Page 1

SAM9X60-EK
SAM9X60-EK User's Guide
Scope
This user's guide introduces the SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit (SAM9X60-EK) and describes the development and
debugging capabilities running on SAM9 Arm®-based embedded MPUs.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 1
Page 2

SAM9X60-EK
Table of Contents
Scope............................................................................................................................................................. 1
1. Introduction............................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1. Document Layout......................................................................................................................... 3
1.2. Recommended Reading...............................................................................................................3
2. Product Overview....................................................................................................................................4
2.1. SAM9X60-EK Features................................................................................................................ 4
2.2. Evaluation Kit Specifications........................................................................................................ 5
2.3. Power Sources............................................................................................................................. 5
2.4. Connectors on Board................................................................................................................... 5
2.5. Default Jumper Settings............................................................................................................... 8
2.6. Kit Content....................................................................................................................................8
3. Function Blocks.......................................................................................................................................9
3.1. Power Supply Topology and Power Distribution...........................................................................9
3.2. Processor................................................................................................................................... 13
3.3. On-board Memories................................................................................................................... 28
3.4. Peripherals................................................................................................................................. 32
3.5. User Interaction and Debugging.................................................................................................48
4. Installation and Operation..................................................................................................................... 55
4.1. System and Configuration Requirements...................................................................................55
4.2. Board Setup............................................................................................................................... 55
5. Erratum................................................................................................................................................. 56
6. Appendix. Schematics and Layouts...................................................................................................... 57
7. Revision History.................................................................................................................................... 64
7.1. DS50002907A - 10/2019............................................................................................................64
The Microchip Website.................................................................................................................................65
Product Change Notification Service............................................................................................................65
Customer Support........................................................................................................................................ 65
Microchip Devices Code Protection Feature................................................................................................ 65
Legal Notice................................................................................................................................................. 65
Trademarks.................................................................................................................................................. 66
Quality Management System....................................................................................................................... 66
Worldwide Sales and Service.......................................................................................................................67
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 2
Page 3

1. Introduction
1.1 Document Layout
The document is organized as follows:
• Chapter 1. “Introduction”
• Chapter 2. “Product Overview” – Important information about the SAM9X60-EK board
• Chapter 3. “Function Blocks” – Specifications of the SAM9X60-EK and high-level description of the major
components and interfaces
• Chapter 4. “Installation and Operation” – Instructions on how to get started with the SAM9X60-EK
• Appendix. “Schematics and Layouts” – SAM9X60-EK schematics and layout diagrams
1.2 Recommended Reading
The following Microchip document is available and recommended as a supplemental reference resource:
• SAM9X60 Datasheet. Lit. Number DS60001579
SAM9X60-EK
Introduction
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 3
Page 4

2. Product Overview
The SAM9X60-EK follows the Microchip MPU strategy for low cost evaluation kits, showcasing all the features that
the SAM9X60 MPU can offer.
2.1 SAM9X60-EK Features
Table 2-1. SAM9X60-EK Features
Characteristic Specification Featured Components
Processor 228-ball TFBGA, 11x11 mm, 0.65 mm pitch Microchip SAM9X60
SAM9X60-EK
Product Overview
External clock
Memory
SD/MMC One standard 4-bit SD card interface –
USB
CAN Two CAN interfaces Microchip MCP2542
Ethernet One ETH port Microchip KSZ8081
Wi-Fi/BT One optional Wi-Fi® /Bluetooth® interface Slot for Microchip ATWILC3000
Audio One ClassD audio port –
Display One 24-bit LCD interface –
Camera One 12-bit Image Sensor Interface –
IO One expander IO Microchip MCP23008
Debug port
MPU: 24 MHz, 32.768 KHz
Misc. osc.: 25 MHz
One 16-bit, 2-Gbit DDR2
One NAND Flash
One QSPI Flash
One EEPROM
Two stacked Type-A connectors with power switches
One Micro-B USB Device
One J-Link-OB + CDC
One JTAG interface
DSC1001CI5
DSC6083CE2A
Winbond W972GG6KB-25
Micron MT29F08BA
Microchip SST26VF064B
Microchip 24AA02E48
2 * Microchip MIC2025
Embedded J-Link-OB through the CDC
interface (ATSAM3U4C TFBGA100)
Board monitor
Expansion
Power management
Board supply From USB A or from external connector –
Backup battery SuperCap –
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
One RGB (Red, Green, Blue) LED
Four push button switches
One PIO connector
One mikroBUS™ connector
Two power regulators
Two power consumption measurement devices
User Guide
–
–
–
Hundreds of possible Click
extensions featuring Microchip
functions inside
Microchip MIC2800, MCP1725
Microchip PAC1934, PAC1710
™
DS50002907A-page 4
Page 5

2.2 Evaluation Kit Specifications
CAUTION
Table 2-2. Evaluation Kit Specifications
Characteristic Specification
Board SAM9X60-EK
Board supply voltage External or USB-powered
SAM9X60-EK
Product Overview
Temperature
Relative humidity 0 to 90% (non-condensing)
Main board dimensions 150 × 125 × 20 mm
RoHS status Compliant
Board identification SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
2.3 Power Sources
Two options are available to power up the SAM9X60-EK board:
• Powering through an external AC to DC +5V wall adapter connector (J1)
• Powering through the USB Micro-B connector on the USBA port (J7 – default choice)
Table 2-3. Electrical Characteristics
Electrical Parameters Value
Input voltage 5VDC
Maximum input voltage (limits) 6VDC
Maximum 3.3VDC current 300 mA
Operating: 0°C to +70°C
Storage: –40°C to +85°C
The SAM9X60-EK board runs at a 3.3V voltage level logic. The maximum voltage that the I/O pins can
tolerate is 3.3V. Providing higher voltages (e.g., 5V) to an I/O pin could damage the board.
2.4 Connectors on Board
The fully-featured SAM9X60-EK board integrates multiple peripherals and interface connectors, as shown in the
following figures.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 5
Page 6

Figure 2-1. SAM9X60-EK Top Connectors
D1
J8
J1
Q5
Q1
R9
R249
R245
R236
R242
R8
R34
R48
R49
FB6
C113
R153
D7
C69
C77
J2
C85D2C88
R128
R91
Y6
C56
C128
C126
R171
R181
J16
R19
R18
VDD_3V3_3 U
C150
U27
R116
C120
Q12
R114
C117
R149
C90
R221
TP4
R225
R224
R231
R230
R218
TP6
R213
C127
VBUS_USBC
Q3
R16
C173
Y10
C152
R235
R238
C2
R10
C6
L1
R7
R250
C176
J7
C4
U6
C122
R94
R93
R84
C58
C116
Q10
Q11
J5
Y2
SW1
R156
R158
R74
R72
SW2
R53
R54
R45
R41
R32
R67
R62
SW3
R97
R98C54
C136
Y8
R162
R110
R111
R109
Y7
C131
D4
R177
C141
C99
J14
FB13
J22
J24
C8
C172
R251
R237
D8
FB1
U1
R11
R29
C18
C1
C19
R246
R234
C148
R239
R258
R256
U2
C5
R4
R13
R12
U4
R243
R233
R241
R257
R47
R36
R35
U9
R265
FB8
C119
R92
R90
C60
R189
J3
R155
U10
J20
C76
C70
Y3
R188
J13
R126
C86
U11
R27
R28
Y1
R197
D3
R20
R119
U5
R22
R24
R21 C27
C25
C23
Y5
C91
R88
R86
R159
R157
U8
R85
R82
R75
R71
R65
R66
R203
R201
R199
Q15
Q14
Q13
U21
C125
C129
C55
U26
R59
R52
R145
R44
R40
R31
R142
R68
R64
R196
U7
R191
R185
J17
R136
R175
J9
R118
R107
C57
R112
R108
R113
C100
R137
R172
FB9
R161
R138
Q7
Q6
D5
J11
R173
R170
R169
Q9
Q8
R174
R182
D6
U24
Y9
U28
R17
Q2
TP9
C149
R1
R6
C106
VDDIOM
C61
VDD_3V3
U32
R117
U20
C124
C123
C121
U19
C118
C115
C114
R187
TP2
R127
R122
R220
R223
R222
C92
C93
R215
R216
R219
R227
R229
R226
R228
U23
TP5
TP7
R26
R190
C105
U17
U15
C103
C97
U14
C104
C102
C101
C130
R160
R176
FB10
C142
C138
R179
R178
FB11
C137
R183
R180
VDDCORE
VBUS_USBA
VBUS_USBB
C9
C3
C20
C22
C7
R148
R150
R33
C12
C11
D9
R132
R133
R79
R80
C29
SW4
R195
R58
R141
R146
U13
U12
C95
C132
R5
R2
Q4
C17
VBUS_JLINK
C171
C151
J18
U3
R96
R95
R154
R89
R87
R37
C179
R259
R260
J19
R130
R124
R152
R81
R77
R69
C75
C62
R70
C24
R194
J21
LD1
VDD_WILC
R207 R202
R105
R104
R135
R134
J6
J10
U22
C134
C133
R139
J12
R3
R15
R240
J23
R83
C53
C59
U31
R115
R123
C26
R212
C96
TP8
C135
J4
U16
VDD_MAIN_5V
Configuration
Jumpers
ISI
Connector
2 x CAN
Connector
CLASSD Audio
Connector
JTAG 20-pin
IDC Connector
UART
DEBUG
JLINK USB
Micro-B
External
Power Jack
MikroBus
USB 2.0
Micro-B
Stacked USB
type A
Ethernet
10/100
4 x User Buttons
I2C and PCM audio header
to/from ATWILC3000
Place to solder the
Wi-Fi / BT Module
SD Card
Connector
Raspberry Pi
Connector
™
SAM9X60-EK
Product Overview
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 6
Page 7

Figure 2-2. SAM9X60-EK Bottom Connectors
C156
R247
C13
C63
R121
C84
R125
C51
R129
C50
C40
R208
C98
R164
R253
C167
R23
C34
C28
R101
R100
R102
R264
R14
C175
C10
C155
PAD2
R270
Q16
C82
C73
R232
R186
C67
R192
C42
C33
C43
C45
C143
R63
R50
R57
R55
R43
R39
R144
R168
R166
R261
R263
R262
C170
C178
R266
C177
R248
C168
C165
C163
C164
C161
C160
U29
FB5
PAD1
C16
C14
C162
C153
R244
C157U25
C79
C71
C68
C81
C78
C72
R120
C66
C65
R131
C83
FB2
C64
C35
C37
C36
C32
C49
C47
FB3
C44
C46
C39
R106
R206
R60
R46
R56
R38
R73
R61
R78
C94
R167
R165
R163
C140
C139
R255
C174
R252
C169
C159
C15
C21
C166
C38
C48
C52
C87
C41
R25
R103
R99
R147
R209
R211
C158
C89
C74
C145
C147
PAD4
PAD3
R268
U30
FB7
C154
C146
C80
C31
R30
R204
C144
R200
R143
R51
R42
R76
R140
R214
R217
R210
J15
FB12
R254
LCD
Connector
SAM9X60-EK
Product Overview
Table 2-4. SAM9X60-EK Board Interface Connectors
Connector Interfaces to
J1 External power jack
J4 Standard SDMMC connector
J6 Dual CAN
J7 USB 2.0 Micro-B (USB-A)
J8A Stacked Type-A USB (USB-B)
J8B Stacked Type-A USB (USB-B)
J10 (not populated) ATWILC3000 GPIO
J9 (not populated) ATWILC3000 UART
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 7
Page 8

SAM9X60-EK
Product Overview
...........continued
Connector Interfaces to
J5 Ethernet 10/100 RJ45 (port 1)
J11 Audio external power
J12 ClassD audio output
J14 mikroBUS socket
J15 LCD connector
J16 External GPIO
J17 ISI Camera Connector
J18 PCB connector for factory-programming the SAM3U/J-Link-OB (not to be used by end user)
J22 USB 2.0 Micro-B, J-Link-OB/J-Link-CDC
J23 JTAG, 20-pin IDC
J24 FTDI connector (UART debugger)
2.5 Default Jumper Settings
Table 2-5. SAM9X60-EK Jumper Settings
Jumper State Function
J2 Closed VDDBU current measurement
J3
J13
J19
(not populated)
J20
J21
Closed Disable the SHDN function and always keep the board powered on
Open (default) Normal behavior, the PMIC can be powered down by the MPU
Closed Booting from on-board memories is permanently disabled
Open (default) Booting from on-board memories is disabled only when SW4 is pressed
Closed
Open (default) Normal SAM3U operation (runs the J-Link interface)
Closed
Open (default)
Closed Disable UART communication (CDC) between MPU and SAM3U
Open (default)
Erase SAM3U firmware (not populated, reserved for factory configuration and
should never be used by the end user)
J-Link on-board interface is disabled. MPU debugging is done through J23, the 20pin SAM-ICE™ connector (i.e., an external JTAG interface is required)
J-Link on-board interface is enabled. MPU debugging is done through it (i.e., using
the SAM3U MCU and the micro USB connector J22)
Enable UART communication (CDC) between MPU and SAM3U (PD20 port must
be high as well)
2.6 Kit Content
The SAM9X60 evaluation kit includes the following:
• The SAM9X60-EK board
• USB-A to USB Micro-B cable
• 50-position FFC/FPC cable
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 8
Page 9

3. Function Blocks
SAM9X60
600 MHz
ARM926EJ-S CPU
BGA 228
On Board Memories
NAND Flash
4Gb (512M x 8)
MT29F4G08ABAEAWP
QSPI Flash
64Mb (8M x 8)
SST26VF064B
I2C EEPROM
2Kb (256 x 8)
24AA025E48
DDR2 SDRAM
2Gb
W972GG6KB
External connections
ETHERNET PHY
RMII
KSZ8081RNAIA
RJ45
Connector
Camera
ISI
Connector
LCD
Connector
2 x CAN
2 x MCP2542
2 x CAN
2 x Connector
CLASS D
Audio Amplifier
Analog Audio
Connector
RASPBERRY PI
Connector
SD Card
Connector
Wi-Fi / BLE
ATWILC3000
mikroBUS
Connector
USB A,B&C
Connectors
RGB LED'sUSER Buttons
SAM9X60 - EVALUATION KIT
Power Supply
5V INPUT
Connector
PMIC
MIC2800
Voltage & Current
Measurement
PAC1710
PAC1934
Backup Power
3V3 SUPERCAP
Program and debug
UART
DEBUG
Connector
On Board
Programmer
ATSAM3U4CA
J-TAG
Connector
USBA
SAM-BA
This section covers the specifications of the SAM9X60-EK and provides a high-level description of the board's major
components and interfaces. This document is not intended to provide detailed documentation about the processor or
about any other component used on the board. It is expected that the user will refer to the appropriate documents of
these devices to access detailed information.
Figure 3-1. SAM9X60-EK Block Diagram
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
3.1 Power Supply Topology and Power Distribution
budget for all the devices on the board and a correct power-up sequence for the MPU. The power-up and powerdown sequences indicated in the SAM9X60 datasheet must be respected for a reliable operation of the device.
3.1.1 Input Power Options
The SAM9X60-EK board can be powered through:
This section describes the implementation and the circuitry that ensures adequate voltage stability and current
The +5V from the wall adapter is protected through an NCP349 positive overvoltage controller switch. The controller
is able to disconnect the system from its output pin when incorrect input operating conditions are detected (5.83V
max).
The USB-powered operation comes from the USB device port connected to a PC or a 5VDC supply. The USB supply
is enough to power the board in most applications. It is important to note that when the USB supply is used, the USB
port has limited power. If USB Host port is required for the application, it is recommended that the external DC supply
be used.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
• an external AC to DC +5V wall adapter connected via a 2.1 mm center-positive plug into the power jack of the
board (J1). The recommended output capacity of the power adapter is 2A,
• USB port A (J7).
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 9
Page 10

0.1uF
50V
0402
C3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C9
GND
IN
1
IN_PAD
7
EN
6
GND
2
FLAG
3
OUT2
5
OUT1
4
NCP349MNAETBG
U1
2
3
1
2.1mm
EJ508A
J1
VDD_MAIN_5V_
GND
EXT_5V DC_5V
180R 0603
FB1
USB_5V
0.1uF
50V
0402
C7
2
71
6
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q1A
5
8 4
3
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q1B
2
71
6
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q2A
5
8 4
3
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q2B
GND GND GND GND
GND GND GND
100µF
16V
Radial, Can
C4
GND
USBA_VBUS_5V
10uF
25V
1206
C1
10uF
25V
1206
C2
10uF
25V
1206
C8
100k
0402
5%
R2
100k
0402
5%
R3
100k
0402
5%
R5
PIC101
PIC102
COC1
PIC201
PIC202
COC2
PIC301
PIC302
COC3
PIC401
PIC402
COC4
PIC701
PIC702
COC7
PIC801
PIC802
COC8
PIC901
PIC902
COC9
PIFB101
PIFB102
COFB1
PIJ101
PIJ102
PIJ103
COJ1
PIQ101
PIQ102
PIQ106
PIQ107
COQ1A
PIQ103
PIQ104
PIQ105
PIQ108
COQ1B
PIQ201
PIQ202
PIQ206
PIQ207
COQ2A
PIQ203
PIQ204
PIQ205
PIQ208
COQ2B
PIR201
PIR202
COR2
PIR301
PIR302
COR3
PIR501
PIR502
COR5
PIU101
PIU102
PIU103
PIU104
PIU105
PIU106
PIU107
COU1
PIC201
PIC301
PIQ101
PIQ202
PIQ205
PIR202
PIU104
PIU105
PIC101
PIJ101
PIU101
PIU107
PIC102
PIC202
PIC302
PIC402
PIC702
PIC802
PIC902
PIJ102
PIR201
PIR301
PIR501
PIU102
PIU106
PIJ103
PIQ102
PIQ105
PIQ203
PIQ206
PIQ207
PIQ208
PIR302
PIQ103
PIQ106
PIQ107
PIQ108
PIU103
PIC801
PIC901
PIFB102
PIQ201
PIR502
PIC701
PIFB101
PIC401
PIQ104
PIQ204
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
The switch between the two powering options is made by four transistors that ensure the separation between the two
when both are plugged. The switch prioritizes powering from the wall adapter to maximize power transfer.
The following figure shows the input power supply topology.
Figure 3-2. Input Power Options
Note: USB-powered operation eliminates additional wires and batteries. It is the preferred mode of operation for any
project that requires only a 5V source at up to 500 mA.
3.1.2 Power Management Integrated Circuit
The MIC2800 is a high-performance power management IC providing three output voltages with maximum efficiency.
Integrating a 2-MHz DC/DC converter with an LDO post-regulator, the MIC2800 gives two high-efficiency outputs with
a second, 300 mA LDO for maximum flexibility. The DC-to-DC converter uses small values of L and C to reduce
board space while still retaining efficiency over 90% at load currents up to 600 mA. For more information about the
MIC2800, refer to the product web page.
Each LDO has an independent Enable (EN) pin thus allowing a proper power-up sequence for the MPU. The 20 KΩ
resistor in series and the 0.1 µF capacitor in parallel with the EN1 input make a low-pass filter and introduce the
necessary delay between the 3.3V and 1.15V rails needed for the proper operation of the MPU. The diode (D1 in
Figure 3-3) ensures that the capacitor fast discharges during the power-down sequence.
Detailed information on the SAM9X60 MPU power supplies and power-up/down considerations are described in
section “Electrical Characteristics” in the SAM9X60 device datasheet (see 1.2 Recommended Reading).
The MIC2800-G8S comes preset to supply all the voltage rails needed by the system:
• 1.8V DC/DC supplies SAM9X60 DDR2 pads (VDDIOM) and devices.
• 1.15V LDO1 supplies SAM9X60 Core (VDDCORE).
• 3.3V LDO2 supplies SAM9X60 I/O pads.
The figure below shows the power management scheme.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 10
Page 11

Figure 3-3. Power Management Integrated Circuit
GND GNDGND GND
VDD_1V15
VDD_MAIN_5V
2.2uH
L1
GND
GNDGND
VDD_1V8
GND
GND
GND
MIC2800_nRST
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C17
0.1uF
50V
0402
C18
0.1uF
50V
0402
C19
LOWQ
1
BIAS
2
SGND
3
PGND
4
SW
5
VIN
6
VIN
7
LDO2
8
FB
9
LDO
10
LDO1
11
POR
12
CSET
13
CBYP
14
EN1
15
EN2
16
U3
MIC2800-G8SYML-TR
600mA
300mA
300mA
VDD_3V3_LDO
POWER_EN
10uF
25V
1206
C10
10uF
25V
1206
C11
10uF
25V
1206
C12
10uF
25V
1206
C21
10uF
25V
1206
C22
10nF
16V
0402
C20
1N4148
D1
20k 0402 1%
R11
100k
0402
5%
R29
PIC1001
PIC1002
COC10
PIC1101
PIC1102
COC11
PIC1201
PIC1202
COC12
PIC1701
PIC1702
COC17
PIC1801
PIC1802
COC18
PIC1901
PIC1902
COC19
PIC2001
PIC2002
COC20
PIC2101
PIC2102
COC21
PIC2201
PIC2202
COC22
PID101
PID102
COD1
PIL101
PIL102
COL1
PIR1101
PIR1102
COR11
PIR2901
PIR2902
COR29
PIU301
PIU302
PIU303
PIU304
PIU305
PIU306
PIU307
PIU308
PIU309
PIU3010
PIU3011
PIU3012
PIU3013
PIU3014
PIU3015
PIU3016
COU3
PIC1002
PIC1102
PIC1202
PIC1702
PIC1802
PIC1902
PIC2002
PIC2102
PIC2202
PIU303
PIU304
PIU3012
POMIC28000nRST
PIC1701
PIU3014
PIC1801
PIU302
PIC1901
PID101
PIR1102
PIU3015
PIC2001
PIU3013
PIL101
PIU305
PIR2901
PIU301
PID102
PIR1101
PIU3016
NLPOWER0EN
PIC1101
PIC1201
PIL102
PIU309
PIU3010
PIC2201
PIU3011
PIC2101
PIU308
PIC1001
PIR2902
PIU306
PIU307
POMIC28000nRST
10k
0402
5%
R19
1k
0402
5%
R18
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J3
GND GND
GND
VDD_MAIN_5V VDD_MAIN_5V
SHDN
POWER_EN
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP2
GND
MIC2800_nRST
STARTB
VDD_3V3
100k
0402
5%
R15
100k
0402
5%
R16
100k
0402
5%
R17
3
1
2
BSS138N
Q3
3
1
2
BSS138N
Q4
3
1
2
BSS138N
Q5
PIJ301
PIJ302
COJ3
COJP2
PIQ301
PIQ302
PIQ303
COQ3
PIQ401
PIQ402
PIQ403
COQ4
PIQ501
PIQ502
PIQ503
COQ5
PIR1501
PIR1502
COR15
PIR1601
PIR1602
COR16
PIR1701
PIR1702
COR17
PIR1801
PIR1802
COR18
PIR1901
PIR1902
COR19
PIJ302
PIQ302
PIQ402
PIQ502
PIQ503
PIR1701
POMIC28000nRST
PIJ301
PIR1801
PIQ301
PIR1901
PIQ403
PIR1601
NLPOWER0EN
PIR1902
POSHDN
PIQ303
PIQ401
PIQ501
PIR1501
PIR1802
NLSTARTB
PIR1702
PIR1502
PIR1602
POMIC28000nRST
POSHDN
WARNING
3.1.3 Shutdown Circuitry
The processor can assert the SHDN signal to shut down the PMIC and enter Power-down mode. This is done by
pulling both enable pins of the PMIC to GND through a Field Effect Transistor (FET) scheme.
Jumper J3 must not be set to enable this functionality. By setting jumper JP2/J3, the user can shut down the MPU
without powering down its power rails.
Figure 3-4. Shutdown Circuitry
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
3.1.4 Battery Unit
A 3.3V battery (supercapacitor) is implemented to permanently maintain the VDDBU voltage.
This function allows the user to shut down the MPU and the system, thus entering a low power mode, and still keep
the custom configuration that was previously set in the MPU backup area. While in Shut-down mode, the board can
be woken up by action on the SW2 button (WAKE UP), which signals the MPU to resume operations.
Jumper JP1/J2 must be in place for proper operation of the MPU, and can be removed if the user wants to bring the
MPU back to the initial configuration, by resetting the General Purpose Backup Registers (GPBR).
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
Make sure the board is powered off before removing the JP1/J2 jumper.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 11
Page 12
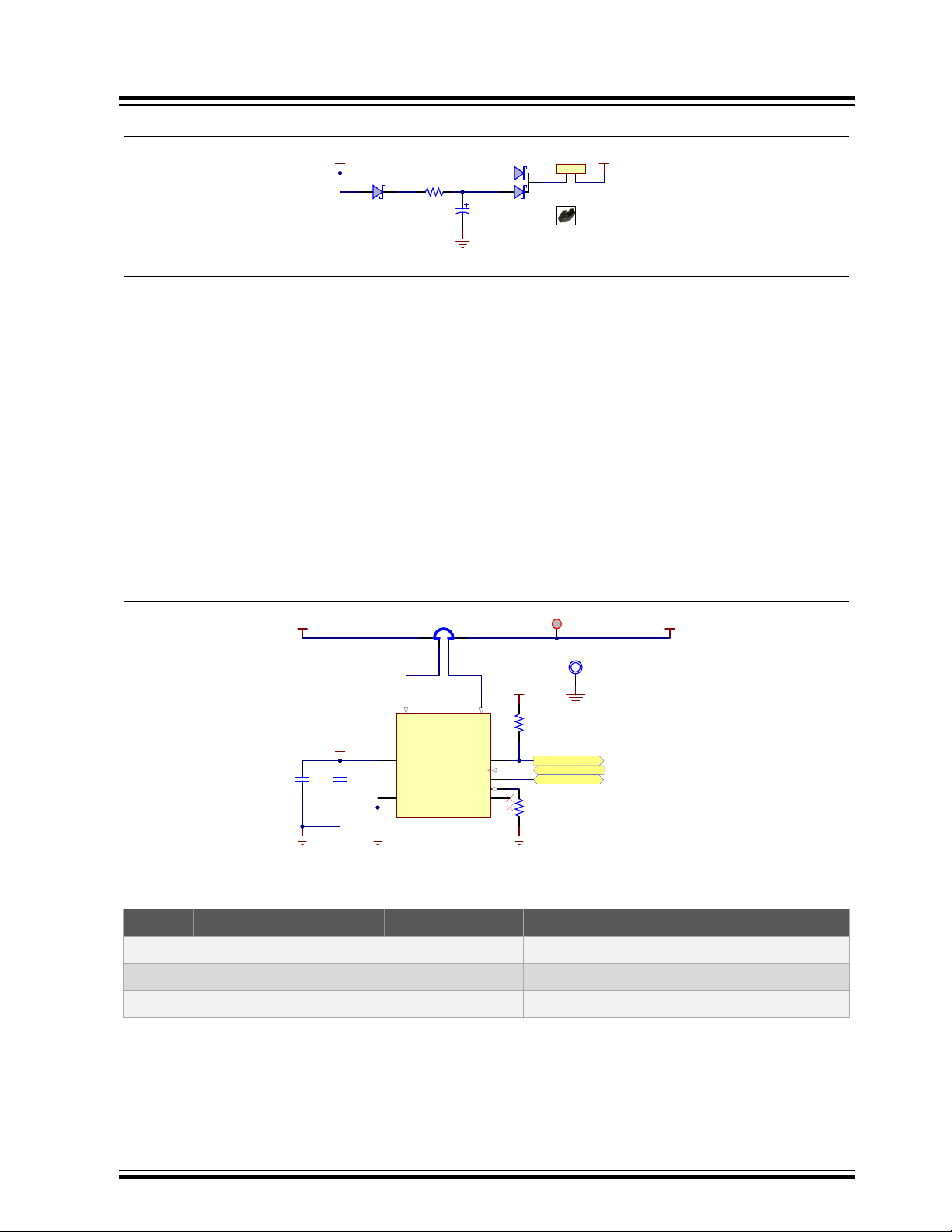
Figure 3-5. Battery Unit
220mF
3.3V
P8.3L11.7D6.8H1.8
C23
1
2
3
BAT54C
D2
PMEG6010ER
D3
VDDBU
GND
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP1
VDD_3V3
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J2
100R
0402
1%
R20
PIC2301
PIC2302
COC23
PID201
PID202
PID203
COD2
PID301
PID302
COD3
PIJ201
PIJ202
COJ2
COJP1
PIR2001
PIR2002
COR20
PIC2302
PIC2301
PID202
PIR2002
PID203
PIJ202
PID302
PIR2001
PID201
PID301
PIJ201
I2C ADR : 1001_101[R/W]
GND GND GND
10k
0402
5%
R4
VDD_3V3
VDD_MAIN_5V_ VDD_MAIN_5V
PAC1710_TWCK
PAC1710_TWD
VDD_MAIN_5V
GND
PAC1710_INT
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
0.25W
R1
SENSE+
1
SENSE-
2
NC
3
NC
4
GND
5
ADDR_SEL
6
ALERT#
7
SMDATA
8
SMCLK
9
VDD
10
PAD
11
PAC1710
U2
5V_P 5V_N
TP LOOP Black TH
TP1
4.7uF
10V
0402
C5
0.1uF
50V
0402
C6
VDD_3V3_LDO
100R
0402
1%
R6
PIC501
PIC502
COC5
PIC601
PIC602
COC6
PIR101
PIR102
PIR103
PIR104
COR1
PIR401
PIR402
COR4
PIR601
PIR602
COR6
PITP101
COTP1
PIU201
PIU202
PIU203
PIU204
PIU205
PIU206
PIU207
PIU208
PIU209
PIU2010
PIU2011
COU2
PIVDD0MAIN05V01
COVDD0MAIN05V
PIR104
PIU202
NL5V0N
PIR103
PIU201
NL5V0P
PIC501
PIC601
PIR602
PITP101
PIU205
PIU2011
PIR601
PIU206
PIU203
PIU204
PIR401
PIU207
POPAC17100INT
PIU209
POPAC17100TWCK
PIU208
POPAC17100TWD
PIR402
PIC502
PIC602
PIU2010
PIR102
PIVDD0MAIN05V01
PIR101
POPAC17100INT
POPAC17100TWCK
POPAC17100TWD
3.1.5 Current Measurement
Two Microchip DC power/energy monitors are embedded on the SAM9X60-EK board:
• one single high-side current sense monitor PAC1710
• one four-channel current sense monitor PAC1934
Both chips communicate with the MPU via a Two-wire Interface (TWI) and both output their ALERT# signal to a port
expander.
The PAC1710 is a single high-side bidirectional current sensing monitor with precision voltage measurement
capabilities. The power monitor measures the voltage developed across an external sense resistor to represent the
high-side current of a battery or voltage regulator. The PAC1710 also measures the SENSE+ pin voltage and
calculates average power over the integration period. The PAC1710 can be programmed to assert the ALERT# pin
when high and low limits are exceeded for current sense and bus voltage. For more information about the PAC1710,
refer to the product web page.
One current sense resistor is populated on board for measuring voltage and current on the main 5V power rail.
Figure 3-6. PAC1710 Current Measurement
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-1. PAC1710 Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared PIO Signal Description
PA31 PAC1710_TWCK Power TWI TWI clock
PA30 PAC1710_TWD Power TWI TWI data
– PAC1710_INT – Interrupt – to port expander U6
The PAC1934 is a four-channel power/energy monitor with current sensor amplifier and bus voltage monitors that
feed high resolution ADCs. Digital circuitry performs power calculations and energy accumulation. The PAC1934
enables energy monitoring with integration periods from 1 ms to up to 36 hours. Bus voltage, sense resistor voltage,
and accumulated proportional power are stored in registers for retrieval by the system master or embedded
controller. For more information about the PAC1934, refer to the product web page.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 12
Page 13

I2C ADR : 0010_111[R/W]
8.45k
0603
1%
R14
10k
0402
5%
R13
10k
0402
5%
R12
PAC1934_TWCK
PAC1934_TWD
VDDCORE
VDDIOM
VDD_3V3
PAC1934_INT
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R7
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R8
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R9
SENSE1_P
SENSE1_N
SENSE2_N
SENSE2_P
SENSE3_P
SENSE3_N
4.7uF
10V
0402
C13
0.1uF
50V
0402
C14
4.7uF
10V
0402
C15
0.1uF
50V
0402
C16
GND
GND
GND
VDD_3V3_LDOVDD_3V3_LDO
ADDRSEL
6
SLOW/ALERT
1
VDD
2
GND
3
VDD/IO
15
SENSE3-
7
SENSE3+
8
SENSE4-
9
SENSE4+
10
SENSE1+
11
SENSE1-
12
SENSE2+
13
SENSE2-
14
PWRDN
16
SM_DATA
5
SM_CLK
4
EP
17
U4 PAC1934
VDD_3V3_LDO
VDD_1V15
VDD_1V8
VDD_3V3
VDDIOM
VDDCORE
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R10
SENSE4_P
SENSE4_N
VDD_3V3 VDD_3V3_MPU
PIC1301
PIC1302
COC13
PIC1401
PIC1402
COC14
PIC1501
PIC1502
COC15
PIC1601
PIC1602
COC16
PIR701
PIR702
PIR703
PIR704
COR7
PIR801
PIR802
PIR803
PIR804
COR8
PIR901
PIR902
PIR903
PIR904
COR9
PIR1001
PIR1002
PIR1003
PIR1004
COR10
PIR1201
PIR1202
COR12
PIR1301
PIR1302
COR13
PIR1401
PIR1402
COR14
PIU401
PIU402
PIU403
PIU404
PIU405
PIU406
PIU407
PIU408
PIU409
PIU4010
PIU4011
PIU4012
PIU4013
PIU4014
PIU4015
PIU4016
PIU4017
COU4
PIVDD03V301
COVDD03V3
PIVDDCORE01
COVDDCORE
PIVDDIOM01
COVDDIOM
PIC1301
PIC1401
PIC1501
PIC1601
PIR1401
PIU403
PIU4017
PIR1301
PIU4016
PIR1402
PIU406
PIR1201
PIU401
POPAC19340INT
PIU404
POPAC19340TWCK
PIU405
POPAC19340TWD
PIR704
PIU4012
NLSENSE10N
PIR703
PIU4011
NLSENSE10P
PIR804
PIU4014
NLSENSE20N
PIR803
PIU4013
NLSENSE20P
PIR904
PIU407
NLSENSE30N
PIR903
PIU408
NLSENSE30P
PIR1004
PIU409
NLSENSE40N
PIR1003
PIU4010
NLSENSE40P
PIR701
PIR801
PIR901
PIR1002
PIC1302
PIC1402
PIC1502
PIC1602
PIR1001
PIR1202
PIR1302
PIU402
PIU4015
PIR902
PIVDD03V301
PIR802
PIVDDCORE01
PIR702
PIVDDIOM01
POPAC19340INT
POPAC19340TWCK
POPAC19340TWD
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Four current sense resistors are populated on board for measuring voltage and current consumption on the power
rails:
• 3.3V VDD_3V3_MPU - MPU on the 3.3V rail
• 3.3V VDD_3V3_SYS - rest of the system on the 3.3V rail
• 1.8V VDDIOM - MPU and DDR2 memory
• 1.15V VDDCORE – MPU core
Figure 3-7. PAC1934 Current Measurement
Table 3-2. PAC1934 Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared PIO Signal Description
PA31 PAC1934_TWCK Power TWI TWI clock
PA30 PAC1934_TWD Power TWI TWI data
– PAC1934_INT – Interrupt – to port expander U6
3.2 Processor
The SAM9X60 is a high-performance, ultra-low power ARM926EJ-S CPU-based embedded microprocessor (MPU)
running up to 600 MHz, with support for multiple memories such as SDRAM, LPSDRAM, LPDDR, DDR2, QSPI and
e.MMC Flash. The device integrates powerful peripherals for connectivity and user interface applications, and offers
security functions (tamper detection, etc.), TRNG, as well as high-performance crypto accelerators for AES and SHA.
Refer to the SAM9X60 datasheet for more information (see 1.2 Recommended Reading).
3.2.1 Power Supply
The PMIC (main regulator) provides all power supplies required by the SAM9X60 device:
• 1.15V for VDDCORE
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
Decoupling capacitors are placed close to the MPU power pins to stabilize the voltage rails.
• 1.8V for VDDIOM
• 3.3V for VDDIOP0, VDDIOP1, VDDANA, VDDNF, VDDQSPI, VDDIN33 and VDDBU
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 13
Page 14

Figure 3-8. Processor Power Supplies
GND
0.1uF16V0201
C32
0.1uF16V0201
C33
SAM9X60 P OWER SUPPLY
4.7uF10V0402
C31
VDDCORE
L6
VDDCORE
F6
VDDCORE
F11
VDDIOM
G14
VDDIOM
C10
VDDIOM
C13
VDDANA
C4
VDDIN33
P13
VDDOUT25
P10
VDDIN33
L11
GND
J8
GND
E7
GND
G12
GNDANA
B4
GNDIN33
R13
VDDNF
K14
VDDIOP0
G3
GND
E10
GND
B13
GND
K5
GND
G5
GND
N15
VDDQSPI
C7
VDDIOP0
K3
GND
H8
GND
H9
GNDIN33
M10
GND
K12
GND
T16
GND
A1
GND
A16
GND
T1
VDDBU
P7
GND
M7
VDDIOP1
N3
GND
N2
U5G
SAM9X6_TFBGA-228
VDDOUT25
VDDBU
VDDCORE
VDDIOM
0.1uF16V0201
C34
0.1uF16V0201
C36
0.1uF16V0201
C37
0.1uF16V0201
C38
0.1uF16V0201
C41
0.1uF16V0201
C42
0.1uF16V0201
C43
0.1uF16V0201
C44
0.1uF16V0201
C45
0.1uF16V0201
C46
0.1uF16V0201
C48
0.1uF16V0201
C49
4.7uF10V0402
C47
0.1uF16V0201
C50
0.1uF16V0201
C51
GND
4.7uF10V0402
C35
VDDIN33
VDDIN33
2.2uF10V0402
C52
4.7uF10V0402
C40
4.7uF10V0402
C39
0R 0402
R30
VDD_3V3_MPU
VDD_3V3_MPU
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
3.2.2 Main Configuration and Control
This block depicts the main block for processor configuration and control:
• XIN and XOUT are the Main Clock Oscillator input/output.
• XIN32 and XOUT32 are the Slow Clock Oscillator input/output.
• SHDN is an output signal used to enable and disable an external power supply circuit.
• WKUP is an event detection input pin used to wake up the processor from Shutdown state.
• JTAGSEL is an input that when pulled high enables the JTAG boundary scan.
• TCK, TDI, TDO, TMS and RTCK are used for JTAG communication.
• nRST is the processor main reset input.
• HHSD_A/B/C are the three USB ports embedded inside the MPU.
• RTUNE is used for USB external tuning.
• TST input is reserved for processor manufacturing tests.
• ADVREFP and ADVREFN are the positive and negative reference points for the embedded analog comparator.
A small low-pass filter is placed to reduce the input noise and improve accuracy.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 14
Page 15

Figure 3-9. Processor Main Configuration and Control
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TDI
JTAG_TDO
JTAG_TMS
JTAG_RTCK
USBA_N
USBA_P
USBB_N
USBB_P
USBC_N
USBC_P
0R
0402
R26
VDDBU
5.62k
0402 1%
R23
SHDN
WAKE_UP
XIN
XOUT
XIN32
XOUT3 2
GND
GND
SAM9X60 CONFIG
GND
1uF
10V
0201
C28
10R
0201
1%
R25
0R 0402
R22
DNP
VDD_3V3_MPU
MPU_nRST
XIN
R10
XOUT
T10
XIN32
T9
XOUT32
R9
SHDN
R11
WKUP
T11
JTAGSEL
P9
nRST
R1
TST
J9
HHSDPA
T12
HHSDMA
R12
HHSDPB
T13
HHSDMB
T14
HHSDPC
P12
HHSDMC
N12
TCK
R3
TDI
F3
TDO
H5
TMS
F5
RTCK
T2
ADVREFP
D5
RTUNE
P11
ADVREFN
C5
U5F
SAM9X6_TFBGA-228
0.1uF
50V
0402
C29
GND
TP2
VDD_3V3
GND
XIN
GND
24MHz
18pF
ABM8G-24.000MHZ-18-D2Y-T
Y1
DNP
27pF
0402
C24
DNP
27pF0402
C25
DNP
1M
0402
5%
R21
DNP
STB
1
GND
2
OUT
3
VDD
4
24MHz
DSC1001CI5-024.0000
Y3
GND
XOUT
0R
0402
R28
32.768Khz
ABS06-32.768KHZ-T
Y2
GND
XIN32
XOUT32
20pF
0402
C26
20pF0402
C27
1M
0402
5%
R24
DNP
0R
0402
R27
DNP
0R
0402
R91
DNP
XIN
XOUT
51R
0402
R149
3.2.3 Clock Circuitry
The embedded MPU generates its necessary clocks based on two oscillators: one slow clock (SLCK) oscillator
running at 32.768 kHz and one main clock oscillator running at 24 MHz.
The main clock oscillator is implemented with a MEMS (Micro Electro-Mechanical System) device DSC1001.
For evaluation purposes, we leave users the freedom to mount a crystal instead, using the PCB footprint reservation
(Y1). In that case, resistors R149 and R28 should be removed, resistors R27 and R91 should be populated and
capacitors C24 and C25 should be populated with the appropriate load capacitance for the selected crystal.
Figure 3-10. Processor Clock Circuitry
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 15
Page 16
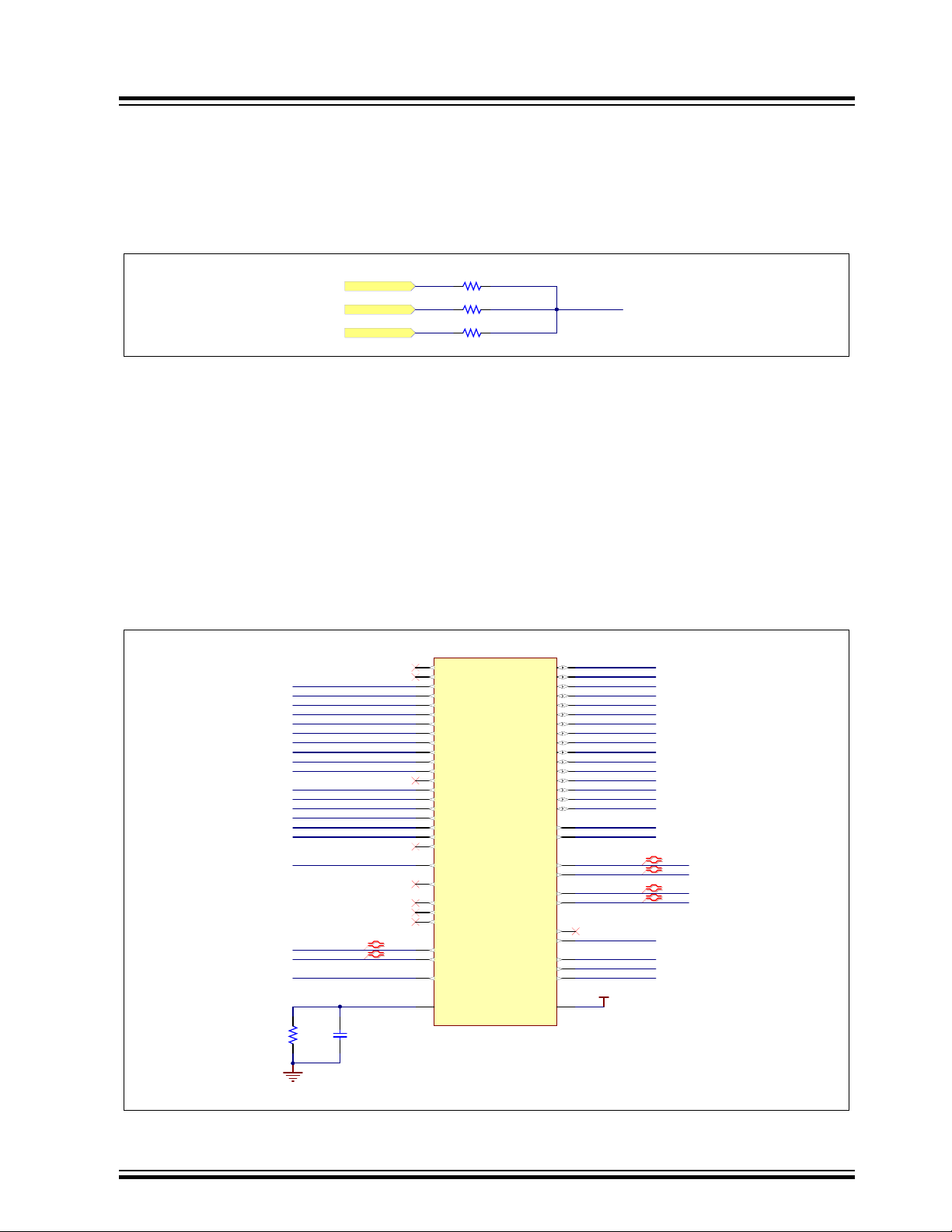
3.2.4 Reset Circuitry
MIC2800_nRST
JTAG_nRST
100R 04021%
R185
100R 04021%
R190
100R 04021%
R191
USER_nRST
MPU_nRST
DDR_A2
DDR_A3
DDR_A4
DDR_A5
DDR_A6
DDR_A7
DDR_A8
DDR_A9
DDR_A10
DDR_A11
DDR_A13
DDR_A14
DDR_A15
DDR_D3
DDR_D6
DDR_D4
DDR_D1
DDR_D5
DDR_D2
DDR_D7
DDR_D0
DDR_D12
DDR_D15
DDR_D13
DDR_D8
DDR_D9
DDR_D10
DDR_D14
DDR_D11
DDR_DQM0
DDR_DQM1
DDR_DQS0_P
DDR_DQS0_N
DDR_DQS1_P
DDR_DQS1_N
DDR_RAS
DDR_CAS
DDR_WE
DDR_CS
DDR_CLK_P
DDR_CLK_N
DDR_CKE
22pF
50V
0402
C62
DDR_A16
DDR_A17
DDR_A18
20k
0402
1%
R119
GND
DDR_SDA10
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
SDCKn
B14
SDCK
A15
SDCKE
F13
nWR0
E8
SDA10
D12
nRD
F12
nWR1
A10
DDR_CAL
B8
A1
G16
A15
G15
A8
F16
A4
B12
A0
B10
A13
B11
A10
C11
A6
A12
A2
A13
A17
F14
A12
A11
A19
H14
A16
E14
A18
C16
A3
D15
A7
B16
A5
E11
A14
C15
A9
D14
A11
E13
D10
F9
D9
D8
D13
B9
D14
D11
D6
J16
D11
A9
D8
G9
D12
F10
D3
H11
D4
J14
D1
H10
D7
J13
D0
H16
D2
H15
D5
J11
D15
C9
DDR_VREF
A14
nCS1
E16
nCS0
F15
DQS1
D9
SDWE
D16
nDQS1
E9
RAS
E15
nDQS0
H13
DQS0
H12
CAS
C12
DQM1
C8
DQM0
G11
nWR3
L14
U5E
SAM9X6_TFBGA-228
DDR_VREF
Three reset sources for the SAM9X60 MPU are placed on the board:
• Power-on Reset from the power management unit MIC2800
• User push button reset SW3
• External JTAG or J-Link-OB reset from an in-circuit emulator
Figure 3-11. Processor Reset Circuitry
3.2.5 DDR Controller (MPDDRC)
The SAM9X60 embeds a Multi-Port DDR-SDRAM Controller (MPDDRC) to drive DDR2 and LPDDR1 memories.
Note the following regarding the command and control signal connections between the DDR Controller and the DDR
Memory:
• Addresses A0, A1 and A12 are not used on the controller side.
• Addresses A2 to A11 are connected to A0 to A9 on the memory side.
• Signal SDA10 must be connected to A10.
• Addresses A13 to A15 are connected to the last three addresses on the memory side.
• A16 to A18 are connected to BA0 to BA2.
It is recommended to double-check the design schematic against the information provided in the datasheet.
Figure 3-12. Processor DDR Controller
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 16
Page 17

4.7k
0201
1%
R120
4.7k
0201
1%
R121
0.1uF
16V
0201
C63
0.1uF
16V
0201
C66
GND
4.7uF
10V
0402
C65
GND
VDDIOM
DDR_VREF
LCD_D17_PC17
LCD_D18_PC18
LCD_D19_PC19
LCD_D20_PC20
LCD_D21_PC21
LCD_D22_PC22
LCD_D23_PC23
LCD_PCLK_PC30
LCD_VSYNC/CS_PC27
LCD_HSYNC/WE_PC28
LCD_DATA_ENABLE_PC29
LCD_IRQ1_PC25
LCD_PWM_PC26
FLEXCOM5_IO1_RX_PA21
FLEXCOM5_IO0_TX_PA22
SDMMC0_DAT2_PA19
SDMMC0_CMD_PA16
SDMMC0_DAT3_PA20
SDMMC0_CLK_PA17
SDMMC0_DAT0_PA15
SDMMC0_DAT1_PA18
SDMMC0_CD_PA23
CLASSD_L0_PA24
CLASSD_L1_PA25
CLASSD_L2_PA26
CLASSD_L3_PA27
WILC3000_ENABLE_PA29
WILC3000_INTERRUPT_PA28
CAN/FLEXCOM_RX_PA06
CAN/FLEXCOM_TX_PA05
FLEXCOM0_IO0_PA00
FLEXCOM0_IO1_PA01
FLEXCOM6_TWD_PA30
FLEXCOM6_TWCK_PA31
CAN/DBGU_TX_PA10
CAN/DBGU_RX_PA09
PA02
PA03
PA04
PA07
PA08
PA11
PA12
PA13
PA14
PC31
SAM9X60 PORT PA
SAM9X60 PORT PC
LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12
LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13
LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14
LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15
LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00
LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02
LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04
LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06
LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08
LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10
LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01
LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03
LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05
LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07
LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09
LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11
LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24
LCD_D16_ISI_nRST_PC16
PA0
P2
PA1
M3
PA2
P1
PA3
L3
PA4
N1
PA5
L4
PA6
M2
PA7
K6
PA8
M1
PA9
G8
PA10
L2
PA11
H7
PA12
L1
PA13
J6
PA14
K1
PA15
H6
PA16
K2
PA17
J3
PA18
J1
PA19
J5
PA20
J2
PA21
G6
PA22
G1
PA23
J4
PA24
F8
PA25
H1
PA26
F7
PA27
H2
PA28
F1
PA29
H3
PA30
G2
PA31
H4
U5A
SAM9X6_TFBGA-228
PC0
M4
PC1
P4
PC2
N5
PC3
P5
PC4
L5
PC5
R4
PC6
M6
PC7
T3
PC8
N8
PC9
T4
PC10
P6
PC11
N6
PC12
R5
PC13
L7
PC14
T5
PC15
J7
PC16
R6
PC17
K8
PC18
T6
PC19
L8
PC20
P8
PC21
M8
PC22
R7
PC23
K9
PC24
R8
PC25
L9
PC26
T8
PC27
M9
PC28
N9
PC29
L10
PC30
T7
PC31
M13
U5C
SAM9X6_TFBGA-228
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
The MPDDRC I/Os embed an automatic impedance matching control to avoid overshoots and to reach the best
performance levels depending on the bus load and external memories. A serial termination connection scheme,
where the driver has an output impedance matched to the characteristic impedance of the line, is used to improve
signal quality and reduce EMI. This is done using the ZQ calibration procedure to calibrate the SAM9X60 DDR I/O
drive strength. The pin name where the ZQ resistor must be connected is DDR_CAL and, as indicated in the
SAM9X60 datasheet for DDR2 case, the resistor value is 20 KOhms.
The DDR_VREF pin serves as a voltage reference input for the DDR I/Os when DDR2 or LPDDR external SDRAM
memories are used.
Figure 3-13. DDR Reference Voltage
3.2.6 PIOs
The following sections depict all the signals connected to the SAM9X60 MPU ports.
See Table 3-3 for details about each port’s functions.
Figure 3-14. Processor PIOs PA and PC
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 17
Page 18

LCD_IRQ2_PB17
ETH0_TXCK_PB04
ETH0_TX0_PB09
ETH0_TXEN_PB07
ETH0_TX1_PB10
ETH0_RX1_PB01
ETH0_RX0_PB00
ETH0_RXER_PB02
ETH0_RXDV_PB03
ETH0_MDC_PB06
ETH0_MDIO_PB05
ETH0_IRQ_PB08
NAND_IO0_PD06
NAND_IO1_PD07
NAND_IO2_PD08
NAND_IO3_PD09
NAND_IO4_PD10
NAND_IO5_PD11
NAND_IO6_PD12
NAND_IO7_PD13
NAND_CLE_PD03
NAND_ALE_PD02
NAND_nWE_PD01
NAND_nRE_PD00
NAND_nCS_PD04
NAND_RB_PD05
USBB_EN_5V_PD15
USBC_EN_5V_PD16
MBUS_AD4_PB15
USBA_VBUSDETECT_PB16
MBUS_RST_PB14
NRST_PB25
SEL_FNCT1_PD19
SEL_FNCT2_PD20
MCP23008_INT_PD17
PB19
PB20
PB21
PB22
PB23
PB24
MBUS_INT_PB18
PB11
PB12
PB13
CAN_STBY_PD21
SAM9X60 PORT PB
SAM9X60 PORT PD
LCD_ID_PD14
USER_BUTTON_PD18
PB0
F4
PB1
C1
PB2
D3
PB3
D1
PB4
E3
PB5
E1
PB6
D2
PB7
A5
PB8
E6
PB9
A2
PB10
A3
PB11
D6
PB12
C2
PB13
A4
PB14
F2
PB15
B5
PB16
B3
PB17
B1
PB18
E4
PB19
C6
PB20
A6
PB21
A7
PB22
B7
PB23
B6
PB24
A8
PB25
E2
U5B
SAM9X6_TFBGA-228
PD0
R14
PD1
T15
PD2
P15
PD3
N14
PD4
R16
PD5
N11
PD6
K16
PD7
J12
PD8
K15
PD9
J10
PD10
L16
PD11
K11
PD12
L15
PD13
J15
PD14
L12
PD15
M16
PD16
M14
PD17
N16
PD18
L13
PD19
P16
PD20
M11
PD21
M15
U5D
SAM9X6_TFBGA-228
22R 0402 1%
R31
22R 0402 1%
R32
22R 0402 1%
R38
22R 0402 1%
R39
22R 0402 1%
R40
22R 0402 1%
R41
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT3_PA04
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT2_PA03
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT1_PA02
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT0_PA11
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CMD_PA12
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CK_PA13
FLEXCOM5_IO4_BT_RTS_PA07
FLEXCOM5_IO3_BT_CTS_PA08
PA02
PA03
PA04
PA07
PA08
PA11
PA12
PA13
PA14
22R 0402 1%
R42
22R 0402 1%
R43
22R 0402 1%
R44
22R 0402 1%
R45
22R 0402 1%
R46
22R 0402 1%
R50
22R 0402 1%
R51
22R 0402 1%
R52
22R 0402 1%
R53
22R 0402 1%
R54
22R 0402 1%
R55
22R 0402 1%
R56
22R 0402 1%
R57
22R 0402 1%
R58
22R 0402 1%
R59
EXT40_GPIO_PA02
EXT40_GPIO_PA03
EXT40_GPIO_PA04
EXT40_SPI_MOSI_PA12
EXT40_SPI_MISO_PA11
EXT40_SPI_SCLK_PA13
EXT40_GPIO_PA14
EXT40_NPCS1_PA07
EXT40_NPCS2_PA08
MBUS_NPCS0_PA14
MBUS_SPCK_PA13
MBUS_MISO_PA11
MBUS_MOSI_PA12
QSPI_IO0_PB21
QSPI_IO1_PB22
QSPI_IO2_PB23
QSPI_IO3_PB24
QSPI_SCK_PB19
QSPI_CS_PB20
22R 0402 1%
R69
22R 0402 1%
R70
22R 0402 1%
R71
22R 0402 1%
R72
PB19
PB20
PB21
22R 0402 1%
R74
22R 0402 1%
R75
22R 0402 1%
R77
22R 0402 1%
R79
22R 0402 1%
R80
22R 0402 1%
R81
PB22
PB23
PB24
PC31
EXT40_I2SMCK_PB23
EXT40_CLK1_PC31
EXT40_I2SWS_PB20
EXT40_I2SCK_PB19
EXT40_GPIO_PB24
EXT40_I2SDIN_PB21
EXT40_I2SDOUT_PB22
ETH0_PCK1_PC31
LED_RED_PB11
LED_GREEN_PB12
LED_BLUE_PB13
EXT40_CLK2_PB13
EXT40_PWM1_PB12
EXT40_PWM0_PB11
0R 0402
R66
0R 0402
R63
0R 0402
R60
PB11
PB12
PB13
MBUS_PWM_PB13
0R 0402
R65
22R 0402 1%
R82
22R 0402 1%
R85
22R 0402 1%
R86
22R 0402 1%
R88
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Figure 3-15. Processor PIOs PB and PD
Some of the ports were multiplexed to accommodate more devices on the evaluation kit and to showcase all the
functions the SAM9X60 MPU can address off a single PIO wire.
Most of the ports that share multiple functions are split through passive resistors placed on the board as close to the
MPU as possible, therefore no other hardware change must be made. In most cases, the user can use only one of
their functions at a time, or can develop a composite driver enabling the use of multiple functions at the same time.
Figure 3-16. Processor PIO Muxing
Table 3-3. Processor PIOs Pin Assignment and Signal Description
Pad Power Rail Function I/O Type
PA0 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) FLEXCOM0_IO0
PA1 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) FLEXCOM0_IO1
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
TWI Data (TWD) bidirectional line shared between the LCD,
EEPROMs and external 40-pin header
TWI Clock (TWCK) output line shared between the LCD, EEPROMs
and external 40-pin header
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 18
Page 19

...........continued
Pad Power Rail Function I/O Type
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
PA2 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA3 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA4 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA51VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA61VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA7 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA8 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
SDMMC1_DAT1
GPIO GPIO going to the external 40-pin header
FLEXCOM0_IO3
GPIO GPIO going to the external 40-pin header
FLEXCOM0_IO2
GPIO GPIO going to the external 40-pin header
FLEXCOM1_IO0 UART Transmit (TX) output line going to the external 40-pin header
CANTX1
FLEXCOM1_IO1 UART Receive (RX) input line going to the external 40-pin header
CANRX1
FLEXCOM4_IO4 First SPI Chip Select (nCS) output line for the external 40-pin header
FLEXCOM5_IO4 SPI Request to Send (RTS) output line for the BT module
FLEXCOM4_IO5
FLEXCOM5_IO3 SPI Clear to Send (CTS) input line for the BT module
SDIO Data 1 (I/O1) bidirectional line for the ATWILC3000 Wi-Fi/BT
module
SDIO Data 2 (I/O2) bidirectional line for the ATWILC3000 Wi-Fi/BT
module
SDIO Data 3 (I/O3) bidirectional line for the ATWILC3000 Wi-Fi/BT
module
CAN Transmit (CANTX) output line going to the second CAN
transceiver MCP2542
CAN Receive (CANRX) input line going to the second CAN
transceiver MCP2542
Second SPI Chip Select (nCS) output line for the external 40-pin
header
PA92VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA102VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA11 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA12 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA13 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
PA14 VDDIOP0 (3.3V)
DRXD DEBUG UART Receive (DRX) input line
CANRX0
DTXD DEBUG UART Transmit (DTX) input line
CANTX0
FLEXCOM4_IO1
SDMMC1_DAT0
FLEXCOM4_IO0
SDMMC1_CMD
FLEXCOM4_IO2
SDMMC1_CK
FLEXCOM4_IO3 SPI Chip Select (nCS) output line for the mikroBUS connector
GPIO GPIO going to the external 40-pin header
CAN Receive (CANRX) input line going to the first CAN transceiver
MCP2542
CAN Transmit (CANTX) output line going to the first CAN transceiver
MCP2542
SPI Master Input Slave Output (MISO) input line shared between the
mikroBUS and external 40-pin connectors
SDIO Data 0 (I/O0) bidirectional line going to the ATWILC3000 WiFi/BT module
SPI Master Output Slave Input (MOSI) output line shared between the
mikroBUS and external 40-pin connectors
SDIO Command (CMD) bidirectional line going to the ATWILC3000
Wi-Fi/BT module
SPI Source Clock (SCLK) output line shared between the mikroBUS
and external 40-pin connectors
SDIO Data 0 (I/O0) bidirectional line going to the ATWILC3000 WiFi/BT module
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 19
Page 20

SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
...........continued
Pad Power Rail Function I/O Type
PA15 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) SDMMC0_DAT0 SDIO Data 0 (I/O0) bidirectional line going to the SD card connector
PA16 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) SDMMC0_CMD
PA17 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) SDMMC0_CK SDIO Clock (CLK) output line going to the SD card connector
PA18 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) SDMMC0_DAT1 SDIO Data 1 (I/O1) bidirectional line going to the SD card connector
PA19 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) SDMMC0_DAT2 SDIO Data 2 (I/O2) bidirectional line going to the SD card connector
PA20 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) SDMMC0_DAT3 SDIO Data 3 (I/O3) bidirectional line going to the SD card connector
PA21 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) FLEXCOM5_IO1
PA22 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) FLEXCOM5_IO0
PA23 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) GPIO
PA24 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) CLASSD_L0 CLASSD Left Output L0
PA25 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) CLASSD_L1 CLASSD Left Output L1
PA26 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) CLASSD_L2 CLASSD Left Output L2
PA27 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) CLASSD_L3 CLASSD Left Output L3
PA28 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) GPIO / WKUP4
PA29 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) GPIO
SDIO Command (CMD) bidirectional line going to the SD card
connector
UART Receive (RX) input line shared between the mikroBUS
connector and the BT transceiver on the ATWILC3000 module
UART Transmit (TX) output line shared between the mikroBUS
connector and the BT transceiver on the ATWILC3000 module
GPIO used as input to detect when an SD card has been inserted in
the SD connector
GPIO Input used to signal any interrupt coming from the WILC300 WiFi/BT module
GPIO Output used to enable the WILC300 Wi-Fi/BT module by
enabling its power supply
PA30 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) FLEXCOM6_IO0
PA31 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) FLEXCOM6_IO1
PB0 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_RX0 RMII Ethernet Receive Data 0 signal going to KSZ8081
PB1 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_RX1 RMII Ethernet Receive Data 1 signal going to KSZ8081
PB2 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_RXER RMII Ethernet Receive Error signal going to KSZ8081
PB3 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_RXDV RMII Ethernet Receive Data Valid signal going to KSZ8081
PB4 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_TXCK RMII Ethernet Transmit Clock signal going to KSZ8081
PB5 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_MDIO RMII Ethernet Management Data I/O signal going to KSZ8081
PB6 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_MDC RMII Ethernet Management Data Clock signal going to KSZ8081
PB7 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_TXEN RMII Ethernet Receive Data Valid signal going to KSZ8081
PB8 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_TXER RMII Ethernet Transmit Coding Error signal going to KSZ8081
PB9 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_TX0 RMII Ethernet Transmit Data 0 signal going to KSZ8081
PB10 VDDANA (3.3V) E0_TX1 RMII Ethernet Transmit Data 1 signal going to KSZ8081
PB11 VDDANA (3.3V) PWM0
TWI Data (TWD) bidirectional signal shared between PAC1934,
PAC1710, MPC23008 and the mikroBUS connector
TWI Clock (TWCK) Bidirectional signal shared between PAC1934,
PAC1710, MPC23008 and the mikroBUS connector
PWM signal shared between the LD1 red LED and the 40-pin
connector
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 20
Page 21

...........continued
Pad Power Rail Function I/O Type
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
PB12 VDDANA (3.3V) PWM1
PB13 VDDANA (3.3V) PWM2
PB14 VDDANA (3.3V) GPIO GPIO output used as the reset signal for the mikroBUS connector
PB15 VDDANA (3.3V) AD4 Analog input for the mikroBUS connector
PB16 VDDANA (3.3V) GPIO
PB17 VDDANA (3.3V) GPIO GPIO input used to signal any interrupt request from the LCD
PB18 VDDANA (3.3V) GPIO
QSCK QSPI Serial Clock (SCK) signal going to SST26VF064B
PB19 VDDQSPI (3.3V)
I2SMCC_CK I2S Bit Clock (CK) signal going to the 40-pin connector
QCS QSPI Chip Select (CS) signal going to SST26VF064B
PB20 VDDQSPI (3.3V)
I2SMCC_WS I2S Word Select (WS) signal going to the 40-pin connector
QIO0 QSPI Data I/O 0 (IO0) signal going to SST26VF064B
PB21 VDDQSPI (3.3V)
I2SMCC_DIN0 I2S Data IN 0 (DIN0) signal going to the 40-pin connector
QIO1 QSPI Data I/O 1 (IO1) signal going to SST26VF064B
PB22 VDDQSPI (3.3V)
I2SMCC_DOUT0 I2S Data Out 0 (DOUT0) signal going to the 40-pin connector
PWM signal shared between the LD1 green LED and the 40-pin
connector
PWM signal shared between the LD1 blue LED, the mikroBUS and
the 40-pin connectors
GPIO input used to detect if the board has been connected to a host
on the USBA port
GPIO input used to signal any interrupt request from the mikroBUS
connector
PB23 VDDQSPI (3.3V)
PB24 VDDQSPI (3.3V)
PB25 VDDIOP0 (3.3V) NRST_OUT Output signal used to reset all the devices on the board
PC0 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC1 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC2 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC3 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
QIO2 QSPI Data I/O 2 (IO2) signal going to SST26VF064B
I2SMCC_MCK I2S Master Clock (MCK) signal going to the 40-pin connector
QIO3 QSPI Data I/O 3 (IO3) signal going to SST26VF064B
GPIO GPIO signal going to the 40-pin connector
LCDDAT0 LCD Data Output 0 (DAT0) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_D0
LCDDAT1 LCD Data Output 1 (DAT1) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_D1
LCDDAT2 LCD Data Output 2 (DAT2) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_D2
LCDDAT3 LCD Data Output 3 (DAT3) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_D3
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 0 (D0) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 1 (D1) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 2 (D2) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 3 (D3) signal going to the ISI
connector
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 21
Page 22

...........continued
Pad Power Rail Function I/O Type
LCDDAT4 LCD Data Output 4 (DAT4) signal going to the LCD connector
PC4 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
ISI_D4
LCDDAT5 LCD Data Output 5 (DAT5) signal going to the LCD connector
PC5 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
ISI_D5
LCDDAT6 LCD Data Output 6 (DAT6) signal going to the LCD connector
PC6 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
ISI_D6
LCDDAT7 LCD Data Output 7 (DAT7) signal going to the LCD connector
PC7 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
ISI_D7
LCDDAT8 LCD Data Output 8 (DAT8) signal going to the LCD connector
PC8 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
ISI_D8
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 4 (D4) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 5 (D5) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 6 (D6) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 7 (D7) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 8 (D8) signal going to the ISI
connector
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
PC9 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC10 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC11 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC12 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC13 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC14 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
PC15 VDDIOP1 (3.3V)
LCDDAT9 LCD Data Output 9 (DAT9) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_D9
LCDDAT10 LCD Data Output 10 (DAT10) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_D10
LCDDAT11 LCD Data Output 11 (DAT11) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_D11
LCDDAT12 LCD Data Output 12 (DAT12) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_PCK
LCDDAT13 LCD Data Output 13 (DAT13) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_VSYNC
LCDDAT14 LCD Data Output 14 (DAT14) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_HSYNC
LCDDAT15 LCD Data Output 15 (DAT15) signal going to the LCD connector
ISI_MCK
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 9 (D9) signal going to the ISI
connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 10 (D10) signal going to the
ISI connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 11 (D11) signal going to the
ISI connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Data Input 12 (D12) signal going to the
ISI connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Vertical Synchronization (VSYNC) signal
going to the ISI connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Horizontal Synchronization (HSYNC)
signal going to the ISI connector
Image Sensor Interface (ISI) Main Clock (MCK) signal going to the ISI
connector
PC16 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT16 LCD Data Output 16 (DAT16) signal going to the LCD connector
PC17 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT17 LCD Data Output 17 (DAT17) signal going to the LCD connector
PC18 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT18 LCD Data Output 18 (DAT18) signal going to the LCD connector
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 22
Page 23

SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
...........continued
Pad Power Rail Function I/O Type
PC19 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT19 LCD Data Output 19 (DAT19) signal going to the LCD connector
PC20 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT20 LCD Data Output 20 (DAT20) signal going to the LCD connector
PC21 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT21 LCD Data Output 21 (DAT21) signal going to the LCD connector
PC22 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT22 LCD Data Output 22 (DAT22) signal going to the LCD connector
PC23 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDAT23 LCD Data Output 23 (DAT23) signal going to the LCD connector
PC24 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDISP
PC25 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) GPIO
PC26 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDPWM
PC27 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDVSYNC
PC28 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDHSYNC
PC29 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDDEN LCD Data Enable (EN) output signal going to the LCD connector
PC30 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) LCDPCK LCD Pixel Clock (PCK) output signal going to the LCD connector
PC31 VDDIOP1 (3.3V) PCK1
PD0 VDDNF (3.3V) NANDOE
PD1 VDDNF (3.3V) NANDWE
PD2 VDDNF (3.3V) A21/NANDALE
LCD Display ON/OFF (DISP) output signal going to the LCD
connector
GPIO input used to signal any interrupt request from the LCD
connector
LCD PWM for Contrast Control (PWM) output signal going to the LCD
connector
LCD Vertical Synchronization (VSYNC) output signal going to the
LCD connector
LCD Horizontal Synchronization (HSYNC) output signal going to the
LCD connector
Programmable Clock Output that can be used as a clock source for
either the RMII Ethernet PHY KSZ8081 or the 40-pin connector
NAND Flash Output Enable (OE) output signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Write Enable (OE) output signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Address Latch Enable (ALE) output signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
PD3 VDDNF (3.3V) A22/NANDCLE
PD4 VDDNF (3.3V) NCS3
PD5 VDDNF (3.3V) NWAIT
PD6 VDDNF (3.3V) D16
PD7 VDDNF (3.3V) D17
PD8 VDDNF (3.3V) D18
PD9 VDDNF (3.3V) D19
PD10 VDDNF (3.3V) D20
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
NAND Flash Command Latch Enable (CLE) output signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Chip Select (CLE) output signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Ready/busy# (R/B#) input pin provides a hardware
method of detecting PROGRAM or ERASE cycle completion from
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Data 0 (D0) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Data 1 (D1) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Data 2 (D2) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Data 3 (D3) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Data 4 (D4) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 23
Page 24

...........continued
Pad Power Rail Function I/O Type
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
PD11 VDDNF (3.3V) D21
PD12 VDDNF (3.3V) D22
PD13 VDDNF (3.3V) D23
PD14 VDDNF (3.3V) GPIO
PD15 VDDNF (3.3V) GPIO GPIO used as output for enabling the 5V supply on the USBB port
PD16 VDDNF (3.3V) GPIO GPIO used as output for enabling the 5V supply on the USBC port
PD17 VDDNF (3.3V) GPIO
PD18 VDDNF (3.3V) GPIO GPIO used as input to probe the changes of the user button
PD19 VDDNF (3.3V) GPIO
PD20 VDDNF (3.3V) GPIO
NAND Flash Data 5 (D5) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Data 6 (D6) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
NAND Flash Data 7 (D7) Bidirectional signal going to
MT29F4G08ABAEA
GPIO used to identify the type of LCD connected by reading the
information stored on an EEPROM placed on the LCD through the
OneWire interface
GPIO used as input to signal any interrupt request from the
MCP23008 GPIO expander
GPIO used as output for selecting between the functions of PA05 and
(1)
PA06
HIGH = UART to 40-pin connector LOW = CAN1 communication
GPIO used as output for selecting between the functions of PA10 and
(2)
PA09
HIGH = Enable DEBUG UART
LOW = CAN0 communication
PD21 VDDNF (3.3V) D31
Note:
1. The selection of the functions of ports PA5 and PA6 must also comply with the state of PD19 as this signal
commands an analog switch placed on the board.
2. The selection of the functions of ports PA9 and PA10 must also comply with the state of PD20 as this signal
commands an analog switch placed on the board.
3.2.7 Dedicated Two-wire Interfaces
The SAM9X60-EK features two dedicated TWIs to access the devices present on board.
The TWI interface uses only two lines, namely serial data (TWD) and serial clock (TWCK). According to the standard,
the TWI clock rate is limited to 400 kHz in Fast mode and 100 kHz in Normal mode, but a configurable baud rate
generator permits the output data rate to be adapted to a wide range of core clock frequencies. The TWI supports
both Master and Slave modes.
One interface is used to access the devices placed in the lower left side of the board:
• The PAC1934 voltage monitor (address: 0010_111[R/W])
• The PAC1710 voltage monitor (address: 1001_101[R/W])
• The MCP23008 Port Expander (address: 0100_000[R/W])
• And any device placed on the mikroBUS connector
GPIO used as output to place the CAN transceivers in or out of
standby
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 24
Page 25

MCP23008_TWD
MCP23008_TWCK
FLEXCOM6_TWD_PA30
FLEXCOM6_TWCK_PA31
22R 0402 1%
R87
22R 0402 1%
R89
22R 0402 1%
R90
22R 0402 1%
R93
22R 0402 1%
R94
22R 0402 1%
R95
2.2k
0402
5%
R84
2.2k
0402
5%
R83
VDD_3V3 VDD_3V3
22R 0402 1%
R92
22R 0402 1%
R96
PAC1934_TWCK
PAC1934_TWD
PAC1710_TWCK
PAC1710_TWD
MBUS_TWD
MBUS_TWCK
FLEXCOM0_IO0_PA00
FLEXCOM0_IO1_PA01
22R 0402 1%
R64
22R 0402 1%
R67
22R 0402 1%
R68
22R 0402 1%
R73
22R 0402 1%
R76
22R 0402 1%
R78
2.2k
0402
5%
R62
2.2k
0402
5%
R61
VDD_3V3 VDD_3V3
EEPROM_TWCK
EEPROM_TWD
EXT40_TWD
EXT40_TWCK
LCD_ISI_TWD
LCD_ISI_TWCK
SAM9X60-EK
Figure 3-17. Board Lower Left TWI Interface
The second interface is used to access the devices placed in the upper right side of the board:
• The 24AA025E48 serial EEPROM (address: 1010_011[R/W])
• The LCD or camera connected on the ISI connector
• And any device connected on the external 40-pin connector
Figure 3-18. Board Upper Right TWI Interface
Function Blocks
3.2.8 I/O Expander
The SAM9X60-EK features an 8-bit I/O expander with serial TWI interface MCP23008.
The MCP23008 consists of multiple 8-bit configuration registers for input, output and polarity selection. The system
master can enable the I/Os as either inputs or outputs by writing the I/O configuration bits.
The data for each input or output is kept in the corresponding input or output register. The polarity of the Input Port
register can be inverted with the Polarity Inversion register. All registers can be read by the system master.
The interrupt output can be configured to activate under two (mutually exclusive) conditions:
• When any input state differs from its corresponding input port register state (indicating to the system master that
an input state has changed)
• When an input state differs from a preconfigured register value
The Interrupt Capture register captures port values at the time of the interrupt, thereby saving the condition that
caused the interrupt.
The Power-on Reset (POR) sets the registers to their default values and initializes the device state machine.
The MCP23008 communicates with the MPU via a TWI bus.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 25
Page 26

Figure 3-19. Processor IO Expander
EXT40_GP7
EXT40_GP6
EXT40_GP5
USBB_OVCU
R
USBC_OVCU
R
PAC1934_INT
PAC1710_INT
MCP23008_TWCK
MCP23008_TW
D
VDD_3V3
GND
VDD_3V3
MCP23008_INT_PD17
NRST_PB25
GND
0.1uF
50V
040
2
C53
100
k
040
2
5
%
R35
DNP
100
k
040
2
5
%
R36
DNP
100
k
040
2
5
%
R37
DNP
100
k
040
2
5
%
R49
100
k
040
2
5
%
R48
100
k
040
2
5
%
R47
100
k
040
2
5
%
R34
10k
040
2
5
%
R33
I2C ADR : 0100_000[R/W]
A
2
1
A
1
2
A
0
3
RESET
4
GP6
1
5
GP7
1
6
VSS
1
7
VDD
1
8
N
C
5
N
C
6
INT
7
N
C
8
GP0
9
GP5
1
4
GP4
1
3
GP3
1
2
GP2
1
1
GP1
1
0
SCL
1
9
SDA
2
0
E
P
2
1
MCP2300
8
U
6
Table 3-4. I/O Expander Signal Descriptions
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
PIO Signal Name Signal Description
GP0 PAC1710_INT PAC1710 interrupt to MPU
GP1 PAC1934_INT PAC1934 interrupt to MPU
GP2 – –
GP3 USBB_OVCUR USB B overcurrent indicator
GP4 USBC_OVCUR USB C overcurrent indicator
GP5 EXT40_GP5 Free use GPIO
GP6 EXT40_GP6 Free use GPIO
GP7 EXT40_GP7 Free use GPIO
INT MCP23008_INT_PD17 MCP23008 Interrupt to MPU
RESET – nRST
SCL MCP23008_TWCK MCP23008 TWI clock
SDA MCP23008_TWD MCP23008 TWI data
3.2.9 Special Function Selectors
Some ports shared between different interfaces are separated using dedicated signal buffers to avoid any possible
interference on the lines.
Ports PA05 and PA06 are shared between the CAN1 transceiver and a UART interface going to the 40-pin connector.
The selection is done using port PD19:
• HIGH = UART to 40-pin connector
• LOW = CAN1 communication
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 26
Page 27

GND
GND
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
GND
GND
22R 0402 1%
R140
22R 0402 1%
R142
22R 0402 1%
R144
22R 0402 1%
R146
SEL_FNCT1_PD19
CAN/FLEXCOM_RX_PA06
CAN/FLEXCOM_TX_PA05
EXT40_TXD
EXT40_RXD
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ126USG
U16
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ125USG
U14
0.1uF
50V0402
C102
0.1uF
50V0402
C104
CAN1_TX
CAN1_RX
GND
GND
22R 0402 1%
R141
22R 0402 1%
R143
22R 0402 1%
R145
22R 0402 1%
R147
SEL_FNCT2_PD20
DBGU_TX_PA10
DBGU_RX_PA09
CAN/DBGU_TX_PA10
CAN/DBGU_RX_PA09
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ126USG
U17
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ125USG
U15 VDD_3V3
GND
VDD_3V3
GND
0.1uF
50V0402
C103
0.1uF
50V0402
C105
CAN0_TX
CAN0_RX
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Figure 3-20. Selection between CAN1 or EXT40 UART
Ports PA09 and PA10 are shared between the CAN0 transceiver and the DEBUG UART interface going to the
DEBUG connector. The selection is done using port PD20:
• HIGH = DEBUG UART communication
• LOW = CAN0 communication
Figure 3-21. Selection between CAN0 or DBGU UART
Ports PA21 and PA22 are shared between a UART interface going to the mikroBUS connector and the UART
interface used to access and configure the Bluetooth functions of the ATWILC3000 module. The selection is done
using port PA29:
• HIGH = ATWILC3000 UART communication
• LOW = MikroBUS CAN communication
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 27
Page 28

Figure 3-22. Selection between mikroBUS UART or ATWILC3000 Bluetooth UART
FLEXCOM5_IO1_RX_PA21
FLEXCOM5_IO0_TX_PA22
GND
GND
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
GND
GND
MBUS_RX
MBUS_TX
22R 0402 1%
R156
22R 0402 1%
R157
22R 0402 1%
R158
22R 0402 1%
R159
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ125USG
U21
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ126USG
U23
WILC3000_ENABLE_PA29
0.1uF
50V0402
C125
0.1uF
50V0402
C129
WILC_BT_TX
WILC_BT_RX
When developing an application, the designer must keep in mind to first configure the values for the selection ports
(PA29, PD19 and PD20) to ensure the signal takes the desired path.
3.3 On-board Memories
The SAM9X60 features a DDR/SDR memory interface and an External Bus Interface (EBI) to enable interfacing to a
wide range of external memories and to almost any type of parallel peripheral.
This section describes the memory devices mounted on the SAM9X60-EK board:
• One DDR2 SDRAM
• One NAND Flash
• One QSPI Flash
• One serial EEPROM
Additional memory can be added to the board by:
• Installing an SD or MMC card in the SD/MMC slot,
• Using the USB ports.
Support is dependent upon driver support in the OS.
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
3.3.1 DDR2/SDRAM
One DDR2/SDRAM (2-Gbit W972GG6KB = 16 Mwords x 16 bits x 8 banks) is used as main system memory, totaling
256 KBytes of SDRAM on the board. The memory bus is 16 bits wide and operates with a frequency of up to 200
MHz.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 28
Page 29

Figure 3-23. DDR2/SDRAM
A0
M8
A1
M3
A2
M7
A3
N2
A4
N8
A5
N3
A6
N7
A7
P2
A8
P8
A9
P3
A10
M2
A11
P7
A12
R2
A13
R8
BA0
L2
BA1
L3
BA2
L1
CKE
K2
CK_P
J8
CK_N
K8
RAS
K7
CAS
L7
WE
K3
CS
L8
DQ0
G8
DQ1
G2
DQ2
H7
DQ3
H3
DQ4
H1
DQ5
H9
DQ6
F1
DQ7
F9
DQ8
C8
DQ9
C2
DQ10
D7
DQ11
D3
DQ12
D1
DQ13
D9
DQ14
B1
DQ15
B9
LDQS_P
F7
LDQS_N
E8
UDQS_P
B7
UDQS_N
A8
LDM
F3
UDM
B3
ODT
K9
NC1
A2
NC2
E2
NC3
R3
NC4
R7
VDD1
A1
VDD2
E1
VDD3
J9
VDD4
M9
VDD5
R1
VDDQ1
A9
VDDQ2
C1
VDDQ3
C3
VDDQ4
C7
VDDQ5
C9
VDDQ6
E9
VDDQ7
G1
VDDQ8
G3
VDDQ9
G7
VDDQ10
G9
VDDL
J1
VREF
J2
VSS1
A3
VSS2
E3
VSS3
J3
VSS4
N1
VSS5
P9
VSSQ1
A7
VSSQ2
B2
VSSQ3
B8
VSSQ4
D2
VSSQ5
D8
VSSQ6
E7
VSSQ7
F2
VSSQ8
F8
VSSQ9
H2
VSSQ10
H8
VSSDL
J7
W972GG6KB-25
U10
GND
0.1uF 16V 0201
C71
0.1uF 16V 0201
C72
0.1uF 16V 0201
C73
0.1uF 16V 0201
C74
0.1uF 16V 0201
C78
0.1uF 16V 0201
C79
0.1uF 16V 0201
C80
1000pF 25V 0402
C81
1000pF 25V 0402
C82
DDR_A2
DDR_A3
DDR_A4
DDR_A5
DDR_A6
DDR_A7
DDR_A8
DDR_A9
DDR_A10
DDR_A11
DDR_A13
DDR_A14
DDR_A15
DDR_A16
DDR_A17
DDR_A18
DDR_D0
DDR_D1
DDR_D2
DDR_D3
DDR_D4
DDR_D5
DDR_D6
DDR_D7
DDR_D8
DDR_D9
DDR_D10
DDR_D11
DDR_D12
DDR_D13
DDR_D14
DDR_D15
DDR_RAS
DDR_CAS
DDR_WE
DDR_CS
DDR_CKE
DDR_CLK_P
DDR_CLK_N
GND
DDR_DQM0
DDR_DQM1
DDR_DQS0_P
DDR_DQS0_N
DDR_DQS1_P
DDR_DQS1_N
VDDIOM
VDDIOM
VDDIOM
DDR_SDA10
GND
i BYTELANE0
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.5mm]
i
ADDR-CTL
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
i BYTELANE1
4.7uF 10V 0402
C67
4.7uF 10V 0402
C68
0.1uF 50V 0402
C69
0.1uF 50V 0402
C70
0.1uF 50V 0402
C75
0.1uF 50V 0402
C76
0.1uF 50V 0402
C77
10nF 16V 0402
C64
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DDR_VREF
100Ω ± 10% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
50Ω ± 10% single-ended trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
3.3.2 NAND FLASH
The SAM9X60-EK has native support for NAND Flash memory through its NAND Flash Controller. The board
implements one MT29F4G08ABA 4Gb x 8 NAND Flash connected to Chip Select three (NCS3) of the
microcontroller. That makes a 512-Mbyte memory space.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 29
Page 30

Figure 3-24. NAND Flash
NAND_CLE_PD03 NAND_IO0_PD06
NAND_IO1_PD07
NAND_IO2_PD08
NAND_IO3_PD09
NAND_IO4_PD10
NAND_IO5_PD11
NAND_IO6_PD12
NAND_IO7_PD13
NAND_ALE_PD02
NAND_nWE_PD01
NAND_nRE_PD00
NAND_nCS_PD04_enabled
NAND_RB_PD05
0.1uF
50V
0402
C58
0.1uF
50V
0402
C59
0.1uF
50V
0402
C60
0.1uF
50V
0402
C61
GND
GND
i
NAND-Flash
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
i
NAND-Flash
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
NC
1
NC
2
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
R/B
7
RE
8
CE
9
NC
10
NC
11
Vcc
12
Vss
13
NC
14
NC
15
CLE
16
ALE
17
WE
18
WP
19
NC
20
NC
21
NC
22
NC
23
NC
24
Vss1
25
NC
26
NC
27
NC
28
I/O0
29
I/O1
30
I/O2
31
I/O3
32
NC
33
Vcc1
34
NC
35
Vss
36
Vcc
37
DNU
38
Vcc1
39
NC
40
I/O4
41
I/O5
42
I/O6
43
I/O7
44
NC
45
NC
46
DNU
47
Vss1
48
MT29F4G08ABAEAWP:E TR
TSOP-48
U9
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
10k
0402
5%
R116
10k
0402
5%
R117
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R114
10k
0402
5%
R115
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-5. NAND Flash Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared PIO Signal Description
PD6 NAND_IO0_PD06 – Data 0
PD7 NAND_IO0_PD07 – Data 1
PD8 NAND_IO0_PD08 – Data 2
PD9 NAND_IO0_PD09 – Data 3
PD10 NAND_IO0_PD10 – Data 4
PD11 NAND_IO0_PD11 – Data 5
PD12 NAND_IO0_PD12 – Data 6
PD13 NAND_IO0_PD13 – Data 7
PD1 NAND_nWE_PD01 – Write Enable
PD4 NAND_nCS_PD04_enabled –
PD2 NAND_ALE_PD02 – Address Latch Enable
PD3 NAND_CLE_PD03 – Command Latch Enable
PD0 NAND_nRE_PD00 – Output Enable
PD5 NAND_RB_PD05 – Ready/Busy#
3.3.3 QSPI Serial Flash
The SAM9X60-EK board features one Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI) memory SST26VF064B.
A QSPI bus is a synchronous serial data link that provides communication with external devices in Master mode.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
Chip Select (through a Disable Boot control buffer – see 3.5.5
Disable Boot)
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 30
Page 31

CE
1
SO/SIO1
2
WP/SIO23VSS
4
SI/SIO0
5
SCK
6
HOLD/SIO3
7
VDD
8
SST26VF064B
U8
0.1uF
50V
0402
C55
GND
QSPI_CS_PB20_enabled
QSPI_IO0_PB21
QSPI_IO1_PB22
QSPI_IO2_PB23
QSPI_IO3_PB24
QSPI_SCK_PB19
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
10k
0402
5%
R106
10k
0402
5%
R99
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R100
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R101
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R102
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R103
DNP
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
The QSPI can be used in SPI mode to interface with serial peripherals (such as ADCs, DACs, LCD controllers, CAN
controllers and sensors), or in Serial Memory mode to interface with serial Flash memories.
The QSPI allows the system to execute code directly from a serial Flash memory (XIP, or Execute In Place,
technology) without code shadowing to RAM. The Flash memory communication protocol is serial, however it is seen
in the system as a conventional parallel memory (ROM, SRAM, DRAM, embedded Flash memory, etc.).
With the support of the Quad SPI protocol, the QSPI allows the system to use high-performance serial Flash
memories which are small and inexpensive, instead of larger and more expensive parallel Flash memories.
Figure 3-25. QSPI Serial Flash
Table 3-6. QSPI Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared PIO Signal Description
PB19 QSPI0_SCK_PB19 I2SMCC_CK QSPI Clock
PB20 QSPI0_CS_PB20_enabled I2SMCC_WS
PB21 QSPI0_IO0_PB21 I2SMCC_DIN0 Data0
PB22 QSPI0_IO1_PB22 I2SMCC_DOUT0 Data1
PB23 QSPI0_IO2_PB23 I2SMCC_MCL Data2
PB24 QSPI0_IO3_PB24 – Data3
3.3.4 Serial EEPROM with Unique MAC Address
The SAM9X60-EK board embeds one Microchip 24AA025E48 serial EEPROM. The 24AA025E48 features 2048 bits
of serial Electrically-Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM) organized as 256 words of eight bits
each and is accessed via an I2C-compatible (2-wire) serial interface. In addition, the 24AA025E48 incorporates an
easy and inexpensive method to obtain a globally unique MAC or EUI address (EUI-48™). For more information
about the 24AA025E48, refer to the product web page.
The EUI-48 addresses can be assigned as the actual physical address of a system hardware device or node, or it
can be assigned to a software instance. These addresses are factory-programmed by Microchip and unique. They
are permanently write-protected in an extended memory block located outside the standard 2-Kbit memory array.
Chip Select (through a Disable Boot control buffer – see
3.5.5 Disable Boot)
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 31
Page 32

A0
5
A1
4
SDA
3
SCL
1
VCC
6
VSS
2
24AA025E48
U7
0.1uF
50V
0402
C54
GND
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
GND
EEPROM_TWCK
EEPROM_TWD
10k
0402
5%
R97
10k
0402
5%
R98
10k
0402 5%
R104
DNP
10k
0402 5%
R105
DNP
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Figure 3-26. EEPROM 24AA02E48
Table 3-7. EEPROM PIO Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared PIO Signal Description
PA00 EEPROM_TWD TWI and SPI TWI data
PA01 EEPROM_TWCK TWI and SPI TWI clock
In the SAM9X60-EK usage context, the EEPROM device is used as a “software label” to store board information
such as chip type, manufacturer name and production date, using the last two 16-byte blocks in memory. The
information contained in these blocks should not be modified.
3.4 Peripherals
Several interfaces and connectors are implemented in the SAM9X60-EK with the purpose of enabling the user to test
all the features that the MPU can offer and to facilitate a reference design for future customer applications.
This section describes the following peripherals mounted on the SAM9X60-EK board:
• Ethernet 10/100 port (GMAC)
• USB host/device
• Wi-Fi/Bluetooth module (optional)
• Controller Area Network (CAN) interface
• Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) interface
• Image Sensor Interface (ISI)
• Audio Class D (CLASSD) amplifier
• Secure Digital Multimedia Card (SDMMC)
• mikroBUS interface
• GPIO interface
3.4.1 Ethernet 10/100 Port (GMAC)
The KSZ8081 is a single-supply 10Base-T/100Base-TX Ethernet physical-layer transceiver for transmission and
reception of data over standard CAT-5 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. The KSZ8081 is a highly-integrated PHY
solution. It reduces board cost and simplifies board layout by using on-chip termination resistors for the differential
pairs and by integrating a low-noise regulator to supply the 1.2V core, and by offering 1.8/2.5/3.3V digital I/O interface
support.
The KSZ8081RNA is connected over the Reduced Media Independent Interface (RMII) directly to the RMII-compliant
MAC inside the SAM9X60 MPU. As the power-up default, the KSZ8081RNA uses a 25 MHz MEMS oscillator to
generate all required clocks, including the 50-MHz RMII reference clock output for the MAC. For more information
about the KSZ8081RNx, refer to the product web page.
An individual unique 48-bit MAC address (Ethernet hardware address) is allocated to this product and is stored in the
Microchip 24AA025E48 TWI serial EEPROM described in 3.3.4 Serial EEPROM with Unique MAC Address.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 32
Page 33

ETH_TX_P
1k
0402
5%
R123
1k
0402
5%
R122
2.2uF 16V0603
C85
180R
BLM18PG181SN1D
FB2
GND
VDD_3V3
TXP
6
TXM
5
RXP
4
RXM
3
VDD_1V2
1
GND
22
PADDLE
25
REXT
9
XI
8
XO
7
REF_CLK
16
TXD1
21
TXD0
20
TXEN
19
RXD1
12
RXD0
13
RXER
17
CRS_DV/PHYAD[1_0]
15
MDC
11
MDIO
10
INTRP
18
VDDA_3V3
2
VDDIO
14
LED0/ANEN_SPEED
23
RST
24
KSZ8081RNAIA-TR
U11
6.49k 0402 1%
R124
1 3
25MHz
ECS-250-20-33-CKM-TR
Y5
DNP
GNDGND
VDD_3V3
GND
10k
0402
5%
R129
ETH_LED
10k
0402
5%
R127
GND
VDD_3V3
ETH_TX_N
ETH_RX_P
ETH_RX_N
20pF
50V
0402
C92
DNP
20pF
50V
0402
C91
DNP
ETH_XI
ETH_XO
ETH_XI
VDD_3V3
GND
ETH0_TXCK_PB04
i
Ethernet 10/100
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.5mm]
NRST_PB25
TP4
ETH0_TX0_PB09
ETH0_TXEN_PB07
ETH0_TX1_PB10
ETH0_RX1_PB01
ETH0_RX0_PB00
ETH0_RXER_PB02
ETH0_RXDV_PB03
ETH0_MDC_PB06
ETH0_MDIO_PB05
ETH0_IRQ_PB08
GND
ETH0_PCK1_PC31
10uF
25V
1206
C87
10uF
25V
1206
C89
GND
0.1uF 50V0402
C86
0.1uF
50V
0402
C88
0.1uF
50V
0402
C90
0.1uF
50V
0402
C93
0R 0402
R130
0R 0402
R126
DNP
0R
0402
R128
DNP
0R
0402
R133
DNP
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
51R
0402
R132
EN
1
GND2OUT
3
VDD
4
DSC6102HI2B-025.000
Y6
100Ω ±5Ω differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
50Ω ± 10% single-end ed trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Additionally, for monitoring and control purposes, a LED functionality is carried on the RJ45 connectors to indicate
activity, link, and speed status.
Figure 3-27. Ethernet Interface
Table 3-8. Ethernet PHY 10/100 Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared Signal Description
PB04 ETH_TXCK_PB24 – Transmit clock
PB07 ETH_TXEN_PB10 – Transmit enable
PB03 ETH_RXDV_PB03 – Receive data valid
PB02 ETH_RXER_PB02 – Receive error
PB00 ETH_RX0_PB00 – Receive data 0
PB01 ETH_RX1_PB01 – Receive data 1
PB09 ETH_TX0_PB09 – Transmit data 0
PB10 ETH_TX1_PB10 – Transmit data 1
PB06 ETH_MDC_PB06 – Management data clock
PB05 ETH_MDIO_PB05 – Management data in/out
PB08 ETH_IRQ_PB08 – Interrupt
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 33
Page 34

Figure 3-28. Ethernet PHY Connector
GND_ETH
ETH_LED
EARTH_ETH
GND_ETH
GND
EARTH_ETH
180R
BLM18PG181SN1D
FB3
TD-
2
TCT
4
TD+
1
RD-
6
RCT
5
RD+
3
4X 75R
1nF,2kV
SHLD
8
NC
7
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
4
5
7
8
Right
12
11
9
10
Left
SHLD
13
SHLD
14
1
2
3
6
RJ45 J00-0045NL
J5
0.1uF
50V
0402
C83
0.1uF
50V
0402
C84
0R
0402
R131
470R
0402
5%
R125
VDD_3V3
ETH_TX_P
ETH_TX_N
ETH_RX_P
ETH_RX_N
Table 3-9. Ethernet RJ45 Connector J5 Pin Assignment
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Pin No Signal Name Signal Description
1 TD+ Transmit
2 TD- Transmit
3 RD+ Receive
4 Decoupling capacitor –
5 Decoupling capacitor –
6 RD- Receive
7 NC –
8 EARTH / GND Common ground
9 ACT LED LED activity
10 ACT LED LED activity
11 LINK LED LED link connection
12 LINK LED LED link connection
13 EARTH / GND Common ground
14 EARTH / GND Common ground
15 NC –
16 NC –
3.4.2 USB Host/Device
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a hot-pluggable general-purpose high-speed I/O standard for computer
peripherals. The standard defines connector types, cabling, and communication protocols for interconnecting a wide
variety of electronic devices. The USB 2.0 Specification defines data transfer rates as high as 480 Mbps (also known
as High Speed USB). A USB host bus connector uses four pins: a power supply pin (5V), a differential pair (D+ and
D- pins) and a ground pin.
The SAM9X60-EK board features three USB communication ports named USB-A to USB-C™.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 34
Page 35

USBA_N
USBA_P
20pF
50V
0402
C106
200k
0402
1%
R150
USBA_N
USBA_P
USBA_VBUSDETECT_PB16
EARTH_USB_A
USBA_VBUS_5V
180R
FB5
100k
0402
5%
R148
DIFF90
DIFF90
VBUS_USBA
ID
4
VBUS
1
GND
5
D-
2
D+
3
0
USB2.0 MICRO-B FEMALE
J7
90Ω ±15% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
The USB-A port can act only as a USB device interface and can be accessed via the USB Micro-B connector (J7).
Two resistors are placed on its power rail to form a voltage divider, converting 5V into 3.3V that is then used to signal
the presence of a USB host to the MPU.
In the case of board bring-up, USB-A is the default port used to connect to the MPU over SAM-BA (SAM Boot
Assistance). For more information, refer to the product web page.
The USB-A port is also used as a secondary power source, as mentioned in 3.1 Power Supply Topology and Power
Distribution. In most cases, this port is limited to 500 mA.
Figure 3-29. USB-A Port
Table 3-10. USB-A Connector Signal Descriptions
Pin No Signal Name Signal Description
1 USBA_VBUS_5V First port 5V power
2 USBA_N First port data minus
3 USBA_P First port data plus
4 ID – (not used)
5 GND First port ground
Table 3-11. USB-A PIO Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared Signal Description
PB16 USBA_VBUSDETECT_PB16 – VBUS detection
The USB-B and USB-C ports are connected to the stacked USB Type-A connector (J8) and each port can act both as
device and as host.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 35
Page 36

Figure 3-30. USB-B and USB-C Ports
VBUS1
1
GND1
4
D1-
2
D1+
3
0
J8A
VBUS2
5
GND2
8
D2-
6
D2+
7
J8B
EARTH_USB_B
USBB_VBUS_5V
USBC_VBUS_5V
USBB_N
USBB_P
USBC_N
USBC_P
USBC_N
USBC_P
USBB_N
USBB_P
180R
FB7
DIFF90
DIFF90
DIFF90
DIFF90
90Ω ±15% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
90Ω ±15% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
Table 3-12. USB-B and USB-C Connector Signal Descriptions
Pin No Signal Name Signal Description
0 EARTH_USB_B Connector chassis connected to ground
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
1 USBB_VBUS_5V Second port 5V power
2 USBB_N Second port data minus
3 USBB_P Second port data plus
4 GND Second port ground
5 USBC_VBUS_5V Third port 5V power
6 USBC_N Third port data minus
7 USBC_P Third port data plus
8 GND Third port ground
In Host mode, the USB Host ports B and C are equipped with 500-mA high-side power switches to enable selfpowered and bus-powered applications. The USBx_EN_5V_PDxx signal controls the current limiting power switch
MIC2025, which in turn supplies power to a client device. Per the USB specification, bus-powered USB 2.0 devices
are limited to a maximum of 500 mA, therefore the MIC2025 limits the current and indicates an overcurrent with the
USBx_OVCUR signal. For more information about the MIC2025, refer to the product web page.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 36
Page 37

Figure 3-31. USB Power Switches
USBB_VBUS_5V
USBB_OVCUR
USBB_EN_5V_PD15
VDD_MAIN_5V
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C118
0.1uF
50V
0402
C115
VBUS_USBB
USBC_VBUS_5V
USBC_OVCUR
USBC_EN_5V_PD16
VDD_MAIN_5V
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C124
0.1uF
50V
0402
C121
VBUS_USBC
100µF
16V
Radial, Can
C116
100µF
16V
Radial, Can
C122
10uF
25V
1206
C119
10uF
25V
1206
C120
10uF
25V
1206
C123
10uF
25V
1206
C113
10uF
25V
1206
C114
10uF
25V
1206
C117
180R
FB6
180R
FB8
10k
0402
5%
R152
10k
0402
5%
R153
10k
0402
5%
R154
10k
0402
5%
R155
EN
1
FLG
2
GND
3
NC4NC
5
OUT
6
IN
7
OUT
8
USB Power Switch
U19
MIC2025-1YM
EN
1
FLG
2
GND
3
NC4NC
5
OUT
6
IN
7
OUT
8
USB Power Switch
U20
MIC2025-1YM
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-13. USB Power Switch PIO Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared Signal Description
PD14 USBA_EN_5V_PD14 – Power switch enable (active high)
GP2 expander USBA_OVCUR – Indicates overcurrent (open drain)
PD15 USBA_EN_5V_PD15 – Power switch enable (active high)
GP3 expander USBB_OVCUR – Indicates overcurrent (open drain)
PD16 USBC_EN_5V_PD16 – Power switch enable (active high)
GP4 expander USBC_OVCUR – Indicates overcurrent (open drain)
3.4.3 Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Module (Optional)
The user has the option to solder an ATWILC3000-MR110CA Wi-Fi/BT module with a chip antenna.
The ATWILC3000-MR110PA WLAN PHY is designed to achieve a reliable and power-efficient physical layer
communication as specified by IEEE® 802.11 b/g/n in Single Stream mode with a 20-MHz bandwidth. Advanced
algorithms are used to achieve maximum throughput in a real-world communication environment with impairments
and interference. The PHY implements all required functions such as FFT, filtering, FEC (Viterbi decoder), frequency
and timing acquisition and tracking, channel estimation and equalization, carrier sensing and clear channel
assessment, as well as automatic gain control. The module is available in a fully certified, 22.428 x 17.732 mm, 36pin module package. For more information about the ATWILC3000, refer to the product web page.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 37
Page 38

Figure 3-32. Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Interface
GND
GND GND
VDD_3V3
GNDGND
10k
0402
5%
R168
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
OUT
1
GND
2
OE
3
VDD
4
32.768kHz
ASH7KW-32.768KHZ-L-T
Y7
DNP
GPIO20
GPIO19
GPIO18
GPIO17
1
2
3
HDR-2.54 Female 1x3
J9
DNP
UART_TXD
UART_RXD
GND
RTS/SDA
CTS/SCL
VDD_3V3
GND GND
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT3_PA04
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT2_PA03
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT1_PA02
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT0_PA11
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CMD_PA12
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CK_PA13
FLEXCOM5_IO4_BT_RTS_PA07
FLEXCOM5_IO3_BT_CTS_PA08
WILC3000_INTERRUPT_PA28
WILC3000_ENABLE
NRST_PB25
VDD_3V3_WILC VDD_3V3
180R
FB9
2.2uF
16V
0603
C134
VDD_3V3
GND
GPIO17
GPIO18
GPIO19
GPIO20
CTS/SCL
RTS/SDA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
HDR-2.54 Female 1x8
J10
DNP
VDD_3V3
2 1
43
GREEN
RED
0805
D4
VDD_WILC
0.1uF
50V
0402
C130
0.1uF
50V
0402
C133
0.1uF
50V
0402
C135
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C136
0R 0402
R169
0R 0402
R170
0R 0402
R171
0R 0402
R173
0R
0402
R174
1k
0402
5%
R160
1k
0402
5%
R161
100k
0402
5%
R162
100k 0402 5%
R163
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R164
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R165
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R166
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R167
DNP
47uF
16V
1206
C131
47uF
16V
1206
C132
DNP
WILC_BT_TX
WILC_BT_RX
WILC_LED_RED
WILC_LED_GREEN
WILC_LED_RED
WILC_LED_GREEN
VBAT
18
VDDIO
12
BT_TXD
8
BT_RXD
9
BT_RTS
10
BT_CTS
11
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
GND1GND13GND21GND28GND36PADDLE
37
GPIO21
35
GPIO0
34
GPIO17
29
GPIO18
30
GPIO19
31
GPIO3
14
GPIO20
32
GPIO4
15
SD_CLK/GPIO8
22
SD_CMD/SPI_SCK
23
SD_DAT0/SPI_MISO
24
SD_DAT1/SPI_SSN
25
SD_DAT2/SPI_MOSI
26
SD_DAT3/GPIO7
27
SDIO/SPI_CFG
2
RTC_CLK
20
CHIP_EN
19
IRQN
33
RESETN
7
UART_TXD
16
UART_RXD
17
ATWILC3000-MR110CA
U24
DNP
GND
2
NC
3
VDD4Output
1
DSC6083CE2A-032K768
Y8
51R
0402
R175
51R
0402
R172
DNP
i
SDMMC1
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
50Ω ± 10% single-ended trace i mpedance
Routing top or bottom
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-14. Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared Signal Description
PA11 SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT0_PA11 – SDIO data
PA02 SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT1_PA02 – SDIO data
PA03 SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT2_PA03 – SDIO data
PA04 SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT3_PA04 – SDIO data
PA12 SDMMC1_WILC3000_CMD_PA12 – SDIO command
PA13 SDMMC1_WILC3000_CK_PA13 – SDIO clock
PA21 FLEXCOM1_IO1_RX_PA21 – Bluetooth serial TX
PA22 FLEXCOM1_IO0_TX_PA22 – Bluetooth serial RX
PA07 FLEXCOM1_IO1_RTS_PA07 – Bluetooth serial RTS
PA08 FLEXCOM1_IO1_CTS_PA08 – Bluetooth serial CTS
PB25 NRST_PB25 – Module reset
PA28 WILC3000_INTERUPT_PA28 – Interrupt
PA29 WILC3000_ENABLE_PA29 – Chip enable
Special care must be taken when powering the ATWILC3000 wireless module. Due to the nature of the wireless
transmission, the module draws a lot of current from its supply rail. In the worst-case scenario, the module can draw
up to 300 mA. The main PMIC on the board, the MIC2800, has a maximum output capacity of 300 mA on its 3.3V
rail, therefore it is not fit to power this module alongside the other components on the board.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
(RX into SAM9X60)
(TX from SAM9X60)
DS50002907A-page 38
Page 39

VDD_MAIN_5V
VIN
1
VIN
2
SHDN
3
GND
4
PWRGD
5
CDELAY
6
SENSE
7
VOUT
8
EP
9
MCP1725/3.3V
U22
2.2uF
16V
0603
C126
2.2uF
16V
0603
C127
1000pF
25V
0402
C128
WILC3000_ENABLE
WILC3000_ENABLE_PA29
VDD_3V3_WILC
15pF
50V
0402
C97
VDD_MAIN_5VVDD_3V3
0R 0402
R135
GND GND GND GND
15pF
50V
0402
C101
VDD_MAIN_5VVDD_3V3
0R 0402
R138
GND GND GND GND
62R
1210
1%
R134
62R
1210
1%
R136
4700pF
50V
0402
C94
GND
62R
1210
1%
R137
62R
1210
1%
R139
4700pF
50V
0402
C98
GND
GND
CAN0_P
CAN0_N
CAN1_N
CAN1_P
CAN_STBY_PD21
RXD
4
TXD1VSS
2
VDD
3
VIO5CANL
6
CANH
7
STBY
8
EP
9
MCP2542
U12
RXD
4
TXD1VSS
2
VDD
3
VIO5CANL
6
CANH
7
STBY
8
EP
9
MCP2542
U13
0.1uF
50V
0402
C95
0.1uF
50V
0402
C96
0.1uF
50V
0402
C99
0.1uF
50V
0402
C100
CAN1_TX
CAN1_RX
CAN0_TX
CAN0_RX
1
2
3
4
5
TERMINAL 1x5
J6
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
To address this issue, the module is fitted with its own separate power supply, the MCP1725, which is a 500-mA Low
Dropout (LDO) linear regulator that provides high current and low output voltages in a very small package. For more
information about the MCP1725, refer to the product web page.
The MCP1725 was chosen because it can supply the current required by the module, and because it features a
shutdown input pin (SHDN) and a Power Good output pin (PWRGD):
• The SHDN input allows to shut down the wireless module if it is unused, therefore saving power.
• The PWRGD output ensures that the ATWILC3000 wireless module is kept in reset until its power rails are
stable.
Figure 3-33. Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Enable
Note: Enabling the ATWILC3000 module prevents the Flexcom UART from being used with the mikroBUS
connector (this is switched by U23).
3.4.4 Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface
Two MCP2542 transceivers are placed on the SAM9X60-EK.
The MCP2542 is a high-speed CAN transceiver that provides the interface between the Controller Area Network
(CAN) protocol controller and the physical two-wire bus. For more information about the MCP2542, refer to the
product web page.
Figure 3-34. Dual CAN Interface
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 39
Page 40

SAM9X60-EK
Table 3-15. CAN Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared Signal Description
PD21 CAN_STBY_PD21 – Dual CAN standby
PA10 CAN0_TX_PA10 – CAN transmit port 0
PA09 CAN0_RX_PA09 – CAN receive port 0
PA05 CAN1_TX_PA05 – CAN transmit port 1
PA06 CAN1_RX_PA06 – CAN receive port 1
Table 3-16. CAN Connector J6 Signal Description
Pin No Signal Name Signal Description
1 CANH Differential positive port 0
2 CANL Differential negative port 0
3 GND Common ground
4 CANH Differential positive port 1
5 CANL Differential negative port 1
Function Blocks
CAN1 function and UART on the external 40-pin connector are shared and selectable through the
SEL_FNCT1_PD19 PIO.
CAN0 function and Debug UART are shared and selectable through the SEL_FNCT2_PD20 PIO.
3.4.5 Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Interface
The SAM9X60-EK board provides a connector with 24 bits of data and control signals to the LCD interface.
Optional displays such as AC320005-5 (refer to the product web page) can be connected to the board.
In order to operate correctly with various LCD modules, two voltage lines are available: 3.3V and 5VDC (default). The
selection is made with 0R resistors.
J15 is a 1.27-mm pitch, 50-pin header. It gives access to the LCD signals.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 40
Page 41

Figure 3-35. LCD Connector
LCD_D17_PC17
LCD_D18_PC18
LCD_D19_PC19
LCD_D20_PC20
LCD_D21_PC21
LCD_D22_PC22
LCD_D23_PC23
GND
LCD_PCLK_PC30
LCD_VSYNC/CS_PC27
LCD_HSYNC/WE_PC28
LCD_DATA_ENABLE_PC29
LCD_ISI_TWD
LCD_ISI_TWCK
LCD_IRQ1_PC25
LCD_IRQ2_PB17
LCD_PWM_PC26
NRST_PB25
0R0402
R217
DNP
0R0402
R214
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
MNT
FFC
FFC/FPC 50P Female
J15
VDD_3V3
VDD_MAIN_5V
i
LCD
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.5mm]
TP5
TP6
TP7
TP8
LCD_ID_PD14
0R 0402
R208
DNP
0R 0402
R209
DNP
0R 0402
R210
DNP
0R 0402
R211
DNP
LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12
LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13
LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14
LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15
LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00
LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02
LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04
LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06
LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08
LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10
LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01
LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03
LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05
LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07
LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09
LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11
LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24
LCD_D16_ISI_nRST_PC16
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-17. LCD Connector J15 Signal Descriptions
Pin No LCD pin PIO Signal Function
1 ID PD18 LCDID_PD18 ID LCD module
2 GND – GND Ground
3 LCDDAT0 PC0 LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00 Data line
4 LCDDAT1 PC1 LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01 Data line
5 LCDDAT2 PC2 LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02 Data line
6 LCDDAT3 PC3 LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03 Data line
7 GND – GND Ground
8 LCDDAT4 PC4 LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04 Data line
9 LCDDAT5 PC5 LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05 Data line
10 LCDDAT6 PC6 LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06 Data line
11 LCDDAT7 PC7 LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07 Data line
12 GND – GND Ground
13 LCDDAT8 PC8 LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08 Data line
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 41
Page 42

...........continued
Pin No LCD pin PIO Signal Function
14 LCDDAT9 PC9 LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09 Data line
15 LCDDAT10 PC10 LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10 Data line
16 LCDDAT11 PC11 LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11 Data line
17 GND – GND Ground
18 LCDDAT12 PC12 LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12 Data line
19 LCDDAT13 PC13 LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13 Data line
20 LCDDAT14 PC14 LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14 Data line
21 LCDDAT15 PC15 LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15 Data line
22 GND – GND Ground
23 LCDDAT16 PC16 LCD_D16_PC16 Data line
24 LCDDAT17 PC17 LCD_D17_PC17 Data line
25 LCDDAT18 PC18 LCD_D18_PC18 Data line
26 LCDDAT19 PC19 LCD_D19_PC19 Data line
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
27 GND – GND Ground
28 LCDDAT20 PC20 LCD_D20_PC20 Data line
29 LCDDAT21 PC21 LCD_D21_PC21 Data line
30 LCDDAT22 PC22 LCD_D22_PC22 Data line
31 LCDDAT23 PC23 LCD_D23_PC23 Data line
32 GND – GND Ground
33 LCDPCK PC30 LCD_PCLK_PC30 Pixel clock
34 LCDVSYNC PC27 LCD_VSYNC/CS_PC27 Vertical synchronization
35 LCDHSYNC PC28 LCD_HSYNC/WE_PC28 Horizontal synchronization
36 LCDDEN PC29 LCD_DATA_ENABLE_PC29 Data enable
37 SPI_SPCK – NC Test point to access the SPI interface via DNP
resistor (see Figure 3-35)
38 SPI_MOSI – NC Test point to access the SPI interface via DNP
resistor (see Figure 3-35)
39 SPI_MISO – NC Test point to access the SPI interface via DNP
resistor (see Figure 3-35)
40 SPI_NPCS0 – NC Test point to access the SPI interface via DNP
resistor (see Figure 3-35)
41 LCDDISP PC24 LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24 Display enable signal
42 TWD PA00 LCD_TWD I2C data line (maXTouch)
43 TWCK PA01 LCD_TWCK I2C clock line (maXTouch)
44 GPIO PC25 LCD_IRQ1_PC25 maXTouch interrupt line
45 GPIO PB17 LCD_IRQ2_PB17 Interrupt line for other I2C devices
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 42
Page 43

...........continued
WARNING
22R 0402 1%
R215
22R 0402 1%
R216
22R 0402 1%
R218
22R 0402 1%
R219
22R 0402 1%
R220
22R 0402 1%
R222
22R 0402 1%
R224
22R 0402 1%
R226
22R 0402 1%
R227
22R 0402 1%
R225
22R 0402 1%
R223
22R 0402 1%
R221
22R 0402 1%
R229
22R 0402 1%
R228
22R 0402 1%
R231
22R 0402 1%
R230
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
Header 2x15
J17
LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12
LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13
LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14
LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15
LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00
LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02
LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04
LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06
LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08
LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10
LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01
LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03
LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05
LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07
LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09
LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11
22R 0402 1%
R212
22R 0402 1%
R213
VDD_3V3
LCD_ISI_TWDLCD_ISI_TWCK
LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24
180R
FB12
ISI_D0
ISI_D1 ISI_D2
ISI_D3 ISI_D4
ISI_D5 ISI_D6
ISI_D7 ISI_D8
ISI_D9 ISI_D10
ISI_D11
ISI_MCK
ISI_VSYNC
ISI_HSYNC
ISI_PCK
LCD_ISI_TWDLCD_ISI_TWCK
ISI_ENISI_nRST
LCD_D16_ISI_nRST_PC16
GNDGND
Pin No LCD pin PIO Signal Function
46 LCDPWM PC26 LCD_PWM_PC26 Backlight control
47 RESET PB25 NRST_PB25 Reset for both display and maXTouch
48 Main_5V/3.3V VCC VCC 3.3V or 5V supply (0R)
49 Main_5V/3.3V VCC VCC 3.3V or 5V supply (0R)
50 GND _ GND Ground
3.4.6 Image Sensor Interface (ISI)
The SAM9X60-EK board provides a connector (J17) for connecting a 12-bit external camera. A TWI connection is
also included for controlling the camera.
The ISI interface and LCD interface are mutually exclusive and should be used one at a time.
J17 is a 30-pin, 2.54-mm pitch header. It gives access to the ISI signals.
Figure 3-36. ISI Expansion Header
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-18. ISI Connector J17 Signal Descriptions
Pin No ISI Pin PIO Signal Function
1 Main_3V3 VCC VCC 3.3V supply
2 GND – GND Ground
3 Main_3V3 VCC VCC 3.3V supply
4 GND – GND Ground
5 ISI_nRST PC16 LCD_RESET_PC16 Camera reset line
6 ISI_EN PC24 LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24 Camera enable
7 ISI_TWCK PA00 LCD_TCKD TWI interface clock line
8 ISI_TWD PA01 LCD_TWD TWI interface data line
9 GND – GND Ground
10 ISI_MCK PC15 LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15 Master clock line
11 GND – GND Ground
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 43
Page 44

SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
...........continued
Pin No ISI Pin PIO Signal Function
12 ISI_VSYNC PC13 LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13 Vertical synchronization
13 GND – GND Ground
14 ISI_HSYNC PC14 LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14 Horizontal synchronization
15 GND – GND Ground
16 ISI_PCK PC12 LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12 Clock line
17 GND – GND Ground
18 ISI_D0 PC00 LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00 Data line
19 ISI_D1 PC01 LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01 Data line
20 ISI_D2 PC02 LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02 Data line
21 ISI_D3 PC03 LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03 Data line
22 ISI_D4 PC04 LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04 Data line
23 ISI_D5 PC05 LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05 Data line
24 ISI_D6 PC06 LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06 Data line
25 ISI_D7 PC07 LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07 Data line
26 ISI_D8 PC08 LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08 Data line
27 ISI_D9 PC09 LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09 Data line
28 ISI_D10 PC10 LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10 Data line
29 ISI_D11 PC11 LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11 Data line
30 GND – GND Ground
3.4.7 Audio Class D (CLASSD) Amplifier
The Audio Class D (CLASSD) Amplifier is a digital input, Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) output stereo Class D
amplifier. CLASSD features a high-quality interpolation filter embedding a digitally-controlled gain, an equalizer and a
de-emphasis filter.
On its input side, CLASSD is compatible with most common audio data rates. On the output side, its PWM output can
drive either:
• high-impedance single-ended or differential output loads (Audio DAC application), or
• external MOSFETs through an integrated non-overlapping circuit (Class D power amplifier application).
For more information, refer to the SAM9X60 datasheet (see 1.2 Recommended Reading).
The output stage of the CLASSD amplifier featured on the SAM9X60-EK can be powered either from the on-board
5V power rail or an outside power supply. The selection is made by changing the jumper (JP3) position on J11:
• 2-3 shorted = on-board 5V power supply
• 1-2 shorted = external power supply
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 44
Page 45

Figure 3-37. Audio Class D Mono Amplifier
3
1
2
SSM3J56ACT
Q6
3
1
2
SSM3K56ACT
Q7
10000pF
25V
0402
C141
1N4148W
D5
10uF
25V
1206
C137
10uF
25V
1206
C139
10uF
25V
1206
C140
GND GND
GND
3
1
2
SSM3J56ACT
Q8
3
1
2
SSM3K56ACT
Q9
10000pF
25V
0402
C142
1N4148W
D6
GND GND
180R
FB10
180R
FB11
1
2
3
4
TERMINAL 1x4
J12
GND
VDD_MAIN_5V
CLASSD_L0_PA24
CLASSD_L1_PA25
CLASSD_L2_PA26
CLASSD_L3_PA27
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP3
0R
0402
R177
0R
0402
R178
0R
0402
R181
0R
0402
R182
10uF
25V
1206
C138
VDD_AUDIO
LEFT_P
LEFT_N
10k
0402
5%
R176
10k
0402
5%
R179
10k
0402
5%
R180
10k
0402
5%
R183
1
2
3
HDR-2.54 Male 1x3
J11
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-19. Class D Output Connector J12 Signal Description
Pin No Signal Name Signal Description
1 LEFT_N Negative level
2 LEFT_P Positive level
3 GND Ground
4 External power Input external power
3.4.8 Secure Digital Multimedia Card (SDMMC)
The SD (Secure Digital) card is a non-volatile memory card format used as a mass storage memory in mobile
devices.
The SAM9X60 has one Secure Digital Multimedia Card (SDMMC) interface that supports the MultiMedia Card
(e.MMC) Specification V4.51, the SD Memory Card Specification V3.0, and the SDIO V3.0 specification. It is
compliant with the SD Host Controller Standard V3.0 Specification.
A standard MMC/SD card connector, connected to the SDMMC interface, is mounted on the top side of the board.
The SDMMC0 communication is based on an 8-pin interface (clock, command, four data and power lines). It includes
a card detection switch.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 45
Page 46

Figure 3-38. SDMMC Connector
VDD_3V3
SDMMC0_DAT2_PA19
SDMMC0_CMD_PA16
SDMMC0_DAT3_PA20
SDMMC0_CLK_PA17
SDMMC0_DAT0_PA15
SDMMC0_DAT1_PA18
SDMMC0_CD_PA23
GND
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C56
GND
i
SDMMC
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
4.7uF
10V
0402
C57
10k
0402
5%
R107
10k
0402
5%
R108
10k
0402
5%
R109
10k
0402
5%
R110
10k
0402
5%
R111
10k
0402
5%
R112
10k
0402
5%
R113
10k
0402
5%
R118
DAT3
1
CMD
2
VSS1
3
VDD
4
CLK
5
VSS2
6
DAT0
7
DAT1
8
DAT2
9
CD
10
WP
11
SHIELD
12
SD
J4
GND GND
MBUS_PWM_PB13
MBUS_INT_PB18
MBUS_RX
MBUS_TX
MBUS_TWCK
MBUS_TWD
MBUS_AD4_PB15
MBUS_RST_PB14
MBUS_NPCS0_PA14
MBUS_SPCK_PA13
MBUS_MISO_PA11
MBUS_MOSI_PA12
VDD_3V3 VDD_MAIN_5V
AN
1
RST
2
CS
3
SCK
4
MISO
5
MOSI
6
+3.3V
7
GND
8
PWM
16
INT
15
RX
14
TX
13
SCL
12
SDA
11
+5V
10
GND
9
mikroBUS HOST
J14
3.4.9 mikroBUS Interface
The SAM9X60-EK hosts a pair of 8-pin female headers (J14) implementing a mikroBUS socket. For details, refer to
the mikroBUS documentation on https://www.mikroe.com/mikrobus.
Figure 3-39. mikroBUS Interface
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-20. mikroBUS Connector J14 Pin Assignment
Function PIO Mbus Signal Pin # Pin # Mbus Signal PIO Function
Analog input PB15 AN 1 16 PWM PB13 PWM
Reset PB14 RST 2 15 INT PB18 Interrupt
SPI
Chip Select
SPI clock PA13 SPI_SPCK 4 13 UART_TX PA22 UART transmit (input from SAM into Mbus)
PA14 SPI_NPCS 3 14 UART_RX PA21 UART receive (output from Mbus into
SAM)
SPI MISO PA11 SPI_MISO 5 12 TWI_SCL PA31 TWI clock
SPI MOSI PA12 SPI_MOSI 6 11 TWI_SDA PA30 TWI data
VCC _ 3V3 Supply 7 10 5V Supply _ VDD
GROUND _ GND 8 9 GND _ Ground
Note: Enabling the ATWILC3000 interface prevents the UART functionality from being used with the mikroBUS
connector. See 3.4.3 Wi-Fi/Bluetooth Module (Optional).
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 46
Page 47

3.4.10 GPIO Interface
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
HDR-2.54 Male 2x20
TSW-120-07-G-D
J16
VDD_3V3 VDD_MAIN_5V
EXT40_GP5
EXT40_TWD
EXT40_TWCK
EXT40_I2SMCK_PB23
EXT40_GPIO_PA02
EXT40_GP6
EXT40_GP7
EXT40_SPI_MOSI_PA12
EXT40_SPI_MISO_PA11
EXT40_SPI_SCLK_PA13
EXT40_CLK1_PC31
EXT40_CLK2_PB13
EXT40_PWM1_PB12
EXT40_I2SWS_PB20
EXT40_TXD
EXT40_RXD
EXT40_I2SCK_PB19
EXT40_GPIO_PA14
EXT40_NPCS1_PA07
EXT40_NPCS2_PA08
EXT40_PWM0_PB11
EXT40_GPIO_PB24
EXT40_I2SDIN_PB21
EXT40_I2SDOUT_PB22
EXT40_GPIO_PA03
EXT40_GPIO_PA04
The SAM9X60-EK board features a 40-pin connector (Raspberry Pi® compatible) for free use.
Figure 3-40. GPIO Connector
Table 3-21. GPIO Connector J16 Pin Assignment
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Signal Pin No Pin No Signal
+3V3 1 2 +5V
EXT40_TWD 3 4 +5V
EXT40_TWCK 5 6 Ground
EXT40_I2SMCK_PB23 7 8 EXT40_TXD
GND 9 10 EXT40_RXD
EXT40_GPIO_PA02 11 12 EXT40_I2SCK_PB19
EXT40_GPIO_PA03 13 14 Ground
EXT40_GPIO_PA04 15 16 EXT40_GP5
+3V3 17 18 EXT40_GP6
EXT40_SPI_MOSI_PA12 19 20 Ground
EXT40_SPI_MISO_PA11 21 22 EXT40_GPIO_PA14
EXT40_SPI_SCLK_PA13 23 24 EXT40_NPCS1_PA07
GND 25 26 EXT40_NPCS2_PA08
NC 27 28 NC
EXT40_CLK1_PC31 29 30 Ground
EXT40_CLK2_PB13 31 32 EXT40_PWM0_PB11
EXT40_PWM1_PB12 33 34 Ground
EXT40_I2SWS_PB20 35 36 EXT40_GPIO_PB24
EXT40_GP7 37 38 EXT40_I2SDIN_PB21
GND 39 40 EXT40_I2SDOUT_PB22
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 47
Page 48

3.5 User Interaction and Debugging
5V_FTDI
FTDI_CTS
FTDI_RTS
TP10
TP11
1
2
3
4
5
6
HDR-2.54 Male 1x6
TSW-106-07-G-S
J24
5V_FTDI5V_FTDI
100k
0402
5%
R263
100k
0402
5%
R264
100k
0402
5%
R261
DNP
100k
0402
5%
R262
DNP
22R 0402 1%
R266
22R 0402 1%
R268
0.1uF
50V
0402
C177
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C178
5V_FTDI
DBGU_TX_PA10
DBGU_RX_PA09
DBGU_RX_PA09
DBGU_TX_PA10 FTDI_TX
FTDI_RX
B2
1
GND
2
VCCA
3
A2
4
A1
5
OE
6
VCCB
7
B1
8
TXS0102
U30
JTAG_CONN_TDI
JTAG_CONN_TMS
JTAG_CONN_TCK
JTAG_CONN_RTCK
JTAG_CONN_TDO
JTAG_CONN_nRST
VDD_3V3
100R
0402
1%
R265
100k
0402
5%
R256
100k
0402
5%
R257
100k
0402
5%
R260
100k
0402
5%
R258
DNP
100k
0402
5%
R259
DNP
JTAG_CONN_TCK
JTAG_CONN_TDO
JTAG_CONN_TMS
JTAG_CONN_TDI
JTAG_CONN_nRST
JTAG_CONN_RTCK
GND
VDD_3V3
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
HDR-2.54 Male 2x10
302-R201
J23
The SAM9X60-EK includes two main debugging interfaces to provide debug-level access to the SAM9X60-EK:
• One UART through the USB/J-Link-OB CDC feature
• Two JTAG interfaces, one connected directly to the MPU using connector J23 and one through the J-Link-OB
interface USB port J21
3.5.1 Serial Debug Com Port (FTDI)
The SAM9X60-EK board features a dedicated serial port for debugging, accessible through header J24. Various
interfaces can be used as a USB/Serial DBGU port bridge, such as the FTDI TTL-232R USB-to-TTL serial cable.
Figure 3-41. Serial Debug Com Port
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-22. Debug Com Port Signal Descriptions
PIO Signal Name Shared Signal Description
PA09 DBGU_RX_PA09 DEBUG Receive data
PA10 DBGU_TX_PA10 DEBUG Transmit data
3.5.2 Debug JTAG
A 20-pin JTAG header (J23) is provided on the SAM9X60-EK board to facilitate software development and debugging
using various JTAG emulators. The interface signals have a voltage level of 3.3V.
Figure 3-42. JTAG Connector
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 48
Page 49

Table 3-23. JTAG/ICE Connector J23 Pin Assignment
LED1_3U
LED2_3U
39R 0402 1%
R247
0.1uF
50V
0402
C157
10nF 16V0402
C148
1N4148
D8
4.7uF
10V
0402
C156
12MHz
Y9
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C154
39R 0402 1%
R248
6.8k 0402 1%
R240
ID
4
VBUS
1
GND
5
D-
2
D+
3
0
USB2.0 MICRO-B FEMALE
J22
0.1uF
50V
0402
C163
10k 0402 5%
R237
0.1uF
50V
0402
C164
10pF 50V0402
C150
150R
R236
10nF
16V
0402
C149
0.1uF
50V
0402
C168
ATSAM3U4CA-CU
VDDANA
K2
ADVREF
J3
GNDANA
K3
AD12BVREF
K4
PA22/PGMD14
H4
PA30
J4
PB3J5PB4
K5
VDDCORE_3
E7
PA13/PGMD5
H5
GND2
F6
PA15/PGMD7
H6
PA16/PGMD8
J6
PA17/PGMD9
K7
PB16F7PB15
G7
PA18/PGMD10
H7
PA19/PGMD11
J7
PA20/PGMD12
K8
PA21/PGMD13
J8
PA23/PGMD15
K9
XIN32
A10
PA24
H8
PA25
K10
PA26
J9
PA0/PGMNCMD
J10
PA1/PGMRDY
H9
PA2/PGMNOE
H10
PA3/PGMNVALID
G8
PA4/PGMM0
G10
PA5/PGMM1
G9
PA6/PGMM2
F8
NRST
B7
VDDCORE_4
H1
GND1
E2
VDDIO_3
E6
VDDCORE_5
G5
DFSDM
D1
GND3
G6
VDDUTMIB3VDDIN
A8
FWUP
D8
ERASE
D6
TEST
D7
XIN
A2
XOUT32
B10
TDI
B9
VDDOUT
A9
PA12/PGMD4
D10
TDO/TRACESWO
B8
TMS/SWDIO
C7
TCK/SWCLK
A7
PA7/PGMM3
F10
PB24
B6
PA8/PGMD0
E10
VDDIO_2
F5
PA14/PGMD6
K6
PB23A6PB22
C6
PB14
C4
PB10
B4
PB9
E4
GNDPLL
C3
PB8J2PB7K1PB6
J1
PB13G4PB12
F2
PB11
G1
PB2G2PB1F1PB0
G3
PA10/PGMD2
E8
VDDIO_1
F3
VDDCORE_1
B1
PA31
F4
PA29
E1
PA28
E3
VDDCORE_2
D4
GNDUTMI
B2
DFSDP
C1
DHSDM
D2
DHSDP
C2
NRSTB
C8
XOUT
A3
VDDPLL
D3
PA11/PGMD3
D9
PA9/PGMD1
E9
PB20D5PB19C5PB18B5PB17
A4
PB5
H2
PA27
H3
PB21
A5
VDDBU
C10
GNDBU
E5
VBG
A1
JTAGSEL
C9
VDDCORE_6
F9
U27
ATSAM3U4CA-CU TFBGA-100
0.1uF
50V
0402
C162
2 1
43
GREEN
RED
0805
D9
0.1uF
50V
0402
C166
180R
FB13
0.1uF
50V
0402
C159
8.2pF 0402
C152
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C158
4.7uF
10V
0402
C161
0.1uF
50V
0402
C155
0.1uF
50V
0402
C153
0.1uF
50V
0402
C165
0.1uF
50V
0402
C169
8.2pF 0402
C151
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C167
GND
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
VDD_3V3_3U
EARTH_JLINK GND
GND
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
GNDGND
VDD_3V3_3U
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
VBUS_JLINK
VDD_3V3_3U
VDD_3V3_3U
GND
ENSPI
NRST_3U
TDI_3U
TDO_3U
TCK_3U
TMS_3U
Xin_SAM3
Xout_SAM3
TRESIN
TRESOUT
TRSTOUT
TRSTIN
150R
R242
150R
R243
150R
R244
10k
0402
5%
R250
VDDout
VDDout
DIS_CDC
DIS_JLINK
ENSPI
JLINK_RTCK_IN
JLINK_TCK_IN
JLINK_TDO_IN
JLINK_TMS_IN
JLINK_TDI_IN
JLINK_nRST
JLINK_UART_RX
JLINK_UART_TX
0.1uF
50V
0402
C160
JLINK_USBHS_N
JLINK_USBHS_P
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP5
DNP
GND
0R
0402
R233
0R 0402
R239
DNP
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J19
DNP
100R
0402
1%
R234
100R
0402
1%
R235
100R 04021%
R238
1k
0402 5%
R246
1k
0402 5%
R249
100k 0402 5%
R245
DIFF90
Xin_SAM3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C170
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
GND
TP9
51R
0402
R251
90Ω ±15% differential trace impe dance
Routing top or bottom
STB
1
GND
2
OUT
3
VDD
4
12.00 MHz
DSC6011JI1A-012.0000
Y10
BOT TOP
SideSide
1 2
3 4
7 8
9 10
11 12
13
15
14
16
J18
pads on PCB
Signal Pin No Pin No Signal
+3.3V 2 1 +3V3
GND 4 3 NC
GND 5 5 TDI
GND 8 7 TMS
GND 10 9 TCK
GND 12 11 RTCK
GND 14 13 TDO
GND 16 15 nRST
GND 18 17 NC
GND 20 19 NC
3.5.3 Embedded Debugger (J-Link-OB) Interface
The SAM9X60-EK includes a built-in SEGGER J-Link-On-Board (J-Link-OB) device. The functionality is implemented
with an ATSAM3U4C microcontroller in an LFBGA100 package. The ATSAM3U4C provides the functions of the
JTAG interface and a bridge from USB to Serial debug port (known as CDC, or communication class device). The bicolored LED (D9) shows the status of the J-Link-On-Board device.
The J-Link-OB device is designed to provide an efficient, low-cost, on-board alternative to the standard J-Link or
SAM-ICE.
Its own dedicated USB port acts as a power source for this block (which is separated from the rest of the system) and
provides the communication link to program and debug the MPU.
Figure 3-43. J-Link-OB with J-Link-CDC Interface
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS50002907A-page 49
User Guide
Page 50
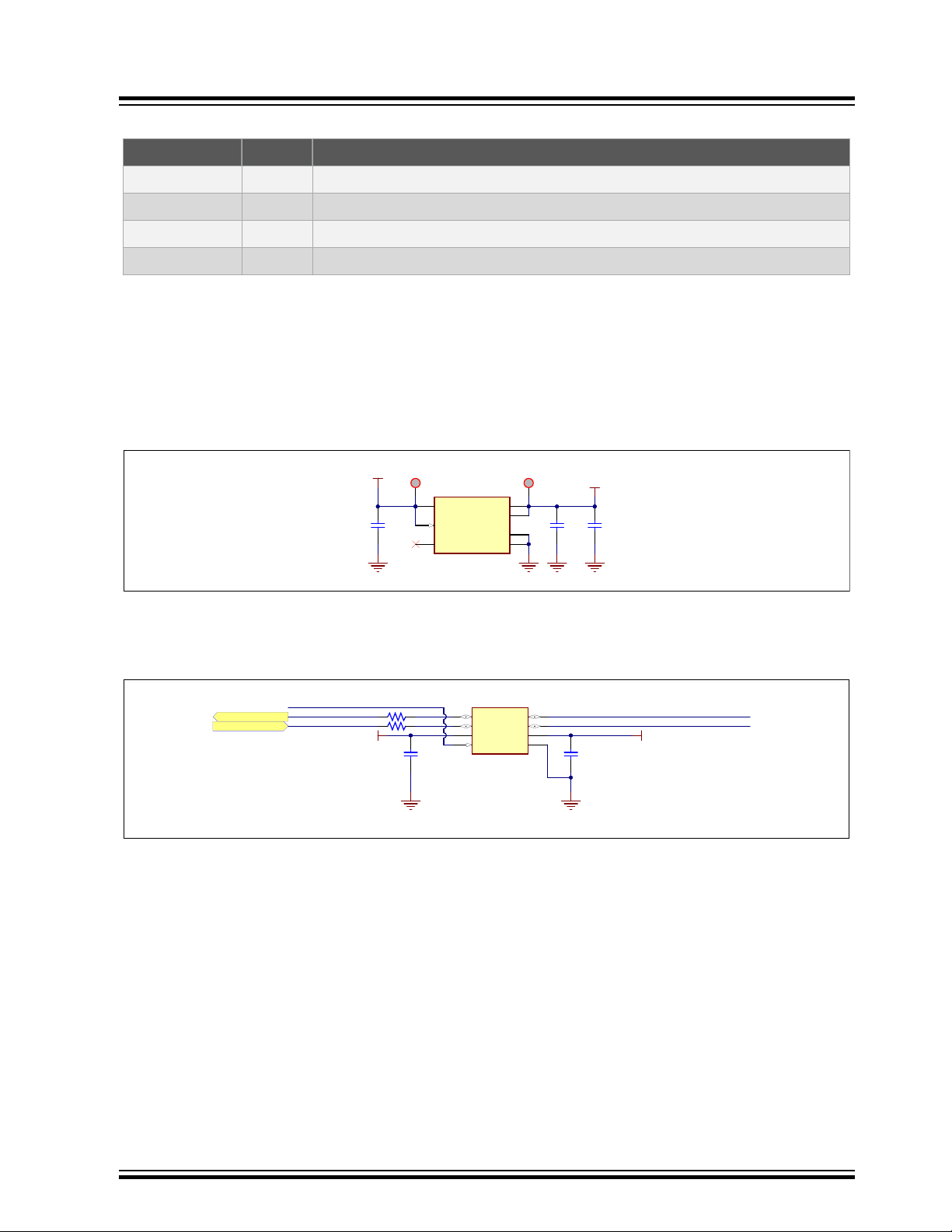
2.2uF
16V
0603
C171
2.2uF
16V
0603
C172
0.1uF
50V
0402
C173
VBUS_JLINK
VDD_3V3_3U
VBUS_JLINK VDD_3V3_3U
EP
7
VIN
6
VOUT
1
GND
3
EN
4
NC
5
VOUT
2
MIC5528 3V3
U28
22R 0402 1%
R252
22R 0402 1%
R254
0.1uF
50V
0402
C174
GNDGND
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C175
VDD_3V3_3U
DIS_CDC
JLINK_UART_TX
JLINK_UART_RX
DBGU_TX_PA10
DBGU_RX_PA09
B2
1
GND
2
VCCA
3
A2
4
A1
5
OE
6
VCCB
7
B1
8
TXS0102
U29
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Table 3-24. J-Link-OB and J-Link-CDC LED D9 Status
LED D9 State Description
Red and Green Off J-Link (SAM3U device) is not programmed, or J20 and J21 are installed.
Red On J-Link (SAM3U device) is programmed but J-Link is disabled (J20 installed).
Green Flashing J-Link is operational but the USB port is not connected.
Green On J-Link-OB is connected and ready.
The ATSAM3U microcontroller is powered only through the J-Link USB connector. This way, the programmer IC is
separated from the rest of the system and the user can have a better reading of the power that the system is drawing
when interrogating the power measurement devices placed on the board.
The MIC5528 has been selected to convert the 5V coming from the USB connector into the 3.3V rail needed by the
microcontroller. The MIC5528 is a simple low-power, low dropout regulator designed for optimal performance in a
very small footprint. It is capable of sourcing up to 500 mA of output current while only drawing 38 μA of operating
current. For more information about the MIC5528, refer to the product web page.
Figure 3-44. J-Link-OB Power Supply
If the user does not require the on-board programming feature, this section can be left unpowered, with no impact on
the rest of the system. A level shifter has been placed on the DEBUG UART line between the SAM9X60 MPU and
the on-board programmer to properly separate the two voltage domains.
Figure 3-45. J-Link-OB Level Shifter
Jumper JP6/J20 disables the J-Link-OB JTAG functionality. When installed (J20 shorted), a quad analog switch (U31/
U32) routes the JTAG interface of the SAM9X60 to the 20-pin header J23.
• Jumper JP6/J20 not installed: J-Link-OB-ATSAM3U4C is enabled and fully functional.
• Jumper JP6/J20 installed: J-Link-OB-ATSAM3U4C is disabled and an external JTAG controller can be used
through the 20-pin JTAG port J23.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 50
Page 51

Figure 3-46. Disable J-Link CDC
DIS_CDC
10k
0402
5%
R241
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP7
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J21
0.1uF
50V
0402
C176
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C179
VDD_3V3
JLINK_nRST
JLINK_RTCK_IN
JTAG_nRST
JTAG_RTCK
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TDI
JTAG_TDO
JTAG_TMS
JLINK_TCK_IN
JLINK_TDO_IN
JLINK_TMS_IN
JLINK_TDI_IN
NC
1
1OE
2
1Y41A
3
2OE
5
2Y72A
6
3Y103A
11
NC
9
4Y
13
3OE
12
GND
8
4A
14
4OE
15
VCC
16
IDTQS3VH125
U32
S
1
I0A
2
I1A
3
YA
4
I0B
5
I1B
6
YB
7
GND
8
YC
9
I1C
10
I0C
11
YD
12
I1D
13
I0D
14
E
15
VCC
16
IDTQS3VH257PAG
U31
100k 0402 5%
R270
3
1
2
BSS138N
Q16
DIS_JLINK
DIS_JLINK
JTAG_CONN_TCK
JTAG_CONN_TDO
JTAG_CONN_TMS
JTAG_CONN_TDI
JTAG_CONN_nRST
JTAG_CONN_RTCK
DIS_JLINK
10k
0402
5%
R232
VDD_3V3_3U
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP6
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J20
Figure 3-47. JTAG Switch
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
In addition to the J-Link-OB functionality, the ATSAM3U4C microcontroller provides a bridge to a debug serial port
(DBGU) of the main board processor. The port is made accessible over the same USB connection used by JTAG by
implementing a Communication Device Class (CDC), which allows a terminal communication with the target device.
This feature is enabled/disabled by jumper J21.
• Jumper J21 not installed: the J-Link-OB CDC function is enabled and fully functional.
• Jumper J21 installed: the J-Link-OB CDC function is disabled.
The USB CDC converts the USB device into a serial communication device. The target device running the CDC is
recognized by the host as a serial interface (USB2COM, virtual COM port) without the need of installing a special
host driver (the CDC is standard). All PC software using a COM port work without modifications with this virtual COM
port. Under Microsoft® Windows®, the device shows up as a COM port; under Linux®, as a /dev/ACMx device. This
enables the user to use host software which was not designed to be used with USB, such as a terminal program.
Figure 3-48. Disable J-Link JTAG
3.5.4 Push Button Switches
The SAM9X60-EK features four push buttons:
• One User push button (SW1) connected to PIO_PD18. This is left at user usage.
• One Wake-up push button (SW2) connected to the SAM9X60 WKUP pin; when pressed, the processor recovers
from shutdown.
• One Board Reset push button (SW3); when pressed, the processor is reset.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 51
Page 52

1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW1
1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW3
VDDBU
USER_BUTTON_PD18
USER_nRST
WAKE_UP
0.1uF
0402
C143
VDD_3V3
GND GND
1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW4
1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW2
0.1uF
0402
C144
GND GND
GND
0.1uF
0402
C145
GND
GND
DIS_BOOT
100R 0402
1%
R197
100R 0402
1%
R192
100k
0402
5%
R194
10k
0402
5%
R186
DIS_BOOT
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
• One Disable Boot push button (SW4); if kept pressed during power-up, the processor is prevented from booting
off the on-board memories (QSPI and NAND Flash), thereby enabling booting from other sources or into ROM
Code.
Figure 3-49. User Push Buttons
3.5.5 Disable Boot
On-board push button SW4 and/or jumper J13 control the selection (CS#) of the bootable memory components
(QSPI and NAND FLASH) using a non-inverting 3-state buffer.
The rule of operation is:
• SW4 (DISABLE_BOOT) or J13 shorted = booting from QSPI and NAND FLASH is disabled.
• LED D6 indicates the state of the DIS_BOOT signal.
– Red = on-board boot memories are disabled.
– Green = on-board boot memories are enabled.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 52
Page 53

Figure 3-50. Disable Boot
DIS_BOOT
GND
2 1
43
GREEN
RED
0805
D7
1k
0402
5%
R187
1k
0402
5%
R188
GND GND
DIS_BOOT
0.1uF
0402
C146
0.1uF
0402
C147
NAND_nCS_PD04
QSPI_CS_PB20
NAND_nCS_PD04_enabled
QSPI_CS_PB20_enabled
GND
GND
GND
DIS_BOOT
DIS_BOOT
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
100k
0402
5%
R189
GND
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J13
DIS_BOOT
100k
0402
5%
R204
VDD_3V3
GND
3
1
2
TN2106
Q10
3
1
2
TN2106
Q11
3
1
2
TN2106
Q12
A
2
GND
3
Y
4
VCC
5
OE
1
74AHC1G126
U25
74HC1G126SE-7
A
2
GND
3
Y
4
VCC
5
OE
1
74AHC1G126
U26
74HC1G126SE-7
SAM9X60-EK
Function Blocks
Note: The “Disable Boot” mechanism does not disable booting from the SD card connector. The user must remove
the SD card in order to disable booting from it.
3.5.6 RGB LED
The SAM9X60-EK board features one RGB LED. The three LED cathodes are controlled via GPIO PWM pins.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 53
Page 54

LED_RED_PB11
LED_GREEN_PB12
LED_BLUE_PB13
VDD_3V3
2.2k 0402
5%
R203
GND
GND
100R
0402
1%
R206
GND
100R
0402
1%
R200
GND
GND
GND
CLV1A-FKB-CK1N1G1BB7R4S3
LD1
1k 0402
5%
R199
1k 0402
5%
R201
100R
0402
1%
R195
10k
0402
5%
R196
10k
0402
5%
R202
10k
0402
5%
R207
DNP
3
1
2
TN2106
Q13
3
1
2
TN2106
Q14
3
1
2
TN2106
Q15
SAM9X60-EK
Figure 3-51. User LEDs
Table 3-25. RGB LED PIOs
Signal PIO Function
LED_RED_PB11 PB11 PWMH1
Function Blocks
LED_GREEN_PB12 PB12 PWML1
LED_BLUE_PB13 PB13 PWML0
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 54
Page 55

4. Installation and Operation
4.1 System and Configuration Requirements
The SAM9X60-EK requires the following:
• Personal Computer
• USB cable (provided in the kit box)
4.2 Board Setup
Follow these steps before using the SAM9X60-EK:
1. Unpack the board, taking care to avoid electrostatic discharge.
2. Check the default jumper settings (see 2.5 Default Jumper Settings).
3. Connect the Micro-USB cable to connector J7 (USB-A port).
4. Connect the other end of the cable to a free port on your PC.
5. Open a terminal (console 115200, N, 8, 1) on your PC.
6. Reset the board. A startup message appears on the console.
SAM9X60-EK
Installation and Operation
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 55
Page 56

5. Erratum
GND_ETH
ETH_LED
EARTH_ETH
TD-
2
TCT
4
TD+
1
RD-
6
RCT
5
RD+
3
4X 75R
1nF,2kV
SHLD
8
NC
7
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
4
5
7
8
Right
12
11
9
10
Left
SHLD
13
SHLD
14
1
2
3
6
RJ45 J00-0045NL
J5
0.1uF
50V
0402
C83
0.1uF
50V
0402
C84
Rev. B
470R
0402
5%
R125
VDD_3V3
ETH_TX_P
ETH_TX_N
ETH_RX_P
ETH_RX_N
GND_ETH
ETH_LED
EARTH_ETH
TD-
2
TCT
4
TD+
1
RD-
6
RCT
5
RD+
3
4X 75R
1nF,2kV
SHLD
8
NC
7
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
4
5
7
8
Right
12
11
9
10
Left
SHLD
13
SHLD
14
1
2
3
6
RJ45 J00-0045NL
J5
0.1uF
50V
0402
C83
0.1uF
50V
0402
C84
Rev. 2
470R
0402
5%
R125
VDD_3V3
ETH_TX_P
ETH_TX_N
ETH_RX_P
ETH_RX_N
1. On SAM9X60-EK Rev. B, the Ethernet activity LED on RJ45 connector J5 is inoperative due to an incorrect
LED connection. This issue is solved in Rev. 2, as shown in the following picture. Nevertheless, the Ethernet
port is perfectly operational on Rev. B boards.
Figure 5-1. RJ45 Connector Right LED Connection Change from Rev. B to Rev. 2
SAM9X60-EK
Erratum
2. SAM9X60-EK Rev. B has the DSC1001DI5-025.0000 in the place of Y6 while SAM9X60-EK Rev. 2 features
the new DSC6102HI2B-025.000.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 56
Page 57

6. Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
1 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:08AM
01 - Block Diagram.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Block Diagram
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
This appendix contains the following schematics and layouts for the SAM9X60-EK board:
• Block Diagram
• Power Supply
• SAM9X60 Processor
• Processor I/Os
• Processor I/O Expansions
• On-board Memories
• USB Interfaces
• Ethernet MAC
• Wi-Fi/Bluetooth
• SDMMC, CAN and CLASSD
• Expansion Connectors
• User Interaction
• On-board J-Link
Figure 6-1. Block Diagram
SAM9X60-EK
Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 57
Page 58

Figure 6-2. Power Supply
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
2 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:08AM
02 - Power supply.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Power supply
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
10k
0402
5%
R19
1k
0402
5%
R18
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J3
GND GND
GND
VDD_MAIN_5V VDD_MAIN_5V
SHDN
220mF
3.3V
P8.3L11.7D6.8H1.8
C23
1
2
3
BAT54C
D2
PMEG6010ER
D3
VDDBU
GND
POWER_EN
0.1uF
50V
0402
C3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C9
GND
IN
1
IN_PAD
7
EN
6
GND
2
FLAG
3
OUT2
5
OUT1
4
NCP349MNAETBG
U1
2
3
1
2.1mm
EJ508A
J1
VDD_MAIN_5V_
GND
EXT_5V DC_5V
180R 0603
FB1
USB_5V
0.1uF
50V
0402
C7
2
71
6
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q1A
5
8 4
3
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q1B
2
71
6
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q2A
5
8 4
3
SIA923AEDJ-T1-GE3
Q2B
GND GND GND GND
GND GND GND
Shunt2.54mm 1x2
JP2
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP1
I2CADR : 1001_101[R/W]
GND GND GND
10k
0402
5%
R4
VDD_3V3
VDD_MAIN_5V_ VDD_MAIN_5V
PAC1710_TWCK
PAC1710_TWD
VDD_MAIN_5V
GND
PAC1710_INT
1 2
3
4
0.01R
12061%0.25W
R1
SENSE+
1
SENSE-
2
NC
3
NC
4
GND
5
ADDR_SEL
6
ALERT#
7
SMDATA
8
SMCLK
9
VDD
10
PAD
11
PAC1710
U2
5V_P 5V_N
TP LOOP Black TH
TP1
4.7uF
10V
0402
C5
0.1uF
50V
0402
C6
GND GNDGND GND
VDD_1V15
VDD_MAIN_5V
2.2uH
L1
GND
GNDGND
VDD_1V8
GND
GND
GND
MIC2800_nRST
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C17
0.1uF
50V
0402
C18
0.1uF
50V
0402
C19
I2CADR : 0010_111[R/W]
8.45k
0603
1%
R14
10k
0402
5%
R13
10k
0402
5%
R12
PAC1934_TWCK
PAC1934_TWD
VDDCORE
VDDIOM
VDD_3V3
PAC1934_INT
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R7
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R8
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R9
SENSE1_P
SENSE1_N
S
E
NS
E
2_
N
SENSE2_P
SENSE3_P
SENSE3_N
4.7uF
10V
0402
C13
0.1uF
50V
0402
C14
4.7uF
10V
0402
C15
0.1uF
50V
0402
C16
GND
GND
GND
600mA
300mA
300mA
VDD_3V3_LDO
POWER_EN
100µF
16V
Radial, Can
C4
GND
VDD_3V3_LDOVDD_3V3_LDO
VDD_3V3_LDO
GND
MIC2800_nRST
STARTB
USBA_VBUS_5V
10uF
25V
1206
C10
10uF
25V
1206
C11
10uF
25V
1206
C12
10uF
25V
1206
C1
10uF
25V
1206
C2
10uF
25V
1206
C21
10uF
25V
1206
C22
10uF
25V
1206
C8
VDD_3V3
SENSE2+
13
S
E
NS
E
1-
12
SENSE1+
11
VDD
2
SENSE2-
14
VDD I/O
15
PWRDN
16
SENSE3-
7
ADDRSEL
6
SLOW/ALERT
1
SM_CLK
4
S
ENSE3
+
8
SENSE4-
9
SENSE4+
10
SM_DATA
5
GND
3
EP
17
PAC1934
U4
VDD_3V3_LDO
VDD_1V15
VDD_1V8
VDD_3V3
VDDIOM
VDDCORE
VDD_3V3
10nF
16V
0402
C20
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J2
100R
0402
1%
R20
100R
0402
1%
R6
1N4148
D1
20k 0402 1%
R11
100k
0402
5%
R29
100k
0402
5%
R2
100k
0402
5%
R3
100k
0402
5%
R5
100k
0402
5%
R15
100k
0402
5%
R16
100k
0402
5%
R17
1 2
3
4
0.01R
1206
1%
R10
S
E
NS
E
4_
P
SENSE4_N
VDD_3V3 VDD_3V3_MPU
Input Power Options
PMIC
Shut-down
Power Measurement
Battery Unit
LOWQ
1
BIAS
2
SGND
3
PGND
4
SW
5
VIN
6
VIN
7
LDO2
8
FB
9
LDO
10
LDO1
11
POR
12
CSET
13
CBYP
14
EN1
15
EN2
16
MIC2800-G8SYML-TR
U3
3
1
2
TN2106
Q3
3
1
2
TN2106
Q4
3
1
2
TN2106
Q5
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
3 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:08AM
03 - Processor SAM9X60.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Processor SAM9X60
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
GND
0.1uF16V0201
C32
0.1uF16V0201
C33
SAM9X60 POWER SUPPLY
4.7uF10V0402
C31
VDDOUT25
VDDBU
VDDCORE
VDDIOM
0.1uF16V0201
C34
0.1uF16V0201
C36
0.1uF16V0201
C37
0.1uF16V0201
C38
0.1uF16V0201
C41
0.1uF16V0201
C42
0.1uF16V0201
C43
0.1uF16V0201
C44
0.1uF16V0201
C45
0.1uF16V0201
C46
0.1uF16V0201
C48
0.1uF16V0201
C49
4.7uF10V0402
C47
0.1uF16V0201
C50
0.1uF16V0201
C51
GND
Decoupling caps should be placed as close as possible to their corresponding power balls
Place C19 close to L11 or P13, and place C30 close to P10
4.7uF10V0402
C35
VDDIN33
VDDIN33
2.2uF10V0402
C52
4.7uF10V0402
C40
4.7uF10V0402
C39
0R 0402
R30
VDD_3V3_MPU
VDD_3V3_MPU
MIC2800_nRST
JTAG_nRST
100R 04021%
R185
100R 04021%
R190
100R 04021%
R191
USER_nRST
MPU_nRST
SAM9X60 Core SAM9X60 Reset
SAM9X60 ClocksSAM9X60 Power
0.1uF
50V
0402
C29
GND
TP2
VDD_3V3
GND
XIN
GND
24MHz
18pF
ABM8G-24.000MHZ-18-D2Y-T
Y1
DNP
27pF
0402
C24
DNP
27pF0402
C25
DNP
1M
0402
5%
R21
DNP
STB1GND
2
OUT3VDD
4
24MHz
DSC1001CI5-024.0000
Y3
GND
XOUT
0R
0402
R28
32.768Khz
ABS06-32.768KHZ-T
Y2
GND
XIN32
XOUT32
20pF
0402
C26
20pF0402
C27
1M
0402
5%
R24
DNP
0R
0402
R27
DNP
0R
0402
R91
DNP
XIN
XOUT
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TDI
JTAG_TDO
JTAG_TMS
JTAG_RTCK
USBA_N
USBA_P
USBB_N
USBB_P
USBC_N
USBC_P
0R
0402
R26
VDDBU
5.62k
0402 1%
R23
SHDN
WAKE_UP
XIN
XOUT
XIN32
XOUT32
GND
GND
SAM9X60 CONFIG
GND
1uF
10V
0201
C28
10R
0201
1%
R25
0R 0402
R22
DNP
VDD_3V3_MPU
MPU_nRST
4.7k
0201
1%
R120
4.7k
0201
1%
R121
0.1uF
16V
0201
C63
0.1uF
16V
0201
C66
GND
4.7uF
10V
0402
C65
GND
DDR_A2
DDR_A3
DDR_A4
DDR_A5
DDR_A6
DDR_A7
DDR_A8
DDR_A9
DDR_A10
DDR_A11
DDR_A13
DDR_A14
DDR_A15
DDR_D3
DDR_D6
DDR_D4
DDR_D1
DDR_D5
DDR_D2
DDR_D7
DDR_D0
DDR_D12
DDR_D15
DDR_D13
DDR_D8
DDR_D9
DDR_D10
DDR_D14
DDR_D11
DDR_DQM0
DDR_DQM1
DDR_DQS0_P
DDR_DQS0_N
DDR_DQS1_P
DDR_DQS1_N
DDR_RAS
DDR_CAS
DDR_WE
DDR_CS
DDR_CLK_P
DDR_CLK_N
DDR_CKE
22pF
50V
0402
C62
DDR_A16
DDR_A17
DDR_A18
20k
0402
1%
R119
GND
VDDIOM
DDR_SDA10
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
SAM9X60 DDR Controller
DDR_VREF
DDR_VREF
DDR_VREF
51R
0402
R149
SAM9X60 DDR I/Os
SDCKn
B14
SDCK
A15
SDCKE
F13
nWR0
E8
SDA10
D12
nRD
F12
nWR1
A10
DDR_CAL
B8
A1
G16
A15
G15
A8
F16
A4
B12
A0
B10
A13
B11
A10
C11
A6
A12
A2
A13
A17
F14
A12
A11
A19
H14
A16
E14
A18
C16
A3
D15
A7
B16
A5
E11
A14
C15
A9
D14
A11
E13
D10
F9
D9
D8
D13
B9
D14
D11
D6
J16
D11
A9
D8
G9
D12
F10
D3
H11
D4
J14
D1
H10
D7
J13
D0
H16
D2
H15
D5
J11
D15
C9
DDR_VREF
A14
nCS1
E16
nCS0
F15
DQS1
D9
SDWE
D16
nDQS1
E9
RAS
E15
nDQS0
H13
DQS0
H12
CAS
C12
DQM1
C8
DQM0
G11
nWR3
L14
SAM9X60-V/DWB
U5E
XIN
R10
XOUT
T10
XIN32
T9
XOUT32
R9
SHDN
R11
WKUP
T11
JTAGSEL
P9
nRST
R1
TST
J9
HHSDPA
T12
HHSDMA
R12
HHSDPB
T13
HHSDMB
T14
HHSDPC
P12
HHSDMC
N12
TCK
R3
TDI
F3
TDO
H5
TMS
F5
RTCK
T2
ADVREFP
D5
RTUNE
P11
ADVREFN
C5
SAM9X60-V/DWB
U5F
VDDCORE
L6
VDDCORE
F6
VDDCORE
F11
VDDIOM
G14
VDDIOM
C10
VDDIOM
C13
VDDANA
C4
VDDIN33
P13
VDDOUT25
P10
VDDIN33
L11
GND
J8
GND
E7
GND
G12
GNDANA
B4
GNDIN33
R13
VDDNF
K14
VDDIOP0
G3
GND
E10
GND
B13
GND
K5
GND
G5
GND
N15
VDDQSPI
C7
VDDIOP0
K3
GND
H8
GND
H9
GNDIN33
M10
GND
K12
GND
T16
GND
A1
GND
A16
GND
T1
VDDBU
P7
GND
M7
VDDIOP1
N3
GND
N2
SAM9X60-V/DWB
U5G
SAM9X60-EK
Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
Figure 6-3. SAM9X60 Processor
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 58
Page 59
Figure 6-4. Processor I/Os
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
4 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:09AM
04 - Processor IOs.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Processor IOs
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
LCD_D17_PC17
LCD_D18_PC18
LCD_D19_PC19
LCD_D20_PC20
LCD_D21_PC21
LCD_D22_PC22
LCD_D23_PC23
LCD_PCLK_PC30
LCD_VSYNC/CS_PC27
LCD_HSYNC/WE_PC28
LCD_DATA_ENABLE_PC29
LCD_IRQ1_PC25
LCD_IRQ2_PB17
LCD_PWM_PC26
FLEXCOM5_IO1_RX_PA21
FLEXCOM5_IO0_TX_PA22
SDMMC0_DAT2_PA19
SDMMC0_CMD_PA16
SDMMC0_DAT3_PA20
SDMMC0_CLK_PA17
SDMMC0_DAT0_PA15
SDMMC0_DAT1_PA18
SDMMC0_CD_PA23
CLASSD_L0_PA24
CLASSD_L1_PA25
CLASSD_L2_PA26
CLASSD_L3_PA27
WILC3000_ENABLE_PA29
WILC3000_INTERRUPT_PA28
ETH0_TXCK_PB04
ETH0_TX0_PB09
ETH0_TXEN_PB07
ETH0_TX1_PB10
ETH0_RX1_PB01
ETH0_RX0_PB00
ETH0_RXER_PB02
ETH0_RXDV_PB03
ETH0_MDC_PB06
ETH0_MDIO_PB05
ETH0_IRQ_PB08
NAND_IO0_PD06
NAND_IO1_PD07
NAND_IO2_PD08
NAND_IO3_PD09
NAND_IO4_PD10
NAND_IO5_PD11
NAND_IO6_PD12
NAND_IO7_PD13
NAND_CLE_PD03
NAND_ALE_PD02
NAND_nWE_PD01
NAND_nRE_PD00
NAND_nCS_PD04
NAND_RB_PD05
CAN/FLEXCOM_RX_PA06
CAN/FLEXCOM_TX_PA05
FLEXCOM0_IO0_PA00
FLEXCOM0_IO1_PA01
USBB_EN_5V_PD15
USBC_EN_5V_PD16
MBUS_AD4_PB15
USBA_VBUSDETECT_PB16
MBUS_RST_PB14
NRST_PB25
FLEXCOM6_TWD_PA30
FLEXCOM6_TWCK_PA31
SEL_FNCT1_PD19
SEL_FNCT2_PD20
CAN/DBGU_TX_PA10
CAN/DBGU_RX_PA09
MCP23008_INT_PD17
PA02
PA03
PA04
PA07
PA08
PA11
PA12
PA13
PA14
PB19
PB20
PB21
PB22
PB23
PB24
MBUS_INT_PB18
PC31
PB11
PB12
PB13
CAN_STBY_PD21
SAM9X60 PORTPA
SAM9X60 PORTP C
SAM9X60 PORT PB
SAM9X60 PORTPD
LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12
LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13
LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14
LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15
LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00
LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02
LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04
LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06
LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08
LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10
LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01
LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03
LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05
LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07
LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09
LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11
LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24
LCD_ID_PD14
USER_BUTTON_PD18
LCD_D16_ISI_nRST_PC16
SAM9X60 PIOs
22R 0402 1%
R31
22R 0402 1%
R32
22R 0402 1%
R38
22R 0402 1%
R39
22R 0402 1%
R40
22R 0402 1%
R41
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT3_PA04
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT2_PA03
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT1_PA02
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT0_PA11
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CMD_PA12
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CK_PA13
FLEXCOM5_IO4_BT_RTS_PA07
FLEXCOM5_IO3_BT_CTS_PA08
PA02
PA03
PA04
PA07
PA08
PA11
PA12
PA13
PA14
22R 0402 1%
R42
22R 0402 1%
R43
22R 0402 1%
R44
22R 0402 1%
R45
22R 0402 1%
R46
22R 0402 1%
R50
22R 0402 1%
R51
22R 0402 1%
R52
22R 0402 1%
R53
22R 0402 1%
R54
22R 0402 1%
R55
22R 0402 1%
R56
22R 0402 1%
R57
22R 0402 1%
R58
22R 0402 1%
R59
EXT40_GPIO_PA02
EXT40_GPIO_PA03
EXT40_GPIO_PA04
EXT40_SPI_MOSI_PA12
EXT40_SPI_MISO_PA11
EXT40_SPI_SCLK_PA13
EXT40_GPIO_PA14
EXT40_NPCS1_PA07
EXT40_NPCS2_PA08
MBUS_NPCS0_PA14
MBUS_SPCK_PA13
MBUS_MISO_PA11
MBUS_MOSI_PA12
QSPI_IO0_PB21
QSPI_IO1_PB22
QSPI_IO2_PB23
QSPI_IO3_PB24
QSPI_SCK_PB19
QSPI_CS_PB20
22R 0402 1%
R69
22R 0402 1%
R70
22R 0402 1%
R71
22R 0402 1%
R72
PB19
PB20
PB21
22R 0402 1%
R74
22R 0402 1%
R75
22R 0402 1%
R77
22R 0402 1%
R79
22R 0402 1%
R80
22R 0402 1%
R81
PB22
PB23
PB24
PC31
EXT40_I2SMCK_PB23
EXT40_CLK1_PC31
EXT40_I2SWS_PB20
EXT40_I2SCK_PB19
EXT40_GPIO_PB24
EXT40_I2SDIN_PB21
EXT40_I2SDOUT_PB22
ETH0_PCK1_PC31
LED_RED_PB11
LED_GREEN_PB12
LED_BLUE_PB13
EXT40_CLK2_PB13
EXT40_PWM1_PB12
EXT40_PWM0_PB11
0R 0402
R66
0R 0402
R63
0R 0402
R60
PB11
PB12
PB13
MBUS_PWM_PB13
0R 0402
R65
22R 0402 1%
R82
22R 0402 1%
R85
22R 0402 1%
R86
22R 0402 1%
R88
SAM9X60 PIO Muxing
PA0
P2
PA1
M3
PA2
P1
PA3
L3
PA4
N1
PA5
L4
PA6
M2
PA7
K6
PA8
M1
PA9
G8
PA10
L2
PA11
H7
PA12
L1
PA13
J6
PA14
K1
PA15
H6
PA16
K2
PA17
J3
PA18
J1
PA19
J5
PA20
J2
PA21
G6
PA22
G1
PA23
J4
PA24
F8
PA25
H1
PA26
F7
PA27
H2
PA28
F1
PA29
H3
PA30
G2
PA31
H4
SAM9X60-V/DWB
U5A
PB0
F4
PB1
C1
PB2
D3
PB3
D1
PB4
E3
PB5
E1
PB6
D2
PB7
A5
PB8
E6
PB9
A2
PB10
A3
PB11
D6
PB12
C2
PB13
A4
PB14
F2
PB15
B5
PB16
B3
PB17
B1
PB18
E4
PB19
C6
PB20
A6
PB21
A7
PB22
B7
PB23
B6
PB24
A8
PB25
E2
SAM9X60-V/DWB
U5B
PC0
M4
PC1
P4
PC2
N5
PC3
P5
PC4
L5
PC5
R4
PC6
M6
PC7
T3
PC8
N8
PC9
T4
PC10
P6
PC11
N6
PC12
R5
PC13
L7
PC14
T5
PC15
J7
PC16
R6
PC17
K8
PC18
T6
PC19
L8
PC20
P8
PC21
M8
PC22
R7
PC23
K9
PC24
R8
PC25
L9
PC26
T8
PC27
M9
PC28
N9
PC29
L10
PC30
T7
PC31
M13
SAM9X60-V/DWB
U5C
PD0
R14
PD1
T15
PD2
P15
PD3
N14
PD4
R16
PD5
N11
PD6
K16
PD7
J12
PD8
K15
PD9
J10
PD10
L16
PD11
K11
PD12
L15
PD13
J15
PD14
L12
PD15
M16
PD16
M14
PD17
N16
PD18
L13
PD19
P16
PD20
M11
PD21
M15
SAM9X60-V/DWB
U5D
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
5 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:09AM
05 - Processor IO Expansions.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Processor IO Expansions
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
FLEXCOM0_IO0_PA00
FLEXCOM0_IO1_PA01
22R 0402 1%
R64
22R 0402 1%
R67
22R 0402 1%
R68
22R 0402 1%
R73
22R 0402 1%
R76
22R 0402 1%
R78
2.2k
0402
5%
R62
2.2k
0402
5%
R61
VDD_3V3 VDD_3V3
MCP23008_TWD
MCP23008_TWCK
EEPROM_TWCK
EEPROM_TWD
FLEXCOM6_TWD_PA30
FLEXCOM6_TWCK_PA31
22R 0402 1%
R87
22R 0402 1%
R89
22R 0402 1%
R90
22R 0402 1%
R93
22R 0402 1%
R94
22R 0402 1%
R95
2.2k
0402
5%
R84
2.2k
0402
5%
R83
VDD_3V3 VDD_3V3
22R 0402 1%
R92
22R 0402 1%
R96
PAC1934_TWCK
PAC1934_TWD
PAC1710_TWCK
PAC1710_TWD
EXT40_TWD
EXT40_TWCK
LCD_ISI_TWD
LCD_ISI_TWCK
MBUS_TWD
MBUS_TWCK
Upper Right Board TWI
Lower Left Board TWI
EXT40_GP7
EXT40_GP6
EXT40_GP5
USBB_OVCUR
USBC_OVCUR
PAC1934_INT
PAC1710_INT
MCP23008_TWCK
MCP23008_TWD
VDD_3V3
GND
VDD_3V3
MCP23008_INT_PD17
NRST_PB25
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C53
100k
0402
5%
R35
DNP
100k
0402
5%
R36
DNP
100k
0402
5%
R37
DNP
100k
0402
5%
R49
100k
0402
5%
R48
100k
0402
5%
R47
100k
0402
5%
R34
10k
0402
5%
R33
Port Expander
GND
GND
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
GND
GND
22R 0402 1%
R140
22R 0402 1%
R142
22R 0402 1%
R144
22R 0402 1%
R146
SEL_FNCT1_PD19
CAN/FLEXCOM_RX_PA06
CAN/FLEXCOM_TX_PA05
EXT40_TXD
EXT40_RXD
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ126USG
U16
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ125USG
U14
0.1uF
50V0402
C102
0.1uF
50V0402
C104
GND
GND
22R 0402 1%
R141
22R 0402 1%
R143
22R 0402 1%
R145
22R 0402 1%
R147
SEL_FNCT2_PD20
DBGU_TX_PA10
DBGU_RX_PA09
CAN/DBGU_TX_PA10
CAN/DBGU_RX_PA09
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ126USG
U17
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ125USG
U15
VDD_3V3
GND
VDD_3V3
GND
0.1uF
50V0402
C103
0.1uF
50V0402
C105
FLEXCOM5_IO1_RX_PA21
FLEXCOM5_IO0_TX_PA22
GND
GND
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
GND
GND
MBUS_RX
MBUS_TX
22R 0402 1%
R156
22R 0402 1%
R157
22R 0402 1%
R158
22R 0402 1%
R159
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ125USG
U21
OE1
1
OE2
7
IN1
2
OUT2
3
GND
4
VCC
8
OUT1
6
IN2
5
NL27WZ126USG
U23
WILC3000_ENABLE_PA29
0.1uF
50V0402
C125
0.1uF
50V0402
C129
WILC_BT_TX
WILC_BT_RX
CAN1_TX
CAN1_RX
CAN0_TX
CAN0_RX
I2CADR : 0100_000[R/W]
A2
1
A1
2
A0
3
RESET
4
GP6
15
GP7
16
VSS
17
VDD
18
NC
5
NC
6
INT
7
NC
8
GP0
9
GP5
14
GP4
13
GP3
12
GP2
11
GP1
10
SCL
19
SDA
20
EP
21
MCP23008
U6
CAN1 / EXT40 UART Selection
CAN0 / DEBUG UART Selection
MikroBUS UART / WILC BT UART Selection
SAM9X60-EK
Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
Figure 6-5. Processor I/O Expansions
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 59
Page 60

Figure 6-6. On-board Memories
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
6 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:10AM
06 - On Board Memories.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
On Board Memories
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
CE
1
SO/SIO1
2
WP/SIO23VSS
4
SI/SIO0
5
SCK
6
HOLD/SIO3
7
VDD
8
SST26VF064B
U8
0.1uF
50V
0402
C55
GND
QSPI_CS_PB20_enabled
QSPI_IO0_PB21
QSPI_IO1_PB22
QSPI_IO2_PB23
QSPI_IO3_PB24
QSPI_SCK_PB19
NAND_CLE_PD03 NAND_IO0_PD06
NAND_IO1_PD07
NAND_IO2_PD08
NAND_IO3_PD09
NAND_IO4_PD10
NAND_IO5_PD11
NAND_IO6_PD12
NAND_IO7_PD13
NAND_ALE_PD02
NAND_nWE_PD01
NAND_nRE_PD00
NAND_nCS_PD04_enabled
NAND_RB_PD05
0.1uF
50V
0402
C58
0.1uF
50V
0402
C59
0.1uF
50V
0402
C60
0.1uF
50V
0402
C61
GND
GND
i
NAND-Flash
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
i
NAND-Flash
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
NC
1
NC
2
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
R/B
7
RE
8
CE
9
NC
10
NC
11
Vcc
12
Vss
13
NC
14
NC
15
CLE
16
ALE
17
WE
18
WP
19
NC
20
NC
21
NC
22
NC
23
NC
24
Vss1
25
NC
26
NC
27
NC
28
I/O0
29
I/O1
30
I/O2
31
I/O3
32
NC
33
Vcc1
34
NC
35
Vss
36
Vcc
37
DNU
38
Vcc1
39
NC
40
I/O4
41
I/O5
42
I/O6
43
I/O7
44
NC
45
NC
46
DNU
47
Vss1
48
MT29F4G08ABAEAWP:E TR
TSOP-48
U9
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
10k
0402
5%
R106
10k
0402
5%
R116
10k
0402
5%
R117
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R99
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R100
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R101
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R102
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R103
DNP
10k
0402
5%
R114
10k
0402
5%
R115
4Gb NAND Flash
A0
5
A1
4
SDA
3
SCL
1
VCC
6
VSS
2
24AA025E48
U7
0.1uF
50V
0402
C54
GND
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
GND
EEPROM_TWCK
EEPROM_TWD
10k
0402
5%
R97
10k
0402
5%
R98
10k
0402 5%
R104
DNP
10k
0402 5%
R105
DNP
Serial Quad I/O Flash
TWI EEPROM
0.1uF 16V 0201
C71
0.1uF 16V 0201
C72
0.1uF 16V 0201
C73
0.1uF 16V 0201
C74
0.1uF 16V 0201
C78
0.1uF 16V 0201
C79
0.1uF 16V 0201
C80
1000pF 25V 0402
C81
1000pF 25V 0402
C82
DDR_A2
DDR_A3
DDR_A4
DDR_A5
DDR_A6
DDR_A7
DDR_A8
DDR_A9
DDR_A10
DDR_A11
DDR_A13
DDR_A14
DDR_A15
DDR_A16
DDR_A17
DDR_A18
DDR_D0
DDR_D1
DDR_D2
DDR_D3
DDR_D4
DDR_D5
DDR_D6
DDR_D7
DDR_D8
DDR_D9
DDR_D10
DDR_D11
DDR_D12
DDR_D13
DDR_D14
DDR_D15
DDR_RAS
DDR_CAS
DDR_WE
DDR_CS
DDR_CKE
DDR_CLK_P
DDR_CLK_N
DDR_DQM0
DDR_DQM1
DDR_DQS0_P
DDR_DQS0_N
DDR_DQS1_P
DDR_DQS1_N
VDDIOM
VDDIOM
VDDIOM
DDR_SDA10
GND
i
BYTELANE0
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
i
ADDR-CTL
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
i
BYTELANE1
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
4.7uF 10V 0402
C67
4.7uF 10V 0402
C68
0.1uF 50V 0402
C69
0.1uF 50V 0402
C70
0.1uF 50V 0402
C75
0.1uF 50V 0402
C76
0.1uF 50V 0402
C77
10nF 16V 0402
C64
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
2Gb DDR2-800 SDRAM 16bit
DDR_VREF
I2CADR : 1010_011[R/W]
GND
i
QSPI
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
A0
M8
A1
M3
A2
M7
A3
N2
A4
N8
A5
N3
A6
N7
A7
P2
A8
P8
A9
P3
A10
M2
A11
P7
A12
R2
A13
R8
BA0
L2
BA1
L3
BA2
L1
CKE
K2
CK_P
J8
CK_N
K8
RAS
K7
CAS
L7
WE
K3
CS
L8
DQ0
G8
DQ1
G2
DQ2
H7
DQ3
H3
DQ4
H1
DQ5
H9
DQ6
F1
DQ7
F9
DQ8
C8
DQ9
C2
DQ10
D7
DQ11
D3
DQ12
D1
DQ13
D9
DQ14
B1
DQ15
B9
LDQS_P
F7
LDQS_N
E8
UDQS_P
B7
UDQS_N
A8
LDM
F3
UDM
B3
ODT
K9
NC1
A2
NC2
E2
NC3
R3
NC4
R7
VDD1
A1
VDD2
E1
VDD3
J9
VDD4
M9
VDD5
R1
VDDQ1
A9
VDDQ2
C1
VDDQ3
C3
VDDQ4
C7
VDDQ5
C9
VDDQ6
E9
VDDQ7
G1
VDDQ8
G3
VDDQ9
G7
VDDQ10
G9
VDDL
J1
VREF
J2
VSS1
A3
VSS2
E3
VSS3
J3
VSS4
N1
VSS5
P9
VSSQ1
A7
VSSQ2
B2
VSSQ3
B8
VSSQ4
D2
VSSQ5
D8
VSSQ6
E7
VSSQ7
F2
VSSQ8
F8
VSSQ9
H2
VSSQ10
H8
VSSDL
J7
W972GG6KB-25
WBGA-84
U10
100Ω± 10% differential trace impedanc e
Routing top or bottom
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
100Ω± 10% differential trace impedanc e
Routing top or bottom
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
100Ω± 10% differential trace impedanc e
Routing top or bottom
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
7 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:10AM
07 - USB ports.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
USB interfaces
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
USBA_N
USBA_P
20pF
50V
0402
C106
200k
0402
1%
R150
GND
GND GND
USBA_N
USBA_P
USBA_VBUSDETECT_PB16
EARTH_USB_A
EARTH_USB_B GND
USBB_VBUS_5V
USBC_VBUS_5V
GND
USBB_N
USBB_P
USBC_N
USBC_P
USBC_N
USBC_P
USBB_N
USBB_P
USBA_VBUS_5V
USBB_VBUS_5V
USBB_OVCUR
USBB_EN_5V_PD15
VDD_MAIN_5V
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C118
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C115
GND
VBUS_USBB
USBC_VBUS_5V
USBC_OVCUR
USBC_EN_5V_PD16
VDD_MAIN_5V
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C124
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C121
GND
VBUS_USBC
GND
GND
100µF
16V
Radial, Can
C116
100µF
16V
Radial, Can
C122
10uF
25V
1206
C119
10uF
25V
1206
C120
10uF
25V
1206
C123
10uF
25V
1206
C113
10uF
25V
1206
C114
10uF
25V
1206
C117
180R
FB5
180R
FB7
180R
FB6
180R
FB8
100k
0402
5%
R148
10k
0402
5%
R152
10k
0402
5%
R153
10k
0402
5%
R154
10k
0402
5%
R155
DIFF90
DIFF90
DIFF90
DIFF90
DIFF90
DIFF90
VBUS_USBA
ID
4
VBUS
1
GND
5
D-
2
D+
3
0
USB2.0MICRO-B FEMALE
J7
USB-A port
USB-B port
USB-C port
USB-B power switch
USB-C power switch
VBUS1
1
GND1
4
D1-
2
D1+
3
0
USB2.0STD-A DUAL FEMALE
J8A
VBUS2
5
GND2
8
D2-
6
D2+
7
USB2.0STD-A DUAL FEMALE
J8B
EN
1
FLG2GND
3
NC4NC
5
OUT6IN
7
OUT
8
USB Power Switch
U19
MIC2025-1YM
EN
1
FLG2GND
3
NC4NC
5
OUT6IN
7
OUT
8
USB Power Switch
U20
MIC2025-1YM
90Ω ±15% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
90Ω ±15% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
90Ω ±15% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
SAM9X60-EK
Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
Figure 6-7. USB Interfaces
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 60
Page 61

Figure 6-8. Ethernet MAC
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
8 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:10AM
08 - Ethernet MAC.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Ethernet MAC
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
ETH_TX_P
1k
0402
5%
R123
1k
0402
5%
R122
2.2uF 16V0603
C85
180R
BLM18PG181SN1D
FB2
GND_ETH
GND
VDD_3V3
TXP
6
TXM
5
RXP
4
RXM
3
VDD_1V2
1
GND
22
PADDLE
25
REXT
9
XI
8
XO
7
REF_CLK
16
TXD1
21
TXD0
20
TXEN
19
RXD1
12
RXD0
13
RXER
17
CRS_DV/PHYAD[1_0]
15
MDC
11
MDIO
10
INTRP
18
VDDA_3V3
2
VDDIO
14
LED0/ANEN_SPEED
23
RST
24
KSZ8081RNAIA-TR
U11
6.49k 0402 1%
R124
ETH_LED
EARTH_ETH
1 3
25MHz
ECS-250-20-33-CKM-TR
Y5
DNP
GNDGND
VDD_3V3
GND
10k
0402
5%
R129
ETH_LED
10k
0402
5%
R127
GND
VDD_3V3
ETH_TX_N
ETH_RX_P
ETH_RX_N
GND_ETH
GND
EARTH_ETH
180R
BLM18PG181SN1D
FB3
20pF
50V
0402
C92
DNP
20pF
50V
0402
C91
DNP
ETH_XI
ETH_XO
ETH_XI
VDD_3V3
GND
ETH0_TXCK_PB04
i
Ethernet 10/100
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.5mm]
NRST_PB25
TP4
ETH0_TX0_PB09
ETH0_TXEN_PB07
ETH0_TX1_PB10
ETH0_RX1_PB01
ETH0_RX0_PB00
ETH0_RXER_PB02
ETH0_RXDV_PB03
ETH0_MDC_PB06
ETH0_MDIO_PB05
ETH0_IRQ_PB08
GND
ETH0_PCK1_PC31
10uF
25V
1206
C87
10uF
25V
1206
C89
GND
TD-
2
TCT
4
TD+
1
RD-
6
RCT
5
RD+
3
4X 75R
1nF,2kV
SHLD
8
NC
7
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
4
5
7
8
Right
12
11910
Left
SHLD
13
SHLD
14
1
2
3
6
RJ45 J00-0045NL
J5
0.1uF
50V
0402
C83
0.1uF
50V
0402
C84
0.1uF 50V0402
C86
0.1uF
50V
0402
C88
0.1uF
50V
0402
C90
0.1uF
50V
0402
C93
0R 0402
R130
0R 0402
R126
DNP
0R
0402
R128
DNP
0R
0402
R133
DNP
0R
0402
R131
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
DIFF100
Ethernet PHYEthernet Connector
51R
0402
R132
470R
0402
5%
R125
VDD_3V3
EN
1
GND2OUT
3
VDD
4
DSC6102HI2B-025.000
Y6
100Ω ±5Ω differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
50Ω± 10% single-end ed trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
9 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:10AM
09 - Wi-Fi BT module.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Wi-Fi BT
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
GND
GND GND
VDD_3V3
GNDGND
10k
0402
5%
R168
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
OUT
1
GND2OE
3
VDD
4
32.768kHz
ASH7KW-32.768KHZ-L-T
Y7
DNP
GPIO20
GPIO19
GPIO18
GPIO17
1
2
3
HDR-2.54Female 1x3
J9
DNP
UART_TXD
UART_RXD
GND
RTS/SDA
CTS/SCL
VDD_3V3
GND GND
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT3_PA04
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT2_PA03
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT1_PA02
SDMMC1_WILC3000_DAT0_PA11
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CMD_PA12
SDMMC1_WILC3000_CK_PA13
FLEXCOM5_IO4_BT_RTS_PA07
FLEXCOM5_IO3_BT_CTS_PA08
WILC3000_INTERRUPT_PA28
WILC3000_ENABLE
NRST_PB25
VDD_3V3_WILC VDD_3V3
180R
FB9
2.2uF
16V
0603
C134
VDD_MAIN_5V
VIN
1
VIN
2
SHDN
3
GND
4
PWRGD
5
CDELAY
6
SENSE
7
VOUT
8
EP
9
MCP1725/3.3V
U22
2.2uF
16V
0603
C126
GND
2.2uF
16V
0603
C127
GND
1000pF
25V
0402
C128
WILC3000_ENABLE
WILC3000_ENABLE_PA29
VDD_3V3
GND
GPIO17
GPIO18
GPIO19
GPIO20
CTS/SCL
RTS/SDA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
HDR-2.54Female 1x8
J10
DNP
VDD_3V3_WILC
VDD_3V3
2 1
43
GREEN
RED
0805
D4
VDD_WILC
0.1uF
50V
0402
C130
0.1uF
50V
0402
C133
0.1uF
50V
0402
C135
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C136
0R 0402
R169
0R 0402
R170
0R 0402
R171
0R 0402
R173
0R
0402
R174
1k
0402
5%
R160
1k
0402
5%
R161
100k
0402
5%
R162
100k 0402 5%
R163
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R164
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R165
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R166
DNP
100k 0402 5%
R167
DNP
47uF
16V
1206
C131
47uF
16V
1206
C132
DNP
WILC_BT_TX
WILC_BT_RX
WILC_LED_RED
WILC_LED_GREEN
WILC_LED_RED
WILC_LED_GREEN
VBAT
18
VDDIO
12
BT_TXD
8
BT_RXD
9
BT_RTS
10
BT_CTS
11
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
GND
1
GND
13
GND
21
GND28GND
36
PADDLE
37
GPIO21
35
GPIO0
34
GPIO17
29
GPIO18
30
GPIO19
31
GPIO3
14
GPIO20
32
GPIO4
15
SD_CLK/GPIO8
22
SD_CMD/SPI_SCK
23
SD_DAT0/SPI_MISO
24
SD_DAT1/SPI_SSN
25
SD_DAT2/SPI_MOSI
26
SD_DAT3/GPIO7
27
SDIO/SPI_CFG
2
RTC_CLK
20
CHIP_EN
19
IRQN
33
RESETN
7
UART_TXD
16
UART_RXD
17
ATWILC3000-MR110CA
U24
DNP
GND2NC
3
VDD4Output
1
DSC6083CE2A-032K768
Y8
WiFi / BT MODULE
WiFi / BT ENABLE
51R
0402
R175
51R
0402
R172
DNP
i
SDMMC1
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
SAM9X60-EK
Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
Figure 6-9. Wi-Fi/Bluetooth
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 61
Page 62

Figure 6-10. SDMMC, CAN and CLASSD
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
10 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:11AM
10 - SDMMC, CAN & CLASSD.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
SDMMC, CAN & CLASSD
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
15pF
50V
0402
C97
VDD_MAIN_5VVDD_3V3
0R 0402
R135
GND GND GND GND
15pF
50V
0402
C101
VDD_MAIN_5VVDD_3V3
0R 0402
R138
GND GND GND GND
62R
1210
1%
R134
62R
1210
1%
R136
4700pF
50V
0402
C94
GND
62R
1210
1%
R137
62R
1210
1%
R139
4700pF
50V
0402
C98
GND
GND
CAN0_H
CAN0_L
CAN1_L
CAN1_H
CAN_STBY_PD21
RXD
4
TXD1VSS
2
VDD
3
VIO5CANL
6
CANH
7
STBY
8
EP
9
MCP2542
U12
RXD
4
TXD1VSS
2
VDD
3
VIO5CANL
6
CANH
7
STBY
8
EP
9
MCP2542
U13
0.1uF
50V
0402
C95
0.1uF
50V
0402
C96
0.1uF
50V
0402
C99
0.1uF
50V
0402
C100
CAN1_TX
CAN1_RX
CAN0_TX
CAN0_RX
SDMMC
3
1
2
SSM3J56ACT
Q6
3
1
2
SSM3K56ACT
Q7
10000pF
25V
0402
C141
1N4148W
D5
10uF
25V
1206
C137
10uF
25V
1206
C139
10uF
25V
1206
C140
GND GND
GND
3
1
2
SSM3J56ACT
Q8
3
1
2
SSM3K56ACT
Q9
10000pF
25V
0402
C142
1N4148W
D6
GND GND
180R
FB10
180R
FB11
1
2
3
4
TERMINAL 1x4
J12
GND
VDD_MAIN_5V
CLASSD_L0_PA24
CLASSD_L1_PA25
CLASSD_L2_PA26
CLASSD_L3_PA27
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP3
0R
0402
R177
0R
0402
R178
0R
0402
R181
0R
0402
R182
10uF
25V
1206
C138
VDD_AUDIO
LEFT_P
LEFT_N
10k
0402
5%
R176
10k
0402
5%
R179
10k
0402
5%
R180
10k
0402
5%
R183
CAN
CLASSD
1
2
3
4
5
TERMINAL1x5
J6
1
2
3
HDR-2.54Male 1x3
J11
VDD_3V3
SDMMC0_DAT2_PA19
SDMMC0_CMD_PA16
SDMMC0_DAT3_PA20
SDMMC0_CLK_PA17
SDMMC0_DAT0_PA15
SDMMC0_DAT1_PA18
SDMMC0_CD_PA23
GND
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C56
GND
4.7uF
10V
0402
C57
10k
0402
5%
R107
10k
0402
5%
R108
10k
0402
5%
R109
10k
0402
5%
R110
10k
0402
5%
R111
10k
0402
5%
R112
10k
0402
5%
R113
10k
0402
5%
R118
DNP
DAT3
1
CMD
2
VSS1
3
VDD
4
CLK
5
VSS2
6
DAT0
7
DAT1
8
DAT2
9
CD
10
WP
11
SHIELD
12
SD
J4
i
SDMMC0
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.25mm]
50Ω± 10% single-en ded trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
11 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:11AM
11 - Expansion connectors.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
Expansion connectors
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
GND GND
MBUS_PWM_PB13
MBUS_INT_PB18
MBUS_RX
MBUS_TX
MBUS_TWCK
MBUS_TWD
MBUS_AD4_PB15
MBUS_RST_PB14
MBUS_NPCS0_PA14
MBUS_SPCK_PA13
MBUS_MISO_PA11
MBUS_MOSI_PA12
VDD_3V3 VDD_MAIN_5V
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
HDR-2.54 Male 2x20
TSW-120-07-G-D
J16
VDD_3V3 VDD_MAIN_5V
EXT40_GP5
GND GND
EXT40_TWD
EXT40_TWCK
EXT40_I2SMCK_PB23
EXT40_GPIO_PA02
EXT40_GP6
EXT40_GP7
EXT40_SPI_MOSI_PA12
EXT40_SPI_MISO_PA11
EXT40_SPI_SCLK_PA13
EXT40_CLK1_PC31
EXT40_CLK2_PB13
EXT40_PWM1_PB12
EXT40_I2SWS_PB20
EXT40_TXD
EXT40_RXD
EXT40_I2SCK_PB19
EXT40_GPIO_PA14
EXT40_NPCS1_PA07
EXT40_NPCS2_PA08
EXT40_PWM0_PB11
EXT40_GPIO_PB24
EXT40_I2SDIN_PB21
EXT40_I2SDOUT_PB22
EXT40_GPIO_PA03
EXT40_GPIO_PA04
MikroBUS
LCD ISI Camera
40-pin GPIO
LCD_D17_PC17
LCD_D18_PC18
LCD_D19_PC19
LCD_D20_PC20
LCD_D21_PC21
LCD_D22_PC22
LCD_D23_PC23
GND
LCD_PCLK_PC30
LCD_VSYNC/CS_PC27
LCD_HSYNC/WE_PC28
LCD_DATA_ENABLE_PC29
LCD_ISI_TWD
LCD_ISI_TWCK
LCD_IRQ1_PC25
LCD_IRQ2_PB17
LCD_PWM_PC26
NRST_PB25
0R0402
R217
DNP
0R0402
R214
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
MNT
FFC
FFC/FPC 50P Female
J15
VDD_3V3
VDD_MAIN_5V
i
LCD
Matched Net Lengths [Tolerance = 0.5mm]
TP5
TP6
TP7
TP8
LCD_ID_PD14
0R 0402
R208
DNP
0R 0402
R209
DNP
0R 0402
R210
DNP
0R 0402
R211
DNP
LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12
LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13
LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14
LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15
LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00
LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02
LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04
LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06
LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08
LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10
LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01
LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03
LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05
LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07
LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09
LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11
LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24
LCD_D16_ISI_nRST_PC16
22R 0402 1%
R215
22R 0402 1%
R216
22R 0402 1%
R218
22R 0402 1%
R219
22R 0402 1%
R220
22R 0402 1%
R222
22R 0402 1%
R224
22R 0402 1%
R226
22R 0402 1%
R227
22R 0402 1%
R225
22R 0402 1%
R223
22R 0402 1%
R221
22R 0402 1%
R229
22R 0402 1%
R228
22R 0402 1%
R231
22R 0402 1%
R230
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
Header 2x15
J17
LCD_D12_ISI_PCK_PC12
LCD_D13_ISI_VSYNC_PC13
LCD_D14_ISI_HSYNC_PC14
LCD_D15_ISI_MCK_PC15
LCD_D0_ISI_D0_PC00
LCD_D2_ISI_D2_PC02
LCD_D4_ISI_D4_PC04
LCD_D6_ISI_D6_PC06
LCD_D8_ISI_D8_PC08
LCD_D10_ISI_D10_PC10
LCD_D1_ISI_D1_PC01
LCD_D3_ISI_D3_PC03
LCD_D5_ISI_D5_PC05
LCD_D7_ISI_D7_PC07
LCD_D9_ISI_D9_PC09
LCD_D11_ISI_D11_PC11
22R 0402 1%
R212
22R 0402 1%
R213
VDD_3V3
LCD_ISI_TWDLCD_ISI_TWCK
LCD_ISI_ENABLE_PC24
180R
FB12
ISI_D0
ISI_D1 ISI_D2
ISI_D3 ISI_D4
ISI_D5 ISI_D6
ISI_D7 ISI_D8
ISI_D9 ISI_D10
ISI_D11
ISI_MCK
ISI_VSYNC
ISI_HSYNC
ISI_PCK
LCD_ISI_TWDLCD_ISI_TWCK
ISI_ENISI_nRST
LCD_D16_ISI_nRST_PC16
GNDGND
AN
1
RST
2
CS
3
SCK
4
MISO
5
MOSI
6
+3.3V
7
GND
8
PWM
16
INT
15
RX
14
TX
13
SCL
12
SDA
11
+5V
10
GND
9
mikroBUS HOST
J14
SAM9X60-EK
Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
Figure 6-11. Expansion Connectors
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 62
Page 63

Figure 6-12. User Interaction
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
12 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:11AM
12 - User Interaction.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
User Interaction
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW1
1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW3
VDDBU
USER_BUTTON_PD18
USER_nRST
WAKE_UP
0.1uF
0402
C143
VDD_3V3
GND GND
1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW4
1 4
2 3
TL3301NF260QG
SW2
0.1uF
0402
C144
GND GND
GND
0.1uF
0402
C145
GND
GND
DIS_BOOT
DIS_BOOT
GND
2 1
43
GREEN
RED
0805
D7
1k
0402
5%
R187
1k
0402
5%
R188
GND GND
DIS_BOOT
0.1uF
0402
C146
0.1uF
0402
C147
NAND_nCS_PD04
QSPI_CS_PB20
NAND_nCS_PD04_enabled
QSPI_CS_PB20_enabled
GND
GND
GND
DIS_BOOT
DIS_BOOT
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
VDD_3V3
100R 0402
1%
R197
100R 0402
1%
R192
100k
0402
5%
R189
100k
0402
5%
R194
10k
0402
5%
R186
RUBBER PAD D9.5 H4.8
PAD4
RUBBER PAD D9.5 H4.8
PAD3
RUBBER PAD D9.5 H4.8
PAD2
RUBBER PAD D9.5 H4.8
PAD1
USB A to USB Micro-B Cable
CBL2
GND
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J13
DIS_BOOT
100k
0402
5%
R204
VDD_3V3
DIS_BOOT
PLACEHOLDERS
TM5000 display
LCD Display TM5000B
LCD1
DNP
USER PUSH BUTTONS
JTAG_CONN_TDI
JTAG_CONN_TMS
JTAG_CONN_TCK
JTAG_CONN_RTCK
JTAG_CONN_TDO
JTAG_CONN_nRST
VDD_3V3
100R
0402
1%
R265
100k
0402
5%
R256
100k
0402
5%
R257
100k
0402
5%
R260
100k
0402
5%
R258
DNP
100k
0402
5%
R259
DNP
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
HDR-2.54 Male 2x10
302-R201
J23
JTAG_CONN_TCK
JTAG_CONN_TDO
JTAG_CONN_TMS
JTAG_CONN_TDI
JTAG_CONN_nRST
JTAG_CONN_RTCK
GND
5V_FTDI
FTDI_CTS
FTDI_RTS
TP10
TP11
1
2
3
4
5
6
HDR-2.54 Male 1x6
TSW-106-07-G-S
J24
5V_FTDI5V_FTDI
100k
0402
5%
R263
100k
0402
5%
R264
100k
0402
5%
R261
DNP
100k
0402
5%
R262
DNP
22R 0402 1%
R266
22R 0402 1%
R268
0.1uF
50V
0402
C177
GNDGND
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C178
5V_FTDI
DBGU_TX_PA10
DBGU_RX_PA09
LED_RED_PB11
LED_GREEN_PB12
LED_BLUE_PB13
VDD_3V3
2.2k 0402
5%
R203
GND
GND
100R
0402
1%
R206
GND
100R
0402
1%
R200
GND
GND
GND
CLV1A-FKB-CK1N1G1BB7R4S3
LD1
1k 0402
5%
R199
1k 0402
5%
R201
100R
0402
1%
R195
10k
0402
5%
R196
10k
0402
5%
R202
10k
0402
5%
R207
DNP
RGB LEDs
GND
FTDI DEBUG
FTDI_TX
FTDI_RX
GND
DISABLE BOOT
JTAG
VDD_3V3
B2
1
GND
2
VCCA
3
A2
4
A1
5
OE
6
VCCB
7
B1
8
TXS0102
U30
50pos FFC, FPC
CBL1
3
1
2
TN2106
Q10
3
1
2
TN2106
Q11
3
1
2
TN2106
Q12
3
1
2
TN2106
Q13
3
1
2
TN2106
Q14
3
1
2
TN2106
Q15
A
2
GND3Y
4
VCC
5
OE
1
74AHC1G126
U25
74HC1G126SE-7
A
2
GND3Y
4
VCC
5
OE
1
74AHC1G126
U26
74HC1G126SE-7
Label Need Help Large
LABEL1
USB A to USB Micro-B Cable
CBL3
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
D D
C C
B B
A A
13 of 13
SAM9X60 Evaluation Kit
9/20/2019 11:43:12AM
13 - On Board JLINK.SchDoc
Project Title
Date:
File:
Revision: Sheet
Designed with
Drawn By:
IGn
Sheet Title
On Board JLINK
Engineer:
IGn
2
Size
B
SAM9X60-EK
PartNumber:
Variant Name
Standard_WILC3000_DNP
Sch #:
03-SAM9X60-EK
Altium.com
LED1_3U
LED2_3U
39R 0402 1%
R247
0.1uF
50V
0402
C157
10nF 16V0402
C148
1N4148
D8
4.7uF
10V
0402
C156
2.2uF
16V
0603
C171
12MHz
Y9
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C154
39R 0402 1%
R248
6.8k 0402 1%
R240
ID
4
VBUS
1
GND
5
D-
2
D+
3
0
USB2.0MICRO-B FEMALE
J22
0.1uF
50V
0402
C163
10k 0402 5%
R237
0.1uF
50V
0402
C164
10pF 50V0402
C150
150R
R236
10nF
16V
0402
C149
0.1uF
50V
0402
C168
ATSAM3U4CA-CU
VDDANA
K2
ADVREF
J3
GNDANA
K3
AD12BVREF
K4
PA22/PGMD14
H4
PA30
J4
PB3J5PB4
K5
VDDCORE_3
E7
PA13/PGMD5
H5
G
N
D2
F6
PA15/PGMD7
H6
PA16/PGMD8
J6
PA17/PGMD9
K7
PB16
F7
PB15
G7
PA18/PGMD10
H7
PA19/PGMD11
J7
PA20/PGMD12
K8
PA21/PGMD13
J8
PA23/PGMD15
K9
XIN32
A10
PA24
H8
PA25
K10
PA26
J9
PA0/PGMNCMD
J10
PA1/PGMRDY
H9
PA2/PGMNOE
H10
PA3/PGMNVALID
G8
PA4/PGMM0
G10
PA5/PGMM1
G9
PA6/PGMM2
F8
NRST
B7
VDDCORE_4
H1
GND1
E2
VDDIO_3E6VDDCORE_5
G5
DFSDM
D1
GND3
G6
VDDUTMI
B3
VDDIN
A8
FWUP
D8
ERASE
D6
TEST
D7
XIN
A2
XOUT32
B10
TDI
B9
VDDOUT
A9
PA12/PGMD4
D10
TDO/TRACESWO
B8
TMS/SWDIO
C7
TCK/SWCLK
A7
PA7/PGMM3
F10
PB24
B6
PA8/PGMD0
E10
VDDIO_2
F5
PA14/PGMD6
K6
PB23A6PB22
C6
PB14C4PB10
B4
PB9
E
4
GN
D
PL
L
C3
PB8
J
2
PB7
K1
PB6
J1
PB13
G4
PB12
F2
PB11
G1
PB2G2PB1F1PB0
G3
PA10/PGMD2
E8
VDDIO_1
F3
VDDCORE_1
B1
PA31
F4
PA29
E1
PA28
E3
VDDCORE_2
D4
G
N
D
UT
M
I
B2
DFSDP
C1
DHSDM
D2
DHSDP
C2
NRSTB
C8
XOUT
A3
VDDPLL
D
3
PA11/PGMD3
D9
PA9/PGMD1
E9
PB20
D5
PB19C5PB18B5PB17
A4
PB5
H2
PA27
H3
PB21
A5
VDDBU
C10
GN
DBU
E5
VBG
A1
JTAGSEL
C9
VDDCORE_6
F9
U27
ATSAM3U4CA-CU TFBGA-100
0.1uF
50V
0402
C162
2 1
43
GREEN
RED
0805
D9
0.1uF
50V
0402
C166
180R
FB13
0.1uF
50V
0402
C159
8.2pF0402
C152
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C158
4.7uF
10V
0402
C161
0.1uF
50V
0402
C155
2.2uF
16V
0603
C172
0.1uF
50V
0402
C153
0.1uF
50V
0402
C165
0.1uF
50V
0402
C169
8.2pF0402
C151
DNP
0.1uF
50V
0402
C173
0.1uF
50V
0402
C167
GND
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
GNDGND
VBUS_JLINK
VDD_3V3_3U
VDD_3V3_3U
EARTH_JLINK GND
GND
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
GNDGND
VDD_3V3_3U
GND
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
VBUS_JLINK
VDD_3V3_3U
VDD_3V3_3U
GND
ENSPI
NRST_3U
TDI_3U
TDO_3U
TCK_3U
TMS_3U
Xin_SAM3
Xout_SAM3
TRESIN
TRESOUT
TRSTOUT
TRSTIN
GND
150R
R242
150R
R243
150R
R244
10k
0402
5%
R250
VDDout
VDDout
DIS_CDC
DIS_JLINK
ENSPI
JLINK_RTCK_IN
JLINK_TCK_IN
JLINK_TDO_IN
JLINK_TMS_IN
JLINK_TDI_IN
JLINK_nRST
VBUS_JLINK VDD_3V3_3U
DIS_CDC
10k
0402
5%
R241
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP7
22R 0402 1%
R252
22R 0402 1%
R254
0.1uF
50V
0402
C174
GNDGND
VDD_3V3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C175
VDD_3V3_3U
DIS_CDC
JLINK_UART_RX
JLINK_UART_TX
JLINK_UART_TX
JLINK_UART_RX
0.1uF
50V
0402
C160
JLINK_USBHS_N
JLINK_USBHS_P
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP5
DNP
GND
EP
7
VIN6VOUT
1
GND
3
EN
4
NC
5
VOUT
2
MIC5528 3V3
U28
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J21
0R
0402
R233
0R 0402
R239
DNP
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J19
DNP
100R
0402
1%
R234
100R
0402
1%
R235
100R 04021%
R238
1k
0402 5%
R246
1k
0402 5%
R249
100k 0402 5%
R245
DIFF90
JLINK-OB INTERFACE
LEVEL SHIFTING UART - JLINK-OBJLINK-OB POWER SUPPLY
DIS JLINK CDC
Xin_SAM3
0.1uF
50V
0402
C170
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
GND
TP9
0.1uF
50V
0402
C176
GND
VDD_3V3
GND
0.1uF
50V
0402
C179
GND
VDD_3V3
GND
JLINK_nRST
JLINK_RTCK_IN
JTAG_nRST
JTAG_RTCK
JTAG_TCK
JTAG_TDI
JTAG_TDO
JTAG_TMS
JLINK_TCK_IN
JLINK_TDO_IN
JLINK_TMS_IN
JLINK_TDI_IN
NC
1
1OE
2
1Y41A
3
2OE
5
2Y72A
6
3Y103A
11
NC
9
4Y
13
3OE
12
GND
8
4A
14
4OE
15
VCC
16
IDTQS3VH125
U32
S
1
I0A
2
I1A
3
YA
4
I0B
5
I1B
6
YB
7
GND
8
YC
9
I1C
10
I0C
11
YD
12
I1D
13
I0D
14
E
15
VCC
16
IDTQS3VH257PAG
U31
100k 0402 5%
R270
3
1
2
BSS138N
Q16
DIS_JLINK
DIS_JLINK
JTAG_CONN_TCK
JTAG_CONN_TDO
JTAG_CONN_TMS
JTAG_CONN_TDI
JTAG_CONN_nRST
JTAG_CONN_RTCK
JTAG Switch
DIS_JLINK
10k
0402
5%
R232
GND
VDD_3V3_3U
Shunt 2.54mm 1x2
JP6
12
HDR-2.54 Male 1x2
J20
DIS JLINK JTAG
DBGU_TX_PA10
DBGU_RX_PA09
51R
0402
R251
B2
1
GND
2
VCCA
3
A2
4
A1
5
OE
6
VCCB
7
B1
8
TXS0102
U29
STB1GND
2
OUT3VDD
4
12.00 MHz
DSC6011JI1A-012.0000
Y10
BOT TOP
SideSide
1 2
3 4
7 8
9 10
11 12
131514
16
J18
padson PCB
90Ω ±15% differential trace impedance
Routing top or bottom
SAM9X60-EK
Appendix. Schematics and Layouts
Figure 6-13. On-board J-Link
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 63
Page 64

7. Revision History
7.1 DS50002907A - 10/2019
First issue.
SAM9X60-EK
Revision History
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 64
Page 65

SAM9X60-EK
The Microchip Website
Microchip provides online support via our website at http://www.microchip.com/. This website is used to make files
and information easily available to customers. Some of the content available includes:
• Product Support – Data sheets and errata, application notes and sample programs, design resources, user’s
guides and hardware support documents, latest software releases and archived software
• General Technical Support – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), technical support requests, online
discussion groups, Microchip design partner program member listing
• Business of Microchip – Product selector and ordering guides, latest Microchip press releases, listing of
seminars and events, listings of Microchip sales offices, distributors and factory representatives
Product Change Notification Service
Microchip’s product change notification service helps keep customers current on Microchip products. Subscribers will
receive email notification whenever there are changes, updates, revisions or errata related to a specified product
family or development tool of interest.
To register, go to http://www.microchip.com/pcn and follow the registration instructions.
Customer Support
Users of Microchip products can receive assistance through several channels:
• Distributor or Representative
• Local Sales Office
• Embedded Solutions Engineer (ESE)
• Technical Support
Customers should contact their distributor, representative or ESE for support. Local sales offices are also available to
help customers. A listing of sales offices and locations is included in this document.
Technical support is available through the website at: http://www.microchip.com/support
Microchip Devices Code Protection Feature
Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today,
when used in the intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these
methods, to our knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating
specifications contained in Microchip’s Data Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of
intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code
protection does not mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection
features of our products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital
Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you
may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Legal Notice
Information contained in this publication regarding device applications and the like is provided only for your
convenience and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to ensure that your application meets with
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 65
Page 66

SAM9X60-EK
your specifications. MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION, QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend,
indemnify and hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims, suits, or expenses resulting from such
use. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip intellectual property rights unless
otherwise stated.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Adaptec, AnyRate, AVR, AVR logo, AVR Freaks, BesTime,
BitCloud, chipKIT, chipKIT logo, CryptoMemory, CryptoRF, dsPIC, FlashFlex, flexPWR, HELDO, IGLOO, JukeBlox,
KeeLoq, Kleer, LANCheck, LinkMD, maXStylus, maXTouch, MediaLB, megaAVR, Microsemi, Microsemi logo, MOST,
MOST logo, MPLAB, OptoLyzer, PackeTime, PIC, picoPower, PICSTART, PIC32 logo, PolarFire, Prochip Designer,
QTouch, SAM-BA, SenGenuity, SpyNIC, SST, SST Logo, SuperFlash, Symmetricom, SyncServer, Tachyon,
TempTrackr, TimeSource, tinyAVR, UNI/O, Vectron, and XMEGA are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
APT, ClockWorks, The Embedded Control Solutions Company, EtherSynch, FlashTec, Hyper Speed Control,
HyperLight Load, IntelliMOS, Libero, motorBench, mTouch, Powermite 3, Precision Edge, ProASIC, ProASIC Plus,
ProASIC Plus logo, Quiet-Wire, SmartFusion, SyncWorld, Temux, TimeCesium, TimeHub, TimePictra, TimeProvider,
Vite, WinPath, and ZL are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Adjacent Key Suppression, AKS, Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Any Capacitor, AnyIn, AnyOut, BlueSky, BodyCom,
CodeGuard, CryptoAuthentication, CryptoAutomotive, CryptoCompanion, CryptoController, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, Dynamic Average Matching, DAM, ECAN, EtherGREEN, In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP,
INICnet, Inter-Chip Connectivity, JitterBlocker, KleerNet, KleerNet logo, memBrain, Mindi, MiWi, MPASM, MPF,
MPLAB Certified logo, MPLIB, MPLINK, MultiTRAK, NetDetach, Omniscient Code Generation, PICDEM,
PICDEM.net, PICkit, PICtail, PowerSmart, PureSilicon, QMatrix, REAL ICE, Ripple Blocker, SAM-ICE, Serial Quad
I/O, SMART-I.S., SQI, SuperSwitcher, SuperSwitcher II, Total Endurance, TSHARC, USBCheck, VariSense,
ViewSpan, WiperLock, Wireless DNA, and ZENA are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
The Adaptec logo, Frequency on Demand, Silicon Storage Technology, and Symmcom are registered trademarks of
Microchip Technology Inc. in other countries.
GestIC is a registered trademark of Microchip Technology Germany II GmbH & Co. KG, a subsidiary of Microchip
Technology Inc., in other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies.
©
2019, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
ISBN: 978-1-5224-4875-4
AMBA, Arm, Arm7, Arm7TDMI, Arm9, Arm11, Artisan, big.LITTLE, Cordio, CoreLink, CoreSight, Cortex, DesignStart,
DynamIQ, Jazelle, Keil, Mali, Mbed, Mbed Enabled, NEON, POP, RealView, SecurCore, Socrates, Thumb,
TrustZone, ULINK, ULINK2, ULINK-ME, ULINK-PLUS, ULINKpro, µVision, Versatile are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Arm Limited (or its subsidiaries) in the US and/or elsewhere.
Quality Management System
For information regarding Microchip’s Quality Management Systems, please visit http://www.microchip.com/quality.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 66
Page 67

Worldwide Sales and Service
AMERICAS ASIA/PACIFIC ASIA/PACIFIC EUROPE
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
http://www.microchip.com/support
Web Address:
http://www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Duluth, GA
Tel: 678-957-9614
Fax: 678-957-1455
Austin, TX
Tel: 512-257-3370
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Novi, MI
Tel: 248-848-4000
Houston, TX
Tel: 281-894-5983
Indianapolis
Noblesville, IN
Tel: 317-773-8323
Fax: 317-773-5453
Tel: 317-536-2380
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
Tel: 951-273-7800
Raleigh, NC
Tel: 919-844-7510
New York, NY
Tel: 631-435-6000
San Jose, CA
Tel: 408-735-9110
Tel: 408-436-4270
Canada - Toronto
Tel: 905-695-1980
Fax: 905-695-2078
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8569-7000
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8665-5511
China - Chongqing
Tel: 86-23-8980-9588
China - Dongguan
Tel: 86-769-8702-9880
China - Guangzhou
Tel: 86-20-8755-8029
China - Hangzhou
Tel: 86-571-8792-8115
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2943-5100
China - Nanjing
Tel: 86-25-8473-2460
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-8502-7355
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-3326-8000
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8864-2200
China - Suzhou
Tel: 86-186-6233-1526
China - Wuhan
Tel: 86-27-5980-5300
China - Xian
Tel: 86-29-8833-7252
China - Xiamen
Tel: 86-592-2388138
China - Zhuhai
Tel: 86-756-3210040
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-3090-4444
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-4160-8631
India - Pune
Tel: 91-20-4121-0141
Japan - Osaka
Tel: 81-6-6152-7160
Japan - Tokyo
Tel: 81-3-6880- 3770
Korea - Daegu
Tel: 82-53-744-4301
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Malaysia - Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 60-3-7651-7906
Malaysia - Penang
Tel: 60-4-227-8870
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 63-2-634-9065
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Taiwan - Hsin Chu
Tel: 886-3-577-8366
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-213-7830
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2508-8600
Thailand - Bangkok
Tel: 66-2-694-1351
Vietnam - Ho Chi Minh
Tel: 84-28-5448-2100
Austria - Wels
Tel: 43-7242-2244-39
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Copenhagen
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
Finland - Espoo
Tel: 358-9-4520-820
France - Paris
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Garching
Tel: 49-8931-9700
Germany - Haan
Tel: 49-2129-3766400
Germany - Heilbronn
Tel: 49-7131-72400
Germany - Karlsruhe
Tel: 49-721-625370
Germany - Munich
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Germany - Rosenheim
Tel: 49-8031-354-560
Israel - Ra’anana
Tel: 972-9-744-7705
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Italy - Padova
Tel: 39-049-7625286
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
Norway - Trondheim
Tel: 47-72884388
Poland - Warsaw
Tel: 48-22-3325737
Romania - Bucharest
Tel: 40-21-407-87-50
Spain - Madrid
Tel: 34-91-708-08-90
Fax: 34-91-708-08-91
Sweden - Gothenberg
Tel: 46-31-704-60-40
Sweden - Stockholm
Tel: 46-8-5090-4654
UK - Wokingham
Tel: 44-118-921-5800
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
User Guide
DS50002907A-page 67
 Loading...
Loading...