Page 1

Operating Manual
IPn4G / IPn4Gb
IPn4G LTE Ethernet Bridge/Serial Gateway
Document: IPn4G Operating Manual.v1.4.pdf
FW: v1.1.0 Build1084-16
May 2015
150 Country Hills Landing NW
Calgary, Alberta
Canada T3K 5P3
Phone: (403) 248-0028
Fax: (403) 248-2762
www.microhardcorp.com
Page 2

Important User Information
Warranty
Microhard Systems Inc. warrants that each product will be free of defects in material and workmanship for a
period of one (1) year for its products. The warranty commences on the date the product is shipped by Micro-
hard Systems Inc. Microhard Systems Inc.’s sole liability and responsibility under this warranty is to repair or
replace any product which is returned to it by the Buyer and which Microhard Systems Inc. determines does
not conform to the warranty. Product returned to Microhard Systems Inc. for warranty service will be shipped
to Microhard Systems Inc. at Buyer’s expense and will be returned to Buyer at Microhard Systems Inc.’s ex-
pense. In no event shall Microhard Systems Inc. be responsible under this warranty for any defect which is
caused by negligence, misuse or mistreatment of a product or for any unit which has been altered or modified
in any way. The warranty of replacement shall terminate with the warranty of the product.
Warranty Disclaims
Microhard Systems Inc. makes no warranties of any nature of kind, expressed or implied, with respect to the
hardware, software, and/or products and hereby disclaims any and all such warranties, including but not limited to warranty of non-infringement, implied warranties of merchantability for a particular purpose, any interruption or loss of the hardware, software, and/or product, any delay in providing the hardware, software, and/
or product or correcting any defect in the hardware, software, and/or product, or any other warranty. The Purchaser represents and warrants that Microhard Systems Inc. has not made any such warranties to the Purchaser or its agents MICROHARD SYSTEMS INC. EXPRESS WARRANTY TO BUYER CONSTITUTES MICROHARD
SYSTEMS INC. SOLE LIABILITY AND THE BUYER’S SOLE REMEDIES. EXCEPT AS THUS PROVIDED, MICROHARD
SYSTEMS INC. DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PROMISE.
MICROHARD SYSTEMS INC. PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED OR INTENDED TO BE USED IN
ANY LIFE SUPPORT RELATED DEVICE OR SYSTEM RELATED FUNCTIONS NOR AS PART OF
ANY OTHER CRITICAL SYSTEM AND ARE GRANTED NO FUNCTIONAL WARRANTY.
Indemnification
The Purchaser shall indemnify Microhard Systems Inc. and its respective directors, officers, employees, successors and assigns including any subsidiaries, related corporations, or affiliates, shall be released and discharged from any and all manner of action, causes of action, liability, losses, damages, suits, dues, sums of
money, expenses (including legal fees), general damages, special damages, including without limitation,
claims for personal injuries, death or property damage related to the products sold hereunder, costs and demands of every and any kind and nature whatsoever at law.
IN NO EVENT WILL MICROHARD SYSTEMS INC. BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL,
INCIDENTAL, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, CATASTROPHIC, PUNITIVE OR OTHER DAMAGES WHICH MAY BE
CLAIMED TO ARISE IN CONNECTION WITH THE HARDWARE, REGARDLESS OF THE LEGAL THEORY BEHIND
SUCH CLAIMS, WHETHER IN TORT, CONTRACT OR UNDER ANY APPLICABLE STATUTORY OR REGULATORY
LAWS, RULES, REGULATIONS, EXECUTIVE OR ADMINISTRATIVE ORDERS OR DECLARATIONS OR OTHERWISE,
EVEN IF MICROHARD SYSTEMS INC. HAS BEEN ADVISED OR OTHERWISE HAS KNOWLEDGE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES AND TAKES NO ACTION TO PREVENT OR MINIMIZE SUCH DAMAGES. IN THE EVENT
THAT REGARDLESS OF THE WARRANTY DISCLAIMERS AND HOLD HARMLESS PROVISIONS INCLUDED ABOVE
MICROHARD SYSTEMS INC. IS SOMEHOW HELD LIABLE OR RESPONSIBLE FOR ANY DAMAGE OR INJURY, MICROHARD SYSTEMS INC.'S LIABILITY FOR ANYDAMAGES SHALL NOT EXCEED THE PROFIT REALIZED BY MICROHARD SYSTEMS INC. ON THE SALE OR PROVISION OF THE HARDWARE TO THE CUSTOMER.
Proprietary Rights
The Buyer hereby acknowledges that Microhard Systems Inc. has a proprietary interest and intellectual property rights in the Hardware, Software and/or Products. The Purchaser shall not (i) remove any copyright, trade
secret, trademark or other evidence of Microhard Systems Inc.’s ownership or proprietary interest or confiden-
tiality other proprietary notices contained on, or in, the Hardware, Software or Products, (ii) reproduce or modify any Hardware, Software or Products or make any copies thereof, (iii) reverse assemble, reverse engineer or
decompile any Software or copy thereof in whole or in part, (iv) sell, transfer or otherwise make available to
others the Hardware, Software, or Products or documentation thereof or any copy thereof, except in accor-
dance with this Agreement.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 2
Page 3

Important User Information (continued)
About This Manual
It is assumed that users of the products described herein have either system integration or
design experience, as well as an understanding of the fundamentals of radio communications.
Throughout this manual you will encounter not only illustrations (that further elaborate on the
accompanying text), but also several symbols which you should be attentive to:
Caution or Warning
Usually advises against some action which could result in undesired or
detrimental consequences.
Point to Remember
Highlights a key feature, point, or step which is noteworthy. Keeping
these in mind will simplify or enhance device usage.
Tip
An idea or suggestion to improve efficiency or enhance usefulness.
Information
Information regarding a particular technology or concept.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 3
Page 4

Important User Information (continued)
Regulatory Requirements
To satisfy FCC RF exposure requirements for mobile transmitting devices, a separation distance
of 23cm or greater for the IPn4G utilizing a 3dBi antenna, or 3.5m or greater for the IPn4G
utilizing a 34dBi antenna, should be maintained between the antenna of this device and persons
during device operation. To ensure compliance, operations at closer than this distance is not
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
recommended. The antenna being used for this transmitter must not be co-located in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter.
This device can only be used with Antennas approved for this device. Please contact
Microhard Systems Inc. if you need more information or would like to order an antenna.
MAXIMUM EIRP
FCC Regulations allow up to 36dBm Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP).
Therefore, the sum of the transmitted power (in dBm and not to exceed +30dBm)), the
cabling loss, and omnidirectional antenna gain cannot exceed 36dBm.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 4
Page 5

CSA Class 1 Division 2 Option
CSA Class 1 Division 2 is Available Only on Specifically Marked Units
If marked this for Class 1 Division 2 – then this product is available for use in Class 1, Division 2,
in the indicated Groups on the product.
In such a case the following must be met:
The transceiver is not acceptable as a stand-alone unit for use in hazardous locations. The
transceiver must be mounted within a separate enclosure, which is suitable for the intended
application. Mounting the units within an approved enclosure that is certified for hazardous
locations, or is installed within guidelines in accordance with CSA rules and local electrical and
fire code, will ensure a safe and compliant installation.
Do not connect or disconnect equipment unless power has been switched off or the area is
known to be non-hazardous.
Installation, operation and maintenance of the transceiver should be in accordance with the
transceiver’s installation manual, and the National Electrical Code.
Tampering or replacement with non-factory components may adversely affect the safe use of
the transceiver in hazardous locations, and may void the approval.
The wall adapters supplied with your transceivers are NOT Class 1 Division 2 approved, and
therefore, power must be supplied to the units using the screw-type or locking type connectors
supplied from Microhard Systems Inc. and a Class 1 Division 2 power source within your panel.
If you are unsure as to the specific wiring and installation guidelines for Class 1 Division 2
codes, contact CSA International.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 5
Page 6
Revision History
Revision Description Initials Date
1.0 Initial Release based on firmware v1_1_0-r1010.bin PEH Dec 2012
1.1 Updated Network > LAN (Add Interface), Updated SMS Commands,
Added SMS Alerts, Updated Wireless Config (Virtual Interfaces), AP
Isolation, Updated COM IP Protocol Config (C12.22, GPS), Updated
GPS (UDP Report, GpsGate, Recorder, Load Recorder), Updated Firewall, Updated VPN (Gateway Type etc), Added Modbus, Updated
misc screen shots, misc formatting. Etc. Based on Firmware v1.1.0r1028.bin
1.2 Misc formatting, updates. Updated WiFi antenna to RP-SMA Female. PEH Mar 2013
1.21 Corrected LTE Band Spec PEH Apr 2013
1.22 Added PoE information PEH Apr 2013
1.23 Added/Corrected Digital I/O pins location PEH Apr 2013
1.24 Corrected enclosure drawings PEH Nov 2013
1.3 Firmware v1.1.0-r1060 PEH Dec 2013
1.31 Misc Corrections PEH Oct 2014
1.4 Firmware v1.1.0-r1084-16 PEH May 2015
PEH Mar 2013
© Microhard Systems Inc. 6
Page 7

Table of Contents
1.0 Overview ......................................................................................................... 10
1.1 Performance Features ................................................................................................... 10
1.2 Specifications ................................................................................................................ 11
2.0 QUICK START ................................................................................................. 13
2.1 Installing the SIM Card ................................................................ .................................. 13
2.2 Getting Started with Cellular .......................................................................................... 13
2.3 Getting Started with WiFi ............................................................................................... 17
2.3.1 Setting up WiFi ................................ ................................................................ .... 17
2.3.1 Connecting to WiFi .............................................................................................. 18
3.0 Hardware Features ......................................................................................... 20
3.1 IPn4G ........................................................................................................................... 20
3.1.1 IPn4G Mechanical Drawings ................................................................................ 21
3.1.2 IPn4G Connectors & Indicators ............................................................................ 22
3.1.2.1 Front ...................................................................................................... 22
3.1.2.2 Rear ................................ ...................................................................... 23
4.0 Configuration.................................................................................................. 24
4.0 Web User Interface ...................................................................................................... 24
4.0.1 Logon Window ..................................................................................................... 25
4.1 System ......................................................................................................................... 26
4.1.1 Summary ............................................................................................................. 26
4.1.2 Settings ............................................................................................................... 27
Host Name .......................................................................................................... 27
Syslog Settings .................................................................................................... 28
Date/Time ............................................................................................................ 29
NTP Server Settings ............................................................................................ 29
HTTP/HTTPS Port Settings.................................................................................. 30
4.1.3 Access Control (Users/Passwords) ...................................................................... 31
4.1.4 Services .............................................................................................................. 33
4.1.5 Maintenance ........................................................................................................ 35
Version Information .............................................................................................. 35
Firmware Upgrade ............................................................................................... 35
Reset to Default ................................................................................................... 36
Backup & Restore Configurations ........................................................................ 36
4.1.6 Logout ................................................................................................................. 37
4.1.7 Reboot ................................................................................................................. 38
4.2 Network ....................................................................................................................... 39
4.2.1 Status .................................................................................................................. 39
4.2.2 LAN ..................................................................................................................... 40
DHCP .................................................................................................................. 42
MAC Binding........................................................................................................ 44
4.2.3 WIFI .................................................................................................................... 45
4.2.4 Routes ................................................................................................................. 46
4.2.5 GRE .................................................................................................................... 48
4.2.6 SNMP .................................................................................................................. 51
4.2.7 sdpServer ............................................................................................................ 54
4.2.8 Local Monitor ....................................................................................................... 55
4.2.9 Port (Ethernet) ..................................................................................................... 56
© Microhard Systems Inc. 7
Page 8

Table of Contents
4.3 Carrier .......................................................................................................................... 57
4.3.1 Status .................................................................................................................. 57
4.3.2 Settings ............................................................................................................... 58
IP-Passthrough .................................................................................................... 59
APN (Access Point Name) ................................................................................... 60
4.3.3 Keepalive............................................................................................................. 62
4.3.4 Traffic Watchdog.................................................................................................. 63
4.3.5 Dynamic DNS ...................................................................................................... 64
4.3.6 SMS Config/Alerts ............................................................................................... 65
4.3.7 SMS .................................................................................................................... 68
4.3.8 Data Usage ......................................................................................................... 69
4.4 Wireless ....................................................................................................................... 72
4.4.1 Status .................................................................................................................. 72
4.4.2 Radio1 ................................................................................................................. 73
Radio Phy Configuration ...................................................................................... 73
802.11 Mode........................................................................................................ 73
Channel Frequency ............................................................................................. 73
Radio Virtual Interface ......................................................................................... 74
Operating Mode ................................................................................................... 75
TX Rate ............................................................................................................... 75
TX Power............................................................................................................. 76
SSID .................................................................................................................... 76
AP Isolation ......................................................................................................... 76
Encryption Type ................................................................................................... 77
4.4.3 Hotspot ................................................................................................................ 78
4.5 Comport ....................................................................................................................... 81
4.5.1 Status .................................................................................................................. 81
4.5.2 COM0/1 Settings ................................................................................................. 82
Data Baud Rate ................................................................................................... 83
IP Protocol Config ................................................................................................ 86
TCP Client ...................................................................................................... 86
TCP Server ..................................................................................................... 86
TCP Client/Server ........................................................................................... 87
UDP Point-to-Point .......................................................................................... 87
UDP Point-to-Multipoint (P) ............................................................................. 87
UDP Point-to-Multipoint (MP) .......................................................................... 88
UDP Multipoint-to-Multipoint ............................................................................ 88
SMTP Client .................................................................................................... 89
PPP ................................................................................................................ 90
GPS Transparent Mode .................................................................................. 91
4.6 I/O ................................................................................................................................ 92
4.6.1 Status .................................................................................................................. 92
4.6.2 Output ................................................................................................................. 93
4.7 GPS .............................................................................................................................. 94
4.7.1 Location ............................................................................................................... 94
4.7.2 Settings ............................................................................................................... 95
4.7.3 GPS Report ......................................................................................................... 96
4.7.4 GpsGate .............................................................................................................. 98
4.7.5 Recorder.............................................................................................................. 101
4.7.6 Load Record ........................................................................................................ 102
© Microhard Systems Inc. 8
Page 9

Table of Contents
4.8 Firewall ....................................................................................................................... 103
4.8.1 Status .................................................................................................................. 103
4.8.2 General ............................................................................................................... 104
4.8.3 Rules ................................................................................................................... 105
4.8.4 Port Forwarding ................................................................................................... 107
DMZ .................................................................................................................... 108
4.8.5 MAC-IP List ......................................................................................................... 109
MAC List Configuration ........................................................................................ 109
IP List Configuration............................................................................................. 110
4.8.6 Reset ................................................................................................................... 111
4.9 VPN ............................................................................................................................ 112
4.9.1 Summary ............................................................................................................. 112
4.9.2 Gateway to Gateway............................................................................................ 113
4.9.3 Client to Gateway (L2TP Client) ........................................................................... 118
4.9.4 VPN Client Access ............................................................................................... 120
4.9.5 Certificate Management ....................................................................................... 121
4.9.6 Cisco VPN Client ................................................................................................. 122
4.10 Tools ............................................................................................................................ 123
4.10.1 Discovery ........................................................................................................... 123
4.10.2 Netflow ............................................................................................................... 124
4.10.3 NMS Settings ..................................................................................................... 126
4.10.4 Event Report ...................................................................................................... 130
4.10.4.1 Configuration ....................................................................................... 130
4.10.4.2 Message Structure ............................................................................... 131
4.10.4.3 Message Payload................................................................................. 132
4.10.5 Modbus .............................................................................................................. 133
4.10.5.1 TCP Modbus ........................................................................................ 133
4.10.5.2 Serial (COM) Modbus........................................................................... 135
4.10.5.3 Modbus Data Map ................................................................................ 136
4.10.6 Websocket ......................................................................................................... 137
4.10.7 Site Survey ........................................................................................................ 139
4.10.8 Ping ................................................................................................................... 140
4.10.9 TraceRoute ........................................................................................................ 141
5.0 AT Command Line Interface........................................................................... 142
5.1 AT Command Overview .............................................................................................. 142
5.1.1 Serial Port .......................................................................................................... 142
5.1.2 Telnet................................................................................................................. 143
5.2 AT Command Syntax .................................................................................................. 144
5.3 Supported AT Commands .......................................................................................... 145
Appendices .......................................................................................................... 177
Appendix A: Serial Interface .................................................................................................. 177
Appendix B: IP-Passthrough Example ................................................................................... 178
Appendix C: Port Forwarding Example .................................................................................. 180
Appendix D: VPN (Site to Site) Example ............................................................................... 182
Appendix E: Firewall Rules Example ..................................................................................... 184
Appendix F: GRE Example ................................................................................................... 186
Appendix G: Firmware Recovery Procedure ................................ .......................................... 189
Appendix H: Troubleshooting ................................................................................................ 190
© Microhard Systems Inc. 9
Page 10

1.0 Overview
The IPn4G is a high-performance 4G LTE Cellular Ethernet & Serial Gateway with 802.11 b/g
WiFi capability, RJ45 Ethernet Port, Digital I/O, and two serial communication ports, one a
fully complimented RS232/485/422 serial port.
The IPn4G utilizes the cellular infrastructure to provide network access to wired and wireless
devices anywhere cellular coverage is supported by a cellular carrier. The IPn4G supports up
to 100Mbps when connected to a LTE enabled carrier, or global fallback to 3G/Edge networks
for areas without 4G LTE.
Providing reliable wireless Ethernet bridge functionality as well gateway service for most
equipment types which employ an RS232, RS422, or RS485 interface, the IPn4G can be
used in a limitless number and types of applications such as:
High-speed backbone
IP video surveillance
Voice over IP (VoIP)
Ethernet wireless
extension
WiFi Hotspot
Legacy network/device
migration
SCADA (PLC’s, Modbus,
Hart)
Facilitating internetwork
wireless communications
1.1 Performance Features
Key performance features of the IPn4G include:
Fast 4G LTE Link to Wireless Carrier
Up to 100Mbps Downlink / 50 Mbps Uplink
Fast Data Rates to 802.11b/g WiFi Devices
Digital I/O - 1 Input, 1 Output
DMZ and Port Forwarding
10/100 Ethernet Port (WAN/LAN)
Integrated GPS (TCP Server/UDP Reporting)
User interface via local console, telnet, web browser
communicates with virtually all PLCs, RTUs, and serial devices through either
RS232, RS422, or RS485 interface
Local & remote wireless firmware upgradable
User configurable Firewall with IP/MAC ACL
IP/Sec secure VPN and GRE Tunneling
© Microhard Systems Inc. 10
Page 11
1.0 Overview
1.2 Specifications
For detailed specifications, please see the specification sheets available on the Microhard website @ http:///www.microhardcorp.com for your specific model.
Electrical/General
Cellular:
Supported Bands:
Data Features:
4G LTE B4/B17 (1700/2100/700 MHz)
Global Fallback to:
HSPA+/UMTS 850/AWS/1900/2100 MHz
GPRS 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
4G LTE
Up to 100 Mbps downlink
Up to 50 Mbps uplink
SIM Card: 1.8 / 3.0 V
WiFi:
Frequency: 2.4 GHz
Spread Method: (CCK) QPSK/BPSK
(OFDM) BPSK, QPSK, QAM16, QAM32, QAM64
Data Rates: 802.11b/g
TX Power: Adjustable / Up to 30dBm
Data Encryption: WEP, WPA(PSK), WPA2(PSK), WPA+WPA2 (PSK)
(Subject to Export Restrictions)
General:
Input Voltage: 9 - 30 VDC
Power over Ethernet: Passive PoE on Ethernet Port
Current Consumption:
(@12VDC & 20dB WiFi)
Cellular WiFi Idle (mA) Typical (mA)
On On 350 390
On Off 280 320
Off On 270 320
Serial Baud Rate: 300bps to 921kbps
Ethernet: 10/100 BaseT, Auto - MDI/X, IEEE 802.3
IPn4G IPn4Gb
LTE FDD (Bands 1-5,7,8,13,17,18,19,20)
UMTS | DC-HSPA+ (Bands 1,2,4,5,8)
GSM | GPRS | EDGE (Bands 2,3,5,8)
3GPP Protocol Stack Release 9
LTE: DL 100 Mbps, UL 50 Mbps
HSPA+: DL 21 Mbps, UL 5.7 Mbps
WCDMA: DL/UL 384 kbps
EDGE Class 33: DL/UL 236.8 kbps
GPRS Class 33: DL/UL 85.6kbps
Table 1-2-1: IPn4G Current Consumption
© Microhard Systems Inc. 11
Page 12

1.0 Overview
1.2 Specifications (Continued)
Network Protocols: TCP, UDP, TCP/IP, TFTP, ARP, ICMP, DHCP, HTTP,
HTTPS*, SSH*, SNMP, FTP, DNS, Serial over IP
Operating Modes: Access Point, Client/Station, Repeater, Mesh Point
Management: Local Serial Console, Telnet, WebUI, SNMP, FTP &
Wireless Upgrade
Diagnostics: Status LED’s, RSSI, Ec/No, Temperature, Remote Diagnostics,
Watchdog, UDP Reporting
Digital I/O: 1 Inputs / 1 Outputs
Environmental
Operation Temperature: -40oF(-40oC) to 185oF(85oC)
Humidity: 5% to 95% non-condensing
Mechanical
Dimensions:
2.25” (57mm) X 3.85” (98mm) X 1.5” (45mm)
Weight:
Approx. 250 grams
Connectors:
Antenna: Wi-Fi: RP-SMA Female
Cellular: 2x SMA Female (Main, DIV)
GPS Uses Diversity Antenna
Data: RS232 COM1: DB-9 Female (Digital I/O)
RS232 Data: DB-9 Female
RS485: SMT: 6-Pin Micro MATE-N-LOK AMP 3-794618-6
Mating Connector: 6-Pin Micro MATE-N-LOK AMP 794617-6
Ethernet : RJ-45
PWR, Misc: Power: SMT: 4-Pin Micro MATE-N-LOK AMP 3-794618-4
Mating Connector: 4-Pin Micro MATE-N-LOK AMP 794617-4
© Microhard Systems Inc. 12
Page 13
2.0 Quick Start
Vin-
Vin+
GND
GND
Tx-
Tx+
Rx+
Rx-
In
Out
This QUICK START guide will walk you through the setup and process required to
access the WebUI configuration window and to establish a basic wireless connection
to your carrier.
Note that the units arrive from the factory with the Local Network setting configured
as ‘Static’ (IP Address 192.168.168.1, Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0, and Gateway
192.168.168.1), in DHCP server mode. (This is for the LAN Ethernet Adapter on the
back of the IPn4G unit.
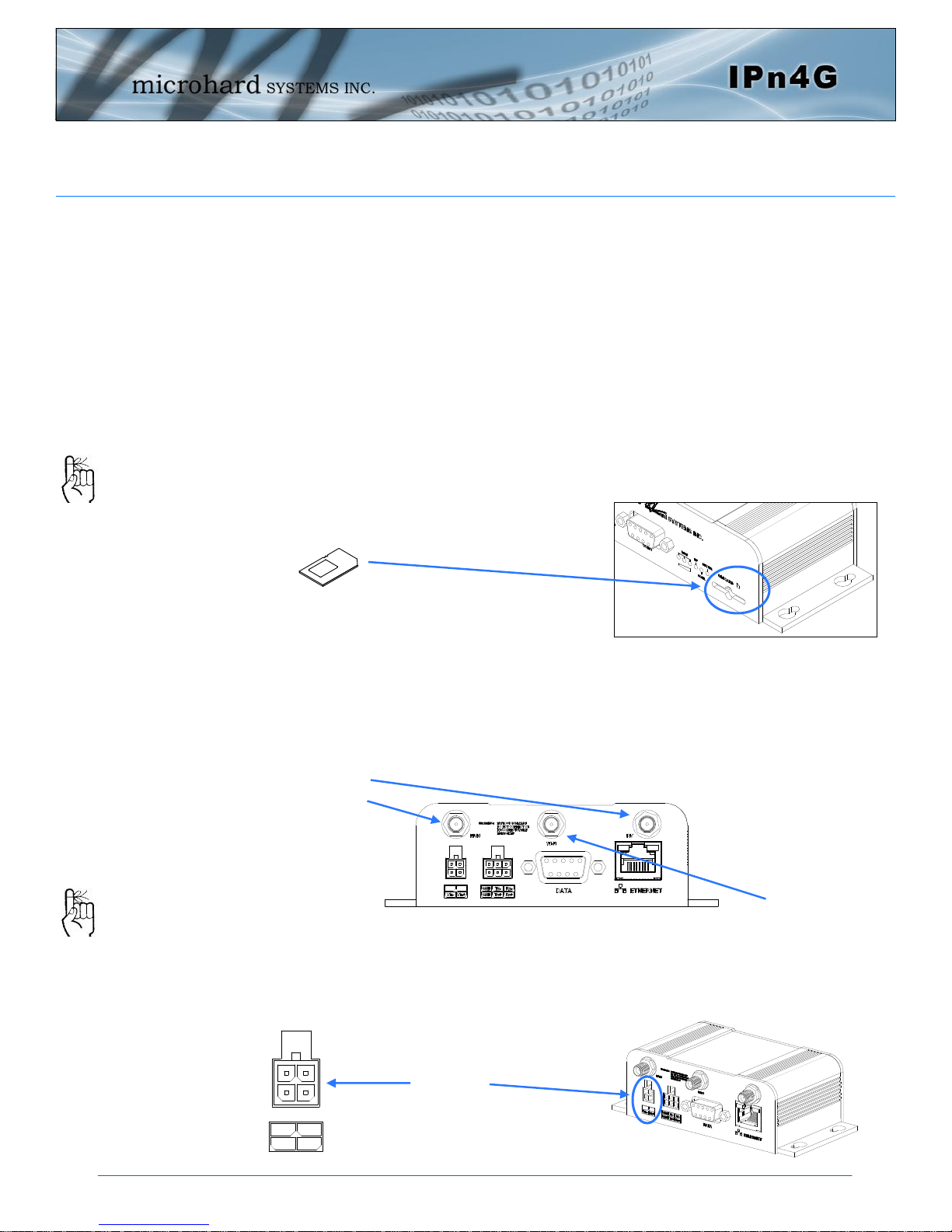
2.1 Installing the SIM Card
Before the IPn4G can be used on a cellular network a valid SIM Card for your
Wireless Carrier must be installed. Insert the SIM Card into the slot as shown
below.
To reset to factory
defaults, press and
hold the CFG button
for 8 seconds with the
IPn4G powered up.
The LED’s will flash
quickly and the IP4G
will reboot with factory
defaults.
SIM Card Slot
Use the MHS-supplied
power adapter or an
equivalent power
source.
The unit can also be
powered via PoE using a
MHS PoE injector.
2.2 Getting Started with Cellular
Connect the Antenna’s to the applicable ANTENNA jack’s of the IPn4G.
Connect the power connector to the power adapter and apply power to the unit,
the RF & SGNL LED’s will flash during boot-up, once they stop, proceed to the
next step.
Cellular
Antenna’s
WiFi Antenna
9-30VDC
© Microhard Systems Inc. 13
Page 14
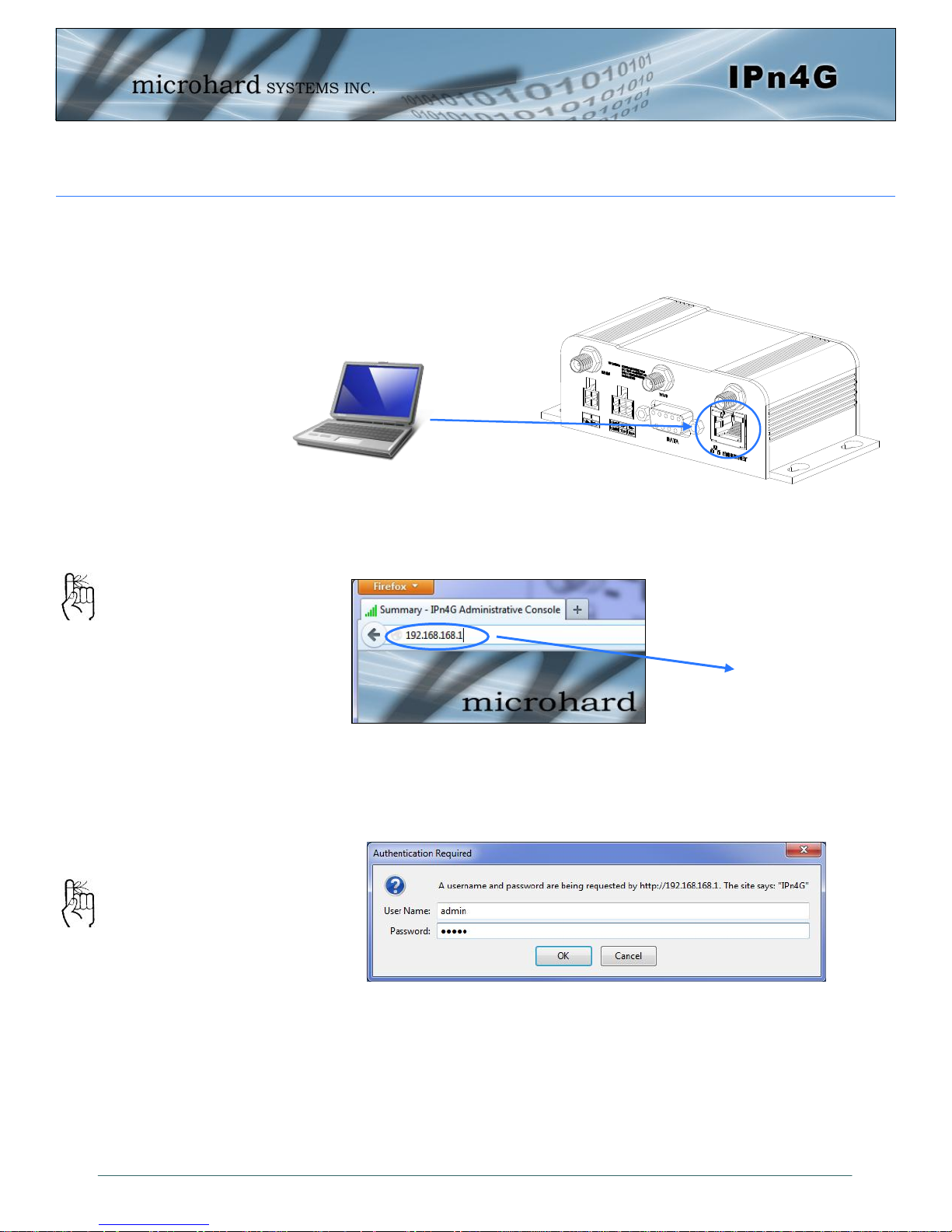
2.0 Quick Start
Connect A PC configured for DHCP directly to the ETHERNET port of the IPn4G,
using an Ethernet Cable. If the PC is configured for DHCP it will automatically
acquire a IP Address from the IPn4G.
Open a Browser Window and enter the IP address 192.168.168.1 into the ad-
dress bar.
The factory default
network settings:
IP: 192.168.168.1
Subnet: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.168.1
The IPn4G will then ask for a Username and Password. Enter the factory defaults
listed below.
192.168.168.1
The factory default login:
User name: admin
Subnet: admin
It is always a good idea to
change the default admin
login for future security.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 14
The Factory default login:
User name: admin
Password: admin
Page 15
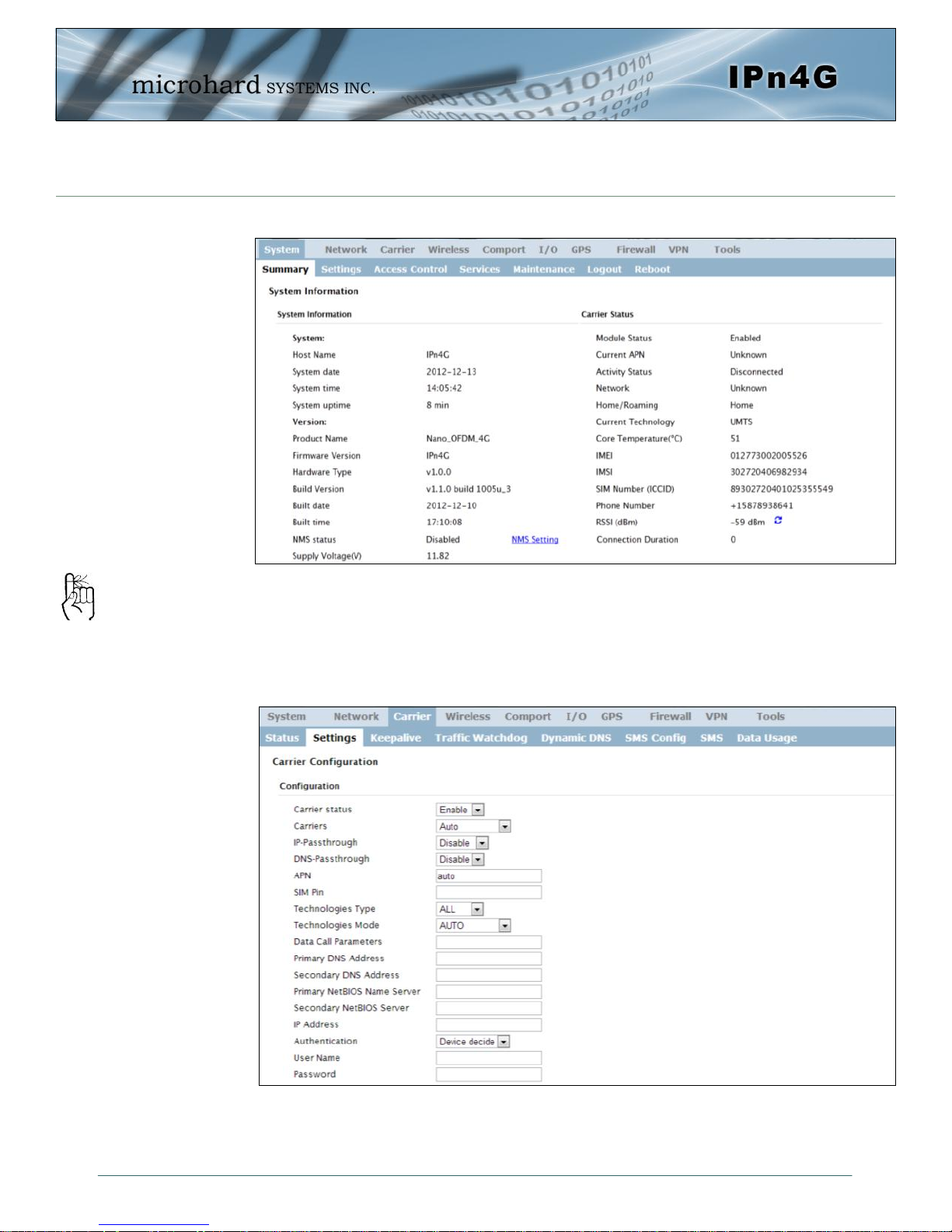
2.0 Quick Start
Once successfully logged in, the System Summary page will be displayed.
As seen above under Carrier Status, the SIM card is installed, but an APN has
not been specified. Setting the APN to auto (default) may provide quick network
Auto APN: Introduced in
firmware version v1.1.0r1038, the IPn4G will
attempt to detect the
carrier based on the SIM
card installed and cycle
through a list of
commonly used APN’s to
provide quick network
connectivity.
connectivity, but may not work with some carriers, or with private APN’s. To set
or change the APN, click on the Carrier > Settings tab and enter the APN supplied by your carrier in the APN field. Some carriers may also require a Username and Password.
Once the APN and any other required information is entered to connect to your
carrier, click on “Submit”. Return to the System > Summary tab.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 15
Page 16
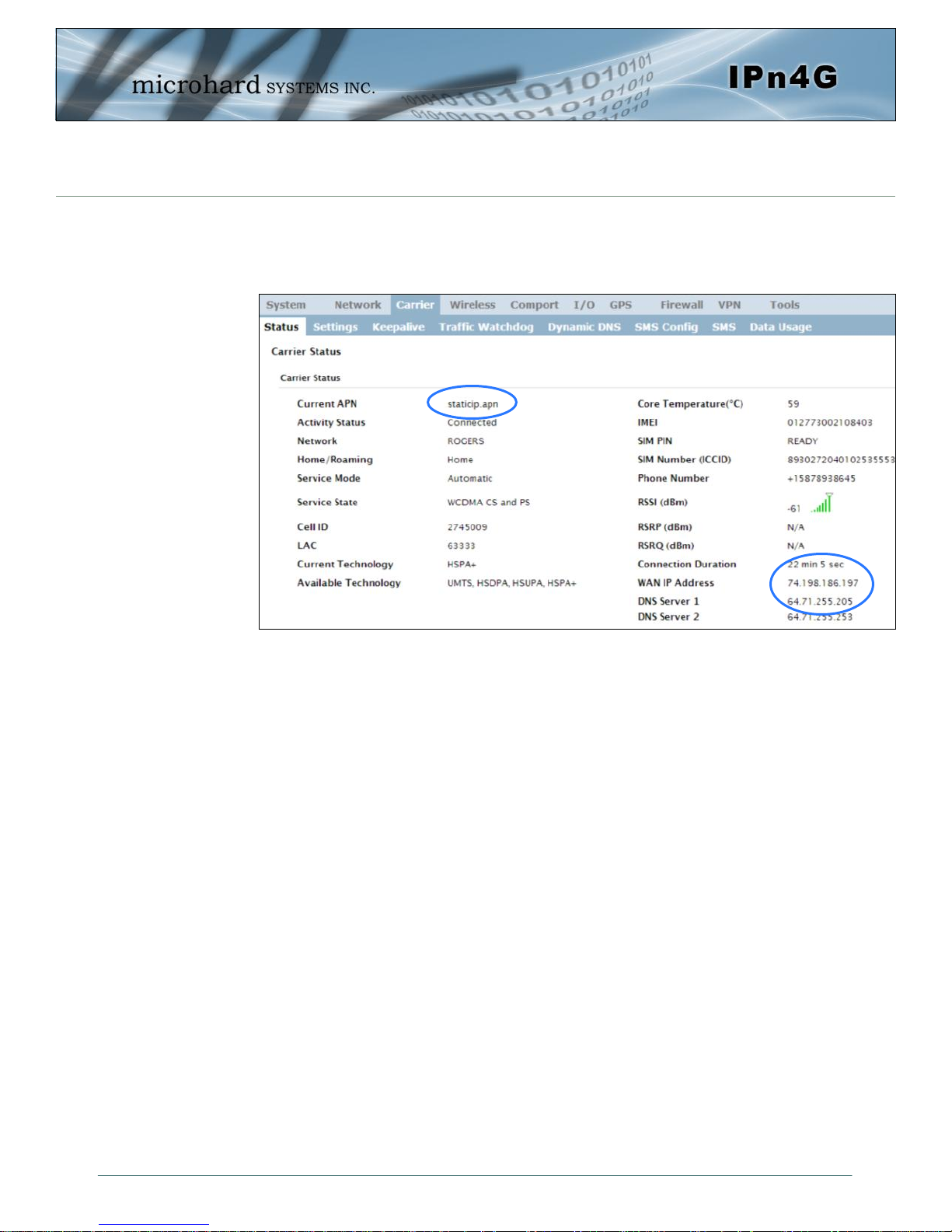
2.0 Quick Start
On the Carrier > Status Tab, verify that a WAN IP Address has been assigned by
your carrier. It may take a few minutes, so try refreshing the page if the WAN
IP Address doesn’t show up right away. The Activity Status should also show
“Connected”.
If you have set a static IP on your PC, you may need to add the DNS Servers
shown in the Carrier Status Menu to you PC to enable internet access.
Congratulations! Your IPn4G is successfully connected to your Cellular Carrier.
The next section gives a overview on enabling and setting up the WiFi Wireless
features of the modem giving 802.11 devices network access.
To access devices connected to IPn4G remotely, one or more of the following
must be configured: IP-Passthrough, Port Forwarding, DMZ. Another option
would be to set up a VPN.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 16
Page 17
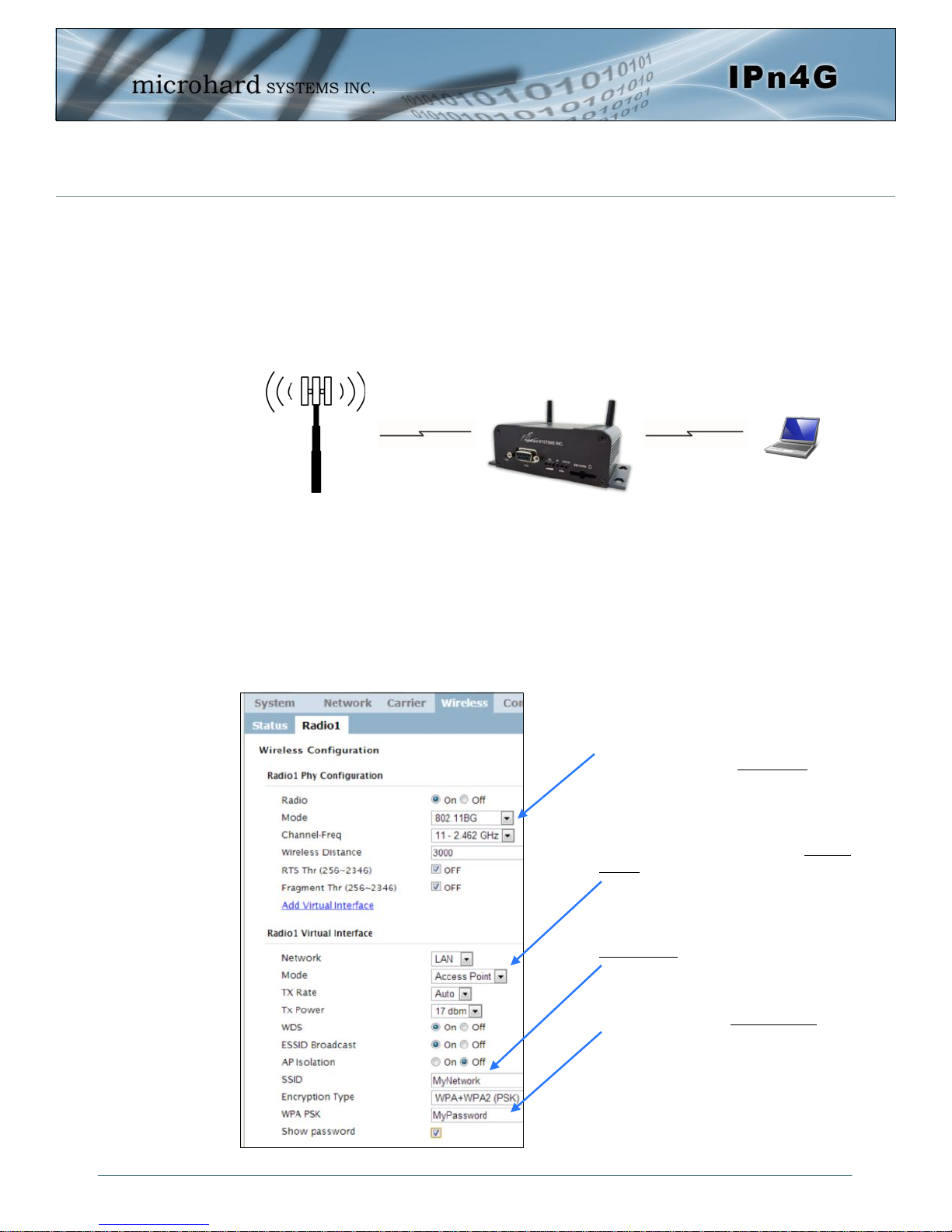
2.0 Quick Start
2.3 Getting Started with WiFi
This Quick Start section walks users through setting up a basic WiFi AP (Access
Point). For additional settings and configuration considerations, refer to the appropriate sections in the manual. This walkthrough assumes all setting are in the factory default state.
2.3.1 Setting up WiFi
Use Section 2.2 Getting Started with Cellular to connect, power up and log in
and configure the Carrier in a IPn4G.
Click on the Wireless > Radio1 Tab to setup the WiFi portion of the IPn4G.
Cell Tower
4G LTE
802.11b/g
In Radio1 Phy Configuration, ensure
the mode is set for 802.11BG.
In the Radio1 Virtual Interface, en-
sure that the Mode is set for Access
Point.
Enter a name for the Wireless Network
under SSID. This example uses
MyNetwork
(Optional) Set a password for the WiFi,
this example uses MyPassword
Click Submit.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 17
Page 18

2.0 Quick Start
2.3.2 Connecting to WiFi
Now that the IPn4G has connection to the Cellular Carrier (See Section 2.2) and
the WiFI has been set up (See Section 2.3), WiFi devices should be able to de-
tect and connect to the IPn4G.
On a WiFi enabled PC/Device, the SSID of MyNetwork, that was created in the
last example should be visible. Connect to that SSID and enter the password.
Once connected the status should change to connected, and network access
should be enabled.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 18
Page 19
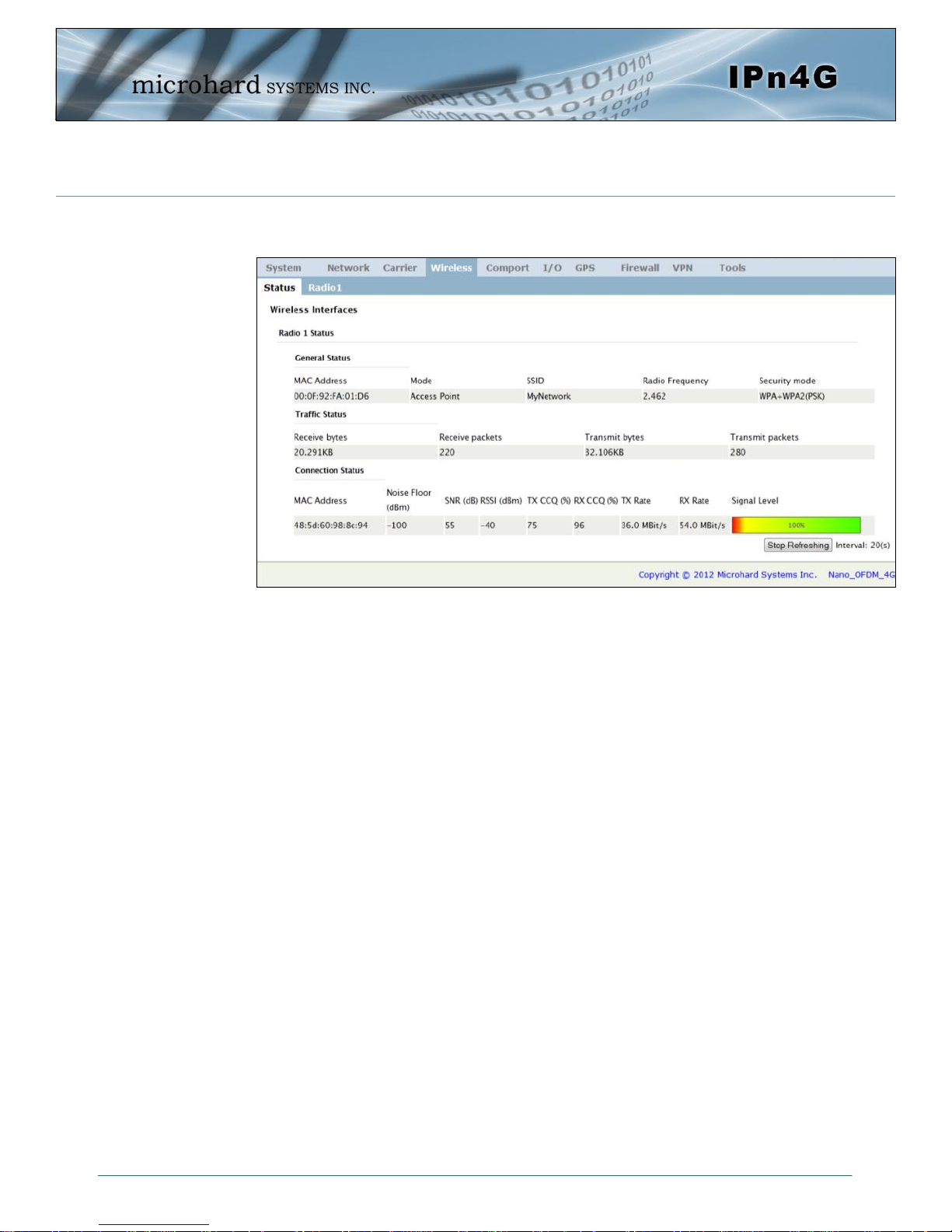
2.0 Quick Start
The status of the WiFi connection should also be visible in the Wireless > Status
tab in the WebUI as seen below.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 19
Page 20

3.0 Hardware Features
3.1 IPn4G
The IPn4G is a fully-enclosed unit ready to be interfaced to external devices.
Any IPn4G may be configured as an Access Point, Station/Client, Repeater or Mesh Node. This
versatility is very convenient from a ’sparing’ perspective, as well for convenience in becoming
very familiar and proficient with using the device: if you are familiar with one unit, you will be
familiar with all units.
The IPn4G features:
Standard Connectors for:
1 Ethernet Ports (RJ45)
COM0 Data Port (RS232/DB9)
COM1 Console Port (RS232/DB9)
4-Pin: MATE-N-LOK Type Connector for Power
6-Pin: MATE-N-LOK Type Connector for RS485 Data
Cellular Antenna (SMA Female Antenna Connection x2)
WiFi Antenna (RP-SMA Female Antenna Connection) (Optional)
Status/Diagnostic LED’s for STATUS, RF, SGNL, RSSI x 3
CFG Button for factory default / firmware recovery operations
Mounting Holes
Image 3-1: Front View of IPn4G
Image 3-2: Rear View of IPn4G
© Microhard Systems Inc. 20
Page 21
3.0 Hardware Features
32.07
52.20
8.60
11.53
56.20
69.81
119.70
Ø7.00
R3.50
108.50
97.70
11.00
5.40
5.60
5.60
5.40
97.70
119.70
37.20
2.60
34.60
119.70
37.20
97.70
11.00
2.60
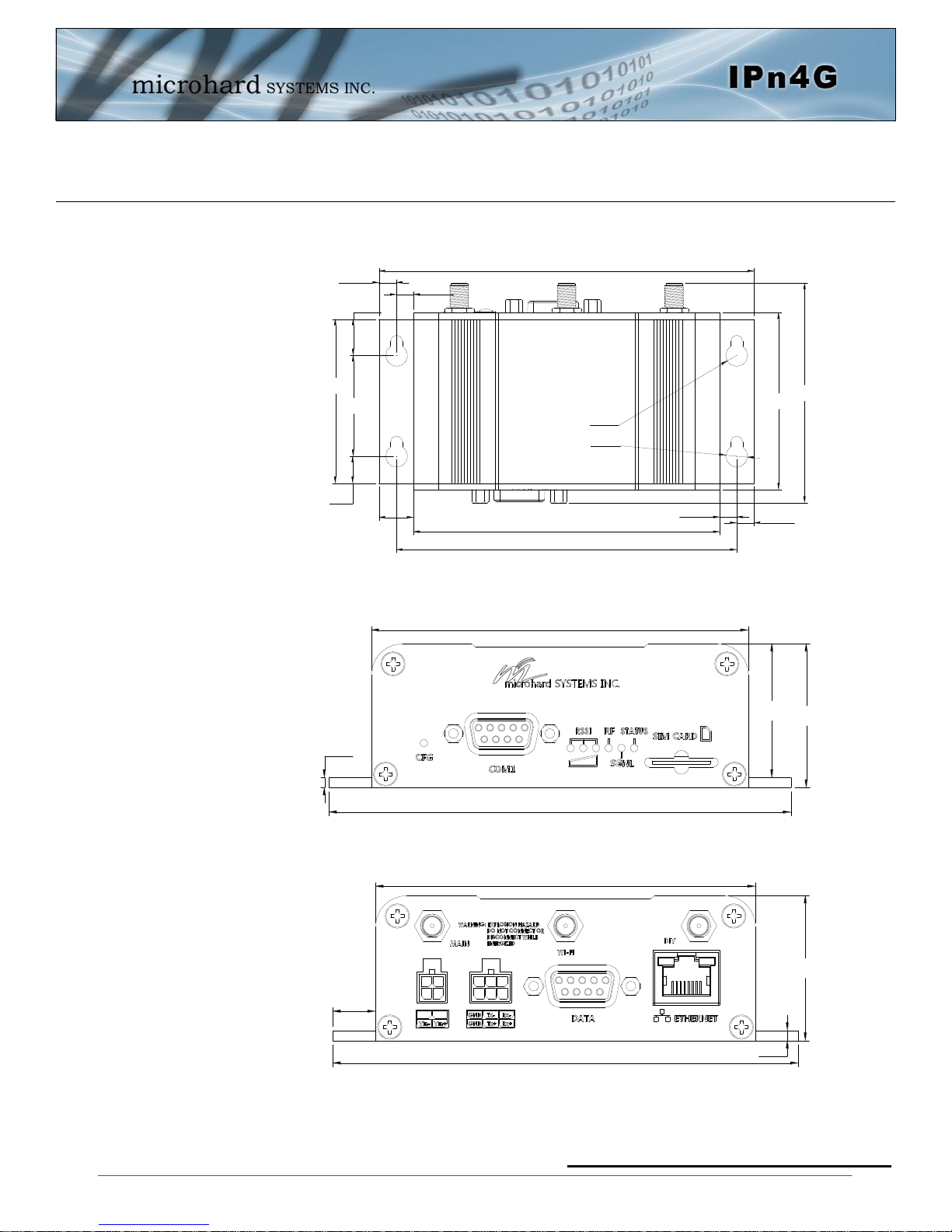
3.1.1 Mechanical Drawings
Drawing 3-1: IPn4G Top View Dimensions
© Microhard Systems Inc. 21
Drawing 3-2: IPn4G Front View Dimensions
O I
Drawing 3-3: IPn4G Rear View Dimensions
Note: All dimension units: Millimeter
Page 22
3.0 Hardware Features
3.1.2 Connectors and Indicators
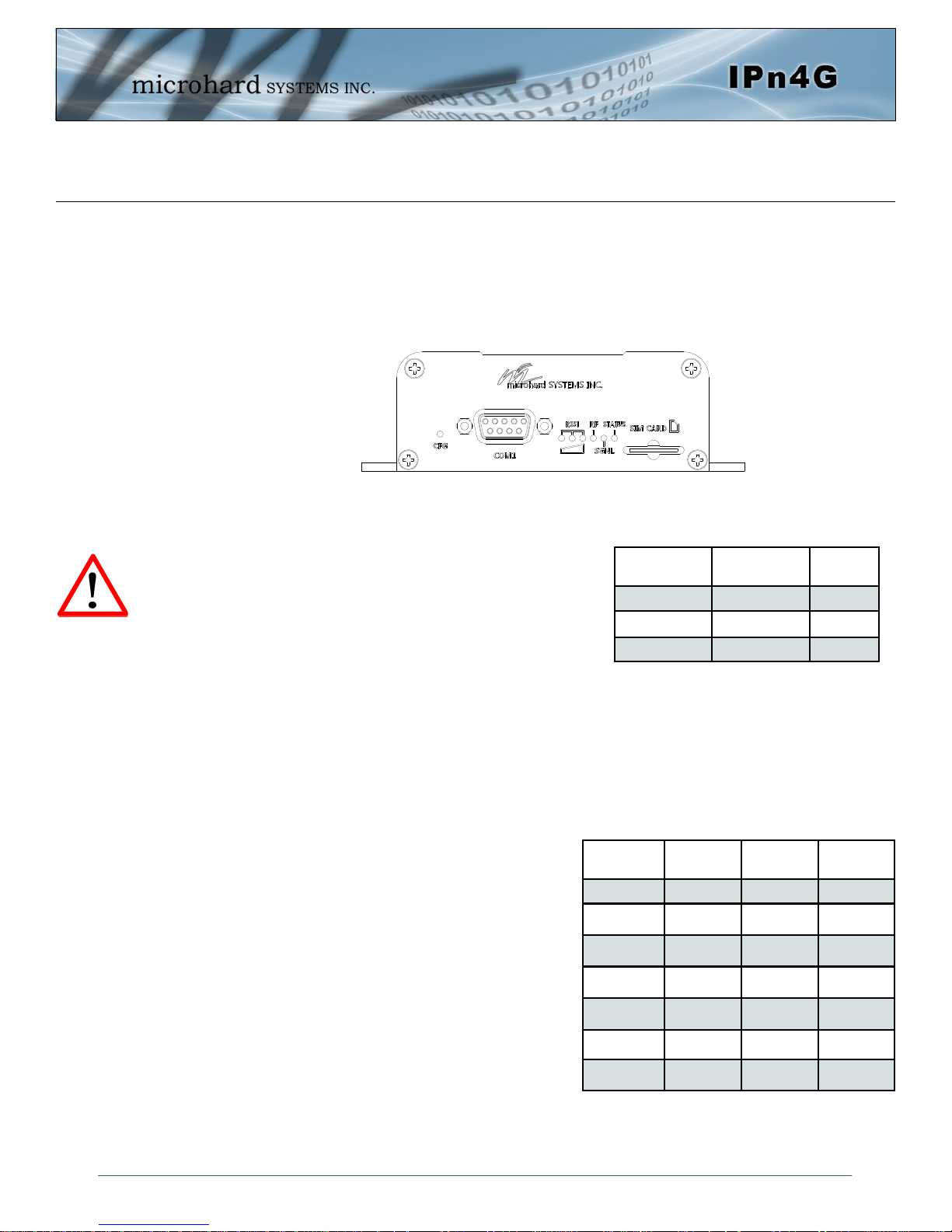
3.1.2.1 Front
On the front of the IPn4G is the COM1 port, CONFIG Button, RSSI, STATUS, RF and SGNL LED’s as
described below:
The COM1 port (RS232) is used for:
AT Command Interface at 115.2kbps and
HyperTerminal (or equivalent).
User data (RS232 - RxD, TxD, and SG)
Caution: Using a
power supply that
does not provide
proper voltage may
damage the IPn4G
unit.
CONFIG (Button) - Holding this button depressed while
powering-up the IPn4G will boot the unit into FILE SYS-
TEM RECOVERY mode. The default IP address for system
recovery (only - not for normal access to the unit) is static:
192.168.1.39.
If the unit has been powered-up for some time (>1 minute), depressing the CFG Button for 8 seconds will
result in FACTORY DEFAULTS being restored, including a static IP address of 192.168.168.1. This IP
address is useable in a Web Browser for accessing the Web User Interface.
RF(Red)/SGNL(Green) LED’s - When the unit is equipped with WiFi, the RF/SGNL LED’s indicate WiFi
activity. In units not equipped with WiFi, the RF/SGNL LED’s indicate carrier (cellular) traffic. Also, during
system bootup, the RF & SGNL LED’s will flash.
Receive Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) (3x
Green) - As the received signal strength increases,
starting with the furthest left, the number of active
RSSI LEDs increases.
STATUS LED (Red) - The Status LED indicates that
power has been applied to the module.
SIM Card - This slot is used to install a SIM card provided by the cellular carrier to enable communication
to their cellular network. Ensure the SIM card is installed properly by paying attention to the diagram
printed above the SIM card slot.
Drawing 3-4: IPn4G Front View
Table 3-1: COM1 Port RS232 Pin Assignment
Signal Level
(dBm)
(-85, 0] ON ON ON
(-90, -85] ON ON FLASH
(-95, -90] ON ON OFF
(-100, -95] ON FLASH OFF
(-105, -100] ON OFF OFF
(-109, -105] FLASH OFF OFF
Other SCANNING SCANNING SCANNING
Signal
Name
RXD 2 O
TXD 3 I
SG 5
RSSI1
(Left)
PIN
#
RSSI2
(Mid)
Input or
Output
RSSI3
(Right)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 22
Table 3-2: RSSI LED’s
Page 23
3.0 Hardware Features
Vin-
Vin+
GND
GND
TxTx+
Rx+
Rx-
In
Out
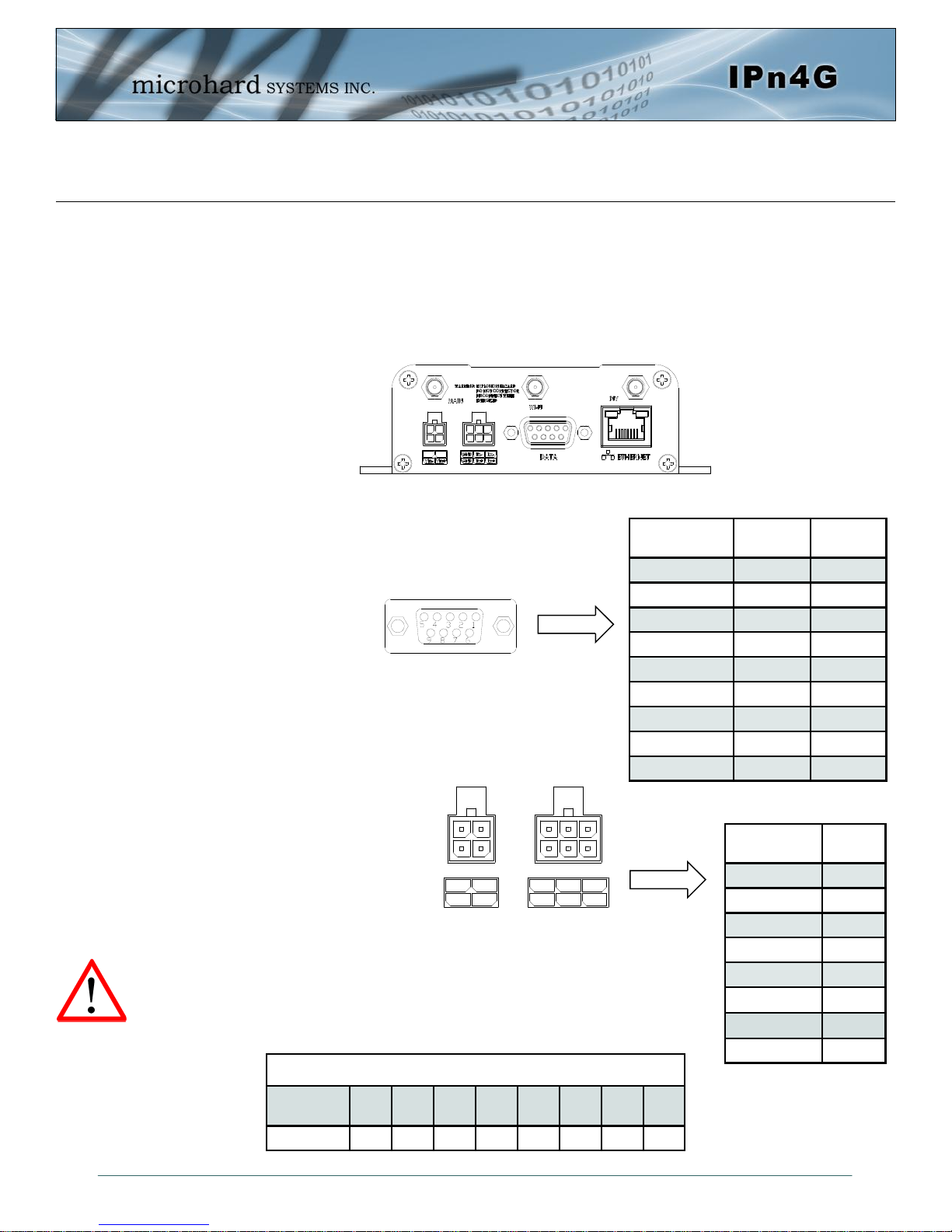
3.1.2 Connectors and Indicators
3.1.2.2 Rear
On the back of the IPn4G is the Data (COM0) port, RS485/422 interface, as well as the power connections.
The unit also has the SMA(F) connectors for the Main (TX/RX), the Diversity (RX) antenna’s, and a RPSMA Female connector for the optional WiFi antenna.
O I
Drawing 3-5: IPn4G Rear View
The DATA (RS232 Port (COM0)) on the rear
of the circuit board is used for:
RS232 serial data (300-921kbps)
The RS422/485 Port is used to interface the IPn4G to a DTE
with the same interface type. Either the RS232 or RS422/485
interface can be used for data traffic, not both.
Vin+/Vin– is used to power the unit. The input Voltage range is
9-30 Vdc.
Digital I/O– The IPn4G has 1 input / 1 output. Inputs have a small wetting
current (Vin) used to detect a contact closure, and prevent false readings by
any noise or intermittent signals, it has a threshold sensitivity of 1.8V.
Maximum recommended load for the output pin is 150mA @ 30 Vdc (Vin).
PoE– The IPn4G can also be powered using Passive PoE on the Ethernet
Port, via a PoE injector.
Caution: Using a
power supply that
does not provide
proper voltage may
damage the modem.
Source
Voltage
9 - 30 Vdc Data Data Data DC+ DC+ Data DC- DC-
© Microhard Systems Inc. 23
Ethernet RJ45 Connector Pin Number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Table 3-5: Ethernet PoE Connections
Name Data Port
DCD 1 O
RXD 2 O
TXD 3 I
DTR 4 I
SG 5
DSR 6 O
RTS 7 I
CTS 8 O
RING 9 O
Table 3-3: Data RS232 Pin Assignment
Name
Tx+ O
Tx1 O
Rx+ I
Rx- I
Vin -
Vin + I
Out O
In I
Table 3-4: Data RS422/485,
Vin, Digital I/O Pin Assignment
Input or
Output
Input or
Output
Page 24
4.0 Configuration
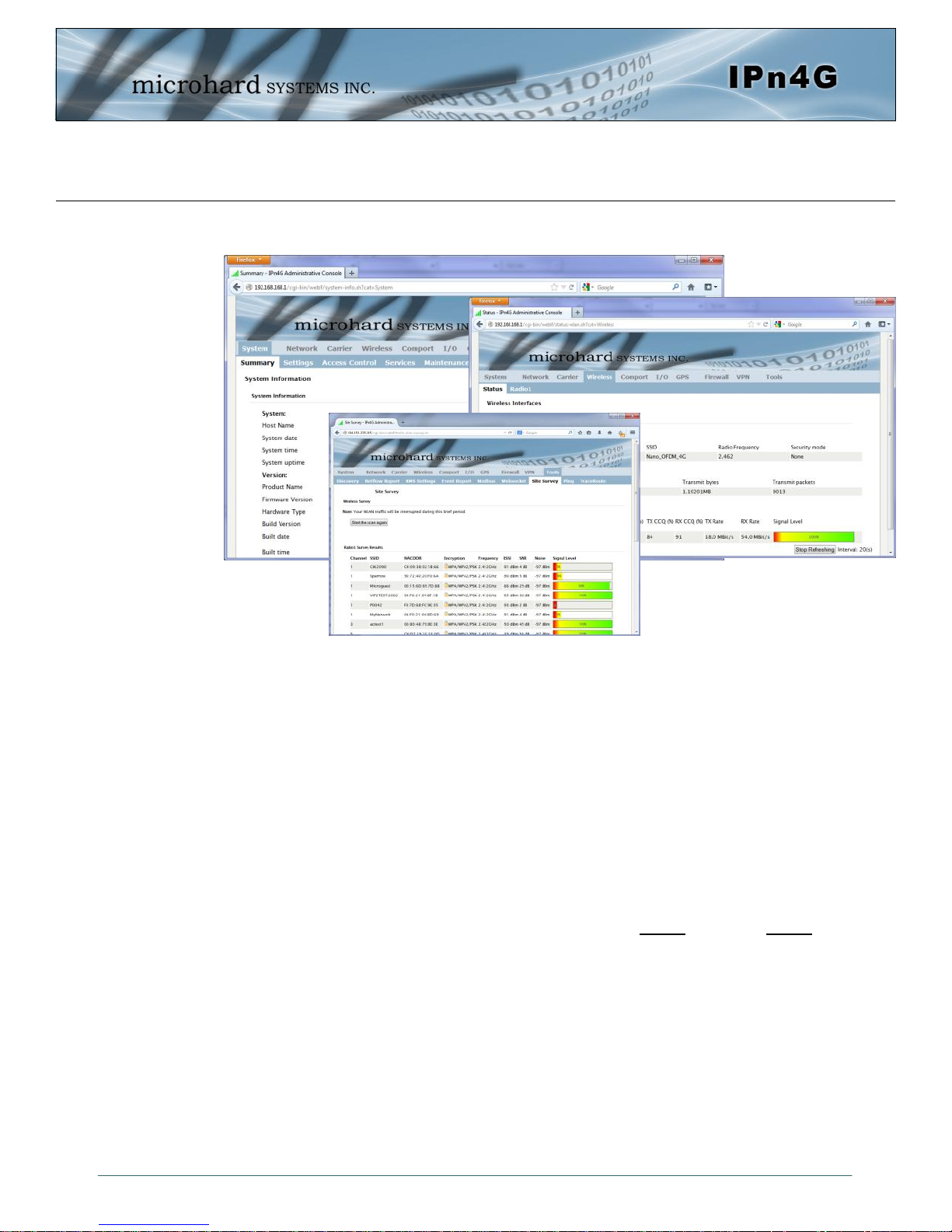
4.0 Web User Interface
Image 4-0-1: WebUI
Initial configuration of an IPn4G using the Web User (Browser) Interface (Web UI) method
involves the following steps:
configure a static IP Address on your PC to 192.168.168.10 (or any address on the
192.168.168.X subnet other than the default IP of 192.168.168.1)
connect the IPn4G ETHERNET port to PC NIC card using an Ethernet cable
apply power to the IPn4G and wait approximately 60 seconds for the system to load
open a web browser and enter the factory default IP address of the unit: 192.168.168.1
logon window appears; log on using default Username: admin Password: admin
use the web browser based user interface to configure the IPn4G as required.
refer to Section 2.0: Quick Start for step by step instructions.
In this section, all aspects of the Web Browser Interface, presented menus, and available
configuration options will be discussed.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 24
Page 25
4.0 Configuration
For security, do not allow
the web browser to
remember the User Name
or Password.
It is advisable to change
the login Password. Do
not FORGET the new
password as it cannot be
recovered.
4.0.1 Logon Window
Upon successfully accessing the IPn4G using a Web Browser, the Logon window will appear.
Image 4-0-2: Logon Window
The factory default User Name is: admin
The default password is: admin
Note that the password is case sensitive. It may be changed (discussed further along in this
section), but once changed, if forgotten, may not be recovered.
When entered, the password appears as ’dots’ as shown in the image below. This display
format prohibits others from viewing the password.
The ‘Remember my password’ checkbox may be selected for purposes of convenience,
however it is recommended to ensure it is deselected - particularly once the unit is deployed in
the field - for one primary reason: security.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 25
Image 4-0-3: Logon Window : Password Entry
Page 26
4.0 Configuration
4.1 System
The main category tabs located at the top of the navigation bar separate the configuration of the
IPn4G into different groups based on function. The System Tab contains the following sub
menu’s:
Summary - Status summary of entire radio including network settings,
version information, and radio connection status.
Settings - Host Name, Default System Mode (Bridge or Router),
System Time/Date, HTTP Port for the WebUI,
Access Control - Change passwords, create new users
Services - Enable/Disable RSSI LED’s, SSH and Telnet services
Maintenance - Version information, firmware Upgrades, reset to defaults,
configuration backup and restore.
Reboot - Remotely reboot the system.
Logout - Logout of the current browser session.
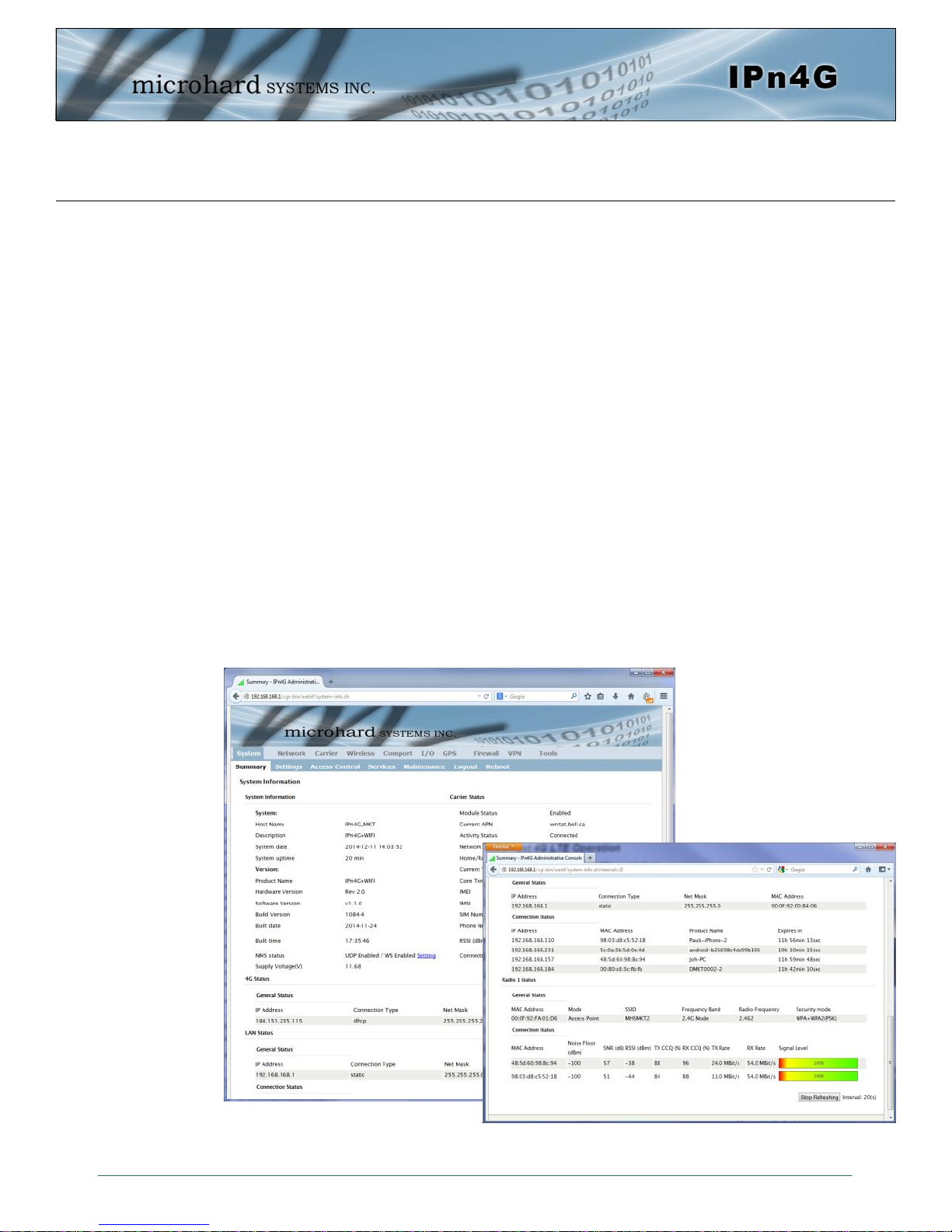
4.1.1 System > Summary
The System Summary screen is displayed immediately after initial login, showing a summary
and status of all the functions of the IPn4G in a single display. This information includes System
Status, Carrier Status, 4G & LAN network information, version info and WiFi radio status as
seen below.
Image 4-1-1: System Info Window
© Microhard Systems Inc. 26
Page 27
4.0 Configuration
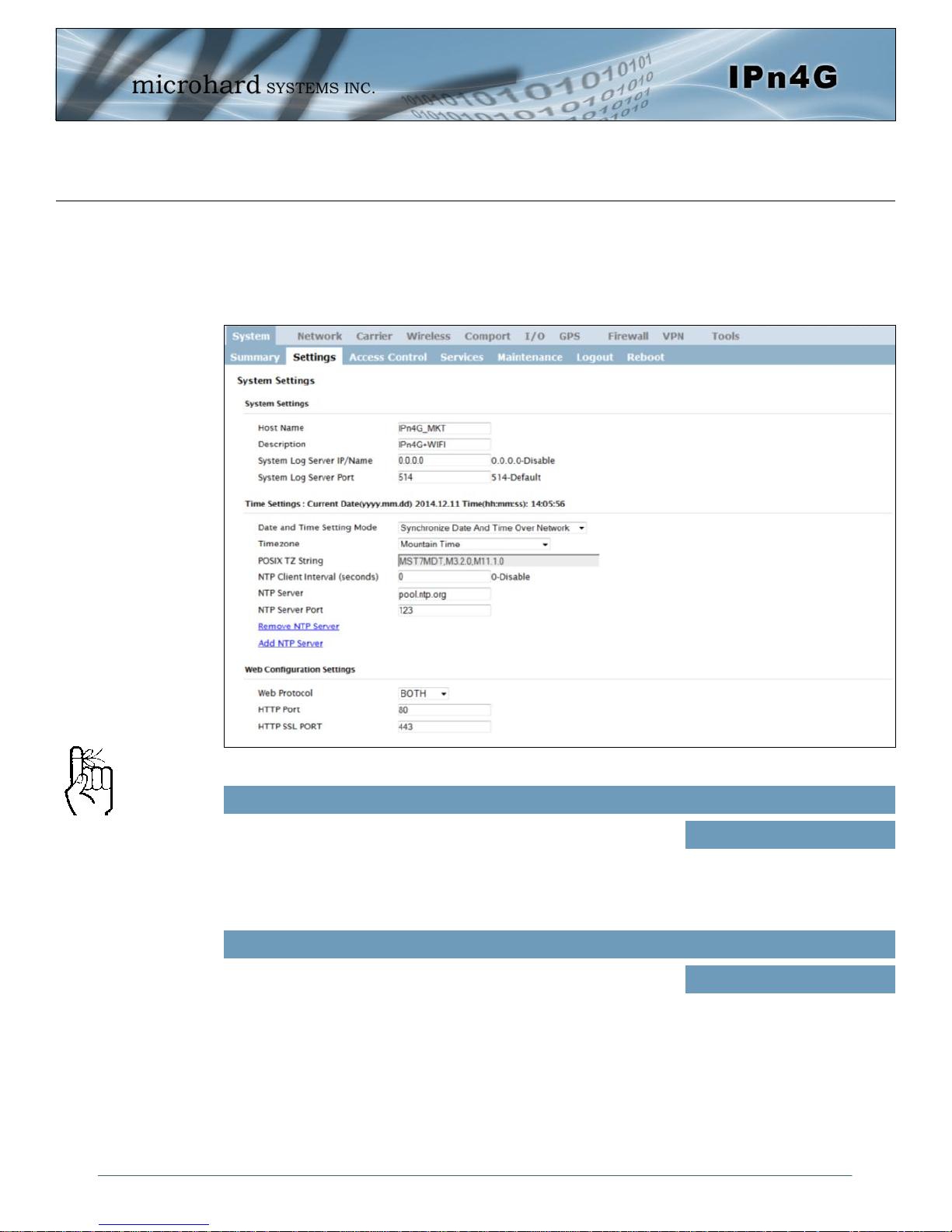
4.1.2 System > Settings
System Settings
Options available in the System Settings menu allow for the configuration of the Host Name.
Image 4-1-2: System Settings > System Settings
Host Name
The Host Name must not be
confused with the Network
Name (SSID) (Wireless
Configuration menu).
The Host Name is a convenient identifier for a specific IPn4G unit. This
feature is most used when accessing units remotely: a convenient
cross-reference for the unit’s WAN IP address. This name appears
when logged into a telnet session, or when the unit is reporting into
Microhard NMS System.
Values (characters)
IPn4G+wifi (varies)
Description
The description field is a general purpose text field that can be used to
provide additional information about the device such as a secondary
identifier, address or phone number for a contact person.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 27
Values (characters)
IPn4G+wifi (varies)
Page 28

4.0 Configuration
System Log Server IP/Name
The modem can be configured to report system level events to a third
party Syslog server, as shown below. Syslog data can then be filtered
and depending on the features of the Syslog server application, alerts
can be generated accordingly.
The screenshot below shows a sample from a simple Syslog Server
application.
Values
0.0.0.0
Enter the UDP port number on the Syslog Server where the actual
service is running. Consult with the documentation of your chosen
Syslog Server for the correct port number. The most common port is
514, which has been set as the default.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 28
Image 4-1-3: System Settings > Syslog Server Example
System Log Server Port
Values (UDP Port #)
514
Page 29

4.0 Configuration
Time Settings
The IPn4G can be set to use a local time source, thus keeping time on its own, or it can be
configured to synchronize the date and time via a NTP Server. The options and menus available
will change depending on the current setting of the Date and Time Setting Mode, as seen below.
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
can be used to synchronize the
time and date or computer
systems with a centralized,
referenced server. This can
help ensure all systems on a
network have the same time
and date.
Image 4-1-3: System Settings > Time Settings
Date and Time Setting Mode
Select the Date and Time Setting Mode required. If set for ‘Use Local
Time’ the unit will keep its own time and not attempt to synchronize
with a network server. If ‘Synchronize Date And Time Over Network’ is
selected, a NTP server can be defined.
Date
The calendar date may be entered in this field. Note that the entered
value is lost should the IPn4G lose power for some reason. (Only
displayed if set to ‘Use Local Time Source’)
Time
The time may be entered in this field. Note that the entered value is
lost should the VIP Series lose power for some reason. (Only
displayed if set to ‘Use Local Time Source’)
If connecting to a NTP time server, specify the timezone from the
dropdown list.
Values (selection)
Use Local Time Source
Synchronize Date And Time
Over Network
Values (yyyy-mm-dd)
2014.12.17 (varies)
Values (hh:mm:ss)
13:27:28 (varies)
Timezone
Values (selection)
(varies)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 29
Page 30

4.0 Configuration
POSIX TZ String
This displays the POSIX TZ String used by the unit as determined by
the timezone setting.
Values (read only)
(varies)
NTP Client Interval
By default the modem only synchronizes the time and date during
system boot up (default: 0), but it can be modified to synchronize at a
regular interval. This process does consume data and should be set
accordingly.
Values (seconds)
0
NTP Server
Enter the IP Address or domain name of the desired NTP time server.
Values (address)
pool.ntp.org
NTP Port
Enter the IP Address or domain name of the desired NTP time server.
Web Configuration Settings
The last section of the System Setting menu allows the configuration of the HTTP and HTTPS
Ports used for the web server of the WEBUI.
Values (port#)
123
Select the type of web protocol used for the WebUI configuration.
Select between HTTP (basic) and HTTPS (SSL, secure), or Both that
are running on the modem.
The default web server ports for the web based configuration tools for
HTTP is TCP:80 and for HTTPS is TCP:443. If changes are required,
keep in mind it must be specified in a internet browser to access the
unit. (example: http://192.168.168.1:8080).
It may be required to configure Firewall rules to allow modified
port numbers that have been changed from the defaults.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 30
Image 4-1-4: System Settings > Web Configuration Settings
Web Protocol
Values (port#)
HTTP / HTTPS / BOTH
HTTP / HTTPS Port
Values (port#)
HTTP: 80
HTTPS:443
Page 31

4.0 Configuration
4.1.3 System > Access Control
Password Change
The Password Change menu allows the password of the user ‘admin’ to be changed. The
‘admin’ username cannot be deleted, but additional users can be defined and deleted as
required as seen in the Users menu below.
Enter a new password for the ‘admin’ user. It must be at least 5
characters in length. The default password for ‘admin’ is ‘admin’.
The exact password must be entered to confirm the password change,
if there is a mistake all changes will be discarded.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 31
Image 4-1-5: Access Control > Password Change
New Password
Values (characters)
admin
min 5 characters
Confirm Password
Values (characters)
admin
min 5 characters
Page 32

4.0 Configuration
4.1.3 System > Access Control
Users
Different users can be set up with customized access to the WebUI. Each menu or tab of the
WebUI can be disabled on a per user basis as seen below.
Enter the desired username. Minimum or 5 character and maximum of
32 character. Changes will not take effect until the system has been
restarted.
Passwords must be a minimum of 5 characters. The Password must
be re-entered exactly in the Confirm Password box as well.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 32
Image 4-1-6: Access Control > Users
Username
Values (characters)
(no default)
Min 5 characters
Max 32 characters
Password / Confirm Password
Values (characters)
(no default)
min 5 characters
Page 33

4.0 Configuration
4.1.4 System > Services
Available Services
Certain services in the IPn4G can be disabled or enabled for either security considerations or
resource/power considerations. The Enable/Disable options are applied after a reboot and will
take affect after each start up. The Start/Restart/Stop functions only apply to the current session
and will not be retained after a power cycle.
Image 4-1-7: System > Services
The IPn4G has the ability to turn off the RSSI LED’s. The RSSI value
can still be read from the unit, but the status will not be visible on the
unit itself .
For testing purposes the IPn4G has an internal iperf server that can be
used to test unit performance. The user must install a iperf client to
use this functionality.
Using the SSH Service Enable/Disable function, you can disable the
SSH service (Port 22) from running on the IPn4G.
RSSI LED
Values (selection)
Start / Restart / Stop
Throughput Test Server
Values (selection)
Start / Restart / Stop
SSH Service
Values (selection)
Start / Restart / Stop
© Microhard Systems Inc. 33
Page 34

4.0 Configuration
Telnet Service
Using the Telnet Service Enable/Disable function, you can disable the
Telnet service (Port 23) from running on the IPn4G.
Using the FTP Service Enable/Disable function, you can disable the
FTP service (Port 21) from running on the IPn4G. This port is reserved
for internal use / future use.
Custom SSH Port. Reserved for internal use.
Values (characters)
Start / Restart / Stop
FTP Server
Values (selection)
Start / Restart / Stop
Microhard Sh
Values (selection)
Start / Restart / Stop
© Microhard Systems Inc. 34
Page 35

4.0 Configuration
4.1.5 System > Maintenance
Version Information
Detailed version information can be found on this display. The Product Name, Firmware
Version, Hardware Type, Build Version, Build Date and Build Time can all be seen here, and
may be requested from Microhard Systems to provide technical support.
Image 4-1-8: Maintenance > Version Information / Firmware Upgrade
Firmware Upgrade
Occasional firmware updates may be released by Microhard Systems which may include fixes
and/or new features. The firmware can be updated wirelessly using the WebUI.
Erase Current Configuration
Check this box to erase the configuration of the IPn4G unit during the
upgrade process. This will upgrade, and return the unit to factory
defaults, including the default IP Addresses and passwords. Not
checking the box will retain all settings during a firmware upgrade
procedure.
Values (check box)
unchecked
Firmware Image
Use the Browse button to find the firmware file supplied by Microhard
Systems. Select “Upgrade Firmware” to start the upgrade process.
This can take several minutes.
Values (file)
(no default)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 35
Page 36

4.0 Configuration
4.1.5 System > Maintenance
Reset to Default
The IPn4G may be set back to factory defaults by using the Reset to Default option under
System > Maintenance > Reset to Default. *Caution* - All settings will be lost!!!
Backup & Restore Configuration
The configuration of the IPn4G can be backed up to a file at any time using the Backup
Configuration feature. The file can the be restored using the Restore Configuration feature. It is
always a good idea to backup any configurations in case of unit replacement. The configuration
files cannot be edited offline, they are used strictly to backup and restore units.
Use this field to name the configuration file. The .config extension will automatically be added to the
configuration file.
Use the ‘Browse’ button to find the backup file that needs to be restored to the unit. Use the ‘Check
Restore File’ button to verify that the file is valid, and then the option to restore the configuration is
displayed, as seen above. The option is available to keep the current carrier settings rather than replace
them with the settings contained in the Config file.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 36
Image 4-1-9: Maintenance > Reset to Default / Backup & Restore Configuration
Name this Configuration / Backup Configuration
Restore Configuration file / Check Restore File / Restore
Page 37

4.0 Configuration
4.1.6 System > Logout
The logout function allows a user to end the current configuration session and prompt for a login
screen.
Image 4-1-10: System > logout
© Microhard Systems Inc. 37
Page 38

4.0 Configuration
4.1.7 System > Reboot
The IPn4G can be remotely rebooted using the System > Reboot menu. As seen below a button
‘OK, reboot now’ is provided. Once pressed, the unit immediately reboots and starts its boot up
procedure.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 38
Image 4-1-11: System > Reboot
Page 39

4.0 Configuration
4.2 Network
4.2.1 Network > Status
The Network Status display gives a overview of the currently configured network interfaces
including the Connection Type (Static/DHCP), IP Address, Net Mask, Default Gateway, DNS,
and IPv4 Routing Table.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 39
Image 4-2-1: Network > Network Status
Page 40

4.0 Configuration
4.2.2 Network > LAN
Network LAN Configuration
The Ethernet port (RJ45) on the back of the IPn4G is the LAN port, used for connection of
devices on a local network. By default, this port has a static IP Address of 192.168.168.1. It
also, by default is running a DHCP server to provide IP Addresses to devices that are connected
to the physical port, and devices connected by a WiFi connection (if equipped).
DHCP: Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol
may be used by
networked devices
(Clients) to obtain unique
network addresses from a
DHCP server.
Advantage:
Ensures unique IP
addresses are assigned,
from a central point
(DHCP server) within a
network.
Disadvantage:
The address of a
particular device is not
‘known’ and is also
subject to change.
STATIC addresses must
be tracked (to avoid
duplicate use), yet they
may be permanently
assigned to a device.
LAN Add/Edit Interface
The IPn4G has the capability to have multiple SSID’s for the WiFi radio (optional). New
Interfaces can be added for additional SSID’s, providing, if required, separate subnets for each
SSID. By default any additional interfaces added will automatically assign IP addresses to
connecting devices via DHCP. Additional interfaces can only be used by additional WIFI SSID’s
(virtual interfaces).
Image 4-2-3: Network > Add/Edit LAN Interface
Image 4-2-2: Network > LAN
© Microhard Systems Inc. 40
Page 41

4.0 Configuration
Spanning Tree (STP)
Within any IP network,
each device must have its
own unique IP address.
A SUBNET MASK is a bit
mask that separates the
network and host (device)
portions of an IP address.
The ‘unmasked’ portion
leaves available the
information required to
identify the various
devices on the subnet.
A GATEWAY is a point
within a network that acts
as an entrance to another
network.
In typical networks, a
router acts as a gateway.
DNS: Domain Name
Service is an Internet
service that translates
easily- remembered
domain names into their
not-so-easilyremembered IP
addresses.
Being that the Internet is
based on IP addresses,
without DNS, if one
entered the domain name
www.microhardcorp.com
(for example) into the
URL line of a web
browser, the website
‘could not be found’).
Spanning Tree (STP) is used by default to detect and prevent
Values (selection)
any loops from occurring.
On
Off
Connection Type
This selection determines if the IPn4G will obtain an IP address
from a DHCP server on the attached network, or if a static IP
address will be entered. If a Static IP Address is chosen, the
fields that follow must also be populated.
Values (selection)
DHCP
Static
IP Address
If ‘Static’ Connection Type is selected, a valid IPv4 Address for
the network being used must be entered in the field. If ‘DHCP’
is chosen this field will not appear and it will be populated
automatically from the DHCP server.
Values (IP Address)
192.168.168.1
Netmask
If ‘Static’ Connection Type is selected, the Network Mask must
be entered for the Network. If ‘DHCP’ is chosen this field will
not appear and it will be populated automatically from the
DHCP server.
Values (IP Address)
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
If the IPn4G is integrated into a network which has a defined
gateway, then, as with other hosts on the network, this
gateway’s IP address will be entered into this field. If there is a
DHCP server on the network, and the Connection Type (see
previous page) is selected to be DHCP, the DHCP server will
populate this field with the appropriate gateway address.
A simple way of looking at what the gateway value should be is: If a device has a packet of data
is does not know where to send, send it to the gateway. If necessary - and applicable - the
gateway can forward the packet onwards to another network.
Values (IP Address)
(no default)
LAN DNS Servers
DNS (Domain Name Service) Servers are used to resolve
domain names into IP addresses. If the Connection Type is set
for DHCP the DHCP server will populate this field and the value
set can be viewed on the Network > Status page.
Values (IP Address)
(no default)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 41
Page 42

4.0 Configuration
LAN DHCP
A IPn4G may be configured to provide dynamic host control protocol (DHCP) service to all
Prior to enabling this
service, verify that there
are no other devices either wired (e.g. LAN) or
wireless (e.g. another VIP
Series unit) with an active
DHCP SERVER service.
(The Server issues IP
address information at the
request of a DHCP Client,
which receives the
information.)
attached (either wired or wireless (WiFi)-connected) devices. By default the DHCP service is
enabled, so devices that are connected to the physical Ethernet LAN ports, as well as any
devices that are connected by WiFi will be assigned an IP by the IPn4G. The LAN DHCP
service is available for each interface, and is located in the add/edit interface menus.
Image 4-2-4: Network > Add/Edit Interface DHCP
The option is used to enable or disable the DHCP service for
devices connected to the LAN Port and devices connected
through a Wireless connection. This includes VIP connected as
clients and other wireless devices such as 802.11 connections.
Select the starting address DHCP assignable IP Addresses.
The first octets of the subnet will be pre-set based on the LAN
IP configuration, and can not be changed.
Set the maximum number of IP addresses that can be assigned
by the IPn4G.
The DHCP lease time is the amount of time before a new
request for a network address must be made to the DHCP
Server.
DHCP
Values (selection)
On / Off
Start
Values (IP Address)
192.168.168.100
Limit
Values (integer)
150
Lease Time
Values (minutes)
(minutes)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 42
Page 43

4.0 Configuration
Alternate Gateway
Specify an alternate gateway for DHCP assigned devices if the default
gateway is not to be used.
Specify a preferred DNS server address to be assigned to DHCP
devices.
Specify the alternate DNS server address to be assigned to DHCP
devices.
Enter the Domain Name for the DHCP devices.
Enter the address of the WINS/NBNS (NetBIOS) Server. The WINS
server will translate computers names into their IP addresses, similar
to how a DNS server translates domain names to IP addresses.
Values (IP Address)
(IP Address)
Preferred DNS Server
Values (IP Address)
(IP Address)
Alternate DNS Server
Values (IP Address)
(IP Address)
Domain Name
Values (string)
(IP Address)
WINS/NBNS Servers
Values (IP/Domain)
(no default)
Select the method used to resolve computer names to IP addresses.
Four name resolution methods are available:
B-node: broadcast
P-node: point-to-point
M-node: mixed/modified
H-node: hybrid
© Microhard Systems Inc. 43
WINS/NBT Node Type
Values (selection)
none
b-node
p-node
m-node
h-node
Page 44

4.0 Configuration
Static IP Addresses (for DHCP)
In some applications it is important that specific devices always have a predetermined IP
address. This section allows for MAC Address binding to a IP Address, so that whenever the
device that has the specified MAC address, will always get the selected IP address. In this
situation, all attached (wired or wireless) devices can all be configured for DHCP, but still get a
known IP address.
Image 4-2-5: Network > MAC Address Binding
Name
The name field is used to give the device a easily recognizable
name.
Values (characters)
(no default)
MAC Address
Enter in the MAC address of the device to be bound to a set IP
address. Set the IP Address in the next field. Must use the
format: AB:CD:DF:12:34:D3. It is not case sensitive, but the
colons must be present.
Values (MAC Address)
(no default)
IP Address
Enter the IP Address to be assign to the device specified by the
MAC address above.
Static Addresses
This section displays the IP address and MAC address currently assigned through the DCHP
service, that are bound by it’s MAC address. Also shown is the Name, and the ability to remove
the binding by clicking “Remove _______”.
Active DHCP Leases
This section displays the IP Addresses currently assigned through the DCHP service. Also
shown is the MAC Address, Name and Expiry time of the lease for reference.
Using the “Release All” button, all DHCP leases are released and any connected devices must
request new leases.
Values (IP Address)
(minutes)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 44
Page 45

4.0 Configuration
4.2.3 Network > WIFI
Network WIFI Configuration
The WIFI menu is used to define (if required) a virtual interface in which to bind a WIFI
connection. This connection can then be bound to the Wireless Radio in the Wireless > Radio1
menu. If this interface is not bound to the Wireless interface it has no operation or purpose.
The WIFI interface can be used setup a separate WIFI connection for connected devices
(separating them from the devices connected to the LAN), this would be the same as adding
another interface under the LAN configuration. In this mode the IPn4G would be operating as a
Access Point (AP) providing network access to any connected devices. A separate DHCP
server must be defined if it is required to provide DHCP services to connecting devices.
In most cases the WIFI interface would be setup to allow the IPn4G to operate as a Client to
another Access Point (AP). Using this menu it can be decided to use DHCP to obtain an IP
address and related networking information from the connected Access Point, or it could be
setup with a static IP address that is part of the AP’s network.
When connected as a Client the IPn4G would be able to use the WIFI network for data rather
than the cellular connection. However unless an appropriate default route(s) was set to
manage this connection there would be no way to predict which interface is used for
data.
WIFI Configuration
The description of each of the parameters for setting up a WIFI interface is identical to those of
adding/editing a virtual LAN interface, which is discussed in the last section.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 45
Image 4-2-2: Network > WIFI
Page 46

4.0 Configuration
4.2.4 Network > Routes
Static Routes Configuration
It may be desirable to have devices on different subnets to be able to talk to one another. This
can be accomplished by specifying a static route, telling the IPn4G where to send data.
Image 4-2-6: Network > Routes
Routes can be names for easy reference, or to describe the route
being added.
Enter the network IP address for the destination.
Specify the Gateway used to reach the network specified above.
Enter the Netmask for the destination network.
Name
Values (characters)
(no default)
Destination
Values (IP Address)
(192.168.168.0)
Gateway
Values (IP Address)
192.168.168.1
Netmask
Values (IP Address)
255.255.255.0
© Microhard Systems Inc. 46
Page 47

4.0 Configuration
Metric
In some cases there may be multiple routes to reach a destination.
The Metric can be set to give certain routes priority, the lower the
metric is, the better the route. The more hops it takes to get to a
destination, the higher the metric.
Define the exit interface. Is the destination a device on the LAN, or the
WAN (for the IPn4G would be the cellular connection)?
Values (Integer)
0
Interface
Values (Selection)
LAN
WAN (4G)
WIFI
None
© Microhard Systems Inc. 47
Page 48

4.0 Configuration
4.2.5 Network > GRE
GRE Configuration
The IPn4G supports GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) Tunneling which can encapsulate a
wide variety of network layer protocols not supported by traditional VPN. This allows IP packets
to travel from one side of a GRE tunnel to the other without being parsed or treated like IP
packets.
Refer to Appendix G:
GRE Example for a
working example of how
to setup GRE on your
Image 4-2-7: Network > GRE Summary
Each GRE tunnel must have a unique name. Up to 10 GRE tunnels
are supported by the IPn4G.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 48
Image 4-2-8: Network > Edit/Add GRE Tunnel
Name
Values (Chars(32))
gre
Page 49

4.0 Configuration
Enable
Enable / Disable the GRE Tunnel.
Enable / Disable Multicast support over the GRE tunnel.
Set the TTL (Time-to-live) value for packets traveling through the GRE
tunnel.
Enter a key is required, key must be the same for each end of the GRE
tunnel.
Enable / Disable ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) support over the GRE
tunnel.
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
Multicast
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
TTL
Values (value)
1 - 255
Key
Values (chars)
(none)
ARP
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
Local Setup
The local setup refers to the local side of the GRE tunnel, as opposed to the remote end.
Gateway IP Address
This is the WAN IP Address of the IPn4G, this field should be populated
with the current WAN IP address.
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
Tunnel IP Address
This is the IP Address of the local tunnel.
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
Netmask
Enter the subnet mask of the local tunnel IP address.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 49
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
Page 50

4.0 Configuration
Subnet IP Address
Enter the subnet address for the local network.
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask for the local network/subnet.
Remote Setup
The remote setup tells the IPn4G about the remote end, the IP address to create the tunnel to,
and the subnet that is accessible on the remote side of the tunnel.
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
Gateway IP Address
Enter the WAN IP Address of the IPn4G or other GRE supported device in
which a tunnel is to be created with at the remote end.
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
Subnet IP Address
The is the IP Address of the remote network, on the remote side of the
GRE Tunnel.
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
Subnet Mask
The is the subnet mask for the remote network/subnet.
IPsec Setup
Refer to the IPsec setup in the VPN Site to Site section of the manual for more information.
Values (IP Address)
(varies)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 50
Page 51

4.0 Configuration
4.2.6 Network > SNMP
The IPn4G may be configured to operate as a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
agent. Network management is most important in larger networks, so as to be able to manage
resources and measure performance. SNMP may be used in several ways:
SNMP: Simple Network
Management Protocol
provides a method of
managing network
devices from a single PC
running network
management software.
Managed networked
devices are referred to as
SNMP agents.
A SNMP management system (a PC running SNMP management software) is required for this
service to operate. This system must have full access to the IPn4G. Communications is in the
form of queries (information requested by the management system) or traps (information
initiated at, and provided by, the SNMP agent in response to predefined events).
Objects specific to the IPn4G are hosted under private enterprise number 21703.
An object is a variable in the device and is defined by a Management Information Database
(MIB). Both the management system and the device have a copy of the MIB. The MIB in the
management system provides for identification and processing of the information sent by a
device (either responses to queries or device-sourced traps). The MIB in the device relates
subroutine addresses to objects in order to read data from, or write data to, variables in the
device.
An SNMPv1 agent accepts commands to retrieve an object, retrieve the next object, set and
object to a specified value, send a value in response to a received command, and send a value
in response to an event (trap).
SNMPv2c adds to the above the ability to retrieve a large number of objects in response to a
single request.
SNMPv3 adds strong security features including encryption; a shared password key is utilized.
Secure device monitoring over the Internet is possible. In addition to the commands noted as
supported above, there is a command to synchronize with a remote management station.
The pages that follow describe the different fields required to set up SNMP on the IPn4G. MIBS
may be requested from Microhard Systems Inc.
The MIB file can be downloaded directly from the unit using the ‘Get MIB File’ button on the
Network > SNMP menu.
configure remote devices
monitor network performance
detect faults
audit network usage
detect authentication failures
© Microhard Systems Inc. 51
Page 52

4.0 Configuration
SNMP Settings
Image 4-2-9: Network > SNMP
If disabled, an SNMP service is not provided from the device.
Enabled, the device - now an SNMP agent - can support SNMPv1, v2,
& v3.
Read Only Community Name
Effectively a plain-text password mechanism used to weakly
authenticate SNMP queries. Being part of the community allows the
SNMP agent to process SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c requests. This
community name has only READ priority.
Read Only Community Name
Also a plain-text password mechanism used to weakly authenticate
SNMP queries. Being part of the community allows the SNMP agent to
process SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c requests. This community name has
only READ/WRITE priority.
SNMP Operation Mode
Values (selection)
Disable / V1&V2c&V3
Values (string)
public
Values (string)
private
SNMP V3 User Name
Defines the user name for SNMPv3.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 52
Values (string)
V3user
Page 53

4.0 Configuration
V3 User Read Write Limit
Defines accessibility of SNMPv3; If Read Only is selected, the
SNMPv3 user may only read information; if Read Write is
selected, the SNMPv3 user may read and write (set) variables.
V3 User Authentication Level
Defines SNMPv3 user’s authentication level:
NoAuthNoPriv: No authentication, no encryption.
AuthNoPriv: Authentication, no encryption.
AuthPriv: Authentication, encryption. (Not supported)
V3 User Authentication Password
SNMPv3 user’s authentication password. Only valid when V3 User
Authentication Level set to AuthNoPriv or AuthPriv (Not supported).
V3 User Privacy Password
SNMPv3 user’s encryption password. Only valid when V3 User
Authentication Level set to AuthPriv (see above). Authpriv is
currently not supported on the IPn4G(b).
Select which version of trap will be sent should a failure or alarm
condition occur.
Values (selection)
Read Only / Read Write
Values (selection)
NoAuthNoPriv
AuthNoPriv
AuthPriv (Not supported)
Values (string)
00000000
Values (string)
00000000
SNMP Trap Version
Values (string)
V1 Traps V2 Traps
V3 Traps V1&V2 Traps
V1&V2&V3 Traps
If enabled, an authentication failure trap will be generated upon
authentication failure.
The community name which may receive traps.
Defines a host IP address where traps will be sent to (e.g. SNMP
management system PC IP address).
© Microhard Systems Inc. 53
Auth Failure Traps
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
Trap Community Name
Values (string)
TrapUser
Trap Manage Host IP
Values (IP Address)
0.0.0.0
Page 54

4.0 Configuration
4.2.7 Network > sdpServer
sdpServer Settings
Microhard Radio employ a discovery service that can be used to detect other Microhard Radio’s
on a network. This can be done using a stand alone utility from Microhard System’s called ‘IP
Discovery’ or from the Tools > Discovery menu. The discovery service will report the MAC
Address, IP Address, Description, Product Name, Firmware Version, Operating Mode, and the
SSID.
Image 4-2-10: Network > sdpServer Settings
Use this option to disable or enable the discovery service.
Specify the port running the discovery service on the IPn4G unit.
Discovery Service Status
Values (selection)
Disable / Discoverable /
Changable
Server Port Settings
Values (Port #)
20097
© Microhard Systems Inc. 54
Page 55

4.0 Configuration
4.2.8 Network > Local Monitor
The Local Device Monitor allows the IPn4G to monitor a local device connected locally to the
Ethernet port or to the locally attached network. If the IPn4G cannot detect the specified IP or a
DHCP assigned IP, the unit will restart the DHCP service, and eventually restart the modem to
attempt to recover the connection.
Image 4-2-11: Network Configuration , Local Monitor
Status
Enable or disable the local device monitoring service.
Select the IP mode. By selecting a fixed IP address the service will monitor
the connection to that specific IP. If auto detect is selected, the IPn4G will
detect and monitor DHCP assigned IP address.
This field is only shown if Fixed Local IP is selected for the IP Mode. Enter
the static IP to be monitored in this field.
The status timeout is the maximum time the IPn4G will wait to detect the
monitored device. At this time the IPn4G will restart the DHCP service. (565535 seconds)
This field defines the amount of time the IPn4G will wait to detect the
monitored device before it will reboot the modem. (30-65535 seconds)
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
IP Mode
Values (selection)
Fixed local IP
Auto Detected IP
Local IP Setting
Values (IP)
0.0.0.0
Status Timeout
Values (seconds)
10
Waiting DHCP Timeout
Values (seconds)
60
© Microhard Systems Inc. 55
Page 56

4.0 Configuration
4.2.9 Network > Port
Ethernet Port Configuration
This menu shows the current status and allows the configuration of the Ethernet Port (LAN).
Image 4-2-11: Network > Ethernet Port Configuration
Mode
Select between Auto, where the IPn4G will decide the best port settings
based on a negotiation with the connected device. It can also be set to
manual where the Speed and Duplex can be set manually.
Values (selection)
Auto / Manual
Speed
If the mode above is set to manual it is possible to select the speed at
which the LAN port is to operate. Chose between 10MBit/s or 100Mbit/s.
Values (selection)
100Mbit/s / 10Mbit/s
Duplex
If the mode above is set to manual it is possible to select the duplex mode
of the Ethernet port. Choose between Full and Half duplex.
Ethernet Port Status
The Ethernet Port Status shows the current status of the Ethernet port, and in the case of ‘Auto’,
will also show the current port configuration.
Values (selection)
Full / Half
© Microhard Systems Inc. 56
Page 57

4.0 Configuration
4.3 Carrier
4.3.1 Carrier > Status
The Carrier Status window provides complete overview information related to the Cellular Carrier portion of
the IPn4G. A variety of information can be found here, such as Activity Status, Network (Name of Wireless
Carrier connected) , Data Service Type (WCDMA/HSPA/HSPA+/LTE etc), Frequency band, Phone
Number etc.
Not all statistics parameters displayed are applicable.
The Received and Transmitted bytes and packets indicate the respective amount of data which has been
moved through the radio.
The Error counts reflect those having occurred on the wireless link.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 57
Image 4-3-1: Carrier > Status
Page 58

4.0 Configuration
4.3 Carrier
4.3.2 Carrier > Settings
The Carrier Menu provides all the options for configuring the IPn4G to communicate with a
Cellular Carrier. In addition to setting up the SIM card, there are several tools such as the Traffic
Watchdog and Data Usage Alerts that can be used to ensure your modem is functioning and
performing as required. The parameters within the Carrier Configuration menu must be input
properly; they are the most basic requirement required by your cellular provider for network
connectivity.
Carrier Status is used to Enable or Disable the connection to the
Cellular Carrier. By default this option is enabled.
This option is used to prevent the modem from roaming. This is
important as there is usually a significant charge for roaming data. This
option can be used to prevent this from happening. This is generally
used in mobile applications.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 58
Image 4-3-2: Carrier > Settings
Carrier Status
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
Data Roaming
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
Page 59

4.0 Configuration
Carriers
In some cases, a user may want to lock onto certain carrier to avoid
data roaming. There were four options presented to a user to choose
from, Auto, SIM based, Scan & Select and Fixed.
Auto will allow the IPn4G to pick the carrier automatically. Data roaming is
permitted.
SIM based will only allow the IPn4G to connect to the network indicated by
the SIM card used in the unit.
Manual will scan for available carriers and allow a user to select from the
available carriers. It takes 2 to 3 minutes to complete a scan.
Fixed allows a user to enter the carrier code (numerical) directly and then the
IPn4G will only connect to that carrier.
IP pass-through allows the WAN IP address to be assigned to the
device connected to the RJ45 LAN Port. In this mode the IPn4G is for
the most part transparent and forwards all traffic to the device
connected to the Ethernet port except that listed below:
The WebUI port (Default Port:TCP 80), this port is retained for remote
management of the IPn4G. This port can be changed to a different port
under the System > Settings Menu.
The SNMP Listening Port (Default Port: UDP 161).
Refer to the Appendix for an example of how to configure IP-Passthrough.
Values (Selection)
Auto
Based on SIM
Manual
Fixed
IP-Passthrough
Values (selection)
Disable
Ethernet
IP-Passthrough Mode
This field is only visible once IP Passthrough has been selected
above. This gives the user the option to manually configure the IPPassthrough feature of the modem. (It is recommended to only use
this option if you are an advanced user and the automatic settings do
not work for your application or carrier)
IP-Passthrough Gateway
This field is used to specify the Gateway to be used for IP Passthrough
if set to manual mode. As mentioned above it is recommended to use
the Auto mode for IP-Passthrough.
IP-Passthrough Netmask
This field is used to specify the Netmask to be used for IP Passthrough
if set to manual mode. As mentioned above it is recommended to use
the Auto mode for IP-Passthrough.
IP-Passthrough Local IP
This is a read only field that displays the current IP address assigned by
the cellular carrier that will be assigned (DHCP) or needs to be
configured (Static) on the attached device.
Values (selection)
Auto / Manual
Values
(no default)
Values
(no default)
Values (selection)
(current carrier IP to be
assigned to attached
device).
© Microhard Systems Inc. 59
Page 60

4.0 Configuration
DNS-Passthrough
When enabled DNS-Passthrough will pass on the WAN assigned DNS
information to the end device.
Values (selection)
Enable / Disable
APN (Access Point Name)
The APN is required by every Carrier in order to connect to their
networks. The APN defines the type of network the IPn4G is
connected to and the service type. Most Carriers have more than one
APN, usually many, dependant on the types of service offered.
Auto APN (default) may allow the unit to quickly connect to a carrier, by cycling through a predetermined
list of common APN’s. Auto APN will not work for private APN’s or for all carriers.
Values (characters)
auto
SIM Pin
The SIM Pin is required for some international carriers. If supplied and
required by the cellular carrier, enter the SIM Pin here.
Values (characters)
(none)
Technologies Type
Set to ALL by default, the Technologies field allows the selection of
3GPP technologies (LTE), and or 3GPP2 technology (CDMA).
Values (selection)
ALL / 3GPP / 3GPP2
Technologies Mode
The Technologies Mode option allows a user the ability to specify what
type of Cellular networks to connect to.
Sets the modems connect string if required by the carrier. Not usually
required in North America.
If let blank the IPn4G with use the DNS server as specified
automatically by the service provider.
Values (selection)
AUTO / LTE Only / WCDMA
Only / GSM Only
Data Call Parameters
Values (string)
(none)
Primary DNS Address
Values (IP Address)
(none)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 60
Page 61

4.0 Configuration
Secondary DNS Address
If let blank the IPn4G with use the DNS server as specified
automatically by the service provider.
Primary NetBIOS Name Server
Enter the Primary NetBIOS Name Server if required by the carrier.
Secondary NetBIOS Name Server
Enter the Secondary NetBIOS Name Server if required by the carrier.
In some cases the Static IP address must be entered in this
field if assigned by a wireless carrier. In most cases the IP will
be read from the SIM card and this field should be left at the
default value.
Values (IP Address)
(none)
Values (IP Address)
(none)
Values (IP Address)
(none)
IP Address
Values (IP Address)
(none)
Authentication
Sets the authentication type required to negotiate with peer.
PAP - Password Authentication Protocol.
CHAP - Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol.
A User Name may be required for authentication to a remote
peer. Although usually not required for dynamically assigned IP
addresses from the wireless carrier, but required in most cases
for static IP addresses. Varies by carrier.
Enter the password for the user name above. May not be
required by some carriers, or APN’s
Values (Selection)
Device decide (AUTO)
PAP
CHAP
User Name
Values (characters)
Carrier/peer dependant
Password
Values (characters)
Carrier/peer dependant
© Microhard Systems Inc. 61
Page 62

4.0 Configuration
4.3 Carrier
4.3.3 Carrier > Keepalive
The Keep alive tab allows for the configuration of the keep alive features of the IPn4G. The
IPn4G can either do a ICMP or HTTP keep alive by attempting to reach a specified address at a
regular interval. If the IPn4G cannot reach the intended destination, it will reset the unit in an
attempt to obtain a new connection to the carrier.
Image 4-3-3: Carrier > Keepalive
Enable or Disable the keep alive functions in the IPn4G.
Select the type of keep alive used. ICMP uses a “ping” to reach
a select destination.
Specify a IP Address or Domain that is used to test the IPn4G
connection. (Use the ‘Test’ button to ensure that a reachable
host is used.)
The Interval value determines the frequency, or how often, the
IPn4G will send out PING messages to the Host.
Keep Alive Status
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
Type
Values (Selection)
ICMP / HTTP
Host Name
Values (IP or Domain)
8.8.8.8
Interval
Values (seconds)
300
Count
The Count field is the maximum number of PING errors such as “Host
unreachable” the IPn4G will attempt before the unit will reboot itself to
attempt to correct connection issues. If set to zero (0), the unit will
never reboot itself.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 62
Values (number)
10
Page 63

4.0 Configuration
4.3 Carrier
4.3.4 Carrier > Traffic Watchdog
The Wireless Traffic Watchdog will detect if there has been no wireless traffic, or communication
with the Cellular carrier for a configurable amount of time. Once that time has elapsed, the unit
will reset, and attempt to re-establish communication with the cellular carrier.
Image 4-3-4: Carrier > Traffic Watchdog
Enable or Disable the Traffic Watchdog.
The Check Interval tells the IPn4G how often (in seconds) to
check for wireless traffic to the cellular carrier. (1-60000
seconds)
The Reboot Timer will reset the unit if there has been no
Cellular RF activity in the configured time. (300 –60000
seconds)
Traffic Watchdog
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
Check Interval
Values (seconds)
1
Reboot Time Limit
Values (seconds)
600
© Microhard Systems Inc. 63
Page 64

4.0 Configuration
4.3 Carrier
4.3.5 Carrier > Dynamic DNS
Unless a carrier issues a Static IP address, it may be desirable to use a dynamic DNS service to
track dynamic IP changes and automatically update DNS services. This allows the use of a
constant resolvable host name for the IPn4G.
Image 4-3-5: Carrier > Traffic Watchdog
This selection allows the use of a Dynamic Domain Name
Server (DDNS), for the IPn4G.
This is a list of supported Dynamic DNS service providers. Free
and premium services are offered, contact the specific
providers for more information.
‘customized_ddns’ can be selected to configure your own
DDNS service if required.
Enter a valid user name for the DDNS service selected above.
Enter a valid password for the user name of the DDNS service
selected above.
DDNS Status
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
Service
Values (selection)
changeip
dyndns
eurodyndns
hn
noip
ods
ovh
regfish
tzo
zoneedit
User Name
Values (characters)
(none)
Password
Values (characters)
(none)
This is the host or domain name for the IPn4G as assigned by
the DDNS provider.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 64
Host
Values (domain name)
(none)
Page 65

4.0 Configuration
4.3 Carrier
4.3.6 Carrier > SMS Config
SMS messages can be used to remotely reboot or trigger events in the IPn4G. SMS alerts can
be set up to get SMS messages based on system events such as Roaming status, RSSI,
Ethernet Link Status or IO Status.
System SMS Command
Image 4-3-6: SMS > SMS Configuration
This option allows a user to enable or disable to use of the
following SMS commands to reboot or trigger events in the
IPn4G:
MSC#REBOOT Reboot system
MSC#NMS Send NMS UDP Report
MSC#WEB Send web client inquiry
MSC#MIOP1 open I/O ouput1
MSC#MIOP2 open I/O ouput2
MSC#MIOP3 open I/O ouput3
MSC#MIOP4 open I/O ouput4
MSC#MIOC1 close I/O ouput1
MSC#MIOC2 close I/O ouput2
MSC#MIOC3 close I/O ouput3
MSC#MIOC4 close I/O ouput4
MSC#EURD0 trigger event report0
MSC#EURD1 trigger event report1
MSC#EURD2 trigger event report2
MSC#EURD3 trigger event report3
MSC#GPSR0 trigger gps report0
MSC#GPSR1 trigger gps report1
MSC#GPSR2 trigger gps report2
MSC#GPSR3 trigger gps report3
SMS Commands are case sensitive.
If enabled, the IPn4G will only accept and execute commands
originating from the phone numbers in the Phone Filter List. Up
to 6 numbers can be added.
Status
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
Set Phone Filter
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
© Microhard Systems Inc. 65
Page 66

4.0 Configuration
System SMS Alerts
Image 4-3-7: SMS > SMS Alerts
Enable SMS Alerts. IF enabled SMS alerts will be send when
conditions are met as configured to the phone numbers listed.
SMS Alerts can be sent to up to 6 different phone numbers that
are listed here.
SMS alerts, when active, will be sent out at the frequency
defined here.
A text field that allows up to 30 characters to add an alias or
other information that will be included with the SMS message.
Status
Values (Selection)
Enable / Disable
Received Phone Numbers
Values (Selection)
(no default)
Time Interval(s)
Values (Seconds)
300
Device Alias
Values (characters)
300
© Microhard Systems Inc. 66
Page 67

4.0 Configuration
RSSI Check
Enable or disable the RSSI alerts.
Set the low threshold for RSSI alerts. When the RSSI drops
below this value, an alert will be sent indicating poor service.
Enable or disable SMS Alerts for Roaming Status.
The IPn4G can send alerts based on the roaming status. Data
rates during roaming can be expensive and it is important to
know when a device has started roaming.
Values (Selection)
Disable RSSI check
Enable RSSI check
Low Threshold (dBm)
Values (dBm)
-99
Carrier Network
Values (Selection)
Disable Roaming Check
Enable Roaming Check
Home / Roaming Status
Values (Selection)
In Roaming
Changed or In Roaming
Changed to Roaming
Enable or disable SMS Alerts for the Ethernet Link status of the
LAN RJ45 port.
The status of the Ethernet Link of the LAN (RJ45) can be used
to send SMS Alerts. The link status may indicate an issue with
the connected device.
SMS Alerts can be sent based on the state changes of the
Digital I/O lines.
Ethernet
Values (Selection)
Disable Ethernet check
Enable Ethernet check
Ethernet Link Status
Values (Selection)
Changed
In no-link
Changed or in no-link
Changed to no-link
I/O Status
Values (Selection)
Disable IO Check
Enable: INPUT Changed
Enable: Output Changed
Enable: INPUT or OUTPUT
Changed.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 67
Page 68

4.0 Configuration
4.3 Carrier
4.3.7 Carrier > SMS
SMS Command History
The SMS menu allows a user to view the SMS Command History and view the SMS messages
on the SIM Card.
Image 4-3-8: SMS > SMS Command History
Send SMS Message
The SMS messages can be sent directly from the IPn4G WebUI interface. Also, the SMS
message history can be viewed.
Image 4-3-9: SMS > SMS Send
© Microhard Systems Inc. 68
Page 69

4.0 Configuration
4.3.8 Carrier > Data Usage
The Data Usage tool on the IPn4G allows users to monitor the amount of cellular data
consumed. Since cellular devices are generally billed based on the amount of data used, alerts
can be triggered by setting daily and/or monthly limits. Notifications can be sent using SMS or
Email, allowing a early warning if configurable limits are about to be exceeded. The usage data
reported by the Data Usage Monitor may not match the data reported by the carrier, but it gives
the users an idea of the bandwidth consumed by the IPn4G.
If enabled the IPn4G will track the amount of cellular data
consumed. If disabled, data is not recorded, even in the Current
Data Usage display.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 69
Image 4-3-10: Carrier > Data Usage
Status
Values (selection)
Disable
Enable
Page 70

4.0 Configuration
Monthly/Daily Over Limit
Select the notification method used to send alerts when daily or
monthly thresholds are exceeded. If none is selected, notifications
will not be sent, but data usage will be recorded for reference
purposes.
Image 4-3-11: Data Usage > SMS Config
Monthly/Daily Data Unit
Select the data unit to be used for data usage monitoring.
Select the data limit for the day or month, used in connection with
the data unit is the previous field. If you want to set the limit to 250
Mbytes, select M Bytes for the data unit, and 250 for the data limit.
Values (selection)
None
Send Notice SMS
Send Notice Email
Values (selection)
Bytes / K Bytes / M Bytes
G Bytes
Data Limit
Values (1-65535)
500
For Monthly tracking, select the day the billing/data cycles begins.
On this day each month the IPn4G will reset the data usage monitor
numbers.
If SMS is selected as the notification method, enter the phone
number to send any SMS messages generated when the data
usage exceeds the configured limits.
Image 4-3-12: Data Usage > Email Config
Period Start Day
Values (1-31)
1 (Day of Month)
Phone Number
Values (phone)
+1403
© Microhard Systems Inc. 70
Page 71

4.0 Configuration
Mail Subject
If Email is selected as the notification method, enter the desired
email subject line for the notification email sent when daily and/or
monthly usage limits are exceeded.
If Email is selected as the notification method, enter the SMTP
server details for the account used to send the Email notifications.
Domain or IP address with the associated port as shown.
If Email is selected as the notification method, enter the username
of the Email account used to send Emails.
If Email is selected as the notification method, enter the password
of the Email account used to send Emails. Most email servers
require authentication on outgoing emails.
Enter the email address of the individual or distribution list to send
the email notification to.
Values (string)
Daily/Monthly Data Usage
Notice
Mail Server(IP/Name)
Values (xxx:port)
smtp.gmail.com:465
Username
Values (username)
@gmail.com
Password
Values (string)
***
Mail Recipient
Values (xx@xx.xx)
host@
© Microhard Systems Inc. 71
Page 72

4.0 Configuration
4.4 Wireless (WiFi)
4.4.1 Wireless > Status
The Status window gives a summary of all radio or wireless related settings and connections.
The General Status section shows the Wireless MAC address of the current radio, the
Operating Mode (Access Point, Client, MESH etc), the SSID being used, frequency channel
information and the type of security used.
Traffic Status shows statistics about the transmitted and received data.
The IPn4G shows information about all Wireless connections in the Connection Status section.
The Wireless MAC address, Noise Floor, Signal to Noise ratio (SNR), Signal Strength (RSSI),
The transmit and receive Client Connection Quality (CCQ), TX and RX data rates, and a
graphical representation of the signal level or quality.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 72
Image 4-4-1: Wireless > Status
Page 73

4.0 Configuration
4.4.2 Wireless > Radio1
Radio1 Phy Configuration
The top section of the Wireless Configuration allows for the configuration of the physical radio
module. You can turn the radio on or off, and select the channel bandwidth and frequency as
seen below.
Image 4-4-2: Wireless > Radio Configuration
This option is used to turn the radio module on or off. If turned
off Wireless connections can not be made. The default is On.
The Mode defines which wireless standard to use for the
wireless network. The IPn4G supports 802.11b/g modes as
seen here. Select the appropriate operating mode from the list.
The Channel-Freq setting allows configuration of which channel
to operate on, auto can be chosen where the unit will
automatically pick a channel to operate. If a link cannot be
established it will try another channel.
Radio
Values (selection)
On / Off
Mode
Values (selection)
802.11B ONLY
802.11BG
Channel-Freq
2.4 GHz Channels
Auto
Channel 01 : 2.412 GHz
Channel 02 : 2.417 GHz
Channel 03 : 2.422 GHz
Channel 04 : 2.427 GHz
Channel 05 : 2.432 GHz
Channel 06 : 2.437 GHz
Channel 07 : 2.442 GHz
Channel 08 : 2.447 GHz
Channel 09 : 2.452 GHz
Channel 10 : 2.457 GHz
Channel 11 : 2.462 GHz
Channel 12 : 2.467 GHz
© Microhard Systems Inc. 73
Page 74

4.0 Configuration
Wireless Distance
The Wireless Distance parameter allows a user to set the
expected distance the WiFi signal needs to travel. The default
is 3km, so the IPn4G will assume that the signal may need to
travel up to 3km so it sets various internal timeouts to account
for this travel time. Longer distances will require a higher
setting, and shorter distances may perform better if the setting
is reduced.
Values (meters)
3000
RTS Thr (256 ~ 2346)
Once the RTS Threshold defined packet size is reached, the
system will invoke RTS/CTS flow control. A large RTS
Threshold will improve bandwidth, while a smaller RTS
Threshold will help the system recover from interference or
collisions caused by obstructions.
Values (selection)
On / OFF
Fragment Thr (256 ~ 2346)
The Fragmentation Threshold allows the system to change the
maximum RF packet size. Increasing the RF packet size
reduces the need to break packets into smaller fragments.
Increasing the fragmentation threshold slightly may improve
performance if a high packet error rate is experienced.
Radio1 Virtual Interface
The bottom section of the Wireless Configuration provides for the configuration of the Operating
Mode of the Wireless Interface, the TX power, Wireless Network information, and Wireless
Encryption. The IPn4G can support multiple virtual interfaces. These interfaces provide different
SSID’s for different users, and can also be assigned to separate subnets (Network Interfaces) to
prevent groups from interacting.
Values (selection)
On / OFF
© Microhard Systems Inc. 74
Image 4-4-3: Wireless > Radio1 Virtual Interface Configuration
Page 75

4.0 Configuration
Network
Choose between LAN or WAN for the Virtual Interface. If
Values (selection)
additional Network Interfaces have been defined in the
Network > LAN section, the Interface name will also appear
here.
LAN
WAN
(Additional Interfaces…)
Mode
Access Point - An Access Point may provide a wireless data
connection to many clients, such as stations, repeaters, or
other supported wireless devices such as laptops etc.
If more than 1 Virtual Interface (more than 1 SSID) has been
defined, the IPn4G can ONLY operate as a Access Point, and
will be locked into this mode.
Station/Client - A Station may sustain one wireless connection, i.e. to an Access Point.
Repeater - A Repeater can be connected to an Access Point to extend the range and provide
a wireless data connection to many clients, such as stations.
Mesh Point - Units can be configured as a Mesh “Node”. When multiple units are configured
as a Mesh node, they automatically establish a network between each other. SSID for each
radio in a Mesh network must be the same.
Values (selection)
Access Point
Client
Repeater
Mesh Point
This setting determines the rate at which the data is to be
wirelessly transferred.
The default is ‘Auto’ and, in this configuration, the unit will
transfer data at the highest possible rate in consideration of the
receive signal strength (RSSI).
Setting a specific value of transmission rate has the benefit of
‘predictability’ of that rate, but if the RSSI drops below the
required minimum level to support that rate, communications will
fail.
TX Rate
802.11 b/g
Auto
1 Mbps (802.11b,g)
2 Mbps (802.11b,g)
5.5 Mbps (802.11b,g)
11 Mbps (802.11b,g)
6 Mbps (802.11g)
9 Mbps (802.11g)
12 Mbps (802.11g)
18 Mbps (802.11g)
24 Mbps (802.11g)
36 Mbps (802.11g)
48 Mbps (802.11g)
54 Mbps (802.11g)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 75
Page 76

4.0 Configuration
TX Power
Refer to FCC (or as
otherwise applicable)
regulations to ascertain,
and not operate beyond,
the maximum allowable
transmitter output
power and effective
isotropic radiated power
(EIRP).
SSID: Service Set
Identifier. The ‘name’ of a
wireless network. In an
open wireless network,
the SSID is broadcast; in
a closed system it is not.
The SSID must be known
by a potential client for it
to be able to access the
wireless network.
This setting establishes the transmit power level which will be
presented to the antenna connectors at the rear of the IPn4G.
Unless required, the Tx Power should be set not for maximum,
but rather for the minimum value required to maintain an
adequate system fade margin.
Wireless distribution system (WDS) is a system enabling the
wireless interconnection of access points. WDS preserves the
MAC addresses of client frames across links between access
points
Disabling the SSID broadcast helps secure the wireless
network. Enabling the broadcast of the SSID (Network Name)
will permit others to ‘see’ the wireless network and perhaps
attempt to ‘join’ it.
When AP Isolation is enabled wireless devices connected to
this SSID will not be able to communicate with each other. In
other words if the IPn4G is being used as a Hot Spot for many
wireless clients, AP Isolation would provide security for those
clients by not allowing access to any other wireless device.
Values (selection)
11 dBm
12 dBm
13 dBm
14 dBm
15 dBm
16 dBm
17 dBm
18 dBm
19 dBm
20 dBm
21 dBm
22 dBm
23 dBm
24 dBm
25 dBm
26 dBm
27 dBm
28 dBm
29 dBm
30 dBm
Values (selection)
On / Off
ESSID Broadcast
Values (selection)
On / Off
AP Isolation
Values (selection)
On / Off
WDS
All devices connecting to the IPn4G in a given network must
Change the default value
for the Network Name to
something unique for your
network. Do this for an
added measure of
security and to
differentiate your network
from others which may be
operating nearby.
use the SSID of the IPn4G. This unique network address is not
only a security feature for a particular network, but also allows
other networks - with their own unique network address - to
operate in the same area without the possibility of undesired
data exchange between networks.
In Mesh Networks, this must be the same for all IPn4G, or VIP
Series units participating, similar to the SSID for other wireless
networks.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 76
SSID
Values (string)
wlan0
MESH ID
Values (string)
(no default)
Page 77

4.0 Configuration
Encryption Type
WEP: Wired Equivalency
Privacy is a security
protocol defined in
802.11b. It is commonly
available for Wi-Fi
networks and was
intended to offer the
equivalent security of a
wired network, however, it
has been found to be not
as secure as desired.
Operating at the data link
and physical layers, WEP
does not provide
complete end-to-end
security.
Security options are dependent on the version type. This
Values (selection)
section describes all available options. Export versions may not
have all optional available to meet regulatory requirements set
government policies.
Disabled
WEP
WPA (PSK)
WPA2 (PSK)
WPA+WPA2 (PSK)
WEP: Wired Equivalency Protocol (WEP) encryption adds some overhead to the data, thereby
negatively effecting throughput to some degree.
The image below shows the associated configuration options:
Image 4-4-4: Encryption Type > WEP
Key Generation
4 complex WEP keys may be generated based on the supplied Passphrase
Procedure: Input a Key Phrase, select the type of Key to be generated using the
Generate Key soft button.
Using the same Passphrase on all IPn4G/VIP Series units within the network will
generate the same Keys on all units. All units must operate with the same Key
selected.
Alternately, key phrases may be entered manually into each Key field.
WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA/WPA2). It provides stronger security than WEP does. The
configuration is essentially the same as for WEP (described above), without the option for
automatic Key generation.
Show Password
Check this box to show the currently configured password for
WPA/WPA2 encryption passphrase.
Values (selection)
unchecked
© Microhard Systems Inc. 77
Page 78

4.0 Configuration
4.4.3 Wireless > HotSpot
The Wireless Hotspot configuration is used when providing public hotspot services and it is
required to use a server or web based authentication service to verify users.
Image 4-4-5: Wireless > Hotspot
Use this option to enable or disable the hotspot authentication
service.
This is the RADIUS name of your Hotspot as given by your
Hotspot Service Provider.
This field is used to specify which configured network is bonded
to the hotspot. Sub networks can be created in the Network >
LAN menu, which are dedicated to the hotspot devices.
*The DHCP service for the network used should be turned off
as all IP address assignments will be made by the hotspot
service provider.*
Hotspot Status
Values (selection)
Enable / Disable
Radius NAS ID
Values
Microhard_1
Hotspot Network
Values
Varies
© Microhard Systems Inc. 78
Page 79

4.0 Configuration
Hotspot IP Address
Specify the IP Address of the Hotspot application. All hotspot
clients will get an IP address in the same network as the
Hotspot.
Specify the Netmask of the Hotspot application. All hotspot
clients will get an IP address in the same network as the
Hotspot.
Provide your service providers 1st DNS Server address.
As assigned by the Hotspot Service Provider, the name or IP
address of the primary RADIUS Server.
Values
192.168.182.0
Hotspot Netmask
Values
255.255.255.0
DNS Domain
Values
Key.chillispot.info
Radius Server 1
Values
radius.hotspotsystem.com
Radius Server 2
As assigned by the Hotspot Service Provider, the name or IP
address of the alternate RADIUS Server.
The Radius Authentication Port Number. The default is 1812.
This is provided by your Hotspot service provider.
The Radius Account Port Number. The default is 1813. This is
provided by your Hotspot service provider.
As given by your service provider. The address of the UAM
Server, the authentication portal.
Values
radius2.hotspotsystem.com
Radius Auth Port
Values
1812
Radius Acct Port
Values
1813
Redirect URL
Values
https://
customer.hotspotsystem.com/
customer/hotspotlogin.php
© Microhard Systems Inc. 79
Page 80

4.0 Configuration
UAM Secret
This is a secret password between the Redirect URL and the
Hotspot given by the hotspot provider.
Also called a shared key, this is the RADIUS password
assigned by you Hotspot provider.
Values
hotsys123
Radius Secret
Values
hotsys123
© Microhard Systems Inc. 80
Page 81

4.0 Configuration
4.5 Comport
4.5.1 Comport > Status
The Status window gives a summary of the serial ports on the IPn4G. The Status window shows
if the com port has been enabled, how it is configured (Connect As), and the connection status.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 81
Image 4-5-1: Comport > Status
Page 82

4.0 Configuration
4.5.2 Comport > COM0/1
This menu option is used to configure the serial device server for the serial communications
port. Serial device data may be brought into the IP network through TCP, UDP, or multicast; it
may also exit the IPn4G network on another VIP Series’ serial port. The fully-featured RS232
interface supports hardware handshaking.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 82
Image 4-5-2: Comport > Settings Configuration
Page 83

4.0 Configuration
Com0/1 Port Status
Note: Most PCs do not
readily support serial
communications greater
than 115200bps.
Select operational status of the Com0/1 Serial Port. The port is
disabled by default.
Determines which serial interface shall be used to connect to
external devices: RS232, RS485, or RS422. When an interface
other than RS232 is selected, the DE9 port will be inactive.
The serial baud rate is the rate at which the modem is to
communicate with the attached local asynchronous device.
Values (selection)
Disabled / Enable
Channel Mode
Values (selection)
RS232
RS485
RS422
Data Baud Rate
Values (bps)
921600
460800
230400
115200
57600
38400
28800
19200
14400
9600
7200
4800
3600
2400
1200
600
300
Software flow control
(XON/XOFF) is not
supported.
Data Format
This setting determines the format of the data on the serial port.
The default is 8 data bits, No parity, and 1 Stop bit.
Values (selection)
8N1
8N2
8E1
8O1
7N1
7N2
7E1
7O1
7E2
7O2
Flow Control
Flow control may be used to enhance the reliability of serial data communications, particularly at
higher baud rates. If the attached device does not support hardware handshaking, leave this
setting at the default value of ‘None’. When CTS Framing is selected, the IPn4G uses the CTS
signal to gate the output data on the serial port.
Values (selection)
None
Hardware
CTS Framing
Drawing 4A: CTS Output Data Framing
© Microhard Systems Inc. 83
Page 84

4.0 Configuration
Pre-Data Delay
Refer to Drawing 6A on the preceding page.
Values (time (ms) )
100
Post-Data Delay
Refer to Drawing 6A on the preceding page.
Values (time (ms) )
100
Date Mode
This setting defines the serial output data framing. In
Transparent mode (default), the received data will be output
promptly from the IPn4G.
When set to Seamless, the serial port server will add a gap between data frames to comply with
the MODBUS protocol for example. See ‘Character Timeout’ below for related information.
Values (selection)
Seamless / Transparent
Character Timeout
In Seamless mode (see Data Mode described on the preceding
page), this setting determines when the serial server will
consider the recently-received incoming data as being ready to
transmit. As per the MODBUS standard, frames will be marked
as ‘bad’ if the time gap between frames is greater than 1.5
characters, but less than the Character Timeout value.
Values (characters)
0
The serial server also uses this parameter to determine the time gap inserted between frames.
It is measured in ‘characters’ and related to baud rate.
Example: If the baud rate is 9600bps, it takes approximately 1ms to move one character. With
the Character Timeout set to 4, the timeout period is 4ms. When the calculated time is less than
3.5ms, the serial server will set the character timeout to a minimum value of 3.5ms.
If the baud rate is greater than 19200bps, the minimum character timeout is internally set to
750us (microseconds).
Maximum Packet Size
Defines the buffer size that the serial server will use to receive
data from the serial port. When the server detects that the
Character Timeout criteria has been met, or the buffer is full, it
packetizes the received frame and transmits it.
Values (bytes)
1024
Priority
This setting effects the quality of service associated with the
data traffic on the COM port.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 84
Values (selection)
Normal / Medium / High
Page 85

4.0 Configuration
No-Connection Data
When enabled the data will continue to buffer received on the
serial data port when the radio loses synchronization. When
disabled the IPn4G will disregard any data received on the
serial data port when radio synchronization is lost.
This option will enable or disable the MODBUS decoding and
encoding features.
The field allows the MODBUS TCP Protection Status flag to be
enabled or disabled. If enabled the MODBUS data will be
encrypted with the MODBUS Protection Key.
MODBUS TCP Protection Key
MODBUS encryption key used for the MODBUS TCP
Protection Status feature.
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
MODBUS TCP Status
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
MODBUS TCP Protection
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
Values (string)
1234
© Microhard Systems Inc. 85
Page 86

4.0 Configuration
IP Protocol Config
UDP: User Datagram
Protocol does not provide
sequencing information
for the packets sent nor
does it establish a
’connection’ (‘handshakin
g’) and is therefore most
suited to communicating
small packets of data.
TCP: Transmission
Control Protocol in
contrast to UDP does
provide sequencing
information and is
connection-oriented; a
more reliable protocol,
particularly when large
amounts of data are being
communicated.
Requires more bandwidth
than UDP.
This setting determines which protocol the serial server will use
Values (selection)
to transmit serial port data over the IPn4G network.
The protocol selected in the IP Protocol Config field will
determine which configuration options appear in the remainder
of the COM0/COM1 Configuration Menu.
TCP Client
TCP Server
TCP Client/Server
UDP Point-to-Point
UDP Point-to-Multipoint (P)
UDP Point-to-Multipoint(MP)
UDP Multipoint-to-Multipoint
SMTP Client (COM0)
PPP (COM0)
GPS Transparent Mode
TCP Client: When TCP Client is selected and data is received on its serial port, the IPn4G
takes the initiative to find and connect to a remote TCP server. The TCP session is terminated
by this same unit when the data exchange session is completed and the connection timeout has
expired. If a TCP connection cannot be established, the serial port data is discarded.
Remote Server Address
IP address of a TCP server which is ready to accept serial port data through a TCP
connection. For example, this server may reside on a LAN network server.
Default: 0.0.0.0
Remote Server Port
A TCP port which the remote server listens to, awaiting a session connection
request from the TCP Client. Once the session is established, the serial port data is
communicated from the Client to the Server.
Default: 20001
Outgoing Connection Timeout
This parameter determines when the IPn4G will terminate the TCP connection if the
connection is in an idle state (i.e. no data traffic on the serial port).
Default: 60 (seconds)
TCP Server: In this mode, the IPn4G Series will not INITIATE a session, rather, it will wait for a
Client to request a session of it (it’s being the Server—it ‘serves’ a Client). The unit will ‘listen’
on a specific TCP port. If a session is established, data will flow from the Client to the Server,
and, if present, from the Server to the Client. If a session is not established, both Client-side
serial data, and Server-side serial data , if present, will be discarded.
Local Listening Port
The TCP port which the Server listens to. It allows a TCP connection to be created
by a TCP Client to carry serial port data.
Default: 20001
Incoming Connection Timeout
Established when the TCP Server will terminate the TCP connection is the
connection is in an idle state.
Default: 300 (seconds)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 86
Page 87

4.0 Configuration
TCP Client/Server: In this mode, the IPn4G will be a combined TCP Client and Server,
meaning that it can both initiate and serve TCP connection (session) requests. Refer to the
TCP Client and TCP Server descriptions and settings described previously as all information,
combined, is applicable to this mode.
A UDP or TCP port is an
application end-point.
The IP address identifies
the device and, as an
extension of the IP
address, the port
essentially ‘fine tunes’
where the data is to go
‘within the device’.
Be careful to select a port
number that is not
predetermined to be
associated with another
application type, e.g.
HTTP uses port 80.
Multicast is a one-tomany transmission of
data over an IP network.
It is an efficient method of
transmitting the same
data to many recipients.
The recipients must me
members of the specific
multicast group.
TTL: Time to Live is the
number of hops a packet
can travel before being
discarded.
In the context of multicast,
a TTL value of 1 restricts
the range of the packet to
the same subnet.
UDP Point-to-Point: In this configuration the IPn4G will send serial data to a specificallydefined point, using UDP packets. This same IPn4G will accept UDP packets from that same
point.
UDP Point-to-Multipoint (P): This mode is configured on an IPn4G which is to send multicast
UDP packets; typically, the Access Point in the IPn4G network.
IP Protocol Config (Continued…)
Remote IP Address
IP address of distant device to which UDP packets are sent when data received at
serial port.
Default: 0.0.0.0
Remote Port
UDP port of distant device mentioned above.
Default: 20001
Listening Port
UDP port which the IP Series listens to (monitors). UDP packets received on this
port are forwarded to the unit’s serial port.
Default: 20001
Multicast IP Address
A valid multicast address this unit uses to send multicast UDP packets upon
receiving data from the serial port. The default value is a good example of a valid
multicast address.
Default: 224.1.1.1
Multicast Port
A UDP port that this IP Series will send UDP packets to. The Multipoint (MP - see
the UDP Point-to-Multipoint (MP) description) stations should be configured to listen
to this point in order to receive multicast packets from this IPn4G unit.
Default: 20001
Listening Port
The UDP port that this unit receives incoming data on from multiple remote units.
Default: 20011
Time to Live
Time to live for the multicast packets.
Default: 1 (hop)
© Microhard Systems Inc. 87
Page 88

4.0 Configuration
UDP Point-to-Multipoint (MP): This protocol is selected on the units which are to receive
multicast UDP packets, typically the Remote units. See the previous description of UDP Point-to
-Multipoint (P).
In a Point-to-Multipoint
(PMP) network topology
which is to utilize UDP
multicast, typically the
MASTER would be
configured as ’(P)’ (the
POINT) and the
REMOTES would be
configured as ’(MP)’ (the
MULTIPOINTS).
UDP Multipoint-to-Multipoint
IP Protocol Config (Continued…)
Remote IP Address
The IP address of a distant device (IPn4G or, for example, a PC) to which the unit
sends UDP packets of data received on the serial port. Most often this is the IP
address of the Access Point.
Default: 0.0.0.0
Remote Port
The UDP port associated with the Remote IP Address (above). In the case of this
‘Remote’ being the VIP Series Station, the value in this field should match the
Listening Port of the Access Point (see UDP Point-to-Multipoint (P)).
Default: 20011
Multicast IP Address
A valid MULTICAST address that this unit will use to receive multicast UDP packets
sent by a UDP Point-to-Multipoint (P) unit. Note that the default value for this field
matches the default Multicast IP Address of the UDP Point-to-Multipoint (P)
configuration described on the previous page.
Default: 224.1.1.1
Multicast Port
The UDP port that this unit will use, along with the Multicast IP Address detailed
above, to receive the multicast UDP packets sent by the UDP Point-to-Multipoint (P)
unit.
Default: 20001
Multicast IP Address
A valid multicast address the unit will use to send multicast UDP packets upon
receiving them at its serial port.
Default: 224.1.1.1
Multicast Port
UDP port that the packets are sent to. Multipoint stations should be configured
to listen to this port in order to receive multicast packets.
Default: 20011
Time to Live
Time to live for the multicast packets.
Default: 1 (hop)
Listening Multicast IP Address
A valid multicast address the unit is to listen to receive multicast UDP packets
sent by another UDP Multipoint-to-Multipoint unit.
Default: 224.1.1.1
Listening Multicast Port
UDP port that the unit will listen to for multicast UDP packets sent by another
UDP Multipoint-to-Multipoint unit.
Default: 20011
© Microhard Systems Inc. 88
Page 89

4.0 Configuration
SMTP Client: If the IPn4G has Internet access, this protocol may be used to send the data
received on the serial port (COM1), in a selectable format (see Transfer Mode (below)), to an email addressee. Both the SMTP Server and the e-mail addressee must be ‘reachable’ for his
feature to function.
SMTP: Simple Mail
Transport Protocol is a
protocol used to transfer
mail across an IP
network.
IP Protocol Config (Continued…)
Mail Subject
Enter a suitable ‘e-mail subject’ (e-mail heading).
Default: COM1 Message
Mail Server (IP/Name)
IP address or ‘Name’ of SMTP (Mail) Server.
Default: 0.0.0.0
Mail Recipient
A valid e-mail address for the intended addressee, entered in the proper format.
Default: host@
Message Max Size
Maximum size for the e-mail message.
Default: 1024
Timeout (s)
How long the unit will wait to gather data from the serial port before sending an
e-mail message; data will be sent immediately upon reaching Message Max
Size.
Default: 10
Transfer Mode
Select how the data received on COM1 is to be sent to the email addressee.
Options are: Text, Attached File, Hex Code.
Default: Text
© Microhard Systems Inc. 89
Page 90

4.0 Configuration
PPP: COM0 can be configured as a PPP server for a serial connection with a PC or other device. The
attached PC could then use a dedicated serial (Windows - dialup/modem) type PPP connection to access
the network resources of the IPn4G. Note: COM1 does not support this mode.
IP Protocol Config (Continued…)
PPP Mode
Can be set for Active or Passive. If set for Active, the PPP server will initiate the PPP
connection with a PPP client. The server will periodically send out link requests following PPP
protocol. If set to Passive, the PPP server will not initiate the PPP connection with PPP client.
The server will wait passively for the client to initiate connection.
Default: Passive
Expected String
When a client (PC or device) initiates a PPP session with the modem, this is the handshaking
string that is expected in order to allow a connection. Generally this doe not need to be
changed.
Default: CLIENT
Response String
This is the handshaking string that will be sent by the modem once the expected string is
received. Generally this does not need to be changed.
Default: CLIENTSERVER
PPP LCP Echo Failure Number
The PPP server will presume the peer to be dead if the LCP echo-requests are sent without
receiving a valid LCP echo-reply. If this happens, PPP server will terminate the connection.
Use of this option requires a non-zero value for the LCP Echo Interval parameter. This option
can be used to enable PPP server to terminate after the physical connection has been
broken (e.g., the modem has hung up).
Default: 0
PPP LCP Echo Interval
The PPP server will send an LCP echo-request frame to the peer every ‘n’ seconds. Normally
the peer should respond to the echo-request by sending an echo-reply. This option can be
used with the LCP-echo-failure option to detect that the peer is no longer connected.
Default: 0
PPP Local IP
Enter the local PPP IP Address, the IP Address of the IPn4G COM0 Port.
Default: 192.168.0.1
PPP Host IP
Enter the PPP Host IP here. This is the IP of the PC or attached device.
Default: 192.168.0.99
PPP Idle Timeout(s)
It is the timeout for tearing down the ppp connection when there is no data traffic within the
time interval. When there is data coming, new ppp connection will be created.
Default: 30
© Microhard Systems Inc. 90
Page 91

4.0 Configuration
GPS Transparent Mode: When in GPS Transparent Mode, GPS data is reported out the serial
port at 1 second intervals. Sample output is shown below:
IP Protocol Config (Continued…)
Image 4-5-3: Comport > GPS Transparent Mode
© Microhard Systems Inc. 91
Page 92

4.0 Configuration
4.6 I/O
4.6.1 I/O > Status
The IPn4G has 1 status input, which can be used with various alarms and sensors for
monitoring, telling the modem when certain events have occurred, such as an intrusion alarm on
a door, a temperature threshold has been exceed, or a generator has failed, out of fuel. Also
included is 1 output, that can be used to drive external relays to remotely control equipment and
devices. The Digital I/O pins are available on the back connector shared with the input power.
Image 4-6-1: I/O > Status
Input Status
The WebUI will display the current state the input. The I/O pins are all normally open so an open
status indicates that there is nothing connected to the input pin, or that an event has not
occurred to trigger the input. The inputs have a small wetting current (Vin) used to detect a
contact closure, and prevent false readings by any noise or intermittent signals, it has a
threshold sensitivity of 1.8V.
Output Status
The WebUI will display the current state of each control output. Using the Output menu
discussed in the next section, a user can remotely control the status of the output pins.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 92
Page 93

4.0 Configuration
4.6.2 I/O > OUTPUT
The Output menu is used to open or close the output pin, allowing a user to remotely trigger an
The output pin on the IPn4G can be used to provide output signals, which can be used to drive
an external relay to control an external device. Maximum recommended load for the Output Pin
is 150mA @ 32 VDC (Vin)
Image 4-6-2: I/O > OUTPUT
© Microhard Systems Inc. 93
Page 94

4.0 Configuration
4.7 GPS
4.7.1 GPS > Location
Location Map
The location map shows the location on the IPn4G. The unit will attempt to get the GPS
coordinates from the built in GPS receiver, and if unsuccessful, will use the Cell ID location
reported by the Cellular Carrier.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 94
Image 4-7-1: GPS > Location Map
Page 95

4.0 Configuration
4.7.2 GPS > Settings
The IPn4G can be polled for GPS data via GPSD standards and/or provide customizable
reporting to up to 4 different hosts using UDP or Email Reporting.
Image 4-7-2: GPS > Settings
Enable or disable the GPS polling function of the IPn4G.
The IPn4G contains an embedded GPS feature in the cellular
module. To use the GPS features of the IPn4G a cellular antenna
must be connected to the Diversity Antenna Port.
Specify the TCP port on the IPn4G where the GPS service is
running and remote systems can connect and poll for GPSD data.
GPS Status
Values
Disable / Enable
GPS Source
Values
Embedded Carrier GPS
TCP Port
Values
2947
© Microhard Systems Inc. 95
Page 96

4.0 Configuration
4.7.3 GPS > Report
The IPn4G can provide customizable reporting to up to 4 hosts using UDP or Email Reporting.
Enable UDP and/or Email or disable GPS Reporting. Up to 4
reports can be set up and configured independently.
The interval timer specifies the frequency at which the GPS data is
reported in seconds.
© Microhard Systems Inc. 96
Image 4-7-3: GPS > GPS Report
Report Define
Values (selection)
Disable
UDP Report
Email Report
Time Interval
Values (seconds)
600
Page 97

4.0 Configuration
Message 1-4
The Message field allows customization of up to 4 different GPS messages
to be sent to the specified host.
None - Message is not used, no data will be sent
ALL - Sends all of the below
GGA - GPS Fix Data
GSA - Overall Satellite Data
GSV - Detailed Satellite Data
RMC - Recommended Min Data for GPS
VTG - Vector Track & Ground Speed
GPSGate - For use with GPSGate Tracking Software
The trigger condition defines the conditions that must be met before a GPS
update is reported. If OR is chosen, the Repeater Timer OR the Distance
trigger conditions must be met before an update is sent. The AND
condition, requires that both the Repeat timer AND the Distance trigger
conditions be met before an update is sent.
The distance parameter allows the GPS data to only be sent when
a specified distance has been traveled since the last report.
Values (selection)
None
ALL NMEA
GGA
GSA
GSV
RMC
VTG
Latitude/Longitude
GPSGate UDP Protocol
Trigger Set
Values (selection)
Only Timer
Timer AND Distance
Timer OR Distance
Distance Set
Values (meters)
1000
UDP Remote IP / Port
This is the IP Address and port of the remote host in which the UDP
packets are to be sent.
If an Email report is chosen, the subject line of the Email can be
defined here.
If an Email report is to be sent, the outgoing mail server must be
defined, and the port number.
Some outgoing mail servers required username and password to
prevent an account being used for spam. Enter the login credentials
here.
Some outgoing mail servers require a username and password to
prevent an account being used for spam. Enter the login credentials
here.
Values (Address/Port)
0.0.0.0 / 20175
Mail Subject
Values (characters)
1000
Mail Server
Values (Address:port)
smtp.gmail.com:465
Username / Password
Values (characters)
Username / password
Mail Recipient
Values (characters)
host@email.com
© Microhard Systems Inc. 97
Page 98

4.0 Configuration
4.7.4 GPS > GpsGate
The IPn4G is compatible with GpsGate - GPS Tracking Software, which is a 3rd party mapping
solution used for various GPS services including vehicle and asset tracking The IPn4G can
communicate with GpsGate via Tracker Mode and TCP/IP. (UDP reporting can also send
information to GpsGate, see the GPS > Report - UDP Reports)
Image 4-7-4: GPS > GpsGate Tracker Mode
GpsGate - Tracker Mode
Enable GpsGate Tracker Mode or TCP modes. In tracker mode
The IPn4G and GpsGate software will communicate via TCP/IP,
however if a connection is not available it will attempt to use SMS
messaging.
Server Command Channel
By default IPn4G and GpsGate will use TCP and SMS to ensure
communication between each other. It is also possible to specify
TCP or SMS communication only. Initial setup in Tracker mode
must be via SMS.
TCP Alive Mode / Alive Time Interval
TCP alive mode will keep TCP connection alive if tracker is not
enabled or the tracker interval is too long. The default is 150
seconds.
Mode Set
Values (selection)
Disable
Enable Tracker Mode
Enable TCP Send Mode
Values (seconds)
TCP and SMS
TCP Only
SMS Only
Values (seconds)
150
© Microhard Systems Inc. 98
Page 99

4.0 Configuration
Setup Phone Filter
A phone number filter can be applied to prevent SMS commands
not intended for the IPn4G from being processed.
Use this parameter to enable or disable the motion trigger in the
IPn4G.
When enabled, the IPn4G will send the current status of the Digital
I/O inputs and/or outputs to the GpsGate Server.
When GPS Invalid, Sending Data
Specify what happens when the GPS data is invalid, either use the
last valid position or do not use the last valid position.
Values (selection)
Disable: Accept All
Enable Filter
Motion Trigger
Values (selection)
Disable
Enable Motion Trigger
Send IO Status
Values (selection)
Disable
Send Input Status
Send Output Status
Send Input&Output Status
Values (selection)
Not Use Last Valid Position
Use Last Valid Position
GpsGate - TCP Mode
Image 4-7-5: GPS > GpsGate TCP Mode
© Microhard Systems Inc. 99
Page 100

4.0 Configuration
Mode Set
Enable GpsGate Tracker Mode or TCP modes. In TCP Mode the
IPn4G will establish a connection with the GpsGate Server directly
without the SMS setup process. If the TCP connection is not
available, the IPn4G will continue to try to connect every few
seconds.
Enter the IP Address of the server running the GpsGate application.
Enter the TCP Port of the server running the GpsGate application.
Define the interval at which the IPn4G will send data to the
GpsGate Server.
Values (selection)
Disable
Enable Tracker Mode
Enable TCP Send Mode
Server Address / IP
Values (IP Address)
192.168.168.1
Server Port
Values (Port)
30175
Server Interval
Values (seconds)
60
Motion Distance
Set the motion threshold in which the IPn4G will be triggered to
send location data.
When enabled, the IPn4G will send the current status of the Digital
I/O inputs and/or outputs to the GpsGate Server.
When GPS Invalid, Sending Data
Specify what happens when the GPS data is invalid, either use the
last valid position or do not use the last valid position.
Values (meters)
100
Send IO Status
Values (selection)
Disable
Send Input Status
Send Output Status
Send Input&Output Status
Values (selection)
Not Use Last Valid Position
Use Last Valid Position
© Microhard Systems Inc. 100
 Loading...
Loading...