Page 1
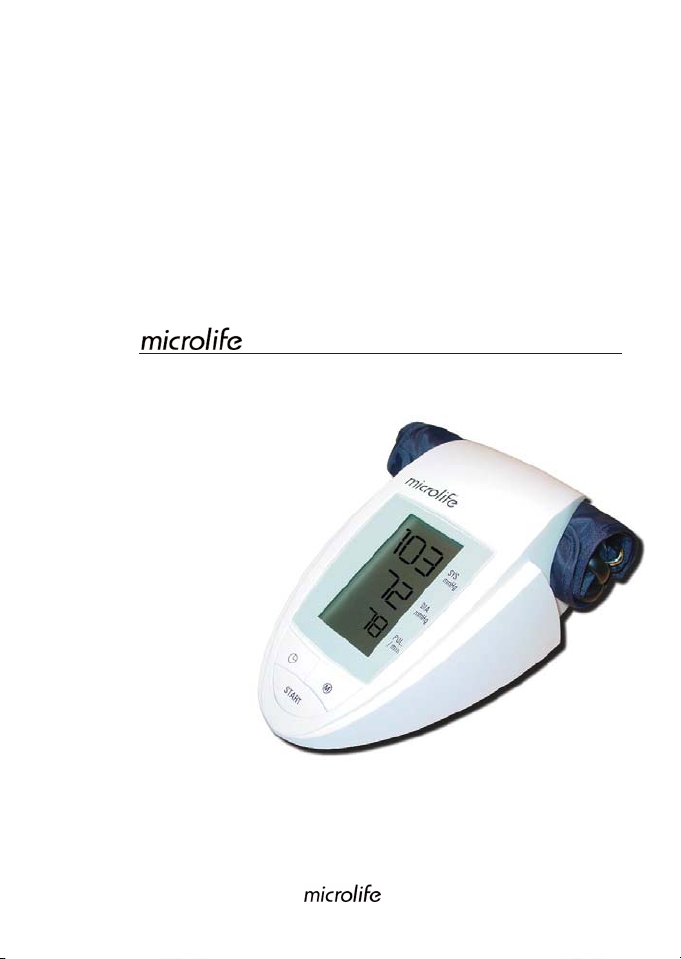
Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor
Model # 3AA1-1: For upper arm
Instruction Manual
Tensiómetro automático
Instrucciones de uso
PLEASE NOTE:
THIS MEDICAL INSTRUMENT MUST BE USED ACCORDING TO
INSTRUCTIONS TO ENSURE ACCURATE READINGS.
Questions? Call toll free at 1-800-568-4147
Page 2

Automatic Blood Pressure Monitor
Instruction Manual
Table of contents
1. Introduction
1.1. Features of your blood pressure monitor
1.2. Important information about self measurement
2. Important information on blood pressure and its measurement
2.1. How does high/low blood pressure arise?
2.2. Which values are normal?
2.3. What can be done if regular high/low values are obtained?
3. Components of your blood pressure monitor
4. Operation of your blood pressure monitor
4.1. Inserting the batteries
4.2. Using an A/C power adapter
4.3. Tube connection
Measurement Procedure
5.1. Before measurement
5.2. Common sources of error
5.3. Fitting the cuff
5.4. Setting the time and date
5.5. Measuring procedure
5.6. Memory – displaying the last measurement
5.7. Discontinuing a measurement
6. Error Messages/Troubleshooting
7. Care and maintenance
8. Warrantee
9. Certifications
10. Technical specifications
1
Page 3

1. Introduction
1.1.Features of your microlife automatic blood pressure monitor,
model # 3AA1-1
Your microlife blood pressure monitor is a fully automatic digital blood pressure measuring
device for use on the upper arm. It enables very fast and reliable measurement of the
systolic and diastolic blood pressure as well as the pulse by way of the oscillometric
method. This device offers clinically proven accuracy and has been designed to be user
friendly.
Before using, please read this instruction manual carefully and then keep it in a safe
place. Please contact your doctor for further questions on the subject of blood pressure
and its measurement.
Attention!
1.2.Important information about self-measurement
• Self-measurement means Control,
not diagnosis or treatment. Unusual values
must always be discussed with your doctor.
Under no circumstances should you
alter the dosages of any drugs prescribed by your doctor.
•
The pulse display is not suitable for checking the frequency of heart pacemakers!
• In cases of irregular heartbeat (Arrhythmia), measurements made with this instrument
should only be evaluated after consultation with your doctor.
Electromagnetic interference:
The device contains sensitive electronic components. Avoid strong electrical or
electromagnetic fields in the direct vicinity of the device (e.g. mobile telephones,
microwave ovens). These can lead to temporary impairment of the measuring accuracy.
2
Page 4

2. Important information on blood pressure and its measurement
2.1. How does high/low blood pressure arise?
Your level of blood pressure is determined in the circulatory center of the brain and
adjusts to a variety of situations through feedback from the nervous system. To adjust
blood pressure, the strength and frequency of the heart (Pulse), as well as the width of
circulatory blood vessels is altered. Blood vessel width is effected by fine muscles in the
blood vessel walls.
Your level of arterial blood pressure changes periodically during heart activity: During the
“blood ejection” (Systole) the value is highest (systolic blood pressure value). At the end
of the heart’s “rest period” (Diastole) pressure is lowest (diastolic blood pressure value).
Blood pressure values must lie within certain normal ranges in order to prevent particular
diseases.
2.2. Which values are normal?
Blood pressure is too high if at rest, your diastolic pressure is above 90mmHg and/or the
systolic blood pressure is over 160mmHg. In this case, please consult your doctor
immediately. Long-term values at this level endanger your health due to continual damage
to the blood vessels in your body.
Should the systolic blood pressure values lie between 140mmHg and 160mmHg and/or
the diastolic blood pressure values lie between 90mmHg and 95mmHg. Consult your
doctor. Regular self-checks will be necessary.
With blood pressure values that are too low, (i.e. systolic values under 105mmHg and/or
diastolic values under 60mmHg), consult your doctor.
Even with normal blood pressure values, a regular self-check with your blood pressure
monitor is recommended. You can detect possible changes in your values early and react
appropriately.
If you are undergoing medical treatment to control your blood pressure, keep a record of
values along with time of day and date. Show these values to your doctor.
Never use the
results of your measurements to independently alter the drug doses prescribed
by your doctor.
3
Page 5
☞Further information
• If your values are mostly normal under resting conditions but exceptionally high under
conditions of physical or psychological stress, it is possible that you are suffering from
so-called “labile hypertension.” Consult your doctor.
•
Correctly measured diastolic blood pressure values above 120mmHg and
require immediate medical treatment.
2.3. What can be done if regular high or low values are obtained?
a) Consult your doctor.
b) Increased blood pressure values (various forms of hypertension) are associated with
considerable health risks over time. Arterial blood vessels in your body are endangered
due to constriction caused by deposits in the vessel walls (Arteriosclerosis). A deficient
supply of blood to important organs (heart, brain, muscles) can result from
arteriosclerosis. Furthermore, the heart will become structurally damaged with
increased blood pressure values.
c) There are many different causes of high blood pressure. We differentiate between the
common primary (essential) hypertension, and secondary hypertension. The latter
group can be ascribed to specific organ malfunctions. Please consult your doctor for
information about the possible origins of your own increased blood pressure values.
d) There are measures which you can take to reduce and even prevent high blood
pressure. These measures must be permanent lifestyle changes.
A) Eating habits
• Strive for a normal weight corresponding to your age. See your doctor for your ideal
weight.
•Avoid excessive consumption of common salt.
Range Systolic Diastolic Measures
Blood pressure Blood pressure
Hypotension (low) lower than 100 lower than 60 Consult your doctor
Normal range between 100 and 140 between 60 and 90 Monitor regularly
Mild hypertension (high) between 140 and 160 between 90 and 100 Consult your doctor
Moderately serious between 160 and 180 between 100 and 110 Consult your doctor
hypertension (higher)
urgent!
Serious hypertension higher than 140 higher than 110 Consult your doctor
(very high)
urgent!
Specific systolic higher than 140 lower than 90 Consult your doctor
hypertension
4
Which values are normal? : (World Health Organization)
Page 6
•Avoid fatty foods.
B) Previous illnesses
• Consistently follow all medical instructions for treating illness such as:
• Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus or sugar diabetes)
• Fat metabolism disorder
• Gout
C) Habits
• Give up smoking completely.
• Drink only moderate amounts of alcohol.
• Restrict your caffeine consumption (coffee, tea, chocolate).
D) Your Physical condition
• After a medical examination, and with your doctor’s approval and direction;
exercise.
• Choose sports which require stamina and avoid those which require strength.
•Avoid reaching the limit of your performance.
• With previous illnesses and/or an age of over 40 years, please consult your doctor
before beginning your exercise routine. You must receive advise regarding the type and
extent of exercise that is appropriate for you.
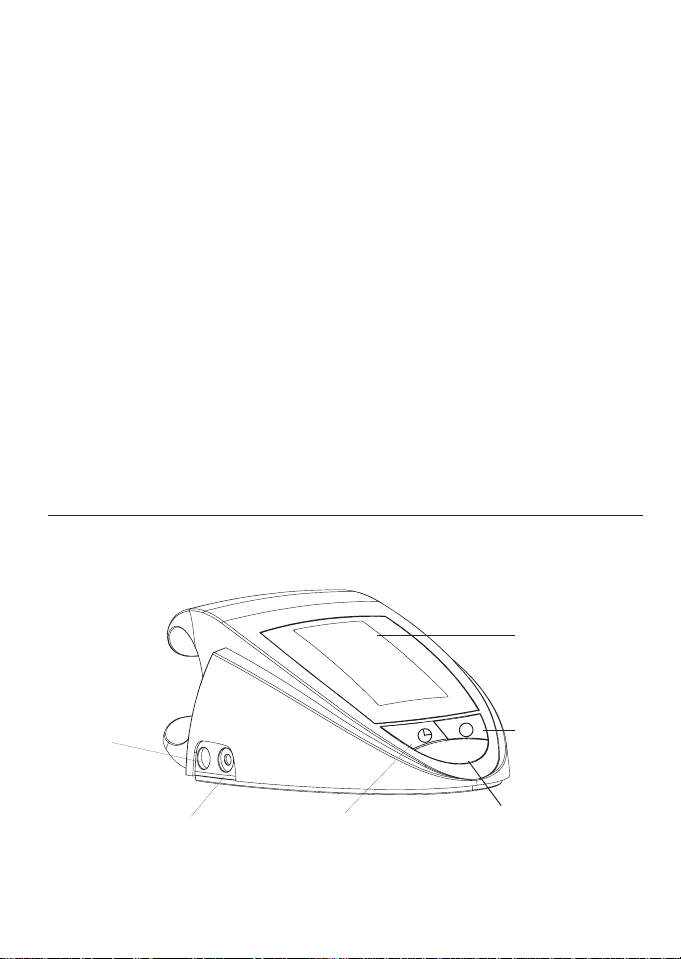
3. Components of your blood pressure monitor
a) Measuring unit
Memory Button
Cuff Jack
Socket
Display
Time & Select
User
START/STOP Button
AC/DC Power
Socket
5
120
85
72
Start
M
Page 7
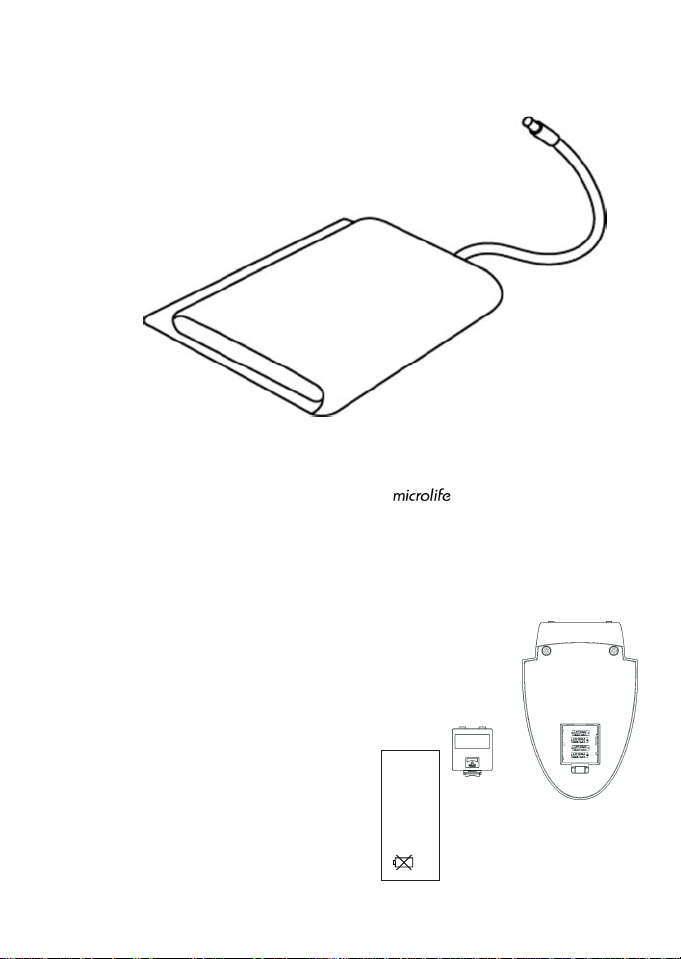
b) Upper arm cuffs:
Type S101 for arm circumference 22–30 cm or
8
11/
16
” -11
13 /
16
” (included)
Type S102 for arm circumference 30–38 cm
11
13
/
16
” -15” (order as a special accessory)
Please Note:
Do not force cuff connection into the opening. Make sure the cuff connection is not pushed
into the AC adapter port. If the cuff is too small, call for further information.
4. Operation of your blood pressure monitor
4.1. Inserting the batteries
After you have unpacked your device insert the batteries. The battery compartment is
located on the back side of the device (see illustration).
a) Remove cover as illustrated.
b) Insert the batteries (4 AA, 1.5 V), following the
indicated polarity. (+ -)
c) If the low battery indicator appears in the
display, the batteries are discharged and the
unit will not function.
d) If batteries are inserted incorrectly, the display
may function eratically or not at all.
Check battery polarity.
Low Battery Indicator
6
Page 8
Attention!
• After the low battery indicator appears, the device won’t function until the batteries
have been replaced.
• Please use “AA” Long-Life or Alkaline 1.5V Batteries.
•
Do not use rechargable batteries.
• If the blood pressure monitor is not used for long periods, remove the batteries from
the device.
Functional check: Hold the On/Off button down to test all the display elements. When
functioning correctly many icons will appear.
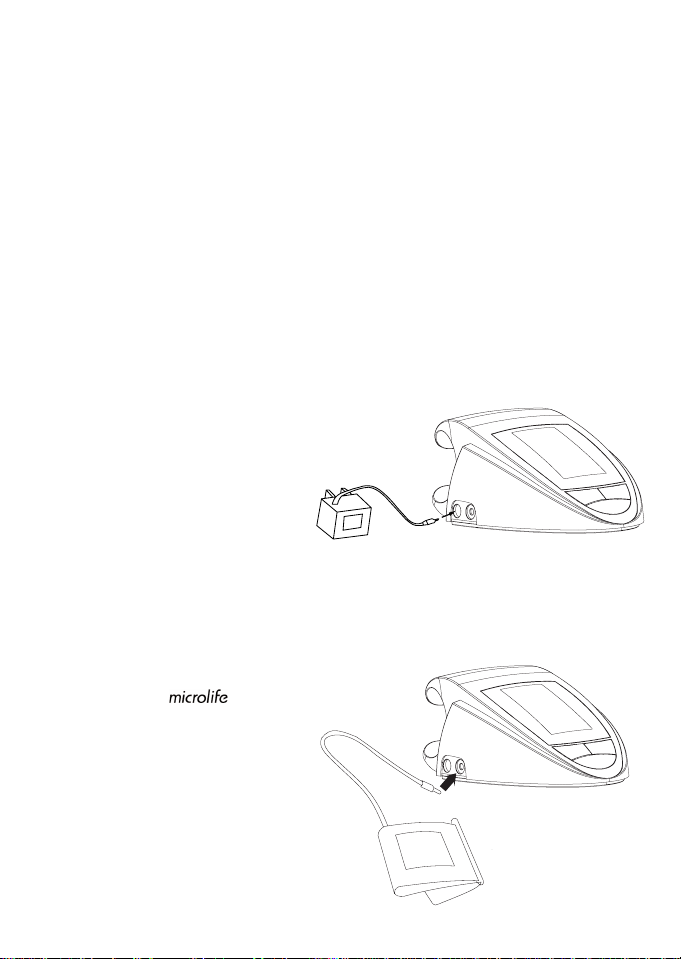
4.2. Using an AC/DC power adapter (special accessory)
It is possible to operate this blood pressure instrument with an AC/DC adaptor. (output 6 V
DC / 600 mA with DIN plug). Make certain that you use an adaptor which fulfills the legal
requirements and electronic requirements in the U.S. (UL standard)
a) Push the plug into the socket at the left side
of the instrument.
b) Plug the AC adaptor into a 110 V
power socket (U.S. or Canada).
c) Test that power is available by
pressing the On/Off button.
Note:
• No power is taken from the batteries while the AC/DC adaptor is connected to the
instrument.
• If the power is interrupted during a measurement (e.g. by removal of the adaptor from
the wall socket), the instrument must be reset by removing the plug from the
instrument.
• Please consult if you have questions
relating to the AC/DC adaptor.
4.3. Tube connection
Insert the cuff tube into the opening
provided on the side of the instrument,
as shown in the diagram.
Right Opening
Left Opening
7
Page 9

5. Measurement Procedure
Please note: You should always be seated before and during measurement.
5.1. Before measurement:
•Avoid eating and smoking as well as all forms of exertion directly before
measurement. These factors influence the measurement result. Find time to relax by
sitting in an armchair in a quiet atmosphere for about ten minutes before
measurement.
• Remove any garment that fits closely to your upper arm.
• Always measure on the same arm (normally left).
• Always perform measurements at the same time of day, since blood pressure changes
during the course of the day.
5.2. Common sources of error:
Note:
Comparable blood pressure measurements always require the same conditions!
These are normally quiet conditions.
•Efforts by the patient to support the arm can increase the blood pressure. Make sure
you are in a comfortable, relaxed position and do not activate any muscles in the
measurement arm during measurement. Use a cushion for support and rest your arm
on a table.
• If the upper arm artery lies considerably lower or higher than the heart, a false higher
or lower blood pressure will be measured!
*A variation of 6” between cuff and heart level can result in a reading error
of + or - 10mm Hg.
• Cuffs that do not fit properly result in false measurement values. Selecting the correct
cuff is extremely important. The cuff size is dependent upon the circumference or
distance arround your upper arm measured in the center. The permissible range is
printed on the cuff. If this is not suitable for your use, please contact .
Note: Use only clinically approved cuffs. e cuffs are specially
manufactured and tested.
•A loose cuff or a sideways protruding air pocket causes false measurement values.
• Repeated measurements without rest allows blood to accumulate in the arm. This can
lead to false results. Measurements should be done after a 5 minute rest to ensure
accuracy.
8
Page 10

5.3. Fitting the cuff
a) Pass the end of the cuff through the flat
metal ring so that a loop is formed. The
velcro closer must be facing outwards.
(Ignore this step if the cuff has already been
prepared.)
b) Place the cuff over the left upper arm so that
the tube is closer to your lower arm.
c) Lay the cuff on the arm as illustrated. Make
certain that the lower edge of the cuff lies
approximately 3/4” to 1”(2 to 3cm) above the
elbow and that the tube is closer to the inner
side of the arm.
Important! The 1” white mark on the cuff
must lie exactly over the artery which runs
down the inner side of the arm.
d) Tighten the cuff by pulling the end and close
the cuff by affixing the velcro.
e) There should be little free space between the
arm and the cuff. You should able to fit 2
fingers between your arm and the cuff.
Clothing must not restrict the arm. Any piece
of clothing which does must be removed.
f) Lay your arm on a table (palm upward) so the
cuff is at the same height as your heart.
Make sure the tube is not kinked.
g) Remain seated quietly for two minutes
before you begin the measurement.
3
/4”-1”
tube
Left Arm
9
Page 11

Comment:
If it is not possible to fit the cuff to your left arm,
it can also be placed on your right arm. However,
all measurements should be made using the
same arm.
5.4. Setting the time and date
This blood pressure monitor incorporates an integrated clock with date display. Time and
date are recorded along with pressure and pulse. After new batteries have been inserted,
the clock begins to run from the following setting: 1999-01-01 00:00 O’clock.
You must then re-enter the date and current time. Please proceed as follows (Example:
Entering 2002-06-15 Time 09:30 AM):
1. Press the User/Time button for at least 3 seconds.
The display now indicates the set year, all characters are blinking.
2. The correct year can be entered by pressing the
MEMORY button. Each click will change the clock 1 year.
3. Press the User/Time button again. The display
now switches to the current date, during which the
first character (month) blinks.
Note: Holding the button down speeds up the procedure.
4. The current month can now be entered by pressing
the MEMORY button. (Example: pressing 5 x
advances 5 months)
5. Press the User/Time button again. The last two
characters (day) are now blinking.
6. The current day can now be entered by pressing
the MEMORY button. (Example: 14 x presses
advances the day from the 1st to 15th)
7. Press the User/Time button again. The display
now switches to the current time, during which the
first character (Hour) blinks.
8. The corresponding hour can now be entered by
pressing the MEMORY button. (Example: 9 x
presses)
Cuff on
right arm
10
Page 12

11
9. Press the User/Time button again. The last two
characters (Minutes) now blink.
10. The minutes can now be entered by pressing the
MEMORY button. (Example: 30 x presses
advances the time from 0 to 30 minutes)
5.5. Reading the set date
After all settings have been made, click the User/Time
button once. The date is briefly displayed and then the
time. The input is now confirmed and the clock begins
to run.
5.6. Measuring procedure
After the cuff has been appropriately positioned
the measurement can begin:
a) Press the ON/OFF/START button. The pump
begins to inflate the cuff. In the display, the
increasing cuff pressure is continually displayed.
b) After automatically reaching an individual
pressure, the pump stops and the pressure
slowly falls. The cuff pressure is displayed during
the measurement.
c) When the device has detected your pulse, the
heart symbol in the display begins to blink and a
beep tone is audible for every pulse beat.
d) When the measurement has been concluded, a
long beep tone sounds. The measured systolic
and diastolic blood pressure values, as well as
the pulse are now displayed.
e) The measurement results are displayed until you
switch the device off. If no button is pressed for 5
minutes, the device switches off automatically.
Measuring
Pumping
Pressure
Measurement
complete
Systolic
Diastolic
Pulse
Page 13

12
5.7. Memory – displaying the last 14 measurements
The measured results are stored in the instrument until a new
measurement is carried out or the batteries are removed. With the
unit in the OFF position, press and hold the MEMORY button for at least
3-seconds. The screen will show the last reading along with time and date.
The MR symbol is displayed in the lower left. Release the button.The last
reading will be displayed. Each time you press the memory button an
earlier measurement will be displayed along with time and date.
5.8. Discontinuing a measurement
If it is necessary to interrupt a blood pressure
measurement for any reason (e.g the patient
feels unwell), the ON/OFF button can be pressed
at any time. The device then immediately lowers
the cuff pressure automatically.
☞Further information
Measurements should not occur soon after each other, since
the results will be inaccurate. Wait several minutes in a relaxed position,
sitting or lying, before you repeat a measurement.
6. Error Messages/Troubleshooting
If an error occurs during a measurement, the
measurement is discontinued and a corresponding
error code is displayed.
(example: error no. 1)
Error No. Possible cause(s) / Solutions
ERR 1 The systolic pressure was determined. The
tube may have loosened, or no pulse was
detected.
*Ensure cuff connections are tight with
proper cuff placement. See section (5.3)
ERR 2 Unnatural pressure impulses. Reason:
The arm was moved during the
measurement (Artefact).
Repeat measurement keeping arm still.
MR
MR
Last
reading
14 readings
in memory
14
Page 14

13
Repeat measurement keeping arm still.
If inflation of the cuff takes too long, the
cuff is not correctly seated or the hose
connection’s not tight.
Check connections and repeat.
The difference between systolic and
diastolic is excessive. Measure again
carefully following proper cuff procedures
and ensure measurement under quiet
conditions.
Other possible errors and their solutions
If problems occur when using the device, the following points should be checked:
Malfunction Remedy
• Check battery installation.
• If the display is unusual, remove the batteries
and then exchange them for new ones.
Check polarity.
• Check the connection of the cuff tube and
connect properly.
1. Fit the cuff correctly on the arm. (see 5.3)
2. Before starting measurement make sure
that the cuff is not too tight and that clothing
is not exerting pressure on the arm. Take
articles of clothing off if necessary.
3. Measure blood pressure again in complete
peace and quiet.
• Please read the following information and
the points listed under “Common sources of
error”.(5.2) Repeat the measurement.
• Blood pressure changes constantly. The
observed readings may accurately reflect
your pressure.
• Record daily values and consult your doctor.
• Pressure readings in your doctor’s office may
be higher due to anxiety.
•Check cuff connections.
Ensure the unit has not been tampered with.
ERR 3
ERR 5
The display remains blank when the instrument
is switched on although the batteries are in
place.
The pressure does not rise although the pump
is running.
The device frequently fails to measure,
or the values measured are too low or high.
Every measurement results in different values,
although the device functions normally and
normal values are displayed.
Blood pressure values differ from those
measured by my doctor
After the instrument has inflated the cuff the
pressure falls very slowly, or not at all. (No
reasonable measurement possible).
Page 15

14
7. Care and maintenance
a) Do not expose the device to either extreme
temperatures, humidity, dust or direct
sunlight.
b) The cuff contains a sensitive air-tight bubble.
Handle this cuff carefully and avoid all types
of stress through twisting or buckling.
c) Clean the device with a soft, dry cloth. Do not
use gas, thinners or similar solvents. Spots
on the cuff can be removed carefully with a
damp cloth and soapsuds.
The cuff must
not be washed in a dishwasher,
clothes washer, or submerged in water.
d) Handle the tube carefully. Do not pull on it.
Do not allow the tubing to kink and keep it
away from sharp edges.
e) Do not drop the monitor or treat it roughly in
any way. Avoid strong vibrations.
f)
Never open the monitor! This invalidates
the manufacturer’s warrantee.
8. Warrantee
Your blood pressure monitor 3AA1-1 is warranteed for 5 years from date of
purchase. This warrantee includes the instrument and the cuff. The warrantee does not
apply to damage caused by improper handling, accidents, not following the operating
instructions or alterations made to the instrument by third parties. There are no user
servicable parts inside. Batteries or damage from old batteries is not covered by the
warrantee. The warrantee is only valid upon presentation of the warrantee card.
Please note: According to international standards, your monitor should be
checked for calibration every 2 years
☞Further information
Blood pressure is subject to fluctuations even in healthy people.
Comparable measurements always require the same conditions (quiet
conditions)!
Page 16

15
If fluctuations in readings are larger than 15 mmHg, and/or you hear irregular
pulse tones, consult your doctor.
In order to receive market clearance from governmental bodies, this device was subjected
to strict clinical tests. The computer program used to measure blood pressure values was
tested by experienced cardiac specialists in Germany.
The manufacture of your blood pressure monitor is in accordence with the
terms of the European standard for blood pressure measuring devices (see technical data)
under the supervision of the Technical Monitoring Association Essen (RWTüV-Essen).
Never attempt to repair the instrument yourself!
Any unauthorized opening of the instrument invalidates all warrantee claims!
9. Certifications
Device standard:
This device is manufactured to meet the
European and United States standards for
non-invasive blood pressure monitors:
EN1060-1 / 1995
EN1060-3 / 1997
DIN 58130, NIBP – clinical investigation
ANSI / AAMI SP10, NIBP – requirements
Electromagnetic compatibility: Device fulfills the stipulations of the
European standard EN 60601-1-2
Clinical testing: Clinical performance tests were carried out
in the U.S. and Germany according to the
DIN 58130/1997 procedure N6
(sequential) and AAMI standard (US).
The stipulations of the EU-Guidelines 93/42/EWG for Medical Products Class IIa have
been fulfilled.
Page 17

16
10. Technical specifications:
Weight:
483 g (with batteries)
Size: 124 (W) x 205 (L) x 81 (H) mm
Storage temperature: –5 to +50°C (23°F - 122°F)
Humidity: 15 to 85% relative humidity maximum
Operation temperature: 10 to 40°C ( 50°F - 104°F)
Display: LCD-Display (Liquid Crystal Display)
Measuring method: oscillometric
Pressure sensor: capacitive
Measuring range:
SYS/DIA:
30 to 280 mmHg
Pulse: 40 to 200 per minute
Cuff pressure display range: 0–299 mmHg
Memory: Automatically stores the last 14
measurements.
Measuring resolution: 1 mmHg
Accuracy: pressure within ± 3 mmHg
pulse ± 5 % of the reading
Power source: a) 4 AA bateries, 1.5 V
b) AC adaptor 6 V DC 600 mA
(voltage 4.5 V DC to 6 V DC)
Accessories: cuff type S101 for arm circumference
11/
22–30 cm (8
16
” -11
13 /
”)
16
(included)
cuff type S102 for arm circumference
30–38 cm (11
13
/
” - 15”)
16
(call microlife for details)
Made in China. Technical alterations reserved!
USA, Inc.
Toll free: 800-568-4147
Email: custserv@microlifeusa.com
www.microlifeusa.com
Page 18

17
Tensiómetro automático
Instrucciones de uso
Page 19

18
1. Introducción
1.1. Características del modelo 3AA1-1
1.2. Información importante sobre las automediciones
2. Información importante sobre la presión sanguínea y su medición
2.1. ¿Cómo se origina la tensión arterial alta/baja?
2.2. ¿Cuales son los valores normales?
2.3. ¿Qué podemos hacer si se miden regularmente valores altos/bajos?
3. Los diversos componentes del tensiómetro
4. Puesta en funcionamiento del tensiómetro
4.1. Colocación de las pilas
4.2. Uso de un adaptador para corriente eléctrica
4.3. Conexión del tubo
4.4. Adjuste de la hora y la fecha
5. Desarrollo de una medición
5.1. Antes de la medición
5.2. Fuentes de error comunes
5.3. Ajuste del brazalete
5.4. Procedimiento de medición
5.5. Indicación del último valor medido – Memoria
5.6. Interrupción de la medición
6. Mensaje de error/funcionamiento defectuoso
7. Cuidados y mantenimiento, recalibración
8. Garantía
9. Referencia a estándares
10. Especificaciones técnicas
Page 20

19
1. Introducción
1.1. Características del modelo 3AA1-1
El modelo 3AA1-1 es un tensiómetro digital totalmente automático con un método
de medición oscilométrico que permite una medición rápida y fiable de la presión
arterial sistólica, diastólica y de la frecuencia del latido cardiaco.
El modelo 3AA1-1 dispone de una pantalla de cristal líquido de grandes
dimensiones, gracias a la cual es posible visualizar claramente el estado de
funcionamiento y la presión del brazalete durante toda la medición.
El aparato le ofrece una altísima precisión en la medición, clínicamente comprobada,
y ha sido diseñado de tal modo que su uso resulta sencillo.
Lea atentamente las instrucciones de uso antes de utilizar el aparato y guárdelas
para posibles consultas futuras.
Atención:
1.2. Información importante sobre las automediciones
• No lo olvide: automedición significa control, no diagnóstico o tratamiento.
Los valores inusuales deben ser discutidos siempre con su médico. No modifique
bajo ninguna circunstancia las dosis de cualquier medicamento que le haya
recetado su médico.
• El indicador de pulsaciones
no es apropiado para medir la frecuencia de los
marcapasos.
• En casos de irregularidad cardiaca (arritmia), las mediciones realizadas con este
instrumento deben ser evaluadas sólo, previa consulta con el médico.
Interferencia electromagnética:
El aparato contiene componentes electrónicos sensibles (microordenador). Por ello,
evite los campos eléctricos o electromagnéticos fuertes en la proximidad directa del
aparato (por ejemplo, teléfonos móviles, microondas); pueden dar lugar a la pérdida
temporal de la exactitud de medición.
Page 21

20
2. Información importante sobre la presión sanguínea y su medición
2.1. ¿Cómo se origina la tensión arterial alta/baja?
El nivel de la tensión arterial se determina en una zona del cerebro, en el llamado centro
circulatorio, y se adapta a cada situación concreta por retroalimentación, a través del
sistema nervioso.
Para ajustar la tensión arterial se modifican la potencia y la frecuencia cardiacas (pulso),
así como la anchura de los vasos sanguíneos. Esto último se efectúa mediante los
músculos de las paredes de los vasos sanguíneos.
El nivel de la tensión arterial cambia periódicamente junto con la actividad cardiaca:
durante la impulsión de la sangre (sístole) el valor es máximo (valor sistólico de la tensión
arterial); al final del «periodo de relajación» del corazón (diástole), mínima (valor diastólico
de la tensión arterial).
Para evitar ciertas enfermedades, los valores de la tensión arterial deben estar situados
entre unos valores límite determinados.
2.2. ¿Cuales son los valores normales?
Se produce un fenómeno de hipertensión cuando en condiciones de reposo del
organismo,la presión diastólica supera los 90 mmHg, o cuando la presión sistólica supera
los 160 mmHg, entonces deberá dirigirse inmediatamente al médico, porque la
persistencia de estos valores pone en peligro su estado de salud, a causa del progresivo
deterioramiento de los vasos sanguíneos que se produciría.
Se deberá dirigir al médico también cuando el valor de la presión sistólica se encuentre
entre 140 mmHg y 160 mmHg o cuando el valor de la presión diastólica se encuentre
entre 90 mmHg y 95 mmHg. Además, se deberá autocontrolar regularmente.
También cuando los valores de la presión sean excesivamente bajos: una presión sistólica
inferior a 105 mmHg o una presión diastólica por debajo de 60 mmHg, será necesario
consultar con el médico.
Cuando los valores estén dentro de la normalidad, es aconsejable efectuar regularmente
un autocontrol usando el tensiómetro, de este modo, será posible averiguar eventuales
variaciones de los valores y tomar las medidas oportunas.
Cuando se esté siguiendo una terapia médica para regular la presión sanguínea , será
necesario tomar regularmente nota de los valores de la presión que vayamos midiendo
siempre a la misma hora. Las anotaciones pueden servir como soporte al examen médico.
No use nunca los resultados de sus mediciones para alterar por su cuenta el
tratamiento prescrito por su médico.
Page 22

21
Tabla de los valores normales de la presión sanguínea (Unidad de medida mmHg)
Nivel Presión sistólica Presión diastólica Medidas a tomar
Hipotensión Inferior a 105 Inferior a 60 Consultar al médico
Niveles normales Entre 105 y 140 Entre 60 y 90 Autocontrol
Valores limites de
hipertensión Entre 140 y 160 Entre 90 y 95 Consultar al médico
Ligera hipertensión Superior a 160 Entre 95 y 105 Consultar al médico
Hipertensión mediana Superior a 160 Entre 105 y 115 Consultar al médico
Hipertensión grave Superior a 160 Superior a 115 Consultar al médico
Page 23

22
☞Otras informaciones
• En presencia de valores mayoritariamente normales en condiciones de reposo, pero
excepcionalmente altos en condiciones de esfuerzo físico o psíquico, puede
presentarse una «hipertensión lábil», si ésta persiste acudir al médico.
•Valores de la presión diastólica medidos correctamente superiores a 120 mmHg,
requieren un tratamiento médico de inmediato.
2.3. ¿Qué podemos hacer si se miden regularmente valores altos/bajos?
a) Consultar con el médico.
b) A medio-largo plazo, un aumento considerable de la tensión arterial (diversas formas
de hipertensión), supone considerables riesgos para la salud. Estos riesgos son
relativos a los vasos sanguíneos, los cuales se ven amenazados por los depósitos que
se forman en sus paredes y que los van estrechando (arteriosclerosis). Ello puede
comportar un aporte insuficiente de riego sanguíneo a los órganos principales
(corazón, cerebro, músculos). Además, largos periodos de presión arterial elevada
pueden provocar daños estructurales en su corazón.
c) Las causas de la hipertensión pueden ser múltiples: es necesario antes de todo,
diferenciar entre la hipertensión primaria (esencial) que es frecuente y la hipertensión
secundaria. La segunda puede ser debida a disfunciones orgánicas específicas. A fin
de establecer las posibles causas de los valores altos obtenidos en la medición de la
presión, consulte con el médico.
d) Hay ciertas medidas que se pueden adoptar no sólo para reducir la tensión arterial
elevada que haya sido diagnosticada por el médico, sinó como prevención
A) Hábitos alimenticios
• Mantener el peso y forma correctos, según su edad y reducir el sobrepeso.
• Evitar el consumo excesivo de sal.
• Evitar los alimentos grasos.
B) Enfermedades previas
• Seguir coherentemente el tratamiento indicado por el médico, para la corrección de
patologías ya existentes, como por ejemplo, diabetes (diabetes mellitus), disfunciones
del metabolismo, gota.
C) Hábitos
• Renunciar completamente al tabaco.
• Moderar el consumo de alcohol.
• Limitar el consumo de cafeina (café).
Page 24

23
D) Constitución física
• Practicar regularmente alguna actividad deportiva, tras una visita médica
preliminar.
• Practicar preferentemente una actividad deportiva que requiera más resistencia
que fuerza.
• Evitar llegar al límite de sus posibilidades físicas.
• En caso de padecer patologías o si se han superado los 40 años de edad, antes de
iniciar cualquier actividad consulte con el médico para determinar el tipo, la intensidad
y forma de practicar deporte.
3. Los diversos componentes del tensiómetro
a) Aparato de medición
b) Brazalete:
modelo MDS9872 para un brazo de 22–30 cm de contorno
modelo MD9873 para un brazo de 30–38 cm de contorno
(accesorio opcional).
brazalete
Time Button
START/STOP Button
Pantalla de cristal líquido
Botón de encendido/
apagado y de
MEMORIA
Conexión del
tubo del brazalete
Toma de
corriente AC/DC
Page 25

24
4. Puesta en funcionamiento del tensiómetro
4.1. Colocación de las pilas
Una vez desempaquetado el aparato, inserte primero las pilas. El compartimento de la
batería está situado en la parte inferior del aparato (vea la ilustración).
a) Levantar la tapa como indica la figura.
b) Coloque las 4 pilas AA de 1,5 V. vigilando de
colocar correctamente los polos positivo y
negativo.
c) Cuando en la pantalla, aparece la señal de
agotamiento de la carga de las pilas (tensión
por debajo de 4,5 V) significa que éstas están
agotadas y deben ser sustituidas.
Advertencia:
• Cuando se visualiza la señal de agotamiento
de las pilas, el aparato se bloquea hasta la
sustitución de las mismas: deberán ser
cambiadas todas.
• Se desaconseja el uso de pilas recargables.
• Si el aparato lleva mucho tiempo sin ser
usado, renueve las pilas.
Control del funcionamiento: a fin de controlar
juntos todos los elementos de la pantalla,
preste atención a la tecla de acceso y verifique
que los datos corresponden a la representación
que sale al lado.
Page 26

4.2. Uso de un adaptador para corriente eléctrica
Es posible utilizar el tensiómetro con un alimentador (salida 6VDC/600 mA con conector
DIN). El alimentador utilizado deberá reunir las disposiciones legales, (símbolo CE en la
etiqueta).
a) Inserte el conector DIN en la toma de corriente
situado en el lateral izquierdo del aparato.
b) Enchufe el transformador a una toma eléctrica
a 230 V.
c) Verifique, accionando la tecla O/I la presencia
de tensión.
Atención:
• Cuando el aparato está conectado al
transformador, no consume corriente de las
pilas.
• En caso de fallo de la red eléctrica durante la
medición (p.ej. desconexión del transformador
de la red eléctrica) el aparato deberá ser
«reiniciado», de modo que extraiga el conector
de su toma y reinsértelo cuando se haya
recuperado la tensión eléctrica.
• Si tiene dudas sobre el transformador, diríjase
a un vendedor especializado.
4.3. Conexión del tubo
Introduzca el tubo del brazalete en la toma que se
encuentra a la izquierda del aparato, como indica
la ilustración.
4.4. Adjuste de la hora y la fecha
5. Desarrollo de una medición
5.1. Antes de la medición
• No coma, ni fume y evite hacer cualquier esfuerzo antes de efectuar la medición. Son
factores que alteran el resultado. Antes de medir la presión arterial, relájese en un
ambiente tranquilo sentado en un sillón por espacio de 10 minutos.
• Si lleva ropa que le presione el brazo, quítesela.
• Efectuar la medida siempre sobre el mismo brazo (generalmente el izquierdo) y evitar
cuanto sea posible moverlo durante la medición.
25
Page 27

• Tenga la precaución de tomar la medición siempre a la misma hora, dado que la
presión arterial cambia en el transcurso del día.
5.2. Fuentes de error comunes
Nota:
A fin de obtener valores de medición de la presión de la sangre comparables,
éstos deberán ser obtenidos en idénticas condiciones.
• Por norma, la medición siempre debe efectuarse en condiciones de reposo.
Cada esfuerzo hecho por el paciente para sostener el brazo puede comportar un
aumento de la presión sanguínea. Mantenga el cuerpo en una posición relajada, debe
sentarse cómodamente y evitar contraer durante la medición los músculos del brazo
utilizado. Es necesario apoyar el brazo en un cojín.
• Si el brazalete se coloca muy por debajo o por encima de la altura del corazón, la
medición se verá alterada indicando una presión mayor o menor, respecto a los valores
reales (por cada 15 cm. de desnivel el resultado de la medición se altera en 10 mmHg).
• Además si el brazalete es demasiado estrecho o corto, puede ser causa de errores en
la medición.
Será realmente importante seleccionar el brazalete adecuado. Las dimensiones de
éste deberán estar adecuadas a la circunferencia del brazo, medida a la mitad de este,
entre el hombro y el codo con los músculos relajados. Una vez ajustado el brazalete, el
brazo debe poder ser flexionado. En el caso de que la circunferencia del brazo del
paciente no esté comprendida en tales medidas, brazaletes de medidas especiales
(accesorios) pueden encontrarse en establecimientos especializados.
Atención: Usar solamente brazaletes comprobados clínicamente.
• Un brazalete mal ajustado o una cámara de aire asomando por los lados son causas
de mediciones falsas.
• Repitiendo muchas veces la medición en el brazo escogido, se provoca un acúmulo de
sangre, ello puede comportar alteraciones en el resultado. Será por lo tanto oportuno
en el caso de repetir la medición de la presión arterial hacer una pausa de 5 minutos
entre cada medición o en todo caso levantar el brazo en alto a fin de que refluya la
sangre acumulada (esté así al menos 5 minutos).
5.3. Ajuste del brazalete
a) Pasar el extremo del brazalete (con tope de
goma integrado) a través del arco metálico,
formando un lazo. El cierre de velcro se
26
Page 28

encuentra en el exterior. (si el brazalete ya
está preparado como se ha descrito, sáltese
este paso).
b) Colocar el brazalete en el brazo izquierdo de
tal modo que el tubo sea dirigido hacia el
antebrazo.
c) Colocar el brazalete en el brazo como está
indicado en la figura, teniendo cuidado de
que el borde inferior del brazalete se
encuentre 2–3 cm por encima del codo y que
la salida del tubo de goma del brazalete esté
situada en el lado interno del brazo.
d) Extender la extremidad libre del brazalete y
cerrarlo con el cierre de velcro.
e) Entre el brazo y el brazalete no deberá
quedar espacio libre, que condicione el
resultado de la medición. Además el brazo no
deberá estar comprimido por alguna pieza de
ropa (p.ej.un pullover) en ese caso quítesela.
f) Asegurar el brazalete con el cierre de velcro
de modo que se adhiera cómodamente al
brazo pero que no esté demasiado estrecho.
Extender el brazo sobre la mesa (la palma de
la mano deberá estar mirando hacia arriba)
de modo que el brazalete se encuentre a la
altura del corazón. Tenga cuidado de no
doblar el tubo.
g) Permanezca sentado tranquilamente dos
minutos antes de empezar la medición.
Nota:
En el caso de que no fuera posible colocar el
brazalete en el brazo izquierdo, se podrá colocar
en el derecho. Lo importante es que la medición
se haga siempre sobre el mismo brazo.
2–3 cm
tubo da
goma
27
Page 29
5.4. Procedimiento de medición
El aparato va provisto de lógica difusa, es decir:
la presión inicial necesaria de inflado del
brazalete se regula automáticamente.
a) Apriete el botón 0/I y MEMORIA para poner
el aparato en funcionamiento, la bomba
iniciará el inflado del brazalete. El visor
indicará si la presión del brazalete va
subiendo.
b) Una vez alcanzada la presión inicial del
brazalete, la bomba se para y la presión
empezará lentamente a disminuir. Veremos
visualizada la presión del brazalete y un valor
de control.
c) Durante la verificación del latido cardíaco,
en el visor empieza a destellar el símbolo del
corazón y por cada latido se oirá un bip.
d) Apenas terminada la medición, se oirá un bip
prolongado. El visor indicará la presión
sistólica y diastólica además de la frecuencia
del latido cardíaco del paciente.
e) El resultado de la medición continuará
visualizándose hasta que el aparato se
apague. Si no se acciona ninguna tecla en un
periodo de 5 minutos el aparato se apaga
automáticamente con el fin de preservar las
baterías.
5.5. Indicación del último valor medido
Los datos de la medición son memorizados por el
aparato hasta la próxima medición o hasta que se
sustituyan las baterías. Para recuperar los valores de
la última medición, bastará pulsar la tecla de
MEMORIA durante 3 segundos.
5.6. Interrupción de la medición
Si por cualquier motivo la medición de la presión
MR
28
Page 30

sanguínea se tiene que interrumpir (p.ej. en caso de malestar del paciente), bastará pulsar
en cualquier momento la tecla 0/I. La presión del brazalete descenderá inmediatamente.
6. Mensaje de error/funcionamiento defectuoso
En caso de errores se visualizarán los siguientes mensajes:
Error nº Posible(s) causa(s)
ERR 1 Se ha determinado la presión sistólica y
después la presión del brazalete ha
descendido por debajo de 20 mmHg.Tal
situación puede ocurrir p.ej. cuando
después de haber medido la presión
sistólica se ha desconectado el tubo del
brazalete.
Otras posibles causas: no ha sido posible
detectar el pulso.
ERR 2 Impulsos anormales de presión
comprometen el resultado de la medición.
Causas: el brazo se ha estado moviendo
durante la medición.
ERR 3 El inflado del brazalete dura demasiado
tiempo.
El brazalete está mal puesto o quizá la
conexión del tubo no garantice la
capacidad hermética.
Problemas de mal funcionamiento y su corrección
En caso de mal funcionamiento de alguno de los elementos del aparato, compruebe los
siguientes puntos y tome las medidas indicadas.
Funcionamiento defectuoso Remedio
Cuando el aparato se pone en marcha y la
pantalla no se enciende aún cuando las
pilas estén puestas.
1. Verificar la correcta colocación de los
polos de las pilas, corrigiéndola si fuera
necesario.
2.En caso de mal funcionamiento del visor,
repita la operación de colocación de las
baterías o bien sustitúyalas.
29
Page 31
☞Otras indicaciones al respecto
En la presión arterial se producen oscilaciones aún en indivi-duos sanos.
Sin embargo es importante recalcar en este punto que a fin de obtener mediciones
comparativas entre ellos, éstas deben de realizarse siempre en las mismas condiciones,
(condiciones de reposo y tranquilidad). Si las variaciones son mayores de 15 mmHg a
pesar de haber tenido en cuenta las mencionadas condiciones y se escuchan pulsaciones
irregulares repetidamente, (señales de bip), acuda al médico.
En caso de problemas de carácter técnico referentes al tensiómetro, deberá
obligatoriamente dirigirse al establecimiento donde lo compró, en ningún caso intente
repararlo.
La manipulación del aparato por personas no autorizadas, comporta de inmediato la
pérdida de la garantía.
No hay presión a pesar de que la bomba
está funcionando.
Algunas veces el aparato no mide los valores de la presión sanguínea o bien da valores muy bajos o muy altos.
En cada medición los resultados son distintos, a pesar de que el aparato funciona
correctamente e indica valores normales.
Los valores de la presión sanguínea medidos con el aparato, son diferentes a los
determinados por el médico.
Después del inflado del brazalete la presión no desciende o desciende muy lentamente. (La medición se desarrolla de forma
incorrecta).
•Comprobar la conexión del tubo del brazalete y si es necesario conectarlo correctamente.
1. Colocar correctamente el brazalete
alrededor del brazo.
2. Antes de iniciar la medición, asegúrese
de que el brazalete no esté muy estrecho
o que alguna prenda de ropa no provoque
una presión excesiva sobre la zona de
medición, en ese caso quítese la prenda.
3. Repita la medición de la presión san-
guínea con toda tranquilidad.
•Repase las notas indicadas en el apartado
«frecuentes errores» y repita la medición.
•Registrar la evolución cotidiana de los valores y consultar con el médico.
•Falta la junta de plástico del conector del
tubo: la junta puede venir como pieza de
recambio.
Colocar la junta en el conector del tubo,
insértelo correctamente y repita la
medición.
30
Page 32

7. Cuidados y mantenimiento, recalibración
a) Evite exponer el tensiómetro a temperaturas extremas, a la
humedad, al polvo y a la irradiación de los rayos del sol.
b) Evite las caídas, trátelo con cuidado y no le de golpes fuertes.
c) Limpiar el aparato con un trapo suave y seco, no utilizar
detergentes ni disolventes.
d) Evite plegar excesivamente el brazalete y el tubo.
e) Cuando no se use el aparato durante mucho tiempo,
cambie las pilas.
f) Quite las manchas del brazalete o la goma
con un paño húmedo. No lavar el brazalete.
g)
No abrir nunca el aparato, si lo hace pierde
la calibración hecha por el fabricante.
Recalibración
Los componentes de un aparato de medición son particularmente
sensibles, deben periódicamente pasar un control donde se verifica su precisión. Las
normas legales referentes a los tensiómetros indican que se debe controlar la calibración
cada dos años. Puede pedir información detallada a su vendedor especializado.
8. Garantía
El fabricante se reserva el derecho de realizar modificaciones en las especificaciones
técnicas
Para el tensiómetro 3AA1-1 concedemos la
garantía de 5 año a partir de la fecha de
adquisición (comprobada por la fecha de factura) . La garantía incluye el aparato y el
brazalete. La garantía no cubre los daños ocasionados por el mal uso del aparato o por
factores accidentales, en caso de no seguir las instrucciones de uso así como en el caso
de manipulación del aparato por terceros.
Fecha y sello del establecimiento vendedor:
9. Estándares de referencia
Estándar del aparato: El aparato cumple los requerimientos del estándar
europeo sobre instrumentos de control de la
presión arterial no invasivos
EN1060-1 / 12:95
EN1060-3 / 09:97
31
Page 33

DIN 58130, NIBP – investigación clínica
ANSI / AAMI SP10, NIBP – requerimientos
Compatibilidad electromagnética: El aparato cumple las especificaciones del estándar
europeo EN 60601-1-2
Ensayo clínico: El test de funcionamiento clínico ha sido realizado
en Alemania de acuerdo con el procedimiento
DIN 58130 / 1997 N6 (secuencial).
Cumple las especificaciones de la directiva de la UE 93/42/CEE para productos médicos de la clase IIa.
10. Especificaciones técnicas
Peso: 465 gramos con las pilas.
Dimensiones: medidas 131 mm ancho.x 174 mm largo x 73 mm
alto.
Conservación:
Temperatura:
Entre –5˚C y 50˚C.
Humedad: 15–85 % máxima humedad relativa.
Pantalla: Pantalla LCD de cristal líquido.
Procedimiento de medición: Oscilométrica.
Elemento manosensible: Capacitivo.
Gama de medición:
Presión, sistólica /diastólica:
De 30 a 280 mmHg.
Latido cardiaco: De 40 a 200 latidos minuto.
Presión del brazalete: De 0 a 299 mmHg, a partir de 300 mmHg se
visualiza «HI».
Visualización:
Mínimo visualizado:
1 mmHg.
Precisión de la medición:
Presión:
±3 mmHg.
Pulso: ± 5% del valor medido (en la escala entre 40 y
200 p/min.)
Alimentación eléctrica: a) 4 pilas UM-3 dim. AA, 1,5 V.
b) alimentador para corriente 6 VDC 600 mA
(voltaje 4.5 VDC to 6 VDC)
Accesorios: Brazalete modelo MDS9872 para contorno de
brazo de 22-30 cm.
Brazalete modelo MDS9873 para contorno de
brazo de 30-38 cm.
El fabricante se reserva el derecho de realizar modificaciones en las especificaciones técnicas
32
 Loading...
Loading...