Page 1

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
Data Sheet
64/80-Pin High Performance,
64-Kbyte Enhanced FLASH
Microcontrollers with A/D
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A
Page 2

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip's Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protect ion features of our
products. Attempts to break microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect
to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such
use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical
components in life support systems is not authorized except
with express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual
property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, dsPIC,
K
EELOQ, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART , PRO MA TE and
PowerSmart are registered trademarks of Microchip
Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
FilterLab, microID, MXDEV, MXL AB, PICMASTER, SEEVAL
and The Embedded Control Solutions Company are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
Accuron, Application Maestro, dsPICDEM, dsPICDEM.net,
ECONOMONITOR, FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB, InCircuit Serial Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, microPort,
Migratable Memory, MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM,
PICC, PICkit, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, PowerCal, PowerInfo,
PowerMate, PowerTool, rfLAB, rfPIC, Select Mode,
SmartSensor, SmartShunt, SmartT el and T otal Endurance are
trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the
U.S.A. and other countries.
Serialized Quick Turn Programming (SQTP) is a service mark
of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2003, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received QS-9000 quality system
certification for its worldwide headquarters,
design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona in July 1999
and Mountain View, California in March 2002.
The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are QS-9000 compliant for its
PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals,
non-volatile memory and analog products. In
addition, Microchip’s quality system for the
design and manufacture of development
systems is ISO 9001 certified.
®
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ
®
code hopping
DS39612A-page ii Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
64/80-Pin High Performance, 64-Kbyte Enhanced FLASH
Microcontrollers with A/D
High Performance RISC CPU:
• Linear program memory addressing to 64 Kbytes
• Linear data memory addressing to 4 Kbytes
• 1 Kbyte of data EEPROM
• Up to 10 MIPs operation:
- DC - 40 MHz osc./clock input
- 4 MHz - 10 MHz osc./clock input with PLL active
• 16-bit wide instructions, 8-bit wide data path
• Priority levels for interrupts
• 31-level, software accessible hardware stack
• 8 x 8 Single Cycle Hardware Multiplier
Peripheral Features:
• High current sink/so ur ce 25 mA/25 mA
• Four external interrup t pin s
• Timer0 module: 8-bit/16-bit tim er/counter
• Timer1 module: 16-bit timer/counter
• Timer2 module: 8-bit timer/counter
• Timer3 module: 16-bit timer/counter
• Timer4 module: 8-bit timer/counter
• Secondary oscilla to r c lo ck option - Timer1/Timer3
• Two Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) mo dul es :
- Capture is 16-bit, max. resolution 6.25 ns (T
- Compare is 16-bit, max. resolution 100 ns (T
- PWM output: PWM re sol ution is 1 to 10-bit
• Three Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM (ECCP)
modules:
- Same Capture/ Compare features as CCP
- One, two, or four PWM ou tp uts
- Selectable polarity
- Programmabl e dead-time
- Auto shutdown on ext er nal event
- Auto Restart
• Master Synchronous Se rial Por t (MSSP) module
with two modes of operation:
- 3-wire SPI™ (supports all 4 SPI modes)
2
C™ Master and Slave mo de
-I
• Two Enhanced USART modules:
- Supports RS-485, R S-2 32, and LIN 1.2
- Auto wake-up on START bit
- Auto baud detec t
• Parallel Slave Port (PSP) module
CY/16)
CY)
External Memory Interface (PIC18F8X2X Devices Only):
• Address capability of up to 2 Mbytes
• 16-bit interface
Analog Features:
• 10-bit, up to 16-channel Analog-to-Digital
Converter (A/D):
- Auto acquisition
- Conversion av ai labl e during SLEEP
• Programmable 16 -level Low Voltage Detection
(LVD) module:
- Supports interrupt on Low Voltage Detection
• Programmable Brown-out Reset (BOR)
• Dual analog comparat or s:
- Programmabl e i nput/output configuration
Special Microcontroller Features:
• 100,000 erase/write cycle Enhanced FLASH
program memory typical
• 1,000,000 erase/write cycle Data EEPROM
memory typical
• 1 second program m in g t ime
• FLASH/Data EEPROM Retention: > 100 years
• Self-reprogramm a bl e under software control
• Power-on Reset (POR) , P ower-up Timer (PWRT)
and Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST)
• Watchdog Timer (WDT) with its own On-Chip
RC Oscillator for reliable operation
• Programmable co de protection
• Power saving SLEEP mode
• Selectable oscillator options including:
- 4X Phase Lock Loop (of primary oscillator)
- Secondary Oscillator (32 kHz) clock inp ut
• In-Circuit Serial Programming™ (ICSP™) via two pins
•MPLAB
®
In-Circuit Debug (ICD 2) via tw o pins
CMOS Technology:
• Low power, high speed FLASH technology
• Fully static design
• Wide operating voltage range (2.0V to 5.5V)
• Industrial and Extended temperature ranges
Program Memory Data Memory
Device
PIC18F6525 48K 24576 3840 1024 53 12 2/3 14 Y 2 2/3 N
PIC18F6621 64K 32768 3840 1024 53 12 2/3 14 Y 2 2/3 N
PIC18F8525 48K 24576 3840 1024 69 16 2/3 14 Y 2 2/3 Y
PIC18F8621 64K 32768 3840 1024 69 16 2/3 14 Y 2 2/3 Y
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 1
Bytes
# Single
Word
Instructions
SRAM
(bytes)
EEPROM
(bytes)
I/O
10-bit
A/D
(ch)
CCP/
ECCP
PWM
MSSP/
SPI/
Master I
2
C
EUSART
Timers
8-bit/16-bit
EMI
Page 4
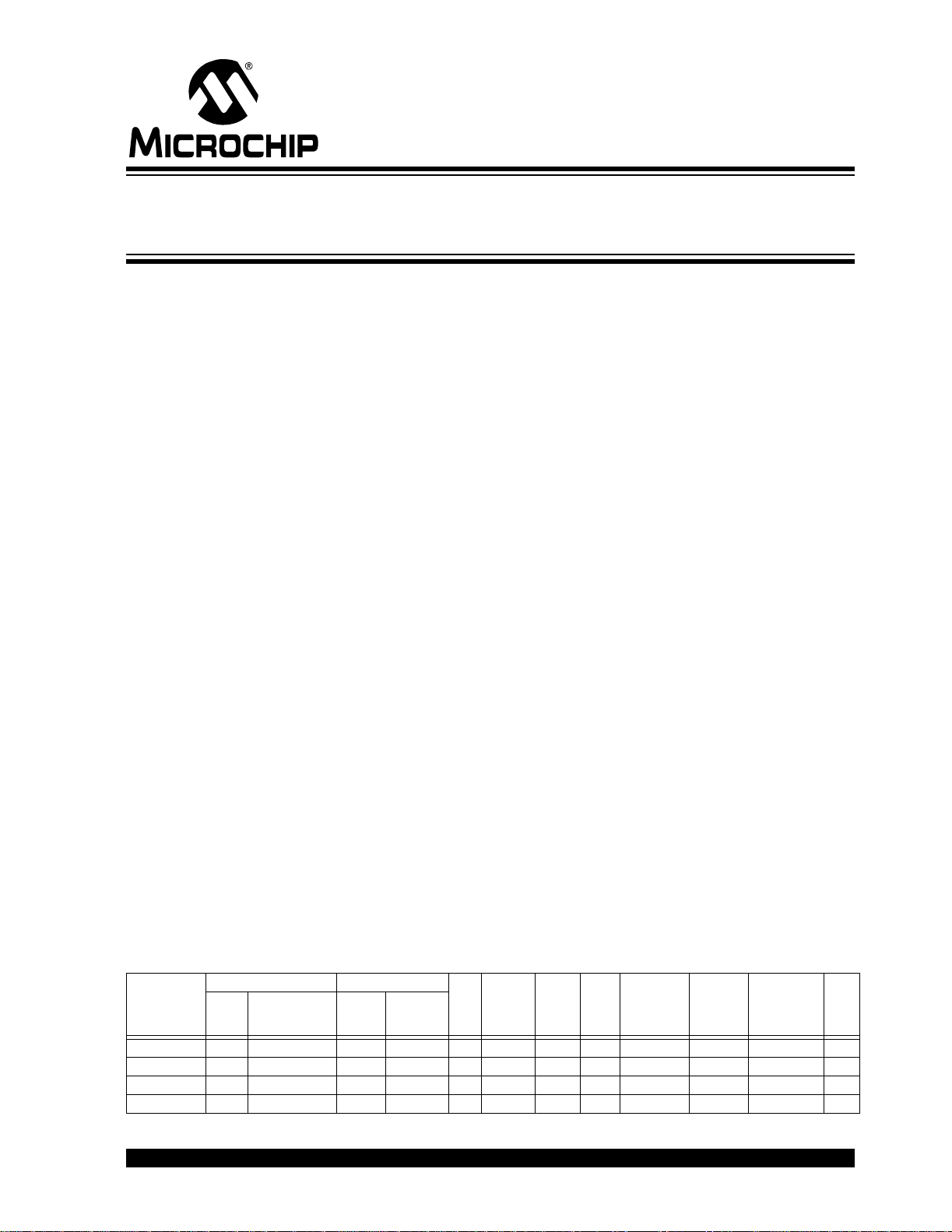
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
Pin Diagrams
64-Pin TQFP
RE3/P3C
RE2/CS/P2B
(1)
/P2A
(1)
RE4/P3B
RE5/P1C
RE6/P1B
RE7/CCP2
RD0/PSP0
VDDVSS
RD1/PSP1
RD2/PSP2
RD3/PSP3
RD4/PSP4
RD5/PSP5
RD6/PSP6
RD7/PSP7
RE1/WR/P2C
RE0/RD
/P2D
RG0/CCP3/P3A
RG1/TX2/CK2
RG2/RX2/DT2
RG3/CCP4/P3D
/VPP/RG5
MCLR
RG4/CCP5/P1D
V
VDD
RF7/SS
RF6/AN11
RF5/AN10/CV
RF2/AN7/C1OUT
REF
RF4/AN9
RF3/AN8
64
63 62 61
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
SS
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
DD
AV
RF0/AN5
RF1/AN6/C2OUT
PIC18F6525
PIC18F6621
REF-
AVSS
RA2/AN2/V
RA3/AN3/VREF+
RA1/AN1
RA0/AN0
54 53 52 5158 57 56 5560 59
27 28
SS
V
VDD
RA5/AN4/LVDIN
50 49
31
29 30 32
(1)
/P2A
(1)
RA4/T0CKI
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
RC6/TX1/CK1
RC7/RX1/DT1
RB0/INT0
RB1/INT1
RB2/INT2
RB3/INT3
RB4/KBI0
RB5/KBI1/PGM
RB6/KBI2/PGC
SS
V
OSC2/CLKO/RA6
OSC1/CLKI
V
DD
RB7/KBI3/PGD
RC5/SDO
RC4/SDI/SDA
RC3/SCK/SCL
RC2/CCP1/P1A
RC1/T1OSI/CCP2
Note 1: CCP2/P2A are multiplexed with RC1 when CCP2MX is set, or RE7 when CCP2MX is not set.
DS39612A-page 2 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5
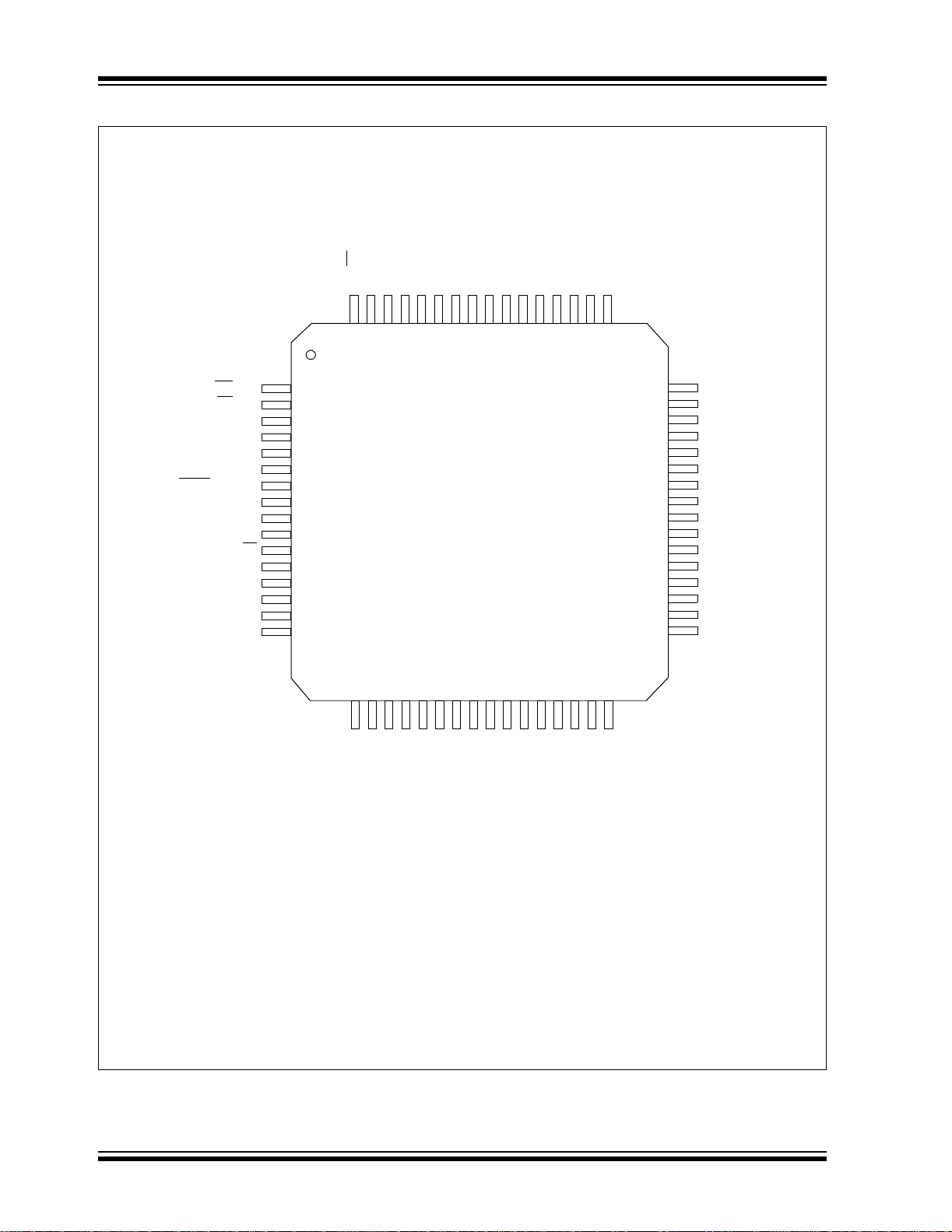
Pin Diagrams (Cont.’d)
80-Pin TQFP
RH2/A18
RH3/A19
RE1/AD9/WR/P2C
RE0/AD8/RD
RG0/CCP3/P3A
RG3/CCP4/P3D
MCLR
RG4/CCP5/P1D
RF5/AN10/CVREF
RF2/AN7/C1OUT
RH7/AN15/P1B
RH6/AN14/P1C
/P2D
RG1/TX2/CK2
RG2/RX2/DT2
/VPP/RG5
V
VDD
RF7/SS
RF6/AN11
RF4/AN9
RF3/AN8
SS
(2)
(2)
(1)
/P2A
(1)
(2)
(2)
RE4/AD12/P3B
(2)
RE5/AD13/P1C
RE6/AD14/P1B
RE7/AD15/CCP2
PIC18F8525
PIC18F8621
RD0/AD0/PSP0
(2)
RE2/AD10/CS/P2B
RE3/AD11/P3C
RH0/A16
RH1/A17
7980
78
77 76 75
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
VDDVSS
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
RD1/AD1/PSP1
RD2/AD2/PSP2
RD3/AD3/PSP3
RD4/AD4/PSP4
RD5/AD5/PSP5
RD6/AD6/PSP6
RD7/AD7/PSP7
RJ0/ALE
RJ1/OE
68 67 66 6572 71 70 6974 73
33 34
35 36
64 63 62 61
37
40
39
38
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
RJ2/WRL
RJ3/WRH
RB0/INT0
RB1/INT1
RB2/INT2
RB3/INT3/CCP2
RB4/KBI0
RB5/KBI1/PGM
RB6/KBI2/PGC
VSS
OSC2/CLKO/RA6
OSC1/CLKI
V
DD
RB7/KBI3/PGD
RC5/SDO
RC4/SDI/SDA
RC3/SCK/SCL
RC2/CCP1/P1A
RJ7/UB
RJ6/LB
(1)
/P2A
(1)
(2)
(2)
RH5/AN13/P3B
RH4/AN12/P3C
RF1/AN6/C2OUT
RF0/AN5
DD
AV
REF-
AVSS
RA2/AN2/V
RA3/AN3/VREF+
RA1/AN1
RA0/AN0
SS
V
(1)
VDD
/P2A
(1)
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/AN4/LVDIN
RC6/TX1/CK1
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
RC1/T1OSI/CCP2
RJ5/CE
RJ4/BA0
RC7/RX1/DT1
Note 1: CCP2/P2A are multiplexed with RC1 when CCP2MX is set; with RE7 when CCP2MX is cleared and the device is
configured in Microcontroller mode; or with RB3 when CCP2MX is cleared in all other Program Memory modes.
2: P1B/P1C/P3B /P3C are multiplexed with RE6:RE3 when ECCPMX is set, and with RH7:RH4 when ECCPMX is
not set.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 3
Page 6

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
Table of Contents
1.0 Device Overview ..........................................................................................................................................................................7
2.0 Oscillator Configurations............................................................................................................................................................ 21
3.0 Reset..........................................................................................................................................................................................31
4.0 Memory Organization.................................................................................................................................................................41
5.0 FLASH Program Memory...................................... ................ ..................................................................................................... 63
6.0 External Memory Interface......................................................................................................................................................... 73
7.0 Data EEPROM Memory................................... ................. ................. ................. ....................................................................... 81
8.0 8 X 8 Hardware Multiplier........................... ................. ................. ................................. .............................................................87
9.0 Interrupts.................................................................................................................................................................................... 89
10.0 I/O Ports................... ................. ...............................................................................................................................................105
11.0 Timer0 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 133
12.0 Timer1 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 137
13.0 Timer2 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 143
14.0 Timer3 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 145
15.0 Timer4 Module ......................................................................................................................................................................... 149
16.0 Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) Modules .................................................................................................................................151
17.0 Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM (ECCP) Module................................................................................................................159
18.0 Master Synchronous Serial Port (MSSP) Module .................................................................................................................... 175
19.0 Enhanced Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (USART).................................................................. 215
20.0 10-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) Module ......................................................................................................................235
21.0 Comparator Module................................................................. ......... .... .. .... ....... .... .... .. .... ......................................................... 243
22.0 Comparator Voltage Reference Module................................................................................................................................... 249
23.0 Low Voltage Detect ..................................................................................................................................................................253
24.0 Special Features of th e CPU.............. ................ ................. ................. .................................................................................... 259
25.0 Instruction Set Summary.......................................................................................................................................................... 277
26.0 Development Support............................................................................................................................................................... 319
27.0 Electrical Characteristics.......................................................................................................................................................... 325
28.0 DC and AC Characteristics Graphs and Tables....................................................................................................................... 359
29.0 Packaging Inform a tio n..... ................. ................ ................. ....................................................................................................... 361
Appendix A: Revision History............................................................................................................................................................. 365
Appendix B: Device Differences......................................................................................................................................................... 365
Appendix C: Conversion Considerations ........................................................... .. ....... .... .. .... .. .... ....................................................... 366
Appendix D: Migration from Mid-Range to Enhanced Devices..........................................................................................................366
Appendix E: Migration from High-End to Enhanced Devices............................................................................................................. 367
Index .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 369
On-Line Support.................................................................... .. .... .... .. ......... .... .. .... ....... .... ...................................................................379
Systems Information and Upgrade Hot Line......................................................................................................................................379
Reader Response.............................................................................................................................................................................. 380
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X Product Identification System............................................................................................................................. 381
DS39612A-page 4 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
It is our intention to provide our valued customers with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip
products. To this end, we will continue to improve our publications to better suit your needs. Our publications will be refined and
enhanced as new volumes and updates are introduced.
If you have any questions or c omm ents regarding t his publication, p lease c ontact the M arket ing Co mmunications Department via
E-mail at docerrors@mail.microchip.com or fax the Reader Response Form in the back of this data sheet to (480) 792-4150.
We welcome your feedback.
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please register at our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page.
The last character of the literature number is the version number, (e.g., DS30000A is version A of document DS30000).
Errata
An errata sheet, describing minor operational differences from the data sheet and recommended workarounds, may exist for current
devices. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the revision
of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
• Microchip’s Worldwide Web site; http://www.microchip.com
• Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
• The Microchip Corporate Literature Center; U.S. FAX: (480) 792-7277
When contacting a sales office or the literature center, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include liter-
ature number) you are using.
Customer Notification System
Register on our web site at www.microchip.com/cn to receive the most current information on all of our products.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 5
Page 8

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
NOTES:
DS39612A-page 6 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
1.0 DEVICE OVERVIEW
This documen t conta i ns dev ic e spec if i c in for m at i on fo r
the following devices:
• PIC18F6525
• PIC18F6621
• PIC18F8525
• PIC18F8621
This family offers the advantages of all
PIC18 microcontrollers - namely, high computational
performance at an economical price - with the
addition of high endurance enhanced FLASH program
memory. The PIC18F6X2X/ 8X2X famil y also provi des
an enhanced range of program memory options and
versatile analog fea tures that mak e it ideal fo r complex,
high performance applications.
1.1 Key Features
1.1.1 EXPANDED MEMORY
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X family provides ample room
for application code, and includes members with
48 Kbytes or 64 Kbytes of code space.
Other memory features are:
• Data RAM and Data EEPROM: The
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X family also provides plenty of
room for application data. The devices have
3840 bytes of data RAM as well as 1024 bytes of
data EEPROM for lon g term retention of non-volatile
data.
• Memory Endurance: The enhanced FLASH cells
for both program memory and data EEPROM are
rated to last for many thousands of erase/write
cycles - up to 100,000 for program memory, and
1,000,000 for EEPROM. Data retention without
refresh is conservatively estimated to be greater
than 40 years.
1.1.2 EXTERNAL MEMORY INTERFACE
In the unlikely event t hat 64 Kbytes of program memo ry
is inadequate for an application, the PIC18F8X2X
members of the family also implement an external
memory interface. This allows the controller’s internal
program counter to address a memory space of up to
2 MBytes, permitting a level of data access that few
8-bit devices can claim.
With the addition of new operati ng mode s, the ext ernal
memory interface offers many new options, including:
• Operating the microcontr oller entirely f rom external
memory
• Using combinations of on-chip and external
memory, up to the 2-Mbyte limit
• Using external FLASH me mory for reprogrammable
application code or large data tables
• Using external RAM devices for storing large
amounts of variable data
1.1.3 EASY MIGRATION
Regardless of the memory size, all devices share the
same rich set of peripherals, allowing for a smooth
migration path as applications grow and evolve.
The consistent pinout scheme used throughout the
entire family also aids in migrating to the next larger
device. This is true when moving between the 64-pin
members, between the 80-pin members, or even
jumping fr om 64-pin to 80-pin devic es.
1.1.4 OTHER SPECI AL FE A TU RES
• Communications: The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X family
incorporates a range of serial communication
peripherals, including 2 independent enhanced
USARTs and a Master SSP module capable of both
SPI and I2C (Master and Slave) mod es of op era tio n.
Also, for PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices, one of the
general purpose I/O port s can be recon figured as an
8-bit parallel slave port for direct processor to
processor communi ca tio ns.
• CCP Modules: All devices in the family incorporate
two Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) modules and
three enhanced CCP modu les to maximize flexibility
in control applications. Up to four different time
bases may be used to perform several different
operations at once. Each of the three ECCPs offer
up to four PWM outputs, allowing for a total of 12
PWMs. The ECCPs also offer many beneficial features, including polarity selection, programmable
dead-time, auto shutdown and restart, and
Half-Bridge and Full-Bridge Output mo des.
• Analog Features: All devices in the family feature
10-bit A/D converters with up to 16 input channels,
as well a s the a bility t o perfor m conver sions du ring
SLEEP mode and auto-acquisition conversions.
Also included are dual analog comparators with
programmable input and output configuration, a
programmable Low Voltage Detect module, and a
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 7
Page 10

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
1.2 Details on Individual Family Members
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X dev ices a re available in 64-pi n
and 80-pin packages. They are differentiated from
each other in four ways:
1. FLASH program memory (48 Kbytes for
PIC18FX525 devices and 64 Kbytes for
PIC18FX621 devices)
2. A/D channels (12 for PIC18F6X2X devices ,
16 for PIC1 8F8X2X)
3. I/O ports (7 on PIC18F6X2X devices, 9 on
PIC18F8X2X)
4. External program memory interface (present
only on PIC18F8X2X devices)
All other features for devic es in the PIC1 8F6X2X/8 X2X
family are identical. These are summarized in
Table 1-1.
Block diagrams of the PIC18F6X2X and PIC18F8X2X
devices are provided in Figure 1-1 and Figure 1-2,
respectively. The pinouts for these device families are
listed in Table 1-2.
TABLE 1-1: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X DEVICE FEATURES
Features PIC18F6525 PIC18F6621 PIC18F8525 PIC18F8621
Operating Frequency
Program Memory (Bytes) 48K 64K 48K 64 K
Program Memory (Instruction s) 24576 32768 24576 3 276 8
Data Memory (Bytes) 3840 3840 3840 384 0
Data EEPROM Memory (Bytes) 1024 1024 1024 1024
External Memory Interface No No Yes Yes
Interrupt Sources 17 17 17 17
I/O Ports Ports A, B, C, D,
Timers 5 5 5 5
Capture/Compare/PWM Modules 2 2 2 2
Enhanced Capture/Compare/
PWM Module
Serial Communications MSSP,
Parallel Communications PSP PSP PSP PSP
10-bit Analog-to-Digital Module 12 input channels 12 input channels 16 input channels 16 input channels
RESETS (and Delays) POR, BOR,
Programmable Low Voltage
Detect
Programmable Brown-out Reset Yes Yes Y es Yes
Instruction Set 77 Instructions 77 Instructions 77 Instructions 77 Instructions
Package 64-pin TQFP 64-pin TQFP 80-pin TQFP 80-pin TQFP
DC - 40 MHz DC - 40 MHz DC - 40 MHz DC - 40 MHz
Ports A, B, C, D,
E, F, G
3333
Addressable
EUSART (2)
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full,
Stack Underflow
(PWRT, OST)
Yes Yes Yes Yes
E, F, G
MSSP,
Addressable
EUSART (2)
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full,
Stack Underflow
(PWRT, OST)
Ports A, B, C, D, E,
F, G, H, J
MSSP,
Addressable
EUSART (2)
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full,
Stack Underflow
(PWRT, OST)
Ports A, B, C, D, E,
F, G, H, J
MSSP,
Addressable
EUSART (2)
POR, BOR,
RESET Instruction,
Stack Full,
Stack Underflow
(PWRT, OST)
DS39612A-page 8 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11

FIGURE 1-1: PIC18F6525/662 1 BLO CK D IA GRA M
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 9
Page 12

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 1-2: PIC18F8525/8621 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Data Bus<8>
PORTA
21
Address Latch
Program Memory
(48/64Kbytes)
Data Latch
OSC2/CLKO
OSC1/CLKI
21
16
Instruction
Decode &
Control
Timing
Generation
Precision
Bandgap
Reference
Table Pointer<21>
inc/dec logic
20
PCLATU
PCU
Program Counter
Table Latch
8
Power-up
Oscillator
Start-up Timer
Power-on
Watchdog
Brown-out
Te st Mod e
8
PCLATH
PCH PCL
31 Level Stack
ROM Latch
IR
Timer
Reset
Timer
Reset
Select
8
4
Decode
BITOP
3
8
Data Latch
Data RAM
(3.8 Kbytes)
Address Latch
12
Address<12>
12 4
FSR0
FSR1
FSR2
inc/dec
logic
8 x 8 Multiply
W
8
8
ALU<8>
8
Bank0, FBSR
PRODLPRODH
RA3/AN3/VREF+
RA4/T0CKI
RA5/AN4 /LVDIN
PORTB
12
8
8
8
PORTC
RB0/INT0
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
RC2/CCP1/P1A
RC3/SCK/SCL
RC4/SDI/SDA
RC5/SDO
RC6/TX1/CK1
RC7/RX1/DT1
PORTH
10-bit
LVD
Note 1: CCP2/P2A are multiplexed with RC1 when CCP2MX is set; with RE7 when CCP2MX is cleared and the device is configured in
Microcontroller mode; or with RB3 when CCP2MX is cleared in all other Program Memory modes.
2: P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C are multiplexed with RE6:RE3 when ECCPMX is set, and with RH7:RH4 when ECCPMX is not set.
3: RG5 is multiplexed with MCLR
4: External memory interface pins are multiplexed with PORTD (AD7:AD0), PORTE (AD15:AD8) and PORTH (A19:A16).
Timer2Timer1 Timer3 Timer4Timer0
MSSP
CCP4 CCP5
, and is only available when the MCLR Resets are disabled.
EUSART1Comparator
ADC
EUSART2
PORTJ
RH0:RH3/AD19
RH4/AN12/P3C
RH5/AN13/P3B
RH6/AN14/P1C
RH7/AN15/P1B
RJ0/ALE
RJ1/OE
RJ2/WRL
RJ3/WRH
RJ4/BA0
RJ5/CE
RJ6/LB
RJ7/UB
(4)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
DS39612A-page 10 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
T ABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Name
Pin Number
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
Pin
Type
Buffer
Type
Description
/VPP/RG5
MCLR
MCLR
VPP
RG5
OSC1/CLKI
OSC1
CLKI
OSC2/CLKO/RA6
OSC2
CLKO
RA6
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X de vices when ECCP MX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microcontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is not set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
79
I
P
I
39 49
IICMOS/ST
40 50
O
O
I/O
ST
—
ST
CMOS
—
—
TTL
Master Clear (input) or programming
voltage (output).
Master Clea r (Res et) inpu t. Thi s pi n is an
active low RESET to the device.
Programming voltage input.
Digital input.
Oscillator crystal or external clock input.
Oscillator crystal input or ex te rn al cl ock
source input. ST buffer when configured
in RC mode; otherwise CMOS.
External clock source input. Always
associated with pin func t io n O SC 1 (see
OSC1/CLKI, OSC2/CLKO pins).
Oscillator crystal or clock out put.
Oscillator crystal output.
Connects to crystal or resonator in
Crystal Oscillator mod e.
In RC mode, OSC2 pin ou tp uts CLKO
which has 1/4 the freque ncy of OSC1
and denotes the instru ct ion cycle rate.
General purpose I/O pin.
DD)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 11
Page 14

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
RA0/AN0
24 30
RA0
AN0
RA1/AN1
23 29
RA1
AN1
RA2/AN2/V
REF-
22 28
RA2
AN2
REF-
V
RA3/AN3/V
REF+
21 27
RA3
AN3
V
REF+
RA4/T0CKI
28 34
RA4
T0CKI
RA5/AN4/LVDIN
27 33
RA5
AN4
LVDIN
RA6 See the OSC2/CLKO/RA6 pin.
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devices when ECCPMX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microc ontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/ P3B /P3C for PIC18F8 X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is no t set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
Pin
Type
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Buffer
Type
TTL
I
Analog
TTL
I
Analog
TTL
I
Analog
I
Analog
TTL
I
Analog
I
Analog
I/OIST/OD
ST
I/O
I
I
TTL
Analog
Analog
Description
PORTA is a bi-directional I/O port.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 0.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 1.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 2.
A/D reference voltage (Low) input.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 3.
A/D reference voltage (High) input.
Digital I/O – Open drain when
configured as output.
Timer0 external clock input.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 4.
Low Voltage Detect input.
DD)
DS39612A-page 12 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
RB0/INT0
48 58
RB0
INT0
RB1/INT1
47 57
RB1
INT1
RB2/INT2
46 56
RB2
INT2
RB3/INT3/CCP2/P2A
45 55
RB3
INT3
(1)
CCP2
(1)
P2A
RB4/KBI0
44 54
RB4
KBI0
RB5/KBI1/PGM
43 53
RB5
KBI1
PGM
RB6/KBI2/PGC
42 52
RB6
KBI2
PGC
RB7/KBI3/PGD
37 47
RB7
KBI3
PGD
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X de vices when ECCP MX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microcontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is not set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
Pin
Type
I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
Buffer
Type
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
ST
—
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
ST
TTL
ST
ST
TTL
ST
ST
Description
PORTB is a bi-directional I/O port. PORTB
can be software programmed for internal
weak pull-ups on all inputs.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 0.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 1.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 2.
Digital I/O.
External interrupt 3.
Capture2 input, Compare2 output,
PWM2 output.
Enhanced CCP2 output P2A.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
Low voltage ICSP programming
enable pin.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
In-Circuit Debugger and
ICSP programming cloc k.
Digital I/O.
Interrupt-on-change pin.
In-Circuit Debugger and
ICSP programming data.
DD)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 13
Page 16
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
RC0/T1OSO/T13CKI
30 36
RC0
T1OSO
T13CKI
RC1/T1OSI/CCP2/P2A
29 35
RC1
T1OSI
(2)
CCP2
(2)
P2A
RC2/CCP1/P1A
33 43
RC2
CCP1
P1A
RC3/SCK/SCL
34 44
RC3
SCK
SCL
RC4/SDI/SDA
35 45
RC4
SDI
SDA
RC5/SDO
36 46
RC5
SDO
RC6/TX1/CK1
31 37
RC6
TX1
CK1
RC7/RX1/DT1
32 38
RC7
RX1
DT1
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devices when ECCPMX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microc ontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/ P3B /P3C for PIC18F8 X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is no t set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
Pin
Type
I/O
O
I
I/O
I
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
Buffer
Type
ST
—
ST
ST
CMOS
ST
—
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
Description
PORTC is a bi-directional I/O port.
Digital I/O.
Timer1 oscillator output.
Timer1/Timer3 external clock input.
Digital I/O.
Timer1 oscillator input.
Capture2 input, Compare2 output,
PWM2 output.
Enhanced CCP2 output P2A.
Digital I/O.
Capture1 input, Compare1 output,
PWM1 output.
Enhanced CCP1 output P1A.
Digital I/O.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for
SPI mode.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for
2
C mode.
I
Digital I/O.
SPI data in.
2
C data I/O.
I
Digital I/O.
SPI data out.
Digital I/O.
USART 1 asynchronous transmit.
USART 1 synchronous clock
(see RX1/DT1).
Digital I/O.
USART 1 asynchronous receive.
USART 1 synchronous data
(see TX1/CK1).
DD)
DS39612A-page 14 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
RD0/AD0/PSP0
RD0
(3)
AD0
58 72
PSP0
RD1/AD1/PSP1
RD1
(3)
AD1
55 69
PSP1
RD2/AD2/PSP2
RD2
(3)
AD2
54 68
PSP2
RD3/AD3/PSP3
RD3
(3)
AD3
53 67
PSP3
RD4/AD4/PSP4
RD4
(3)
AD4
52 66
PSP4
RD5/AD5/PSP5
RD5
(3)
AD5
51 65
PSP5
RD6/AD6/PSP6
RD6
(3)
AD6
50 64
PSP6
RD7/AD7/PSP7
RD7
(3)
AD7
49 63
PSP7
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X de vices when ECCP MX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microcontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is not set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
Pin
Type
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Buffer
Type
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
TTL
TTL
Description
PORTD is a bi-directional I/O port. These
pins have TTL i nput buffer s wh en external
memory is enabled.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 0.
Parallel slave port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 1.
Parallel slave port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 2.
Parallel slave port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 3.
Parallel slave port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 4.
Parallel slave port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 5.
Parallel Slave Port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 6.
Parallel slave port data.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 7.
Parallel slave port data.
DD)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 15
Page 18
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
RE0/AD8/RD
RE0
(3)
AD8
/P2D
24
RD
P2D
RE1/AD9/WR/P2C
RE1
(3)
AD9
13
WR
P2C
RE2/AD10/CS
RE2
(3)
AD10
/P2B
64 78
CS
P2B
RE3/AD11/P3C
RE3
(3)
AD11
(4)
P3C
RE4/AD12/P3B
RE4
(3)
AD12
(4)
P3B
RE5/AD13/P1C
RE5
(3)
AD13
(4)
P1C
RE6/AD14/P1B
RE6
(3)
AD14
(4)
P1B
RE7/AD15/CCP2/P2A
RE7
(3)
AD15
(5)
CCP2
(5)
P2A
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devices when ECCPMX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microc ontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/ P3B /P3C for PIC18F8 X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is no t set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
63 77
62 76
61 75
60 74
59 73
Pin
Type
I/O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
Buffer
Type
ST
TTL
TTL
—
ST
TTL
TTL
ST
ST
TTL
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
—
ST
TTL
ST
—
Description
PORTE is a bi-directional I/O port.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 8.
Read control for paralle l slave port.
Enhanced CCP2 output P2D.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 9.
Write control for parallel slave port.
Enhanced CCP2 output P2C.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 10.
Chip select control for parallel slave port.
Enhanced CCP2 output P2B.
Digital I/O.
External memory address/data 11.
Enhanced CCP3 output P3C.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 12.
Enhanced CCP3 output P3B.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 13.
Enhanced CCP1 output P1C.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 14.
Enhanced CCP1 output P1B.
Digital I/O.
External memory addre ss/data 15.
Capture2 input, Compare2 output,
PWM2 output.
Enhanced CCP2 output P2A.
DD)
DS39612A-page 16 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
RF0/AN5
RF0
AN5
RF1/AN6/C2OUT
RF1
AN6
C2OUT
RF2/AN7/C1OUT
RF2
AN7
C1OUT
RF3/AN8
RF1
AN8
RF4/AN9
RF1
AN9
RF5/AN10/CV
RF1
AN10
CVREF
RF6/AN11
RF6
AN11
RF7/SS
RF7
SS
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
REF
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X de vices when ECCP MX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microcontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is not set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
Pin Number
18 24
17 23
16 18
15 17
14 16
13 15
12 14
11 13
Pin
Type
I/O
I
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
I/O
I
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
I/O
I
Buffer
Type
ST
Analog
ST
Analog
ST
ST
Analog
ST
ST
Analog
ST
Analog
ST
Analog
Analog
ST
Analog
ST
TTL
Description
PORTF is a bi-directional I/O port.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 5.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 6.
Comparator 2 output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 7.
Comparator 1 output.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 8.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 9.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 10.
Comparator V
Digital I/O.
Analog input 11.
Digital I/O.
SPI slave select input.
REF output.
DD)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 17
Page 20

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
RG0/CCP3/P3A
RG0
CCP3
P3A
RG1/TX2/CK2
RG1
TX2
CK2
RG2/RX2/DT2
RG2
RX2
DT2
RG3/CCP4/P3D
RG3
CCP4
P3D
RG4/CCP5/P1D
RG4
CCP5
P1D
RG5 7 9 — — See MCLR
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devices when ECCPMX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microc ontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/ P3B /P3C for PIC18F8 X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is no t set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
Pin Number
35
46
57
68
810
Pin
Type
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
Buffer
Type
ST
ST
—
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
—
Description
PORTG is a bi-directional I/O port.
Digital I/O.
Capture3 input, Compare3 output,
PWM3 output.
Enhanced CCP3 output P3A.
Digital I/O.
USART 2 asynchronous transmit.
USART 2 synchronous clock
(see RX2/DT2).
Digital I/O.
USART 2 asynchronous receive.
USART 2 synchronous data
(see TX2/CK2).
Digital I/O.
Capture4 input, Compare4 output,
PWM4 output.
Enhanced CCP3 output P3D.
Digital I/O.
Capture5 input, Compare5 output,
PWM5 output.
Enhanced CCP1 output P1D.
/VPP/RG5 pin.
DD)
DS39612A-page 18 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
RH0/A16
RH0
A16
RH1/A17
RH1
A17
RH2/A18
RH2
A18
RH3/A19
RH3
A19
RH4/AN12/P3C
RH4
AN12
(7)
P3C
RH5/AN13/P3B
RH5
AN13
(7)
P3B
RH6/AN14/P1C
RH6
AN14
(7)
P1C
RH7/AN15/P1B
RH7
AN15
(7)
P1B
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
Pin Number
—79
—80
—1
—2
—22
—21
—20
—19
Pin
Type
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
O
I/O
I
O
Buffer
Type
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
TTL
ST
Analog
—
ST
Analog
—
ST
Analog
—
ST
Analog
—
Description
PORTH is a bi-directional I/O port
Digital I/O.
External memory address 16.
Digital I/O.
External memory address 17.
Digital I/O.
External memory address 18.
Digital I/O.
External memory address 19.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 12.
Enhanced CCP3 output P3C.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 13.
Enhanced CCP3 output P3B.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 14.
Enhanced CCP1 output P1C.
Digital I/O.
Analog input 15.
Enhanced CCP1 output P1B.
(6)
.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 19
Page 22

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 1-2: PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
Pin Number
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X
RJ0/ALE
—62
RJ0
ALE
RJ1/OE
—61
RJ1
OE
RJ2/WRL
—60
RJ2
WRL
RJ3/WRH
—59
RJ3
WRH
RJ4/BA0
—39
RJ4
BA0
RJ5/CE
—40
RJ5
CE
RJ6/LB
—41
RJ6
LB
RJ7/UB
—42
RJ7
UB
SS 9, 25,
V
41, 56
V
DD 10, 26,
38, 57
(8)
AV
SS
(8)
AVDD
Legend: TTL = TTL compatible input CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output
Note 1: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX (CONFIG3H<0>) is not set (all Program
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels Analog = Analog input
I = Input O = Output
P = Power OD = Open Drain (no P diode to V
Memory modes except Microcontroller).
2: Default assignment for CCP2/P2A when CCP2MX is set (all devices).
3: External memory interface functions are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
4: Default assignment for P1B/P1C/P3B/P3C for PIC18F8X2X devices when ECCPMX (CONFIG3H<1>) is set, and for all
PIC18F6X2X devices.
5: Alternate assignment for CCP2/P2A in PIC18F8X2X devices when CCP2MX is not set (Microc ontroller mode).
6: PORTH and PORTJ (and their multiplexed functions) are only available on PIC18F8X2X devices.
7: Alternate assignment for P1B/P1C/ P3B /P3C for PIC18F8 X2X devic es when ECCPM X (CON FIG3H<1>) is no t set.
8: AV
DD must be connected to a positive supply and AVSS must be connected to a ground reference for proper operation of
the part in User or ICSP modes. See parameter D001A for details.
20 26 P — Ground reference for analog modul es.
19 25 P — Positive supply for analog modules.
11, 31,
51, 70
12, 32,
48, 71
Pin
Type
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Buffer
Type
PORTJ is a bi-directional I/O port
ST
O
TTL
ST
O
TTL
ST
O
TTL
ST
O
TTL
ST
O
TTL
ST
O
TTL
ST
O
TTL
ST
O
TTL
Digital I/O.
External memory address latch enable.
Digital I/O.
External memory output enable.
Digital I/O.
External memory write low control.
Digital I/O.
External memory write high control.
Digital I/O.
System bus byte addres s 0 control.
Digital I/O
External memory access indicator.
Digital I/O.
External memory low byte select.
Digital I/O.
External memory high byte select.
Description
(6)
P — Ground reference for logic and I/O pins.
P — Po sit iv e supply for logic and I/O pins.
DD)
.
DS39612A-page 20 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
2.0 OSCILLATOR CONFIGURATIONS
2.1 Oscillator Types
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices can be operated in
twelve different Oscillator modes. The user can program four configuration bits (FOSC3, FOSC2, FOSC1,
OSC0) to select one of these eight modes:
and F
1. LP Low Power Crystal
2. XT Crystal/Resonator
3. HS High Speed Crystal/Resonator
4. RC Ex tern al R esi st or/C apacitor
5. EC External Clock
6. ECIO External Clock with I/O pin
enabled
7. HS+PLL High Speed Crystal/Resonator
with PLL enabled
8. RCIO External Resist or/C apacitor with
I/O pin enabled
9. ECIO+SPLL External Clock with software
controlled PLL
10. ECIO+PLL External Clock with PLL and I/O
pin enabled
11. HS+SPLL High Speed Crystal/Resonator
with software control
12. RC IO E x tern al Resi stor/Capacitor with
I/O pin enabled
2.2 Crystal Oscillator/Ceramic Resonators
In XT , LP, HS, HS+PLL or HS+SPLL Oscillator modes, a
crystal or ceramic resonator is connected to the OSC1
and OSC2 pins to establish oscil lation. Figure 2-1 shows
the pin connections.
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X oscillator design requires the
use of a parallel cut crysta l.
Note: Use of a series cut crystal may give a fre-
quency out of the crystal manufacturers
specifications.
FIGURE 2-1: CRYSTAL/CERAMIC
RESONATOR OPERATION
(HS, XT OR LP
CONFIGURATION)
(1)
C1
(1)
C2
Note 1: See Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 for
2: A series resistor (R
3: R
OSC1
To
Internal
XTAL
(2)
RS
OSC2
recommended values of C1 and C2.
AT strip cut crystals.
F varies with the Oscillator mode chosen.
(3)
RF
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
S) may be required for
Logic
SLEEP
T ABLE 2-1: CAPACITOR SELECTION FOR
CERAMIC RESONATORS
Ranges Tested:
Mode Freq C1 C2
XT 455 kHz
2.0 MHz
4.0 MHz
HS 8.0 MHz
16.0 MHz
These values are for design guid ance only.
See notes following this table.
Resonators Used:
2.0 MHz Murata Erie CSA2.00MG ± 0.5%
4.0 MHz Murata Erie CSA4.00MG ± 0.5%
8.0 MHz Murata Erie CSA8.00MT ± 0.5%
16.0 MHz Murata Erie CSA16.00MX ± 0.5%
All resonators used did not have bui lt-in capacitors.
Note 1: Higher capacita nce increa ses the st ability
of the oscillator but also increases the
start-up time.
2: When operating below 3V V
using certain ceramic resonators at any
voltage, it may be necessary to use high
gain HS mode, try a lower frequency
resonator, or switch to a crystal oscillator.
3: Since each resonator/crystal has its own
characteristics, the user should consul t the
resonator/crystal manufacturer for appropriate values of external components, or
verify oscillator performance.
68 - 100 pF
15 - 68 pF
15 - 68 pF
10 - 68 pF
10 - 22 pF
68 - 100 pF
15 - 68 pF
15 - 68 pF
10 - 68 pF
10 - 22 pF
DD, or when
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 21
Page 24

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 2-2: CAPACITOR SELECTION FOR
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
Ranges Tested:
Mode Freq C1 C2
LP 32.0 kHz 33 pF 33 pF
200 kHz 15 pF 15 pF
XT 200 kHz 47-68 pF 47-68 pF
1.0 MHz 15 pF 15 pF
4.0 MHz 15 pF 15 pF
HS 4.0 MHz 15 pF 15 pF
8.0 MHz 15-33 pF 15-33 pF
20.0 MHz 15-33 pF 15-33 pF
25.0 MHz TBD TBD
These values are for de sign guid ance only.
See notes following this table.
Crystals Used
32.0 kHz Epson C-001R32.768K-A ± 20 PPM
200 kHz STD XTL 200.000KHz ± 20 PPM
1.0 MHz ECS ECS-10-13-1 ± 50 PPM
4.0 MHz ECS ECS-40-20-1 ± 50 PPM
8.0 MHz Epson CA-301 8.000M-C ± 30 PPM
20.0 MHz Epson CA-301 20.000M-C ± 30 PPM
Note 1: Higher capacitanc e increase s the stabi lity
of the oscillator but also increases the
start-up time.
2: Rs (see Figure 2-1) may be required in
HS mode, as we ll as XT mode , to avoid
overdriving crystals with low drive level
specification.
3: Since each resonator/crystal has its own
characteristics, the user should consult the
resonator/crystal manufacturer for appropriate values of external components, or
verify oscillator performance.
An external clock sourc e may also be conne cted to th e
OSC1 pin in the HS, XT and LP modes as shown in
Figure 2-2.
FIGURE 2-2: EXTERNAL CLOCK INPUT
OPERATION (HS, XT OR LP
OSC CONFIGURATION)
Clock from
Ext. System
Open
OSC1
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
OSC2
2.3 RC Oscillator
For timing insensitive applications, the “RC” and
“RCIO” device options offer additional cost savings.
The RC oscillator frequency is a function of the supply
voltage, the resistor (R
ues and the operating temperature. In addition to this,
the oscillator frequency will vary from uni t to unit due to
normal process parameter variation. Furthermore, the
difference in le ad fram e c apacitance betwee n package
types will also affect the oscillation frequency, especially for low C
EXT values. The user also needs to take
into account variation due to tolerance of external R
and C components used. Figure 2-3 shows how the
R/C combination is connected.
In the RC Oscillator mode, the oscillator frequency
divided by 4 is available on the OSC2 pin. This signal
may be used f or t e st pu r pos es or t o sy nc hr o n iz e ot he r
logic.
FIGURE 2-3: RC OSCILLATOR MODE
VDD
REXT
CEXT
VSS
F
Recommended values: 3 kΩ ≤ REXT ≤ 100 kΩ
The RCIO Oscillator mode functions like the RC mode
except that the OSC2 pin becomes an additional general purpose I/O pin. The I/O pin becomes bit 6 of
PORTA (RA6).
EXT) and capacitor (CEXT) val-
OSC1
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
OSC2/CLKO
OSC/4
C
EXT > 20pF
Internal
Clock
DS39612A-page 22 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
2.4 External Clock Input
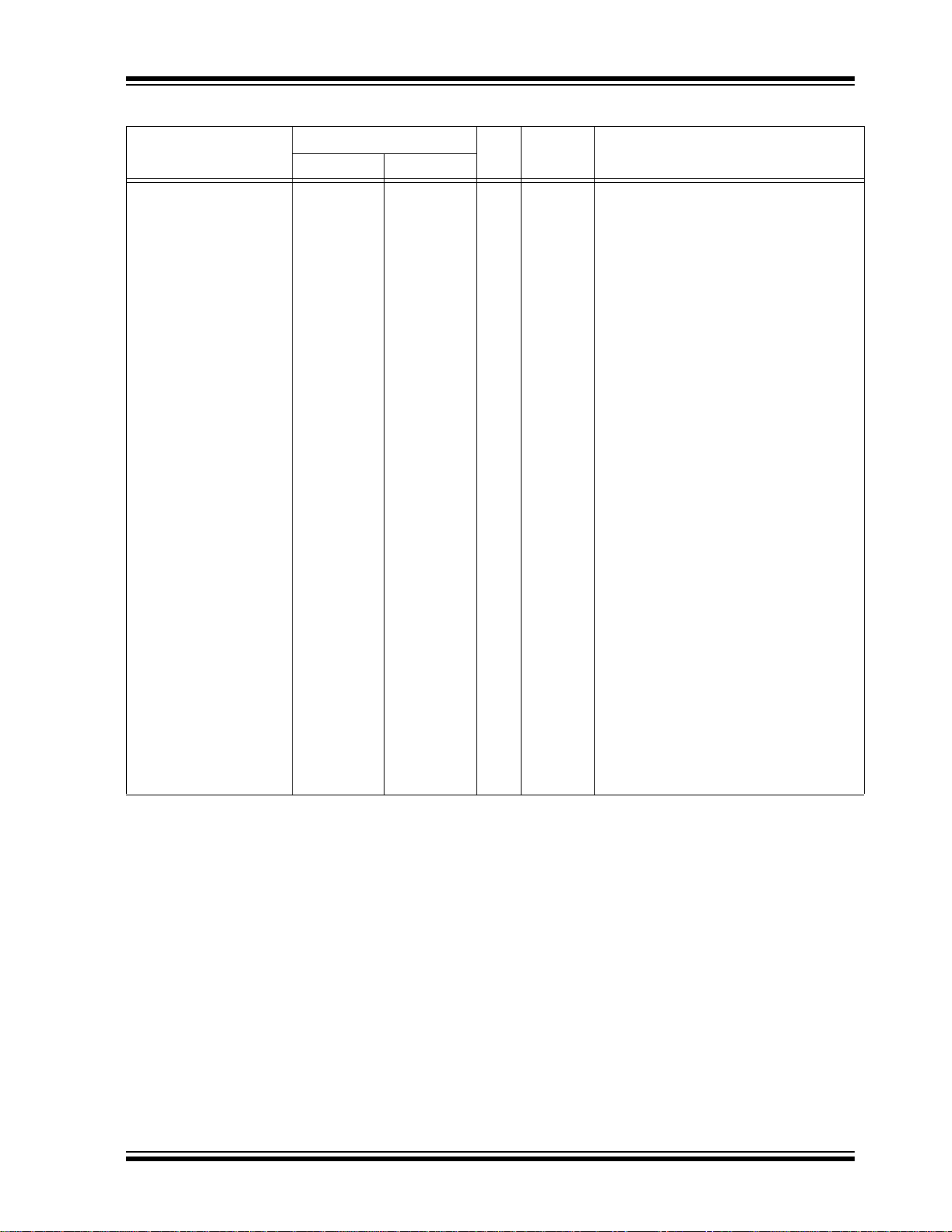
The EC, ECIO, EC+PLL and EC+SPLL Oscillator
modes require an external clock source to be connected to the OSC 1 pin. T he feed back device b etwee n
OSC1 and OSC2 is turned off in these modes to save
current. There is a maximum 1.5 µs start-up r equired
after a Power-on Reset or Wak e-up from SLEEP mode.
In the EC Oscillator mode, the oscillator frequency
divided by 4 is available on the OSC2 pin. This signal
may be used f or t e st pu r pos es or t o sy nc hr o n iz e ot he r
logic. Figure 2-4 shows the pin connections for the EC
Oscillator mode.
FIGURE 2-4: EXTERNAL CLOCK INPUT
OPERATION
(EC CONFIGURATION)
Clock from
Ext. System
F
OSC/4
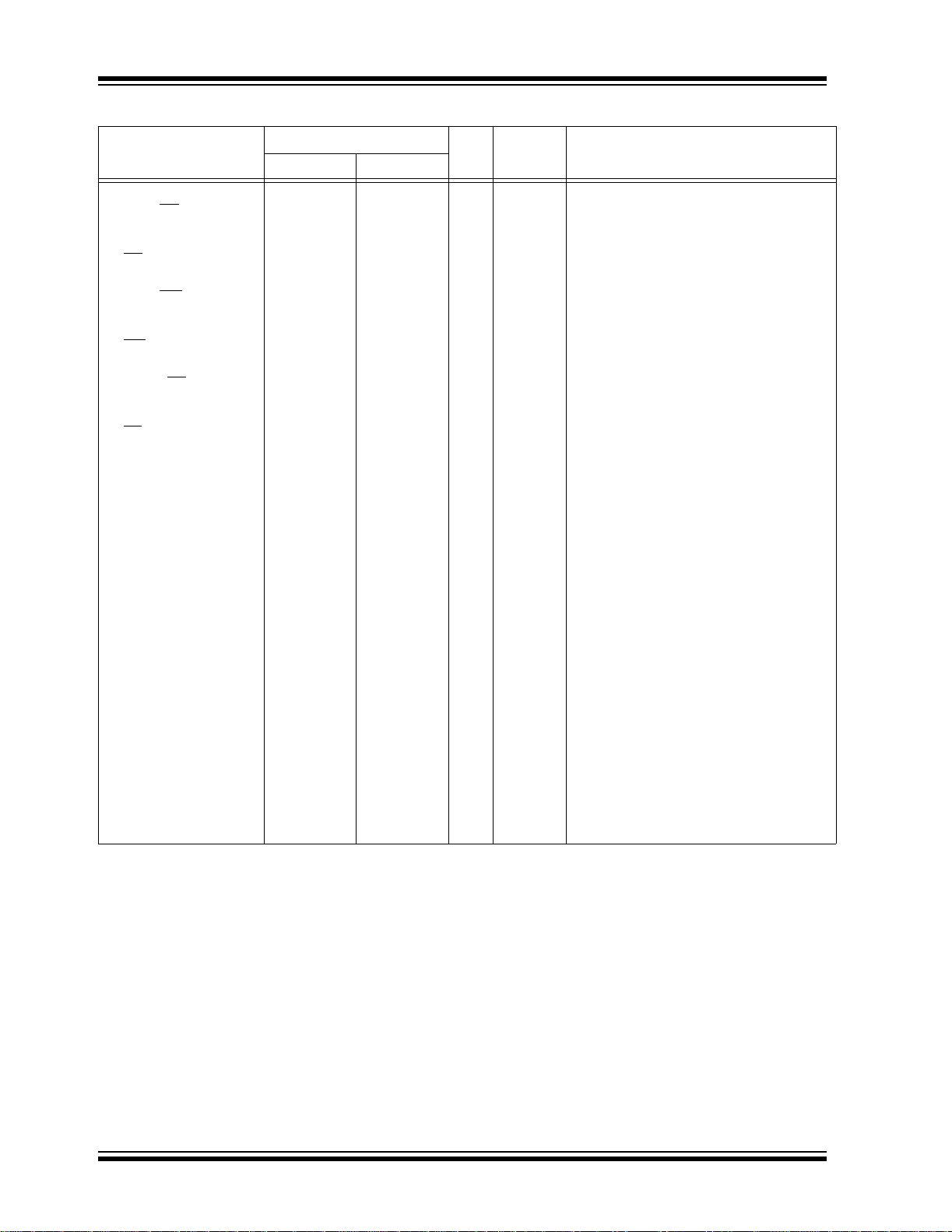
The ECIO Oscillator mode functions like the EC mode
except that the OSC2 pin becomes an additional general purpose I/O pin. The I/O pin becomes bit 6 of
PORTA (RA6). Figure 2-5 shows the pin connections
for the ECIO Oscillator mode.
FIGURE 2-5: EXTERNAL CLOCK INPUT
Clock from
Ext. System
RA6
OSC1
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
OSC2
OPERATION
(ECIO CONFIG URATION)
OSC1
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
I/O (OSC2)
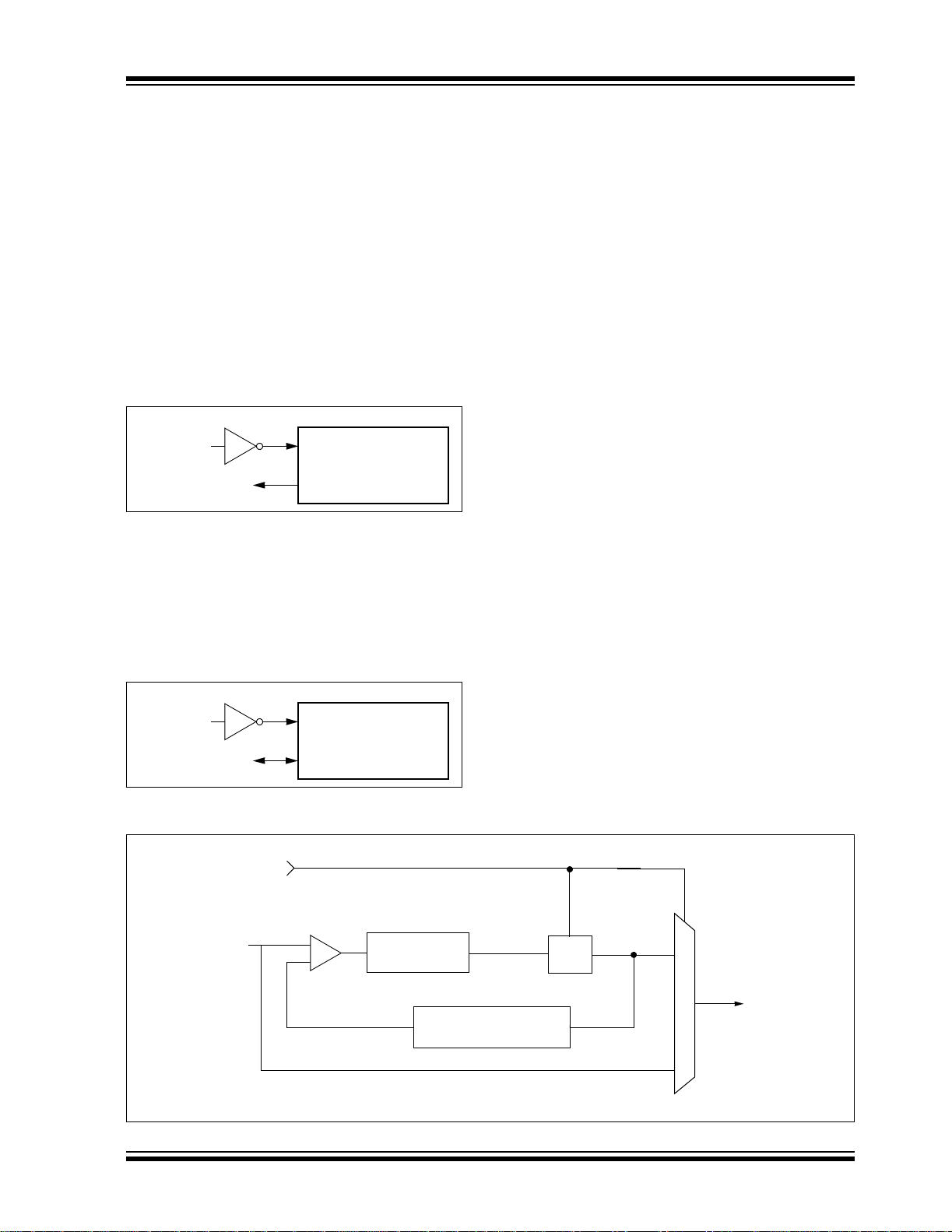
2.5 Phase Locked Loop (PLL)
A phase locked loop circuit is provided as a
programmable option for us ers that want to multip ly the
frequency of the in com in g osc il lat or s ig nal by 4 . For an
input clock frequency of 10 MHz, the internal clock
frequency will b e multipli ed to 40 MHz. This is usefu l for
customers who are concerned with EMI due to high
frequency crystals.
The PLL can only be enabled when the oscillator configuration bits are pro grammed fo r High Spee d Oscill ator or External Clock mode. If they are programmed for
any other mode, the PLL is no t enabled and the s ystem
clock will come directly from OSC1. There are two
types of PLL modes - Software Controlled PLL and
Configuration bits Controlled PLL. In Software Controlled PLL mode, PIC18 F6X2X/8X2X executes at regular clock frequency after all RESET conditi ons. During
execution, the application can enable PLL and switch
to 4x clock frequency operation by setting the PLLEN
bit in the OSCCON register. In Configuration bits Controlled PLL, the PLL operation cann ot be chan ged “onthe-fly”. To enable or disable it, the controller must
either cycle through a Power-on Re set, or switch the
clock source from the main oscillator to the Timer1
oscillator and bac k again ( see Section2.6 for details on
oscillator switching).
The type of PLL is selected by programming
OSC<3:0> configuration bit s in CO NFIG1 H Conf igur a-
F
tion register. The Oscillator mode is specified during
device programming.
A PLL lock timer is used to ensure that the PLL has
locked before device execution starts. The PLL lock
timer has a time-out that is called T
PLL.
FIGURE 2-6: PLL BLOCK DIAGRAM
PLL Enable
Phase
Comparator
F
IN
FOUT
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 23
Loop
Filter
Divide by 4
VCO
SYSCLK
MUX
Page 26
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
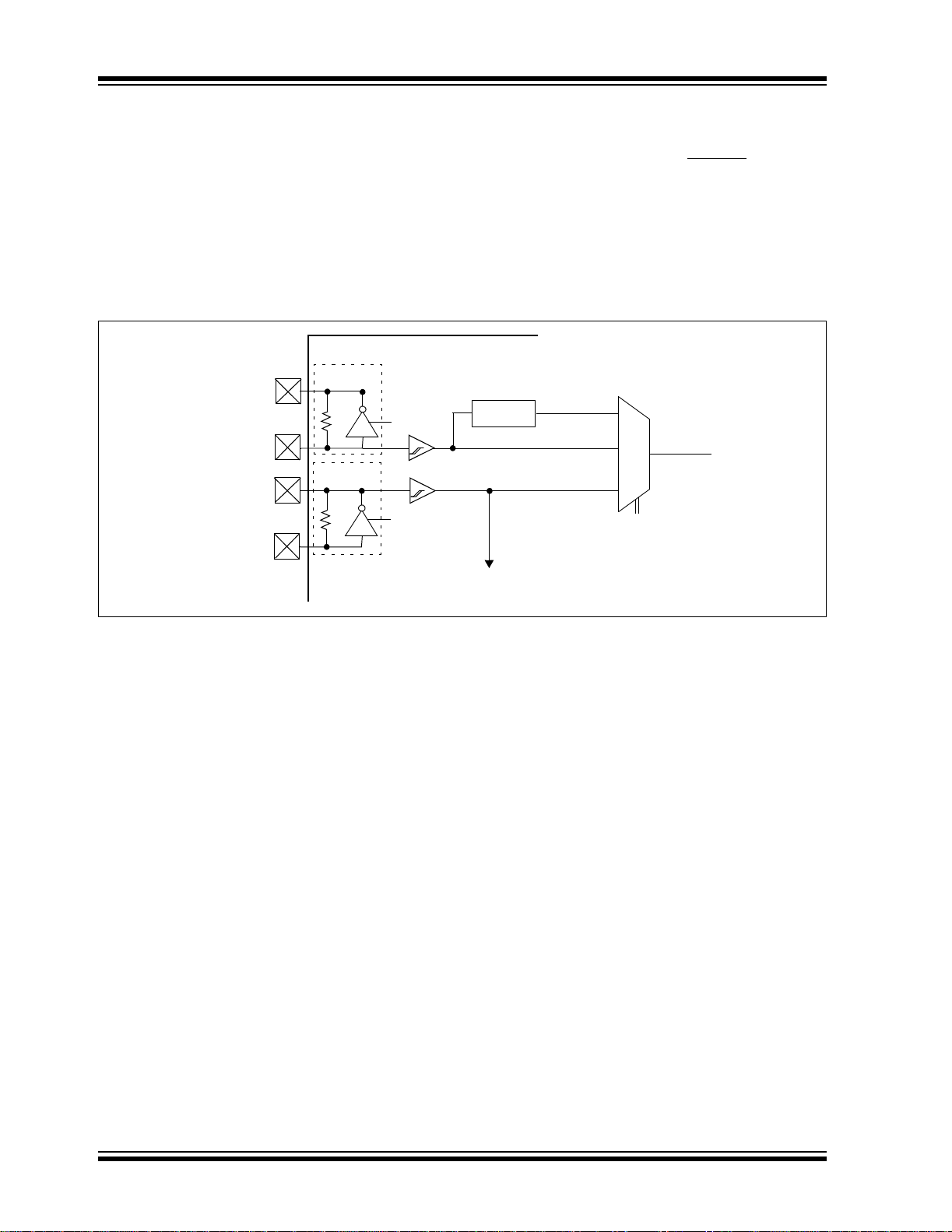
2.6 Oscillator Switching Feature
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices include a feature that
allows the system c lock sour ce to be swit ched from the
main oscillator to an alternate low frequency clock
source. For the PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices, this
alternate c lock source is th e Timer1 osci llat or. If a low
frequency crystal (32 kHz, for example) has been
attached to the Timer1 oscillator pins and the Timer1
oscillator has been ena bled, the devi ce can swit ch to a
FIGURE 2-7: DEVICE CLOCK SOURCES
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
OSC2
OSC1
T1OSO
T1OSI
Main Oscillator
SLEEP
Timer1 Oscillator
T1OSCEN
Enable
Oscillator
Low Power Execution mode. Fig ure2-7 shows a block
diagram of the system clock sources. The clock
switching feature is enabled by programming the
Oscillator Switching Enable (OSCSEN
) bit in the
CONFIG1H Configuration register to a ‘0’. Clock
switching is disabled in an erased device. See
Section 12.0 for further details of the Timer1 oscillator.
See Section 24.0 for Configuration register details.
4 x PLL
TOSC
TT1P
TOSC/4
MUX
Clock
Source
TSCLK
Clock Source Option
for Other Modules
DS39612A-page 24 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
2.6.1 SYSTEM CLOCK SWITCH BIT
The system clock sourc e sw it ching is performed under
software control. The system clock switch bits,
SCS1:SCS0 (OSCCON<1:0>), control the clock
switching. When the SCS0 bit is ‘0’, the system clock
source comes from the main oscillator that is selected
by the F
ration register. When the SCS0 bit is set, the system
clock sourc e will c ome fro m the Timer1 oscill ator. The
SCS0 bit is cleared on all forms of RESET.
When F
mode, SCS1 bit can be u sed to s elect bet ween primar y
oscillator/clock and P LL ou tput . SCS1 b it w ill o nly hav e
an effect on the system clock if the PLL is enabled
(PLLEN = 1) and locked (LOCK = 1), else it will be
forced cleared. When programmed with Configuration
Controlled PLL, SCS1 bit will be forced clear.
OSC configuration bits in CONFIG1H Configu-
OSC bits are programmed for Software PLL
REGISTER 2-1: OSCCON REGISTER
U-0 U-0 U-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
— — — — LOCK PLLEN SCS1 SCS0
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7-4 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 3 LOCK: Phase Lock Loop Lock Status bit
1 = Phase lock loop output is stable as system clock
0 = Phase lock loop output is not stable and output cannot be used as system clock
bit 2 PLLEN
bit 1 SCS1: System Clock Switch bit 1
bit 0 SCS0
(1)
: Phase Lock Loop Enable bit
1 = Enable phase lock loop output as system clock
0 = Disable phase lock loop
When PLLEN and LOCK bits are set:
1 = Use PLL output
0 = Use primary oscillator/clock input pin
When PLLEN or LOCK bit is cleared:
Bit is forced clear.
(2)
: System Clock Switch bit 0
When OSCSEN configuration bit = 0 and T1OSCEN bit = 1:
1 = Switch to Timer1 oscillator/clock pin
0 = Use primary oscillator/clock input pin
OSCSEN and T1OSCEN are in other states:
When
Bit is forced clear.
Note: The Timer1 oscillator must be enabled
and operating to switch the system clock
source. The Timer1 oscillator is enabled
by setting the T1OSCEN bit in the Timer1
Control register (T1CON). If the Timer1
oscillator is not enabled, then any write to
the SCS0 bit will be ignored (SCS0 bit
forced cleared) and the main osci llator w ill
continue to be the system clock source.
Note 1: PLLEN bit is forced set when configured for ECIO+PLL and HS+PLL. This bit is
writable for ECIO+SPLL and HS+SPLL modes only; forced cleared for all other
Oscillator modes.
2: The setting of SCS0 = 1 supersedes SCS1 = 1.
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 25
Page 28

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
2.6.2 OSCILLATOR TRANSITIONS
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices con tai n circuit ry to prevent
“glitches” when switching between oscillator sources.
Essentially, the circuitry waits for eight rising edges of
the clock source that the processor is swit ching to. This
ensures that the n ew c lo ck s ourc e is s t able and that its
pulse width will not be less than the shortest pulse
width of the two clock sources.
A timing diagram indicating the transition from the main
oscillator to the Timer1 oscillator is s hown in Figure2-8.
The Timer1 oscillator is assumed to be running all the
time. After the SCS0 bit is set, the processor i s frozen at
the next occurring Q1 cycle. After eight synchronization
cycles are counted from the Timer1 oscillator, operation
resumes. No additional delays are required after the
synchronization cycles.
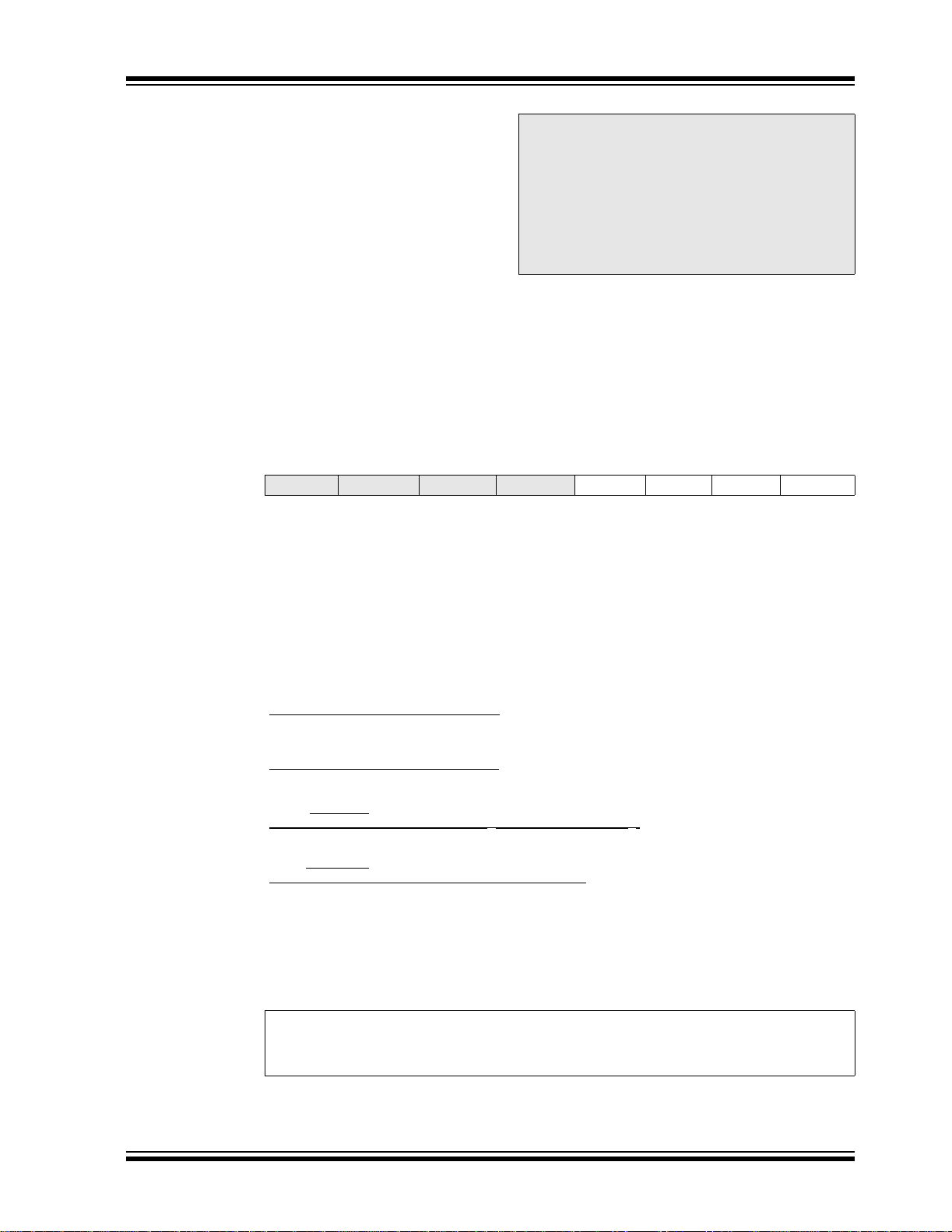
FIGURE 2-8: TIMING DIAGRAM FOR TRANSITION FROM OSC1 TO TIMER1 OSCILLATOR
Q4 Q1
Q1
T1OSI
OSC1
Internal
System
Clock
SCS
(OSCCON<0>)
Program
Counter
Note: T
Q1
TOSC
TDLY
DLY is delay from SCS high to first count of transition circuit.
TT1P
21345678
TSCS
PC + 2PC
Q3Q2Q1Q4Q3Q2
Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1
PC + 4
The sequence of events that takes place when switching from the Timer1 oscillator to the main oscillator will
depend on the mode of the main oscillator. In addition
to eight clock cycles of the main oscillator, additional
delays may take place.
If the main oscillator is configured for an external crystal (HS, XT, LP), then the transition will t ak e pl ac e aft er
an oscillator st art-up time (T
OST) has occurred. A timing
diagram, indicating the transit ion from th e T imer1 os cillator to the main oscillator for HS, XT and LP modes, is
shown in Figure 2-9.
FIGURE 2-9: TIMING FOR TRANSITION BETWEEN TIMER1 AND OSC1 (HS, XT, LP)
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2
T1OSI
OSC1
Internal
System Clock
Program
Counter
Note 1: T
SCS
OST = 1024 TOSC (drawing not to scale).
(OSCCON<0>)
Q3 Q4
PC PC + 2
Q1
TOST
TOSC
TT1P
12345678
TSCS
Q3
PC + 6
DS39612A-page 26 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 29
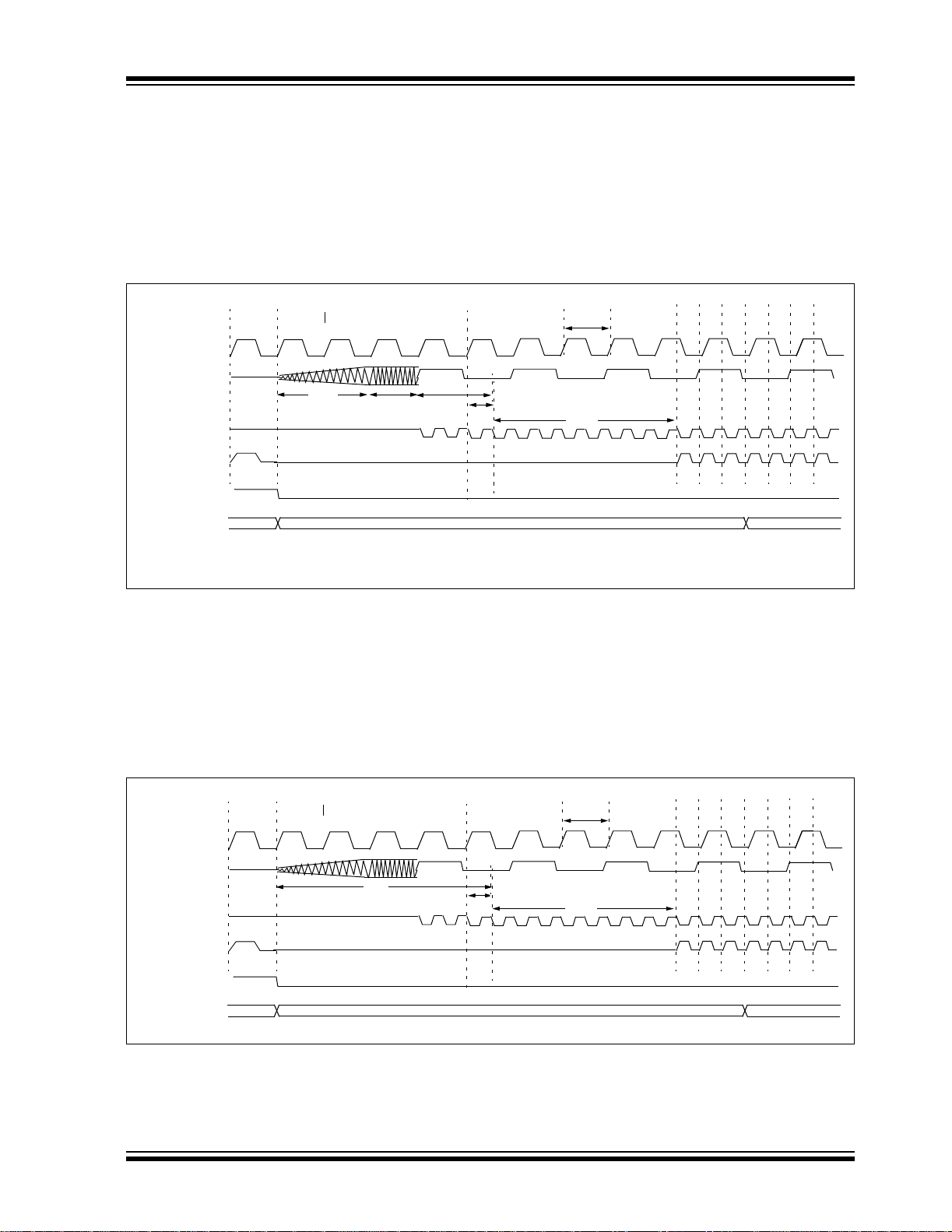
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
If the main oscillator is configured for HS mode with
PLL active, an oscillator start-up time (T
additional PLL time -out (T
PLL) will occur . The PLL tim e-
out is typically 2 ms and allows the PLL to lock to the
main oscillator frequency. A timing diagram, indicating
the transition from the Timer1 oscillator to the main
oscillator for HS-PLL mode, is shown in Figure 2-10.
FIGURE 2-10: TIMING FOR TRANSITION BETWEEN TIMER1 AND OSC1
(HS WITH PLL ACTIVE, SCS1 = 1)
OST) plus an
T1OSI
OSC1
PLL Clock
Input
Internal System
Program Counter
Note 1: T
Clock
(OSCCON<0>)
SCS
OST = 1024 TOSC (drawing not to scale).
Q4 Q1
TOST
PC PC + 2
TPLL
TOSC
TT1P
TSCS
12345678
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2
If the main oscillator is configured for EC mode with PLL
active, only PLL time-out (T
PLL) will occur . The PLL time-
out is typically 2 ms and allows the PLL to lock to the
main oscillator frequency. A timing diagram, indicating
the transition from the Timer1 oscillator to the main
oscillator for EC with PLL active, is shown in Figure 2-1 1.
FIGURE 2-11: TIMING FOR TRANSITION BETWEEN TIMER1 AND OSC1
(EC WITH PLL ACTIVE, SCS1 = 1)
Q3
PC + 4
Q4
T1OSI
OSC1
PLL Clock
Input
Internal System
Program Counter
Clock
(OSCCON<0>)
SCS
Q4 Q1
TPLL
TOSC
PC PC + 2
TT1P
TSCS
12345678
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2
Q3
PC + 4
Q4
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 27
Page 30

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
If the main oscillato r is c onfigur ed in th e RC, R CIO, EC
or ECIO modes, th ere is no os cillator start-up time-out.
Operation will resume after eight cycles of the main
oscillator have been counted. A timing diagram, indicating the transition from the Timer1 oscillator to the
main oscillator for RC, RCIO, EC and ECIO modes, is
shown in Figure 2-12.
FIGURE 2-12: TIMING FOR TRANSITION BETWEEN TIMER1 AND OSC1 (RC, EC)
Q3 Q4 Q1 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 Q3
T1OSI
OSC1
Internal System
Clock
(OSCCON<0>)
Note: RC Oscillator mode assumed.
SCS
Program
Counter
PC
2.7 Effects of SLEEP Mode on the On-Chip Oscillator
When the device e xecutes a SLEEP i nstructio n, the onchip clocks and oscillator are turn ed off and the device
is held at the beginning of an instruction cycle (Q1
state). With the oscillator off, the OSC1 and OSC2
TT1P
TOSC
1
45678
23
TSCS
PC + 2
switching currents have been removed, SLEEP mode
achieves the lowest current consumption of the device
(only leakage currents). Enabling any on-chip feature
that will operate during SL EEP will incre ase the current
consumed during SLEEP. The user can wake from
SLEEP through external RESET, Watchdog Timer
Reset, or through an interrupt.
signals will stop oscillating. Since all the transistor
TABLE 2-3: OSC1 AND OSC2 PIN STATES IN SLEEP MODE
OSC Mode OSC1 Pin OSC2 Pin
RC Floating, external resistor should pull high At logic low
RCIO Floating, external resistor should pull high Configured as PORTA, bit 6
ECIO Floating Configured as PORTA, bit 6
EC Floating At logic low
LP, XT, and HS Feedback inverter disabled, at
quiescent voltage level
Note: See Table 3-1 in Section 3.0, “Reset” for time-outs due to SLEEP and MCLR
Feedback invert er di sa bled, at
quiescent voltage level
Reset.
Q4
PC + 4
DS39612A-page 28 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 31

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
2.8 Power-up Delays
Power-up delays are con trolled by two time rs so that no
external RESET circuitry is required for most applications. The delays ensure that the device is kept in
RESET until the device power sup ply and clock are st able. For additional information on RESET operation,
see Section 3.0, “Reset”.
The first timer is the Power-up Timer (PWRT) which
optionally provid es a fix ed delay of 72 ms (nominal) on
power-up only (POR and BOR). The second timer is
the Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST), intended to keep
the chip in RESET until the crystal oscillator is stable.
With the PLL enabled (HS+PLL and EC+PLL Oscillator
mode), the time-out sequence following a Power-on
Reset is different from other Oscillator modes. The
time-out sequence is as follows: First, the PWRT timeout is invoked after a POR time delay has expired.
Then, the Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) is invoked.
However, this is still not a sufficient amount of time to
allow the PLL to lock at high frequencies. The PWRT
timer is used to provide an additional fixed 2 ms (nominal) time-out to allow the PLL a mple time to lock to the
incoming clock frequ enc y.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 29
Page 32

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
NOTES:
DS39612A-page 30 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 33
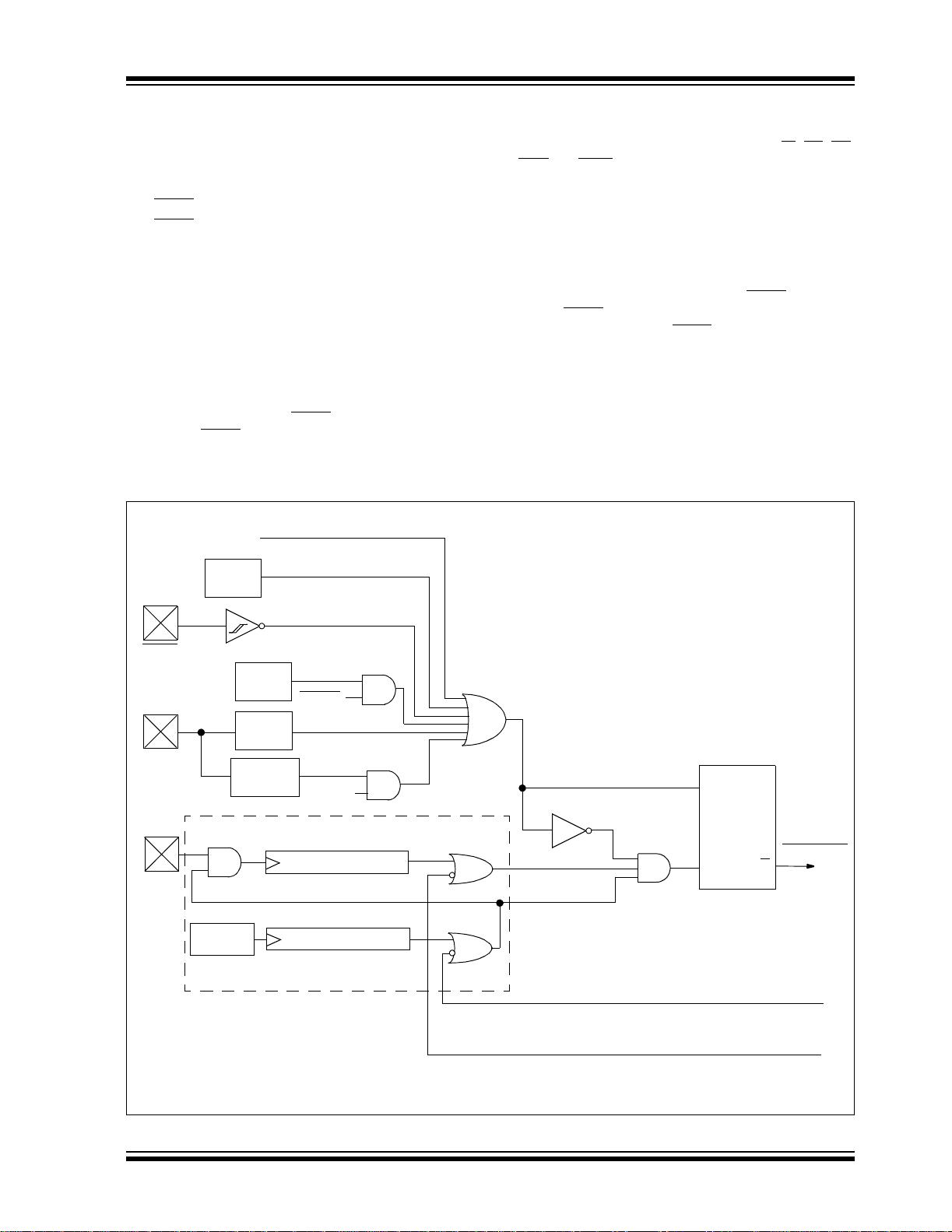
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
t
3.0 RESET
Most registers are not affected by a WDT wake-up
since this is viewed as the resumption of normal oper-
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices differentiate between
various kinds of RESET:
a) Power-on Reset (POR)
b) MCLR
Reset during normal operation
c) MCLR Reset during SLEEP
d) Watchdog Timer (WDT) Reset (during normal
operation)
e) Programmable Brown-out Reset (BOR)
f) RESET Instruction
g) Stack Full Reset
h) Stack Underflow Reset
ation. Status bits from the RCON register, RI, TO, PD,
and BOR, are set or cleared differently in different
POR
RESET situations as indicated in Table 3-2. These bits
are used in software to determine the nature of the
RESET. See Table 3-3 for a full description of the
RESET states of all registers.
A simplified block di agram of the On-Chip Reset Circu it
is shown in Figure 3-1.
The enhanced MCU devices have a MCLR
in the MCLR
ignore small puls es. T he MC LR
Reset path. The filter will detect and
pin is not driv en lo w b y
any internal RESETS, including the WDT.
Most registers are una ffected b y a RESET. Their status
is unknown on POR and unchanged by all other
RESETS. The other registers are forced to a “RESET
state” on Power-on Reset, MCL R
out Reset, MCLR
Reset during SLEEP and by the
, WDT Reset, Brown-
RESET instruction.
FIGURE 3-1: SIMPLIFIED BLOCK DIAGRAM OF ON-CHIP RESET CIRCUIT
RESET Instruction
noise filter
MCLR
VDD
OSC1
Stack
Pointer
Brown-out
OST/PWRT
On-chip
RC OSC
Stack Full/Underflow Reset
External Reset
WDT
Time-out
Reset
WDT
Module
DD Rise
V
Detect
Reset
(1)
SLEEP
Power-on Reset
BOREN
OST
10-bit Ripple Counter
PWRT
10-bit Ripple Counter
S
R
Chip_Rese
Q
Enable PWRT
Enable OST
Note 1: This is a separate oscillator from the RC oscillator of the CLKI pin.
2: See Table 3-1 for time-out situations.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 31
(2)
Page 34

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
3.1 Power-on Reset (POR)
A Power-on Reset pulse is generated on-chip when
DD rise is detected. To take advantage of the POR c ir-
V
cuitry, tie the MCLR
tor to V
DD. This will eliminate external RC components
pin through a 1 kΩ to 10 kΩ resis-
usually needed to create a Power-on Reset delay. A
minimum rise rate for V
DD is specified (parameter
D004). For a slow rise time, see Figure 3-2.
When the device st arts normal operation (i.e ., ex its the
RESET condition), device operating parameters (voltage, frequency, temperature, etc.) must be met to
ensure operation. If these conditions are not met, the
device must be held in RESET until the operating
conditions are met.
FIGURE 3-2: EXTERNAL POWER-ON
RESET CIRCUIT (FOR
SLOW V
DD
V
D
R
R1
C
Note 1: External Power-on Reset circuit is required
only if the V
The diode D helps discharge the capacitor
quickly when V
2: R < 40 kΩ is recommended to make sure
that the voltage drop across R does not
violate the device’s electrical specification.
3: R1 = 1 kΩ to 10 kΩ will limit any current
flowing into MCLR
C in the event of MCLR/
due to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) or
Electrical Overstress (EOS).
DD power-up slope is too slow.
DD POWER-UP)
MCLR
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
DD powers down.
from external capacitor
VPP pin breakdown,
3.2 Power-up Timer (PWRT)
The Power-up Timer provides a fixed nominal time-out
(parameter #33) only on power-up from the POR. The
Power-up Timer operates on an internal RC oscillator.
The chip is kept in RESET as long as the PWRT is
active. The PWR T’ s time delay al lows VDD to rise to an
acceptable level. A configuration bit is provided to
enable/disable the PWRT.
The power-up time delay will vary fr om chip-to-ch ip due
DD, temperature and process variation. See DC
to V
parameter #33 for details.
3.3 Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST)
The Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) provides 1024
oscillator cycle (from OSC1 input) delays after the
PWRT delay is over (para meter #32). Th is ensures th at
the crystal oscillator or resonator has started and
stabilized.
The OST time-out is invoked only for XT, LP and HS
modes and only on Power-on Reset, or wake-up from
SLEEP.
3.4 PLL Lock Time-out
With the PLL enabled, the time-ou t sequen ce foll owin g
a Power-on Reset is different from other Oscillator
modes. A portion of the Po wer-up Timer is used to provide a fixed time-out th at is suff icient for the PLL to lock
to the main oscillator fre quenc y. This PLL lock time-out
PLL) is typically 2 ms and follows the oscillator
(T
start-up time-out.
3.5 Brown-out Reset (BOR)
A configuration bit, BOREN, can disable (if clear/
programmed) or enable (if set) the Brown-out Reset
circuitry. If V
DD falls below parameter D005 for greater
than parameter #35, the brown-out situation will reset
the chip. A RESET may not occur if VDD falls below
parameter D005 for less than p aram et er #35 . The chip
will remain in Brown-out Reset until VDD rises abo ve
DD. If the Power-up Timer is enabled, it will be
BV
invoked after V
DD rises above BVDD; it then will keep
the chip in RESET for an additional time delay
(parameter #33). If VDD drops below BVDD while the
Power-up Timer is running, the chip will go back into a
Brown-out Reset and the Power-up Timer will be
initialized . Once V
DD rises above BVDD, the Power-up
Timer will execute the additional time delay.
3.6 Time-out Sequence
On power-up, the time-out sequence is as follows:
First, PWRT time-out is invoked after the POR time
delay has expi red. Then, OST is activ ated. The total
time-out will vary based on oscillator configuration and
the status of th e PWRT. For example, in RC mode with
the PWRT disabled, there will be no time-out at all.
Figure 3-3, Figure 3-4, Figure 3-5, Figure 3-6 and
Figure 3-7 depict time-out sequences on power-up.
Since the time-outs occur from the POR pulse, the
time-outs will expire if MCLR
Bringing MCLR
high will begin execution immediately
(Figure 3-5). This is useful for testing purposes or to
synchronize more than one PIC18F6X2X/8X2X device
operating in parallel.
Table 3-2 shows the RESET conditions for some
Special Function Registers, while Table 3-3 shows the
RESET conditions for all of the registers.
is kept low long enough.
DS39612A-page 32 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 35

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 3-1: TIME-OUT IN VARIOUS SITUATIONS
Oscillator
Configuration
HS with PLL enabled
HS, XT, LP 72 ms + 1024 TOSC 1024 TOSC 72 ms
EC 72 ms 1.5 µs72 ms
External RC 72 ms — 72 ms
Note 1: 2 ms is the nominal time required for the 4x PLL to lock.
2: 72 ms is the nominal power-up timer delay, if implemented.
3: 1.5 µs is the recovery time from SLEEP. There is no recovery time from oscillator switch.
(1)
PWRTE = 0 PWRTE = 1
72 ms + 1024 TOSC
Power-up
+ 2ms
(2)
1024 TOSC
+ 2 ms
72 ms
Brown-out
(2)
+ 1024 TOSC
+ 2 ms
(2)
+ 1024 TOSC 1024 TOSC
(2)
(2)
Wake-up from
SLEEP or
Oscillator Switch
1024 TOSC + 2 ms
(3)
1.5 µs
—
REGISTER 3-1: RCON REGISTER BITS AND POSITIONS
R/W-0 U-0 U-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-0 R/W-0
IPEN
bit 7 bit 0
Note 1: Refer to Section 4.14 (page 61) for bit definitions.
— —RITO PD POR BOR
(1)
TABLE 3-2: STATUS BITS, THEIR SIGNIFICANCE AND THE INITIALIZATION CONDITION FOR
RCON REGISTER
Condition
Power-on Reset 0000h 111 0 0 u u
Reset during normal
MCLR
operation
Software Reset during normal operation 0000h 0uu u u u u
Stack Full Reset dur ing normal operation 0000h uu u u u u 1
Stack Underflow Reset during normal
operation
Reset during SLEEP 0000h u10 u u u u
MCLR
WDT Reset 0000h 101 u u u u
WDT Wake-up PC + 2 u0 0 u u u u
Brown-out Reset 0000h 111 1 0 u u
Interrupt wake-up from SLEEP PC + 2
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
Note 1: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEH or GIEL bits are set, the PC is loaded with the
interrupt vector (0008h or 0018h).
Program
Counter
0000h uuu u u u u
0000h uuu u u 1 u
(1)
TO PD POR BOR STKFUL STKUNF
RI
u10 u u u u
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 33
Page 36

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 3-3: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS
Resets
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
TOSU PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---0 0000 ---0 0000 ---0 uuuu
TOSH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TOSL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
STKPTR PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 00-0 0000 uu-0 0000 uu-u uuuu
PCLATU PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
PCLATH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PCL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 PC + 2
TBLPTRU PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
TBLPTRH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TBLPTRL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TABLAT PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PRODH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PRODL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
INTCON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 000x 0000 000x uuuu uuuu
INTCON2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
INTCON3 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1100 0000 1100 0000 uuuu uuuu
INDF0 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
POSTINC0 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
POSTDEC0 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
PREINC0 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
PLUSW0 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
FSR0H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---- 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu
FSR0L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
WREG PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
INDF1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
POSTINC1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
POSTDEC1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
PREINC1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
PLUSW1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Shaded cells indicate condi tions do not apply for the designated device.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wa ke-up is du e to an interru pt and the GI EL or GIEH bit is set, the PC i s loaded wit h the interrup t
vector (0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are
updated with the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the
hardware stack.
4: See Table 3-2 for RESET value for specific condition.
5: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA, and TRISA are enabled in ECIO and RCIO Oscillator modes only. In all other
Oscillator modes, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
6: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are not available on all devices. When unimplemente d, they are rea d ‘0’.
7: If MCLR
function is disabled, PORTG<5> is a read only bit.
WDT Reset
RESET Instruction
Stack Rese ts
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(2)
(1)
(1)
(1)
DS39612A-page 34 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 37

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 3-3: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
Resets
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
FSR1H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---- 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu
FSR1L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
BSR PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---- 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu
INDF2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
POSTINC2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
POSTDEC2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
PREINC2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
PLUSW2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X N/A N/A N/A
FSR2H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---- 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu
FSR2L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
STATUS PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---x xxxx ---u uuuu ---u uuuu
TMR0H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
TMR0L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T0CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
OSCCON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---- 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu
LVDCON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0101 --00 0101 --uu uuuu
WDTCON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---- ---0 ---- ---0 ---- ---u
(4)
RCON
TMR1H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
TMR1L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T1CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0-00 0000 u-uu uuuu u-uu uuuu
TMR2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PR2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
T2CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -000 0000 -000 0000 -uuu uuuu
SSPBUF PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
SSPADD PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSPSTAT PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSPCON1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
SSPCON2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wa ke-up is du e to an interru pt and the GI EL or GIEH bit is set, the PC i s loaded wit h the interrup t
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are
4: See Table 3-2 for RESET value for specific condition.
5: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA, and TRISA are enabled in ECIO and RCIO Oscillator modes only. In all other
6: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are not available on all devices. When unimplemente d, they are rea d ‘0’.
7: If MCLR
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0--1 11qq 0--1 qquu u--1 qquu
Shaded cells indicate condi tions do not apply for the designated device.
vector (0008h or 0018h).
updated with the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the
hardware stack.
Oscillator modes, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
function is disabled, PORTG<5> is a read only bit.
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
WDT Reset
RESET Instruction
Stack Rese ts
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 35
Page 38

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 3-3: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
Resets
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
ADRESH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
ADRESL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
ADCON0 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
ADCON1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
ADCON2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0-00 0000 0-00 0000 u-uu uuuu
CCPR1H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR1L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP1CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
CCPR2H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR2L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP2CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
CCPR3H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCPR3L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
CCP3CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
ECCP1AS PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
CVRCON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
CMCON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TMR3H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
TMR3L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
T3CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PSPCON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 ---- 0000 ---- uuuu ----
SPBRG1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
RCREG1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TXREG1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TXSTA1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 -010 0000 -010 uuuu -uuu
RCSTA1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 000x 0000 000x uuuu uuuu
EEADRH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---- --00 ---- --00 ---- --uu
EEADR PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
EEDATA PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
EECON2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xx-0 x000 uu-0 u000 uu-0 u000
EECON1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xx-x x000 uu-u u000 uu-u u000
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Shaded cells indicate condi tions do not apply for the designated device.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wa ke-up is du e to an interru pt and the GI EL or GIEH bit is set, the PC i s loaded wit h the interrup t
vector (0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are
updated with the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the
hardware stack.
4: See Table 3-2 for RESET value for specific condition.
5: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA, and TRISA are enabled in ECIO and RCIO Oscillator modes only. In all other
Oscillator modes, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
6: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are not available on all devices. When unimplemente d, they are rea d ‘0’.
7: If MCLR
function is disabled, PORTG<5> is a read only bit.
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
WDT Reset
RESET Instruction
Stack Rese ts
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
DS39612A-page 36 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 39

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 3-3: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
Resets
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
IPR3 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --11 1111 --11 1111 --uu uuuu
PIR3 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
PIE3 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
IPR2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -1-1 1111 -1-1 1111 -u-u uuuu
PIR2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -0-0 0000 -0-0 0000 -u-u uuuu
PIE2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -0-0 0000 -0-0 0000 -u-u uuuu
IPR1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
PIR1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PIE1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
MEMCON
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0-00 --00 0-00 --00 u-uu --uu
TRISJ PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISG PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---1 1111 ---1 1111 ---u uuuu
TRISF PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISE PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISD PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISC PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISB PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
TRISA
(5,6)
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -111 1111
(5)
LATJ PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATH PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATG PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---x xxxx ---u uuuu ---u uuuu
LATF PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATE PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATD PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATC PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATB PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
LATA
(5,6)
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -xxx xxxx
(5)
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Shaded cells indicate condi tions do not apply for the designated device.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
2: When the wa ke-up is du e to an interru pt and the GI EL or GIEH bit is set, the PC i s loaded wit h the interrup t
vector (0008h or 0018h).
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are
updated with the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the
hardware stack.
4: See Table 3-2 for RESET value for specific condition.
5: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA, and TRISA are enabled in ECIO and RCIO Oscillator modes only. In all other
Oscillator modes, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
6: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are not available on all devices. When unimplemente d, they are rea d ‘0’.
7: If MCLR
function is disabled, PORTG<5> is a read only bit.
WDT Reset
RESET Instruction
Stack Rese ts
-111 1111
-uuu uuuu
(5)
(5)
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
-uuu uuuu
-uuu uuuu
(1)
(1)
(5)
(5)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 37
Page 40

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 3-3: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED)
Resets
MCLR
Register Applicable Devices
PORTJ PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTH
PORTG
PORTF PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PORTE PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PORTD PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTC PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTB PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
PORTA
SPBRGH1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
BAUDCON1 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -1-0 0-00 -1-0 0-00 -1-u u-uu
SPBRGH2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
BAUDCON2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -1-0 0-00 -1-0 0-00 -1-u u-uu
ECCP1DEL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TMR4 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
PR4 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 1111 1111 1111 1111 uuuu uuuu
T4CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -000 0000 -000 0000 -uuu uuuu
CCPR4H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu
CCPR4L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu
CCP4CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
CCPR5H PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu
CCPR5L PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu
CCP5CON PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X --00 0000 --00 0000 --uu uuuu
SPBRG2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
RCREG2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TXREG2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
TXSTA2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 -010 0000 -010 uuuu -u1u
RCSTA2 PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 000x 0000 000x uuuu uuu-
ECCP3AS PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
ECCP3DEL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
ECCP2AS PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
ECCP2DEL PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X 0000 0000 0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
Legend: u = unchanged, x = unknown, - = unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’, q = value depends on condition.
Note 1: One or more bits in the INTCONx or PIRx registers will be affected (to cause wake-up).
(7)
(5,6)
2: When the wa ke-up is du e to an interru pt and the GI EL or GIEH bit is set, the PC i s loaded wit h the interrup t
3: When the wake-up is due to an interrupt and the GIEL or GIEH bit is set, the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL are
4: See Table 3-2 for RESET value for specific condition.
5: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA, and TRISA are enabled in ECIO and RCIO Oscillator modes only. In all other
6: Bit 6 of PORTA, LATA and TRISA are not available on all devices. When unimplemente d, they are rea d ‘0’.
7: If MCLR
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X xxxx xxxx xxxx uuuu uuuu uuuu
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X ---x xxxx ---u uuuu ---u uuuu
PIC18F6X2X PIC18F8X2X -xxx 0000
Shaded cells indicate condi tions do not apply for the designated device.
vector (0008h or 0018h).
updated with the current value of the PC. The STKPTR is modified to point to the next location in the
hardware stack.
Oscillator modes, they are disabled and read ‘0’.
function is disabled, PORTG<5> is a read only bit.
Power-on Reset,
Brown-out Reset
(5)
WDT Reset
RESET Instruction
Stack Rese ts
-uuu 0000
(5)
Wake-up via WDT
or Interrupt
-uuu uuuu
(5)
DS39612A-page 38 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 41

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 3-3: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR TIED TO VDD VIA 1 kΩ RESISTOR)
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
TPWRT
PWRT TIME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
TOST
FIGURE 3-4: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
PWRT TI ME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
TPWRT
NOT TIED TO VDD): CASE 1
TOST
FIGURE 3-5: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
TPWRT
PWRT TIME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RESET
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 39
NOT TIED TO VDD): CASE 2
TOST
Page 42

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 3-6: SLOW RISE TIME (MCLR TIED TO VDD VIA 1 kΩ RESISTOR)
5V
VDD
MCLR
INTERNAL POR
0V
PWRT
T
1V
PWRT TIME-OUT
OST TIME-OUT
INTERNAL RES ET
TOST
FIGURE 3-7: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POR W/ PLL ENABLED
(MCLR
TIED TO VDD VIA 1 kΩ RESISTOR)
DS39612A-page 40 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 43

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.0 MEMORY ORGANIZATION
There are three memory blocks in PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
devices. They are:
• Program Memory
• Data RAM
• Data EEPROM
Data and program m emory use sep arate bus ses which
allows for concur rent access of these blocks. Add itional
detailed information for FLASH program memory and
data EEPROM is provided in Section 5.0 and
Section 7.0, respectively.
In addition to on -chip FLASH, the PIC18 F8X2X devices
are also capable of accessing external program memory through an external mem ory bus. Depending on the
selected operating mode (discussed in Section 4.1.1),
the controllers may access either internal or external
program memory exclusively, or both internal and
external memory in selected blocks. Additional information on the external memory interface is provided in
Section 6.0.
4.1 Program Memory Organization
A 21-bit program counter is capable of addressing the
2-Mbyte program memory space. Accessing a location
between the physically implemented memory and the
2-Mbyte address will cause a read of all ‘0’s (a NOP
instruction).
The PIC18F6525 and PIC18F8525 each have
48 Kbytes of on-chip FLASH memory, while the
PIC18F6621 and PIC18F8621 have 64 Kbytes of
FLASH. This means that PIC18FX525 devices can
store internally up to 24,576 single word instructions,
and PIC18FX621 de vices can sto re up to 32,768 single
word instructions.
The RESET vector address is at 0000h, and the
interrupt vector addresses are at 0008h and 0018h.
Figure 4-1 shows the program memory map for
PIC18FX525 devices, while Figure 4-2 shows the
program memory map for PIC18FX621 devices.
4.1.1 PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PROGRAM MEMORY MODES
PIC18F8X2X devices differ significantly from their
PIC18 predecessors in their utilization of program
memory. In addition to available on-chip FLASH program memory, these controllers can also address up to
2 Mbytes of external program memory through the
external memory interface. There are four distinct
operating modes available to the controllers:
• Microprocessor (MP)
• Microprocessor with Boot Block (MPBB)
• Extended Microcontroller (EMC)
• Microcontroller (MC)
The Program Memory mode is determined by setting
the two Least Significant bits of the CONFIG3L
Configuration Byte register as shown in Register 4-1.
(See also Section 24.1 for additional details on the
device configuration bits.)
The Program Memory modes operate as follows:
•The Microprocessor Mode permits access only
to external program memory; the contents of the
on-chip FLASH memory are ignored. The 21-bit
program counter permits access to a 2-MByte
linear program memory space.
• The Microprocessor with Boot Block Mode
accesses on-chip FLASH memory from addresses
000000h to 0007FFh. Above this, external program
memory is accessed all the way up to the 2 -M Byte
limit. Program execution automatically switches
between the two memories as required.
• The Microcontroller Mode accesses only
on-chip FLASH memory. Attempts to read above
the physical limit of the on-chip FLASH (BFFFh for
the PIC18FX525, FFFFh for the PIC18FX621)
causes a read of all ‘0’s (a NOP instruction).
The Microcontroller mode is also the only operating
mode available to PIC18F6X2X devices.
•The Extended Microcontroller Mode allows
access to both internal and external program
memories as a single block. The device can
access its entire on-chip FLASH memory; above
this, the device accesses external program memory up to the 2-MByte program space limit. As
with Boot Block mode, ex ecution automatically
switches between the two memories as required.
In all modes, the microcontroller has complete access
to data RAM and EEPROM.
Figure 4-3 compare s t he me mo ry m aps of the different
Program Memory modes. The differences between
on-chip and external memory access limitations are
more fully explained in Table 4-1.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 41
Page 44
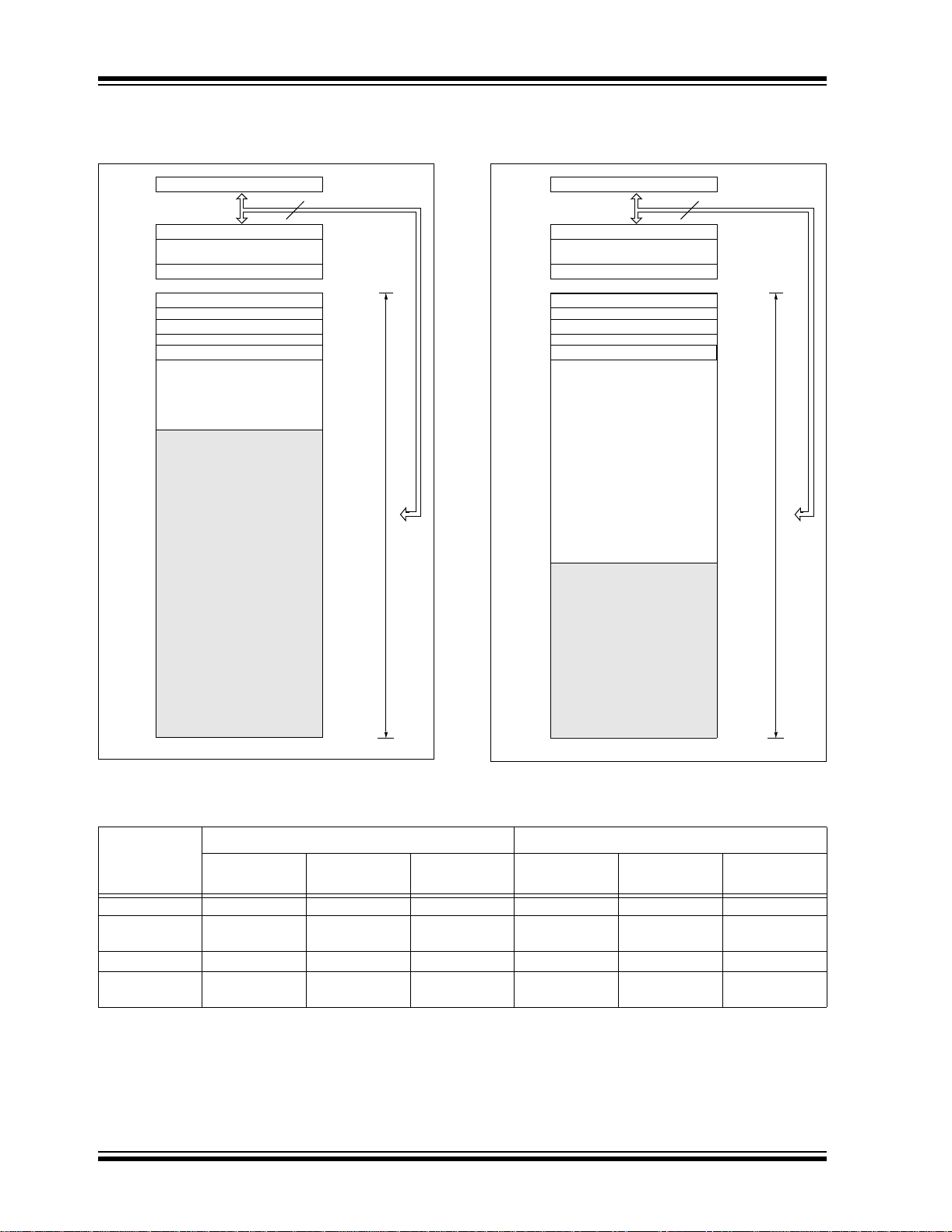
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 4-1: INTERNAL PROGRAM
MEMORY MAP AND
STACK FOR PIC18FX525
PC<20:0>
CALL,RCALL,RETURN
RETFIE,RETLW
Stack Level 1
Stack Level 31
RESET Vector
High Priority Interrupt Vector
Low Priority Interrupt Vector
On-Chip FLASH
Program Memory
Read ‘0’
21
•
•
•
000000h
000008h
000018h
00BFFFh
00C000h
FIGURE 4-2: INTERNAL PROGRAM
MEMORY MAP AND
STACK FOR PIC18FX621
PC<20:0>
CALL,RCALL,RETURN
RETFIE,RETLW
Stack Level 1
Stack Level 31
RESET Vector
High Priority Interrupt Vector
Low Priori ty In t e r r u pt Vector
On-Chip FLASH
Program Memory
User Memory Space
21
•
•
•
000000h
000008h
000018h
00FFFFh
010000h
User Memory Space
Read ‘0’
1FFFFFh
200000h
1FFFFFh
200000h
TABLE 4-1: MEMORY ACCESS FOR PIC18F8X2X PROGRAM MEMORY MODES
Internal Program Memory External Program Memory
Operating Mode
Microprocessor No Access No Access No Access Yes Yes Y es
Microprocessor
w/ Boot Block
Microcontroller Yes Yes Yes No Access No Access No Ac cess
Extended
Microcontroller
Execution
From
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Table Read
From
Table Write To
Execution
From
Table Read
From
Table Write To
DS39612A-page 42 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 45

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
REGISTER 4-1: CONFIG3L CONFIGURATION BYTE
R/P-1 U-0 U-0 U-0 U-0 U-0 R/P-1 R/P-1
WAIT — — — — —PM1PM0
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 WAIT: External Bus Data Wait Enable bit
1 = Wait selections unavailable, device will not wait
0 = Wait programmed by WAIT1 and WAIT0 bits of MEMCOM register (MEMCOM<5:4>)
bit 6-2 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 1-0 PM1:PM0: Processor Data Memory Mode Select bits
11 = Microcontroller mode
10 = Microprocessor mode
01 = Microcontroller with Boot Block mode
00 = Extended Microcontroller mode
Note 1: This mode is available only on PIC18F8X2X devices.
Legend:
R = Readable bit P = Programmable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value after erase ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
(1)
(1)
(1)
FIGURE 4-3: MEMORY MAPS FOR PIC18F6X2X/8X2X PROGRAM MEMORY MODES
Microprocessor
000000h
Program Space Execution
1FFFFFh
Note 1: PIC18F8525 and PIC18F6525.
2: PIC18F8621 and PIC18F6621.
3: This mode is available only on PIC18F8X2X devices.
(3)
Mode
On-Chip
Program
Memory
(No
access)
External
Program
Memory
External
Memory FLASH
On-Chip
000000h
0007FFh
000800h
1FFFFFh
Microprocessor
with Boot Block
(3)
Mode
External
Program
Memory
External
Memory FLASH
On-Chip
Program
Memory
On-Chip
000000h
00BFFFh
00FFFFh
00C000h
010000h
1FFFFFh
Microcontroller
Mode
On-Chip
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
Program
Memory
Reads
‘0’s
On-Chip
FLASH
000000h
00BFFFh
00FFFFh
00C000h
010000h
1FFFFFh
Extended
Microcontroller
(1)
(2)
(1)
(2)
Mode
External
Program
Memory
External
Memory
(3)
On-Chip
Program
Memory
On-Chip
FLASH
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 43
Page 46

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.2 Return Address Stack
The return address s tack allows any combination of up
to 31 program calls and interrupts to occur. The PC
(Program Counter) is pushed onto the stack when a
CALL or RCALL instruction is executed, or an interrupt
is Acknowledged. The PC value is pulled off the stack
on a RETURN, RETLW, or a RETFIE instruction.
PCLATU and PCLATH are not affected by any of the
RETURN or CALL instructions.
The stack operates as a 31-word by 21-bit RAM and a
5-bit stack pointer, with the stack pointer initialized to
00000b after all RESETS. There is no RAM associate d
with stack poi nter 00000 b. This is o nly a RESET v alue.
During a CALL type instruc tion caus ing a push o nto the
stack, the stack pointer is first incremented and the
RAM location pointed to by the stack pointer is written
with the contents of the PC. During a RETURN type
instruction causing a pop from the stack, the contents
of the RAM location pointed to by the STKPTR are
transferred to the PC and then the stack pointer is
decremented.
The stack space is not part of either program or data
space. The stac k p oi n ter i s r e adab l e a n d wr i tab le, a nd
the address on the top of the stac k is readab le and writable through SFR registers. Data can also be pushed
to, or popped from the stack using the top-of-stack
SFRs. Status bits indicate if the stack pointer is at, or
beyond the 31 levels provided.
4.2.1 TOP-OF-STACK ACCESS
The top of the stack is readable and writable. Three
register locations, TOSU, TOSH and TOSL hold the
contents of the stack location pointed to by the
STKPTR register. This allows users to implement a
software stack if necessary. After a CALL, RCALL or
interrupt, the software can read the pushed value by
reading the TOSU, TOSH and TOSL registers. These
values can be placed on a us er defined s oftware st ack.
At return time, the software can replace the TOSU,
TOSH and TOSL and do a return.
The user must disable the global interrupt enable bits
during this time to prevent inadvertent stack
operations.
4.2.2 RETURN STACK POINTER (STKPTR)
The STKPTR register contains the stack pointer value,
the STKFUL (stack full) status bit, and the STKUNF
(stack underflow) status bits. Register 4-2 shows the
STKPTR register. The value of the stack pointer can be
0 through 31. The stack pointer increments when values are pushed onto the stack and decrements when
values are popped off the stack. At RESET, the stack
pointer value will be ‘0’. The user may read and write
the stack pointer value. This feature can be used by a
real-time operating system for return stack
maintenance.
After the PC is pus hed on to the st ack 31 tim es (wi thout
popping any values off the stack), the STKFUL bit is
set. The STKFUL bit can on ly be cleared in so ftware or
by a POR.
The action that takes place when the stack becomes
full depends on the state of the STVREN (Stack Overflow Reset Enable) configuration bit. Refer to
Section 25.0 for a description of the device configuration bits. If STVREN is set (default), the 31st push will
push the (PC + 2) value onto the st ack, set the STKFU L
bit, and reset the device. The STKFUL bit will remain
set and the stack pointer will be set to ‘0’.
If STVREN is cleared, the STKFUL bit will be set on the
31st push and the stack pointer will increment to 31.
Any additional pushes will not overwrite the 31st push,
and STKPTR will remain at 31.
When the stack has been popped enough times to
unload the stac k, the next pop will ret urn a value of zero
to the PC and sets the STKUNF bit, while the stack
pointer remains at ‘0’. The STKUNF bit will remain set
until cleared in software or a POR occurs.
Note: Returning a value of zero to the PC on an
underflow has the effect of vectoring the
program to the RESET vector, where the
stack conditions can be verified and
appropriate actions can be taken.
DS39612A-page 44 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 47

REGISTER 4-2: STKPTR REGISTER
R/C-0 R/C-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
(1)
STKFUL
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 STKFUL: Stack Full Flag bit
1 = Stack became full or overflowed
0 = Stack has not become full or overflowed
bit 6 STKUNF: Stack Underflow Flag bit
1 = Stack underflow occurred
0 = Stack underflow did not occur
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4-0 SP4:SP0: Stack Pointer Location bits
Note 1: Bit 7 and bit 6 can only be cleared in user software or by a POR.
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
STKUNF
(1)
— SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 4-4: RETURN ADDRESS STACK AND ASSOCIATED REGISTERS
Return Address S t ac k
11111
11110
TOSLTOSHTOSU
0x340x1A0x00
Top-of-Stack
4.2.3 PUSH AND POP INSTRUCTIONS
Since the Top-of-Stack (TOS) is readable and writabl e,
the ability to push valu es onto the stack and pull va lues
off the sta ck, withou t disturbi ng normal program ex ecution, is a desirable optio n. To push the current PC value
onto the stack, a PUSH instruction can be executed.
This will i ncrem ent th e stack point er and load the cu rrent PC value onto the stack. TOSU, TOSH and TOSL
can then be modified to place a return address on the
stack.
The ability to pull the TOS value off of the stack and
replace it with the value that was previously pushed
onto the stack, without disturbing normal execution, is
achieved by using the POP inst ruction. T he POP instru ction discards the current TOS by decrementing the
stack pointer. The previous value pushed onto the
stack then becomes the TOS value.
11101
0x001A34
0x000D58
00011
00010
00001
00000
4.2.4 STACK FULL/UNDERFLOW RESETS
These RESETS are enabled by programming the
STVREN configuration bit. When the STVREN bit is
disabled, a full or underf low condition will set the appropriate STKFUL or STKUNF bit, but not cause a device
RESET. When the STVREN bit is enabled, a full or
underflow condition wil l set the appropri ate STKFUL or
STKUNF bit and then cause a device RESET. The
STKFUL or STKUNF bits are only cleared by the user
software or a POR Reset.
STKPTR<4:0>
00010
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 45
Page 48

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.3 Fast Register Stack
A “fast interrupt return” optio n is available for in terrupts.
A fast register stack is provided for the STATUS,
WREG and BSR registers and is onl y one in depth. The
stack is not readable or writable and is loaded with the
current value of the corresponding register when the
processor vectors for an interrupt. The values in the
registers are then loaded back into the working registers if the FAST RETURN instruction is used to return
from the interrupt.
A low or high priority interrupt source will push values
into the stack registers. If both low and high priority
interrupts are enabled, the stack registers cannot be
used reliably for low priority interrupts. If a high priority
interrupt occurs while servicing a low priority interrupt,
the stack register values stored by the low priority
interrupt will be overwritten.
If high priority int errupts are not dis abled duri ng low priority inter rupts, users must save th e key registers in
software during a low priority interrupt.
If no interrupts are used, the fast register stack can be
used to restore the STATUS, W REG and BSR regis ters
at the end of a subr out ine ca ll. To use the fast registe r
stack for a subroutine call, a FAST CALL instruction
must be executed.
Example 4-1 shows a source code example that uses
the fast register stack.
4.4 PCL, PCLATH and PCLATU
The program counter ( PC) spe ci fie s th e ad dre ss of th e
instruction to fetch for execution. The PC is 21 bits
wide. The low byte is called the PCL register; this register is readable and writable. The high byte is called
the PCH register. This register contains the PC<15:8>
bits and is not directly readable or writable; updates to
the PCH register may be performed through the
PCLATH register. The upper byte is called PCU. This
register contains th e PC<20 :16> bit s an d is not d irectly
readable or writable; updates to the PCU register may
be performed through the PCLATU register.
The PC addresses bytes in the program memory. To
prevent the PC from becoming misaligned with word
instructions, the LSB of the PCL is fixed to a value of
‘0’. The PC increments by 2 to address sequential
instructions in the program memo ry.
The CALL, RCALL, GOTO and program branch
instructions write to the program counter directly. For
these instructions, the contents of PCLATH and
PCLATU are not transferred to the program counter.
The contents of PCLATH and PCLATU will be transferred to the program counter by an operation that
writes PCL. Similarly, the upper two bytes of the program counter will be transferred to PCLATH and
PCLATU by an operation that reads PCL. This is useful
for computed offsets to the PC (see Section4.8.1).
EXAMPLE 4-1: FAST REGISTER STACK
CODE EXAMPLE
CALL SUB1, FAST ;STATUS, WREG, BSR
•
•
SUB1 •
•
•
RETURN FAST ;RESTORE VALUES SAVED
;SAVED IN FAST REGISTER
;STACK
;IN FAST REGISTER STACK
FIGURE 4-5: CLOCK/INSTRUCTION CYCLE
Q2 Q3 Q4
OSC1
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
PC
OSC2/CLKO
(RC mode)
Q1
PC
Execute INST (PC-2)
Fetch INST (PC)
Q1
Execute INST (PC)
Fetch INST (PC+2)
4.5 Clocking Scheme/Instruction
Cycle
The clock input (from OSC1) is internally divided by
four to generate four non-overlapping quadrature
clocks, namely Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4. Internally, the program counter (PC) is incremented every Q1, the
instruction is fetched from the program memory and
latched into the instruction register in Q4. The instruction is decoded and executed during the following Q1
through Q4. The clocks and instruction execution flow
are shown in Figure4-5.
Q2 Q3 Q4
PC+2
Q2 Q3 Q4
Q1
PC+4
Execute INST (PC+2)
Fetch INST (PC+4)
Internal
Phase
Clock
DS39612A-page 46 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 49

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.6 Instruction Flow/Pipelining
An “Instruction Cycle” consists of four Q cycles (Q1,
Q2, Q3 and Q4). The instruc ti on fe tch and execute are
pipelined such that fetch takes one instruction cycle,
while decode and execute take another instruction
cycle. However, due to the pipelining, each instruction
effectively executes in one cycle. If an instruction
causes the program counter to change (e.g., GOTO),
A fetch cycle begins with the program counter (PC)
incrementing in Q1.
In the execution cy cle, the fetch ed instruction i s latched
into the “Instruction Register” (IR) in cycle Q1. This
instruction is then decoded and executed during the
Q2, Q3, and Q4 cycles. Dat a memory is read during Q2
(operand read) and written during Q4 (destination
write).
then two cycles are re quired to com plete the inst ruction
(Example 4-2).
EXAMPLE 4-2: INSTRUCTION PIPELINE FLOW
TCY0TCY1TCY2TCY3TCY4TCY5
1. MOVLW 55h
2. MOVWF PORTB
3. BRA SUB_1
4. BSF PORTA, BIT3 (Forced NOP)
5. Instruction @ address SUB_1
All instructions are si ngle cycl e exc ept fo r any program branc hes. The se t ake two cy cles sinc e the fetch instru ction
is “flushed” from the pipeline, while the new instruction is being fetched and then executed.
Fetch 1 Execute 1
Fetch 2 Execute 2
Fetch 3 Execute 3
Fetch 4 Flush (NOP)
Fetch SUB_1 Execute SUB_1
4.7 Instructions in Program Memory
word boundaries, the data contained in the instruction
is a word address. The word address is written to
The program memory is addressed in bytes. Instructions are stored as two bytes or four bytes in program
memory. The Least Significant Byte of an instruction
word is always stored in a program memory location
with an even address (LSB = 0). Figure 4-6 shows an
example of how instructi on words are stored in the program memory. To maintain alignment with instruction
boundaries, the PC increments in steps of 2 and the
LSB will always read ‘0’ (see Section 4.4).
PC<20:1> which accesses the desired byte address in
program memory. Instruction #2 in Figure 4-6 shows
how the instruction “GOTO 000006h” is encod ed in the
program memory. Program branch instructions, which
encode a relative address offset, operate in the same
manner . The offset value stored in a br an ch ins truc tio n
represents the number of single word instructions that
the PC will be offset by. Section 25.0 provides further
details of the instruction set.
The CALL and GOTO instructions have an absolute
program memory address embedded into the
instruction. Since instructions are always stored on
FIGURE 4-6: INSTRUCTIONS IN PROGRAM MEMORY
LSB = 1 LSB = 0 ↓
0Fh 55h 000008h
EFh 03h 00000Ah
F0h 00h 00000Ch
C1h 23h 00000Eh
F4h 56h 000010h
Instruction 1:
Instruction 2:
Instruction 3:
Program Memory
Byte Locations
MOVLW 055h
GOTO 000006h
MOVFF 123h, 456h
→
Word Address
000000h
000002h
000004h
000006h
000012h
000014h
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 47
Page 50

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.7.1 TWO-WORD INSTRUCTIONS
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices have four two-word
instructions: MOVFF, CALL, GOTO and LFSR. The
second word of these instructions has the 4 MSBs set
to ‘1’s and is a special kind of NOP instruction. The
lower 12 bits of the second word contain data to be
used by the instruction. If the first word of the instruction is executed, the data in the second word is
accessed. If the second word of the instruction is executed by itself (first word was skipped), it w ill execute as
a NOP. This action is necessary when the two-word
instruction is preceded by a conditional instruction that
changes the PC. A program example that demonstrates this concept is shown in Example 4-3. Refer to
Section 25.0 for further details of the instruction set.
EXAMPLE 4-3: TWO-WORD INSTRUCTIONS
CASE 1:
Object Code Source Code
0110 0110 0000 0000 TSTFSZ REG1 ; is RAM location 0?
1100 0001 0010 0011 MOVFF REG1, REG2 ; No, execute 2-word instruction
1111 0100 0101 0110 ; 2nd operand holds address of REG2
0010 0100 0000 0000 ADDWF REG3 ; continue code
CASE 2:
Object Code Source Code
0110 0110 0000 0000 TSTFSZ REG1 ; is RAM location 0?
1100 0001 0010 0011 MOVFF REG1, REG2 ; Yes
1111 0100 0101 0110 ; 2nd operand becomes NOP
0010 0100 0000 0000 ADDWF REG3 ; continue code
4.8 Lookup Tables
Lookup tables are implemented two ways. These are:
• Computed GOTO
• Table Reads
4.8.1 COMPUTED GOTO
A computed GOTO is accomplish ed by adding an offset
to the program counter (ADDWF PCL).
A lookup table can be formed with an ADDWF PCL
instruction and a group of RETLW 0xnn instructions.
WREG is loaded with an offset into the table before
executing a call to tha t t able. The first instructi on of th e
called routine is the ADDWF PCL instruction. The next
instruction executed will be one of the RETLW 0xnn
instructions that returns the value 0xnn to the calling
function.
The offset value (va lue in WREG) specifie s the number
of bytes that the program counter should advance.
In this method, only one data byte may be stored in
each instruction location and room on the return
address stack is required.
4.8.2 TABLE READS/TABLE WRITES
A better method of storing data in program memory
allows 2 bytes of data to be stored in each instruction
location.
Lookup table data may be stored 2 bytes per program
word by using ta ble read s and writes . The t abl e point er
(TBLPTR) specifies the byte address and the table
latch (TABLAT) contains the data that is read from, or
written to program memory. Data is transferred to/from
program memory, one byte at a time.
A description of the table read/table write operation is
shown in Section 5.0.
DS39612A-page 48 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 51

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.9 Data Memory Organization
The data memory i s impl emented as static RAM. Each
register in the data memory has a 12-bit address,
allowing up to 4096 byt es of data mem ory. Figure 4-7
shows the data memory organization for the
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devices.
The data memory map is divided into 16 banks that
contain 256 bytes each. The lower 4 bits of the Bank
Select Register (BSR<3:0>) select which bank will be
accessed. The upper 4 bits for the BSR are not
implemented.
The data memory contains Special Function Registers
(SFR) and General Purpose Registers (GPR). The
SFRs are used for control and status of the controller
and peripheral functio ns, while GPRs are us ed for data
storage and scratch pad operations in the user’s application. The SFRs start at the last location of Bank 15
(0FFFh) and extend downwards. Any remaining space
beyond the SFRs in the bank may be implemented as
GPRs. GPRs start at the first location of Bank 0 and
grow upwards. Any re ad of a n un im pl em ente d l oc atio n
will read as ‘0’s.
The entire data memory may be accessed directly or
indirectly. Direct addressing may require the use of the
BSR register. Indirect addressing requires the use of a
File Select Register (FSRn) and a corresponding Indirect File Operand (INDFn). Each FSR holds a 12-bit
address value that can be used to access any location
in the data memory map without banking.
The instruction set and architecture allow operations
across all banks. This m ay be accompli shed by indirec t
addressing or by the us e of t he MOVFF instruction. The
MOVFF instruction is a two-word/two-cycle instruction
that moves a value from one register to another.
To ensure that commonly used registers (SFRs and
select GPRs) can be accessed in a single cycle
regardless of the current BSR values, an Access Bank
is implemented. A s egment of Ban k 0 and a segm ent of
Bank 15 comprise the Access RAM. Section 4.10
provides a detailed description of the Access RAM.
4.9.1 GENERAL PURPOSE REGISTER FILE
The register file can b e access ed eithe r dire ctly o r indirectly. Indirect addressing operates using a File Select
Register and correspond ing Ind irect Fi le Ope rand. Th e
operation of indirect addressing is shown in
Section 4.12.
Enhanced MCU devices may have banked memory in
the GPR area. GPRs are not initialized by a Power-on
Reset and are unchanged on all other RESETS.
Data RAM is available for use as general purpose registers by all instructions. The top section of Bank 15
(F60h to FFFh) contains SFRs. All other banks of data
memory contain GPRs, starting with Bank 0.
4.9.2 SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTERS
The Special Function Registers (SFRs) are registers
used by the CPU an d peripheral modul es for controllin g
the desired operation of the device. These reg isters are
implemented as static RAM. A list of these registers is
given in Table 4-2 and Table 4-3.
The SFRs can be classified into two sets: those associated with the “core” function and those related to the
peripheral functions. Those registers related to the
“core” are described i n this section, while tho se rel ate d
to the operation of the peripheral features are
described in the section of that peripheral feature. The
SFRs are typically distributed among the peripherals
whose functions they control.
The unused SFR locations are unimplemented and
read as ‘0’s. The addresses for the SFRs are listed in
Table 4-2.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 49
Page 52

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 4-7: DATA MEMORY MAP FOR PIC18F6X2X/8X2X DEVICES
BSR<3:0>
= 0000
= 0001
= 0010
= 0011
= 0100
= 1110
= 1111
When a = 1,
the BSR is used to specify the
RAM location that the instruction
uses.
Bank 0
Bank 1
Bank 2
Bank 3
Bank 4
Bank 5
to
Bank 13
Bank 14
Bank 15
Data Memory Map
00h
Access RAM
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
00h
FFh
GPRs
GPRs
GPRs
GPRs
GPRs
GPRs
GPRs
Unused
SFRs
000h
05Fh
060h
0FFh
100h
1FFh
200h
2FFh
300h
3FFh
400h
4FFh
500h
DFFh
E00h
EFFh
F00h
F5Fh
F60h
FFFh
Access Bank
Access RAM low
Access RAM high
(SFRs)
When a = 0,
the BSR is ignored and the
Access Bank is used.
The first 128 bytes are General
Purpose RAM (from Bank 0).
The second 128 bytes are
Special Function Registers
(from Bank 15).
00h
5Fh
50h
FFh
DS39612A-page 50 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 53

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 4-2: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER MAP
Address Name Address Name Address Name Address Name
FFFh TOSU FDFh INDF2
FFEh TOSH FDEh POSTINC2
FFDh TOSL FDDh POSTDEC2
FFCh STKPTR FDCh PREINC2
FFBh PCLATU FDBh PLUSW2
FFAh PCLATH FDAh FSR2H FBAh CCP2CON F9Ah TRISJ
FF9h PCL FD9h FSR2L FB9h CCPR3H F99h TRISH
FF8h TBLPTRU FD8h STATUS FB8h CCPR3L F98h TRISG
FF7h TBLPTRH FD7h TMR0H FB7h CCP3CON F97h TRISF
FF6h TBLPTRL FD6h TMR0L FB6h ECCP1AS F96h TRISE
FF5h TABLAT FD5h T0CON FB5h CVRCON F95h TRISD
FF4h PRODH FD4h —
FF3h PRODL FD3h OSCCON FB3h TMR3H F93h TRISB
FF2h INTCON FD2h LVDCON FB2h TMR3L F92h TRISA
FF1h INTCON2 FD1h WDTCON FB1h T3CON F91h LATJ
FF0h INTCON3 FD0h RCON FB0h PSPCON F90h LATH
FEFh INDF0
FEEh POSTINC0
FEDh POSTDEC0
FECh PREINC0
FEBh PLUSW0
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
FCFh TMR1H FAFh SPBRG1 F8Fh LATG
FCEh TMR1L FAEh RCREG1 F8Eh LATF
FCDh T1CON FADh TXREG1 F8Dh LATE
FCCh TMR2 FACh TXSTA1 F8Ch LATD
FCBh PR2 FABh RCSTA1 F8Bh LATC
FEAh FSR0H FCAh T2CON FAAh EEADRH F8Ah LATB
FE9h FSR0L FC9h SSPBUF FA9h EEADR F89h LATA
FE8h WREG FC8h SSPADD FA8h EEDATA F88h PORTJ
FE7h INDF1
FE6h POSTINC1
FE5h POSTDEC1
FE4h PREINC1
FE3h PLUSW1
(3)
FC7h SSPSTAT FA7h EECON2 F87h PORTH
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
FC6h SSPCON1 FA6h EECON1 F86h PORTG
FC5h SSPCON2 FA5h IPR3 F85h PORTF
FC4h ADRESH FA4h PIR3 F84h PORTE
FC3h ADRESL FA3h PIE3 F83h PORTD
FE2h FSR1H FC2h ADCON0 FA2h IPR2 F82h PORTC
FE1h FSR1L FC1h ADCON1 FA1h PIR2 F81h PORTB
FE0h BSR FC0h ADCON2 FA0h PIE2 F80h PORTA
Note 1: Unimplemented registers are read as ‘0’.
2: This register is not available on PIC18F6X2X devices.
3: This is not a physical register.
(3)
FBFh CCPR1H F9Fh IPR1
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(1)
FBEh CCPR1L F9Eh PIR1
FBDh CCP1CON F9Dh PIE1
FBCh CCPR2H F9Ch MEMCON
FBBh CCPR2L F9Bh —
FB4h CMCON F94h TRISC
(2)
(1)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 51
Page 54
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 4-2: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER MAP (CONTINUED)
Address Name Address Name Address Name Address Name
F7Fh SPBRGH1 F5Fh
F7Eh BAUDCON1 F5Eh
F7Dh SPBRGH2 F5Dh
F7Ch BAUDCON2 F5Ch
(1)
F7Bh
F7Ah
—
—
(1)
F5Bh
F5Ah
F79h ECCP1DEL F59h
F78h TMR4 F58h
F77h PR4 F57h
F76h T4CON F56h
F75h CCPR4H F55h
F74h CCPR4L F54h
F73h CCP4CON F53h
F72h CCPR5H F52h
F71h CCPR5L F51h
F70h CCP5CON F50h
F6Fh SPBRG2 F4Fh
F6Eh RCREG2 F4Eh
F6Dh TXREG2 F4Dh
F6Ch TXSTA2 F4Ch
F6Bh RCSTA2 F4Bh
F6Ah ECCP3AS F4Ah
F69h ECCP3DEL F49h
F68h ECCP2AS F48h
F67h ECCP2DEL F47h
F66h
F65h
F64h
F63h
F62h
F61h
F60h
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
F46h
F45h
F44h
F43h
F42h
F41h
F40h
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
Note 1: Unimplemented registers are read as ‘0’.
2: This register is not available on PIC18F6X2X devices.
3: This is not a physical register.
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
F3Fh
F3Eh
F3Dh
F3Ch
F3Bh
F3Ah
F39h
F38h
F37h
F36h
F35h
F34h
F33h
F32h
F31h
F30h
F2Fh
F2Eh
F2Dh
F2Ch
F2Bh
F2Ah
F29h
F28h
F27h
F26h
F25h
F24h
F23h
F22h
F21h
F20h
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
F1Fh
F1Eh
F1Dh
F1Ch
F1Bh
F1Ah
F19h
F18h
F17h
F16h
F15h
F14h
F13h
F12h
F11h
F10h
F0Fh
F0Eh
F0Dh
F0Ch
F0Bh
F0Ah
F09h
F08h
F07h
F06h
F05h
F04h
F03h
F02h
F01h
F00h
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
DS39612A-page 52 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 55

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 4-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TOSU
TOSH Top-of-Stack High Byte (TOS<15:8>) 0000 0000 34, 44
TOSL Top-of-Stack Low Byte (TOS<7:0>) 0000 0000 34, 44
STKPTR STKFUL STKUNF
PCLATU
PCLATH Holding Register for PC<15:8> 0000 0000 34, 46
PCL PC Low Byte (PC<7:0>) 0000 0000 34, 46
TBLPTRU
TBLPTRH Program Memory Table Pointer High Byte (TBLP T R<15:8>) 0000 0000 34, 71
TBLPTRL Program Memory T able Pointer Low Byte (TBLPT R<7:0>) 0000 0000 34, 71
TABLAT Program Memory T able Latch 0000 0000 34, 71
PRODH Product Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 34, 87
PRODL Product Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 34, 87
INTCON GIE/GIEH PEIE/GIEL TMR0IE INT0IE RBIE TMR0IF INT0IF RBIF 0000 0000 34, 91
INTCON2 RBPU
INTCON3 INT2IP INT1IP INT3IE INT2IE INT1IE INT3IF INT2IF INT1IF 1100 0000 34, 93
INDF0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory - value of FSR0 not changed (not a physical register) n/a 58
POSTINC0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory - value of FSR0 post-incremented
POSTDEC0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory - value of FSR0 post-decremented
PREINC0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory - value of FSR0 pre-incremented (not a physical register) n/a 58
PLUSW0 Uses contents of FSR0 to address data memory - value of FSR0 pre-incremented
FSR0H
FSR0L Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 0 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 34, 58
WREG Working Register xxxx xxxx 34
INDF1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory - value of FSR1 not changed (not a physical register) n/a 58
POSTINC1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory - value of FSR1 post-incremented
POSTDEC1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory - value of FSR1 post-decremented
PREINC1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory - value of FSR1 pre-incremented (not a physical register) n/a 58
PLUSW1 Uses contents of FSR1 to address data memory - value of FSR1 pre-incremented
FSR1H
FSR1L Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 1 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 35, 58
BSR
INDF2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory - value of FSR2 not changed (not a physical register) n/a 58
POSTINC2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory - value of FSR2 post-incremented
POSTDEC2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory - value of FSR2 post-decremented
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: RA6 and associated bits are configured as port pins in RCIO and ECIO Oscillator mode only and read ‘0’ in all other
2: Bit 21 of the TBLPTRU allows access to the device configur ation bits.
3: These registers are unused on PIC18F6X2X devices; always maintain these clear.
4: RG5 is available only if MCLR
— — — Top-of-Stack Upper Byte (TOS<20:16>) ---0 0000 34, 44
— Return Stack Pointer 00-0 0000 34, 45
— — bit 21 Holding Register for PC<20:16> --10 0000 34, 46
— —bit 21
INTEDG0 INTEDG1 INTEDG2 INTEDG3 TMR0IP INT3IP RBIP 1111 1111 34, 92
(not a physical register)
(not a physical register)
(not a physical register) - value of FSR0 offset by value in WREG
— — — — Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 0 High Byte ---- 0000 34, 58
(not a physical register)
(not a physical register)
(not a physical register) - value of FSR1 offset by value in WREG
— — — — Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 1 High Byte ---- 0000 35, 58
— — — — Bank Select Register ---- 0000 35, 57
(not a physical register)
(not a physical register)
Oscillator modes.
(2)
Program Memory Table Pointer Upper Byt e (TB LP T R<2 0:1 6> ) --00 0000 34, 71
function is disabled in configuration.
Value on
POR, BOR
n/a 58
n/a 58
n/a 58
n/a 58
n/a 58
n/a 58
n/a 58
n/a 58
Details
on page:
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 53
Page 56

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 4-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED)
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PREINC2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory - value of FSR2 pre-incremented
PLUSW2 Uses contents of FSR2 to address data memory - value of FSR2 pre-incremented
FSR2H
FSR2L Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 2 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 35, 58
STATUS
TMR0H Timer0 Register High Byte 0000 0000 35, 135
TMR0L Timer0 Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 35, 135
T0CON TMR0ON T08BIT T0CS T0SE PSA T0PS2 T0PS1 T0PS0 1111 1111 35, 133
OSCCON
LVDCON
WDTCON
RCON IPEN
TMR1H Timer1 Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 35, 141
TMR1L Timer1 Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 35, 141
T1CON RD16
TMR2 Timer2 Register 0000 0000 35, 144
PR2 Timer2 Period Register 1111 1111 35, 144
T2CON
SSPBUF SSP Receive Buffer/Transmit Register xxxx xxxx 35, 183
SSPADD SSP Address Register in I
SSPSTAT SMP CKE D/A
SSPCON1 WCOL SSPOV SSPEN CKP SSPM3 SSPM2 SSPM1 SSPM0 0000 0000 35, 177
SSPCON2 GCEN ACKSTAT ACKDT ACKEN RCEN PEN RSEN SEN 0000 0000 35, 187
ADRESH A/D Result Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 242
ADRESL A/D Result Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 242
ADCON0
ADCON1
ADCON2 ADFM
CCPR1H Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 1 High Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 174
CCPR1L Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 1 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 174
CCP1CON P1M1 P1M0 DC1B1 DC1B0 CCP1M3 CCP1M2 CCP1M1 CCP1M0 0000 0000 36, 159
CCPR2H Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 2 High Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 174
CCPR2L Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 2 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 174
CCP2CON P2M1 P2M0 DC2B1 DC2B0 CCP2M3 CCP2M2 CCP2M1 CCP2M0 0000 0000 36, 159
CCPR3H Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 3 High Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 174
CCPR3L Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM Register 3 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 174
CCP3CON P3M1 P3M0 CCP3X CCP3Y CCP3M3 CCP3M2 CCP3M1 CCP3M0 0000 0000 36, 159
ECCP1AS ECCP1ASE ECCP1AS2 ECCP1AS1 ECCP1AS0 PSS1AC1 PSS1AC0 PSS1BD1 PSS1BD0 0000 0000 36, 171
CVRCON CVREN CVROE CVRR CVRSS CVR3 CVR2 CVR1 CVR0 0000 0000 36, 249
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: RA6 and associated bits are configured as port pins in RCIO and ECIO Oscillator mode only and read ‘0’ in all other
(not a physical register)
(not a physical register) - value of FSR2 offset by value in WREG
— — — — Indirect Data Memory Address Pointer 2 High Byte ---- 0000 35, 58
— — —NOVZDCC---x xxxx 35, 60
— — — — — — —SCS---- ---0 25, 35
— — IRVST LVDEN LVDL3 LVDL2 LVDL1 L VD L0 --00 0101 35, 255
— — — — — — —SWDTE---- ---0 35, 269
— —RITO PD POR BOR 0--1 11qq 35, 61,
— T1CKPS1 T1CKPS0 T1OSCEN T1SYNC TMR1CS TMR1ON 0-00 0000 35, 141
— T2OUTPS3 T2OUTPS2 T2OUTPS1 T2OUTPS0 TMR2ON T2CKPS1 T2CKPS0 -000 0000 35, 144
2
C Slave mode. SSP Baud Rate Reload Register in I2C Master mode. 0000 0000 35, 183
PSR/WUA BF 0000 0000 35, 176
— — CHS3 CHS2 CHS1 CHS0 GO/DONE ADON --00 0000 36, 235
— — VCFG1 VCFG0 PCFG3 PCFG2 PCFG1 PCFG0 --00 0000 36, 236
— ACQT2 ACQT1 ACQT0 ADCS2 ADCS1 ADCS0 0-00 0000 36, 237
Oscillator modes.
2: Bit 21 of the TBLPTRU allows access to the device configur ation bits.
3: These registers are unused on PIC18F6X2X devices; always maintain these clear.
4: RG5 is available only if MCLR
function is disabled in configuration.
Value on
POR, BOR
n/a 58
n/a 58
Details
on page:
103
DS39612A-page 54 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 57

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 4-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED)
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
CMCON C2OUT C1OUT C2INV C1INV CIS CM2 CM1 CM0 0000 0000 36, 243
TMR3H Timer3 Register High Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 147
TMR3L Timer3 Register Low Byte xxxx xxxx 36, 147
T3CON RD16 T3CCP2 T3CKPS1 T3CKPS0 T3CCP1 T3SYNC
PSPCON IBF OBF IBOV PSPMODE
SPBRG1 USART1 Baud Rate Generator 0000 0000 36, 219
RCREG1 USART1 Receive Re gi st er 0000 0000 36, 226
TXREG1 USART1 Transmit Register 0000 0000 36, 224
TXSTA1 CSRC TX9 TXEN SYNC
RCSTA1 SPEN RX9 SREN CREN ADDEN FERR OERR RX9D 0000 000x 36, 217
EEADRH
EEADR Data EEPROM Address Register 0000 0000 36, 85
EEDATA Data EEPROM Data Register 0000 0000 36, 85
EECON2 Data EEPROM Control Register 2 (not a physical register) ---- ---- 36, 85
EECON1 EEPGD CFGS
IPR3
PIR3
PIE3
IPR2
PIR2
PIE2
IPR1 PSPIP ADIP RCIP TXIP SSPIP CCP1IP TMR2IP TMR1IP 1111 1111 37, 100
PIR1 PSPIF ADIF RCIF TXIF SSPIF CCP1IF TMR2IF TMR1IF 0000 0000 37, 94
PIE1 PSPIE ADIE RCIE TXIE SSPIE CCP1IE TMR2IE TMR1IE 0000 0000 37, 97
MEMCON
(3)
TRISJ
(3)
TRISH
TRISG
TRISF Data Direction Control Register for PORTF 1111 1111 37, 118
TRISE Data Direction Control Register for PORTE 1111 1111 37, 115
TRISD Data Direction Control Register for PORTD 1111 1111 37, 112
TRISC Data Direction Control Register for PORTC 1111 1111 37, 110
TRISB Data Direction Control Register for PORTB 1111 1111 37, 107
TRISA
(3)
LATJ
(3)
LATH
LATG
LATF Read PORTF Data Latch, Write PORTF Data Latch xxxx xxxx 37, 121
LATE Read PORTE Data Latch, Write PORTE Data Latch xxxx xxxx 37, 118
LATD Read PORTD Data Latch, Write PORTD Data Latch xxxx xxxx 37, 115
LATC Read PORTC Data Latch, Write PORTC Data Latch xxxx xxxx 37, 112
LATB Read PORTB Data Latch, Write PORTB Data Latch xxxx xxxx 37, 110
LATA
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: RA6 and associated bits are configured as port pins in RCIO and ECIO Oscillator mode only and read ‘0’ in all other
2: Bit 21 of the TBLPTRU allows access to the device configur ation bits.
3: These registers are unused on PIC18F6X2X devices; always maintain these clear.
4: RG5 is available only if MCLR
— — — — — — EE Adr Register High ---- --00 36, 85
— FREE WRERR WREN WR RD xx-0 x000 36, 82
— — RC2IP TX2IP TMR4IP CCP5IP CCP4IP CCP3IP --11 1111 37, 102
— — RC2IF TX2IF TMR4IF CCP5IF CCP4IF CCP3IF --00 0000 37, 96
— — RC2IE TX2IE TMR4IE CCP5IE CCP4IE CCP3IE --00 0000 37, 99
—CMIP— EEIP BCLIP LVDIP TMR3IP CCP2IP -1-1 1111 37, 101
—CMIF— EEIF BCLIF LVDIF TMR3IF CCP2IF -0-0 0000 37, 95
—CMIE— EEIE BCLIE LVDIE TMR3IE CCP2IE -0-0 0000 37, 98
(3)
EBDIS —WAIT1WAIT0— —WM1WM00-00 --00 37, 73
Data Direction Control Register for PORTJ 1111 1111 37, 129
Data Direction Control Register for PORTH 1111 1111 37, 126
— — — Data Direction Control Register for PORTG ---1 1111 37, 121
— TRISA6
Read PORTJ Data Latch, Write PORTJ Data Latch xxxx xxxx 37, 129
Read PORTH Data Latch, Write PORTH Data Latch xxxx xxxx 37, 126
— — — Read PORTG Data Latch, Write PORTG Data Latch ---x xxxx 37, 123
—LATA6
Oscillator modes.
(1)
Data Direction Control Register for PORTA -111 1111 37, 123
(1)
Read PORTA Dat a Latch, Write PORTA Data Latch
function is disabled in configuration.
— — — — 0000 ---- 36, 131
— BRGH TRMT TX9D 0000 -010 36, 216
TMR3CS TMR3ON 0000 0000 36, 147
(1)
Value on
POR, BOR
-xxx xxxx 37, 107
Details
on page:
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 55
Page 58

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 4-3: REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED)
File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
(3)
PORTJ
PORTH
PORTG
PORTF Read PORTF pins, Write PORTF Data Latch xxxx xxxx 38, 121
PORTE Read PORTE pins, Write PORTE Data Latch xxxx xxxx 38, 118
PORTD Read PORTD pins, Write PORTD Data Latch xxxx xxxx 38, 115
PORTC Read PORTC pins, Write PORTC Data Latch xxxx xxxx 38, 112
PORTB Read PORTB pins, Write PORTB Data Latch xxxx xxxx 38, 110
PORTA
SPBRGH1 Enhanced USART1 Baud Rate Generator High Byte 0000 0000 38, 219
BAUDCON1
SPBRGH2 Enhanced USART2 Baud Rate Generator High Byte 0000 0000 38, 219
BAUDCON2
ECCP1DEL P1RSEN P1DC6 P1DC5 P1DC4 P1DC3 P1DC2 P1DC1 P1DC0 0000 0000 38, 170
TMR4 Timer4 Register 0000 0000 38, 150
PR4 Timer4 Period Register 1111 1111 38, 150
T4CON
CCPR4H Capture/Compare/PWM Register 4 High Byte xxxx xxxx 38, 155
CCPR4L Capture/Compare/PWM Register 4 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 38, 155
CCP4CON
CCPR5H Capture/Compare/PWM Register 5 High Byte xxxx xxxx 38, 155
CCPR5L Capture/Compare/PWM Register 5 Low Byte xxxx xxxx 38, 155
CCP5CON
SPBRG2 USART2 Baud Rate Generator 0000 0000 38, 219
RCREG2 USART2 Receive Re gi st er 0000 0000 38, 226
TXREG2 USART2 Transmit Register 0000 0000 38, 224
TXSTA2 CSRC TX9 TXEN SYNC SENDB BRGH TRMT TX9D 0000 -010 38, 224
RCSTA2 SPEN RX9 SREN CREN ADEN FERR OERR RX9D 0000 000x 38, 224
ECCP3AS ECCP3ASE ECCP3AS2 ECCP3AS1 ECCP3AS0 PSS3AC1 PSS3AC0 PSS3BD1 PSS3BD0 0000 0000 38, 171
ECCP3DEL P3RSEN P3DC6 P3DC5 P3DC4 P3DC3 P3DC2 P3DC1 P3DC0 0000 0000 38, 170
ECCP2AS ECCP2ASE ECCP2AS2 ECCP2AS1 ECCP2AS0 PSS2AC1 PSS2AC0 PSS2BD1 PSS2BD0 0000 0000 38, 171
ECCP2DEL P2RSEN P2DC6 P2DC5 P2DC4 P2DC3 P2DC2 P2DC1 P2DC0 0000 0000 38, 170
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, - = unimplemented, q = value depends on condition
Note 1: RA6 and associated bits are configured as port pins in RCIO and ECIO Oscillator mode only and read ‘0’ in all other
Read PORTJ pins, Write PORTJ Data Latch xxxx xxxx 38, 129
(3)
Read PORTH pins, Write PORTH Data Latch xxxx xxxx 38, 126
— —
—RA6
— RCIDL — SCKP BRG16 — WUE ABDEN -1-1 0-00 38, 218
— RCIDL — SCKP BRG16 — WUE ABDEN -1-0 0-00 38, 218
— TOUTPS3 TOUTPS2 TOUTPS1 TOUTPS0 TMR4ON T4CKPS1 T4CKPS0 -000 0000 38, 149
— — CCPxX CCPxY CCPxM3 CCPxM2 CCPxM1 CCPxM0 --00 0000 38, 151
— — CCPxX CCPxY CCPxM3 CCPxM2 CCPxM1 CCPxM0 --00 0000 38, 151
Oscillator modes.
2: Bit 21 of the TBLPTRU allows access to the device configur ation bits.
3: These registers are unused on PIC18F6X2X devices; always maintain these clear.
4: RG5 is available only if MCLR
(1)
(4)
RG5
Read PORTA pins, Write PORTA Data Latch
function is disabled in configuration.
Read PORTG pins, Write PORTG Data Latc h --0x xxxx 38, 123
(1)
Value on
POR, BOR
-x0x 0000 38, 107
Details
on page:
DS39612A-page 56 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 59

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.10 Access Bank
The Access Bank is an architectural enhancement,
which is very useful for C compiler code optimization.
The techniques used by the C compiler may also be
useful for programs written in assembly.
This data memory region can be used for:
• Intermediate computational values
• Local variables of subroutines
• Faster context saving/switching of variables
• Common variables
• Faster evaluation/control of SFRs (no banking)
The Access Bank is comprised of the upper 160 bytes
in Bank 15 (SFRs) and the lower 96 bytes in Bank 0.
These two sections will be referred to as Access RAM
High and Access RAM Low, respectively. Figure 4-7
indicates the Access RAM areas.
A bit in the instruction word spec ifie s if the opera tion is
to occur in the bank spec ifi ed by the BSR register or in
the Access Bank. This bit is denoted by the ‘a’ bit (for
access bit).
When forced in the Access Bank (a = 0), the last
address in Access RAM Low is followed by the first
address in Access RAM High. Access RAM High maps
the Special Function R egisters so that these r egisters
can be accessed without any software overhead. This is
useful for testing status flags and modifying control bits.
4.1 1 Bank Select Register (BSR)
The need for a large general purpose memory space
dictates a RAM banking scheme. The data memory is
partitioned into sixteen banks. When using direct
addressing, the BSR should be configured for the
desired bank.
BSR<3:0> holds the upper 4 bits of the 12-bit RAM
address. The BSR<7:4> bits will always read ‘0’s, and
writes will have no effect.
A MOVLB instruction has been provided in the
instruction set to assist in selecting banks.
If the currently selected bank is not implemented, any
read will return all ‘0’s and all writes are ignored. The
ST ATUS register bits will be set/c le ared as ap prop ria te
for the instruction performed.
Each Bank extends up to FFh (256 bytes). All data
memory is implemented as static RAM.
A MOVFF instruction ignores the BSR since the 12-bit
addresses are embedded into the instruction word.
Section 4.12 provides a d escription of ind irect address ing which allows linear addressing of the entire RAM
space.
FIGURE 4-8: DIRECT ADDRESSING
Direct Addressing
BSR<3:0> 7
Bank Select
Note 1: For register file map detail, see Table4-2.
(2)
2: The access bit of the instruction can be used t o force an override of the selected bank (BSR<3:0>) to the
registers of the Access Bank.
3: The MOVFF instruction embeds the entire 12-bit address in the instruction.
Location Select
From Opcode
Data
Memory
(3)
(1)
(3)
0
00h 01h 0Eh 0Fh
000h
0FFh
100h
1FFh
E00h
EFFh
Bank 0 Bank 1 Bank 14 Bank 15
F00h
FFFh
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 57
Page 60

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.12 Indirect Addressing, INDF and FSR Registers
Indirect addressing is a mode of addressing dat a memory, where the data memory address in the instruction
is not fixed. An FSR regis ter i s u sed as a poi nte r to th e
data memory location that i s to be read or written. Since
this pointer is in RAM, the cont en t s c an be mo difi ed by
the program. This can be useful for data tables in the
data memory and for software stacks. Figure 4-9
shows the operation of indirect addressing. This shows
the moving of the value to the data memory address
specified b y the value of the FSR register.
Indirect addressing is possible by using one of the INDF
registers. Any instruction using the INDF register actually accesses the register pointed to by the File Select
Register, FSR. Reading the INDF register itself indirectly
(FSR = 0), will read 00h. Writing to the INDF register
indirectly, results in a no operation. The FSR register
contains a 12-bit address whic h is shown in Figure4-10.
The INDFn register is not a physical register. Addressing INDFn actually addresses the register whose
address is contained in the FSRn register (FSRn is a
pointer). T his is indirect addressing.
Example 4-4 shows a sim ple use of in direct addres sing
to clear the RAM in Bank 1 (locations 100h-1FFh) in a
minimum number of instructions.
EXAMPLE 4-4: HOW TO CLEAR RAM
(BANK 1) USING
INDIRECT ADDRESSING
LFSR FSR0 ,0x100 ;
NEXT CLRF POSTINC0 ; Clear INDF
; register and
; inc pointer
BTFSS FSR0H, 1 ; All done with
; Bank1?
GOTO NEXT ; NO, clear next
CONTINUE ; YES, continue
There are three indirect addressing registers. To
address the entire data memory space (4096 bytes),
these registers are 12 bits wide. To store the 12 bits of
addressing information, two 8-bit registers are
required. These indirect addres si ng regi ste r s are:
1. FSR0: composed of FSR0H:FSR0L
2. FSR1: composed of FSR1H:FSR1L
3. FSR2: composed of FSR2H:FSR2L
In addition, there are registers INDF0, INDF1 and
INDF2, which are not physically implemented. Reading
or writing to these registers activates indirect addressing, with the value in the corresponding FSR register
being the a ddress of the data. If an instruction writes a
value to INDF0, th e v al ue will be w ritten to the address
pointed to by FSR 0H:FSR0L. A read f rom INDF 1 reads
the data from the address pointed to by
FSR1H:FSR1L. INDFn can be used in code anywhere
an operand can be used.
If INDF0, INDF1, or INDF2 are read indirectly via an
FSR, all ‘0’s are read (zero bit is set). Similarly, if
INDF0, INDF1, or INDF2 are written to indirectly, the
operation will be equivale nt to a NOP instruction and the
ST ATUS bits are not affected.
4.12.1 INDIRECT ADDRESSING OPERATION
Each FSR register has an INDF register associated
with it, plus four addition al register addresses. Perform ing an operation on one of these five registers determines how the FSR will be modified during indirect
addressing.
When data access is done to one of the five INDFn
locations, the address selected will configure the FSRn
register to:
• Do nothing to FSRn after an indirect access (no
change) - INDFn.
• Auto-decrement FSRn after an indirect access
(post-decrement) - POSTDECn.
• Auto-increment FSRn after an indirect access
(post-increment) - POSTINCn.
• Auto-increment FSRn before an indirect access
(pre-increment) - PREINCn.
• Use the value in the WREG register as an offset
to FSRn. Do not mo dify the va lue of the WREG or
the FSRn register after an indirect access (no
change) - PLUSWn.
When using the auto-increment or auto-decrement features, the effect on the FSR is not reflected in the
STATUS register. For example, if the indirect address
causes the FSR to equal ‘0’, the Z bit will not be set.
Incrementing or decrementing an FSR affects all 12
bits. That is, whe n FSRnL overflows from an increment,
FSRnH will be incremented automatically.
Adding these features allows the FSRn to be used as a
stack pointer in ad diti on to it s us es for t abl e ope rati ons
in data memo ry.
Each FSR has an address associated with it that performs an indexed indirect access. When a data access
to this INDFn location (PLUSWn) occurs, the FSRn is
configured to add th e s ig ned v alu e in the WREG register and the value in F S R to f orm the add res s befo re a n
indirect access. The FSR value is not changed.
If an FSR register contains a value that poin ts to one of
the INDFn, an indirect read will read 00h (zero bit is
set), whil e an i ndi re ct wri te will be equ ival ent t o a NOP
(ST ATUS bits are not affected).
If an indirect addressing operation is done where the
target address is an FSRnH or FSRnL register,
the write operation will dominate over the pre- or
post-increment/decrement functions.
DS39612A-page 58 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 61

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 4-9: INDIRECT ADDRESSING OPERATION
RAM
Instruction
Executed
Opcode Address
12
File Address = Access of an Indirect Addressing Register
0h
FFFh
BSR<3:0>
Instruction
Fetched
Opcode
12
4
8
File
FIGURE 4-10: INDIRECT ADDRESSING
Indirect Addressing
FSR Register11
Location Select
Data
Memory
12
FSR
0
0000h
(1)
0FFFh
Note 1: For register file map detail, see Table 4-2.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 59
Page 62

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.13 STATUS Register
The STATUS register, shown in Register 4-3, contains
the arithmetic status of the ALU. The STATUS register
can be the destination for any instruction, as with any
other register. If the STATUS register is the destination
for an instruction t hat affect s the Z, DC, C, OV, or N bits,
then the write to these five bits is disabled. These bits
are set or cleared according to the device logic.
Therefore, the result of an instruction with the STATUS
register as destina tion may be different t han inte nde d.
REGISTER 4-3: STATUS REGISTER
U-0 U-0 U-0 R/W-x R/W-x R/W-x R/W-x R/W-x
— — —NOVZDCC
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 N: Negative bit
This bit is used for signed arithmetic (2’s complement). It indicates whether the result was
negative (ALU MSB = 1).
1 = Result was negative
0 = Result was positive
bit 3 OV: Overflow bit
This bit is used for signed arithmetic (2’s complement). It indicates an overflow of the
7-bit magnitude which causes the sign bit (bit 7) to change state.
1 = Overflow occurred for signed arithmetic (in this arithmetic operation)
0 = No overflow occurred
bit 2 Z: Zero bit
1 = The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is zero
0 = The result of an arithmetic or logic operation is not zero
bit 1 DC: Digit Carry/Borrow
For ADDWF, ADDLW, SUBLW, and SUBWF instructions.
1 = A carry-out from the 4th low order bit of the result occurred
0 = No carry-out from the 4th low order bit of the result
Note: For borrow,
complement of the second operand. Fo r rot ate (RRF, RLF) i ns truc tio ns , t his b it is
loaded with either bit 4 or bit 3 of the source register.
bit
the polarity is reverse d. A su btra cti on i s exec ute d by addi ng t he two’s
For example, CLRF STATUS will clear the upper three
bits and set t he Z bit. T his leaves the STATUS regist er
as 000u u1uu (where u = unchanged).
It is recommended, therefore, that only BCF, BSF,
SWAPF, MOVFF and MOVWF instructions are used to
alter the STATUS register because these instructions
do not affect the Z, C, DC, OV, or N bits from the
STATUS register. For other instructions not affecting
any STATUS bits, see Table 25-2.
Note: The C and DC bits operate as a borrow
and digit borrow bit respectively, in
subtraction.
bit 0 C: Carry/Borrow
For ADDWF, ADDLW, SUBLW, and SUBWF instructions.
1 = A carry-out from the Most Significant bit of the result occurred
0 = No carry-out from the Most Significant bit of the result occurred
Note: For borrow,
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
DS39612A-page 60 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
bit
the polarity is reverse d. A su btra cti on i s exec ute d by addi ng t he two’s
complement of the second operand. Fo r rot ate (RRF, RLF) i ns truc tio ns , t his b it is
loaded with either the high or low order bit of the source register.
Page 63

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
4.14 RCON Register
The Reset Control (RCON) register contains flag bits
that allow differentiation between the sources of a
device RESET. These flags include the TO
BOR
and RI bits. This re gister is reada ble and w ritabl e.
REGISTER 4-4: RCON REGISTER
R/W-0 U-0 U-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-0 R/W-0
IPEN
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 IPEN: Interrupt Priority Enable bit
1 = Enable priority levels on interrupts
0 = Disable priority levels on interrupts (PIC16CXXX Compatibility mode)
bit 6-5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 RI
bit 3 TO
bit 2 PD
bit 1 POR
bit 0 BOR
: RESET Instruction Flag bit
1 = The RESET instruction was not executed
0 = The RESET instruction was executed causing a device RESET
(must be set in software after a Brown-out Reset occurs)
: Watchdog Time-out Flag bit
1 = After power-up, CLRWDT instruction, or SLEEP instruction
0 = A WDT time-out occurred
: Power-down Detection Flag bit
1 = After power-up or by the CLRWDT instruction
0 = By execution of the SLEEP instruction
: Power-on Reset Status bit
1 = A Power-on Reset has not occurred
0 = A Power-on Reset occurred
(must be set in software after a Power-on Reset occurs)
: Brown-out Reset Status bit
1 = A Brown-out Reset has not occurred
0 = A Brown-out Reset occurred
(must be set in software after a Brown-out Reset occurs)
, PD, POR,
— —RITO PD POR BOR
Note: It is recommended that th e POR bit be set
after a Power-on Reset has been
detected, so that subsequent Power-on
Resets may be detected.
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 61
Page 64

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
NOTES:
DS39612A-page 62 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 65

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
5.0 FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
The FLASH program memory is readable, writ able, and
erasable, during normal operation over the entire V
range.
A read from program memory is executed on one byte
at a time. A write to program memory is executed on
blocks of 8 byt es at a time. Program memory is erased
in blocks of 64 bytes at a time. A bulk erase operation
may not be issued from user code.
Writing or erasing program memory will cease instruction fetches until the operation is complete. The program memory cannot be ac cessed du ring the write or
erase, therefore, code cannot execute. An internal
programming timer terminates program memory writes
and erases.
A value written to progra m memory does not nee d to be
a valid instruction. Executing a program memory
location that forms an invalid instruction results in a
NOP.
DD
5.1 Table Reads and Table Writes
In order to read and write program memory, there are
two operations that allow the processor to move bytes
between the program memory sp ace and the dat a RAM:
• Table Read (TBLRD)
• Table Write (TBLWT)
The program memory space is 16 bits wide, while the
data RAM space is 8 bits wide. Table reads and table
writes move data between these two memory spaces
through an 8-bit register (TABLAT).
Table read operations retrieve data from program
memory and places it into the data RAM space.
Figure 5-1 shows the operation of a table read with
program memory and data RAM.
Table write operations store data from the data memory
space into holding registers in program memory. The
procedure to write the contents of the holding registers
into program memory is detailed in Section 5.5, “Writing
to FLASH Program Memory”. Figure 5-2 shows the
operation of a table write with program memory and data
RAM.
Table operations work with byte entities. A table block
containing data, rather than program instructions, is not
required to be word aligned. Therefore, a table block can
start and end at any byte address. If a t able write is being
used to write executable code into program memory,
program instructions will need to be word aligned.
FIGURE 5-1: TABLE READ OPERATION
Table Pointer
TBLPTRU
Note 1: Table Pointer register points to a byte in program memory.
TBLPTRH TBLPTRL
(1)
Program Memory
(TBLPTR)
Instruction: TBLRD*
Program Memory
Table Latch (8-bit)
TABLAT
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 63
Page 66

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 5-2: TABLE WRITE OPERATION
Instruction: TBLWT*
Program Memory
Table Pointer
TBLPTRU
Note 1: Table pointer actually points to one of eight holding registers, the address of which is determined by
TBLPTRH TBLPTRL
TBLPTRL<2:0>. The process for physically writing data to the program memory array is discussed in
Section 5.5.
(1)
Program Memory
(TBLPTR)
Holding Registers
Table Latch (8-bit)
TABLAT
5.2 Control Registers
Several control registers are used in conjunction with
the TBLRD and TBLWT instructions. These include the:
• EECON1 register
• EECON2 register
• TABLAT register
• TBLPTR registers
5.2.1 EECON1 AND EECON2 REGISTERS
EECON1 is the control register for memory accesses.
EECON2 is not a physical register. Reading EECON2
will read all ‘0’s. The EECON2 register is used
exclusively in the memory write and erase sequences.
Control bit EEPGD determines if the access will be a
program or data EEPROM memory access. When
clear, any subsequent operations will operate on the
data EEPROM memory. When set, any subsequent
operations will operate on the program memory.
Control bit CFGS determin es if the access will be to the
configuration/calibration registers or to program
memory/data EEPROM memory. When set,
subsequent operations will operate on configuration
registers regardless of EEPGD (see Section 24.0,
“Special Fea tures of the CPU” ). When clear, memory
selection access is determined by EEPGD.
The FREE bit, when set, will allow a program memory
erase operation. When the FREE bit is set, the erase
operation is initiated on the next WR command. When
FREE is clear , only wr ite s are enab led .
The WREN bit, when set, will allow a write operation.
On power-up, the WREN bit is c lear . T he WRERR bit is
set when a write operation is interrupted by a MCLR
Reset or a WDT Time-out Reset during normal operation. In these situations, the user can check the
WRERR bit and rewrite the location. It is necessary to
reload the data and address regi sters (EEDATA a nd
EEADR) due to RESET values of zero.
The WR control bit initiates write operations. The bit
cannot be cleared, only set, in software; it is cleared in
hardware at the completion of the write operation. The
inability to clear the WR bit in software prevents the
accidental or premature termination of a write
operation.
Note: Interrupt flag bit, EEIF in the PIR2 registe r ,
is set when the write is complete. It must
be cleared in software.
DS39612A-page 64 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 67

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
REGISTER 5-1: EECON1 REGISTER (ADDRESS FA6h)
R/W-x R/W-x U-0 R/W-0 R/W-x R/W-0 R/S-0 R/S-0
EEPGD CFGS — FREE WRERR WREN WR RD
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 EEPGD: FLASH Program or Data EEPROM Memory Select bit
1 = Access FLASH program memory
0 = Access data EEPROM memory
bit 6 CFGS: FLASH Program/Data EEPROM or Configuration Select bit
1 = Access Configuration registers
0 = Access FLASH program or data EEPROM memory
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 FREE: FLASH Row Erase Enable bit
1 = Erase the program memory row addressed by TBLPTR on the next WR command
(cleared by completion of erase operation)
0 = Perform write only
bit 3 WRERR: FLASH Program/Data EEPROM Error Flag bit
1 = A write operation is prematurely terminated
(any RESET during self-timed programming in normal operation)
0 = The write operation completed
Note: When a WRERR occurs, the EEPGD and CFGS bits are not cleared. This allows
tracing of the error condition.
bit 2 WREN: FLASH Program/Data EEPROM Write Enable bit
1 = Allows write cycles to FLASH program/data EEPROM
0 = Inhibits write cycles to FLASH program/data EEPROM
bit 1 WR: Write Control bit
1 = Initiates a data EEPROM erase/write cycle or a program memory erase cycle or write cycle.
(The operation is self-tim ed and the bit is cleared by hardw are once writ e is complete. The
WR bit can only be set (not cleared) in software.)
0 = Write cycle to the EEPROM is complete
bit 0 RD: Read Control bit
1 = Initiates an EEPROM read
(Read takes one cyc le. RD is cleared in ha rdware. The RD bit can only be set (not cleare d)
in software. RD bit cannot be set when EEPGD = 1.)
0 = Does not initiate an EEPROM read
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 65
Page 68

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
5.2.2 TABLAT - TABLE LATCH REGISTER
The Table Latch (TABLAT) is an 8-bit register mapped
into the SFR space. The Table Latch register is used to
hold 8-bit data during data transfers between program
memory and data RAM.
5.2.3 TBLPTR - TABLE POINTER REGISTER
The Table Pointer register (TBLPTR) address es a byte
within the program memory. The TBLPTR is comprised
of three SFR registers : Table Pointer Upper Byte, Table
Pointer High Byte and Table Pointer Low Byte
(TBLPTRU:TBLPTRH:TBLPTRL). These three registers join to form a 22-bit wide pointer. The low order
21 bits allow the device to address up to 2 Mbytes of
program memory sp ace. Th e 22nd b it allow s acce ss to
the device ID, the user ID and the configuration bits.
The table pointer, TBLPTR, is used by the TBLRD and
TBLWT instructions. These instructions can update the
TBLPTR in one of four ways based on the table operation. These operations are shown in Table 5-1. These
operations on the TBLPTR only affect the low order
21 bits.
5.2.4 TABLE POINTER BOUNDARIES
TBLPTR is used in reads, writes, and erases of the
FLASH program memory.
When a TBLRD is executed, all 22 bits of the TBLPTR
determine which byte is read from program memory
into TABL AT .
When a TBLWT is executed, th e three LSbs o f the Table
Pointer register (TBLP TR<2:0>) determine which of the
eight program memory holding registers is written to.
When the timed write to program memory (long write)
begins, the 19 MSbs of the TBLPTR (TBLPTR<21:3>)
will determine which program memory block of 8 bytes
is written to. For more detail, see Section 5.5, “Writing
to FLASH Program Memory”.
When an erase of program memory is executed, the
16 MSbs of the T able Pointer register (TBLPTR<21:6>)
point to the 64-byte block that will be erased . The Least
Significant bits (TBLPTR<5:0>) are ignored.
Figure 5-3 describes the relevant boundaries of
TBLPTR based on FLASH program memory
operations.
TABLE 5-1: TABLE POINTER OPERATIONS WITH TBLRD AND TBLWT INSTRUCTIONS
Example Operation on Table Pointer
TBLRD*
TBLWT*
TBLRD*+
TBLWT*+
TBLRD*TBLWT*-
TBLRD+*
TBLWT+*
TBLPTR is incremented after the read/write
TBLPTR is decremented after the read/write
TBLPTR is incremented before the read /write
TBLPTR is not modified
FIGURE 5-3: TABLE POINTER BOUNDARIES BASED ON OPERATION
21 16 15 87 0
TBLPTRU
ERASE - TBLPTR<20:6>
WRITE - TBLP TR<21:3>
TBLPTRLTBLPTRH
READ - TBLPTR<21:0>
DS39612A-page 66 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 69

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
5.3 Reading the FLASH Program Memory
The TBLRD instruction is used to retrieve da ta from p ro-
gram memory and places i t into dat a RA M. Table reads
from program memory are performed one byte at a
time.
TBLPTR points to a byte address in program space.
Executing TBLRD places the byte pointed to into
TABLAT. In addition, TBLPTR can be modified
automatically for the next table read operation.
The internal program memory is typically organize d by
words. The Least Significant b it of th e address selects
between the high and low bytes of the word. Figure 5-4
shows the interface between the internal program
memory and the TABLAT.
FIGURE 5-4: READS FROM FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
Program Memory
(Even Byte Address)
(Odd Byte Address)
TBLPTR = xxxxx1
Instruction Register
(IR)
FETCH
TBLRD
EXAMPLE 5-1: READING A FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY WORD
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; Load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the word
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
READ_WORD
TBLRD*+ ; read into TABLAT and increment
MOVF TABLAT, W ; get data
MOVWF WORD_EVEN
TBLRD*+ ; read into TABLAT and increment
MOVFW TABLAT, W ; get data
MOVWF WORD_ODD
TBLPTR = xxxxx0
TABLAT
Read Register
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 67
Page 70

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
5.4 Erasing FLASH Program Memory
The minimum eras e block is 32 wo rds or 64 b ytes. Only
through the use of an external programmer, or through
ICSP control, can larger blocks of program memory be
bulk erased. Word erase in the FLASH array is not
supported.
When initiating an erase sequence from the microcontroller itself, a blo ck of 64 bytes of program memo ry
is erased. The Most Significant 16 bits of the
TBLPTR<21:6> point to the block being erased.
TBLPTR<5:0> are ignored.
The EECON1 register comma nds the erase operation.
The EEPGD bit must be set to point to the FLASH program memory. The WREN bit must be set to enable
write operations. The F REE bit is set to select an erase
operation.
For protection, the wri te i ni tiat e s equ enc e f or EECO N2
must be used.
A long write is necessary for erasing the internal
FLASH. Instruction execution is halted while in a long
5.4.1 FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY ERASE SEQUENCE
The sequence of events for erasing a block of internal
program memory location is:
1. Load Table Pointer register with address of row
being erased.
2. Set the EECON1 register for the erase operation:
• set EEPGD bit to point to program memory;
• clear the CFGS bit to access program memory;
• set WREN bit to enable writes;
• set FREE bit to enable the erase.
3. Disable interrupt s.
4. Write 55h to EECON2.
5. Write AAh to EECON2.
6. Set the WR bit. This will begin the row erase
cycle.
7. The CPU will stall for duration of the erase
(about 2 ms using internal timer).
8. Re-enable interrupts.
write cycle. The long write will be terminated by the
internal programming timer.
EXAMPLE 5-2: ERASING A FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY ROW
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; load TBLPTR with the base
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the memory block
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the memory block
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
ERASE_ROW
ERASE_ROW
Required MOVLW 55h
Required MOVLW 55h
Sequence MOVWF EECON2 ; write 55H
Sequence MOVWF EECON2 ; write 55H
MOVWF TBLPTRL
BSF EECON1,EEPGD ; point to FLASH program memory
BSF EECON1,EEPGD ; point to FLASH program memory
BCF EECON1,CFGS ; access FLASH program memory
BCF EECON1,CFGS ; access FLASH program memory
BSF EECON1,WREN ; enable write to memory
BSF EECON1,WREN ; enable write to memory
BSF EECON1,FREE ; enable Row Erase operation
BSF EECON1,FREE ; enable Row Erase operation
BCF INTCON,GIE ; disable interrupts
BCF INTCON,GIE ; disable interrupts
MOVLW AAh
MOVLW AAh
MOVWF EECON2 ; write AAH
MOVWF EECON2 ; write AAH
BSF EECON1,WR ; start erase (CPU stall)
BSF EECON1,WR ; start erase (CPU stall)
BSF INTCON,GIE ; re-enable interrupts
BSF INTCON,GIE ; re-enable interrupts
DS39612A-page 68 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 71

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
5.5 Writing to FLASH Program Memory
The minimum programmi ng block is 4 words or 8 bytes .
Word or byte programming is not supported.
Table writes are used internally to load the holding
registers needed to program the FLASH memory.
There are 8 holding registers used by the Table Writes
for programming.
Since the Table Latch (TABLAT) is only a single byte,
the TBLWT instruction has to be executed 8 times for
each programming operation. All of the table write
operations will e ssenti ally be sh ort wr ites bec ause only
the holding registers are w ritte n. At the end of upda ting
8 registers, the EECON1 register must be w ritten to, to
start the programming operation with a long write.
The long write is necessary for programming the internal FLASH. Instruction execution is halted while in a
long write cycle. The long write will be terminated by
the internal programming timer.
The EEPROM on-chip timer controls the write time.
The write/erase voltages are generated by an on-chip
charge pump, rated to operate over the voltage range
of the device for byte or word operations.
FIGURE 5-5: TABLE WRITES TO FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
TABLAT
Write Register
8 8 8
TBLPTR = xxxxx2
TBLPTR = xxxxx0
8
TBLPTR = xxxxx1
TBLPTR = xxxxx7
Holding Register
Holding Register
Program Memory
5.5.1 FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY WRITE
SEQUENCE
The sequence of events for programming an internal
program memory location should be:
1. Read 64 bytes into RAM.
2. Update data values in RAM as necessary.
3. Load Table Pointer register with address being
erased.
4. Do the row erase procedure.
5. Load Table Pointer register with address of first
byte being written.
6. Write the first 8 bytes into the holding registers
with auto-increment.
7. Set the EECON1 register for th e write operatio n:
• set EEPGD bit to point to program memory;
• clear the CFGS bit to access program memory;
• set WREN to enable byte writes.
Holding Register
8. Disable interrupt s.
9. Write 55h to EECON2.
10. Write AAh to EECON2.
1 1. Set the WR bit. Thi s will beg in the w rite cy cl e.
12. Th e CPU wil l st all for d uration o f the w rite (abo ut
2 ms using internal timer).
13. Re-enable interrupts.
14. Repeat steps 6-14 seven times to write 64 bytes.
15. Verify the memory (table read).
This procedure will require about 18 ms to update one
row of 64 bytes of memory. An example of the required
code is given in Example 5-3.
Note: Before setting the WR bit, the Table
Pointer address needs to be within the
intended address range of the eight bytes
in the holding register.
Holding Register
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 69
Page 72

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
EXAMPLE 5-3: WRITING TO FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
MOVLW D'64 ; number of bytes in erase block
MOVWF COUNTER
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_HIGH ; point to buffer
MOVWF FSR0H
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF FSR0L
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; Load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the memory block
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
READ_BLOCK
MODIFY_WORD
ERASE_BLOCK
Required MOVWF EECON2 ; write 55H
Sequence MOVLW AAh
WRITE_BUFFER_BACK
PROGRAM_LOOP
WRITE_WORD_TO_HREGS
TBLRD*+ ; read into TABLAT, and inc
MOVF TABLAT, W ; get data
MOVWF POSTINC0 ; store data
DECFSZ COUNTER ; done?
BRA READ_BLOCK ; repeat
MOVLW DATA_ADDR_HIGH ; point to buffer
MOVWF FSR0H
MOVLW DATA_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF FSR0L
MOVLW NEW_DATA_LOW ; update buffer word
MOVWF POSTINC0
MOVLW NEW_DATA_HIGH
MOVWF INDF0
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER ; load TBLPTR with the base
MOVWF TBLPTRU ; address of the memory block
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH
MOVWF TBLPTRH
MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF TBLPTRL
BSF EECON1,EEPGD ; point to FLASH program memory
BCF EECON1,CFGS ; access FLASH program memory
BSF EECON1,WREN ; enable write to memory
BSF EECON1,FREE ; enable Row Erase operation
BCF INTCON,GIE ; disable interrupts
MOVLW 55h
MOVWF EECON2 ; write AAH
BSF EECON1,WR ; start erase (CPU stall)
BSF INTCON,GIE ; re-enable interrupts
TBLRD*- ; dummy read decrement
MOVLW 8 ; number of write buffer groups of 8 bytes
MOVWF COUNTER_HI
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_HIGH ; point to buffer
MOVWF FSR0H
MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_LOW
MOVWF FSR0L
MOVLW 8 ; number of bytes in holding register
MOVWF COUNTER
MOVFW POSTINC0, W ; get low byte of buffer data
MOVWF TABLAT ; present data to table latch
TBLWT+* ; write data, perform a short write
; to internal TBLWT holding register.
DECFSZ COUNTER ; loop until buffers are full
BRA WRITE_WORD_TO_HREGS
DS39612A-page 70 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 73

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
EXAMPLE 5-3: WRITING TO FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY (CONTINUED)
PROGRAM_MEMORY
Required MOVWF EECON2 ; write 55H
Sequence MOVLW AAh
BSF EECON1,EEPGD ; point to FLASH program memory
BCF EECON1,CFGS ; access FLASH program memory
BSF EECON1,WREN ; enable write to memory
BCF INTCON,GIE ; disable interrupts
MOVLW 55h
MOVWF EECON2 ; write AAH
BSF EECON1,WR ; start program (CPU stall)
BSF INTCON,GIE ; re-enable interrupts
DECFSZ COUNTER_HI ; loop until done
BRA PROGRAM_LOOP
BCF EECON1,WREN ; disable write to memory
5.5.2 WRITE VERIFY
Depending on the application, good programming
practice may dictate that the value written to the memory should be verified against the original value. This
should be used in applications where excessive writes
can stress bits near the specification limit.
WDT Time-ou t Reset duri ng normal ope ration. In th ese
situations, users ca n check the WRERR bit and rewri te
the location.
5.5.4 PROTECTION AGAINST SPURIOUS WRITES
To protect against spurious writes to FLASH program
5.5.3 UNEXPECTED TERMINATION OF WRITE OPERATION
If a write is termin ate d b y a n u npl anned event, such as
memory, the write initiate sequence must also be followed. See Section 24.0, “Special Features of the
CPU” for more detail.
loss of power or an unexpected RESET, the memory
location just pr ogrammed shou ld be verifi ed and rep rogrammed if needed. The WRERR bit is set when a
write operation is interrupted by a MCLR
Reset or a
5.6 FLASH Program Operation During Code Protection
See Section 24.0, “Special Features of the CPU” for
details on code prote cti on o f FLASH program memory.
TABLE 5-2: REGISTERS ASSOCIATED WITH PROGRAM FLASH MEMORY
Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TBLPTRU
TBPLTRH Program Memory Table Pointer High Byte (TBLPTR<15:8>) 0000 0000 0000 0000
TBLPTRL Program Memory Table Pointer High Byte (TBLPTR<7:0>) 0000 0000 0000 0000
TABLAT Program Memory Table Latch 0000 0000 0000 0000
INTCON GIE/GIEH PEIE/GIEL
EECON2 EEPROM Control Register 2 (not a physical register) — —
EECON1 EEPGD CFGS — FREE WRERR WREN WR
IPR2
PIR2
PIE2
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, r = reserved, - = unimplemented, read as ‘0’.
— — bit21 Program Memory Table Pointer Upper Byte
(TBLPTR<20:16>)
TMR0IE INTE RBIE TMR0IF INTF RBIF 0000 0000 0000 0000
RD xx-0 x000 uu-0 u000
— CMIP —EEIPBCLIP LVDIP TMR3IP CCP2IP ---1 1111 ---1 1111
— CMIF —EEIFBCLIF LVDIF TMR3IF CCP2IF ---0 0000 ---0 0000
— CMIE —EEIEBCLIE LVDIE TMR3IE CCP2IE ---0 0000 ---0 0000
Shaded cells are not used during FLASH/EEPROM access.
Val ue on:
POR, BOR
--00 0000 --00 0000
Value on
all other
RESETS
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 71
Page 74

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
NOTES:
DS39612A-page 72 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 75

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
6.0 EXTERNAL MEMORY INTERFACE
Note: The external memory interface is not
implemented on PIC18F6X2X (64-pin) devices.
The external memory interface is a feature of the
PIC18F8X2X devices that allows the controller to
access external memory devices (such as FLASH,
EPROM, SRAM, etc.) as program or data memory.
The physical implementation of the interface uses 27
pins. These pins are res erved for external ad dress/data
bus functions; they are multiplexed with I/O port pins on
four ports. Three I/O ports are multiplexed with the
address/data bus, while the fourth port is multiplexed
with the bus control signals. The I/O port functions are
enabled when the EBDIS bit in the MEMCON register
is set (see Register 6-1). A list of the multiplexed pins
and their functions is provided in Table 6-1.
As implemented in the PIC18F8X2X d evice s, the int erface operates in a similar manner to the external
memory interface introduced on PIC18C601/801
microcontrollers. The most notable difference is that
the interface on PIC18F8X2X devices only operates in
16-bit modes. The 8-bit mode is not supported.
For a more complete discussion of the operating
modes that use the external memory interface, refer to
Section 4.1.1, “PIC18F6X2X/8X2X Program Memory
Modes”.
6.1 Program Memory Modes and the External Memory Interface
As previously noted, PIC18F8X2X controllers are
capable of operating in any one of four Program Memory modes using combinations of on-chip and external
program memory. The functions of the multiplexe d po rt
pins depends on the Program Memory mode selected,
as well as the setting of the EBDIS bit.
In Microprocessor Mode, the external bus is always
active and the port pins have only the external bus
function.
In Microcontroller Mode, the bus is not active and
the pins have their port functions only. Writes to the
MEMCOM register are not perm itted.
In Microprocessor with Boot Block or Extended
Microcontroller Mode, the external program memory
bus shares I/O port functions on the pins. When the
device is fetching or doing table read/table write operations on the external program memory space, the
pins will have the external bus function. If the device is
fetching and accessin g inte rnal program memory locations only, the EBDIS control bit will change the pins
from external memory to I/O port functions. When
EBDIS = 0, the pins function as the external bus.
When EBDIS = 1, the pins function as I/O ports.
REGISTER 6-1: MEMCON REGISTER
R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 U-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
EBDIS
bit7 bit0
bit 7 EBDIS: External Bus Disable bit
1 = External system bus disabled, all external bus drivers are mapped as I/O ports
0 = External system bus enabled and I/O ports are disabled
bit 6 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 5-4 WAIT1:WAIT0: Table Reads and Writes Bus Cycle Wait Count bits
11 = Table reads and writes will wait 0 T
10 = Table reads and writes will wait 1 TCY
01 = Table reads and writes will wait 2 TCY
00 = Table reads and writes will wait 3 TCY
bit 3-2 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 1-0 WM1:WM0: TBLWRT Operation with 16-bit Bus bits
1x =Word Write mode: TABLAT<0> and TABLAT<1> word output, WRH active when
TABLAT<1> writte n
01 =Byte Select mode: TABLAT data copied on both MS and LS Byte, WRH
will activate
00 = Byte Write mode: TABLA T data copied on both MS and LS Byte, WRH or WRL will activate
Note: The MEMCON register is unimplemented and reads all ‘0’s when the device is in
—WAIT1WAIT0— —WM1WM0
Microcontroller mode.
CY
and (UB or LB)
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 73
Page 76

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
If the device fetches or accesses external memory
while EBDIS = 1, the pins will switch to external bus. If
the EBDIS bit is set by a program executing from
external memory, the action of setting the bit will be
delayed until the program branches into the internal
memory. At that time, the pins will change from
external bus to I/O ports.
When the device is exec uting out of internal memory
(EBDIS = 0) in Microprocessor with Boot Block mode
or Extended Microcontroll er mode, the control signals
will NOT be active. They will go to a state where th e
AD<15:0> and A<19:16> are tri-state; the CE
WRH
, WRL, UB and LB signals are ‘1’, and ALE an d
BA0 are ‘0’.
TABLE 6-1: PIC18F8X2X EXTERNAL BUS - I/O PORT FUNCTIONS
Name Port Bit Function
RD0/AD0 PORTD bit 0 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 0 or Data bit 0
RD1/AD1 PORTD bit 1 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 1 or Data bit 1
RD2/AD2 PORTD bit 2 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 2 or Data bit 2
RD3/AD3 PORTD bit 3 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 3 or Data bit 3
RD4/AD4 PORTD bit 4 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 4 or Data bit 4
RD5/AD5 PORTD bit 5 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 5 or Data bit 5
RD6/AD6 PORTD bit 6 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 6 or Data bit 6
RD7/AD7 PORTD bit 7 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 7 or Data bit 7
RE0/AD8 PORTE bit 0 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 8 or Data bit 8
RE1/AD9 PORTE bit 1 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 9 or Data bit 9
RE2/AD10 PORTE b it 2 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 10 or Data bit 10
RE3/AD11 PORTE bit 3 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 11 or Data bit 11
RE4/AD12 PORTE b it 4 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 12 or Data bit 12
RE5/AD13 PORTE b it 5 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 13 or Data bit 13
RE6/AD14 PORTE b it 6 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 14 or Data bit 14
RE7/AD15 PORTE b it 7 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 15 or Data bit 15
RH0/A16 PORTH bit 0 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 16
RH1/A17 PORTH bit 1 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 17
RH2/A18 PORTH bit 2 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 18
RH3/A19 PORTH bit 3 Input/Output or System Bus Address bit 19
RJ0/ALE PORTJ bit 0 Input/Output or System Bus Address Latch Enable (ALE) Control pin
RJ1/OE
RJ2/WRL
RJ3/WRH
RJ4/BA0 PORTJ bit 4 Input/Output or System Bus Byte Address bit 0
RJ5/CE
RJ6/LB
RJ7/UB
PORTJ bit 1 Input/Output or System Bus Output Enable (OE) Control pin
PORTJ bit 2 Input/Out put or System Bus Write Low (WRL) Control pin
PORTJ bit 3 Input/Output or System Bus Write High (WRH) Control pin
PORTJ bit 5 Input/Output or System Bus Chip Enable (CE) Control pin
PORTJ bit 6 Input/Output or System Bus Lower Byte Enable (LB) Control pin
PORTJ bit 7 Input/Output or System Bus Upper Byte Enable (UB) Control pin
, OE,
DS39612A-page 74 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 77

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
6.2 16-bit Mode
The external memory interface implemented in
PIC18F8X2X devices operates only in 16-bit mode.
The mode selection is not software configurable but is
programmed via the configuration bits.
The WM1:WM0 bits in the MEMCON register determine three types of connections in 16-bit mode. They
are referred to as:
• 16-bit Byte Write
• 16-bit Word Write
• 16-bit Byte Select
These three different configurations allow the designer
maximum flexibility in using 8-bit and 16-bit memory
devices.
For all 16-bit modes, the Address Latch Enable (ALE)
pin indicates that the address b its A15:A0 are availabl e
on the external memory interface bus. Following the
address latch, the Output Enable signal (OE
enable both bytes of program memory at once to form
a 16-bit instruction word. The Chip Enable signal (CE)
is active at any time that the microcontroller accesses
external memory, whether reading or writing; it is inactive (asserted high) whenever the device is in SLEEP
mode.
) will
In Byte Select mode, JEDEC standard FLASH memories will require BA0 for the byte address line and one
I/O line, to select between Byte and Word mode. The
other 16-bit modes do not need BA0. JEDEC st a nda rd
static RAM memo ri es wil l us e t he U B
or LB signals for
byte selection.
6.2.1 16-BIT BYTE WRITE MODE
Figure 6-1 shows an example of 16-bit Byte Write
mode for PIC18F8X2X devices. This mode is used for
two separate 8-bit memories connected for 16-bit operation. This generally includes basic EPROM and
FLASH devices. It allows table writes to byte-wide
external memories.
During a TBLWT instruction cycle, the TABLAT data is
presented on the upper and lower bytes of the
AD15:AD0 bus. The appropriate WRH
line is strobed on the LSb of the TBLPTR.
or WRL control
FIGURE 6-1: 16-BIT BYTE WRITE MODE EXAMPLE
D<7:0>
PIC18F8X2X
AD<7:0>
AD<15:8>
ALE
A<19:16>
CE
OE
WRH
WRL
Note 1: This signal only applies to table writes. See Section 5.1, “Table Reads and Writes”.
373
373
A<19:0>
D<15:8>
A<x:0>
D<7:0>
CE
(MSB)
OE OEWR
(LSB)
A<x:0>
D<7:0>
(1)
WR
Address Bus
Data Bus
Control Lines
D<7:0>
CE
(1)
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 75
Page 78

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
6.2.2 16-BIT WORD WRITE MODE
Figure 6-2 shows an example of 16-bit Word Write
mode for PIC18F8X2X devices. This mode is used for
word-wide memories which includes some of the
EPROM and FLASH type memo ries. T his mod e allo ws
opcode fetches and t a ble reads from all forms of 1 6-b it
memory, and table writes to any type of word-wide
external memories. This method makes a distinction
between TBLWT cycles to even or odd addresses.
During a TBLWT cycle to an even address
(TBLPTR<0> = 0), the TABLAT data is transferred to a
holding latch and the external address data bus is tri-
During a TBLWT cycle to an odd address
(TBLPTR<0> = 1), the TA BLAT data is presented on
the upper byte of the AD15:AD0 bus. The contents of
the holding latch are pre sented on the lower byte of the
AD15:AD0 bus.
The WRH
WRL
the LSbit of the TBLPTR but it is left unconnected.
Instead, the UB
bytes. The obvious limitation to this method is that the
table write must be done in pairs on a specific word
boundary to correctly write a word location.
stated for the data portion of the bus cycle. No write
signals are activated.
FIGURE 6-2: 16-BIT WORD WRITE MODE EXAMPLE
PIC18F8X2X
AD<7:0>
AD<15:8>
ALE
A<19:16>
CE
OE
WRH
373
373
A<20:1>
D<15:0>
signal is strobed for each write cycle; the
pin is unused. The signal on the BA0 pi n indicates
and LB signals are active to s elect both
A<x:0>
D<15:0>
Address Bus
Data Bus
Control Lines
JEDEC Word
EPROM Memory
WR
(1)
CE
OE
Note 1: This signal only applies to table writes. See Section 5.1, “Table Reads and Writes”.
DS39612A-page 76 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 79

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
6.2.3 16-BIT BYTE SELECT MODE
Figure 6-3 shows an example of 16-bit Byte Select
mode for PIC18F8X2X devices. Thi s mode allows tabl e
write operations to word-wide external memories with
byte selection capability. This generally includes both
word-wide FLASH and SRAM devices.
During a TBLWT cycle, the TABLAT data is prese nted
FLASH and SRAM devices use different control signal
combinations to implement Byte Select mode. JEDEC
standard FLASH memo ries req uire th at a co ntrolle r I/O
port pin be connected to the memory’s BY TE/WORD
pin to provide the select si gna l. The y als o use the BA0
signal from the controller as a byte address. JEDEC
standard static RAM memories, on the other hand, use
the UB
on the upper an d lower byte of th e AD1 5:AD0 b us. Th e
signal is strobed for each write cycle; the WRL
WRH
pin is not used. The BA0 or UB/LB signals are used to
select the byte to be written based on the Least
Significant bit of the TBLPTR register.
FIGURE 6-3: 16-BIT BYTE SELECT MODE EXAMPLE
PIC18F8X2X
AD<7:0>
AD<15:8>
ALE
A<19:16>
OE
WRH
WRL
BA0
I/O
LB
UB
373
373
A<20:1>
138
A<20:1>
(2)
or LB signals to select the byte.
A<x:1>
CE
A0
BYTE/WORD
A<x:1>
CE
LB
UB
JEDEC Word
FLASH Memory
D<15:0>
OE
JEDEC Word
SRAM Memory
D<15:0>
(1)
WR
OE
WR
(1)
D<15:0>
D<15:0>
Address Bus
Data Bus
Control Lines
Note 1: This signal only applies to table writes. See Section 5.1, “Table Reads and Writes”.
2: Demultiplexing is only required when multiple memory devices are accessed.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 77
Page 80

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
6.2.4 16-BIT MODE TIMING
The presentation of control signals on the external
memory bus is different for the various operating
modes. Typical signal timing diagrams are shown in
Figure 6-4 through Figure6-6.
FIGURE 6-4: EXTERNAL MEMORY BUS TIMING FOR TBLRD (MICROPROCESSOR MODE)
Apparent Q
Actual Q
A<19:16>
AD<15:0>
BA0
ALE
OE
WRH
WRL
CE
Memory
Cycle
Instruction
Execution
Q2Q1 Q3 Q4 Q2Q1 Q3 Q4 Q4Q4 Q4 Q4
Q2Q1 Q3 Q4 Q2Q1 Q3 Q4 Q2Q1 Q3 Q4
00h
3AABh
‘1’ ‘1’
‘1’
‘0’
Opcode Fetch
MOVLW 55h
from 007556h
TBLRD Cycle1
0E55h
CF33h
from 199E67h
TBLRD Cycle2
0Ch
Table Read
of 92h
9256h
1 T
‘1’
‘0’
CY Wait
FIGURE 6-5: EXTERNAL MEMORY BUS TIMING FOR
TBLRD
(EXTENDED MICROCONTROLLER MODE)
Q2Q1 Q3 Q4 Q2Q1 Q3 Q4
A<19:16>
AD<15:0>
CE
ALE
OE
Memory
Cycle
Instruction
Execution
DS39612A-page 78 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Opcode Fetch Opcode Fetch Opcode Fetch
TBLRD*
from 000100h
INST(PC-2)
MOVLW 55h
from 000102h
TBLRD Cycle1
Q2Q1 Q3 Q4
0Ch
CF33h
TBLRD 92h
from 199E67h
TBLRD Cycle2
Q2Q1 Q3 Q4
9256h
ADDLW 55h
from 000104h
MOVLW
Page 81

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 6-6: EXTERNAL MEMORY BUS TIMING FOR SLEEP (MICROPROCESSOR MODE)
A<19:16>
AD<15:0>
CE
ALE
OE
Memory
Cycle
Instruction
Execution
Q2Q1 Q3 Q4 Q2Q1 Q3 Q4
00h
3AAAh
Opcode Fetch
SLEEP
from 007554h
INST(PC-2)
0003h
00h
3AABh
Opcode Fetch
MOVLW 55h
from 007556h
SLEEP
0E55h
Q1
SLEEP Mode,
Bus Inactive
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 79
Page 82

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
NOTES:
DS39612A-page 80 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 83

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
7.0 DATA EEPROM MEMORY
The data EEPROM is re adable and writable durin g normal operation over the entire V
memory is not directly mapped in the register file
space. Instead, it is indirectly addressed through the
Special Function Registers (SFR).
There are five SFRs used to read and write the
program and data EEPROM memory. These registers
are:
• EECON1
• EECON2
• EEDATA
• EEADRH
• EEADR
The EEPROM data memory allows byte read and write.
When interfacing to the data memory block, EEDATA
holds the 8-bit data for read/write. EEADR and
EEADRH hold the address of the EEPROM location
being accessed. These devices have 1024 bytes of
data EEPROM with an address range from 00h to
3FFh.
The EEPROM data memory is rated for high erase/
write cycles. A byt e write autom atically er ases the loc ation and writes the new data (erase-before-write). The
write time is controlled by an on-chip timer. The write
time will vary with vo ltag e and tempe rat ure, as wel l as
from chip to chip. Please refer to parameter D122
(Section 27.0, “Electrical Characteristics”) for exact
limits.
DD range. The data
7.1 EEADR and EEADRH
The address register pair can address up to a maximum of 1024 bytes of data EEPROM. The two MSbits
of the address are stored in EEADRH, while the
remaining eight LSbits are stored in EEADR. The six
Most Significant bits of EEADRH are unused and are
read as ‘0’.
7.2 EECON1 and EECON2 Registers
EECON1 is the control register for EEPROM memory
accesses.
EECON2 is not a physical register. Reading EECON2
will read all ‘0’s. The EECON2 register is used
exclusively in the EEPROM write sequence.
Control bits RD and WR initiate read and write operations, respectively. These bits cannot be cleared, only
set in soft ware. They are clea red in hardware at the
completion of the read or write operation. The inability
to clear the WR bit in software prevents the accidental
or premature termination of a write operation.
The WREN bit, when set, will allow a write operation.
On power-up, the WREN bit is c lear . Th e WRERR bit is
set when a write operation is interrupted by a MCLR
Reset or a WDT Time-out Reset during normal
operation. In these situations, the user can check the
WRERR bit and rewrite the location. It is necessary to
reload the data and address regi sters (EEDATA a nd
EEADR) due to the RESET condition forcing the
contents of the registers to zero.
Note: Interrupt flag bit, EEIF in the PIR2 registe r ,
is set when write is complete. It must be
cleared in software.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 81
Page 84

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
REGISTER 7-1: EECON1 REGISTER (ADDRESS FA6h)
R/W-x R/W-x U-0 R/W-0 R/W-x R/W-0 R/S-0 R/S-0
EEPGD CFGS — FREE WRERR WREN WR RD
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 EEPGD: FLASH Program/Data EEPROM Memory Select bit
1 = Access FLASH program memory
0 = Access data EEPROM memory
bit 6 CFGS: FLASH Program/Data EEPROM or Configuration Select bit
1 = Access Configuration or Calibration registers
0 = Access FLASH program or data EEPROM memory
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 FREE: FLASH Row Erase Enable bit
1 = Erase the program memory row addressed by TBLPTR on the next WR command
(cleared by completion of erase operation)
0 = Perform write only
bit 3 WRERR: FLASH Program/Data EEPROM Error Flag bit
1 = A write operation is prematurely terminated
(any MCLR
0 = The write operation completed
Note: When a WRERR occurs, the EEPGD or FREE bits are not cleared. This allows
or any WDT Reset during self-timed programming in normal operation)
tracing of the error condition.
bit 2 WREN: FLASH Program/Data EEPROM Write Enable bit
1 = Allows write cycles to FLASH program/data EEPROM
0 = Inhibits write cycles to FLASH program/data EEPROM
bit 1 WR: Write Control bit
1 = Initiates a data EEPROM erase/write cycle or a program memory erase cycle or write cycle.
(The operation is self-tim ed and the bit is clea red by hardware on ce write is complete. The
WR bit can only be set (not cleared) in software.)
0 = Write cycle to the EEPROM is complete
bit 0 RD: Read Control bit
1 = Initiates an EEPROM read
(Read takes one cyc le. RD is cleared in ha rdware. The RD bit can only be set (not cleare d)
in software. RD bit cannot be set when EEPGD = 1.)
0 = Does not initiate an EEPROM read
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
DS39612A-page 82 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 85

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
7.3 Reading the Data EEPROM Memory
T o read a d ata memory loca tion, the user must write the
address to the EEADRH:EEADR register pair , clear the
EEPGD control bit (EECON1<7>), clear the CFGS
EXAMPLE 7-1: DATA EEPROM READ
MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDRH ;
MOVWF EEADRH ; Upper bits of Data Memory Address to read
MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDR ;
MOVWF EEADR ; Lower bits of Data Memory Address to read
BCF EECON1, EEPGD ; Point to DATA memory
BCF EECON1, CFGS ; Access EEPROM
BSF EECON1, RD ; EEPROM Read
MOVF EEDATA, W ; W = EEDATA
7.4 Writing to the Data EEPROM Memory
To write an EEPROM data location, the address must
first be written to the EEADRH:EEADR register pair
and the data written to the EEDATA register. Then the
sequence in Example7-2 must be followed to initiate
the write cycle.
The write will not initiate if the above sequence is not
exactly followed (write 55h to EECON2, write AAh to
EECON2, then set WR bit) for each byte. It is strongly
recommended that interrupts be disabled during this
code segment.
Additionally, the WREN bit in EECON1 must be set to
enable writes. This mechanism prevents accidental
writes to data EEPROM due to unexpected code
execution (i.e., runaway programs). The WREN bit
control bit (EECON1<6>), and then set the RD control
bit (EECON1<0>). The data is available for the very
next instruction cycle; therefore, the EEDATA register
can be read by the next instruction. EEDATA will hold
this value until another read operation or until it is
written to by the user (during a write operation).
should be kept clear at all times except when updating
the EEPROM. The WREN bit is not cleared
by hardware
After a write sequence has been initiated, EECON1,
EEADRH, EEADR and EEDATA cannot be modified.
The WR bit will be inhibited from being set unless the
WREN bit is set. The WREN bit must be set on a previous instruction. Both WR and WREN cannot be set
with the same instruction.
At the completion of the write cycle, the WR bit is
cleared in hardware and th e EEPROM Write Complete
Interrupt Flag bit (EEIF) is set. The user may either
enable this interrupt or poll this bit. EEIF must be
cleared by software.
EXAMPLE 7-2: DATA EEPROM WRITE
MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDRH ;
MOVWF EEADRH ; Upper bits of Data Memory Address to write
MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDR ;
MOVWF EEADR ; Lower bits of Data Memory Address to write
MOVLW DATA_EE_DATA ;
MOVWF EEDATA ; Data Memory Value to write
BCF EECON1, EEPGD ; Point to DATA memory
BCF EECON1,CFGS ; Access EEPROM
Required MOVWF EECON2 ; Write 55h
Sequence MOVLW AAh ;
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 83
BSF EECON1, WREN ; Enable writes
BCF INTCON, GIE ; Disable Interrupts
MOVLW 55h ;
MOVWF EECON2 ; Write AAh
BSF EECON1, WR ; Set WR bit to begin write
BSF INTCON, GIE ; Enable Interrupts
; User code execution
BCF EECON1, WREN ; Disable writes on write complete (EEIF set)
Page 86

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
7.5 Write Verify
Depending on the application, good programming
practice may dictate that the value written to the memory should be verified against the original value. This
should be used in applications where excessive writes
can stress bits near the specification limit.
7.6 Protection Against Spurious Write
There are conditions when the device may not want to
write to the data EEPROM memory. To protect against
spurious EEPROM writes, various mechanisms have
been built -in. On powe r-up, the WR EN bit is cl eared.
Also, the Power-up Timer (72 ms duration) prevents
EEPROM write.
The write initiate se quence and the WREN bit together
help prevent an accidental write during brown-out,
power glitch, or software malfunction.
7.7 Operation During Code Protect
Data EEPROM memory has its own code protect
mechanism. External read and write operations are
disabled if either of these mechanisms are enabled.
The microcontroller i tself can both re ad and wr ite to the
internal data EEPROM regardless of the state of the
code protect configuration bit. Refer to Section 24.0,
“Special Features of the CPU” for additional
information.
7.8 Using the Data EEPROM
The data EEPROM is a hi gh en dura nc e, byt e addressable array that has been optimized for the storage of
frequently changing information (e.g., program variables or other data that are updated often). Frequently
changing values will typically be updated more often
than specification D1 24. If this is not the ca se, an array
refresh must be performed. For this reason, variables
that change infrequently (such as constants, IDs, calibration, etc.) should be stored in FLASH program
memory.
A simple data EEPROM refresh routine is shown in
Example 7-3.
Note: If data EEPROM is only used to store con-
stants and/or data that changes rarely, an
array refresh is likely not required. See
specification D124.
EXAMPLE 7-3: DATA EEPROM REFRESH ROUTINE
CLRF EEADR ; Start at address 0
CLRF EEADRH ;
BCF EECON1,CFGS ; Set for memory
BCF EECON1,EEPGD ; Set for Data EEPROM
BCF INTCON,GIE ; Disable interrupts
Loop ; Loop to refresh array
BSF EECON1,WREN ; Enable writes
BSF EECON1,RD ; Read current address
MOVLW 55h ;
MOVWF EECON2 ; Write 55h
MOVLW AAh ;
MOVWF EECON2 ; Write AAh
BSF EECON1,WR ; Set WR bit to begin write
BTFSC EECON1,WR ; Wait for write to complete
BRA $-2
INCFSZ EEADR,F ; Increment address
BRA Loop ; Not zero, do it again
INCFSZ EEADRH, F ; Increment the high address
BRA Loop ; Not zero, do it again
BCF EECON1,WREN ; Disable writes
BSF INTCON,GIE ; Enable interrupts
DS39612A-page 84 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 87

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
TABLE 7-1: REGISTERS ASSOCIATED WITH DATA EEPROM MEMORY
Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
INTCON GIE/GIEH PEIE/GIEL
EEADRH
EEADR EEPROM Address Register 0000 0000 0000 0000
EEDATA EEPROM Data Register 0000 0000 0000 0000
EECON2 EEPROM Control Register 2 (not a physical register) — —
EECON1 EEPGD
IPR2
PIR2
PIE2
Legend: x = unknown, u = unchanged, r = reserved, - = unimplemented, read as ‘0’.
— — — — — — EE Addr Register High ---- --00 ---- --00
CFGS — FREE WRERR WREN WR RD xx-0 x000 uu-0 u000
— CMIP —EEIPBCLIP LVDIP TMR3IP CCP2IP ---1 1111 ---1 1111
— CMIF —EEIFBCLIF LVDIF TMR3IF CCP2IF ---0 0000 ---0 0000
— CMIE —EEIEBCLIE LVDIE TMR3IE CCP2IE ---0 0000 ---0 0000
Shaded cells are not used during FLASH/EEPROM access.
TMR0IE INT0IE RBIE TMR0IF INT0IF RBIF 0000 0000 0000 0000
Value on:
POR, BOR
Val ue on
all other
RESETS
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 85
Page 88

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
NOTES:
DS39612A-page 86 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 89

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
8.0 8 X 8 HARDWARE MULTIPLIER
8.1 Introduction
An 8 x 8 hardware multiplier is included in the ALU of
the PIC18F6X 2X/8X2X devices . By making the multiply a hardware operation, it completes in a single
instruction cycl e. This is an unsigned mul tiply that gives
a 16-bit result. The result is store d in the 16-b it produc t
register pair (PR ODH:PRODL). The m ultip lier d oes not
affect any flags in the ALUSTA register.
Making the 8 x 8 multiplier execute in a single cycle
gives the following advantages:
• Higher computational throughput
• Reduces code size requ irements for multiply
algorithms
The performance increas e allows the device to be used
in applications previously reserved for Digital Signal
Processors.
Ta ble 8-1 shows a perf ormance comparison be tween
enhanced devices using the sin gle cycle hardw are multiply, and performing the same function without the
hardware multiply.
8.2 Operation
Example 8-1 shows the sequence to do an 8 x 8
unsigned multiply. Only one instruction is required
when one argument of the multiply is already loaded in
the WREG register.
Example 8-2 shows the sequence t o do an 8 x 8 signed
multiply. To account for the sign bits of the arguments,
each argument’s Most Significant bit (MSb) is tested
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 87
Page 90

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
Example 8-3 shows the sequence to do a 16 x 16
unsigned multiply. Equation 8-1 shows the algorithm
that is used. The 32-bit re sult is st ored in four re gisters,
RES3:RES0.
EQUATION 8-1: 16 x 16 UNSIGNED
MULTIPLICATION
ALGORITHM
RES3:RES0 = ARG1H:ARG1L • ARG2H:ARG2L
= (ARG1H
(ARG1H
(ARG1L
(ARG1L
• ARG2H • 2
• ARG2L • 2
• ARG2H • 2
• ARG2L)
16
) +
8
) +
8
) +
EXAMPLE 8-3: 16 x 16 UNSIGNED
MULTIPLY ROUTINE
MOVF ARG1L, W
MULWF ARG2L ; ARG1L * ARG2L ->
MOVFF PRODH, RES1 ;
MOVFF PRODL, RES0 ;
;
MOVF ARG1H, W
MULWF ARG2H ; ARG1H * ARG2H ->
MOVFF PRODH, RES3 ;
MOVFF PRODL, RES2 ;
;
MOVF ARG1L, W
MULWF ARG2H ; ARG1L * ARG2H ->
MOVF PRODL, W ;
ADDWF RES1, F ; Add cross
MOVF PRODH, W ; products
ADDWFC RES2, F ;
CLRF WREG ;
ADDWFC RES3, F ;
;
MOVF ARG1H, W ;
MULWF ARG2L ; ARG1H * ARG2L ->
MOVF PRODL, W ;
ADDWF RES1, F ; Add cross
MOVF PRODH, W ; products
ADDWFC RES2, F ;
CLRF WREG ;
ADDWFC RES3, F ;
Example 8-4 shows the sequence to do a 16 x 16
signed multiply. Equation 8-2 shows the algorithm
used. The 32-bit result is stored in four registers,
RES3:RES0. To account for the sign bits of the arguments, each argum ent p ai rs’ M ost S ign ificant bit (MSb)
is tested and the appropriate subtractions are done.
; PRODH:PRODL
; PRODH:PRODL
; PRODH:PRODL
; PRODH:PRODL
EQUATION 8-2: 16 x 16 SIGNED
MULTIPLICATION
ALGORITHM
RES3:RES0
= ARG1H:ARG1L
= (ARG1H
(ARG1H
(ARG1L
(ARG1L
• ARG2H<7> • ARG1H:ARG1L • 2
(-1
• ARG1H<7> • ARG2H:ARG2L • 2
(-1
• ARG2H:ARG2L
• ARG2H • 2
• ARG2L • 2
• ARG2H • 2
• ARG2L) +
16
) +
8
) +
8
) +
EXAMPLE 8-4: 16 x 16 SIGNED
MULTIPLY ROUTINE
MOVF ARG1L, W
MULWF ARG2L ; ARG1L * ARG2L ->
MOVFF PRODH, RES1 ;
MOVFF PRODL, RES0 ;
;
MOVF ARG1H, W
MULWF ARG2H ; ARG1H * ARG2H ->
MOVFF PRODH, RES3 ;
MOVFF PRODL, RES2 ;
;
MOVF ARG1L, W
MULWF ARG2H ; ARG1L * ARG2H ->
MOVF PRODL, W ;
ADDWF RES1, F ; Add cross
MOVF PRODH, W ; products
ADDWFC RES2, F ;
CLRF WREG ;
ADDWFC RES3, F ;
;
MOVF ARG1H, W ;
MULWF ARG2L ; ARG1H * ARG2L ->
MOVF PRODL, W ;
ADDWF RES1, F ; Add cross
MOVF PRODH, W ; products
ADDWFC RES2, F ;
CLRF WREG ;
ADDWFC RES3, F ;
;
BTFSS ARG2H, 7 ; ARG2H:ARG2L neg?
BRA SIGN_ARG1 ; no, check ARG1
MOVF ARG1L, W ;
SUBWF RES2 ;
MOVF ARG1H, W ;
SUBWFB RES3
;
SIGN_ARG1
BTFSS ARG1H, 7 ; ARG1H:ARG1L neg?
BRA CONT_CODE ; no, done
MOVF ARG2L, W ;
SUBWF RES2 ;
MOVF ARG2H, W ;
SUBWFB RES3
;
CONT_CODE
:
; PRODH:PRODL
; PRODH:PRODL
; PRODH:PRODL
; PRODH:PRODL
16
) +
16
)
DS39612A-page 88 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 91

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
9.0 INTERRUPTS
The PIC18F6X2X/8X2X devic es have multiple in terrupt
sources and an interrupt priority feature that allows
each interrupt source to be assigned a high or a low priority level. The high priority interrupt vector is at
000008h, while the low priority interrupt vector is at
000018h. High priorit y interrupt event s will overrid e any
low priority interrupts that may be in progress.
There are t hirteen r egisters which are used to c ontrol
interrupt operation. They are:
• RCON
•INTCON
• INTCON2
• INTCON3
• PIR1, PIR2, PIR3
• PIE1, PIE2, PIE3
• IPR1, IPR2, IPR3
It is recommended that the Microchip header files sup-
plied with MPLAB
names in these registers. This allows the assembler/
compiler to automatical ly ta ke care of the pla ceme nt of
these bits within the specified register.
Each interrupt source has three bits to control its
operation. The functions of these bits are:
• Flag bit to indicate that an interrupt event
occurred
• Enable bit that allows program execution to
branch to the interrupt vector address when the
flag bit is set
• Priority bit to select high priority or low priority
The interrupt priority feature is enabled by setting the
IPEN bit (RCON<7>). When interrupt priority is
enabled, there are two bits which enable in terrupt s gl obally. Setting the GIEH bit (INTCON<7>) enables all
interrupts that hav e the priority bit set. Setting the GIEL
bit (INTCON<6>) enables all interrupts that have the
priority bit cleared. When the interrupt flag, enable bit
and appropriate global interrupt enable bit are set, the
interrupt will vec tor imm ediat ely to addre ss 00 0008h or
000018h, depending on the priority level. Individual
interrupts can be disabled through their corresponding
enable bits.
®
IDE be used for the symbolic bit
When the IPEN bit is cleared (default state), the interrupt priority feature is disabled and interrupts are
compatible with PICmicro
patibility mode, th e interrupt priority bits for each sourc e
have no effect. INTCON<6> is the PEIE bit which
enables/disables all peripheral interrupt sources.
INTCON<7> is the GIE bit which enables/disables all
interrupt sources. All interrupts branch to address
000008h in Compatibility mode.
When an interrupt is responded to, the global interrupt
enable bit is cleared to disable further interrupts. If the
IPEN bit is cleared, this is the GIE bit. If interru pt priority
levels are used, this wi ll be either the GIEH or G IEL bit.
High priority interrupt sources can interrupt a low
priority interrupt.
The return address is pushed onto the stack and the
PC is loaded with the interrupt vector address
(000008h or 000018h). Once in the Interrupt Service
Routine, the source(s) of the interrupt can be determined by polling the interrupt flag bits. The interrupt
flag bits must be cleared in s oftware be fore re-enab ling
interrupts to avoid recursive interrupts.
The “return from interrupt” instruction, RETFIE, exits
the interrupt routine and set s the GIE bit (GIEH or GI EL
if priority levels are used) which re-enables interrupts.
For external interrupt events, such as the INT pins or
the PORTB input chang e interrupt, the i nterrupt latenc y
will be three to four instruction cycles. The exact
latency is the same for one or two-cycle instructions.
Individual interrupt flag bits are set regardless of the
status of their corresponding enable bit or the GIE bit.
®
mid-range device s. In Com-
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 89
Page 92

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
FIGURE 9-1: INTERRUPT LOGIC
Peripheral Interrupt Flag bit
Peripheral Interrupt Enable bit
Peripheral Interrupt Priority bit
TMR1IF
TMR1IE
TMR1IP
XXXXIF
XXXXIE
XXXXIP
High Priority Interrupt Generation
Low Priority Interrupt Generation
Peripheral Interrupt Flag bit
Peripheral Interrupt Enable bit
Peripheral Interrupt Priority bit
TMR1IF
TMR1IE
TMR1IP
XXXXIF
XXXXIE
XXXXIP
Additional Peripheral Interrupts
Additional Peripheral Interrupts
TMR0IF
TMR0IE
TMR0IP
RBIF
RBIE
RBIP
INT1IF
INT1IE
INT1IP
INT2IF
INT2IE
INT2IP
IPE
TMR0IF
TMR0IE
TMR0IP
INT0IF
INT0IE
INT1IF
INT1IE
INT1IP
INT2IF
INT2IE
INT2IP
IPEN
GIEL/PEIE
RBIF
RBIE
RBIP
IPEN
Wake-up if in SLEEP mode
GIEL/PEIE
GIE/GEIH
Interrupt to CPU
Vector to Location
0008h
GIEH/GIE
Interrupt to CPU
Vector to Location
0018h
DS39612A-page 90 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 93

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
9.1 INTCON Registers
The INTCON registers are readable and writable
registers which c ontai n various enable, priority a nd flag
bits.
REGISTER 9-1: INTCON REGISTER
R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-x
GIE/GIEH PEIE/GIEL TMR0IE INT0IE RBIE TMR0IF INT0IF RBIF
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 GIE/GIEH: Global Interrupt Enable bit
When IPEN (RCON<7>) =
1 = Enables all unmasked interrupts
0 = Disables all interrupts
When IPEN (RCON<7>) =
1 = Enables all high priority interrupts
0 = Disables all interrupts
bit 6 PEIE/GIEL: Peripheral Interrupt Enable bit
When IPEN (RCON<7>) =
1 = Enables all unmasked peripheral interrupts
0 = Disables all peripheral interrupts
When IPEN (RCON<7>) =
1 = Enables all low priority peripheral interrupts
0 = Disables all low priority peripheral interrupts
bit 5 TMR0IE: TMR0 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the TMR0 overflow interrupt
0 = Disables the TMR0 overflow interrupt
bit 4 INT0IE: INT0 External Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the INT0 external interrupt
0 = Disables the INT0 external interrupt
bit 3 RBIE: RB Port Change Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the RB port change interrupt
0 = Disables the RB port change interrupt
bit 2 TMR0IF: TMR0 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR0 register has overflowed (must be cleared in software)
0 = TMR0 register did not overflow
bit 1 INT0IF: INT0 External Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The INT0 external interrupt occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = The INT0 external interrupt did not occur
bit 0 RBIF: RB Port Change Interrupt Flag bit
1 = At least one of the RB7:RB4 pins changed state (must be cleared in software)
0 = None of the RB7:RB4 pins have changed state
Note: A mismatch condition will continue to set this bit. Reading PORTB will end the
mismatch condition and allow the bit to be cleared.
0:
1:
0:
1:
Note: Interrupt flag bits are s et when an i nter rupt
condition occurs, rega rdless of the state of
its corresponding enable bit or the global
enable bit. User software should ensure
the appropriate interrupt flag bits are clear
prior to enabling an interrupt. This feature
allows for software polling.
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 91
Page 94

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
REGISTER 9-2: INTCON2 REGISTER
R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1
RBPU INTEDG0 INTEDG1 INTEDG2 INTEDG3 TMR0IP INT3IP RBIP
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 RBPU
bit 6 INTEDG0: External Interrupt 0 Edge Select bit
bit 5 INTEDG1: External Interrupt 1 Edge Select bit
bit 4 INTEDG2: External Interrupt 2 Edge Select bit
bit 3 INTEDG3: External Interrupt 3 Edge Select bit
bit 2 TMR0IP: TMR0 Overflow Interrupt Priority bit
bit 1 INT3IP: INT3 External Interrupt Priority bit
bit 0 RBIP: RB Port Change Interrupt Priority bit
: PORTB Pull-up Enable bit
1 = All PORTB pull-ups are disabled
0 = PORTB pull-ups are enabled by individual port latch values
1 = Interrupt on rising edge
0 = Interrupt on falling edge
1 = Interrupt on rising edge
0 = Interrupt on falling edge
1 = Interrupt on rising edge
0 = Interrupt on falling edge
1 = Interrupt on rising edge
0 = Interrupt on falling edge
1 = High priority
0 = Low priority
1 = High priority
0 = Low priority
1 = High priority
0 = Low priority
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
Note: Interrupt flag bits are set when an interr upt c ond iti on oc curs , rega rdle ss of the st a te
of its correspo nding en abl e bit or the globa l ena ble bi t. U ser so ftware s hould ensu re
the appropriate interrup t flag bits are clear prior to enab ling an interrupt. T his featu re
allows for software polling.
DS39612A-page 92 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 95

REGISTER 9-3: INTCON3 REGISTER
R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
INT2IP INT1IP INT3IE INT2IE INT1IE INT3IF INT2IF INT1IF
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 INT2IP: INT2 External Interrupt Priority bit
1 = High priority
0 = Low priority
bit 6 INT1IP: INT1 External Interrupt Priority bit
1 = High priority
0 = Low priority
bit 5 INT3IE: INT3 External Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the INT3 external interrupt
0 = Disables the INT3 external interrupt
bit 4 INT2IE: INT2 External Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the INT2 external interrupt
0 = Disables the INT2 external interrupt
bit 3 INT1IE: INT1 External Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the INT1 external interrupt
0 = Disables the INT1 external interrupt
bit 2 INT3IF: INT3 External Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The INT3 external interrupt occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = The INT3 external interrupt did not occur
bit 1 INT2IF: INT2 External Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The INT2 external interrupt occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = The INT2 external interrupt did not occur
bit 0 INT1IF: INT1 External Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The INT1 external interrupt occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = The INT1 external interrupt did not occur
PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
Legend: Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
Note: Interrupt flag bits are set when an interr upt c ond iti on oc c urs , rega rdle ss of the state
of its correspo nding en abl e bit or the globa l ena ble bi t. U ser so ftware s hould ensu re
the appropriate interrup t flag bits are clear prior to enab ling an interrupt. T his featu re
allows for software polling.
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 93
Page 96

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
9.2 PIR Registers
The PIR registers conta in the ind ividu al flag bi ts fo r the
peripheral interrupts. Due to the number of peripheral
interrupt sources, there are three Peripheral Interrupt
Flag registers (PIR1, PIR2 and PIR3).
Note 1: Interrupt flag bits are set when an interru pt
condition occurs, regardl ess of the state of
its corresponding enable bit or the global
enable bit, GIE (INTCON<7>).
2: User software sh ould ensure the ap propri-
ate interrupt flag bits are cleared prior to
enabling an interrupt and after servicing
that interrupt.
REGISTER 9-4: PIR1: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REQUEST (FLAG) REGISTER 1
R/W-0 R/W-0 R-0 R-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
(1)
PSPIF
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 PSPIF: Parallel Slave Port Read/Write Interrupt Flag bit
1 = A read or a write operation has taken place (must be cleared in software)
0 = No read or write has occurred
Note 1: Enabled only in Microcontroller mode for PIC 18F8X2X devices.
bit 6 ADIF: A/D Converter Interrupt Flag bit
1 = An A/D conversion completed (must be cleared in software)
0 = The A/D conversion is not complete
bit 5 RC1IF: USART1 Receive Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The USART1 receive buffer, RCREGx, is full (cleared when RCREGx is read)
0 = The USART1 receive buffer is empty
bit 4 TX1IF: USART Transmit Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The USART1 transmit buffer, TXREGx, is empty (cleared when TXREGx is written)
0 = The USART1 transmit buffer is full
bit 3 SSPIF: Master Synchronous Serial Port Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The transmission/reception is complete (must be cleared in software)
0 = Waiting to transmit/receive
bit 2 CCP1IF: CCP1 Interrupt Flag bit
Capture mode:
1 = A TMR1 register capture occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = No TMR1 register capture occurred
Compare mode:
1 = A TMR1 register compare match occurred (must be c leared in software)
0 = No TMR1 register compare match occurred
PWM mode:
Unused in this mode.
bit 1 TMR2IF: TMR2 to PR2 Match Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR2 to PR2 match occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = No TMR2 to PR2 match occurred
bit 0 TMR1IF: TMR1 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR1 register overflowed (must be cleared in software)
0 = TMR1 register did not overflow
ADIF RC1IF TX1IF SSPIF CCP1IF TMR2IF TMR1IF
(1)
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
DS39612A-page 94 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 97

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
REGISTER 9-5: PIR2: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REQUEST (FLAG) REGISTER 2
U-0 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
—CMIF— EEIF BCLIF LVDIF TMR3IF CCP2IF
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 6 CMIF: Comparator Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The comparator input has changed (must be cleared in software)
0 = The comparator input has not changed
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 EEIF: Data EEPROM/FLASH Write Operation Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The write operation is complete (must be cleared in software)
0 = The write operation is not complete, or has not been started
bit 3 BCLIF: Bus Collision Interrupt Flag bit
1 = A bus collision occurred while the SSP module (configured in I
was transmitting (must be cleared in softwar e)
0 = No bus collision occurred
bit 2 LVDIF: Low Voltage Detect Interrupt Flag bit
1 = A low voltage condition occurred (must be cleared in software )
0 = The device voltage is above the Low Voltage Detect trip point
bit 1 TMR3IF: TMR3 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR3 register overflowed (must be cleared in software)
0 = TMR3 register did not overflow
bit 0 CCP2IF: CCP2 Interrupt Flag bit
Capture mode:
1 = A TMR1 or TMR3 register capture oc curred (must be cleared in software)
0 = No TMR1 or TMR3 register capture occurred
Compare mode:
1 = A TMR1 or TMR3 register compare match occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = No TMR1 or TMR3 register compare match occurred
PWM mode:
Unused in this mode.
2
C Master mode)
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 95
Page 98

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
REGISTER 9-6: PIR3: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REQUEST (FLAG) REGISTER 3
U-0 U-0 R-0 R-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
— — RC2IF TX2IF TMR4IF CCP5IF CCP4IF CCP3IF
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7-6 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 5 RC2IF: USART2 Receive Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The USART2 receive buffer, RCREGx, is full (cleared when RCREGx is read)
0 = The USART2 receive buffer is empty
bit 4 TX2IF: USART2 Transmit Interrupt Flag bit
1 = The USART2 transmit buffer, TXREGx, is empty (cleared when TXREGx is written)
0 = The USART2 transmit buffer is full
bit 3 TMR4IF: TMR3 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit
1 = TMR4 register overflowed (must be cleare d in softwar e)
0 = TMR4 register did not overflow
bit 2-0 CCPxIF: CCPx Interrupt Flag bit (ECCP3, CCP4 and CCP5)
Capture mode:
1 = A TMR1 or TMR3 register capture oc curred (must be cleared in software)
0 = No TMR1 or TMR3 register capture occurred
Compare mode:
1 = A TMR1 or TMR3 register compare match occurred (must be cleared in software)
0 = No TMR1 or TMR3 register compare match occurred
PWM mode:
Unused in this mode.
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
DS39612A-page 96 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 99

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
9.3 PIE Registers
The PIE registers contain the individual enable bits for
the peripheral interrupts. Due to the number of peripheral interrupt sources, there are three Peripheral Interrupt Enable registers (PIE1, PIE2 and PIE3). When the
IPEN bit (RCON<7>) is ‘0’, the PEIE bit must be set to
enable any of these peripheral interrupts.
REGISTER 9-7: PIE1: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER 1
R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
(1)
PSPIE
bit 7 bit 0
ADIE RC1IE TX1IE SSPIE CCP1IE TMR2IE TMR1IE
bit 7 PSPIE: Parallel Slave Port Read/Writ e Interru pt Enab le bit
1 = Enables the PSP read/write interrupt
0 = Disables the PSP read/write interrupt
Note 1: Enabled only in Microcontroller mode for PIC18F8X2X devices.
bit 6 ADIE: A/D Converter Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the A/D interrupt
0 = Disables the A/D interrupt
bit 5 RC1IE: USART1 Receive Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the USART1 receive interrupt
0 = Disables the USART1 receive interrupt
bit 4 TX1IE: USART1 Transmit Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the USART1 transmit interrupt
0 = Disables the USART1 transmit interrupt
bit 3 SSPIE: Master Synchronous Serial Port Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the MSSP interrupt
0 = Disables the MSSP interrupt
bit 2 CCP1IE: CCP1 Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the CCP1 interrupt
0 = Disables the CCP1 interrupt
bit 1 TMR2IE: TMR2 to PR2 Match Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt
0 = Disables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt
bit 0 TMR1IE: TMR1 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the TMR1 overflow interrupt
0 = Disables the TMR1 overflow interrupt
(1)
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
2003 Microchip Technology Inc. Advance Information DS39612A-page 97
Page 100

PIC18F6X2X/8X2X
REGISTER 9-8: PIE2: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER 2
U-0 R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0
—CMIE— EEIE BCLIE LVDIE TMR3IE CCP2IE
bit 7 bit 0
bit 7 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 6 CMIE: Comparator Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the comparator interrupt
0 = Disables the comparator interrupt
bit 5 Unimplemented: Read as ‘0’
bit 4 EEIE: Data EEPROM/FLASH Write Operation Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the write operation interrupt
0 = Disab les the write operation interrupt
bit 3 BCLIE: Bus Collision Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the bus collision interrupt
0 = Disables the bus collision interrupt
bit 2 LVDIE: Low Voltage Detect Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the Low Voltage Detect interrupt
0 = Disables the Low Voltage Detect interrupt
bit 1 TMR3IE: TMR3 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the TMR3 overflow interrupt
0 = Disables the TMR3 overflow interrupt
bit 0 CCP2IE: CCP2 Interrupt Enable bit
1 = Enables the CCP2 interrupt
0 = Disables the CCP2 interrupt
Legend:
R = Readable bit W = Writable bit U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’
- n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set ‘0’ = Bit is cleared x = Bit is unknown
DS39612A-page 98 Advance Information 2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...