
TC7650
Chopper Stabilized Operational Amplifier
Features
• Low Input Offset Voltage: 0.7µV Typ
• Low Input Offset Voltage Drift: 0.05µV/°C Max
• Low Input Bias Current: 10pA Max
• High Impedance DifferentialCMOS Inputs: 10
12
• High Open Loop Voltage Gain:120dB Min.
• Low Input NoiseVoltage: 2.0µVp-p
• High Slew Rate: 2.5V/µsec.
• Low Power Operation:20mW
• Output Clamp Speeds Recovery Time
• Compensated Internally for Stable Unity Gain
Operation
• Direct Replacement for ICL7650
• Available in 8-Pin Plastic DIP and 14-Pin Plastic
DIP Packages
Applications
• Instrumentation
• Medical Instrumentation
• Embedded Control
• Temperature Sensor Amplifier
• Strain GageAmplifier
Package Type
8-Pin DIP
1
C
A
Ω
–
INPUT
+
INPUT
2
TC7650CPA
3
V
SS
4
14-Pin DIP
C
B
1
C
A
2
NC
3
–
INPUT
+
INPUT
V
NC
SS
4
TC7650CPD
5
6
7
8
C
B
V
7
DD
6
OUTPUT
OUTPUT CLAMP
5
14
INT/EXT
13
EXT CLK IN
12
INT CLK OUT
V
11
DD
10
OUTPUT
9
OUTPUT CLAMP
C
8
RETN
Device Selection Table
Part
Number
TC7650CPA 8-PinPDIP 0°C to +70°C 5µV
TC7650CPD 14-Pin PDIP 0°C to +70°C 5µV
Package
Temperature
Range
Max V
NC = NO INTERNAL CONNECTION
OS
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21463B-page 1
TC7650
General Description
The TC7650 CMOS chopper stabilized operational
amplifier practically removes offset voltage error terms
from system errorcalculations.The 5µVmaximum V
OS
specification, for example, represents a 15 times
improvement over the industry standard OP07E. The
50nV/°C offset drift specification is over25 times lower
than the OP07E. The increased performance eliminates V
trim procedures, periodic potentiometer
OS
adjustmentandthereliability problemscausedbydamaged trimmers.
The TC7650 performance advantages are achieved
without the additional manufacturing complexity and
cost incurred with laser or "zener zap" V
trim tech-
OS
niques.
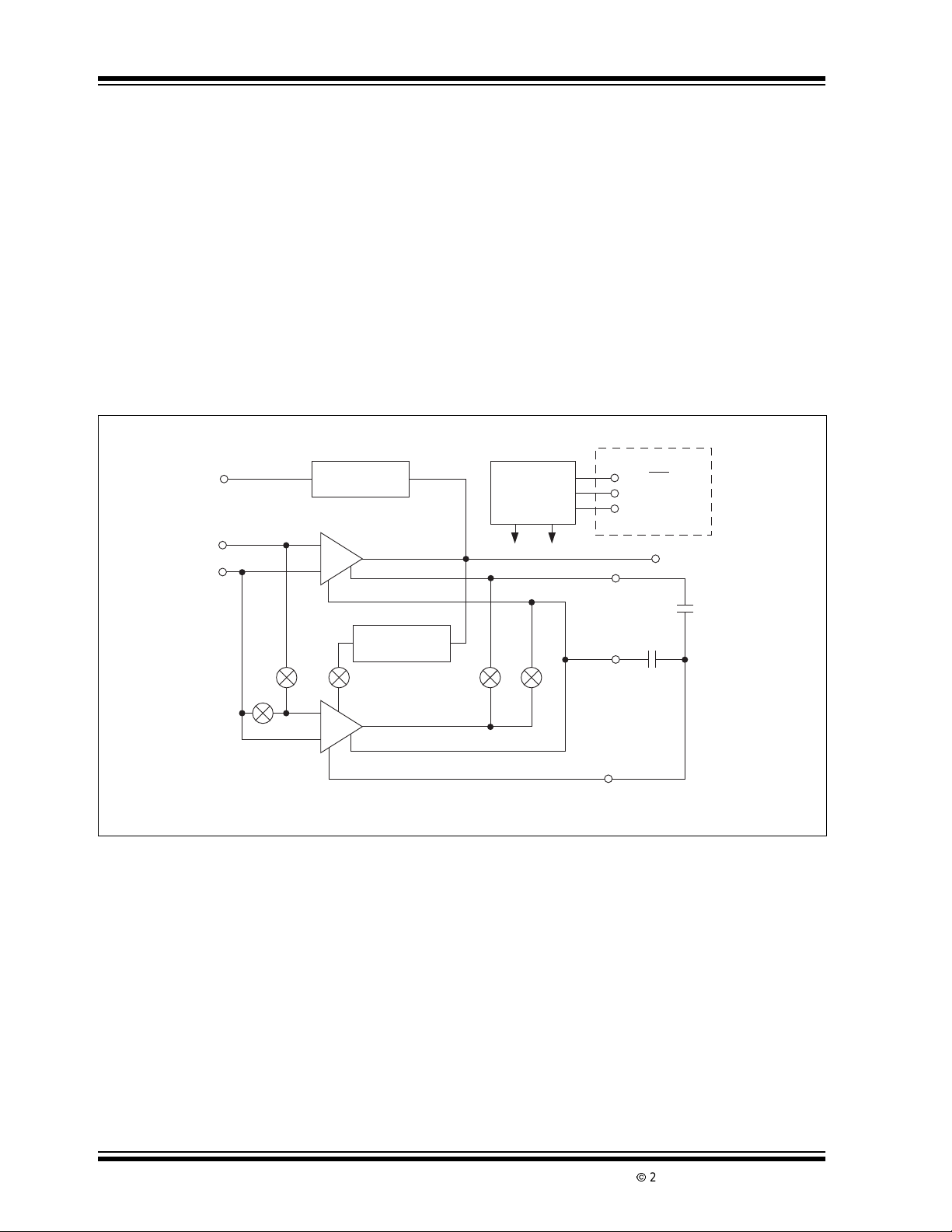
Functional Block Diagram
Output
Clamp
Inputs
Output Clamp
Circuit
Main
Amplifier
The TC7650 nulling scheme corrects both DC V
OS
errors and VOSdrift errors with temperature. A nulling
amplifieralternately correctsitsown V
main amplifier V
error. Offset nulling voltages are
OS
errorsandthe
OS
stored on two user supplied external capacitors. The
capacitors connect to the internal amplifier V
OS
null
points. The main amplifier input signal is never
switched. Switching spikes are not present at the
TC7650 output.
The 14-pin dual-in-line package (DIP) has an external
oscillatorinput to drive the nulling circuitry for optimum
noise performance. Both the 8 and 14-pin DIPs have
an output voltage clamp circuit to minimize overload
recoverytime.
14-Pin DIP Only
Oscillator
AB
INT/EXT
EXT CLK IN
CLK OUT
Output
NULL
Null
Amplifier
A
Null
*
For 8-Pin DIP, connect to V
Intermod
Compensation
BB
ss
BA
C
B
C
A
TC7650
*C
RETN
DS21463B-page 2
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.
TC7650
1.0 ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
*Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the dev ice.
These are stress ratingsonly and functional operation ofthe
device at these or any ot her conditions above those indi-
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Total SupplyVoltage (VDDto VSS) .......................+18V
Input Voltage.................... (V
+0.3V)to (VSS–0.3V)
DD
cated in the operation sections of the specifications is not
implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions
for ex tended periods my affect device reliability.
StorageTemperature Range..............-65°C to +150°C
Voltage on Oscillator Control Pins...............V
DD
to V
SS
Duration of Output Short Circuit.....................Indefinite
Current Into Any Pin............................................10mA
WhileOperating(Note 3)............................100µA
Package Power Dissipat ion (T
≤ 70°C)
A
8-Pin Plastic DIP.......................................730mW
14-Pin Plastic DIP.....................................800mW
Operating Temper ature Range
C Device .......................................... 0°C to +70°C
TC7652 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
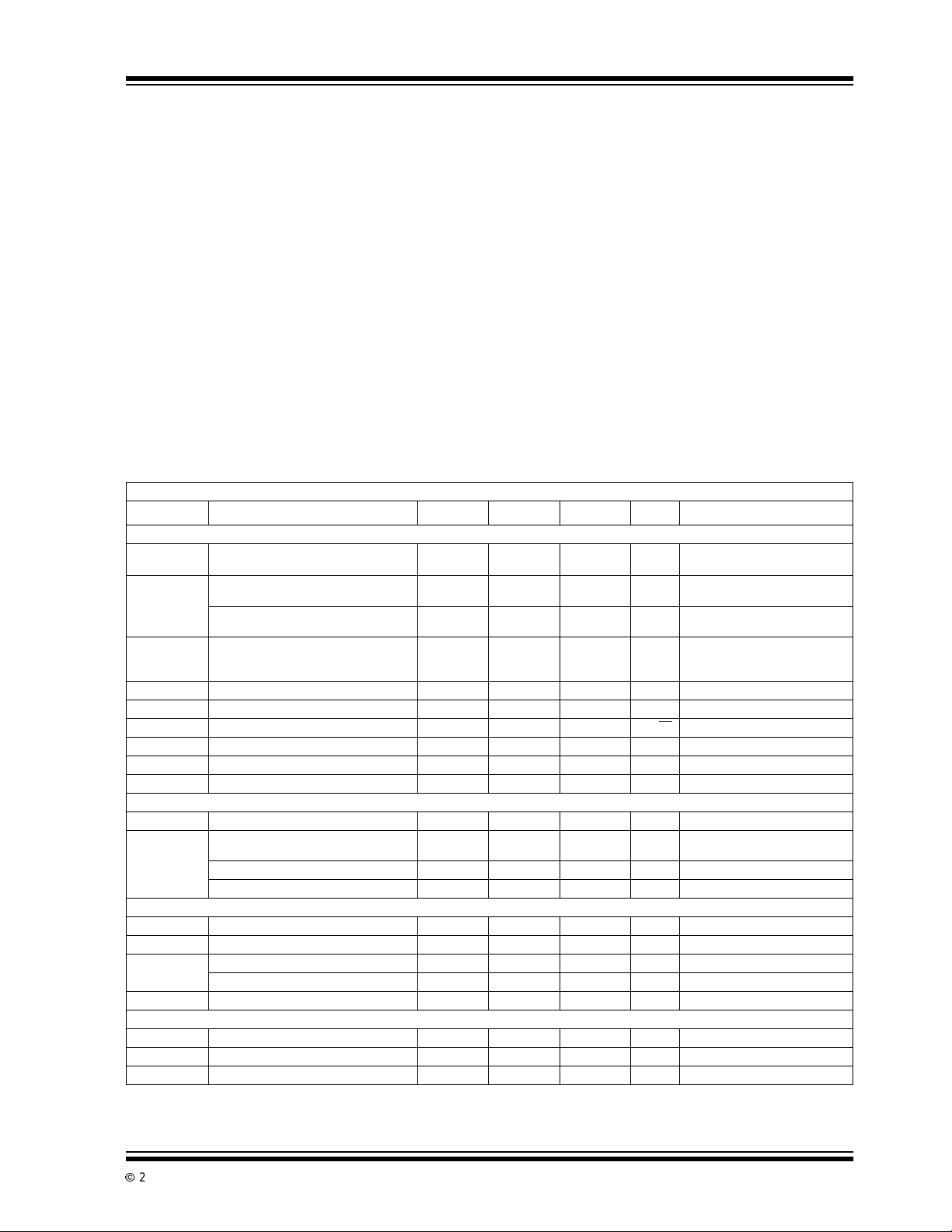
Electrical Characteristics: VDD=+5V,VSS=-5V,CA=CB=0.1µF, TA= +25°C, unless otherwise indicated.
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ Max Units Test Conditions
Input
V
OS
∆V
/∆T Input Offset Voltage A verage
OS
I
BIAS
I
OS
e
NP-P
I
N
R
IN
CMVR Common Mode Voltage Range -5 -5.2 to +2 +1.6 V
CMRR Common Mode Rejection Ratio 120 130 — dB CMVR = -5V to +1.5V
Output
A Large Signal Voltage Gain 120 130 — dB R
V
OUT
Dynamic
B
W
S
R
t
R
f
CH
Supply
V
DD,VSS
I
S
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio 120 130 dB V
Note 1: See " Output Clamp" discussion.
Input Offset Voltage —
Temperature Coefficient
Offset Voltage vs. Time — 100 — nV/
Input Bias Current —
Input Offset Current — 0.5 — pA
Input Noise Voltage — 2 — µV
Input Noise Current —
Input Resistance — 10
Output Voltage Swing (Note 2)±4.7
Clamp ON Current 25 70 200 µAR
Clamp OFF Current — 1 — pA -4V < V
Unity Gain Bandwidth — 2.0 — MHz Unity Gain (+1)
Slew Rate — 2.5 — V/µsec CL= 50pF, RL= 10kΩ
Rise Time — 0.2 — µsec
Overshoot — 20 — %
Internal Chopping Frequency 120 200 375 Hz Pins 12–14 Open (DIP)
Operating Supply Range 4.5 — 16 V
Supply Current — 2 3.5 mA No Load
2: Output clamp not connected. See typical characteristics curves for output swing versus clamp current characteristics.
3: Limiting input current to 100µA is recommended to avoid latch-up problems.
—
— 0.01 0.05 µV/°C Operating Temperature Range
—
—
—
±0.7
±1.0
1.5
35
100
0.01
±4.85
±4.95
±5
—
10
150
400
12
—pA/√Hz f=10Hz
—
—
—µVTA= +25°C
Over Operating Temp Range
month
pA
TA= +25°C
pA
0°C ≤ T
pA
P-PRS
Ω
V
V
A
-25°C ≤ T
= 100Ω, 0 to 10Hz
=10kΩ
L
RL=10kΩ
R
= 100kΩ
L
= 100kΩ (Note 1)
L
OUT
=±3Vto±8V
S
≤ +70°C
A
≤ +85°C
<+4V(Note 1)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21463B-page 3
TC7650
2.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
ThedescriptionsofthepinsarelistedinTable2-1.
TABLE 2-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Pin Number
Symbol Description
8-pin DIP 14-pin DIP
1,8 2,1 C
A,CB
Nulling capacitor pins
2 4 -INPUT Inverting Input
3 5 +INPUT Non-inverting Input
47 V
SS
59OUTPUT
Negative Power Supply
Output VoltageClamp
CLAMP
6 10 OUTPUT Output
711 V
DD
Positive Power Supply
— 3,6 NC No internal connection
—8C
RETN
Capacitor current return pin
— 12 INT CLK OUT Internal Clock Output
— 13 EXT CLK IN External Clock Input
— 14 INT/EXT
Select Internal or External Clock
3.0 DETAILED DESCRIPTION
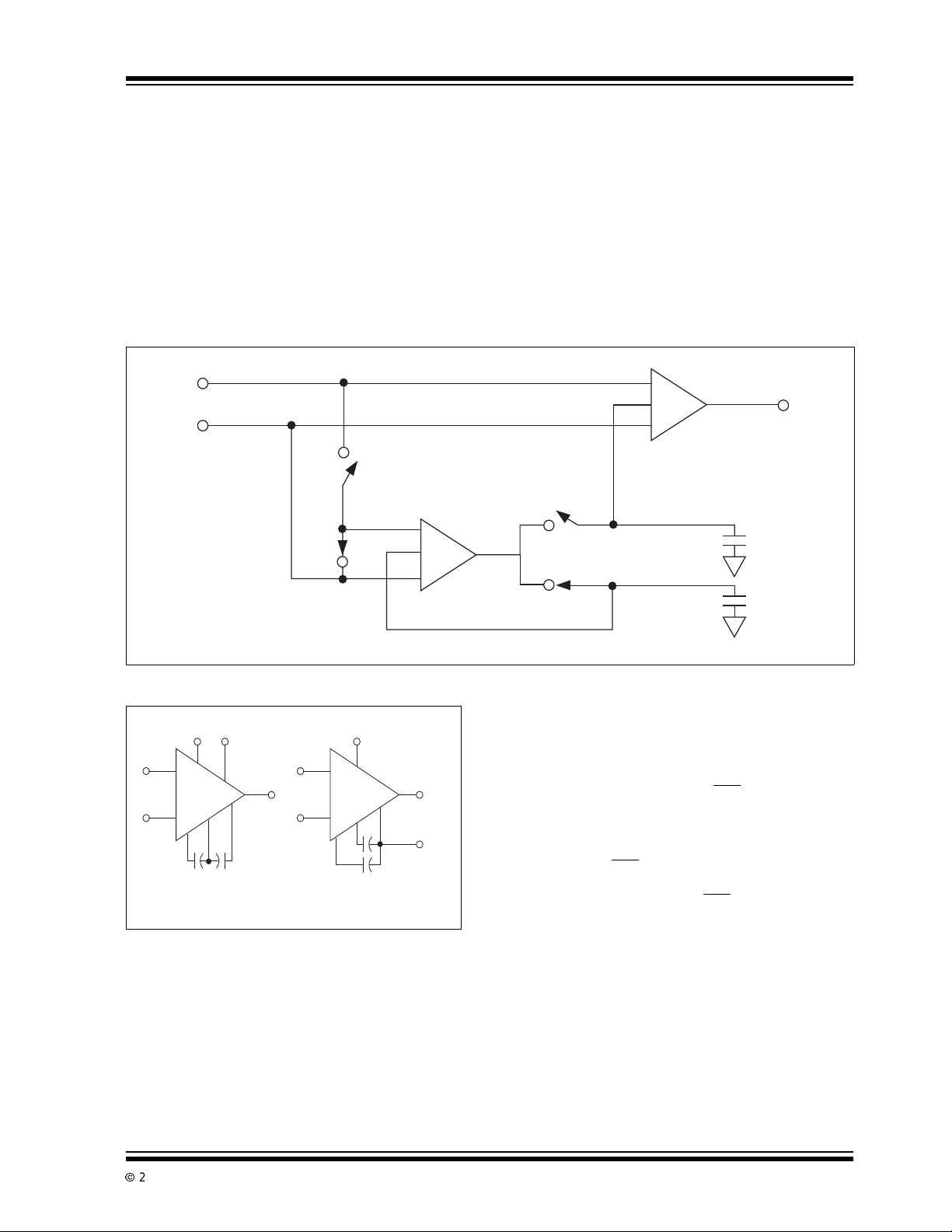
3.1 Theory of Operation
Figure 3-1 shows the major elements of the TC7650.
There are two amplifiers (the main amplifier and the
nulling amplifier), and both have offset null capability.
The main amplifier is connected full-time from the input
to the output. The nullingamplifier, underthe control of
the chopping frequency oscillator and clock circuit,
alternatelynulls itselfandthemainamplifier.Twoexternal capacitors provide the required storage of the nulling potentials and the necessary nulling loop time
constants. The nulling arrangement operates over the
full common mode and power supply ranges, and is
also independentofthe output level, thus giving exceptionally high CMRR, PSRR and A
Careful balancing of the input switches minimizes
chopper frequency charge injection at the input terminals, and the feed forward type injection into the compensationcapacitor that can cause outputspikes in this
type of circuit.
The circuit's offset voltage compensation is easily
shown. With the nulling inputs shorted, a voltage
almost identical to the nulling amplifier offset voltage is
stored on C
. The effective offset voltage at the null
A
amplifier input is:
EQUATION 3-1:
V
OSE
----------------- -V
=
AN1+
1
OSN
VOL
.
After the nulling amplifier is zeroed, the main amplifier
is zeroed; the A s witches open and B switches close.
The output voltage equation i s:
EQUATION 3-2:
V
OUT=AM[VOSM
+(V+-V-)+AN(V+-V-)+ANV
OSE
]
EQUATION 3-3:
V
+
OSMVOSN
V
OUTAMAN
V+V-–()
---------------- -------------------------- -+=
A
N
As desired, the device offset voltages are reduced by
the high open loop gai n of the nulling amplifier.
3.2 Output Stage/Loading
The output circuit is a high impedance stage (approximately 18kΩ). With loads less than this, the chopper
amplifier behaves in some ways like a trans-conductance amplifier whose open-loop gain isproportional to
load resistance. For example, the open loop gain will
be 17dB lower with a 1kΩ load than with a 10kΩ load.
If the amplifier is used strictly for DC, the lower gain is
of little consequence, since the DC gain is typically
greaterthan 120dB, even with a1kΩ load. In wideband
applications, the best frequency response will be
achieved with a load resistor of 10kΩ or higher. This
resultsin a s mooth 6dB/octave response from 0.1Hz to
2MHz, with phase shifts of less than 10° in the transi-
DS21463B-page 4
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.
TC7650
tion region, where the main amplifier takes over from
the null amplifier. The clock frequency sets the transition region.
ing sum and difference frequencies, and causing disturbances to the gain and phase versus frequency
characteristics near the chopping frequency. These
effects are substantially reduced in the TC7650 by
3.3 Intermodulation
Previous chopper stabilized amplifiers have suffered
from intermodulation effects between the chopper frequency and input signals. These arise because the
finite AC gain of the amplifier results in a small AC signal at the input. This is seen by the zeroing circuit as an
feeding the nulling circuit with a dynamic current corresponding to the compensation capacitor current in such
a way as to cancel that portion of the input signal due
to a finite AC gain. The intermodulation and gain/phase
disturbances are held to very low values, and can generally be ignored.
error signal, which is chopped and fed back, thus inject-
FIGURE 3-1: TC7650 CONTAI NS A NULLING AND MAIN AMPLIFIER. OFFSET CORRECTION
+
V
Analog Input
VOLTAGES ARE STORED ON TWO EXTERNAL CAPACITORS
+
Null
.
Main
Amplifier
-
-
V
B
A
TC7650
+
Null
-
B
A
Null
Gain = A
M
C
B
C
A
Amplifier
V
OUT
Gain = A
FIGURE 3-2: NULLING CAPACITOR
CONNECTION
2
-
TC7650
3
+
1
V
DD
7
6
4
C
B
8
C
A
V
SS
V
V
DD
SS
11
4
-
TC7650
5
+
2
14-PIN PACKAGE 8-PIN PACKAGE
CAC
7
10
1
8
B
3.4 Nulling Capacitor Connection
The offset voltage correction capacitors are connected
to C
and CB. The common capacitor connection is
A
made to V
capacitorreturn (C
The common connection should be made through a
separatePCtraceorwiretoavoidvoltagedrops.The
capacitorsoutside foil, if possible,shouldbe connected
to C
RETN
(Pin 4) on the 8-pin packages and to
SS
,Pin8)onthe14-pinpackages.
RETN
or VSS.
, Offset = V
N
OSN
3.5 Clock Operation
The internal oscillator is set for a 200Hz nominal choppingfrequencyonboththe8-and14-pinDIPs.Withthe
14-pin DIP TC7650, the 200 Hz internal chopping frequency is available at the internal clock output (Pin 12).
A 400Hz nominal signal will be present at the external
clockinput pin (Pin 13) with INT/EXT
is the internalclock signal before adivide-by-twooperation.
The 14-pin DIP device can be driven by an external
clock. The INT/EXT
input (Pin 14) hasan internal pullup and may be l eft open for internal clock operation. If
an external clock is used, INT/EXT
(Pin 7) to disable the internal clock. Theexternal clock
signal is appliedto the external clock input (Pin 13).
The external clock amplitude should swing between
V
and ground for power supplies up to ±6V and
DD
between V
+
and V+-6V for higher supply voltages.
At low frequencies the external clock duty cycle is not
critical, since an internal divide-by-two gives the
desired 50% switching duty cycle. The offset storage
correction capacitorsare charged only whenthe external clock input is high. A 50% t o 80% external clock
highoropen. This
must be tied to V
SS
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21463B-page 5

TC7650
7
positive duty cycle is desired for frequencies above
500Hz to ensure transients settle before the internal
switches open.
The external clock input can also be used as a strobe
input. If a strobe signal is connected at the external
clockinputsothatitisLOWduringthetimeanoverload
signalis applied, neither capacitor will be charged. The
leakage currents at t he capacitors pins arevery low. At
25°C a typical TC7650 willdrift less than 10µV/sec.
3.6 Output Clamp
Chopper-stabilized systems can show long recovery
times from overloads. If the output is driven to either
supply rail, output saturation occurs. The inputs are no
longer held at a "virtual ground." The V
treatsthedifferential signalas an offset and tries to correct it by charging the external capacitors. The nulling
circuit also saturates. Once the input signal returns to
normal, the response time is lengthened by the long
recovery time of the nulling amplifier and external
capacitors.
Through an external clamp connection, the TC7650
eliminates the overload recovery problem by reduci ng
the feedback network gain before the output voltage
reaches either supply rail.
FIGURE 3-3: INTERNAL CLAMP CIRCUIT
Internal
Positive Clamp Bias ≈ V+ - V
P-Channel
Output
Clamp Pin
N-Channel
null circuit
OS
≈ V+ - 0.
T
FIGURE 3-5: INVERTING AMPLIFIER WITH
OPTIONAL CLAMP
R
2
R
Input
*
Connect To V
On 8-Pin DIP.
1
–
R
Clamp
TC7650
R
+
C
µ
0.1 F
C
*
(R
For Full Clamp
Effect
µ
0.1 F
Output
R2) ‡ 100 kΩ
1
The output clamp circuit is shown in Figure 3-3, with
typical inverting and non-inverting circuit connections
shown in Figures 3-4 and 3-5. Output voltage versus
clamp circuit current characteristics are shown in the
typicaloperatingcurves.Fortheclamptobe fully effective, the i mpedance across the clampoutput should be
greater than 100kΩ.
3.7 Latch-Up Avoidance
Junction-isolated CMOS circuits inherently include a
parasitic 4-layer (p-n-p-n) structure which has characteristics similar to an SCR. Under certain circumstances this junction may be triggered into a lowimpedance state,resultingin excessive supply current.
To avoid this condition, no voltage greater t han 0.3V
beyond the supply rails should be applied to anypin.In
general, the amplifier supplies must be established
either at the sametime or before any input signals are
applied. If this is not possible, the drive circuits must
limit input current flow to under 0.1mA to avoid latchup.
FIGURE 3-4: NON-INVERTING AMPLIFIER
WITH OPTIONAL CLAMP
*
Connect To V
On 8-Pin DIP.
Input
R3 + (R1/R2) ‡ 100 kΩ
For Full Clamp Effect
DS21463B-page 6
SS
0.1µF
C
+
R
TC7650
Clamp
*
C
R
3
Output
R
2
R
1
3.8 Thermoelectric Potentials
Precision DC measurements are ultimately limited by
thermoelectric potentials developed in thermocouple
junctions of dissimilar metals, alloys, silicon, etc.
Unless all junctions are at the same temperature, thermoelectric voltages, typically around 0.1µV/°C, but up
to tens of µV/°C for some materials, will be generated.
In ordertorealizethebenefitsextremely-lowoffsetvoltages provide, it is essential to take s pecial precautions
to avoid temperature gradients. All components should
be enclosed to eliminate air movement, especially
thosecaused by power dissipatingelementsinthe system. Low thermoelectric co-efficient connections
should be used where possible andpower supply voltages and power dissipation should be kept to a minimum. High impedance loads are preferable, and
separationfrom surrounding heatdissipatingelements
is advised.
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC7650
t
3.9 Pin Compatibility
On the 8-pin mini-DIP TC7650, the external null storage capacitors are connected to pins 1and 8. Onmost
other operational amplifiers these are left open or are
used for offset potentiometer or compensation capacitor connections.
For OP05 and OP07 operational amplifiers, t he
replacement of the offset null potentiometer between
pins 1 and8 by two capacitors from the pinsto V
SS
will
convert the OP05/07 pin configurations for TC7650
operation. For LM108 devices, the compensation
capacitoris replaced by the external nulling capacitors.
The LM101/748/709 pinouts are modified similarly by
removing any circuit connections to Pin 5. On the
TC7650, Pin 5 is the output clamp connection.
Other operational amplifiers may use this pin as an offset or compensation point.
The minor modifications needed to retrofit a TC7650
into existing sockets operating at reduced power supply voltages make pr ototyping and circuit verification
straightforward.
3.10 Input Guarding
High impedance, low leakage CMOS inputs allow the
TC7650 to make measurements of high-impedance
sources. Stray leakage paths can increase input currents and decrease input resistance unless inputs are
guarded.A guard is aconductivePCtrace surrounding
the input terminals. The ring connects to a low impedance point at the same potential as the inputs. Stray
leakagesare absorbed by the lowimpedance ring. The
equal potential between ring and inputs prevents input
leakagecurrents. Typicalguardconnections are shown
in Figure 3-6.
The 14-pin DIP configuration has been specifically
designed to ease input guarding. The pins adjacent to
the inputs are unused.
In applications r equiring low leakage currents, boards
should be cleaned thoroughly and blown dry after soldering. Protective coatings will prevent future board
contamination.
FIGURE 3-6: INPUT GUARD CONNECTION
Inverting Amplifier
Input
R
1
R3*
R
2
-
+
Output
Noninverting Amplifier
R
2
*
R
R
1
NOTE: R3 =
3
Input
R
1 R2
R1 + R
-
+
Should Be Low
Impedence For
Optimum Guarding
2
Output
Follower
R3*
-
Outpu
Input
+
3.11 Component Selection
The two required capacitors,CAand CB, have optimum
values, depending on the clock or choppingfrequency.
For the preset internal clock, the correctvalue is 0.1µF.
To maintain the same relationship between the chopping frequency and the nulling time constant, the
capacitor values should be scaled in proportion to the
external clock, if used. High quality film typecapacitors
(such as Mylar) are preferred; ceramic or other lower
grade capacitors may be suitablein some applications.
For fast settling on initial turn-on, low dielectricabsorption capacitors (such as polypropy lene) should be
used. With c eramic capacitors, several seconds may
be r equired to settle to 1µV.
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21463B-page 7

TC7650
(
g)
4.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Note: The graphs andtables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range ( e.g., outside specified power supplyrange) and therefore outside the warranted range.
1 mA
0.1 mA
0.01 mA
0.01 A
CLAMP CURRENT
0.01 nA
TA = +25˚C
V
= ±5V
S
1 Am
0.1 A
m
m
1 nA
0.1 nA
1 pA
4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 5.0
3.0
TA = +25˚C
2.6
2.2
1.8
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
1.4
1.0
5 6 7 8 9 101112 131415
Positive Clamp Current
vs. Output Voltage
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Supply Current vs.
Supply Voltage
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
Negative Clamp Current
1 mA
1 Am
m
m
1 nA
1 pA
-4.0 -4.1 -4.2
TA = +25˚C
V
= ±5V
S
0.1 mA
0.01 mA
0.1 A
0.01 A
CLAMP CURRENT
0.1 nA
0.01 nA
Gain/Phase vs. Frequency
30
20
10
0
–10
–20
GAIN (dB)
–30
–40
CLOSED-LOOP
–50
GAIN = 20
–60
1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
vs. Output Voltage
-4.4 -4.5 -4.6 -4.7 -4.8 -4.9 -5.0
-4.3
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
PHASE
FREQUENCY (H )
z
GAIN
225
180
135
90
45
0
-45
-90
-135
-180
de
PHASE
DS21463B-page 8
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

5.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
5.1 Package Marking Information
Package marking information not avai lable atthistime.
5.2 Package Dimensions
8-Pin Plastic DIP
PIN 1
.260 (6.60)
.240 (6.10)
TC7650
.045 (1.14)
.030 (0.76)
.200 (5.08)
.140 (3.56)
.150 (3.81)
.115 (2.92)
14-Pin PDIP (Narrow)
.400 (10.16)
.348 (8.84)
.110 (2.79)
.090 (2.29)
.022 (0.56)
.015 (0.38)
.770 (19.56)
.745 (18.92)
.070 (1.78)
.040 (1.02)
.040 (1.02)
.020 (0.51)
.260 (6.60)
.240 (6.10)
PIN 1
.015 (0.38)
.008 (0.20)
Dimensions: inches (mm)
.310 (7.87)
.290 (7.37)
.400 (10.16)
.310 (7.87)
.310 (7.87)
.290 (7.37)
3˚MIN.
.200 (5.08)
.140 (3.56)
.150 (3.81)
.115 (2.92)
.110 (2.79)
.090 (2.29)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21463B-page 9
.070 (1.78)
.045 (1.14)
.022 (0.56)
.015 (0.38)
.040 (1.02)
.020 (0.51)
.015 (0.38)
.008 (0.20)
.400 (10.16)
.310 (7.87)
Dimensions: inches (mm)
3
˚
MIN.

TC7650
DS21463B-page 10
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC7650
SALES AND SUPPORT
Data Sheets
Products supported by a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences
and r ecommended workarounds. To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please contact one of
the following:
1. Your localMicrochip sales office
2. The Microchip Corporate Literature CenterU.S. FAX: ( 480) 792-7277
3. The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Please specify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (include Literature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the mostcurrent information on our products.
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21463B-page 11

TC7650
NOTES:
DS21463B-page 12
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. Itis your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporat ed with respect
to the accuracy or use ofsuch information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such
use or otherwise. Use ofMicrochip’sproductsascriticalcomponents in life support systems is not authorized except with
express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly orotherwise, under any intellectual property
rights.
Trademarks
TheMicrochipnameandlogo,theMicrochiplogo,FilterLab,
K
EELOQ,microID,MPLAB,PIC,PICmicro,PICMASTER,
PICSTART, PRO MATE , S EEVAL and The Embedded C ontrol
SolutionsCompany areregiste red trademarksof MicrochipTechnologyIncorp or ated intheU.S.A .andother c ountries.
dsPIC, ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLA B,
In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, microPort,
Migratable Memory, MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM,
MXDEV, PICC, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, rfPIC, Select Mode
and Total Enduranceare trademarksof MicrochipTechnology
Incorporated in theU.S.A.
Serialized Quick Turn Programming (SQTP) is a service mark
of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2002, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received QS-9000 quality system
certification for its worldwide headquarters,
design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona inJuly 1999
and Mountain View, California inMarch 2002.
The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are QS-9000 compliant for its
®
PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals,
non-volatile memory and analog products. In
addition, Microchip’s quality system for the
design and manufacture of development
systems is ISO9001 certified.
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ®code hopping
2002 Microchip TechnologyI nc. DS21463B - page 13

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200 Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: http://www.microchip.com
Rocky Mountain
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7966 Fax: 480-792-7456
Atlanta
500 Sugar Mill Road, Suite 200B
Atlanta, GA 30350
Tel: 770-640-0034 Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
2 Lan Drive, Suite 120
Westford, MA 01886
Tel: 978-692-3848 Fax: 978-692-3821
Chicago
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 630-285-0071 Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
4570 Westgrove Drive, Suite 160
Addison, TX 75001
Tel: 972-818-7423 Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Tri-Atria Office Building
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190
Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Tel: 248-538-2250 Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
2767 S. Albright Road
Kokomo, Indiana 46902
Tel: 765-864-8360 Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
18201 Von Karman, Suite 1090
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 949-263-1888 Fax: 949-263-1338
New York
150 Motor Parkway, Suite 202
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Tel: 631-273-5305 Fax: 631-273-5335
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First Street, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408-436-7950 Fax: 408-436-7955
Toro nto
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699 Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd
Suite 22, 41Rawson Street
Epping 2121, NSW
Australia
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Beijing Liaison Office
Unit 915
Bei Hai Wan Tai Bldg.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Beidajie
Beijing, 100027, No. China
Tel: 86-10-85282100 Fax: 86-10-85282104
China - Chengdu
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Chengdu Liaison Office
Rm. 2401, 24th Floor,
Ming Xing Financial Tower
No. 88 TIDU Street
Chengdu 610016, China
Tel: 86-28-6766200 Fax: 86-28-6766599
China - Fuzhou
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Fuzhou Liaison Office
Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza
No. 71 Wusi Road
Fuzhou 350001, China
Tel: 86-591-7503506 Fax: 86-591-7503521
China - Shanghai
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd.
Room 701, Bldg. B
Far East International Plaza
No. 317 Xian Xia Road
Shanghai, 200051
Tel: 86-21-6275-5700 Fax: 86-21-6275-5060
China - Shenzhen
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Liaison Office
Rm. 1315, 13/F , Shenzhen Kerry Centre,
Renminnan Lu
Shenzhen 518001, China
Tel: 86-755-2350361 Fax: 86-755-2366086
Hong Kong
Microchip Technology Hongkong Ltd.
Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza
223 Hing F ong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T., HongKong
Tel: 852-2401-1200 Fax: 852-2401-3431
India
Microchip Technology Inc.
India Liaison Office
Divyasree Chambers
1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Bangalore, 560 025, India
Tel: 91-80-2290061 Fax: 91-80-2290062
Japan
Microchip Technology Japan K.K.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shinyokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama-shi
Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea
Microchip Technology Korea
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3Floor
Samsung-Dong, K angnam-Ku
Seoul, Korea 135-882
Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-5934
Singapore
Microchip Technology Singapore Pte Ltd.
200 Middle Road
#07-02 Prime Centre
Singapore, 188980
Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Ta iw an
Microchip Technology Taiwan
11F-3, No. 207
Tung Hua North Road
Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
EUROPE
Denmark
Microchip Technology Nordic ApS
Regus Business Centre
Lautrup hoj 1-3
Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Tel: 45 4420 9895 Fax: 45 4420 9910
France
Microchip Technology SARL
Parc d’Activite du Moulinde Massy
43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Batiment A - ler Etage
91300 Massy, France
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany
Microchip Technology GmbH
Gustav-Heinemann Ring 125
D-81739 Munich, Germany
Tel: 49-89-627-144 0 Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy
Microchip Technology SRL
Centro Direzionale Colleoni
Palazzo Taurus 1 V. Le Colleoni 1
20041 Agrate Brianza
Milan, Italy
Tel: 39-039-65791-1 Fax: 39-039-6899883
United Kingdom
Arizona Microchip Technology Ltd.
505 Eskdale Road
Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham
Berkshire,England RG415TU
Tel: 44 118 921 5869 Fax: 44-118 921-5820
03/01/02
DS21463B-page 14
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...