Datasheet TC1072-1.8VCH713, TC1072-2.5VCH713, TC1072-2.6VCH713, TC1072-2.7VCH713, TC1072-2.85VCH713 Datasheet (Microchip) [ru]
...Page 1
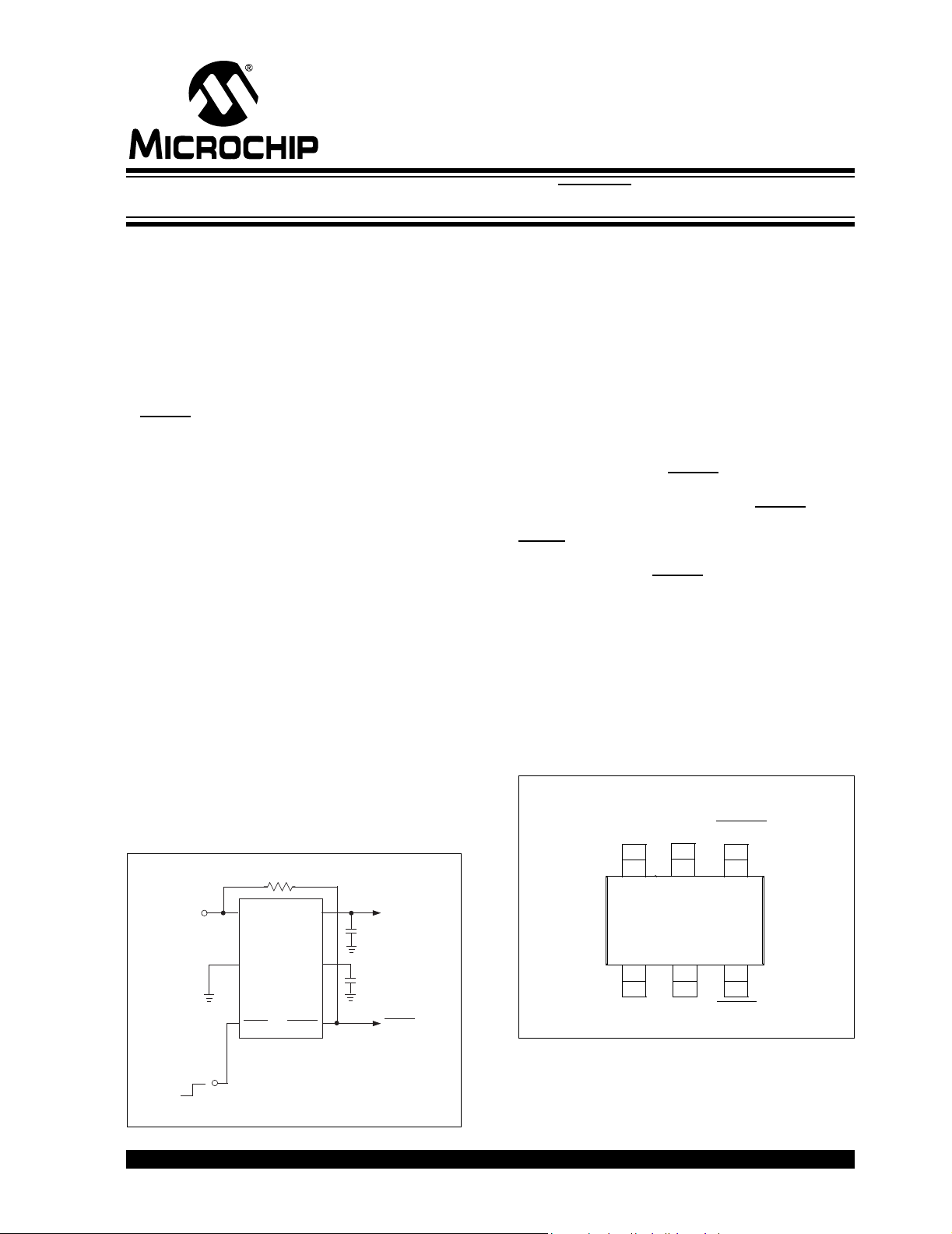
TC1072/TC1073
R
6
1
4
2
3
6-Pin SOT-23
V
OUT
ERROR
SHDNGNDV
IN
5
Bypass
50mA and 100mA CMOS LDOs with Shutdown, ERROR Output and V
Features:
• 50 µA Ground Current for Longer Battery Life
• Very Low Dropout Voltage
• Choice of 50 mA (TC1072) and 100 mA (TC1073)
Output
• High Output Voltage Accuracy
• Standard or Custom Output Voltages
• Power-Saving Shutdown Mode
• ERROR
Output Can Be Used as a Low Battery
Detector or Processor Reset Generator
• Bypass Input for Ultra Quiet Operation
• Overcurrent and Overtemperature Protection
• Space-Saving 6-Pin SOT-23 Package
• Pin Compatible Upgrades for Bipolar Regulators
• Standard Output Voltage Options:
- 1.8V, 2.5V, 2.6V, 2.7V, 2.8V, 2.85V, 3.0V,
3.3V, 3.6V, 4.0V, 5.0V
• Other output voltages are available. Please
contact Microchip Technology Inc. for details.
Applications:
• Battery Operated Systems
• Portable Computers
• Medical Instruments
• Instrumentation
• Cellular/GSM/PHS Phones
• Linear Post-Regulators for SMPS
• Pagers
General Description
The TC1072 and TC1073 are high accuracy (typically
±0.5%) CMOS upgrades for older (bipolar) low dropout
regulators. Designed specifically for battery-operated
systems, the devices’ CMOS construction eliminates
wasted ground current, significantly extending battery
life. Total supply current is typically 50 µA at full load
(20 to 60 times lower than in bipolar regulators).
The devices’ key features include ultra low noise
operation (plus optional Bypass input); very low
dropout voltage (typically 85 mV, TC1072 and 180 mV,
TC1073 at full load) and fast response to step changes
in load. An error output (ERROR
) is asserted when the
devices are out-of-regulation (due to a low input
voltage or excessive output current). ERROR
used as a low battery warning or as a processor
signal (with the addition of an external RC
RESET
network). Supply current is reduced to 0.5 µA (max)
and both V
and ERROR
OUT
are disabled when the
shutdown input is low. The devices incorporate both
overtemperature and overcurrent protection.
The TC1072 and TC1073 are stable with an output
capacitor of only 1 µF and have a maximum output
current of 50 mA, and 100 mA, respectively. For higher
output current versions, please see the TC1185,
TC1186, TC1187 (I
TC1108 and TC1173 (I
= 150 mA) and TC1107,
OUT
= 300 mA) data sheets.
OUT
Package Type
Bypass
REF
can be
Typical Application Circuit
R
P
V
1
IN
V
IN
TC1072
TC1073
2
GND
3
Shutdown Control
(from Power Control Logic)
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 1
SHDN
V
OUT
Bypass
ERROR
6
5
4
+
1 µF
C
BYPASS
470 pF
V
OUT
ERRO
Page 2
TC1072/TC1073
TC V
OUT
= (V
OUTMAX
– V
OUTMIN
) x 10
6
V
OUT
x ΔT
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
† Note: Stresses above those listed under "Absolute
Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to
the device. These are stress ratings only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions
Absolute Maximum Ratings†
Input Voltage .........................................................6.5V
Output Voltage...........................(-0.3V) to (V
+ 0.3V)
IN
above those indicated in the operation sections of the
specifications is not implied. Exposure to Absolute
Maximum Rating conditions for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Power Dissipation................Internally Limited (Note 6)
Maximum Voltage on Any Pin ........ VIN +0.3V to -0.3V
Operating Temperature Range...... -40°C < T
< 125°C
J
Storage Temperature..........................-65°C to +150°C
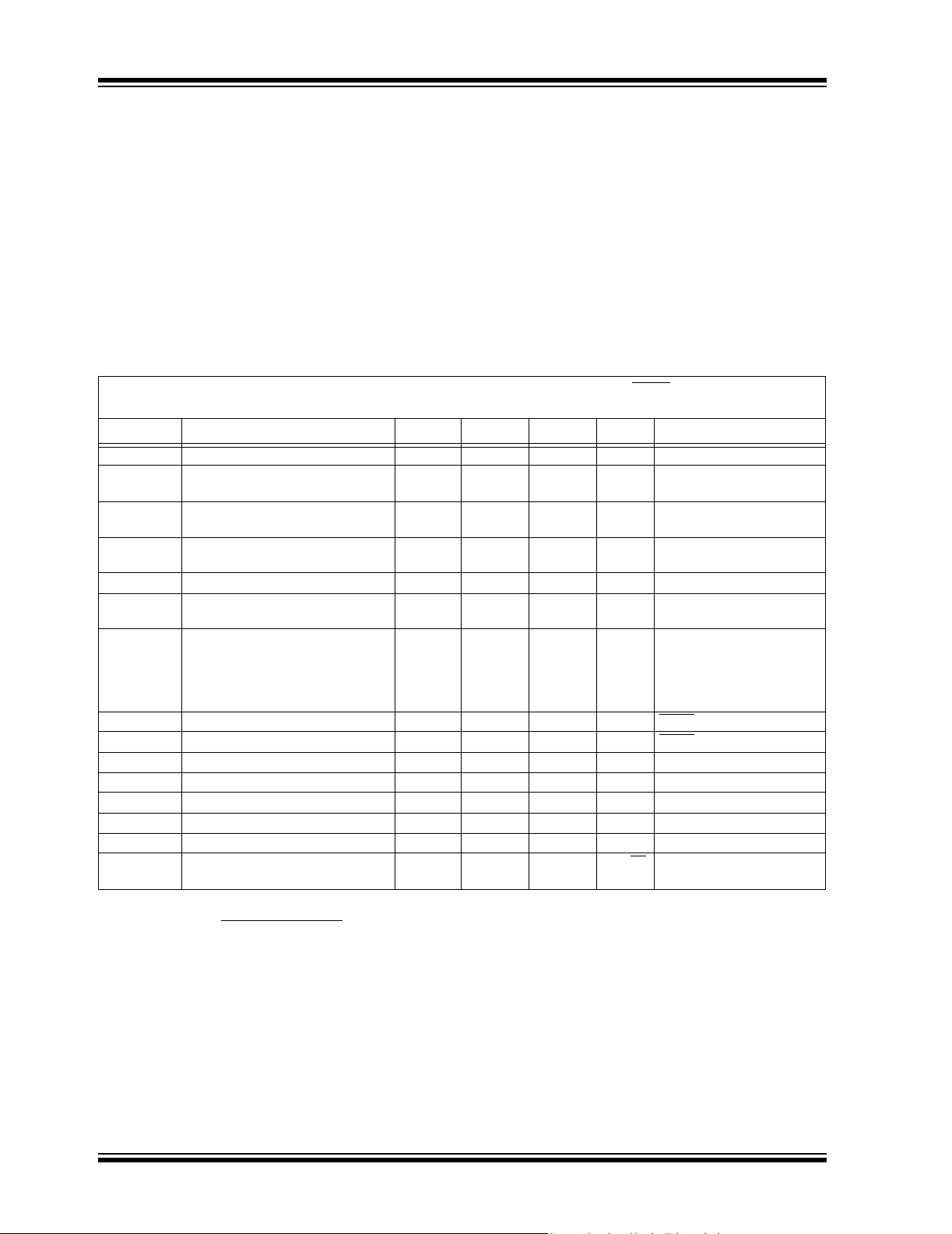
TC1072/TC1073 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, VIN=V
Boldface type specifications apply for junction temperatures of -40°C to +125°C.
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
V
IN
I
OUTMAX
V
OUT
TCV
OUT
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
OUT/VOUT
V
IN-VOUT
I
IN
I
INSD
Input Operating Voltage 2.7 — 6.0 V Note 9
Maximum Output Current 50
Output Voltage VR –
V
Temperature Coefficient —
OUT
/ΔVINLine Regulation — 0.05 0.35 %(VR + 1V) ≤ VIN ≤ 6V
Load Regulation — 0.5 2.0 %IL = 0.1 mA to I
Dropout Voltage —
Supply Current — 50 80 µA SHDN
Shutdown Supply Current — 0.05 0.5 µA SHDN
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio — 64 — dB F
I
OUTSC
ΔV
T
SD
ΔT
OUT
SD
Output Short Circuit Current — 300 450 mA V
/ΔPDThermal Regulation — 0.04 — V/W Notes 5, 6
Thermal Shutdown Die Temperature — 160 — °C
Thermal Shutdown Hysteresis — 10 — °C
eN Output Noise — 260 — nV/√Hz
Note 1: VR is the regulator output voltage setting. For example: VR= 2.5V, 2.7V, 2.85V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V, 4.0V, 5.0V.
2:
+ 1V, IL= 0.1 mA, CL=3.3μF, SHDN
OUT
100
—
—
—
—
VR ±0.5% VR + 2.5% V Note 1
2.5%
—
40
2
20
—
—
—
65
85
180
—
—
—
—
120
250
>VIH, TA=+25°C.
mAmATC1072
TC1073
ppm/°C Note 2
(Note 3)
mV I
=0.1mA
L
I
=20mA
L
IL=50mA
IL= 100 mA (Note 4),
TC1073
RE
OUT
IL=I
470 pF from Bypass to GND
=VIH, IL= 0 (Note 8)
=0V
≤ 1kHz
=0V
OUTMAX
OUTMAX
3: Regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low duty cycle pulse testing. Load regulation is tested over a load range
from 0.1 mA to the maximum specified output current. Changes in output voltage due to heating effects are covered by the thermal
regulation specification.
4: Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its nominal value.
5: Thermal Regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time T after a change in power dissipation is applied, excluding load or
line regulation effects. Specifications are for a current pulse equal to I
6: The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable junction temperature and the
thermal resistance from junction-to-air (i.e., T
thermal shutdown. Please see Section 5.0 “Thermal Considerations” for more details.
7: Hysteresis voltage is referenced by V
8: Apply for Junction Temperatures of -40°C to +85°C.
9: The minimum VIN has to justify the conditions = VIN≥ VR+V
, TJ, θJA). Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation causes the device to initiate
A
.
R
DROPOUT
at VIN=6V for T=10 ms.
LMAX
and VIN≥ 2.7V for IL= 0.1 mA to I
OUTMAX
.
DS21354D-page 2 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3
TC1072/TC1073
TC V
OUT
= (V
OUTMAX
– V
OUTMIN
) x 10
6
V
OUT
x ΔT
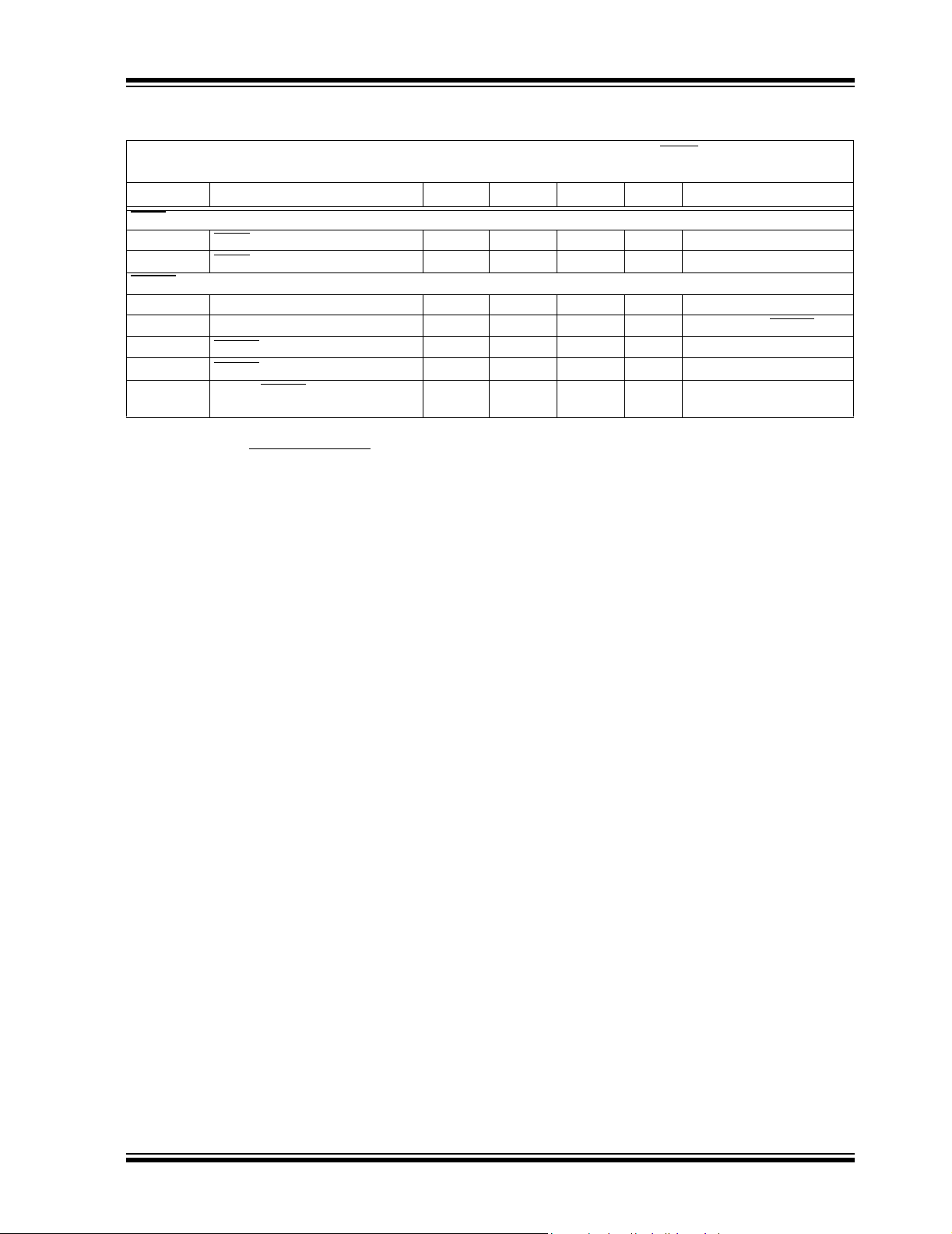
TC1072/TC1073 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, VIN=V
Boldface type specifications apply for junction temperatures of -40°C to +125°C.
+ 1V, IL= 0.1 mA, CL=3.3μF, SHDN
OUT
>VIH, TA= +25°C.
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
SHDN Input
V
IH
V
IL
ERROR
V
INMIN
V
OL
V
TH
V
HYS
t
DELAY
Note 1: VR is the regulator output voltage setting. For example: VR= 2.5V, 2.7V, 2.85V, 3.0V, 3.3V, 3.6V, 4.0V, 5.0V.
SHDN
Input High Threshold 45 — — %VINVIN= 2.5V to 6.5V
Input Low Threshold — — 15 %VINVIN= 2.5V to 6.5V
SHDN
Open Drain Output
Minimum VIN Operating Voltage 1.0 — — V
Output Logic Low Voltage — — 400 mV 1 mA Flows to ERROR
ERROR Threshold Voltage — 0.95 x V
— V See Figure 4-2
R
ERROR Positive Hysteresis — 50 — mV Note 7
V
to ERROR
OUT
2:
3: Regulation is measured at a constant junction temperature using low duty cycle pulse testing. Load regulation is tested over a load range
from 0.1 mA to the maximum specified output current. Changes in output voltage due to heating effects are covered by the thermal
regulation specification.
4: Dropout voltage is defined as the input to output differential at which the output voltage drops 2% below its nominal value.
5: Thermal Regulation is defined as the change in output voltage at a time T after a change in power dissipation is applied, excluding load or
line regulation effects. Specifications are for a current pulse equal to I
6: The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of ambient temperature, the maximum allowable junction temperature and the
thermal resistance from junction-to-air (i.e., T
thermal shutdown. Please see Section 5.0 “Thermal Considerations” for more details.
7: Hysteresis voltage is referenced by V
8: Apply for Junction Temperatures of -40°C to +85°C.
9: The minimum VIN has to justify the conditions = VIN≥ VR+V
Delay — 2.5 — ms Vout falling from VR to
VR-10%
at VIN=6V for T=10 ms.
LMAX
, TJ, θJA). Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation causes the device to initiate
A
.
R
and VIN≥ 2.7V for IL= 0.1 mA to I
DROPOUT
OUTMAX
.
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 3
Page 4
TC1072/TC1073
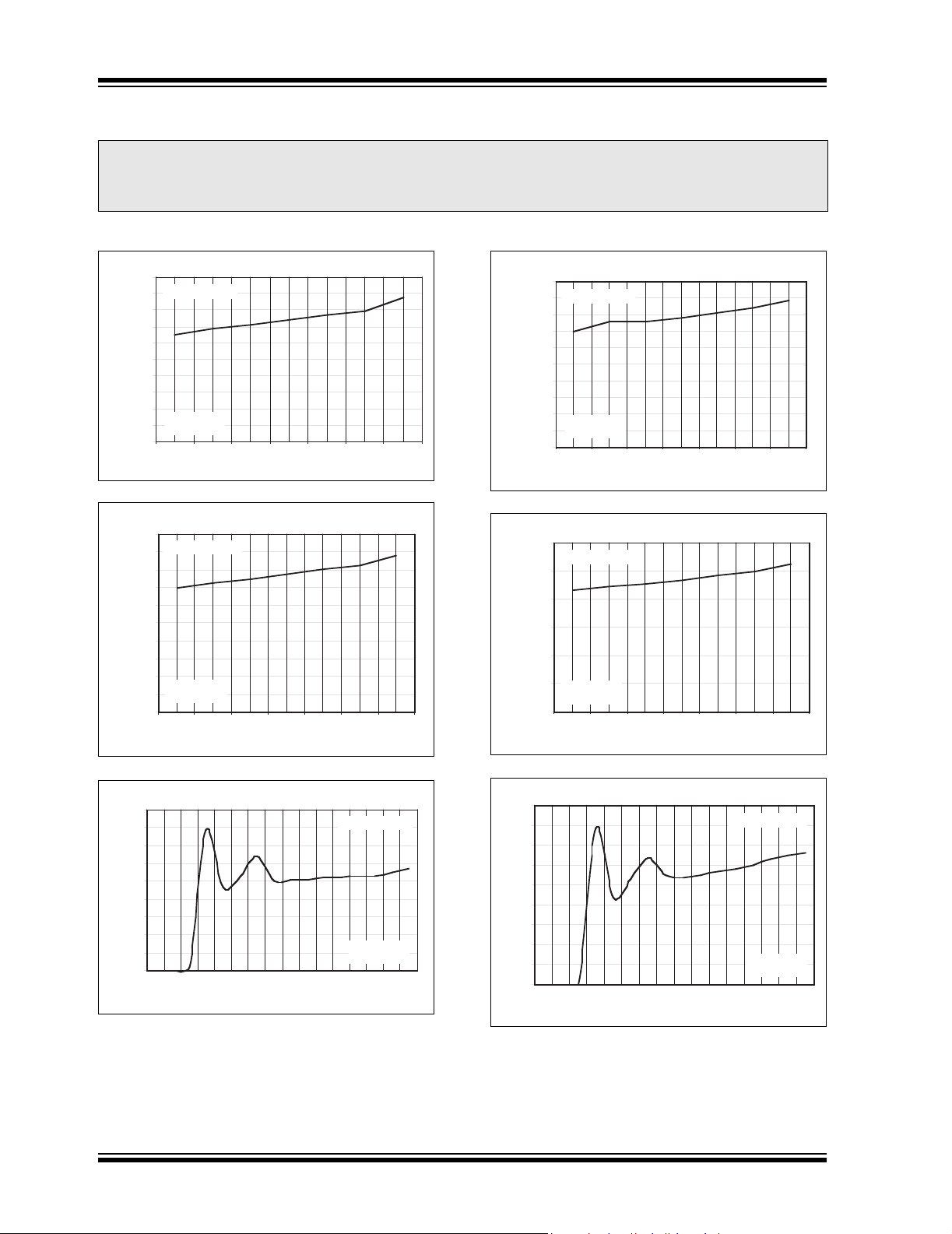
2.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS CURVES
Note: The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
Note: Unless otherwise specified, all parts are measured at temperature = +25°C.
0.020
0.018
0.016
0.014
0.012
0.010
0.008
0.006
0.004
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.002
0.000
0.200
0.180
0.160
0.140
0.120
0.100
0.080
0.060
0.040
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.020
0.000
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature (V
I
= 10mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 125
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature (V
I
= 100mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUT
OUT
= 3.3V)
= 3.3V)
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature (V
0.100
I
0.090
0.080
0.070
0.060
0.050
0.040
0.030
0.020
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.010
0.000
0.300
0.250
0.200
0.150
0.100
0.050
DROPOUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.000
= 50mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 125
Dropout Voltage vs. Temperature (V
I
= 150mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 0 20 50 70 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUT
OUT
= 3.3V)
= 3.3V)
(V
90
80
70
A)
µ
60
50
40
30
GND CURRENT (
20
10
0
Ground Current vs. VIN (V
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
V
(V)
IN
OUT
= 3.3V)
I
LOAD
C
C
= 10mA
= 1µF
IN
OUT
= 1µF
90
80
70
A)
µ
60
50
40
30
GND CURRENT (
20
10
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
Ground Current vs. V
V
(V)
IN
= 3.3V)
IN
OUT
I
= 100mA
LOAD
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
DS21354D-page 4 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5
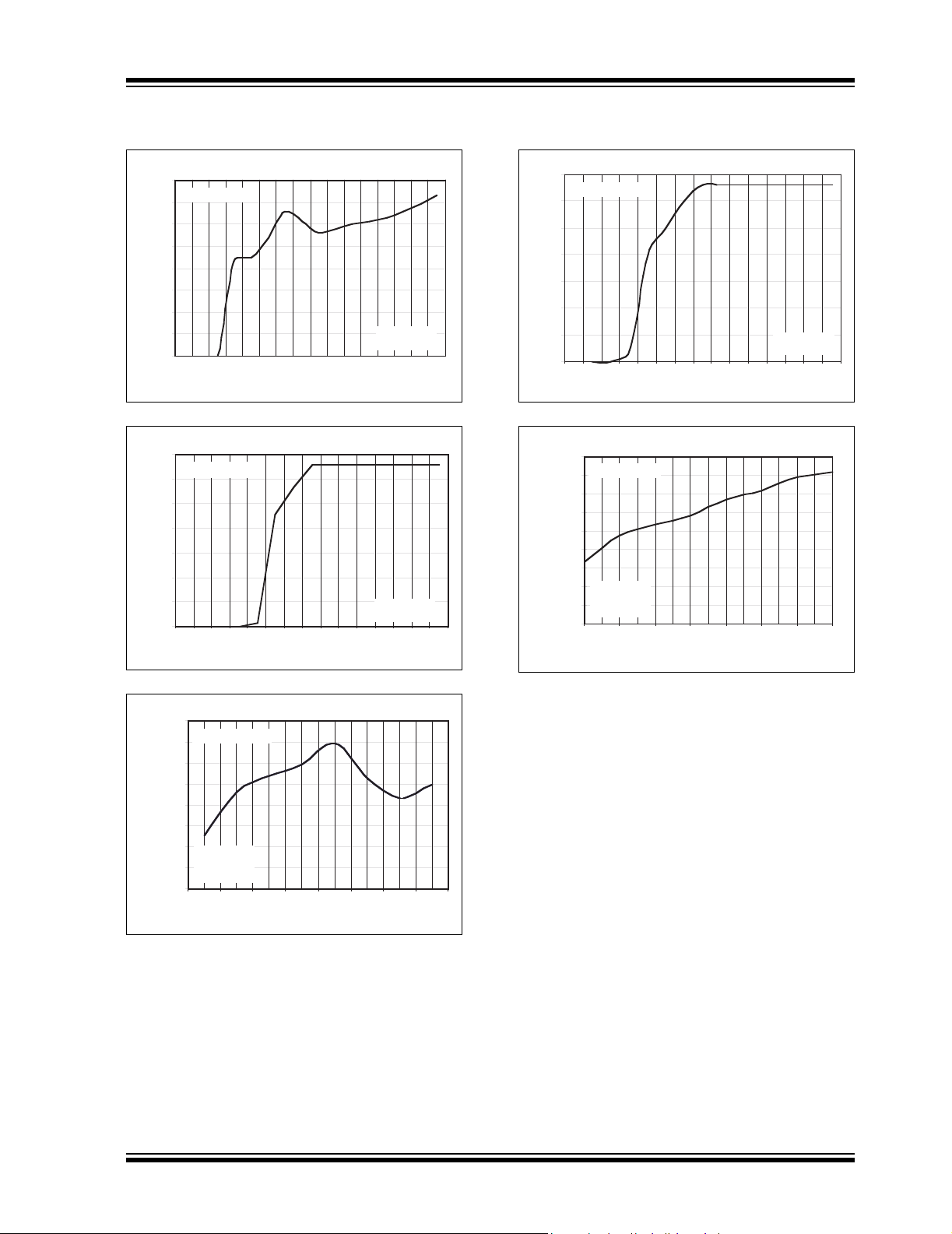
TC1072/TC1073
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
I
LOAD
= 100mA
C
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
= 1µF
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7
VIN (V)
V
OUT
(V)
V
OUT
vs.
V
IN
(V
OUT
= 3.3V)
3.274
3.276
3.278
3.280
3.282
3.284
3.286
3.288
3.290
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
I
LOAD
= 150mA
C
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
= 1µF
VIN = 4.3V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
V
OUT
(V)
Output Voltage vs. Temperature (V
OUT
= 3.3V)
Note: Unless otherwise specified, all parts are measured at temperature = +25°C.
80
70
Ground Current vs. VIN (V
I
= 150mA
LOAD
60
50
40
30
20
GND CURRENT (µA)
10
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7 7.5
VIN (V)
OUT
= 3.3V)
C
C
= 1µF
IN
OUT
= 1µF
3.5
I
= 0
LOAD
3
2.5
2
(V)
OUT
1.5
V
1
0.5
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7
V
vs.
V
(V
OUT
= 3.3V)
IN
OUT
C
= 1µF
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
V
(V)
IN
3.320
3.315
Output Voltage vs. Temperature (V
I
= 10mA
LOAD
3.310
3.305
3.300
(V)
3.295
OUT
V
3.290
3.285
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
3.280
OUT
VIN = 4.3V
3.275
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 1 25
TEMPERATURE (°C)
OUT
= 3.3V)
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 5
Page 6
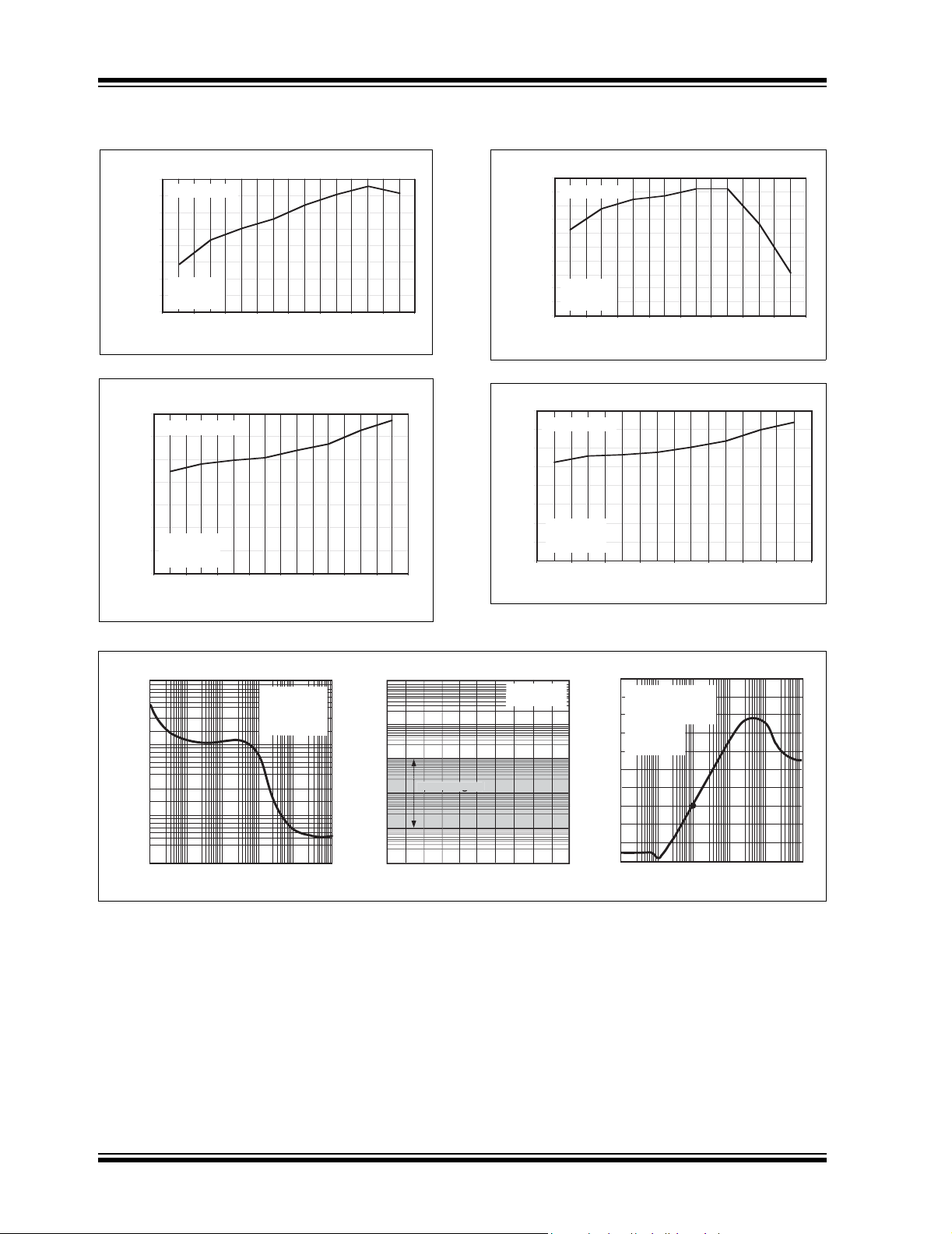
TC1072/TC1073
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
GND CURRENT (
µ
A)
I
LOAD
= 10mA
V
IN
= 6V
C
IN
= 1µF
C
OUT
= 1µF
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Temperature
vs. Quiescent Current
(V
OUT
= 5V)
Stable Region
S
n
K
Note: Unless otherwise specified, all parts are measured at temperature = +25°C.
(V
OUT
= 5V)
(V)
OUT
V
4.994
4.992
4.990
4.988
4.986
4.984
4.982
4.980
4.978
4.976
4.974
Output Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 150mA
LOAD
V
= 6V
IN
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 -10 0 2 0 40 85 125
(V)
OUT
V
5.025
5.020
5.015
5.010
5.005
5.000
4.995
4.990
4.985
Output Voltage vs. Temperature
I
= 10mA
LOAD
V
= 6V
IN
C
= 1µF
IN
C
= 1µF
OUT
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
(V
= 5V)
OUT
NOISE (µV/√Hz)
10.0
Output Noise vs. Frequency
1.0
0.1
0.0
0.01K
0.1K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
R
LOAD
= 1µF
C
OUT
CIN = 1µF
C
= 0
BYP
1K 10K 100K
= 50Ω
1000K
Stability Region vs. Load Current
1000
100
(Ω)
10
ESR
OUT
C
1
table Regio
0.1
0.01
10
203040
0
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Temperature vs. Quiescent Current (V
80
I
LOAD
70
60
50
40
30
20
V
IN
GND CURRENT (µA)
C
IN
10
C
OUT
0
-40 -20 -10 0 20 40 85 125
C
= 1µF
OUT
to 10µF
50 60 70 80 90 100
= 150mA
= 6V
= 1
µ
= 1µF
F
TEMPERATURE (°C)
-30
I
-35
V
V
-40
V
-45
C
C
-50
-55
-60
PSRR (dB)
-65
-70
-75
-80
0.01K
OUT
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
10mA
OUT =
= 4V
IN
DC
= 100mV
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
AC
= 0
0.1K
=
=
3V
1µF
p-p
1K 10K
FREQUENCY (Hz)
= 5V)
100K
1000
DS21354D-page 6 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7
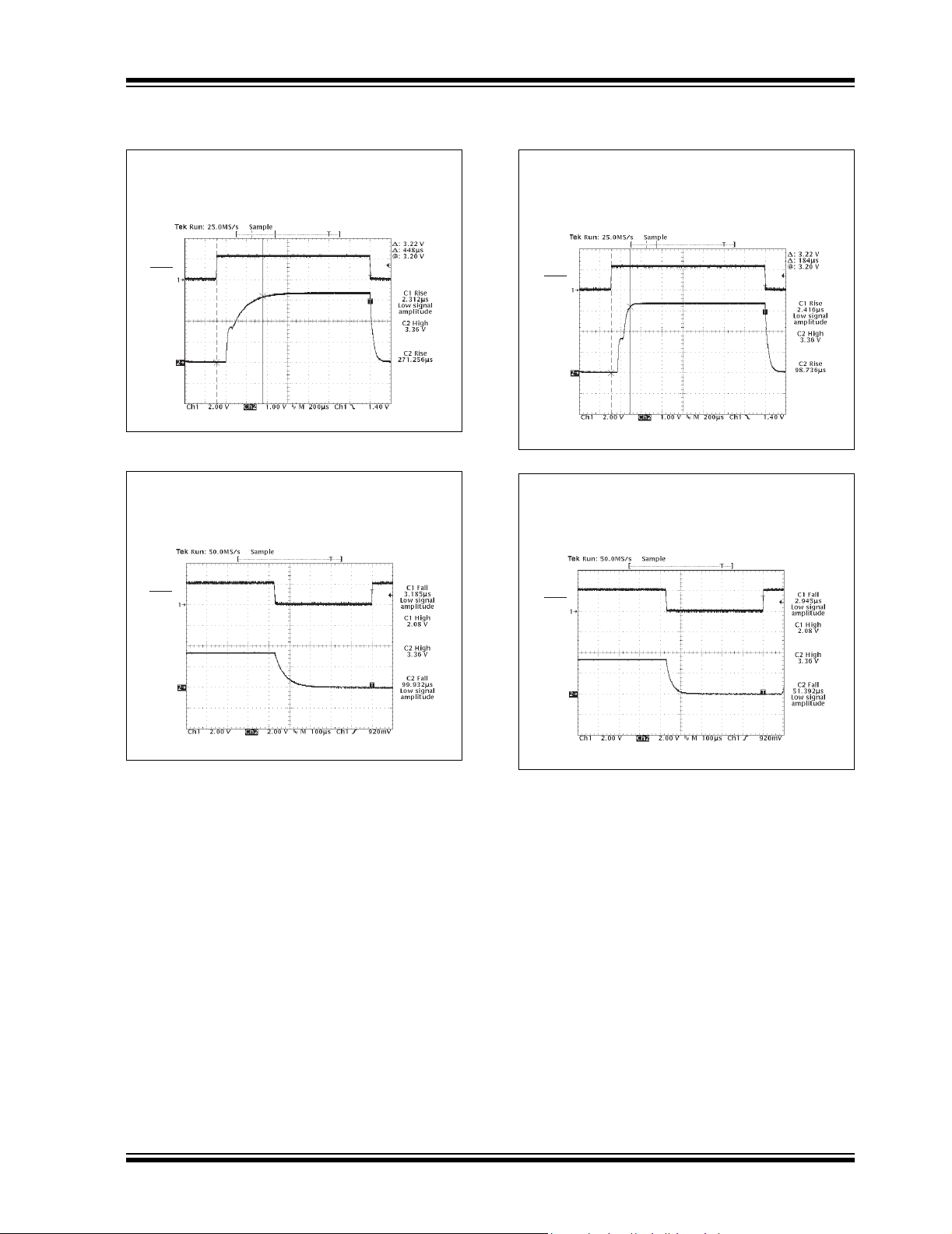
TC1072/TC1073
V
OUT
Measure Rise Time of 3.3V LDO with Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
OUT
= 1µF, C
BYP
= 470pF, I
LOAD
= 100mA
VIN = 4.3V, Temp = 25°C, Rise Time = 448µS
V
SHDN
Measure Fall Time of 3.3V LDO with Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
OUT
= 1µF, C
BYP
= 470pF, I
LOAD
= 50mA
VIN = 4.3V, Temp = 25°C, Fall Time = 100µS
V
OUT
V
SHDN
Note: Unless otherwise specified, all parts are measured at temperature = +25°C.
Measure Rise Time of 3.3V LDO without Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
VIN = 4.3V, Temp = 25°C, Rise Time = 184µS
V
SHDN
V
OUT
Measure Fall Time of 3.3V LDO without Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
VIN = 4.3V, Temp = 25°C, Fall Time = 52µS
OUT
OUT
= 1µF, C
= 1µF, C
BYP
BYP
= 0pF, I
= 0pF, I
LOAD
LOAD
= 100mA
= 100mA
V
SHDN
V
OUT
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 7
Page 8

TC1072/TC1073
Measure Rise Time of 5.0V LDO with Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
OUT
= 1µF, C
BYP
= 470pF, I
LOAD
= 100mA
VIN = 6V, Temp = 25°C, Rise Time = 390µS
V
OUT
V
SHDN
Note: Unless otherwise specified, all parts are measured at temperature = +25°C.
Measure Rise Time of 5.0V LDO without Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
V
SHDN
V
OUT
V
= 6V, Temp = 25°C, Rise Time = 192µS
IN
OUT
= 1µF, C
BYP
= 0pF, I
LOAD
= 100mA
Measure Fall Time of 5.0V LDO with Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
V
SHDN
V
OUT
= 6V, Temp = 25°C, Fall Time = 167µS
V
IN
OUT
= 1µF, C
BYP
= 470pF, I
LOAD
= 50mA
Measure Fall Time of 5.0V LDO without Bypass Capacitor
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
V
SHDN
V
OUT
= 6V, Temp = 25°C, Fall Time = 88µS
V
IN
OUT
= 1µF, C
BYP
= 0pF, I
LOAD
= 100mA
DS21354D-page 8 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

TC1072/TC1073
I
LOAD
V
OUT
Load Regulation of 3.3V LDO
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
OUT
= 2.2µF, C
BYP
= 470pF,
VIN = V
OUT
+ 0.25V, Temp = 25°C
I
LOAD
= 50mA switched in at 10kHz, V
OUT
is AC coupled
Load Regulation of 3.3V LDO
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
OUT
= 2.2µF, C
BYP
= 470pF,
V
IN
= V
OUT
+ 0.25V, Temp = 25°C
I
LOAD
= 150mA switched in at 10kHz, V
OUT
is AC coupled
I
LOAD
V
OUT
Note: Unless otherwise specified, all parts are measured at temperature = +25°C.
Load Regulation of 3.3V LDO
Conditions: CIN = 1µF, C
VIN = V
I
= 100mA switched in at 10kHz, V
LOAD
I
LOAD
V
OUT
Conditions: VIN = 4V, + 1V Squarewave @ 2.5kHz
= 2.2µF, C
OUT
+ 0.25V, Temp = 25°C
OUT
is AC coupled
OUT
Line Regulation of 3.3V LDO
BYP
= 470pF,
V
IN
V
OUT
CIN = 0µF, C
I
LOAD
= 1µF, C
OUT
= 100mA, VIN & V
= 470pF,
BYP
are AC coupled
OUT
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 9
Page 10

TC1072/TC1073
Note: Unless otherwise specified, all parts are measured at temperature = +25°C.
Line Regulation of 5.0V LDO
Conditions: VIN = 6V, + 1V Squarewave @ 2.5kHz
V
IN
V
OUT
CIN = 0µF, C
I
LOAD
= 1µF, C
OUT
= 100mA, VIN & V
= 470pF,
BYP
are AC coupled
OUT
Thermal Shutdown Response of 5.0V LDO
Conditions: VIN = 6V, CIN = 0µF, C
V
OUT
I
was increased until temperature of die reached about 160°C, at
LOAD
which time integrated thermal protection circuitry shuts the regulator
off when die temperature exceeds approximately 160°C. The regulator
remains off until die temperature drops to approximately 150°C.
OUT
= 1µF
DS21354D-page 10 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11

3.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
TC1072/TC1073
The descriptions of the pins are listed in
Table 3-1.
TABLE 3-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Pin No.
(6-Pin SOT-23)
1V
2 GND Ground terminal.
3 SHDN
4ERROROut-of-Regulation Flag. (Open drain output).
5 Bypass Reference bypass input.
6V
Symbol Description
IN
OUT
Unregulated supply input.
Shutdown control input.
Regulated voltage output.
3.1 Input Voltage Supply (VIN)
Connect unregulated input supply to the VIN pin. If
there is a large distance between the input supply and
the LDO regulator, some input capacitance is
necessary for proper operation. A 1 µF capacitor
connected from V
most applications.
to ground is recommended for
IN
3.2 Ground (GND)
Connect the unregulated input supply ground return to
GND. Also connect the negative side of the 1 µF typical
input decoupling capacitor close to GND and the
negative side of the output capacitor C
OUT
to GND.
3.4 Out-Of-Regulation Flag (ERROR
ERROR goes low when V
approximately – 5%.
is out-of-tolerance by
OUT
)
3.5 Reference Bypass Input (Bypass)
Connecting a 470 pF to this input further reduces
output noise.
3.6 Regulated Voltage Output (V
Connect the output load to V
connect the positive side of the LDO output capacitor
as close as possible to the V
of the LDO. Also
OUT
pin.
OUT
OUT
)
3.3 Shutdown Control Input (SHDN
The regulator is fully enabled when a logic-high is
applied to SHDN
a logic-low is applied to SHDN
output voltage falls to zero, ERROR
and supply current is reduced to 0.5 µA (maximum).
. The regulator enters shutdown when
. During shutdown,
is open-circuited
)
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 11
Page 12

TC1072/TC1073
V
TH
V
OUT
ERROR
V
IH
V
OL
HYSTERESIS (VH)
t
DELAY
4.0 DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The TC1072 and TC1073 are precision fixed output
voltage regulators. (If an adjustable version is desired,
please see the TC1070/TC1071/TC1187 data sheet.)
Unlike bipolar regulators, the TC1072 and TC1073’s
supply current does not increase with load current. In
addition, V
over the entire 0 mA to I
important consideration in RTC and CMOS RAM
battery back-up applications).
Figure 4-1 shows a typical application circuit. The
regulator is enabled any time the shutdown input
) is at or above VIH, and shutdown (disabled)
(SHDN
when SHDN
controlled by a CMOS logic gate, or I/O port of a
microcontroller. If the SHDN
should be connected directly to the input supply. While
in shutdown, supply current decreases to 0.05 µA
(typical), V
circuited.
Shutdown Control
(to CMOS Logic or Tie
to VIN if unused)
remains stable and within regulation
OUT
OUTMAX
load current range, (an
is at or below VIL. SHDN may be
input is not required, it
+
1 µF
C1
C3, 470 pF
R1
1M
0.2 µF
C2
is open-
V
OUT
BATTLOW
or RESET
falls to zero volts, and ERROR
OUT
+
Battery
V
IN
+
1 µF
GND
SHDN
C2 Required Only
if ERROR is used as a
Processor RESET Signal
TC1072
TC1073
(See Text)
V
OUT
Bypass
ERROR
V+
FIGURE 4-2: Error
Output Operation.
4.2 Output Capacitor
A 1 µF (minimum) capacitor from V
recommended. The output capacitor should have an
effective series resistance greater than 0.1Ω and less
than 5.0Ω, and a resonant frequency above 1 MHz. A
1 µF capacitor should be connected from V
there is more than 10 inches of wire between the
regulator and the AC filter capacitor, or if a battery is
used as the power source. Aluminum electrolytic or
tantalum capacitor types can be used. (Since many
aluminum electrolytic capacitors freeze at
approximately -30°C, solid tantalums are
recommended for applications operating below -25°C.)
When operating from sources other than batteries,
supply-noise rejection and transient response can be
improved by increasing the value of the input and
output capacitors and employing passive filtering
techniques.
to ground is
OUT
IN
to GND if
4.3 Bypass Input
FIGURE 4-1: Typical Application Circuit.
A 470 pF capacitor connected from the Bypass input to
ground reduces noise present on the internal
4.1 ERROR
Open-Drain Output
reference, which in turn significantly reduces output
noise. If output noise is not a concern, this input may be
ERROR
regulation by more than –5% (typical). This condition
may be caused by low input voltage, output current
limiting, or thermal limiting. The ERROR
value (e.g. ERROR
is driven low whenever V
=VOL at 4.75V (typical) for a 5.0V
falls out of
OUT
output voltage
left unconnected. Larger capacitor values may be
used, but results in a longer time period to rated output
voltage when power is initially applied.
regulator and 2.85V (typical) for a 3.0V regulator).
ERROR
output operation is shown in Figure 4-2.
Note that ERROR is active tDELAY (typically, 2.5 µs)
after V
above VTH by V
As shown in
battery low flag, or as a processor RESET
falls to VTH, and inactive when V
OUT
HYS
.
Figure 4-1, ERROR can be used as a
rises
OUT
signal (with
the addition of timing capacitor C2). R1 x C2 should be
chosen to maintain ERROR
RESET
input for at least 200 ms to allow time for the
below VIH of the processor
system to stabilize. Pull-up resistor R1 can be tied to
V
, VIN or any other voltage less than (VIN + 0.3V).
OUT
DS21354D-page 12 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13

TC1072/TC1073
Where:
PD
≈
(V
INMAX
– V
OUTMIN)ILOADMAX
P
D
V
INMAX
V
OUTMIN
I
LOADMAX
= Worst-case actual power dissipation
= Minimum regulator output voltage
= Maximum output (load) current
= Maximum voltage on V
IN
P
DMAX
= (T
JMAX
– T
AMAX
)
θ
JA
where all terms are previously defined.
P
DMAX
= (T
JMAX
– T
AMAX
)
θ
JA
= (125 – 55)
220
= 318 mW
5.0 THERMAL CONSIDERATIONS
5.1 Thermal Shutdown
Integrated thermal protection circuitry shuts the
regulator off when die temperature exceeds 160°C.
The regulator remains off until the die temperature
drops to approximately 150°C.
5.2 Power Dissipation
The amount of power the regulator dissipates is
primarily a function of input and output voltage, and
output current. The following equation is used to
calculate worst-case actual power dissipation:
EQUATION 5-1:
The maximum allowable power dissipation
Equation 5-2) is a function of the maximum ambient
(
temperature (T
perature (T
JMAX
tion-to-air (θ
of approximately 220°C/Watt.
), the maximum allowable die tem-
AMAX
) and the thermal resistance from junc-
). The 6-Pin SOT-23 package has a θ
JA
JA
Equation 5-1 can be used in conjunction with
Equation 5-2 to ensure regulator thermal operation is
within limits. For example:
Given:
= 3.0V ±5%
V
INMAX
V
OUTMIN
I
LOADMAX
T
JMAX
T
AMAX
= 2.7V – 2.5%
= 40 mA
= 125°C
= 55°C
Find: 1. Actual power dissipation
2. Maximum allowable dissipation
Actual power dissipation:
P
≈
(V
D
= [(3.0 x 1.05) – (2.7 x 0.975)] x 40 x 10
INMAX
– V
OUTMIN)ILOADMAX
–3
= 20.7 mW
Maximum allowable power dissipation:
In this example, the TC1072 dissipates a maximum of
20.7 mW; below the allowable limit of 318 mW. In a
similar manner,
Equation 5-1 and Equation 5-2 can be
used to calculate maximum current and/or input
voltage limits.
EQUATION 5-2:
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 13
5.3 Layout Considerations
The primary path of heat conduction out of the package
is via the package leads. Therefore, layouts having a
ground plane, wide traces at the pads, and wide power
supply bus lines combine to lower θ
increase the maximum allowable power dissipation
limit.
and therefore
JA
Page 14

TC1072/TC1073
1
& = part number code + threshold voltage
2
(two-digit code)
3
represents year and quarter code
4
represents production lot ID code
W, Width of
Carrier Tape
User Direction of Feed
P,Pitch
Standard Reel Component
Orientation
Reverse Reel Component
Orientation
PIN 1
Device
Marking
PIN 1
Carrier Tape, Number of Components per Reel and Reel Size
Package Carrier Width (W) Pitch (P) Part Per Full Reel Reel Size
6-Pin SOT-23 8 mm 4 mm 3000 7 in
6.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
6.1 Package Marking Information
6.2 Taping Form
(V)
1.8 EY FY
2.5 E1 F1
2.6 ET FT
2.7 E2 F2
2.8 EZ FZ
2.85 E8 F8
3.0 E3 F3
3.3 E4 F4
3.6 E9 F9
4.0 E0 F0
5.0 E6 F6
TC1072
Code
TC1073
Code
DS21354D-page 14 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

TC1072/TC1073
6-Lead Plastic Small Outline Transistor (CH) [SOT-23]
Notes:
1. Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed 0.127 mm per side.
2. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ASME Y14.5M.
BSC: Basic Dimension. Theoretically exact value shown without tolerances.
Note: For the most current package drawings, please see the Microchip Packaging Specification located at
http://www.microchip.com/packaging
Units MILLIMETERS
Dimension Limits MIN NOM MAX
Number of Pins N 6
Pitch e 0.95 BSC
Outside Lead Pitch e1 1.90 BSC
Overall Height A 0.90 – 1.45
Molded Package Thickness A2 0.89 – 1.30
Standoff A1 0.00 – 0.15
Overall Width E 2.20 – 3.20
Molded Package Width E1 1.30 – 1.80
Overall Length D 2.70 – 3.10
Foot Length L 0.10 – 0.60
Footprint L1 0.35 – 0.80
Foot Angle φ 0° – 30°
Lead Thickness c 0.08 – 0.26
Lead Width b 0.20 – 0.51
b
E
4
N
E1
PIN 1 ID BY
LASER MARK
D
1
2
3
e
e1
A
A1
A2
c
L
L1
φ
Microchip Technology Drawing C04-028B
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 15
Page 16

TC1072/TC1073
NOTES:
DS21354D-page 16 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

APPENDIX A: REVISION HISTORY
Revision D (February 2007)
• Page 1: Ground current changed to 50 µA.
• Package type changed from SOT-23A to SOT-23.
• Added voltage options.
•T
• Section 3.0 “Pin Descriptions”: Added pin
• Section 4.1 “ERROR Open-Drain Output”:
• Changed Figure 4-2.
• Updated Packaging Information.
Revision C (January 2006)
• Undocumented changes.
Revision B (May 2002)
• Undocumented changes.
added to Table 1-1.
DELAY
descriptions.
Defined t
DELAY
.
TC1072/TC1073
Revision A (March 2002)
• Original Release of this Document.
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 17
Page 18

TC1072/TC1073
NOTES:
DS21354D-page 18 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

TC1072/TC1073
PART NO. — X XXXXX
Threshold PackageTemperature
Range
Device
Device TC1072: CMOS LDO with Shutdown, ERROR Output & V
REF
Bypass
TC1073: CMOS LDO with Shutdown, ERROR
Output & V
REF
Bypass
Threshold voltage
(typical)
1.8 = 1.8V
2.5 = 2.5V
2.6 = 2.6V
2.7 = 2.7V
2.8 = 2.8V
2.85 = 2.85V
3.0 = 3.0V
3.3 = 3.3V
3.6 = 3.6V
4.0 = 4.0V
5.0 = 5.0V
Temperature Range V = -40° C to +125° C
Package CH713 = Plastic small outline transistor (CH) SOT-23,
6 lead, (tape and reel).
Examples:
a) TC1072-1.8VCH713: 1.8V
b) TC1072-2.5VCH713 2.5V
c) TC1072-2.6VCH713 2.6V
d) TC1072-2.7VCH713 2.7V
e) TC1072-2.8VCH713 2.8V
f) TC1072-2.85VCH713 2.85V
g) TC1072-3.0VCH713 3.0V
h) TC1072-3.3VCH713 3.3V
i) TC1072-3.6VCH713 3.6V
j) TC1072-4.0VCH713 4.0V
k) TC1072-5.0VCH713 5.0V
a) TC1073-1.8VCH713: 1.8V
b) TC1073-2.5VCH713 2.5V
c) TC1073-2.6VCH713 2.6V
d) TC1073-2.7VCH713 2.7V
e) TC1073-2.8VCH713 2.8V
f) TC1073-2.85VCH713 2.85V
g) TC1073-3.0VCH713 3.0V
h) TC1073-3.3VCH713 3.3V
i) TC1073-3.6VCH713 3.6V
j) TC1073-4.0VCH713 4.0V
k) TC1073-5.0VCH713 5.0V
X.X
Vol tag e
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM
To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office.
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 19
Page 20

TC1072/TC1073
NOTES:
DS21354D-page 20 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is provided only for your convenience
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR
OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION,
QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability
arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at
the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend, indemnify and
hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims,
suits, or expenses resulting from such use. No licenses are
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip
intellectual property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Accuron,
dsPIC, KEELOQ, KEELOQ logo, microID, MPLAB, PIC,
PICmicro, PICSTART, PRO MATE, PowerSmart, rfPIC, and
SmartShunt are registered trademarks of Microchip
Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
AmpLab, FilterLab, Linear Active Thermistor, Migratable
Memory, MXDEV, MXLAB, PS logo, SEEVAL, SmartSensor
and The Embedded Control Solutions Company are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, CodeGuard,
dsPICDEM, dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, ECAN,
ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB,
In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, Mindi, MiWi,
MPASM, MPLAB Certified logo, MPLIB, MPLINK, PICkit,
PICDEM, PICDEM.net, PICLAB, PICtail, PowerCal,
PowerInfo, PowerMate, PowerTool, REAL ICE, rfLAB,
rfPICDEM, Select Mode, Smart Serial, SmartTel, Total
Endurance, UNI/O, WiperLock and ZENA are trademarks of
Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other
countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2007, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2002 certification for its worldwide
headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in Chandler and
Tempe, Arizona, Gresham, Oregon and Mountain View, California. The
Company’s quality system processes and procedures are for its PIC
MCUs and dsPIC® DSCs, KEELOQ
EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and analog
products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design and
manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
®
code hopping devices, Serial
© 2007 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21354D-page 21
®
Page 22

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
http://support.microchip.com
Web Address:
www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Duluth, GA
Tel: 678-957-9614
Fax: 678-957-1455
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Farmington Hills, MI
Tel: 248-538-2250
Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
Kokomo, IN
Tel: 765-864-8360
Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
Santa Clara
Santa Clara, CA
Tel: 408-961-6444
Fax: 408-961-6445
Toronto
Mississauga, Ontario,
Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699
Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Asia Pacific Office
Suites 3707-14, 37th Floor
Tower 6, The Gateway
Habour City, Kowloon
Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8528-2100
Fax: 86-10-8528-2104
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8665-5511
Fax: 86-28-8665-7889
China - Fuzhou
Tel: 86-591-8750-3506
Fax: 86-591-8750-3521
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2401-1200
Fax: 852-2401-3431
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-8502-7355
Fax: 86-532-8502-7205
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-5407-5533
Fax: 86-21-5407-5066
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
Fax: 86-24-2334-2393
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8203-2660
Fax: 86-755-8203-1760
China - Shunde
Tel: 86-757-2839-5507
Fax: 86-757-2839-5571
China - Wuhan
Tel: 86-27-5980-5300
Fax: 86-27-5980-5118
China - Xian
Tel: 86-29-8833-7250
Fax: 86-29-8833-7256
ASIA/PACIFIC
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-4182-8400
Fax: 91-80-4182-8422
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-4160-8631
Fax: 91-11-4160-8632
India - Pune
Tel: 91-20-2566-1512
Fax: 91-20-2566-1513
Japan - Yokohama
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166
Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea - Gumi
Tel: 82-54-473-4301
Fax: 82-54-473-4302
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or
82-2-558-5934
Malaysia - Penang
Tel: 60-4-646-8870
Fax: 60-4-646-5086
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 63-2-634-9065
Fax: 63-2-634-9069
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan - Hsin Chu
Tel: 886-3-572-9526
Fax: 886-3-572-6459
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-536-4818
Fax: 886-7-536-4803
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2500-6610
Fax: 886-2-2508-0102
Thailand - Bangkok
Tel: 66-2-694-1351
Fax: 66-2-694-1350
EUROPE
Austria - Wels
Tel: 43-7242-2244-39
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Copenhagen
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
France - Paris
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Munich
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
Spain - Madrid
Tel: 34-91-708-08-90
Fax: 34-91-708-08-91
UK - Wokingham
Tel: 44-118-921-5869
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
12/08/06
DS21354D-page 22 © 2007 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

 Loading...
Loading...