Page 1
M
MCP6141/2/3/4
600 nA, Non-Unity Gain Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Op Amps
Features
• Low Quiescent Current: 600 nA/Amplifier (typ.)
• Stable for gains of 10 V/V or higher
• Rail-to-Rail Input: -0.3V (min.) to V
+ 0.3V (max.)
DD
• Rail-to-Rail Output:
+10 mV (min.) to VDD-10 mV (max.)
-V
SS
• Gain Bandwidth Product: 100 kHz (typ.)
• Wide Supply Voltage Range: 1.4V to 5.5V (max.)
• Available in Single, Dual and Quad
• Chip Select (CS
) with MCP6143
Applications
• Toll Booth Tags
• Wearable Products
• Temperature Measurement
• Battery-Powered
Available Tools
• Spice macro models (at www.microchip.com)
• FilterLab
®
Software (at www.microchip.com)
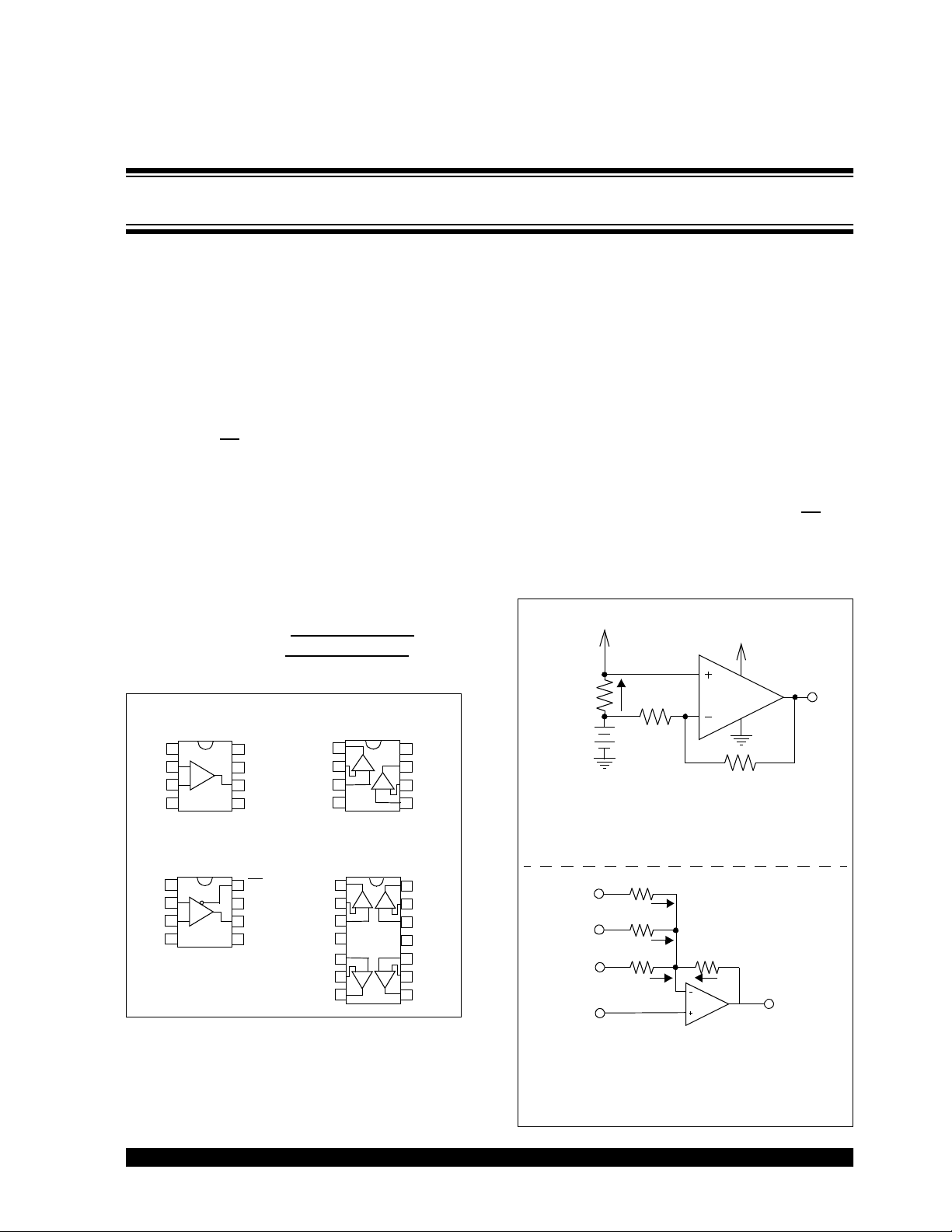
Package Types
MCP6141
PDIP, SOIC, MSOP
NC
1
-IN
2
+
+IN
3
V
4
SS
MCP6143
PDIP, SOIC, MSOP
NC
1
2
-
-IN
+
3
+IN
V
4
SS
8
NC
7
V
OUT
6
NC
5
CS
8
V
7
OUT
6
NC
5
OUTA
DD
DD
MCP6142
PDIP, SOIC, MSOP
1
A
-
+
2
-INA
+INA
V
SS
PDIP, SOIC, TSSOP
OUTA
-INA1
+INA1
V
DD
+INB
-INB
3
4
MCP6144
1
A
2
-
+
3
4
5
-
+
6
B
7OUTB1
B
-
+
D
-
+
-
+
C
8
7
6
5
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
V
DD
OUTB
-INB
+INB
OUTD
-IND
+IND
V
SS
+INC
-INC
OUTC
Description
The MCP6141/2/3/4 family of non-unity gain stable
operational amplifiers (op amps) from Microchip
Technology, Inc. operate with a single supply voltage
as low as 1.4V, while drawing less than 1 µA (max.) of
quiescent current per amplifier. These devices are also
designed to support rail-to-rail input and output swing.
The MCP6141/2/3/4 op amps have a gain bandwidth
product of 100 kHz (typ.) and are stable for gains of
10 V/V or higher. This specification makes these
devices appropriate for battery-powered applications
where higher frequency responses from the amplifier
are required.
The MCP6141/2/3/4 family of op amps are offered in
single (MCP6141), single with a Chip Select (CS
) feature (MCP6143), dual (MCP6142) and quad
(MCP6144) configurations.
Typical Applications
V
DD
I
1k Ω
DD
+1.4V
to
5.5V
R
I
100 k Ω
High Side Battery Current Sensor
R
G
1
n
R
V
V
V
V
REF
1
1
R
2
2
R
3
3
------+
I
1
I
2
I
3
MCP614X
Summing Amplifier
1
1R
G
n
----- -
+ 10V/V≥=
F
R
1
MCP614X
R
F
R
I
R
F
1
----- -
R
2
V
DD
= 1 MΩ
F
10V/V≥=
I
F
1
----- -++
R
3
V
SS
V
OUT
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 1
Page 2
MCP6141/2/3/4
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1.1 Maximum Ratings†
V
- VSS.........................................................................7.0V
DD
All inputs and outputs........................ V
Difference Input voltage ....................................... |V
Output Short Circuit Current ..................................continuous
Current at Input Pins ....................................................±2 mA
Current at Output and Supply Pins ............................±30 mA
-0.3V to VDD +0.3V
SS
DD
- VSS|
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Name Function
+IN/+INA/+INB/+INC/+IND Non-inverting Inputs
-IN/-INA/-INB/-INC/-IND Inverting Inputs
V
DD
V
SS
OUT/OUTA/OUTB/OUTC/OUTD Outputs
CS
NC No internal connection
Positive Power Supply
Negative Power Supply
Chip Select
Storage temperature ..................................... -65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature, T
............................................ +150°C
J
ESD protection on all pins (HBM:MM).................. ≥ 4kV:200V
†Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a
stress rating only and functional operation of the device at
those or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operational listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
DC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise indicated, all limits are specified for VDD = +1.4V to +5.5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25°C,
V
= VDD/2, R
CM
Input Offset
Input Offset Voltage V
Drift with Temperature ∆V
Power Supply Rejection PSRR 70 85 — dB
Input Bias Current and Impedance
Input Bias Current I
Input Bias Current Over-Temperature I
Input Offset Current I
Common Mode Input Impedance Z
Differential Input Impedance Z
Common Mode
Common-Mode Input Range VCMR V
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio CMRR 62 80 — dB V
Open Loop Gain
DC Open Loop Gain (large signal) A
Output
Maximum Output Voltage Swing VOL, VOHVSS + 10 — V
Output Short Circuit Current I
Power Supply
Supply Voltage V
Quiescent Current per amplifier I
= 1 MΩ to V
L
/2, and V
DD
OUT
~ VDD/2.
Parameters Sym Min Typ Max Units Conditions
VCM = V
SS
OS
OS
B
B
OS
CM
DIFF
OL
O
DD
Q
-3.0 — +3.0 mV
/∆T— ±1.5 — µV/°CT
= -40°C to +85°C
A
—1.0— pA
——100pAT
= -40°C to +85°C
A
—1.0— pA
—10
—10
− 0.3 — V
SS
60 75 — dB V
60 80 — dB V
95 115 — dB R
—21—mAV
13
||6 — Ω||pF
13
||6 — Ω||pF
+ 0.3 V
DD
− 10 mV RL = 50 kΩ to V
DD
= 5V,
DD
V
= -0.3V to 5.3V
CM
= 5V,
DD
V
= 2.5V to 5.3V
CM
= 5V,
DD
V
= -0.3V to 2.5V
CM
= 50 kΩ to V
L
100 mV < V
(V
− 100 mV)
DD
OUT
1.4 — 5.5 V
0.3 0.6 1.0 µA IO = 0
OUT
= 2.5V, VDD = 5 V
DD
<
DD
/2,
/2
21668A-page 2 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3

MCP6141/2/3/4
AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise indicated, all limits are specified for VDD = +5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25 °C,
V
= VDD/2, R
CM
Gain Bandwidth Product GBWP — 100 — kHz
Slew Rate SR — 24 — V/ms
Phase Margin PM — 60 — ° G = +10
Input Voltage Noise E
Input Voltage Noise Density e
Input Current Noise Density i
SPECIFICATIONS FOR MCP6143 CHIP SELECT FEATURE
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise indicated, all limits are specified for V
V
= VDD/2, R
CM
CS Low Specifications
CS Logic Threshold, Low V
CS
Input Current, Low I
CS High Specifications
CS Logic Threshold, High V
CS
Input Current, High I
CS Input High, GND Current I
Amplifier Output Leakage, CS High — 20 — pA CS = V
Dynamic Specifications
CS Low to Amplifier Output High
Turn-on Tim e
High to Amplifier Output High Z
CS
Hysteresis V
= 1 MΩ to V
L
/2, CL = 60 pF, and V
DD
OUT
~ VDD/2.
Parameters Sym Min Typ Max Units Conditions
— 5.0 — µVp-p f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
—170—nV/√Hz f = 1 kHz
—0.6—fA/√Hz f = 1 kHz
= +1.4V to +5.5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25 °C,
DD
~ VDD/2.
= 1 MΩ to V
L
/2, CL = 60 pF, and V
DD
n
n
n
OUT
Parameters Sym Min Typ Max Units Conditions
CSL
CSH
t
ON
t
OFF
HYST
IL
V
SS
—5.0—pACS = V
VDD - 0.3 — V
IH
—5.0—pACS = V
Q
—20—pACS = V
—2.050msCS low = VSS + 0.3V, G = +1 V/V,
—10—µsCS high = VDD - 0.3V, G = +1 V/V
—0.6— VV
—VSS + 0.3 V For entire VDD range
SS
DD
V For entire VDD range
DD
DD
DD
V
= 0.9 VDD/2
OUT
V
= 0.1 VDD/2
OUT
= 5V
DD
TEMPERATURE SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise indicated, all limits are specified for V
Parameters Symbol Min Typ Max Units Conditions
Temperature Ranges
Specified Temperature Range T
Operating Temperature Range T
Storage Temperature Range T
A
A
A
-40 — +85 °C
-40 — +125 °C Note 1
-65 — +150 °C
Thermal Package Resistances
Thermal Resistance, 8L-PDIP θ
Thermal Resistance, 8L-SOIC θ
Thermal Resistance, 8L-MSOP θ
Thermal Resistance, 14L-PDIP θ
Thermal Resistance, 14L-SOIC θ
Thermal Resistance, 14L-TSSOP θ
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
—
—
—
—
—
—
Note 1: The MCP6141/2/3/4 family of op amps operates over this extended range, but with reduced performance.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 3
85
163
206
70
108
100
= +1.4V to +5.5V, V
DD
—
—
—
—
—
—
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
SS
= GND.
Page 4
MCP6141/2/3/4
2.0 TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
Note: The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
and V
OUT~VDD
/2.
= +5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25°C, VCM = VDD/2, R
DD
= 1 MΩ to V
L
DD
/2, C
= 60 pF,
L
16%
1200 Samples
14%
VDD = 5.5 V
12%
10%
8%
6%
4%
2%
Percentage of Occurrences
0%
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
Input Offset Voltage (mV)
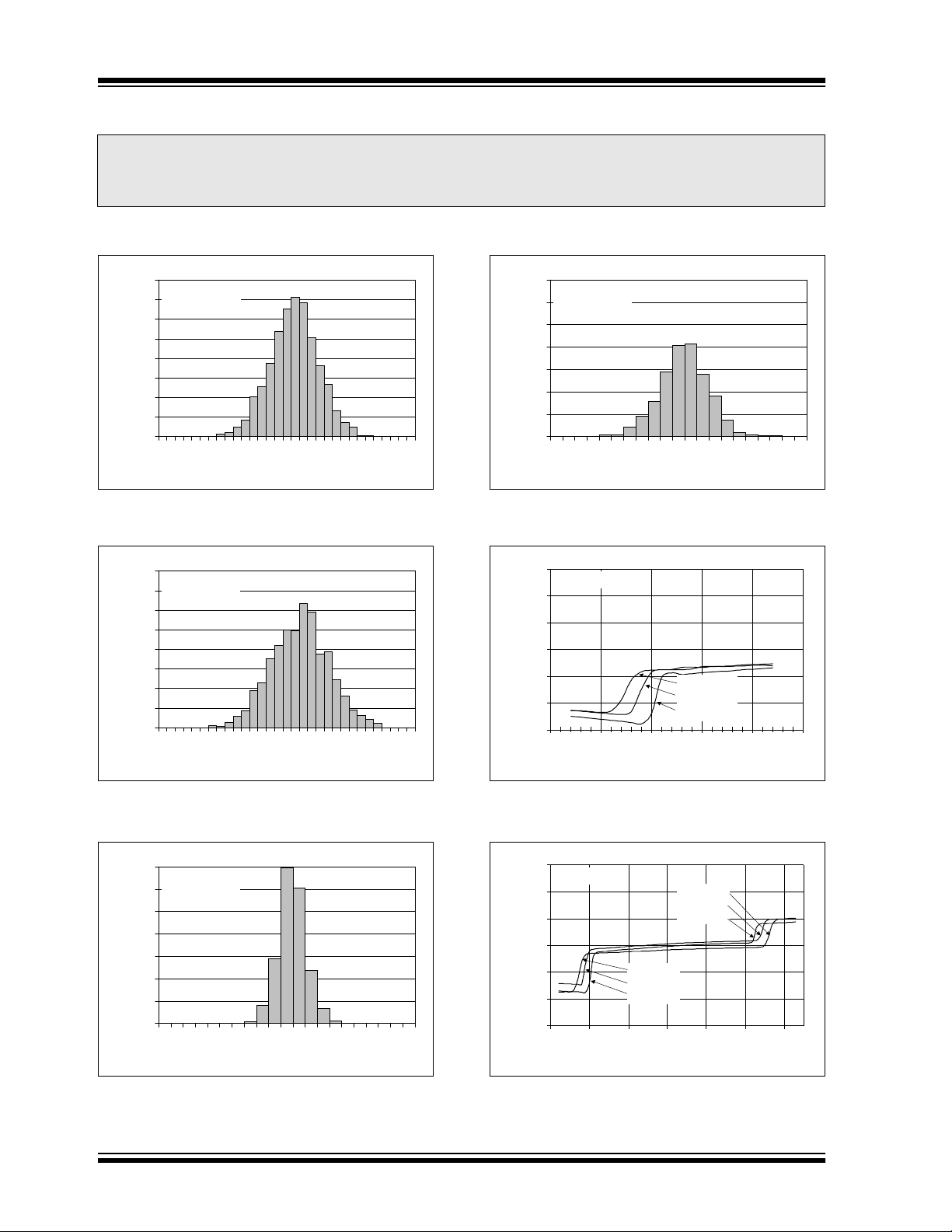
FIGURE 2-1: Histogram of Input Offset
Voltage with V
16%
1200 Samples
14%
VDD = 1.4 V
12%
10%
8%
6%
4%
2%
Percentage of Occurrences
0%
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
= 5.5V.
DD
Input Offset Voltage (mV)
35%
1200 Samples
30%
VDD = 1.4 V
25%
20%
15%
10%
5%
Percentage of Occurrences
0%
-10 -5 0 5 10
Input Offset Voltage Drift (µV/°C)
FIGURE 2-4: Histogram of Input Offset
Voltage Drift with V
600
VDD = 1.4 V
400
200
0
-200
-400
Input Offset Voltage (µV)
-600
-0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0
Common Mode Input Voltage (V)
= 1.4V.
DD
TA = +85°C
= +25°C
T
A
T
= -40°C
A
FIGURE 2-2: Histogram of Input Offset
Voltage with V
35%
1200 Samples
30%
VDD = 5.5 V
25%
20%
15%
10%
5%
Percentage of Occurrences
0%
-10 -5 0 5 10
= 1.4V.
DD
Input Offset Voltage Drift (µV/°C)
FIGURE 2-3: Histogram of Input Offset
Voltage Drift with V
= 5.5V.
DD
FIGURE 2-5: Input Offset Voltage vs.
Common Mode Input Voltage vs. Temperature
with V
= 1.4V.
DD
600
VDD = 5.5 V
400
200
0
-200
-400
Input Offset Voltage (µV)
-600
-0.5 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5
TA = +85°C
T
T
Common Mode Input Voltage (V)
= +25°C
A
= -40°C
A
TA = +85°C
= +25°C
T
A
= -40°C
T
A
FIGURE 2-6: Input Offset Voltage vs.
Common Mode Input Voltage vs. Temperature
with V
= 5.5V.
DD
21668A-page 4 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5
MCP6141/2/3/4
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
and V
OUT~VDD
500
450
400
350
300
Input Offset Voltage (µV)
250
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5
/2.
VDD = 1.4 V
Output Voltage (V)
= +5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25°C, VCM = VDD/2, R
DD
RL = 50 k:
VDD = 5.5 V
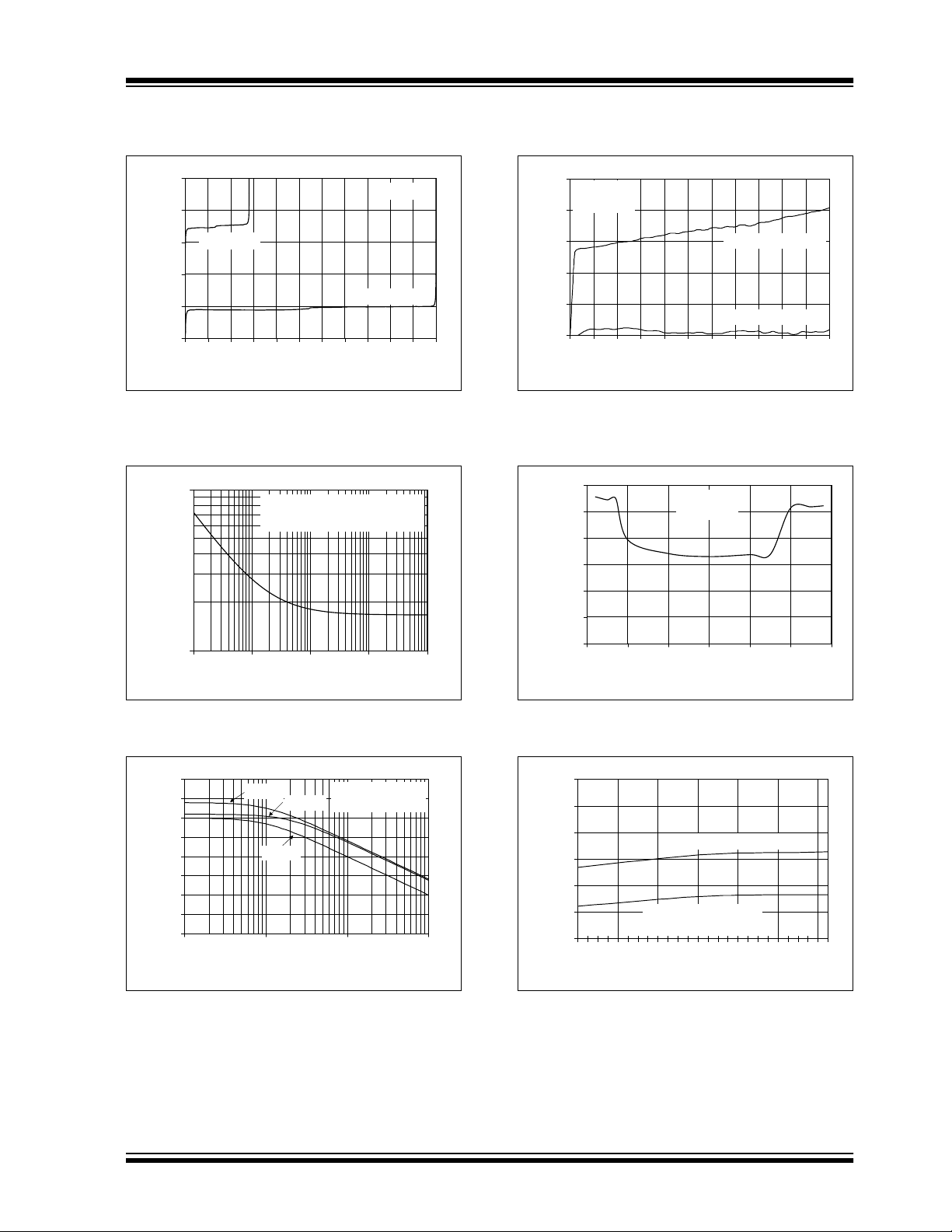
FIGURE 2-7: Input Offset Voltage vs. Output Voltage vs. Power Supply Voltage.
1,000
Hz)
(nV/
Input Noise Voltage Density
100
0.1 1 10 100 1000
Eni = 4.7 µV
= 167 nV/Hz, f = 1 kHz
e
ni
Frequency (Hz)
, f = 0.1 to 10 Hz
P-P
= 1 MΩ to V
L
50
TA = 85°C
V
= 5.5 V
DD
40
30
20
10
0
Input Bias, Offset Currents (pA)
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5
Common Mode Input Voltage (V)
/2, C
DD
Input Bias Current
Input Offset Current
= 60 pF,
L
FIGURE 2-10: Input Bias, Offset Currents vs. Common Mode Input Voltage with Temperature = 85°C.
300
250
200
Hz)
150
(nV/
100
50
Input Noise Voltage Density
0
-0.5 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5
Common Mode Input Voltage (V)
f = 1 kHz
VDD = 5.0 V
FIGURE 2-8: Input Noise Voltage Density vs. Frequency.
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
CMRR, PSRR (dB)
30
20
1 10 100 1000
PSRR-
CMRR
10 100
Frequency (Hz)
PSRR+
VDD = 5.0 V
Referred to Input
FIGURE 2-9: Common Mode Rejection Ratio, Power Supply Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency.
FIGURE 2-11: Input Noise Voltage Density vs. Common Mode Input Voltage.
100
95
90
85
80
CMRR, PSRR (dB)
75
70
-40-20 0 20406080
CMRR (VDD = 5.0 V,
V
CM
Ambient Temperature (°C)
PSRR (VCM = VSS)
= -0.3 V to +5.3 V)
FIGURE 2-12: Common Mode Rejection Ratio, Power Supply Rejection Ratio vs. Ambient Temperature.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 5
Page 6
MCP6141/2/3/4
k
k
r
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
and V
OUT~VDD
50
40
30
(pA)
20
10
Input Bias and Offset Currents
0
/2.
VCM = V
DD
VDD = 5.5 V
25 35 45 55 65 75 85
Ambient Temperature (°C)
= +5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25°C, VCM = VDD/2, R
DD
Input Bias
Current
Input Offset
Current
FIGURE 2-13: Input Bias and Offset Currents vs. Ambient Temperature.
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
Open-Loop Gain (dB)
VDD = 5.5 V
-20
0.1
0.01
Phase
1
Frequency (Hz)
Gain
10
100
1
1000
10k
10000
100
100000
0
-30
-60
-90
-120
-150
-180
Open-Loop Phase (°)
-210
= 1 MΩ to V
L
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
(mA)
0.3
0.2
0.1
Quiescent Current per amplifie
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5. 5 6.0 6.5 7.0
TA = 85°C
TA = 25°C
TA = -40°C
Power Supply Voltage (V)
DD
/2, C
= 60 pF,
L
FIGURE 2-16: Quiescent Current Vs. Power Supply Voltage vs. Temperature.
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
DC Open-Loop Gain (dB)
70
60
100
VDD = 5.5 V
V
= 0.5 V to 5.0 V
OUT
VDD = 1.4 V
V
= 0.5 V to 0.9 V
OUT
1k 10k 100k
Load Resistance (:)
FIGURE 2-14: Open Loop Gain, Phase vs.
Frequency with V
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
DC Open Loop Gain (dB)
60
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5
= 5.5V.
DD
RL = 50 k:
V
= 100 mV to VDD - 100 mV
OUT
Power Supply Voltage (V)
FIGURE 2-15: DC Open Loop Gain vs. Power Supply Voltage.
FIGURE 2-17: DC Open Loop Gain vs. Load Resistance vs. Power Supply Voltage.
140
RL = 50 k:
130
120
110
100
(dB)
90
80
70
60
Small Signal DC Open Loop Gain
0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30
Output Voltage Headroom;
V
DD-VOUT
VDD = 5.5 V
VDD = 1.4 V
or V
OUT-VSS
(V)
FIGURE 2-18: Small Signal DC Open Loop Gain vs. Output Voltage Headroom vs. Power Supply.
21668A-page 6 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

MCP6141/2/3/4
p
p
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
and V
OUT~VDD
140
130
120
(dB)
110
100
90
Channel-to-Channel Separation
/2.
Input-Referred
1000 10000
Frequency (Hz)
= +5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25°C, VCM = VDD/2, R
DD
FIGURE 2-19: Channel to Channel Separation vs. Frequency (MCP6142 and MCP6144 only).
120
Gain Bandwidth Product
100
80
60
(kHz)
40
20
Gain Bandwidth Product
0
-40-20 0 20406080
Phase Margin
VDD = 5.5 V
Ambient Temperature (°C)
10k1k
90
75
60
45
30
Phase Margin (°)
15
0
180
160
140
120
100
80
(kHz)
60
40
20
Gain Bandwidth Product
0
-0.5
Phase Margin
Gain Bandwidth Product
0.0
0.5
1.0
Common Mode Input Voltage (V)
= 1 MΩ to V
L
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
DD
4.0
/2, C
4.5
= 60 pF,
L
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
5.0
5.5
FIGURE 2-22: Gain Bandwidth Product, Phase Margin vs. Common Mode Input Voltage.
120
100
80
60
(kHz)
40
20
Gain Bandwidth Product
VDD = 1.4 V
C
= 60 pF
L
0
-40-200 20406080
Gain Bandwidth Product
Phase Margin
Ambient Te mperature ( °C)
90
75
60
45
30
Phase Margin (°)
15
0
Phase Margin (°)
FIGURE 2-20: Gain Bandwidth Product,
Phase Margin vs. Ambient Temperature with
V
= 5.5V.
DD
12
10
8
6
4
Frequency (kHz)
Closed Loop Gain
2
0
0.00 0.00 0.00
10
Closed Loop Gain Frequency
Phase Margin
G = +10 V/V
VDD = 5.5 V
Load Capacitance (F)
90
75
60
45
30
15
0
1n100
Phase Margin (°)
FIGURE 2-21: Closed Loop Gain
Frequency, Phase Margin vs. Load Capacitance
with V
DD
=5.5V.
FIGURE 2-23: Gain Bandwidth Product,
Phase Margin vs. Ambient Temperature with
= 1.4V.
V
DD
40
35
30
25
20
(pA)
15
+ISC, VDD = 1.4 V
10
-ISC, VDD = 1.4 V
5
Output Short Circuit Current
0
-40-200 20406080
Ambient Temperature (°C)
-ISC, VDD = 5.5 V
+ISC, VDD = 5.5 V
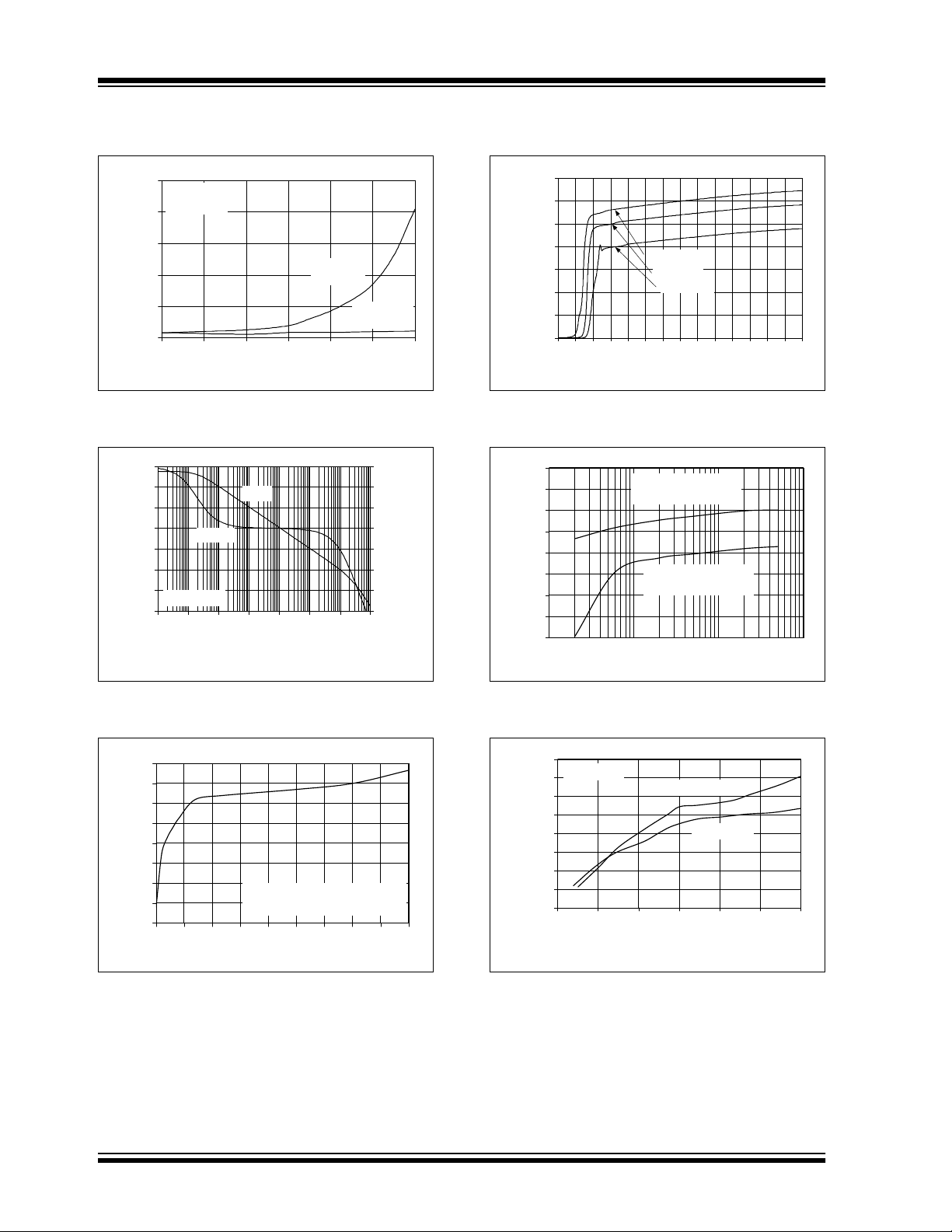
FIGURE 2-24: Output Short Circuit Current vs. Ambient Temperature vs. Power Supply Voltage.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 7
Page 8
MCP6141/2/3/4
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
and V
OUT~VDD
/2.
= +5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25°C, VCM = VDD/2, R
DD
50
45
40
Falling Edge
35
30
25
20
15
Slew Rate (V/ms)
10
Rising Edge
5
0
-40-20 0 20406080
Ambient Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2-25: Slew Rate vs. Ambient Temperature.
1,000
100
VOL-VSS, VDD = 1.4 V
10
1
Output Voltage Headroom (mV)
1.E-05 1.E-04 1.E-03 1.E-02
10µ 10m1m100µ
Output Current Magnitude (A)
VOL-VSS, VDD = 5.5 V
= 1 MΩ to V
L
DD
/2, C
= 60 pF,
L
10
VDD = 5.5 V
1
Output Voltage Swing (VP-P)
0.1
100 1k 10k
100 1000 10000
VDD = 1.4 V
Frequency (Hz)
FIGURE 2-28: Output Voltage Swing vs. Frequency vs. Power Supply Voltage.
4.0
VDD = 5.5 V
3.5
RL = 50 k:
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
Output Voltage Headroom (mV)
0.0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80
VOL - V
SS
VDD - V
OH
Ambient Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2-26: Output Voltage Headroom vs. Output Current Magnitude vs. Power Supply Voltage.
0.08
0.06
0.04
0.02
0.00
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
Output Voltage (20 mV/div)
-0.08
0.E+00 1.E-04 2.E-04 3.E-04 4.E-04 5.E-04 6.E-04 7.E-04 8.E-04 9.E-04 1.E-03
G = +11 V/V
RL = 50 k:
Time (100 µs/div)
FIGURE 2-27: Small Signal Non-Inverting Pulse Response vs. Time.
FIGURE 2-29: Output Voltage Headroom
vs. Ambient Temperature with V
0.08
0.06
0.04
0.02
0.00
-0.02
-0.04
-0.06
Output Voltage (20 mV/div)
-0.08
0.E+00 1.E-04 2.E-04 3.E-04 4.E-04 5.E-04 6.E-04 7.E-04 8.E-04 9.E-04 1.E-03
Time (100 µs/div)
= 5.5V.
DD
G = -10 V/V
= 50 k:
R
F
FIGURE 2-30: Small Signal Inverting Pulse Response vs. Time.
21668A-page 8 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

MCP6141/2/3/4
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
and V
OUT~VDD
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
Output Voltage (V)
1.0
0.5
0.E+00 2.E-04 4.E-04 6.E-04 8.E-04 1.E-03 1.E-03 1.E-03 2.E-03 2.E-03 2.E-03
0.0
/2.
G = +11 V/V
RL = 50 k:
Time (200 µs/div)
= +5V, VSS = GND, TA = 25°C, VCM = VDD/2, R
DD
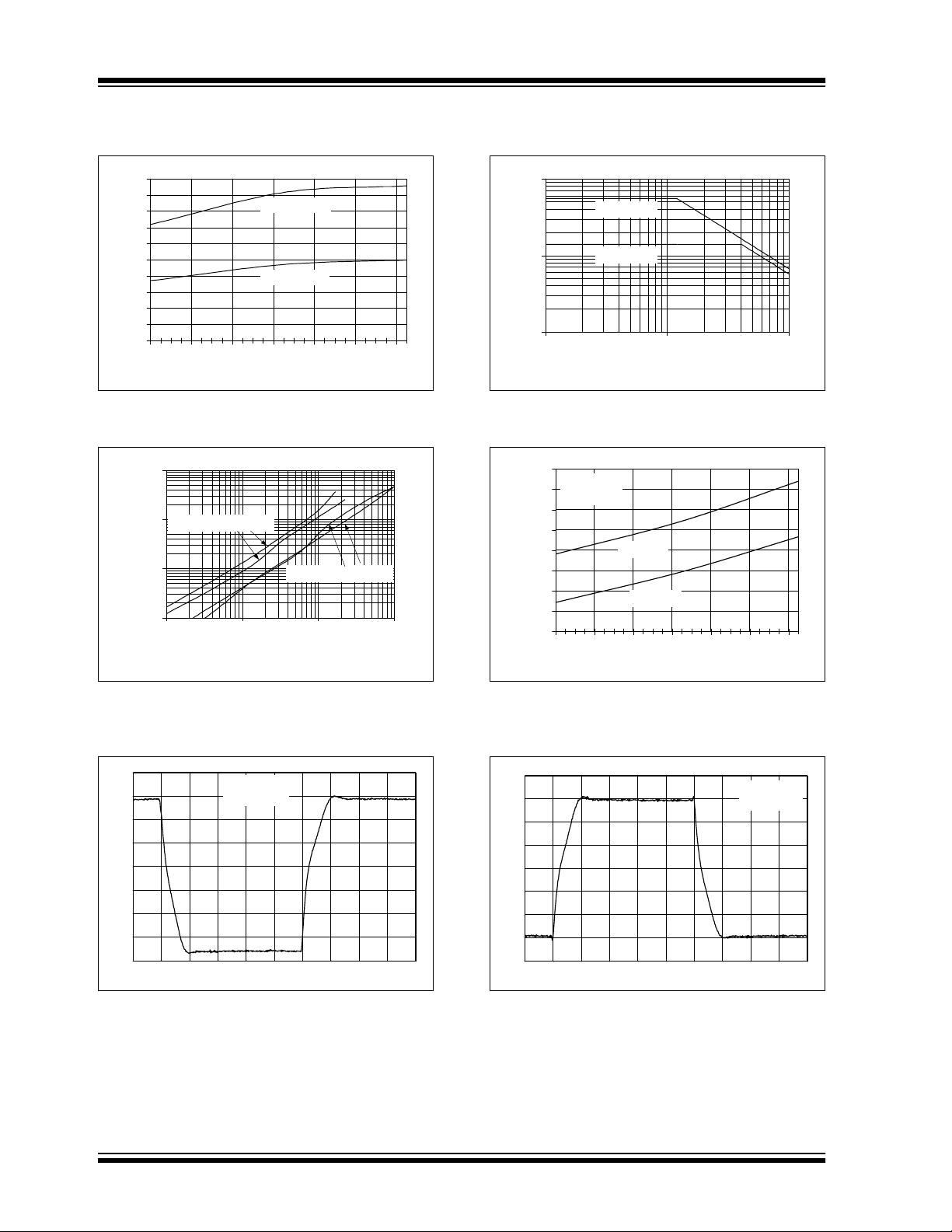
FIGURE 2-31: Large Signal Non-Inverting Pulse Response vs. Time.
27.5
25.0
V
on V
OUT
22.5
20.0
17.5
15.0
12.5
10.0
7.5
5.0
2.5
0.E+00 1.E-03 2.E-03 3.E-03 4.E-03 5.E-03 6.E-03 7.E-03 8.E-03 9.E-03 1.E-02
0.0
Chip Select Voltage (V)
G = +11 V/V
V
= 3.0 V
IN
V
Hi-Z
OUT
CS Voltage
Time (1 ms/div)
OUT
on
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
FIGURE 2-34: Large Signal Inverting Pulse Response vs. Time.
Output Voltage (V)
= 1 MΩ to V
L
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
Output Voltage (V)
1.0
0.5
0.E+00 2.E-04 4.E-04 6.E-04 8.E-04 1.E-03 1.E-03 1.E-03 2.E-03 2.E-03 2.E-03
0.0
5.5
5.0
V
on
OUT
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
Output Voltage (V)
1.0
G = +11 V/V
0.5
VIN = 3.0 V
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
Time (200 µs/div)
Hysteresis
CS swept
high to low
Chip Select Voltage (V)
/2, C
DD
CS swept
low to high
= 60 pF,
L
G = -10 V/V
RF = 50 k:
V
HI-Z
OUT
FIGURE 2-32: Chip Select (CS
) to
Amplifier Output Response Time
(MCP6143 only).
6
G = +11 V/V
5
4
3
2
1
0
Input, Output Voltages (V)
0.E+00 5.E-03 1.E-02 2.E-02 2.E-02 3.E-02
-1
V
OUT
V
IN
Time (5 ms/div)
FIGURE 2-33: The MCP6141/2/3/4 family
shows no phase reversal (for information only–
the Maximum Absolute Input Voltage is still
V
- 0.3V and V
SS
DD
+ 0.3V).
FIGURE 2-35: Output Voltage vs. Chip
Select (CS
) Voltage (MCP6143 only).
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 9
Page 10
MCP6141/2/3/4
3.0 APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The MCP6141/2/3/4 family of operational amplifiers
are fabricated on Microchip’s state-of-the-art CMOS
process. They are stable for noise gain of 10 V/V or
higher. Microchip also produces a unity gain stable
product, the MCP6041/2/3/4 family, which has similar
specifications. The MCP6041/2/3/4 family has a bandwidth of 1.4 kHz at a noise gain of 10 V/V, while the
MCP6141/2/3/4 family has a bandwidth of 10 kHz at a
noise gain of 10 V/V. These devices are suitable for a
wide range of applications requiring very low power
consumption. With these op amps, the power supply
pin needs to be bypassed with a 0.1 µF capacitor.
3.1 Rail-to-Rail Input
The input stage of these devices uses two differential
input stages in parallel; one operates at low V
mon mode input voltage) and the other at high V
With this topology, the MCP6141/2/3/4 family operates
with V
Offset Voltage is measured at both V
and V
up to 300 mV past either supply rail. The Input
CM
+ 0.3V to ensure proper operation.
DD
CM=VSS
3.2 Output Loads and Battery Life
The MCP6141/2/3/4 op amp family has low quiescent
current, which supports battery-powered applications.
There is minimal quiescent current glitch when chip
select (CS
sive current draw and reduced battery life when the
part is turned off or on.
Heavy resistive loads at the output can cause excessive battery drain. Driving a DC voltage of 2.5V across
a 100 kΩ load resistor will cause the supply current to
increase by 25 µA, depleting the battery 43 times as
fast as I
High frequency signals (fast edge rate) across capacitive loads will also significantly increase supply current.
For instance, a 0.1 µF capacitor at the output presents
an AC impedance of 15.9 kΩ (1/2πfC) to a 100 Hz
sinewave. It can be shown that the average power
drawn from the battery by a 5.0 V
(1.77 Vrms) under these conditions is:
EQUATION
P
This will drain the battery 18 times as fast as IQ alone.
) is raised or lowered. This prevents exces-
(0.6 µA typ) alone.
Q
SUPPLY
V
–()I
DDVSS
5V()0.6µA5.0V
V
()=
+ fC
Q
Lp p–()
100Hz 0.1µF⋅⋅+()=
pp–
3.0 µW50µW+=
CM
sinewave
p-p
L
(com-
CM
-0.3V
3.3 Rail-to-Rail Output
The MCP6141/2/3/4 family Maximum Output Voltage
Swing defines the maximum swing possible under a
particular output load. According to the specification
table, the output can reach up to 10 mV of either supply
rail with a 50 kΩ load.
3.4 Input Voltage and Phase Reversal
The MCP6141/2/3/4 op amp family uses CMOS transistors at the input. It is designed to prevent phase
reversal when the input pins exceed the supply voltages. Figure 2-33 shows an input voltage exceeding
both supplies without output phase reversal.
The maximum operating V
inputs is V
-0.3V and VDD + 0.3V. Voltage on the
SS
that can be applied to the
CM
input that exceeds this absolute maximum rating can
cause excessive current to flow in or out of the input
.
pins. Current beyond ±2 mA can cause possible reliability problems. Applications that exceed this rating
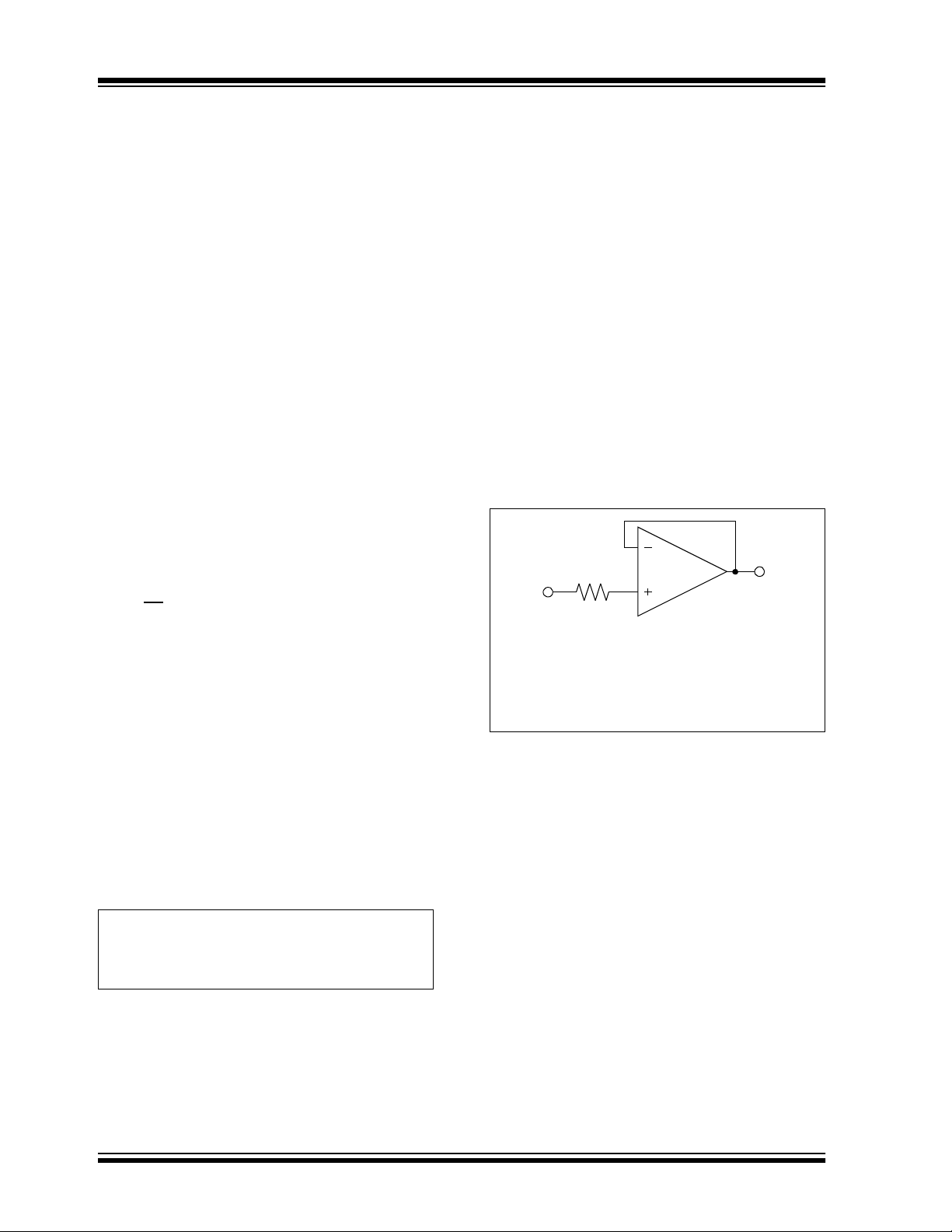
must be externally limited with an input resistor, as
shown in Figure 3-1.
R
IN
V
IN
Maximum expected V
()V
≥
R
--------------------------- ------------ ------------------------------ ----------
IN
V
SS
R
≥
----------------------------- ------------ ------------------------------ ---- -
IN
MCP614X
IN
2 mA
Minimum expected V
()–
2 mA
FIGURE 3-1: An input resistor, R
V
OUT
–
DD
IN
,
IN
should be used to limit excessive input current if
the inputs exceed the absolute maximum
specification.
3.5 Stability
The MCP6141/2/3/4 op amp family is designed to give
high bandwidth and faster slew rate for circuits with
high noise (G
stable MCP6041/2/3/4 op amp family has lower AC
performance, but it is preferable for low noise gain
applications.
Noise gain is defined to be the gain from a voltage
source at the non-inverting input to the output when all
other voltage sources are zeroed (shorted out). Noise
gain is independent of signal gain and depends only on
components in the feedback loop.
) or signal gain. The related unity-gain
n
21668A-page 10 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11

MCP6141/2/3/4
R
G
V
IN
Non-inverting noise gain: 1 + RF/R
V
IN
R
G
Inverting noise gain: 1 + R
R
F
MCP614X
R
F
MCP614X
F/RG
V
≥ +10 V/V
G
≥ +10 V/V
V
OUT
OUT
FIGURE 3-2: Noise gain for inverting and non-inverting amplifier configuration.
Figure 3-2 shows non-inverting and inverting amplifier
circuits. In order for the amplifiers to be stable, the
noise gain should meet the specified requirement:
Note that the integrator circuit in Figure 3-3 becomes
unity gain at high frequencies because of the capacitor. Therefore, this circuit is unstable for the
MCP6141/2/3/4.
3.6 Capacitive Load and Stability
Driving capacitive loads can cause stability problems
with voltage feedback op amps. Figure 2-21 shows how
increasing the load capacitance will decrease the phase
margin. While a phase margin above 60° is ideal, 45° is
on the verge of instability. As can be seen, up to
C
= 150 pF can be placed on the MCP6141/2/3/4 op
L
amp outputs without any problems, while 250 pF creates a 45° phase margin.
When the op amp is required to drive large capacitive
loads (C
Figure 3-4) at the output of the amplifier improves the
phase margin. This resistor makes the output load
resistive at higher frequencies, which improves the
phase margin. The bandwidth reduction caused by the
capacitive load, however, is not changed. To select
R
ISO
macro model and bench testing to adjust R
there is a minimum frequency response peaking.
>150 pF), a small series resistor (R
L
ISO
in
, start with 1 kΩ, then use the MCP6141 SPICE
until
ISO
EQUATION
R
Gn1
Note that an inverting signal gain of G = -9 V/V corresponds to a noise gain G
Figure 3-3 shows a unity gain buffer and integrator that
are unstable when used with the MCP6141/2/3/4 family. However, they are suitable for the MCP6041/2/3/4
family.
MCP604X
V
IN
R
V
IN
F
-------+ 10V/V≥=
R
G
= +10 V/V.
n
V
OUT
Unity gain buffer:
Unstable for MCP614X
C
MCP604X
V
OUT
R
2
V
IN
R
1
MCP614X
R
ISO
V
OUT
C
L
FIGURE 3-4: Amplifier circuit for heavy capacitive loads.
3.7 The MCP6143 Chip Select (CS) Option
The MCP6143 is a single amplifier with a chip select
(CS
) option. When CS is pulled high, the supply current
drops to 20 pA (typ.) and goes through the CS
V
. When this happens, the amplifier is put into a high
SS
impedance state. By pulling CS
enabled. If the CS
pin is left floating, the amplifier will
low, the amplifier is
not operate properly. Figure 3-5 shows the output
voltage and supply current response to a CS
pin to
pulse.
Integrator:
Unstable for MCP614X
FIGURE 3-3: Typical Circuits that are not suitable for the MCP6141/2/3/4 family.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 11
Page 12
MCP6141/2/3/4
CS
V
OUT
Hi-Z
V
IL
t
ON
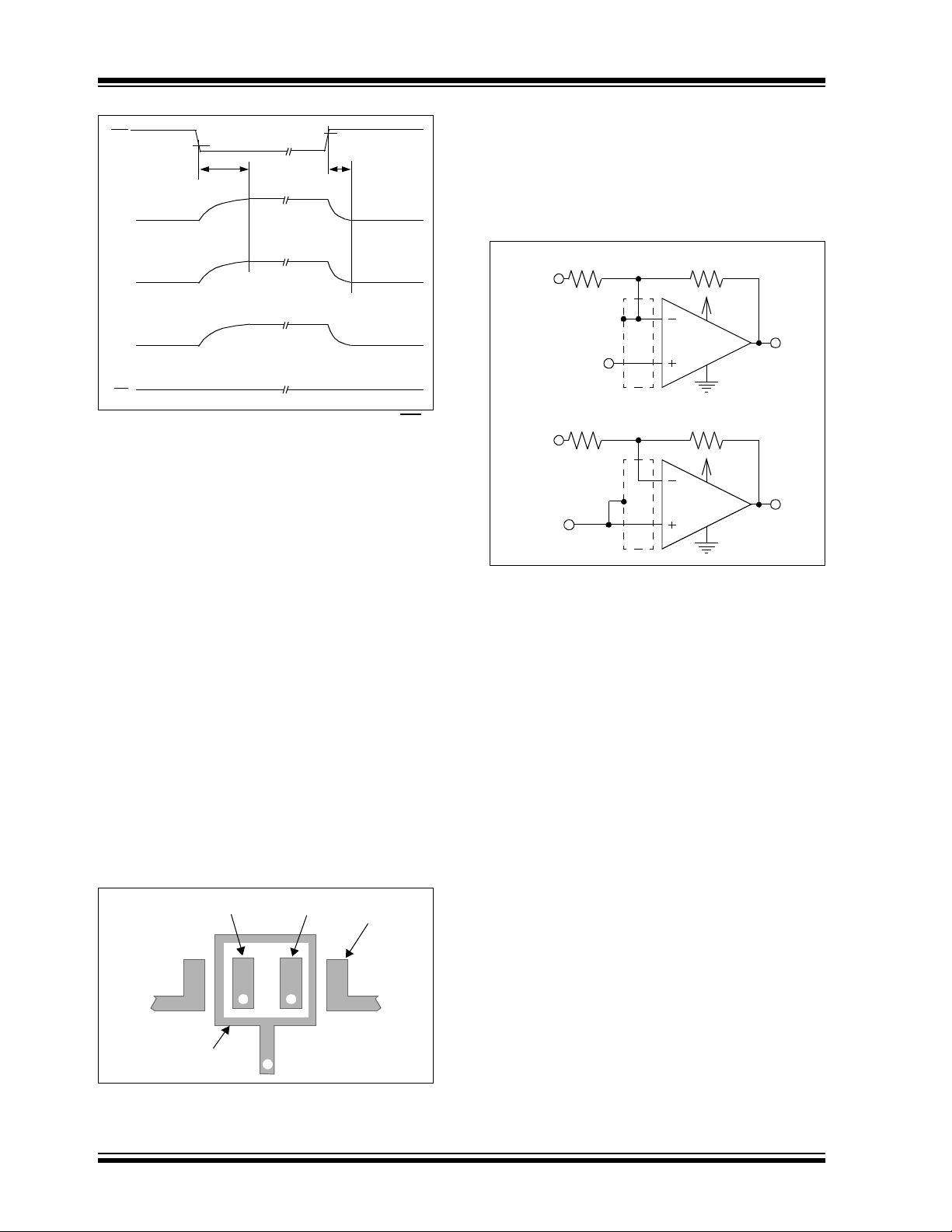
Circuit schematics for different guard ring implementa-
V
IH
t
OFF
Hi-Z
tions are shown in Figure 3-7. Figure 3-7A biases the
guard ring to the input common mode voltage, which is
most effective for non-inverting gains. Figure 3-7B
biases the guard ring to a reference voltage (V
REF
which can be ground), which is useful for inverting
gains and precision photo sensing circuits.
,
0.6 µA, typ
I
I
I
VSS
VDD
CS
5 pA, typ
0.6 µA, typ
20 pA, typ
5 pA, typ
5pA, typ
20 pA, typ
5pA, typ
FIGURE 3-5: Timing Diagram for the CS function on the MCP6143 op amp.
3.8 Layout Considerations
Good PC board layout techniques will help you achieve
the performance shown in the specifications and typical
performance curves. It will also assist in minimizing
Electro-Magnetic Compatibility (EMC) issues.
3.8.1 SURFACE LEAKAGE
In applications where low input bias current is critical,
PC board surface leakage effects and signal coupling
from trace to trace need to be considered.
Surface leakage is caused by a difference in voltage
between traces, combined with high humidity, dust or
other contamination on the board. Under low humidity
conditions, a typical resistance between nearby traces
12
is 10
Ω. A 5V difference would cause 5 pA of current
to flow, which is greater than the input current of the
MCP6141/2/3/4 family at 25°C (1 pA, typ).
The simplest technique to reduce surface leakage is
using a guard ring around sensitive pins (or traces).
The guard ring is biased at the same voltage as the
sensitive pin or trace. Figure 3-6 shows an example of
a typical layout.
Figure 3-7A
V
DD
MCP614X
V
REF
Figure 3-7B
V
DD
MCP614X
V
REF
FIGURE 3-7: Two possible guard ring connection strategies to reduce surface leakage effects.
3.8.2 COMPONENT PLACEMENT
In order to help prevent crosstalk:
• Separate digital components from analog components, and low speed devices from high speed
devices.
• Keep sensitive traces short and straight. Separate
them from interfering components and traces.
This is especially important for high frequency
(low rise time) signals.
• Use a 0.1 µF supply bypass capacitor within 0.1”
(2.5 mm) of the V
to the ground plane.
pin. It must connect directly
DD
IN- IN+
V
SS
Guard Ring
FIGURE 3-6: Example of Guard Ring layout.
21668A-page 12 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13
MCP6141/2/3/4
3.8.3 SIGNAL COUPLING
The input pins of the MCP6141/2/3/4 family of op amps
are high impedance, which allows noise injection. This
noise can be capacitively or magnetically coupled. In
either case, using a ground plane helps reduce noise
injection.
When noise is coupled capacitively, the ground plane
provides shunt capacitance to ground for high frequency signals (Figure 3-8 shows the equivalent circuit). The coupled current, I
(V
TRACE 2
) on the victim trace when the trace to ground
plane capacitance (C
resistor (R
) is small. Increasing the distance between
T2
, produces a lower voltage
M
) is large and the terminating
SH2
traces and using wider traces also helps.
C
V
TRACE 1
I
M
C
SH1
C
SH2
V
M
TRACE 2
R
T2
FIGURE 3-8: Equivalent circuit for
capacitive coupling between traces on a PC
board (with ground plane).
When noise is coupled magnetically, the ground plane
reduces the mutual inductance between traces. This
occurs because the ground return current at high frequencies will follow a path directly beneath the signal
trace. Increasing the separation between traces makes
a significant difference. Changing the direction of one
of the traces can also reduce magnetic coupling.
If these techniques are not enough, it may help to place
guard traces next to the victim trace. They should be on
both sides of the victim trace and be as close as possible. Connect the guard traces to ground plane at both
ends and in the middle for long traces.
3.9 Typical Applications
3.9.1 BATTERY CURRENT SENSING
The MCP6141/2/3/4 op amps’ Common Mode Input
Range, which goes 300 mV beyond both supply rails,
supports their use in high side and low side battery
current sensing applications. The very low quiescent
current (0.6 µA, typ.) help prolong battery life, while the
rail-to-rail output allows you to detect low currents.
Figure 3-9 shows a high side battery current sensor circuit. The feedback and input resistors are sized to minimize power losses. The battery current (I
the 1 kΩ resistor causes its top terminal to be more
negative than the bottom terminal. This keeps the com-
mon mode input voltage of the op amp ≤ V
within its allowed range. The output of the op amp can
reach V
- 0.1 mV (see Figure 2-26), which is a
DD
smaller error than the offset voltage.
V
1k Ω
+1.4 V
to
DD
I
DD
100 kΩ
V
DD
MCP614X
V
5.5 V
1MΩ
FIGURE 3-9: High Side Battery Current Sensor.
3.9.2 SUMMING AMPLIFIER
The rail-to-rail input and output, the 600 nA (typ.) quiescent current and the wide bandwidth make the
MCP6141/2/3/4 family of operational amplifiers fit well
in a summing amplifier circuit, as shown in Figure 3-10.
SS
) through
DD
, which is
DD
R
1
I
1
R
2
I
2
R
3
I
3
R
F
I
F
-
+
V
OUT
V
V
V
V
REF
1
2
3
MCP614X
FIGURE 3-10: Summing amplifier circuit.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 13
Page 14

MCP6141/2/3/4
In this configuration, the amplifier outputs the sum of
the three input voltages. The ratio of the sum and the
output voltage is defined using the feedback and input
resistors. V
family of amplifiers is stable for noise gain (G
V or higher. The G
amplifier is calculated as shown below:
EQUATION
is used to offset the output voltage. This
REF
and the signal gain of the summing
n
n
) of 10 V/
Noise Gain:
1
------
R
1
----- -++
R
2
3
1
G
n
1R
------
+ 10 V/V≥=
F
R
1
Signal Gain:
R
–
F
V
V
01
V
02
V
03
V
04
V
OUTV01V02V03V04
V
OUT
R
F
+++=
V
-----------------------
×=
---------
–
---------
–
---------
REFV1
R
1
R
1
R
F
×=
V
2
R
2
R
F
×=
V
3
R
3
R
R
F
------
R
2
V
–
REFV2
-----------------------
R
2
R
F
×=
------+++
V
REF
R
3
V
REFV3
-----------------------++ V
–
R
3
F
1
------
R
1
–
1
+=
REF
At a noise gain of 10 V/V, the amplifier bandwidth is
approximately 10 kHz. The bandwidth to quiescent current ratio of MCP6141/2/3/4 makes this device an
appropriate choice for battery-powered applications.
21668A-page 14 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

4.0 SPICE MACRO MODEL
The Spice macro model for the MCP6141, MCP6142,
MCP6143 and MCP6144 simulates the typical amplifier performance of offset voltage, DC power supply
rejection, input capacitance, DC common mode rejection, open loop gain over frequency, phase margin, output swing, DC power supply current, power supply
current change with supply voltage, input common
mode range, output voltage range vs. load and input
voltage noise.
The characteristics of the MCP6141, MCP6142,
MCP6143 and MCP6144 amplifiers are similar in terms
of performance and behavior. This single op amp
macro model supports all four devices, with the exception of the chip select function of the MCP6143, which
is not modeled.
The listing for this macro model is shown on the next
page. The most recent revision of the model can be
downloaded from Microchip’s web site at
w
ww.microchip.com.
MCP6141/2/3/4
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 15
Page 16

MCP6141/2/3/4
Software License Agreement
The software supplied herewith by Microchip Technology I ncorporated (the “Company”) is intended and supplied to you, the Company’s customer, for use solely and exclusively on Microchip products.
The software is owned by the Company and/or its supplier, and is protected under applicable copyright laws. All rights are reserved.
Any use in violation of the foregoing restrictions may subject the user to criminal sanctions under applicable laws, as well as to civil
liability for the breach of the terms and conditions of this license.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED IN AN “AS IS” CONDITION. NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. THE COMPANY SHALL NOT, IN ANY CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
.SUBCKT MCP6141 1 2 3 4 5
* | | | | |
* | | | | Output
* | | | Negative Supply
* | | Positive Supply
* | Inverting Input
* Non-inverting Input
*
* Macromodel for the MCP6141/2/3/4 op amp family:
* MCP6141 (single)
* MCP6142 (dual)
* MCP6143 (single w/ CS; chip select is not modeled)
* MCP6144 (quad)
*
* Revision History:
* REV A: 06-Sep-02, KEB (created model)
*
* Recommendations:
* Use PSPICE (or SPICE 2G6; other simulators may require translation)
* For a quick, effective design, use a combination of: data sheet
* specs, bench testing, and simulations with this macromodel
* For high impedance circuits, set GMIN=100F in the .OPTIONS
* statement
*
* Supported:
* Typical performance at room temperature (25 degrees C)
* DC, AC, Transient, and Noise analyses.
* Most specs, including: offsets, DC PSRR, DC CMRR, input impedance,
* open loop gain, voltage ranges, supply current, ... , etc.
*
* Not Supported:
* Chip select (MCP6143)
* Variation in specs vs. Power Supply Voltage
* Distortion (detailed non-linear behavior)
* Temperature analysis
* Process variation
* Behavior outside normal operating region
*
* Input Stage
V10 3 10 -300M
R10 10 11 258K
R11 10 12 258K
C11 11 12 3.53P
C12 1 0 6.00P
E12 1 14 POLY(4) 20 0 21 0 26 0 27 0 1.00M 117 117 1 1
I12 14 0 1.50P
M12 11 14 15 15 NMI L=2.00U W=5.00U
C13 14 2 6.00P
M14 12 2 15 15 NMI L=2.00U W=5.00U
I14 2 0 500E-15
C14 2 0 6.00P
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 16
Page 17

I15 15 4 300N
V16 16 4 200M
D16 16 15 DL
V13 3 13 50.0M
D13 14 13 DL
*
* Noise, PSRR, and CMRR
I20 21 20 423U
D20 20 0 DN1
D21 0 21 DN1
G26 0 26 POLY(1) 3 4 308U -56.0U
R26 26 0 1
G27 0 27 POLY(2) 1 3 2 4 -979U 178U 178U
R27 27 0 1
*
* Open Loop Gain, Slew Rate
G30 0 30 POLY(1) 12 11 0 1.00K
R30 30 0 1
E31 31 0 POLY(1) 3 4 29.3 1.05
D31 30 31 DL
E32 0 32 POLY(1) 3 4 57.0 2.04
D32 32 30 DL
G33 0 33 POLY(1) 30 0 0 562
R33 33 0 1
C33 33 0 838M
G34 0 34 POLY(1) 33 0 0 1.00
R34 34 0 1.00
C34 34 0 8.53U
G35 0 35 POLY(2) 34 0 33 34 0 1.00 1.22
R35 35 0 1.00
*
* Output Stage
G50 0 50 POLY(1) 57 5 0 1.00
D51 50 51 DL
R51 51 0 1K
D52 52 50 DL
R52 52 0 1K
G53 3 0 POLY(1) 51 0 300N 1M
G54 0 4 POLY(1) 52 0 300N -1M
E55 55 0 POLY(2) 3 0 51 0 -10M 1 -100M
D55 57 55 DLS
E56 56 0 POLY(2) 4 0 52 0 10M 1 -100M
D56 56 57 DLS
G57 0 57 POLY(3) 3 0 4 0 35 0 0 17.8U 17.8U 35.5U
R57 57 0 28.2K
R58 57 5 1.00
C58 5 0 2.00P
*
* Models
.MODEL NMI NMOS
.MODEL DL D N=1 IS=1F
.MODEL DLS D N=10M IS=1F
.MODEL DN1 D IS=1F KF=1.17E-18 AF=1
*
.ENDS MCP6141
MCP6141/2/3/4
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 17
Page 18

MCP6141/2/3/4
5.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
5.1 Package Marking Information
8-Lead PDIP (300 mil)
XXXXXXXX
XXXXXNNN
YYWW
8-Lead SOIC (150 mil)
XXXXXXXX
XXXXYYWW
NNN
8-Lead MSOP
XXXXXX
YWWNNN
Example:
MCP6141
I/P058
0223
Example:
MCP6142
I/SN0223
058
Example:
6143I
223058
Legend: XX...X Customer specific information*
YY Year code (last 2 digits of calendar year)
WW Week code (week of January 1 is week ‘01’)
NNN Alphanumeric traceability code
Note: In the event the full Microchip part number cannot be marked on one line, it will
be carried over to the next line thus limiting the number of available characters
for customer specific information.
* Standard marking consists of Microchip part number, year code, week code, traceability code (facility
code, mask rev#, and assembly code). For marking beyond this, certain price adders apply. Please
check with your Microchip Sales Office.
21668A-page 18 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

5.1 Package Marking Information (Continued)
14-Lead PDIP (300 mil) (MCP6144) Example:
MCP6141/2/3/4
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
YYWWNNN
14-Lead SOIC (150 mil) (MCP6144)
XXXXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXXX
YYWWNNN
14-Lead TSSOP (MCP6144)
XXXXXX
YYWW
NNN
MCP6144-I/P
0223058
Example:
MCP6144ISL
0223058
Example:
6144ST
0223
058
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 19
Page 20

MCP6141/2/3/4
8-Lead Plastic Dual In-line (P) – 300 mil (PDIP)
E1
D
2
n
E
β
eB
Number of Pins
Pitch
Top to Seating Plane A .140 .155 .170 3.56 3.94 4.32
Molded Package Thickness A2 .115 .130 .145 2.92 3.3 0 3.68
Base to Seating P lane A1 .015 0.38
Shoulder to Shoulder Width E .300 .313 .325 7.62 7.94 8.26
Molded Package Width E1 .240 .250 .260 6.10 6.35 6.60
Overall Length D .360 .373 .385 9.14 9.46 9.78
Tip to Seating Plane L .125 .130 .135 3.18 3.30 3.43
Lead Thickness
Upper Lead Width B1 .045 .058 .070 1.14 1.46 1.78
Lower Lead Width B .014 .018 .022 0.36 0.46 0.56
Overall Row Spacing § eB .310 .370 .430 7.87 9.40 1 0.92
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-001
Drawing No. C04-018
Dimension Limits MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
1
α
A
c
Units INCHES* MILLIMETERS
n
p
c
α
β
.008 .012 .015 0.20 0.29 0.38
A1
B1
B
88
.100 2.54
51015 51015
51015 51015
A2
L
p
21668A-page 20 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

8-Lead Plastic Small Outline (SN) – Narrow, 150 mil (SOIC)
E
E1
p
D
2
MCP6141/2/3/4
B
Number of Pins
Pitch
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Paramete r
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-012
Drawing No. C04-057
n
45°
c
β
n
p
φ
c
α
β
1
h
A
φ
L
048048
A1
MILLIMETERSINCHES*Units
1.27.050
α
A2
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
88
1.751.551.35.069.061.053AOverall Height
1.551.421.32.061.056.052A2Molded Package Thickness
0.250.180.10.010.007.004A1Standoff §
6.206.025.79.244.237.228EOverall Width
3.993.913.71.157.154.146E1Molded Package Width
5.004.904.80.197.193.189DOverall Length
0.510.380.25.020.015.010hChamfer Distance
0.760.620.48.030.025.019LFoot Length
0.250.230.20.010.009.008
0.510.420.33.020.017.013BLead Width
1512015120
1512015120
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 21
Page 22

MCP6141/2/3/4
8-Lead Plastic Micro Small Outline Package (MS) (MSOP)
p
B
n 1
c
(F)
β
Dimension Limits
Number of Pins
Pitch
Overall Height
Molded Package Thickness
Standoff §
Overall Width
Molded Package Width
Overall Length
Foot Length
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Lead Width
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
*Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not
exceed .010" (0.254mm ) per side.
Drawing No. C04-111
E1
E
D
2
A
Units
n
p
A
A2
A1
E
E1
D
L
φ
c
B
α
β
MIN
.030
.002
.184
.114
.114
.016
.004
.010
φ
L
INCHES
NOM
.026
.034
.193
.118
.118
.022
.037.035FFootprint (Reference)
0
.006
.012
A1
8
.044
.038
.006
.200
.122
.122
.028
6
.008
.016
7
7
MILLIMETERS*
MINMAX NOM
0.65
0.76
0.05
4.67
2.90
2.90
0.40
0
0.10
0.25
0.86
4.90
3.00
3.00
0.55
0.15
0.30
α
A2
MAX
8
1.18
0.97
0.15
.5.08
3.10
3.10
0.70
1.000.950.90.039
6
0.20
0.40
7
7
21668A-page 22 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

14-Lead Plastic Dual In-line (P) – 300 mil (PDIP)
E1
D
2
MCP6141/2/3/4
n
E
β
eB
Number of Pins
Pitch
Top to Seating Plane A .140 .155 .170 3.56 3.94 4.32
Molded Package Thickness A2 .115 .130 .145 2.92 3.30 3.68
Base to Seating Plane A1 .015 0.38
Shoulder to Shoulder Width E .300 .313 .325 7.62 7.94 8.26
Molded Package Width E1 .240 .250 .260 6.10 6.35 6.60
Overall Length D .740 .750 .760 18.80 19 .05 19.30
Tip to Seating Plane L .125 .130 .135 3.18 3.30 3.43
Lead Thickness
Upper Lead Width B1 .045 .058 .070 1.14 1.46 1.78
Lower Lead Width B .014 .018 .022 0.36 0.46 0.56
Overall Row Spacing § eB .310 .370 .430 7.87 9.40 10.92
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-001
Drawing No. C04-005
1
A
c
A1
Dimension Limits MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
Units INCHES* MILLIMETERS
n
p
c
α
β
.008 .012 .015 0.20 0.29 0.38
5 10 1 5 5 10 15
5 10 1 5 5 10 15
B1
B
14 14
.100 2.54
α
A2
L
p
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 23
Page 24

MCP6141/2/3/4
14-Lead Plastic Small Outline (SL) – Narrow, 150 mil (SOIC)
E
E1
p
D
2
B
n
1
45°
c
β
Number of Pins
Pitch
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Paramete r
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-012
Drawing No. C04-065
h
A
φ
L
n
p
φ
c
α
β
A1
048048
α
MILLIMETERSINCHES*Units
1.27.050
A2
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
1414
1.751.551.35.069.061.053AOverall Height
1.551.421.32.061.056.052A2Molded Package Thickness
0.250.180.10.010.007.004A1Standoff §
6.205.995.79.244.236.228EOverall Width
3.993.903.81.157.154.150E1Molded Package Width
8.818.698.56.347.342.337DOverall Length
0.510.380.25.020.015.010hChamfer Distance
1.270.840.41.050.033.016LFoot Len gth
0.250.230.20.010.009.008
0.510.420.36.020.017.014BLead Width
1512015120
1512015120
21668A-page 24 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25

MCP6141/2/3/4
14-Lead Plastic Thin Shrink Small Outline (ST) – 4.4 mm (TSSOP)
E
E1
p
D
2
n
B
1
A
c
φ
β
Number of Pins
Pitch
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.005” (0.127mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent : MO-153
Drawing No. C04-087
n
p
φ
c
α
β
L
MILLIMETERS*INCHESUnits
0.65.026
α
A2A1
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
1414
1.10.043AOverall Height
0.950.900.85.037.035.033A2Molded Package Thickness
0.150.100.05.006.004.002A1Standoff §
6.506.386.25.256.251.246EOverall Width
4.504.404.30.177.173.169E1Molded Package Width
5.105.004.90.201.197.193DMolded Package Length
0.700.600.50.028.024.020LFoot Len gth
840840
0.200.150.09.008.006.004
0.300.250.19.012.010.007B1Lead Width
10501050
10501050
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. 21668A-page 25
Page 26

MCP6141/2/3/4
NOTES:
21668A-page 26 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27

MCP6141/2/3/4
ON-LINE SUPPORT
Microchip provides on-line support on the Microchip
World Wide Web site.
The web site is used by Microchip as a means to make
files and information easily available to customers. To
view the site, the user must have access to the Internet
and a web browser, such as Netscape
Internet Explorer. Files are also available for FTP
download from our FTP site.
Connecting to the Microchip Internet Web Site
The Microchip web site is available at the following
URL:
www.microchip.com
The file transfer site is available by using an FTP service to connect to:
ftp://ftp.microchip.com
The web site and file transfer site provide a variety of
services. Users may download files for the latest
Development Tools, Data Sheets, Application Notes,
User's Guides, Articles and Sample Programs. A variety of Microchip specific business information is also
available, including listings of Microchip sales offices,
distributors and factory representatives. Other data
available for consideration is:
• Latest Microchip Press Releases
• Technical Support Section with Frequently Asked
Questions
• Design Tips
• Device Errata
• Job Postings
• Microchip Consultant Program Member Listing
• Links to other useful web sites related to
Microchip Products
• Conferences for products, Development Systems,
technical information and more
• Listing of seminars and events
®
or Microsoft
SYSTEMS INFORMATION AND
UPGRADE HOT LINE
The Systems Information and Upgrade Line provides
system users a listing of the latest versions of all of
Microchip's development systems software products.
®
Plus, this line provides information on how customers
can receive the most current upgrade kits.The Hot Line
Numbers are:
1-800-755-2345 for U.S. and most of Canada, and
1-480-792-7302 for the rest of the world.
092002
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21668A-page 27
Page 28

MCP6141/2/3/4
READER RESPONSE
It is our intention to provide you with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip product. If you wish to provide your comments on organization, clarity, subject matter, and ways in which our documentation
can better serve you, please FAX your comments to the Technical Publications Manager at (480) 792-4150.
Please list the following information, and use this outline to provide us with your comments about this document.
To :
RE: Reader Response
From:
Application (optional):
Would you like a reply? Y N
Device:
Questions:
1. What are the best features of this document?
2. How does this document meet your hardware and software development needs?
3. Do you find the organization of this document easy to follow? If not, why?
Technical Publications Manager
Name
Company
Address
City / State / ZIP / Country
Telephone: (_______) _________ - _________
MCP6141/2/3/4
Literature Number:
Total Pages Sent ________
FAX: (______) _________ - _________
DS21668A
4. What additions to the document do you think would enhance the structure and subject?
5. What deletions from the document could be made without affecting the overall usefulness?
6. Is there any incorrect or misleading information (what and where)?
7. How would you improve this document?
DS21668A-page 28 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 29

MCP6141/2/3/4
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM
To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office.
PART NO. X /XX
Device
PackageTemper atu re
Range
Device: MCP6141: CMOS Single Op Amp
MCP6141T: CMOS Single Op Amp
MCP6142: CMOS Dual Op Amp
MCP6142T: CMOS Dual Op Amp
MCP6143: CMOS Single Op Amp w/CS
MCP6143T: CMOS Single Op Amp w/CS
MCP6144: CMOS Quad Op Amp
MCP6144T: CMOS Quad Op Amp
(Tape and Reel for SOIC, MSOP)
(Tape and Reel for SOIC and TSSOP)
(Tape and Reel for SOIC and MSOP)
(Tape and Reel for SOIC and TSSOP)
Function
Function
Examples:
a) MCP6141-I/P: Industrial tempe rature,
PDIP package.
b) MCP6141T-I/SN: Tape and Reel, Indus-
trial temperature, SOIC package.
a) MCP6142-I/SN: Industrial temperature,
SOIC package .
b) MCP6142-I/MS: Industrial temperature,
MSOP package.
a) MCP6143-I/MS: Industrial temperature,
MSOP package.
b) MCP6143-I/P: Industrial tempe rature,
PDIP package.
Temperature Range: I = -40°C to +85°C
Package: MS = Plastic MSOP, 8-lead
P = Plastic DIP (300 mil Bo dy), 8-lead, 14-lead
SN = Plastic SOIC (150 mil Body), 8-lead
SL = Plastic SOIC (150 mil Body), 14-lead
ST = Plastic TSSOP ( 4.4mm Body), 14-lead
a) MCP6144-I/SL: Industrial temperature,
SIOC package .
b) MCP6144T-I/ST: Tape and Reel, Indus-
trial temperature, TSSOP package.
Sales and Support
Data Sheets
Products supported by a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences and recommended workarounds. To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please contact one of the following:
1. Your local Microchip sales office
2. The Microchip Corporate Literature Center U.S. FAX: (480) 792-7277
3. The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Please specify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (include Literature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21668A-page 29
Page 30

MCP6141/2/3/4
NOTES:
DS21668A-page 30 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 31

Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
assumed by Micr ochip Technology Incorporated with respect
to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual propert y rights arising from such
use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical components in life support systems is not authorized except with
express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual property
rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, K
EELOQ
MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART and PRO MATE are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A. and other countries.
FilterLab, microID, MXDEV, MXLAB, PICMASTER, SEEVAL
and The Embedded Control Solutions Company are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
dsPIC, dsPICDEM.net, ECONOMONITOR, FanSense,
FlexROM, fuzzyLAB, In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP,
ICEPIC, microPort, Migratable Memory, MPASM, MPLIB,
MPLINK, MPSIM, PICC, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, rfPIC, Select
Mode and Total Endurance are trademarks of Microchip
Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
Serialized Quick Turn Programming (SQTP) is a service mark
of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2002, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
,
Microchip received QS-9000 quality system
certification for its worldwide headquarters,
design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona in July 1999
and Mountain View, California in March 2002.
The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are QS-9000 compliant for its
PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals,
non-volatile memory and analog products. In
addition, Microchip’s qua lity system for the
design and manufacture of development
systems is ISO 9001 certified.
®
8-bit MCUs, KEEL
®
code hopping
OQ
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21668A - page 31
Page 32

M
W
ORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler B lvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200 Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: http://www.microchip.com
Rocky Mountain
2355 West Chandler B lvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7966 Fax: 480-792-4338
Atlanta
500 Sugar Mill Road, Suite 200B
Atlanta, GA 30350
Tel: 770-640-0034 Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
2 Lan Drive, Suit e 120
Westford, MA 01886
Tel: 978-692-3848 Fax: 978-692-3821
Chicago
333 Pierce Road, S uite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 630-285-0071 Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
4570 Westgrove Drive, Suite 160
Addison, TX 75001
Tel: 972-818-7423 Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Tri-Atria Office Building
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190
Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Tel: 248-538-2250 Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
2767 S. Albright Road
Kokomo, Indiana 46902
Tel: 765-864-8360 Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
18201 Von Karman, Suite 10 90
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 949-263-1888 Fax: 949-263-1338
New York
150 Motor Parkwa y, Suite 202
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Tel: 631-273-5305 Fax: 631-273-5335
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First S treet, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408-436-7950 Fax: 408-436-7955
Toro nt o
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699 Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd
Suite 22, 41 Rawson Street
Epping 2121, NSW
Australia
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Beijing Liaison Office
Unit 915
Bei Hai Wan Tai Bldg.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Beidajie
Beijing, 100027, No. China
Tel: 86-10-852821 00 Fax: 86-10-85282104
China - Chengdu
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Chengdu Liaison Office
Rm. 2401, 24th Floor,
Ming Xing Financial Tower
No. 88 TIDU Street
Chengdu 610016, China
Tel: 86-28-867662 00 Fax: 86-28-86766599
China - Fuzhou
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Fuzhou Liaison Office
Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza
No. 71 Wusi Road
Fuzhou 350001, China
Tel: 86-591-75035 06 Fax: 86-591-7503521
China - Shanghai
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd.
Room 701, Bldg. B
Far East International Plaza
No. 317 Xian Xia Road
Shanghai, 200051
Tel: 86-21-6275-5700 Fax: 86-21-6275 -5060
China - Shenzhen
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Shenzhen L iaison Office
Rm. 1315, 13/F, Shenzhen Kerry Centre,
Renminnan Lu
Shenzhen 518001, Ch ina
Tel: 86-755-23503 61 Fax: 86-755-2366086
China - Hong Kong SAR
Microchip Technology Hongkong Ltd.
Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-120 0 Fax: 852-2401-3431
India
Microchip Technology Inc.
India Liaison Office
Divyasree Chambers
1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Bangalore, 560 025, India
Tel: 91-80-229006 1 Fax: 91-80-2290062
Japan
Microchip Technology Japan K.K.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shinyokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama-shi
Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea
Microchip Technology Korea
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku
Seoul, Korea 135-882
Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-5934
Singapore
Microchip Technology Singapore Pte Ltd.
200 Middle Road
#07-02 Prime Centre
Singapore, 188980
Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Ta iw an
Microchip Technology (Barbados) Inc.,
Taiwan Branch
11F-3, No. 207
Tung Hua North Road
Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
EUROPE
Austria
Microchip Technology Austria GmbH
Durisolstrasse 2
A-4600 Wels
Austria
Tel: 43-7242-2244-399
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark
Microchip Technology Nordic ApS
Regus Business Centre
Lautrup hoj 1-3
Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Tel: 45 4420 9895 Fax: 45 4420 9910
France
Microchip Technology SARL
Parc d’Activite du Moulin de Massy
43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Batiment A - ler Etage
91300 Massy, France
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany
Microchip Technology GmbH
Steinheilstrasse 10
D-85737 Ismaning, Germany
Tel: 49-89-627-144 0 Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy
Microchip Technology SRL
Centro Direzionale Colleoni
Palazzo Taurus 1 V. Le Colleoni 1
20041 Agrate Brianza
Milan, Italy
Tel: 39-039-65791-1 Fax: 39-039-689988 3
United Kingdom
Microchip Ltd.
505 Eskdale Road
Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham
Berkshire, England RG41 5TU
Tel: 44 118 921 5869 Fax: 44-118 921-5820
08/01/02
DS21668A-page 32 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...