Microchip Technology TC1186-5.0VCT, TC1186-3.6VCT, TC1186-3.3VCT, TC1186-3.0VCT, TC1186-2.8VCT Datasheet
...
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
50mA, 100mA and 150mA CMOS LDOs with Shutdown and ERROR Output
Features
• Extremely Low Ground Current forLonger
Battery Life
• Very Low Dropout Voltage
• Choice of 50mA (TC1054),100mA (TC1055)and
150mA (TC1186) Output
• High Output Voltage Accuracy
• Standard or Custom Output Voltages
• Power-Saving Shutdown Mode
• ERROR
Detector, or Processor Reset Generator
• Over Current and O ver Temperature Protection
• Space-Saving 5-Pin SOT-23A Package
• Pin Compatible Upgrades for Bipolar Regulators
Output Can Be Used as a Low Battery
Applications
• Battery Operated Systems
• PortableComputers
• Medical Instruments
• Instrumentation
• Cellular/GSM/PHSPhones
• Linear Post-Regulators for SMPS
• Pagers
Device Selection Table
Part Number Package
TC1054-xxVCT 5-Pin SOT-23A -40°C to +125°C
TC1055-xxVCT 5-Pin SOT-23A -40°C to +125°C
TC1186-xxVCT 5-Pin SOT-23A -40°C to +125°C
NOTE: xx indicates outputvoltages
Available Output Voltages: 1.8, 2.5, 2.7, 2.8, 2.85, 3.0, 3.3,
3.6, 4.0, 5.0.
Other output voltages are available. Please contact Microchip
T echnology Inc. for details.
Junction
Temp. Range
Package Type
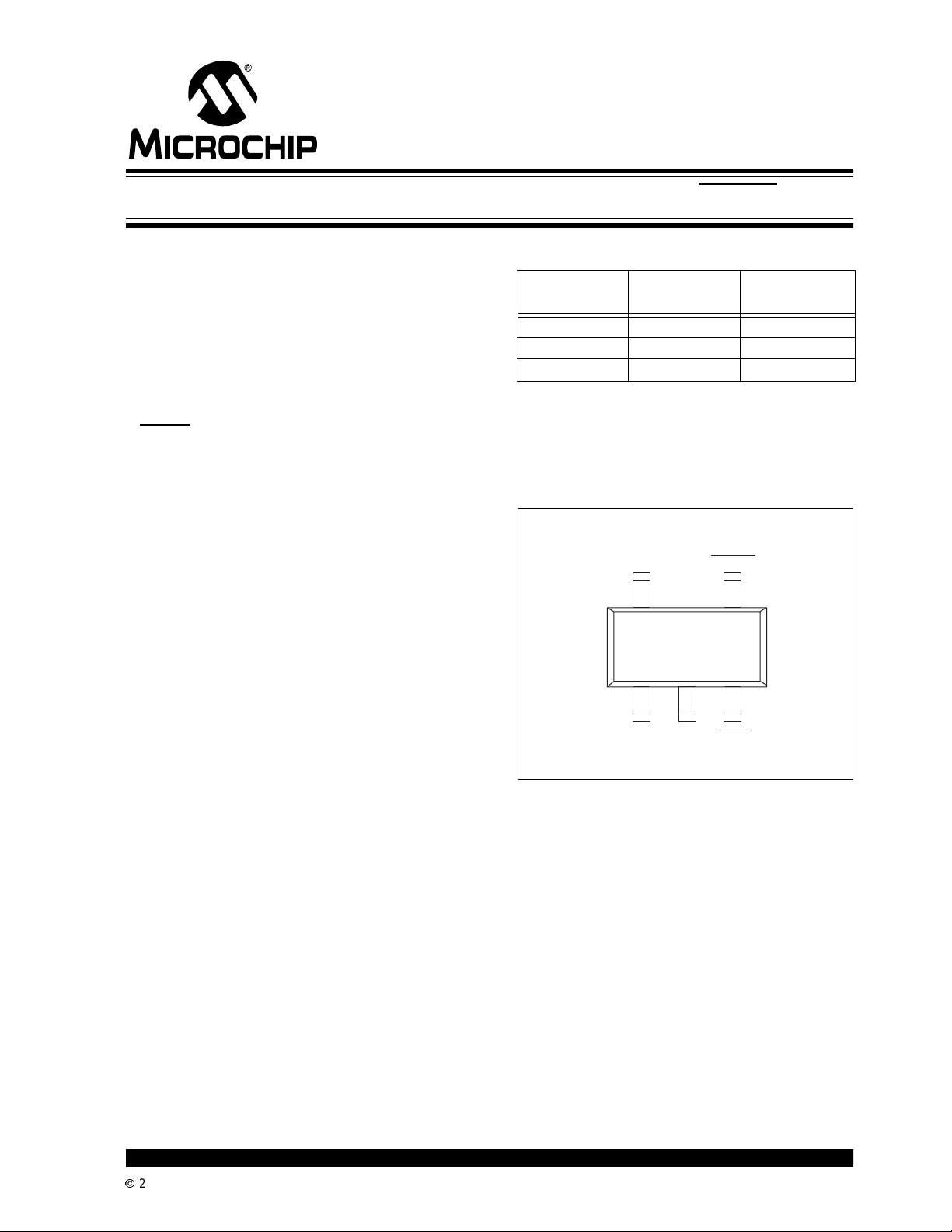
5-Pin SOT-23A
V
OUT
5
ERROR
4
TC1054
TC1055
TC1186
13
2
V
IN
NOTE: 5-Pin SOT-23A is equivalentto the EIAJ (SC-74A)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 1
GND
SHDN
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
General Description
The TC1054, TC1055 and TC1186 are high accuracy
(typically ±0.5%) CMOS upgrades for older (bipolar)
low dropout regulators. Designed specifically for
battery-operated systems, the devices’ CMOS
construction eliminates wasted ground current,
significantly extending battery life. Total supply current
is typically 50µA at full load (20 to 60 times lower than
in bipolar regulators).
The devices’ key features include ultra low noise
operation, very l ow dropout voltage – typically 85mV
(TC1054); 180mV (TC1055); and 270mV (TC1186) at
full l oad — and fast response to step changes in load.
An error output (ERROR
are out-of-regulation (due to a low input voltage or
excessive output current). ERROR
low battery war ning or as a processor RESET
(with the addition of an external RC network). Supply
current is reduced to 0.5µA (max) and both V
ERROR
are disabled when the shutdown input is low.
The devices i ncorporate both over-temperature and
over-current protection.
The TC1054, TC1055 and TC1186 are stable with an
output capacitor of only 1µF and have a maximum
output current of 50mA, 100mA and 150mA,
respectively. For higher output current regulators,
please see the TC1173 (I
) is asserted when thedevices
canbeusedasa
signal
and
OUT
= 300mA) data sheet.
OUT
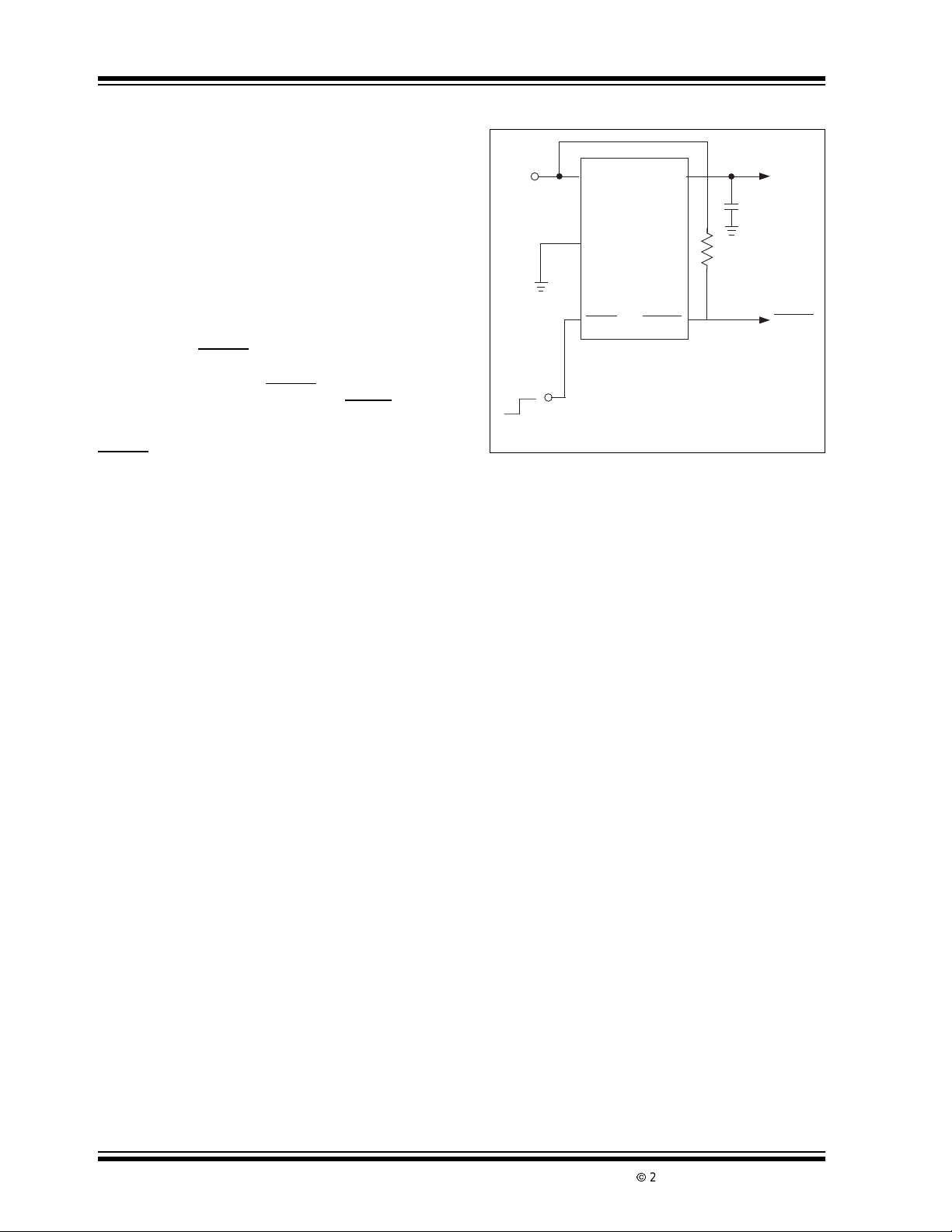
Typical Application
V
IN
(from Power Control Logic)
1
V
IN
2
GND
3
SHDN
Shutdown Control
TC1054
TC1055
TC1186
V
OUT
ERROR
5
4
V
OUT
+
1µF
ERROR
DS21350B-page 2
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
1.0 ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
Input Voltage......................................................... 6.5V
Output Voltage...........................(-0.3V) to (V
+0.3V)
IN
*Stresses above those listed under "Absolute Maximum
Ratings" may cause permanentdamage to the device. These
are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device
at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operation sections of the specifications is not implied.
Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
Power Dissipation............... Internally Limited (Note 6)
Maximum Voltage on Any Pin ........ V
OperatingTemperature Range...... -40°C < T
+0.3V to -0.3V
IN
< 125°C
J
Storage Temperature. ........................ -65°C to +150°C
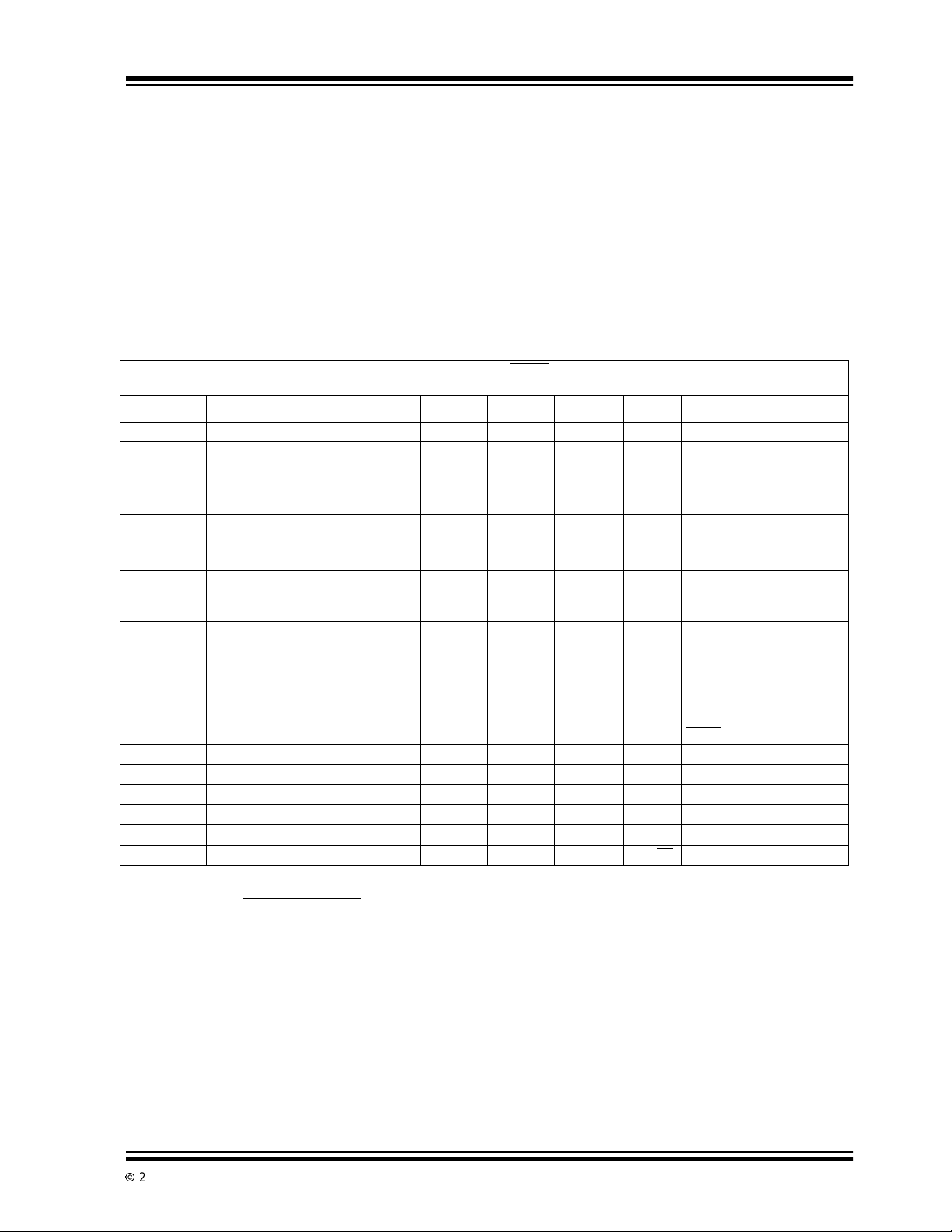
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: VIN=V
type specifications apply for junction temperatures of -40°C to +125°C.
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
V
IN
I
OUTMAX
V
OUT
TCV
OUT
/∆VINLine Regulation — 0.05 0.35 %(VR+1V)≤ VIN ≤ 6V
∆V
OUT
∆V
OUT/VOUT
V
IN-VOUT
I
IN
I
INSD
Input OperatingVoltage 2.7 — 6.0 V Note 8
Maximum Output Current 50
Output Voltage VR–2.5% VR±0.5% VR+2.5% V Note 1
V
T emperature Coefficient —
OUT
Load Regulation TC1054; TC1055
Dropout Voltage
Supply Curre nt — 50 80 µA SHDN =VIH,IL=0
Shutdown Supply Current — 0.05 0.5 µA SHDN =0V
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio — 64 — dB F
I
OUTSC
/∆PDThermal Regulation — 0.04 — V/W Notes 5, 6
∆V
OUT
T
SD
∆T
SD
Output Short Circuit Current — 300 450 mA V
Thermal Shutdown Die Temperature — 160 — °C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis — 10 — °C
eN Output Noise — 260 — nV/√Hz
Note 1: VRis the regulator output voltage setting. For example: VR= 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.7V, 2.85V, 3.0V, 3.3V,3.6V, 4.0V, 5.0V.
2:
TC V
=(V
OUT
OUTMAX–VOUTMIN
V
3: Regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low duty cycle pulse testing. Load regulation is tested over a load range
from 0.1mA to the maximum specified output current. Changes in output voltage due to heating effects are covered by the thermal
regulation specification.
4: Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its nominal value.
5: Thermal Regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time T after a change in power dissipation is applied, excluding load or
line regulation effects. Specifications are for a current pulse equal to I
6: The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable junction temperature and the
thermal resistance from junction-to-air (i.e., T
thermal shutdown. Please see Section 4.0 Thermal Considerations for more details.
7: Hysteresis voltage is referenced by V
8: Them inimum V
OUT
has to justify the conditions: VIN≥ VR+V
IN
+1V,IL=100µA, CL=3.3µF, SHD N >VIH,TA= 25°C, unless otherwise noted. Boldface
OUT
mA TC1054
TC1055
TC1186
ppm/°C Note 2
%IL= 0.1mA to I
IL= 0.1mA to I
TC1186
100
150
—
—
—
—
—
—
20
40
0.5
0.5
—
—
—
—
—
2
3
(Note 3)
mV I
=100µA
L
I
=20mA
L
I
=50mA
L
I
=100mA
L
I
=150mA(Note 4)
L
≤ 1kHz
RE
=0V
OUT
IL=I
OUTMAX
.
OUTMAX
TC1055; TC1186
TC1186
6
)x 10
x ∆T
—
—
—
—
—
, θJA). Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation causes the device to initiate
A,TJ
.
R
2
65
85
180
270
LMAX
andVIN≥ 2.7V for IL=0.1mAtoI
DROPOUT
—
—
120
250
400
at VIN= 6V for T = 10 msec.
OUTMAX
OUTMAX
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 3

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186 ELECTRICAL SPECI FICATIONS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Characteristics: VIN=V
type specifications apply for junctiontemperaturesof -40°C to +125°C.
+1V,IL=100µA, CL=3.3µF, SHDN >VIH,TA= 25°C, unless otherwise noted. Boldface
OUT
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
SHDN
Input
V
IH
V
IL
ERROR
V
INMIN
V
OL
V
TH
V
HYS
Note 1: VRis the regulator output voltage setting. For example: VR= 1.8V, 2.5V , 2.7V, 2.85V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V, 4.0V, 5.0V.
SHDN Input High Threshold 45 — — %VINVIN=2.5Vto6.5V
SHDN Input Low Threshold — — 15 %VINVIN=2.5Vto6.5V
Output
Minimum VIN Operating Voltage 1.0 — — V
Output Logic Low Voltage
ERROR ThresholdVoltage — 0.95 x V
— — 400 mV 1 mA Flows to ERROR
— V SeeFigure3-2
R
ERROR Positive Hysteresis — 50 — mV Note 7
2:
TC V
=(V
OUT
OUTMAX–VOUTMIN
V
x ∆T
3: Regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low duty cycle pulse testing. Load regulation is tested over a load range
from 0.1mA to the maximum specified output current. Changes in output voltage due to heating effects are covered by the thermal
regulation specification.
4: Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its nominal value.
5: Thermal Regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time T after a change in power dissipation is applied, excluding load or
line regulation effects. Specifications are for a current pulse equal to I
6: The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable junction temperature and the
thermal resistance from junction-to-air (i.e., T
thermal shutdown. Please see Section 4.0 Thermal Considerations for more details.
7: Hysteresis voltage is referenced by V
8: Theminimum V
OUT
has to justify the conditions: VIN≥ VR+V
IN
)x 10
6
at VIN= 6V for T = 10 msec.
LMAX
, θJA). Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation causes the device to initiate
A,TJ
.
R
and VIN≥ 2.7V for IL= 0.1mA to I
DROPOUT
OUTMAX
.
DS21350B-page 4
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.
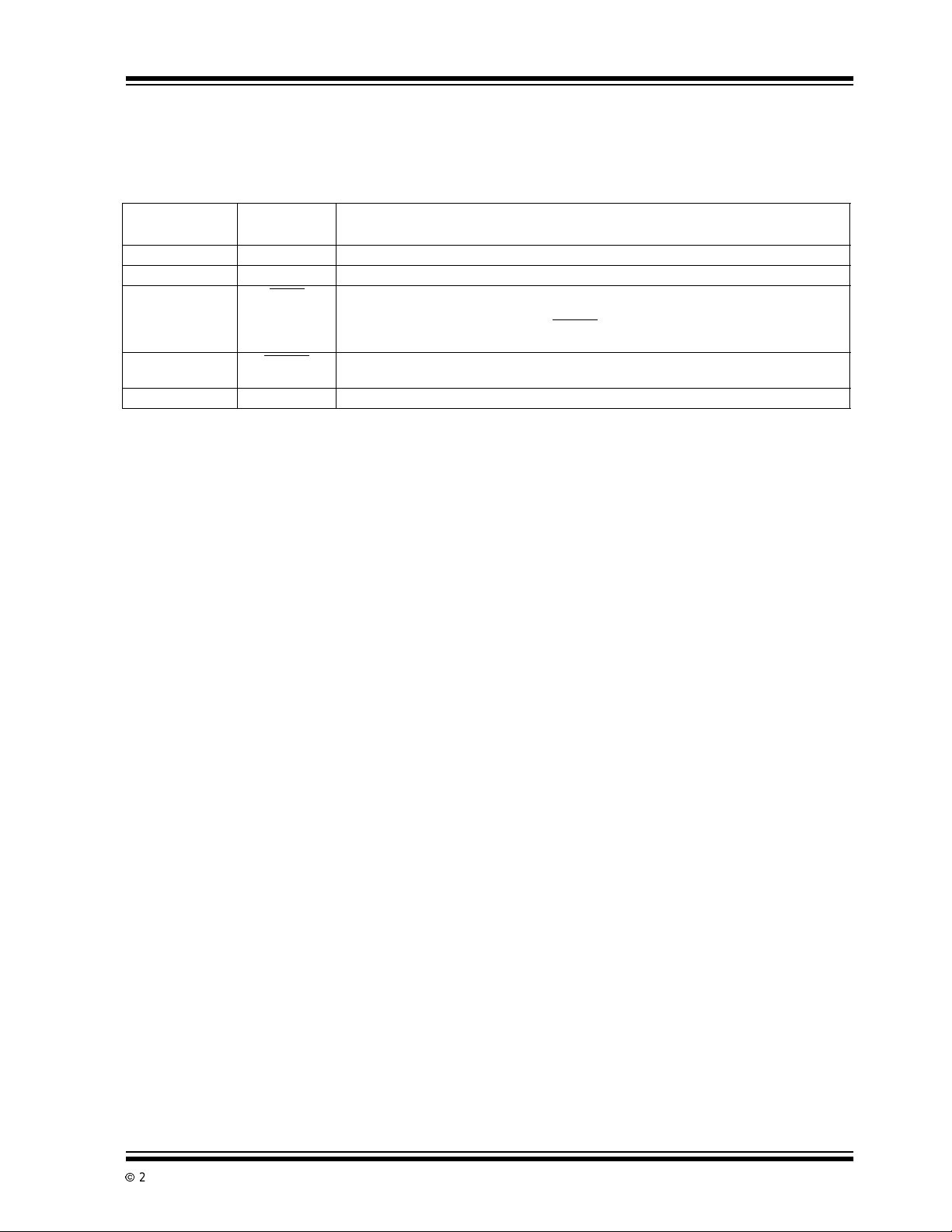
2.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
The descriptions of the pins are listed in Table 2-1.
TABLE 2-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
Pin No.
(5-Pin SOT-23A)
1V
2 GND Ground terminal.
3 SHDN
4 ERROR
5V
Symbol Description
IN
OUT
Unregulated supply input.
Shutdown control input. The regulator is fully enabled when a logic high is applied to this
input. The regulator entersshutdown when a logic low is applied to this input.During
shutdown, outputvoltage falls to zero, ERROR
reducedto0.5µA(max).
Out-of-Regulation Flag.(Open drain output).This output goes low when V
tolerance by approximately – 5%.
Regulated voltage output.
is open circuited and supply current is
is out-of-
OUT
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 5
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
3.0 DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The TC1054, TC1055 and TC1186 are precision fixed
output voltage regulators. (If an adjustable version is
desired, please see the TC1070/TC1071/TC1187 data
sheet.) Unlike bipolar regulators, the TC1054, TC1055
and TC1186supplycurrentdoesnot increasewith load
current. In addition, V
regulation over the entire 0mA to I
load current range, (an important consideration in RTC
and CMOS RAM battery back-up applications).
Figure 3-1 shows a typical application circuit. The
regulator is enabled any time the shutdown input
(SHDN
)isatoraboveVIH, and shutdown (disabled)
when SHDN
is at or below VIL. SHDN may be
controlled by a CMOS logic gate, or I/O port of a
microcontroller. If the SHDN
should be connected directly to the input supply. While
in shutdown, supply current decreases to 0.05µA
(typical), V
fallsto zero volts, and ERROR is open-
OUT
circuited.
FIGURE 3-1: TYPICAL APPLICATION
+
1µF
+
Battery
Shutdown Control
(to CMOS Logic or Tie
to V
if unused)
IN
if ERROR is used as a
Processor RESET Signal
remains stable and within
OUT
OUTMAX
input is not required, it
CIRCUIT
TC1054
TC1055
TC1186
(See Text)
V
OUT
ERROR
V+
V
IN
GND
SHDN
C2 Required Only
+
R1
1M
1µF
C1
0.2µF
C2
operating
V
OUT
BATTLOW
or RESET
3.1 ERROR Open Drain Output
ERROR is driven low whenever V
regulation by more than – 5% ( typical). This condition
may be caused by low input voltage, output current
limiting, or thermal limiting. The ERRO R
5% below rated V
outputvoltagevalue(e.g.ERROR
regardless of t he programmed
OUT
=VOLat 4.75V (typ.)
for a 5. 0V regulator and 2.85V (typ.) for a 3.0V
regulator). ERROR
output operation is shown in
Figure 3-2.
Note that ERROR
inactive when V
isactivewhen V
rises above VTHby V
OUT
OUT
As shown in Figure 3-1, ERROR
battery low flag, or as a processor RESET
the addition of timing capacitor C2). R1 x C2 should be
chosen to maintain ERROR
RESET
inputfor at least 200 msec to allow time for the
below VIHof the processor
system to stabilize. Pull-up resistor R1 can be tied to
V
OUT,VIN
or any other voltageless than (VIN+0.3V).
FIGURE 3-2: ERROR OUTPUT
OPERATION
V
OUT
V
TH
ERROR
V
IH
V
OL
falls out of
OUT
threshold is
fallsto VTH, and
.
HYS
canbeusedasa
signal (with
HYSTERESIS (VH)
3.2 Output Capacitor
A1µF(min)capacitorfromV
recommended. The output capacitor should have an
effective s eries resistance greater than 0.1Ω and less
than 5.0Ω, and a resonant frequency above 1MHz. A
1µF capacitor should be connected from V
there i s more than 10 inches of wire between the
regulator and the AC filter capacitor, or if a battery is
used as the power source. Aluminum electrolytic or
tantalum capacitor types can be used. (Since many
aluminum electrolytic capacitors freeze at approximately -30°C, solid tantalums are recommended for
applications operating below -25°C.) When operating
from sources other than batteries, supply-noise
rejection and transient response can be improved by
increasing the value of the input and output capacitors
and employing passive filtering techniques.
to ground is
OUT
to GND if
IN
DS21350B-page 6
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
4.0 THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
4.1 Thermal Shutdown
Integrated thermal protection circuitry shuts the
regulator off when die temperature exceeds 160°C.
The regulator remains off until the die temperature
drops to approximately 150°C.
4.2 Power Dissipation
The amount of power the regulator dissipates is
primarily a function of input and output voltage, and
output current. The following equation is used to
calculate worst case actual power dissipation:
EQUATION 4-1:
≈ (V
P
D
INMAX–VOUTMIN)ILOADMAX
Where:
= Worst case actual power dissipation
P
D
= Maximum voltage on V
V
INMAX
V
I
LOADMAX
= Mi nimum regulator output voltage
OUTMIN
= Maximum output ( load) current
The maximum al lowable power dissipation
(Equation 4-2) is a function of the maximum ambient
temperature (T
temperature (T
junction-to-air (θ
a θ
of approximately 220°C/Watt.
JA
), the maximum allowable die
AMAX
) and the t hermal resistance from
JMAX
). The 5-Pin SOT-23A package has
JA
IN
Equation 4-1 can be used in conjunction with
Equation 4-2 to ensure regulator thermal operation i s
within limits. For example:
Given:
V
INMAX
V
OUTMIN
I
LOADMAX
T
JMAX
T
AMAX
=3.0V±5%
=2.7V–2.5%
=40mA
= 125°C
=55°C
Find: 1. Actual power dissipation
2. Maximum allowable dissipation
Actual power dissipation:
P
D ≈ (V
INMAX–VOUTMIN)ILOADMAX
= [ (3.0 x 1.05) – (2.7 x .975)]40 x 10
–3
= 20.7mW
Maximum allowable power dissipation:
P
DMAX
=(T
JMAX–TAMAX
θ
)
JA
= (125 – 55)
220
=318mW
In this example, the TC1054 dissipates a maximum of
20.7mW; below the allowable limit of 318mW. In a
similar manner, Equation 4-1 and Equation 4-2 can be
used to calculate maximum current and/or input
voltage limits.
EQUATION 4-2:
P
Where all terms are previously defined.
DMAX
=(T
JMAX–TAMAX
4.3 Layout Considerations
)
θ
JA
The primary path of heat conduction out of the package
is via the package leads. Therefore, layouts having a
ground plane, wi de traces at the pads, and wide power
supply bus lines combine to lower θ
and therefore,
JA
increase the maximum allowable power dissipation
limit.
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 7

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
5.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Unless Otherwise Specified, All Parts Are Measured At Temperature = 25°C)
Note: The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samplesandareprovidedforinformational purposesonly.Theperformancecharacteristicslistedhereinare
not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outsidethe specified
operating range ( e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
0.020
0.018
0.016
0.014
0.012
0.010
0.008
0.006
0.004
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.002
0.000
0.200
0.180
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 10mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 12 5
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 100mA
LOAD
0.160
0.140
0.120
0.100
0.080
0.060
0.040
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
C
= 1µF
0.020
0.000
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
(V
OUT
= 3.3V)
0.100
0.090
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 50mA
LOAD
(V
= 3.3V)
OUT
0.080
0.070
0.060
0.050
0.040
0.030
0.020
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
C
= 1µF
0.010
0.000
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
(V
= 3.3V)
OUT
0.300
0.250
0.200
0.150
0.100
0.050
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.000
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 150mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
(V
= 3.3V)
OUT
90
80
70
A)
µ
60
50
40
30
20
GND CURRENT (
10
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
DS21350B-page 8
Ground Current vs. V
V
(V)
IN
(V
= 3.3V)
IN
OUT
I
LOAD
C
IN
C
OUT
= 10mA
= 1µF
= 1µF
90
80
70
A)
µ
60
50
40
30
GND CURRENT (
20
10
0
Ground Current vs. V
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
(V
= 3.3V)
IN
OUT
I
= 100mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
(V)
V
IN
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
5.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
(Unless Otherwise Specified, All Parts Are Measured At Temperature = 25°C)
80
70
Ground Current vs. VIN (V
I
= 150mA
LOAD
60
50
40
30
20
GND CURRENT (µA)
10
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
V
(V)
IN
OUT
= 3.3V)
C
C
IN
OUT
= 1µF
= 1µF
(V)
OUT
V
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
V
vs.
V
(V
IN
VIN (V)
OUT
= 3.3V)
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
OUT
I
= 0
LOAD
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7
V
vs.
V
(V
IN
VIN (V)
OUT
= 3.3V)
3.5
I
LOAD
3.0
2.5
2.0
(V)
OUT
1.5
V
1.0
0.5
0.0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7
3.290
I
LOAD
3.288
3.286
3.284
(V)
3.282
OUT
V
3.280
3.278
C
IN
C
3.276
3.274
OUT
V
IN
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
OUT
= 100mA
Output Voltage vs. Temperature (V
= 150mA
= 1µF
= 1µF
= 4.3V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
C
C
OUT
= 1µF
IN
OUT
= 3.3V)
= 1µF
3.320
3.315
Output Voltage vs. Temperature (V
I
= 10mA
LOAD
3.310
3.305
3.300
(V)
3.295
OUT
V
3.290
3.285
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
V
OUT
= 4.3V
IN
3.280
3.275
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 12 5
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUT
= 3.3V)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 9

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
Stable Region
S
n
K
5.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
(Unless Otherwise Specified, All Parts Are Measured At Temperature = 25°C)
Output Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 10mA
LOAD
V
= 6V
IN
= 1µF
C
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 12 5
Temperature
I
= 10mA
LOAD
TEMPERATURE (°C)
vs. Quiescent Current
(V)
V
OUT
A)
µ
5.025
5.020
5.015
5.010
5.005
5.000
4.995
4.990
4.985
70
60
50
40
30
20
GND CURRENT (
V
= 6V
IN
10
= 1µF
C
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
0
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
(V
(V
OUT
OUT
= 5V)
= 5V)
4.994
4.992
4.990
4.988
4.986
(V)
4.984
OUT
4.982
V
4.980
4.978
4.976
4.974
80
70
A)
60
µ
50
40
30
20
GND CURRENT (
10
0
Output Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 150mA
LOAD
V
= 6V
IN
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
Temperature vs. Quiescent Current (V
I
= 150mA
LOAD
V
= 6V
IN
C
= 1µF
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
(V
= 5V)
OUT
= 5V)
OUT
NOISE (µV/√Hz)
10.0
1.0
Output Noise vs. Frequency
0.1
0.0
0.01K
0.1K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
R
LOAD
= 1µF
C
OUT
= 1µF
C
IN
1K 10K 100K
= 50Ω
1000K
Stability Region vs. Load Current
1000
100
(Ω)
10
ESR
OUT
C
table Regio
1
0.1
0.01
10
203040
0
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
C
= 1µF
OUT
to 10µF
50 60 70 80 90 100
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
-30
I
10mA
OUT =
-35
-40
-45
-50
= 4V
V
IN
DC
= 100mV
V
IN
AC
= 3V
V
OUT
= 0
C
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
-55
-60
PSRR (dB)
-65
-70
-75
-80
0.1K
0.01K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
p-p
1K 10K
100K
1000
DS21350B-page 10
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
5.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
Conditions: C
VSHDN
VOUT
Conditions: C
VSHDN
Measure Rise Time of 3.3V LDO
= 1µF, C
IN
Temp = 25
Measure Rise Time of 5.0V LDO
= 1µF, C
IN
Temp = 25
= 1µF, I
OUT
°C, Fall Time = 184µS
= 1µF, I
OUT
°C, Fall Time = 192µS
= 100mA, VIN = 4.3V,
LOAD
= 100mA, VIN = 6V,
LOAD
Conditions: C
VSHDN
VOUT
Conditions: C
VSHDN
Measure Fall Time of 3.3V LDO
= 1µF, C
IN
Temp = 25
= 1µF, I
OUT
°C, Fall Time = 52µS
LOAD
= 100mA, VIN = 4.3V,
Measure Fall Time of 5.0V LDO
= 1µF, C
IN
Temp = 25
= 1µF, I
OUT
°C, Fall Time = 88µS
LOAD
= 100mA, VIN = 6V,
VOUT
Thermal Shutdown Response of 5.0V LDO
Conditions: V
VOUT
I
was increased until temperature of die reached about 160°C, at
LOAD
which time integrated thermal protection circuitry shuts the regulator
off when die temperature exceeds approximately 160°C. The regulator
remains off until die temperature drops to approximately 150°C.
= 6V, CIN = 0µF, C
IN
OUT
= 1µF
VOUT
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 11
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
6.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
6.1 Package Marking Information
“1” & “2” = part number code + temperature range and
voltage
(V)
1.8 CY DY PY
2.5 C1 D1 P1
2.7 C2 D2 P2
2.8 CZ DZ PZ
2.85 C8 D8 P8
3.0 C3 D3 P3
3.3 C5 D5 P5
3.6 C9 D9 P9
4.0 C0 D0 P0
5.0 C7 D7 P7
“3” represents year and quarter code
“4” represents l ot ID number
TC1054
Code
TC1055
Code
6.2 Taping Form
Component Taping Orientation for 5-Pin SOT-23A (EIAJ SC-74A) Devices
TC1186
Code
User Direction of Feed
DS21350B-page 12
Device
Marking
W
PIN 1
Standard Reel Component Orientation
TR Suffix Device
(Mark Right Side Up)
Carrier Tape, Number of Components Per Reel and Reel Size
Package Carrier Width (W) Pitch (P) Part Per Full Reel Reel Size
5-Pin SOT-23A 8 mm 4 mm 3000 7 in
P
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.
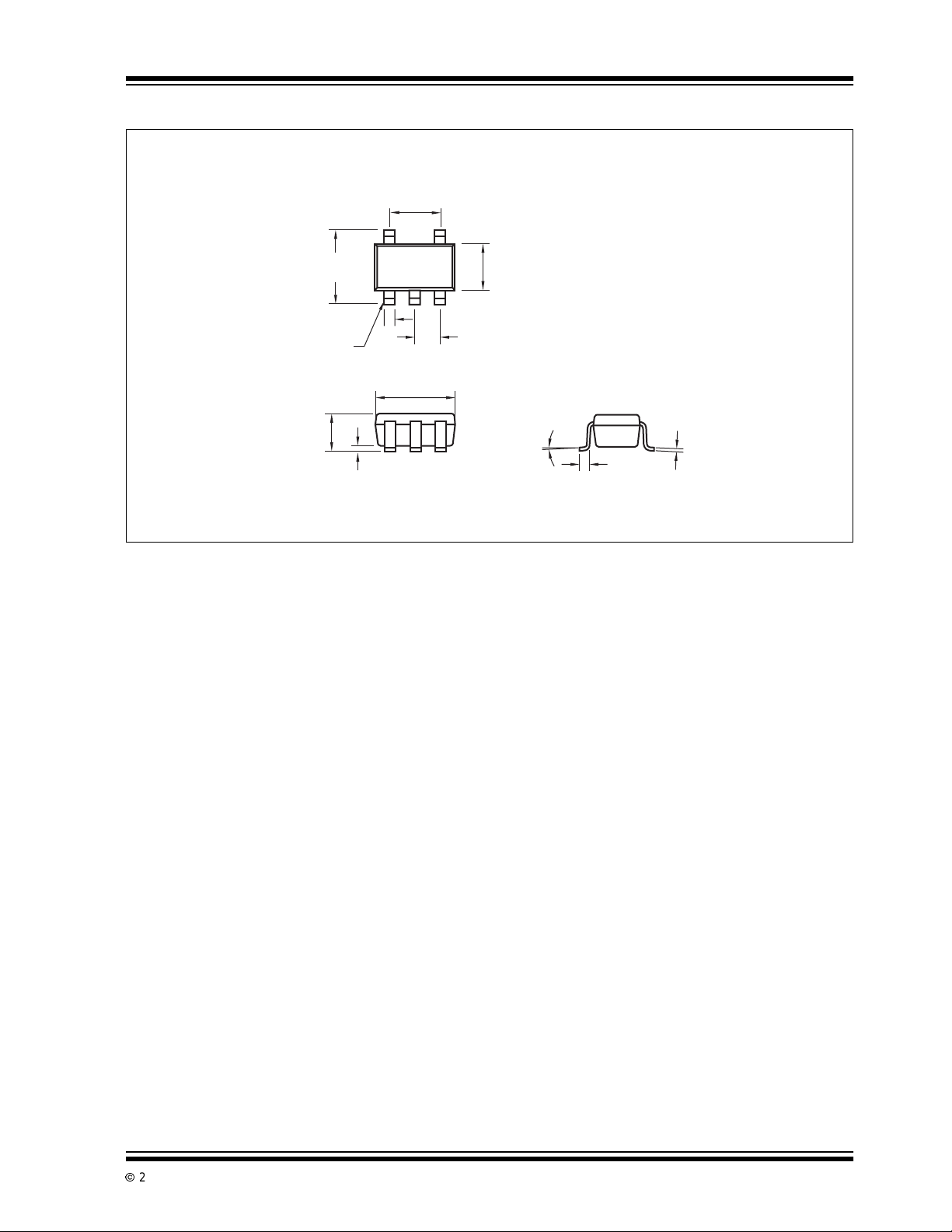
6.3 Package Dimensions
SOT-23A-5
TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
.075 (1.90)
REF.
.122 (3.10)
.098 (2.50)
.020 (0.50)
.012 (0.30)
.057 (1.45)
.035 (0.90)
PIN 1
.006 (0.15)
.000 (0.00)
.122 (3.10)
.106 (2.70)
.071 (1.80)
.059 (1.50)
.037 (0.95)
REF.
10° MAX.
.010 (0.25)
.004 (0.09)
.024 (0.60)
.004 (0.10)
Dimensions: inches (mm)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 13

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
NOTES:
DS21350B-page 14
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
SALES AND SUPPORT
Data Sheets
Products supportedby a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences and recommendedworkarounds.To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particulardevice, please contactoneof the following:
1. Your local Microchip sales office
2. The Microchip Corporate Literature CenterU.S.FAX: (480) 792-7277
3. The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Pleasespecify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (includeLiterature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21350B-page 15

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
NOTES:
DS21350B-page 16 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.

TC1054/TC1055/TC1186
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect
to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such
use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical components in life support systems is not authorized except with
express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual property
rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, FilterLab,
K
EELOQ,microID,MPLAB,PIC,PICmicro,PICMASTER,
PICSTART, PRO MATE, SEEVAL and The Embedded Control
SolutionsCompany areregiste red trademarksof MicrochipTechnologyIncorp or ated in the U.S.A. and other countries .
dsPIC, ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, Fle xR OM , fuzz yLAB,
In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, microPort,
Migratable Memory, MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM,
MXDEV,MXLAB, PICC, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, rfPIC, Select
Mode and Total Endurance are trademarks of Microchip
TechnologyIncorporated in the U.S.A.
Serialized Quick Turn Programming (SQTP) is a service mark
of Microchip TechnologyIncorporated in t he U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2002, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserve d.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received QS-9000 quality system
certification for its worldwide headquarters,
design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona in July 1999
and Mountain View,California in March 2002.
The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are QS-9000 compliant for its
®
PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals,
non-volatile memory and analog products. In
addition, Microchip’s quality system for the
design and manufacture of development
systemsisISO 9001certified.
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21350B-page 17
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ®code hopping

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200 Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: http://www.microchip.com
Rocky Mountain
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7966 Fax: 480-792-7456
Atlanta
500 Sugar Mill Road, Suite 200B
Atlanta, GA 30350
Tel: 770-640-0034 Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
2 Lan Drive, Suite 120
Westford, MA 01886
Tel: 978-692-3848 Fax: 978-692-3821
Chicago
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 630-285-0071 Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
4570 Westgrove Drive, Suite 160
Addison, TX 75001
Tel: 972-818-7423 Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Tri-Atria Office Building
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190
Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Tel: 248-538-2250 Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
2767 S. Albright Road
Kokomo, Indiana 46902
Tel: 765-864-8360 Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
18201 Von Karman, Suite 1090
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 949-263-1888 Fax: 949-263-1338
New York
150 Motor Parkway, Suite 202
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Tel: 631-273-5305 Fax: 631-273-5335
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First Street, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408-436-7950 Fax: 408-436-7955
Toronto
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699 Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd
Suite 22, 41 Rawson Street
Epping 2121, NSW
Australia
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Beijing Liaison Office
Unit 915
Bei Hai Wan Tai Bldg.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Beidajie
Beijing, 100027, No. China
Tel: 86-10-85282100 Fax: 86-10-85282104
China - Chengdu
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Chengdu Liaison Office
Rm. 2401, 24th Floor,
Ming Xing Financial Tower
No. 88 TIDU Street
Chengdu 610016, China
Tel: 86-28-86766200 Fax: 86-28-86766599
China - Fuzhou
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Fuzhou Liaison Office
Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza
No. 71 Wusi Road
Fuzhou 350001, China
Tel: 86-591-7503506 Fax: 86-591-7503521
China - Shanghai
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd.
Room 701, Bldg. B
Far East International Plaza
No. 317 Xian Xia Road
Shanghai, 200051
Tel: 86-21-6275-5700 Fax: 86-21-6275-5060
China - Shenzhen
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Liaison Office
Rm. 1315, 13/F , Shenzhen Kerry Centre,
Renminnan Lu
Shenzhen 518001, China
Tel: 86-755-2350361 Fax: 86-755-2366086
China - Hong K ong SAR
Microchip Technology Hongkong Ltd.
Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-1200 Fax: 852-2401-3431
India
Microchip Technology Inc.
India Liaison Office
Divyasree Chambers
1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Bangalore, 560 025, India
Tel: 91-80-2290061 Fax: 91-80-2290062
Japan
Microchip Technology Japan K.K.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shinyokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama-shi
Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea
Microchip Technology Korea
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku
Seoul, Korea 135-882
Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-5934
Singapore
Microchip Technology Singapore Pte Ltd.
200 Middle Road
#07-02 Prime Centre
Singapore, 188980
Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan
Microchip Technology Taiwan
11F-3, No. 207
Tung HuaNorth Road
Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
EUROPE
Denmark
Microchip Technology Nordic ApS
Regus Business Centre
Lautrup hoj 1-3
Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Tel: 45 4420 9895 Fax: 45 4420 9910
France
Microchip Technology SARL
Parc d’Activite du Moulin de Massy
43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Batiment A - ler Etage
91300 Massy, France
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany
Microchip Technology GmbH
Gustav-Heinemann Ring 125
D-81739 Munich, Germany
Tel: 49-89-627-144 0 Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy
Microchip Technology SRL
Centro Direzionale Colleoni
Palazzo Taurus 1 V. Le Colleoni 1
20041 Agrate Brianza
Milan, Italy
Tel: 39-039-65791-1 Fax: 39-039-6899883
United Kingdom
Microchip Ltd.
505 Eskdale Road
Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham
Berkshire, EnglandRG41 5TU
Tel: 44 118 921 5869 Fax: 44-118921-5820
05/01/02
DS21350B-page 18
*DS21350B*
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...