Page 1

PICDEM
TM
4
User’s Guide
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A
Page 2

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip's Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digit al Millennium Copyright Act. If suc h a cts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications. No
representation or warranty is given and no liability is assumed by
Microchip T echnology Incorporated with respect to the accuracy
or use of such information, or infringement of patents or other
intellectual property rights arising from such use or otherwise.
Use of Microchip’s products as critical components in life
support systems is not authorized except with express written
approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or
otherwise, under any intellectual property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, K
EELOQ,
MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART, PRO MATE and
PowerSmart are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
FilterLab, microID, MXDEV , MXLAB, PICMASTE R, SEEVAL
and The Embedded Control Solutions Company are registered
trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Accuron, Application Maestro, dsPIC, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, FlexROM,
fuzzyLAB, In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC,
microPort, Migratable Memory, MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK,
MPSIM, PICC, PICkit, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, Powe rCal,
PowerInfo, PowerMate, PowerTool, rfLAB, rfPIC, Select Mode,
SmartSensor, SmartShunt, SmartT el and Total Endurance are
trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
and other countries.
Serialized Quick Turn Programming (SQTP) is a service mark of
Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2003, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received QS-9000 quality system
certification for its worldwide headquarters,
design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona in July 1999
and Mountain View, California in March 2002.
The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are QS-9000 compliant for its
PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals,
non-volatile memory and analog products. In
addition, Microchip’s quality system for the
design and manufacture of development
systems is ISO 9001 certified.
®
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ
®
code hoppin g
DS51337A - page ii 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3

Tabl e of Conten ts
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1 Welcome .........................................................................................1
1.2 PICDEM 4 Demonstration Board ........................... ..... ....................2
1.3 Sample Devices ....................................... ..... .... ..............................3
1.4 Sample Programs ............. .... ..... ............................................... .... ..3
1.5 PICDEM 4 User’s Guide .................................................................3
1.6 Reference Documents ....................................................................3
Chapter 2. Getting Started
2.1 PICDEM 4 as a Stand-Alone Board –
Preprogrammed Device ..................................................................5
2.2 PICDEM 4 Used with an In-Circuit Emulat or or
In-Circuit Debugger ....................................... .... ..... ..... ....................6
PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
Chapter 3. Tutorial
3.1 Tutorial Firmware Operation ...........................................................7
3.2 Source Code and Application Notes ...............................................8
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page iii
Page 4

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
Appendix A. Hardware Detail
A.1 Processor Sockets ............................... .... .....................................11
A.2 LED DISPLAY ...............................................................................11
A.3 Power Supply ................................................................................11
A.4 RS-232 Serial Port ........................................................................11
A.5 Switches ........................................................................................ 12
A.6 Oscillator Options ..........................................................................12
A.7 Analog Input ..................................................................................12
A.8 ICD Connector ..............................................................................12
A.9 Serial EEPROM ............................................................................13
A.10 Motor .............................................................................................13
A.11 LIN .................................................................................................16
A.12 Supercapacitor ..............................................................................17
A.13 Real-Time Clock ....................................... ..... ..... .... .......................18
A.14 LCD Display ..................................................................................18
A.15 Device Configuration Overview .....................................................19
A.16 Board Layout and Schematics ......................................................20
Index..........................................................................................................23
Worldwide Sal e s a nd Se rvice...... .. ... ........................................... .. ... .......24
DS51337A-page iv 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5

1.1 WELCOME
Thank you for purchasing the PICDEM 4 demonstration board from Microchip
Technology Incorporated. The PICDEM 4 demonstrates the capabilities of the 8-, 14-,
and 18-pin PIC16XXXX and PIC18XXXX devices.
The PICDEM 4 can be used stand-alone with a programmed part, with an In-Circuit
Emulator (e.g., MPLAB
Sample programs are provided to demonstrate the unique features of the supported
devices.
The PICDEM 4 Kit comes with the following:
1. PICDEM 4 Demonstration Board (Figure 1-1)
2. Sample Devices
3. CD-ROM, which contains:
If you are missing any part of the kit, please contact your nearest Microchip sales office
listed in the back of this publication for help.
PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
Chapter 1. Introduction
®
ICE), or with an In-Circuit Debugger (e.g., MPLAB ICD 2).
a) Sample Programs
b) PICDEM 4 Demonstration Board User’s Guide
c) Application Notes
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 1
Page 6
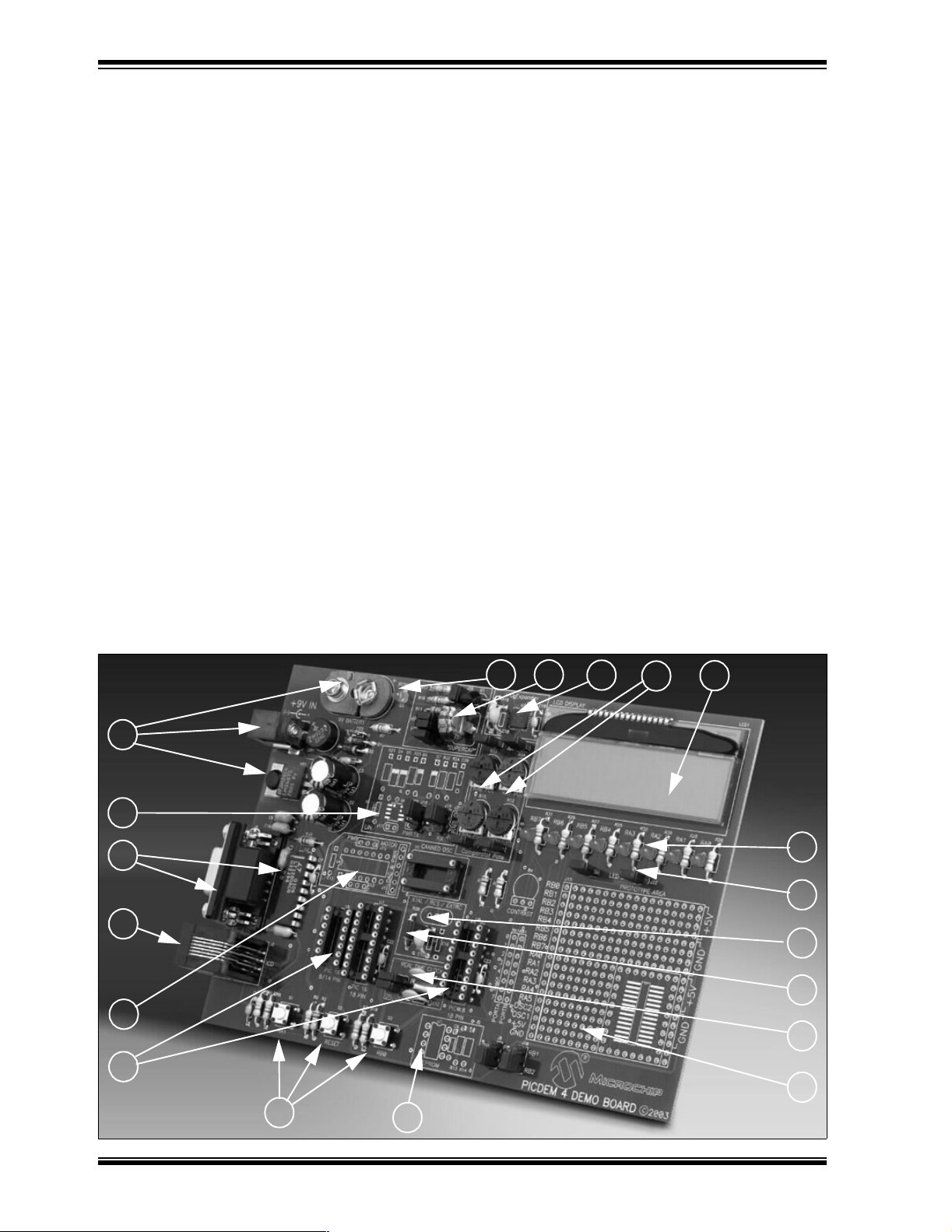
PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
1.2 PICDEM 4 DEMONSTRATION BOARD
The PICDEM 4 demonstration board has the following hardware features:
1. 8-, 14- and 18-pin DIP sockets. (Although 3 sockets are provided, only one
device may be used at a time.)
2. On-board +5V regulator for direct input from 9V, 100 mA AC/DC wall adapter or
9V battery, or hooks for a +5V , 100 mA regulated DC supply.
3. RS-232 connection and associated hardware for direct connection to RS-232
interface.
4. In-Circuit Debugger (ICD) connector.
5. Four 5 k
6. Three push button switches for external stimulus and RESET.
7. Green power-on indicator LED.
8. Eight red LEDs connected to PORTA and PORTB.
9. Jumpers J21 and J22 to disconnect LEDs from PORTA and PORTB.
10. Unpopulated holes provided for crystal connection.
11. 32.768 kHz crystal for Timer1 Real-Time Clock operation.
12. Jumper J14 to disconnect on-board RC oscillator (R20 and C15, approx. 2 MHz).
13. Unpopulated holes for EEPROM.
14. 2 x 16 LCD display.
15. Prototype area for user hardware.
16. PIC16LF72 I/O expander.
17. Supercapacitor circuitry.
18. Unpopulated holes for a LIN transceiver.
19. Unpopulated holes for a motor driver.
Ω pots for devices with analog inputs and comparators.
FIGURE 1-1: PICDEM 4 HARDWARE
2
18
3
4
19
1
6
13
7
17
16
5
14
8
9
10
12
11
15
DS51337A-page 2 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

1.3 SAMPLE DEVICES
Two FLASH devices are included. The device types may change, but will generally
include PIC16XXXX and PIC18XXXX 18-pin DIP devices.
1.4 SAMPLE PROGRAMS
The PICDEM 4 Kit includes a CD-ROM with sample demonstration programs. These
programs may be used with the included sample devices, with an In-Circuit Emulator
(ICE), or with an In-Circuit Debugger (ICD). For each type of device (PIC16XXXX or
PIC18XXXX), demo source code (several ASM files) and compiled code (one HEX file)
are provided.
1.5 PICDEM 4 USER’S GUIDE
This document describes the PICDEM 4 demonstration board, tutorial and demonstration software. Detailed information on individual microcontrollers may be found in the
device’s respective data sheet. Detailed information on In-Circuit Emulator (ICE) or
In-Circuit Debugger (ICD) systems may be found in the respective tool’s user’s guide.
Chapter 1: Introduction – This chapter introduces the PICDEM 4 and provides a brief
description of the hardware.
Chapter 2: Getting Started – This chapter goes through a basic step-by-step process
for getting your PICDEM 4 up and running as a stand-alone board, or with an ICE or
ICD.
Chapter 3: Tutorial – This chapter provides a detailed description of the tutorial
program.
Appendix A: Hardware Detail – This appendix describes in detail the hardware of the
PICDEM 4 board.
Introduction
1.6 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
Reference Documents may be obtained by contacting your nearest Microchip sales
office (listed in the back of this document), or by download from the Microchip web site
(www.microchip.com).
• Technical Library CD-ROM (DS00161) or individual data sheets:
- PIC16F627A/628A/648A Data Sheet (DS40044)
- PIC18F1220/1320 Data Sheet (DS39605)
- PICmicro
- PICmicro
• MPLAB
• MPASM User’s Guide with MPLINK and MPLIB (DS33014)
• PRO MATE
• PICSTART
• MPLAB
• MPLAB
• Microchip Third Party Guide (DS00104)
TM
Mid-Range MCU Family Reference Manual (DS33 023 )
®
18C MCU Family Reference Manual (DS39500)
®
IDE Simulator, Editor User’s Guide (DS51025)
®
II User’s Guide (DS 30 082)
®
Plus User’s Guide (DS51028)
®
ICE Emulator User’s Guide (DS51159)
®
ICD 2 In-Circuit Debugger Quick Start Guide (DS51268)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 3
Page 8

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
NOTES:
DS51337A-page 4 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
Chapter 2. Getting Started
The PICDEM 4 may be used as a stand-alone board with a preprogrammed device,
with an In-Circuit Emulator (ICE), or with an In-Circuit Debugger (ICD). For a list of
PICmicro microcontroller compatible ICEs or ICDs, please refer to the Development
Systems Ordering Guide or the Microchip Third Party Guide.
2.1 PICDEM 4 AS A STAND-ALONE BOARD – PREPROGRAMMED DEVICE
The PICDEM 4 may be demonstrated immediately by following the steps listed below:
• Place the preprogrammed sample device in the appropriate socket on the
PICDEM 4 board.
• Apply power to the PICDEM 4. For information on acceptable power sources,
see Appendix A.
Note: In the event that the preprogrammed PICDEM 4 demonstration board does
not operate, check the following conditions:
- J8/J10 must be connected for the appropriate device
- J3, J4, J7, J9, and J24 - J27 must be ON
- J23 and J28 must be OFF
The status of all other jumpers will not affect the preprogrammed
demonstration.
To reprogram the sample device, the following will be necessary:
1. Program source code.
User source code may be used to program the device or, if this has previously been
done, the sample program may be restored from the file on the included CD-ROM.
2. An assembler, such as MPASM
compiler, such as MPLAB C18 (PIC18XXXX devices only).
Source code must be assembled or compiled into a HEX file before it can be programmed into the device. Microchip Technology’s MPASM assembler or MPLAB
C18 C compiler may be used. Both are compatible with MPLAB IDE; however,
other assemblers/compilers may be used. For a list of these PICmicro MCU
compatible language tools, please refer to the Microchip Third Party Guide.
3. A device programmer, such as PRO MATE II, PICSTAR T Plus, or MPLAB ICD 2
(programmer functionality available with MPLAB IDE v6.00 or greater).
Once the sample program is in HEX file format, a programmer may be used to program a FLASH device. Microchip T echnology’s PRO MATE II device programmer,
PICSTART Plus development programmer, or MPLAB ICD 2 may be used. All are
compatible with MPLAB IDE. However, other programmers may be used. For a list
of these PICmicro MCU compatible programmers, please refer to the Microchip
Third Party Guid e.
If the code protection bit(s) have not been programmed, the on-chip program
memory can be read out for verification purposes.
TM
assembler (available with MPLAB IDE), or a
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 5
Page 10

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
2.2 PICDEM 4 USED WITH AN IN-CIRCUIT EMULATOR OR IN-CIRCUIT DEBUGGER
To use PICDEM 4 with an In-Circuit Emulator (ICE) or In-Circuit Debugger (ICD), refer
to the tool’s user’s guide for instructions on how to power-up and configure the
ICE/ICD, as well as how to connect to target boards (e.g., Figure 2-1).
FIGURE 2-1: PICDEM 4 CONNECTED TO MPLAB ICD 2 USING USB
Configure the PICDEM 4 for the desired oscillator as described in Table 2-1. Refer to
the ICE/ICD user’s guide for any oscillator configuration requirements.
TABLE 2-1: OSCILLATOR SELECTION
Oscillator Selection on
PICDEM 4
RC J14 ON, Y3 empty, Y1 empty
Crystal J14 OFF, Y1 empty, crystal in Y3, caps in C15 and C16
Canned Oscillator J14 OFF, oscillator in Y1 (Y3, C15, C16 empty)
Device Internal Oscillator J14 OFF, Y1 empty, Y3 empty
Resonator - no internal caps J14 OFF, Y1 empty, resonator in Y3, caps in C15 and C16
Resonator - with internal
caps
DS51337A-page 6 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
J14 OFF, Y1 empty, resonator in Y3, C15 and C16 empty
Modification on PICDEM 4
Page 11

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
Chapter 3. Tutorial
The tutorial program is preprogrammed into the sample device (for example,
p16PDEM4_Demo.hex for a PIC16XXXX device and p18PDEM4_Demo.hex for a
PIC18XXXX device). Also, this program is on the included CD-ROM program disk for
user reference (i.e., if the sample device has been reprogrammed with another
program, the tutorial may be reprogrammed into the device).
For detailed information on the PICDEM 4 hardware, please refer to Appendix A.
3.1 TUTORIAL FIRMWARE OPERATION
The PIC18F tutorial firmware is made up of two components, which are individually
displayed on the LCD. The PIC
system clock source.
1. Voltmeter
This mode uses the A/D module to measure the voltage of the R33 pot and displays a voltage between 0.00V and 5.00V on the LCD. Voltage is continually
updated until the mode is exited by pressing SW3 (RB0).
2. Clock
Once this mode is entered from the main menu, a real-time clock will start counting from 00:00:00. The Timer1 module and a 32 kHz clock crystal is used to
establish a Real-Time Clock. By pressing SW1, the clock time can be set to the
user's preference. After SW1 has been pressed, the cursor will flash over the
hours digits. Press SW1 and the cursor will now flash over the minutes digits.
SW3 is used to increment hours and minutes whenever the cursor is flashing
over either. After the minutes have been set, press SW1 and the time will be set
and the LCD is returned to an active clock display.
The PIC16F tutorial firmware is made up of one component, which uses the comparator
module and potentiometers R12, R15, R33, and R34. Turning the potentiometers will
vary the voltages to the PIC16 inputs, thereby changing the results of the comparator
outputs. The LCD will be used for displaying these results.
®
microcontroller’s internal RC oscillator is used as the
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 7
Page 12

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
FIGURE 3-1: PIC18F TUTORIAL PROGRAM FLOW CHART
Power-up
"Microchip
Voltmeter
SW1 = Next
SW3 = Now
Real-Time Clock
SW1 = Next
SW3 = Now
PICDEM 4"
SW3
SW1
SW3
SW1 SW3
Volts = 1.93V
SW3 = Exit Test
00:00:00
SW1 = Set
SW3 = Menu
00:00:00
SW1 = -> SW3 = ++
SW3
SW1
SW1 (2x)
3.2 SOURCE CODE AND APPLICATION NOTES
In addition to the assembled tutorial programs (HEX files), source code used to create
these HEX files is included on the PICDEM 4 CD-ROM. Both source code and related
HEX file are found in device specific directories.
Application Notes are also included on the CD-ROM for additional examples of use.
For information on how to reprogram the device with new or modified code, or how to
restore the tutorial program, please see Section 2.1.
DS51337A-page 8 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
Appendix A. Hardware Detail
The PICDEM 4 hardware is uncomplicated and is intended to illustrate the ease of use
of various PICmicro MCUs. The PICDEM 4 features the following hardware elements.
Note: Many of the following hardware sections will require specific demo board
jumper configurations. If a jumper is not listed in a particular section, then
that jumper has no effect on the circuitry within the hardware section you
are working. Figure A-1 shows a diagram of the PICDEM 4 silkscreen with
all necessary jumpers highlighted. Also, refer to the schematic for circuit
connections.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 9
Page 14

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
FIGURE A-1: PICDEM 4 DEMONSTRATION BOARD PARTS LAYOUT (SILKSCREEN)
J22
J21
J15
J10
J8
J25
J24
J28
J4
J3
J23
J19 J20
J16 J18
J27
J26
J14
J7
J9
J11
J17
J12
J13
DS51337A-page 10 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

A.1 PROCESSOR SOCKETS
Although three sockets are provided, only one device may be used at a time.
• 8- or 14-pin socket (U5) used for 8- or 14-pin devices (8-pin devices are inserted
in the upper 8 pins of U5)
• 18-pin PIC16 socket (U7)
• 18-pin PIC18 socket (U8)
A.2 LED DISPLAY
Eight red LEDs are connected to PORTA and PORTB of U7 and U8, while five of the
eight LEDs are connected to U5. PORTA and PORTB pins are set high to light the
LEDs. These LEDs may be disconnected from PORTA and PORTB by removing
jumpers J21 and J22.
One green LED is provided to determine whether there is power to the PICDEM 4
board (LED on) or not (LED off).
A.3 POWER SUPPLY
There are three ways to supply power to PICDEM 4:
• A 9V battery can be plugged into J2.
• A 9V, 100 mA unregulated AC or DC supply can be plugged into J1. A power
supply can be purchased through Microchip, Part # AC162039.
• A +5V, 100 mA regulated DC supply can be connected to the hooks provided.
Hardware Detail
Note 1: There are two jumpers (J3 and J4) associated with the power
MPLAB ICE 2000 users have a regulated +5V power supply available in the logic probe
connector and can easily connect to the hooks on PICDEM 4 (Red probe to +5V and
Black probe to GND).
MPLAB ICD 2 users may use the ICD to power the target board to 5V , up to 200 mA, if
the MPLAB ICD 2 is connected to the PC with a serial cable.
A.4 RS- 2 32 SERIAL PORT
An RS-232 level shifting IC has been provided with all necessary hardware to support
connection of an RS-232 host through the DB9 connector. The port is configured as
DCE, and can be connected to a PC using a straight through cable.
The PIC16/PIC18 RX and TX pins are tied to the RX and TX lines of the LT1280ACN.
Unlike previous demo boards, the RS-232 chip has an ON/OFF pin which is connected
to I/O pin RB3. For RS-232 operation, these jumpers must be configured as follows:
PIC16
• J18/19 - Upper two pins ON
• J20 - OFF (if populated)
supply circuit. These jumpers must be on for all functions,
with the exception of the Supercapacitor Circuit. Refer to
Section A.12 “Supercapacitor” for further details.
2: The PICDEM 4 kit does not include a power supply.
PIC18
• J18/19 - Lower two pins ON
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 11
Page 16

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
A.5 SWITCHES
Three switches provide the following functions:
• S1 - Active low switch connected to RA4
• S2 - MCLR
• S3 - Active low switch connected to RB0
Switch S2 has a debounce capacitor, whereas S1 and S3 do not, allowing the user to
investigate debounce techniques.
When pressed, the switches are grounded; when idle, they are pulled high (+5V).
A.6 OSCILLATOR OPTIONS
• RC oscillator (2 MHz approximately) supplied. This oscillator may be disabled by
removing jumper J14.
• Pads provided for user furnished crystal/resonator and two capacitors (Y3).
• Socket provided for a canned oscillator (Y1).
• 32.768 kHz (watch type) crystal for Timer1 (Y2). This oscillator can be disabled by
removing jumpers J7 and J9.
A.7 ANALOG INPUT
to hard reset the processor
There are four 5 kΩ potentiometers (R12, R15, R33, R34) on the PICDEM 4 board.
These are all connected to PORTA (RA0-RA3), and can be adjusted from V
to provide an analog input to the devices with an A/D or Comparator module.
Potentiometers R12, R15, R33, and R34 all have individual jumpers. For a potentiometer to function, its specific jumper must be on. The jumper removed will allow for other
I/O functi ons to t ake plac e. For all of the pot entiomet ers to be f unctiona l, thes e jumpers
must be configured as follows:
• J22 - OFF (PORTA LEDs)
•J24 - ON
•J25 - ON
• If J26 is ON, then J23 is OFF
• If J27 is ON, then J28 is OFF
The above conditions will enab le all potent iom ete rs .
A.8 ICD CONNECTOR
By way of the modular connector (J5), the MPLAB ICD 2 can be connected for low cost
debugging. The ICD connector utilizes RB6 and RB7 of the microcontroller for in-circuit
debugging. For ICD operation, the Real-time Clock connections to the microcontroller
must be disabled. For ICD operation, these jumpers must be configured as follows:
• J7 - OFF (RTC)
• J9 - OFF (RTC)
• J21 - OFF (PORTB LEDs)
SS to VDD
DS51337A-page 12 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

A.9 SERIAL EEPROM
For EEPROM operation, these jumpers must be configured as follows:
PIC16
• J8/10 - Upper two pins ON
• J21 - OFF (PORTB LEDs)
PIC18
• J8/10 - Lower two pins ON
• J21 - OFF (PORTB LEDs)
For more information on the serial EEPROM, please refer to the most recent version of
the Technical Library CD-ROM.
A.10 MOTOR
There are three headers (J11, J12, and J13) for the motor driver circuit. These will allow
for external power and load connections. For motor control operation, these jumpers
must be configured as follows:
J11
Hardware Detail
• Left 2 pins: Board PWR
• Right 2 pins: External PWR
J13
• Left 2 pins: Board GND
• Right 2 pins: External GND
J12
• Connect External Power Source and Load. Lower pin (1) is PWR, top pin is GND.
•J19 - OFF
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 13
Page 18

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
A.10.1 PICDEM 4 Motor Control Demo
The TC4467 devices are a family of four output CMOS buffers/MOSFET drivers. The
PICmicro MCU PWM output is connected to these drivers to create a variety of possible
driving conditions. The following figures show a few of these possible configurations.
The driver can directly drive the small load, or can act as a MOSFET driver for a bigger
load request.
FIGURE A-2: SINGLE OUTPUT MODE PWM
PA
RB3
TC4467
L
PA
RB3
1Y
1Y
TC4467
PA
TC4467
RB3
L
L = Load
A = Amplifier
1Y
L
A
FIGURE A-3: DIRECT H-BRIDGE DRIVER IN ECCP HALF-BRIDGE
OUTPUT MODE
PA
RB3
PB
RB2
TC4467
1Y
2Y
L
L = Load
A = Amplifier
DS51337A-page 14 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

FIGURE A-4: HALF-BRIDGE MODE PWM
Hardware Detail
PA
RB3
PB
RB2
PA
RB3
PB
RB2
TC4467
TC4467
1Y
2Y
2Y
1Y
A
A
A
A
L
L
L = Load
A = Amplifier
FIGURE A-5: DUAL OUTPUT PWM IN H-BRIDGE CONFIGURATION
PA
TC4467
RB3
PB
RB2
L = Load
A = Amplifier
1Y
2Y
A
A
A
L
A
PA
RB3
PB
RB2
TC4467
1Y
2Y
A
A
A
L
A
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 15
Page 20

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
A.11 LIN
The PICDEM 4 is designed with an optional LIN circuit (not populated). This circuit
provides the essential circuitry to interface a PICmicro microcontroller to a Local
Interconnect Network (LIN). The circuit includes a MCP201 LIN transceiver, reverse
voltage protection, and over voltage protection.
Jumpers J16, J17, J18, J19, and J20 are provided to set up and connect a PICmicro
microcontroller on PICDEM 4 to the LIN bus. External jumper J16 provides the connection to the LIN bus. With the MCP201 installed, power to the PICDEM 4 can be supplied
from the LIN bus battery connection via J16; shorting J17 enables bus power to the
circuitry beyond the LIN interface circuit (refer to the MCP201 voltage regulator
specifications for maximum conditions).
Jumpers J18, J19, and J20 provide connections to the microcontroller on the
PICDEM 4. Shorting the appropriate pins (shown on the schematic) can connect either
a PIC16 or PIC18 device to the LIN transceiver. J18 connects the LIN TX pin to either
a PIC16 or PIC18 microcontroller. J19 connects the LIN RX pin to either a PIC16 or
PIC18 microcontroller. J20 provides an additional receive connection for PIC16
devices. For LIN operation, these jumpers must be configured as follows:
•J17 - ON
PIC18
• J18/J19 - Lower two pins ON
•J21 - OFF
PIC16
• J18/J19 - Upper two pins ON
•J20 - ON
•J21 - OFF
DS51337A-page 16 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

A.12 SUPERCAPACITOR
The 0.33F (C5) Supercapacitor is used to demonstrate the low power capabilities of
PICmicro devices. This circuit requires all other peripherals to be disconnected from
the circuit. The Supercapacitor code, included on your PICDEM 4 CD, is configured so
that the device will remain in SLEEP most of the time, while a 32 kHz watch crystal (Y2)
connected to Timer1 keeps the PICmicro MCU running.
The device wakes up every second and toggles a port pin, and a second port pin indicates the power start-up. If a power source is present, a high level is maintained;
otherwise, in the absence of power, the pin will go low.
In the event of a power failure, the Supercapacitor will supply the PICmicro MCU with
power through an internal protection diode on a port pin. If the user desires to measure
the Supercapacitor supply time, they will have to observe the power signals with an
oscilloscope or another demo board.
Note: The Supercapacitor circuit described in this manual is used only to demon-
strate the low power cap ability of the device. Th e Supercap acitor is us ed as
an example for the low power source. DO NOT use this circuit as a
general design practice.
For Supercapacitor operation, these jumpers must be configured as follows:
• J3 - OFF (Power Supply)
• J4 - OFF (Power Supply)
• J22 - OFF (PORTA LEDs)
• J23 - ON (Supercapacitor)
• J26 - OFF (Potentiometer)
• J27 - OFF (Potentiometer)
• J28 - ON (LVD)
Hardware Detail
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 17
Page 22

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
A.13 REAL-TIME CLOCK
This circui t all ows the user to conf igur e a PI Cmicr o MC U in eithe r th e U7 or U8 sock et
for timekeeping, using a 32.768 kHz clock crystal connected to Timer1’s T1OSO and
T1OSI pins. ICD operation will not be functional when the Real-Time Clock circuit is
enabled. For RTC operation, these jumpers must be configured as follows:
•J7 - ON
•J9 - ON
•J21 - OFF
A.14 LCD DISPLAY
An LCD display with two lines, 16 characters per line, is connected to the I/O Expander
(U3), which can be driven by all three device sockets.
A 10K pot may be installed into R4 to adjust contrast on the LCD. If this is done, R5 and
R6 need to be removed.
The LCD is connected to the I/O Expander by three control lines (E, R/W, RS), and four
data lines (DB7:DB4). For LCD operation, these jumpers must be configured as
follows:
PIC16
• J8/10 - Upper two pins ON
• J21 - OFF (PORTB LEDs)
PIC18
• J8/10 - Lower two pins ON
• J21 - OFF (PORTB LEDs)
DS51337A-page 18 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

A.15 DEVICE CONFIGURATION OVERVIEW
Table A-1 lists the I/O features and port connections for each processor type.
TABLE A-1: PORT CONNECTIONS
Connection Type
LEDs RA0:RA2, RB4, RB5 ALL ALL
RS-232 RB1/RB4 RB2/RB5 RB1/RB4
S1 RA4 RA4 RA4
S2 RA5 RA5 RA5
S3 RB0 RB0 RB0
R33 Pot RA0 RA0 RA0
R34 Pot RA1 RA1 RA1
R15 Pot RA2 RA2 RA2
R12 Pot N/A RA3 RA3
LCD RB1/RB4 RB1/RB4 RB1/RB4
EEPROM RB1/RB4 RB1/RB4 RB1/RB4
ICD N/A RB6/RB7 RB6/RB7
LIN N/A RB2/RB5/RB1 RB1/RB4
MOTOR RB2/RB3 RB2/RB3 RB2/RB3
RTC N/A RB6/RB7 RB6/RB7
CANNED OSC OSC1 OSC1 OSC1
RC OSCILLATOR OS C1 OSC1 OSC1
CRYSTAL/RESONATOR OSC1/OSC2 OSC1/OSC2 OSC1/OSC2
SUPERCAPACITOR
CIRCUITS
PIC12/PIC16
8- or 14-Pin
N/A RA2/RA3 RA2/RA3
Hardware Detail
Device
PIC16 18-Pin PIC18 18-Pin
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 19
Page 24

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
A.16 BOARD LAYOUT AND SCHEMATICS
The following figures show the parts layout (silkscreen) and schematics for the
PICDEM 4 board.
FIGURE A-6: PICDEM 4 PARTS LAYOUT
J22
J21
J15
J10
J8
J25
J24
J20
J28
J3
J4
J23
J19
J18
J16
J27
J26
J14
J9
J7
J11
J17
J12
J13
DS51337A-page 20 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25

FIGURE A-7: PICDEM 4 SCHEMATIC SHEET 1
Hardware Detail
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 21
Page 26

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
FIGURE A-8: PICDEM 4 SCHEMATIC SHEET 2
Note: The Supercapacitor circuit described in this manual is used only to demonstrate the low power capability of the
device. The Supercapacitor is used as an example for the low power source. DO NOT use this circuit as a
general design practice.
DS51337A-page 22 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27

PICDEM 4 User’s Guide
Index
A
A/D Input ........................................................... ...... ..2
B
Board ............................................................ 1, 2, 5, 9
Parts Layout ...............................................10, 20
Power Supply ............................................... 5, 11
Silkscreen .................................................. 10, 20
C
Clock ......................................................................... 7
D
Demonstration Board. See Board
Demonstration Programs. See Sample Programs
E
EEPROM, Serial .......................................................2
H
Hardware ..................................................................9
K
Kit Components ........................................................ 1
L
LCD .........................................................................18
LEDs
Green Power ................................................ 2, 11
Red Display ................................................. 2, 11
LIN, Transceiver ........................................................ 2
M
Microchip Third Party Guide ......................................3
MPASM Assembler ...................................................5
MPASM Assembler User’s Guide with
MPLINK Linker and MPLIB Librarian ................. 3
MPLAB C18 ..............................................................5
MPLAB ICD 2 ........................................1, 5, 6, 11, 12
MPLAB ICD 2 Quick Start Guide .............................. 3
MPLAB ICE ..................................................... 1, 6, 11
MPLAB ICE User’s Guide .........................................3
MPLAB IDE ............................................................... 5
MPLAB IDE User’s Guide .........................................3
O
Oscillator Options .................................................... 12
Oscillator Selection ...................................................6
P
PIC16F62XA Data Sheet ..........................................3
PIC16XXXX ...............................................................1
Tutorial Program ............ ...... ...... ..... ...... ............. 7
PIC18F1X20 Data Sheet ................................... ...... ..3
PIC18XXXX ...............................................................1
Tutorial Program ............ ...... ...... ..... ...... ............. 7
PICDEM 4 Board. See Board
PICDEM 4 Kit. See Kit Components
PICmicro 18C MCU Family Reference Manual ......... 3
PICmicro Mid-Range MCU Family
Reference Manual ..............................................3
PICSTART Plus ........................................................5
PICSTART Plus User’s Guide ................................... 3
PRO MATE II ............................................................5
PRO MATE II User’s Guide ....................................... 3
Push Buttons. See Switches
R
Reference Documents ..............................................3
RS-232 ................................................................ 2, 11
S
Sample Devices ....................................................1, 3
Sample Programs .................................................1, 3
Sockets ...................................................................11
Supercapacitor .......................................................... 2
Switches ..............................................................2, 12
T
Tutorial ...................................................................... 7
V
Voltmeter ................................................................... 7
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. DS51337A-page 23
Page 28

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200 Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: http://www.microchip.com
Atlanta
3780 Mansell Road, Suite 130
Alpharetta, GA 30022
Tel: 770-6 40- 003 4 Fax: 770- 640 -03 07
Boston
2 Lan Drive, Suite 120
Westford, MA 01886
Tel: 978-6 92- 384 8 Fax: 978- 692 -38 21
Chicago
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 630-285-0071 Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
4570 Westgrove Drive, Suite 160
Addison, TX 75001
Tel: 972-8 18- 742 3 Fax: 972- 818 -29 24
Detroit
Tri-Atria Office Building
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190
Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Tel: 248-538-2250 Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
2767 S. Albright Road
Kokomo, Indiana 46902
Tel: 765-864-8360 Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
18201 Von Karman, Suite 1090
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 949-2 63- 188 8 Fax: 949- 263 -13 38
Phoenix
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7966 Fax: 480-792-4338
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First Street, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408-4 36- 795 0 Fax: 408- 436 -79 55
Toronto
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Cana da
Tel: 905-673-0699 Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd
Marketing Support Division
Suite 22, 41 Rawson Street
Epping 2121, NSW
Australia
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beij ing
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Beijing Liaison Office
Unit 915
Bei Hai Wan Tai Bldg.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Beidajie
Beijing, 100027, No. China
Tel: 86-10-85282100 Fax: 86-10-85282104
China - Chengdu
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Chengdu Liaison Office
Rm. 2401-2402, 24th Floor,
Ming Xing Financial Tower
No. 88 TIDU Street
Chengdu 610016, China
Tel: 86-28-86766200 Fax: 86-28-86766599
China - Fuzhou
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Fuzhou Liaison Office
Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza
No. 71 Wusi Road
Fuzhou 350001, China
Tel: 86-591-7503506 Fax: 86-591-7503521
China - Hong Kong SAR
Microchip Technology Hongkong Ltd.
Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-1200 Fax: 852-2401-3431
China - Shanghai
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd.
Room 701, Bldg. B
Far East International Plaza
No. 317 Xian Xia Road
Shanghai, 200051
Tel: 86-21-6275-5700 Fax: 86-21-6275-5060
China - Shenzhen
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Shenzhen Liaison Office
Rm. 1812, 18/F, Building A, United Plaza
No. 5022 Binhe Road, Futian District
Shenzhen 518033, China
Tel: 86-755-82901380 Fax: 86-755-82966626
China - Qingdao
Rm. B505A, Fullhope Plaza,
No. 12 Hong Kong Central Rd.
Qingdao 266071, China
Tel: 86-532-5027355 Fax: 86-532-5027205
India
Microchip Technology Inc.
India Liaison Office
Marketing Support Division
Divyasree Chambers
1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Bangalore, 560 025, India
Tel: 91-80-2290061 Fax: 91-80-2290062
Japan
Microchip Technology Japan K.K.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shinyokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama-shi
Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea
Microchip Technology Korea
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku
Seoul, Korea 135-882
Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-5934
Singapore
Microchip Technology Singapore Pte Ltd.
200 Middle Road
#07-02 Prime Centre
Singapore, 188980
Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan
Microchip Technology (Barbados) Inc.,
Taiwan Branch
11F-3 , No . 207
Tung Hua North Road
Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
EUROPE
Austria
Microchip Technology Austria GmbH
Durisolstrasse 2
A-4600 Wels
Austria
Tel: 43-7242-2244-399
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark
Microchip Technology Nordic ApS
Regus Business Centre
Lautrup hoj 1-3
Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Tel: 45 4420 9895 Fax: 45 4420 9910
France
Microchip Technology SARL
Parc d’Activite du Moulin de Massy
43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Batiment A - ler Etage
91300 Massy, France
Tel: 33-1-69-53 -63-20 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany
Microchip Technology GmbH
Steinheilstrasse 10
D-85737 Ismaning, Germany
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy
Microchip Technology SRL
Via Quasimodo, 12
20025 Legnano (MI)
Milan, Italy
Tel: 39-0331-742611 Fax: 39-0331-466781
United Kingdom
Microchip Ltd.
505 Eskdale Road
Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham
Berkshire, England RG41 5TU
Tel: 44 118 921 5869 Fax: 44-118 921-5820
03/25/03
DS51337A-page 24 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...