Page 1

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck
Development Board
User’s Guide
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A
Page 2

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is provided only for your convenience
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR
OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION,
QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability
arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at
the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend, indemnify and
hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims,
suits, or expenses resulting from such use. No licenses are
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip
intellectual property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Accuron,
dsPIC, K
EELOQ, microID, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART,
PRO MATE, PowerSmart, rfPIC and SmartShunt are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A. and other countries.
AmpLab, FilterLab, Migratable Memory, MXDEV, MXLAB,
SEEVAL, SmartSensor and The Embedded Control Solutions
Company are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, CodeGuard,
dsPICDEM, dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, ECAN,
ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB,
In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, Linear Active
Thermistor, Mindi, MiWi, MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK, PICkit,
PICDEM, PICDEM.net, PICLAB, PICtail, PowerCal,
PowerInfo, PowerMate, PowerTool, REAL ICE, rfLAB,
rfPICDEM, Select Mode, Smart Serial, SmartTel, Total
Endurance, UNI/O, WiperLock and ZENA are trademarks of
Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other
countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2006, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2002 certification for its worldwide
headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in Chandler and
Tempe, Arizona, Gresham, Oregon and Mountain View, California. The
Company’s quality system processes and procedures are for its PIC
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ
microperipherals, no nvolatile memory and analog products. In addition,
Microchip’s quality system for the design and manufacture of
development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
®
code hopping devices, Serial EEPROMs,
DS70181A-page ii © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
®
Page 3

dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
Table of Contents
Preface ........................................................................................................................... 1
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................ 7
1.2 dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board Kit ........................................ 8
1.3 dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board Features .............................. 8
Chapter 2. Hardware Overview
2.1 Connectors ................................................................................................... 11
2.2 User Interface Hardware .............................................................................. 14
2.3 Program or Debug Selection Switch (SW2) ................................................. 17
Chapter 3. Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
3.1 Tutorial Overview ......................................................................................... 19
3.2 Creating the Project ...................................................................................... 19
3.3 Building the Code ......................................................................................... 26
3.4 Programming the Chip ................................................................................. 28
3.5 Debugging the Code .................................................................................... 33
Chapter 4. Demonstration Program Operation
4.1 Demonstration Program ............................................................................... 37
4.2 Demonstration Code .................................................................................... 39
4.3 Other Code Examples .................................................................................. 40
Appendix A. Schematic and Layouts
Index ............................................................................................................................. 45
Worldwide Sales and Service .................................................................................... 46
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page iii
Page 4

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
NOTES:
DS70181A-page iv © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5

dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
Preface
NOTICE TO CUSTOMERS
All documentation becomes dated, and this manual is no exception. Microchip tools and
documentation are constantly evolving to meet customer needs, so some actual dialogs
and/or tool descriptions may differ from those in this document. Please refer to our web site
(www.microchip.com) to obtain the latest documentation available.
Documents are identified with a “DS” number. This number is located on the bottom of each
page, in front of the page number. The numbering convention for the DS number is
“DSXXXXXA”, where “XXXXX” is the document number and “A” is the revision level of the
document.
For the most up-to-date information on development tools, see the MPLAB
Select the Help menu, and then Topics to open a list of available on-line help files.
®
IDE on-line help.
This document contains general information that is useful to know before using the
dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board.
Items discussed in this preface include:
• About this Guide
• Conventions Used in this Guide
• Warranty Registration
• Recommended Reading
• The Microchip Web Site
• Development Systems Customer Change Notification Service
• Customer Support
• Document Revision History
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
This document describes how to use the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development
Board development tool. The manual layout is as follows:
• Chapter 1. “Introduction” – This chapter introduces the dsPICDEM™ SMPS
Buck Development Board and provides a brief descriptions of the hardware.
• Chapter 2. “Hardware Overview” – This chapter describes the dsPICDEM™
SMPS Buck Development Board hardware.
• Chapter 3. “Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device” – This chapter goes through a
basic step by step process for getting your dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board up and running with the MPLAB
a dsPIC30F2020 device.
• Chapter 4. “Demonstration Program Operation” – This chapter describes the
operation of the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board.
• Appendix A. “Schematic and Layouts” – This section illustrates the
dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board layout and provides hardware
schematic diagrams.
®
In-Circuit Debugger 2 (ICD 2) using
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 1
Page 6
dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
CONVENTIONS USED IN THIS GUIDE
This manual uses the following documentation conventions:
DOCUMENTATION CONVENTIONS
Description Represents Examples
Arial font:
Italic characters Referenced books MPLAB
Emphasized text ...is the only compiler...
Initial caps A window the Output window
A dialog the Settings dialog
A menu selection select Enable Programmer
Quotes A field name in a window or
dialog
Underlined, italic text with
right angle bracket
Bold characters A dialog button Click OK
N‘Rnnnn A number in verilog format,
Text in angle brackets < > A key on the keyboard Press <Enter>, <F1>
Courier New font:
Plain Courier New Sample source code #define START
Italic Courier New A variable argument file.o, where file can be
Square brackets [ ] Optional arguments mcc18 [options] file
Curly brackets and pipe
character: { | }
Ellipses... Replaces repeated text var_name [,
A menu path File>Save
A tab Click the Power tab
where N is the total number of
digits, R is the radix and n is a
digit.
Filenames autoexec.bat
File paths c:\mcc18\h
Keywords _asm, _endasm, static
Command-line options -Opa+, -Opa-
Bit values 0, 1
Constants 0xFF, ‘A’
Choice of mutually exclusive
arguments; an OR selection
Represents code supplied by
user
®
IDE User’s Guide
“Save project before build”
4‘b0010, 2‘hF1
any valid filename
[options]
errorlevel {0|1}
var_name...]
void main (void)
{ ...
}
DS70181A-page 2 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

WARRANTY REGISTRATION
Please complete the enclosed Warranty Registration Card and mail it promptly.
Sending in the Warranty Registration Card entitles users to receive new product
updates. Interim software releases are available at the Microchip web site.
RECOMMENDED READING
This user's guide describes how to use the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development
Board. Other useful documents are listed below. The following Microchip documents
are available and recommended as supplemental reference resources.
Readme Files
For the latest information on using other tools, read the tool-specific Readme files in
the Readmes subdirectory of the MPLAB IDE installation directory. The Readme files
contain update information and known issues that may not be included in this user’s
guide.
THE MICROCHIP WEB SITE
Microchip provides online support via our web site at www.microchip.com. This web
site is used as a means to make files and information easily available to customers.
Accessible by using your favorite Internet browser, the web site contains the following
information:
• Product Support – Data sheets and errata, application notes and sample
programs, design resources, user’s guides and hardware support documents,
latest software releases and archived software
• General Technical Support – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), technical
support requests, online discussion groups, Microchip consultant program
member listing
• Business of Microchip – Product selector and ordering guides, latest Microchip
press releases, listing of seminars and events, listings of Microchip sales offices,
distributors and factory representatives
Preface
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 3
Page 8

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMS CUSTOMER CHANGE NOTIFICATION SERVICE
Microchip’s customer notification service helps keep customers current on Microchip
products. Subscribers will receive e-mail notification whenever there are changes,
updates, revisions or errata related to a specified product family or development tool of
interest.
To register, access the Microchip web site at www.microchip.com, click on Customer
Change Notification and follow the registration instructions.
The Development Systems product group categories are:
• Compilers – The latest information on Microchip C compilers and other language
tools. These include the MPLAB C18 and MPLAB C30 C compilers; MPASM™
and MPLAB ASM30 assemblers; MPLINK™ and MPLAB LINK30 object linkers;
and MPLIB™ and MPLAB LIB30 object librarians.
• Emulators – The latest information on Microchip in-circuit emulators.This
includes the MPLAB ICE 2000 and MPLAB ICE 4000.
• In-Circuit Debuggers – The latest information on the Microchip in-circuit
debugger, MPLAB ICD 2.
• MPLAB
Integrated Development Environment for development systems tools. This list is
focused on the MPLAB IDE, MPLAB SIM simulator, MPLAB IDE Project Manager
and general editing and debugging features.
• Programmers – The latest information on Microchip programmers. These include
the MPLAB PM3 and PRO MATE
Plus and PICkit
®
IDE – The latest information on Microchip MPLAB IDE, the Windows®
®
™
1 development programmers.
II device programmers and the PICSTART®
DS70181A-page 4 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

CUSTOMER SUPPORT
Users of Microchip products can receive assistance through several channels:
• Distributor or Representative
• Local Sales Office
• Field Application Engineer (FAE)
• Technical Support
Customers should contact their distributor, representative or field application engineer
(FAE) for support. Local sales offices are also available to help customers. A listing of
sales offices and locations is included in the back of this document.
Technical support is available through the web site at: http://support.microchip.com
Preface
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 5
Page 10

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
DOCUMENT REVISION HISTORY
Revision A (October 2006)
• Initial Release of this Document.
DS70181A-page 6 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11
Modern power supplies are becoming smaller, more efficient, more flexible and less
costly. These desirable enhancements have come about as digital signal controllers
have been incorporated into Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS) designs. Buck
converters are used when the desired output voltage is smaller than the input voltage.
This chapter introduces and provides an overview of the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck
Development Board. Topics covered include:
•Overview
• dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board Kit
• dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board Features
1.1 OVERVIEW
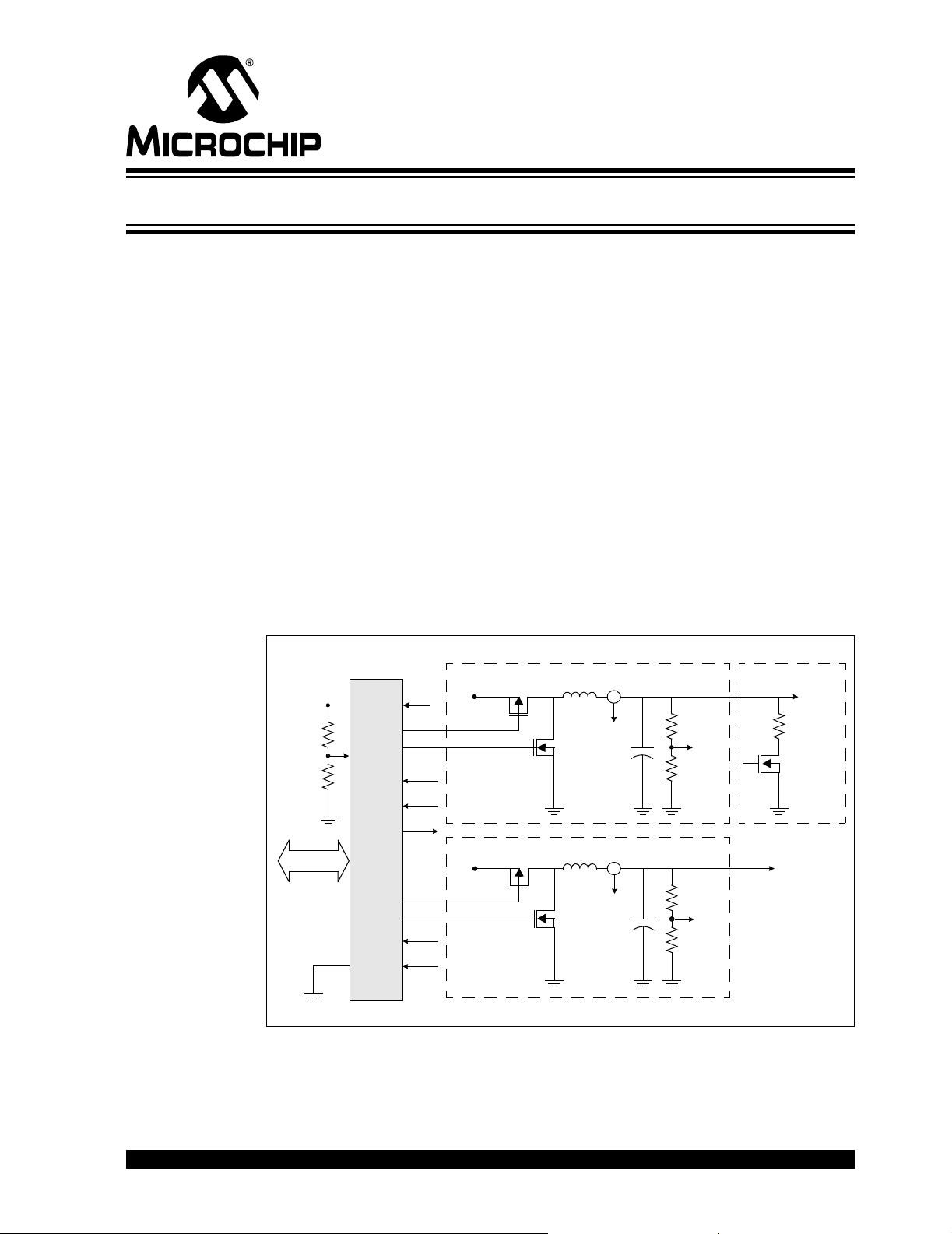
Figure 1-1 is a block diagram of the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board, A
dsPIC30F2020 DSC controls two independent DC/DC synchronous buck converters,
providing closed-loop Proportional, Integral, Derivative (PID) control in software to
maintain desired output voltage levels. The dsPIC
sary memory and peripherals for A/D conversion, PWM generation and general
purpose I/O, precluding the need to perform these functions in external circuitry.
dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
Chapter 1. Introduction
®
DSC device provides the neces-
USER’S GUIDE
FIGURE 1-1: SYNCHRONOUS BUCK CONVERTER BLOCK DIAGRAM
LOADBUCK CONVERTER 1
IN
V
Communication
AN4
dsPIC30F2020
AN0
AN1
OC1
AN2
AN3
V
DD
PWM1H
PWM1L
I1
V1
Vg
PWM2H
PWM2L
I2
V2
VIN
I1
V1
VG
BUCK CONVERTER 2
VIN
I2
V2
VOUT1
VOUT2
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 7
Page 12

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
dsPIC DSC SMPS devices are specifically designed to provide low-cost, efficient control of a wide range of power supply topologies. Their specialized peripherals facilitate
closed-loop feedback control of switched mode power supplies while also providing
communications for remote monitoring and supervisory control.
The dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board aids in rapid development of multiple buck converters using dsPIC30F1010/2020 Digital Signal Controllers. The
dsPIC30F1010/2020 devices offer these features and capabilities:
• Integrated program and data memory on a single chip
• Ultra fast interrupt response time and hardware interrupt priority logic
• 2000 ksps, on-chip ADC with four dedicated sample/hold circuits for multiple loop
control
• Four independent, high-resolution PWM generators specially designed to support
different power topology
• Four analog comparators for system protection
• On-chip system communications (I
• On-chip RC oscillator for lower system cost
• High-current sink/source I/O pins: 25 mA/25mA
• 30 MIPS performance CPU
1.2 dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD KIT
2
C/SPI/UART)
The dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board kit contains these items:
• dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
• dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board CD containing example code and
relevant documentation
1.3 dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD FEATURES
The dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board incorporates these features:
1.3.1 Power Stages
• Two synchronous buck converter power stages
• Voltage/current measurement for digital control of buck converters
• In-rush current limiting
• Switchable 5Ω/5W resistive load on VOUT1
• Buck Converter 1 output (VOUT1) on J1 connector for external loading
• Buck Converter 2 output (VOUT2) on J2 connector for external loading
1.3.2 Input/Output Controls
• Three 5 kΩ Potentiometers (R29,R30 and R35)
• Two push button switches (S2 and S4)
• Master Clear push button switch (S3)
• LED indicator (LED3)
DS70181A-page 8 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13

Introduction
1.3.3 Development Board Power
• Auxiliary power input (P1and P2) – 7V to 15V (9V nominal)
• 9 volt power input (J2)
Note: This power input is compatible with the 9 volt power supply that is part of
the MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger (DV164007).
• LED power-on indicator (LED1)
• On-board 5V DC, low-dropout regulator
1.3.4 Communication Ports
• One RS232 port (J6)
• MPLAB ICD 2 programming connector (J5)
• SW2 selection of programming interface to the MPLAB ICD 2
Debugger/Programmer
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 9
Page 14

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
NOTES:
DS70181A-page 10 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

Chapter 2. Hardware Overview
This chapter describes the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
hardware elements and identifies the hardware components. The topics covered
include:
• Connectors
• User Interface Hardware
• Program or Debug Selection Switch (SW2)
2.1 CONNECTORS
Figure 2-1 shows the hardware connection (MPLAB ICD 2 and power supply) to the
dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board.
dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
FIGURE 2-1: dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD
CONNECTED TO MPLAB
Expansion
Header
6
®
ICD 2 AND POWER SUPPLY
ICD Connector
3
RS232 Connector
VOUT Connectors
5
4
VOUT2
VOUT1
Input Power Connector
1
2
TABLE 2-1: BUCK CONVERTER BOARD CONNECTORS
No Hardware Elements
1 Input Power Connector (J2)
2 RS232 connector (J6)
3 Programming/debugging connector (J5)
4 VOUT1 Connector (J1)
5 VOUT2 Connector (J3)
6 Expansion Header (J7)
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 11
Page 16

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
2.1.1 Input Power Connector
The dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board obtains +9V power from a power
connector for a +9V AC/DC wall adapter as well as auxiliary power connection points
(AUX PWR IN). A separate +5V DC regulator provides the operating voltage (V
required by the dsPIC30F2020 device.
2.1.2 ICD Connector
An RJ11 female connector (J5) connects the MPLAB® ICD 2 to the dsPIC30F2020
device for programming and debugging.
2.1.3 RS-232 Serial Port
An RS-232 serial communication port (J6) is provided for monitoring and controlling the
power supply by a remote processor. The PGM DEBUG switch (SW2) must be in set
in program mode position (PGM) to communicate via the UART.
2.1.4 VOUT1
An external load can be connected to VOUT1 through connector J1. An on-board 5Ω
5 watt resistor is connected at the output of VOUT1 through MOSFET U6 to optionally
load the first buck converter circuit. This load can be enabled or disabled in software.
See Figure A-3: “dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board Schematic 2 of 3”
DD)
2.1.5 VOUT2
An external load can be connected to VOUT2 through connector J1.See Figure
A-4: “dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board Schematic 3 of 3”
2.1.6 Expansion Header
Header J7 is an expansion connector that matches the dsPIC30F2020 device pins (see
Table 2-2 for pin usage information).
DS70181A-page 12 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

Hardware Overview
TABLE 2-2: DEVICE PINS IN EXPANSION CONNECTOR
Pin Number
Primary
Assignment Primary Use
1MCLR
Master Clear (Reset)
2 AN0/RB0 Analog Input 0 (Buck Converter 1 current)
3 AN1/RB1 Analog Input 1 (Buck Converter 1 voltage)
4 AN2/RB2 Analog Input 2 (Buck Converter 2 current)
5 AN3/RB3 Analog Input 3 (Buck Converter 2 voltage)
6 AN4/RB4 Analog Input 4 (Input Voltage)
7 AN5/RB5 Analog Input 5 (Potentiometer R29)
8V
SS Ground reference for logic and I/O pins
9 AN6/OSCI/RB6 Analog Input 6 (Potentiometer R30)
10 AN7/OSCO/RB7 Analog Input 7 (Potentiometer R35)
11 EMUD1/RE7 ICD secondary communication channel data
12 EMUC1/RE6 ICD secondary communication channel clock
13 V
DD Positive supply for logic and I/O pins
14 OC2/RF6 Compare output
15 OC1/RD0 Compare output
16 RA9 Port A pin (LED3)
17 U1TX/PGC/RF7 UART1 Receive
18 U1RX/PGD/RF8 UART1 Transmit
19 V
SS Ground reference for logic and I/O pins
20 VDD Positive supply for logic and I/O pins
21 PWM3H/RE5 PWM 3 High Output (Push Button Switch S2)
22 PWM3L/RE4 PWM 3 Low Output (Push Button Switch S4)
23 PWM2H/RE3 PWM 2 High Output (Buck Converter 2)
24 PWM2L/RE2 PWM 2 Low Output (Buck Converter 2)
25 PWM1H/RE1 PWM 1 High Output (Buck Converter 1)
26 PWM1L/RE0 PWM 1 Low Output (Buck Converter 1)
27 AV
28 AV
SS Ground reference for analog module
DD Positive supply for analog module
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 13
Page 18

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
2.2 USER INTERFACE HARDWARE
Figure 2-2 identifies the hardware elements that comprise the user interface (jumpers,
switches, LEDs and potentiometers) on the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development
Board.
FIGURE 2-2: JUMPERS/LED/SWITCHES/POTENTIOMETER
Jumpers
MCLR Reset Switch
S3
JP1JP3 JP4 JP2 JP5 J4 J8
LED1 LED3 R29 R30 R35
Potentiometers
S2 S4
SwitchesLEDs
2.2.1 Jumpers
The dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board has seven jumpers that determine
how features on the buck converters are used. Table 2-3 lists these jumpers and their
functions.
TABLE 2-3: JUMPER DESCRIPTIONS
Jumper Description
JP1 Buck Converter 1 Input Select
ON: Connects the Input power to buck converter 1
OFF: Input to buck converter 1 is left open
JP2 Buck Converter 1 Load Drive
ON: Turn ON buck converter 1 load (5
OFF: On board load is disabled
JP3 Buck Converter 2 Input Select
ON: Connects the Input power to buck converter 2
OFF: Input to buck converter 2 is left open
Ω/5W) using OC1/RD0 pin
DS70181A-page 14 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

Hardware Overview
TABLE 2-3: JUMPER DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Jumper Description
JP4 Buck Converter 1 Synchronous MOSFET Drive
ON: Enable Synchronous MOSFET drive for buck converter 1
OFF: Disable Synchronous MOSFET drive for buck converter 1
JP5 Buck Converter 2 Synchronous MOSFET Drive
ON: Enable Synchronous MOSFET drive for buck converter 2
OFF: Disable Synchronous MOSFET drive for buck converter 2
J4 Buck Converter 1 Current Sense Position Select
Jumper J4 is connected to the buck converter 1 output bulk capacitor. It allows the
user to select the current sense resistor position for different applications.
Position Function
1-2 Current sense resistor senses output load of converter 1
2-3 Current sense resistor senses inductor current of converter 1
J8 Buck Converter 2 Current Sense Position Select
Jumper J8 is connected to the buck converter 2 output bulk capacitor. It allows the
user to select the current sense resistor position for different applications.
Position Function
1-2 Current sense resistor senses load current of converter 2
2-3 Current sense resistor senses inductor current of converter 2
2.2.2 Switches, LEDs and Potentiometers
The dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board has 2 switches, 3 potentiometers
and one LED for user applications. The board also has one power ON status LED and
device reset switch.
TABLE 2-4: PUSH BUTTONS, POTENTIOMETERS AND LEDS
Label Hardware Elements
S2, S4 Push button switches connected to port pins RE5 and RE4, respectively, for user
applications. When momentarily depressed, the switch connects the respective
port pin to ground (Logical ‘0’).
R29, R30,
R35
LED3 User programmable LED; programmed by writing to port pin RE9.
LED1 Power-on status LED; indicates status of 5V regulator.
S3 Reset switch. When momentarily depressed, the switch asserts the MCLR
User potentiometers connected to analog input pins (AN5, AN6 and AN7),
respectively, for user applications.
®
to the dsPIC
DSC device for Reset.
signal
2.2.3 Test Points
The dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board provides seven power test points
that can be used to debug the power stage and eight PWM test points that can be used
to check the PWM signal and gate drive to buck converter 1 and 2. These test points
are described in Table 2-5 and Table 2-6, respectively.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 15
Page 20

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
FIGURE 2-3: TEST POINTS
Power Test Points
P2 P1 TP2 TP1 P14 P9 P3
P8 P6 P5 P7 P10 P13 P12 P11
PWM Test Points
.
TABLE 2-5: POWER TEST POINTS
Test Point Description
TP1 5V DC Regulator Output
TP2 5V DC Regulator Output Ground
P1 Input Supply Voltage
P2 Input Supply Ground
P3 Buck Converter Output Ground
P9 Buck Converter 1 Switching Point
P14 Buck Converter 2 Switching Point
Note 1: All ground test points are shorted
.
(1)
(1)
(1)
TABLE 2-6: PWM TEST POINTS
Test Point
P5 Buck Switch PWM signal (Buck Converter 1)
P6 Synchronous Switch PWM signal (Buck Converter 1)
P7 Buck Switch PWM signal (Buck converter 2)
P8 Synchronous Switch PWM signal (Buck Converter 2)
P10 Buck Switch Gate Drive (Buck Converter 1)
P11 Synchronous Switch Gate Drive (Buck Converter 1)
P12 Buck Switch Gate Drive (Buck Converter 2)
P13 Synchronous Switch Gate Drive (Buck Converter 2)
Signal
DS70181A-page 16 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

Hardware Overview
2.3 PROGRAM OR DEBUG SELECTION SWITCH (SW2)
The dsPIC30F2020 device program pins (PGC/PGD) are multiplexed with the UART
pins (U1RX and U1TX). A DIP switch (SW2) selects whether the default programming
pin pair (PGC/PGC) are used to program the device. Because PGC and PGD are
multiplexed with the UART pins, the pins can only be used to program the device.
Debugging is not possible with PGC/EMUC and PGD/EMUD.
When SW2 is in the PGM position, the PGC/PGD and PGC1/PGD1 pins are connected
to the ICD 2. This configuration allows you to program the device with either the default
programming pin pair (PGC/PGD) or the first set of auxiliary programming pins
(PGC1/PGD1). Emulation and debugging in not possible when SW2 is in the PGM
position and the default programming/emulation pins are selected (via the
Configuration bits).
When SW2 is in the DEBUG position, PGC1/EMUC1 and PGD1/EMUD1 must be
selected as the debugging pin pair in the Configuration bit settings window. Both
programming and debugging are possible in this configuration.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 17
Page 22

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
NOTES:
DS70181A-page 18 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

Chapter 3. Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
This chapter is a self-paced tutorial to get you started using the dsPICDEM™ SMPS
Buck Development Board with its on-board dsPIC30F2020 device. Information is provided on these topics:
• Tutorial Overview
• Creating the Project
• Building the Code
• Programming the Chip
• Debugging the Code
3.1 TUTORIAL OVERVIEW
The tutorial demonstrates the main features of MPLAB IDE Integrated Development
Environment and the MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger as they are used with the
dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board. On completing this tutorial, you should
be able to:
• Create a project using the Project Wizard.
• Assemble and link the code and set the Configuration bits.
• Set up MPLAB IDE to use the MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger.
• Program the chip with the MPLAB ICD 2.
• View the code execution.
• View registers in a Watch window.
• Set a breakpoint and make the code halt at a chosen location.
• Use the function keys to Reset, Run, Halt and Single Step the code.
Before you begin the tutorial, run the install program on the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck
Development Board CD. The default installation location is:
c:\Program Files\Microchip\Sync Buck Board\Firmware\DualBuck
dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
3.2 CREATING THE PROJECT
The first step is to create a project and workspace in MPLAB IDE. Usually, you will have
one project in one workspace.
Note: These instructions presume the use of MPLAB IDE 7.43 or newer.
A project contains the files needed to build an application (source code, linker script
files, etc.) along with their associations to various build tools and build options.
A workspace contains one or more projects and information on the selected device,
debug tool and/or programmer, open windows and their location, and other IDE
configuration settings. MPLAB IDE provides a Project Wizard to help create new
projects.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 19
Page 24

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
3.2.1 Select a dsPIC DSC Device
• Start MPLAB IDE.
• Close any workspace that might be open (File>Close Workspace
• From the Project menu, select Project Wizard.
• From the Welcome screen, click Next> to display the Project Wizard Step One
dialog as shown in the Figure 3-1.
FIGURE 3-1: PROJECT WIZARD, STEP 1, SELECT A DEVICE
).
• From the Device: pull-down list, select dsPIC30F2020 and click Next>. The
Project Wizard Step Two dialog displays as shown in Figure 3-2.
DS70181A-page 20 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25

Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
FIGURE 3-2: PROJECT WIZARD STEP 2, SELECT LANGUAGE
TOOLSUITE
3.2.2 Select Language Toolsuite
• From the Active Toolsuite: pull-down menu, select Microchip ASM30 Toolsuite.
This tool suite includes the assembler and linker that will be used.
Note: If you are creating a project with source files written in a language other
than Microchip assembly, choose the appropriate language tool suite from
the drop-down selections.
• In the Toolsuite Contents block, select MPLAB ASM30 Assembler
(pic30-as.exe).
• In the Location block, click Browse... and navigate to:
C:\Program Files\Microchip\MPLAB ASM30 Suite\bin\pic30-as.exe
• With MPLAB LINK 30 Object Linker (pic30-Id.exe) selected in Toolsuite Con-
tents, click Browse... and navigate to:
C:\Program Files\Microchip\MPLAB ASM30 Suite\bin\pic30-id.exe
•Click Next> to continue. The Project Wizard Step Three dialog displays as shown
in Figure 3-3.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 21
Page 26

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
FIGURE 3-3: PROJECT WIZARD, STEP 3, NAME YOUR PROJECT
3.2.3 Name Your Project
• In the Project Name text box, type DualBuck.
•Click Browse... and navigate to C:\DualBuck to place your project in the tutorial
folder (create this folder if it does not already exist).
•Click Next> to continue. The Project Wizard Step Four dialog displays as shown
in Figure 3-4.
DS70181A-page 22 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27

Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
FIGURE 3-4: PROJECT WIZARD, STEP 4, ADD FILES TO PROJECT
3.2.4 Add Files to Project
• In the left window, navigate to c:\...\Firmware\DualBuck and select these
files:
SMPS_PID_Control.s
isr_traps.s
p30f2020.gld
p30f2020.inc
•Click Add>> to include these files in the project. The files appear with check
boxes in the right-hand window.
• Check each box (to instruct the Project Wizard to copy these files to the project
directory).
•Click Next> to continue.
• When the summary screen displays, click Finish.
• When the Save Workspace As window displays, type DualBuck.mcw in the
“File name” field and save the workspace in C:\DualBuck (see Figure 3-5).
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 23
Page 28

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
FIGURE 3-5: SAVE WORKSPACE WINDOW
After the project wizard completes, the MPLAB IDE project window shows the
isr_traps.s and SMPS_PID_Control.s files in the Source Files folder, the
p30f2020.inc file in the Header Files folder and the p30f2020.gld file in the Linker
Scripts folder (Figure 3-6).
FIGURE 3-6: MPLAB
®
IDE PROJECT WINDOW
DS70181A-page 24 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 29

Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
A project and workspace has now been created in MPLAB IDE. DualBuck.mcw is the
workspace file and DualBuck.mcp is the project file. Double click the
SMPS_PID_Controls.s file in the project window to open the file. MPLAB IDE should
now look similar to Figure 3-7.
FIGURE 3-7: MPLAB
®
IDE WORKSPACE WINDOWS
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 25
Page 30

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
3.3 BUILDING THE CODE
In this project, building the code consists of assembling the SMPS_PID_Controls.s
and isr_traps.s files to create their respective object files,
and isr_traps.o, and then linking the object files to create the DualBuck.hex and
DualBuck.cof output files. The .hex file contains the data necessary to program the
device and the .cof file contains additional information that lets you debug at the
source code level.
Before building, there are settings required to tell MPLAB IDE where to find the include
files and to reserve space for the extra debug code when the MPLAB ICD 2 is used.
The following line is near the top of the SMPS_PID_Controls.s file:
.include "p30f2020.inc"
This line causes a standard include file to be used. Microchip provides these files with
all the Special Function Register (SFR) labels already defined for convenience. To build
the code, select Build Options>Project
displays, as shown in Figure 3-8.
FIGURE 3-8: BUILD OPTIONS
from the Project menu. The Build Options dialog
SMPS_PID_Controls.o
DS70181A-page 26 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 31

Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
3.3.1 Identify Assembler Include Path
• Select the General tab.
• At the Assembler Include Path, $(AINDIR) box, click Browse... and navigate to:
C:\Program Files\Microchip\MPLAB ASM30 Suite\Support\Inc
This path tells MPLAB IDE where to find the include files
•Click Apply and then click OK.
Note: The p30f2020.inc file was included when you added files to the project
folder (section Section 3.2.4 “Add Files to Project”). Selecting an
Assembler Include Path in the manner described here allows you to link to
the latest .inc file included with MPLAB IDE. Skip this step to use the
.inc file in the project folder.
3.3.2 Link for ICD 2
It is necessary to tell the linker that the code should be built with the intention to debug.
This sets aside RAM for the MPLAB ICD 2 to use during debugging. If this step is not
done, the MPLAB ICD 2 will not function properly in Debug mode.
• On the Project Manager toolbar, select “Debug” from the drop-down box (see
Figure 3-9)
FIGURE 3-9: LINK PROJECT FOR MPLAB
®
ICD 2
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 27
Page 32

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
3.3.3 Build the Project
•Select Project>Build All.
• Observe the progress of the build in the Output window as shown in Figure 3-10.
FIGURE 3-10: BUILD OUTPUT WINDOW
3.4 PROGRAMMING THE CHIP
The MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger can be used to program and debug the
dsPIC30F2020 device in-circuit on the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board.
Note: Before proceeding, make sure that the USB driver for the MPLAB ICD 2 has
been installed on your PC (see the “MPLAB
User’s Guide” (DS51331) for more details regarding the installation of
MPLAB ICD 2).
3.4.1 Setup the Device Configuration
• Use the Configure>Configuration Bits menu to display the configuration settings.
• Set up the Configuration bits as shown in Figure 3-11.
FIGURE 3-11: CONFIGURATION SETTINGS
®
ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger
DS70181A-page 28 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 33

Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
3.4.2 Connect the MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger
• Before connecting the MPLAB ICD 2 make sure SW2 is in the DEBUG position.
• Connect the MPLAB ICD 2 to the PC with the USB cable as shown in
Figure 3-12).
• Connect the MPLAB ICD 2 to the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
with the short RJ-11 (telephone) cable.
• Apply +9V power to the board.
FIGURE 3-12: dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD
CONNECTED TO MPLAB
®
ICD 2 IN-CIRCUIT DEBUGGER
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 29
Page 34

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
3.4.3 Enable MPLAB ICD 2 Connection
• From the Debugger menu, click Select Tool>MPLAB ICD 2 to designate the
MPLAB ICD 2 as the debug tool in MPLAB IDE.
•Select Debugger>Connect to connect the debugger to the device. The MPLAB
ICD 2 should report that it found the dsPIC30F2020 device, as shown in
Figure 3-13.
•Select Debugger>Settings
• Select the Program tab.
•Check Allow ICD 2 to select memories and ranges, as shown in Figure 3-14.
This setting will speed up operations by programming only a small part of the total
program memory.
Note: The MPLAB ICD 2 may need to download the new firmware if this is the first
time the MPLAB ICD 2 is being used with a dsPIC30F device. If any errors
are shown, double click the error message to get more information.
to display the MPLAB ICD 2 Debugger settings.
FIGURE 3-13: ENABLING MPLAB
®
ICD 2
DS70181A-page 30 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 35

Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
FIGURE 3-14: SETTING PROGRAM MEMORY SIZE
3.4.4 Program the dsPIC30F2020
• From the Debugger menu, select Program. The Output window (Figure 3-15)
displays the program steps as they occur.
• Observe the process in the Output window. When “MPLAB ICD 2 Ready”
displays, the device is programmed and ready to run.
•Use the Debugger>Reset
code.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 31
menu to reset the code, then Debugger>Run to run the
Page 36

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
FIGURE 3-15: PROGRAMMING THE DSPIC30F2020 DEVICE
DS70181A-page 32 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 37

3.5 DEBUGGING THE CODE
The MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger can be used to run, halt and step the code. A
breakpoint can be set to halt the program after the code has executed the instruction
at the breakpoint. The contents of the RAM and registers can be viewed whenever the
processor has been halted.
The MPLAB ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger uses the following function keys to access the
main debugging functions:
<F5> Halt
<F6> Reset
<F7> Single Step
<F9> Run
In addition, there are more functions available by right clicking on a line of source code.
The most important of these are “Set Breakpoint” and “Run to Cursor”.
3.5.1 Display the Code
• From the View menu, select View>Program Memory.
• On the Program Memory window, select the Symbolic tab, as shown in
Figure 3-16.
• Press <F5> to halt the processor and press <F6> to reset. The program memory
now shows a green arrow pointing to the line of code at address 0.
The instruction at this location is goto 0x000100. This code is added by the linker to
make the program branch to the start of the code in the Lab1.c file. From location
0x000100 executable code starts.
Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
FIGURE 3-16: PROGRAM MEMORY WINDOW
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 33
Page 38

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
3.5.2 Step the Program
• Press <F7> to single step the code. The green arrow now points to the code
below _reset in the SMPS_PID_Control.s source code, as shown in
Figure 3-17.
• Right click two lines below the green arrow and choose “Run to Cursor”. The
green arrow then points to the line on which you right clicked.
• From the View menu, select View>Watch
Figure 3-18.
•From the Add SFR pull-down list, display DTR1.
•Click Add SFR to add the DTR1 register to the Watch window.
• Next, select PWMCON1 from the pull-down list and click Add SFR.
• Repeat for the ADCON register.
• You will be able to view these registers change as you step through the code.
FIGURE 3-17: SOURCE CODE WINDOW
to open a Watch window as shown in
FIGURE 3-18: WATCH WINDOW DISPLAY
DS70181A-page 34 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 39

3.5.3 Set Break Point
• To set a breakpoint, right click a code line and select “Set Breakpoint” from the
pop-up menu.
As an example, find the following line of code and set a breakpoint on this line.
cp0 VIN_GOOD_FLAG
A red stop sign should appear in the gutter (gray bar on the left) of the source
code window, as shown in Figure 3-19.
• Press <F9> to run the code. The program halts on the instruction following the
breakpoint
Note: An alternate method is to simply double click the line. This feature may
need to be enabled using the Edit>Properties
FIGURE 3-19: SETTING BREAKPOINT
Using the dsPIC30F2020 Device
menu.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 35
Page 40

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
NOTES:
DS70181A-page 36 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 41

Chapter 4. Demonstration Program Operation
The dsPIC30F2020 device supplied with the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development
Board is pre-programmed with a demonstration program that illustrates simultaneous
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control of the output voltage for the two buck circuits on the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board. This code is available on
the CD that is provided with the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board kit. It
can also be downloaded from the Microchip web site (www.microchip.com).
This section covers the following topics:
• Demonstration Program
• Demonstration Code
• Other Code Examples
4.1 DEMONSTRATION PROGRAM
The demonstration program provides simultaneous closed-loop control of the output
voltage from both buck circuits on the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board.
One PID loop controls a target voltage output (VOUT1) at 5V. The other PID loop controls a target voltage output (VOUT2) at 3.3V.
The PID control scheme consists of seven parameters. The main parameters are:
1. Proportional Error Gain (P-Gain) – This parameter produces a correction fac-
tor that is proportional to the magnitude of the output voltage error.
2. Integral Error Gain (I-Gain) – This parameter uses the cumulative voltage error
to generate a correction factor that eliminates any residual error due to limitations
in offset voltages and measurement resolution.
3. Derivative Error Gain (D-Gain) – This parameter produces a correction factor
that is proportional to the rate of change of the output error voltage, which helps
the system respond quickly to changes in system conditions.
Additional control parameters that are summed with the P, I, and D Gain terms are:
4. Second Derivative, or Jerk Error, Gain (J-Gain) – This parameter produces a
correction factor that is proportional to the change in the differential error (i.e., the
derivative of the derivative). J-Gain is a high frequency term that tends to provide
quick response to an impulse event.
5. Feed Forward Gain – This parameter produces a correction factor based on the
desired output voltage that is computed based on the magnitude of the input voltage, inductor current, and circuit attributes (i.e. inductor and capacitor values).
This term allows the control loop to be proactive rather than reactive. In other
words, when the input voltage changes, feed forward gain responds so that the
control loop does not have to wait until the output voltage changes before making
the appropriate gain correction.
6. Dead Time Gain – This parameter produces a correction factor, which compen-
sates for the fact that the feed forward gain term does not account for the energy
lost due to the dead time of the PWM signal (the time when both MOSFETs are
off).
7. Current-Limit Gain – This parameter limits the cumulative control gain when the
current is approaching its upper limit.
dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 37
Page 42

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
The demonstration program requires no manual preparation except to connect 9V
power to the board. You can verify the VOUT1 and VOUT2 voltage levels by measuring
them at the output terminals (J1 and J3, respectively).
If you installed the software that came on the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development
Board CD, the demonstration program source code is located in the following folder on
your PC.
C:\Program Files\Microchip\Sync Buck Board\Firmware\DualBuck
Instructions for programming the dsPIC30F2020 are provided in the Readme file that
is included in the DualBuck folder. Chapter 3 also describes how to program the
dsPIC30F2020 using the ICD 2. Figure 4-1 illustrates the program flow of the
demonstration program.
FIGURE 4-1: SMPS DEMONSTRATION PROGRAM FLOW CHART
START
Initialization Routines:
• Peripherals – ADC, PWM, Timers, GPIO, etc.
• Variables – PID Gain Terms, Data Buffers
• Constants – Desired Voltage, Current Limit, etc.
• Interrupts – ADC, Timers
• Set Soft Start Flag
• System Stabilization
Soft Start Routine
Soft
Start
Routine
Yes
Idle Loop Functions:
• Check VIN
• Check Soft Start Flag
• Check/Reset Fault Timers and Flags
• Perform non-critical functions here (e.g. user
application tasks)
Does
Fault Condition
Exist
?
No
Is
Soft Start
Active
?
No
Fault-Check Routine
Yes
Disable
Outputs
ADC Interrupt
ADC Interrupt Routines:
• Measure VOUT
• Calculate PID Gain Parameters
• Update PWM Duty Cycle
END
DS70181A-page 38 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 43

4.2 DEMONSTRATION CODE
4.2.1 System Initialization
When power is applied to the board, the program starts by executing these system
initialization routines:
• Peripherals – The required peripherals (PWM, ADC, Timers, GPIO) are
configured and enabled.
• Variables – Program variables are defined. RAM locations and register usage are
also defined and documented.
• Constants – Program constants are defined, including reference setpoints for
both VOUT1 and VOUT2, input voltage, current limits, fault conditions, PWM
periods and Timer periods.
• Interrupts – The ADC and Timer Interrupts are set up and enabled.
• Soft Start – The Soft Start flag is set
• System Stabilization – All outputs are discharged to ensure a stable value at
startup.
4.2.2 Fault Check
The program checks the ADC for input undervoltage and output overvoltage conditions. If a fault occurs, the PWM outputs are disabled until the fault condition is cleared.
If no fault is detected, the program proceeds.
Demonstration Program Operation
4.2.3 Soft Start
If the Soft Start flag is set, the Soft Start Routine ramps up the output voltage in an
open-loop fashion to bring the system within the operating range of the PID control
loop. This routine ensures that the output does not overshoot the desired voltage. It
also limits the current at startup.
4.2.4 ADC Interrupt
The ADC Interrupt is the heart of the demo program. This routine takes up approximately 75% of the execution time. It performs all the PID calculations and applies any
needed corrections to the output
Two simultaneous PID loops are being processed (one for VOUT1 and the other for
VOUT2). Each loop has its own variables, constants and peripheral initialization.
Key points to note are:
• The ADC Interrupt can occur at any time during program execution, and
• It takes priority over any other tasks that the program is performing.
4.2.5 System Idle Loop
All auxiliary functions are performed in the System Idle routine. This is the time available to the CPU while the demo program is waiting for an ADC Interrupt. Non-critical
functions can be performed in this loop. During this time the input voltage, fault timers
and Soft Start flag are checked.
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 39
Page 44

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
4.3 OTHER CODE EXAMPLES
There are several other code examples included on the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck
Development Board CD. Please refer to the Readme files located in each code example folder for details on what each code example demonstrates. Check the Microchip
website (www.microchip.com) for the latest updates to these code examples and for
additional code examples.
DS70181A-page 40 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 45

dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
Appendix A. Schematic and Layouts
This Appendix provides a layout drawing of the printed circuit board followed by
schematics for the dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board.
FIGURE A-1: dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD LAYOUT
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 41
Page 46

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
FIGURE A-2: dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD SCHEMATIC 1 OF 3
RXD
TXD
P1L
VDD
P1H
RE5
P2L
P2H
RE4
RA9
VDD
OC1
0.1uF
C19
MCLR
VDD
OC2
AN0
AN4
AN1
AN2
AN3
MCLR
AN5
2.2K
2.2K
R32
R24
RXD
TXD
VDD
AN6
AN7
EMUD1
EMUC1
RXD
EMUD1
TXD
EMUC1
VDD
0.1uF
C16
0.1uF
C21
0.1uF
C12
VDD
C20
0.1uF
0.1uF
C15
VDD
VDD
VDD
MCLR
RE5
C17
0.1uF
VDD
C14
0.1uF
C18
0.1uF
VDD VDD
RE4
AN7
C32
0.01uF
P1H
P1L
P2H
P2L
P6
P5
P7
P8
VDD
MCLR
AN1
AN0
AN2
AN3
RE5
RE4
AN5
C8
0.1uF
AN4
0.01uF
C11
500pF
C10
0.01uF
C23
500pF
C13
TXD
RXD
RA9
VDD
AN6
AN7
OC1
OC2
VDD
EMUC1
EMUD1
VDD
AN6
C31
0.01uF
VDD
AN5
C9
0.01uF
VDD
RA9
DS70181A-page 42 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 47

Schematic and Layouts
FIGURE A-3: dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD SCHEMATIC 2 OF 3
J1
VOUT1
0.1uF
C5
C4
C24
5R 5W
330uF 16V
330uF 16V
U6
3
4
R5
1
IN4001
D6
4.7K
R17
JP2
1K 1%
R7
VDD
R1
0.050 R 1%
L1
39uH
P9
U1
IRFR5305
P10
1N4746A 18V
D9
1K 1%
R10
MBRS340
D4
U5
27R
R12
P11
U2:B
4.7K
R14
R9
27R
JP4
VDD
C2
100 uF 10V
U2:A
4.7K
C35
1.0uF
1N4746A 18V
JP1
VIN
D5
3K 1%
R6
C28
470uF 25V
C37
470uF 25V
R13
VIN
470RR2470R
1K 1%
R11
R4
P1L
AN1
AN0
P1H
AN4
OC1
D7
C22
1N4001MOD
470uF 15V
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 43
Page 48

dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board
FIGURE A-4: dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK DEVELOPMENT BOARD SCHEMATIC 3 OF 3
J3
VOUT2
330uF 16V
0.1uF
330uF 16V
C7
C25
C6
R36
L2
P14
IRFR5305
1K 1%
R20
VDD
0.050R 1%
39uH
D8
U12
P13
1N4746A 18V
D10
1K 1%
R22
MBRS340
U15
27R
R18
P12
U11:B
4.7K
R34
27R
R15
U11:A
4.7K
C34
D11
JP3
C33
C36
VIN
R19
1.0uF
1N4746A 18V
470uF 25V
470uF 25V
JP5
470R
470R
R8
R3
P2L
AN3
AN2
P2H
DS70181A-page 44 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 49

dsPICDEM™ SMPS BUCK
Index
DEVELOPMENT BOARD
USER’S GUIDE
B
Block Diagram
Synchronous Buck Converter ............................. 7
Board Features .......................................................... 8
C
Communication Ports................................................. 9
Connectors............................................................... 11
Current Limit Gain.................................................... 37
Customer Notification Service.................................... 4
Customer Support...................................................... 5
D
Dead Time Gain....................................................... 37
Derivative Error Gain (D-Gain)................................. 37
Development Board Power........................................ 9
Documentation
Conventions........................................................ 2
Layout ................................................................. 1
E
Expansion Header ................................................... 12
F
Feed Forward Gain.................................................. 37
I
ICD Connector ......................................................... 12
Input Power Connector ............................................ 12
Input/Output Controls................................................. 8
Integral Error Gain (I-Gain) ...................................... 37
Internet Address......................................................... 3
J
Jerk Error Gain (J-Gain)........................................... 37
Jumper Descriptions ................................................ 14
K
Kit
dsPICDEM™ SMPS Buck Development Board.. 8
M
Microchip Internet Web Site....................................... 3
P
PID Control............................................................... 37
Power Stages............................................................. 8
Power Test Points.................................................... 16
Program/Debug Switch ...................................... 16
Proportional Error Gain (P-Gain).............................. 37
PWM Test Points ..................................................... 16
, 17
R
Reading, Recommended ........................................... 3
RS-232 Serial Port ................................................... 12
S
Second Derivative Gain (J-Gain) ............................. 37
Synchronous Buck Converter Block Diagram............ 7
T
Test Points ............................................................... 15
V
VOUT1 ..................................................................... 12
VOUT2 ..................................................................... 12
W
Warranty Registration ................................................ 3
WWW Address........................................................... 3
© 2006 Microchip Technology Inc. DS70181A-page 45
Page 50

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
http://support.microchip.com
Web Address:
www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Alpharetta, GA
Tel: 770-640-0034
Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Farmington Hills, MI
Tel: 248-538-2250
Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
Kokomo, IN
Tel: 765-864-8360
Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
Santa Clara
Santa Clara, CA
Tel: 408-961-6444
Fax: 408-961-6445
Toronto
Mississauga, Ontario,
Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699
Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Asia Pacific Office
Suites 3707-14, 37th Floor
Tower 6, The Gateway
Habour City, Kowloon
Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8528-2100
Fax: 86-10-8528-2104
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8665-5511
Fax: 86-28-8665-7889
China - Fuzhou
Tel: 86-591-8750-3506
Fax: 86-591-8750-3521
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-8502-7355
Fax: 86-532-8502-7205
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-5407-5533
Fax: 86-21-5407-5066
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
Fax: 86-24-2334-2393
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8203-2660
Fax: 86-755-8203-1760
China - Shunde
Tel: 86-757-2839-5507
Fax: 86-757-2839-5571
China - Wuhan
Tel: 86-27-5980-5300
Fax: 86-27-5980-5118
China - Xian
Tel: 86-29-8833-7250
Fax: 86-29-8833-7256
ASIA/PACIFIC
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-4182-8400
Fax: 91-80-4182-8422
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-4160-8631
Fax: 91-11-4160-8632
India - Pune
Tel: 91-20-2566-1512
Fax: 91-20-2566-1513
Japan - Yokohama
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166
Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea - Gumi
Tel: 82-54-473-4301
Fax: 82-54-473-4302
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or
82-2-558-5934
Malaysia - Penang
Tel: 60-4-646-8870
Fax: 60-4-646-5086
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 63-2-634-9065
Fax: 63-2-634-9069
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan - Hsin Chu
Tel: 886-3-572-9526
Fax: 886-3-572-6459
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-536-4818
Fax: 886-7-536-4803
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2500-6610
Fax: 886-2-2508-0102
Thailand - Bangkok
Tel: 66-2-694-1351
Fax: 66-2-694-1350
EUROPE
Austria - Wels
Tel: 43-7242-2244-39
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Copenhagen
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
France - Paris
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Munich
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
Spain - Madrid
Tel: 34-91-708-08-90
Fax: 34-91-708-08-91
UK - Wokingham
Tel: 44-118-921-5869
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
10/19/06
DS70181A-page 46 © 2006 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...