Page 1

PSMC Designer
User’s Guide
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B
Page 2

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
YSTEM
CERTIFIED BY DNV
== ISO/TS 16949 ==
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is provided only for your convenience
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR
OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION,
QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability
arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at
the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend, indemnify and
hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims,
suits, or expenses resulting from such use. No licenses are
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip
intellectual property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, dsPIC,
FlashFlex, K
PICSTART, PIC
and UNI/O are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
FilterLab, Hampshire, HI-TECH C, Linear Active Thermistor,
MTP, SEEVAL and The Embedded Control Solutions
Company are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Silicon Storage Technology is a registered trademark of
Microchip Technology Inc. in other countries.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, BodyCom,
chipKIT, chipKIT logo, CodeGuard, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, dsSPEAK, ECAN,
ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, HI-TIDE, In-Circuit Serial
Programming, ICSP, Mindi, MiWi, MPASM, MPF, MPLAB
Certified logo, MPLIB, MPLINK, mTouch, Omniscient Code
Generation, PICC, PICC-18, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, PICkit,
PICtail, REAL ICE, rfLAB, Select Mode, SQI, Serial Quad I/O,
Total Endurance, TSHARC, UniWinDriver, WiperLock, ZENA
and Z-Scale are trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
GestIC and ULPP are registered trademarks of Microchip
Technology Germany II GmbH & Co. KG, a subsidiary of
Microchip Technology Inc., in other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2012-2013, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in
the U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
ISBN: 9781620772737
EELOQ, KEELOQ logo, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro,
32
logo, rfPIC, SST, SST Logo, SuperFlash
QUALITY MANAGEMENT S
DS40001671B-page 2 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2009 certification for its worldwide
headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in Chandler and
Tempe, Arizona; Gresham, Oregon and design centers in California
and India. The Company’s quality system processes and procedures
are for its PIC
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and
analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design
and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
®
MCUs and dsPIC® DSCs, KEELOQ
®
code hopping
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. PSMC Designer Overview
1.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 9
Chapter 2. Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.1 Introduction ................................................................................................... 11
2.2 Function Selection ........................................................................................ 12
2.3 Device Selection ........................................................................................... 12
2.4 PSMC Selection ........................................................................................... 12
2.5 PSMC Enable ............................................................................................... 12
2.6 Interrupt Enables .......................................................................................... 12
2.6.1 Timed Event Interrupt Enable .................................................................... 12
2.6.2 Auto-Shutdown Interrupt Enable ............................................................... 12
2.7 Comments .................................................................................................... 12
2.8 Copy and Show Button ................................................................................. 13
2.8.1 PSMC SFR Displays ................................................................................. 13
2.9 Paste Button ................................................................................................. 13
2.10 Clear Button ............................................................................................... 13
2.11 Pull-down Menu .......................................................................................... 13
2.11.1 Save Assy ............................................................................................... 13
2.11.2 Save C ..................................................................................................... 13
2.11.3 Load Code ............................................................................................... 14
2.12 Clock .......................................................................................................... 14
2.12.1 Clock Source ........................................................................................... 14
2.12.2 Prescale .................................................................................................. 14
2.13 Timer .......................................................................................................... 14
2.13.1 Sync Source ............................................................................................ 15
2.13.2 Timer Interrupt ......................................................................................... 15
2.14 Blanking ...................................................................................................... 15
2.14.1 Blanking Times ........................................................................................ 16
2.14.2 Rising Event Trigger ................................................................................ 16
2.14.3 Falling Event Trigger ............................................................................... 17
2.14.4 Asynchronous Input Pin Polarity ............................................................. 17
2.15 Period Event ............................................................................................... 17
2.15.1 Synchronous Selection ............................................................................ 17
2.15.2 Asynchronous Selection .......................................................................... 18
2.15.3 Asynchronous Polarity (not available on PIC16(L)F1782/3) .................... 18
2.15.4 Interrupt ................................................................................................... 18
2.16 Rising Event ............................................................................................... 18
2.16.1 Synchronous Selection ............................................................................ 19
2.16.2 Asynchronous Selection .......................................................................... 19
2.16.3 Interrupt ................................................................................................... 20
PSMC DESIGNER
USER’S GUIDE
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 3
Page 4

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
2.17 Falling Event ............................................................................................... 20
2.17.1 Synchronous Selection ............................................................................20
2.17.2 Asynchronous Selection ..........................................................................21
2.17.3 Asynchronous Polarity (not available on PIC16(L)F1782/3) ....................21
2.17.4 Interrupt ....................................................................................................21
2.18 Modulation .................................................................................................. 21
2.18.1 Modulation Source Selection ...................................................................22
2.18.2 Modulation Enable ...................................................................................22
2.19 PSMC Modes ............................................................................................. 22
2.19.1 Dead-Band Control ..................................................................................23
2.19.2 SPWM: Single PWM Mode ......................................................................23
2.19.3 SPWMC: Single PWM Mode with Complementary Outputs ....................24
2.19.4 PP: Push-Pull Mode .................................................................................25
2.19.5 PPC: Push-Pull with Complementary Output ...........................................25
2.19.6 FBPP: Full-Bridge Push-Pull ....................................................................26
2.19.7 FBPPC: Full-Bridge Push-Pull with Complementary Mode Outputs ........27
2.19.8 PS: Pulse-Skipping Mode ........................................................................27
2.19.9 PSC: Pulse-Skipping with Complementary Output ..................................28
2.19.10 ECCPR: ECC PWM Full-Bridge Mode, Reverse Direction ....................29
2.19.11 ECCPF: ECC PWM Full-Bridge Mode, Forward Direction .....................30
2.19.12 FDC: Fixed Duty Cycle Mode ................................................................30
2.19.13 Fine Frequency Adjust ...........................................................................31
2.19.14 FDCC: Fixed Duty Cycle with Complementary Output ..........................31
2.19.15 3PH: 3-Phase PWM ...............................................................................32
2.20 Output Control ............................................................................................ 33
2.20.1 Output Enable ..........................................................................................34
2.20.2 Output Steering ........................................................................................34
2.20.3 Output Steering Synchronization .............................................................34
2.20.4 Output Polarity .........................................................................................35
2.20.5 Shutdown Level .......................................................................................35
2.21 Auto-Shutdown ........................................................................................... 35
2.21.1 Shutdown Enable .....................................................................................35
2.21.2 Shutdown Sources ...................................................................................35
2.21.3 Shutdown Override ..................................................................................35
2.21.4 Auto/Manual Restart ................................................................................35
2.22 Sync Control (not available on the PIC16(L)F1782/3) ................................ 36
Chapter 3. PSMC Tips
3.1 Variable Period with Fixed Off-time .............................................................. 37
3.2 3-Phase Variable Duty Cycle ....................................................................... 38
3.3 Center Weighted Variable PWM .................................................................. 39
DS40001671B-page 4 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5

PSMC DESIGNER
USER’S GUIDE
Preface
NOTICE TO CUSTOMERS
All documentation becomes dated, and this manual is no exception. Microchip tools and
documentation are constantly evolving to meet customer needs, so some actual dialogs
and/or tool descriptions may differ from those in this document. Please refer to our web site
(www.microchip.com) to obtain the latest documentation available.
Documents are identified with a “DS” number. This number is located on the bottom of each
page, in front of the page number. The numbering convention for the DS number is
“DSXXXXXA”, where “XXXXX” is the document number and “A” is the revision level of the
document.
For the most up-to-date information on development tools, see the MPLAB IDE online help.
Select the Help menu, and then Topics to open a list of available online help files.
INTRODUCTION
This chapter contains general information that will be useful to know before using the
PSMC Designer. Items discussed in this chapter include:
• Conventions Used in this Guide
• The Microchip Web Site
• Customer Support
• Document Revision History
DOCUMENT LAYOUT
This document describes how to use the PSMC Designer. The document is organized
as follows:
• Chapter 1. “PSMC Designer Overview”
• Chapter 2. “Main PSMC Configuration GUI”
• Chapter 3. “PSMC Tips”
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 5
Page 6

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
CONVENTIONS USED IN THIS GUIDE
This manual uses the following documentation conventions:
DOCUMENTATION CONVENTIONS
Description Represents Examples
Arial font:
Italic characters Referenced books MPLAB IDE User’s Guide
Emphasized text ...is the only compiler...
Initial caps A window the Output window
A dialog the Settings dialog
A menu selection select Enable Programmer
Quotes A field name in a window or
dialog
Underlined, italic text with
right angle bracket
Bold characters A dialog button Click OK
N‘Rnnnn A number in verilog format,
Text in angle brackets < > A key on the keyboard Press <Enter>, <F1>
Courier New font:
Plain Courier New Sample source code #define START
Italic Courier New A variable argument file.o, where file can be
Square brackets [ ] Optional arguments mcc18 [options] file
Curly brackets and pipe
character: { | }
Ellipses... Replaces repeated text var_name [,
A menu path File>Save
A tab Click the Power tab
where N is the total number of
digits, R is the radix and n is a
digit.
Filenames autoexec.bat
File paths c:\mcc18\h
Keywords _asm, _endasm, static
Command-line options -Opa+, -Opa-
Bit values 0, 1
Constants 0xFF, ‘A’
Choice of mutually exclusive
arguments; an OR selection
Represents code supplied by
user
“Save project before build”
4‘b0010, 2‘hF1
any valid filename
[options]
errorlevel {0|1}
var_name...]
void main (void)
{ ...
}
DS40001671B-page 6 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

THE MICROCHIP WEB SITE
Microchip provides online support via our web site at www.microchip.com. This web
site is used as a means to make files and information easily available to customers.
Accessible by using your favorite Internet browser, the web site contains the following
information:
• Product Support – Data sheets and errata, application notes and sample
programs, design resources, user’s guides and hardware support documents,
latest software releases and archived software
• General Technical Support – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), technical
support requests, online discussion groups, Microchip consultant program
member listing
• Business of Microchip – Product selector and ordering guides, latest Microchip
press releases, listing of seminars and events, listings of Microchip sales offices,
distributors and factory representatives
CUSTOMER SUPPORT
Users of Microchip products can receive assistance through several channels:
• Distributor or Representative
• Local Sales Office
• Field Application Engineer (FAE)
• Technical Support
Customers should contact their distributor, representative or field application engineer
(FAE) for support. Local sales offices are also available to help customers.
Technical support is available through the web site at:
http://www.microchip.com/support.
Preface
DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY
Revision A (December 2012)
• Initial Release of this Document.
Revision B (June 2013)
• Updated Figure 2-3, Figure 2-6, Figure 2-7, Figure 2-18, and Figure 2-19.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 7
Page 8

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
NOTES:
DS40001671B-page 8 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

Chapter 1. PSMC Designer Overview
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The PSMC peripheral is a sophisticated programmable switch mode controller
intended to operate power conversion applications with little or no software
intervention. The peripheral capabilities range from simple, single channel PWM
generation to multi-channel complementary waveforms with dead bands between
transitions. PWM modes include:
•PWM
• Push-Pull
• Full-bridge
• Push-Pull Full-bridge
• Pulse skipping
• High resolution fixed duty cycle
• 6-step 3-phase operation
Every mode, except the 6-step, has a complementary output mode, which drives at
least two channels that are the complement of each other.
The PSMC also supports various driver and feedback configurations with the following
programmable features:
• Dead band – delays the output drive for a time after the complement of that output
turns off
• Blanking – Suppresses feedback signals for a time after the drive transitions on
and off
• Asynchronous inputs – pulse Start and Stop events can be triggered by external
asynchronous signals in combination with, or independent of, an internal time
base
• Shutdown – immediate safe shutdown driven by an external asynchronous Fault
signal
• Modulation – the PWM can be operated as a carrier and modulated by an
independent input
There are thirty Special Function Registers (SFRs) in the PSMC configuration setup.
Setting all thirty registers with the appropriate values for desired operation can be a
daunting task. The PSMC Designer GUI was created to simplify that effort.
The GUI divides the PSMC into up to eleven major functions. These functions are
shown in relation to each other in block diagram format in the main GUI window.
Clicking on a block opens the control GUI for that function. The user is guided through
the PSMC configuration design by completing signal paths and control options within
each function by selecting switch positions. Entry boxes for times and frequencies
appear within the diagrams where numeric entry is required.
There are two options for transferring the completed PSMC configuration to your
project. One is to copy the code into the clipboard buffer which can then be pasted into
your source code. The other transfer method is to generate an output file that can be
included by reference in your source code. Include files are also the means by which
PSMC configurations are stored for later retrieval by the PSMC designer.
PSMC DESIGNER
USER’S GUIDE
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 9
Page 10

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
Although a brief description of each function is included at the beginning of each
function section, please refer to the device data sheet for a more detailed description
of the PSMC operation. The sections of this guide are arranged in the same order of
progression that a user would follow when creating a PSMC configuration.
DS40001671B-page 10 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11
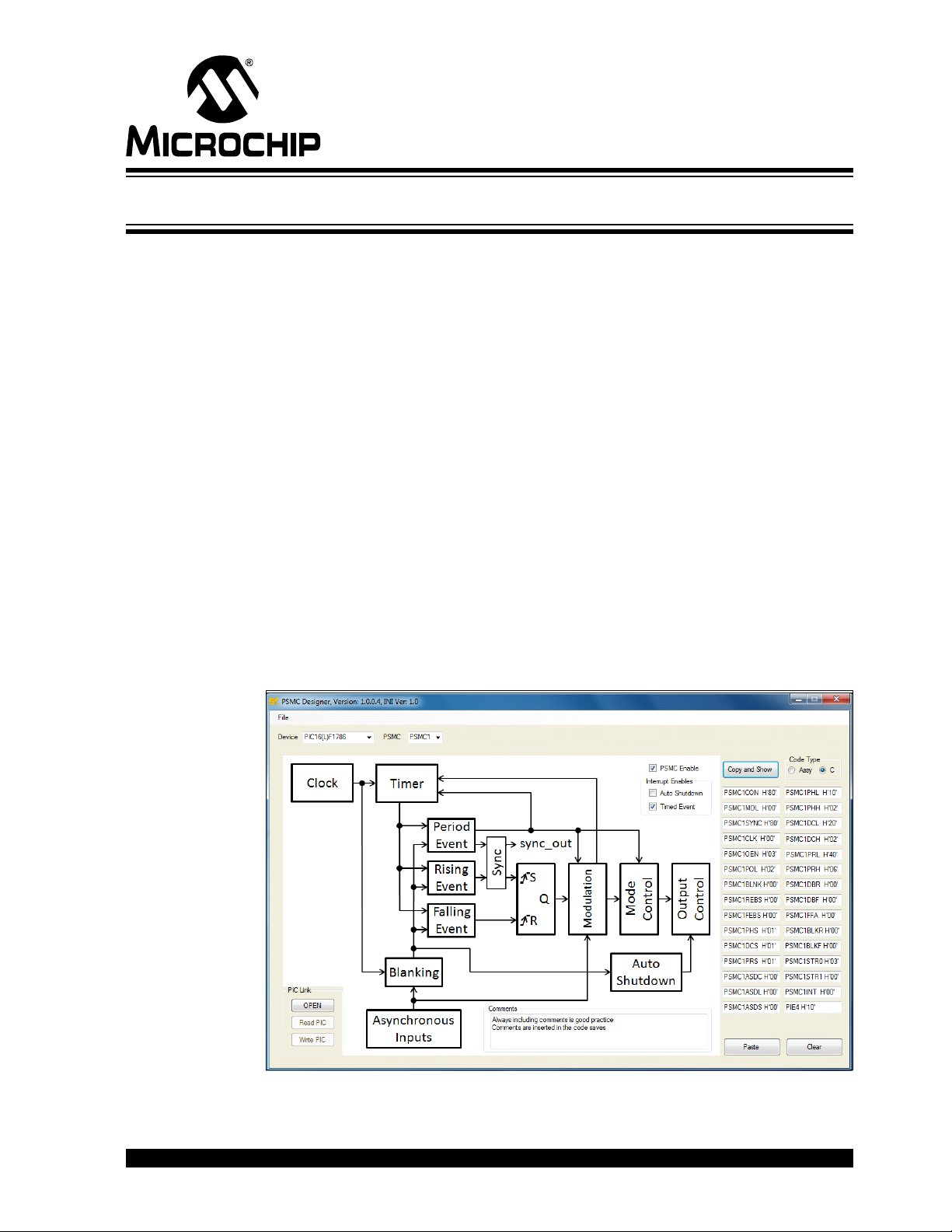
Chapter 2. Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.1 INTRODUCTION
Figure 2-1 shows the main PSMC Designer user interface, referred to hereafter as the
main GUI. Here you will see the eleven major functions of the PSMC:
1. Clock 2. Timer
3. Blanking 4. Period Event
5. Rising Event 6. Falling Event
7. Modulation 8. PSMC Modes
9. Output Control 10. Auto-Shutdown
11. Sync Output Control (not available
on the PIC16(L)F1782/3)
The main GUI also contains the following:
1. Device Selection 2. PSMC Selection
3. Copy and Show Button 4. Paste Button
5. Clear Button 6. Copy and Show Button
7. PSMC SFR Displays 8. PSMC Enable
9. Interrupt Enables 10. Pull-down Menu
11. Comments
PSMC DESIGNER
USER’S GUIDE
FIGURE 2-1: MAIN PSMC DESIGNER GUI
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 11
Page 12

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
2.2 FUNCTION SELECTION
As you move your cursor around the display, you will notice that the cursor shape
changes to a hand whenever it is within the bounds of one of the function blocks.
Clicking on the mouse when the cursor is a hand will open a control GUI for the function
to which the hand is pointing. When you are finished configuring that block you can
either close the associated GUI or leave it open. All functions remain active whether or
not they are visible.
2.3 DEVICE SELECTION
Selecting the device is the first step in creating a PSMC configuration. The Device
combination box lists all devices with PSMC peripherals. Make the selection by
scrolling through the list to the desired device. The device selection also configures
controls for all PSMC instances in that device with the proper input and output names
associated with that device.
2.4 PSMC SELECTION
Selecting the desired PSMC instance is the second step in creating a PSMC
configuration. Make the selection by scrolling through the list to the desired PSMC
instance. The PSMC selection also configures all other controls with the proper input
and output names associated with that PSMC instance.
2.5 PSMC ENABLE
This checkbox in the main GUI enables or disables the currently selected PSMC of the
currently selected device.
2.6 INTERRUPT ENABLES
The interrupt enable checkboxes in the main GUI enable or disable the corresponding
bit of the PIEx register for the currently selected PSMC of the currently selected device.
2.6.1 Timed Event Interrupt Enable
The timed event enable is the summary enable bit for the timed event interrupts.
2.6.2 Auto-Shutdown Interrupt Enable
The auto-shutdown enable is the enable bit for auto-shutdown events.
2.7 COMMENTS
The comments section in the lower center of the main GUI is where user comments
about the PSMC configuration can be entered. Each PSMC instance has its own
comment data, which is displayed when that PSMC is selected. Comments entered in
this box are included as comments in the saved file output.
DS40001671B-page 12 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13

2.8 COPY AND SHOW BUTTON
The Copy and Show button does two things: It shows all SFR values in the PSMC
instance configuration, and it copies those values to the clipboard. The clipboard format
is consistent with the type selected by the Code Type radio buttons. C and Assembly
are the two options. The clipboard capture can be pasted into your source code,
however, code for only the presently selected PSMC instance is in the clipboard.
Multiple copy and paste operations are required when working with multiple PSMC
instances. A better method for saving multiple PSMC instances of the same device is
the File Save option. Files can be saved in either C or Assembly format (see Save Assy
or Save C).
2.8.1 PSMC SFR Displays
The PSMC SFRs are displayed by name and value in the 30 text boxes between the
Copy and Show button and the Paste button. Only the SFRs for the selected PSMC
instance are displayed as indicated by each of the SFR name prefixes.
2.9 PASTE BUTTON
The Paste button transfers SFR values of the PSMC instance, from which they were
copied with the Copy and Show button, to the presently selected PSMC instance. In
this manner, one PSMC configuration can be created then quickly copied to other
desired PSMC instances. It is usually easier to make a few changes to a copied
configuration than it is to re-enter the entire configuration for each PSMC instance.
Note that the Paste button will not paste values copied from your source code.
Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.10 CLEAR BUTTON
The Clear button clears all SFRs in the presently selected PSMC instance to zero. All
GUIs of the various functions adjust accordingly.
2.11 PULL-DOWN MENU
In the upper left of the main GUI display there is a pull-down menu titled “File”. This
pull-down menu includes the following:
• Save Assy Code
• Save C Code
• Load Code
A file selection dialog will appear when the desired menu item is selected for both
saving and loading code. A comment section, that includes the device number and
clock frequency, is included in the saved code. This is used to reconstruct those parts
of the configuration when the code is loaded back into the designer tool.
2.11.1 Save Assy
Selecting the Save Assy code menu option creates an include file containing assembly
configuration code for all PSMCs in the selected device that have been configured. Any
PSMC instance in the selected device that is clear will not be included in the output.
2.11.2 Save C
Selecting the Save C code menu option creates an include file containing C
configuration code for all PSMCs in the selected device that have been configured. Any
PSMC instance in the selected device that is clear will not be included in the output.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 13
Page 14
PSMC Designer User’s Guide
2.11.3 Load Code
Selecting the Load Code menu option retrieves the SFR information from the file and
sets the device selection and all PSMC instance configurations contained in the code
file. The load algorithm automatically recognizes whether the code was saved as C or
assembly and reads it accordingly.
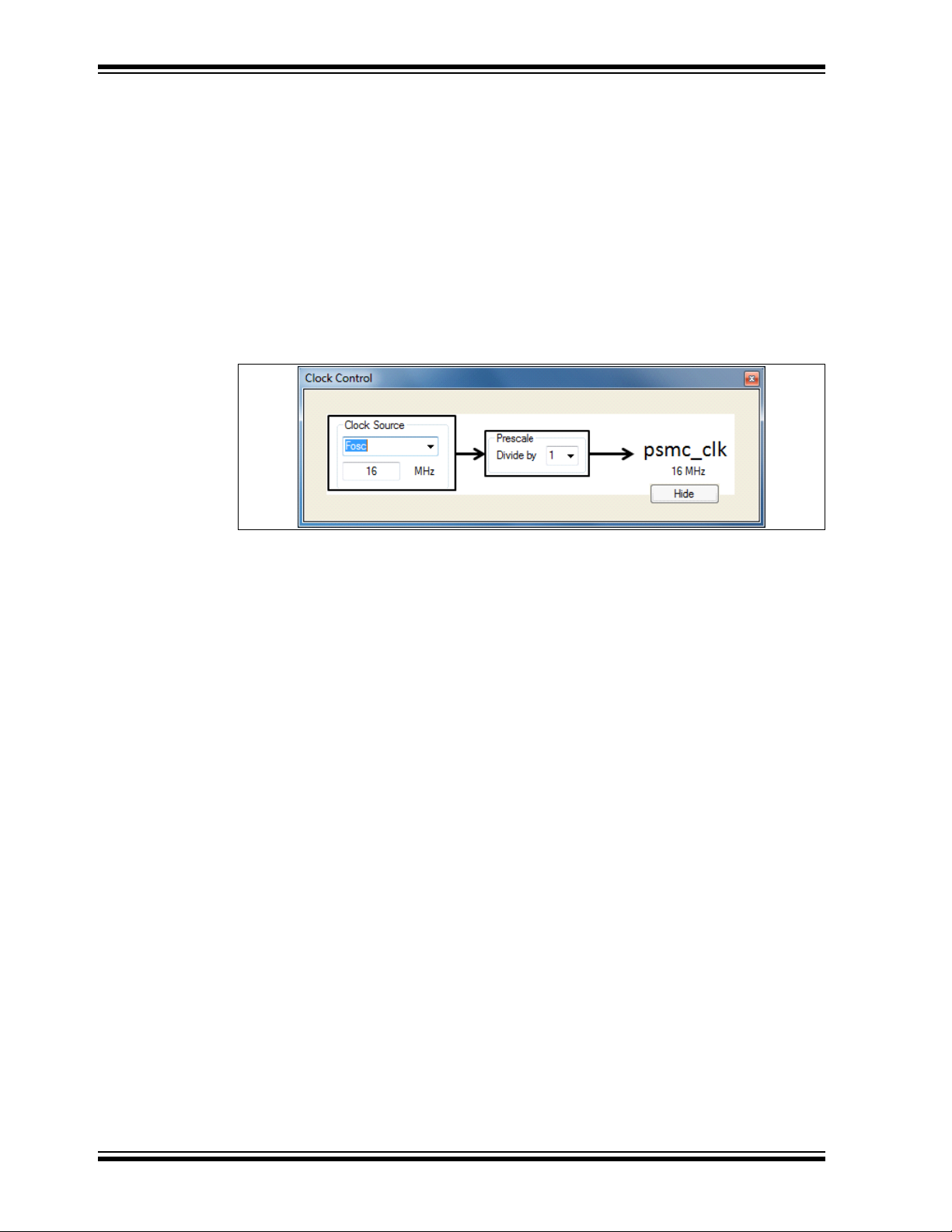
2.12 CLOCK
The clock control determines the rate at which the synchronous event timer, blanking
timers, and dead-band timers all increment. The clock selections should be made first
since the times in the aforementioned controls are all affected by the clock selections.
The clock control GUI is shown in Figure 2-2.
FIGURE 2-2: CLOCK CONTROL
2.13 TIMER
2.12.1 Clock Source
The clock source selects one of three PSMC clock sources:
OSC – internal system oscillator
•F
• 64 MHz – 64 MHz clock derived from the 16 MHz HFINTOC by multiplying by 4.
• PSMCxCLK pin – The I/O pin designated as the PSMC clock input.
When either the F
specified by entering the number in MHz in the text box below the clock selection
combination box. Selecting 64 MHz forces the frequency to 64 MHz, which cannot be
altered.
OSC or PSMCxCLK pin is selected, then the actual frequency is
2.12.2 Prescale
The prescale selection determines which of four dividers is used to reduce the selected
clock source to the psmc_clk output frequency. The four selections are:
• Divide by 1
• Divide by 2
• Divide by 4
• Divide by 8
The timer control GUI, shown in Figure 2-3, is opened by clicking on the timer block in
the main GUI. The timer is a 16-bit counter to which the synchronous period event,
rising event, and falling event count registers are compared to create their synchronous
events.
DS40001671B-page 14 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
FIGURE 2-3: TIMER CONTROL
2.13.1 Sync Source
PSMCs in the device can be synchronized to a master PSMC by routing the sync_out
signal from the master as one of the timer Reset inputs. The sync source selection
determines the Reset source and thereby also determines which PSMC is the master.
The number of selections varies by the number of PSMC instances in the device.
2.13.2 Timer Interrupt
The timer overflow can be selected as a timed interrupt source by clicking on the switch
image at the CY terminal of the timer. Connecting this switch connects the timer carry
out to the PMSC timed interrupt summary bit in the device PIRx register. Enabling the
timer interrupt also requires checking the timed event interrupt enable box on the main
window.
2.14 BLANKING
The blanking control GUI, shown in Figure 2-4, is opened by clicking on the blanking
block in the main GUI. Blanking suppresses the selected inputs for a programmable
period of time which starts at either a rising event or falling event or both.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 15
Page 16

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-4: BLANKING CONTROL
All asynchronous inputs pass through blanking. Rising and falling events are used as
the blanking triggers because these are the two events that signal the output power
drivers to turn on and off. When a power driver switches it can cause spurious
transients in the system that can cause false event triggers if not suppressed. A
blanked input is suppressed for all of the following:
• Period event
• Rising event
• Falling event
• Shutdown event
Modulation sources are the only inputs that are not affected by blanking.
Note that, in Figure 2-4, the signal names entering the blanking control on the left are
the same names, but appended by a “_B” when leaving on the right. You will notice that
the input signal identifiers in the other GUIs are also appended with a “_B”, as a
reminder that those inputs pass through the blanking function and may be blanked.
2.14.1 Blanking Times
The blanking time is entered in the appropriate text box in microseconds. The blanking
count value is calculated from the entered time based on the psmc_clk frequency. If
the calculated count value exceeds the maximum allowed then a warning dialog will
appear indicating the limit. If the psmc_clk frequency is changed then a new time
based on the new frequency and existing count will be displayed in the text box.
2.14.2 Rising Event Trigger
Click on the switch at the blanking time output to enable or disable the rising event
blanking trigger. Asynchronous inputs are selected for rising event blanking individually
by closing the switch to the AND gate output in their path.
DS40001671B-page 16 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

2.14.3 Falling Event Trigger
Click on the switch at the blanking time output to enable or disable the falling event
blanking trigger. Asynchronous inputs are selected for falling event blanking
individually by closing the switch to the AND gate output in their path.
2.14.4 Asynchronous Input Pin Polarity
One of the asynchronous inputs comes directly from an I/O pin. For example, RB0 is
that input in Figure 2-4. There is a buffer between the input label and the first AND gate.
The polarity of the I/O pin input is selectable by clicking on the output of the buffer.
When the buffer output is a line, clicking on it will change the line to a bubble indicating
that the signal is inverted. Clicking on the bubble will change the output to a line.
2.15 PERIOD EVENT
The period event GUI, shown in Figure 2-5, is opened by clicking on the period event
block in the main GUI. The period event determines the frequency of the PSMC PWM
waveform. Each period event resets the timer. The period event source can be
synchronous or asynchronous.
FIGURE 2-5: PERIOD CONTROL
Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.15.1 Synchronous Selection
Synchronous period event selection is made by clicking on the X leading to the upper
input to the output OR gate. When clicked, the X is replaced by a straight line leading
from the period time selection box to the output OR gate. Synchronous period events
can be deselected by clicking on the input line to the OR gate to change it back to a
line terminated with an X.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 17
Page 18

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
The synchronous period event frequency is determined by the time or frequency
entered in the Period Time/Period Freq text box. The Radio button below the box
selects time or frequency as the display. When a value is entered the period count
value is calculated based on the psmc_clk frequency. If the display mode is changed
then the value changes to correspond with the existing count. Likewise, if the
psmc_clk frequency is changed then the period value will be changed to correspond
with the existing count.
2.15.2 Asynchronous Selection
Asynchronous period events are selected by clicking on any X leading to the 7-wide
OR gate of the control. Inputs are identified by source signal name appended by a “_B”,
which indicates that the signal first passed through the blanking function. Input
selections vary by device. When all selections are open, then the connection to the
output OR gate is shown as open. This connection cannot be changed by clicking.
Instead, it closes automatically when any asynchronous input is selected.
2.15.3 Asynchronous Polarity (not available on PIC16(L)F1782/3)
The output from the 7-wide OR gate can be clicked to change the polarity of the
asynchronous event. Figure 2-5 shows the polarity control enabled to invert the signal.
The default polarity is not inverted, in which case the output will be shown as a straight
line. The cursor will change to a hand when moved to the polarity selection area. The
cursor will not change in devices that do not have this feature.
2.15.4 Interrupt
The synchronous period event can be selected as a timed interrupt source by clicking
on the switch image leading to the line labeled as interrupt. Closing this switch connects
the synchronous period event out to the PMSC timed interrupt summary bit in the
device PIRx register. Enabling the synchronous period event interrupt also requires
checking the timed event interrupt enable box on the main window.
2.16 RISING EVENT
The rising event control GUI, shown in Figure 2-6, is opened by clicking on the rising
event block in the main GUI. The rising event starts the active drive of the PWM output.
The rising event source can be synchronous or asynchronous. In most applications the
rising event will be synchronous at 0 us after period event. In this case, starting a PWM
drive by an asynchronous input is accomplished by enabling that input in the period
control. One application for synchronous times greater than 0 is center weighted PWM.
See Center Weighted Variable PWM in Chapter 3. “PSMC Tips”.
DS40001671B-page 18 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
FIGURE 2-6: RISING EVENT CONTROL
2.16.1 Synchronous Selection
Synchronous rising event selection is made by clicking on the X leading to the upper
input to the output OR gate. When clicked, the X is replaced by a straight line leading
from the rising event time selection box to the output OR gate. Synchronous rising
events can be deselected by clicking on the input line to the OR gate to change it back
to a line terminated with an X.
The Radio button below the text box selects time or percent as the display. When time
is selected then the time entered in the text box will determine the number of
microseconds the synchronous rising event will occur after the period event. When a
time value is entered then the rising event count value is calculated based on the
psmc_clk frequency. If the display mode is changed then the displayed value changes
to correspond with the existing count. Likewise, if the psmc_clk frequency is changed
then the rising event displayed value will be changed to correspond with the existing
count except when the percent display mode is selected. The count remains constant
and the displayed value changes to avoid invalid time entries as a result of a change
to the psmc_clk value.
Entering the value as percent determines the percentage of the period the rising event
will occur after the period event. When the percent value is entered then the rising
event count is calculated based on the existing period count value. Unlike the time
value, the percent value remains constant when the psmc_clk or period values are
changed. This is possible because the new rising event count, as a result of changes
to the psmc_clk, will always be valid.
2.16.2 Asynchronous Selection
Asynchronous rising events are selected by clicking on any X leading to the 7-wide OR
gate of the control. Inputs are identified by source signal name appended by a “_B”,
which indicates that the signal first passed through the blanking function. Input
selections vary by device. When all selections are open then the connection to the
output OR gate is shown as open. This connection cannot be changed by clicking.
Instead it closes automatically when any asynchronous input is selected.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 19
Page 20

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
2.16.3 Interrupt
The synchronous rising event can be selected as a timed interrupt source by clicking
on the switch image leading to the line labeled as interrupt. Closing this switch connects
the synchronous rising event out to the PMSC timed interrupt summary bit in the device
PIRx register. Enabling the synchronous rising event interrupt also requires checking
the timed event interrupt enable box on the main window.
2.17 FALLING EVENT
The falling event control GUI, shown in Figure 2-7, is opened by clicking on the falling
event block in the main GUI. The falling event terminates the active PWM drive output.
The falling event source can be synchronous or asynchronous.
FIGURE 2-7: FALLING EVENT CONTROL
2.17.1 Synchronous Selection
Synchronous falling event selection is made by clicking on the X leading to the upper
input to the output OR gate. When clicked, the X is replaced by a straight line leading
from the falling event time selection box to the output OR gate. Synchronous falling
events can be deselected by clicking on the input line to the OR gate to change it back
to a line terminated with an X.
The Radio button below the text box selects time or percent as the display. When time
is selected then the time entered in the text box will determine the number of
microseconds the synchronous falling event will occur after the rising event. When a
time value is entered, then the falling event count value is calculated based on the
psmc_clk frequency and the rising event count. If the display mode is changed, then
the displayed value changes to correspond with the existing count. Likewise, if either
the psmc_clk frequency or rising event value is changed, then the falling event
displayed value will be changed to correspond with the existing count except when the
percent display mode is selected. The count remains constant and the displayed value
changes to avoid invalid time entries as a result of a change to any of the psmc_clk,
period, or rising event values.
DS40001671B-page 20 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
Entering the value as percent determines the active pulse width as a percentage of the
period. The active pulse width is the time from when the PWM output goes active (rising
event) to the time the PWM output is terminated (falling event). When the percent value
is entered then the falling event count is calculated based on the existing period count
and rising event values. Unlike the time value, the percent value remains constant
when the psmc_clk or period values are changed. This is possible when the rising
event time is zero (most applications) because the new falling event count, as a result
of changes to the psmc_clk and period, will always be valid. In the unlikely event that
a percentage value is entered that causes the falling event count to exceed the period
count, then a warning dialog will appear and the falling event count will be adjusted to
the maximum valid count.
2.17.2 Asynchronous Selection
Asynchronous falling events are selected by clicking on any X leading to the 7-wide OR
gate of the control. Inputs are identified by source signal name appended by a “_B”,
which indicates that the signal first passed through the blanking function. Input
selections vary by device. When all selections are open then the connection to the
output OR gate is shown as open. This connection cannot be changed by clicking.
Instead it closes automatically when any asynchronous input is selected.
2.17.3 Asynchronous Polarity (not available on PIC16(L)F1782/3)
The output from the 7-wide OR gate can be clicked to change the polarity of the
asynchronous event. Figure 2-7 shows the polarity control enabled to invert the signal.
The default polarity is not inverted and the output will be shown as a straight line. The
cursor will change to a hand when moved to the output selection area. The cursor will
not change in devices that do not have this feature.
2.17.4 Interrupt
The synchronous falling event can be selected as a timed interrupt source by clicking
on the switch image leading to the line labeled as interrupt. Closing this switch connects
the synchronous falling event out to the PMSC timed interrupt summary bit in the
device PIRx register. Enabling the synchronous falling event interrupt also requires
checking the timed event interrupt enable box on the main window.
2.18 MODULATION
The modulation control, shown in Figure 2-8, is opened by clicking on the modulation
block in the main GUI. Modulation is used in applications that need to gate the PWM
output on and off. For example, infrared communications typically have a carrier PWM
frequency to pulse the IR emitters which is then modulated on and off by the
intelligence data.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 21
Page 22

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-8: MODULATION CONTROL
2.18.1 Modulation Source Selection
The modulation source is selected from one of the external asynchronous PSMC inputs
or peripheral outputs internal to the device. Modulation sources are mutually exclusive.
The selection is made by choosing the desired source from those available in the
Modulation Source combination box. Note that when modulation is enabled and the
modulation source is low, then the Timer is held in Reset. This ensures that the first
PWM pulse enabled by the modulation going high is a complete PWM period.
Synchronization with the period event ensures that the last PWM pulse is also a
complete period. It should be apparent that modulation should only be used when the
PWM Q signal is completely synchronous (no asynchronous inputs to the period, rising,
or falling events) to avoid an incomplete cycle of the first PWM period after modulation
starts.
2.18.2 Modulation Enable
Modulation is enabled by clicking the enable switch to the On position. When enabled,
the modulation signal gates the Q output from the PWM SR latch to the PWM mode
input. Note that the PWM coming into the modulation function is labeled Q and going
out it is labeled MQ. Modes that use the PWM signal take their input from the
modulation function MQ output.
When the modulation enable switch is in the Off position, the MQ gate is always
enabled, thereby passing the unmodulated Q out to the mode inputs.
2.19 PSMC MODES
The mode function is where the simple PWM signal derived from the rising and falling
events becomes something more. There are five PWM modes, one High Resolution
Frequency mode, and one Six-Step mode that simplifies steering pairs of outputs to the
six PWM channels.
All modes, except the Six-Step mode, have a corresponding complementary output
mode making a total of thirteen modes (2 x 6 + 1 = 13). The complementary modes
include two dead-band controls: one triggered by the rising edge of the PWM signal
and one triggered by the falling edge.
Modes are selected by clicking on the corresponding tab in the mode selection GUI.
The tabs are labeled with the acronym of the mode control contained therein.
There are up to six PWM output channels. Not all modes use all six channels. Unused
channels are indicated by an output line that begins with an X. The sections that follow
detail each of the thirteen modes.
DS40001671B-page 22 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.19.1 Dead-Band Control
Each of the six complementary modes contains two dead-band control blocks. One
control delays the turn-on of the normal PWM output(s) and the other control delays the
turn-on of the complementary PWM output(s). Dead-band control does not delay the
turn-off of either normal or complementary outputs.
2.19.1.1 WHAT IS DEAD BAND?
Complementary outputs are generally used to drive power devices connected in series
between the power rails. The complementary outputs drive the two power devices such
that only one is on at a time, connecting one of the power rails to the load. When the
PWM output is active, then one rail is connected to the output. When the complement
is active, then the other rail is connected to the output. The turn-on time of a power
device is generally faster than the turn-off time. It is necessary therefore, to disable the
drives to both power devices for at least the activation difference to prevent both
devices from conducting at the same time. This is accomplished with the dead-band
time.
Click on either dead-band block to open the rising or falling dead-band control GUI
shown in Figure 2-9. To enable dead band, click the switch to connect the AND gate
output to the dead-band output. Enter the desired dead-band time in the text box.
Dead band operates as follows: When the input transitions from high-to-low the output
goes low immediately. When the input transitions from low-to-high then the output
transition is delayed by the dead-band time.
Note that the dead-band controls are identical for all modes. In other words, changes
made to the rising dead-band control in one mode will appear in the rising dead-band
control of all other modes. The same is true for the falling dead-band control.
FIGURE 2-9: DEAD-BAND CONTROL
2.19.2 SPWM: Single PWM Mode
Single PWM mode is selected by clicking on the SPWM tab, as shown in Figure 2-10.
This mode directs the single PWM signal to the six output channels. This mode enables
output steering which is a means of enabling or disabling any combination of the six
channels. Output steering selection is discussed in the output control section. Output
steering can be used to switch the output from one pin to another pin or to enable
several outputs simultaneously, so they can be connected in parallel to boost the output
current drive.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 23
Page 24

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-10: SINGLE PWM MODE
2.19.3 SPWMC: Single PWM Mode with Complementary Outputs
The Single PWM Complementary mode is selected by clicking on the SPWMC tab, as
shown in Figure 2-11. This is identical to Single PWM mode, except the output
channels are divided into two groups of three. One group has the PWM signal and the
other group has the complement of the PWM signal.
Click on either dead-band block to open the dead-band control. See
Section 2.19.1 “Dead-Band Control” for more information.
FIGURE 2-11: SINGLE PWM COMPLEMENTARY MODE
DS40001671B-page 24 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.19.4 PP: Push-Pull Mode
The Push-Pull mode is selected by clicking on the PP tab as shown in Figure 2-12. The
Push-pull mode is similar to the PWM mode, except that the PWM output alternates
between Channel A and Channel B every PWM period.
FIGURE 2-12: PUSH-PULL MODE
2.19.5 PPC: Push-Pull with Complementary Output
Push-Pull Complementary mode is selected by clicking on the PPC tab, as shown in
Figure 2-13. This mode is identical to the Push-Pull mode with the addition of two
complementary outputs on Channel E and Channel F.
Click on either dead-band block to open the dead-band control. See
Section 2.19.1 “Dead-Band Control” for more information.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 25
Page 26

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-13: PUSH-PULL COMPLEMENTARY MODE
2.19.6 FBPP: Full-Bridge Push-Pull
Full-Bridge Push-Pull mode is selected by clicking on the FBPP tab, as shown in
Figure 2-14. Full-Bridge Push-Pull mode is identical to Push-Pull mode, except that
there are four channels, two of which are active at a time with the same waveform.
Channels A and C alternate with Channels B and D every period event.
FIGURE 2-14: FULL-BRIDGE PUSH-PULL MODE
DS40001671B-page 26 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.19.7 FBPPC: Full-Bridge Push-Pull with Complementary Mode Outputs
Full-Bridge Push-Pull Complementary mode is selected by clicking on the FBPPC tab
as shown in Figure 2-15. This mode is identical to full-bridge push-pull with the addition
of two complementary outputs on Channel E and Channel F. Channel E is the
complement of Channels A and C. Channel F is the complement of Channels B and D.
Click on either dead-band block to open the dead-band control. See
Section 2.19.1 “Dead-Band Control” for more information.
FIGURE 2-15: FULL-BRIDGE PUSH-PULL COMPLEMENTARY
2.19.8 PS: Pulse-Skipping Mode
Pulse-Skipping mode is selected by clicking on the PS tab as shown in Figure 2-16.
Pulse-Skipping mode uses the asynchronous rising event output to enable the PWM
output. When the asynchronous input is low at the period event then PWM output for
that period is suppressed, otherwise the PWM output occurs as it normally would in the
Single PWM mode. Pulse-Skipping mode is generally used in hysteretic power
conversion applications. Channel A is the only available output in Pulse-Skipping
mode.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 27
Page 28

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-16: PULSE-SKIPPING MODE
2.19.9 PSC: Pulse-Skipping with Complementary Output
Pulse-skipping with complementary output is selected by clicking on the PSC tab as
shown in Figure 2-17. Pulse-skipping with complementary output is identical to
Pulse-Skipping mode with the complement of the PWM output to Channel B.
Click on either dead-band block to open the dead-band control. See
Section 2.19.1 “Dead-Band Control” for more information.
FIGURE 2-17: PULSE-SKIPPING COMPLEMENTARY
DS40001671B-page 28 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 29

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.19.10 ECCPR: ECC PWM Full-Bridge Mode, Reverse Direction
ECC compatible PWM mode, reverse direction, is selected by clicking on the ECCPR
tab as shown in Figure 2-18. This is a full-bridge driver with two of four outputs,
Channels A and D, active. The Channel A output is the PWM drive and the Channel D
output is true without Pulse-Width Modulation. This mode is intended to drive the high
side and low side of opposite sides of an H-bridge power device configuration. Such
configurations are used in brushed DC motor applications that need both speed and
direction control. This mode is compatible with the Full-Bridge mode of the ECCP
peripheral.
The mode can be changed to the forward direction mode by clicking on the direction
switch or clicking on the ECCPF tab.
When the motor is running and the direction is changed, then the change is
synchronized with the period event and dead-band time is inserted to prevent
shoot-through on either side of the H-bridge. Click on either dead-band block to open
the corresponding dead-band control. See Section 2.19.1 “Dead-Band Control” for
more information.
FIGURE 2-18: ECC PWM FULL-BRIDGE REVERSE
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 29
Page 30

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
2.19.11 ECCPF: ECC PWM Full-Bridge Mode, Forward Direction
ECC compatible PWM mode, forward direction, is selected by clicking on the ECCPF
tab as shown in Figure 2-19. This mode is a full-bridge driver with two of four outputs,
Channels B and C, active. The Channel B output is the PWM drive and the Channel C
output is true without Pulse-Width Modulation. This mode is intended to drive the high
side and low side of opposite sides of an H-bridge power device configuration. Such
configurations are used in brushed DC motor applications that need speed and
direction control. This mode is compatible with the Full-Bridge mode of the ECCP
peripheral.
The mode can be changed to the reverse direction mode by clicking on the direction
switch or clicking on the ECCPR tab.
When the motor is running and the direction is changed, then the change is
synchronized with the period event and dead-band time is inserted to prevent
shoot-through on either side of the H-bridge. Click on either dead-band block to open
the corresponding dead-band control. See Section 2.19.1 “Dead-Band Control” for
more information.
FIGURE 2-19: ECC PWM FULL-BRIDGE FORWARD
2.19.12 FDC: Fixed Duty Cycle Mode
Fixed Duty Cycle mode is selected by clicking on the FDC tab as shown in Figure 2-20.
The Fixed Duty Cycle mode is used to generate frequencies with a much higher
resolution than is possible with the period count alone. This mode provides only 50%
duty cycle waveforms and should be used only with synchronous period time
generation. This mode is generally used in fluorescent lamp ballast controls. Course
frequency is determined with the period count (see synchronous period control).
DS40001671B-page 30 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 31

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
FIGURE 2-20: FIXED DUTY CYCLE
2.19.13 Fine Frequency Adjust
After the course frequency is determined with the clock and period controls, the
frequency is fine tuned with the Fine Frequency Adjust control. Click on the FFA box to
open the fine frequency adjust control shown in Figure 2-21.
The combination box in the center of the fixed frequency adjust control shows 16
possible selections based on the psmc_clk frequency and period count. Selections
can be made by frequency or time by clicking on the desired display mode radio button.
When any of the clock frequency, period frequency, or selection mode is changed, then
the selection list and displayed selection are updated to correspond to the change.
Note that the displayed frequency is twice the output waveform frequency because the
fixed 50% duty cycle is derived by dividing the adjusted period frequency by two.
FIGURE 2-21: FINE FREQUENCY ADJUST CONTROL
2.19.14 FDCC: Fixed Duty Cycle with Complementary Output
Fixed Duty Cycle Complementary Output mode is selected by clicking on the FDCC tab
as shown in Figure 2-22. The Fixed Duty Cycle with Complementary Output mode is
identical to the Fixed Duty Cycle mode with Channel B output as the complement to
Channel A.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 31
Page 32

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-22: FIXED DUTY CYCLE COMPLEMENTARY OUTPUT
2.19.15 3PH: 3-Phase PWM
3-Phase PWM mode is selected by clicking on the 3PH tab as shown in Figure 2-23.
3-Phase PWM is a special mode that generates the waveform for 6-step 3-phase
systems such as those for driving brushless DC motors. These systems have three half
bridges requiring two drive outputs each for a total of six channels. This mode uses the
steering control bits to drive two of the six channels at a time: one half-bridge high side
drive and another half-bridge low side drive both on.
A diagram is presented in the top center of the control that indicates the power voltages
applied to the system in each phase. Phases are labeled U, V and W. The phase U half
bridge is driven by channels A (high side) and B (low side) as indicated to the right of
the phase labels. Phases V and W are labeled similarly. You can also select which side
of the half bridge receives the Pulse-Width Modulation: High side, low side, or both.
Modulation is selected by the two check boxes to the left of the diagram.
Clicking on a radio button at the top of the diagram will select that phase drive
configuration. For example, as shown in Figure 2-23, high side modulation is checked
and radio button 1 is selected, thereby driving phase U high with modulation, phase V
low with no modulation, and phase W floating. The channel connections to achieve this
configuration are shown on the right.
DS40001671B-page 32 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 33

Main PSMC Configuration GUI
FIGURE 2-23: 3-PHASE PWM
2.20 OUTPUT CONTROL
Channels are directed to the output pins through the output control. Open the output
control GUI shown in Figure 2-24 by clicking on the output control block in the main
GUI.
There are four selections for each channel in this control:
1. Output enable – switch furthest to the right
2. Output steering – input to the buffer on the left
3. Output polarity – bubble on output of the buffer figure
4. Shutdown level – switch at input to MUX
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 33
Page 34

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-24: OUTPUT CONTROL
2.20.1 Output Enable
The output enable switch selects between the PORT latch output and the PSMC
channel. When the PORT latch output is selected, then the output pin is not affected by
the PSMC. When the PSMC channel is selected, then the pin is not affected by the
PORT latch.
2.20.2 Output Steering
Two modes, SPWM and SPWMC, include steering. Steering gives the ability to steer
the PWM output to one or more of the six outputs. Steering differs from the output
enable because when steering is disabled then the pin output is forced false regardless
of the PORT latch level.
Modes other than SPWM and SPWMC do not include steering and therefore, all
steering controls are shown as connected for those modes and cannot be
disconnected.
2.20.3 Output Steering Synchronization
The checkbox in the lower left of the control selects period event steering
synchronization. When the PWM is active and steering is changed, then the
synchronized steering change takes effect at the period event immediately following
the change. When steering synchronization is not enabled then steering changes take
effect immediately without waiting for the period event.
DS40001671B-page 34 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 35

2.20.4 Output Polarity
The output polarity control determines the active-true level of the channel output. The
active time starts at the rising event and ends at the falling event. Polarity is selected
by clicking on the output of the channel buffer. The output will appear as a bubble for
active-low polarity and as a line for active-high polarity.
2.20.5 Shutdown Level
Shutdown level is the level forced on the output when a shutdown condition is active.
The shutdown level for a channel is selected by clicking on the switch at the input of
the shutdown MUX. Note that the polarity control is ahead of the shutdown MUX so that
the shutdown output level is not affected by the polarity control.
2.21 AUTO-SHUTDOWN
Auto-shutdown provides the ability to suspend the PWM output immediately upon an
external input or program control. The auto-shutdown control, shown in Figure X
Auto-Shutdown, is opened by clicking on the auto-shutdown block in the main GUI.
2.21.1 Shutdown Enable
Shutdown is enabled by clicking on the switch at the output of the control. When
shutdown is enabled then a high on any shutdown source will force the PSMC outputs
to a predetermined state until the shutdown source goes low and the PSMC is
restarted.
Main PSMC Configuration GUI
2.21.2 Shutdown Sources
Shutdown sources are selected by clicking on the broken lines leading to the 8-input
OR gate. The broken line will change to an unbroken line indicating that the connection
is made. Remove source selections by clicking on the unbroken OR gate input line.
The ASE switch is a software control bit that provides software generated shutdown
events. You can preset this bit by clicking on the switch.
2.21.3 Shutdown Override
Clicking on the ASDOV switch changes the state of the auto-shutdown override bit.
When set, this bit forces a shutdown condition that remains in effect as long as the bit
is set. Manual and automatic restarts have no affect while the ASDOV bit is set.
2.21.4 Auto/Manual Restart
Clicking on the ARSEN switch selects between automatic and manual restart. When
restart is automatic then the PSMC will resume operation after all shutdown sources
are low. When restart is manual, then the ASE bit must be cleared by software to restart
the PSMC. The ASE bit can only be cleared if all input sources are low. In either case,
PSMC operation resumes on the first period event after the shutdown is cleared.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 35
Page 36

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 2-25: AUTO-SHUTDOWN
2.22 SYNC OUTPUT CONTROL (NOT AVAILABLE ON THE PIC16(L)F1782/3)
Slaves select the sync source as shown in Section 2.13 “Timer”. The sync output of
PIC16(L)F1783/3 devices is fixed to the period event output. All other devices can
select either the period event or rising event as the sync output.
The sync output control, shown in Figure 2-26, is opened by clicking on the sync block
of the main GUI. The synchronization signal output to other PSMC sync inputs may
come directly from the period event or from the rising edge event. Clicking on the
double-pole switch selects between the two possibilities.
When the switch selects the period event as the master PSMC sync source then all
slave PSMCs will synchronize their period events to the master. This requires the
period time for all slave PSMCs to be as long as or longer than the period time of the
master.
When the switch selects the rising event as the master PSMC sync source, then the
master PSMC rising event defaults to the master PSMC period event, and the slave
PSMCs period is delayed by the master PSMC rising event time. Delaying slaves in this
manner retains the 0 to 100% duty cycle range of the master and slave in phase
delayed applications.
FIGURE 2-26: SYNC CONTROL
DS40001671B-page 36 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 37

Chapter 3. PSMC Tips
The following sections provide useful tips for getting the most out of the PSMC
peripheral.
3.1 VARIABLE PERIOD WITH FIXED OFF-TIME
Some power supply designs use a fixed off-time and then vary the duty cycle by
asynchronous feedback to terminate drive time and also start a new period. The first
configuration that comes to mind is shown in Figure 3-1 and is setup as follows:
- Period event: Asynchronous feedback
- Rising event: Synchronous time set to desired fixed off-time
- Falling event: Asynchronous feedback – same source as period event
FIGURE 3-1: FIXED OFF-TIME WITH RISING EVENT DELAY
PSMC DESIGNER
USER’S GUIDE
This will not work because the timing of the asynchronous event relative to the
psmc_clk may cause the rising event to be suppressed.
An alternate method, shown in Figure 3-2 with Falling Event Delay, uses a fixed falling
event delay, which avoids the timing issue is setup as follows:
- Period event: Asynchronous feedback
- Rising event: Synchronous time set to zero
- Falling event: Synchronous time set to desired fixed off-time
- Shutdown level: Low
- Output polarity: Inverted
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 37
Page 38

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 3-2: FIXED OFF-TIME WITH FALLING EVENT DELAY
This method inverts the output so that the synchronous duty cycle becomes the
off-time, and the off-time after the duty cycle end becomes the on-time. Use
auto-shutdown to start and stop the application.
3.2 3-PHASE VARIABLE DUTY CYCLE
3-Phase applications such as power supplies, AC induction motors, and tri-color LED
lighting, require three PWMs with a fixed-phase offset from each other. These
applications also require a variance of the PWM duty cycle from 0 to 100%. The rising
event phase-delay alone cannot be used to offset the waveforms because the rising
event delay subtracts from the time available for the duty cycle. For example, if a period
has 100 microseconds and the rising event time is 30 microseconds then the falling
event time after the rising event can be no larger than 70 microseconds, which is a
maximum duty cycle of 70%.
Phase delay can be implemented without losing duty cycle range by selecting the rising
event sync output option. When that option is selected then the synchronous rising
event time defaults to zero. In other words, the rising event time is the master’s phase
delayed sync output and the master’s synchronous rising edge event occurs at the
master’s period event.
Now consider how this affects the three PSMCs generating the three PWMs in the
three phase waveform:
• The first PSMC is the master for the second PSMC
• The second PSMC is the slave of the first PSMC but is also the master to the third
PSMC
• The third PSMC is the slave of the second PSMC and master of none
Setup for the three PSMCs of a PIC16(L)F1786 is as follows:
- Select the PIC16(L)F1786 and PSMC1
- Click on the Sync function: Set rising event as the sync output
- Click on the Timer function: Set the sync source to Off
- Click on the Period Event function: Set the period event time to the desired
value. Click on the upper input line to the output OR gate to make the
synchronous connection.
- Click on the Rising Event function: Set the rising event delay to the desired
phase offset. Click on the upper input line to the output OR gate to make the
synchronous connection.
- Click on the Falling Event function: Set the falling event duty cycle to the
desired value. Click on the upper input line to the output OR gate to make the
synchronous connection.
- Click on the Modulation function: Enable modulation and set the source to
CM4 SYNC
DS40001671B-page 38 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 39

PSMC Tips
- Click on the Mode Control function: Click on the tab to set the desired PWM
mode
- Click on the Output Control function: Connect the steering (if needed),
channel polarity, and desired outputs to pins
- Check the PSMC enable box
- Write in the comments section notes about Phase 1 of this 3-phase setup
- Copy this setup using the Copy and Show button
Select PSMC2
- Paste the configuration copied from PSMC1 by clicking on the Paste button
- Click on the Timer function: Change the sync source to PSMC1
- Click on the Modulation function: Disable modulation
- Click on the Output Control function: Change if necessary the steering,
polarity, and channel outputs to pins
- Write in the comments section notes about Phase 2 of this 3-phase setup
- All other settings are the same as PSMC1 and need not be changed
Select PSMC3
- Paste the configuration copied from PSMC1 by clicking on the Paste button
- Click on the Timer function: Change the sync source to PSMC2
- Click on the Output Control function: Change if necessary the steering, polarity, and channel outputs to pins
- Write in the comments section notes about Phase 3 of this 3-phase setup
- All other settings are the same as PSMC2 and need not be changed
Use the file pull-down menu to save the three-phase configuration setup as a C or
Assembly code include file.
If your project initialization routine does not include the I/O pin initialization for the
PSMC outputs, then add that initialization code to your project. Also add the reference
to your project to include the PSMC configuration file.
Modulation has been used in this setup so that the 3-phase output starts in order with
PSMC1 operating first when the modulation source is high. In this example,
Comparator 4 sync output is used as the modulation source. The 3-Phase PWM is
started by Comparator 4 output high and stopped by Comparator 4 output low. This is
accomplished by software setting the C4POL bit to start the PWM and clearing the
C4POL bit to stop the PWM. The C4ON and C4SYNC bits should both be cleared. All
other Comparator 4 control bits are don’t care.
3.3 CENTER WEIGHTED VARIABLE PWM
Some applications benefit from a PWM that spreads from the middle of the period
instead of expanding from the start of the period. This is sometimes referred to as
center weighted PWM. Center weighted PWM can be accomplished by setting the
rising event time to the middle of the period minus half the PWM width and setting the
falling event time to the middle of the period plus half the PWM width (Figure 3-3).
Irregular PWM widths are avoided during the change, because the new settings are
held until the PxLD bit (bit 6 of the PSMCxCON register) is set. The transfer to the
counters is performed synchronous with the PWM period, ensuring that both new
settings take effect in the same period.
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 39
Page 40

PSMC Designer User’s Guide
FIGURE 3-3: CENTER WEIGHTED PWM
DS40001671B-page 40 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 41

NOTES:
PSMC Designer User’s Guide
2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc. DS40001671B-page 41
Page 42

Worldwide Sales and Service
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
http://www.microchip.com/
support
Web Address:
www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Duluth, GA
Tel: 678-957-9614
Fax: 678-957-1455
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Cleveland
Independence, OH
Tel: 216-447-0464
Fax: 216-447-0643
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Farmington Hills, MI
Tel: 248-538-2250
Fax: 248-538-2260
Indianapolis
Noblesville, IN
Tel: 317-773-8323
Fax: 317-773-5453
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
Santa Clara
Santa Clara, CA
Tel: 408-961-6444
Fax: 408-961-6445
Toronto
Mississauga, Ontario,
Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699
Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Asia Pacific Office
Suites 3707-14, 37th Floor
Tower 6, The Gateway
Harbour City, Kowloon
Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8569-7000
Fax: 86-10-8528-2104
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8665-5511
Fax: 86-28-8665-7889
China - Chongqing
Tel: 86-23-8980-9588
Fax: 86-23-8980-9500
China - Hangzhou
Tel: 86-571-2819-3187
Fax: 86-571-2819-3189
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2943-5100
Fax: 852-2401-3431
China - Nanjing
Tel: 86-25-8473-2460
Fax: 86-25-8473-2470
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-8502-7355
Fax: 86-532-8502-7205
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-5407-5533
Fax: 86-21-5407-5066
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
Fax: 86-24-2334-2393
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8864-2200
Fax: 86-755-8203-1760
China - Wuhan
Tel: 86-27-5980-5300
Fax: 86-27-5980-5118
China - Xian
Tel: 86-29-8833-7252
Fax: 86-29-8833-7256
China - Xiamen
Tel: 86-592-2388138
Fax: 86-592-2388130
China - Zhuhai
Tel: 86-756-3210040
Fax: 86-756-3210049
ASIA/PACIFIC
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-3090-4444
Fax: 91-80-3090-4123
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-4160-8631
Fax: 91-11-4160-8632
India - Pune
Tel: 91-20-2566-1512
Fax: 91-20-2566-1513
Japan - Osaka
Tel: 81-6-6152-7160
Fax: 81-6-6152-9310
Japan - Tokyo
Tel: 81-3-6880- 3770
Fax: 81-3-6880-3771
Korea - Daegu
Tel: 82-53-744-4301
Fax: 82-53-744-4302
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or
82-2-558-5934
Malaysia - Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 60-3-6201-9857
Fax: 60-3-6201-9859
Malaysia - Penang
Tel: 60-4-227-8870
Fax: 60-4-227-4068
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 63-2-634-9065
Fax: 63-2-634-9069
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan - Hsin Chu
Tel: 886-3-5778-366
Fax: 886-3-5770-955
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-213-7828
Fax: 886-7-330-9305
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2508-8600
Fax: 886-2-2508-0102
Thailand - Bangkok
Tel: 66-2-694-1351
Fax: 66-2-694-1350
EUROPE
Austria - Wels
Tel: 43-7242-2244-39
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Copenhagen
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
France - Paris
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Munich
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
Spain - Madrid
Tel: 34-91-708-08-90
Fax: 34-91-708-08-91
UK - Wokingham
Tel: 44-118-921-5869
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
11/29/12
DS40001671B-page 42 2012-2013 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...