Page 1

Low Pin Count Demo Board
User’s Guide
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A
Page 2

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digit al Millennium Copyright Act. If suc h a c t s
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is provided only for your convenience
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE,
RELATED TO THE INFORMATION, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION, QUALITY, PERFORMANCE,
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR PURPOSE.
Microchip disclaims all liability arising from this information and
its use. Use of M icrochip’s prod ucts as critical components in
life support systems is not authorized except with express
written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed,
implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip intellectual property
rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Accuron,
dsPIC, K
EELOQ, microID, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART,
PRO MATE, PowerSmart, rfPIC, and SmartShunt are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A. and other countries.
AmpLab, FilterLab, Migratable Memory, MXDEV, MXLAB,
PICMASTER, SEEVAL, SmartSensor and The Embedded
Control Solutions Company are registered trademarks of
Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, ECAN, ECONOMONITOR,
FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB, In-Circuit Serial
Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, Linear Active Thermistor,
MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM, PICkit, PICDEM,
PICDEM.net, PICLAB, PICtail, PowerCal, PowerInfo,
PowerMate, PowerTool, rfLAB, rfPICD EM, Select Mode,
Smart Serial, SmartTel, Total Endurance and WiperLock are
trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the
U.S.A. and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2005, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2002 quality system certification for
its worldwide headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona and Mountain View, California in
October 2003. The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are for its PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and
analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design
and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
®
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ
®
code hopping
DS51556A-page ii © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3

LOW PIN COUNT DEMO BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
Tabl e of Conten ts
Preface ...........................................................................................................................1
Chapter 1. Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board Overview
1.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Highlight s .................... .. ............. .. .............. .. .. ............. ... ............. .. .. ............. ... 7
1.3 Devices S u pp o rted by the LPC D e mo Board .................... ............. .. .............. 7
1.4 LPC Demo B o a rd O verview ...................... .. ............. .. .............. .. ............. .. ..... 8
1.5 Running the PICkit™ 2 Flash Starter Kit Default Demonstration ................... 8
Chapter 2. Mid-Range PICmicro® Architectural Overvie w
2.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 9
2.2 Memory Organization ...................................................................................10
2.3 Instruct io n fo rma ts ...... .. ............. .. .............. .. .. ............. ... ............. .. .. ............. . 10
2.3.1 Assembler Basics ......................................................................................11
Chapter 3. LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.1 Introduction ................................................................................................... 13
3.2 LPC Demo B o a rd le ss o n s ................ ............. .. .............. .. ............. .. ............. . 13
3.2.1 Lesson 1: Hello World (Light a LED) .......................................................................14
3.2.2 Lesson 2: Delay Loop (Blink a LED) ....................................................................... 15
3.2.3 Lesson 3: Rotate (Move the LED) ...........................................................................17
3.2.4 Lesson 4: Analog-to-Digital .....................................................................................19
3.2.5 Lesson 5: Variable Speed Rotate ...........................................................................22
3.2.6 Lesson 6: Switch Debouncing ................................................................................23
3.2.7 Lesson 7: Reversible Variable Speed Rotate ......................................................... 25
3.2.8 Lesson 8: Function Calls ........................................................................................26
3.2.9 Lesson 9: Timer0 ....................................................................................................27
3.2.10 Lesson 10: Interrupts ............................................................................................29
3.2.11 Lesson 11: Indirect Data Addressing ....................................................................31
3.2.12 Lesson 12: Look-up Table (ROM Array) ...............................................................33
Appendix A. Hardware Schematics
A.1 Introduction .................................................................................................. 37
Worldwide Sales and Service ....................................................................................38
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page iii
Page 4

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
NOTES:
DS51556A-page iv © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5

LOW PIN COUNT DEMO
BOARD USER’S GUIDE
Preface
NOTICE TO CUSTOMERS
All documentation becomes dated, and this manual is no exception. Microchip tools and
documentation are constantly evolving to meet customer needs, so some actual dialogs
and/or tool descriptions may differ from those in this document. Please refer to our web site
(www.microchip.com) to obtain the latest documentation available.
Documents are identified with a “DS” number. This number is located on the bottom of each
page, in front of the page number. The numbering convention for the DS number is
“DSXXXXXA”, where “XXXXX” is the document number and “A” is the revision level of the
document.
For the most up-to-date information on development tools, see the MPLAB
Select the Help menu, and then Topics to open a list of available on-line help files.
®
IDE on-line help.
INTRODUCTION
This chapter contains general information that will be useful to know before using the
Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board. Items discussed in this chapter include:
• About this Guide
• Warranty Registration
• Recommended Reading
• Troubleshooting
• The Microchip Web Site
• Development Systems Customer Notification Service
• Customer Support
DOCUMENT LAYOUT
This document describes how to use the Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide as
a development tool to emulate and debug firmware on a target board. The manual
layout is as follows:
• Chapter 1. “Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board Overview” – An overview of
Microchip’s Low Pin Count Demo Board.
• Chapter 2. “Mid-Ra nge PICm icro
the Mid-range PICmicro
• Chapter 3. “ LPC Demo Boa rd Lesso ns” – Contains a variety of lessons that
demonstrate how to utilize and experiment with the Low Pin Count Demo Board.
®
Architecture.
®
Architectural Overview” – An overview of
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 1
Page 6
Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
CONVENTIONS USED IN THIS GUIDE
This manual uses the following docum entat io n conven tion s:
DOCUMENTATION CONVENTIONS
Description Represents Examples
Arial font:
Italic characters Referenced books MPLAB
Emphasized text ...is the only comp ile r...
Initial caps A window the Output window
A dialog the Settings dialog
A menu selection select Enable Programmer
Quotes A field name in a window or
dialog
Underlined, italic text with
right angle bracket
Bold characters A dialog button Click OK
N‘Rnnnn A number in verilog format,
Text in angle brackets < > A key on the keyboard Press <Enter>, <F1>
Courier font:
Plain Courier Sample source code #define START
Italic Courier A variable argument file.o, where file can be
Square brackets [ ] Optional arguments mcc18 [options] file
Curly brackets and pipe
character: { | }
Ellipses... Replaces r epeated text var_name [,
A menu path File>Save
A tab Click the Power tab
where N is the tota l number of
digits, R is th e radi x and n is a
digit.
Filenames autoexec.bat
File paths c:\mcc18\h
Keywords _asm, _endasm, static
Command-line options -Opa+, -Opa-
Bit values 0, 1
Constants 0xFF, ‘A’
Choice of mutually exclusive
arguments; an OR selection
Represents code supplied by
user
“Save project before build”
4‘b0010, 2‘hF1
any valid filename
[options]
errorlevel {0|1}
var_name...]
void main (void)
{ ...
}
®
IDE User’s Guide
DS51556A-page 2 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

WARRANTY REGISTRATION
Please complete the enclosed Warranty Registration Card and mail it promptly.
Sending in the Warranty Registration Card entitles users to receive new product
updates. Interim software releases are available at the Microchip web site.
RECOMMENDED READING
This user’s guide describes how to use the Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board. Other
useful documents are listed below. The following Microchip documents are available
and recommended as supplemental reference resources.
Readme for Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board
For the latest information on using the Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board, read the
“Readme for Low Pin Count Demo Board.txt” file (an ASCII text file) in the
PICkit 2 installation directory. The Readme file contains update information and known
issues that may not be included in this user’s guide.
Readme Files
For the latest information on using other tools, read the tool-specific Readme files in
the Readmes subdirectory of the MPLAB IDE installation directory. The Readme files
contain update information and known issues that may not be included in this user’s
guide.
PICkit™ 2 Microcontroller Programmer User’s Guide (DS51553)
Consult this document for instr ucti ons on how to use the PICkit2 Microcontroller
Programmer hardware and software.
PIC16F685/687/689/690 Data Sheet (DS41262)
Consult this document for information regarding the PIC16F685/687/689/690 20-pin
Flash based, 8-bit CMOS Microcontroller device specifications.
MPLAB
Consult this document for more information pertaining to the installation and features
of the MPLAB Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Software.
®
IDE, Simulator, Editor User’s Guide (DS51025)
Preface
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 3
Page 8

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
THE MICROCH IP WEB SITE
Microchip provides online support via our web site at www.microchip.com. This web
site is used as a means to make files and information easily available to customers.
Accessible by using your favorite Internet browser, the web site contains the following
information:
• Product Support – Data sheets and errata, application notes and sample
programs, design resources, user’s guides and hardware support documents,
latest software releases and archived software
• General Technical Support – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), technical
support requests, online discussion groups, Microchip consultant program
member listin g
• Business of Microchip – Product selector and ordering guides, latest Microchip
press releases, listing of seminars and events, listings of Microchip sales offices,
distributors and factory representatives
DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMS CUSTOMER CHANGE NOTIFICATION SERVICE
Microchip’s customer notification service helps keep customers current on Microchip
products. Subscribers will receive e-mail notification whenever there are changes,
updates, revisions or errata related to a specified product family or development tool of
interest.
To register, access the Microchip web site at www.microchip.com, click on Customer
Change Notification and follow the registration instructions.
The Development Systems product group categories are:
• Compilers – The latest information on Microchip C compilers and other language
tools. These include the MPLAB C18 and MPLAB C30 C compilers; MPASM™
and MPLAB ASM30 assemblers; MPLINK™ and MPLAB LINK30 object linkers;
and MPLIB™ and MPLAB LIB30 object librarians.
• Emulators – The latest information on Microchip in-circuit emulators.This
includes the MPLAB ICE 2000 and MPLAB ICE 4000.
• In-Circuit Debuggers – The latest information on the Microchip in-circuit
debugger, MPLAB ICD 2.
• MPLAB
Integrated Development Environment for development systems tools. This list is
focused on the MPLAB IDE, MPLAB SIM simulator, MPLAB IDE Project Manager
and general editing and debugging features.
• Programmers – The latest information on Microchip programmers. These include
the MPLAB PM3 and PRO MATE
Plus and PICkit
®
IDE – The latest information on Microchip MPLAB IDE, the Windows®
®
®
1 development programmers.
II device programmers and the PICSTART®
DS51556A-page 4 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

CUSTOMER SUPPORT
Users of Microchip products can receive assistance through several channels:
• Distributor or Representative
• Local Sales Office
• Field Application Engineer (FAE)
• Technical Support
• Development Systems Information Line
Customers should contact their distributor, representative or field application engineer
(FAE) for support. Local sales offices are also available to help customers. A listing of
sales offices and locations is included in the back of this document.
Technical support is available through the web site at: http://support.microchip.com
In additi on, t her e is a De velo pment Sys tem s In form at ion Li ne w hic h lis t s th e la tes t ve r-
sions of Microchip’s development systems software products. This line also provides
information on how customers can receive currently available upgrade kits.
The Development Systems Information Line numbers are:
1-800-755-2345 – United States and most of Canada
1-480-792-7302 – Other Interna tio nal Loca tio ns
Preface
DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY
Revision A (May 2005)
• Initial Release of this Document.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 5
Page 10

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
NOTES:
DS51556A-page 6 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11

LOW PIN COUNT DEMO BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
Chapter 1. Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board Overview
1.1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter introduces the Low Pin Count (LPC) Demo Board and describes the LPC
Demo Board features.
1.2 HIGHLIGHTS
This chapter discusses:
• Devices supported by the LPC Demo Board
• The LPC Demo Board Overview
• Running the PICkit™ 2 Starter Kit Default Demonstration
1.3 DEVICES SUPPORTED BY THE LPC DEMO BOARD
For a list of supported devices, see the LPC Demo Board README file on the PICkit™ 2
Starter Kit CD-ROM.
8-pin DIP Flash Devices:
PIC12F508 PIC12F629 PIC12F635
PIC12F509 PIC12F675 PIC12F683
PIC12F510
14-pin DIP Flash Devices:
PIC16F505 PIC16F630 PIC16F684
PIC16F506 PIC16F676 PIC16F688
20-pin DIP Flash Devices:
PIC16F685 PIC16F689 PIC16F785
PIC16F687 PIC16F690
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 7
Page 12
Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
r
1.4 LPC DEMO BOARD OVERVIEW
The Low Pin Count Demo Board Works with the PICkit™ 2 Microcontroller
Programmer to help the user get up to speed quickly using PICmicro
This user’s guide is written in the form of Lessons intended for a person with some
exposure to assembly language but has never used a PICmicro
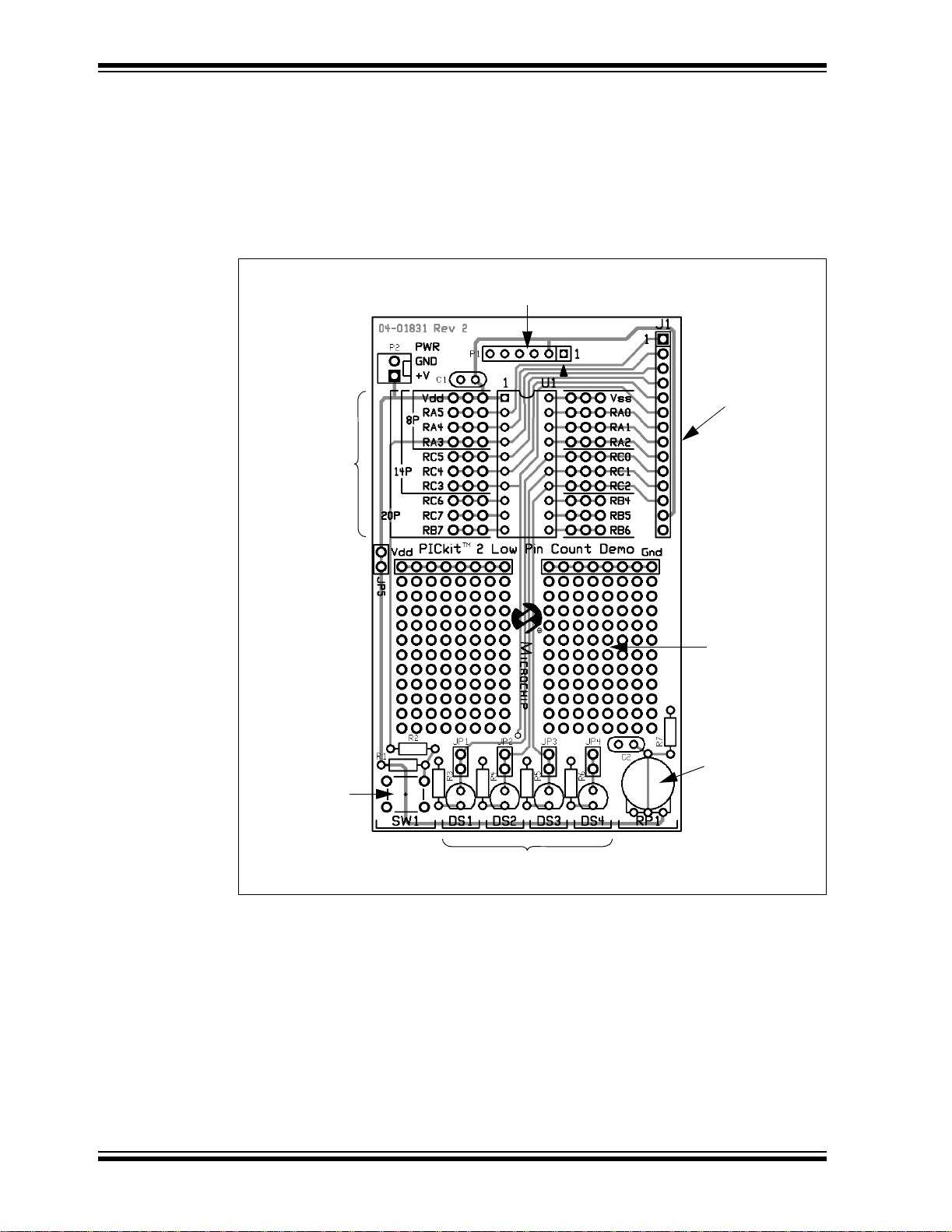
The LPC Demo Board overview is shown in Figure 1-1.
FIGURE 1-1: LPC DEMO BOARD
®
microcontr ollers.
®
microcontroller.
PICkit™ 2 Programming Header
14-pin Expansion
Header
20-pin
DIP Socket
Generous
Prototyping
Area
Potentiomete
Push Button
LEDs
1.5 RUNNING THE PICkit™ 2 STARTER KIT DEFAULT DEMONSTRATION
The Low Pin Count Demo Board comes preprogrammed with a demonstration program.
To use this program, connect the PICkit™ 2 Starter Kit to the PC’s USB port using the
USB cable. Start the PICkit™ 2 Microcontroller Programmer application and check the
target power box. The demo program will blink the four red lights in succession. Press
the Push Button Switch, labeled SW1, and the sequence of the lights will reverse. Rotate
the potentiometer , labeled RP1, and th e light sequence will blink at a different rate. This
demo program is developed through the first 7 lessons in this guide.
DS51556A-page 8 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13
LOW PIN COUNT DEMO BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
Chapter 2. Mid-Range PICmicro® Architectural Overview
2.1 INTRODUCTION
This chapt er describes the Mid-range PICmicro® Architectural Overview for the LPC
Demo Board.
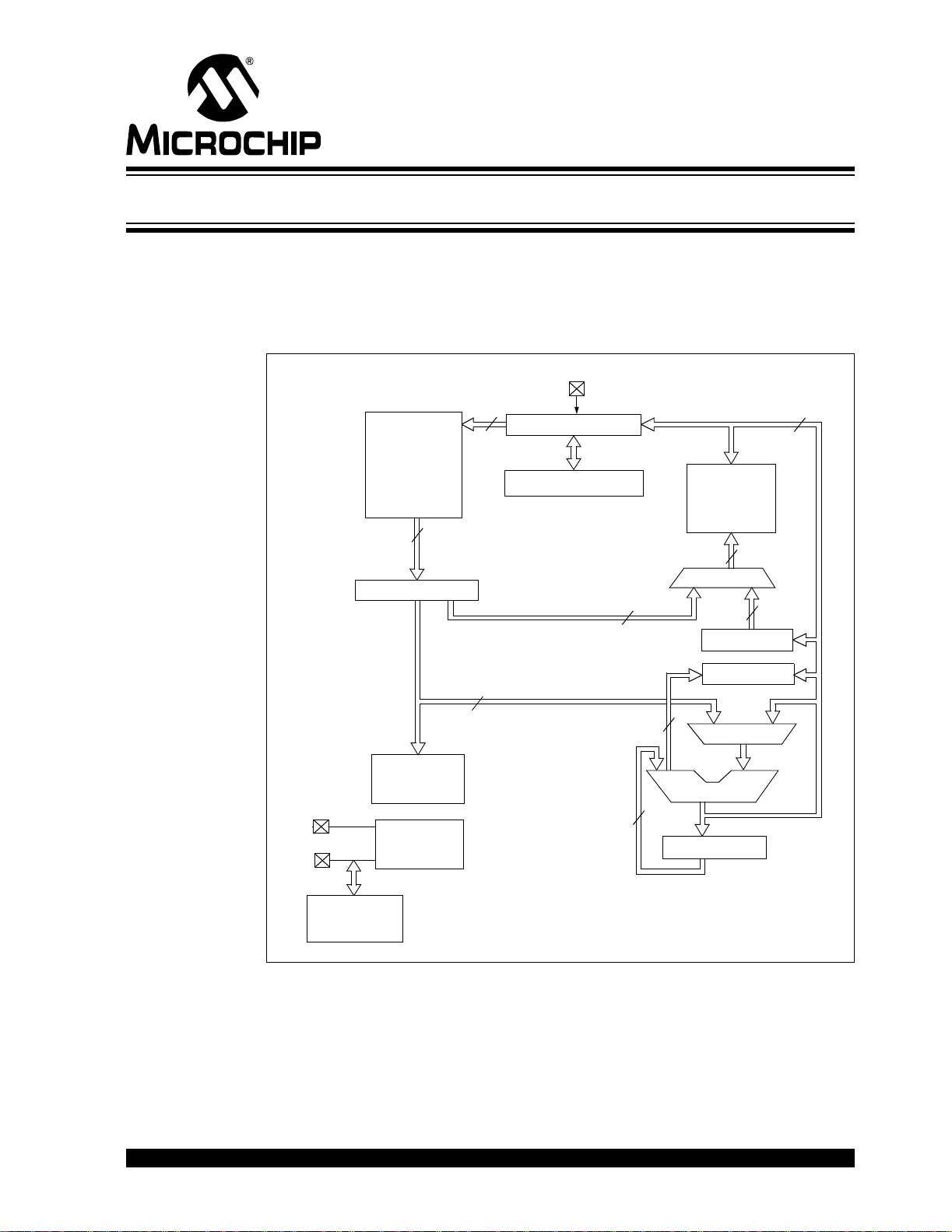
FIGURE 2-1: SIMPLIFIED MID-RANGE PICmicro
INT
13
Program Counter
8-Level Stack (13-bit)
Direct Addr
7
Program
Bus
OSC1/CLKI
OSC2/CLKO
Flash
4k x 14
Program
Memory
14
Instruction Reg
8
Instruction
Decode and
Control
Timing
Generation
®
BLOCK DIAGRAM
Data Bus
RAM
256 bytes
File
Registers
RAM Addr
9
Addr MUX
8
FSR Reg
Status Reg
3
8
MUX
ALU
W Reg
8
Indirect
Addr
Internal
Oscillator
Block
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 9
Page 14

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
2.2 MEMORY ORGANIZATION
PICmicro® microcontrollers are designed with separate program and data memory
areas. This allows faster execution as the address and data busses are separate and
do not have to do double duty.
Data Memory is held in file regi ster s. Ins truc tions referr ing to fil e regi sters us e 7 bit s,
so only 128 file registers can be addressed. Multiple file registers are arranged into
“pages”. Two extra bits RP0 and RP1 (in the Status register) allow accessing multiple
pages. These two bits effectively become the top two bits of the file register address.
The additional pages may or may not be implemented, depending on the device.
Mid-range devices reserve the first 32 addresses of each page for Special Function
Registers (SFRs). SFRs are how the program interacts with the peripherals. The
controls and data registers are memory mapped into the SFR space. Addresses above
0x20 to the end of each page are General Purpose Registers (GPRs), where program
variables may be stored.
Some frequently used registers may be accessed from any bank. For example, the
Status register is always available no matter which bank is selected via the RP bits. The
last 16 bytes (0x70-0x7F) may also be accessed from any bank.
Program Memory is accessed via a 13-b it Program Counter (P C). The lo wer 8 bit s are
accessible via SFR (PCL), and the upper 5 are at a PCLATH. See the
PIC16F685/687/689/690 Data Sheet’s (DS41262) Section on PCL and PCLATH for
more details on the PC. PCLATH becomes important when program memory size
exceeds 1k instructions, and also for the table look-up in Lesson 12.
Mid-range PICmicro
otherwise noted, the lessons in this manual use the Internal Oscillator running at 4 MHz.
®
MCUs may be clocked by a number of different devices. Unless
2.3 INSTRUCTION FORMATS
Most instructions follow one of three formats: Byte oriented instructions, Bit oriented
instructions and Literal instructions.
Byte instructions contain 7-bit data address, a destination bit, and 6-bit op code. The
data address plus the RP0 and RP1 bits create a 9-bit data memory address for one
operand. The other operand is the Working register (called W or Wreg). After the
instruction executes, the destination bit (d) specifies whether the result will be stored in
W or back in the original file register. For example:
ADDWF data,f
adds the contents of Wreg and data, with the result going back into data.
Bit instructions operate on a specific bit within a file register. They contain 7 bits of data
address, 3-bit number and the remaining 4 bits are op code. These instructions may
set or clear a specific bit within a file register. They may also be used to test a specific
bit within a file register. For example:
BSF STATUS,RP0
set the RP0 bit in the Status register.
Literal instructions contain the data operand within the instruction. The Wreg becomes
the other operand. Calls and GOTO’s use 11 bits as a literal address.
MOVLW'A'
Moves the ASCII value of ‘A’ (0x41) into Wreg.
DS51556A-page 10 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

Mid-Range PICmicro® Architectural Overview
2.3.1 Assembler Basics
Numbers in the Assembler
Unless otherwise specified, the assembler assumes any numeric constants in
the progr am are hexa decimal (b ase 16). Bi nary (bas e 2), Octa l (base 8) , Decimal
(base 10), and ASCII coding are also supported.
Hexadecimal: 12 or 0x12 or H'12'
Decimal .12 or D'12'
Octal O'12'
Binary B'00010010'
ASCII A'c' or 'c'
(Origin)
Org
Org tells the Assembler where to start generating code. Normally we start coding
at address ‘0000’, but it could be anywhere. Baseline devices have a Reset
vector at the last location in program memory, so it’s good practice to have a
GOTO instruction pointing to the beginning of the program.
End
End tells the assembler to stop assembling. There must be one at the end of the
program. It does not necessarily have to be at the end of the file, but nothing after
the end statement will be assembled.
Defining Data Memory Locations
There are three ways to name a location (see Example 2-1).
EXAMPLE 2-1: DEFINING DATA MEMORY
#define Length 0x20 ;c-like syntax
Length equ 0x20 ;equate 0x20 with the symbol
cblock 0x20 ;start a block of variables
Length ;this will be at address 0x20
Width ;this will be at address 0x21
Area:2 ;this is 2 bytes long, starting at
;address 0x22
Girth ;this will be at address 0x24
endc
Unless there is a reason to want a name to a specific location, the cblock/endc
method is preferred. The advantage is that as variables come and go through the
development process, the cblock keeps the block to a minimum. Using one of the other
methods, you may have to go back and find an unused location.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 11
Page 16

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
NOTES:
DS51556A-page 12 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

LOW PIN COUNT DEMO BOARD
Chapter 3. LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.1 INTRODUCTION
The following lessons cover basic LPC Demo Board features. Refer to applicable
documents as needed. Any updates to the applicable documents are available on
Microchip’s web site.
The code and hex files are installed in C:\Microchip\PICkit 2 Lessons\. They
may also be found on the PICkit™ 2 CD-ROM under directory \PICkit 2 Lessons\.
3.2 LPC DEMO BOARD LESSONS
• Lesson 1: Hello World (Light a LED)
• Lesson 2: Delay Loop (Blink a LED)
• Lesson 3: Rotate (Move the LED)
• Lesson 4: Analog-to-Digital
• Lesson 5: Variable Speed Rotate
• Lesson 6: Switch Debounce
• Lesson 7: Reversible Variable Speed Rotate
• Lesson 8: Function Calls
• Lesson 9: Timer0
• Lesson 10: Interrupts
• Lesson 11: Indirect Data Addressing
• Lesson 12: Look-up Table (ROM Array)
USER’S GUIDE
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 13
Page 18

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
3.2.1 Lesson 1: Hello World (Light a LED)
The first lesson shows how to turn on a LED. This is the PICmicro® microcontroller
version of “Hello World” and discusses the I/O pin structures.
New Instructions
BSF Bit set
BCF Bit clear
The LEDs are connected to I/O pins RC0 through RC3. When one of these I/O pins
drive high, the LED turns on. The I/O pins can be configured for input or output. On
start-up, the default is input. The TRIS bits use the convention of ‘0’ for output and ‘1’
for input. We want digital output so these must be configured.
EXAMPLE 3-1: PICkit 2, LESSON 1: “HELLO WORLD”
; PICkit 2 Lesson 1 - 'Hello World'
;
#include <p16F690.inc>
__config (_INTRC_OSC_NOCLKOUT & _WDT_OFF & _PWRTE_OFF &
_MCLRE_OFF & _CP_OFF & _BOD_OFF & _IESO_OFF & _FCMEN_OFF)
org 0
Start
BSF STATUS,RP0 ;select Register Page 1
BCF TRISC,0 ;make I/O Pin C0 an output
BCF STATUS,RP0 ;back to Register Page 0
BSF PORTC,0 ;turn on LED C0
GOTO $ ;wait here
end
Now lets look at the program that makes this happen.
; Starts a comment. Any text on the line following the semicolon
is ignored.
#include Brings in an include file defining all the Special Function
Registers available on the PIC16F690. Also, it defines valid
memory areas. These definitions match the names used in the
device data sheet.
__Config Defines the Configuration Word. The labels are defined in the
p16F690.inc file. The labels may be logically ANDed
together to form the word.
Org 0 T ells the assembler where to start generating code. Code may
be generated for any area of the part. Mid-range PICmicro
®
microcontroller de vi ce s start at addres s ‘0’, also called the
Reset vecto r.
BCF TRISC,0 Tells the processor to clear a bit in a file register. TRISC is the
Tri-state register for pin 0 of PORTC. A ‘1’ in the register
makes the pin an input; a ‘0’ makes it an output. We want to
make it an output, so the bit must be cleared.
BSF PORTC,0 Tells the processor to set pin 0 of PORTC. This will force the
I/O pin to a high condition turning on the LED.
GOTO $ Tells the processor to go to the current instruction.
For more information, refer to the I/O Ports Section of the PIC16F685/687/689/690
Data Sheet (DS41262).
DS51556A-page 14 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.2 Lesson 2: Delay Loop (Blink a LED)
The first lesson showed how to turn on a LED, this lesson shows how to make it blink.
While this might seem a trivial change from Lesson 1, the reasons will soon become
apparent.
New Instructions
CLRF Clear file register
INCF Increment file register
DECF Decrement file register
INCFSZ Increment file register, Skip next instruction if zero
DECFSZ Decrement file register, Skip next instruction if zero
GOTO Jump to a new location in the program
EXAMPLE 3-2: PICkit 2, LESSON 2: BLINK
Loop
BSF PORTC,0 ;turn on LED C0
BCF PORTC,0 ;turn off LED C0
GOTO Loop ;do it again
While adding a BCF instruction a nd ma ki ng it lo op w il l ma k e it bl in k, it w il l bl i nk so fas t
you won’t see it. It will only look dim. That loop requires 4 instruction times to execute.
The first instruction turns it on. The second one turns it off. The GOTO takes two instruc tion times, which means it will be on for 25% of the time.
As configured, the PICmicro executes 1 million instructions per second. At this rate, the
blinking needs to be slowed down so that the blinking can be seen, which can be done
by using a delay loop.
Note: Counting cycles – Relating clock speed to instruction speed. The processor
requires 4 clocks to execute an instruction. Since the internal oscillator as
used in these lessons runs at 4 MHz, the instruction rate is 1 MHz.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 15
Page 20

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
Increment or Decrement a File Register
The INCFSZ and DECFSZ instructions add or subtract one from the contents of
the file register and skips the next instruction when the result is zero. One use is
in the delay loop as shown in Example 3-3.
CLRF Clears the counter location.
DECFSZ Decrements the location, and if the result is zero, the next
instruction is skipped.
EXAMPLE 3-3: DELAY LOOP
Short Loop
CLRF Delay
Loop
DECFSZ Delay,f
GOTO Loop
Long Loop
CLRF Delay1
CLRF Delay2
Loop
DECFSZ Delay1,f
GOTO Loop
DECFSZ Delay2,f
GOTO Loop
The GOTO Loop (in Example 3-3) backs up and does it again. This loop takes 3
instruction times; one for the decrement and two for the GOTO (see note) and the
counter will force it to go around 256 times, which takes it a total of 768 instruction times
(768 μs) to execute.
Even that is still too fast for t he eye to see. It can be slowed do wn even more by a dding
a second loop around this one.
The inner loop still takes 768 μs plus 3 for the outer loop, but now it’s executed another
256 times, 771 * 256 = 197376 μs = 0.197s.
Note: GOTO instructions take two instructions due to the pipelined design of the
processor. The processor fetches the next instruction while executing the
current instruction. When a program branch occurs, t he fetched instruction
is not executed.
Open Blink.asm and build the lesson. Next, import the hex file into the PICkit 2 and
program the device. Note the LED now flashes at about a 2 Hz rate.
DS51556A-page 16 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.3 Lesson 3: Rotate (Move the LED)
Building on Lessons 1 and 2, which showed how to light up a LED and then make it
blink with a delay loop, this lesson adds rotation. It will light up DS4 and then shift it to
DS3, then DS2, then DS1 and back to DS4.
New Instructions
MOVLW Loads Wreg with a literal value
MOVWF Moves the contents of Wreg to a file register
MOVF Moves the contents of a file register, either to Wreg or back
into the file register (see note)
RRF Rotate file register right
RLF Rot ate file register left
Note: Moving a file register to itself looks like a NOP at first. However, it has a
useful side effect in that the Z flag is set to reflect the value. In other words,
MOVF fileregister,f is a convenient way to test whether or not the
value is zero without affecting the contents of the Wreg.
Rotate Program Flow
• First, initialize the I/O port and the Display,
• Copy the Display variable to the I/O Port, then
• Delay for a little while
• Rotate the display
FIGURE 3-1: ROTATE PROGRAM FLOW
Initialize I/O Port
Put Up Display
Delay
Rotate Display
Did it overflow?
No
Reset Display
Yes
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 17
Page 22

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
Rotate
The rotate instructions (RRF or RLF) shift all the bits in the file register right or left by
one position, through the Carry bit. The Carry bit is shifted into the byte and receives
the bit shifted out of the byte. The Carry bit should be cleared before rotation so
unwanted bits are not introduced into the display byte. The Carry bit also indicates
when the display byte is empty. When it is, reinsert the ‘1’ at bit 3.
PICmicro MCUs have two rotate instructions: Rotate Left (RLF) and Rotate Right (RRF).
These instructions rotate the contents of a file register and Carry bit one place.
FIGURE 3-2: ROTATE LEFT
Carry
File Register
EXAMPLE 3-4: ROTATE EXAMPLE
Start
BSF STATUS,RP0 ;select Register Page 1
CLRF TRISC ;make I/O PORTC all output
BCF STATUS,RP0 ;back to Register Page 0
MOVLW 0x08
MOVWF Display
MainLoop
MOVF Display,w ;Copy the display to the LEDs
MOVWF PORTC
OndelayLoop ;Delay .197S
DECFSZ Delay1,f
GOTO OndelayLoop
DECFSZ Delay2,f
GOTO OndelayLoop
BCF STATUS,C ;ensure the carry bit is clear
RRF Display,f ;Rotate Display right
BTFSC STATUS,C ;Did the bit rotate into the carry?
BSF Display,3 ;yes, put it into bit 3.
GOTO MainLoop
DS51556A-page 18 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.4 Lesson 4: Analog-to-Digital
This lesson shows how to configure the ADC, run a conversion, read the analog voltage
controlled by the potentiometer (RP1) on the board, and display the high order 4 bits
on the display.
The PIC16F690 has an on board Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) with 10 bits of
resolution on any of 11 channels. The converter can be referenced to the device’s V
or an external voltage reference. The LPC Demo Board references it to V
DD as
provided by the USB cable. The answer from the ADC is represented by a ratio of the
voltage to the reference.
ADC = V/V
REF * 1023
Converting the answer from the ADC back to voltage requires solving for V.
V = ADC/1023 * V
REF
Two of the three factors on the right side of the equation are constants and may be
calculated in advance. This eliminates the need to actually divide, but still requires fixed
or floating point multiply to solve the equation on the fly.
However, sometimes, such as when reading a sensor, calculating the voltage is only
the first step. There may be additional math to calculate the meaningful data from the
sensor. For example, when reading a thermistor, calculating the voltage is only the first
step on the way to getting the temperature.
There are other means to convert ADC values, including a straight table look-up or a
piece-wise linear interpolation. Each of these represents different speed/memory
trade-offs.
The schematic (Appendix A. “Hardware Schematics”) shows the wiper on the
potentiometer is connected to pin RA0 on the PIC16F690.
Here’s the checklist for this lesson:
• Configure PORTA as an analog input, TRISA<0> = 1, ANSEL<0> = 1
• Select clock scaling in ADCON1.
• Select channel, justification and V
REF source in ADCON0.
DD
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 19
Page 24

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
3.2.4.1 ADCON1
ADCON1 selects the ratio between processor clock speed and conversion speed. This
is important because the ADC needs at least 1.6 μs per bit. Accuracy degrades if the
clock speed is too high. As the processor clock speed increases, an increasingly large
divider is necessary to keep the conversion speed. Four MHz is fastest at 8:1 ratio with
a conversion speed of 2 μs per bit. Refer to the “T
Frequencies” Table in the Analog-to-Digital Section of the PIC16F685/687/689/690
Data Sheet (DS41262) for recommended configurations.
AD vs. Device Operating
REGISTER 3-1: ADCON1 – A/D CONTROL REGISTER 1 (ADDRESS: 9Fh)
U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 U-0 U-0 U-0 U-0
— ADCS2 ADCS1 ADCS0 — — — —
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 6-4 ADCS<2:0>: A/D Conversion Clock Select bits
000 =F
001 =F
010 =F
x11 =F
100 =F
101 =F
110 =F
bit 3-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
OSC/2
OSC/8
OSC/32
RC (clock derived from a dedicated internal oscillator = 500 kHz max)
OSC/4
OSC/16
OSC/64
DS51556A-page 20 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.4.2 ADCON0
ADCON0 controls the ADC operation. Bit 0 turns on the ADC module. Bit 1 starts a
conversion and bits <5:2> selects which channel the ADC will operate. VCFG bit< 6>
selects the ADC reference, w hich may be either V
on V
REF. ADFM bit <7> selects whether the 10 bits are right or left justified in the 16 bits.
For purposes of this lesson, the ADC must be turned on and pointed to RA0. Choose
the internal voltage reference and 8T
OSC conversion clock.
The ADC needs about 5 μs, after changing channels, to allow the ADC sampling
capacitor to settle. Finally, we can start the conversion by setting the GO bit in ADCON0.
The bit also serves as the DONE
flag. That is, the ADC w ill clear the same bit when the
conversion is complete. The answer is then available in ADRESH:ADRESL.
This lesson takes the high order 4 bits of the result and copies them to the display LEDs
attached to PORTC.
See the Analog-to-Digital section in the PIC16F685/687/689/690 Data Sheet
(DS41262) for more details on the ADC module.
DD or a separate reference voltage
REGISTER 3-2: ADCON0 – A/D CONTROL REGISTER (ADDRESS: 1Fh)
R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
ADFM VCFG CHS3 CHS2 CHS1 CHS0 GO/DONE
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 ADFM: A/D Result Formed Select bit
1 = Right justified
0 = Left justified
bit 6 VCFG: Voltage Reference bit
REF pin
1 = V
0 = V
DD
bit 5-2 CHS<3:0>: Analog Channel Select bits
0000 = Channel 00 (AN0)
0001 = Channel 01 (AN1)
0010 = Channel 02 (AN2)
0011 = Channel 03 (AN3)
0100 = Channel 04 (AN4)
0101 = Channel 05 (AN5)
0110 = Channel 06 (AN6)
0111 = Channel 07 (AN7)
1000 = Channel 08 (AN8)
1001 = Channel 09 (AN9)
1010 = Channel 10 (AN10)
1011 = Channel 11 (AN11)
1100 =CV
1101 =VP6
1110 = Reserved. D o not use.
1111 = Reserved. D o not use.
bit 1 GO/DONE
1 = A/D conversion cycle in progress. Setting this bit starts an A/D co nversion cycle.
This bit is automatically cleared by har dware when the A/D conver sion has completed.
0 = A/D conversion comple ted/ not in progress
bit 0 ADON: A/D Enable bit
1 = A/D converter module is enabled
0 = A/D converter is shut off and consu m es no operating current
REF
: A/D Conversion Status bit
ADON
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bi t , read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘ 1’ = Bi t is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 21
Page 26

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
3.2.5 Lesson 5: Variable Speed Rotate
Lesson 5 combines Lessons 3 and 4 by using the Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
to control the speed of rotation.
New Instructions
BTFSS Bit test, skip if set
BTFSC Bit test, skip if clear
A conversion is run on every pass through the main loop. The result controls the length
of the outer loop (see Example 3-5).
EXAMPLE 3-5: VARIABLE SPEED ROTATE EXAMPLE
...
BSF ADCON0,GO ;start conversion
BTFSS ADCON0,GO ;this bit will change to zero when the
;conversion is complete
GOTO $-1
MOVF ADRESH,w ;Copy the display to the LEDs
ADDLW 1
MOVWF Delay2
A2DDelayLoop
DECFSZ Delay1,f ;Delay Loop shortened by the ADResult as
;controlled by the Pot.
GOTO A2DDelayLoop
DECFSZ Delay2,f
GOTO A2DDelayLoop
FIGURE 3-3: VARIABLE SPEED ROTATE PROGRAM FLOW
Initialize I/O Port
Initialize ADC
Put Up Display
Get ADC Result
Delay Using ADC
Rotate Display
Did it overflow?
Yes
No
Reset Display
DS51556A-page 22 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.6 Lesson 6: Switch Debouncing
Mechanical switches play an imp ortant and extens iv e role in pr ac tica lly every
computer, microprocessor and microcontroller application. Mechanical switches are
inexpensive, simple and reliable. In addition, switches can be very noisy. The apparent
noise is caused by the closing and opening action that seldom results in a clean
electrical transition. The connection makes and breaks several, perhaps even
hundreds, of times before the final switch state settles.
The problem is known as switch bounce. Some of the intermittent activity is due to the
switch contacts actually bouncing off each other. Imagine slapping two billiard balls
together. The hard non-resilient material doesn’t absorb the kinetic energy of motion.
Instead, the energy dissipates over time and friction in the bouncing action against the
forces push the billiard balls together. Hard metal switch contacts react in much the
same way. Also, switch contacts are not perfectly smooth. As the contacts move
against each other, the imperfections and impurities on the surfaces cause the
electrical connection to be interrupted. The result is switch bounce.
The consequences of uncorrected switch bounce can range from being just annoying
to catastrophic. For example, imagine advancing the TV channel, but instead of getting
the next channel, the selection skips one or two. This is a situation a designer should
strive to avoid.
Switch bounce has been a problem even before the earliest computers. The classic
solution involved filtering, such as through a resistor-capacitor circuit, or through
re-settable shift registers (see Figures 3-4 and 3-5). These methods are still effective
but they involve additional cost in material, installation and board real estate. Why
suffer the additional expense when software is free and program memory is abundant.
FIGURE 3-4: FILTERING DEBOUNCE SOLUTION
+V
R2
R1
C
SW
Filtered
Switch
Output
1
FIGURE 3-5: SHIFT REGISTER DEBOUNCE SOLUTION
+V
R1
Filtered
Switch
Output
SW
D
CLK
Qn
CLR
Debounce
Clock
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 23
Page 28

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
One of the simplest ways to switch debounce is to sample the switch until the signal is
stable or continue to sample the signal until no more bounces are detected. How long
to continue sampling requires some investigation. However, 5 mS is usually plenty
long, while still reacting fast enough that the user won’t notice it.
Lesson 6 shows how to sample the line at a 1 mS rate waiting for a number of
sequential state changes, which is a simple matter of counting to 5, then resetting the
counter every time it’s still in the original unchanged state.
The Switch on the LPC Demo Board doesn’t bounce much, but it is good practice to
debounce all switches in the system.
FIGURE 3-6: SIMPLE SWITCH DEBOUNCE PROGRAM FLOW
Yes
Increment Counter
Is Counter = 5?
Yes
Change State
Reset Counter
Switch has
changed states?
No
Delay 1 mS
No
Reset Counter
DS51556A-page 24 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 29

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.7 Lesson 7: Reversible Variable Speed Rotate
Lesson 7 combines Lessons 5 and 6 using the button to reverse the direction of rotation
when the button is pressed and adjusting the potentiometer to control the speed of
rotation.
The program needs to keep track of rotation direction and new code needs to be added
to rotate in the other direction.
Lesson 5 rotates right and checks for a ‘1’ in the Carr y bi t t o det ermi ne w hen to rest a rt
the sequence. In Lesson 7, we’ll also need to rotate left and check for a ‘1’ in bit 4 of
the display. When the ‘1’ shows up in bit 4 of the display, re-insert it into the bit 0
position.
EXAMPLE 3-6: REVERSIBLE VARIABLE SPEED ROTATE EXAMPLE
Original Version:
Rotate
RRF Display,f
BTFSC STATUS,C ;Did the bit rotate into the carry?
BSF Display,3 ;yes, put it into bit 3.
Bidirectional Version:
Rotate
BCF STATUS,C ;ensure the carry bit is clear
BTFSS Direction,0
GOTO RotateLeft
RotateRight
RRF Display,f
BTFSC STATUS,C ;Did the bit rotate into the carry?
BSF Display,3 ;yes, put it into bit 3.
GOTO MainLoop
RotateLeft
RLF Display,f
BTFSC Display,4 ;did it rotate out of the display
BSF Display,0 ;yes, put it into bit 0
GOTO MainLoop
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 25
Page 30

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
3.2.8 Lesson 8: Function Calls
Lesson 8 shows the reversible LEDs but with the Delay Loop rewritten as a function.
New Instructions
CALL Invokes functions or subroutines
RETURN Terminates functions or subroutines
RETLW Terminates functions or subroutines
Functions or Subroutines are invoked with the CALL instruction and terminated with a
RETURN or RETLW instruction. RETURN jumps back to the original program at the
location following the CALL. RETLW also returns to the calling program, but loads Wreg
with a constant.
The mid-range PICmicro MCU device’s CALL stack can hold up to 8 return addresses.
If a ninth CALL is made, it will overwrite the first one and then the program will not be
able to RETURN all the way back.
Passing Arguments
Arguments to the subroutine may be passed in a number of ways. Wreg is a convenient
place to pass one byte and the FSR may be used to pass another byte, if not otherwise
used. If more data must be passed, a buffer must be allocated.
When the Delay function is pulled out to a subroutine, the ADC result is moved into
Wreg, then the CALL transfers control to the Delay subroutine. The RETURN transfers
control to the MOVLW following the CALL.
EXAMPLE 3-7: FUNCTION CALL EXAMPLE
MOVF ADRESH,w
CALL Delay ;call delay function
;returns here when done
...
GOTO xxx
; Delay function.
; Delay time is Wreg value * 771 uS
Delay
MOVWF Delay2
DelayLoop
DECFSZ Delay1,f
GOTO DelayLoop
DECFSZ Delay2,f
GOTO DelayLoop
RETURN
DS51556A-page 26 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 31

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.9 Lesson 9: Timer0
Timer0 is a counter implemented in the processor. It may be used to count processor
clock cycles or external events. Lesson 9 configures it to count instruction cycles and
set a flag when it rolls over. This frees up the processor to do meaningful work rather
than just wasting cycles.
Timer0 is an 8-bit counter with an optional prescaler, which is configured to divide by
256 before reaching the Timer0 counter.
FIGURE 3-7: TIMER0 SIMPLIFIED
Clock/4 or
T0CKI pin
Prescaler may be configured
to divide by 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64,
128 or 256.
Note: See PIC16F690 Timer0 section for more details.
TMR0 is a Special Function Register (SFR) and may be read or modified by the
program. The Prescaler is not a SFR and thus cannot be read or modified by the
program. However, writing to TMR0 clears the Prescaler.
The timer may be fed either by the same clock that drives the processor or by an
external event. Driven by the processor clock, it increments once for every instruction
cycle. This is a convenient method of marking time, better than delay loops, as it allows
the processor to work on the problem rather than waste cycles in delay loops.
The prescaler is configured through the OPTION_REG, see Figure 3-8.
FIGURE 3-8: PRESCALER CONFIGURATION THROUGH OPTION_REG
X X T0CS T0SE PSA PS2 PS1 PS0
bit 7 bit 0
Prescaler T0IFTMR0
Flag set when
TMR0 overflows.
Must be cleared
in software.
Legend:
X: Don’t cares – not Timer0 related.
T0CS: Timer0 Clock Source 0 for Instruction Clock.
T0SE: Timer0 Source Edge – Don’t care when connected to instruction clock.
PSA: Prescaler Assignment 0 assigns to Timer0.
PS: Prescaler rate select ‘111’ – full prescaler, divide by 256.
Lesson 9 configures Timer0 with the Prescaler for a maximum delay on Timer0. The
prescaler will divide the processor clock by 256 and Timer0 will divide that by 256
again. Thus, Timer0 Flag will be set every 65536 μs (0.0000001 second * 256 * 256),
or about 15 times a second. The main program sits in a loop waiting for the rollover and
when it does, it increments the display and then loops back.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 27
Page 32

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
EXAMPLE 3-8: TIMER0 EXAMPLE
ORG 0
BSF STATUS,RP0
MOVLW b'00000111' ;configure Timer0. Sourced from the
;Processor clock
MOVWF OPTION_REG ;Maximum Prescaler
CLRF TRISC ;Make PORTC all output
CLRF Display
BCF STATUS,RP0
ForeverLoop
BTFSS INTCON,T0IF ;wait here until Timer0 rolls over
GOTO ForeverLoop
BCF INTCON,T0IF ;flag must be cleared in software
INCF Display,f ;increment display variable
MOVF Display,w ;send to the LEDs
MOVWF PORTC
GOTO ForeverLoop
END
DS51556A-page 28 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 33

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.10 Lesson 10: Interrupts
New Instructions
RETFIE Return from Interrupt
SWAPF Swap nibbles in file register
Interrupt Sources
Most of the peripherals can generate an interrupt; also some of the I/O pins may be
configured to generate an interrupt when they change state.
When a peripheral needs service, it sets its interrupt flag. Each interrupt flag is ANDed
with its enable bit and then these are ORed together to form a Master Interrupt. This
master interrupt is ANDed with the Global Interrupt Enable (GIE). See the Interrupt
Logic Figure in the PIC16F685/687/689/690 Data Sheet (DS41262) for a complete
drawing of the interrupt logic. The enable bits allow the PICmicro to limit the interrupt
sources to certain peripherals.
FIGURE 3-9: INTERRUPT LOGIC SIMPLIFIED
Interrupt Flag
Interrupt Enable
Master Interrupt
Global Interrupt Enable
Other Interrupt Sources
When the master interrupt line is asse rted, the PICmicro finishes the current
instruction, stores the nex t addres s on the CALL stack then jumps to the Interrupt
Service Routine (ISR). It also clears the GIE bit, preventing another interrupt from
occurring while servicing the current one.
Save Current Context
The first thing the ISR must do is to save the current context of the processor so it can
be restored before returning to the main program. Any SFR that may be changed in the
ISR must be saved, which means the Wreg and Status registers at the very least. The
last 16 bytes of each PIC16F690 file register page are unbanked and are good places
to save the context, as they may be accessed from any register page without regard to
the RP0 and RP1 bits in the Status register. The location of unbanked registers may
vary from part to part. Check the register map to find the unbanked region for a specific
part.
Identify Triggering Event
Next, the ISR has to figure out what triggered the interrupt. It has to check the interrupt
flags to determine what caused the interrupt. When it finds the source, then it can
service the peripheral.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 29
Page 34

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
Restore Context
Once the peripheral is serviced, it needs to restore the context and resume the main
program. Restoring the context is a little harder than it might seem at first. The obvious
method doesn’t work because the MOVF W_Temp,w may affect the Z flag, which was
restored in the previous instruction. Instead, a pair of SWAPF instructions can restore
Wreg without affecting the flags in the Status register. SWAPF exchanges the high and
low nibbles. The first SWAPF switches the nibbles in the file register and the second one
switches them back and puts the result in Wreg.
EXAMPLE 3-9: CONTEXT RESTORE
;incorrect context restore
MOVF STATUS_Temp,w
MOVWF STATUS
MOVF W_Temp ;this may change the Z bit
;in the Status register
;good context restore
MOVF STATUS_Temp,w
MOVWF STATUS
SWAPF W_Temp,f ;swap in place
SWAPF W_Temp,w ;swap with Wreg destination
Finally, RETFIE transfers control back to the original program and sets the GIE bit,
re-enabling interrupts.
FIGURE 3-10: SWAPF INSTRUCTION
Before
After
1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1
1 0 1 00 0 1 1
DS51556A-page 30 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 35

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.11 Lesson 11: Indirect Data Addressing
The FSR (File Select Register) allows the specifying of a file register address. A
subsequent read or write to the INDF (Indirect File regist er ) refers to the file registe r
addressed by the FSR.
This may be used to implement a moving average filter. The moving average keeps a
list of the last n values and averages them together. The Filter needs two parts: A
circular queue and a function to calculate the average.
FIGURE 3-11: MOVING AVERAGES
Conceptual View
Time
n 105 102 101 104 99 103 105 107 103
n + 1 106 105 102 101 104 99 103 105 103
n + 2 110 106 105 102 101 104 99 103 104
The rest move down one
Newest value inserted here
Average
Implementation View
Time
n 107 105 101 104 99 101 102 105 103
Pointer to oldest value
n + 1 106 105 102 101 99 101 102 105 103
Older value overwritten, pointer advanced
n + 2 106 110 103 99 99 101 102 105 104
Pointer advanced
Average
Calculating averages in a mid-range PICmicro is best accomplished by using the FSR
to keep track of where the next value will be inserted. This ensures the oldest value is
always overwritten with the newest and doesn’t waste time moving values within the
memory.
EXAMPLE 3-10: FILE SELECT REGISTER EXAMPLE
;insert new value into a queue, enter with new value in
;Wreg
MOVF temp ;save the latest value
MOVF QueuePointer,w
MOVWF FSR ;load FSR with the queue pointer
MOVF temp,w
MOVWF INDF ;Write the latest value to the queue
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 31
Page 36

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
Lesson 11 adds a Moving Average Filter to the Analog-to-Digital code in Lesson 4.
Twisting the potentiometer changes the value read by the Analog-to-Digital. The filtered
value is then sent to the LED display. The filter only runs every 0.2 seconds to slow
down the display changes and make it visible. The display appears to count from the
old potentiometer position to the new position.
The filter averages the last 8 readings. Choosing a power of two for the number of
samples allows division by simple rotates instead of longhand.
Rather than summing the array every time, it’s faster to keep a running sum, then
subtract out the oldest value in the queue and adding in the new value.
DS51556A-page 32 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 37

LPC Demo Board Lessons
3.2.12 Lesson 12: Look-up Table (ROM Array)
Lesson 8 introduced function calls. Lesson 12 shows how function calls and calculated
modification of the Program Counter may be used to implement a Look-up Table (see
Example 3-11).
It is sometimes useful to implement a table to convert from one value to another.
Expressed in a high-level language it might look like this:
y = function(x);
That is for every value of x, it returns the corresponding y value.
Look-up tables are a fast way to convert an input to meaningful data because the
transfer function is pre-calculated and “looked up” rather than calculated on the fly.
PICmicro MCUs implement these by directly modifying the Program Counter. For
example, a function that converts hexadecimal numbers to the ASCII equivalent. We
can strip out the individual nibble and call the Look-up Table. The index advances the
program counter to the appropriate RETLW instruction to load Wreg with the constant
and returns to the calling program.
EXAMPLE 3-11: LOOK-UP TABLE
;Enter with index in Wreg
Look-upTable
ADDWF PCL,f ;jump to
RETLW '0' ;index 0
RETLW '1' ;index 1
...
RETLW 'F' ;index 15
Calling the Look-up Table works most of the time. However, if the table falls across a
256 byte page boundary, or if somehow the Look-up Table is called with an out of
bounds index value, it will jump to a location out of the table.
Good programming practices dictate a few additional instructions. First, since the table
is only sixteen entries, make sure a number no larger than 16 is passed in. The simplest
way to do this is to logically AND the contents of Wreg before modifying PCL: ANDLW
0x0F. More complex error recovery schemes may be appropriate, depending on the
application.
In addition, there are some nuances to be aware of should the table cross a 256 word
boundary. The Program Counter is 13 bits wide, but only the lower 8 bits are
represented in PCL (see Figure 3-12). The remaining 5 bits are stored in PCLATH.
However, an overflow of the lower 8 bits is not automatically carried over into PCLATH.
Instead, be sure to check for and handle that case in our code. See the PCL and
PCLATH Section in the PIC16F685/687/689/690 Data Sheet (DS41262) for more
details of how PCLATH is used.
FIGURE 3-12: PC LOADING AS DESTINATION OF INSTRUCTION
PCH PCL
12 8 7 0
PC
PCLATH<4:0>
5
8
Instruction with
PCL as
Destination
ALU Result
PCLATH
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 33
Page 38

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
This lesson uses the Look-up T able to implement a binary to Gray code converter. Gray
code is a binary code in which only a single bit changes from one sequence to the next.
They are frequently used in encoder applications to avoid wild jumps between states.
Binary encoders are typically implemented an opaque disk sensed by light sensors.
Due to different threshold levels on different bits, bits may change at slightly differently
times yielding momentary invalid results. Gray code prevents this because only one bit
changes from one sequence to the next. The current code is correct until it transitions
to the next.
The algorithm to convert between binary and Gray code is fairly complex. For a small
number of bits, the table look-up is smaller and faster.
This lesson also takes the Analog-to-Digital value and converts it to Gray code
displayed on the LEDs. The code changes one bit at a time as the potentiometer
rotates across its range (see Example 3-12).
Gray Code Converter
Decimal
0 0000
1 0001
2 0011
3 0010
4 0110
5 0111
6 0101
7 0100
8 1100
9 1101
10 1111
11 1110
12 1010
13 1011
14 1001
15 1000
Binary
DS51556A-page 34 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 39

LPC Demo Board Lessons
EXAMPLE 3-12: CONVERT BINARY TO GRAY CODE
; Convert 4 bit binary to 4 bit Gray code
;
BinaryToGrayCode
ANDLW 0x0F ;mask off invalid entries
MOVWF temp
MOVLW high TableStart ;get high order part of the beginning of
;the table
MOVWF PCLATH
MOVLW low TableStart ;load starting address of table
ADDWF temp,w ;add offset
BTFSC STATUS,C ;did it overflow?
INCF PCLATH,f ;yes: increment PCLATH
MOVWF PCL ;modify PCL
TableStart
RETLW b'0000' ;0
RETLW b'0001' ;1
RETLW b'0011' ;2
RETLW b'0010' ;3
RETLW b'0110' ;4
RETLW b'0111' ;5
RETLW b'0101' ;6
RETLW b'0100' ;7
RETLW b'1100' ;8
RETLW b'1101' ;9
RETLW b'1111' ;10
RETLW b'1110' ;11
RETLW b'1010' ;12
RETLW b'1011' ;13
RETLW b'1001' ;14
RETLW b'1000' ;15
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 35
Page 40

Low Pin Count Demo Board User’s Guide
NOTES:
DS51556A-page 36 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 41

Appendix A. Hardware Schematics
A.1 INTRODUCTION
This appendix contains the Low Pin Count Demo Board Diagrams.
FIGURE A-1: LOW PIN COUNT DEMO BOARD SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
PICKITTM 2 USER’S GUIDE
RP1
10 KΩ
R3
R4
R5
470Ω
DS1
JP1
470Ω
DS2
JP2
SW1
R1
10 KΩ
R2
1 KΩ
JP5
μF
C2
0.1
R7
1KΩ
470Ω
DS3
JP3
R6
470Ω
DS4
JP4
+V
RA3
+V
U1
PIC16F690/P
C1
0.1 μF
20
SS
V
DD
V
RA0
RB4
RC2
RC1
RC0
RA1
RA0
1918171615
2
131211
14
REF/ICSPCLK
RC2/AN6/P1D
RC0/AN4/C2IN+
RC1/AN5/C12IN-
RB4/AN10/SDI/SDA
RA2/AN2/T0CLKI/INT/C1OUT
RA1/AN1/C12IN-/V
RA0/AN0/C1IN+/ICSPDAT/ULPWU
RA4/AN3/T1G/OSC2/CLKOUT
RA5/T1CKI/OSC1/CLKIN
RC5/CCP1/P1A
RC4/C2OUT/P1B
RC3/AN7/P1C
RC6/AN8/SS
RA3/MCLR/VPP
678
5
341
RC6
RC5
RC4
RC3
RA5
RA4
RA3 RA2
RB5
RB6/SCK/SCK
RB5/AN11/RX/DT
RB7/RX/CK
RC7/AN9/SDO
9
10
RC7
RB7 RB6
1
TM
P1
ICSP
PP
V
+V
VDD
GND
RC0
65432
T1G
ICSPDAT
ICSPCLK
RC1
RC3
RC2
RA5
RA4
RA3
RC5
RC4
RC3
RA0
RA1
RA2
RC0
RC1
RC2
+5V
GND
J1
432
1
RA5
RA4
RA3
RC5
RC4
RC3
RA0
RA1
98765
RA2
RC0
P2
RC1
+V
+V
PWR
RC2
1
1413121110
2
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51556A-page 37
Page 42

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
http://support.microchip.com
Web Address:
www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Alpharetta, GA
Tel: 770-640-0034
Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Farmington Hills, MI
Tel: 248-538-2250
Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
Kokomo, IN
Tel: 765-864-8360
Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
San Jose
Mountain View, CA
Tel: 650-215-1444
Fax: 650-961-0286
Toronto
Mississauga, Ontario,
Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699
Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8528-2100
Fax: 86-10-8528-2104
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8676-6200
Fax: 86-28-8676-6599
China - Fuzhou
Tel: 86-591-8750-3506
Fax: 86-591-8750-3521
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-5407-5533
Fax: 86-21-5407-5066
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
Fax: 86-24-2334-2393
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8203-2660
Fax: 86-755-8203-1760
China - Shunde
Tel: 86-757-2839-5507
Fax: 86-757-2839-5571
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-502-7355
Fax: 86-532-502-7205
ASIA/PACIFIC
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-2229-0061
Fax: 91-80-2229-0062
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-5160-8631
Fax: 91-11-5160-8632
Japan - Kanagawa
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166
Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or
82-2-558-5934
Malaysia - Penang
Tel:011-604-646-8870
Fax:011-604-646-5086
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 011-632-634-9065
Fax: 011-632-634-9069
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-536-4818
Fax: 886-7-536-4803
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2500-6610
Fax: 886-2-2508-0102
Taiwan - Hsinchu
Tel: 886-3-572-9526
Fax: 886-3-572-6459
EUROPE
Austria - Weis
Tel: 43-7242-2244-399
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Ballerup
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
France - Massy
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Ismaning
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
England - Berkshire
Tel: 44-118-921-5869
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
04/20/05
DS51556A-page 38 © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...