meklējiet
medicīnisku palīdzību!
psiholoģiska stresa apstākļos, iespējams, ka Jūs sirgstat no tā saucamās «labilās
hipertensijas». Konsultējieties ar ārstu, ja Jums ir aizdomas, ka tas ir Jūsu gadījums.
•
Pareizi izmērīta diastoliskā asinsspiediena rādītāja, kas ir virs 120 mmHg, gadījumā ir
nepieciešama neatliekama medicīniskā ārstēšana.
27
Page 31

2.3.
Kas darāms, kad tiek iegūti augsti/zemi rādītāji?
a)
Lūdzu, konsultējieties ar ārstu.
b)
Paaugstināti asinsspiediena rādītāji (dažādas hipertensijas formas), kas tiek novēroti
ilgstoša perioda vai vidēji ilga perioda garumā, var radīt nozīmīgu risku Jūsu veselībai. Tas
ir saistīts ar organisma arteriālajiem asinsvadiem, kuri var tikt bojāti asinsvadu sieniņās
uzkrājušos nogulšņu dēļ (arterioskleroze). Tas var izraisīt nepietiekamu asins pievadīšanu
svarīgiem orgāniem (sirds, smadzenes, muskuļi). Ja ilgstoši saglabājas paaugstināti
asinsspiediena rādītāji, sirds struktūra var tikt bojāta.
c)
Ir daudz dažādu iemeslu, kāpēc paaugstinās asinsspiediens. Mēs izšķiram bieži sastopa mo
primāro (būtisko) hipertensiju un sekundāro hipertensiju. Konsultējieties ar savu ārstu, lai
gūtu informāciju par Jūsu paaugstināto asinsspiediena rādītāju iespējamajiem cēloņiem.
d)
Ir pasākumi, kurus Jūs varat veikt, ne tikai, lai samazinātu medicīniskā ceļā noteikto
paaugstināto asinsspiedienu, bet arī, lai novērstu tā rašanos. Šie pasākumi ir Jūsu parastā
dzīvesveida daļa:
A)
Ēšanas paradumi
•
Tiecieties uzturēt Jūsu vecumam atbilstošu normālu svaru. Tieciet vaļā no liekā svara!
•
Izvairieties pārmērīgi lietot uzturā parasto sāli.
•
Izvairieties no taukainiem ēdieniem.
B)
Iepriekšējās slimības
Pastāvīgi sekojiet visām medicīniskajām instrukcijām tādu iepriekšēju saslimšanu ārstēšanai, kā:
•
Diabēts (Diabetes mellitus)
•
Tauku apmaiņas traucējumi
•
Podagra
C)
Paradumi
•
Pilnībā atmetiet smēķēšanu
•
Lietojiet tikai mērenas alkohola devas
•
Samaziniet kofeīna (kafijas) lietošanu uzturā
D)
Fiziskā uzbūve
•
Veicot iepriekšēju medicīnisko apskati, regulāri nodarbojieties ar sportu.
•
Izvēlieties uz izturību vērstu sporta veidu un izvairieties no tiem, kas prasa spēka pielietošanu.
•
Izvairieties no pārmērīgas slodzes.
28
Page 32

•
Ar iepriekšējām slimībām un/vai vecumā pāri 40 gadiem, konsultējieties ar ārstu pirms
sporta nodarbību uzsākšanas. Ārsts ieteiks Jums piemērotā sporta veidu un slodzes.
3.
Dažādas asinsspiediena mērītāja komplekta sastāvdaļas
Attēlā ir parādīts no kā sastāv BP AG1-20:
a)
Mērierīce:
Manometrs
Manšete
Stetoskopa galviņa
Manšete
b)
AC-1M modelis, ar rokas apkārtmēru 22 - 32 cm vai
AC-1L modelis, ar rokas apkārtmēru 32 - 42 cm (pieejams kā speciālais piederums)
4.
4.1.
•
•
•
•
:
Mērījumu veikšana
Pirms mērīšanas
Izvairieties no ēšanas, smēķēšanas, kā arī no dažāda veida piepūles tieši pirms mērījumu
veikšanas. Visi šie apstākļi var ietekmēt mērījumu rezultātus. Mēģiniet rast laiku atpūtai,
sēžot atzveltnes krēslā mierīgā atmosfērā aptuveni desmit minūtes pirms mērīšanas.
Noņemiet apģērbu, kas cieši pieguļ Jūsu rokas augšdaļai.
Mēriet vienmēr uz vienas rokas (parasti kreisās).
Centieties veikt mērījumus regulāri vienā dienas laikā, jo dienas gaitā asinsspiediens mainās.
Somiņa
Uzgaļi ausīm
Stetoskops
Gumijas bumbieris
un vārsti
29
Page 33

Visbiežākie kļūmju avoti
4.2.
:
Asinsspiediena mērījumiem, kurus izmantojat salīdzināšanai, ir nepieciešami vienādi
Piezīme
nosacījumi! Parasti tie ir mierīgi nosacījumi.
•
Pacienta mēģinājumi atbalstīt roku var paaugstināt asinsspiedienu. Pārliecinieties, ka Jums ir
ērti, Jūs atrodaties atslābinātā stāvoklī un nedarbināt nevienu no mērāmās rokas muskuļiem
mērījumu veikšanas laikā. Ja nepieciešams, izmantojiet spilvenu atbalstam.
•
Ja rokas artērija atrodas ievērojami zemāk (augstāk) par sirds līmeni, tiks parādīts kļūmīgi
augstāks (zemāks) asinsspiediena mērījums! (Atšķirība augstumā par 15 cm atbilst mērījuma
novirzei par 10 mmHg).
•
Manšetes, kas ir pārāk šauras vai pārāk īsas var sniegt nepareizus mērījumu rādītājus. Ir svarīgi
izvēlēties atbilstošu manšeti. Manšetes izmērs ir atkarīgs no rokas apkārtmēra (tiek mērīts
rokas vidusdaļā). Pieļaujamais izmērs ir uzdrukāts uz manšetes. Ja tas Jums nav piemērots,
sazinieties ar tirgotāju. Piezīme: Izmantojiet tikai klīniski atzītas originālās manšetes!
•
Vaļīga vai nelīdzeni uzģērbta manšete var sniegt nepareizus mērījumu rezultātus.
4.3.
Manšetes uzvilkšana
a)
Aptiniet manšeti apkārt kreisajam augšdelmam tā, lai
caurule būtu vērsta apakšdelma virzienā.
b)
Uzlieciet manšeti kā parādīts attēlā. Pārliecinieties, ka
manšetes apakšējā mala ir aptuveni 2 - 3 cm virs elkoņa
un ka gumijas caurule iziet no manšetes rokas iekšējā
pusē. Svarīgi! Atzīmei (3 cm gara līnija) ir jābūt tieši uz
2 - 3 cm
artērijas, kas tek pa rokas iekšējo pusi.
c)
Aizvelciet manšetes brīvo galu un aizsprādzējiet to.
d)
Starp roku un manšeti nedrīkst palikt brīva vieta, jo tas
caurule
var ietekmēt rezultātus. Taču sprādze nedrīkst aprobežot
roku. Jebkurš apģērba gabals, kas aprobežo rokas
kustības (piemēram, džemperis) ir jānoģērbj.
e)
Nostipriniet manšeti ar liplentes palīdzību tādā veidā, lai tā
ir ērti un ne pārāk cieši uzģērbta. Novietojiet roku uz galda
30
Page 34

(ar delnu uz augšu) tā, lai manšete būtu vienā līmenī ar
sirdi. Pārliecinieties, ka caurule nav savijusies.
f)
Pasēdiet pāris minūtes mierīgi pirms mērīšanas veikšanas.
Komentārs
Ja neizdodas uzvilkt manšeti uz kreisās rokas, to iespējams
uzģērbt uz labās. Tomēr visi mērījumi ir jāveic, izmantojot
vienu un to pašu roku.
4.4.
4.4.1.
Stetoskopa galviņu nedrīkst novietot UZ manšetes vai tās
IEKŠPUSĒ, to drīkst novietot zem manšetes vai 1 - 2 cm zem tās.
Stetoskopa galviņa ir novietota pareizi, ja Korotkova toņi kļūst
stiprāki «skaļāki». Pārliecinieties, ka stetoskopa galviņa saskaras
ar ādu un atrodas virs pleca artērijas. Pareizi uzģērbiet austiņas
uz abām ausīm, lai pārbaudītu Korotkova toņus mērīšanas
laikā. Pirms lietojat stetoskopu, pārliecinieties, ka membrāna,
austiņas un caurule nav ieplaisājušas. Nepareiza stetoskopa
izvietošana vai bojājums var sniegt sagrozītas skaņas vai trokšņu
pārraidīšanu, tas savukārt neļaus saņemt precīzus rādījumus.
4.4.2.
Noslēdziet gaisa vārstu uz gumijas bumbiera, pagriežot to
pulksteņa rādītāja kustības virzienā. Neaizgrieziet pārāk cieši.
Vienmērīgi saspiediet ar roku piepūšanas bumbieri līdz rādītāja
bultiņa uz mērinstrumenta būs 30 mmHg virs parastā sistoliskā
asinsspiediena rādītāja. Ja Jūs neesat pārliecināti par parasto
rādītāju, tad sākumam piepūtiet līdz 200 mmHg.
:
Mērīšanas procedūra
Stetoskopa galviņas novietošana zem manšetes
Manšetes piepūšana
31
Page 35

4.4.3.
Sistoliskā asinsspiediena rādījums
Lēni atveriet vārstu, griežot skrūvi pretēji pulksteņa rādītāja
kustības virzienam un turiet stetoskopa galviņu uz pleca artērijas.
Atbilstošs gaisa izlaišanas ātrums ir svarīgs, lai saņemtu precīzu
rādījumu, tādēļ Jums ir jātrenē un jāapgūst gaisa izlaišana ar
ieteicamo ātrumu – 2 - 3 mmHg sekundē vai pazemināšanos par
1 - 2 atzīmēm uz spiediena mērinstrumenta pēc katra sirdspuksta.
Nav ieteicams atstāt manšeti piepūstu ilgāk nekā tas ir nepieciešams. Kad no manšetes tiek
izlaists gaiss, Jums ir uzmanīgi jāklausās ar stetoskopu. Atzīmējiet rādījumu, kas ir redzams
uz mērinstrumenta, kad Jūs saklausāt neskaidrus, ritmiskus sitienus vai dobjas skaņas. Tas
ir sistoliskā asinsspiediena rādījums. Uzmanīgi klausieties un iemācieties atpazīt pulsa skaņu
(Korotkova toņus).
4.4.4.
Diastoliskā asinsspiediena rādījums
Ļaujiet spiedienam kristies, izlaižot gaisu ar tādu pat ātrumu. Kad tiek sasniegts Jūsu diastoliskā
asinsspiediena rādītājs pulsējoša skaņa izbeidzas. Pilnībā izlaidiet gaisu no manšetes vārsta.
Noņemiet manšeti no rokas un stetoskopu no ausīm.
4.4.5.
Jūsu rādījumu ierakstīšana
Atkārtojiet mērīšanu vismaz divreiz. Neaizmirstiet pierakstīt Jūsu rādījumus un laiku, kad tika
veikts mērījums, nekavējoties pēc mērījumu izdarīšanas. Piemērots laiks – pirmais, ko darāt rītā
vai tieši pirms vakara ēdienreizes. Atcerieties, ka vienīgi Jūsu ārsts ir pietiekoši kvalificēts, lai
analizētu Jūsu asinsspiedienu.
☞
Papildus informācija
Mērījumus nedrīkst veikt vienu pēc otra, citādi rezultāti var būt nepareizi. Uzgaidiet dažas
minūtes miera stāvoklī sēdus vai guļus, tad atkārtojiet mērīšanu.
5.
Citi iespējamās problēmas un to novēršana
Ja, lietojot ierīci, rodas problēmas, ir jāpārbauda šādus aspektus, un, ja nepieciešams, ir jāveic
attiecīgi pasākumi:
32
Page 36

Problēma
Pārraidītās skaņas ir slikti dzirdamas,
traucētas vai pastāv papildus trokšņi.
Spiediens nepaaugstinās, neskatoties
uz to, ka gumijas bumbieris piepūšas.
Izpūšanas ātrums var uzstādīt tikai
2 - 3 mmHg/sekundē, noregulējot
gaisa izpūšanas vārstu.
Rādītājs miera stāvoklī atrodas uz
atzīmes 0+/-3 mmHg.
☞
PAPILDUS INFORMĀCIJA
Asinsspiediena līmenis var svārstīties pat veseliem cilvēkiem. Tādēļ ir svarīgi veikt
salīdzināmos mērījumus tajos pašos apstākļos (miera apstākļos)! Ja, neskatoties uz
visiem šiem aspektiem, svārstīšanās pārsniedz 15 mmHg un/vai vairākas reizes Jūs saklausāt
nevienmērīgu pulsu, konsultējieties ar ārstu.
Jums ir jākonsultējas ar tirgotāju vai aptiekāru, ja ar asinsspiediena mērītāju rodas tehniska
rakstura problēmas. Nekad nemēģiniet remontēt ierīci patstāvīgi! Ierīces neatļautas
atvēršanas gadījumā garantija kļūst nederīga!
Pasākums
1.
Pārbaudiet vai austiņas nav aizsitušās vai ieplaisājušas.
Ja nav, tad pārliecinieties, vai tās labi pieguļ un nav
no lietotas.
2.
Pārbaudiet, vai caurule nav bojāta vai sagriezusies.
3.
Pārbaudiet, vai uz stetoskopa galviņas un diafragmas
nav plaisu.
4.
Pārliecinieties, ka stetoskopa galviņa pieskaras
ādai
atbilstošā veidā un atrodas uz pleca artērijas
mērīšanas laikā. Notīriet vai nomainiet bojātās detaļas,
lai gūtu pareizus rādījumus.
1.
Pārliecinieties, ka vārsts ir noslēgts.
2. Pārliecinieties, ka manšete ir labi savienota ar
gumijas bumbieri un manometru.
3. Pārbaudiet, vai nav noplūdes manšetē, vadā vai
bumbierī. Nomainiet bojātās detaļas, ja tādas ir.
•
Izjauciet bumbiera vārstu, lai pārliecinātos, ka nekas
neaizsprosto gaisa plūsmu vārstā. Ja tas joprojām
nedarbojas, nomainiet to, lai gūtu pareizus rādījumus.
1. Pārliecinieties, ka vārsts ir atvērts, lai veiktu nulles
stāvokļa pārbaudi.
2. Ja joprojām saglabājas novirze lielāka par 3 mmHg,
sazinieties ar tirgotāju, lai veiktu atkārtotu manometra
kalibrēšanu.
33
Page 37

6.
Kopšana un uzglabāšana, atkārtota kalibrēšana
Pareizi izmantojot un uzglabājot šo asinsspiediena mērītāja ierīci, tā nodrošinās gadiem ilgu
kalpošanu. Sekojiet vispārīgiem nosacījumiem:
•
Nenometiet.
•
Nekad nepiepūtiet vairāk par 300 mmHg.
•
Nepakļaujiet ierīci izteikti zemas vai augstas temperatūras, mitruma vai tiešu saules staru iedarbībai.
•
Nekad nepieskarieties manšetes audumam ar asiem priekšmetiem, jo tie var bojāt audumu.
•
Pirms uzglabāšanas pilnībā izlaidiet gaisu no manšetes.
•
Nekādā gadījumā nedemontējiet manometru.
•
Uzglabājiet visu ierīci komplektā ietilpstošajā somiņā, lai uzglabātu visas detaļas tīras.
•
Uzglabāšana pie šādas temperatūras: -20 - +70 °C ar relatīvo mitrumu 85 % (bez kondensācijas).
•
Notīriet manometru un gumijas bumbieri ar mitru drāniņu. Nav nepieciešams sterilizēt, jo manometra daļas parasti nenokļūst tiešā saskarē ar pacienta ķermeni mērījumu veikšanas laikā.
•
No sākuma noņemiet bumbieri un noslaukiet liplenti, bumbieri un caurules ar mitru drāniņu.
Manšeti drīkst mazgāt ar ziepēm un aukstu ūdeni. Tikai noskalojiet manšeti ar tīru ūdeni un
izžāvējiet to dabiskā ceļā.
Periodiska kalibrēšana
Laiku pa laikam ir jāpārbauda jutīgo mērierīču precizitāte. Tādēļ mēs iesakām veikt periodisku
statiskā asinsspiediena displeja pārbaudi ik pēc 2 gadiem.
Tirgotājs var sniegt vairāk informācijas šajā jautājumā.
7.
Garantija
Šim asinsspiediena mērītājam ir 2 gadu garantija, skaitot no iegādes datuma. Garantija
attiecas uz ierīci un manšeti. Tā nav attiecināma uz bojājumiem, kas radušies nepareizas
lietošanas, negadījuma, norādījumu nesekošanas vai trešo personu veikto ierīces modifikāciju
rezultātā. Garantija ir derīga tikai uzrādot tirgotāja aizpildītu garantijas talonu.
Ražotājs: Microlife AG, Šveice Serviss:
Izplatītājs Latvijā: UAB Microlife Maskavas iela 17/19, Rīga, LV-1050
Maskavas iela 17/19, Rīga, LV-1050 Mob. tālr.: +371 29188395
34
Page 38

8.
Atsauce uz standartiem
Ierīces standarts:
un ANSI / AAMI SP09
Šī ierīce atbilst Direktīvas par medicīniskām ierīcēm 93/42/EEC prasībām.
9.
www.microlife.lv
Sīkāka lietotāja informācija par produktu, kā arī ar pakalpojumiem ir pieejama vietnē www.microlife.lv
10.
Tehniskās specifikācijas
:
Svars
:
Izmērs
Uzglabāšanas temperatūra
Lietošanas temperatūra: 0 - 46 °C
Mērīšanas diapazons
Mērīšanas izšķirtspēja: 2 mmHg
Precizitāte
: ±
±
Gaisa iepūšanas avots
Spiediena krišanas ātrums: 2 - 3 mmHg/sek
Gaisa noplūde
Kļūme histerēzes dēļ: 0 - 4 mmHg ietvaros
Piederumi
ar iekšēju kameru
2.
3. stetoskops
4. somiņa
Tiesības uz tehniskām izmaiņām saglabātas.
: <±
: 1.
450 g
175 x 170 x 103 mm
:
-20 °C līdz +70 °C; maksimālais relatīvais mitrums 85 %
:
0 - 300 mmHg
3 mmHg ietvaros 18 - 33 °C temperatūrā;
6 mmHg ietvaros 34 - 46 °C temperatūrā
:
200 cm3 apjoms rada 300 mmHg spiedienu 4 - 10 sekundēs.
manšete (pieaugušo izmērs ar rokas apkārtmēru 22 - 32 cm)
gumijas bumbieris un vārsts
Ierīce atbilst EN 1060-1/-2
4 mmHg/min
35
Page 39

Aneroidne vererõhu mõõtmise komplekt
Kasutusjuhend
36
Page 40

Sisukord
1.
Sissejuhatus
1.1.
BP AG1-20 omadused
1.2.
Oluline teave iseendal vererõhu mõõtmise kohta
2. Oluline teave vererõhu ja selle mõõtmise kohta
2.1.
Kuidas tekib kõrge/madal vererõhk?
2.2.
Millised vererõhuväärtused on normaalsed?
2.3.
Mida saab teha, kui mõõdetud vererõhuväärtused on regulaarselt kõrged/madalad?
3. Vererõhu mõõtmise komplekti komponendid
4. Vererõhu mõõtmine
4.1.
Enne mõõtmist
4.2.
Sagedasemad veaallikad
4.3.
Manseti asetamine
4.4.
Mõõtmisprotseduur
4.4.1.
4.4.2.
4.4.3.
4.4.4.
4.4.5.
5. Häired / rikete leidmine
6. Hooldus ja teenindus, ümberkalibreerimine
7. Garantii
8. Standardid
9. www.microlife.ee
10. Tehnilised andmed
Asetage stetoskoobi otsik manseti alla
Manseti täitmine
Süstoolse vererõhu näit
Diastoolse vererõhu näit
Tulemuste ülesmärkimine
EE
37
Page 41

1.
Sissejuhatus
1.1.
BP AG1-20 omadused
Õlavarrele asetatava aneroidse vererõhu mõõtmise komplektiga BP AG1-20 ei mõõdeta
vererõhku automaatselt, vaid mehhaaniliselt.
Lisaks soodsale hinnale on seade usaldusväärne ja kindla kvaliteediga. Tänu kaasaegsele
nõelamehhanismile ja täisõhuventiilidega ergonoomilisele kummiballoonile on BP AG1-20-ga
saadud mõõtmistulemused täpsed ja omavahel võrreldavad. Peale selle tagavad omaduste
püsimise vastupidav nailonmansett, suurepärase kvaliteediga ühendusosad ja aneroidne vererõhu mõõtmisviis. Vererõhumõõtjat saab hoida lukuga nailonkotis, mida on mugav kaasas kanda.
Enne kui hakkate aparaati kasutama, lugege kasutusjuhend hoolikalt läbi ja hoidke seda kindlas
kohas. Kui teil tekib lisaküsimusi vererõhu ja selle mõõtmise kohta, pöörduge arsti poole.
Tähelepanu!
1.2.
Oluline informatsioon iseendal vererõhu mõõtmise kohta
•
Ärge unustage: iseendal vererõhu mõõtmine tähendab kontrolli, mitte diagnoosimist
ega ravi. Tavalisest erinevatest väärtustest tuleb alati rääkida arstile. Mitte ühelgi juhul
ei tohi muuta arsti määratud ravimiannuseid.
2.
Oluline informatsioon vererõhu ja selle mõõtmise kohta
2.1.
Kuidas tekib kõrge/madal vererõhk?
Vererõhu väärtus määratakse kindlaks ühes teatud ajupiirkonnas, mida nimetatakse vereringe keskuseks. Situatsiooniga kohanemine toimub närvisüsteemi tagasisidemehhanismi abil.
Et vererõhku reguleerida, muudetakse südamelöökide (pulsi) tugevust ja sagedust ning
ühtlasi veresoonte laiust. Viimast muudetakse veresoonte seintes olevate peente lihaste abil.
Arteriaalne vererõhk muutub südametegevuse ajal periooditi: vere väljutuse (süstoli) ajal on
see maksimaalne (süstoolse vererõhu väärtus), südame puhkeperioodi lõpus (diastolis) aga
minimaalne (diastoolse vererõhu väärtus). Vererõhk peab jääma normi piiresse, et hoida ära
teatud haiguste kujunemist.
38
Page 42

Millised vererõhuväärtused on normaalsed?
2.2.
Vererõhk on liiga kõrge, kui diastoolse vererõhu väärtus ületab puhkeolekus 90 mmHg ja/või
süstoolse vererõhu väärtus 140 mmHg. Sellisel juhul pöörduge viivitamatult arsti poole. Pikka
aega püsiv kõrge rõhk ohustab tervist, kahjustades pidevalt veresooni.
Pöörduge arsti poole ka juhul, kui vererõhk on liiga madal, st süstoolne vererõhk alla
100 mmHg ja/või diastoolne vererõhk alla 60 mmHg.
Ka normaalsete vererõhuväärtuste puhul soovitatakse iseendal vererõhku regulaarselt jälgida.
Nii saate võimalikud muutused varakult avastada ja sellele reageerida.
Kui te võtate vererõhuravimeid, märkige oma vererõhuväärtused üles korrapäraselt iga päev
kindlatel kellaaegadel. Näidake saadud tulemusi oma arstile. Ärge kunagi kasutage
mõõtmistulemusi selleks, et ise muuta arsti määratud ravimiannuseid.
Vererõhuväärtuste klassifikatsiooni tabel (ühikud mmHg) Maailma Tervishoiuorganisatsiooni
andmeil:
Vahemik Süstoolne Diastoolne Soovitus
liiga madal vererõhk
optimaalne vererõhk
1.
normaalne vererõhk
2.
pisut kõrgenenud vererõhk
3.
liiga kõrge vererõhk
4.
väga kõrge vererõhk
5.
ohtlikult kõrge vererõhk
6.
☞
Lisainformatsioon
•
Kui teie vererõhuväärtused on puhkeolekus enamasti normi piires, kuid füüsilise või
< 100 < 60
100 - 120 60 - 80
120 - 130 80 - 85
130 - 140 85 - 90
140 - 160 90 - 100
160 - 180 100 - 110
≥ 180 ≥ 110
Pidage nõu arstiga
Iseseisev kontroll
Iseseisev kontroll
Pidage nõu arstiga
Pöörduge arsti poole
Pöörduge arsti poole
Pöörduge viivitamatult
arsti poole!
psüühilise koormuse puhul erandlikult kõrged, võib teil olla nn labiilne hüpertensioon.
Kahtluse korral pöörduge arsti poole.
•
Õigesti mõõdetud diastoolse vererõhu väärtused üle 120 mmHg vajavad koheselt ravi.
39
Page 43

2.3.
Mida saab teha, kui mõõdetud vererõhuväärtused on regulaarselt kõrged/madalad?
a)
Palun konsulteerige arstiga.
b)
Kõrgenenud vererõhk (hüpertensiooni eri vormid) ohustab tervist nii keskmiselt kui ka
pikaajaliselt. Niisugune seisund mõjutab organismi veresooni (artereid), põhjustades
veresoonte seintele tekkivate ladestuste (arterioskleroosi) tagajärjel veresoonte
ahenemist. Selle tagajärg võib olla elutähtsate organite (süda, aju, lihased) ebapiisav
varustamine verega. Peale selle kahjustab pidevalt kõrge vererõhk südamekudet.
c)
Kõrgenenud vererõhu tekkel on palju põhjusi. Eristatakse tavalist primaarset
(essentsiaalset) hüpertensiooni ja sekundaarset hüpertensiooni. Viimast rühma saab
seostada teatud kindla organi talitluse häiretega. Palun rääkige oma arstiga, et selgitada
välja teie vererõhutõusu põhjused.
d)
On võimalik kasutada abinõusid, mis mitte ainult ei alanda vererõhku, vaid hoiavad ka
selle tõusu ära. Need abinõud on osa teie üldisest eluviisist:
A)
Toitumisharjumused
•
Saavutage eale vastav normaalne kehakaal. Vähendage ülekaalu!
•
Vältige liigset söögisoola tarbimist.
•
Vältige rasvaseid toite.
B)
Kaasuvad haigused
Järgige kogu aeg juhiseid, mis olete saanud järgnevalt nimetatud kaasnevate haiguste raviks:
•
suhkruhaigus (Diabetes mellitus)
•
rasvade ainevahetuse häired
•
podagra
C)
Harjumused
•
Jätke suitsetamine lõplikult maha
•
Jooge alkoholi vaid mõõdukas koguses
•
Piirake kofeiini (kohvi) tarbimist
D)
Füüsiline seisund
•
Hakake korrapäraselt tegema sporti, ent kõigepealt tehke kindlaks oma tervislik seisund.
•
Valige spordialad, mis nõuavad vastupidavust, mitte jõudu.
•
Vältige sportimist oma võimete piiril.
40
Page 44

•
Kaasnevate haigustega ja/või üle 40-aastased inimesed peaksid enne sportlikku tegevust
konsulteerima arstiga. Arst annab nõu, milline spordiala valida ning kui intensiivne võib
treening olla.
3.
Aneroidse vererõhu mõõtmise komplekti osad
Pildil on kujutatud vererõhuaparaat BP AG1-20, mille koostisosad on:
a)
Vererõhumõõtja:
Stetoskoobi otsik
Mansett
b)
Tüüp AC-1M, õlavarrele ümbermõõduga 22 - 32 cm või
Tüüp AC-1L, õlavarrele ümbermõõduga 32 - 42 cm
(saadaval lisatarvikuna)
4.
Mõõtmine
4.1.
Enne mõõtmist
•
Enne vererõhu mõõtmist vältige söömist, suitsetamist ja igasugust pingutust. Kõik
Manomeeter
Mansett
:
Pehme kott
Kõrvaotsik
Stetoskoop
Kummiballoon
ja õhuventiil
41
Page 45

need tegurid mõjutavad mõõtmise tulemust. Võtke endale aega ja lõdvestuge, istudes
tugitoolis rahulikus õhkkonnas ligikaudu kümme minutit enne mõõtmist.
•
Eemaldage kõik riided, mis on tihedalt õlavarre ümber.
•
Mõõtke rõhku alati samal käel (tavaliselt vasakul).
•
Püüdke mõõta korrapäraselt iga päev samal kellaajal, kuna vererõhk muutub päeva jooksul.
4.2.
Sagedasemad vigade põhjused
Märkus: Et saada võrreldavad vererõhuväärtused, tuleb alati mõõta samades
tingimustes! St üldjuhul puhkeolekus.
•
Kõik patsiendi pingutused toetada kätt võivad vererõhuväärtust suurendada. Veenduge,
et olete mugavas lõdvestunud asendis ja ärge mõõtmise ajal pingutage lihaseid sellel käel,
kust mõõdate rõhku. Kui vaja, kasutage toestuseks patja.
•
Kui käearter asetseb südame suhtes tunduvalt madalamal (kõrgemal), saadakse ekslikult kõr gem
(madalam) vererõhuväärtus! (iga 15 cm kõrguse erinevus annab mõõtmisvea 10 mmHg).
•
Kasutades liiga kitsast või lühikest mansetti, võib saada vale vererõhuväärtuse. Õige
manseti valik on äärmiselt tähtis. Manseti suurus oleneb käe ümbermõõdust (mõõdetud
keskosas). Lubatud vahemik on trükitud mansetile. Kui see ei sobi teile, pöörduge
müügiesindaja poole. Märkus: kasutage ainult kliiniliselt tunnustatud originaalmansette!
•
Lõtv mansett või külgedele väljuvad õhutaskud põhjustavad valesid mõõtmistulemusi.
4.3.
Manseti asetamine
a) Tõmmake mansett üle vasaku käe nii, et vooliku ots on
suunatud käelaba poole.
b) Asetage mansett ümber käe, nagu joonisel näidatud.
Veenduge, et manseti alumine serv on ligikaudu 2 - 3 cm
küünarnukist kõrgemal ja kummist voolik väljub mansetist
käe siseküljel. Oluline! Märgistus (u. 3 cm pikkune riba) peab
asetsema täpselt arteril, mis kulgeb käsivarre sisepinnal.
c) Tõmmake manseti vaba ots pingule ja sulgege sulguriga.
d) Käe ja manseti vahele ei tohi jääda vaba ruumi, see võib
2 - 3 cm
Voolik
42
Page 46

mõjutada mõõtmistulemust. Riided ei tohi kätt pigistada.
Kõik sellised riided (näiteks kampsun) tuleb ära võtta.
e) Sulgege mansett takjakinnitusega nii, et see asetseb
mugavalt ega ole liiga tihedalt ümber. Asetage käsi laua
peale (peopesa ülespoole) nii, et mansett oleks südamega
samal kõrgusel. Veenduge, et voolik poleks niverdunud.
f) Jääge paariks minutiks rahulikult istuma, enne kui alustate
mõõtmist.
Kommentaar:
Kui vasakule käele pole võimalik mansetti asetada, võib selle
panna paremale käele. Ent kõik mõõtmised tuleb teha samal käel.
4.4.
Mõõtmisprotseduur
4.4.1.
Asetage stetoskoobi otsik manseti alla
Stetoskoobi otsikut ei tohi panna manseti PEALE ega VAHELE,
vaid see tuleb asetada manseti alla või sellest 1 - 2 cm allapoole.
Stetoskoobi otsik on asetatud õigesti, kui Korotkovi toone on
kuulda kõige tugevamini («valjemini»). Veenduge, et stetoskoobi
otsik on kontaktis nahaga ja asub õlavarrearteri kohal. Et mõõtmise
ajal Korotkovi toone kuulda, tuleb kõrvaotsikud asetada õigesti.
Enne stetoskoobi kasutust kontrollige, et membraan, kõrvaotsikud
ja voolikud oleksid terved. Kui stetoskoop on valesti ühendatud
või kahjustatud, võivad helid moonduda või halvasti levida, mille
tagajärjeks võivad olla ebatäpsed mõõtmistulemused.
4.4.2.
Manseti täitmine
Sulgege kummiballooni õhuventiil, keerates kruvi kellaosuti
liikumise suunas. Ärge keerake kruvi kinni liiga kõvasti. Pumbake
kummiballooni ühe käega ühtlase sagedusega nii, et see ületaks
oodatud süstoolse vererõhu väärtust vähemalt 30 mmHg. Kui te ei
tea seda väärtust, täitke mansett ligikaudu 200 mmHg-ni.
43
Page 47

4.4.3.
Süstoolse vererõhu näit
Avage õhuventiil aeglaselt, keerates kruvi kellaosutile vastupidises
suunas ja hoidke stetoskoobi otsikut õlavarrearteri kohal. Täpsete
tulemuste saamiseks on oluline, et rõhku langetataks õige
kiirusega. Seega peate harjutades omandama, kuidas langetada
rõhku kiirusega 2 - 3 mmHg sekundis või üks kaks mõõtevahemikku ühe südamelöögi kohta. Mansetti ei tohi täidetuna hoida
kauem, kui vaja. Kui mansett hakkab tühjenema, peate stetoskoobiga hoolega kuulatlema südametoone. Fikseerige mõõdikunäit
kohe, kui kuulete nõrka, rütmilist tooni. See ongi süstoolse vererõhu
näit. Kuulake hoolikalt ja tutvuge pulsi (Korotkovi) toonidega.
4.4.4.
Diastoolse vererõhu näit
Jätkake rõhu langetamist aeglaselt, sama kiirusega. Kui rõhk on langenud teie diastoolse rõhu
näiduni, rütmilised toonid lõppevad. Nüüd tühjendage mansett täielikult. Võtke mansett käe
ümbert ära ja eemaldage kõrvaotsikud kõrvadest.
4.4.5.
Tulemuste ülesmärkimine
Korrake mõõtmist vähemalt kaks korda. Ärge unustage tulemusi ja mõõtmise kellaaega üles
märkida kohe, kui olete mõõtmise lõpetanud. Sobivaim mõõtmisaeg on hommikul pärast
ärkamist või vahetult enne õhtusööki. Ärge unustage, et ainult arst oskab teie seisundit teie
vererõhunäitude alusel analüüsida.
☞
Lisainformatsioon
Rõhku ei tohi mõõta mitu korda järjest, pidamata vahet, kuna see võib põhjustada valesid tulemusi.
Enne kui mõõtmist kordate, oodake mõned minutid lõdvestunud asendis, kas istudes või lamades.
5.
Teised võimalikud häired ja nende kõrvaldamine
Kui seadme kasutamise ajal tekib probleeme, tuleb kontrollida järgmisi punkte ja vajaduse korral
võtta tarvitusele vastavad abinõud:
44
Page 48

Probleem
Heli ülekanne on nõrk, heli
on moondunud või on
kuulda lisamüra
Kummiballooni pumbates
rõhk ei suurene
Õhku vabastavat ventiili
avades ei õnnestu rõhku
langetada kiirusel
2 - 3 mmHg sekundis
Tühja manseti puhul ei
näita osuti 0 +/- 3 mmHg
☞
Lisateave
Vererõhu tase kõigub ka täiesti tervetel isikutel. Et saada võrreldavaid väärtusi, on oluline
mõõta vererõhku alati samades tingimustes (rahulikes oludes)! Kui kõiki neid tegureid on
arvestatud, ent kõikumine on siiski suurem kui 15 mmHg ja/või te kuulete aeg-ajalt ebaregulaarseid pulsilööke, pidage palun nõu arstiga.
Kui vererõhuaparaadiga tekib tehnilisi probleeme, küsige nõu müügiesindajalt või apteekrilt.
Ärge mingil juhul parandage vererõhuaparaati ise!
Kui seade on ilma loata lahti võetud, muutuvad kõik tema garantiid kehtetuks!
Mida teha
1.
Kontrollige, kas kõrvaotsikud on ummistunud või mõranenud.
Järgmise võimalusena kontrollige, kas need pole liiga kulunud,
et täpselt kõrva sobituda.
2. Kontrollige voolikut, kas see pole niverdunud või katki.
3. Kontrollige stetoskoobi otsiku membraani või tugiosa mõrade
suhtes.
4. Kontrollige, kas stetoskoobi otsik on mõõtmise ajal vastu nahka
ja õlavarrearteri kohal. Puhastage või asendage kõik defektsed
osad, et saada täpseid mõõtmistulemusi.
1. Kontrollige, kas õhuventiil on suletud.
2. Veenduge, et mansett on ballooni ja vooliku külge õigesti
ühendatud.
3. Kontrollige manseti, ballooni ja vooliku juures võimalikke
lekkekohti. Kõrvaldage võimalikud defektsed kohad.
• Ühendage õhuventiil kummiballooni küljest lahti ja kontrollige,
kas ventiilis on õhuvoolu takistust. Eemaldage see ja korrake
mõõtmist.
1. Veenduge, et algseisu kontrollides oleks õhuventiil avatud.
2. Kui viga on endiselt rohkem kui 3 mmHg, pöörduge
manomeetri ümberkalibreerimiseks müügiesindaja poole.
45
Page 49

6.
Hooldus ja teenindus, ümberkalibreerimine
Õige hoolduse ja remondi puhul on see aparaat töökorras aastaid. Järgige alltoodud põhireegleid.
•
Ärge laske aparaadil maha kukkuda.
•
Ärge mansetti täites kunagi ületage rõhku 300 mmHg.
•
Kaitske aparaati liiga kõrge temperatuuri, niiskuse ja otsese päikesevalguse eest.
•
Ärge ühelgi juhul puudutage mansetti terava esemega - see võib mansetti kahjustada.
•
Kasutuste vahelisel ajal tühjendage mansett alati täielikult.
•
Ärge ühelgi juhul võtke manomeetrit osadeks lahti.
•
Hoidke kõiki vererõhumõõtja osasid alati kaasasoleva koti sees, et osad püsiksid puhtana.
•
Säilitustingimused: -20 - +70 °C suhtelise niiskuse 85 % juures (mittekondenseeruv).
•
Puhastage manomeetrit ja kummiballooni niiske riidelapiga. Steriliseerimine ei ole vajalik,
kuna manomeetri osad ei tohiks mõõtmise ajal sattuda kokkupuutesse patsiendi kehaga.
•
Eemaldage kõigepealt seesmine kummiosa ning pühkige niiske lapiga takjariba, kummiosa
ja voolikud puhtaks. Mansetti saab pesta seebi ja külma veega. Loputage mansett üle puhta
veega ja kuivatage seda õhu käes.
Perioodiline ümberkalibreerimine
Tundlike mõõteaparaatide täpsust tuleb teatud ajavahemike järel kontrollida. Seetõttu soovitame
staatilise rõhunäidiku regulaarset kontrolli iga kahe aasta järel. Teie müügiesindaja annab teile
meeleldi rohkem teavet selle kohta.
7.
Garantii
Vererõhuaparaadi BP AG1-20 garantii kestab kaks aastat alates ostmiskuupäevast. Garantii
hõlmab aparaadi ja manseti. Garantii ei kehti, kui seadet on valesti käsitsetud, õnnetusjuhtumite
puhul ning siis, kui pole järgitud kasutusjuhiseid või on seadet muudetud kolmanda osapoole
poolt. Garantii kehtib ainult siis, kui näidatakse ette müügiesindaja täidetud garantiikaart.
Vastutava müügiesindaja nimi ja ettevõtte aadress:
Maaletooja: Allium UPI OÜ - Vae 16, Laagri - 76401 Harjumaa
Tel: 679 1827 - www.microlife.ee - info@allium.upi.ee
46
Page 50

8.
Standardnäitajad
Aparaadi standard:
EN 1060–1/-2; ANSI / AAMI SP09
See seade vastab kõigile Meditsiiniseadme Direktiivi 93/42/EEC nõuetele.
9.
www.microlife.ee
Üksikasjalikku informatsiooni meie toodete ja teenuste kohta leiate Microlife kodulehelt
www.microlife.ee.
10.
Tehnilised andmed
:
Kaal
:
Suurus
Hoidmistemperatuur
Töötemperatuur
Mõõtevahemik
Mõõteresolutsioon: 2 mmHg
Täpsus
: ±
±
Inflatsiooni allikas
Rõhu langetamise kiirus: 2 - 3 mmHg/sek
Õhuleke
: <±
Hüstereetiline viga: 0 - 4 mmHg
Lisatarvikud
(täiskasvanu käele ümbermõõduga 22 - 32 cm)
2. kummiballoon ja õhuventiil
3. stetoskoop
4. pehme kott
Võimalikud on tehnilised modifikatsioonid.
:
:
:
:
: 1.
Vastab Euroopa standardi nõuetele:
450 g
175 x 70 x 103 mm
-20 °C kuni +70 °C; suhteline niiskus maksimaalselt 85 %
0 - 46 °C
0 - 300 mmHg
3 mmHg temperatuuri 18 - 33 °C juures;
6 mmHg temperatuuri 34 - 46 °C juures
maht vähemalt 200 cc, 300 mmHg saavutatakse 4 - 10 sekundiga
M-mansett, seesmise kummikotiga
4 mmHg/min
47
Page 51

Механический прибор для измерения артериального
давления
Руководство по пользованию
48
Page 52

Содержание
1. Введение.
1.1. Особенности
1.2. Важные указания по самостоятельному измерению кровяного давления
2. Важная информация о кровяном давлении и его измерении.
2.1. Kак возникает повышенное или пониженное давление?
2.2. Kакое давление является нормальным?
2.3. Что делать, если регулярно определяется повышенное или пониженное давление?
3. Cоставные части прибора для измерения давления.
4. Процедура измерения.
4.1. Перед измерением
4.2. Часто встречающиеся ошибки
4.3. Наложение манжеты
4.4. Процедура измерения
4.4.1. Подсоединение трубки стетоскопа к головке стетоскопа
4.4.2.
4.4.3.
4.4.4.
4.4.5.
5. Возможные неисправности и методы их устранения.
6. Уход за прибором.
7. Гарантия.
8. Соответствие стандартам.
9. www.microlife.ru
10. Технические данные.
Накачивание манжеты
Измерение систолического артериального давления
Измерение диастолического артериального давления
3апись произведенных измерений
RU
49
Page 53

1. Введение.
1.1. Особенности
Комплект для измерения артериального давления является неавтоматическим,
механическим прибором для измерения давления, использующимся на плечевой
зоне. Он предоставляет достоверные результаты и превосходные эксплуатационные
характеристики при экономичной цене. При помощи своего современного безостановочного
механизма с игольчатым клапаном и эргономичного резинового баллона, снабженного
клапанами, BP AG1-20 обеспечивает Вам точные и согласованные измерения. Кроме
того, его износостойкая капроновая манжета, высококачественная опора и анероидный
измеритель давления обеспечивают согласованную работу. Весь прибор хранится в
нейлоновой сумке с застежкой для портативности.
Пожалуйста, внимательно прочтите это руководство и сохраните его. Если у вас
имеются дополнительные вопросы в отношении кровяного давления и его изме ре ния,
проконсультируйтесь у вашего врача.
Информация по безопасности.
1.2. Важные указания по самостоятельному измерению кровяного давления.
• ѕомните о следующем: самостоятельные измерения выполняются для контроля,
а не для постановки диагноза или лечения. Обращающие на себя внимание значения
кровяного давления обязательно должны быть обсуждены с врачом. Hи в коем случае
не изменяйте самостоятельно прописанные вашим врачом лекарства или их дозировку.
2. Важная информация о кровяном давлении и его измерении.
2.1. Kак возникает повышенное или пониженное давление?
Уровень кровяного давления определяется в особом участке мозга, так называемом
центре кровообращения, и регулируется им в зависимости от ситуации путем посылки
ответных сигналов по нервным путям. Для регулировки кровяного давления изменяется
сила и частота сердцебиения (пульс), а также ширина кровяных сосудов (ширина сосудов
50
Page 54

изменяется маленькими мышцами в стенках сосудов). Уровень артериального давления
периодически изменяется в процессе сердечной деятельности: во время «выброса крови»
(систолы) значение давления максимально (систолическое значение давления), в конце
фазы покоя (диастолы) - минимально (диастолическое значение давления). Значения
кровяного давления должны находиться в определенном нормальном диапазоне, что
необходимо для предотвращения некоторых заболеваний.
2.2. Kакое давление является нормальным?
Kровяное давление считается слишком высоким, если в состоянии покоя диастолическое
давле ние составляет более 90 мм ртутного столба и/или си столическое давление
составляет более 140 мм ртутного столба. В этом случае рекомендуется незамедлительно
обратиться к врачу. Длительное сохранение да вления на таком уровне представляет
опасность для вашего здо ро вья, так как оно вызывает прогрессирующее повреждение
кровяных сосудов в вашем организме.
K врачу также следует обратитьс
сис толическом давлении менее 100 мм рт. ст. и/или диастолическом давлении менее 60 мм рт.
ст. Даже если измеренные значения давления находятся в норме, рекомендуем с помощью
вашего прибора регулярно контролировать свое кровяное давление, чтобы своевременно
распознать возможные отклонени
Если вы проходите курс лечения по регулированию кровяного давления, регулярно
выполняйте измерения кровяного давления в определенные часы и записывайте их в
журнал. Впоследствии покажите эти записи вашему врачу. Ни в коем случае не
из меняйте самостоятельно на основе результатов изме рения давления прописанные
вашим врачом медикаменты или их дозировку.
Таблица значений артериального давления крови (в единицах mmHg) согласно
классификации Всемирной Организации 3дравоохранения:
я
и при слишком низком кровяном давлении, а именно при
я
давления и предпринять необходимые действия.
51
Page 55

Диапазон Систолическое Диастолическое Рекомендация
артериальное давление
слишком низкое
1.
оптимальное артериальное
давление
2.
артериальное давление
в норме
3.
артериальное давление
слегка повышено
4.
артериальное давление
слишком высокое
5.
артериальное давление
чрезмерно высокое
6.
артериальное давление
угрожающе высокое
< 100 < 60
100 - 120 60 - 80
120 - 130 80 - 85
130 - 140 85 - 90
140 - 160 90 - 100
160 - 180 100 - 110
≥ 180 ≥ 110
Обратитесь к врачу
Самостоятельный
контроль
Самостоятельный
контроль
Обратитесь к врачу
Обратитесь за
медицинской помощью
Обратитесь за
медицинской помощью
Срочно обратитесь за
медицинской помощью!
☞ Прочие указания
•
Если значения давления, измеренные в состоянии покоя, не являются необычными,
а в состоянии физического или душевного переутомления вы наблюдаете чрезмерно
повышенные значения, это может указывать на наличие так называемой артериальной
лабильной гипертонии. В любом случае, обсудите результаты с Вашим врачом.
•
Если при правильном измерении артериального давления диастолическое кровяное
давление составляет более 120 мм рт. ст., необходимо незамедлительно вызвать врача.
2.3. Что делать, если регулярно определяется повышенное или пониженное кровяное
давление?
a) Обратитесь к врачу.
б) Повышенные значения артериального давления (различные формы гипертонии),
наблюдаемые в течение некоторого периода, связаны с существенными опасностями для
здоровья. Повышенное давление оказывает негативное влияние на кровеносные сосуды,
которые подвергаются опасности повреждения в результате отложений в стенках
сосудов (атеросклероз). Это может привести к недостаточному кровоснабжению важных
органов (сердца, мозга, мышц). Кроме того, возникают нарушения в структуре сердца.
52
Page 56

в) Повышенное артериальное давление может быть вызвано множеством причин. Различают
часто встречаемую первичную (эссенциальную) гипертонию и вторичную гипертонию.
Вторичная гипертония может приводить к неправильной работе органов. В отношении
возможных причин повышенного давления проконсультируйтесь у Вашего врача.
г) Чтобы предупредить и снизить повышенное кровяное давление, можно произвести
некоторые изменения образа жизни. Эти изменения должны стать частью Вашего образа
жизни, и к ним относятся:
A) Привычки в отношении питания
•
Стремитесь поддерживать нормальный вес, соответствующий Вашему возрасту, как
предписал Ваш врач. Снижайте избыточный вес!
•
Избегайте чрезмерного потребления поваренной соли. (Многие консервированные
продукты содержат много соли).
• Избегайте потребления жирной пищи. (Консервированные продукты часто являются жирными).
Б) Имеющиеся заболевания
Последовательно, в соответствии с предписаниями врача, выполняйте лечение имеющихся
заболеваний, например:
•
сахарного диабета (Diabetes mellitus)
•
нарушений жирового обмена
•
подагры
В) Привычки
•
Полностью откажитесь от курения
•
Ограничьте потребление алкоголя
•
Ограничьте потребление кофеина (кофе, чая, шоколада и т.д.)
Г) Физическое состояние организма
•
Предварительно пройдя врачебное обследование, регулярно занимайтесь спортом.
•
Отдавайте предпочтение нагрузкам на выносливость и избегайте силовых видов спорта.
•
Не допускайте полного изнеможения.
•
Если у Вас имеются какие-либо заболевания и/или если Вы старше 40 лет, перед началом
занятий спортом обратитесь к врачу. Он поможет Вам разработать подходящую для Вас
программу упражнений.
53
Page 57

3. Составные части прибора для измерения кровяного давления.
Ниже изображен прибор для измерения кровяного давления, состоящий из следующих частей:
а) Прибор
Манометр
Сумка-чехол
Ушные оливы
Стетоскоп
Манжета
Головка
фонендоскопа
б) Манжета
Тип AC-1 M размер 22 - 32 см или
Tип AC-1 L размер 32 - 42 см
(можно приобрести по специальному заказу)
4. Bыполнение измерения.
4.1. Перед измерением.
•
Hепосредственно перед измерением кровяного давления избегайте приема пищи,
курения и всевозможных прочих усилий. Bсе эти факторы влияют на результаты
измерений. Лучше всего посидите в кресле приблизительно 10 минут в спокойной
обстановке, чтобы снять внутреннее напряжение.
54
Нагнетатель с
клапаном откачки
Page 58

Освободите левую руку от одежды. Hе закатывайте рукав, т.к. он сдавит вашу руку и
•
это приведет к неточности при измерении.
•
Измеряйте давление всегда на одной и той же руке (обычно левой).
•
Cтарайтесь выполнять измерения регулярно в одно и то же время суток, так как
кровяное давление изменяется в течение дня.
4.2. Часто совершаемые ошибки.
Примечание: Для получения сравнимых результатов измерения всегда требуются
одинаковые условия! Обычно это условия покоя.
•
Kаждое напряжение пациента, например, упор на руку, может повысить кровяное
давление. Уделите внимание тому, чтобы тело было приятно расслаблено, и не
напрягайте во время измерения мускулы на измеряемой руке.
•
Убедитесь, что точка входа воздушной трубки в манжету располагается над локтевой
ямкой и находится на уровне сердца. Eсли эта точка находится выше уровня сердца
на 15 см, прибор покажет значение верхнего давления примерно на 10 мм рт.ст. ниже
истинного значения вашего давления и наоборот.
•
Bыбор правильного размера манжеты является важным условием, которое может
повлиять на точность измерения. Pазмер манжеты зависит от окружности плеча руки.
ѕредупреждение. Используйте только клинически апробированную оригинальную
манжету!
•
Cвободно или криво одетая манжета может являться причиной неправильных показаний.
4.3. Hаложение манжеты.
a) Оберните манжету вокруг левой руки так, чтобы
трубка была направлена к нижней части руки.
б) Наложите манжету на руку, как показано на рисунке.
Убедитесь, что нижний край манжеты находится на
расстоянии приблизительно 2 - 3 см выше локтевого
сгиба и что резиновая трубка выходит из манжеты с
внутренней стороны руки.
2 - 3 cm
трубка
55
Page 59

в) Затяните свободный конец манжеты и застегните
манжету на «липучку».
г) Она должна быть затянута на плече, но не слишком
туго. Любую одежду, которая ограничивает руку
(например, свитер), следует снять.
д) Положите руку на стол (ладонью вверх) так, чтобы
манжета находилась на уровне сердца. Убедитесь,
что трубка не перекручена.
Примечание:
Если невозможно надеть манжету на левую руку, ее
можно разместить и на правой. Однако все измерения
должны проводиться на одной и той же руке.
4.4. Процедура измерения
4.4.1. Установите рабочую часть стетоскопа
под манжету. Pабочая часть стетоскопа не должна
устанавливаться на манжету или в нее, он должен быть
расположен либо под манжетой, либо на 1 - 2 см ниже
манжеты. Pабочая часть стетоскопа считается установленной
правильно тогда, когда тон Короткова слышен как самый
сильный (
«громкий»). Удостоверьтесь, что рабочая часть
стетоскопа находится в контакте с кожей и расположена
выше плечевой артерии. Правильно вставляйте наушники для
проверки тона Короткова во время измерения.
Перед использованием стетоскопа удостоверьтесь в отсутствии трещин в мембране,
наушниках и трубке. Неправильная установка или повреждение стетоскопа вызовут
искажение тона или плохую передачу тона, что приведет к неточным измерениям.
56
Page 60

4.4.2. Накачивание манжеты
3акройте воздушный клапан, расположенный на резиновом баллоне,
повернув винт по часовой стрелке. Не затягивайте слишком туго.
Сжимайте резиновый баллон в руке равномерно до тех пор, пока
указатель датчика не превысит на 30 мм рт.столба Ваше обычное
систолическое давление. Eсли Вы не уверены в этой величине,
сперва накачайте манжету до давления 200 мм рт.столба.
4.4.3. Измерение систолического артериального давления
Медленно откройте воздушный клапан, поворачивая винт
против часовой стрелки, и держите рабочую часть стетоскопа
над плечевой артерией. Для получения точных показаний важна
правильная скорость выпуска воздуха из манжеты, поэтому Вам
следует начать и использовать в дальнейшем скорость выпуска
воздуха 2 - 3 мм рт. ст./сек или опускаться на одно или два
деления на датчике при каждом сокращении сердца.
Вам не следует допускать, чтобы манжета оставалась накачанной дольше, чем это необходимо. Когда манжета начинает выпускать воздух, Вы должны внимательно слушать тоны через
стетоскоп. 3аметьте показание на датчике как только Вы услышите четкий, ритмичный стук
или биение. Ёто значение является величиной систолического артериального давления.
Слушайте внимательно и ознакомьтесь с тоном сердечных сокращений (Короткова).
4.4.4. Измерение диастолического артериального давления
Позволяйте давлению падать при той же скорости выпуска воздуха. Когда достигнуто
значение диастолического артериального давления, звук биения перестает быть
слышимым. Полностью выпустите воздух из манжеты. Снимите манжету с руки и извлеките
наушники стетоскопа из ушей.
4.4.5. 3апись произведенных измерений
Повторите измерения как минимум два раза. Не забудьте записать свои измерения, а также
время и дату измерения сразу же после проведения измерений. Подходящим временем
измерения является утро, сразу же после сна или непосредственно перед ужином.
57
Page 61

Помните, что только Ваш терапевт имеет квалификацию, достаточную для того, чтобы
интерпретировать показания Вашего аретиального давления.
☞ ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ
Не следует повторять измерения одно за другим через короткий промежуток времени,
так как результаты измерения от этого искажаются. Прежде чем повторять измерение,
подождите 1 минуту сидя или лежа.
5. Возможные неисправности и методы их устранения.
Eсли во время использования устройства имеют место проблемы, необходимо проверить
следующие моменты и предпринять соответствующие меры в случае необходимости:
Неисправность
Плохая передача тона,
искажения или посторонний
шум.
При накачивании манжеты
резиновым баллоном давление
не увеличивается.
58
Средство устранения
1. Проверьте, не забились ли наушники и не являются
ли они треснутыми. Eсли нет, удостоверьтесь, что
они плотно прилегают и не изношены.
2. Проверьте, не имеет ли трубка трещин и не
перекручена ли она.
3. Проверьте, не имеется ли трещин в крышке и
мембране рабочей части стетоскопа.
4. Удостоверьтесь, что рабочая часть стетоскопа
находится в надлежащем контакте с кожей и
располагается над плечевой артерией во время
измерения. Во избежание неточных измерений,
прочистите или замените неисправные детали.
1. Удостоверьтесь, что клапан закрыт
2. Удостоверьтесь, что манжета правильно
подсоединена к резиновому баллону и манометру.
3. Проверьте, не имеют ли манжета, трубка и
резиновый баллон утечек. При обнаружен ии
неисправности замените неисправные детали.
Page 62

Скорость выпуска воздуха
не может быть установлена
на 2-3 мм рт. ст./сек
регулировки клапана
выпуска воздуха.
В состоянии покоя указатель
не находится на отметке
0 +/- 3 мм рт.столба.
☞ Прочие указания
Уровень артериального давления подвержен колебаниям даже у здоровых людей.
Следовательно, является важным, чтобы сравниваемые между собой измерения всегда
производились в одних и тех же условиях (отдыха)!
Eсли, тем не менее, в приборе для измерения кровяного давления возникли неполадки
технического характера, просим обратиться в торговую организацию или аптеку, в которой вы
приобрели прибор. Ни в коем случае не пытайтесь самостоятельно ремонтировать прибор!
В случае самостоятельного вскрытия прибора гарантия утрачивает силу!
6. Уход за прибором.
При надлежащем уходе и техническом обслуживании измерительный прибор будет служить
Вам годами. Следуйте общим правилам, приведенным ниже:
•
Не роняйте прибор.
•
Никогда не надувайте за 300 мм рт. столба.
•
Не подвергайте устройство воздействию крайне высоких/низких температур, влажности
или прямых солнечных лучей.
•
Никогда не прикасайтесь к ткани, из которой изготовлена манжета, острыми инструмен тами,
поскольку при этом могут возникнуть повреждения.
•
Xраните манжету, полностью выпустив из нее воздух.
•
Ни при каких обстоятельствах не разбирайте манометр.
•
Отсоедините клапан от «груши» для того, чтобы
проверить, не имеется ли препятствий для воздуха
внутри клапана. Удалите препятствия и повторите
попытку снова. Eсли клапан не работает должным
образом, замените его во избежание получения
неточных результатов измерений.
1. Удостоверьтесь, что при проверке установки нуля
клапан полностью открыт.
2. Eсли отклонение от нулевого значения превышает
3 мм рт. столба, обратитесь к торговой организации
для повторной калибровки манометра.
59
Page 63

•
Xраните все устройство в сумке для хранения для того, чтобы его детали оставались в чистоте.
•
Температурные условия хранения: -20 - +70 °С при относительной влажности 85 % (без
конденсации).
•
Протирайте манометр и резиновый баллон мягкой тряпочкой. Стерильная обработка
не является необходимой, поскольку части манометра не должны вступать в
непосредственный контакт с частями тела пациента во время измерения.
•
Сперва удалите резиновый баллон и протрите застежку-
трубки влажной тряпочкой. Манжета может быть вымыта при помощи мыла и холод ной
воды. Потом ополосните манжету чистой водой и оставьте ее сохнуть на воздухе.
Периодическая калибровка прибора
Точность чувствительных измерительных приборов должна время от времени проверяться. По
этой причине рекомендуем периодически, раз в два года, проверять индикацию статического
давления. Более подробную информацию о проверке вы можете получить в специализированной
торговой организации, в которой вы приобрели прибор или сервисном центре Микролайф.
«
липучкуї, резиновый баллон и
7. Гарантия.
Измерителю артериального давления гарантируется 2 года работы с даты приобретения.
Эта гарантия относится к прибору и манжете. Гарантия не относится к повреждениям,
вызванным неправильным обращением, случайными причинами, невыполнением инструкций
по эксплуатации и модификациями прибора, выполненными третьей стороной.
Гарантия действует только в случае предъявления гарантийного талона, заполненного
сотрудником торговой организации.
Фамилия ответственного сотрудника и адрес торговой организации:
8. Соответствие стандартам.
Cтандарт прибора: EN 1060-1/-2
ANSI / AAMI SP09
Данный прибор соответствует требованиям директивы ЕЭС о медицинском оборудовании
93/42/EEC.
60
Page 64

9. www.microlife.ru
Подробную полезную информацию о сервисных возможностях наших термометров и
тонометров, Вы найдете на нашей странице www.microlife.ru.
10. Tехнические данные.
Bес: 450 г.
Pазмеры: 175 x 70 x 103 мм
Tемпература хранения: от -20 °C до +70 °C; отн. влажность в пределах 85 %
Tемпература пользования: от 0 - 46 °C
Диапазон измерения: от 0 - 300 мм рт. ст.
Pазрешающая способность
измерительного прибора: 2 мм рт. столба
Погрешность: ± 3 мм рт. столба в пределах от 18 - 33 °C;
± 6 мм рт. столба в пределах от 34 - 46 °C
Источник давления воздуха: объем как минимум 200 куб. см создает
давление 300 мм рт. столба за 4 - 10 с.
Скорость выпуска воздуха: 2 - 3 мм рт. столба/с.
Утечка воздуха: < ± 4 мм рт. столба/мин
Погрешность запаздывания: в пределах от 0 - 4 мм рт. столба
Принадлежности: 1. манжета M (взрослый размер с окружностью плеча
22 - 32 см) с внутренней камерой
2. нагнетатель с клапаном откачки
3. стетоскоп
4. сумка-чехол
Могут быть внесены технические изменения.
61
Page 65

Aneroid verenpainemittari pakkaus
Käyttöohjeet
62
Page 66

Sisällysluettelo
1. Esittely
1.1. Verenpainemittarin toiminnot
1.2. Tärkeää tietoa verenpaineen kotimittauksesta
2. Tärkeää tietoa verenpaineesta ja sen mittaamisesta
2.1. Miten korkea/matala verenpaine ilmenee?
2.2. Mitkä ovat normaalit verenpainearvot?
2.3.
Mitä voidaan tehdä, jotta saavutetaan normaalit korkeat/matalat verenpainearvot?
3. Verenpainemittauspakkauksen osat
4. Mittauksen suorittaminen
4.1. Ennen mittausta
4.2. Yleiset virhelähteet
4.3. Mansetin pukeminen
4.4. Verenpaineen mittaaminen
4.4.1. Rintakappaleen asettaminen mansetin alle
4.4.2. Mansetin täyttö
4.4.3. Systolisen verenpaineen lukeminen
4.4.4. Diastolisen verenpaineen lukeminen
4.4.5. Tulosten tallentaminen
5. Virheilmoitukset / virhetoiminnot
6. Hoito, huolto ja uudelleenkalibrointi
7. Takuu
8. Käytetyt standardit
9. www.microlife.fi
10. Tekniset tiedot
FI
63
Page 67

1. Esittely
1.1. Verenpainemittarin toiminnot
Aneroidi verenpainemittari ei ole automaattimittari vaan mekaaninen verenpaineen olkavarresta
tapahtuvaan mittaamiseen tarkoitettu laite.
Sillä voidaan mitata luotettavasti, hyvin ja edullisesti. Kehittynyt jatkuva ruuvimekanismi
ja ergonominen pumppausosa täydellisine venttiileineen tarjoavat käyttäjälleen tarkan ja
yhtenäisen mittauksen. Kestävä, nylon mansetti, korkeatasoinen varustus ja aneroidi äänentoisto
tarjoavat yhtenäisen toiminnan.
Ennen kuin otat mittarin käyttöösi, niin lue käyttöohjeet huolellisesti ja säilytä ne turvallisessa
paikassa. Jos sinulla on lisäkysymyksiä verenpaineesta tai sen mittamisesta, niin ota yhteyttä
lääkäriisi.
Huomio!
1.2. Tärkeää tietoa verenpaineen kotimittauksesta
• Äläunohda:kotimittaus tarkoittaa kontrollia ei diagnoosia tai hoitoa. Keskustele aina
poikkeavista arvoista lääkärisi kanssa. Älä missään olosuhteissa muuta minkään lääkärisi
määräämän lääkkeen annostusta keskustelematta siitä ensin lääkärisi kanssa.
2. Tärkeää tietoa verenpaineesta ja sen mittaamisesta
2.1. Miten korkea/matala verenpaine ilmenee?
Verenpaineen taso määräytyy aivojen osassa nimeltä verenkiertokeskus ja se mukautuu
kulloiseenkin tilanteeseen hermoston antaman palautteen avulla. Elimistö muuttaa sydämen
(pulssin) voimakkuutta ja taajuutta sekä verisuonten tilavuutta verenpaineen säätelemiseksi.
Jälkimmäisen saavat aikaan verisuonten seinämien pienet lihakset.
Valtimoverenpaineentasovaihteleesydämentoiminnanmyötä:«Verentyöntövaiheen»
eli sydämen supistumisvaiheen (systole) aikana verenpaine on korkeimmillaan (systolinen
verenpaine) ja sydämen «lepovaiheen» (diastole) lopussa se on alhaisimmillaan (diastolinen
verenpaine). Verenpainearvojen on hyvä olla normaaliarvojen sisällä terveyden ylläpitämiseksi.
64
Page 68

2.2 Mitkä ovat normaalit verenpainearvot?
Verenpaine on liian korkea, jos diastolinen paine on levossa yli 90 mmHg ja/tai systolinen
verenpaine on yli 140 mmHg. Näissä tapauksissa kääntykää välittömästi lääkärin puoleen. Jos
arvot ovat pitkän aikaa tällä tasolla, ne edistävät elimistönne verisuonten rappeutumista ja
vaarantavat siten terveyttänne.
Jos verenpainearvot ovat liian alhaiset, eli systoliset arvot ovat alle 100 mmHg ja/tai diastoliset
arvot alle 60 mmHg, on myös syytä kääntyä lääkärin puoleen.
Silloinkin kun verenpainearvot ovat normaalit, suositellaan säännöllistä omatoimista tarkastusta
verenpainemittarilla. Näin pystytte havaitsemaan mahdolliset muutokset arvoissa varhain ja ryhtyä
nopeasti tarpeellisiin toimenpiteisiin.
Jos olette lääkehoidossa verenpaineesi kontrolloimiseksi, pidä kirjaa verenpainearvoistasi mittaamalla verenpaine säännöllisesti samaan aikaan päivästä. Näyttäkää nämä arvot lääkärillenne.
Älkää koskaan muuttako omin päin lääkärinne määräämiä lääkeannostuksia
mittaustenne perusteella.
Verenpainearvotaulukko(yksiköt,mmHG)Maailmanterveysjärjestön(WHO)mukaisesti:
Vaihteluväli Systolinen Diastolinen Suositus
liian alhainen paine
1. optimaalinen verenpaine
2. normaali verenpaine
3. lievästi korkea verenpaine
4. liian korka verenpaine
5. avian liian korkea verenpaine
6. vaarallisen korkea verenpaine
< 100 < 60
100 - 120 60 - 80
120 - 130 80 - 85
130 - 140 85 - 90
140 - 160 90 - 100
160 - 180 100 - 110
≥ 180 ≥ 110
Käänny lääkärin puoleen
Omatoiminen seuranta
Omatoiminen seuranta
Käänny lääkärin puoleen
Pyydä lääkinnällistä apua
Pyydä lääkinnällistä apua
Pyydä kiireellisesti
lääkinnällistä apua!
☞ Lisätietoja
• Josverenpainearvosiovatpääasiassaallenormaaliarvojenlepotilassamuttapoikkeusta
pauksissa korkeat, kuten fyysisessä ja psykologisessa stressissä, saatat kärsiä niin
kutsutusta epävakaasta korkeasta verenpaineesta. Ota yhteytää lääkäriisi.
65
Page 69

• Oikeinmitattudiastolinenverenpaineyli120mmHgvaatiikiireellistä lääkinnällistä hoitoa.
2.3. Mitä voidaan tehdä, jotta saavutetaan normaalit korkeat/matalat verenpainearvot?
a) Kääntykää lääkärin puoleen.
b) Pitempiaikaiset kohonneet verenpainearvot (verenpainetaudin eri muodot) voivat olla
huomattava terveysriski. Elimistönne valtimosuonet ovat erityisessä vaarassa suonien
seinämien kalkkeutumisen aiheuttaman ahtautumisen (arterioskleroosi) vuoksi. Seurauksena
voi olla verenpuute tärkeissä elimissä (sydän, aivot, lihakset). Lisäksi pitkän aikaa jatkuvasti
koholla olevat verenpainearvot voivat vahingoittaa sydämen rakennetta.
c) Korkean verenpaineen ilmenemiseen on olemassa monta eri syytä. Me teemme eron yleisen
primaarisen (essentiaalisen) verenpainetaudin ja sekundaarisen verenpainetaudin välillä.
Jälkimmäisen syynä ovat tietyt elimelliset toimintahäiriöt. Kysykää lääkäriltänne kohonneen
verenpaineenne mahdollisista syistä.
d) Voitte myös itse vaikuttaa verenpaineeseenne elintapojanne muuttamalla. Nämä toimet
kuuluvatjokapäiväiseenelämäänne:
A) Syömistavat
• Pyrkikääikäännevastaavaannormaalipainoon.Vähentäkääylipainoa!
• Välttäkääsuolanliiallistakäyttöä.
• Välttäkäärasvaisiaruokia.
B) Aikaisemmat sairaudet
Noudattakaajohdonmukaisestisellaistenaikaisempiensairauksiennehoitoohjeitakuten:
• Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus)
• Metabolinen oireyhtymä
• Kihti
C) Tavat
• Lopetatupakointi
• Käytäalkoholiakohtuullisesti
• Vähennäkahvinjuontiasi(kahvi)
D) Fyysinen yleiskunto
• Peruslääkärintarkastuksenjälkeen,liikusäännöllisesti.
66
Page 70

• Valitseliikuntalajeja,jotkavahvistavatkestävyyttäjavältävoimailulajeja.
• Välttäkääsaavuttamastasuorituskykynneylärajaa.
• Josteilläonollutaikaisempiasairauksiaja/taioletteyli40vuotias,kääntykäälääkärinne
puoleen ennen liikuntaharrastuksen aloittamista. Hän antaa neuvoja teille sopivista
liikuntamuodoista ja liikuntamääristä.
3. Verenpainemittauspakkauksen osat
KuvassaBPAG120verenpainemittaripakkauksenosat:
a) Mittausyksikkö:
Manometri
Mansetti
Rintaosa
b) Mansetti:
Tyyppi AC-1M, olkavarren yläosan ympärysmitta 22 - 32 cm tai
Tyyppi AC-1L, olkavarren yläosan ympärysmitta 32 - 42 cm
(saatava lisätilauksesta)
Säilytyslaukku
Korvaosa
Stetoskooppi
Pumppausosa ja
venttiilit
67
Page 71

4. Mittauksen suorittaminen
4.1. Ennen mittausta
• Vältäfyysisiäaktiviteetteja,syömistäjatupakointiavälittömästiennenmittausta.Kaikkiedellä
mainitut asiat vaikuttavat verenpaineen mittaustuloksiin. Istuudu vähintään 10 minuutiksi
ennen mittausta ja rentoudu rauhallisessa paikassa.
• Poista tiukka vaatetus käsivarrelta. Paidan hihoja ei tule kääriä ylös, jotta vältytään kiristämiseltä.
• Mittaaainasamastakädestä(normaalistivasemmasta).
• Pyrimittaamaanverenpaineainasamaanaikaanpäivästä,koskaverenpainevaihtelee
päivän aikana.
4.2. Yleiset virhelähteet
Huomaa: Verenpainemittausten keskinäinen vertailu edellyttää aina samoja olosuhteita!
Olosuhteiden tulisi yleensä aina olla rauhalliset.
• Potilaanyrityksettukeakäsivarttavoivatlisätäverenpainetta.Varmistakaa,ettäolette
mukavassa, rennossa asennossa ja että ette käytä mitään mittauskäsivarren lihaksista
mittauksen aikana. Tarvittaessa käytä tyynyä tukena.
• Joskädenvaltimoonhuomattavstialempana(korkeammalla)kuinsydänniintuloson
virheellisesti korkeampi (matalampi) mitattaessa (jokainen 15 cm ero antaa 10 mmHg
virheen tulokseen)!
• Liiankapeatailyhytmansettisaaaikaavirhetuloksen.Oikeankokoisenmansetinvalinta
on sen takia erittäin tärkeätä. Mansetin koko määräytyy käsivarren ympärysmitan mukaan
(käsivarren keskivaiheilta mitattuna). Sallittu ympärysmitta-alue on merkitty mansettiin. Jos
kokoalue on väärä, ota yhteys laitteen myyjään.
Huomaa: Käytä ainoastaan kliinisesti hyväksyttyjä alkuperäismansetteja!
• Löysämansettijasivulletyöntyväilmataskuvääristävättuloksen.
4.3. Mansetin pukeminen
a) Pujota mansetti vasempaan käteen, niin että letku on
käsivarren sisäpuolella.
b) Varmista, että mansetin alaosa on noin 2 - 3 cm
kyynärvartesi yläpuolella ja että ilmaletku jää käden
68
Page 72

sisäpuolelle. Tärkeää! Merkki (noin 3 cm pitkä viiva)
on tarkalleen valtimon yläpuolella ja letku sen kohdalla.
c) Kiristä mansetin vapaasta päästä ja lukitse mansetti
paikoilleen.
2 - 3 cm
letku
d) Mansetin pitää olla käden ympärillä niin, että mansetin
ja ihon välissä ei ole ylimääräistä tilaa. Vaatteet eivät
saa kiristää. Kaikki kättä kiristävät vaatteet pitää riisua
(esim. villapusero).
e) Kiinnitä mansetti niin että se istuu kädessä mukavasti,
mutta ei ole liian tiukka. Anna käden levätä pöydällä
(kämmen ylöspäin) niin että mansetti on samalla korkeudella sydämen kanssa. Varmista, että letku ei ole sykkyrällä.
f) Istu hiljaa kaksi minuuttia ennen kuin aloitat mittauksen.
Kommentti:
Jos ei ole mahdollista laittaa mansettia vasempaan käteen, niin sen voi laittaa myös oikeaan
käteen. Joka tapauksessa on tärkeää, että mittaus tehdään aina samasta kädestä.
4.4. Verenpaineen mittaaminen
4.4.1. Rintakappaleen asettaminen mansetin alle
Aseta stetoskoopin rintakappale mansetin alle tai 1 - 2 cm sen
alapuolelle. Rintakappaletta ei saa laittaa mansetin päälle tai
sisään. Rintakappale on asetettu oikein, kun Korrotkoffin äänet
kuuluvat selvästi. Varmista, että rintakappale on ihon kanssa
kosketuksissa ja olkavarsilaskimon yläpuolella. Laita stetoskoopin
korvakappleet korviin, jotta kuulet Korotkoffin äänet mittauksen
aikana. Ennen kuin käytät stetoskooppia, varmista että kalvo,
korvakappaleet ja letku ovat ehjiä. Sopimaton tai vahingoittunut
stetoskooppi voi vääristää äänen tai antaa vain heikon äänen ja näin epätarkan tuloksen.
69
Page 73

4.4.2. Mansetin täyttö
Sulje pumpussa oleva ilmaventtiili kääntämällä ruuvia
myötäpäivään.Äläylikiristä.Pumppaailmapumppuakädellä
tasaisesti, kunnes laitteen viisari osoittaa 30 mmHg yli
normaalin systolisen verenpaineesi. Jos et ole varma arvosta,
niin täytä mansetti 200 mmHg ensin.
4.4.3. Systolisen verenpaineen lukeminen
Avaa hitaasti ilmaventtiili kääntämällä ruuvia vastapäivään ja
pidä stetoskoopin rintakappaletta olkavarsilaskimon yläpuolella.
Sopiva ilman poispäästämisen vauhti on tärkeää tarkan tuloksen
saamiseksi, joten harjoittele, sillä paras ilman poislaskuvauhti on
2 - 3 mmHg /sekuntti tai 1 - 2 merkin pudotus paineen pudotus
mittavälineessäjokasydämenlyönnillä.Äläpidämansettia
täytettynä yhtään kuemmin kuin on tarpeellista. Kun mansetti alkaa
tyhjentyä, sinun pitää kuunnella huolellisesti stetoskoopilla.
Heti kun pulssin ääni on kuultavissa stetoskoopista, lue yläarvo (systolinen) mittarista.
4.4.4. Diastolisen verenpaineen lukeminen
Anna paineen jatkaa tippumistaan samaan aikaa mansetin tyhjentymisen kanssa. Ilmanpaineen
pudotessa, pulssinnopeuden voimakkuus putoaa myös. Viimeinen kuultava pulssin ääni antaa
ala-arvon (diastolinen) lukeman. Tyhjennä mansetin venttiili täydellisesti. Poista mansetti kädestä
ja stetoskooppi korvista.
4.4.5. Tulosten tallentaminen
Toistamittausvähintäänkaksikertaa.Äläunohdakirjatatuloksiajaaikaaheti,kunoletlopettanut
mittaamisen Sopiva mittausaika on tehdä se heti aamulla ensimmäiseksi ennen aamiaista. Muista,
että lääkärisi on ainoa oikea henkilö analysoimaan verenpaine mittaustuloksiasi.
☞ Lisätietoja
Mittausta ei pidä tehdä heti toisen mittauksen perään, koska tulokset voivat olla vääristyneitä. Odota
useita minuutteja rennossa asennossa, istuen tai maaten, ennen kuin toistat mittauksen.
70
Page 74

5. Virheilmoitukset / virhetoiminnot
Jos mittauksen aikana ilmenee jokin vika, niin seuraavat asiat pitää tarkistaa ja jos tarpeellista
niinvastaavamittauspitäätehdäuudelleen:
Virheilmoitus
Äänensiirtoonheikko,
vääristynyt tai siellä on
ylimääräisiä häiriöitä.
Paine ei nouse, vaikka
pumppu pumppaa.
Ilman poispäästämisen tasoa
ei voi asettaa 2- 3 mmHg/s.
säätämällä ilmaventtiiliä.
Mittarin osoitin ei ole
0+/- 3 mmHg lepotilassa.
☞ Lisätietoja
Verenpaineen taso vaihtelee myös terveillä ihmisillä. Sen vuoksi vertaileva mittaus pitää
aina tehdä samoissa olosuhteissa. Jos, kaikki tekijät on otettu huomioon ja verenpaineen
vaihtelu on enemmän kuin 15 mmHg ja /tai kuulet epäsäännöllisen pulssin useissa tapauksissa,
ota yhteyttä lääkäriin
Konsultoi mittarin myyjää, jos mittarissa on teknisiä ongelmia. Älä koskaan yritä itse korjata
mittaria! Jos mittari vahingoittuu ammattitaidottoman henkilön mittarin avaamisen vuoksi, niin
takuu ei ole enää voimassa!
Korjaus
1. Tarkista korvaosat, jotta eivät ole tukossa tai säröillä. Jos ei,
varmista, että ne eivät ole huonosti kiinnitetty.
2. Tarkasta, että letku ei ole rikki tai kierteellä.
3. Tarkista, että välikalvossa tai rintakappaleessa ei ole halkeamia.
4. Varmista, että rintakapple on täysin kiinni ihossa ja olkavarsilaskimon yläpuolella mittauksen aikana. Puhdista tai vaihda
jokainen vahingoittunut osa välttääksesi epätarkan tuloksen.
1. Varmista, että venttiili on kiinni.
2. Varmista, että mansetti on kiinnitetty hyvin pumppuun ja
manometriin.
3. Tarkista, että mansetti, ilmaputki ja pumppu ovat ehjiä. Vaihda
mahdolliset rikkinäiset osat.
•Purkaaventtiili.Tarkistaonkoilmaventtiilitukossa.Poista
tukos ja yritä uudelleen. Jos se ei vieläkään toimi, vaihda laite
välttyäksesi epätarkoilta tuloksilta.
1. Varmista, että venttiili on auki.
2. Jos edelleen enemmän kuin 3 mmHg ero, ota yhteyttä mittarin
myyjään mittarin uudelleen kalibroimiseksi.
71
Page 75

6. Hoito, huolto ja uudelleenkalibrointi
Pitämällähyvinjahuoltamallatätäverenpainemittariasekestäävuosia.Noudataseuraaviaohjeita:
•Äläpudota.
•Äläkoskaantäytämansettiayli300mmHg.
•Äläkoskaaaltistamittariakorkeillelämpötiloille,kosteudelletaisuoralleauringonvalolle.
•Äläkoskaankosketamansettiaterävälläesineellä,koskasevoivahingoittaasitä.
•Tyhjennämansettiainakokonaanennensensäilytykseenlaittoa.
•Äläkoskaanpurkaamanometriämissäänolosuhteissa.
•Säilytäkokolaitteistosäilytyspussissapitääksesikaikkiosatpuhtaina.
•Säilytyslämpötilaolosuhteet:20+70°Cjailmankosteus85%(eikondensoitunut).
•Pyyhi manometri ja pumppu kostealla liinalla. Sterilointi ei ole tarpeellista, niin kauan kuin
manometrin osat eivät ole suorassa kosketuksessa potilaiden kehon kanssa mittauksen aikana.
•Poistakumiosaensinjapyyhisulkija,pumppujaputketkosteallaliinalla.Mansetinvoipestä
saippualla ja kylmällä vedellä, mutta älä huuhdo mansettia juoksevan veden alla ja kuivata
huoneilmassa.
Tarkkuustesti
Suosittelemme instrumentin tarkkuuden testaamista joka 2. vuosi tai mekaanisen iskun jälkeen
(jos instrumentti on esim. päässyt putoamaan). Järjestä testiaika ottamalla yhteyttä mittarin
myyjään.
7. Takuu
Instrumentilla on 2 vuoden takuu ostopäivästä lukien. Takuu on voimassa ainoastaan silloin, kun
korvausvaatimuksen yhteydessä esitetään kauppiaan täyttämä takuukortti (katso takakantta),
joka vahvistaa ostopäivämäärän tai viimeisen voimassaolopäivämäärän. Takuu ei koske kuluvia
osia. Instrumentin avaaminen tai muuttaminen mitätöi takuun. Takuu ei korvaa vaurioita, jotka
aiheutuvat väärästä käsittelystä,
onnettomuuksistataikäyttöohjeidennoudattamattajättämisestä.OtayhteysMicrolifepalveluun:
72
Page 76

8. Käytetyt standardit
Laitteen standardi: Laite vastaa ei-invasiivisten verenpainemittareiden eurooppalaisen
standardinvaatimuksia:EN10601/2;ANSI/AAMISP09
Tämä laite vastaa EU-direktiivin 93/42/EEC lääkinnällisistä laitteista asetettuja vaatimuksia.
9. www.microlife.fi
Yksityiskohtaisetkäyttöohjeetsekäpalvelutlöytyvät:www.microlife.fi
10. Tekniset tiedot
Paino: 450 g
Mitat: 175 x 70 x 103 mm
Käyttölämpötila: -20 - +70 °C; 85 % suhteellinen maksimaalinen kosteus
Säilytyslämpötila: 0 - 46 °C
Mittausalue: 0 - 300 mmHg
Resoluutio: 2 mmHg
Tarkkuus: rajoissa ±3 mmHg in 18 - 33 °C;
rajoissa ±6 mmHg in 34 - 46 °C
Ilmantäyttö: määrä vähintään 200cc paineeseen asti 300 mmHg 4 - 10 s.
Paineen laskunopeus: 2 - 3 mmHg/s.
Ilman vuotoa: < ± 4 mmHg/min
Hystereesi-virhe: rajoissa 0 - 4 mmHg
Tarvikkeet: 1. M-mansetti (aikuisten koko käsivarren ympärysmitta 22 - 32 cm)
kanssa upotekoristeinen virtsarakon
2. Pumppausosa ja venttiilit
3. Stetoskooppi
4. Säilytyslaukku
Oikeus teknisiin muutoksiin pidätetään.
73
 Loading...
Loading...