Page 1
M
2.7V 4-Channel/8-Channel 10-Bit A/D Converters
MCP3004/3008
with SPI™ Serial Interface
Features
• 10-bit resolution
• ± 1 LSB max DNL
• ± 1 LSB max INL
• 4 (MCP3004) or 8 (MCP3008) input channels
• Analog inputs programmable as single-ended or
pseudo-differential pairs
• On-chip sample and hold
• SPI serial interface (modes 0,0 and 1,1)
• Single supply operation: 2.7V - 5.5V
• 200 ksps max. sampling rate at V
• 75 ksps max. sampling rate at V
DD
= 2.7V
DD
= 5V
• Low power CMOS technology
• 5 nA typical standby current, 2 µA max.
• 500 µA max. active current at 5V
• Industrial temp range: -40°C to +85°C
• Available in PDIP, SOIC and TSSOP packages
Applications
• Sensor Interface
• Process Control
• Data Acquisition
• Battery Operated Systems
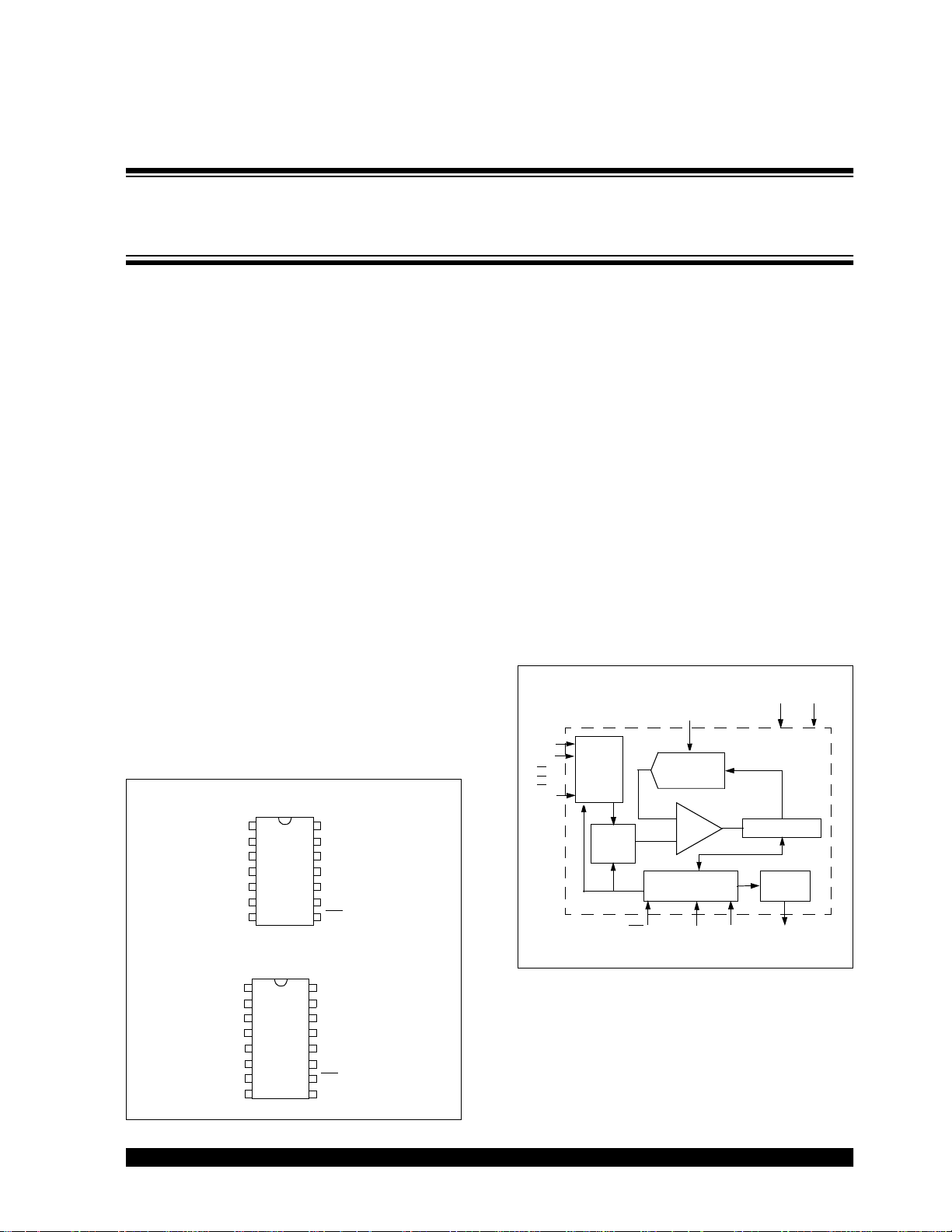
Package Types
PDIP, SOIC, TSSOP
14
MCP3004
13
12
11
10
9
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
V
DD
V
REF
AGND
CLK
D
OUT
D
IN
CS
/SHDN
V
DD
V
REF
AGND
CLK
D
OUT
D
IN
CS/SHDN
DGND
PDIP, SOIC
CH0
CH1
CH2
CH3
NC
NC
DGND
CH0
CH1
CH2
CH3
CH4
CH5
CH6
CH7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
MCP3008
Description
The Microchip Technology Inc. MCP3004/3008
devices are successive approximation 10-bit Analogto-Digital (A/D) converters with on-board sample and
hold circuitry. The MCP3004 is programmable to provide two pseudo-differential input pairs or four singleended inputs. The MCP3008 is programmable to provide four pseudo-differential input pairs or eight singleended inputs. Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) and Integral Nonlinearity (INL) are specified at ±1 LSB. Communication with the devices is accomplished using a
simple serial interface compatible with the SPI protocol.
The devices are capable of conversion rates of up to
200 ksps. The MCP3004/3008 devices operate over a
broad voltage range (2.7V - 5.5V). Low current design
permits operation with typical standby currents of only
5 nA and typical active currents of 320 µA. The
MCP3004 is offered in 14-pin PDIP, 150 mil SOIC and
TSSOP packages, while the MCP3008 is offered in 16pin PDIP and SOIC packages.
Functional Block Diagram
V
V
SS
V
REF
CH0
CH1
CH7*
* Note: Channels 4-7 available on MCP3008 Only
Input
Channel
Max
Sample
and
Hold
CS/SHDN
DAC
Compar ator
Control Logic
D
IN
CLK D
DD
10-Bit SAR
Shift
Regist er
OUT
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 1
Page 2
MCP3004/3008
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
VDD........................................................................7.0V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. V
Storage temperature .......................... -65°C to +150°C
Ambient temp. with power applied .....-65°C to +125°C
Soldering temperature of leads (10 seconds) .. +300°C
ESD protection on all pins .................................. > 4 kV
*Notice: Stresses above those listed under "Maximum
Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. This is
a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at
those or any other conditions above those indicated in the
operation listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure
to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
.....-0.6V to VDD +0.6V
SS
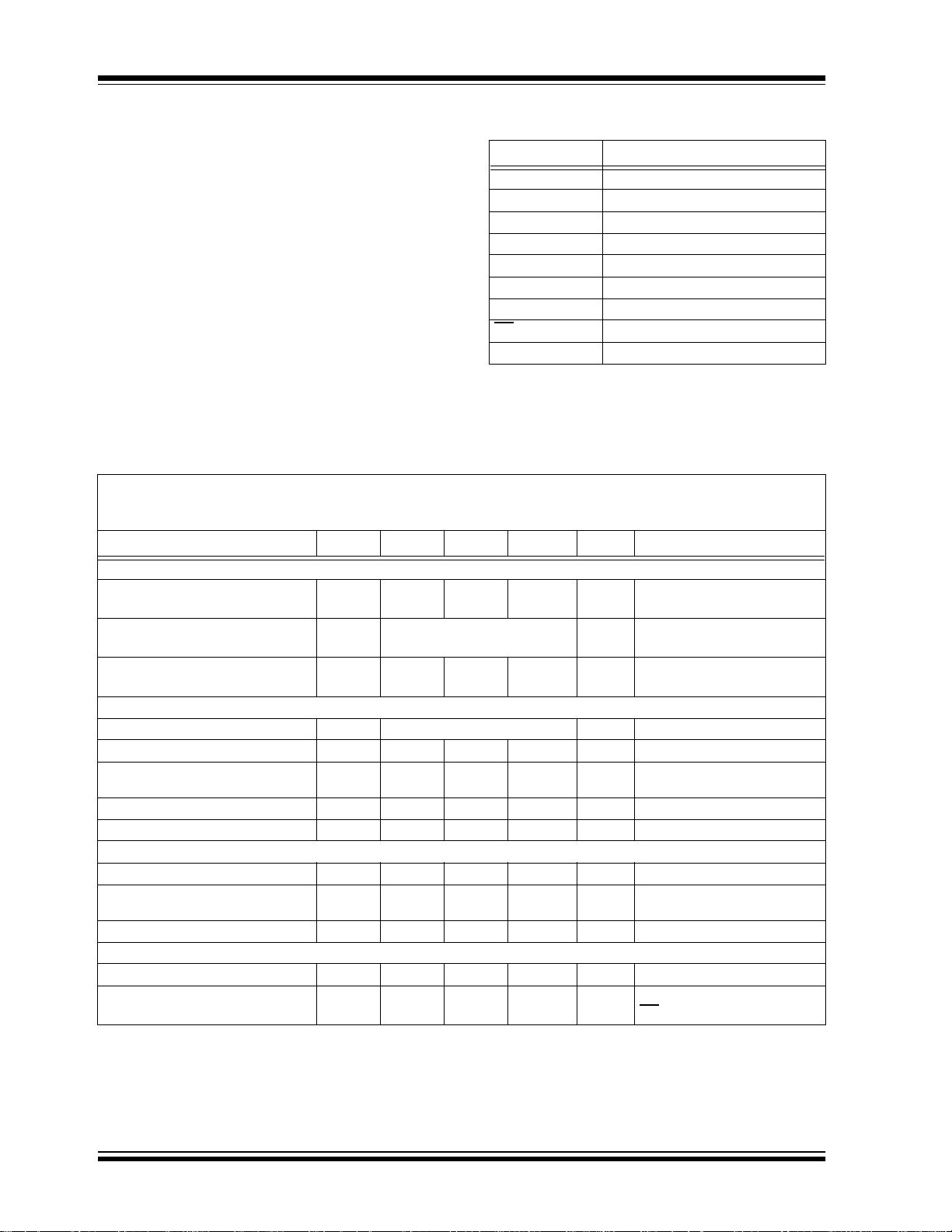
PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Name Function
V
DD
DGND Digital Ground
AGND Analog Ground
CH0-CH7 Analog Inputs
CLK Serial Clock
D
IN
D
OUT
/SHDN Chip Select/Shutdown Input
CS
V
REF
+2.7V to 5.5V Power Supply
Serial Data In
Serial Data Out
Reference Voltage Input
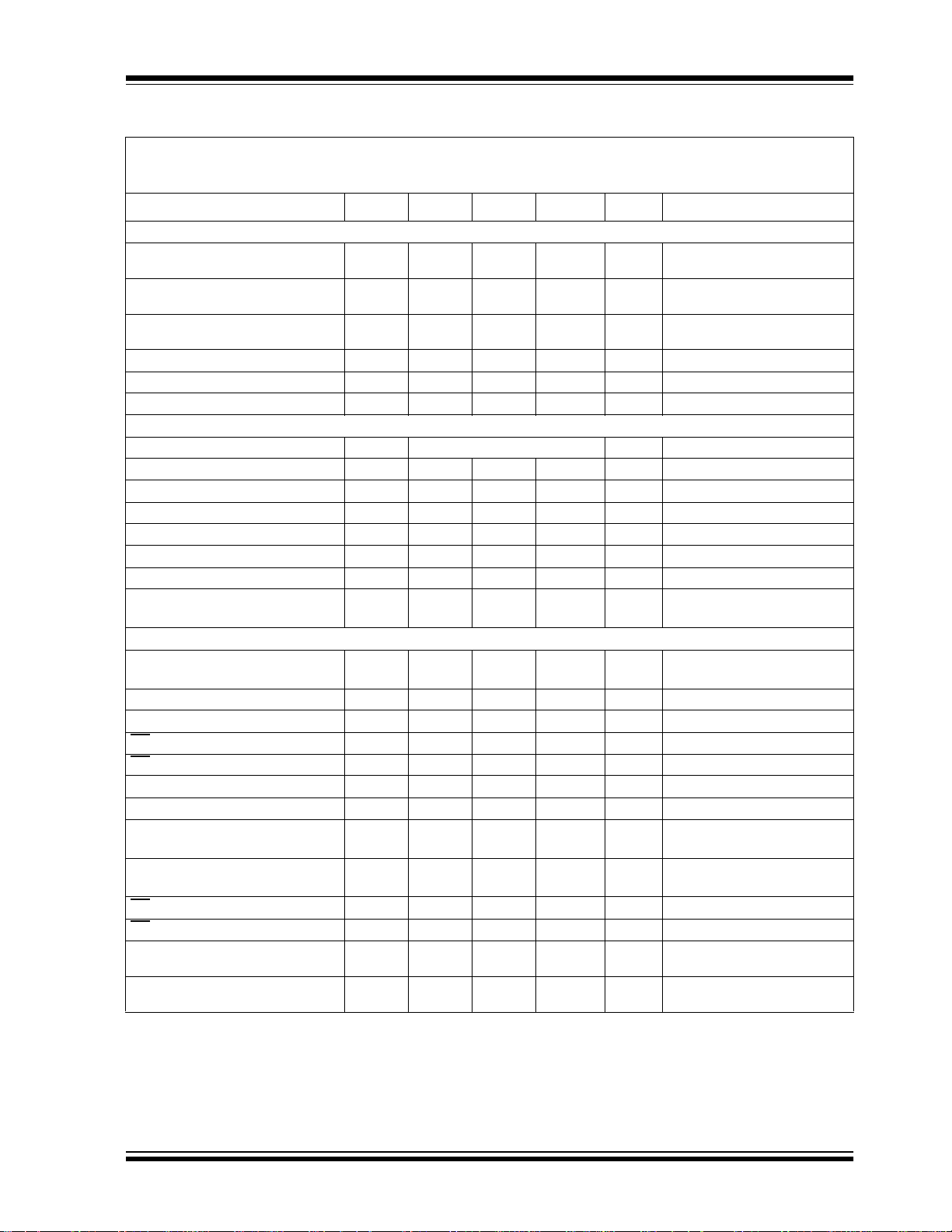
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, all parameters apply at V
T
= -40°C to +85°C, f
AMB
V
= 5V, T
DD
AMB
= 25°C.
= 200 ksps and f
SAMPLE
CLK
= 18*f
. Unless otherwise noted, typical values apply for
SAMPLE
= 5V, V
DD
Parameter Sym Min Typ Max Units Conditions
Conversion Rate
Conversion Time t
CONV
— — 10 clock
cycles
Analog Input Sample Time t
SAMPLE
1.5 clock
cycles
Throughput Rate f
SAMPLE
——20075ksps
ksps
DC Accuracy
Resolution 10 bits
Integral Nonlinearity INL — ±0.5 ±1 LSB
Differential Nonlinearity DNL — ±0.25 ±1 LSB No missing codes over
Offset Error — — ±1.5 LSB
Gain Error — — ±1.0 LSB
Dynamic Performance
Total Harmonic Distortion — -76 dB V
Signal to Noise and Distortion
—61 dBV
(SINAD)
Spurious Free Dynamic Range — 78 dB V
Reference Input
Voltage Range 0.25 — V
Current Drain — 100
0.001
DD
150
3
V Note 2
µA
µA CS
Note 1: This parameter is established by characterization and not 100% tested.
2: See graphs that relate linearity performance to V
REF
levels.
3: Because the sample cap will eventually lose charge, effective clock rates below 10 kHz can affect linearity
performance, especially at elevated temperatures. See Section 6.2, “Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed”,
for more information.
= 5V,
REF
VDD = V
V
= V
DD
REF
REF
= 5V
= 2.7V
temperature
= 0.1V to 4.9V@1 kHz
IN
= 0.1V to 4.9V@1 kHz
IN
= 0.1V to 4.9V@1 kHz
IN
= VDD = 5V
DS21295B-page 2 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (CONTINUED)
MCP3004/3008
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, all parameters apply at V
T
= -40°C to +85°C, f
AMB
V
= 5V, T
DD
AMB
= 25°C.
= 200 ksps and f
SAMPLE
CLK
= 18*f
. Unless otherwise noted, typical values apply for
SAMPLE
= 5V, V
DD
REF
= 5V,
Parameter Sym Min Typ Max Units Conditions
Analog Inputs
Input Voltage Range for CH0 or
CH1 in Single-Ended Mode
Input Voltage Range for IN+ in
pseudo-differential mode
Input Voltage Range for IN- in
pseudo-differential mode
V
SS
IN- — V
-100 — VSS+100 mV
V
SS
—V
REF
REF
+IN-
V
Leakage Current — 0.001 ±1 µA
Switch Resistance — 1000 — Ω See Figure 4-1
Sample Capacitor — 20 — pF See Figure 4-1
Digital Input/Output
Data Coding Format Straight Binary
High Level Input Voltage V
Low Level Input Voltage V
High Level Output Voltage V
Low Level Output Voltage V
Input Leakage Current I
Output Leakage Current I
Pin Capacitance
(All Inputs/Outputs)
CIN,
C
IH
IL
OH
OL
LI
LO
OUT
0.7 V
DD
4.1——VI
——0.4VI
-10 — 10 µA VIN = VSS or V
-10 — 10 µA V
— — 10 pF VDD = 5.0V (Note 1)
——V
—0.3 VDDV
OH
OL
OUT
T
AMB
= -1 mA, VDD = 4.5V
= 1 mA, VDD = 4.5V
= VSS or V
= 25°C, f = 1 MHz
Timing Parameters
Clock Frequency f
Clock High Time t
Clock Low Time t
Fall To First Rising CLK Edge t
CS
Fall To Falling CLK Edge t
CS
Data Input Setup Time t
Data Input Hold Time t
CLK Fall To Output Data Valid t
CLK Fall To Output Enable t
Rise To Output Disable t
CS
Disable Time t
CS
Rise Time t
D
OUT
Fall Time t
D
OUT
CLK
HI
LO
SUCS
CSD
SU
HD
DO
EN
DIS
CSH
R
F
——3.6
1.35
MHz
MHz
VDD = 5V (Note 3)
V
= 2.7V (Note 3)
DD
125 — — ns
125 — — ns
100 — — ns
—— 0 ns
— — 50 ns
— — 50 ns
——125
200
——125
200
nsnsVDD = 5V, See Figure 1-2
V
= 2.7V, See Figure 1-2
DD
nsnsVDD = 5V, See Figure 1-2
V
= 2.7V, See Figure 1-2
DD
— — 100 ns See Test Circuits, Figure 1-2
270 — — ns
— — 100 ns See Test Circuits, Figure 1-2
(Note 1)
— — 100 ns See Test Circuits, Figure 1-2
(Note 1)
Note 1: This parameter is established by characterization and not 100% tested.
2: See graphs that relate linearity performance to V
REF
levels.
3: Because the sample cap will eventually lose charge, effective clock rates below 10 kHz can affect linearity
performance, especially at elevated temperatures. See Section 6.2, “Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed”,
for more information.
DD
DD
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 3
Page 4
MCP3004/3008
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (CONTINUED)
Electrical Characteristics: Unless otherwise noted, all parameters apply at V
T
= -40°C to +85°C, f
AMB
V
= 5V, T
DD
AMB
= 25°C.
= 200 ksps and f
SAMPLE
CLK
= 18*f
. Unless otherwise noted, typical values apply for
SAMPLE
= 5V, V
DD
REF
= 5V,
Parameter Sym Min Typ Max Units Conditions
Power Requirements
Operating Voltage V
Operating Current I
Standby Current I
DD
DD
DDS
2.7 — 5.5 V
— 425
225
550 µA VDD = V
D
unloaded
OUT
V
= V
DD
D
unloaded
OUT
REF
REF
= 5V,
= 2.7V,
—0.005 2 µACS = VDD = 5.0V
Temperature Ranges
Specified Temperature Range T
Operating Temperature Range T
Storage Temperature Range T
A
A
A
-40 — +85 °C
-40 — +85 °C
-65 — +150 °C
Thermal Package Resistance
Thermal Resistance, 14L-PDIP θ
Thermal Resistance, 14L-SOIC θ
Thermal Resistance, 14L-TSSOP θ
Thermal Resistance, 16L-PDIP θ
Thermal Resistance, 16L-SOIC θ
JA
JA
JA
JA
JA
—70 —°C/W
— 108 — °C/W
— 100 — °C/W
—70 —°C/W
—90 —°C/W
Note 1: This parameter is established by characterization and not 100% tested.
2: See graphs that relate linearity performance to V
REF
levels.
3: Because the sample cap will eventually lose charge, effective clock rates below 10 kHz can affect linearity
performance, especially at elevated temperatures. See Section 6.2, “Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed”,
for more information.
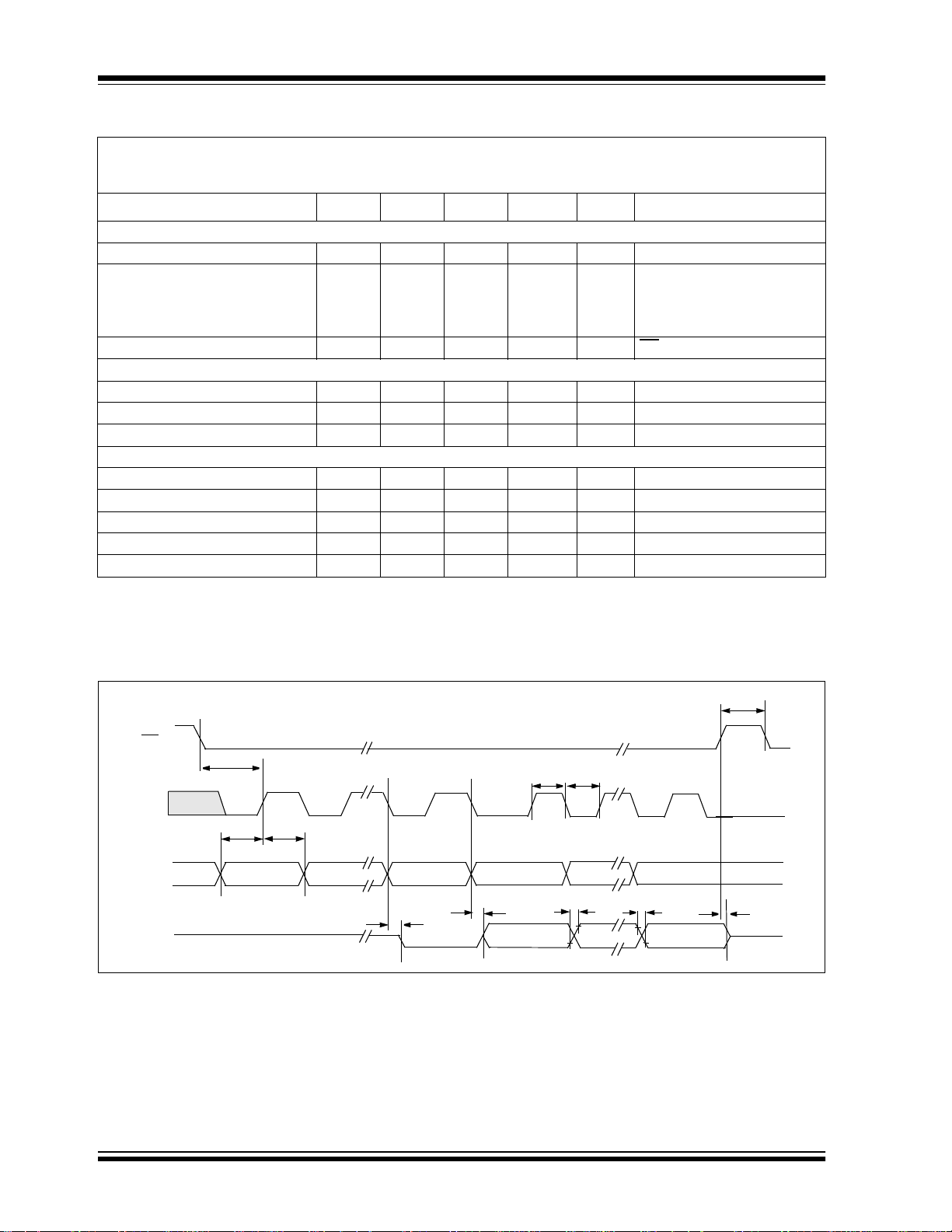
D
CS
CLK
D
OUT
IN
T
SUCS
T
SU
MSB IN
T
HD
FIGURE 1-1: Serial Interface Timing.
T
CSH
THIT
LO
T
T
EN
DO
NULL BIT
T
R
T
F
T
DIS
LSBMSB OUT
DS21295B-page 4 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5
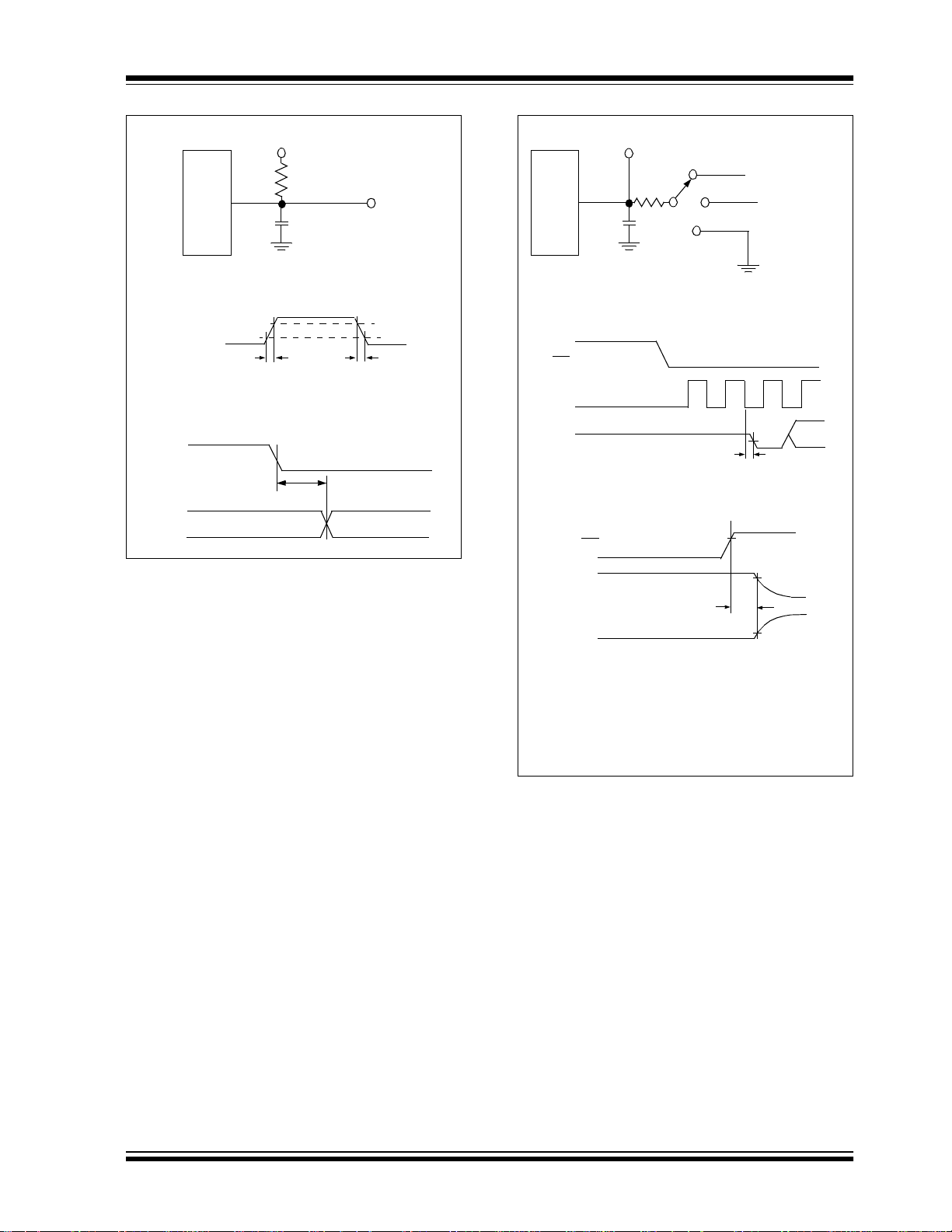
MCP3004/3008
1.4V
3kΩ
D
OUT
C
= 100 pF
L
Voltage Waveforms for tR, t
D
OUT
t
R
Voltage Waveforms for t
CLK
t
DO
D
OUT
FIGURE 1-2: Load Circuit for t
Te s t P o in t
F
V
t
F
DO
, tF, tDO.
R
OH
V
OL
Test P o i n t
V
DD
3kΩ
D
OUT
VDD/2
100 pF
V
SS
Voltage Waveforms for t
t
Waveform 2
DIS
tEN Wave form
Waveform 1
t
DIS
EN
CS
CLK
D
OUT
CS
D
OUT
Waveform 1*
D
OUT
12
Voltage Waveforms for t
V
IH
T
DIS
DIS
3
t
EN
90%
10%
Waveform 2†
* Waveform 1 is for an output with internal
conditions such that the output is high,
unless disabled by the output control.
† Waveform 2 is for an output with internal
conditions such that the output is low,
unless disabled by the output control.
4
B9
FIGURE 1-3: Load circuit for t
and tEN.
DIS
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 5
Page 6

MCP3004/3008
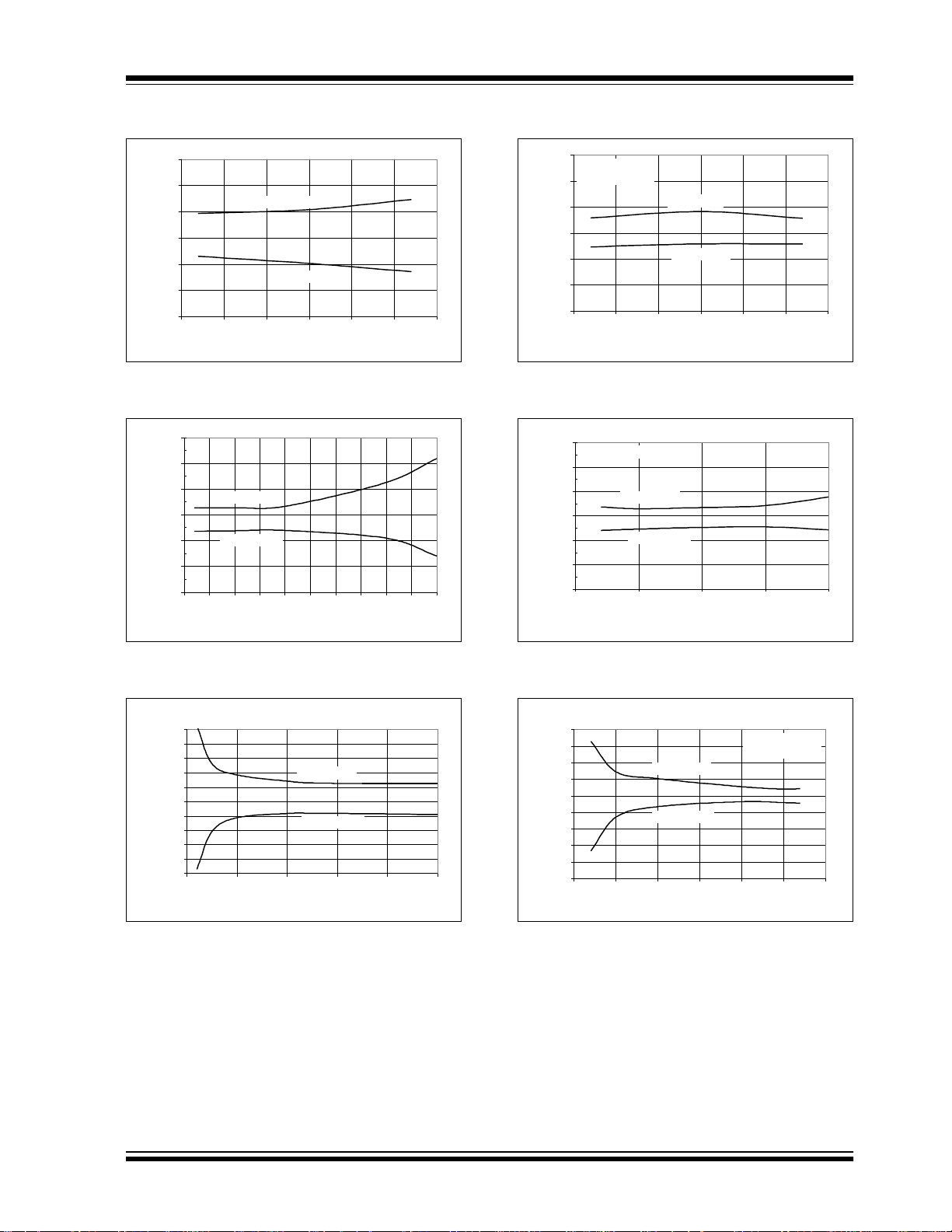
2.0 TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Note: The graphs and tables provided following this note are a statistical summary based on a limited number of
samples and are provided for informational purposes only. The performance characteristics listed herein
are not tested or guaranteed. In some graphs or tables, the data presented may be outside the specified
operating range (e.g., outside specified power supply range) and therefore outside the warranted range.
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
DD
= V
REF
= 5V, f
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
, TA = 25°C.
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
INL (LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
Positive I NL
Negative INL
Sample Rate (ksps)
FIGURE 2-1: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs. Sample Rate.
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
INL(LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
0123456
Positive INL
Negative INL
V
REF
(V)
1.0
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
INL (LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
REF
Positive I NL
Negative INL
0255075100
Sample Rate (ksps)
FIGURE 2-4: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs.
Sample Rate (V
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
INL(LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2. 0 2.5 3.0
= 2.7V).
DD
Positive I NL
Negative INL
V
(V)
REF
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 2.7 V
REF
= 75 ksps
FIGURE 2-2: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs.
.
V
REF
0.5
VDD = V
= 5 V
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
-0.1
INL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
-0.5
REF
f
= 200 ksps
SAMPLE
0 12 8 256 384 512 640 76 8 89 6 1024
Digital Code
FIGURE 2-3: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs. Code (Representative Part).
FIGURE 2-5: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs.
(VDD = 2.7V).
V
REF
0.5
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.0
-0.1
INL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
-0.5
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
0 12 8 256 384 512 640 76 8 89 6 1024
Digital Code
FIGURE 2-6: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs.
Code (Representative Part, V
= 2.7V).
DD
DS21295B-page 6 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7
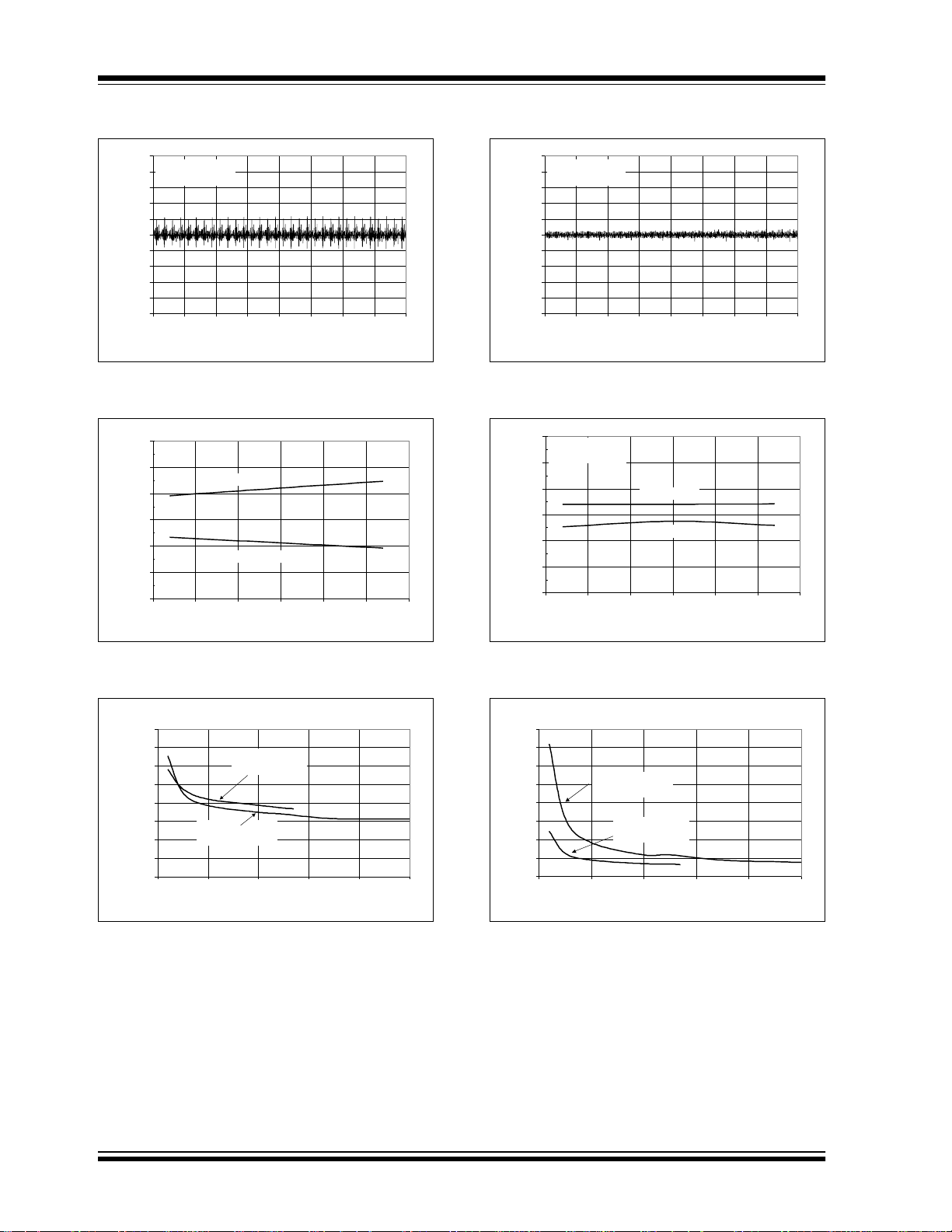
MCP3004/3008
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
INL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
-50-25 0 255075100
Positive I NL
Negative INL
DD
= V
REF
= 5V, f
Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2-7: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs. Temperature.
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
DNL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
Positive D NL
Negative DNL
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 225 250
Sample Rate (ksps)
CLK
= 18* f
, TA = 25°C.
SAMPLE
0.6
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
0.4
0.2
0.0
INL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
-50-25 0 255075100
Positive I NL
Negative INL
Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2-10: Integral Nonlinearity (INL) vs.
Temperature (V
0.6
VDD = V
0.4
0.2
0.0
DNL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
0255075100
= 2.7V).
DD
= 2.7 V
REF
Positive D NL
Negative DNL
Sample Rate (ksps)
FIGURE 2-8: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) vs. Sample Rate.
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
DNL (LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
012345
Positive D NL
Negative DNL
V
(V)
REF
FIGURE 2-9: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
REF
.
vs. V
FIGURE 2-11: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
vs. Sample Rate (V
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
DNL (LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2. 5 3.0
= 2.7V).
DD
Positive D NL
Negative DNL
V
REF
(V)
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 2.7 V
REF
= 75 ksps
FIGURE 2-12: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
vs. V
REF (VDD
= 2.7V).
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 7
Page 8
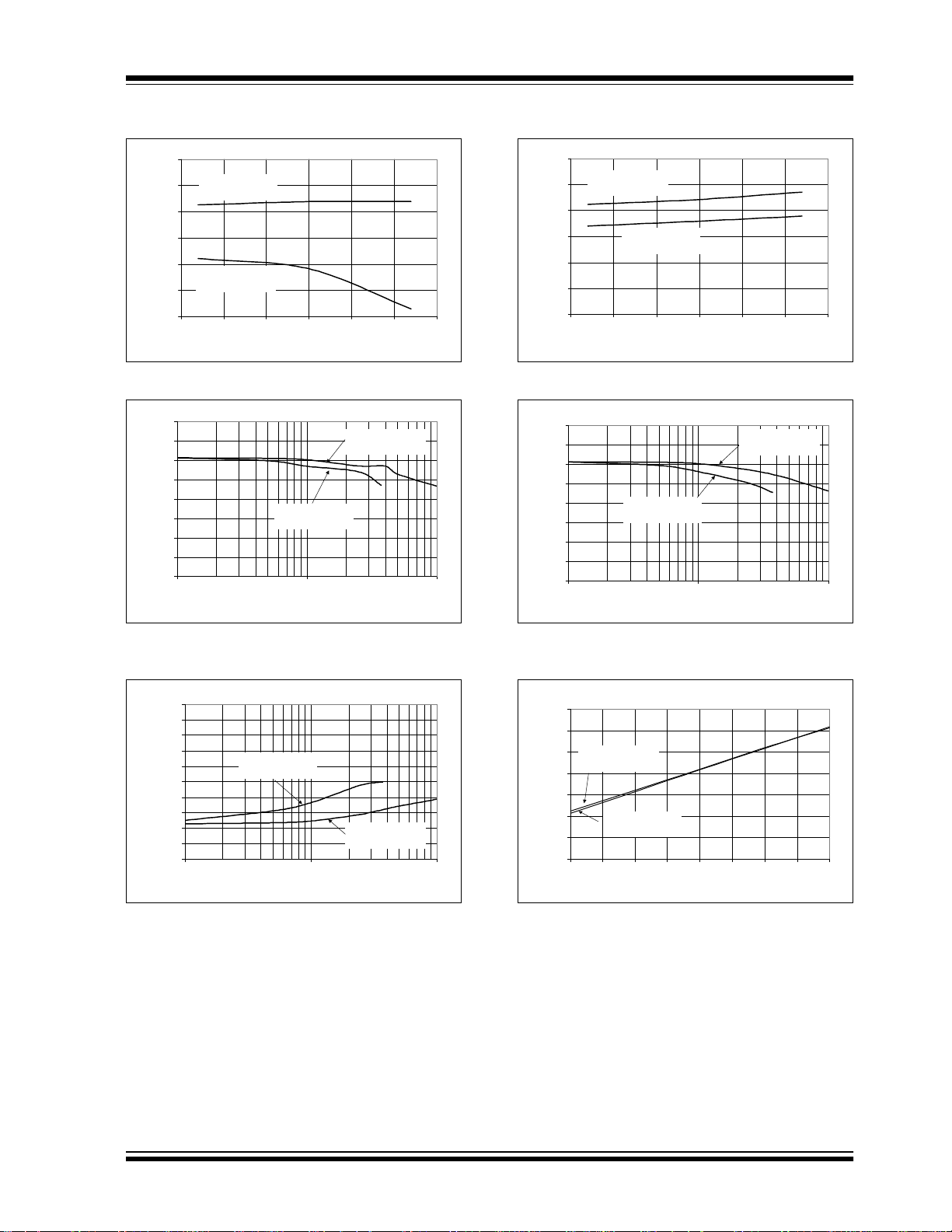
MCP3004/3008
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
1.0
VDD = V
= 5 V
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
DNL (LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
REF
f
= 200 ksps
SAMPLE
0 12 8 256 384 512 640 76 8 89 6 10 24
DD
= V
REF
= 5V, f
Digital Code
FIGURE 2-13: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) vs. Code (Representative Part).
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
DNL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
Positive D NL
Negative DNL
Temperature (°C)
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
-0.2
DNL (LSB)
-0.4
-0.6
-0.8
-1.0
, TA = 25°C.
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
0 12 8 256 384 512 640 76 8 89 6 10 24
Digital Code
FIGURE 2-16: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
vs. Code (Representative Part, V
0.6
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
0.4
0.2
0.0
DNL (LSB)
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
-50-25 0 255075100
Positive D NL
Negative DNL
Temperature (°C)
DD
= 2.7V).
FIGURE 2-14: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) vs. Temperature.
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
-0.5
-1.0
Gain Error (LSB)
-1.5
-2.0
012345
FIGURE 2-15: Gain Error vs. V
VDD = 5 V
f
SAMPLE
VDD = 2.7 V
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
= 200 ksps
V
(V)
REF
.
REF
FIGURE 2-17: Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
VDD = 5 V
f
SAMPLE
V
f
SAMPLE
= 2.7V).
DD
= 200 ksps
= 2.7 V
DD
= 75 ksps
V
REF
(V)
REF
.
vs. Temperature (V
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
Offset Error (LSB)
1
0
0123 45
FIGURE 2-18: Offset Error vs. V
DS21295B-page 8 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9
MCP3004/3008
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
0.0
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
f
SAMPLE
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
REF
= 75 ksps
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
-0.4
Gain Error (LSB)
-0.5
-0.6
-50-25 0 255075100
DD
= V
REF
= 5V, f
Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2-19: Gain Error vs. Temperature.
80
70
60
50
40
30
SNR (dB)
20
10
0
110100
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
Input Frequency (kHz)
= 2.7 V
REF
= 75 ksps
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
CLK
= 18* f
, TA = 25°C.
SAMPLE
1.2
VDD = V
= 5 V
f
SAMPLE
REF
= 200 ksps
VDD = V
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
REF
= 2.7 V
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
Offset Error (LSB)
0.2
0.0
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2-22: Offset Error vs. Temperature.
80
70
60
50
40
30
SINAD (dB)
20
10
0
110100
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
Input Frequency (kHz)
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
FIGURE 2-20: Signal to Noise (SNR) vs. Input Frequency.
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
THD (dB)
-70
-80
-90
-100
110100
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 2.7 V
REF
= 75 ksps
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
Input Frequency (kHz)
FIGURE 2-21: Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) vs. Input Frequency.
FIGURE 2-23: Signal to Noise and Distortion (SINAD) vs. Input Frequency.
70
60
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
VDD = V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
= 2.7 V
50
40
30
SINAD (dB)
20
10
0
-40 -35 -30 -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0
Input Signal Level (dB)
FIGURE 2-24: Signal to Noise and Distortion (SINAD) vs. Input Signal Level.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 9
Page 10
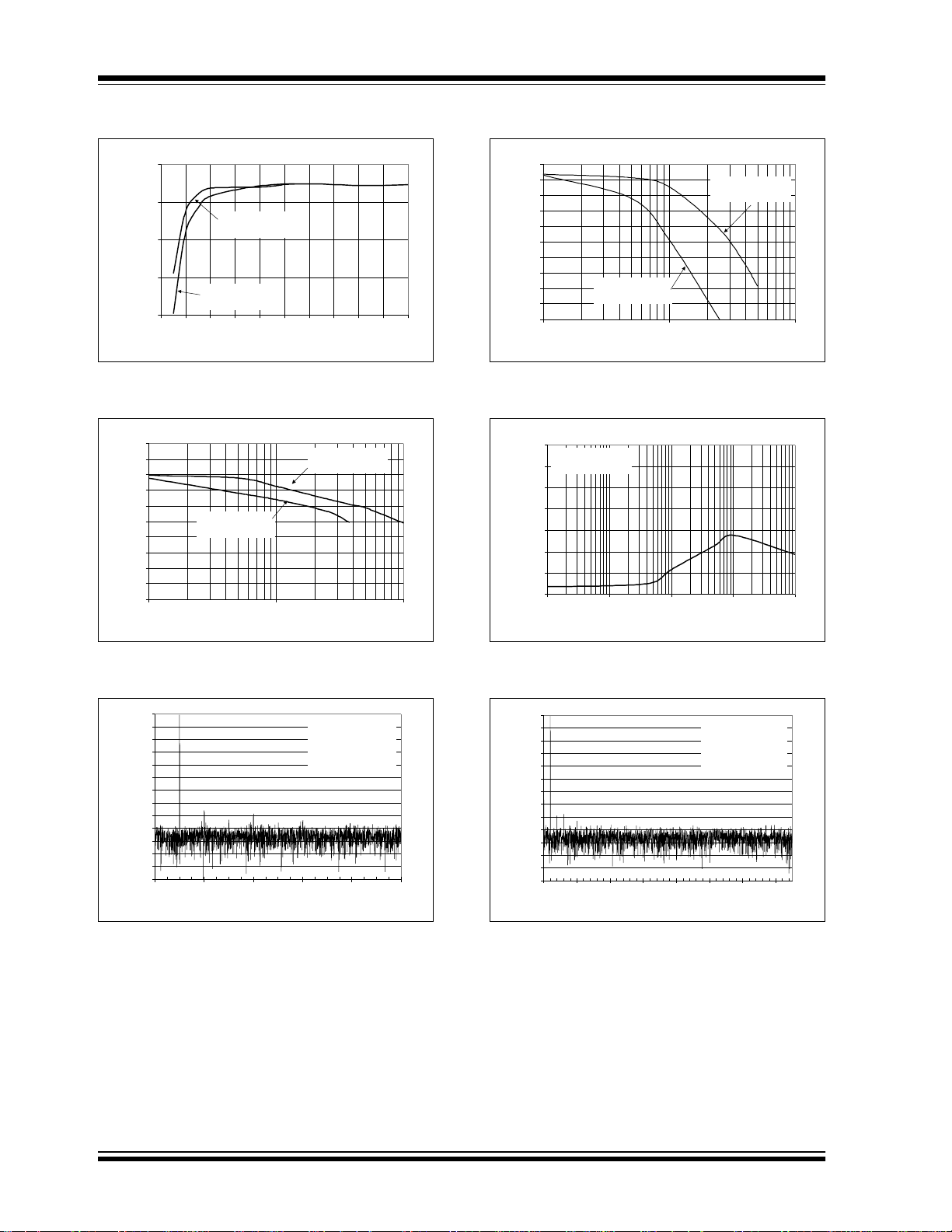
MCP3004/3008
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
10.00
9.75
9.50
ENOB (rms)
9.25
9.00
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4. 5 5.0
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
VDD = V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
= 2.7 V
V
REF
(V)
DD
= V
REF
= 5V, f
FIGURE 2-25: Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
vs. V
.
REF
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
SFDR (dB)
30
20
10
0
110100
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 2.7 V
REF
= 75 ksps
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
Input Frequency (kHz)
CLK
= 18* f
, TA = 25°C.
SAMPLE
10.0
9.8
9.6
9.4
9.2
9.0
8.8
ENOB (rms)
8.6
8.4
8.2
8.0
110100
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 2.7 V
REF
= 75 ksps
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
Input Frequency (kHz)
FIGURE 2-28: Effective Number of Bits (ENOB) vs. Input Frequency.
0
VDD = V
= 5 V
REF
f
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
Power Supply Rejection (dB)
-70
= 200 ksps
SAMPLE
1 10 100 1000 10 000
Ripple Frequency (kHz)
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
FIGURE 2-26: Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) vs. Input Frequency.
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
Amplitude (dB)
-100
-110
-120
-130
0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000
Frequency (Hz)
VDD = V
REF
F
= 200 ksps
SAMPLE
F
= 10.009 7 kHz
INPUT
4096 poi nts
= 5 V
FIGURE 2-27: Frequency Spectrum of 10 kHz
Input (Representative Part).
FIGURE 2-29: Power Supply Rejection (PSR) vs. Ripple Frequency.
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
-80
-90
Amplitude (dB)
-100
-110
-120
-130
0 5000 10000 15000 20000 25000 30000 35000
Frequency (Hz)
VDD = V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
f
= 1.0070 8 kHz
INPUT
4096 poi nts
= 2.7 V
FIGURE 2-30: Frequency Spectrum of 1 kHz
Input (Representative Part, V
= 2.7V).
DD
DS21295B-page 10 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11
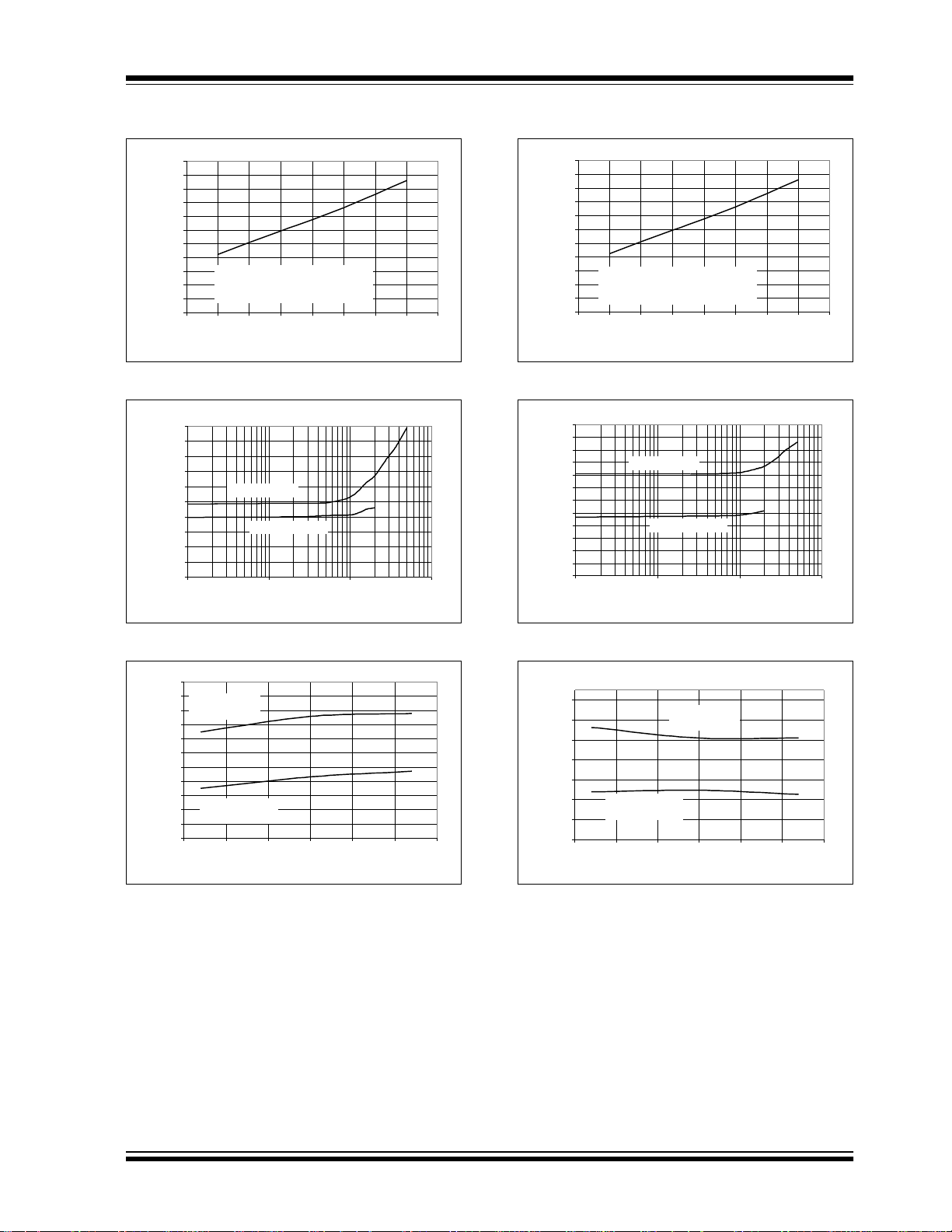
MCP3004/3008
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
550
500
450
400
350
300
(µA)
250
DD
I
200
150
100
FIGURE 2-31: I
500
450
400
350
300
250
(µA)
DD
200
I
150
100
V
= V
REF
DD
All points at f
at V
50
0
2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0
REF
= 3.6 MHz exc ept
CLK
= VDD = 2.5 V, f
= 1.35 MHz
CLK
VDD (V)
vs. VDD.
DD
VDD = V
= 5 V
REF
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
REF
50
0
10 100 1000 10000
Clock Frequency (kHz)
DD
= V
REF
= 5V, f
CLK
= 18* f
SAMPLE
FIGURE 2-34: I
, TA = 25°C.
550
500
450
400
350
300
(µA)
250
DD
I
200
150
V
= V
REF
DD
All points at f
100
at V
REF
2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0
10 100 1000 10000
120
110
100
(µA)
REF
I
50
0
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
= 3.6 MHz exc ept
CLK
= VDD = 2.5 V, f
= 1.35 MHz
CLK
VDD (V)
vs. VDD.
REF
VDD = V
= 5 V
REF
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
REF
Clock Frequency (kHz)
FIGURE 2-32: I
550
500
VDD = V
450
400
350
300
(µA)
250
DD
I
200
150
100
50
0
REF
f
= 3.6 MHz
CLK
VDD = V
f
= 1.35 MHz
CLK
-50-250 255075100
FIGURE 2-33: I
vs. Clock Frequency.
DD
= 5 V
= 2.7 V
REF
Temperature (°C)
vs. Temperature.
DD
FIGURE 2-35: I
140
120
100
80
(µA)
REF
60
I
40
20
VDD = V
f
CLK
0
-50-250 255075100
FIGURE 2-36: I
vs. Clock Frequency.
REF
VDD = V
= 5 V
REF
f
= 3.6 MHz
CLK
= 2.7 V
REF
= 1.35 MHz
Temperature (°C)
vs. Temperature.
REF
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 11
Page 12
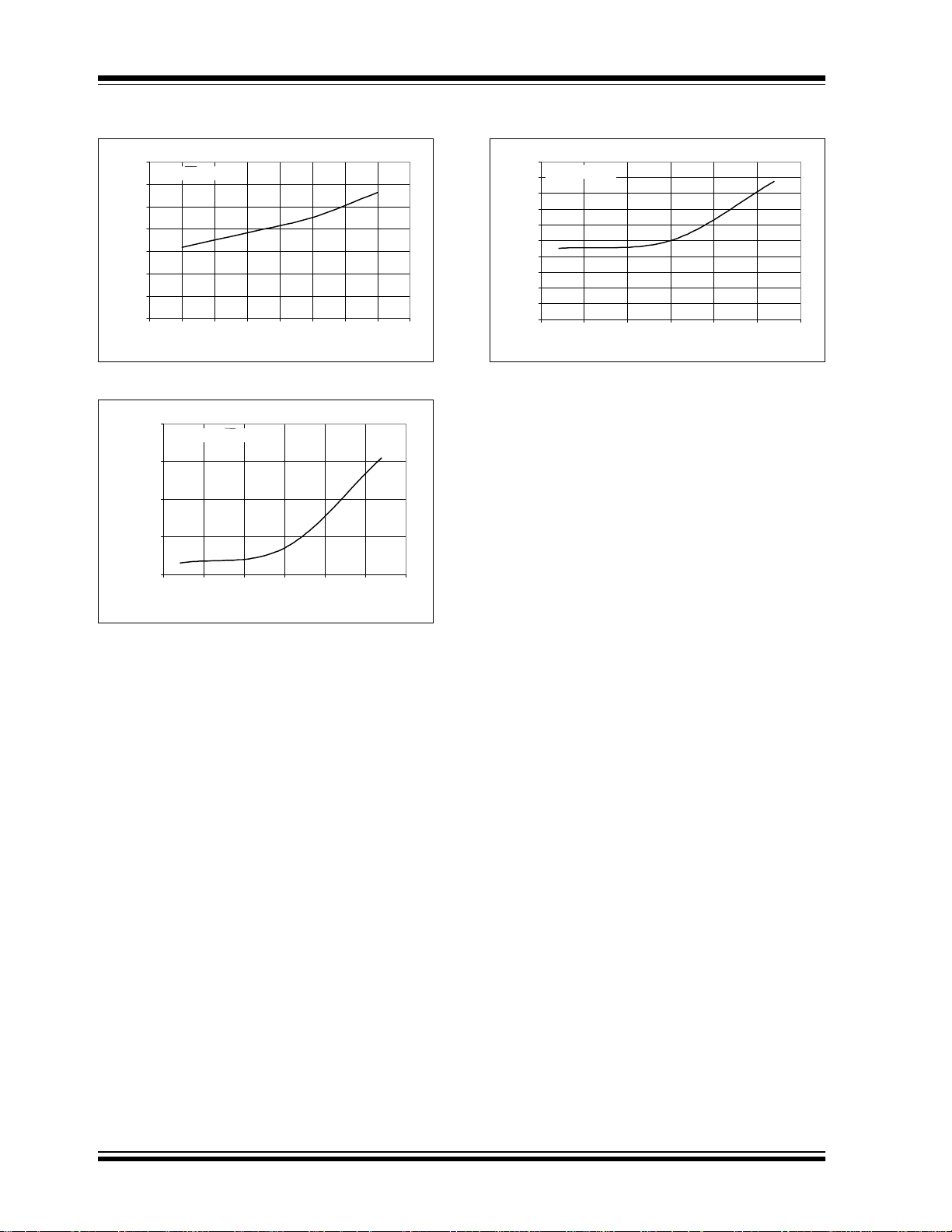
MCP3004/3008
Note: Unless otherwise indicated, V
70
V
= CS = V
REF
60
50
40
(pA)
30
DDS
I
20
10
0
2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0
FIGURE 2-37: I
100.00
10.00
(nA)
1.00
DDS
I
0.10
VDD = V
DD
DDS
= CS = 5 V
REF
VDD (V)
vs. VDD.
DD
= V
REF
= 5V, f
CLK
= 18* f
, TA = 25°C.
SAMPLE
2.0
VDD = V
= 5 V
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
Analog Input Leakage (nA)
0.0
REF
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
Temperature (°C)
FIGURE 2-39: Analog Input Leakage Current vs. Temperature.
0.01
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100
FIGURE 2-38: I
Temperature (°C)
vs. Temperature.
DDS
DS21295B-page 12 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13

MCP3004/3008
3.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
TABLE 3-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Name Function
V
DD
DGND Digital Ground
AGND Analog Ground
CH0-CH7 Analog Inputs
CLK Serial Clock
D
IN
D
OUT
/SHDN Chip Select/Shutdown Input
CS
V
REF
3.1 DGND
Digital ground connection to internal digital circuitry.
3.2 AGND
Analog ground connection to internal analog circuitry.
3.3 CH0 - CH7
Analog inputs for channels 0 - 7, respectively, for the
multiplexed inputs. Each pair of channels can be programmed to be used as two independent channels in
single-ended mode or as a single pseudo-differential
input where one channel is IN+ and one channel is IN.
See Section 4.1, “Analog Inputs”, and Section 5.0,
“Serial Communication”, for information on
programming the channel configuration.
3.4 Serial Clock (CLK)
The SPI clock pin is used to initiate a conversion and
clock out each bit of the conversion as it takes place.
See Section 6.2, “Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed”,
for constraints on clock speed.
3.5 Serial Data Input (DIN)
The SPI port serial data input pin is used to load
channel configuration data into the device.
3.6 Serial Data Output (D
The SPI serial data output pin is used to shift out the
results of the A/D conversion. Data will always change
on the falling edge of each clock as the conversion
takes place.
3.7 Chip Select/Shutdown (CS/SHDN)
The CS/SHDN pin is used to initiate communication
with the device when pulled low. When pulled high, it
will end a conversion and put the device in low power
standby. The CS
between conversions.
+2.7V to 5.5V Power Supply
Serial Data In
Serial Data Out
Reference Voltage Input
)
OUT
/SHDN pin must be pulled high
4.0 DEVICE OPERATION
The MCP3004/3008 A/D converters employ a conventional SAR architecture. With this architecture, a sample is acquired on an internal sample/hold capacitor for
1.5 clock cycles starting on the first rising edge of the
serial clock once CS
this sample time, the device uses the collected charge
on the internal sample and hold capacitor to produce a
serial 10-bit digital output code. Conversion rates of
100 ksps are possible on the MCP3004/3008. See
Section 6.2, “Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed”, for
information on minimum clock rates. Communication
with the device is accomplished using a 4-wire SPIcompatible interface.
4.1 Analog Inputs
The MCP3004/3008 devices offer the choice of using
the analog input channels configured as single-ended
inputs or pseudo-differential pairs. The MCP3004 can
be configured to provide two pseudo-differential input
pairs or four single-ended inputs. The MCP3008 can be
configured to provide four pseudo-differential input
pairs or eight single-ended inputs. Configuration is
done as part of the serial command before each conversion begins. When used in the pseudo-differential
mode, each channel pair (i.e., CH0 and CH1, CH2 and
CH3 etc.) are programmed as the IN+ and IN- inputs as
part of the command string transmitted to the device.
The IN+ input can range from IN- to (V
IN- input is limited to ±100 mV from the V
input can be used to cancel small signal commonmode noise, which is present on both the IN+ and INinputs.
When operating in the pseudo-differential mode, if the
voltage level of IN+ is equal to or less than IN-, the
resultant code will be 000h. If the voltage at IN+ is
equal to or greater than {[V
the output code will be 3FFh. If the voltage level at IN-
is more than 1 LSB below V
IN+ input will have to go below V
output code. Conversely, if IN- is more than 1 LSB
above V
IN+ input level goes above V
For the A/D converter to meet specification, the charge
holding capacitor (C
time to acquire a 10-bit accurate voltage level during
the 1.5 clock cycle sampling period. The analog input
model is shown in Figure 4-1.
This diagram illustrates that the source impedance (R
adds to the internal sampling switch (R
directly affecting the time that is required to charge the
capacitor (C
impedances increase the offset, gain and integral linearity errors of the conversion (see Figure 4-2).
, the 3FFh code will not be seen unless the
SS
SAMPLE
has been pulled low. Following
+ IN-). The
REF
rail. The IN-
SS
+ (IN-)] - 1 LSB}, then
REF
, the voltage level at the
SS
REF
) must be given enough
SAMPLE
). Consequently, larger source
to see the 000h
SS
level.
) impedance,
SS
S
)
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 13
Page 14

MCP3004/3008
4.2 Reference Input
For each device in the family, the reference input
(V
) determines the analog input voltage range. As
REF
the reference input is reduced, the LSB size is reduced
accordingly.
EQUATION
V
REF
LSB Size
The theoretical digital output code produced by the A/D
converter is a function of the analog input signal and the
reference input, as shown below.
CHx
R
SS
VA
=
C
7pF
------------ -
1024
PIN
V
DD
= 0.6V
V
T
= 0.6V
V
T
EQUATION
×
1024 V
Digital Output Code
= analog input voltage
V
IN
V
= reference voltage
REF
------------------------ -- -
=
When using an external voltage reference device, the
system designer should always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for circuit layout. Any instability in the operation of the reference device will have a
direct effect on the operation of the A/D converter.
Sampling
Switch
R
= 1 kΩ
S
C
SAMP LE
= DAC capacitance
= 20 pF
V
SS
I
LEAKAGE
±1 nA
SS
V
IN
REF
Legend
Signal Source
VA
R
CHx
C
=
Source Impedance SS=sampling switch
=
SS
Input Channel Pad
=
Input Pin Capacitance
=
PIN
Threshold Voltage
=
V
T
I
LEAKAGE
C
SAMPLE
R
S
FIGURE 4-1: Analog Input Model.
4
3
2
1
Clock Frequency (Mhz)
0
100 1000 10000
VDD = V
= 2.7 V
REF
f
= 75 ksps
SAMPLE
Input Resistance (Ohms)
VDD = V
f
SAMPLE
= 5 V
REF
= 200 ksps
FIGURE 4-2: Maximum Clock Frequency vs.
Input resistance (R
) to maintain less than a
S
0.1 LSB deviation in INL from nominal
conditions.
Leakage Current At The Pin
=
Due To Various Junctions
sampling switch resist or
=
sample/hold capacitance
=
DS21295B-page 14 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

MCP3004/3008
5.0 SERIAL COMMUNICATION
Communication with the MCP3004/3008 devices is
accomplished using a standard SPI-compatible serial
interface. Initiating communication with either device is
done by bringing the CS
device was powered up with the CS
brought high and back low to initiate communication.
The first clock received with CS
constitute a start bit. The SGL/DIFF
bit and will determine if the conversion will be done
using single-ended or differential input mode. The next
three bits (D0, D1 and D2) are used to select the input
channel configuration. Table 5-1 and Table 5-2 show
the configuration bits for the MCP3004 and MCP3008,
respectively. The device will begin to sample the analog input on the fourth rising edge of the clock after the
start bit has been received. The sample period will end
on the falling edge of the fifth clock following the start
bit.
Once the D0 bit is input, one more clock is required to
complete the sample and hold period (D
care” for this clock). On the falling edge of the next
clock, the device will output a low null bit. The next 10
clocks will output the result of the conversion with MSB
first, as shown in Figure 5-1. Data is always output from
the device on the falling edge of the clock. If all 10 data
bits have been transmitted and the device continues to
receive clocks while the CS
output the conversion result LSB first, as is shown in
Figure 5-2. If more clocks are provided to the device
while CS
transmitted), the device will clock out zeros indefinitely.
If necessary, it is possible to bring CS
leading zeros on the D
often done when dealing with microcontroller-based
SPI ports that must send 8 bits at a time. Refer to
Section 6.1, “Using the MCP3004/3008 with Microcontroller (MCU) SPI Ports”, for more details on using the
MCP3004/3008 devices with hardware SPI ports.
is still low (after the LSB first data has been
line low (see Figure 5-1). If the
pin low, it must be
low and DIN high will
bit follows the start
is a “don’t
IN
is held low, the device will
low and clock in
line before the start bit. This is
IN
TABLE 5-1: CONFIGURE BITS FOR THE
MCP3004
Control Bit
Selections
Single/
* D2 is “don’t care” for MCP3004
D2* D1 D0
Diff
1 X 0 0 single-ended CH0
1 X 0 1 single-ended CH1
1 X 1 0 single-ended CH2
1 X 1 1 single-ended CH3
0 X 0 0 differential CH0 = IN+
0 X 0 1 differential CH0 = IN-
0 X 1 0 differential CH2 = IN+
0 X 1 1 differential CH2 = IN-
Input
Configuration
Channel
Selection
CH1 = IN-
CH1 = IN+
CH3 = IN-
CH3 = IN+
TABLE 5-2: CONFIGURE BITS FOR THE
MCP3008
Control Bit
Selections
Single
/Diff
D2 D1 D0
1 0 0 0 single-ended CH0
1 0 0 1 single-ended CH1
1 0 1 0 single-ended CH2
1 0 1 1 single-ended CH3
1 1 0 0 single-ended CH4
1 1 0 1 single-ended CH5
1 1 1 0 single-ended CH6
1 1 1 1 single-ended CH7
0 0 0 0 differential CH0 = IN+
0 0 0 1 differential CH0 = IN-
0 0 1 0 differential CH2 = IN+
0 0 1 1 differential CH2 = IN-
0 1 0 0 differential CH4 = IN+
0 1 0 1 differential CH4 = IN-
0 1 1 0 differential CH6 = IN+
0 1 1 1 differential CH6 = IN-
Input
Configuration
Channel
Selection
CH1 = IN-
CH1 = IN+
CH3 = IN-
CH3 = IN+
CH5 = IN-
CH5 = IN+
CH7 = IN-
CH7 = IN+
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 15
Page 16

MCP3004/3008
t
CYC
CS
t
SUCS
CLK
HI-Z
D1D2
D0
Null
B9 B8 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 *
Bit
t
SAMPL E
Don’t Care
t
CONV
D
D
IN
OUT
Start
SGL/
DIFF
* After completing the data transfer, if further clocks are applied with CS
first data, then followed with zeros indefinitely. See Figure 5-2 below.
: during this time, the bias current and the comparator powers down while the reference input becomes
** t
DATA
a high impedance node.
FIGURE 5-1: Communication with the MCP3004 or MCP3008.
t
CYC
t
CSH
Start
SGL/
DIFF
D2
HI-Z
t
**
DATA
low, the A/D converter will output LSB
t
CYC
CS
t
SUCS
Power Down
CLK
Start
D
IN
D0D1D2
Don’t Care
SGL/
DIFF
t
SAMPLE
Null
B8 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 B9
B9
Bit
(MSB)
t
CONV
t
DATA
*
**
D
OUT
HI-Z
* After completing the data transfer, if further clocks are applied with CS low, the A/D converter will output zeros
indefinitely.
** t
: During this time, the bias circuit and the comparator powers down while the reference input becomes
DATA
a high impedance node, leaving the CLK running to clock out LSB first data or zeroes.
FIGURE 5-2: Communication with MCP3004 or MCP3008 in LSB First Format.
t
CSH
HI-Z
DS21295B-page 16 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

6.0 APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
6.1 Using the MCP3004/3008 with Microcontroller (MCU) SPI Ports
With most microcontroller SPI ports, it is required to
send groups of eight bits. It is also required that the
microcontroller SPI port be configured to clock out data
on the falling edge of clock and latch data in on the rising edge. Because communication with the MCP3004/
3008 devices may not need multiples of eight clocks, it
will be necessary to provide more clocks than are
required. This is usually done by sending ‘leading
zeros’ before the start bit. As an example, Figure 6-1
and Figure 6-2 shows how the MCP3004/3008 can be
interfaced to a MCU with a hardware SPI port.
Figure 6-1 depicts the operation shown in SPI Mode
0,0, which requires that the SCLK from the MCU idles
in the ‘low’ state, while Figure 6-2 shows the similar
case of SPI Mode 1,1, where the clock idles in the ‘high’
state.
As is shown in Figure 6-1, the first byte transmitted to
the A/D converter contains seven leading zeros before
the start bit. Arranging the leading zeros this way
induces the 10 data bits to fall in positions easily manipulated by the MCU. The MSB is clocked out of the A/D
converter on the falling edge of clock number 14. Once
the second eight clocks have been sent to the device,
the MCU receive buffer will contain five unknown bits
(the output is at high impedance for the first two
clocks), the null bit and the highest order 2 bits of the
conversion. Once the third byte has been sent to the
device, the receive register will contain the lowest order
eight bits of the conversion results. Employing this
method ensures simpler manipulation of the converted
data.
Figure 6-2 shows the same thing in SPI Mode 1,1,
which requires that the clock idles in the high state. As
with mode 0,0, the A/D converter outputs data on the
falling edge of the clock and the MCU latches data from
the A/D converter in on the rising edge of the clock.
MCP3004/3008
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 17
Page 18

MCP3004/3008
CS
MCU latches data from A/D
converter on rising edges of SCLK
SCLK
D
IN
1 2 34 56 78 910111213141516
Data is clocked out of
A/D conver ter on falli ng edges
Star t
SGL/
DIFF
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
D2
DO
D1
Don’t Care
D
OUT
MCU Transmitted Data
MCU Transmitted Data
(Aligned with falling
edge of clock)
MCU Received Data
(Align ed with rising
edge of clock)
X = “Don’t Care” Bits
HI-Z
Star t
00000 1
??? ????
Data stored into MCU receive
register after transmission of first
8 bits
?
Bit
00
SGL/
D2
DIFF
???
Data stored into MCU receive
register after transmission of
second 8 bits
NULL
B9 B8
BIT
??
XXXXDO
(Null)
0
B9 B8
D1
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B 0
XXXXX XXX
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Data stored into MCU receive
register after transmission of last
8 bits
FIGURE 6-1: SPI Communication with the MCP3004/3008 using 8-bit segments (Mode 0,0: SCLK idles low).
CS
SCLK
D
D
OUT
MCU Transmitted Data
(Aligned with falling
edge of clock)
MCU Received Data
(Aligned with rising
edge of clock)
X = “Don’t Care” Bits
MCU latches data from A/D converter
on rising edges of SCLK
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
IN
000 00
????????
Data stored into MCU receive
register after transmission of first
8 bits
Data is clocked out of A/D
converter on falling edges
HI-Z
Start
00
Bit
Start
1
SGL/
DIFF
SGL
/
DIFF
???
Data stored into MCU receive
register after transmission of
second 8 bits
D2
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
DO
D1
NULL
B9
BIT
D1D2
XXXXDO
0
B9 B8
??
(Null)
Don’t Care
B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
B7
B8
XXXXXXXX
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Data stored into MCU receive
register after transmission of last
8 bits
FIGURE 6-2:
SPI Communication with the
MCP3004/3008
using 8-bit segments (Mode 1,1: SCLK idles high).
DS21295B-page 18 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

MCP3004/3008
6.2 Maintaining Minimum Clock Speed
When the MCP3004/3008 initiates the sample period,
charge is stored on the sample capacitor. When the
sample period is complete, the device converts one bit
for each clock that is received. It is important for the
user to note that a slow clock rate will allow charge to
bleed off the sample capacitor while the conversion is
taking place. At 85°C (worst case condition), the part
will maintain proper charge on the sample capacitor for
at least 1.2 ms after the sample period has ended. This
means that the time between the end of the sample
period and the time that all 10 data bits have been
clocked out must not exceed 1.2 ms (effective clock
frequency of 10 kHz). Failure to meet this criterion may
introduce linearity errors into the conversion outside
the rated specifications. It should be noted that during
the entire conversion cycle, the A/D converter does not
require a constant clock speed or duty cycle, as long as
all timing specifications are met.
6.3 Buffering/Filtering the Analog Inputs
If the signal source for the A/D converter is not a low
impedance source, it will have to be buffered or inaccurate conversion results may occur (see Figure 4-2). It is
also recommended that a filter be used to eliminate any
signals that may be aliased back in to the conversion
results, as is illustrated in Figure 6-3, where an op amp
is used to drive, filter and gain the analog input of the
MCP3004/3008. This amplifier provides a low impedance source for the converter input, plus a low pass
filter, which eliminates unwanted high frequency noise.
Low pass (anti-aliasing) filters can be designed using
Microchip’s free interactive FilterLab™ software. FilterLab will calculate capacitor and resistors values, as
well as determine the number of poles that are required
for the application. For more information on filtering signals, see AN699, “Anti-Aliasing Analog Filters for Data
Acquisition Systems”.
V
DD
V
REF
MCP3004
10 µF
1µF
4.096V
Refe rence
0.1 µF
C
R
1
V
IN
R
2
C
MCP1541
MCP601
1
+
-
2
R
4
R
3
1µF
IN+
IN-
FIGURE 6-3: The MCP601 Operational
Amplifier is used to implement a second order
anti-aliasing filter for the signal being converted
by the MCP3004.
6.4 Layout Considerations
When laying out a printed circuit board for use with
analog components, care should be taken to reduce
noise wherever possible. A bypass capacitor should
always be used with this device and should be placed
as close as possible to the device pin. A bypass capacitor value of 1 µF is recommended.
Digital and analog traces should be separated as much
as possible on the board, with no traces running underneath the device or bypass capacitor. Extra precautions should be taken to keep traces with high
frequency signals (such as clock lines) as far as possible from analog traces.
Use of an analog ground plane is recommended in
order to keep the ground potential the same for all
devices on the board. Providing V
devices in a “star” configuration can also reduce noise
by eliminating return current paths and associated
errors (see Figure 6-4). For more information on layout
tips when using A/D converters, refer to AN688, “Lay-
out Tips for 12-Bit A/D Converter Applications”.
V
DD
Connection
connections to
DD
Device 1
FIGURE 6-4: V
Device 2
traces arranged in a ‘Star’
DD
Device 4
Device 3
configuration in order to reduce errors caused by
current return paths.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 19
Page 20

MCP3004/3008
6.5 Utilizing the Digital and Analog Ground Pins
The MCP3004/3008 devices provide both digital and
analog ground connections to provide additional
means of noise reduction. As is shown in Figure 6-5,
the analog and digital circuitry is separated internal to
the device. This reduces noise from the digital portion
of the device being coupled into the analog portion of
the device. The two grounds are connected internally
through the substrate which has a resistance of 5 -10Ω.
If no ground plane is utilized, both grounds must be
connected to V
available, both digital and analog ground pins should
be connected to the analog ground plane. If both an
analog and a digital ground plane are available, both
the digital and the analog ground pins should be connected to the analog ground plane. Following these
steps will reduce the amount of digital noise from the
rest of the board being coupled into the A/D converter.
on the board. If a ground plane is
SS
V
DD
MCP3004/08
Digital Side
-SPI Interface
-Shift Register
-Control Logic
Substrate
DGND AGND
Analog Ground Plane
Analog Side
-Sample Cap
-Capacitor Array
-Comparator
5 - 10Ω
0.1 µF
FIGURE 6-5: Separation of Analog and Digital Ground Pins.
DS21295B-page 20 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

7.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
7.1 Package Marking Information
14-Lead PDIP (300 mil) Example:
MCP3004/3008
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
YYWWNNN
14-Lead SOIC (150 mil)
XXXXXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXXXX
YYWWNNN
14-Lead TSSOP (4.4mm) *
XXXXXXXX
YYWW
NNN
MCP3004-I/P
0212027
Example:
MCP3004ISL
XXXXXXXXXXX
0212027
Example:
3004
I212
027
* Please contact Microchip Factory for B-Grade TSSOP devices
Legend: XX...X Customer specific information*
YY Year code (last 2 digits of calendar year)
WW Week code (week of January 1 is week ‘01’)
NNN Alphanumeric traceability code
Note: In the event the full Microchip part number cannot be marked on one line, it will
be carried over to the next line thus limiting the number of available characters
for customer specific information.
* Standard marking consists of Microchip part number, year code, week code, traceability code (facility
code, mask rev#, and assembly code). For marking beyond this, certain price adders apply. Please check
with your Microchip Sales Office.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 21
Page 22

MCP3004/3008
Package Marking Information (Continued)
16-Lead PDIP (300 mil) (MCP3308)Example:
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
YYWWNNN
16-Lead SOIC (150 mil) (MCP3308)
XXXXXXXXXXXXX
XXXXXXXXXXXXX
YYWWNNN
MCP3008-I/P
0212030
Example:
MCP3008-I/SL
XXXXXXXXXX
0212030
DS21295B-page 22 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

14-Lead Plastic Dual In-line (P) – 300 mil (PDIP)
E1
D
2
MCP3004/3008
n
E
β
eB
Number of Pins
Pitch
Top to Seating Plane A .140 .155 .170 3.56 3.94 4.32
Molded Package Thickness A2 .115 .130 .145 2.92 3.30 3.68
Base to Seating Plane A1 .015 0.38
Shoulder to Shoulder Width E .300 .313 .325 7.62 7.9 4 8.26
Molded Package Width E1 .240 .250 .260 6.10 6.35 6.60
Overall Length D .740 .750 .760 18.80 19.05 19.30
Tip to Seating Plane L .125 .130 .135 3.18 3.30 3.43
Lead Thickness
Upper Lead Width B1 .045 .058 .070 1.14 1.46 1.78
Lower Lead Width B .014 .018 .022 0.36 0.46 0.56
Overall Row Spacing § eB .310 .370 .430 7.87 9.40 10.92
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include m old flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-001
Drawing No. C04-005
1
A
c
A1
Dimension Limits MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
Units INCHES* MILLIMETERS
n
p
c
α
β
.008 .012 .015 0.20 0.29 0.38
5 10 15 5 10 15
5 10 15 5 10 15
B1
B
14 14
.100 2.54
α
A2
L
p
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 23
Page 24

MCP3004/3008
14-Lead Plastic Small Outline (SL) – Narrow, 150 mil (SOIC)
E
E1
p
D
2
B
n
1
45°
c
β
Number of Pins
Pitch
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Paramete r
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-012
Drawing No. C04-065
h
A
φ
L
n
p
φ
c
α
β
A1
048048
α
MILLIMETERSINCHES*Units
1.27.050
A2
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
1414
1.751.551.35.069.061.053AOverall Height
1.551.421.32.061.056.052A2Molded Package Thickness
0.250.180.10.010.007.004A1Standoff §
6.205.995.79.244.236.228EOverall Width
3.993.903.81.157.154.150E1Molded Package Width
8.818.698.56.347.342.337DOverall Length
0.510.380.25.020.015.01 0hChamfer Distance
1.270.840.41.050.033.016LFoot Len gth
0.250.230.20.010.009.008
0.510.420.36.020.017.014BLead Width
1512015120
1512015120
DS21295B-page 24 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25

14-Lead Plastic Thin Shrink Small Outline (ST) – 4.4 mm (TSSOP)
E
E1
p
D
2
n
B
1
MCP3004/3008
A
c
φ
β
Number of Pins
Pitch
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mo ld flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.005” (0.127mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MO-153
Drawing No. C04-087
n
p
φ
c
α
β
L
MILLIMETERS*INCHESUnits
0.65.026
α
A2A1
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
1414
1.10.043AOverall Height
0.950.900.85.037.035.033A2Molded P ackage Thickness
0.150.100.05.006.004.002A1Standoff §
6.506.386.25.256.251.246EOverall Width
4.504.404.30.177.173.169E1Molded Package Width
5.105.004.90.201.197.193DMolded Package Length
0.700.600.50.028.024.020LFoot Len gth
840840
0.200.150.09.008.006.004
0.300.250.19.012.010.007B1Lead Width
10501050
10501050
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 25
Page 26

MCP3004/3008
16-Lead Plastic Dual In-line (P) – 300 mil (PDIP)
E1
D
2
n
E
β
eB
Number of Pins
Pitch
Molded Package Thickness
Lead Thickness
Overall Row Spacing §
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-001
Drawing No. C04-017
1
A
c
A1
n
p
A2
c
eB
α
β
B1
B
0.38.015A1Base to Seating Plan e
α
p
MILLIMETERSINCHES*Units
2.54.100
A2
L
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
1616
4.323.943.56.170.155.14 0ATop to Seating Plane
3.683.302.92.145.130.115
8.267.947.62.325.313.300EShoulder to Shoulder Width
6.606.356.10.260.250.240E1Molded Package Width
19.3019.0518.80.760.750.740DOverall Length
3.433.303.18.135.130.125LTip to Seating Plane
0.380.290.20.015.012.008
1.781.461.14.070.058.045B1Upper Lea d Width
0.560.46.036.022.018.014BLower Lea d Width
10.929.407.87.430.370.310
1510515105
1510515105
DS21295B-page 26 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27

16-Lead Plastic Small Outline (SL) – Narrow 150 mil (SOIC)
E
E1
p
D
2
B
n
45°
1
h
MCP3004/3008
α
c
φ
L
β
Number of Pins
Pitch
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bot tom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Cha racteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include m old flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-012
Drawing No. C04-108
n
p
φ
c
α
β
A
A1
MILLIMETERSINCHES*Units
1.27.050
048048
A2
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
1616
1.751.551.35.069.061.053AOverall Height
1.551.441.32.061.057.052A2Molded Package Thickness
0.250.180.10.010.007.004A1Standoff §
6.206.025.79.244.237.228EOverall Width
3.993.903.81.157.154.150E1Molded Package Width
10.019.919.80.394.3 90. 386DOverall Length
0.510.380.25.020.015.010hChamfer Distance
1.270.840.41.050.033.016LFoot Length
0.250.230.20.010.009.008
0.510.420.33.020.017. 013BLead Width
1512015120
1512015120
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page 27
Page 28

MCP3004/3008
NOTES:
DS21295B-page 28 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 29

MCP3004/008
ON-LINE SUPPORT
Microchip provides on-line support on the Microchip
World Wide Web site.
The web site is used by Microchip as a means to make
files and information easily available to customers. To
view the site, the user must have access to the Internet
and a web browser, such as Netscape
Internet Explorer. Files are also available for FTP
download from our FTP site.
Connecting to the Microchip Internet Web Site
The Microchip web site is available at the following
URL:
www.microchip.com
The file transfer site is available by using an FTP service to connect to:
ftp://ftp.microchip.com
The web site and file transfer site provide a variety of
services. Users may download files for the latest
Development Tools, Data Sheets, Application Notes,
User's Guides, Articles and Sample Programs. A variety of Microchip specific business information is also
available, including listings of Microchip sales offices,
distributors and factory representatives. Other data
available for consideration is:
• Latest Microchip Press Releases
• Technical Support Section with Frequently Asked
Questions
• Design Tips
• Device Errata
• Job Postings
• Microchip Consultant Program Member Listing
• Links to other useful web sites related to
Microchip Products
• Conferences for products, Development Systems,
technical information and more
• Listing of seminars and events
®
or Microsoft
SYSTEMS INFORMATION AND
UPGRADE HOT LINE
The Systems Information and Upgrade Line provides
system users a listing of the latest versions of all of
Microchip's development systems software products.
®
Plus, this line provides information on how customers
can receive the most current upgrade kits.The Hot Line
Numbers are:
1-800-755-2345 for U.S. and most of Canada, and
1-480-792-7302 for the rest of the world.
092002
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page29
Page 30

MCP3004/008
READER RESPONSE
It is our intention to provide you with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip product. If you wish to provide your comments on organization, clarity, subject matter, and ways in which our documentation
can better serve you, please FAX your comments to the Technical Publications Manager at (480) 792-4150.
Please list the following information, and use this outline to provide us with your comments about this document.
To :
RE: Reader Response
From:
Application (optional):
Would you like a reply? Y N
Device:
Questions:
1. What are the best features of this document?
2. How does this document meet your hardware and software development needs?
3. Do you find the organization of this document easy to follow? If not, why?
Technical Publications Manager
Name
Company
Address
City / State / ZIP / Country
Telephone: (_______) _________ - _________
MCP3004/008
Literature Number:
Total Pages Sent ________
FAX: (______) _________ - _________
DS21295B
4. What additions to the document do you think would enhance the structure and subject?
5. What deletions from the document could be made without affecting the overall usefulness?
6. Is there any incorrect or misleading information (what and where)?
7. How would you improve this document?
DS21295B-page30 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 31

MCP3004/3008
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM
To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office.
PART NO. X /XX
Device
Device: MCP3004: 4-Channel 10-Bit Serial A/D Converter
Temperature Range: I = -40°C to +85°C
Package: P = Plastic DIP (300 mil Body), 14-lead, 16-lead
Range
MCP3004T: 4-Channel 10-Bit Serial A/D Converter
MCP3008: 8-Channel 10-Bit Serial A/D Converter
MCP3008T: 8-Channel 10-Bit Serial A/D Converter
SL = Plastic SOIC (150 mil Body), 14-lead, 16-lead
ST = Plastic TSSOP (4.4mm), 14-lead
PackageTem per atu re
(Tape and Reel)
(Tape and Reel)
Examples:
a) MCP3 004-I/P: Industri al Te mperature, P DIP
package.
b) MCP3004-I/SL: Industrial Temperature,
SOIC package.
c) MCP3004-I/ST: Industrial Temperature,
TSSOP package.
d) MCP3004T-I/ST: Industrial Temperature,
TSSOP package, Tape and Reel.
a) MCP3 008-I/P: Industri al Te mperature, P DIP
package.
b) MCP3008-I/SL: Industrial Temperature,
SOIC package.
Sales and Support
Data Sheets
Products supported by a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences and recommended workarounds. To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please contact one of the following:
1. Your local Microchip sales office
2. The Microchip Corporate Literature Center U.S. FAX: (480) 792-7277
3. The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Please specify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (include Literature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B-page31
Page 32

MCP3004/3008
NOTES:
DS21295B-page 32 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 33

Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect
to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such
use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical components in life support systems is not authorized except with
express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual property
rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, K
EELOQ
MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART and PRO MATE are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A. and other countries.
FilterLab, microID, MXDEV, MXLAB, PICMASTER, SEEVAL
and The Embedded Control Solutions Company are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
dsPIC, dsPICDEM.net, ECONOMONITOR, FanSense,
FlexROM, fuzzyLAB, In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP,
ICEPIC, microPort, Migratable Memory, MPASM, MPLIB,
MPLINK, MPSIM, PICC, PICDEM, PICDEM.net, rfPIC, Select
Mode and Total Endurance are trademarks of Microchip
Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
Serialized Quick Turn Programming (SQTP) is a service mark
of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2002, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
,
Microchip received QS-9000 quality system
certification for its worldwide headquarters,
design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona in July 1999
and Mountain View, California in March 2002.
The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are QS-9000 compliant for its
PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals,
non-volatile memory and analog produ cts. In
addition, Microchip’s qua lity system for the
design and manufacture of development
systems is ISO 9001 certified.
®
8-bit MCUs, KEEL
®
code hopping
OQ
2002 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21295B - page 33
Page 34

M
W
ORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler B lvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200 Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: http://www.microchip.com
Rocky Mountain
2355 West Chandler B lvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7966 Fax: 480-792-4338
Atlanta
500 Sugar Mill Road, Suite 200B
Atlanta, GA 30350
Tel: 770-640-0034 Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
2 Lan Drive, Suit e 120
Westford, MA 01886
Tel: 978-692-3848 Fax: 978-692-3821
Chicago
333 Pierce Road, S uite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 630-285-0071 Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
4570 Westgrove Drive, Suite 160
Addison, TX 75001
Tel: 972-818-7423 Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Tri-Atria Office Building
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190
Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Tel: 248-538-2250 Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
2767 S. Albright Road
Kokomo, Indiana 46902
Tel: 765-864-8360 Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
18201 Von Karman, Suite 10 90
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 949-263-1888 Fax: 949-263-1338
New York
150 Motor Parkwa y, Suite 202
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Tel: 631-273-5305 Fax: 631-273-5335
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First S treet, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408-436-7950 Fax: 408-436-7955
Toro nto
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Canada
Tel: 905-673-0699 Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd
Suite 22, 41 Rawson Street
Epping 2121, NSW
Australia
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733 Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Beijing Liaison Office
Unit 915
Bei Hai Wan Tai Bldg.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Beidajie
Beijing, 100027, No. China
Tel: 86-10-852821 00 Fax: 86-10-852 82104
China - Chengdu
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Chengdu Liaison Office
Rm. 2401, 24th Floor,
Ming Xing Financial Tower
No. 88 TIDU Street
Chengdu 610016, China
Tel: 86-28-867662 00 Fax: 86-28-867 66599
China - Fuzhou
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Fuzhou Liaison Office
Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza
No. 71 Wusi Road
Fuzhou 350001, China
Tel: 86-591-75035 06 Fax: 86-591-7503521
China - Shanghai
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd.
Room 701, Bldg. B
Far East International Plaza
No. 317 Xian Xia Road
Shanghai, 200051
Tel: 86-21-6275-5700 Fax: 86-21-6275-5060
China - Shenzhen
Microchip Technology Consulting (Shanghai)
Co., Ltd., Shenzhen L iaison Office
Rm. 1315, 13/F, Shenzhen Kerry Centre,
Renminnan Lu
Shenzhen 518001, Ch ina
Tel: 86-755-23503 61 Fax: 86-755-2366086
China - Hong Kong SAR
Microchip Technology Hongkong Ltd.
Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401-120 0 Fax: 852-2401-3431
India
Microchip Technology Inc.
India Liaison Office
Divyasree Chambers
1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Bangalore, 560 025, India
Tel: 91-80-229006 1 Fax: 91-80-2290 062
Japan
Microchip Technology Japan K.K.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shinyokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Yokohama-shi
Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
Tel: 81-45-471- 6166 Fax: 81-45-471-6122
Korea
Microchip Technology Korea
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku
Seoul, Korea 135-882
Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-593 4
Singapore
Microchip Technology Singapore Pte Ltd.
200 Middle Road
#07-02 Prime Centre
Singapore, 188980
Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Ta iw an
Microchip Technology (Barbados) Inc.,
Taiwan Branch
11F-3, No. 207
Tung Hua North Road
Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
EUROPE
Austria
Microchip Technology Austria GmbH
Durisolstrasse 2
A-4600 Wels
Austria
Tel: 43-7242-2244-399
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark
Microchip Technology Nordic ApS
Regus Business Centre
Lautrup hoj 1-3
Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Tel: 45 4420 9895 Fax: 45 4420 9910
France
Microchip Technology SARL
Parc d’Activite du Moulin de Massy
43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Batiment A - ler Etage
91300 Massy, France
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20 Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany
Microchip Technology GmbH
Steinheilstrasse 10
D-85737 Ismaning, Germany
Tel: 49-89-627-144 0 Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy
Microchip Technology SRL
Centro Direzionale Colleoni
Palazzo Taurus 1 V. Le Colleoni 1
20041 Agrate Brianza
Milan, Italy
Tel: 39-039-65791-1 Fax: 39-039-6899883
United Kingdom
Microchip Ltd.
505 Eskdale Road
Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham
Berkshire, England RG41 5TU
Tel: 44 118 921 5869 Fax: 44-118 921-5820
08/01/02
DS21295B-page 34 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...