Microchip Technology TC1044SEOA, TC1044SCPA, TC1044SCOA, TC1044SMJA, TC1044SIJA Datasheet
...
EVALUATION
KIT
AVAILABLE
Charge Pump DC-TO-DC Voltage Converter
TC1044S
FEATURES
■ Converts +5V Logic Supply to ±5V System
■ Wide Input Voltage Range ....................1.5V to 12V
■ Efficient Voltage Conversion.........................99.9%
■ Excellent Power Efficiency ............................... 98%
■ Low Power Consumption ............ 80µA @ VIN = 5V
■ Low Cost and Easy to Use
— Only Two External Capacitors Required
■ RS-232 Negative Power Supply
■ Available in 8-Pin Small Outline (SOIC) and 8-Pin
Plastic DIP Packages
■ Improved ESD Protection ..................... Up to 10kV
■ No External Diode Required for High Voltage
Operation
■ Frequency Boost Raises F
PIN CONFIGURATION (DIP AND SOIC)
BOOST
CAP
GND
CAP
1
+
2
3
–
4
TC1044SCPA
TC1044SEPA
TC1044SIJA
TC1044SMJA
+
8
V
7
OSC
LOW
6
VOLTAGE (LV)
V
5
OUT
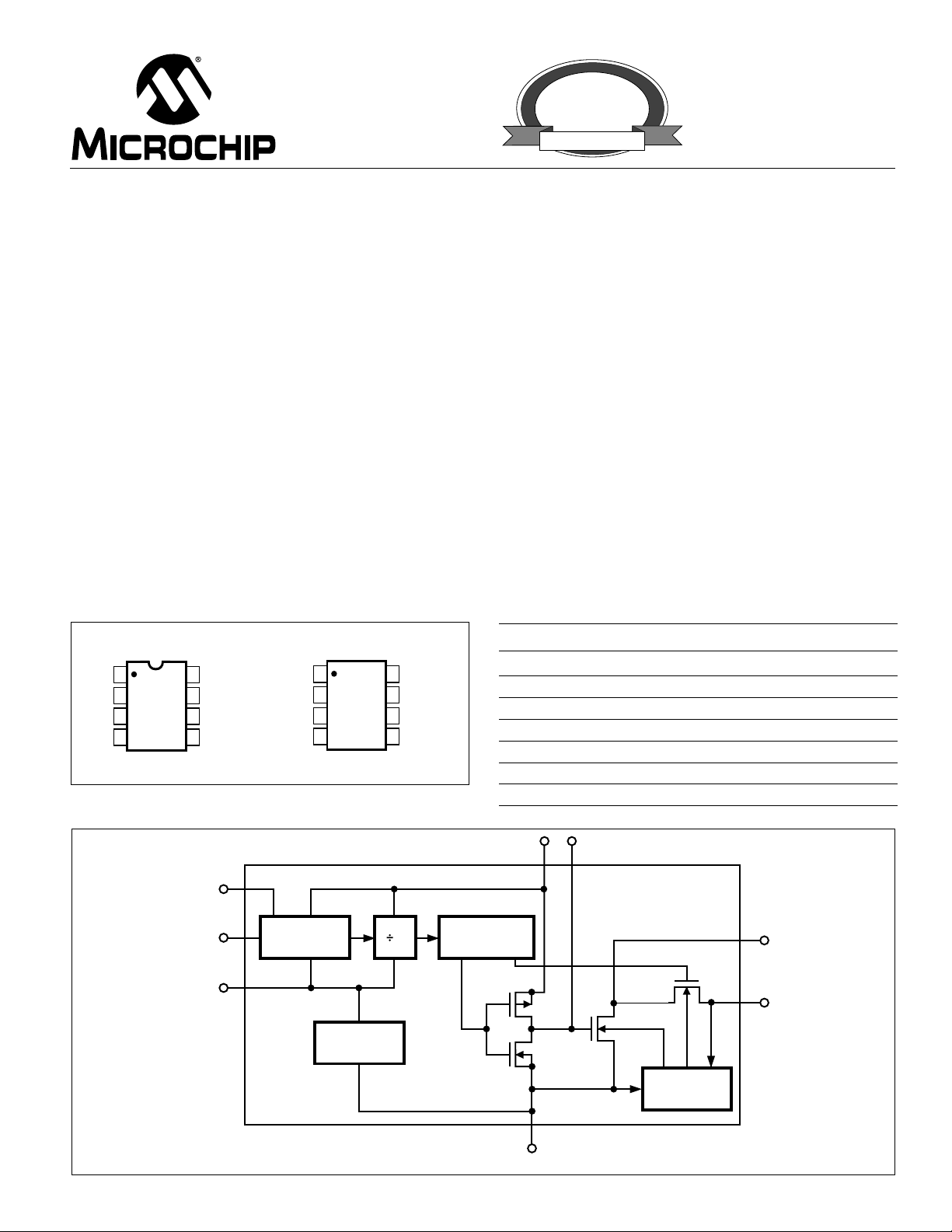
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
BOOST
1
OSC
BOOST
CAP
GND
CAP
to 45kHz
1
+
2
TC1044SCOA
TC1044SEOA
3
–
4
+
8
V
7
OSC
LOW
6
VOLTAGE (LV)
V
5
OUT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TC1044S is a pin-compatible upgrade to the Industry standard TC7660 charge pump voltage converter. It
converts a +1.5V to +12V input to a corresponding –1.5V
to –12V output using only two low cost capacitors, eliminating inductors and their associated cost, size and EMI.
Added features include an extended supply range to 12V,
and a frequency boost pin for higher operating frequency,
allowing the use of smaller external capacitors.
The on-board oscillator operates at a nominal frequency
of 10kHz. Frequency is increased to 45kHz when pin 1 is
connected to V+. Operation below 10kHz (for lower supply
current applications) is possible by connecting an external
capacitor from OSC to ground (with pin 1 open).
The TC1044S is available in both 8-pin DIP and
8-pin small outline (SOIC) packages in commercial and
extended temperature ranges.
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part No. Package Temp. Range
TC1044SCOA 8-Pin SOIC 0°C to +70°C
TC1044SCPA 8-Pin Plastic DIP 0°C to +70°C
TC1044SEOA 8-Pin SOIC – 40°C to +85°C
TC1044SEPA 8-Pin Plastic DIP – 40°C to +85°C
TC1044SIJA 8-Pin CerDIP – 25°C to +85°C
TC1044SMJA 8-Pin CerDIP – 55°C to +125°C
TC7660EV Charge Pump Family Evaluation Kit
+
V
82
CAP
+
OSC
LV
© 2001 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21348A
7
OSCILLATOR
6
TC1044S
RC
INTERNAL
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
2
VOLTAGE–
LEVEL
TRANSLATOR
3
GND
LOGIC
NETWORK
4
5
–
CAP
V
OUT
TC1044S-12 9/16/96
TC1044S
Charge Pump DC-TO-DC Voltage Converter
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Package Power Dissipation (TA ≤ 70°C) (Note 2)
8-Pin CerDIP ..................................................800mW
Supply Voltage ......................................................... +13V
LV, Boost and OSC Inputs
Voltage (Note 1) .........................– 0.3V to (V++ 0.3V)
for V+ < 5.5V
(V+ – 5.5V) to (V++ 0.3V)
for V+ > 5.5V
Current Into LV (Note 1)...................... 20µA for V+ > 3.5V
Output Short Duration (V
≤ 5.5V) .........Continuous
SUPPLY
8-Pin Plastic DIP.............................................730mW
8-Pin SOIC .....................................................470mW
Operating Temperature Range
C Suffix .................................................. 0°C to +70°C
I Suffix...............................................– 25°C to +85°C
E Suffix .............................................– 40°C to +85°C
M Suffix...........................................– 55°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature Range ................– 65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) .................+300°C
*Static-sensitive device. Unused devices must be stored in conductive material. Protect devices from static discharge and static fields. Stresses above those
listed under "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device
at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operation sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS: T
= +25°C, V+ = 5V, C
A
= 0, Test Circuit (Figure 1), unless otherwise
OSC
indicated.
Symbol Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
+
I
+
I
+
V
H2
+
V
L2
R
OUT
F
OSC
P
EFF
V
OUT EFF
Z
OSC
NOTES: 1. Connecting any input terminal to voltages greater than V+ or less than GND may cause destructive latch-up. It is recommended that no
Supply Current RL = ∞ — 80 160 µA
0°C < T
– 40°C < T
< +70°C — — 180
A
< +85°C — — 180
A
– 55°C < TA < +125°C — — 200
Supply Current 0°C < TA < +70°C — — 300 µA
(Boost Pin = V
+
)– 40°C < TA < +85°C — — 350
– 55°C < TA < +125°C — — 400
Supply Voltage Range, High Min ≤ TA ≤ Max, 3 — 12 V
RL = 10 kΩ, LV Open
Supply Voltage Range, Low Min ≤ TA ≤ Max, 1.5 — 3.5 V
RL = 10 kΩ, LV to GND
Output Source Resistance I
= 20mA — 60 100 Ω
OUT
I
= 20mA, 0°C ≤ TA ≤ +70°C — 70 120
OUT
= 20mA, –40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C — 70 120
I
OUT
I
= 20mA, –55°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C — 105 150
OUT
V+ = 2V, I
0°C ≤ T
= 3 mA, LV to GND
OUT
≤ +70°C — — 250 Ω
A
– 55°C ≤ TA ≤ +125°C — — 400
Oscillator Frequency Pin 7 open; Pin 1 open or GND — 10 — kHz
Boost Pin = V
+
—45—
Power Efficiency RL = 5 kΩ; Boost Pin Open 96 98 — %
< TA < T
T
MIN
Boost Pin = V
; Boost Pin Open 95 97 —
MAX
+
—88—
Voltage Conversion Efficiency RL = ∞ 99 99.9 — %
Oscillator Impedance V+ = 2V — 1 — MΩ
V+ = 5V — 100 — kΩ
inputs from sources operating from external supplies be applied prior to "power up" of the TC1044S.
2. Derate linearly above 50°C by 5.5mW/°C.
TC1044S-12 9/16/96
2
© 2001 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21348A
Charge Pump DC-TO-DC Voltage Converter
TC1044S
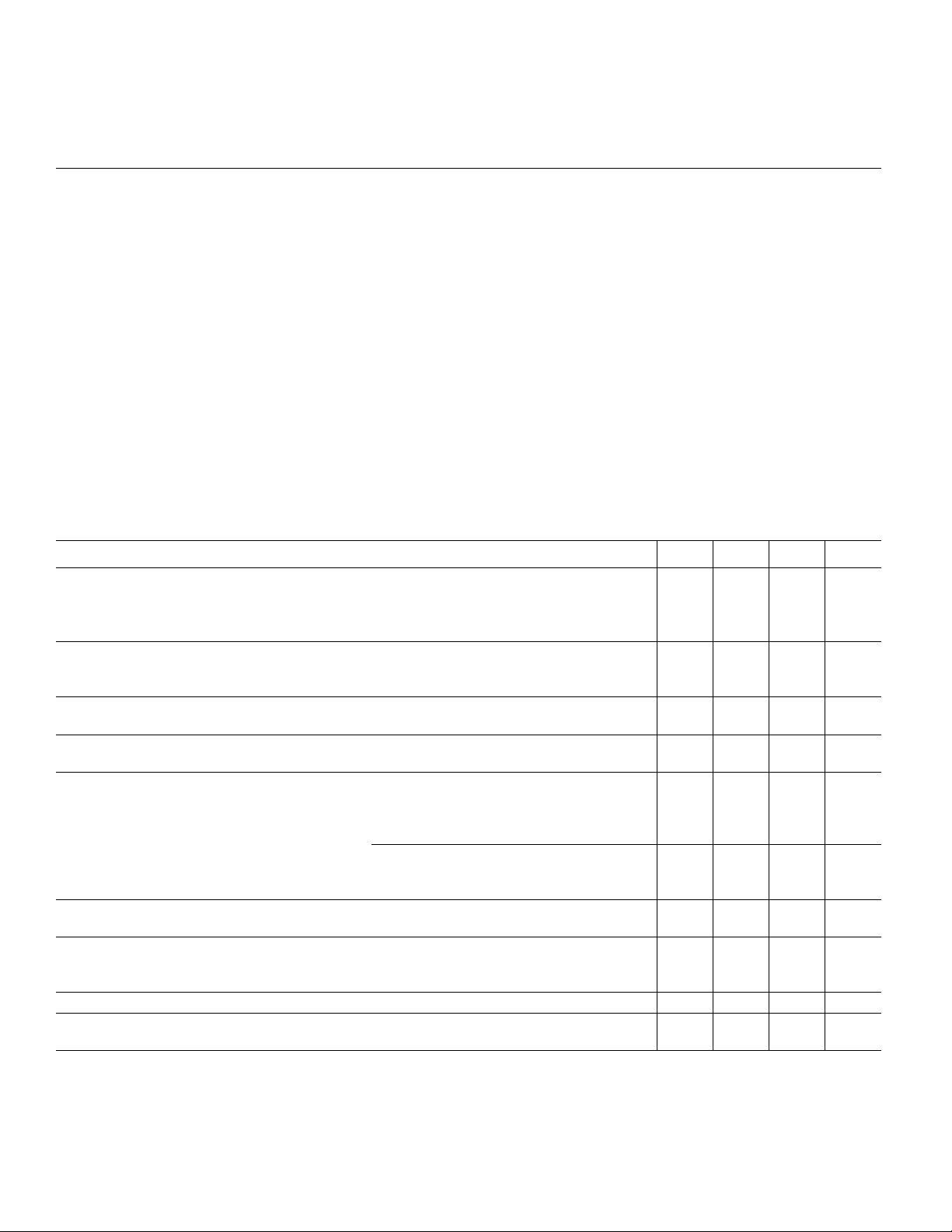
Circuit Description
The TC1044S contains all the necessary circuitry to
implement a voltage inverter, with the exception of two
external capacitors, which may be inexpensive 10 µF polarized electrolytic capacitors. Operation is best understood by
considering Figure 2, which shows an idealized voltage
inverter. Capacitor C1 is charged to a voltage, V+, for the half
cycle when switches S1 and S3 are closed. (Note: Switches
S2 and S4 are open during this half cycle.) During the second
half cycle of operation, switches S2 and S4 are closed, with
S1 and S3 open, thereby shifting capacitor C1 negatively by
V+ volts. Charge is then transferred from C1 to C2, such that
the voltage on C2 is exactly V+, assuming ideal switches and
no load on C2.
The four switches in Figure 2 are MOS power switches;
S1 is a P-channel device, and S2, S3 and S4 are N-channel
devices. The main difficulty with this approach is that in
integrating the switches, the substrates of S3 and S4 must
always remain reverse-biased with respect to their sources,
but not so much as to degrade their ON resistances. In
addition, at circuit start-up, and under output short circuit
conditions (V
and the substrate bias adjusted accordingly. Failure to
accomplish this will result in high power losses and probable
device latch-up.
This problem is eliminated in the TC1044S by a logic
network which senses the output voltage (V
with the level translators, and switches the substrates of
S3 and S4 to the correct level to maintain necessary reverse
bias.
+
V
+
C
1
1µF
= V+), the output voltage must be sensed
OUT
OUT
1
2
3
4
TC1044S
8
7
*
6
5
C
OSC
) together
I
S
+
V
(+5V)
I
L
R
L
S
V
+
GND
1
S
3
Figure 2. Idealized Charge Pump Inverter
S
2
C
1
C
S
4
2
V
= – V
OUT
IN
The voltage regulator portion of the TC1044S is an
integral part of the anti-latch-up circuitry. Its inherent voltage
drop can, however, degrade operation at low voltages. To
improve low-voltage operation, the “LV” pin should be
connected to GND, disabling the regulator. For supply
voltages greater than 3.5V, the LV terminal must be left
open to ensure latch-up-proof operation and prevent device
damage.
Theoretical Power Efficiency
Considerations
In theory, a capacitive charge pump can approach
100% efficiency if certain conditions are met:
(1) The drive circuitry consumes minimal power.
(2) The output switches have extremely low ON
resistance and virtually no offset.
(3) The impedances of the pump and reservoir
capacitors are negligible at the pump frequency.
The TC1044S approaches these conditions for negative voltage multiplication if large values of C1 and C2 are
used. Energy is lost only in the transfer of charge
between capacitors if a change in voltage occurs. The
energy lost is defined by:
NOTE: For large values of C
and C2 should be increased to 100µF.
of C
1
Figure 1. TC1044S Test Circuit
© 2001 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21348A
+
(>1000pF), the values
OSC
C
2
10µF
V
OUT
2
E = 1/2 C1 (V
1
– V
2
)
2
V1 and V2 are the voltages on C1 during the pump and
transfer cycles. If the impedances of C1 and C2 are relatively
high at the pump frequency (refer to Figure 2) compared to
the value of RL, there will be a substantial difference in
voltages V1 and V2. Therefore, it is desirable not only to
make C2 as large as possible to eliminate output voltage
ripple, but also to employ a correspondingly large value for
C1 in order to achieve maximum efficiency of operation.
3
TC1044S-12 9/16/96
TC1044S
Charge Pump DC-TO-DC Voltage Converter
Dos and Don'ts
• Do not exceed maximum supply voltages.
• Do not connect the LV terminal to GND for supply
voltages greater than 3.5V.
• Do not short circuit the output to V+ supply for voltages
above 5.5V for extended periods; however, transient
conditions including start-up are okay.
• When using polarized capacitors in the inverting mode,
the + terminal of C1 must be connected to pin 2 of the
TC1044S and the + terminal of C2 must be connected
to GND.
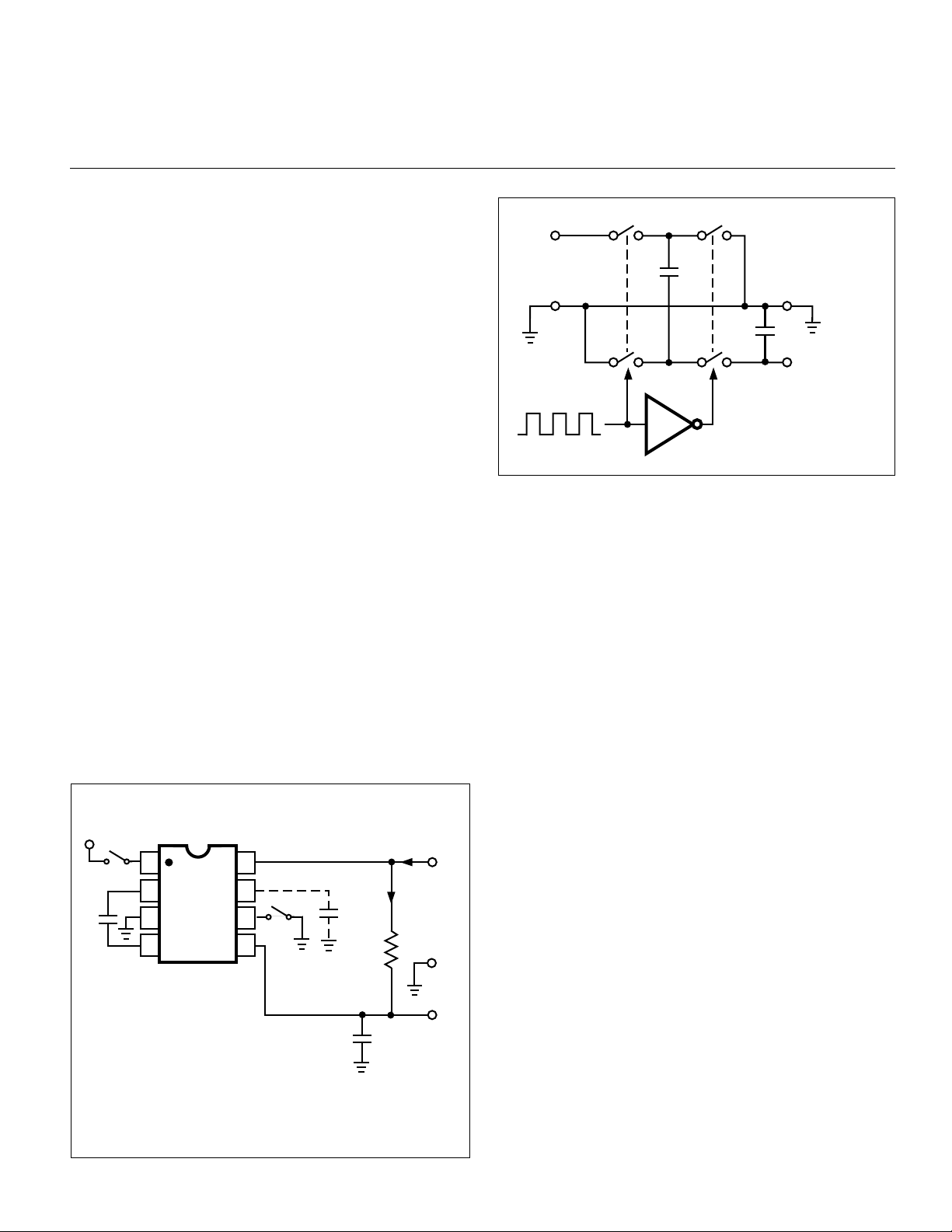
Simple Negative Voltage Converter
Figure 3 shows typical connections to provide a negative supply where a positive supply is available. A similar
scheme may be employed for supply voltages anywhere in
the operating range of +1.5V to +12V, keeping in mind that
pin 6 (LV) is tied to the supply negative (GND) only for supply
voltages below 3.5V.
+
V
The output characteristics of the circuit in Figure 3 are
those of a nearly ideal voltage source in series with 70Ω.
Thus, for a load current of –10mA and a supply voltage of
+5V, the output voltage would be – 4.3V.
The dynamic output impedance of the TC1044S is due,
primarily, to capacitive reactance of the charge transfer
capacitor (C1). Since this capacitor is connected to the
output for only 1/2 of the cycle, the equation is:
2
XC = = 3.18Ω,
2πf C
1
where f = 10 kHz and C1 = 10µF.
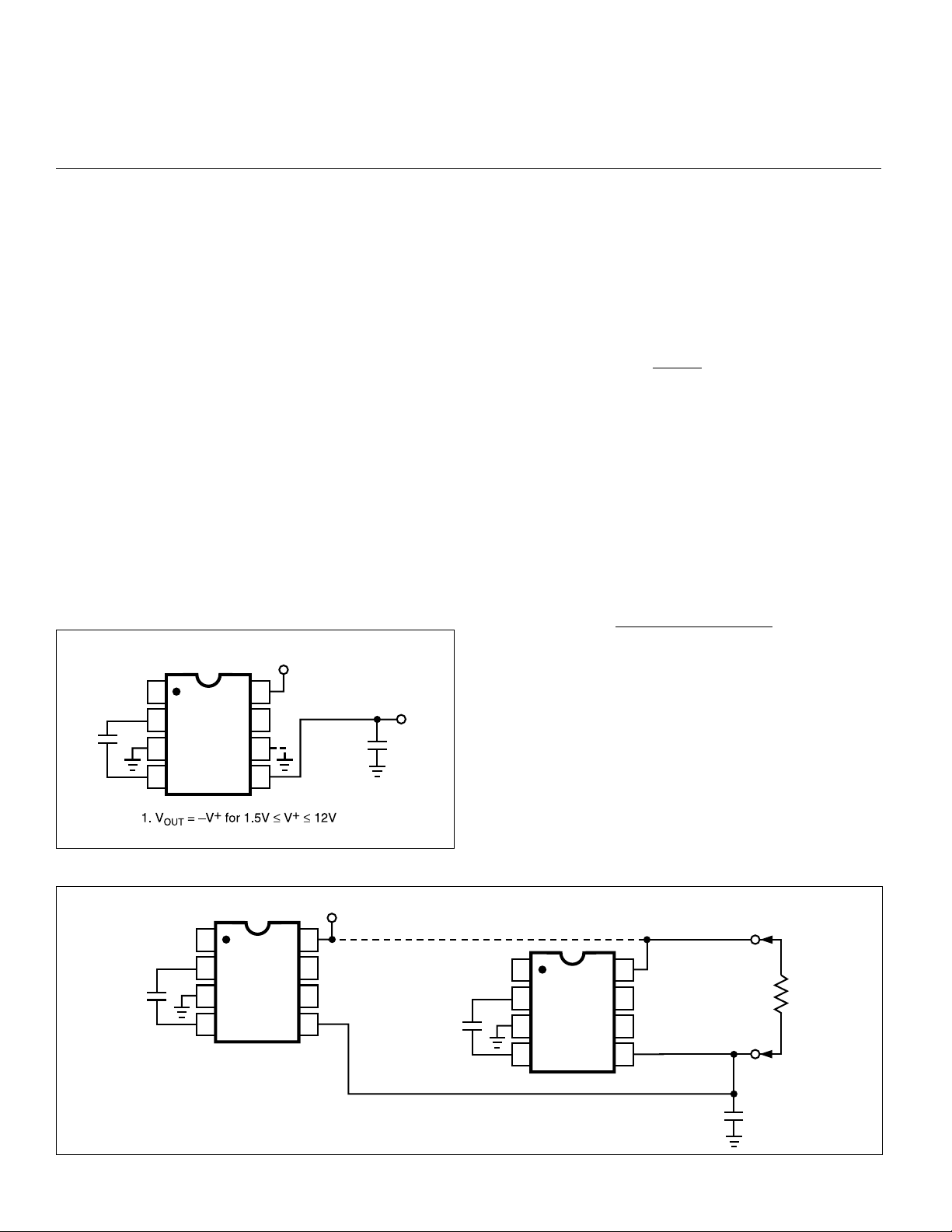
Paralleling Devices
Any number of TC1044S voltage converters may be
paralleled to reduce output resistance (Figure 4). The reservoir capacitor, C2, serves all devices, while each device
requires its own pump capacitor, C1. The resultant output
resistance would be approximately:
R
(of TC1044S)
R
OUT
=
OUT
n (number of devices)
10µF
C
1
NOTES:
*
1
2
+
C
TC1044S
3
4
Figure 3. Simple Negative Converter
1
2
1
3
4
8
7
6
5
TC1044S
"1"
V
*
OUT
C
2
10µF
+
+
V
8
7
6
5
C
1
1
2
3
4
TC1044S
"n"
8
R
7
6
5
L
C
2
+
TC1044S-12 9/16/96
Figure 4. Paralleling Devices Lowers Output Impedance
4
© 2001 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21348A
 Loading...
Loading...