Page 1

IS2083
IS2083 SDK Debugger User's Guide
Introduction
This document describes how to use the SEGGER JLINK debugger to enable software debugging of 8051 MCU core
that is part of the IS2083BM. The SEGGER debugger makes use of IS2083BM 2-wire JTAG interface to download
8051 firmware images into IS2083BM SQI flash. It then controls the IS2083BM SQI CPU register to provide
debugging features. The following chapters describe the software and hardware prerequisites, setup and procedure
to enter the Debugging mode.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 1
Page 2

IS2083
Table of Contents
Introduction.....................................................................................................................................................1
1. Quick References....................................................................................................................................3
1.1. Reference Documentation............................................................................................................3
1.2. Software Prerequisites................................................................................................................. 3
1.3. Hardware Prerequisites................................................................................................................3
2. Software Setup........................................................................................................................................6
2.1. Keil μVision Setup........................................................................................................................ 6
2.2. SDK Settings.............................................................................................................................. 10
3. Hardware Connection............................................................................................................................11
3.1. J-Link Probes Connection.......................................................................................................... 11
4. Start Debugging.................................................................................................................................... 15
4.1. Enabling Debug Mode................................................................................................................15
5. Document Revision History...................................................................................................................18
The Microchip Website.................................................................................................................................19
Product Change Notification Service............................................................................................................19
Customer Support........................................................................................................................................ 19
Microchip Devices Code Protection Feature................................................................................................ 19
Legal Notice................................................................................................................................................. 19
Trademarks.................................................................................................................................................. 20
Quality Management System....................................................................................................................... 20
Worldwide Sales and Service.......................................................................................................................21
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 2
Page 3
1. Quick References
1.1 Reference Documentation
Please go to http://www.microchip.com/IS2083 or http://www.microchip.com/BM83 to get the following documents.
• IS2083 Bluetooth® Stereo Audio SoC Data Sheet
• BM83 Bluetooth® Stereo Audio Module Data Sheet
• BM83 Bluetooth® Audio Development Board User's Guide
• IS2083 SDK User's Guide
1.2 Software Prerequisites
• IS2083 Software Development Kit
• isUpdate tool
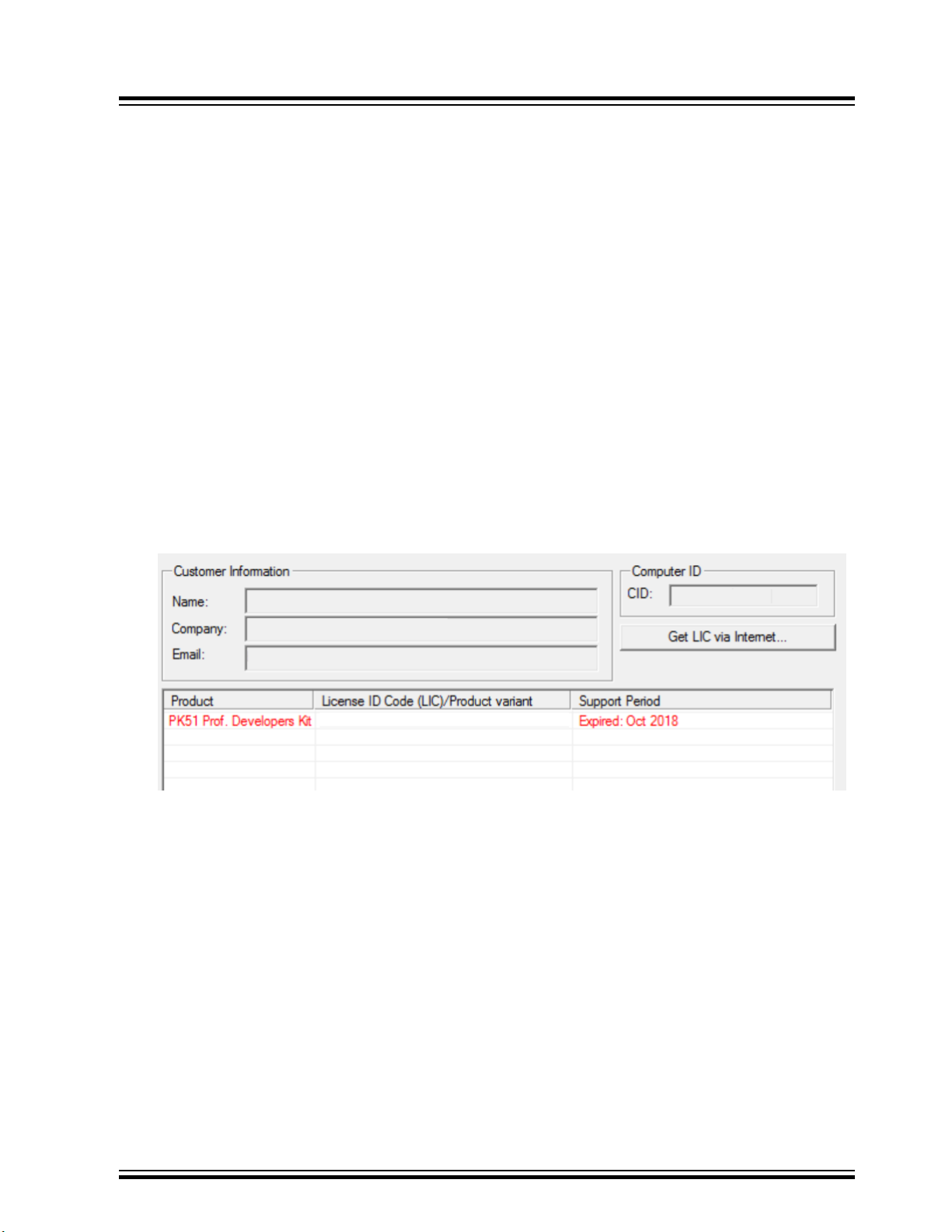
• Please refer to the IS2083 SDK User’s Guide Section 1.2 to know what Keil® μVision® version should be used.
Furthermore, please be sure your PK51 license is valid in the support period. If your license expires on or before
the support period, Keil C51 may not allow you to use the debugger support. It depends on if your license
expiration date is on or before the C51 release date. For example, C51 9.59 released in May 2018. If your
license expired before that, you cannot use the debugger with C51 9.59. On the other hand, if your license
expired after May 2018, you can still use the debugger support. For example, the figure below shows that this
license has expired, but it can still work with C51 9.59 because it is after May 2018.
IS2083
Quick References
– The following DLL files enable debugging in the IS2083BM using Keil μVision:
• JLinkARM.dll
• JLinkIS2083.dll
– Initsession.ini – this file stops the Keil μVision at the first execution of SDK.
Note: The DLL files and Initsession.ini file are available in the following folder:
release-package at http://www.microchip.com/IS2083 or http://www.microchip.com/BM83.
• J-Link Commander (folder path: \Software\Debugger Support\Commander)
– An executable command prompt to check if J-Link probes can communicate with the IS2083BM.
1.3 Hardware Prerequisites
• SEGGER J-Link Debug Probe
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 3
Page 4

Figure 1-1. J-Link Debug Probe
IS2083
Quick References
– J-Link PRO, J-Link ULTRA+, J-Link PLUS and J-Link BASE.
• BM83 EVB
– BM83 EVB provides a two-wire JTAG interface to communicate with the IS2083BM.
• J-Link 6-pin adapter from Microchip
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 4
Page 5

Figure 1-2. J-Link 6-pin Adapter
IS2083
Quick References
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 5
Page 6
2. Software Setup
This section describes the setup procedure of Keil uVision and IS2083 SDK to work with the debug probes.
2.1 Keil μVision Setup
This section describes the step-by-step procedure for Keil μVision setup. The user needs to first set up μVision and
connect to J-Link debug probes and later to the BM83 EVB. See 3.1 J-Link Probes Connection.
2.1.1 File Settings
Visit the Keil website to download and install the required Keil C51 (See IS2083 SDK User Guide, Section 1.2,
Software Prerequisites for the latest SDK Keil supported version.).
IS2083 SDK requires a specific Keil μVision tool to compile and operate with J-Link probes. The .dll files
customized for SEGGER J-Link debugger allows Keil μVision to communicate with the IS2083BM through J-Link
probe.
Note: After Keil μVision installation, ensure that it is not running.
Keil C51 v9.59 requires the following steps, 1 to 3 for file settings. The version v9.60 and above contains the DLL
files. Perform only step 3 for Keil C51 v9.60 and above.
IS2083
Software Setup
Perform the following steps for the setup:
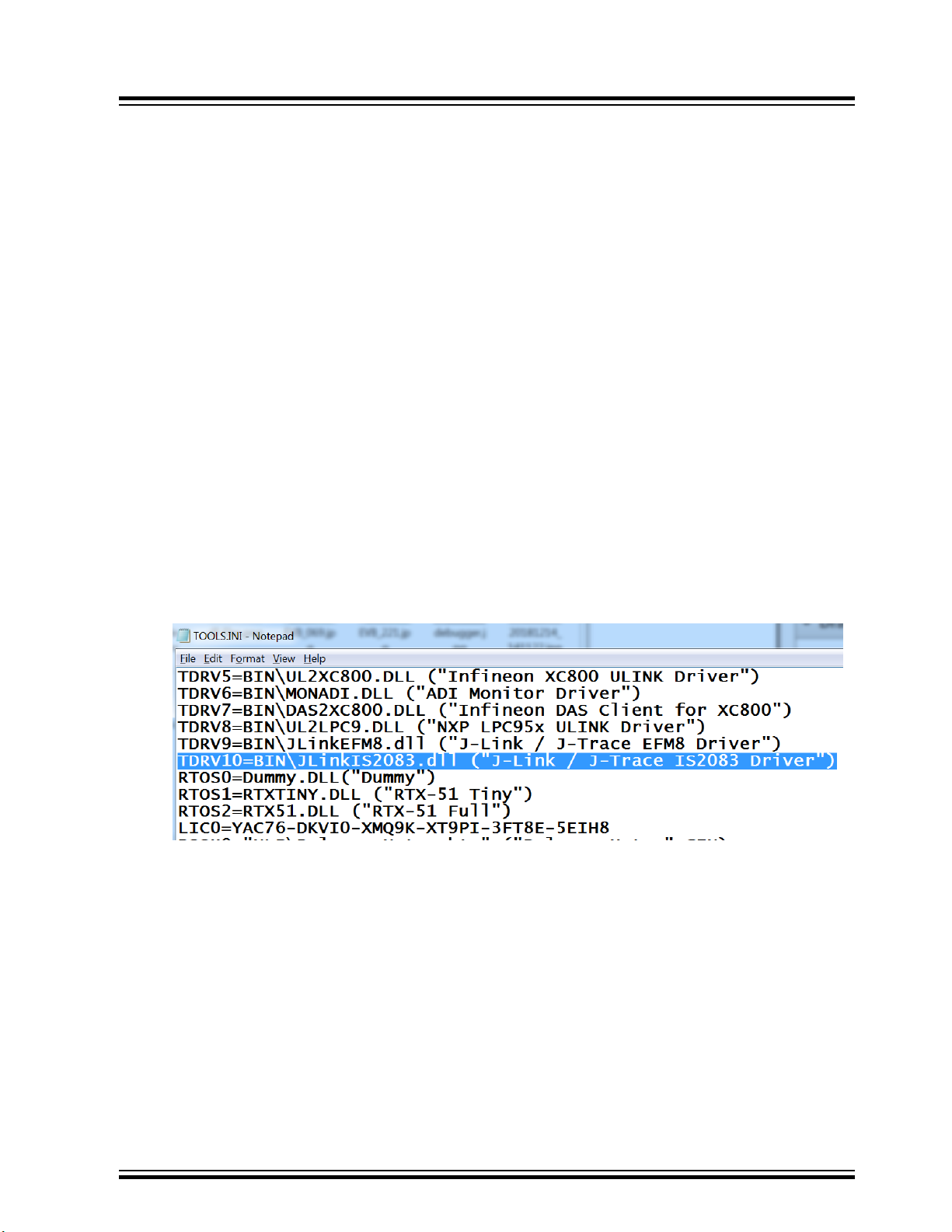
1. Go to C:\Keil_v5\ and use the text editor to open the TOOLS.INI file.
2. Insert the text TDRV10=BIN\JLinkIS2083.dll (J-Link / J-Trace IS2083 Driver) into the file as
shown below:
Figure 2-1. TOOLS.INI
3. Go to C:\Keil_v5\C51\BIN and copy the following files from the debug package to the directory:
– JLinkIS2083.dll
– JLinkARM.dll
2.1.2 Debug Settings
After verifying the J-link connection and Keil file settings, unplug and plug in the power cord to reset the IS2083BM.
This turns the J-Link LED to steady green.
Perform the following steps for debug settings:
1. Launch Keil μVision and double click MSPKv2_Application_IS2083B.uvproj and Keil uVision automatically
loads these SDK project files:
– MSPKv2_App_Pbap
– MSPKv2_App_MSPK
– MSPKv2_App_Basic
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 6
Page 7
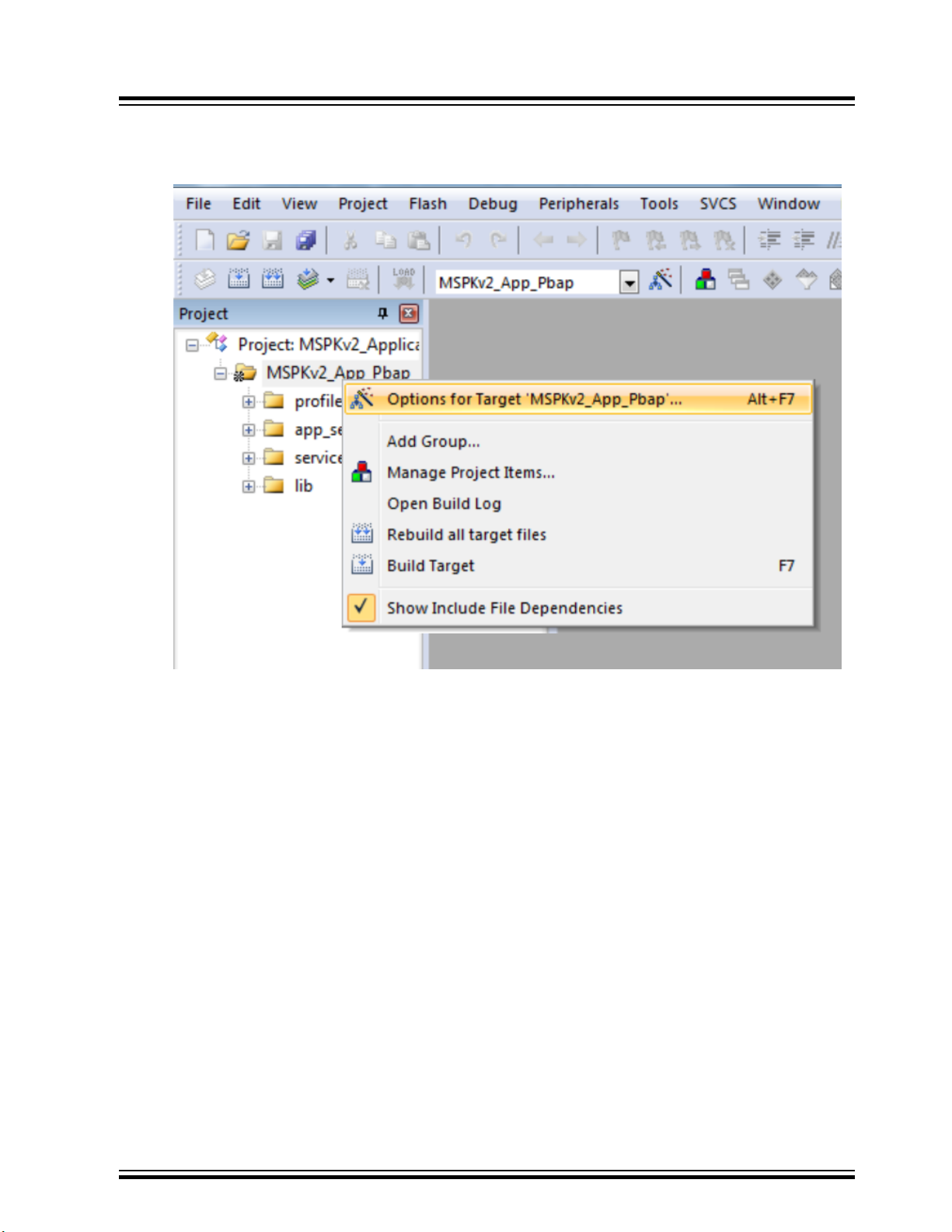
– MSPKv2_App_MSPK_Debug
2. For each of the projects, right-click the "Options for Target.”
Figure 2-2. Build Target
IS2083
Software Setup
3. In the Debug tab, select the highlighted parameters for setup. Replace S8051.DLL with -cIS208x and
DP51.DLL with -pIS208x. Load the InitSession.ini file in “Initialization File” and select the “Load
Application Setup” checkbox.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 7
Page 8

Figure 2-3. Options for Target
IS2083
Software Setup
4. Click the Settings button.
5. Select “Speed” as 12000 kHz and deselect the checkbox "Compare before download". Click OK.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 8
Page 9

Figure 2-4. Debug Settings
IS2083
Software Setup
6. To build the application and start a debug session, click
. Keil μVision is now ready to debug the IS2083BM device.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 9
Page 10

Figure 2-5. Debugging Session
IS2083
Software Setup
2.2 SDK Settings
The 2-wire JTAG debug port (i.e. P1_2 and P1_3) on IS2083BM is multiplexed with I2C function. Before debugging,
the user must enable the buildoption ENABLE_JTAG_DEBUG. This enables SW I2C and disables Low Power mode
for the debugger to run properly. The user can select MSPKv2_App_MSPK_Debug project target, which includes
ENABLE_JTAG_DEBUG buildoption.
ENABLE_JTAG_DEBUG uses SW I2C port (P2_3 and P2_6 by default) instead of HW I2C. SDK enables Low Power
mode, which turns off the debugger clock and then disconnects the debugger. ENABLE_JTAG_DEBUG is used to
disable the Low Power mode to avoid this. Refer to the IS2083 Bluetooth® Stereo Audio SoC Data Sheet for more
details on JTAG program and debug feature.
For information on which SDK features are included in MSPKv2_App_MSPK_Debug project, see the IS2083 SDK
User's Guide, Section 2.2, and Table 2-1.
Figure 2-6. Target Build
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 10
Page 11

3. Hardware Connection
The section describes the procedure to connect the BM83 EVB with the J-Link debug probes.
3.1 J-Link Probes Connection
SEGGER J-Link debug probes can work with Keil μVision to provide software debugging and downloading on the
IS2083BM.
Perform the following steps:
Case 1 – Connecting J-Link Probes to BM83 EVB
Connect the J-Link, BM83 EVB, and 6-pin adapter as shown in the following figures.
Figure 3-1. J-Link Probes to BM83 EVB Connection
IS2083
Hardware Connection
Be sure to have the correct orientation while inserting the 6-pin adapter to a BM83 EVB.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 11
Page 12

Figure 3-2. 6-pin Adapter Connection
IS2083
Hardware Connection
Be sure to unplug jumpers in-between JP307 and JP308 so the HW-I2C interface will not be used:
In order to use Embedded mode, please connect P2_6 of JP309 to P1_3 of JP402, P2_3 of JP309 to P1_2 of JP402.
Then IS2083BM can communicate with ST codec over SW I2C.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 12
Page 13

IS2083
Hardware Connection
Ensure that RST_N of SW402 on BM83 EVB is connected to the BM83 module. J-Link uses this pin to reset the
debugger.
Figure 3-3. RST_N Connection to BM83 Module
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 13
Page 14

Case 2 – Connecting J-Link Probes to application board with IS2083BM
Figure 3-4. J-Link 6-pins connector schematic
IS2083
Hardware Connection
Connect the following pins from your board to the 6pins connector:
Table 3-1. Pin details for the IS2083BM/BM83 board
J-Link 6pin Connector BM83 IS2083BM Description
Pin1 Pin43, RST_N RST_N Reset IS2083BM
Pin2 3V3 3V3_IO 3V3 power
Pin3 Ground Ground Ground
Pin4 Pin46, TDI_CPU TDI_CPU Data
Pin5 Pin47, TCK_CPU TCK_CPU Clock
Pin6 NC NC Not used
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 14
Page 15

4. Start Debugging
The section describes the procedure for IS2083BM file configuration and starting of the debugging on Keil uVision.
4.1 Enabling Debug Mode
SEGGER J-Link debugger downloads the 8051 image and automatically updates the Flash header in the IS2083BM.
Pre-program the IS2083BM device with voice prompt, UI Config and DSP images before using the debugger. It is
recommended to pre-program with the demo package, which contains the following files:
• Embedded mode – Demo_Package_Embedded_Mode_RTP.hex
• Host mode – Demo_Package_MCU_Mode_RTP.hex
Choose one of them according to your desired application mode. Please refer to the BM83 Bluetooth® Audio
Development Board User’s Guide for how to download the image with tools.
Perform the following steps to enable Debugging mode:
1. In the Keil uVision tool, select and build "MSPKv2_App_MSPK_debug".
2. Click the
icon or go to Debug > Start/Stop Debug Session for debugging. Keil μVision uses the DLL files to
communicate to the IS2083BM and then access Flash. J-Link checks for the Flash header and downloads the
complied 8051 images at the correct bank.
3. After Flash, the program counter stops at 0x27_0000, which is the Application_Init. This is the first
function that the application code can execute.
During debugging, 8051 MCU will be halted, once the program counter hits the breakpoint. Program ROM is
suspended and the Bluetooth connection is dropped simultaneously.
IS2083
Start Debugging
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 15
Page 16
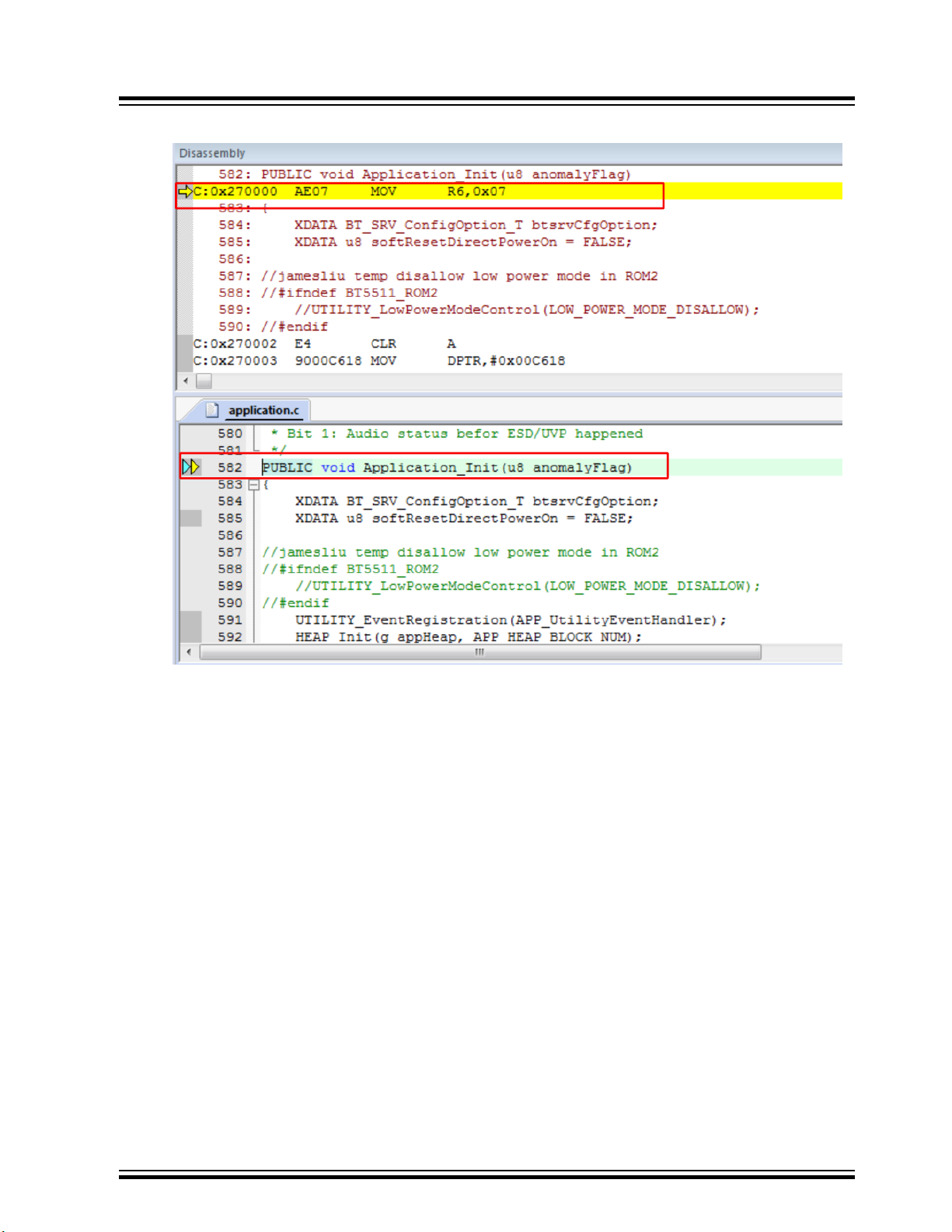
Figure 4-1. Application_Init
IS2083
Start Debugging
4. The following example shows how to add a breakpoint in the function App_init. When the user runs the
debugger, it stops at line94 and Keil μVision provides the local variable of APP_init at the right-hand side.
The user can investigate the global variable by using the Watch window.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 16
Page 17

Figure 4-2. Watch Window
IS2083
Start Debugging
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 17
Page 18

5. Document Revision History
Revision Date Section Description
A 07/2019 Document Initial Revision
IS2083
Document Revision History
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 18
Page 19

IS2083
The Microchip Website
Microchip provides online support via our website at http://www.microchip.com/. This website is used to make files
and information easily available to customers. Some of the content available includes:
• Product Support – Data sheets and errata, application notes and sample programs, design resources, user’s
guides and hardware support documents, latest software releases and archived software
• General Technical Support – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), technical support requests, online
discussion groups, Microchip design partner program member listing
• Business of Microchip – Product selector and ordering guides, latest Microchip press releases, listing of
seminars and events, listings of Microchip sales offices, distributors and factory representatives
Product Change Notification Service
Microchip’s product change notification service helps keep customers current on Microchip products. Subscribers will
receive email notification whenever there are changes, updates, revisions or errata related to a specified product
family or development tool of interest.
To register, go to http://www.microchip.com/pcn and follow the registration instructions.
Customer Support
Users of Microchip products can receive assistance through several channels:
• Distributor or Representative
• Local Sales Office
• Embedded Solutions Engineer (ESE)
• Technical Support
Customers should contact their distributor, representative or ESE for support. Local sales offices are also available to
help customers. A listing of sales offices and locations is included in this document.
Technical support is available through the website at: http://www.microchip.com/support
Microchip Devices Code Protection Feature
Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today,
when used in the intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these
methods, to our knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating
specifications contained in Microchip’s Data Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of
intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code
protection does not mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection
features of our products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital
Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you
may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Legal Notice
Information contained in this publication regarding device applications and the like is provided only for your
convenience and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to ensure that your application meets with
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 19
Page 20

IS2083
your specifications. MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION, QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend,
indemnify and hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims, suits, or expenses resulting from such
use. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip intellectual property rights unless
otherwise stated.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Adaptec, AnyRate, AVR, AVR logo, AVR Freaks, BesTime,
BitCloud, chipKIT, chipKIT logo, CryptoMemory, CryptoRF, dsPIC, FlashFlex, flexPWR, HELDO, IGLOO, JukeBlox,
KeeLoq, Kleer, LANCheck, LinkMD, maXStylus, maXTouch, MediaLB, megaAVR, Microsemi, Microsemi logo, MOST,
MOST logo, MPLAB, OptoLyzer, PackeTime, PIC, picoPower, PICSTART, PIC32 logo, PolarFire, Prochip Designer,
QTouch, SAM-BA, SenGenuity, SpyNIC, SST, SST Logo, SuperFlash, Symmetricom, SyncServer, Tachyon,
TempTrackr, TimeSource, tinyAVR, UNI/O, Vectron, and XMEGA are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
APT, ClockWorks, The Embedded Control Solutions Company, EtherSynch, FlashTec, Hyper Speed Control,
HyperLight Load, IntelliMOS, Libero, motorBench, mTouch, Powermite 3, Precision Edge, ProASIC, ProASIC Plus,
ProASIC Plus logo, Quiet-Wire, SmartFusion, SyncWorld, Temux, TimeCesium, TimeHub, TimePictra, TimeProvider,
Vite, WinPath, and ZL are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Adjacent Key Suppression, AKS, Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Any Capacitor, AnyIn, AnyOut, BlueSky, BodyCom,
CodeGuard, CryptoAuthentication, CryptoAutomotive, CryptoCompanion, CryptoController, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, Dynamic Average Matching, DAM, ECAN, EtherGREEN, In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP,
INICnet, Inter-Chip Connectivity, JitterBlocker, KleerNet, KleerNet logo, memBrain, Mindi, MiWi, MPASM, MPF,
MPLAB Certified logo, MPLIB, MPLINK, MultiTRAK, NetDetach, Omniscient Code Generation, PICDEM,
PICDEM.net, PICkit, PICtail, PowerSmart, PureSilicon, QMatrix, REAL ICE, Ripple Blocker, SAM-ICE, Serial Quad
I/O, SMART-I.S., SQI, SuperSwitcher, SuperSwitcher II, Total Endurance, TSHARC, USBCheck, VariSense,
ViewSpan, WiperLock, Wireless DNA, and ZENA are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
The Adaptec logo, Frequency on Demand, Silicon Storage Technology, and Symmcom are registered trademarks of
Microchip Technology Inc. in other countries.
GestIC is a registered trademark of Microchip Technology Germany II GmbH & Co. KG, a subsidiary of Microchip
Technology Inc., in other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies.
©
2019, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
ISBN: 978-1-5224-4805-1
Quality Management System
For information regarding Microchip’s Quality Management Systems, please visit http://www.microchip.com/quality.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 20
Page 21

Worldwide Sales and Service
AMERICAS ASIA/PACIFIC ASIA/PACIFIC EUROPE
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
http://www.microchip.com/support
Web Address:
http://www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Duluth, GA
Tel: 678-957-9614
Fax: 678-957-1455
Austin, TX
Tel: 512-257-3370
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Novi, MI
Tel: 248-848-4000
Houston, TX
Tel: 281-894-5983
Indianapolis
Noblesville, IN
Tel: 317-773-8323
Fax: 317-773-5453
Tel: 317-536-2380
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
Tel: 951-273-7800
Raleigh, NC
Tel: 919-844-7510
New York, NY
Tel: 631-435-6000
San Jose, CA
Tel: 408-735-9110
Tel: 408-436-4270
Canada - Toronto
Tel: 905-695-1980
Fax: 905-695-2078
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8569-7000
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8665-5511
China - Chongqing
Tel: 86-23-8980-9588
China - Dongguan
Tel: 86-769-8702-9880
China - Guangzhou
Tel: 86-20-8755-8029
China - Hangzhou
Tel: 86-571-8792-8115
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2943-5100
China - Nanjing
Tel: 86-25-8473-2460
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-8502-7355
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-3326-8000
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8864-2200
China - Suzhou
Tel: 86-186-6233-1526
China - Wuhan
Tel: 86-27-5980-5300
China - Xian
Tel: 86-29-8833-7252
China - Xiamen
Tel: 86-592-2388138
China - Zhuhai
Tel: 86-756-3210040
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-3090-4444
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-4160-8631
India - Pune
Tel: 91-20-4121-0141
Japan - Osaka
Tel: 81-6-6152-7160
Japan - Tokyo
Tel: 81-3-6880- 3770
Korea - Daegu
Tel: 82-53-744-4301
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Malaysia - Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 60-3-7651-7906
Malaysia - Penang
Tel: 60-4-227-8870
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 63-2-634-9065
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Taiwan - Hsin Chu
Tel: 886-3-577-8366
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-213-7830
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2508-8600
Thailand - Bangkok
Tel: 66-2-694-1351
Vietnam - Ho Chi Minh
Tel: 84-28-5448-2100
Austria - Wels
Tel: 43-7242-2244-39
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Copenhagen
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
Finland - Espoo
Tel: 358-9-4520-820
France - Paris
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Garching
Tel: 49-8931-9700
Germany - Haan
Tel: 49-2129-3766400
Germany - Heilbronn
Tel: 49-7131-72400
Germany - Karlsruhe
Tel: 49-721-625370
Germany - Munich
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Germany - Rosenheim
Tel: 49-8031-354-560
Israel - Ra’anana
Tel: 972-9-744-7705
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Italy - Padova
Tel: 39-049-7625286
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
Norway - Trondheim
Tel: 47-72884388
Poland - Warsaw
Tel: 48-22-3325737
Romania - Bucharest
Tel: 40-21-407-87-50
Spain - Madrid
Tel: 34-91-708-08-90
Fax: 34-91-708-08-91
Sweden - Gothenberg
Tel: 46-31-704-60-40
Sweden - Stockholm
Tel: 46-8-5090-4654
UK - Wokingham
Tel: 44-118-921-5800
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002892A-page 21
 Loading...
Loading...