查询TC1037供应商查询TC1037供应商
Linear Building Block – Single Comparator in SOT Packages
TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
Features
• TinySOT-23A Packages
• Optimized for Single Supply Operation
• Ultra Low Input Bias Current: Less than 100pA
• Low Quiescent Current: 4µA (TC1037),
Shutdown Mode: 4µA, 0.05µA (TC1038),
6µA (TC1039)
• Shutdown Mode (TC1038)
• 2.0% Accurate IndependentVoltage Reference
(TC1039)
• Rail-to-Rail Inputs and Outputs
• Operation Down to V
DD
=1.8V
Applications
• Power Management Circuits
• Battery Operated Equipment
• Consumer Products
Device Selection Table
Part Number Package
TC1037CECT 5-Pin SOT-23A -40°C to +85°C
TC1038CECH 6-Pin SOT-23A -40°C to +85°C
TC1039CECH 6-Pin SOT-23A -40°C to +85°C
Temperature
Range
General Description
The TC1037/TC1038/TC1039 are single, low-power
comparatorsdesigned for low-power applications.
These comparators are specifically designed for
operation from a single supply. However, operation
from dual supplies also is possible, and power supply
current is independent of the magnitude of the power
supply voltage. The TC1037/TC1038/TC1039 operate
fromtwo1.5ValkalinecellsdowntoV
= 1.8V.Active
DD
supply current is 4µA for the TC1037/TC1038 and 6µA
for the TC1039. Input and output swing of these
devices is rail-to-rail.
An active low shutdown input, SHDN
, is available on
the TC1038 and disables the comparator, placing its
output in a high-impedance state. The TC1038 draws
only 0.05µA (typical) when the shutdown mode is
active.
An internally biased 1.20V bandgap reference i s
included in the TC1039. The reference is accurate to
2.0 percent tolerance. This referenceis independent of
the comparator in the TC1039.
Packaged in a 5-Pin SOT-23A (TC1037) or 6-Pin
SOT-23A (TC1038/TC1039),thesesinglecomparators
are ideal for applications requiring high integration,
small size and low power.
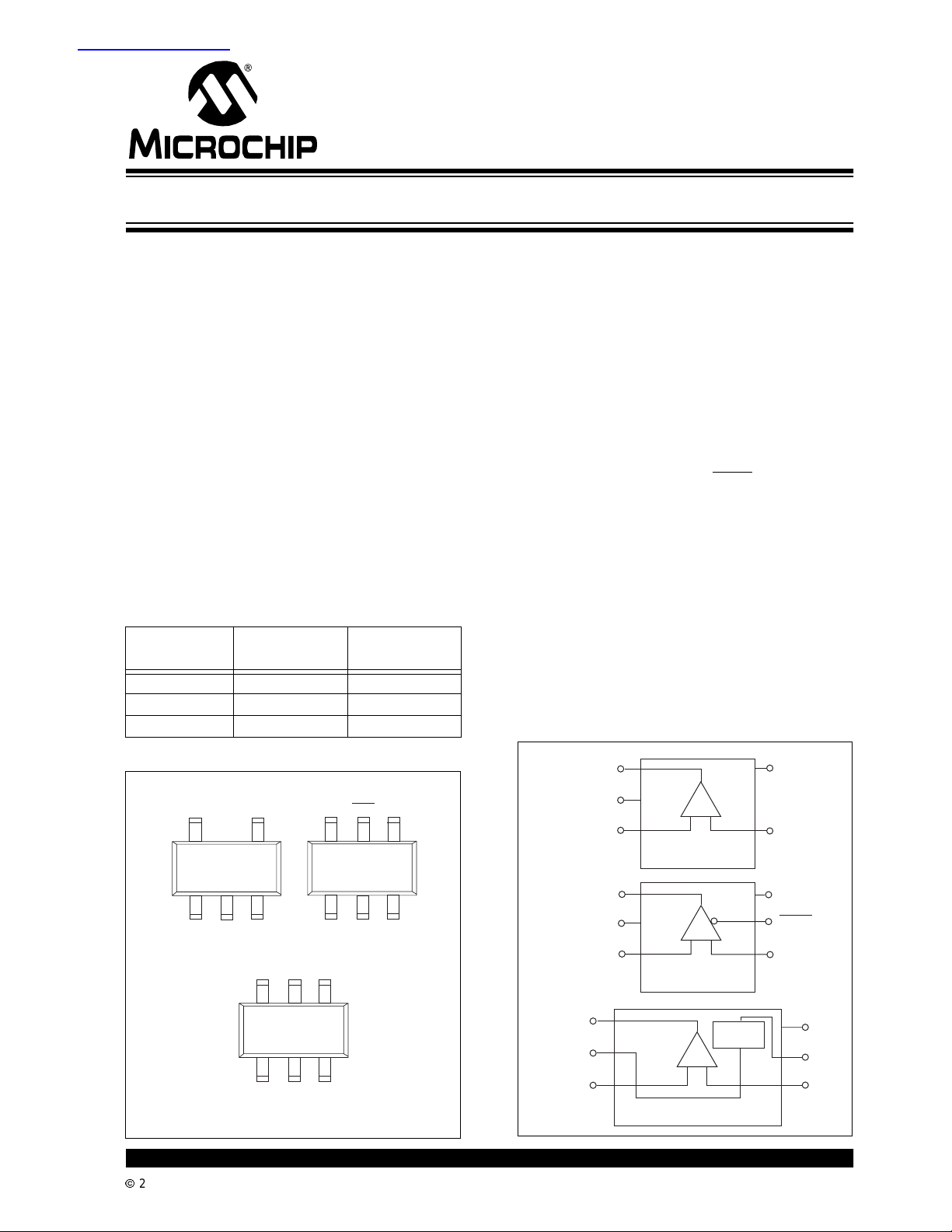
Functional Block Diagram
V
IN+
SS
1
2
3
+
–
5
V
DD
4
IN-
Package Types
5-Pin SOT-23A
V
DD
5
OUTPUT
6-Pin SOT-23A
IN-
4
V
DD
6
IN-SHDN
45
TC1037
TC1037ECT
2
1
OUTPUT
3
V
IN+
SS
6-Pin SOT-23A
V
DD
6
TC1039ECH
1
OUTPUT
NOTE: 5-Pin SOT-23A is equivalent to the EIAJ SC-74A.
6-PinSOT-23A is equivalenttothe EIAJ SC-74.
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 1
V
2
SS
TC1038ECH
1
OUTPUT
IN-REF
45
3
IN+
V
IN+
SS
1
2
3
+
–
2
3
V
IN+
SS
OUTPUT
6
5
4
V
DD
SHDN
IN-
TC1038
OUTPUT
V
SS
IN+
1
Voltage
2
3
+
Reference
–
6
V
5
REF
4
IN-
TC1039
DD

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
1.0 ELECTRICAL
CHARACTERISTICS
*Stresses above those listed under "Absolute Maximum
Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These
are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device
at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Supply Voltage......................................................6.0V
Voltage on Any Pin..........(V
– 0.3V) to (VDD+0.3V)
SS
operation sections of the specifications is not implied.
Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for
extended periods may affectdevice reliability.
Junction Temperature.......................................+150°C
Operating Temperature Range.............-40°C to +85°C
StorageTemperature Range..............-55°C to +150°C
TC1037/TC1038/TC10 39 E LECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: Typical values apply at 25°C and VDD= 3.0V. Minimum and maximum values apply for TA= -40° to
+85°C and V
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
V
DD
I
Q
I
SHDN
Shutdown Input (TC1038 Only)
V
IH
V
IL
I
SI
Comparator
(SD) Output ResistanceinShutdown 20 — — MΩ SHDN =VSS(TC1038 Only)
R
OUT
(SD) Output Capacitance in Shutdown — — 5 pF SHDN =VSS(TC1038 Only)
C
OUT
T
SEL
T
DESEL
V
ICMR
A
VOL
GBWP Gain BandwidthProduct — 90 — kHz V
V
OS
I
B
V
OH
V
OL
CMRR Common Mode Rejection Ratio 66 — — dB TA=25°C;VDD=5V;
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio 60 — — dB TA=25°C;VCM=1.2V;
I
SRC
I
SINK
T
PD1
T
PD2
= 1.8V to 5.5V,unless otherwise specified.
DD
SupplyVoltage 1.8 — 5.5 V
Supply Current, Operating (TC1039)
(TC1037/TC1038)
Supply Current Shutdown Mode
(TC1038Only)
Input High Threshold 80% V
Input Low Threshold — — 20% V
—
—
6
4
10
µAµAAll Outputs Unloaded,
8
SHDN
=VDDfor TC1038
——0.3µA SHDN =V
——V
DD
V
DD
SS
Shutdown Input Current — — ±100 nA
Select Time — 20 — µsec V
DeselectTime — 500 — nsec V
Valid from SHDN =V
OUT
RL=10kΩ to VSS(TC1038 Only)
Valid from SHDN =V
OUT
RL=10kΩ to V
SS
Common Mode Input Voltage Range VSS–0.2 — VDD+0.2 V
Large SignalVoltage Gain — 100 — V/mV RL=10kΩ,VDD=5V
= 1.8V to 5.5V;
DD
Input Offset Voltage –5
–5
V
O=VDD
—+5+5mVmVVDD=3V,VCM=1.5V,TA=25°C,
T
A
to V
SS
= -40°C to 85°C
Input Bias Current — — ±100 pA TA=25°C;
IN+, IN- = V
Output High Voltage VDD–0.3 — — V RL=10kΩ to V
Output Low Voltage — — 0.3 V RL=10kΩ to V
V
CM=VDD
V
=1.8Vto5V
DD
Output Source Current 1 — — mA IN+ = VDD,IN-=V
Output Shorted to V
DD
to V
to V
SS
DD
SS
SS
SS
SS
VDD=1.8V
Output Sink Current 2 — — mA IN+ = VSS,IN-=V
Output Shorted to V
VDD=1.8V
SS
SS
Response Time — 4 — µsec 100mVOverdrive, CL= 100pF
Response Time — 6 — µsec 10mV Overdrive, CL= 100pF
IH
IL
DS21344B-page 2
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
TC1037/TC1038/TC1039 E LECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Characteristics: Typical values apply at 25°C and VDD= 3.0V. Minimum and maximum values applyfor TA=-40°to
+85°Cand V
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Test Conditions
VoltageReference (TC1039Only)
V
REF
I
REF(SOURCE )
I
REF(SINK)
C
L(REF)
E
VREF
e
VREF
= 1.8V to 5.5V, unless otherwise specified.
DD
Reference Voltage 1.176 1.200 1.224 V
Source Current 50 — — µA
Sink Current 50 — — µA
Load Capacitance — — 100 pF
Noise Voltage — 20 — µV
Noise VoltageDensity — 1.0 — µV/√ Hz 1kHz
RMS
100Hz to 100kHz
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 3

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
2.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
The description of the pins are listed in Table 2-1.
TABLE 2-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Pin No.
TC1037
(5-Pin SOT-23A)
1 OUTPUT Comparator output.
2V
3 IN+ Comparator non-inverting input.
4 IN- Comparator inverting input.
5V
Pin No.
TC1038
(6-Pin SOT-23A)
1 OUTPUT Comparator output.
2V
3 IN+ Comparator non-inverting input.
4 IN- Comparator inverting input.
5 SHDN
6V
Symbol Description
SS
DD
Symbol Description
SS
DD
Negative power supply.
Positive power supply.
Negative power supply.
Active low shutdown input (TC1038 only). A low input on this pin disables the comparator
and placesthe output terminal in a high impedance state.
Positive power supply.
Pin No.
TC1039
(6-Pin SOT-23A)
1 OUTPUT Comparator output.
2V
3 IN+ Comparator non-inverting input.
4 IN- Comparator inverting input.
5 REF 1.20V bandgap voltage reference output (TC1039 only).
6V
Symbol Description
SS
DD
Negative power supply.
Positive power supply.
DS21344B-page 4
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
3.0 DETAILED DESCRIPTION
The TC1037/TC1038/TC1039 are a series of very low
power, linear building block products targeted at low
voltage, single supply applications. The TC1037/
TC1038/TC1039 minimum operating voltage is 1.8V
and typical supply current is only 4µA for the TC1037
and TC1038 (fully enabled) and 6µA for the TC1039.
3.1 Comparator
The TC1037/8/9 contain one comparator. The
comparator’s input range extends beyond both supply
voltagesby 200mV and the outputswill swing to within
several millivoltsof thesupplies depending on the load
current being driven.
The comparator exhibits a propagation delay and
supply current which is largely independent of supply
voltage. The low input bias current and offset voltage
makes it suitable for high impedance precision
applications.
The TC1038 comparator is disabled during shutdown
and has a high impedance output.
3.2 Voltage Reference
A 2.0% tolerance, internally biased, 1.20V bandgap
voltage reference is i ncluded in the TC1039. It has a
push-pull output capable of sourcing and sinking at
least 50µA.
3.3 Shutdown Input (TC1038 Only)
SHDN at VILdisables the comparator and reduces the
supply current to less than 0.3µA. The SHDN
cannotbe allowedto float. When not used, connect it to
V
. The comparator’s output is in a high impedance
DD
state when the TC1038 is disabled. The comparator’s
inputs can be driven from rail-to-rail by an external
voltage when the TC1038 is disabled. No latchup will
occur when the device is driven to its enabled state
when SHDN
is set to VIH.
input
4.0 TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
The TC1037/TC1038/TC1039 family lends itself to a
wide variety of applications, particularly in battery
powered systems. It typicallyfindsapplicationin power
management, processor supervisory and interface
circuitry.
4.1 External Hysteresis (Comparator)
Hysteresis can be set externally with two resistors
using positive f eedback techniques (see Figure 4-1).
The design procedure for setting external comparator
hysteresisis as follows:
1. Choose the feedback resistor R
input bias current of the comparator is at most
100pA, the current through R
100nA (i.e., 1000 times the input bias current)
and retain excellent accuracy. The current
through R
R
where VRis a stable r eference voltage.
C
at the comparator’s trip point is VR/
C
2. Determinethehysteresisvoltage (V
the upper and lower thresholds.
3. Calculate R
as follows:
A
EQUATION 4-1:
V
HY
=
-----------
C
V
DD
RAR
4. Choose the rising threshold voltage for V
(V
).
THR
5. Calculate R
as follows:
B
EQUATION 4-2:
V
THR
1
1
–
-------
R
-----------------------------------------------------------=
R
B
---------------------
VRRA×
6. Verify the threshold voltages with these
formulas:
V
rising:
SRC
.Sincethe
C
canbesetto
C
HY
1
–
------R
A
C
)between
SRC
EQUATION 4-3:
1
1
B
1
-------
R
C
V
V
SRC
THR
falling:
VR()RA()
------R
A
-------
++=
R
EQUATION 4-4:
RAVDD×
V
THFVTHR
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 5
--------- ------------- ---
–=
R
C

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
4.2 Precision Battery Monitor
Figure 4-2 is a precision battery low/battery dead
monitoring circuit. Typically, the battery low output
warns the user that a battery dead condition is
imminent. Battery dead typically initiates a forced
shutdown to prevent operation at low internal supply
voltages(which can cause unstablesystemoperation).
The circuit in Figure 4-2 uses a TC1034, a TC1037 and
a TC1039, and only six external resistors. AMP 1 is a
simple buffer, while CMPTR1 and CMPTR2 provide
precision voltage detection using V
Resistors R2 and R4 set the detection threshold for
BATT LOW,
thresholdforBATT FAIL
assert BATT LOW
2.0V (typical). Total current consumed by this circuit i s
typically 16µA at 3V. Resistors R5 and R6 provide
hysteresis for comparators CMPTR1 and CMPTR2,
respectively.
whileresistorsR1and R3 set the detection
.The componentvaluesshown
at 2.2V (typical) and BATT FAIL at
as a reference.
R
4.3 32.768 kHz “Time Of Day Clock”
Crystal Controlled Oscillator
A very stable oscillator driver can be designedby using
a crystalresonatorasthefeedbackelement. Figure 4-3
shows a typical application circuit using this technique
to develop a clockdriverfora Time Of Day (TOD)clock
chip.The value of R
level at which the comparator trips – in this case onehalf of V
be set several times greaterthanthe crystaloscillator’s
period,whichwill ensure a 50% duty cycle by maintaining a DC voltage at the inverting comparator input
equal to the absolute average of the output signal.
. The RC time constant of RCand CAshould
DD
and RBdetermine the DC voltage
A
4.4 Non-Retriggerable One Shot
Multivibrator
Using two comparators, a non-retriggerable one shot
multivibratorcan be designed using t he circuit configuration of Figure 4-4. A key feature of this design is that
the pulse width is independent of the magnitude of the
supply voltage because the charging voltage and the
intercept voltage are a fixed percentage of V
addition,this one shot is capable of pulse width with as
much as a 99% duty cycle and exhibits input lockoutto
ensure that the circuit will not re-trigger before the
outputpulsehascompletelytimedout.The triggerlevel
is the voltage required at the input to raise the voltage
at node A higher than the voltage at node B, and is set
by the resistivedividerR4 and R10 and the impedance
network composed of R1, R2 and R3. When the one
shot has been triggered, the output of CMPTR2is high,
causingthereferencevoltageatthenon-invertinginput
of CMPTR1 to go to V
input pulses from disturbing the circuit until the output
pulse has timed out.
. This prevents any additional
DD
DD
.In
ThevalueofthetimingcapacitorC1mustbesmall
enough to allow CMPTR1 to discharge C1 to a diode
voltage before the feedback signal from CMPTR2
(through R10) switches CMPTR1 to its high state and
allows C1 to start an exponential charge t hrough R5.
Proper circuit action depends upon rapidly discharging
C1 through the voltage set by R6, R9 and D2 to a final
voltage of a small diode drop. Two propagation delays
after the voltage on C1 drops below the level on the
non-invertinginput of CMPTR2,the output of CMPTR1
switches to the positive rail and begins to charge C1
throughR5. The timedelay which sets the outputpulse
width results from C1 charging to the reference voltage
set by R6, R9 and D2, plus four comparator propagation delays. When the voltage across C1 charges
beyond the reference, the output pulse returns to
ground and the input is again ready to accept a trigger
signal.
4.5 Oscillators and Pulse Width
Modulators
Microchip’s linear building block comparators adapt
well to oscillator applications for low frequencies (less
than 100kHz). Figure 4-5 shows a symmetrical square
wave generator using a minimum number of components. The output is set by the RC time constant of R4
and C1, and the totalhysteresisoftheloopissetbyR1,
R2 and R3. The maximum frequencyof the oscillator is
limitedonly by the largesignalpropagationdelayof the
comparator in addition to any capacitive loading at the
output which degrades the slew rate.
To analyzethiscircuit, assume that the output is initially
high. For thisto occur, the voltage at the inverting input
must be less than the voltageat the non-invertinginput.
Therefore, capacitor C1 is discharged. The voltage at
the non-inverting input (V
EQUATION 4-5:
V
H
where, if R1 = R2 = R3, then:
EQUATION 4-6:
)is:
H
R2 VDD()
---------- ------------- ------------- ---------=
R2 R1 R3
V
H
||
()+[]
2VDD()
-------------------=
3
DS21344B-page 6
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
Capacitor C1 will charge up through R4. When the
voltage of the comparator's inverting input is equal to
V
, the comparator output will switch. With the output
H
at ground potential,the value at the non-inverting input
terminal (V
) is reduced by t he hysteresis network to a
L
value given by:
EQUATION 4-7:
V
V
DD
-----------=
L
3
Using the same resistorsas before, capacitor C1 must
now discharge through R4 toward ground. The output
will return to a high state when the voltage across the
capacitor has discharged to a value equal to V
.The
L
period of oscillation will be twice the time it takes for the
RC circuit to charge up to one half its final value. The
period can be calculated from:
EQUATION 4-8:
1
----------------- 2 0. 6 94()R4()C1()=
FREQ
The frequency stability of this circuit should only be a
function of the external component tolerances.
Figure 4-6 shows thecircuitforapulsewidthmodulator
circuit. It is essentially the same as in Figure 4-5 with
the addition of an input control voltage. When the input
control voltage is equal to one-half V
, operation i s
DD
basically the same as described for the free-running
oscillator. If the input controlvoltageismoved above or
below one-halfV
, the duty cycle of theoutputsquare
DD
wave will be altered.Thisis because the addition of the
control voltage at the input has now altered the trip
points. The equations for these trip points are shown in
Figure 4-6 (see V
and VL).
H
Pulse width sensitivity to the input voltage variations
can be increased by reducing the value of R6 from
10KΩ and conversely, sensitivity will be reduced by
increasing the value of R6. The values of R1 and C1
can be varied to produce the desiredcenter frequency.
FIGURE 4-1: COMPARATOR
EXTERNAL HYSTERESIS
CONFIGURATION
R
C
V
SRC
TC1037
R
A
R
B
V
DD
+
–
V
R
V
OUT
FIGURE 4-2: PRECISION BATTERY M ONITOR
To System DC/DC
Converter
V
DD
TC1034
3V
Alkaline
+
AMP1
–
+
TC1039
R2, 330k, 1%
R1, 270k, 1%
V
R
R4, 470k, 1%
R5, 7.5M
V
DD
+
CMPTR1
–
TC1037
V
DD
TC1039
–
CMPTR2
+
R6, 7.5M
R3, 470k, 1%
BATTLOW
BATTFAIL
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 7

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
FIGURE 4-3: 32 .768 kHz “TIME OF DAY” CLOCK OSCILLATOR
32.768kHz
V
DD
R
150k
V
DD
A
+
C
A
100pF
–
R
C
1M
R
150k
B
FIGURE 4-4: NON-RETRIGGERABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
V
DD
R3
TC1037
IN
t
0
R1
IN
100k
GND
1M
100k
R2
R4
1M
A
–
CMPTR1
+
B
R10
61.9k
R5
10M
D1
C1
100pF
R6
562k
C
R9
243k
TC1025
–
CMPTR2
+
R8
10M
D2
TC1037
V
OUT
= 30.52µsec
T
per
R7
1M
OUT
OUT
V
DD
GND
V
C
DD
GND
FIGURE 4-5: SQUARE WAVE G ENERATOR
V
DD
R1
100k
C1
R2
100k
DS21344B-page 8
TC1037
V
DD
–
+
R3
100k
R4
V
=
H
=
V
L
FREQ =
R2 (VDD)
R2 + (R1||R3)
(VDD) (R2||R3)
R1 + (R2||R3)
1
2(0.694)(R4)(C1)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

FIGURE 4-6: PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR
V
DD
TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
R1
V
C
R6
10k
C1
100k
R2
100k
1/4
TC1037
V
DD
–
+
R3
100k
R4
V
(R1R2R6 + R2R3R6) + VC (R1R2R3)
V
V
FREQ =
For Square Wave Generation
Select R1 = R2 = R3
V
DD
=
H
R1R2R6 + R1R3R6 + R2R3R6 + R1R2R3
(R2R3R6) + VC (R1R2R3)
V
=
L
V
=
C
DD
R1R2R6 + R1R3R6 + R2R3R6 + R1R2R3
1
2 (0.694) (R4) (C1)
DD
2
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 9

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
5.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Note: The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a l imited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range ( e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
Comparator Propagation Delay
vs. Supply Voltage
7
= 25
T
°C
A
= 100pF
C
L
sec)
µ
6
Overdrive = 10mV
5
4
3.5
4 4.5 5 5.5
3
DELAY TO RISING EDGE (
2
1.5
2
Overdrive = 50mV
2.5 3
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V) SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
Comparator Propagation Delay
vs. Temperature
7
Overdrive = 100mV
sec)
µ
6
V
DD
V
5
4
DELAY TO FALLING EDGE (
3
-40°C85°C25°C
TEMPERATURE (°C)
DD
V
DD
V
DD
= 5V
= 4V
= 3V
= 2V
Comparator Propagation Delay
vs. Supply Voltage
7
= 25
T
°C
A
C
= 100pF
L
sec)
µ
6
Overdrive = 10mV
5
4
Overdrive = 50mV
3
DELAY TO FALLING EDGE (
2
1.5
2
Overdrive = 100mV
2.5 3
3.5
4 4.5 5 5.5
Comparator Output Swing
vs. Output Source Current
2.5
= 25
°C
T
A
2.0
(V)
OUT
- V
DD
V
1.5
1.0
V
= 1.8V
DD
.5
0
0
12345 6
I
(mA)
SOURCE
V
V
DD
= 3V
DD
= 5.5V
Comparator Propagation Delay
vs. Temperature
7
Overdrive = 100mV
sec)
µ
6
5
4
DELAY TO RISING EDGE (
3
-40°C85°C25°C
TEMPERATURE (°C)
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
Comparator Output Swing
vs. Output Sink Current
2.5
= 25
T
°C
A
2.0
(V)
1.5
SS
- V
1.0
OUT
V
.5
0
012 345
V
I
SINK
DD
= 1.8V
V
DD
(mA)
V
= 5.5V
DD
= 5V
= 4V
= 2V
= 3V
= 3V
6
Comparator Output Short-Circuit
Current vs. Supply Voltage
60
50
40
30
20
10
Sourcing
0
OUTPUT SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT (mA)
0
T
Sinking
12345 6
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
= 85°C
A
TA = -40°C
TA = 25°C
= -40
A
T
= 85°C
T
A
DS21344B-page 10
T
A
C
°
= 25°C
Reference Voltage vs.
1.240
V
1.220
1.200
1.180
1.160
REFERENCE VOLTAGE (V)
1.140
0
Load Current
V
DD
V
= 1.8V
DD
DD
= 1.8V
2468
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
= 3V
V
DD
Sinking
Sourcing
V
DD
V
= 3V
DD
= 5.5V
= 5.5V
Line Transient
Response of V
4
V
3
2
1
0
10
0
SUPPLY AND REFERENCE VOLTAGES (V)
DD
V
REF
100 200
TIME (µsec)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.
REF
300
400

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
5.0 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (CONTINUED)
Reference Voltage
vs. Supply Voltage
1.25
Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
3
TC1037, TC1038
TA = 85°C
Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
5
TC1039
TA = 85°C
1.20
1.15
1.10
REFERENCE VOLTAGE (V)
1.05
1
23
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
= -40°C
T
A
= 25°C
T
A
= -40°C
T
2
1
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
0
4
5
0123456
T
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
= 25°C
A
A
4
3
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
2
0123456
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 11

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
6.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
6.1 Package Marking Information
5-Pin SOT-23A
1 & 2 = part number code + temperature range and
voltage
Part Number Code
TC1037CECT AR
TC1038CECH AS
TC1039CECH AT
3 = year and quarter code
4 = lot ID number
6-Pin SOT-23A
6.2 Taping Form
Component Taping Orientation for 5-Pin SOT-23A (EIAJ SC-74A) Devices
User Direction of Feed
Device
Marking
W
PIN 1
Standard Reel Component Orientation
TR Suffix Device
(Mark Right Side Up)
Carrier Tape, Number of Components Per Reel and Reel Size
Package Carrier Width (W) Pitch (P) Part Per Full Reel Reel Size
5-Pin SOT-23A 8 mm 4 mm 3000 7 in
P
DS21344B-page 12
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

6.3 Ta ping Form ( Continued)
Component Taping Orientation for 6-Pin SOT-23A (EIAJ SC-74) Devices
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Device
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
Marking
TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
User Direction of Feed
W
PIN 1
Standard Reel Component Orientation
For TR Suffix Device
(Mark Right Side Up)
Carrier Tape, Number of Components Per Reel and Reel Size
Package Carrier Width (W) Pitch (P) Part Per Full Reel Reel Size
6-Pin SOT-23A 8 mm 4 mm 3000 7 in
P
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 13

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
6.3 Package Dimensions
SOT-23A-5
.075 (1.90)
REF.
.122 (3.10)
.098 (2.50)
.020 (0.50)
.012 (0.30)
.057 (1.45)
.035 (0.90)
SOT-23A-6
.122 (3.10)
.098 (2.50)
PIN 1
.006 (0.15)
.000 (0.00)
.122 (3.10)
.106 (2.70)
.075 (1.90)
REF.
.071 (1.80)
.059 (1.50)
.037 (0.95)
REF.
10° MAX.
.069 (1.75)
.059 (1.50)
.010 (0.25)
.004 (0.09)
.024 (0.60)
.004 (0.10)
Dimensions: inches (mm)
DS21344B-page 14
.020 (0.50)
.014 (0.35)
.057 (1.45)
.035 (0.90)
.006 (0.15)
.000 (0.00)
.118 (3.00)
.110 (2.80)
.037 (0.95)
REF.
10° MAX.
.024 (0.60)
.004 (0.10)
Dimensions: inches (mm)
.008 (0.20)
.004 (0.09)
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc.

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
Sales and Support
Data Sheets
Products supportedby a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences and recommendedworkarounds.To determine if an errata sheet existsfor a particulardevice, please contact one of the following:
1. Your local Microchip sales office
2. The Microchip CorporateLiterature Center U.S. FAX: (480)792-7277
3. The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Pleasespecify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (includeLiterature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21344B-page15

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
NOTES:
DS21344B-page16 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.

TC1037/TC1038/TC1039
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect
to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such
use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’sproductsascriticalcomponents in life support systems is not authorized except with
express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual property
rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, FilterLab,
K
EELOQ,microID,MPLAB,PIC,PICmicro,PICMASTER,
PICSTART, PRO MATE, SEEV AL and The Embedded Control
SolutionsCompany areregiste red trademarksof MicrochipTechnologyIncorp or ated in the U.S.A. and other countries .
dsPIC, ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB,
In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, microPort,
Migratable Memory, MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM,
MXDEV, PICC, PICDEM, PICDEM.net , rfPIC, Select Mode
and Total Enduranceare trademarksof MicrochipTechnology
Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Serialized Quick Turn Programming (SQTP) is a service mark
of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2002, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received QS-9000 quality system
certification for its worldwide headquarters,
design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona in July 1999
and Mountain View, California in March 2002.
The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are QS-9000 compliant for its
®
PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals,
non-volatile memory and analog products. In
addition, Microchip’s quality system for the
design and manufacture of development
systemsisISO 9001certified.
2002 Microchip TechnologyInc. DS21344B-page 17
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ®code hopping

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200 Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: http://www.microchip.com
Rocky Mountain
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7966 Fax: 480-792-7456
Atlanta
500 Sugar Mill Road, Suite 200B
Atlanta, GA 30350
Tel: 770-640-0034 Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
2 Lan Drive, Suite 120
Westford, MA 01886
Tel: 978-692-3848 Fax: 978-692-3821
Chicago
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 630-285-0071 Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
4570 Westgrove Drive, Suite 160
Addison, TX 75001
Tel: 972-818-7423 Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Tri-Atria Office Building
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190
Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Tel: 248-538-2250 Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
2767 S. Albright Road
Kokomo, Indiana 46902
Tel: 765-864-8360 Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
18201 Von Karman, Suite 1090
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 949-263-1888 Fax: 949-263-1338
New York
150 Motor Parkway, Suite 202
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Tel: 631-273-5305 Fax: 631-273-5335
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First Street, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408-436-7950 Fax: 408-436-7955
Toro nto
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699 Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd
Suite 22, 41 Rawson Street
Epping 2121, NSW
Australia
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Beijing Liaison Office
Unit 915
Bei Hai Wan Tai Bldg.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Beidajie
Beijing, 100027, No. China
Tel: 86-10-85282100 Fax: 86-10-85282104
China - Chengdu
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Chengdu Liaison Office
Rm. 2401, 24th Floor,
Ming Xing Financial Tower
No. 88 TIDU Street
Chengdu 610016, China
Tel: 86-28-6766200 Fax: 86-28-6766599
China - Fuzhou
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Fuzhou Liaison Office
Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza
No. 71 Wusi Road
Fuzhou 350001, China
Tel: 86-591-7503506 Fax: 86-591-7503521
China - Shanghai
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd.
Room 701, Bldg. B
Far East International Plaza
No. 317 Xian Xia Road
Shanghai, 200051
Tel: 86-21-6275-5700 Fax: 86-21-6275-5060
China - Shenzhen
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Liaison Office
Rm. 1315, 13/F , Shenzhen Kerry Centre,
Renminnan Lu
Shenzhen 518001, China
Tel: 86-755-2350361 Fax: 86-755-2366086
Hong Kong
Microchip Technology Hongkong Ltd.
Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-1200 Fax: 852-2401-3431
India
Microchip Technology Inc.
India Liaison Office
Divyasree Chambers
1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Bangalore, 560 025, India
Tel: 91-80-2290061 Fax: 91-80-2290062
Japan
Microchip Technology Japan K.K.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shinyokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama-shi
Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea
Microchip Technology Korea
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku
Seoul, Korea 135-882
Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-5934
Singapore
Microchip Technology Singapore Pte Ltd.
200 Middle Road
#07-02 Prime Centre
Singapore, 188980
Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Ta iw an
Microchip Technology Taiwan
11F-3, No. 207
Tung HuaNorth Road
Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
EUROPE
Denmark
Microchip Technology Nordic ApS
Regus Business Centre
Lautrup hoj 1-3
Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Tel: 45 4420 9895 Fax: 45 4420 9910
France
Microchip Technology SARL
Parc d’Activite du Moulin de Massy
43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Batiment A - ler Etage
91300 Massy, France
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany
Microchip Technology GmbH
Gustav-Heinemann Ring 125
D-81739 Munich, Germany
Tel: 49-89-627-144 0 Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy
Microchip Technology SRL
Centro Direzionale Colleoni
Palazzo Taurus 1 V. Le Colleoni 1
20041 Agrate Brianza
Milan, Italy
Tel: 39-039-65791-1 Fax: 39-039-6899883
United Kingdom
Arizona Microchip Technology Ltd.
505 Eskdale Road
Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham
Berkshire,England RG415TU
Tel: 44 118 921 5869 Fax: 44-118921-5820
03/01/02
DS21344B-page 18
*DS21344B*
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...