Page 1

dsPIC30F5015/5016
Data Sheet
High-Performance
Digital Signal Controllers
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A
Page 2

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection features of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is provided only for your convenience
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE,
RELATED TO THE INFORMATION, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION, QUALITY, PERFORMANCE,
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR PURPOSE.
Microchip disclaims all liability arising from this information and
its use. Use of Microchip’s products as critical components in
life support systems is not authorized except with express
written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed,
implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip intellectual property
rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Accuron,
dsPIC, K
EELOQ, microID, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART,
PRO MATE, PowerSmart, rfPIC, and SmartShunt are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A. and other countries.
AmpLab, FilterLab, Migratable Memory, MXDEV, MXLAB,
PICMASTER, SEEVAL, SmartSensor and The Embedded
Control Solutions Company are registered trademarks of
Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, ECAN, ECONOMONITOR,
FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB, In-Circuit Serial
Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, Linear Active Thermistor,
MPASM, MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM, PICkit, PICDEM,
PICDEM.net, PICLAB, PICtail, PowerCal, PowerInfo,
PowerMate, PowerTool, rfLAB, rfPICDEM, Select Mode,
Smart Serial, SmartTel, Total Endurance and WiperLock are
trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the
U.S.A. and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2005, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2002 quality system certification for
its worldwide headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona and Mountain View, California in
October 2003. The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are for its PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and
analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design
and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
®
8-bit MCUs, KEEL
®
OQ
code hopping
DS70149A-page ii Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3

dsPIC30F5015/5016
dsPIC30F5015/5016 Enhanced Flash
16-bit Digital Signal Controller
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
(DS70030).
(DS70046). For more
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
dsPIC30F
High-Performance Modified RISC CPU:
• Modified Harvard architecture
• C compiler optimized instruction set architecture
with flexible Addressing modes
• 84 base instructions
• 24-bit wide instructions, 16-bit wide data path
• 66 Kbytes on-chip Flash program space
(Instruction words)
• 2 Kbytes of on-chip data RAM
• 1 Kbytes of nonvolatile data EEPROM
• Up to 30 MIPS operation:
- DC to 40 MHz external clock input
- 4 MHz-10 MHz oscillator input with
PLL active (4x, 8x, 16x)
• 36 interrupt sources
- 5 external interrupt sources
- 8 user selectable priority levels for each
interrupt source
- 4 processor trap sources
• 16 x 16-bit working register array
DSP Engine Features:
• Dual data fetch
• Accumulator write back for DSP operations
• Modulo and Bit-Reversed Addressing modes
• Two, 40-bit wide accumulators with optional
saturation logic
• 17-bit x 17-bit single-cycle hardware fractional/
integer multiplier
• All DSP instructions single cycle
• ±16-bit single-cycle shift
Peripheral Features:
• High-current sink/source I/O pins: 25 mA/25 mA
•Timer module with programmable prescaler:
- Five 16-bit timers/counters; optionally pair
16-bit timers into 32-bit timer modules
• 16-bit Capture input functions
• 16-bit Compare/PWM output functions
•3-wire SPITM modules (supports 4 Frame modes)
•I2CTM module supports Multi-Master/Slave mode
and 7-bit/10-bit addressing
• 1 UART modules with FIFO Buffers
• 1 CAN modules, 2.0B compliant
Motor Control PWM Module Features:
• 8 PWM output channels
- Complementary or Independent Output
modes
- Edge and Center-Aligned modes
• 4 duty cycle generators
• Dedicated time base
• Programmable output polarity
• Dead-Time control for Complementary mode
• Manual output control
• Trigger for A/D conversions
Quadrature Encoder Interface Module Features:
• Phase A, Phase B and Index Pulse input
• 16-bit up/down position counter
• Count direction status
• Position Measurement (x2 and x4) mode
• Programmable digital noise filters on inputs
• Alternate 16-bit Timer/Counter mode
• Interrupt on position counter rollover/underflow
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 1
Page 4
dsPIC30F5015/5016
Analog Features:
• 10-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) with
4 S/H Inputs:
- 1 Msps conversion rate
- 16 input channels
- Conversion available during Sleep and Idle
• Programmable Brown-out Detection and Reset
generation
Special Microcontroller Features:
• Power-on Reset (POR), Power-up Timer (PWRT)
and Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST)
• Flexible Watchdog Timer (WDT) with on-chip,
low-power RC oscillator for reliable operation
• Fail-Safe Clock Monitor operation detects clock
failure and switches to on-chip, low-power RC
oscillator
• Programmable code protection
• In-Circuit Serial Programming™ (ICSP™)
• Selectable Power Management modes
- Sleep, Idle and Alternate Clock modes
• Enhanced Flash program memory:
- 10,000 erase/write cycle (min.) for
CMOS Technology:
industrial temperature range, 100K (typical)
• Data EEPROM memory:
- 100,000 erase/write cycle (min.) for
industrial temperature range, 1M (typical)
• Self-reprogrammable under software control
• Low-power, high-speed Flash technology
• Wide operating voltage range (2.5V to 5.5V)
• Industrial and Extended temperature ranges
• Low-power consumption
dsPIC30F Motor Control and Power Conversion Family*
Program
Device Pins
dsPIC30F2010 28 12K/4K 512 1024 3 4 2 6 ch 6 ch Yes 1 1 1 -
dsPIC30F3010 28 24K/8K 1024 1024 5 4 2 6 ch 6 ch Yes 1 1 1 -
dsPIC30F4012 28 48K/16K 2048 1024 5 4 2 6 ch 6 ch Yes 1 1 1 1
dsPIC30F3011 40/44 24K/8K 1024 1024 5 4 4 6 ch 9 ch Yes 2 1 1 -
dsPIC30F4011 40/44 48K/16K 2048 1024 5 4 4 6 ch 9 ch Yes 2 1 1 1
dsPIC30F5015 64 66K/22K 2048 1024 5 4 4 8 ch 16 ch Yes 1 2 1 1
dsPIC30F5016 80 66K/22K 2048 1024 5 4 4 8 ch 16 ch Yes 1 2 1 1
dsPIC30F6010 80 144K/48K 8192 4096 5 8 8 8 ch 16 ch Yes 2 2 1 2
* This table provides a summary of the dsPIC30F5015/5016 peripheral features. Other available devices in the dsPIC30F Motor
Control and Power Conversion Family are shown for feature comparison.
Mem. Bytes/
Instructions
SRAM
Bytes
EEPROM
Bytes
Timer
16-bit
Input
Cap
Output
Comp/Std
PWM
Motor
Control
PWM
A/D 10-bit
1 Msps
Quad
Enc
TM
UART
TM
C
2
I
SPI
CAN
DS70149A-page 2 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 5

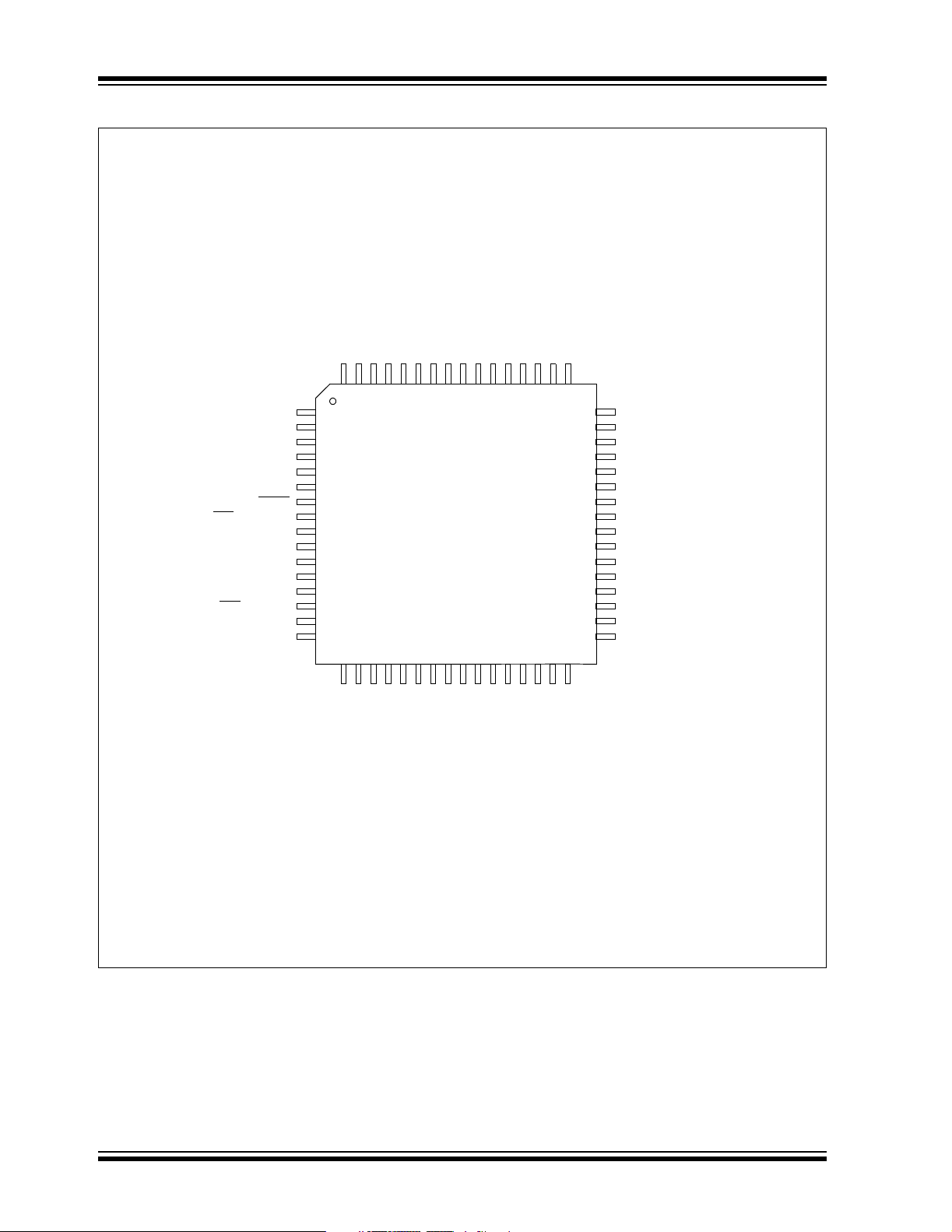
Pin Diagram
80-Pin TQFP
PWM3L/RE4
dsPIC30F5015/5016
DD
CN16/UPDN/RD7
CN14/RD5
PWM2L/RE2
PWM1L/RE0
RG0
RG1
C1TX/RF1
C1RX/RF0
PWM2H/RE3
PWM1H/RE1
V
CN15/RD6
VSS
CN13/RD4
RD12
OC4/RD3
OC3/RD2
CN19/RD13
EMUD2/OC2/RD1
PWM3H/RE5
PWM4L/RE6
PWM4H/RE7
T2CK/RC1
T4CK/RC3
SCK2/CN8/RG6
SDI2/CN9/RG7
SDO2/CN10/RG8
MCLR
SS2/CN11/RG9
SS
V
VDD
FLTA/INT1/RE8
FLTB/INT2/RE9
AN5/QEB/CN7/RB5
AN4/QEA/CN6/RB4
AN3/INDX/CN5/RB3
AN2/SS1
/CN4/RB2
PGC/EMUC/AN1/CN3/RB1
PGD/EMUD/AN0/CN2/RB0
80
79
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2324252627282930313233
22
REF-/RA9
AN7/RB7
V
VREF+/RA10
AN6/OCFA/RB6
DD
AV
75
767877
AVSS
727473
7170696867666564636261
dsPIC30F5016
VSS
AN8/RB8
AN9/RB9
AN11/RB11
AN10/RB10
DD
V
EMUC1/SOSCO/T1CK/CN0/RC14
60
EMUD1/SOSCI/CN1/RC13
59
EMUC2/OC1/RD0
58
IC4/RD11
57
IC3/RD10
56
IC2/RD9
55
IC1/RD8
54
INT4/RA15
53
52
INT3/RA14
SS
V
51
OSC2/CLKO/RC15
50
OSC1/CLKI
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
39
38
37
36
35
34
CN17/RF4
AN12/RB12
AN13/RB13
CN20/RD14
AN14/RB14
CN21/RD15
AN15/CN12/RB15
DD
V
SCL/RG2
SDA/RG3
EMUC3/SCK1/INT0/RF6
SDI1/RF7
EMUD3/SDO1/RF8
U1RX/RF2
U1TX/RF3
40
CN18/RF5
Note: Pinout subject to change.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 3
Page 6
dsPIC30F5015/5016
Pin Diagram
64-Pin TQFP
PWM3L/RE4
PWM2H/RE3
PWM2L/RE2
PWM1H/RE1
SS
UPDN/CN16/RD7
C1TX/RF1
V
VDD
C1RX/RF0
CN15/RD6
IC6/CN14/RD5
IC5/CN13/RD4
OC4/RD3
OC3/RD2
EMUD2/OC2/RD1
PWM1L/RE0
PWM3H/RE5
PWM4L/RE6
PWM4H/RE7
SCK2/CN8/RG6
SDI2/CN9/RG7
SDO2/CN10/RG8
AN5/QEB/CN7/RB5
AN4/QEA/CN6/RB4
AN3/INDX/CN5/RB3
AN2/SS1
AN1/V
AN0/V
MCLR
SS2
/CN11/RG9
/CN4/RB2
REF-/CN3/RB1
REF+/CN2/RB0
VSS
VDD
545352
646362616059585756
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 36
14
15
16
171819202122232425
PGD/EMUD/AN7/RB7
PGC/EMUC/AN6/OCFA/RB6
dsPIC30F5015
DD
AVSS
AV
AN8/RB8
AN9/RB9
55
27
26
SS
V
VDD
AN11/RB11
AN10/RB10
AN12/RB12
504951
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
CN18/RF5
CN17/RF4
AN13/RB13
AN14/RB14
AN15/CN12/RB15
EMUC1/SOSCO/T1CK/CN0/RC14
EMUD1/SOSCI/T4CK/CN1/RC13
EMUC2/OC1/RD0
IC4/INT4/RD11
IC3/INT3/RD10
IC2/FLTB/INT2/RD9
IC1/FLTA/INT1/RD8
V
SS
OSC2/CLKO/RC15
OSC1/CLKI
DD
V
SCL/RG2
SDA/RG3
EMUC3/SCK1/INT0/RF6
U1RX/SDI1/RF2
EMUD3/U1TX/SDO1/RF3
Note: Pinout subject to change.
DS70149A-page 4 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

dsPIC30F5015/5016
Table of Contents
1.0 Device Overview .......................................................................................................................................................................... 7
2.0 CPU Architecture Overview........................................................................................................................................................ 15
3.0 Memory Organization ................................................................................................................................................................. 23
4.0 Address Generator Units............................................................................................................................................................ 35
5.0 Interrupts.................................................................................................................................................................................... 41
6.0 Flash Program Memory.............................................................................................................................................................. 49
7.0 Data EEPROM Memory ............................................................................................................................................................. 55
8.0 I/O Ports ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 59
9.0 Timer1 Module ........................................................................................................................................................................... 65
10.0 Timer2/3 Module ........................................................................................................................................................................ 69
11.0 Timer4/5 Module ....................................................................................................................................................................... 75
12.0 Input Capture Module ................................................................................................................................................................ 79
13.0 Output Compare Module............................................................................................................................................................ 83
14.0 Quadrature Encoder Interface (QEI) Module ............................................................................................................................. 87
15.0 Motor Control PWM Module ....................................................................................................................................................... 93
16.0 SPI™ Module ........................................................................................................................................................................... 103
17.0 I2C Module............................................................................................................................................................................... 107
18.0 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) Module .............................................................................................. 115
19.0 CAN Module............................................................................................................................................................................. 123
20.0 10-bit High-Speed Analog-to-Digital Converter (A/D) Module.................................................................................................. 133
21.0 System Integration ................................................................................................................................................................... 145
22.0 Instruction Set Summary .......................................................................................................................................................... 161
23.0 Development Support............................................................................................................................................................... 169
24.0 Electrical Characteristics .......................................................................................................................................................... 173
25.0 Packaging Information.............................................................................................................................................................. 217
Appendix A: Revision History............................................................................................................................................................. 221
Index ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 223
The Microchip Web Site..................................................................................................................................................................... 229
Customer Change Notification Service .............................................................................................................................................. 229
Customer Support .............................................................................................................................................................................. 229
Reader Response .............................................................................................................................................................................. 230
Product Identification System ............................................................................................................................................................ 231
TO OUR VALUED CUSTOMERS
It is our intention to provide our valued customers with the best documentation possible to ensure successful use of your Microchip
products. To this end, we will continue to improve our publications to better suit your needs. Our publications will be refined and
enhanced as new volumes and updates are introduced.
If you have any questions or comments regarding this publication, please contact the Marketing Communications Department via
E-mail at docerrors@microchip.com or fax the Reader Response Form in the back of this data sheet to (480) 792-4150. We
welcome your feedback.
Most Current Data Sheet
To obtain the most up-to-date version of this data sheet, please register at our Worldwide Web site at:
http://www.microchip.com
You can determine the version of a data sheet by examining its literature number found on the bottom outside corner of any page.
The last character of the literature number is the version number, (e.g., DS30000A is version A of document DS30000).
Errata
An errata sheet, describing minor operational differences from the data sheet and recommended workarounds, may exist for current
devices. As device/documentation issues become known to us, we will publish an errata sheet. The errata will specify the revision
of silicon and revision of document to which it applies.
To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please check with one of the following:
• Microchip’s Worldwide Web site; http://www.microchip.com
• Your local Microchip sales office (see last page)
When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are
using.
Customer Notification System
Register on our web site at www.microchip.com to receive the most current information on all of our products.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 5
Page 8

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS70149A-page 6 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 9

dsPIC30F5015/5016
1.0 DEVICE OVERVIEW
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
This document contains device specific information for
the dsPIC30F5015 and dsPIC30F5016 devices. The
dsPIC30F devices contain extensive Digital Signal
Processor (DSP) functionality within a high-performance
16-bit microcontroller (MCU) architecture.
(DS70030).
(DS70046). For more
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
dsPIC30F
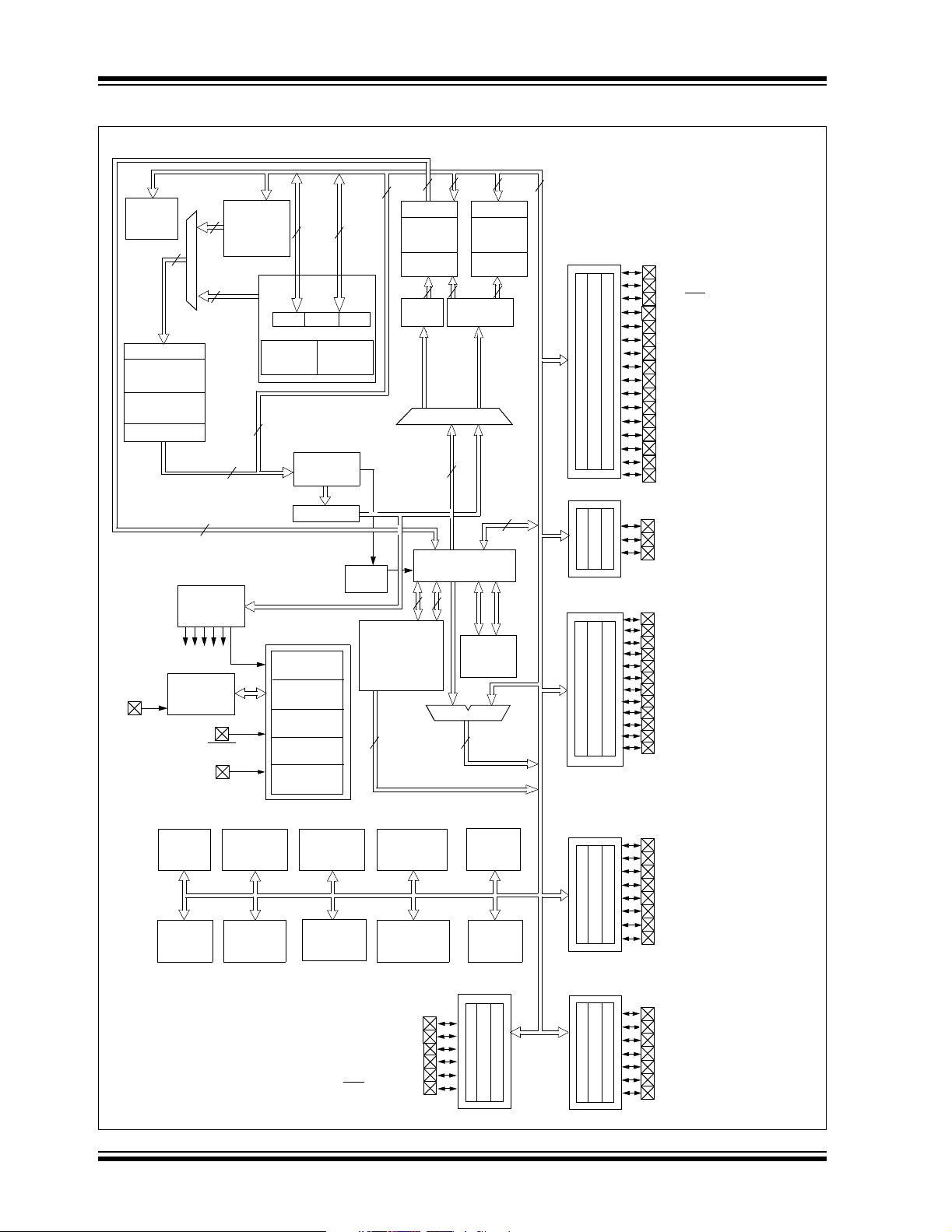
Figure 1-1 is a block diagram of the dsPIC30F5015
device. Following the block diagram, Table 1-1
provides a brief description of the device I/O pinout and
the functions that are multiplexed to the port pins on the
dsPIC30F5015.
Figure 1-2 is a block diagram of the dsPIC30F5016
device. Following the block diagram, Table 1-2
provides a brief description of the device I/O pinout and
the functions that are multiplexed to the port pins on the
dsPIC30F5016.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 7
Page 10
dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 1-1: dsPIC30F5015 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Interrupt
Controller
Address Latch
Program Memory
(66 Kbytes)
Data EEPROM
(1 Kbyte)
Data Latch
Control Signals
to Various Blocks
OSC1/CLKIN
24
16
Instruction
Decode &
Control
Timing
Generation
MCLR
VDD, VSS
AVDD, AVSS
PSV & Table
Data Access
24
Control Block
24
24
Y Data Bus
8
PCU
Program Counter
Stac k
Control
Logic
16
ROM Latch
Power-up
Timer
Oscillator
Start-up Timer
POR/BOR
Reset
Watchdog
Timer
Low-Voltage
Detect
16
PCH PCL
Loop
Control
Logic
IR
Decode
16
Y AGU
DSP
Engine
16
X Data Bus
16
16
Y Data
RAM
(1 Kbyte)
Address
Latch
Effective Address
16
Data LatchData Latch
16
16
X RAGU
X WAGU
16
16 x 16
W Reg Array
16
Divide
ALU<16>
16
16
X Data
RAM
(1 Kbyte)
Address
Latch
16
16
Unit
16
PORTB
PORTC
PORTD
AN0/VREF+/CN2/RB0
AN1/VREF-/CN3/RB1
AN2/SS1/CN4/RB2
AN3/INDX/CN5/RB3
AN4/QEA/CN6/RB4
AN5/QEB/CN7/RB5
PGC/EMUC/AN6/OCFA/RB6
PGD/EMUD/AN7/RB7
AN8/RB8
AN9/RB9
AN10/RB10
AN11/RB11
AN12/RB12
AN13/RB13
AN14/RB14
AN15/CN12/RB15
EMUD1/SOSCI/T4CK/CN1/RC13
EMUC1/SOSCO/T1CK/CN0/RC14
OSC2/CLKO/RC15
EMUC2/OC1/RD0
EMUD2/OC2/RD1
OC3/RD2
OC4/RD3
IC5/CN13/RD4
IC6/CN14/RD5
CN15/RD6
UPDN/CN16/RD7
IC1/FLTA/INT1/RD8
IC2/FLTB/INT2/RD9
IC3/INT3/RD10
IC4/INT4/RD11
CAN1
SPI1,
SPI2
10-bit ADC
Timers
Input
Capture
Module
QEI
SCK2/CN8/RG6
SDI2/CN9/RG7
SDO2/CN10/RG8
SS2
Output
Compare
Module
Motor Control
PWM
SCL/RG2
SDA/RG3
/CN11/RG9
I2C™
UART1
PORTG PORTF
PWM1L/RE0
PWM1H/RE1
PWM2L/RE2
PWM2H/RE3
PWM3L/RE4
PWM3H/RE5
PWM4L/RE6
PWM4H/RE7
PORTE
C1RX/RF0
C1TX/RF1
U1RX/SDI1/RF2
EMUD3/U1TX/SDO1/RF3
CN17/RF4
CN18/RF5
EMUC3/SCK1/INT0/RF6
DS70149A-page 8 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11
dsPIC30F5015/5016
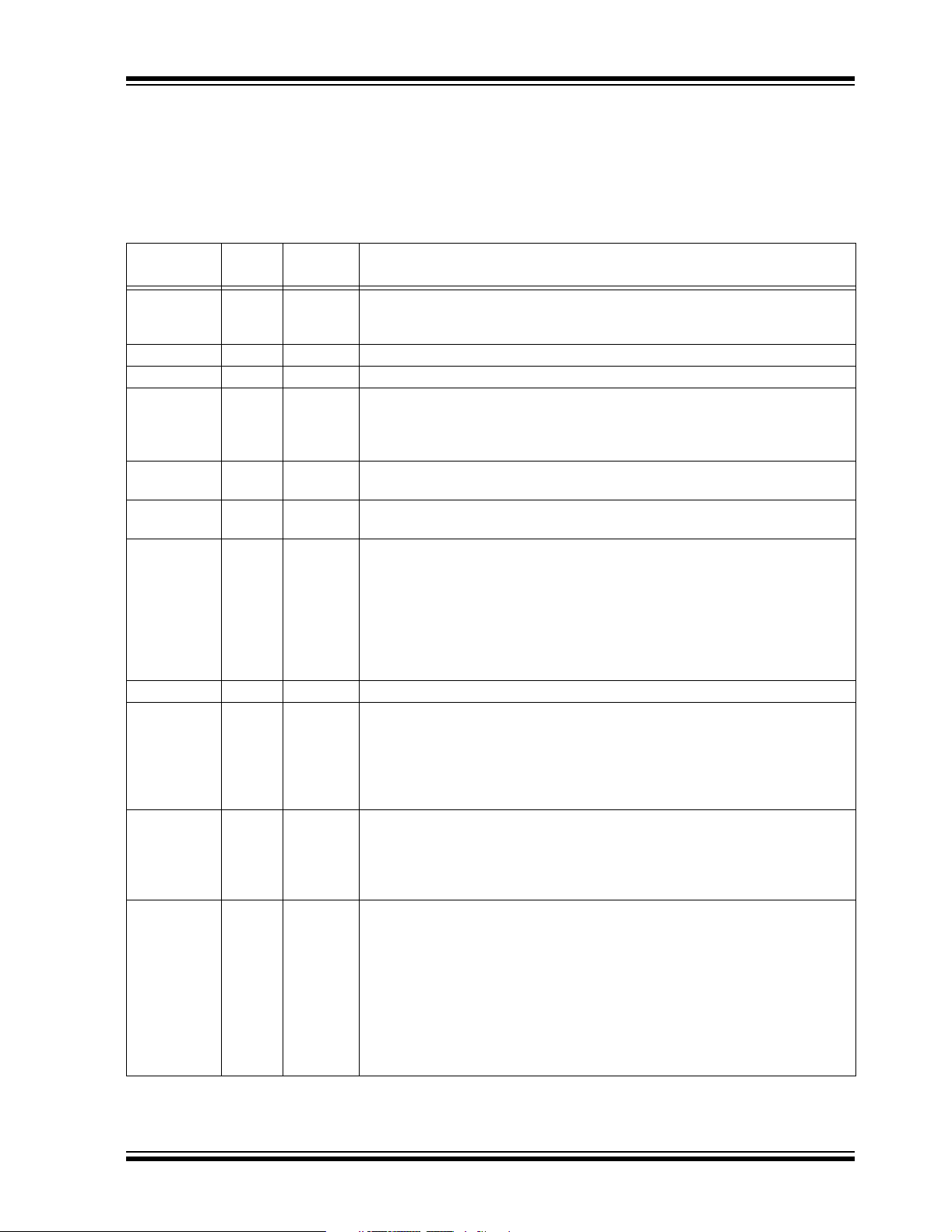
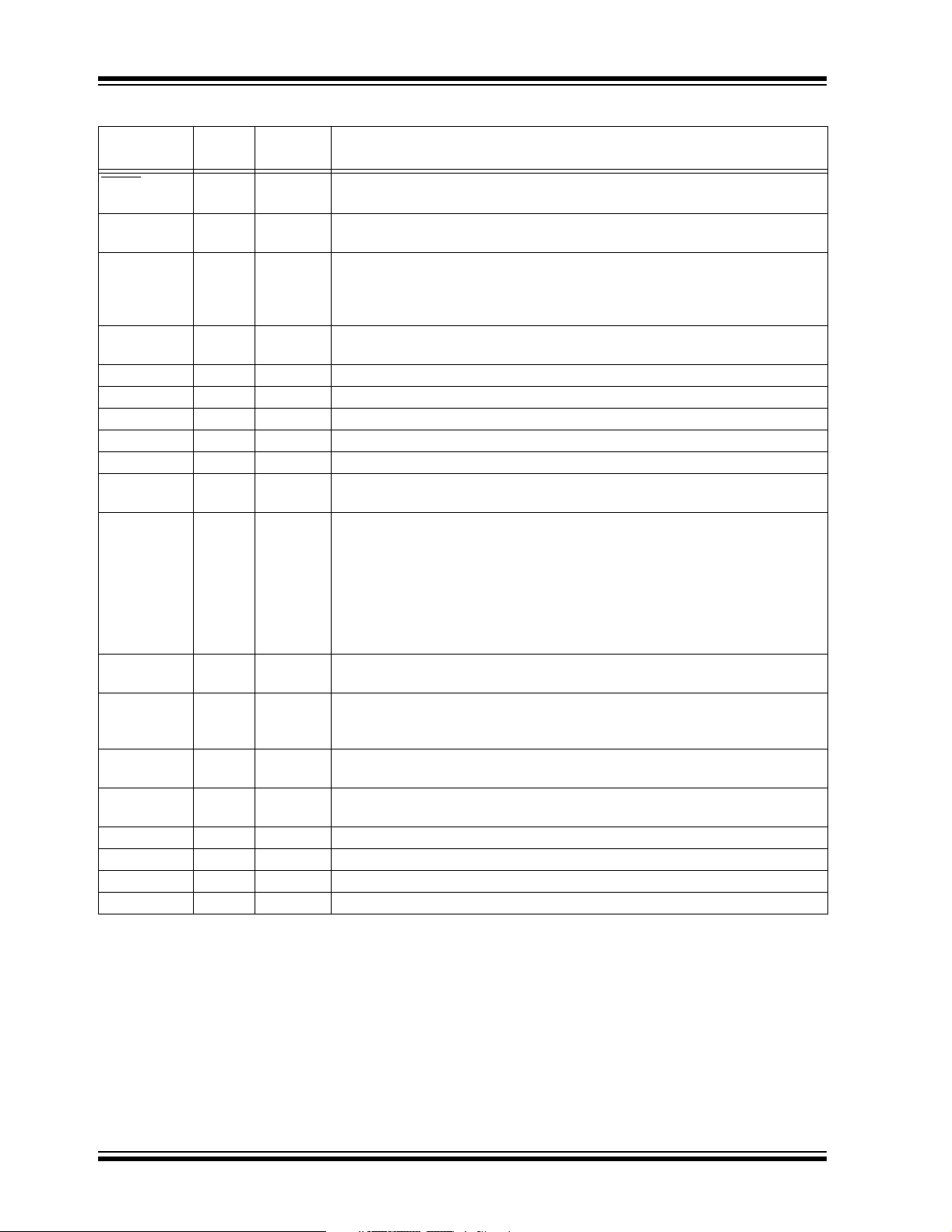
Table 1-1 provides a brief description of the device I/O
pinout and the functions that are multiplexed to the port
pins on the dsPIC30F5015 device. Multiple functions
may exist on one port pin. When multiplexing occurs,
the peripheral module’s functional requirements may
force an override of the data direction of the port pin.
TABLE 1-1: I/O PIN DESCRIPTIONS FOR dsPIC30F5015
Pin Name
AN0-AN15 I Analog Analog input channels.
DD P P Positive supply for analog module.
AV
AVSS P P Ground reference for analog module.
CLKIN
CLKO
CN0-CN18 I ST Input change notification inputs.
C1RX
C1TX
EMUD
EMUC
EMUD1
EMUC1
EMUD2
EMUC2
EMUD3
EMUC3
IC1-IC4 I ST Capture inputs 1 through 4.
INDX
QEA
QEB
UPDN
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
INT4
FLTA
FLTB
PWM1L
PWM1H
PWM2L
PWM2H
PWM3L
PWM3H
PWM4L
PWM4H
Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output Analog = Analog input
Pin
Type
I
O
I
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
I
I
O
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels O = Output
I = Input P = Power
Buffer
Typ e
AN0 and AN1 are also used for device programming data and clock inputs,
respectively.
ST/CMOS—External clock source input. Always associated with OSC1 pin function.
Oscillator crystal output. Connects to crystal or resonator in Crystal
Oscillator mode. Optionally functions as CLKO in RC and EC modes. Always
associated with OSC2 pin function.
Can be software programmed for internal weak pull-ups on all inputs.
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
CMOS
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
CAN1 bus receive pin.
CAN1 bus transmit pin.
ICD Primary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Primary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
ICD Secondary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Secondary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
ICD Tertiary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Tertiary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
ICD Quaternary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Quaternary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
Quadrature Encoder Index Pulse input.
Quadrature Encoder Phase A input in QEI mode.
Auxiliary Timer External Clock/Gate input in Timer mode.
Quadrature Encoder Phase A input in QEI mode.
Auxiliary Timer External Clock/Gate input in Timer mode.
Position Up/Down Counter Direction State.
External interrupt 0.
External interrupt 1.
External interrupt 2.
External interrupt 3.
External interrupt 4.
PWM Fault A input.
PWM Fault B input.
PWM 1 Low output.
PWM 1 High output.
PWM 2 Low output.
PWM 2 High output.
PWM 3 Low output.
PWM 3 High output.
PWM 4 Low output.
PWM 4 High output.
Description
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 9
Page 12
dsPIC30F5015/5016
TABLE 1-1: I/O PIN DESCRIPTIONS FOR dsPIC30F5015 (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
MCLR I/P ST Master Clear (Reset) input or programming voltage input. This pin is an active-
OCFA
OC1-OC4
OSC1
OSC2
PGD
PGC
RB0-RB15 I/O ST PORTB is a bidirectional I/O port.
RC13-RC15 I/O ST PORTC is a bidirectional I/O port.
RD0-RD11 I/O ST PORTD is a bidirectional I/O port.
RE0-RE7 I/O ST PORTE is a bidirectional I/O port.
RF0-RF6 I/O ST PORTF is a bidirectional I/O port.
RG2-RG3
RG6-RG9
SCK1
SDI1
SDO1
SS1
SCK2
SDI2
SDO2
SS2
SCL
SDA
SOSCO
SOSCI
T1CK
T4CK
U1RX
U1TX
DD P — Positive supply for logic and I/O pins.
V
SS P — Ground reference for logic and I/O pins.
V
VREF+ I Analog Analog Voltage Reference (High) input.
V
REF- I Analog Analog Voltage Reference (Low) input.
Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output Analog = Analog input
Pin
Type
I
O
I
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
O
I
I/O
I
O
I
I/O
I/O
O
I
I
I
I
O
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels O = Output
I = Input P = Power
Buffer
Typ e
low Reset to the device.
ST
—
ST/CMOS—Oscillator crystal input. ST buffer when configured in RC mode; CMOS
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
—
ST/CMOS
ST
ST
ST
—
Compare Fault A input (for Compare channels 1, 2, 3 and 4).
Compare outputs 1 through 4.
otherwise.
Oscillator crystal output. Connects to crystal or resonator in Crystal Oscillator
mode. Optionally functions as CLKO in RC and EC modes.
In-Circuit Serial Programming™ data input/output pin.
In-Circuit Serial Programming clock input pin.
PORTG is a bidirectional I/O port.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI™ #1.
SPI #1 Data In.
SPI #1 Data Out.
SPI #1 Slave Synchronization.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI #2.
SPI #2 Data In.
SPI #2 Data Out.
SPI #2 Slave Synchronization.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for I
Synchronous serial data input/output for I
32 kHz low-power oscillator crystal output.
32 kHz low-power oscillator crystal input. ST buffer when configured in RC
mode; CMOS otherwise.
Timer1 external clock input.
Timer4 external clock input.
UART1 Receive.
UART1 Transmit.
Description
2
C™.
2
C.
DS70149A-page 10 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13
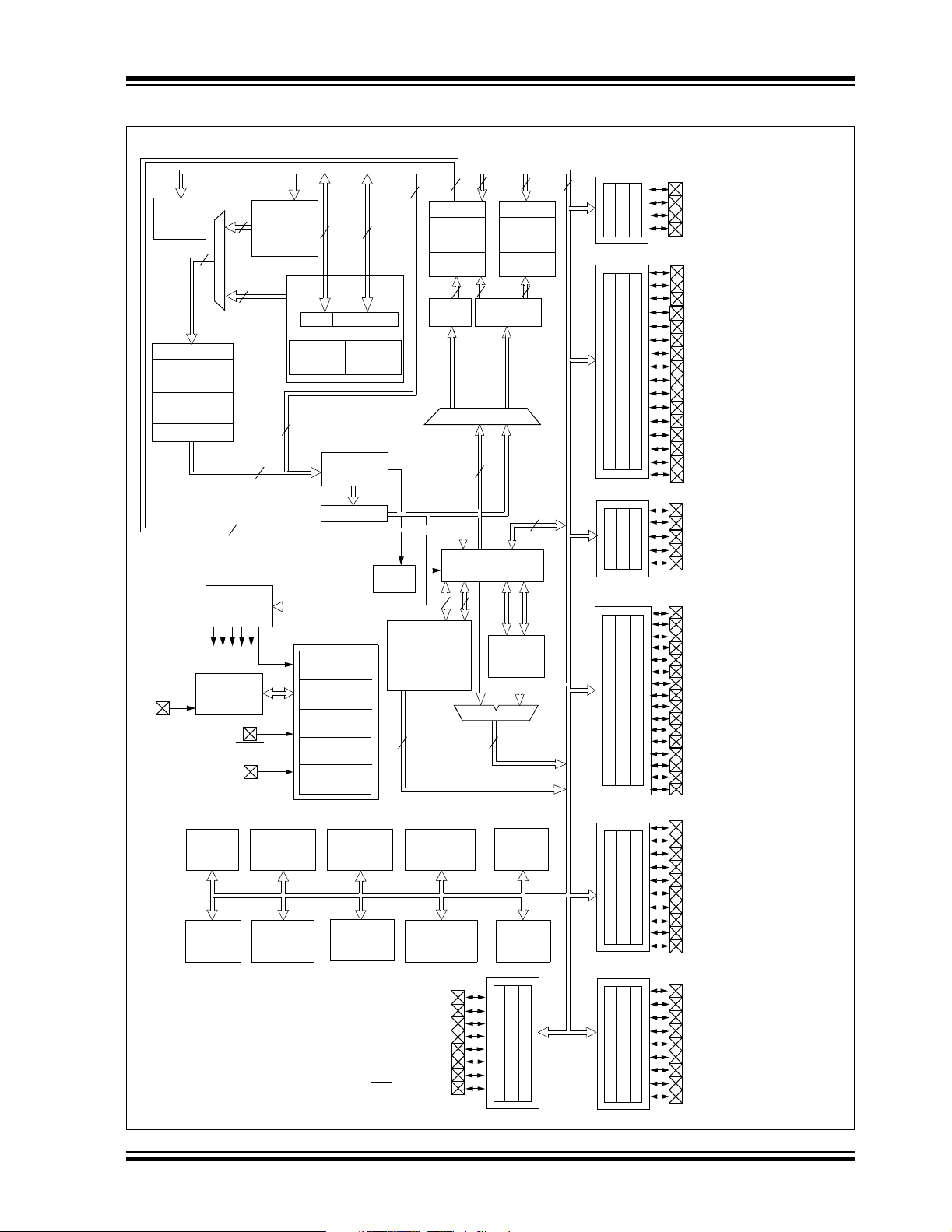
FIGURE 1-2: dsPIC30F5016 BLOCK DIAGRAM
dsPIC30F5015/5016
Interrupt
Controller
Address Latch
Program Memory
(66 Kbytes)
Data EEPROM
(1 Kbyte)
Data Latch
Control Signals
to Various Blocks
OSC1/CLKIN
24
16
Instruction
Decode &
Control
Timing
Generation
MCLR
VDD, VSS
AVDD, AVSS
CAN1
SPI1,
SPI2
PSV & Table
Data Access
24
Control Block
24
24
10-bit ADC
Timers
Y Data Bus
8
PCH PCL
PCU
Program Counter
Stac k
Control
Logic
16
ROM Latch
Power-up
Timer
Oscillator
Start-up Timer
POR/BOR
Reset
Watchdog
Timer
Low-Voltage
Detect
Loop
Control
Logic
IR
Input
Capture
Module
QEI
16
Decode
DSP
Engine
16
Y Data
RAM
(1 Kbyte)
Address
Latch
Y AGU
Effective Address
16
16
Output
Compare
Module
Motor Control
PWM
X Data Bus
16
16
16
16
X RAGU
X WAGU
16
16 x 16
W Reg Array
16
ALU<16>
16
16
Data LatchData Latch
X Data
RAM
(1 Kbyte)
Address
Latch
16
Divide
Unit
I2C™
UART1
16
PORTA
PORTB
16
PORTC
PORTD
PORTE
VREF-/RA9
VREF+/RA10
INT3/RA14
INT4/RA15
PGD/EMUD/AN0/CN2/RB0
PGC/EMUC/AN1/CN3/RB1
AN2/SS1/CN4/RB2
AN3/INDX/CN5/RB3
AN4/QEA/CN6/RB4
AN5/QEB/CN7/RB5
AN6/OCFA/RB6
AN7/RB7
AN8/RB8
AN9/RB9
AN10/RB10
AN11/RB11
AN12/RB12
AN13/RB13
AN14/RB14
AN15/CN12/RB15
T2CK/RC1
T4CK/RC3
EMUD1/SOSCI/CN1/RC13
EMUC1/SOSCO/T1CK/CN0/RC14
OSC2/CLKO/RC15
EMUC2/OC1/RD0
EMUD2/OC2/RD1
OC3/RD2
OC4/RD3
CN13/RD4
CN14/RD5
CN15/RD6
CN16/UPDN/RD7
IC1/RD8
IC2/RD9
IC3/RD10
IC4/RD11
RD12
CN19/RD13
CN20/RD14
CN21/RD15
PWM1L/RE0
PWM1H/RE1
PWM2L/RE2
PWM2H/RE3
PWM3L/RE4
PWM3H/RE5
PWM4L/RE6
PWM4H/RE7
FLTA/INT1/RE8
FLTB/INT2/RE9
RG0
RG1
SCL/RG2
SDA/RG3
SCK2/CN8/RG6
SDI2/CN9/RG7
SDO2/CN10/RG8
SS2
/CN11/RG9
PORTG PORTF
C1RX/RF0
C1TX/RF1
U1RX/RF2
U1TX/RF3
CN17/RF4
CN18/RF5
EMUC3/SCK1/INT0/RF6
SDI1/RF7
EMUD3/SDO1/RF8
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 11
Page 14
dsPIC30F5015/5016
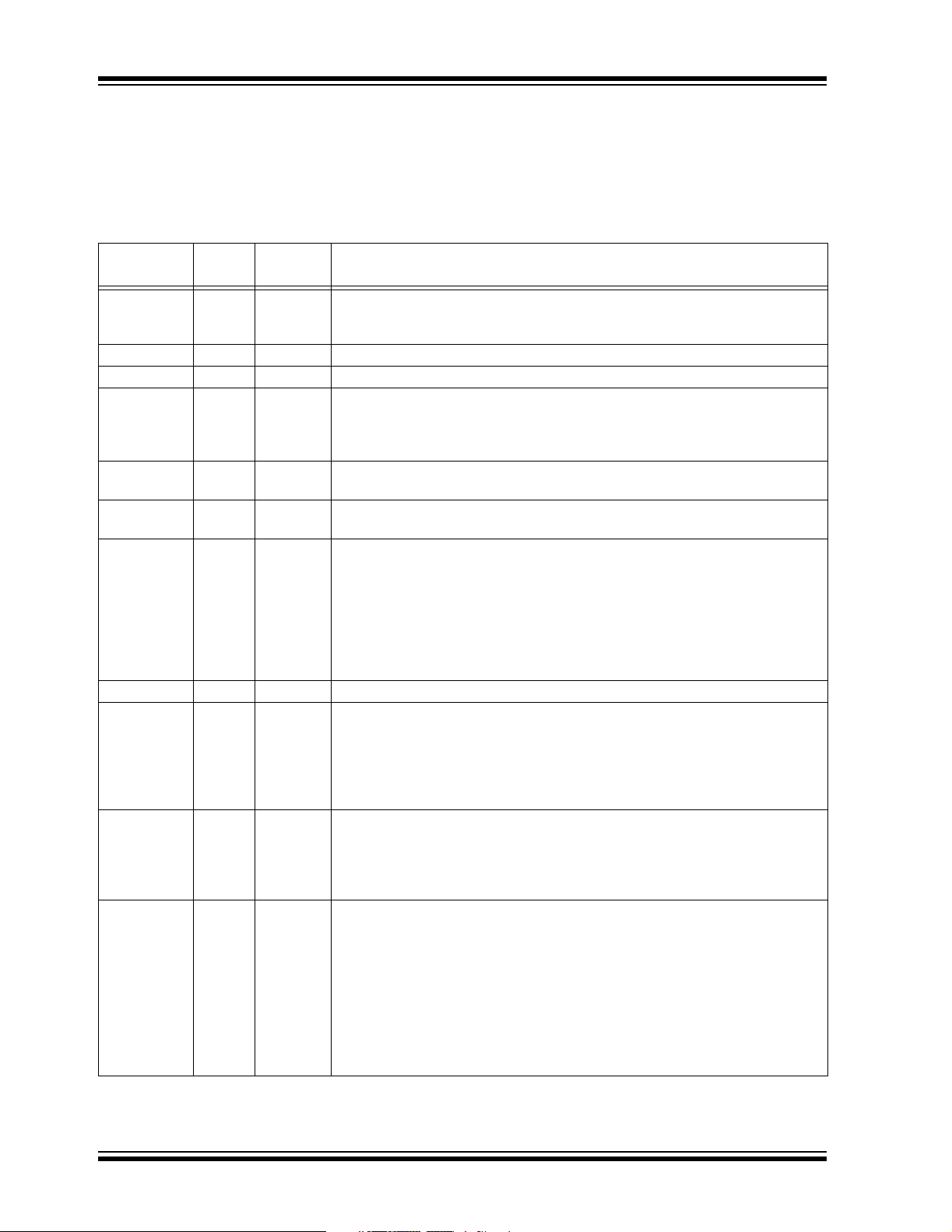
Table 1-1 provides a brief description of the device I/O
pinout and the functions that are multiplexed to the port
pins on the dsPIC30F5016. Multiple functions may
exist on one port pin. When multiplexing occurs, the
peripheral module’s functional requirements may force
an override of the data direction of the port pin.
TABLE 1-2: I/O PIN DESCRIPTIONS For dsPIC30F5016
Pin Name
AN0-AN15 I Analog Analog input channels.
DD P P Positive supply for analog module.
AV
AVSS P P Ground reference for analog module.
CLKIN
CLKO
CN0-CN21 I ST Input change notification inputs.
C1RX
C1TX
EMUD
EMUC
EMUD1
EMUC1
EMUD2
EMUC2
EMUD3
EMUC3
IC1-IC4 I ST Capture inputs 1 through 8.
INDX
QEA
QEB
UPDN
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
INT4
FLTA
FLTB
PWM1L
PWM1H
PWM2L
PWM2H
PWM3L
PWM3H
PWM4L
PWM4H
Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output Analog = Analog input
Pin
Type
I
O
I
O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
I
I
O
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels O = Output
I = Input P = Power
Buffer
Typ e
AN0 and AN1 are also used for device programming data and clock inputs,
respectively.
ST/CMOS—External clock source input. Always associated with OSC1 pin function.
Oscillator crystal output. Connects to crystal or resonator in Crystal
Oscillator mode. Optionally functions as CLKO in RC and EC modes. Always
associated with OSC2 pin function.
Can be software programmed for internal weak pull-ups on all inputs.
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
CMOS
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
CAN1 bus receive pin.
CAN1 bus transmit pin.
ICD Primary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Primary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
ICD Secondary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Secondary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
ICD Tertiary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Tertiary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
ICD Quaternary Communication Channel data input/output pin.
ICD Quaternary Communication Channel clock input/output pin.
Quadrature Encoder Index Pulse input.
Quadrature Encoder Phase A input in QEI mode.
Auxiliary Timer External Clock/Gate input in Timer mode.
Quadrature Encoder Phase A input in QEI mode.
Auxiliary Timer External Clock/Gate input in Timer mode.
Position Up/Down Counter Direction State.
External interrupt 0.
External interrupt 1.
External interrupt 2.
External interrupt 3.
External interrupt 4.
PWM Fault A input.
PWM Fault B input.
PWM 1 Low output.
PWM 1 High output.
PWM 2 Low output.
PWM 2 High output.
PWM 3 Low output.
PWM 3 High output.
PWM 4 Low output.
PWM 4 High output.
Description
DS70149A-page 12 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15
dsPIC30F5015/5016
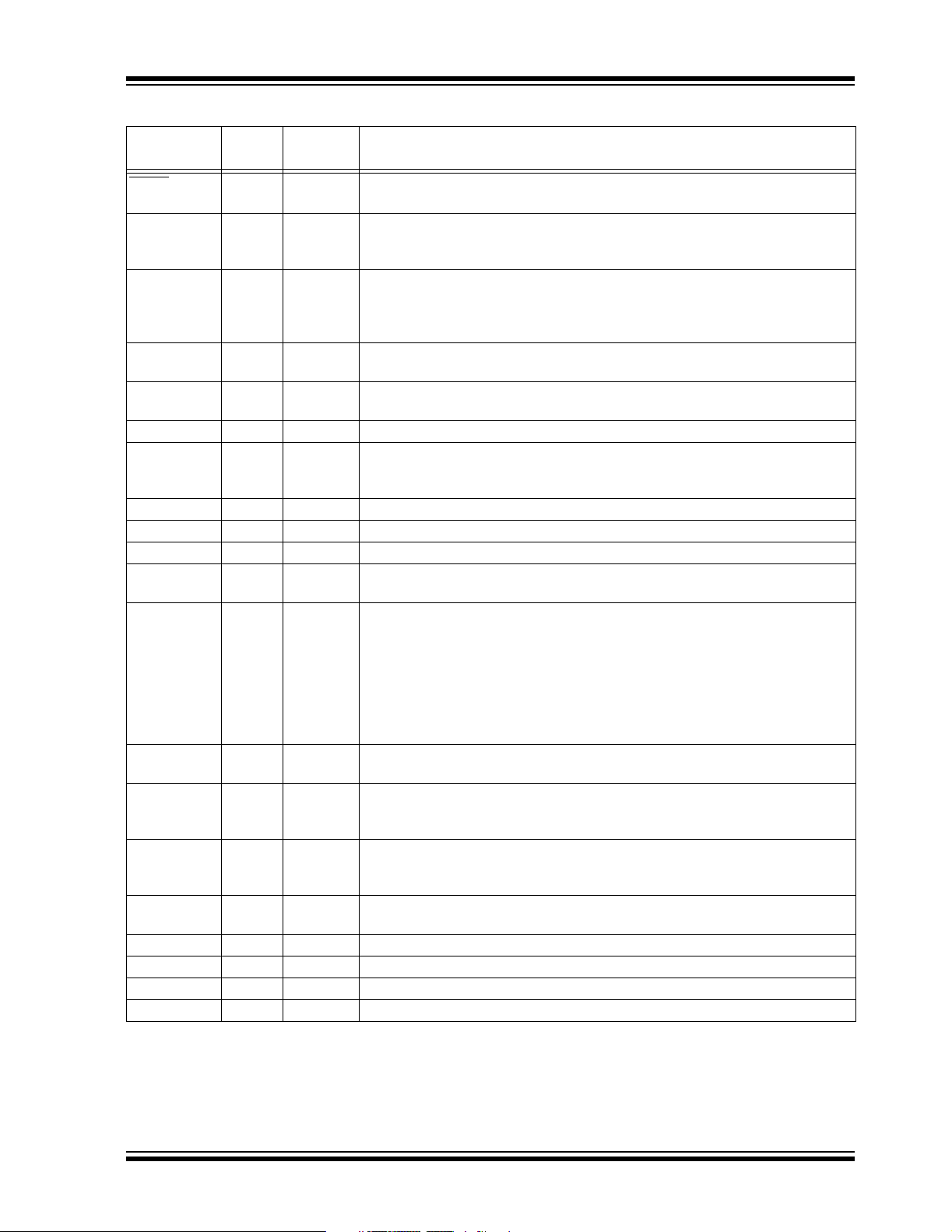
TABLE 1-2: I/O PIN DESCRIPTIONS For dsPIC30F5016 (CONTINUED)
Pin Name
MCLR I/P ST Master Clear (Reset) input or programming voltage input. This pin is an active-
OCFA
OCFB
OC1-OC4
OSC1
OSC2
PGD
PGC
RA9-RA10
RA14-RA15
RB0-RB15 I/O ST PORTB is a bidirectional I/O port.
RC1
RC3
RC13-RC15
RD0-RD15 I/O ST PORTD is a bidirectional I/O port.
RE0-RE9 I/O ST PORTE is a bidirectional I/O port.
RF0-RF8 I/O ST PORTF is a bidirectional I/O port.
RG0-RG3
RG6-RG9
SCK1
SDI1
SDO1
SS1
SCK2
SDI2
SDO2
SS2
SCL
SDA
SOSCO
SOSCI
T1CK
T2CK
T4CK
U1RX
U1TX
DD P — Positive supply for logic and I/O pins.
V
SS P — Ground reference for logic and I/O pins.
V
VREF+ I Analog Analog Voltage Reference (High) input.
V
REF- I Analog Analog Voltage Reference (Low) input.
Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output Analog = Analog input
Pin
Type
I
I
O
I
I/O
I/O
I
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I
O
I
I/O
I
O
I
I/O
I/O
O
I
I
I
I
I
O
ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels O = Output
I = Input P = Power
Buffer
Typ e
low Reset to the device.
ST
ST
—
ST/CMOS—Oscillator crystal input. ST buffer when configured in RC mode; CMOS
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
—
ST
ST
ST
—
ST/CMOS
ST
ST
ST
ST
—
Compare Fault A input (for Compare channels 1, 2, 3 and 4).
Compare Fault B input (for Compare channels 5, 6, 7 and 8).
Compare outputs 1 through 4.
otherwise.
Oscillator crystal output. Connects to crystal or resonator in Crystal Oscillator
mode. Optionally functions as CLKO in RC and EC modes.
In-Circuit Serial Programming™ data input/output pin.
In-Circuit Serial Programming clock input pin.
PORTA is a bidirectional I/O port.
PORTC is a bidirectional I/O port.
PORTG is a bidirectional I/O port.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI™ #1.
SPI #1 Data In.
SPI #1 Data Out.
SPI #1 Slave Synchronization.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for SPI #2.
SPI #2 Data In.
SPI #2 Data Out.
SPI #2 Slave Synchronization.
Synchronous serial clock input/output for I
Synchronous serial data input/output for I
32 kHz low-power oscillator crystal output.
32 kHz low-power oscillator crystal input. ST buffer when configured in RC
mode; CMOS otherwise.
Timer1 external clock input.
Timer2 external clock input.
Timer4 external clock input.
UART1 Receive.
UART1 Transmit.
Description
2
C™.
2
C.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 13
Page 16

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS70149A-page 14 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

dsPIC30F5015/5016
2.0 CPU ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
This document provides a summary of the
dsPIC30F5015/5016 CPU and peripheral function. For
a complete description of this functionality, please refer
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
to the
(DS70030).
(DS70046). For more
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
2.1 Core Overview
The core has a 24-bit instruction word. The Program
Counter (PC) is 23 bits wide with the Least Significant
bit (LSb) always clear (see Section 3.1 “Program
Address Space”), and the Most Significant bit (MSb)
is ignored during normal program execution, except for
certain specialized instructions. Thus, the PC can
address up to 4M instruction words of user program
space. An instruction pre-fetch mechanism is used to
help maintain throughput. Program loop constructs,
free from loop count management overhead, are
supported using the DO and REPEAT instructions, both
of which are interruptible at any point.
The working register array consists of 16x16-bit
registers, each of which can act as data, address or offset registers. One working register (W15) operates as
a software Stack Pointer for interrupts and calls.
The data space is 64 Kbytes (32K words) and is split
into two blocks, referred to as X and Y data memory.
Each block has its own independent Address Generation Unit (AGU). Most instructions operate solely
through the X memory AGU, which provides the
appearance of a single unified data space. The
Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) class of dual source DSP
instructions operate through both the X and Y AGUs,
splitting the data address space into two parts (see
Section 3.2 “Data Address Space”). The X and Y
data space boundary is device specific and cannot be
altered by the user. Each data word consists of 2 bytes,
and most instructions can address data either as words
or bytes.
dsPIC30F
(DS70046).
There are two methods of accessing data stored in
program memory:
The upper 32 Kbytes of data space memory can be
•
mapped into the lower half (user space) of program
space at any 16K program word boundary, defined
by the 8-bit Program Space Visibility Page
(PSVPAG) register. This lets any instruction access
program space as if it were data space, with a limitation that the access requires an additional cycle.
Moreover, only the lower 16 bits of each instruction
word can be accessed using this
• Linear indirect access of 32K word pages within
program space is also possible using any working
register, via table read and write instructions.
Table read and write instructions can be used to
access all 24 bits of an instruction word.
Overhead-free circular buffers (Modulo Addressing)
are supported in both X and Y address spaces. This is
primarily intended to remove the loop overhead for
DSP algorithms.
The X AGU also supports Bit-Reversed Addressing on
destination effective addresses, to greatly simplify input
or output data reordering for radix-2 FFT algorithms.
Refer to Section 4.0 “Address Generator Units” for
details on Modulo and Bit-Reversed Addressing.
The core supports Inherent (no operand), Relative, Literal, Memory Direct, Register Direct, Register Indirect,
Register Offset and Literal Offset Addressing modes.
Instructions are associated with predefined addressing
modes, depending upon their functional requirements.
For most instructions, the core is capable of executing
a data (or program data) memory read, a working register (data) read, a data memory write and a program
(instruction) memory read per instruction cycle. As a
result, 3-operand instructions are supported, allowing
C = A + B operations to be executed in a single cycle.
A DSP engine has been included to significantly
enhance the core arithmetic capability and throughput.
It features a high-speed 17-bit by 17-bit multiplier, a
40-bit ALU, two 40-bit saturating accumulators and a
40-bit bidirectional barrel shifter. Data in the accumulator or any working register can be shifted up to 16 bits
right or 16 bits left in a single cycle. The DSP instructions operate seamlessly with all other instructions and
have been designed for optimal real-time performance.
The MAC class of instructions can concurrently fetch
two data operands from memory, while multiplying two
W registers. To enable this concurrent fetching of data
operands, the data space has been split for these
instructions and linear for all others. This has been
achieved in a transparent and flexible manner, by dedicating certain working registers to each address space
for the MAC class of instructions.
method.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 15
Page 18

dsPIC30F5015/5016
The core does not support a multi-stage instruction
pipeline. However, a single stage instruction pre-fetch
mechanism is used, which accesses and partially
decodes instructions a cycle ahead of execution, in
order to maximize available execution time. Most
instructions execute in a single cycle, with certain
exceptions.
The core features a vectored exception processing
structure for traps and interrupts, with 62 independent
vectors. The exceptions consist of up to 8 traps (of
which 4 are reserved) and 54 interrupts. Each interrupt
is prioritized based on a user assigned priority between
1 and 7 (1 being the lowest priority and 7 being the
highest) in conjunction with a predetermined ‘natural
order’. Traps have fixed priorities, ranging from 8 to 15.
2.2 Programmer’s Model
The programmer’s model is shown in Figure 2-1 and
consists of 16x16-bit working registers (W0 through
W15), 2x40-bit accumulators (AccA and AccB),
STATUS register (SR), Data Table Page register
(TBLPAG), Program Space Visibility Page register
(PSVPAG), DO and REPEAT registers (DOSTART,
DOEND, DCOUNT and RCOUNT), and Program
Counter (PC). The working registers can act as data,
address or offset registers. All registers are memory
mapped. W0 acts as the W register for file register
addressing.
Some of these registers have a shadow register associated with each of them, as shown in Figure 2-1. The
shadow register is used as a temporary holding register
and can transfer its contents to or from its host register
upon the occurrence of an event. None of the shadow
registers are accessible directly. The following rules
apply for transfer of registers into and out of shadows.
• PUSH.S and POP.S
W0, W1, W2, W3, SR (DC, N, OV, Z and C bits
only) are transferred.
• DO instruction
DOSTART, DOEND, DCOUNT shadows are
pushed on loop start, and popped on loop end.
When a byte operation is performed on a working
register, only the Least Significant Byte of the target
register is affected. However, a benefit of memory
mapped working registers is that both the Least and
Most Significant Bytes can be manipulated through
byte-wide data memory space accesses.
2.2.1 SOFTWARE STACK POINTER/ FRAME POINTER
The dsPIC® DSC devices contain a software stack.
W15 is the dedicated software Stack Pointer (SP), and
will be automatically modified by exception processing
and subroutine calls and returns. However, W15 can be
referenced by any instruction in the same manner as all
other W registers. This simplifies the reading, writing
and manipulation of the Stack Pointer (e.g., creating
stack frames).
Note: In order to protect against misaligned
stack accesses, W15<0> is always clear.
W15 is initialized to 0x0800 during a Reset. The user
may reprogram the SP during initialization to any
location within data space.
W14 has been dedicated as a Stack Frame Pointer as
defined by the LNK and ULNK instructions. However,
W14 can be referenced by any instruction in the same
manner as all other W registers.
2.2.2 STATUS REGISTER
The dsPIC DSC core has a 16-bit STATUS register
(SR), the LSB of which is referred to as the SR Low
Byte (SRL) and the MSB as the SR High Byte (SRH).
See Figure 2-1 for SR layout.
SRL contains all the MCU ALU operation Status flags
(including the Z bit), as well as the CPU Interrupt Priority Level Status bits, IPL<2:0>, and the Repeat Active
Status bit, RA. During exception processing, SRL is
concatenated with the MSB of the PC to form a
complete word value which is then stacked.
The upper byte of the SR register contains the DSP
Adder/Subtractor Status bits, the DO Loop Active bit
(DA) and the Digit Carry (DC) Status bit.
2.2.3 PROGRAM COUNTER
The Program Counter is 23 bits wide. Bit 0 is always
clear. Therefore, the PC can address up to 4M
instruction words.
DS70149A-page 16 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 2-1: dsPIC30F5015/5016 PROGRAMMER’S MODEL
D0D15
W0/WREG
W1
W2
W3
W4
DSP Operand
Registers
DSP Address
Registers
W13/DSP Write Back
W5
W6
W7
W8
W9
W10
W11
W12/DSP Offset
W14/Frame Pointer
W15/Stack Pointer
PUSH.S Shadow
DO Shadow
Legend
Working Registers
DSP
Accumulators
PC22
7
22
22
TABPAG
TBLPAG
7
PSVPAG
PSVPAG
AD39 AD0AD31
AccA
AccB
0
Data Table Page Address
0
DOSTART
SPLIM Stack Pointer Limit Register
PC0
Program Space Visibility Page Address
15
RCOUNT
15
DCOUNT
DOEND
AD15
Program Counter
0
0
Repeat Loop Counter
0
DO Loop Counter
0
DO Loop Start Address
DO Loop End Address
15
CORCON
OA OB SA SB
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 17
OAB SAB
SRH
DA DC
IPL2 IPL1
RA
IPL0 OV
SRL
N
0
Core Configuration Register
C
Z
STATUS Register
Page 20
dsPIC30F5015/5016
2.3 Divide Support
The dsPIC DSC devices feature a 16/16-bit signed
fractional divide operation, as well as 32/16-bit and
16/16-bit signed and unsigned integer divide
operations, in the form of single instruction iterative
divides. The following instructions and data sizes are
supported:
1. DIVF – 16/16 signed fractional divide
2. DIV.sd – 32/16 signed divide
3. DIV.ud – 32/16 unsigned divide
4. DIV.sw – 16/16 signed divide
5. DIV.uw – 16/16 unsigned divide
The divide instructions must be executed within a
Repeat loop. Any other form of execution (e.g. a series
of discrete divide instructions) will not function correctly
because the instruction flow depends on RCOUNT. The
divide instruction does not automatically set up the
RCOUNT value, and it must, therefore, be explicitly and
correctly specified in the REPEAT instruction, as shown
in Table 2-1 (REPEAT will execute the target instruction
{operand value+1} times). The Repeat loop count must
be set up for 18 iterations of the DIV/DIVF instruction.
Thus, a complete divide operation requires 19 cycles.
Note: The divide flow is interruptible. However,
the user needs to save the context as
appropriate.
TABLE 2-1: DIVIDE INSTRUCTIONS
Instruction Function
DIVF Signed fractional divide: Wm/Wn → W0; Rem → W1
DIV.sd Signed divide: (Wm+1:Wm)/Wn → W0; Rem → W1
DIV.sw (or DIV.s) Signed divide: Wm/Wn → W0; Rem → W1
DIV.ud Unsigned divide: (Wm+1:Wm)/Wn → W0; Rem → W1
DIV.uw (or DIV.u) Unsigned divide: Wm/Wn → W0; Rem → W1
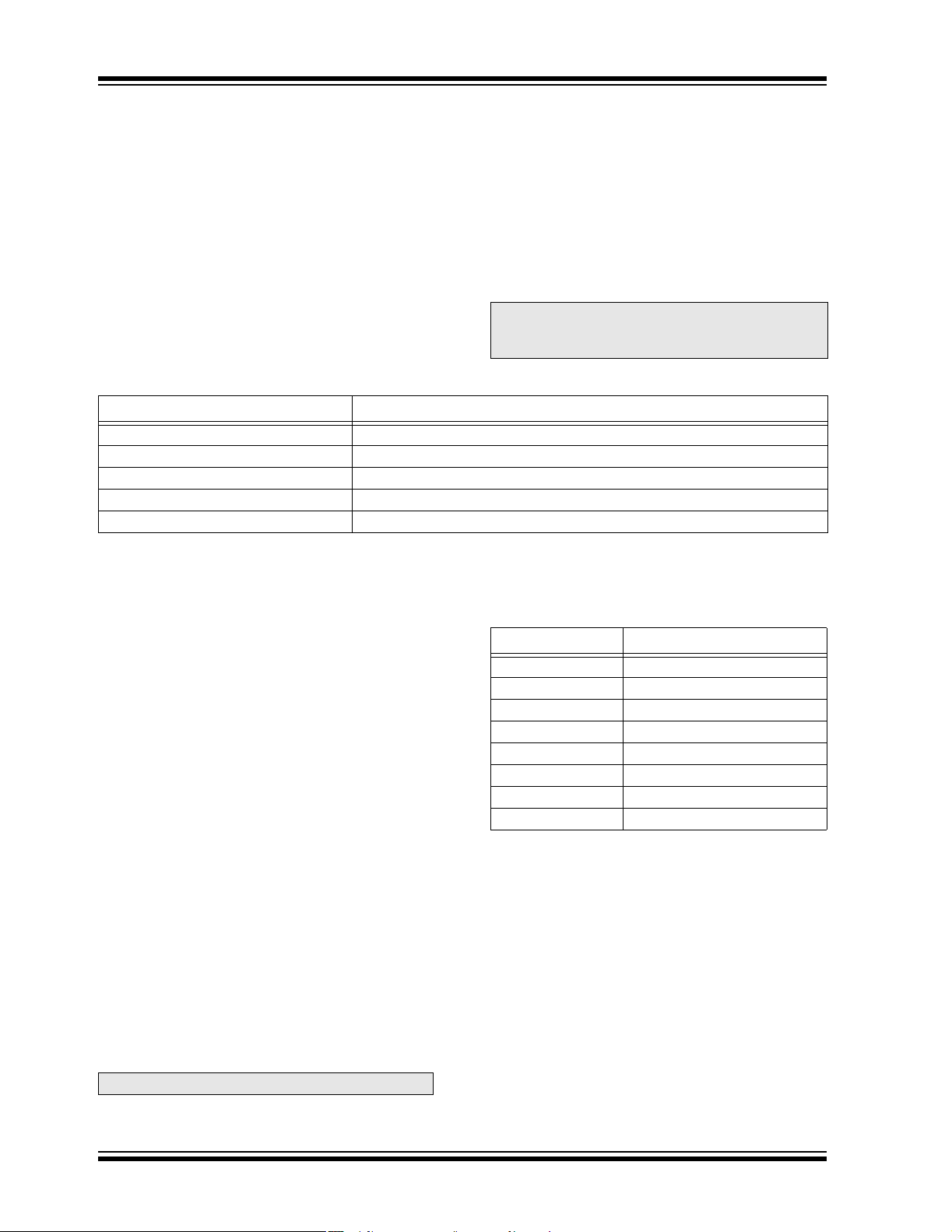
2.4 DSP Engine
The DSP engine consists of a high-speed 17-bit x 17-bit
multiplier, a barrel shifter, and a 40-bit adder/subtractor
(with two target accumulators, round and saturation
logic).
The dsPIC30F devices have a single instruction flow
which can execute either DSP or MCU instructions.
Many of the hardware resources are shared between
the DSP and MCU instructions. For example, the
instruction set has both DSP and MCU multiply
instructions which use the same hardware multiplier.
The DSP engine also has the capability to perform inherent accumulator-to-accumulator operations, which
require no additional data. These instructions are ADD,
SUB and NEG.
The DSP engine has various options selected through
various bits in the CPU Core Configuration register
(CORCON), as listed below:
1. Fractional or Integer DSP Multiply (IF).
2. Signed or Unsigned DSP Multiply (US).
3. Conventional or Convergent Rounding (RND).
4. Automatic Saturation On/Off for AccA (SATA).
5. Automatic Saturation On/Off for AccB (SATB).
6. Automatic Saturation On/Off for Writes to Data
Memory (SATDW).
7. Accumulator Saturation mode Selection
(ACCSAT).
Note: For CORCON layout, see Table 4-2.
A block diagram of the DSP engine is shown in
Figure 2-2.
TABLE 2-2: DSP INSTRUCTION
SUMMARY
Instruction Algebraic Operation
CLR A = 0
ED A = (x – y)
EDAC A = A + (x – y)
MAC A = A + (x * y)
MOVSAC No change in A
MPY A = x * y
MPY.N A = – x * y
MSC A = A – x * y
2
2
DS70149A-page 18 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21
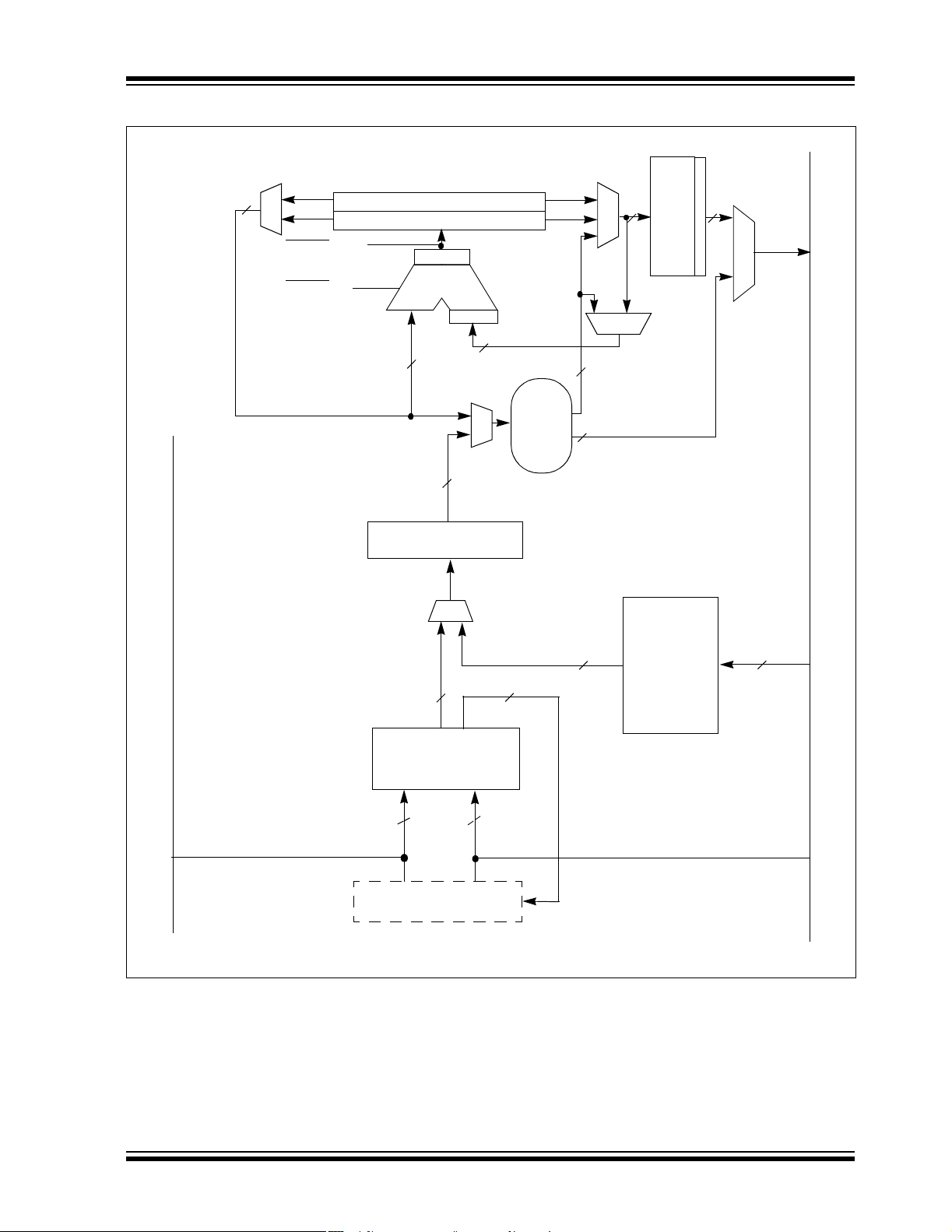
FIGURE 2-2: DSP ENGINE BLOCK DIAGRAM
40
Carry/Borrow Out
Carry/Borrow In
40-bit Accumulator A
40-bit Accumulator B
Saturate
Adder
Negate
dsPIC30F5015/5016
S
a
40
Round
Logic
16
t
u
r
a
t
e
40
40
Barrel
Shifter
32
32
40
16
X Data Bus
16
Zero Backfill
40
Sign-Extend
Y Data Bus
33
17-bit
Multiplier/Scaler
16
To/From W Array
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 19
16
Page 22

dsPIC30F5015/5016
2.4.1 MULTIPLIER
The 17x17-bit multiplier is capable of signed or
unsigned operations and can multiplex its output using
a scaler to support either 1.31 fractional (Q31) or 32-bit
integer results. Unsigned operands are zero-extended
into the 17th bit of the multiplier input value. Signed
operands are sign-extended into the 17th bit of the
multiplier input value. The output of the 17 x 17-bit
multiplier/scaler is a 33-bit value, which is signextended to 40 bits. Integer data is inherently
represented as a signed two’s complement value,
where the MSB is defined as a sign bit. Generally
speaking, the range of an N-bit two’s complement
integer is -2
range is -32768 (0x8000) to 32767 (0x7FFF), including
0. For a 32-bit integer, the data range is -2,147,483,648
(0x8000 0000) to 2,147,483,645 (0x7FFF FFFF).
When the multiplier is configured for fractional multiplication, the data is represented as a two’s complement
fraction, where the MSB is defined as a sign bit and the
radix point is implied to lie just after the sign bit
(QX format). The range of an N-bit two’s complement
fraction with this implied radix point is -1.0 to (1 – 2
For a 16-bit fraction, the Q15 data range is -1.0
(0x8000) to 0.999969482 (0x7FFF), including 0 and
has a precision of 3.01518x10
16x16 multiply operation generates a 1.31 product,
which has a precision of 4.65661x10
The same multiplier is used to support the MCU multiply instructions, which include integer 16-bit signed,
unsigned and mixed sign multiplies.
The MUL instruction may be directed to use byte or
word-sized operands. Byte operands will direct a 16-bit
result, and word operands will direct a 32-bit result to
the specified register(s) in the W array.
N-1
N-1
to 2
– 1. For a 16-bit integer, the data
-5
. In Fractional mode, a
-10
1-N
.
2.4.2 DATA ACCUMULATORS AND
ADDER/SUBTRACTOR
The data accumulator consists of a 40-bit adder/
subtractor with automatic sign extension logic. It can
select one of two accumulators (A or B) as its preaccumulation source and post-accumulation destination. For the ADD and LAC instructions, the data to be
accumulated or loaded can be optionally scaled via the
barrel shifter, prior to accumulation.
2.4.2.1 Adder/Subtractor, Overflow and
Saturation
The adder/subtractor is a 40-bit adder with an optional
zero input into one side and either true or complement
data into the other input. In the case of addition, the
carry/borrow
true data (not complemented), whereas in the case of
subtraction, the carry/borrow
other input is complemented. The adder/subtractor
generates Overflow Status bits, SA/SB and OA/OB,
which are latched and reflected in the STATUS register.
• Overflow from bit 39: this is a catastrophic
overflow in which the sign of the accumulator is
destroyed.
• Overflow into guard bits 32 through 39: this is a
recoverable overflow. This bit is set whenever all
the guard bits are not identical to each other.
The adder has an additional saturation block which
controls accumulator data saturation, if selected. It
uses the result of the adder, the Overflow Status bits
described above, and the SATA/B (CORCON<7:6>)
).
and ACCSAT (CORCON<4>) mode control bits to
determine when and to what value to saturate.
Six STATUS register bits have been provided to
support saturation and overflow; they are:
1. OA:
AccA overflowed into guard bits
2. OB:
AccB overflowed into guard bits
3. SA:
AccA saturated (bit 31 overflow and saturation)
or
AccA overflowed into guard bits and saturated
(bit 39 overflow and saturation)
4. SB:
AccB saturated (bit 31 overflow and saturation)
or
AccB overflowed into guard bits and saturated
(bit 39 overflow and saturation)
5. OAB:
Logical OR of OA and OB
6. SAB:
Logical OR of SA and SB
The OA and OB bits are modified each time data
passes through the adder/subtractor. When set, they
indicate that the most recent operation has overflowed
into the accumulator guard bits (bits 32 through 39).
The OA and OB bits can also optionally generate an
arithmetic warning trap when set and the corresponding overflow trap flag enable bit (OVATEN, OVBTEN) in
the INTCON1 register (refer to Section 5.0 “Inter-
rupts”) is set. This allows the user to take immediate
action, for example, to correct system gain.
input is active-high and the other input is
input is active-low and the
DS70149A-page 20 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 23

dsPIC30F5015/5016
The SA and SB bits are modified each time data passes
through the adder/subtractor, but can only be cleared by
the user. When set, they indicate that the accumulator
has overflowed its maximum range (bit 31 for 32-bit
saturation, or bit 39 for 40-bit saturation) and will be saturated (if saturation is enabled). When saturation is not
enabled, SA and SB default to bit 39 overflow and thus
indicate that a catastrophic overflow has occurred. If the
COVTE bit in the INTCON1 register is set, SA and SB
bits will generate an arithmetic warning trap when
saturation is disabled.
The Overflow and Saturation Status bits can optionally
be viewed in the STATUS register (SR) as the logical
OR of OA and OB (in bit OAB) and the logical OR of SA
and SB (in bit SAB). This allows programmers to check
one bit in the STATUS register to determine if either
accumulator has overflowed, or one bit to determine if
either accumulator has saturated. This would be useful
for complex number arithmetic which typically uses
both the accumulators.
The device supports three Saturation and Overflow
modes.
1. Bit 39 Overflow and Saturation:
When bit 39 overflow and saturation occurs, the
saturation logic loads the maximally positive 9.31
(0x7FFFFFFFFF) or maximally negative 9.31
value (0x8000000000) into the target accumulator. The SA or SB bit is set and remains set until
cleared by the user. This is referred to as ‘super
saturation’ and provides protection against erroneous data or unexpected algorithm problems
(e.g., gain calculations).
2. Bit 31 Overflow and Saturation:
When bit 31 overflow and saturation occurs, the
saturation logic then loads the maximally positive 1.31 value (0x007FFFFFFF) or maximally
negative 1.31 value (0x0080000000) into the
target accumulator. The SA or SB bit is set and
remains set until cleared by the user. When this
Saturation mode is in effect, the guard bits are not
used (so the OA, OB or OAB bits are never set).
3. Bit 39 Catastrophic Overflow
The bit 39 Overflow Status bit from the adder is
used to set the SA or SB bit, which remain set
until cleared by the user. No saturation operation
is performed and the accumulator is allowed to
overflow (destroying its sign). If the COVTE bit in
the INTCON1 register is set, a catastrophic
overflow can initiate a trap exception.
2.4.2.2 Accumulator ‘Write Back’
The MAC class of instructions (with the exception of
MPY, MPY.N, ED and EDAC) can optionally write a
rounded version of the high word (bits 31 through 16)
of the accumulator that is not targeted by the instruction
into data space memory. The write is performed across
the X bus into combined X and Y address space. The
following addressing modes are supported:
1. W13, Register Direct:
The rounded contents of the non-target accumulator are written into W13 as a 1.15 fraction.
2. [W13]+ = 2, Register Indirect with Post-Increment:
The rounded contents of the non-target accumulator are written into the address pointed to by
W13 as a 1.15 fraction. W13 is then
incremented by 2 (for a word write).
2.4.2.3 Round Logic
The round logic is a combinational block, which performs a conventional (biased) or convergent (unbiased)
round function during an accumulator write (store). The
Round mode is determined by the state of the RND bit
in the CORCON register. It generates a 16-bit, 1.15 data
value which is passed to the data space write saturation
logic. If rounding is not indicated by the instruction, a
truncated 1.15 data value is stored and the least
significant word is simply discarded.
Conventional rounding takes bit 15 of the accumulator,
zero-extends it and adds it to the ACCxH word (bits 16
through 31 of the accumulator). If the ACCxL word (bits
0 through 15 of the accumulator) is between 0x8000
and 0xFFFF (0x8000 included), ACCxH is incremented. If ACCxL is between 0x0000 and 0x7FFF,
ACCxH is left unchanged. A consequence of this algorithm is that over a succession of random rounding
operations, the value will tend to be biased slightly
positive.
Convergent (or unbiased) rounding operates in the
same manner as conventional rounding, except when
ACCxL equals 0x8000. If this is the case, the LSb (bit
16 of the accumulator) of ACCxH is examined. If it is ‘1’,
ACCxH is incremented. If it is ‘0’, ACCxH is not modified. Assuming that bit 16 is effectively random in
nature, this scheme will remove any rounding bias that
may accumulate.
The SAC and SAC.R instructions store either a truncated (SAC) or rounded (SAC.R) version of the contents
of the target accumulator to data memory, via the X bus
(subject to data saturation, see Section 2.4.2.4 “Data
Space Write Saturation”). Note that for the MAC class
of instructions, the accumulator write back operation
will function in the same manner, addressing combined
MCU (X and Y) data space though the X bus. For this
class of instructions, the data is always subject to
rounding.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 21
Page 24

dsPIC30F5015/5016
2.4.2.4 Data Space Write Saturation
In addition to adder/subtractor saturation, writes to data
space may also be saturated, but without affecting the
contents of the source accumulator. The data space write
saturation logic block accepts a 16-bit, 1.15 fractional
value from the round logic block as its input, together with
overflow status from the original source (accumulator)
and the 16-bit round adder. These are combined and
used to select the appropriate 1.15 fractional value as
output to write to data space memory.
If the SATDW bit in the CORCON register is set, data
(after rounding or truncation) is tested for overflow and
adjusted accordingly. For input data greater than
0x007FFF, data written to memory is forced to the maximum positive 1.15 value, 0x7FFF. For input data less
than 0xFF8000, data written to memory is forced to the
maximum negative 1.15 value, 0x8000. The MSb of the
source (bit 39) is used to determine the sign of the
operand being tested.
If the SATDW bit in the CORCON register is not set, the
input data is always passed through unmodified under
all conditions.
2.4.3 BARREL SHIFTER
The barrel shifter is capable of performing up to 16-bit
arithmetic or logic right shifts, or up to 16-bit left shifts
in a single cycle. The source can be either of the two
DSP accumulators or the X bus (to support multi-bit
shifts of register or memory data).
The shifter requires a signed binary value to determine
both the magnitude (number of bits) and direction of the
shift operation. A positive value will shift the operand
right. A negative value will shift the operand left. A
value of ‘0’ will not modify the operand.
The barrel shifter is 40 bits wide, thereby obtaining a
40-bit result for DSP shift operations and a 16-bit result
for MCU shift operations. Data from the X bus is presented to the barrel shifter between bit positions 16 to
31 for right shifts, and bit positions 0 to 15 for left shifts.
DS70149A-page 22 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 25
dsPIC30F5015/5016
3.0 MEMORY ORGANIZATION
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
(DS70046). For more
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
(DS70030).
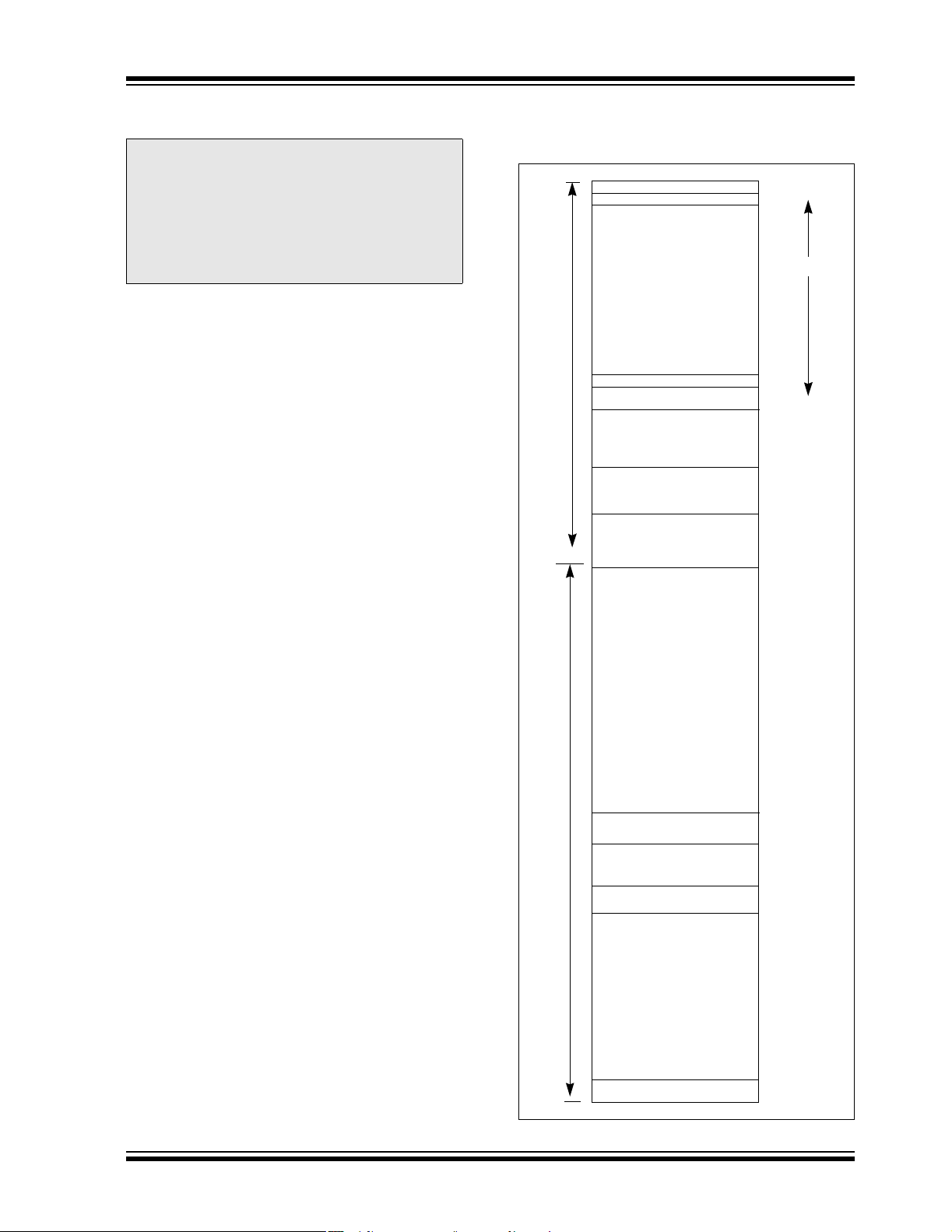
3.1 Program Address Space
The program address space is 4M instruction words. It
is addressable by the 23-bit PC, table instruction
Effective Address (EA), or data space EA, when
program space is mapped into data space, as defined
by Table 3-1. Note that the program space address is
incremented by two between successive program
words, in order to provide compatibility with data space
addressing.
User program space access is restricted to the lower
4M instruction word address range (0x000000 to
0x7FFFFE), for all accesses other than TBLRD/TBLWT,
which use TBLPAG<7> to determine user or configuration space access. In Table 3-1, read/write instructions,
bit 23 allows access to the Device ID, the User ID and
the Configuration bits. Otherwise, bit 23 is always clear.
dsPIC30F
FIGURE 3-1:
Space
User Memory
PROGRAM SPACE
MEMORY MAP FOR
dsPIC30F5015/5016
Reset - GOTO Instruction
Reset - Target Address
Interrupt Vector Table
Reserved
Alternate Vector Table
User Flash
Program Memory
(22K instructions)
Reserved
(Read ‘0’s)
Data EEPROM
(1 Kbyte)
000000
000002
000004
Vector Tables
00007E
000080
000084
0000FE
000100
00AFFE
00B000
7FFBFE
7FFC00
7FFFFE
800000
Reserved
8005BE
Space
Configuration Memory
UNITID (32 instr.)
Reserved
Device Configuration
Registers
Reserved
DEVID (2)
8005C0
8005FE
800600
F7FFFE
F80000
F8000E
F80010
FEFFFE
FF0000
FFFFFE
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 23
Page 26
dsPIC30F5015/5016
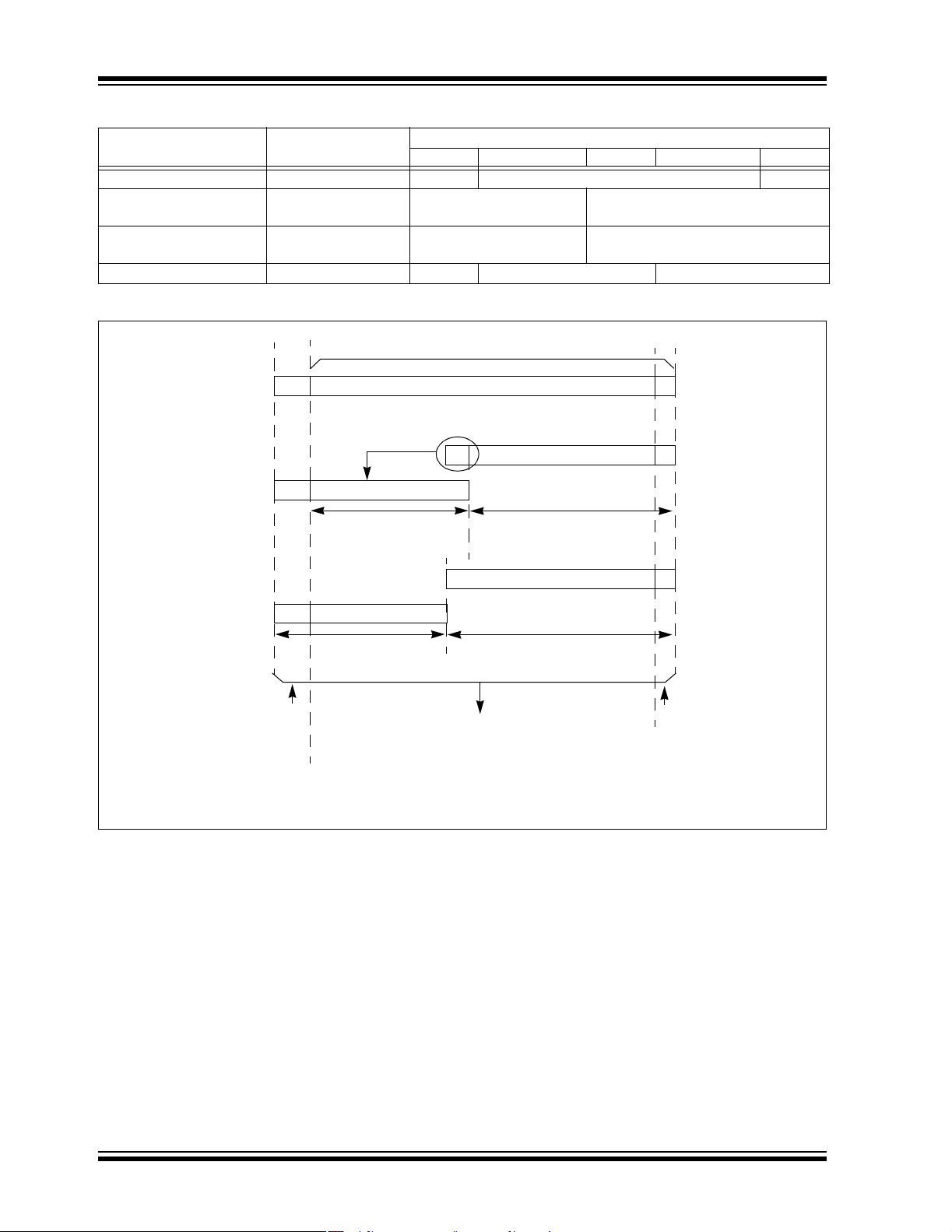
TABLE 3-1: PROGRAM SPACE ADDRESS CONSTRUCTION
Access Type
Access
Space
<23> <22:16> <15> <14:1> <0>
Instruction Access User 0 PC<22:1> 0
TBLRD/TBLWT User
TBLPAG<7:0> Data EA<15:0>
(TBLPAG<7> = 0)
TBLRD/TBLWT Configuration
TBLPAG<7:0> Data EA<15:0>
(TBLPAG<7> = 1)
Program Space Visibility User 0 PSVPAG<7:0> Data EA<14:0>
FIGURE 3-2: DATA ACCESS FROM PROGRAM SPACE ADDRESS GENERATION
23 bits
Using
Program
Counter
0
Program Space Address
0Program Counter
Select
Using
Program
Space
Visibility
Using
Table
Instruction
Note: Program Space Visibility cannot be used to access bits <23:16> of a word in program memory.
0
1/0
User/
Configuration
Space
Select
PSVPAG Reg
8 bits
TBLPAG Reg
8 bits
1
24-bit EA
EA
15 bits
EA
16 bits
Byte
Select
DS70149A-page 24 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 27
dsPIC30F5015/5016
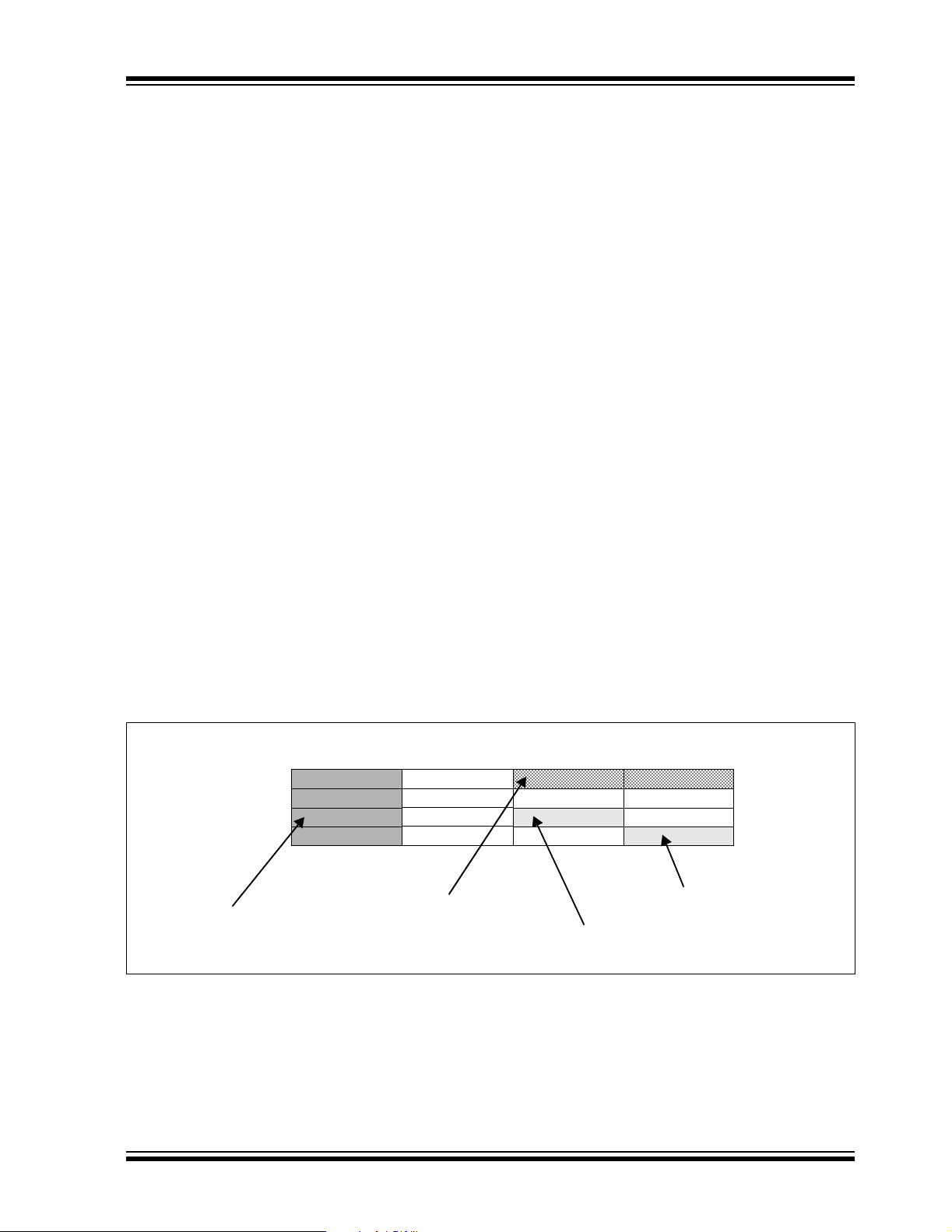
3.1.1 DATA ACCESS FROM PROGRAM MEMORY USING TABLE INSTRUCTIONS
This architecture fetches 24-bit wide program memory.
Consequently, instructions are always aligned. However, as the architecture is modified Harvard, data can
also be present in program space.
There are two methods by which program space can
be accessed; via special table instructions, or through
the remapping of a 16K word program space page into
the upper half of data space (see Section 3.1.2 “Data
Access From Program Memory Using Program
Space Visibility”). The TBLRDL and TBLWTL instruc-
tions offer a direct method of reading or writing the least
significant word of any address within program space,
without going through data space. The TBLRDH and
TBLWTH instructions are the only method whereby the
upper 8 bits of a program space word can be accessed
as data.
The PC is incremented by two for each successive
24-bit program word. This allows program memory
addresses to directly map to data space addresses.
Program memory can thus be regarded as two 16-bit
word wide address spaces, residing side by side, each
with the same address range. TBLRDL and TBLWTL
access the space which contains the least significant
word, and TBLRDH and TBLWTH access the space
which contains the MSB.
Figure 3-2 shows how the EA is created for table operations and data space accesses (PSV = 1). Here,
P<23:0> refers to a program space word, whereas
D<15:0> refers to a data space word.
A set of table instructions are provided to move byte or
word-sized data to and from program space.
1. TBLRDL: Table Read Low
Word:
Read the least significant word of the
program address;
P<15:0> maps to D<15:0>.
Byte:
Read one of the LSBs of the program
address;
P<7:0> maps to the destination byte when byte
select = 0;
P<15:8> maps to the destination byte when byte
select = 1.
2. TBLWTL: Table Write Low (refer to Section 6.0
“Flash Program Memory” for details on Flash
Programming).
3. TBLRDH: Table Read High
Word:
Read the most significant word of the
program address;
P<23:16> maps to D<7:0>; D<15:8> always
be = 0.
Byte:
Read one of the MSBs of the program
address;
P<23:16> maps to the destination byte when
byte select = 0;
The destination byte will always be = 0 when
byte select = 1.
4. TBLWTH: Table Write High (refer to Section 6.0
“Flash Program Memory” for details on Flash
Programming).
FIGURE 3-3: PROGRAM DATA TABLE ACCESS (LEAST SIGNIFICANT WORD)
PC Address
0x000000
0x000002
0x000004
0x000006
Program Memory
‘Phantom’ Byte
(Read as ‘0’).
00000000
00000000
00000000
00000000
23
TBLRDL.W
16
8
TBLRDL.B (Wn<0> = 0)
TBLRDL.B (Wn<0> = 1)
0
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 25
Page 28
dsPIC30F5015/5016
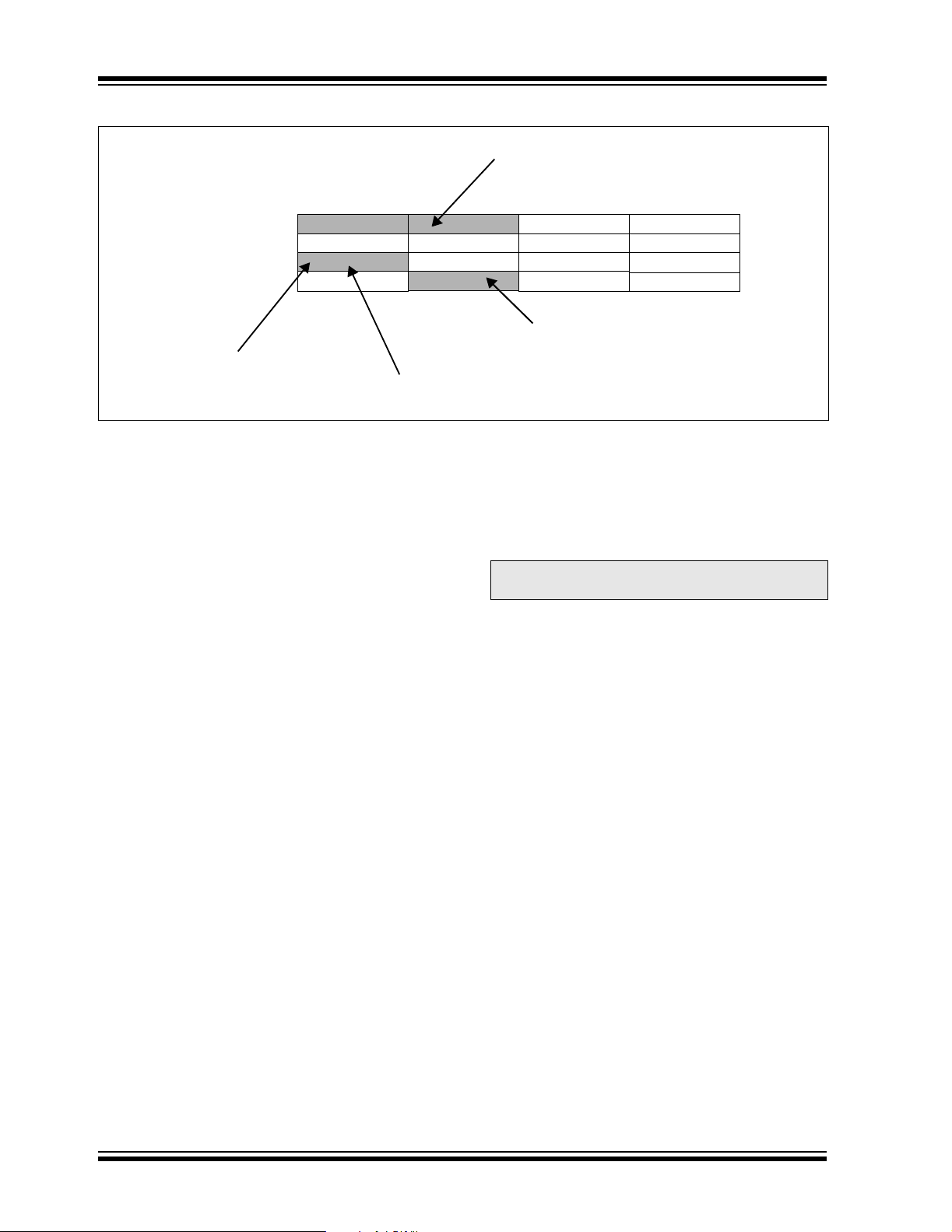
FIGURE 3-4: PROGRAM DATA TABLE ACCESS (MSB)
TBLRDH.W
PC Address
0x000000
0x000002
0x000004
0x000006
Program Memory
‘Phantom’ Byte
(Read as ‘0’)
00000000
00000000
00000000
00000000
23
TBLRDH.B (Wn<0> = 1)
3.1.2 DATA ACCESS FROM PROGRAM MEMORY USING PROGRAM SPACE VISIBILITY
The upper 32 Kbytes of data space may optionally be
mapped into any 16K word program space page. This
provides transparent access of stored constant data
from X data space, without the need to use special
instructions (i.e., TBLRDL/H, TBLWTL/H instructions).
Program space access through the data space occurs
if the MSb of the data space EA is set and program
space visibility is enabled, by setting the PSV bit in the
Core Control register (CORCON). The functions of
CORCON are discussed in Section 2.4 “DSP
Engine”.
Data accesses to this area add an additional cycle to
the instruction being executed, since two program
memory fetches are required.
Note that the upper half of addressable data space is
always part of the X data space. Therefore, when a
DSP operation uses program space mapping to access
this memory region, Y data space should typically contain state (variable) data for DSP operations, whereas
X data space should typically contain coefficient
(constant) data.
Although each data space address, 0x8000 and higher,
maps directly into a corresponding program memory
address (see Figure 3-5), only the lower 16 bits of the
24-bit program word are used to contain the data. The
upper 8 bits should be programmed to force an illegal
instruction to maintain machine robustness. Refer
dsPIC30F Programmer’s Reference Manual
to the
(DS70030) for details on instruction encoding.
16
TBLRDH.B (Wn<0> = 0)
Note that by incrementing the PC by 2 for each
program memory word, the Least Significant 15 bits of
data space addresses directly map to the Least Significant 15 bits in the corresponding program space
addresses. The remaining bits are provided by the
Program Space Visibility Page register,
PSVPAG<7:0>, as shown in Figure 3-5.
Note: PSV access is temporarily disabled during
table reads/writes.
For instructions that use PSV which are executed
outside a Repeat loop:
• The following instructions will require one instruction cycle in addition to the specified execution
time:
- MAC class of instructions with data operand
pre-fetch
- MOV instructions
- MOV.D instructions
• All other instructions will require two instruction
cycles in addition to the specified execution time
of the instruction.
For instructions that use PSV which are executed
inside a Repeat loop:
• The following instances will require two instruction
cycles in addition to the specified execution time
of the instruction:
- Execution in the first iteration
- Execution in the last iteration
- Execution prior to exiting the loop due to an
interrupt
- Execution upon re-entering the loop after an
interrupt is serviced
• Any other iteration of the Repeat loop will allow
the instruction, accessing data using PSV, to
execute in a single cycle.
8
0
DS70149A-page 26 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 29
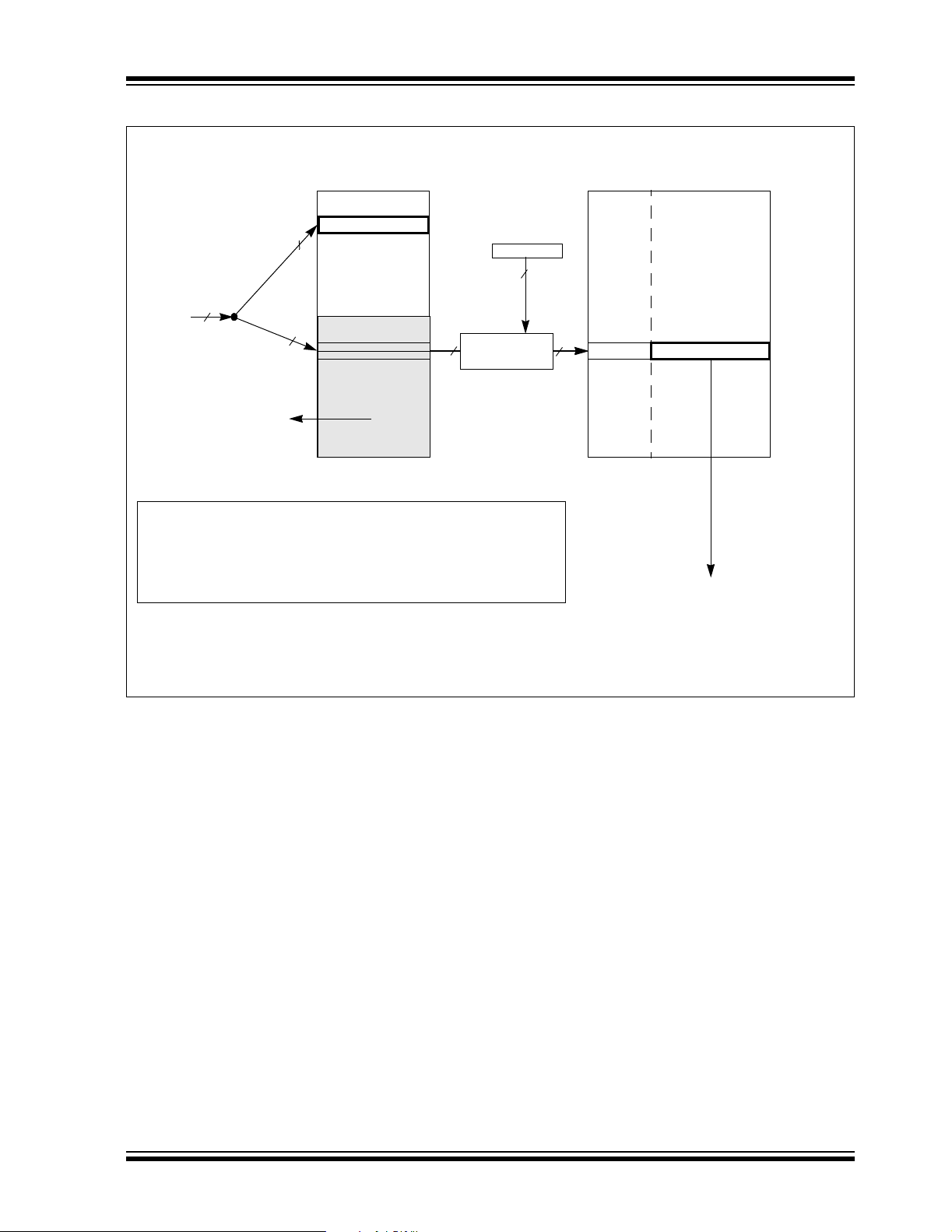
dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 3-5: DATA SPACE WINDOW INTO PROGRAM SPACE OPERATION
Data Space Program Space
0x0000
0x000100
EA<15> =
Data
Space
EA
BSET CORCON,#2 ; PSV bit set
MOV #0x00, W0 ; Set PSVPAG register
MOV W0, PSVPAG
MOV 0x9200, W0 ; Access program memory location
Note: PSVPAG is an 8-bit register, containing bits <22:15> of the program space address
16
EA<15> = 1
Upper Half of Data
Space is Mapped
into Program Space
(i.e., it defines the page in program space to which the upper half of data space is being mapped).
15
0
15
; using a data space access
0x8000
15
0xFFFF
PSVPAG
Address
Concatenation
(1)
0x00
8
23 15 0
23
Data Read
0x001200
0x017FFE
3.2 Data Address Space
The core has two data spaces. The data spaces can be
considered either separate (for some DSP instructions), or as one unified linear address range (for MCU
instructions). The data spaces are accessed using two
Address Generation Units (AGUs) and separate data
paths.
3.2.1 DATA SPACE MEMORY MAP
The data space memory is split into two blocks, X and
Y data space. A key element of this architecture is that
Y space is a subset of X space, and is fully contained
within X space. In order to provide an apparent linear
addressing space, X and Y spaces have contiguous
addresses.
When executing any instruction other than one of the
MAC class of instructions, the X block consists of the
64 Kbyte data address space (including all Y
addresses). When executing one of the MAC class of
instructions, the X block consists of the 64 Kbyte data
address space excluding the Y address block (for data
reads only). In other words, all other instructions
regard the entire data memory as one composite
address space. The MAC class instructions extract the
Y address space from data space and address it using
EAs sourced from W10 and W11. The remaining X
data space is addressed using W8 and W9. Both
address spaces are concurrently accessed only with
the MAC class instructions.
A data space memory map is shown in Figure 3-6.
Figure 3-7 shows a graphical summary of how X and Y
data spaces are accessed for MCU and DSP
instructions.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 27
Page 30
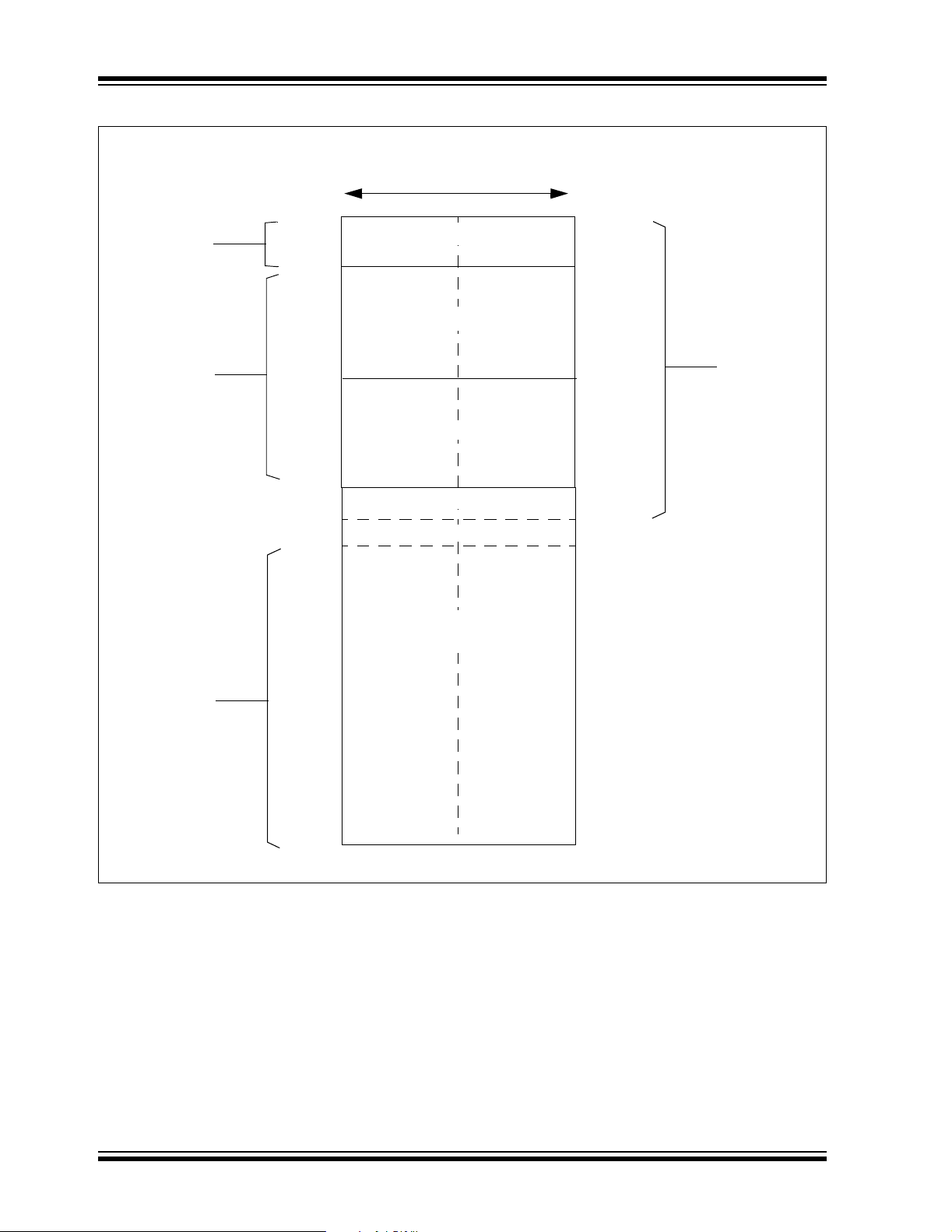
dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 3-6: dsPIC30F5015/5016 DATA SPACE MEMORY MAP
2 Kbyte
SFR Space
2 Kbyte
SRAM Space
MSB
Address
0x0001
0x07FF
0x0801
0x0BFF
0x0C01
0x0FFF 0x0FFE
0x1FFF 0x1FFE
≈
0x8001
16 bits
LSBMSB
SFR Space
X Data RAM (X)
Y Data RAM (Y)
Unimplemented
Unimplemented
0x0000
0x07FE
0x0800
0x0BFE
0x0C00
0x10000x1001
≈
0x8000
LSB
Address
8 Kbyte
Near
Data
Space
Optionally
Mapped
into Program
Memory
0xFFFF
X Data
Unimplemented (X)
0xFFFE
DS70149A-page 28 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 31

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 3-7: DATA SPACE FOR MCU AND DSP (MAC CLASS) INSTRUCTIONS EXAMPLE
SFR SPACE
UNUSED
(Y SPACE)
X SPACE
Non-MAC Class Ops (Read/Write) MAC Class Ops Read-Only
MAC Class Ops (Write)
Indirect EA using any W Indirect EA using W8, W9 Indirect EA using W10, W11
Y SPACE
UNUSED
SFR SPACE
UNUSED
X SPACE
X SPACE
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 29
Page 32

dsPIC30F5015/5016
3.2.2 DATA SPACES
The X data space is used by all instructions and supports all addressing modes. There are separate read
and write data buses. The X read data bus is the return
data path for all instructions that view data space as
combined X and Y address space. It is also the X
address space data path for the dual operand read
instructions (MAC class). The X write data bus is the
only write path to data space for all instructions.
The X data space also supports Modulo Addressing for
all instructions, subject to addressing mode restrictions. Bit-Reversed Addressing is only supported for
writes to X data space.
The Y data space is used in concert with the X data
space by the MAC class of instructions (CLR, ED,
EDAC, MAC, MOVSAC, MPY, MPY.N and MSC) to provide two concurrent data read paths. No writes occur
across the Y bus. This class of instructions dedicates
two W register pointers, W10 and W11, to always
address Y data space, independent of X data space,
whereas W8 and W9 always address X data space.
Note that during accumulator write back, the data
address space is considered a combination of X and Y
data spaces, so the write occurs across the X bus.
Consequently, the write can be to any address in the
entire data space.
The Y data space can only be used for the data prefetch operation associated with the MAC class of
instructions. It also supports Modulo Addressing for
automated circular buffers. Of course, all other instructions can access the Y data address space through the
X data path, as part of the composite linear space.
The boundary between the X and Y data spaces is
defined as shown in Figure 3-6 and is not user
programmable. Should an EA point to data outside its
own assigned address space, or to a location outside
physical memory, an all-zero word/byte will be
returned. For example, although Y address space is
visible by all non-MAC instructions using any addressing mode, an attempt by a MAC instruction to fetch data
from that space, using W8 or W9 (X space pointers),
will return 0x0000.
3.2.3 DATA SPACE WIDTH
The core data width is 16 bits. All internal registers are
organized as 16-bit wide words. Data space memory is
organized in byte addressable, 16-bit wide blocks.
3.2.4 DATA ALIGNMENT
To help maintain backward compatibility with
PICmicro
usage efficiency, the dsPIC30F instruction set supports
both word and byte operations. Data is aligned in data
memory and registers as words, but all data space EAs
resolve to bytes. Data byte reads will read the complete
word, which contains the byte, using the LSb of any EA
to determine which byte to select. The selected byte is
placed onto the LSB of the X data path (no byte
accesses are possible from the Y data path as the MAC
class of instruction can only fetch words). That is, data
memory and registers are organized as two parallel
byte wide entities with shared (word) address decode,
but separate write lines. Data byte writes only write to
the corresponding side of the array or register which
matches the byte address.
As a consequence of this byte accessibility, all effective
address calculations (including those generated by the
DSP operations, which are restricted to word-sized
data) are internally scaled to step through word-aligned
memory. For example, the core would recognize that
Post-Modified Register Indirect Addressing mode,
[Ws++], will result in a value of Ws + 1 for byte
operations and Ws + 2 for word operations.
All word accesses must be aligned to an even address.
Misaligned word data fetches are not supported, so
care must be taken when mixing byte and word operations, or translating from 8-bit MCU code. Should a
misaligned read or write be attempted, an address
error trap will be generated. If the error occurred on a
read, the instruction underway is completed, whereas if
it occurred on a write, the instruction will be executed
but the write will not occur. In either case, a trap will
then be executed, allowing the system and/or user to
examine the machine state prior to execution of the
address fault.
®
devices and improve data space memory
TABLE 3-2: EFFECT OF INVALID
MEMORY ACCESSES
Attempted Operation Data Returned
EA = an unimplemented address 0x0000
W8 or W9 used to access Y data
space in a MAC instruction
W10 or W11 used to access X
data space in a MAC instruction
All effective addresses are 16 bits wide and point to
bytes within the data space. Therefore, the data space
address range is 64 Kbytes or 32K words.
DS70149A-page 30 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
0x0000
0x0000
FIGURE 3-8: DATA ALIGNMENT
15 8 7 0
0001
0003
0005
Byte 1 Byte 0
Byte 3 Byte 2
Byte 5 Byte 4
LSBMSB
0000
0002
0004
Page 33

dsPIC30F5015/5016
All byte loads into any W register are loaded into the
LSB. The MSB is not modified.
A sign-extend (SE) instruction is provided to allow
users to translate 8-bit signed data to 16-bit signed
values. Alternatively, for 16-bit unsigned data, users
can clear the MSB of any W register by executing a
zero-extend (ZE) instruction on the appropriate
address.
Although most instructions are capable of operating on
word or byte data sizes, it should be noted that some
instructions, including the DSP instructions, operate
only on words.
3.2.5 NEAR DATA SPACE
An 8 Kbyte ‘near’ data space is reserved in X address
memory space between 0x0000 and 0x1FFF, which is
directly addressable via a 13-bit absolute address field
within all memory direct instructions. The remaining X
address space and all of the Y address space is
addressable indirectly. Additionally, the whole of X data
space is addressable using MOV instructions, which
support memory direct addressing with a 16-bit
address field.
3.2.6 SOFTWARE STACK
The dsPIC DSC device contains a software stack. W15
is used as the Stack Pointer.
The Stack Pointer always points to the first available
free word and grows from lower addresses towards
higher addresses. It pre-decrements for stack pops and
post-increments for stack pushes, as shown in
Figure 3-9. Note that for a PC push during any CALL
instruction, the MSB of the PC is zero-extended before
the push, ensuring that the MSB is always clear.
Note: A PC push during exception processing
will concatenate the SRL register to the
MSB of the PC prior to the push.
There is a Stack Pointer Limit register (SPLIM) associated with the Stack Pointer. SPLIM is uninitialized at
Reset. As is the case for the Stack Pointer, SPLIM<0>
is forced to ‘0’, because all stack operations must be
word-aligned. Whenever an effective address (EA) is
generated using W15 as a source or destination
pointer, the address thus generated is compared with
the value in SPLIM. If the contents of the Stack Pointer
(W15) and the SPLIM register are equal and a push
operation is performed, a stack error trap will not occur.
The stack error trap will occur on a subsequent push
operation. Thus, for example, if it is desirable to cause
a stack error trap when the stack grows beyond
address 0x2000 in RAM, initialize the SPLIM with the
value, 0x1FFE.
Similarly, a Stack Pointer underflow (stack error) trap is
generated when the Stack Pointer address is found to
be less than 0x0800, thus preventing the stack from
interfering with the Special Function Register (SFR)
space.
A write to the SPLIM register should not be immediately
followed by an indirect read operation using W15.
FIGURE 3-9: CALL STACK FRAME
0x0000
Stack Grows Towards
000000000
Higher Address
PC<15:0>
PC<22:16>
<Free Word>
015
W15 (before CALL)
W15 (after CALL)
POP: [--W15]
PUSH: [W15++]
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 31
Page 34

dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 1000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuu0
0000 0000 0uuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuu0
0000 0000 0uuu uuuu
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0010 0000
— — — — — — — — —PCH
— — — — — — — —TBLPAG
Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
(Home)
Address
SFR Name
W0 0000 W0/WREG
W1 0002 W1
W2 0004 W2
W3 0006 W3
W4 0008 W4
W5 000A W5
W6 000C W6
W7 000E W7
W8 0010 W8
W9 0012 W9
W10 0014 W10
W11 0016 W11
W12 0018 W12
W13 001A W13
W14 001C W14
W15 001E W15
SPLIM 0020 SPLIM
ACCAL 0022 ACCAL
ACCAH 0024 ACCAH
ACCAU 0026 Sign-Extension (ACCA<39>) ACCAU
ACCBL 0028 ACCBL
ACCBH 002A ACCBH
ACCBU 002C Sign-Extension (ACCB<39>) ACCBU
TABLE 3-3: CORE REGISTER MAP
PCL 002E PCL
— — — — — — — —PSVPAG
PSVPAG 0034
RCOUNT 0036 RCOUNT
TBLPAG 0032
PCH 0030
— — — — — — — — —DOSTARTH
— — — — — — — — — DOENDH
— — — US EDT DL2 DL1 DL0 SATA SATB SATDW ACCSAT IPL3 PSV RND IF
DCOUNT 0038 DCOUNT
DOSTARTL 003A DOSTARTL 0
DOENDL 003E DOENDL 0
SR 0042 OA OB SA SB OAB SAB DA DC IPL2 IPL1 IPL0 RA N OV Z C
DOSTARTH 003C
CORCON 0044
DOENDH 0040
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
DS70149A-page 32 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
Note: Refer to
Page 35

dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuu0
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuu1
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuu0
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuu1
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
0000 0000 0000 0000
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
(Home)
Address
SFR Name
MODCON 0046 XMODEN YMODEN — — BWM<3:0> YWM<3:0> XWM<3:0>
XMODSRT 0048 XS<15:1> 0
XMODEND 004A XE<15:1> 1
TABLE 3-3: CORE REGISTER MAP (CONTINUED)
YMODSRT 004C YS<15:1> 0
— — DISICNT<13:0>
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
YMODEND 004E YE<15:1> 1
XBREV 0050 BREN XB<14:0>
Note: Refer to
DISICNT 0052
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 33
Page 36

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS70149A-page 34 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 37

dsPIC30F5015/5016
4.0 ADDRESS GENERATOR UNITS
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
The dsPIC DSC core contains two independent
Address Generator Units (AGU): the X AGU and Y
AGU. The Y AGU supports word-sized data reads for
the DSP MAC class of instructions only. The dsPIC DSC
AGUs support three types of data addressing:
• Linear Addressing
• Modulo (Circular) Addressing
• Bit-Reversed Addressing
Linear and Modulo Data Addressing modes can be
applied to data space or program space. Bit-Reversed
Addressing is only applicable to data space addresses.
(DS70030).
(DS70046). For more
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
4.1 Instruction Addressing Modes
The addressing modes in Table 4-1 form the basis of
the addressing modes optimized to support the specific
features of individual instructions. The addressing
modes provided in the MAC class of instructions are
somewhat different from those in the other instruction
types.
dsPIC30F
4.1.1 FILE REGISTER INSTRUCTIONS
Most file register instructions use a 13-bit address field
(f) to directly address data present in the first 8192 bytes
of data memory (near data space). Most file register
instructions employ a working register W0, which is
denoted as WREG in these instructions. The destination
is typically either the same file register, or WREG (with
the exception of the MUL instruction), which writes the
result to a register or register pair. The MOV instruction
allows additional flexibility and can access the entire
data space during file register operation.
4.1.2 MCU INSTRUCTIONS
The three-operand MCU instructions are of the form:
Operand 3 = Operand 1 <function> Operand 2
where Operand 1 is always a working register (i.e., the
addressing mode can only be Register Direct), which is
referred to as Wb. Operand 2 can be a W register,
fetched from data memory, or a 5-bit literal. The result
location can be either a W register or an address
location. The following addressing modes are
supported by MCU instructions:
• Register Direct
• Register Indirect
• Register Indirect Post-Modified
• Register Indirect Pre-Modified
• 5-bit or 10-bit Literal
Note: Not all instructions support all the address-
ing modes given above. Individual
instructions may support different subsets
of these addressing modes.
TABLE 4-1: FUNDAMENTAL ADDRESSING MODES SUPPORTED
Addressing Mode Description
File Register Direct The address of the file register is specified explicitly.
Register Direct The contents of a register are accessed directly.
Register Indirect The contents of Wn forms the EA.
Register Indirect Post-Modified The contents of Wn forms the EA. Wn is post-modified (incremented or
decremented) by a constant value.
Register Indirect Pre-Modified Wn is pre-modified (incremented or decremented) by a signed constant value
to form the EA.
Register Indirect with Register Offset The sum of Wn and Wb forms the EA.
Register Indirect with Literal Offset The sum of Wn and a literal forms the EA.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 35
Page 38

dsPIC30F5015/5016
4.1.3 MOVE AND ACCUMULATOR INSTRUCTIONS
Move instructions and the DSP Accumulator class of
instructions provide a greater degree of addressing
flexibility than other instructions. In addition to the
addressing modes supported by most MCU instructions, Move and Accumulator instructions also support
Register Indirect with Register Offset Addressing
mode, also referred to as Register Indexed mode.
Note: For the MOV instructions, the addressing
mode specified in the instruction can differ
for the source and destination EA. However, the 4-bit Wb (Register Offset) field is
shared between both source and
destination (but typically only used by
one).
In summary, the following addressing modes are
supported by Move and Accumulator instructions:
• Register Direct
• Register Indirect
• Register Indirect Post-Modified
• Register Indirect Pre-Modified
• Register Indirect with Register Offset (Indexed)
• Register Indirect with Literal Offset
• 8-bit Literal
• 16-bit Literal
Note: Not all instructions support all the address-
ing modes given above. Individual
instructions may support different subsets
of these addressing modes.
4.1.4 MAC INSTRUCTIONS
The dual source operand DSP instructions (CLR, ED,
EDAC, MAC, MPY, MPY.N, MOVSAC and MSC), also
referred to as MAC instructions, utilize a simplified set of
addressing modes to allow the user to effectively
manipulate the data pointers through Register Indirect
tables.
The two source operand pre-fetch registers must be a
member of the set {W8, W9, W10, W11}. For data
reads, W8 and W9 will always be directed to the X
RAGU and W10 and W11 will always be directed to the
Y AGU. The effective addresses generated (before and
after modification) must, therefore, be valid addresses
within X data space for W8 and W9 and Y data space
for W10 and W11.
In summary, the following addressing modes are
supported by the MAC class of instructions:
• Register Indirect
• Register Indirect Post-Modified by 2
• Register Indirect Post-Modified by 4
• Register Indirect Post-Modified by 6
• Register Indirect with Register Offset (Indexed)
4.1.5 OTHER INSTRUCTIONS
Besides the various addressing modes outlined above,
some instructions use literal constants of various sizes.
For example, BRA (branch) instructions use 16-bit
signed literals to specify the branch destination directly,
whereas the DISI instruction uses a 14-bit unsigned
literal field. In some instructions, such as ADD Acc, the
source of an operand or result is implied by the opcode
itself. Certain operations, such as NOP, do not have any
operands.
4.2 Modulo Addressing
Modulo Addressing is a method of providing an automated means to support circular data buffers using
hardware. The objective is to remove the need for
software to perform data address boundary checks
when executing tightly looped code, as is typical in
many DSP algorithms.
Modulo Addressing can operate in either data or program space (since the data pointer mechanism is essentially the same for both). One circular buffer can be
supported in each of the X (which also provides the
pointers into program space) and Y data spaces. Modulo
Addressing can operate on any W register pointer. However, it is not advisable to use W14 or W15 for Modulo
Addressing, since these two registers are used as the
Stack Frame Pointer and Stack Pointer, respectively.
In general, any particular circular buffer can only be
configured to operate in one direction, as there are certain restrictions on the buffer start address (for incrementing buffers) or end address (for decrementing
buffers) based upon the direction of the buffer.
The only exception to the usage restrictions is for buffers which have a power-of-2 length. As these buffers
satisfy the start and end address criteria, they may
operate in a Bidirectional mode, (i.e., address boundary checks will be performed on both the lower and
upper address boundaries).
Note: Register Indirect with Register Offset
Addressing is only available for W9 (in X
space) and W11 (in Y space).
DS700149A-page 36 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 39

dsPIC30F5015/5016
4.2.1 START AND END ADDRESS
The Modulo Addressing scheme requires that a
starting and an ending address be specified and
loaded into the 16-bit Modulo Buffer Address registers:
XMODSRT, XMODEND, YMODSRT and YMODEND
(see Table 3-3).
Note: Y-space Modulo Addressing EA calcula-
tions assume word-sized data (LSb of
every EA is always clear).
The length of a circular buffer is not directly specified. It
is determined by the difference between the
corresponding start and end addresses. The maximum
possible length of the circular buffer is 32K words
(64 Kbytes).
4.2.2 W ADDRESS REGISTER SELECTION
The Modulo and Bit-Reversed Addressing Control register, MODCON<15:0>, contains enable flags, as well
as a W register field to specify the W Address registers.
The XWM and YWM fields select which registers will
operate with Modulo Addressing. If XWM = 15,
X RAGU and X WAGU Modulo Addressing are
disabled. Similarly, if YWM = 15, Y AGU Modulo
Addressing is disabled.
The X Address Space Pointer W register (XWM) to
which Modulo Addressing is to be applied, is stored in
MODCON<3:0> (see Table 3-3). Modulo Addressing is
enabled for X data space when XWM is set to any value
other than 15 and the XMODEN bit is set at
MODCON<15>.
The Y Address Space Pointer W register (YWM) to
which Modulo Addressing is to be applied, is stored in
MODCON<7:4>. Modulo Addressing is enabled for Y
data space when YWM is set to any value other than 15
and the YMODEN bit is set at MODCON<14>.
FIGURE 4-1: MODULO ADDRESSING OPERATION EXAMPLE
Byte
Address
0x1100
MOV #0x1100,W0
MOV W0, XMODSRT ;set modulo start address
MOV #0x1163,W0
MOV W0,MODEND ;set modulo end address
MOV #0x8001,W0
MOV W0,MODCON ;enable W1, X AGU for modulo
MOV #0x0000,W0 ;W0 holds buffer fill value
MOV #0x1110,W1 ;point W1 to buffer
DO AGAIN,#0x31 ;fill the 50 buffer locations
MOV W0, [W1++] ;fill the next location
AGAIN: INC W0,W0 ;increment the fill value
0x1163
Start Addr = 0x1100
End Addr = 0x1163
Length = 0x0032 words
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 37
Page 40

dsPIC30F5015/5016
4.2.3 MODULO ADDRESSING APPLICABILITY
Modulo Addressing can be applied to the Effective
Address (EA) calculation associated with any W register.
It is important to realize that the address boundaries
check for addresses less than or greater than the upper
(for incrementing buffers) and lower (for decrementing
buffers) boundary addresses (not just equal to). Address
changes may, therefore, jump beyond boundaries and
still be adjusted correctly.
Note: The modulo corrected Effective Address is
written back to the register only when PreModify or Post-Modify Addressing mode is
used to compute the Effective Address.
When an address offset (e.g., [W7+W2]) is
used, modulo address correction is performed, but the contents of the register
remains unchanged.
4.3 Bit-Reversed Addressing
Bit-Reversed Addressing is intended to simplify data
re-ordering for radix-2 FFT algorithms. It is supported
by the X AGU for data writes only.
The modifier, which may be a constant value or register
contents, is regarded as having its bit order reversed.
The address source and destination are kept in normal
order. Thus, the only operand requiring reversal is the
modifier.
4.3.1 BIT-REVERSED ADDRESSING IMPLEMENTATION
Bit-Reversed Addressing is enabled when:
1. BWM (W register selection) in the MODCON
register is any value other than 15 (the stack can
not be accessed using Bit-Reversed Addressing)
and
2. the BREN bit is set in the XBREV register and
3. the addressing mode used is Register Indirect
with Pre-Increment or Post-Increment.
N
If the length of a Bit-Reversed buffer is M = 2
then the last ‘N’ bits of the data buffer start address
must be zeros.
XB<14:0> is the Bit-Reversed Address modifier or
‘pivot point’ which is typically a constant. In the case of
an FFT computation, its value is equal to half of the FFT
data buffer size.
Note: All bit-reversed EA calculations assume
word-sized data (LSb of every EA is
always clear). The XB value is scaled
accordingly to generate compatible (byte)
addresses.
When enabled, Bit-Reversed Addressing will only be
executed for Register Indirect with Pre-Increment or
Post-Increment Addressing and word-sized data writes.
It will not function for any other addressing mode or for
byte-sized data, and normal addresses will be generated
instead. When Bit-Reversed Addressing is active, the W
address pointer will always be added to the address
modifier (XB) and the offset associated with the Register
Indirect Addressing mode will be ignored. In addition, as
word-sized data is a requirement, the LSb of the EA is
ignored (and always clear).
Note: Modulo Addressing and Bit-Reversed
Addressing should not be enabled
together. In the event that the user
attempts to do this, Bit-Reversed Addressing will assume priority when active for the
X WAGU, and X WAGU Modulo Addressing will be disabled. However, Modulo
Addressing will continue to function in the
X RAGU.
If Bit-Reversed Addressing has already been enabled
by setting the BREN (XBREV<15>) bit, then a write to
the XBREV register should not be immediately followed
by an indirect read operation using the W register that
has been designated as the Bit-Reversed Pointer.
bytes,
FIGURE 4-2: BIT-REVERSED ADDRESS EXAMPLE
Sequential Address
b15 b14 b13 b12
b15 b14 b13 b12
DS700149A-page 38 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
b11 b10 b9 b8
b7 b6 b5 b4b11 b10 b9 b8
b7 b6 b5 b1
Pivot Point
b3 b2 b1 0
Bit Locations Swapped Left-to-Right
Around Center of Binary Value
b2 b3 b4 0
Bit-Reversed Address
XB = 0x0008 for a 16-word Bit-Reversed Buffer
Page 41

dsPIC30F5015/5016
TABLE 4-2: BIT-REVERSED ADDRESS SEQUENCE (16-ENTRY)
Normal Address Bit-Reversed Address
A3 A2 A1 A0 Decimal A3 A2 A1 A0 Decimal
0000 0 0000 0
0001 1 1000 8
0010 2 0100 4
0011 3 1100 12
0100 4 0010 2
0101 5 1010 10
0110 6 0110 6
0111 7 1110 14
1000 8 0001 1
1001 9 1001 9
1010 10 0101 5
1011 11 1101 13
1100 12 0011 3
1101 13 1011 11
1110 14 0111 7
1111 15 1111 15
TABLE 4-3: BIT-REVERSED ADDRESS MODIFIER VALUES FOR XBREV REGISTER
Buffer Size (Words) XB<14:0> Bit-Reversed Address Modifier Value
4096 0x0800
2048 0x0400
1024 0x0200
512 0x0100
256 0x0080
128 0x0040
64 0x0020
32 0x0010
16 0x0008
80x0004
40x0002
20x0001
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 39
Page 42

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS700149A-page 40 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 43

dsPIC30F5015/5016
5.0 INTERRUPTS
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
The dsPIC30F5015/5016 has 36 interrupt sources and
4 processor exceptions (traps), which must be
arbitrated based on a priority scheme.
The CPU is responsible for reading the Interrupt
Vector Table (IVT) and transferring the address contained in the interrupt vector to the program counter.
The interrupt vector is transferred from the program
data bus into the program counter, via a 24-bit wide
multiplexer on the input of the program counter.
The Interrupt Vector Table (IVT) and Alternate Interrupt Vector Table (AIVT) are placed near the beginning
of program memory (0x000004). The IVT and AIVT
are shown in Figure 5-1.
The interrupt controller is responsible for preprocessing the interrupts and processor exceptions,
prior to their being presented to the processor core.
The peripheral interrupts and traps are enabled, prioritized and controlled using centralized Special Function
Registers:
• IFS0<15:0>, IFS1<15:0>, IFS2<15:0>
All Interrupt Request Flags are maintained in
these three registers. The flags are set by their
respective peripherals or external signals, and
they are cleared via software.
• IEC0<15:0>, IEC1<15:0>, IEC2<15:0>
All Interrupt Enable Control bits are maintained in
these three registers. These control bits are used
to individually enable interrupts from the
peripherals or external signals.
• IPC0<15:0>... IPC11<7:0>
The user assignable priority level associated with
each of these 44 interrupts is held centrally in
these twelve registers.
• IPL<3:0>
The current CPU priority level is explicitly stored
in the IPL bits. IPL<3> is present in the CORCON
register, whereas IPL<2:0> are present in the
STATUS register (SR) in the processor core.
• INTCON1<15:0>, INTCON2<15:0>
Global interrupt control functions are derived from
these two registers. INTCON1 contains the control and status flags for the processor exceptions.
The INTCON2 register controls the external interrupt request signal behavior and the use of the
alternate vector table.
(DS70030).
(DS70046). For more
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
dsPIC30F
Note: Interrupt flag bits get set when an interrupt
condition occurs, regardless of the state of
its corresponding enable bit. User
software should ensure the appropriate
interrupt flag bits are clear prior to
enabling an interrupt.
All interrupt sources can be user assigned to one of
seven priority levels, 1 through 7, via the IPCx
registers. Each interrupt source is associated with an
interrupt vector, as shown in Table 5-1. Levels 7 and 1
represent the highest and lowest maskable priorities,
respectively.
Note: Assigning a priority level of 0 to an inter-
rupt source is equivalent to disabling that
interrupt.
If the NSTDIS bit (INTCON1<15>) is set, nesting of
interrupts is prevented. Thus, if an interrupt is currently
being serviced, processing of a new interrupt is prevented, even if the new interrupt is of higher priority
than the one currently being serviced.
Note: The IPL bits become read-only whenever
the NSTDIS bit has been set to ‘1’.
Certain interrupts have specialized control bits for
features like edge or level triggered interrupts, interrupt-on-change, etc. Control of these features remains
within the peripheral module which generates the
interrupt.
The DISI instruction can be used to disable the
processing of interrupts of priorities 6 and lower for a
certain number of instructions, during which the DISI bit
(INTCON2<14>) remains set.
When an interrupt is serviced, the PC is loaded with the
address stored in the vector location in program
memory that corresponds to the interrupt. There are 63
different vectors within the IVT (refer to Figure 5-2).
These vectors are contained in locations 0x000004
through 0x0000FE of program memory (refer to
Figure 5-2). These locations contain 24-bit addresses,
and in order to preserve robustness, an address error
trap will take place should the PC attempt to fetch any
of these words during normal execution. This prevents
execution of random data as a result of accidentally
decrementing a PC into vector space, accidentally
mapping a data space address into vector space, or the
PC rolling over to 0x000000 after reaching the end of
implemented program memory space. Execution of a
GOTO instruction to this vector space will also generate
an address error trap.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 41
Page 44

dsPIC30F5015/5016
5.1 Interrupt Priority
The user assignable Interrupt Priority (IP<2:0>) bits for
each individual interrupt source are located in the Least
Significant 3 bits of each nibble within the IPCx register(s). Bit 3 of each nibble is not used and is read as a
‘0’. These bits define the priority level assigned to a
particular interrupt by the user.
Note: The user selectable priority levels start at
0, as the lowest priority and level 7, as the
highest priority.
Since more than one interrupt request source may be
assigned to a specific user specified priority level, a
means is provided to assign priority within a given level.
This method is called “Natural Order Priority”.
Natural Order Priority is determined by the position of
an interrupt in the vector table, and only affects
interrupt operation when multiple interrupts with the
same user-assigned priority become pending at the
same time.
Table 5-1 lists the interrupt numbers and interrupt
sources for the dsPIC DSC devices and their
associated vector numbers.
Note 1: The Natural Order Priority scheme has 0
as the highest priority and 53 as the
lowest priority.
2: The Natural Order Priority number is the
same as the INT number.
The ability for the user to assign every interrupt to one
of seven priority levels implies that the user can assign
a very high overall priority level to an interrupt with a
low natural order priority.
TABLE 5-1: INTERRUPT VECTOR TABLE
INT
Number
Highest Natural Order Priority
0 8 INT0 – External Interrupt 0
1 9 IC1 – Input Capture 1
2 10 OC1 – Output Compare 1
3 11 T1 – Timer1
4 12 IC2 – Input Capture 2
5 13 OC2 – Output Compare 2
6 14 T2 – Timer2
7 15 T3 – Timer3
8 16 SPI1
9 17 U1RX – UART1 Receiver
10 18 U1TX – UART1 Transmitter
11 19 ADC – ADC Convert Done
12 20 NVM – NVM Write Complete
13 21 SI2C – I
14 22 MI2C – I2C Master Interrupt
15 23 Input Change Interrupt
16 24 INT1 – External Interrupt 1
17 25 Reserved
18 26 Reserved
19 27 OC3 – Output Compare 3
20 28 OC4 – Output Compare 4
21 29 T4 – Timer4
22 30 T5 – Timer5
23 31 INT2 – External Interrupt 2
24 32 Reserved
25 33 Reserved
26 34 SPI2
27 35 C1 – Combined IRQ for CAN1
28 36 IC3 – Input Capture 3
29 37 IC4 – Input Capture 4
30 38 Reserved
31 39 Reserved
32 40 OC5 – Output Compare 5
33 41 OC6 – Output Compare 6
34 42 OC7 – Output Compare 7
35 43 OC8 – Output Compare 8
36 44 INT3 – External Interrupt 3
37 45 INT4 – External Interrupt 4
38 46 Reserved
39 47 PWM – PWM Period Match
40 48 QEI – QEI Interrupt
41 49 Reserved
42 50 Reserved
43 51 FLTA – PWM Fault A
44 52 FLTB – PWM Fault B
45-53 53-61 Reserved
Lowest Natural Order Priority
Vector
Number
Interrupt Source
2
C™ Slave Interrupt
DS700149A-page 42 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 45

dsPIC30F5015/5016
5.2 Reset Sequence
A Reset is not a true exception because the interrupt
controller is not involved in the Reset process. The
processor initializes its registers in response to a Reset
which forces the PC to zero. The processor then begins
program execution at location 0x000000. A GOTO
instruction is stored in the first program memory location, immediately followed by the address target for the
GOTO instruction. The processor executes the GOTO to
the specified address and then begins operation at the
specified target (start) address.
5.2.1 RESET SOURCES
There are 6 sources of error which will cause a device
Reset.
• Watchdog Time-out:
The Watchdog has timed out, indicating that the
processor is no longer executing the correct flow
of code.
• Uninitialized W Register Trap:
An attempt to use an uninitialized W register as
an Address Pointer will cause a Reset.
• Illegal Instruction Trap:
Attempted execution of any unused opcodes will
result in an illegal instruction trap. Note that a
fetch of an illegal instruction does not result in an
illegal instruction trap if that instruction is flushed
prior to execution due to a flow change.
• Brown-out Reset (BOR):
A momentary dip in the power supply to the
device has been detected which may result in
malfunction.
• Trap Lockout:
Occurrence of multiple trap conditions
simultaneously will cause a Reset.
5.3 Traps
Traps can be considered as non-maskable interrupts
indicating a software or hardware error, which adhere
to a predefined priority, as shown in Figure 5-1. They
are intended to provide the user a means to correct
erroneous operation during debug and when operating
within the application.
Note: If the user does not intend to take correc-
tive action in the event of a trap error
condition, these vectors must be loaded
with the address of a default handler that
simply contains the RESET instruction. If,
on the other hand, one of the vectors
containing an invalid address is called, an
address error trap is generated.
Note that many of these trap conditions can only be
detected when they occur. Consequently, the questionable instruction is allowed to complete prior to trap
exception processing. If the user chooses to recover
from the error, the result of the erroneous action that
caused the trap may have to be corrected.
There are 8 fixed priority levels for traps: Level 8
through Level 15, which implies that IPL3 is always set
during processing of a trap.
If the user is not currently executing a trap, and he sets
the IPL<3:0> bits to a value of ‘0111’ (Level 7), then all
interrupts are disabled, but traps can still be processed.
5.3.1 TRAP SOURCES
The following traps are provided with increasing
priority. However, since all traps can be nested, priority
has little effect.
Math Error Trap:
The math error trap executes under the following three
circumstances:
1. Should an attempt be made to divide by zero,
the divide operation will be aborted on a cycle
boundary and the trap taken.
2. If enabled, a math error trap will be taken when
an arithmetic operation on either Accumulator A
or B causes an overflow from bit 31 and the
Accumulator Guard bits are not utilized.
3. If enabled, a math error trap will be taken when
an arithmetic operation on either Accumulator A
or B causes a catastrophic overflow from bit 39
and all saturation is disabled.
4. If the shift amount specified in a shift instruction
is greater than the maximum allowed shift
amount, a trap will occur.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 43
Page 46

dsPIC30F5015/5016
Address Error Trap:
This trap is initiated when any of the following
circumstances occurs:
1. A misaligned data word access is attempted.
2. A data fetch from our unimplemented data
memory location is attempted.
3. A data access of an unimplemented program
memory location is attempted.
4. An instruction fetch from vector space is
attempted.
Note: In the MAC class of instructions, wherein
the data space is split into X and Y data
space, unimplemented X space includes
all of Y space, and unimplemented Y
space includes all of X space.
5. Execution of a “BRA #literal” instruction or a
“GOTO #literal” instruction, where literal
is an unimplemented program memory address.
6. Executing instructions after modifying the PC to
point to unimplemented program memory
addresses. The PC may be modified by loading
a value into the stack and executing a RETURN
instruction.
Stack Error Trap:
This trap is initiated under the following conditions:
1. The Stack Pointer is loaded with a value which
is greater than the (user programmable) limit
value written into the SPLIM register (stack
overflow).
2. The Stack Pointer is loaded with a value which
is less than 0x0800 (simple stack underflow).
Oscillator Fail Trap:
This trap is initiated if the external oscillator fails and
operation becomes reliant on an internal RC backup.
5.3.2 HARD AND SOFT TRAPS
It is possible that multiple traps can become active
within the same cycle (e.g., a misaligned word stack
write to an overflowed address). In such a case, the
fixed priority shown in Figure 5-2 is implemented,
which may require the user to check if other traps are
pending in order to completely correct the Fault.
‘Soft’ traps include exceptions of priority level 8 through
level 11, inclusive. The arithmetic error trap (level 11)
falls into this category of traps.
‘Hard’ traps include exceptions of priority level 12
through level 15, inclusive. The address error (level
12), stack error (level 13) and oscillator error (level 14)
traps fall into this category.
Each hard trap that occurs must be Acknowledged
before code execution of any type may continue. If a
lower priority hard trap occurs while a higher priority
trap is pending, Acknowledged, or is being processed,
a hard trap conflict will occur.
The device is automatically reset in a hard trap conflict
condition. The TRAPR status bit (RCON<15>) is set
when the Reset occurs, so that the condition may be
detected in software.
FIGURE 5-1: TRAP VECTORS
Reset - GOTO Instruction
Reset - GOTO Address
Reserved
Oscillator Fail Trap Vector
Address Error Trap Vector
Stack Error Trap Vector
Math Error Trap Vector
IVT
Priority
Decreasing
AIVT
Reserved Vector
Reserved Vector
Reserved Vector
Interrupt 0 Vector
Interrupt 1 Vector
—
—
—
Interrupt 52 Vector
Interrupt 53 Vector
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Oscillator Fail Trap Vector
Stack Error Trap Vector
Address Error Trap Vector
Math Error Trap Vector
Reserved Vector
Reserved Vector
Reserved Vector
Interrupt 0 Vector
Interrupt 1 Vector
—
—
—
Interrupt 52 Vector
Interrupt 53 Vector
0x000000
0x000002
0x000004
0x000014
0x00007E
0x000080
0x000082
0x000084
0x000094
0x0000FE
DS700149A-page 44 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 47

dsPIC30F5015/5016
5.4 Interrupt Sequence
All interrupt event flags are sampled in the beginning of
each instruction cycle by the IFSx registers. A pending
Interrupt Request (IRQ) is indicated by the flag bit
being equal to a ‘1’ in an IFSx register. The IRQ will
cause an interrupt to occur if the corresponding bit in
the Interrupt Enable (IECx) register is set. For the
remainder of the instruction cycle, the priorities of all
pending interrupt requests are evaluated.
If there is a pending IRQ with a priority level greater
than the current processor priority level in the IPL bits,
the processor will be interrupted.
The processor then stacks the current program counter
and the low byte of the processor STATUS register
(SRL), as shown in Figure 5-2. The low byte of the
STATUS register contains the processor priority level at
the time prior to the beginning of the interrupt cycle.
The processor then loads the priority level for this interrupt into the STATUS register. This action will disable
all lower priority interrupts until the completion of the
Interrupt Service Routine.
FIGURE 5-2: INTERRUPT STACK
FRAME
0x0000
Higher Address
Stack Grows Towards
PC<15:0>
SRL IPL3 PC<22:16>
<Free Word>
015
W15 (before CALL)
W15 (after CALL)
POP : [--W15]
PUSH : [W15++]
5.5 Alternate Vector Table
In program memory, the Interrupt Vector Table (IVT) is
followed by the Alternate Interrupt Vector Table (AIVT),
as shown in Figure 5-1. Access to the Alternate Vector
Table is provided by the ALTIVT bit in the INTCON2
register. If the ALTIVT bit is set, all interrupt and exception processes will use the alternate vectors instead of
the default vectors. The alternate vectors are organized
in the same manner as the default vectors. The AIVT
supports emulation and debugging efforts by providing
a means to switch between an application and a
support environment, without requiring the interrupt
vectors to be reprogrammed. This feature also enables
switching between applications for evaluation of
different software algorithms at run time.
If the AIVT is not required, the program memory allocated to the AIVT may be used for other purposes.
AIVT is not a protected section and may be freely
programmed by the user.
5.6 Fast Context Saving
A context saving option is available using shadow registers. Shadow registers are provided for the DC, N,
OV, Z and C bits in SR, and the registers W0 through
W3. The shadows are only one level deep. The shadow
registers are accessible using the PUSH.S and POP.S
instructions only.
When the processor vectors to an interrupt, the
PUSH.S instruction can be used to store the current
value of the aforementioned registers into their
respective shadow registers.
If an ISR of a certain priority uses the PUSH.S and
POP.S instructions for fast context saving, then a
higher priority ISR should not include the same instructions. Users must save the key registers in software
during a lower priority interrupt, if the higher priority ISR
uses fast context saving.
Note 1: The user can always lower the priority level
by writing a new value into SR. The Interrupt
Service Routine must clear the interrupt flag
bits in the IFSx register before lowering the
processor interrupt priority in order to avoid
recursive interrupts.
2: The IPL3 bit (CORCON<3>) is always clear
when interrupts are being processed. It is
set only during execution of traps.
The RETFIE (Return from Interrupt) instruction will
unstack the program counter and STATUS registers to
return the processor to its state prior to the interrupt
sequence.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 45
5.7 External Interrupt Requests
The interrupt controller supports five external interrupt
request signals, INT0-INT4. These inputs are edge
sensitive; they require a low-to-high or a high-to-low
transition to generate an interrupt request. The
INTCON2 register has five bits, INT0EP-INT4EP, that
select the polarity of the edge detection circuitry.
5.8 Wake-up from Sleep and Idle
The interrupt controller may be used to wake-up the
processor from either Sleep or Idle modes, if Sleep or
Idle mode is active when the interrupt is generated.
If an enabled interrupt request of sufficient priority is
received by the interrupt controller, then the standard
interrupt request is presented to the processor. At the
same time, the processor will wake-up from Sleep or
Idle and begin execution of the Interrupt Service
Routine (ISR) needed to process the interrupt request.
Page 48

dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0100 0100 0100
0000 0000 0000 0000
0100 0000 0000 0100
0100 0100 0000 0000
0100 0100 0100 0100
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0100 0100
0100 0000 0100 0100
0100 0000 0000 0100
0000 0000 0000 0100
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
— — — — OVATE OVBTE COVTE — — — MATHERR ADDRERR STKERR OSCFAIL —
— — — — — — — — — — INT4EP INT3EP INT2EP INT1EP INT0EP
— — IC4IF IC3IF C1IF SPI2IF — — INT2IF T5IF T4IF OC4IF OC3IF — —INT1IF
— — — FLT BIF F LTAIF — — QEIIF PWMIF — INT4IF INT3IF — — — —
— — IC4IE IC3IE C1IE SPI2IE — — INT2IE T5IE T4IE OC4IE OC3IE — —INT1IE
— — — FLTBIE FLTAIE — — QEIIE PWMIE — INT4IE INT3IE — — — —
— T1IP<2:0> —OC1IP<2:0>— IC1IP<2:0> — INT0IP<2:0>
— T31P<2:0> — T2IP<2:0> — OC2IP<2:0> — IC2IP<2:0>
—ADIP<2:0>— U1TXIP<2:0> — U1RXIP<2:0> — SPI1IP<2:0>
— CNIP<2:0> —MI2CIP<2:0>— SI2CIP<2:0> — NVMIP<2:0>
—OC3IP<2:0>— — — — — — — — — INT1IP<2:0>
— INT2IP<2:0> — T5IP<2:0> — T4IP<2:0> — OC4IP<2:0>
— C1IP<2:0> — SPI2IP<2:0> — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — — IC4IP<2:0> — IC3IP<2:0>
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
—PWMIP<2:0>— — — — — INT41IP<2:0> — INT3IP<2:0>
— FLTAIP<2:0> — — — — — — — — — QEIIP<2:0>
— — — — — — — — — — — — — FLTBIP<2:0>
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
ADR Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
SFR
Name
TABLE 5-2: INTERRUPT CONTROLLER REGISTER MAP FOR dsPIC30F5015
INTCON2 0082 ALTIVT
INTCON1 0080 NSTDIS
IFS0 0084 CNIF MI2CIF SI2CIF NVMIF ADIF U1TXIF U1RXIF SPI1IF T3IF T2IF OC2IF IC2IF T1IF OC1IF IC1IF INT0IF
IEC0 008C CNIE MI2CIE SI2CIE NVMIE ADIE U1TXIE U1RXIE SPI1IE T3IE T2IE OC2IE IC2IE T1IE OC1IE IC1IE INT0IE
IEC1 008E
IFS1 0086
IFS2 0088
IPC0 0094
IPC1 0096
IPC2 0098
IPC3 009A
IEC2 0090
IPC4 009C
IPC5 009E
IPC7 00A2
IPC6 00A0
IPC9 00A6
IPC8 00A4
IPC10 00A8
IPC11 00AA
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Note: Refer to
DS700149A-page 46 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 49

dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0000 0000 0100
0100 0100 0100 0100
0100 0100 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0100
0000 0000 0100 0100
0100 0000 0100 0100
0100 0000 0000 0100
0000 0000 0000 0100
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
— — — — OVATE OVBTE COVTE — — — MATHERR ADDRERR STKERR OSCFAIL —
— — — — — — — — — — INT4EP INT3EP INT2EP INT1EP INT0EP
— — IC4IF IC3IF C1IF SPI2IF — — INT2IF T5IF T4IF OC4IF OC3IF — —INT1IF
— — — FLT BIF F LTAIF — — QEIIF PWMIF — INT4IF INT3IF — — — —
— — IC4IE IC3IE C1IE SPI2IE — — INT2IE T5IE T4IE OC4IE OC3IE — —INT1IE
— — — FLTBIE FLTAIE — — QEIIE PWMIE — INT4IE INT3IE — — — —
— T1IP<2:0> —OC1IP<2:0>— IC1IP<2:0> — INT0IP<2:0>
— T31P<2:0> — T2IP<2:0> — OC2IP<2:0> — IC2IP<2:0>
—ADIP<2:0>— U1TXIP<2:0> — U1RXIP<2:0> — SPI1IP<2:0>
— CNIP<2:0> —MI2CIP<2:0>— SI2CIP<2:0> — NVMIP<2:0>
—OC3IP<2:0>— — — — — — — — — INT1IP<2:0>
— INT2IP<2:0> — T5IP<2:0> — T4IP<2:0> — OC4IP<2:0>
— C1IP<2:0> — SPI2IP<2:0> — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — — IC4IP<2:0> — IC3IP<2:0>
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
—PWMIP<2:0>— — — — — INT41IP<2:0> — INT3IP<2:0>
— FLTAIP<2:0> — — — — — — — — — QEIIP<2:0>
— — — — — — — — — — — — — FLTBIP<2:0>
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
ADR Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
SFR
Name
TABLE 5-3: INTERRUPT CONTROLLER REGISTER MAP FOR dsPIC30F5016
INTCON2 0082 ALTIVT
INTCON1 0080 NSTDIS
IFS0 0084 CNIF MI2CIF SI2CIF NVMIF ADIF U1TXIF U1RXIF SPI1IF T3IF T2IF OC2IF IC2IF T1IF OC1IF IC1IF INT0IF
IEC0 008C CNIE MI2CIE SI2CIE NVMIE ADIE U1TXIE U1RXIE SPI1IE T3IE T2IE OC2IE IC2IE T1IE OC1IE IC1IE INT0IE
IEC1 008E
IFS1 0086
IFS2 0088
IPC0 0094
IPC1 0096
IPC2 0098
IPC3 009A
IEC2 0090
IPC4 009C
IPC5 009E
IPC7 00A2
IPC6 00A0
IPC9 00A6
IPC8 00A4
IPC10 00A8
IPC11 00AA
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Note: Refer to
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 47
Page 50

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS700149A-page 48 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 51

dsPIC30F5015/5016
6.0 FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
(DS70046). For more
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
(DS70030).
The dsPIC30F family of devices contains internal
program Flash memory for executing user code. There
are two methods by which the user can program this
memory:
1. In-Circuit Serial Programming™ (ICSP™)
2. Run-Time Self-Programming (RTSP)
6.1 In-Circuit Serial Programming (ICSP)
dsPIC30F devices can be serially programmed while in
the end application circuit. This is simply done with two
lines for Programming Clock and Programming Data
(which are named PGC and PGD respectively), and
three other lines for Power (V
Master Clear (MCLR
). this allows customers to manufacture boards with unprogrammed devices, and then
program the microcontroller just before shipping the
product. This also allows the most recent firmware or a
custom firmware to be programmed.
DD), Ground (VSS) and
dsPIC30F
6.2 Run-Time Self-Programming (RTSP)
RTSP is accomplished using TBLRD (table read) and
TBLWT (table write) instructions.
With RTSP, the user may erase program memory,
32 instructions (96 bytes) at a time and can write
program memory data, 32 instructions (96 bytes) at a
time.
6.3 Table Instruction Operation Summary
The TBLRDL and the TBLWTL instructions are used to
read or write to bits<15:0> of program memory.
TBLRDL and TBLWTL can access program memory in
Word or Byte mode.
The TBLRDH and TBLWTH instructions are used to read
or write to bits<23:16> of program memory. TBLRDH
and TBLWTH can access program memory in Word or
Byte mode.
A 24-bit program memory address is formed using
bits<7:0> of the TBLPAG register and the Effective
Address (EA) from a W register specified in the table
instruction, as shown in Figure 6-1.
FIGURE 6-1: ADDRESSING FOR TABLE AND NVM REGISTERS
24 bits
Using
Program
Counter
Using
NVMADR
Addressing
Using
Ta bl e
Instruction
User/Configuration
Space Select
0
1/0
NVMADRU Reg
1/0
TBLPAG Reg
NVMADR Reg EA
8 bits 16 bits
Working Reg EA
8 bits
24-bit EA
16 bits
0Program Counter
Byte
Select
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 49
Page 52

dsPIC30F5015/5016
6.4 RTSP Operation
The dsPIC30F Flash program memory is organized
into rows and panels. Each row consists of 32 instructions, or 96 bytes. Each panel consists of 128 rows, or
4K x 24 instructions. RTSP allows the user to erase one
row (32 instructions) at a time and to program
32 instructions at one time.
Each panel of program memory contains write latches
that hold 32 instructions of programming data. Prior to
the actual programming operation, the write data must
be loaded into the panel write latches. The data to be
programmed into the panel is loaded in sequential
order into the write latches; instruction 0, instruction 1,
etc. The addresses loaded must always be from an
even group of 32 boundary.
The basic sequence for RTSP programming is to set up
a Table Pointer, then do a series of TBLWT instructions
to load the write latches. Programming is performed by
setting the special bits in the NVMCON register.
32 TBLWTL and 32 TBLWTH instructions are required to
load the 32 instructions.
All of the table write operations are single-word writes
(2 instruction cycles), because only the table latches
are written.
After the latches are written, a programming operation
needs to be initiated to program the data.
The Flash program memory is readable, writable and
erasable during normal operation over the entire V
range.
DD
6.5 RTSP Control Registers
The four SFRs used to read and write the program
Flash memory are:
•NVMCON
• NVMADR
• NVMADRU
• NVMKEY
6.5.1 NVMCON REGISTER
The NVMCON register controls which blocks are to be
erased, which memory type is to be programmed and
start of the programming cycle.
6.5.2 NVMADR REGISTER
The NVMADR register is used to hold the lower two
bytes of the Effective Address. The NVMADR register
captures the EA<15:0> of the last table instruction that
has been executed and selects the row to write.
6.5.3 NVMADRU REGISTER
The NVMADRU register is used to hold the upper byte
of the Effective Address. The NVMADRU register captures the EA<23:16> of the last table instruction that
has been executed.
6.5.4 NVMKEY REGISTER
NVMKEY is a write-only register that is used for write
protection. To start a programming or an erase
sequence, the user must consecutively write 0x55 and
0xAA to the NVMKEY register. Refer to Section 6.6
“Programming Operations” for further details.
Note: The user can also directly write to the
NVMADR and NVMADRU registers to
specify a program memory address for
erasing or programming.
DS700149A-page 50 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 53

dsPIC30F5015/5016
6.6 Programming Operations
A complete programming sequence is necessary for
programming or erasing the internal Flash in RTSP
mode. A programming operation is nominally 2 msec in
duration and the processor stalls (waits) until the operation is finished. Setting the WR bit (NVMCON<15>)
starts the operation, and the WR bit is automatically
cleared when the operation is finished.
6.6.1 PROGRAMMING ALGORITHM FOR PROGRAM FLASH
The user can erase or program one row of program
Flash memory at a time. The general process is:
1. Read one row of program Flash (32 instruction
words) and store into data RAM as a data
“image”.
2. Update the data image with the desired new
data.
3. Erase program Flash row.
a) Set up NVMCON register for multi-word,
program Flash, erase, and set WREN bit.
b) Write address of row to be erased into
NVMADRU/NVMDR.
c) Write ‘55’ to NVMKEY.
d) Write ‘AA’ to NVMKEY.
e) Set the WR bit. This will begin erase cycle.
f) CPU will stall for the duration of the erase
cycle.
g) The WR bit is cleared when erase cycle
ends.
4. Write 32 instruction words of data from data
RAM “image” into the program Flash write
latches.
5. Program 32 instruction words into program
Flash.
a) Set up NVMCON register for multi-word,
program Flash, program, and set WREN
bit.
b) Write ‘55’ to NVMKEY.
c) Write ‘AA’ to NVMKEY.
d) Set the WR bit. This will begin program
cycle.
e) CPU will stall for duration of the program
cycle.
f) The WR bit is cleared by the hardware
when program cycle ends.
6. Repeat steps 1 through 5 as needed to program
desired amount of program Flash memory.
6.6.2 ERASING A ROW OF PROGRAM
MEMORY
Example 6-1 shows a code sequence that can be used
to erase a row (32 instructions) of program memory.
EXAMPLE 6-1: ERASING A ROW OF PROGRAM MEMORY
; Setup NVMCON for erase operation, multi word write
; program memory selected, and writes enabled
; Init pointer to row to be ERASED
MOV #0x4041,W0 ;
MOV W0
MOV #tblpage(PROG_ADDR),W0 ;
MOV W0
MOV #tbloffset(PROG_ADDR),W0 ; Intialize in-page EA[15:0] pointer
MOV W0, NVMADR ; Intialize NVMADR SFR
DISI #5 ; Block all interrupts with priority <7
MOV #0x55,W0
MOV W0
MOV #0xAA,W1 ;
MOV W1
BSET NVMCON,#WR ; Start the erase sequence
NOP ; Insert two NOPs after the erase
NOP ; command is asserted
NVMCON ; Init NVMCON SFR
,
NVMADRU ; Initialize PM Page Boundary SFR
,
; for next 5 instructions
NVMKEY ; Write the 0x55 key
,
NVMKEY ; Write the 0xAA key
,
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 51
Page 54

dsPIC30F5015/5016
6.6.3 LOADING WRITE LATCHES
Example 6-2 shows a sequence of instructions that
can be used to load the 96 bytes of write latches.
32 TBLWTL and 32 TBLWTH instructions are needed to
load the write latches selected by the Table Pointer.
EXAMPLE 6-2: LOADING WRITE LATCHES
; Set up a pointer to the first program memory location to be written
; program memory selected, and writes enabled
; Perform the TBLWT instructions to write the latches
; 0th_program_word
; 1st_program_word
; 2nd_program_word
; 31st_program_word
MOV #0x0000,W0 ;
MOV W0
MOV #0x6000,W0 ; An example program memory address
MOV #LOW_WORD_0,W2 ;
MOV #HIGH_BYTE_0,W3 ;
TBLWTL W2
TBLWTH W3
MOV #LOW_WORD_1,W2 ;
MOV #HIGH_BYTE_1,W3 ;
TBLWTL W2
TBLWTH W3
MOV #LOW_WORD_2,W2 ;
MOV #HIGH_BYTE_2,W3 ;
TBLWTL W2
TBLWTH W3
•
•
•
MOV #LOW_WORD_31,W2 ;
MOV #HIGH_BYTE_31,W3 ;
TBLWTL W2
TBLWTH W3
TBLPAG ; Initialize PM Page Boundary SFR
,
[W0] ; Write PM low word into program latch
,
[W0++] ; Write PM high byte into program latch
,
[W0] ; Write PM low word into program latch
,
[W0++] ; Write PM high byte into program latch
,
[W0] ; Write PM low word into program latch
,
[W0++] ; Write PM high byte into program latch
,
[W0] ; Write PM low word into program latch
,
[W0++] ; Write PM high byte into program latch
,
Note: In Example 6-2, the contents of the upper byte of W3 has no effect.
6.6.4 INITIATING THE PROGRAMMING SEQUENCE
For protection, the write initiate sequence for NVMKEY
must be used to allow any erase or program operation
to proceed. After the programming command has been
executed, the user must wait for the programming time
until programming is complete. The two instructions
following the start of the programming sequence
should be NOPs.
EXAMPLE 6-3: INITIATING A PROGRAMMING SEQUENCE
DISI #5 ; Block all interrupts with priority <7
MOV #0x55,W0
MOV W0
MOV #0xAA,W1 ;
MOV W1
BSET NVMCON,#WR ; Start the erase sequence
NOP ; Insert two NOPs after the erase
NOP ; command is asserted
NVMKEY ; Write the 0x55 key
,
NVMKEY ; Write the 0xAA key
,
; for next 5 instructions
DS700149A-page 52 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 55

uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
0000 0000 uuuu uuuu
dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
—PROGOP<6:0> 0000 0000 0000 0000
TWRI
— — — —
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
— — — — — — — — NVMADR<23:16>
— — — — — — — — KEY<7:0>
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
File Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 All Resets
TABLE 6-1: NVM REGISTER MAP
NVMCON 0760 WR WREN WRERR
NVMKEY 0766
NVMADR 0762 NVMADR<15:0>
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
NVMADRU 0764
Note: Refer to
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 53
Page 56

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS700149A-page 54 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 57

dsPIC30F5015/5016
7.0 DATA EEPROM MEMORY
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
information on the device instruction set and programming, refer to the
Reference Manual
The data EEPROM memory is readable and writable
during normal operation over the entire V
data EEPROM memory is directly mapped in the
program memory address space.
The four SFRs used to read and write the program
Flash memory are used to access data EEPROM
memory, as well. As described in Section 4.0
“Address Generator Units”, these registers are:
•NVMCON
• NVMADR
• NVMADRU
• NVMKEY
The EEPROM data memory allows read and write of
single words and 16-word blocks. When interfacing to
data memory, NVMADR, in conjunction with the
NVMADRU register, is used to address the EEPROM
location being accessed. TBLRDL and TBLWTL instructions are used to read and write data EEPROM. The
dsPIC30F6010 device has 8 Kbytes (4K words) of data
EEPROM, with an address range from 0x7FF000 to
0x7FFFFE.
A word write operation should be preceded by an erase
of the corresponding memory location(s). The write
typically requires 2 ms to complete, but the write time
will vary with voltage and temperature.
(DS70030).
(DS70046). For more
dsPIC30F Programmer’s
dsPIC30F
DD range. The
A program or erase operation on the data EEPROM
does not stop the instruction flow. The user is responsible for waiting for the appropriate duration of time
before initiating another data EEPROM write/erase
operation. Attempting to read the data EEPROM while
a programming or erase operation is in progress results
in unspecified data.
Control bit WR initiates write operations, similar to program Flash writes. This bit cannot be cleared, only set,
in software. This bit is cleared in hardware at the completion of the write operation. The inability to clear the
WR bit in software prevents the accidental or
premature termination of a write operation.
The WREN bit, when set, will allow a write operation.
On power-up, the WREN bit is clear. The WRERR bit is
set when a write operation is interrupted by a MCLR
Reset, or a WDT Time-out Reset, during normal operation. In these situations, following Reset, the user can
check the WRERR bit and rewrite the location. The
address register NVMADR remains unchanged.
Note: Interrupt flag bit NVMIF in the IFS0 regis-
ter is set when write is complete. It must be
cleared in software.
7.1 Reading the Data EEPROM
A TBLRD instruction reads a word at the current program word address. This example uses W0 as a
pointer to data EEPROM. The result is placed in
register W4, as shown in Example 7-1.
EXAMPLE 7-1: DATA EEPROM READ
MOV #LOW_ADDR_WORD,W0 ; Init Pointer
MOV #HIGH_ADDR_WORD,W1
MOV W1
TBLRDL [ W0 ], W4 ; read data EEPROM
TBLPAG
,
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 55
Page 58

dsPIC30F5015/5016
7.2 Erasing Data EEPROM
7.2.1 ERASING A BLOCK OF DATA EEPROM
In order to erase a block of data EEPROM, the
NVMADRU and NVMADR registers must initially
point to the block of memory to be erased. Configure
NVMCON for erasing a block of data EEPROM, and
set the ERASE and WREN bits in the NVMCON
register. Setting the WR bit initiates the erase, as
shown in Example 7-2.
EXAMPLE 7-2: DATA EEPROM BLOCK ERASE
; Select data EEPROM block, ERASE, WREN bits
MOV #4045,W0
MOV W0
; Start erase cycle by setting WR after writing key sequence
DISI #5 ; Block all interrupts with priority <7
MOV #0x55,W0 ;
MOV W0
MOV #0xAA,W1 ;
MOV W1
BSET NVMCON,#WR ; Initiate erase sequence
NOP
NOP
; Erase cycle will complete in 2mS. CPU is not stalled for the Data Erase Cycle
; User can poll WR bit, use NVMIF or Timer IRQ to determine erasure complete
NVMCON ; Initialize NVMCON SFR
,
; for next 5 instructions
NVMKEY ; Write the 0x55 key
,
NVMKEY ; Write the 0xAA key
,
7.2.2 ERASING A WORD OF DATA EEPROM
The NVMADRU and NVMADR registers must point to
the block. Erase a block of data Flash and set the
ERASE and WREN bits in the NVMCON register.
Setting the WR bit initiates the erase, as shown in
Example 7-3.
EXAMPLE 7-3: DATA EEPROM WORD ERASE
; Select data EEPROM word, ERASE, WREN bits
MOV #4044,W0
MOV W0
; Start erase cycle by setting WR after writing key sequence
DISI #5 ; Block all interrupts with priority <7
MOV #0x55,W0 ;
MOV W0
MOV #0xAA,W1 ;
MOV W1
BSET NVMCON,#WR ; Initiate erase sequence
NOP
NOP
; Erase cycle will complete in 2mS. CPU is not stalled for the Data Erase Cycle
; User can poll WR bit, use NVMIF or Timer IRQ to determine erasure complete
NVMCON
,
; for next 5 instructions
NVMKEY ; Write the 0x55 key
,
NVMKEY ; Write the 0xAA key
,
DS700149A-page 56 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 59

dsPIC30F5015/5016
7.3 Writing to the Data EEPROM
To write an EEPROM data location, the following
sequence must be followed:
1. Erase data EEPROM word.
a) Select word, data EEPROM, erase and set
WREN bit in NVMCON register.
b) Write address of word to be erased into
NVMADRU/NVMADR.
c) Enable NVM interrupt (optional).
d) Write ‘55’ to NVMKEY.
e) Write ‘AA’ to NVMKEY.
f) Set the WR bit. This will begin erase cycle.
g) Either poll NVMIF bit or wait for NVMIF
interrupt.
h) The WR bit is cleared when the erase cycle
ends.
2. Write data word into data EEPROM write
latches.
3. Program 1 data word into data EEPROM.
a) Select word, data EEPROM, program and
set WREN bit in NVMCON register.
b) Enable NVM write done interrupt (optional).
c) Write ‘55’ to NVMKEY.
d) Write ‘AA’ to NVMKEY.
e) Set the WR bit. This will begin program
cycle.
f) Either poll NVMIF bit or wait for NVM
interrupt.
g) The WR bit is cleared when the write cycle
ends.
The write will not initiate if the above sequence is not
exactly followed (write 0x55 to NVMKEY, write 0xAA to
NVMCON, then set WR bit) for each word. It is strongly
recommended that interrupts be disabled during this
code segment.
Additionally, the WREN bit in NVMCON must be set to
enable writes. This mechanism prevents accidental
writes to data EEPROM, due to unexpected code execution. The WREN bit should be kept clear at all times,
except when updating the EEPROM. The WREN bit is
not cleared by hardware.
After a write sequence has been initiated, clearing the
WREN bit will not affect the current write cycle. The WR
bit will be inhibited from being set unless the WREN bit
is set. The WREN bit must be set on a previous instruction. Both WR and WREN cannot be set with the same
instruction.
At the completion of the write cycle, the WR bit is
cleared in hardware and the Nonvolatile Memory Write
Complete Interrupt Flag bit (NVMIF) is set. The user
may either enable this interrupt, or poll this bit. NVMIF
must be cleared by software.
7.3.1 WRITING A WORD OF DATA EEPROM
Once the user has erased the word to be programmed,
then a table write instruction is used to write one write
latch, as shown in Example 7-4.
EXAMPLE 7-4: DATA EEPROM WORD WRITE
; Point to data memory
MOV #LOW_ADDR_WORD,W0 ; Init pointer
MOV #HIGH_ADDR_WORD,W1
MOV W1
MOV #LOW(WORD),W2 ; Get data
TBLWTL W2
; The NVMADR captures last table access address
; Select data EEPROM for 1 word op
MOV #0x4004,W0
MOV W0
; Operate key to allow write operation
DISI #5 ; Block all interrupts with priority <7
MOV #0x55,W0
MOV W0
MOV #0xAA,W1
MOV W1
BSET NVMCON,#WR ; Initiate program sequence
NOP
NOP
; Write cycle will complete in 2mS. CPU is not stalled for the Data Write Cycle
; User can poll WR bit, use NVMIF or Timer IRQ to determine write complete
TBLPAG
,
[ W0] ; Write data
,
NVMCON
,
; for next 5 instructions
NVMKEY ; Write the 0x55 key
,
NVMKEY ; Write the 0xAA key
,
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 57
Page 60

dsPIC30F5015/5016
7.3.2 WRITING A BLOCK OF DATA EEPROM
To write a block of data EEPROM, write to all sixteen
latches first, then set the NVMCON register and
program the block.
EXAMPLE 7-5: DATA EEPROM BLOCK WRITE
MOV #LOW_ADDR_WORD,W0 ; Init pointer
MOV #HIGH_ADDR_WORD,W1
MOV W1
MOV #data1,W2 ; Get 1st data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data2,W2 ; Get 2nd data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data3,W2 ; Get 3rd data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data4,W2 ; Get 4th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data5,W2 ; Get 5th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data6,W2 ; Get 6th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data7,W2 ; Get 7th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data8,W2 ; Get 8th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data9,W2 ; Get 9th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data10,W2 ; Get 10th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data11,W2 ; Get 11th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data12,W2 ; Get 12th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data13,W2 ; Get 13th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data14,W2 ; Get 14th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data15,W2 ; Get 15th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #data16,W2 ; Get 16th data
TBLWTL W2
MOV #0x400A,W0 ; Select data EEPROM for multi word op
MOV W0
DISI #5 ; Block all interrupts with priority <7
MOV #0x55,W0
MOV W0
MOV #0xAA,W1
MOV W1
BSET NVMCON,#WR ; Start write cycle
NOP
NOP
TBLPAG
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data
,
[ W0]++ ; write data. The NVMADR captures last table access address.
,
NVMCON ; Operate Key to allow program operation
,
; for next 5 instructions
NVMKEY ; Write the 0x55 key
,
NVMKEY ; Write the 0xAA key
,
7.4 Write Verify
Depending on the application, good programming
practice may dictate that the value written to the memory should be verified against the original value. This
should be used in applications where excessive writes
can stress bits near the specification limit.
7.5 Protection Against Spurious Write
There are conditions when the device may not want to
write to the data EEPROM memory. To protect against
spurious EEPROM writes, various mechanisms have
been built-in. On power-up, the WREN bit is cleared;
also, the Power-up Timer prevents EEPROM write.
The write initiate sequence and the WREN bit together,
help prevent an accidental write during brown-out,
power glitch or software malfunction.
DS700149A-page 58 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 61

dsPIC30F5015/5016
8.0 I/O PORTS
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
(DS70046).
All of the device pins (except VDD, VSS, MCLR and
OSC1/CLKIN) are shared between the peripherals and
the parallel I/O ports.
All I/O input ports feature Schmitt Trigger inputs for
improved noise immunity.
8.1 Parallel I/O (PIO) Ports
When a peripheral is enabled and the peripheral is
actively driving an associated pin, the use of the pin as
a general purpose output pin is disabled. The I/O pin
may be read, but the output driver for the parallel port
bit will be disabled. If a peripheral is enabled, but the
peripheral is not actively driving a pin, that pin may be
driven by a port.
All port pins have three registers directly associated
with the operation of the port pin. The data direction
register (TRISx) determines whether the pin is an input
or an output. If the data direction bit is a ‘1’, then the pin
is an input. All port pins are defined as inputs after a
Reset. Reads from the latch (LATx), read the latch.
Writes to the latch, write the latch (LATx). Reads from
the port (PORTx), read the port pins and writes to the
port pins, write the latch (LATx).
dsPIC30F
Any bit and its associated data and control registers
that are not valid for a particular device will be
disabled. That means the corresponding LATx and
TRISx registers and the port pin will read as zeros.
When a pin is shared with another peripheral or function that is defined as an input only, it is nevertheless
regarded as a dedicated port because there is no
other competing source of outputs. An example is the
INT4 pin.
The format of the registers for PORTA are shown in
Table 8-2.
The TRISA (Data Direction Control) register controls
the direction of the RA<7:0> pins, as well as the INTx
pins and the V
REF pins. The LATA register supplies
data to the outputs and is readable/writable. Reading
the PORTA register yields the state of the input pins,
while writing the PORTA register modifies the contents
of the LATA register.
A parallel I/O (PIO) port that shares a pin with a peripheral is, in general, subservient to the peripheral. The
peripheral’s output buffer data and control signals are
provided to a pair of multiplexers. The multiplexers
select whether the peripheral or the associated port
has ownership of the output data and control signals of
the I/O pad cell. Figure 8-2 shows how ports are shared
with other peripherals, and the associated I/O cell (pad)
to which they are connected. Table 8-1 and Table 8-2
show the formats of the registers for the shared ports,
PORTB through PORTG.
FIGURE 8-1: BLOCK DIAGRAM OF A DEDICATED PORT STRUCTURE
Dedicated Port Module
Data Bus
WR TRIS
WR LAT+
WR Port
Read LAT
Read Port
Read TRIS
TRIS Latch
QD
CK
Data Latch
QD
CK
I/O Cell
I/O Pad
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 59
Page 62

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 8-2: BLOCK DIAGRAM OF A SHARED PORT STRUCTURE
Data Bus
WR TRIS
WR LAT +
WR Port
Peripheral Module
Peripheral Input Data
Peripheral Module Enable
Peripheral Output Enable
Peripheral Output Data
PIO Module
Read TRIS
QD
CK
TRIS Latch
QD
CK
Data Latch
Read LAT
Read Port
Output Multiplexers
1
Output Enable
0
1
Output Data
0
Input Data
I/O Cell
I/O Pad
8.2 Configuring Analog Port Pins
The use of the ADPCFG and TRIS registers control the
operation of the A/D port pins. The port pins that are
desired as analog inputs must have their corresponding TRIS bit set (input). If the TRIS bit is cleared
(output), the digital output level (VOH or VOL) will be
converted.
When reading the PORT register, all pins configured as
analog input channels will read as cleared (a low level).
Pins configured as digital inputs will not convert an analog input. Analog levels on any pin that is defined as a
digital input (including the ANx pins) may cause the
input buffer to consume current that exceeds the
device specifications.
8.2.1 I/O PORT WRITE/READ TIMING
One instruction cycle is required between a port
direction change or port write operation and a read
operation of the same port. Typically this instruction
would be a NOP.
EXAMPLE 8-1: PORT WRITE/READ
EXAMPLE
MOV 0xFF00, W0 ; Configure PORTB<15:8>
; as inputs
MOV W0, TRISBB ; and PORTB<7:0> as outputs
NOP ; Delay 1 cycle
BTSS PORTB, #13 ; Next Instruction
DS700149A-page 60 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 63

dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
1111 1111 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
— 1110 0000 0000 0000
—
—
—
0000 1111 1111 1111
— 0000 0000 0000 0000
— 0000 0000 0000 0000
—
—
—
—
—
—
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
— — TRISF6 TRISF5 TRISF4 TRISF3 TRISF2 TRISF1 TRISF0
— — RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RF1 RF0
— — LATF6 LATF5 LATF4 LATF3 LATF2 LATF1 LATF0
TABLE 8-1: dsPIC30F5015 PORT REGISTER MAP
Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
SFR
— — TRISE7 TRISE6 TRISE5 TRISE4 TRISE3 TRISE2 TRISE1 TRISE0
— — RE7 RE6 RE5 RE4 RE3 RE2 RE1 RE0
— — LATE7 LATE6 LATE5 LATE4 LATE3 LATE2 LATE1 LATE0
— — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
Name
PORTA 02C2
LATA 02C4
TRISB 02C6 TRISB15 TRISB14 TRISB13 TRISB12 TRISB11 TRISB10 TRISB9 TRISB8 TRISB7 TRISB6 TRISB5 TRISB4 TRISB3 TRISB2 TRISB1 TRISB0
PORTB 02C8 RB15 RB14 RB13 RB12 RB11 RB10 RB9 RB8 RB7 RB6 RB5 RB4 RB3 RB2 RB1 RB0
LATB 02CB LATB15 LATB14 LATB13 LATB12 LATB11 LATB10 LATB9 LATB8 LATB7 LATB6 LATB5 LATB4 LATB3 LATB2 LATB1 LATB0
TRISA 02C0
TRISC 02CC TRISC15 TRISC14 TRISC13
— — — — TRISD11 TRISD10 TRISD9 TRISD8 TRISD7 TRISD6 TRISD5 TRISD4 TRISD3 TRISD2 TRISD1 TRISD0
— — — — RD11 RD10 RD9 RD8 RD7 RD6 RD5 RD4 RD3 RD2 RD1 RD0
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
— — — — — — —
— — — — — — —
— — — — — — —
— — — — — — TRISG9 TRISG8 TRISG7 TRISG6 — — TRISG3 TRISG2 — — 0000 0011 1100 1100
— — — — — — RG9 RG8 RG7 RG6 — —RG3RG2 — — 0000 0000 0000 0000
PORTC 02CE RC15 RC14 RC13
PORTD 02D4
LATC 02D0 LATC15 LATC14 LATC13
TRISD 02D2
LATD 02D6 LATD11 LATD10 LATD9 LATD8 LATD7 LATD6 LATD5 LATD4 LATD3 LATD2 LATD1 LATD0
TRISE 02D8
PORTE 02DA
PORTF 02E0
LATF 02E2
TRISG 02E4
LATE 02DC
TRISF 02EE
PORTG 02E6
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
— — — — — — LATG9 LATG8 LATG7 LATG6 — —LATG3LATG2— — 0000 0000 0000 0000
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
LATG 02E8
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Note: Refer to
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 61
Page 64

dsPIC30F5015/5016
1100 0110 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
1111 1111 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
— 1110 0000 0000 1010
TRISC1
—
TRISC3
1111 1111 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
— 0000 0000 0000 0000
— 0000 0000 0000 0000
RC1
LATC1
—
—
RC3
LATC3
0000 0011 1111 1111
0000 0001 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
TABLE 8-2: dsPIC30F5016 PORT REGISTER MAP
Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
SFR
RF8 RF7 RF6 RF5 RF4 RF3 RF2 RF1 RF0
LATF8 LATF7 LATF6 LATF5 LATF4 LATF3 LATF2 LATF1 LATF0
TRISF8 TRISF7 TRISF6 TRISF5 TRISF4 TRISF3 TRISF2 TRISF1 TRISF0
RE9 RE8 RE7 RE6 RE5 RE4 RE3 RE2 RE1 RE0
LATE9 LATE8 LATE7 LATE6 LATE5 LATE4 LATE3 LATE2 LATE1 LATE0
TRISE9 TRISE8 TRISE7 TRISE6 TRISE5 TRISE4 TRISE3 TRISE2 TRISE1 TRISE0
— — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — —
— — — — — — — — —
— — — TRISA10 TRISA9 — — — — — — — — —
— — — RA10 RA9 — — — — — — — — —
— — — LATA1 0 LATA9 — — — — — — — — —
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
— — — — — —
— — — — — — —
— — — — — — —
— — — — — — —
— — — — — — TRISG9 TRISG8 TRISG7 TRISG6 — — TRISG3 TRISG2 TRISG1 TRISG0 0000 0011 1100 1111
— — — — — — RG9 RG8 RG7 RG6 — — RG3 RG2 RG1 RG0 0000 0000 0000 0000
Name
PORTA 02C2 RA15 RA14
LATA 02C4 LATA15 LATA14
TRISB 02C6 TRISB15 TRISB14 TRISB13 TRISB12 TRISB11 TRISB10 TRISB9 TRISB8 TRISB7 TRISB6 TRISB5 TRISB4 TRISB3 TRISB2 TRISB1 TRISB0
PORTB 02C8 RB15 RB14 RB13 RB12 RB11 RB10 RB9 RB8 RB7 RB6 RB5 RB4 RB3 RB2 RB1 RB0
LATB 02CB LATB15 LATB14 LATB13 LATB12 LATB11 LATB10 LATB9 LATB8 LATB7 LATB6 LATB5 LATB4 LATB3 LATB2 LATB1 LATB0
TRISC 02CC TRISC15 TRISC14 TRISC13
PORTC 02CE RC15 RC14 RC13
LATC 02D0 LATC15 LATC14 LATC13
TRISD 02D2 TRISD15 TRISD14 TRISD13 TRISD12 TRISD11 TRISD10 TRISD9 TRISD8 TRISD7 TRISD6 TRISD5 TRISD4 TRISD3 TRISD2 TRISD1 TRISD0
PORTD 02D4 RD15 RD14 RD13 RD12 RD11 RD10 RD9 RD8 RD7 RD6 RD5 RD4 RD3 RD2 RD1 RD0
LATD 02D6 LATD15 LATD14 LATD13 LATD12 LATD11 LATD10 LATD9 LATD8 LATD7 LATD6 LATD5 LATD4 LATD3 LATD2 LATD1 LATD0
TRISA 02C0 TRISA15 TRISA14
TRISE 02D8
PORTE 02DA
PORTF 02E0
LATF 02E2
LATE 02DC
TRISF 02EE
PORTG 02E6
TRISG 02E4
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
— — — — — — LATG9 LATG8 LATG7 LATG6 — — LATG3 LATG2 LATG1 LATG0 0000 0000 0000 0000
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
LATG 02E8
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Note: Refer to
DS700149A-page 62 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 65

dsPIC30F5015/5016
8.3 Input Change Notification Module
The input change notification module provides the
dsPIC30F devices the ability to generate interrupt
requests to the processor in response to a change-ofstate on selected input pins. This module is capable of
when the clocks are disabled. There are 22 external
signals (CN0 through CN21) that may be selected
(enabled) for generating an interrupt request on a
change-of-state.
Please refer to the pin diagrams for CN pin locations.
detecting input change-of-states, even in Sleep mode
TABLE 8-3: INPUT CHANGE NOTIFICATION REGISTER MAP (BITS 15-8) FOR dsPIC30F5015
SFR
Name
CNEN1 00C0 CN15IE CN14IE CN13IE CN12IE CN11IE CN10IE CN9IE CN8IE
CNEN2 00C2
CNPU1 00C4 CN15PUE CN14PUE CN13PUE CN12PUE CN11PUE CN10PUE CN9PUE CN8PUE
CNPU2 00C6
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Reset State
0000 0000 0000 0000
— — — — — — — — 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
— — — — — — — — 0000 0000 0000 0000
TABLE 8-4: INPUT CHANGE NOTIFICATION REGISTER MAP (BITS 7-0) FOR dsPIC30F5015
SFR
Name
CNEN1 00C0 CN7IE CN6IE CN5IE CN4IE CN3IE CN2IE CN1IE CN0IE
CNEN2 00C2
CNPU1 00C4 CN7PUE CN6PUE CN5PUE CN4PUE CN3PUE CN2PUE CN1PUE CN0PUE
CNPU2 00C6
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Addr. Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
0000 0000 0000 0000
— —
— —
— — — CN18IE CN17IE CN16IE
— — — CN18PUE CN17PUE CN16PUE
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
TABLE 8-5: INPUT CHANGE NOTIFICATION REGISTER MAP (BITS 15-8) FOR dsPIC30F5016
SFR
Name
CNEN1 00C0 CN15IE CN14IE CN13IE CN12IE CN11IE CN10IE CN9IE CN8IE
CNEN2 00C2
CNPU1 00C4 CN15PUE CN14PUE CN13PUE CN12PUE CN11PUE CN10PUE CN9PUE CN8PUE
CNPU2 00C6
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Reset State
0000 0000 0000 0000
— — — — — — — — 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
— — — — — — — — 0000 0000 0000 0000
TABLE 8-6: INPUT CHANGE NOTIFICATION REGISTER MAP (BITS 7-0) FOR dsPIC30F5016
SFR
Name
CNEN1 00C0 CN7IE CN6IE CN5IE CN4IE CN3IE CN2IE CN1IE CN0IE
CNEN2 00C2
CNPU1 00C4 CN7PUE CN6PUE CN5PUE CN4PUE CN3PUE CN2PUE CN1PUE CN0PUE
CNPU2 00C6
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Addr. Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
0000 0000 0000 0000
— —
— —
CN21IE CN20IE CN19IE CN18IE CN17IE CN16IE
CN21PUE CN20PUE CN19PUE CN18PUE CN17PUE CN16PUE
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 63
Page 66

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS700149A-page 64 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 67

dsPIC30F5015/5016
9.0 TIMER1 MODULE
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
This section describes the 16-bit General Purpose
(GP) Timer1 module and associated operational
modes.
Note: Timer1 is a Type A timer. Please refer to
the specifications for a Type A timer in
Section 24.0 Electrical Characteristics
of this document.
The following sections provide a detailed description,
including setup and control registers along with associated block diagrams for the operational modes of the
timers.
The Timer1 module is a 16-bit timer which can serve as
the time counter for the Real-Time Clock, or operate as
a free-running interval timer/counter. The 16-bit timer
has the following modes:
• 16-bit Timer
• 16-bit Synchronous Counter
• 16-bit Asynchronous Counter
Further, the following operational characteristics are
supported:
• Timer gate operation
• Selectable prescaler settings
• Timer operation during CPU Idle and Sleep
modes
• Interrupt on 16-bit Period register match or falling
edge of external gate signal
(DS70046).
dsPIC30F
These operating modes are determined by setting the
appropriate bit(s) in the 16-bit SFR, T1CON. Figure 9-1
presents a block diagram of the 16-bit timer module.
16-bit Timer Mode: In the 16-bit Timer mode, the timer
increments on every instruction cycle up to a match
value, preloaded into the Period register, PR1, then
resets to ‘0’ and continues to count.
When the CPU goes into the Idle mode, the timer will
stop incrementing, unless the TSIDL (T1CON<13>)
bit = 0. If TSIDL = 1, the timer module logic will resume
the incrementing sequence upon termination of the
CPU Idle mode.
16-bit Synchronous Counter Mode: In the 16-bit
Synchronous Counter mode, the timer increments on
the rising edge of the applied external clock signal,
which is synchronized with the internal phase clocks.
The timer counts up to a match value preloaded in PR1,
then resets to ‘0’ and continues.
When the CPU goes into the Idle mode, the timer will
stop incrementing, unless the respective TSIDL bit = 0.
If TSIDL = 1, the timer module logic will resume the
incrementing sequence upon termination of the CPU
Idle mode.
16-bit Asynchronous Counter Mode: In the 16-bit
Asynchronous Counter mode, the timer increments on
every rising edge of the applied external clock signal.
The timer counts up to a match value preloaded in PR1,
then resets to ‘0’ and continues.
When the timer is configured for the Asynchronous mode
of operation and the CPU goes into the Idle mode, the
timer will stop incrementing if TSIDL = 1.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 65
Page 68

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 9-1: 16-BIT TIMER1 MODULE BLOCK DIAGRAM (TYPE A TIMER)
PR1
Equal
T1IF
Event Flag
SOSCO/
T1CK
SOSCI
0
1
TGATE
Reset
LPOSCEN
Comparator x 16
TMR1
QDCKTGATE
Q
Gate
Sync
T
CY
TCS
1 x
0
0 0
1
TSYNC
1
(3)
0
TGATE
TON
Sync
TCKPS<1:0>
2
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
9.1 Timer Gate Operation
The 16-bit timer can be placed in the Gated Time
Accumulation mode. This mode allows the internal T
CY
to increment the respective timer when the gate input
signal (T1CK pin) is asserted high. Control bit TGATE
(T1CON<6>) must be set to enable this mode. The
timer must be enabled (TON = 1) and the timer clock
source set to internal (TCS = 0).
When the CPU goes into the Idle mode, the timer will
stop incrementing, unless TSIDL = 0. If TSIDL = 1, the
timer will resume the incrementing sequence upon
termination of the CPU Idle mode.
9.2 Timer Prescaler
The input clock (FOSC/4 or external clock) to the 16-bit
timer has a prescale option of 1:1, 1:8, 1:64 and 1:256,
selected by control bits, TCKPS<1:0> (T1CON<5:4>).
The prescaler counter is cleared when any of the
following occurs:
• a write to the TMR1 register
• clearing of the TON bit (T1CON<15>)
• device Reset such as POR and BOR
However, if the timer is disabled (TON = 0), then the
timer prescaler cannot be reset since the prescaler
clock is halted.
TMR1 is not cleared when T1CON is written. It is
cleared by writing to the TMR1 register.
9.3 Timer Operation During Sleep Mode
During CPU Sleep mode, the timer will operate if:
• The timer module is enabled (TON = 1) and
• The timer clock source is selected as external
(TCS = 1) and
• The TSYNC bit (T1CON<2>) is asserted to a logic
‘0’, which defines the external clock source as
asynchronous
When all three conditions are true, the timer will continue to count up to the Period register and be reset to
0x0000.
When a match between the timer and the Period register occurs, an interrupt can be generated, if the
respective timer interrupt enable bit is asserted.
DS700149A-page 66 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 69

dsPIC30F5015/5016
9.4 Timer Interrupt
The 16-bit timer has the ability to generate an interrupt
on period match. When the timer count matches the
Period register, the T1IF bit is asserted and an interrupt
will be generated, if enabled. The T1IF bit must be
cleared in software. The Timer Interrupt Flag, T1IF, is
located in the IFS0 Control register in the interrupt
controller.
When the Gated Time Accumulation mode is enabled,
an interrupt will also be generated on the falling edge of
the gate signal (at the end of the accumulation cycle).
Enabling an interrupt is accomplished via the respective
Timer Interrupt Enable bit, T1IE. The Timer Interrupt
Enable bit is located in the IEC0 Control register in the
interrupt controller.
9.5 Real-Time Clock
Timer1, when operating in Real-Time Clock (RTC)
mode, provides time-of-day and event time-stamping
capabilities. Key operational features of the RTC are:
• Operation from 32 kHz LP oscillator
• 8-bit prescaler
• Low power
• Real-Time Clock Interrupts
These operating modes are determined by setting the
appropriate bit(s) in the T1CON Control register.
9.5.1 RTC OSCILLATOR OPERATION
When the TON = 1, TCS = 1 and TGATE = 0, the timer
increments on the rising edge of the 32 kHz LP oscillator output signal, up to the value specified in the Period
register, and is then reset to ‘0’.
The TSYNC bit must be asserted to a logic ‘0’
(Asynchronous mode) for correct operation.
Enabling LPOSCEN (OSCCON<1>) will disable the
normal Timer and Counter modes and enable a timer
carry-out wake-up event.
When the CPU enters Sleep mode, the RTC will continue to operate, provided the 32 kHz external crystal
oscillator is active and the control bits have not been
changed. The TSIDL bit should be cleared to ‘0’ in
order for RTC to continue operation in Idle mode.
9.5.2 RTC INTERRUPTS
When an interrupt event occurs, the respective
interrupt flag, T1IF, is asserted and an interrupt will be
generated, if enabled. The T1IF bit must be cleared in
software. The respective Timer Interrupt Flag, T1IF, is
located in the IFS0 Status register in the interrupt
controller.
Enabling an interrupt is accomplished via the
respective Timer Interrupt Enable bit, T1IE. The Timer
Interrupt Enable bit is located in the IEC0 Control
register in the interrupt controller.
FIGURE 9-2: RECOMMENDED
COMPONENTS FOR
TIMER1 LP OSCILLATOR
RTC
C1
SOSCI
32.768 kHz
XTAL
C2
C1 = C2 = 18 pF; R = 100K
R
dsPIC30FXXXX
SOSCO
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 67
Page 70

dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
1111 1111 1111 1111
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
TMR1 0100 Tim er1 Regist er
TABLE 9-1: TIMER1 REGISTER MAP
DS700149A-page 68 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
PR1 0102 Period Register 1
T1CON 0104 TON —TSIDL — — — — — — TGATE TCKPS1 TCKPS0 —TSYNCTCS —
Note: Refer to
Page 71

dsPIC30F5015/5016
10.0 TIMER2/3 MODULE
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
This section describes the 32-bit General Purpose
(GP) timer module (Timer2/3) and associated operational modes. Figure 10-1 depicts the simplified block
diagram of the 32-bit Timer2/3 module. Figure 10-2
and Figure 10-3 show Timer2/3 configured as two
independent 16-bit timers; Timer2 and Timer3,
respectively.
Note: Timer2 is a Type B timer and Timer3 is a
Type C timer. Please refer to the appropriate timer type in Section 24.0 Electrical
Characteristics of this document.
The Timer2/3 module is a 32-bit timer, which can be
configured as two 16-bit timers, with selectable operating modes. These timers are utilized by other
peripheral modules such as:
• Input Capture
• Output Compare/Simple PWM
The following sections provide a detailed description,
including setup and control registers, along with associated block diagrams for the operational modes of the
timers.
The 32-bit timer has the following modes:
• Two independent 16-bit timers (Timer2 and
Timer3) with all 16-bit operating modes (except
Asynchronous Counter mode)
• Single 32-bit Timer operation
• Single 32-bit Synchronous Counter
Further, the following operational characteristics are
supported:
• ADC Event Trigger
• Timer Gate Operation
• Selectable Prescaler Settings
• Timer Operation during Idle and Sleep modes
• Interrupt on a 32-bit Period register Match
These operating modes are determined by setting the
appropriate bit(s) in the 16-bit T2CON and T3CON
SFRs.
(DS70046).
dsPIC30F
For 32-bit timer/counter operation, Timer2 is the least
significant word and Timer3 is the most significant word
of the 32-bit timer.
Note: For 32-bit timer operation, T3CON control
bits are ignored. Only T2CON control bits
are used for setup and control. Timer2
clock and gate inputs are utilized for the
32-bit timer module, but an interrupt is
generated with the Timer3 Interrupt Flag
(T3IF) and the interrupt is enabled with the
Timer3 Interrupt Enable bit (T3IE).
16-bit Mode: In 16-bit mode, Timer2 and Timer3 can be
configured as two independent 16-bit timers. Each timer
can be set up in either 16-bit Timer mode or 16-bit
Synchronous Counter mode. See Section 9.0 “Timer1
Module”, Timer1 Module, for details on these two
operating modes.
The only functional difference between Timer2 and
Timer3 is that Timer2 provides synchronization of the
clock prescaler output. This is useful for high-frequency
external clock inputs.
32-bit Timer Mode: In the 32-bit Timer mode, the timer
increments on every instruction cycle up to a match
value, preloaded into the combined 32-bit Period register, PR3/PR2, then resets to ‘0’ and continues to count.
For synchronous 32-bit reads of the Timer2/Timer3
pair, reading the least significant word (TMR2 register)
will cause the most significant word to be read and
latched into a 16-bit holding register, termed
TMR3HLD.
For synchronous 32-bit writes, the holding register
(TMR3HLD) must first be written to. When followed by
a write to the TMR2 register, the contents of TMR3HLD
will be transferred and latched into the MSB of the
32-bit timer (TMR3).
32-bit Synchronous Counter Mode: In the 32-bit
Synchronous Counter mode, the timer increments on
the rising edge of the applied external clock signal,
which is synchronized with the internal phase clocks.
The timer counts up to a match value preloaded in the
combined 32-bit Period register, PR3/PR2, then resets
to ‘0’ and continues.
When the timer is configured for the Synchronous
Counter mode of operation and the CPU goes into the
Idle mode, the timer will stop incrementing, unless the
TSIDL (T2CON<13>) bit = 0. If TSIDL = 1, the timer
module logic will resume the incrementing sequence
upon termination of the CPU Idle mode.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 69
Page 72

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 10-1: 32-BIT TIMER2/3 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Data Bus<15:0>
Write TMR2
Read TMR2
ADC Event Trigger
T3IF
Event Flag
T2CK
0
1
TGATE
(T2CON<6>)
Reset
Equal
TMR3HLD
16
16
TMR3
MSB
Comparator x 32
PR3 PR2
16
TMR2
LSB
QD
Q
CK
TGATE(T2CON<6>)
TCS
1 x
Sync
TGATE
TON
TCKPS<1:0>
2
Gate
Sync
TCY
Note: Timer Configuration bit T32, T2CON(<3>), must be set to ‘1’ for a 32-bit timer/counter operation. All control
bits are respective to the T2CON register.
0 1
0 0
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
DS700149A-page 70 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 73

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 10-2: 16-BIT TIMER2 BLOCK DIAGRAM (TYPE B TIMER)
Equal
Reset
T2IF
Event Flag
(1)
T2CK
Note 1: T2CK input is not available on dsPIC30F5015. This input is grounded as shown in Figure 10-3.
0
1
TGATE
PR2
Comparator x 16
TMR2
QDCKTGATE
Q
Gate
Sync
CY
T
1 x
0 1
0 0
TCS
TGATE
TON
FIGURE 10-3: 16-BIT TIMER3 BLOCK DIAGRAM (TYPE C TIMER)
Sync
TCKPS<1:0>
2
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
ADC Event Trigger
T3IF
Event Flag
TGATE
Note: The dsPIC30F5015/5016 devices do not have external pin inputs to Timer3. In these devices, the following
modes should not be used:
1. TCS = 1
2. TCS = 0 and TGATE = 1 (gated time accumulation)
Equal
Reset
0
1
PR3
Comparator x 16
TMR3
Q
QDCKTGATE
Sync
CY
T
TCS
1 x
0 1
0 0
TGATE
TON
TCKPS<1:0>
2
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 71
Page 74

dsPIC30F5015/5016
10.1 Timer Gate Operation
The 32-bit timer can be placed in the Gated Time
Accumulation mode. This mode allows the internal T
to increment the respective timer when the gate input
signal (T2CK pin) is asserted high. Control bit TGATE
(T2CON<6>) must be set to enable this mode. When in
this mode, Timer2 is the originating clock source. The
TGATE setting is ignored for Timer3. The timer must be
enabled (TON = 1) and the timer clock source set to
internal (TCS = 0).
The falling edge of the external signal terminates the
count operation, but does not reset the timer. The user
must reset the timer in order to start counting from zero.
CY
10.2 ADC Event Trigger
When a match occurs between the 32-bit timer (TMR3/
TMR2) and the 32-bit combined Period register (PR3/
PR2), a special ADC trigger event signal is generated
by Timer3.
10.3 Timer Prescaler
The input clock (FOSC/4 or external clock) to the timer
has a prescale option of 1:1, 1:8, 1:64 and 1:256
selected by control bits TCKPS<1:0> (T2CON<5:4>
and T3CON<5:4>). For the 32-bit timer operation, the
originating clock source is Timer2. The prescaler operation for Timer3 is not applicable in this mode. The
prescaler counter is cleared when any of the following
occurs:
• a write to the TMR2/TMR3 register
• clearing either of the TON (T2CON<15> or
T3CON<15>) bits to ‘0’
• device Reset such as POR and BOR
However, if the timer is disabled (TON = 0), then the
Timer2 prescaler cannot be reset, since the prescaler
clock is halted.
TMR2/TMR3 is not cleared when T2CON/T3CON is
written.
10.4 Timer Operation During Sleep Mode
During CPU Sleep mode, the timer will not operate,
because the internal clocks are disabled.
10.5 Timer Interrupt
The 32-bit timer module can generate an interrupt on
period match, or on the falling edge of the external gate
signal. When the 32-bit timer count matches the
respective 32-bit Period register, or the falling edge of
the external “gate” signal is detected, the T3IF bit
(IFS0<7>) is asserted and an interrupt will be generated if enabled. In this mode, the T3IF interrupt flag is
used as the source of the interrupt. The T3IF bit must
be cleared in software.
Enabling an interrupt is accomplished via the
respective Timer Interrupt Enable bit, T3IE (IEC0<7>).
DS700149A-page 72 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 75

uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
1111 1111 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
1111 1111 1111 1111
—
(1)
TCS
dsPIC30F5015/5016
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
—TSIDL— — — — — — TGATE TCKPS1 TCKPS0 T32 —
—TSIDL— — — — — — TGATE TCKPS1 TCKPS0 — — — —
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
TMR2 0106 Timer2 Register
TMR3HLD 0108 Timer3 Holding Register (For 32-bit timer operations only)
TMR3 010A Timer3 Register
TABLE 10-1: TIMER2/3 REGISTER MAP
PR2 010C Period Register 2
T3CON 0112 TON
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Note 1: TCS in T2CON is not available on the dsPIC30F5015.
PR3 010E Period Register 3
T2CON 0110 TON
Note 2: Refer to
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS700149A-page 73
Page 76

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS700149A-page 74 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 77

dsPIC30F5015/5016
11.0 TIMER4/5 MODULE
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
(DS70046).
This section describes the second 32-bit General
Purpose (GP) timer module (Timer4/5) and associated
operational modes. Figure 11-1 depicts the simplified
block diagram of the 32-bit Timer4/5 module.
Figure 11-2 and Figure 11-3 show Timer4/5 configured
as two independent 16-bit timers, Timer4 and Timer5,
respectively.
Note: Timer4 is a Type B timer and Timer5 is a
Type C timer. Please refer to the appropriate timer type in Section 24.0 Electrical
Characteristics of this document.
FIGURE 11-1: 32-BIT TIMER4/5 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Data Bus<15:0>
dsPIC30F
The Timer4/5 module is similar in operation to the
Timer2/3 module. However, there are some
differences, which are listed below:
• The Timer4/5 module does not support the ADC
Event Trigger feature
• Timer4/5 can not be utilized by other peripheral
modules such as Input Capture and Output Compare
The operating modes of the Timer4/5 module are
determined by setting the appropriate bit(s) in the 16-bit
T4CON and T5CON SFRs.
For 32-bit timer/counter operation, Timer4 is the least
significant word and Timer5 is the most significant word
of the 32-bit timer.
Note: For 32-bit timer operation, T5CON control
bits are ignored. Only T4CON control bits
are used for setup and control. Timer4
clock and gate inputs are utilized for the
32-bit timer module, but an interrupt is
generated with the Timer5 Interrupt Flag
(T5IF) and the interrupt is enabled with the
Timer5 Interrupt Enable bit (T5IE).
T5IF
Event Flag
T4CK
Wri te TM R4
Read TMR4
Reset
0
1
TGATE
(T4CON<6>)
Equal
TMR5HLD
16
16
TMR5
MSB
Comparator x 32
PR5 PR4
16
TMR4
LSB
QD
CK
Q
TGATE(T4CON<6>)
Gate
Sync
TCS
1 x
0
Sync
TGATE
TON
1
TCKPS<1:0>
2
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
T
CY
Note: Timer Configuration bit T32, T4CON(<3>), must be set to ‘1’ for a 32-bit timer/counter operation. All
control bits are respective to the T4CON register.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 75
0 0
Page 78

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 11-2: 16-BIT TIMER4 BLOCK DIAGRAM (TYPE B TIMER)
PR4
T4IF
Event Flag
T4CK
Equal
Reset
0
1
TGATE
Comparator x 16
TMR4
QDCKTGATE
Q
Gate
Sync
T
CY
TCS
1 x
0 1
0 0
TGATE
TON
FIGURE 11-3: 16-BIT TIMER5 BLOCK DIAGRAM (TYPE C TIMER)
PR5
Sync
TCKPS<1:0>
2
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
ADC Event Trigger
T5IF
Event Flag
TGATE
Equal
Reset
Comparator x 16
TMR5
0
1
QDCKTGATE
Q
Sync
CY
T
TCS
1 x
0 1
0 0
TGATE
TON
TCKPS<1:0>
2
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
Note: The dsPIC30F5015/5016 devices do not have an external pin input to Timer5. In these devices, the
following modes should not be used:
1. TCS = 1
2. TCS = 0 and TGATE = 1 (gated time accumulation)
DS70149A-page 76 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 79

uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
1111 1111 1111 1111
1111 1111 1111 1111
0000 0000 0000 0000
dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
—TSIDL — — — — — — TGATE TCKPS1 TCKPS0 T45 —TCS —
—TSIDL — — — — — — TGATE TCKPS1 TCKPS0 — — — —
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
TMR4 0114 Tim er 4 R egister
TMR5HLD 0116 Timer5 Holding Register (For 32-bit operations only)
TMR5 0118 Tim er 5 R egister
PR4 011A Period Register 4
PR5 011C Period Register 5
T4CON 011E TON
T5CON 0120 TON
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
TABLE 11-1: TIMER4/5 REGISTER MAP
Note: Refer to
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 77
Page 80

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS70149A-page 78 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 81

dsPIC30F5015/5016
12.0 INPUT CAPTURE MODULE
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
(DS70046).
This section describes the input capture module and
associated operational modes. The features provided by
this module are useful in applications requiring
frequency (period) and pulse measurement. Figure 12-1
depicts a block diagram of the input capture module.
Input capture is useful for such modes as:
• Frequency/Period/Pulse Measurements
• Additional sources of External Interrupts
The key operational features of the input capture
module are:
• Simple Capture Event mode
• Timer2 and Timer3 mode selection
• Interrupt on input capture event
These operating modes are determined by setting the
appropriate bits in the ICxCON register (where
x = 1,2,...,N). The dsPIC30F6010 device has 8 capture
channels.
dsPIC30F
12.1 Simple Capture Event Mode
The simple capture events in the dsPIC30F product
family are:
• Capture every falling edge
• Capture every rising edge
• Capture every 4th rising edge
• Capture every 16th rising edge
• Capture every rising and falling edge
These simple Input Capture modes are configured by
setting the appropriate bits ICM<2:0> (ICxCON<2:0>).
12.1.1 CAPTURE PRESCALER
There are four input capture prescaler settings, specified by bits ICM<2:0> (ICxCON<2:0>). Whenever the
capture channel is turned off, the prescaler counter will
be cleared. In addition, any Reset will clear the
prescaler counter.
FIGURE 12-1: INPUT CAPTURE MODE BLOCK DIAGRAM
From GP Timer Module
ICx
Pin
Prescaler
1, 4, 16
3
Synchronizer
ICM<2:0>
Mode Select
ICBNE, ICOV
ICxCON
Data Bus
Clock
ICI<1:0>
Edge
Detection
Logic
Interrupt
Logic
Set Flag
Set Flag
ICxIF
ICxIF
FIFO
R/W
Logic
Note: Where ‘x’ is shown, reference is made to the registers or bits associated to the respective input
capture channels 1 through N.
T2_CNT
T3_CNT
16 16
10
ICxBUF
ICTMR
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 79
Page 82

dsPIC30F5015/5016
12.1.2 CAPTURE BUFFER OPERATION
Each capture channel has an associated FIFO buffer,
which is four 16-bit words deep. There are two status
flags, which provide status on the FIFO buffer:
• ICBFNE – Input Capture Buffer Not Empty
• ICOV – Input Capture Overflow
The ICBFNE will be set on the first input capture event
and remain set until all capture events have been read
from the FIFO. As each word is read from the FIFO, the
remaining words are advanced by one position within
the buffer.
In the event that the FIFO is full with four capture
events and a fifth capture event occurs prior to a read
of the FIFO, an overflow condition will occur and the
ICOV bit will be set to a logic ‘1’. The fifth capture event
is lost and is not stored in the FIFO. No additional
events will be captured till all four events have been
read from the buffer.
If a FIFO read is performed after the last read and no
new capture event has been received, the read will
yield indeterminate results.
12.1.3 TIMER2 AND TIMER3 SELECTION MODE
Each capture channel can select between one of two
timers for the time base, Timer2 or Timer3.
Selection of the timer resource is accomplished
through SFR bit ICTMR (ICxCON<7>). Timer3 is the
default timer resource available for the input capture
module.
12.1.4 HALL SENSOR MODE
When the input capture module is set for capture on
every edge, rising and falling, ICM<2:0> = 001, the following operations are performed by the input capture
logic:
• The input capture interrupt flag is set on every
edge, rising and falling.
• The interrupt on Capture mode setting bits,
ICI<1:0>, is ignored, since every capture
generates an interrupt.
• A capture overflow condition is not generated in
this mode.
12.2 Input Capture Operation During Sleep and Idle Modes
An input capture event will generate a device wake-up
or interrupt, if enabled, if the device is in CPU Idle or
Sleep mode.
Independent of the timer being enabled, the input
capture module will wake-up from the CPU Sleep or
Idle mode when a capture event occurs, if ICM<2:0> =
111 and the interrupt enable bit is asserted. The same
wake-up can generate an interrupt if the conditions for
processing the interrupt have been satisfied. The
wake-up feature is useful as a method of adding extra
external pin interrupts.
12.2.1 INPUT CAPTURE IN CPU SLEEP
MODE
CPU Sleep mode allows input capture module operation with reduced functionality. In the CPU Sleep
mode, the ICI<1:0> bits are not applicable, and the
input capture module can only function as an external
interrupt source.
The capture module must be configured for interrupt
only on the rising edge (ICM<2:0> = 111) in order for
the input capture module to be used while the device
is in Sleep mode. The prescale settings of 4:1 or 16:1
are not applicable in this mode.
12.2.2 INPUT CAPTURE IN CPU IDLE
MODE
CPU Idle mode allows input capture module operation
with full functionality. In the CPU Idle mode, the Interrupt mode selected by the ICI<1:0> bits is applicable, as
well as the 4:1 and 16:1 capture prescale settings,
which are defined by control bits ICM<2:0>. This mode
requires the selected timer to be enabled. Moreover, the
ICSIDL bit must be asserted to a logic ‘0’.
If the input capture module is defined as
ICM<2:0> = 111 in CPU Idle mode, the input capture
pin will serve only as an external interrupt pin.
12.3 Input Capture Interrupts
The input capture channels have the ability to generate
an interrupt, based upon the selected number of capture events. The selection number is set by control bits
ICI<1:0> (ICxCON<6:5>).
Each channel provides an interrupt flag (ICxIF) bit. The
respective capture channel interrupt flag is located in
the corresponding IFSx Status register.
Enabling an interrupt is accomplished via the respective Capture Channel Interrupt Enable (ICxIE) bit. The
Capture Interrupt Enable bit is located in the
corresponding IEC Control register.
DS70149A-page 80 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 83

uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
0000 0000 0000 0000
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
0000 0000 0000 0000
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
0000 0000 0000 0000
uuuu uuuu uuuu uuuu
0000 0000 0000 0000
dsPIC30F5015/5016
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
IC1BUF 0140 Input 1 Capture Register
IC1CON 0142 — —ICSIDL— — — — — ICTMR ICI<1:0> ICOV ICBNE ICM<2:0>
IC2BUF 0144 Input 2 Capture Register
IC2CON 0146 — —ICSIDL— — — — — ICTMR ICI<1:0> ICOV ICBNE ICM<2:0>
IC3BUF 0148 Input 3 Capture Register
TABLE 12-1: INPUT CAPTURE REGISTER MAP
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 81
IC3CON 014A — —ICSIDL— — — — — ICTMR ICI<1:0> ICOV ICBNE ICM<2:0>
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
IC4BUF 014C Input 4 Capture Register
IC4CON 014E — —ICSIDL— — — — — ICTMR ICI<1:0> ICOV ICBNE ICM<2:0>
Note: Refer to
Page 84

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS70149A-page 82 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 85

dsPIC30F5015/5016
13.0 OUTPUT COMPARE MODULE
The key operational features of the output compare
module include:
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this group
of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be a complete
reference source. For more information on the CPU,
peripherals, register descriptions and general device
functionality, refer to the
Manual
(DS70046).
dsPIC30F Family Reference
This section describes the output compare module and
associated operational modes. The features provided
by this module are useful in applications requiring
operational modes such as:
• Generation of Variable Width Output Pulses
• Power Factor Correction
Figure 13-1 depicts a block diagram of the output compare module.
• Timer2 and Timer3 Selection mode
• Simple Output Compare Match mode
• Dual Output Compare Match mode
• Simple PWM mode
• Output Compare during Sleep and Idle modes
• Interrupt on Output Compare/PWM Event
These operating modes are determined by setting the
appropriate bits in the 16-bit OCxCON SFR (where
x = 1,2,3,...,N). The dsPIC30F6010 device has
8 compare channels.
OCxRS and OCxR in the figure represent the Dual
Compare registers. In the Dual Compare mode, the
OCxR register is used for the first compare and OCxRS
is used for the second compare.
FIGURE 13-1: OUTPUT COMPARE MODE BLOCK DIAGRAM
Set Flag bit
OCxRS
OCxIF
From GP Timer Module
TMR2<15:0
Comparator
0
OCxR
OCTSEL
1
TMR3<15:0>
0
T2P2_MATCH
OCM<2:0>
Mode Select
1
T3P3_MATCH
Output
Logic
3
QS
R
Output Enable
OCx
OCFA
(for x = 1, 2, 3 or 4)
Note: Where ‘x’ is shown, reference is made to the registers associated with the respective output compare
channels 1 through N.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 83
Page 86

dsPIC30F5015/5016
13.1 Timer2 and Timer3 Selection Mode
Each output compare channel can select between one
of two 16-bit timers; Timer2 or Timer3.
The selection of the timers is controlled by the OCTSEL
bit (OCxCON<3>). Timer2 is the default timer resource
for the output compare module.
13.2 Simple Output Compare Match Mode
When control bits OCM<2:0> (OCxCON<2:0>) = 001,
010 or 011, the selected output compare channel is
configured for one of three simple output compare
match modes:
• Compare forces I/O pin low
• Compare forces I/O pin high
• Compare toggles I/O pin
The OCxR register is used in these modes. The OCxR
register is loaded with a value and is compared to the
selected incrementing timer count. When a compare
occurs, one of these compare match modes occurs. If
the counter resets to zero before reaching the value in
OCxR, the state of the OCx pin remains unchanged.
13.3 Dual Output Compare Match Mode
When control bits OCM<2:0> (OCxCON<2:0>) = 100
or 101, the selected output compare channel is configured for one of two dual output compare modes, which
are:
• Single Output Pulse mode
• Continuous Output Pulse mode
13.3.1 SINGLE-PULSE MODE
For the user to configure the module for the generation
of a single output pulse, the following steps are
required (assuming timer is off):
• Determine instruction cycle time T
• Calculate desired pulse width value based on T
• Calculate time to start pulse from timer start value
of 0x0000.
• Write pulse width start and stop times into OCxR
and OCxRS Compare registers (x denotes
channel 1, 2, ...,N).
• Set Timer Period register to value equal to, or
greater than, value in OCxRS Compare register.
• Set OCM<2:0> = 100.
• Enable timer, TON (TxCON<15>) = 1.
To initiate another single pulse, issue another write to
set OCM<2:0> = 100.
CY.
CY.
13.3.2 CONTINUOUS PULSE MODE
For the user to configure the module for the generation
of a continuous stream of output pulses, the following
steps are required:
• Determine instruction cycle time T
• Calculate desired pulse value based on TCY.
• Calculate timer to start pulse width from timer start
value of 0x0000.
• Write pulse width start and stop times into OCxR
and OCxRS (x denotes channel 1, 2, ...,N)
Compare registers, respectively.
• Set Timer Period register to value equal to, or
greater than, value in OCxRS Compare register.
• Set OCM<2:0> = 101.
• Enable timer, TON (TxCON<15>) = 1.
CY.
13.4 Simple PWM Mode
When control bits OCM<2:0> (OCxCON<2:0>) = 110
or 111, the selected output compare channel is configured for the PWM mode of operation. When configured
for the PWM mode of operation, OCxR is the main latch
(read-only) and OCxRS is the secondary latch. This
enables glitchless PWM transitions.
The user must perform the following steps in order to
configure the output compare module for PWM
operation:
1. Set the PWM period by writing to the appropriate
Period register.
2. Set the PWM duty cycle by writing to the OCxRS
register.
3. Configure the output compare module for PWM
operation.
4. Set the TMRx prescale value and enable the
timer, TON (TxCON<15>) = 1.
13.4.1 INPUT PIN FAULT PROTECTION
FOR PWM
When control bits OCM<2:0> (OCxCON<2:0>) = 111,
the selected output compare channel is again
configured for the PWM mode of operation, with the
additional feature of input Fault protection. While in this
mode, if a logic ‘0’ is detected on the OCFA pin, the
respective PWM output pin is placed in the highimpedance input state. The OCFLT bit (OCxCON<4>)
indicates whether a Fault condition has occurred. This
state will be maintained until both of the following
events have occurred:
• The external Fault condition has been removed.
• The PWM mode has been re-enabled by writing
to the appropriate control bits.
DS70149A-page 84 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 87

dsPIC30F5015/5016
13.4.2 PWM PERIOD
The PWM period is specified by writing to the PRx
register. The PWM period can be calculated using
Equation 13-1.
EQUATION 13-1: PWM PERIOD
PWM Period = [(PRx) + 1] • 4 • T
(TMRx Prescale Value)
PWM frequency is defined as 1 / [PWM period].
OSC •
FIGURE 13-1: PWM OUTPUT TIMING
Period
Duty Cycle
TMR3 = PR3
T3IF = 1
(Interrupt Flag)
OCxR = OCxRS
TMR3 = Duty Cycle (OCxR)
When the selected TMRx is equal to its respective
Period register, PRx, the following four events occur on
the next increment cycle:
• TMRx is cleared.
• The OCx pin is set.
- Exception 1: If PWM duty cycle is 0x0000,
- Exception 2: If duty cycle is greater than PRx,
• The PWM duty cycle is latched from OCxRS into
OCxR.
• The corresponding timer interrupt flag is set.
See Figure 13-1 for key PWM period comparisons.
Timer3 is referred to in the figure for clarity.
TMR3 = PR3
T3IF = 1
(Interrupt Flag)
OCxR = OCxRS
TMR3 = Duty Cycle (OCxR)
the OCx pin will remain low.
the pin will remain high.
13.5 Output Compare Operation During CPU Sleep Mode
When the CPU enters the Sleep mode, all internal
clocks are stopped. Therefore, when the CPU enters
the Sleep state, the output compare channel will drive
the pin to the active state that was observed prior to
entering the CPU Sleep state.
For example, if the pin was high when the CPU
entered the Sleep state, the pin will remain high. Likewise, if the pin was low when the CPU entered the
Sleep state, the pin will remain low. In either case, the
output compare module will resume operation when
the device wakes up.
13.6 Output Compare Operation During CPU Idle Mode
When the CPU enters the Idle mode, the output
compare module can operate with full functionality.
The output compare channel will operate during the
CPU Idle mode if the OCSIDL bit (OCxCON<13>) is at
logic ‘0’ and the selected time base (Timer2 or Timer3)
is enabled and the TSIDL bit of the selected timer is
set to logic ‘0’.
13.7 Output Compare Interrupts
The output compare channels have the ability to generate an interrupt on a compare match, for whichever
match mode has been selected.
For all modes except the PWM mode, when a compare
event occurs, the respective interrupt flag (OCxIF) is
asserted and an interrupt will be generated, if enabled.
The OCxIF bit is located in the corresponding IFS
Status register and must be cleared in software. The
interrupt is enabled via the respective Compare
Interrupt Enable (OCxIE) bit, located in the
corresponding IEC Control register.
For the PWM mode, when an event occurs, the respective Timer Interrupt Flag (T2IF or T3IF) is asserted and
an interrupt will be generated, if enabled. The IF bit is
located in the IFS0 Status register and must be cleared
in software. The interrupt is enabled via the respective
Timer Interrupt Enable bit (T2IE or T3IE), located in the
IEC0 Control register. The output compare interrupt
flag is never set during the PWM mode of operation.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 85
Page 88

dsPIC30F5015/5016
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
SFR Name Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
TABLE 13-1: OUTPUT COMPARE REGISTER MAP
— —OCSIDL— — — — — — — — OCFLT OCTSEL OCM<2:0>
OC1RS 0180 Output Compare 1 Secondary Register
OC1R 0182 Output Compare 1 Main Register
OC1CON 0184
— —OCSIDL— — — — — — — — OCFLT OCTSE OCM<2:0>
OC2RS 0186 Output Compare 2 Secondary Register
OC2R 0188 Output Compare 2 Main Register
OC2CON 018A
— —OCSIDL— — — — — — — — OCFLT OCTSEL OCM<2:0>
OC3RS 018C Output Compare 3 Secondary Register
OC3R 018E Output Compare 3 Main Register
OC3CON 0190
— —OCSIDL— — — — — — — — OCFLT OCTSEL OCM<2:0>
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
OC4RS 0192 Output Compare 4 Secondary Register
OC4R 0194 Output Compare 4 Main Register
OC4CON 0196
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Note: Refer to
DS70149A-page 86 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 89

dsPIC30F5015/5016
14.0 QUADRATURE ENCODER INTERFACE (QEI) MODULE
The operational features of the QEI include:
• Three input channels for two phase signals and
index pulse
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
(DS70046).
dsPIC30F
This section describes the Quadrature Encoder Interface (QEI) module and associated operational modes.
The QEI module provides the interface to incremental
encoders for obtaining mechanical position data.
• 16-bit up/down position counter
• Count direction status
• Position Measurement (x2 and x4) mode
• Programmable digital noise filters on inputs
• Alternate 16-bit Timer/Counter mode
• Quadrature Encoder Interface interrupts
These operating modes are determined by setting the
appropriate bits QEIM<2:0> (QEICON<10:8>).
Figure 14-1 depicts the Quadrature Encoder Interface
block diagram.
FIGURE 14-1: QUADRATURE ENCODER INTERFACE BLOCK DIAGRAM
Sleep Input
Synchronize
Det
TQCS
T
CY
QEIM<2:0>
0
1
1
0
TQCKPS<1:0>
2
Prescaler
1, 8, 64, 256
QEA
QEB
INDX
UPDN
Programmable
Digital Filter
UPDN_SRC
QEICON<11>
0
1
Programmable
Digital Filter
Programmable
Digital Filter
PCDOUT
0
1
3
Existing Pin Logic
Up/Down
Quadrature
Encoder
Interface Logic
QEIM<2:0>
Mode Select
TQGATE
3
D
CK
16-bit Up/Down Counter
2
Comparator/
Zero Detect
Max Count Register
Q
Q
(POSCNT)
(MAXCNT)
Reset
Equal
QEIIF
Event
Flag
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 87
Page 90

dsPIC30F5015/5016
14.1 Quadrature Encoder Interface Logic
A typical incremental (a.k.a. optical) encoder has three
outputs: Phase A, Phase B and an index pulse. These
signals are useful and often required in position and
speed control of ACIM and SR motors.
The two channels, Phase A (QEA) and Phase B (QEB),
have a unique relationship. If Phase A leads Phase B,
then the direction (of the motor) is deemed positive or
forward. If Phase A lags Phase B, then the direction (of
the motor) is deemed negative or reverse.
A third channel, termed index pulse, occurs once per
revolution and is used as a reference to establish an
absolute position. The index pulse coincides with
Phase A and Phase B, both low.
14.2 16-bit Up/Down Position Counter Mode
The 16-bit up/down counter counts up or down on
every count pulse, which is generated by the difference
of the Phase A and Phase B input signals. The counter
acts as an integrator, whose count value is proportional
to position. The direction of the count is determined by
the UPDN signal, which is generated by the
Quadrature Encoder Interface logic.
14.2.1 POSITION COUNTER ERROR
CHECKING
Position count error checking in the QEI is provided for
and indicated by the CNTERR bit (QEICON<15>). The
error checking only applies when the position counter
is configured for Reset on the Index Pulse modes
(QEIM<2:0> = 110 or 100). In these modes, the
contents of the POSCNT register are compared with
the values (0xFFFF or MAXCNT + 1, depending on
direction). If these values are detected, an error condition is generated by setting the CNTERR bit and a QEI
count error interrupt is generated. The QEI count error
interrupt can be disabled by setting the CEID bit
(DFLTCON<8>). The position counter continues to
count encoder edges after an error has been detected.
The POSCNT register continues to count up/down until
a natural rollover/underflow. No interrupt is generated
for the natural rollover/underflow event. The CNTERR
bit is a read/write bit and reset in software by the user.
14.2.2 POSITION COUNTER RESET
The Position Counter Reset Enable bit, POSRES
(QEI<2>), controls whether the position counter is reset
when the index pulse is detected. This bit is only
applicable when QEIM<2:0> = 100 or 110.
If the POSRES bit is set to ‘1’, then the position counter
is reset when the index pulse is detected. If the
POSRES bit is set to ‘0’, then the position counter is not
reset when the index pulse is detected. The position
counter will continue counting up or down, and will be
reset on the rollover or underflow condition.
The interrupt is still generated on the detection of the
index pulse and not on the position counter overflow/
underflow.
14.2.3 COUNT DIRECTION STATUS
As mentioned in the previous section, the QEI logic
generates an UPDN signal, based upon the relationship between Phase A and Phase B. In addition to the
output pin, the state of this internal UPDN signal is supplied to a SFR bit, UPDN (QEICON<11>), as a readonly bit. To place the state of this signal on an I/O pin,
the SFR bit, PCDOUT (QEICON<6>), must be ‘1’.
14.3 Position Measurement Mode
There are two measurement modes which are supported and are termed x2 and x4. These modes are
selected by the QEIM<2:0> mode select bits located in
SFR QEICON<10:8>.
When control bits QEIM<2:0> = 100 or 101, the x2
Measurement mode is selected and the QEI logic only
looks at the Phase A input for the position counter
increment rate. Every rising and falling edge of the
Phase A signal causes the position counter to be incremented or decremented. The Phase B signal is still
utilized for the determination of the counter direction,
just as in the x4 mode.
Within the x2 Measurement mode, there are two
variations of how the position counter is reset:
1. Position counter reset by detection of index
pulse, QEIM<2:0> = 100.
2. Position counter reset by match with MAXCNT,
QEIM<2:0> = 101.
When control bits QEIM<2:0> = 110 or 111, the x4
Measurement mode is selected and the QEI logic looks
at both edges of the Phase A and Phase B input signals. Every edge of both signals causes the position
counter to increment or decrement.
Within the x4 Measurement mode, there are two
variations of how the position counter is reset:
1. Position counter reset by detection of index
pulse, QEIM<2:0> = 110.
2. Position counter reset by match with MAXCNT,
QEIM<2:0> = 111.
The x4 Measurement mode provides for finer resolution data (more position counts) for determining motor
position.
DS70149A-page 88 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 91

dsPIC30F5015/5016
14.4 Programmable Digital Noise Filters
The digital noise filter section is responsible for rejecting noise on the incoming capture or quadrature
signals. Schmitt Trigger inputs and a three-clock cycle
delay filter combine to reject low-level noise and large,
short duration noise spikes that typically occur in noise
prone applications, such as a motor system.
The filter ensures that the filtered output signal is not
permitted to change until a stable value has been
registered for three consecutive clock cycles.
For the QEA, QEB and INDX pins, the clock divide
frequency for the digital filter is programmed by bits
QECK<2:0> (DFLTCON<6:4>) and are derived from
the base instruction cycle T
To enable the filter output for channels QEA, QEB and
INDX, the QEOUT bit must be ‘1’. The filter network for
all channels is disabled on POR and BOR.
CY.
14.5 Alternate 16-bit Timer/Counter
When the QEI module is not configured for the QEI
mode, QEIM<2:0> = 001, the module can be configured as a simple 16-bit timer/counter. The setup and
control of the auxiliary timer is accomplished through
the QEICON SFR register. This timer functions
identically to Timer1. The QEA pin is used as the timer
clock input.
When configured as a timer, the POSCNT register
serves as the Timer Count register and the MAXCNT
register serves as the Period register. When a Timer/
Period register match occurs, the QEI interrupt flag will
be asserted.
The only exception between the general purpose timers and this timer is the added feature of external up/
down input select. When the UPDN pin is asserted
high, the timer will increment up. When the UPDN pin
is asserted low, the timer will be decremented.
Note: Changing the operational mode (i.e., from
QEI to Timer or vice versa), will not affect
the Timer/Position Count register contents.
The UPDN control/status bit (QEICON<11>) can be
used to select the count direction state of the Timer
register. When UPDN = 1, the timer will count up. When
UPDN = 0, the timer will count down.
In addition, control bit, UPDN_SRC (QEICON<0>),
determines whether the timer count direction state is
based on the logic state written into the UPDN control/
status bit (QEICON<11>), or the QEB pin state. When
UPDN_SRC = 1, the timer count direction is controlled
from the QEB pin. Likewise, when UPDN_SRC = 0, the
timer count direction is controlled by the UPDN bit.
Note: This timer does not support the External
Asynchronous Counter mode of operation.
If using an external clock source, the clock
will automatically be synchronized to the
internal instruction cycle.
14.6 QEI Module Operation During CPU Sleep Mode
14.6.1 QEI OPERATION DURING CPU
SLEEP MODE
The QEI module will be halted during the CPU Sleep
mode.
14.6.2 TIMER OPERATION DURING CPU
SLEEP MODE
During CPU Sleep mode, the timer will not operate,
because the internal clocks are disabled.
14.7 QEI Module Operation During CPU Idle Mode
Since the QEI module can function as a Quadrature
Encoder Interface, or as a 16-bit timer, the following
section describes operation of the module in both
modes.
14.7.1 QEI OPERATION DURING CPU IDLE
MODE
When the CPU is placed in the Idle mode, the QEI module will operate if the QEISIDL bit (QEICON<13>) = 0.
This bit defaults to a logic ‘0’ upon executing POR and
BOR. For halting the QEI module during the CPU Idle
mode, QEISIDL should be set to ‘1’.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 89
Page 92

dsPIC30F5015/5016
14.7.2 TIMER OPERATION DURING CPU IDLE MODE
When the CPU is placed in the Idle mode and the QEI
module is configured in the 16-bit Timer mode, the
16-bit timer will operate if the QEISIDL bit
(QEICON<13>) = 0. This bit defaults to a logic ‘0’ upon
executing POR and BOR. For halting the timer module
during the CPU Idle mode, QEISIDL should be set
to ‘1’.
If the QEISIDL bit is cleared, the timer will function
normally, as if the CPU Idle mode had not been
entered.
14.8 Quadrature Encoder Interface Interrupts
The Quadrature Encoder Interface has the ability to
generate an interrupt on occurrence of the following
events:
• Interrupt on 16-bit up/down position counter
rollover/underflow
• Detection of qualified index pulse, or if CNTERR
bit is set
• Timer period match event (overflow/underflow)
• Gate accumulation event
The QEI Interrupt Flag bit, QEIIF, is asserted upon
occurrence of any of the above events. The QEIIF bit
must be cleared in software. QEIIF is located in the
IFS2 Status register.
Enabling an interrupt is accomplished via the respective enable bit, QEIIE. The QEIIE bit is located in the
IEC2 Control register.
DS70149A-page 90 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 93

0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
0000 0000 0000 0000
dsPIC30F5015/5016
1111 1111 1111 1111
(DS70046) for descriptions of register bit fields.
— QEISIDL INDX UPDN QEIM<2:0> SWPAB PCDOUT TQGATE TQCKPS<1:0> POSRES TQCS UDSRC
— — — — — IMV<1:0> CEID QEOUT QECK2 QECK1 QECK0 — — — —
dsPIC30F Family Reference Manual
Addr. Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Reset State
SFR
Name
TABLE 14-1: QEI REGISTER MAP
POSCNT 0126 Position Counter<15:0>
MAXCNT 0128 Maximun Count<15:0>
DFLTCON 0124
QEICON 0122 CNTERR
Legend: u = uninitialized bit
Note: Refer to
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 91
Page 94

dsPIC30F5015/5016
NOTES:
DS70149A-page 92 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 95

dsPIC30F5015/5016
15.0 MOTOR CONTROL PWM MODULE
Note: This data sheet summarizes features of this
group of dsPIC30F devices and is not intended to be
a complete reference source. For more information
on the CPU, peripherals, register descriptions and
general device functionality, refer to the
Family Reference Manual
This module simplifies the task of generating multiple,
synchronized Pulse-Width Modulated (PWM) outputs.
In particular, the following power and motion control
applications are supported by the PWM module:
• Three Phase AC Induction Motor
• Switched Reluctance (SR) Motor
• Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor
• Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
(DS70046).
dsPIC30F
The PWM module has the following features:
• 8 PWM I/O pins with 4 duty cycle generators
• Up to 16-bit resolution
• ‘On-the-Fly’ PWM frequency changes
• Edge and Center-Aligned Output modes
• Single-Pulse Generation mode
• Interrupt support for asymmetrical updates in
Center-Aligned mode
• Output override control for Electrically
Commutative Motor (ECM) operation
• ‘Special Event’ comparator for scheduling other
peripheral events
• Fault pins to optionally drive each of the PWM
output pins to a defined state
• Duty cycle updates are configurable to be
immediate or synchronized to the PWM time base
This module contains 4 duty cycle generators, numbered 1 through 4. The module has 8 PWM output pins,
numbered PWM1H/PWM1L through PWM4H/PWM4L.
The eight I/O pins are grouped into high/low numbered
pairs, denoted by the suffix H or L, respectively. For
complementary loads, the low PWM pins are always
the complement of the corresponding high I/O pin.
The PWM module allows several modes of operation
which are beneficial for specific power control
applications.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 93
Page 96

dsPIC30F5015/5016
FIGURE 15-1: PWM MODULE BLOCK DIAGRAM
PWMCON1
PWM Enable and Mode SFRs
PWMCON2
DTCON1 Dead-Time Control SFRs
DTCON2
FLTACON Fault Pin Control SFRs
FLTBCON
OVDCON
PWM Manual
Control SFR
PWM Generator #4
PDC4 Buffer
PDC4
Comparator
16-bit Data Bus
PTMR
Comparator
PTPER
PTPER Buffer
PTCON
PWM Generator
#3
PWM Generator
#2
PWM Generator
#1
Channel 4 Dead-Time
Generator and
Override Logic
Channel 3 Dead-Time
Generator and
Override Logic
Channel 2 Dead-Time
Generator and
Override Logic
Channel 1 Dead-Time
Generator and
Override Logic
Output
Driver
Block
PWM4H
PWM4L
PWM3H
PWM3L
PWM2H
PWM2L
PWM1H
PWM1L
FLTA
FLTB
Comparator
SEVTCMP
SEVTDIR
PTDIR
Special Event
Postscaler
Special Event Trigger
PWM Time Base
Note: Details of PWM Generator #1, #2 and #3 not shown for clarity.
DS70149A-page 94 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 97

dsPIC30F5015/5016
15.1 PWM Time Base
The PWM time base is provided by a 15-bit timer with
a prescaler and postscaler. The time base is accessible
via the PTMR SFR. PTMR<15> is a read-only status
bit, PTDIR, that indicates the present count direction of
the PWM time base. If PTDIR is cleared, PTMR is
counting upwards. If PTDIR is set, PTMR is counting
downwards. The PWM time base is configured via the
PTCON SFR. The time base is enabled/disabled by
setting/clearing the PTEN bit in the PTCON SFR.
PTMR is not cleared when the PTEN bit is cleared in
software.
The PTPER SFR sets the counting period for PTMR.
The user must write a 15-bit value to PTPER<14:0>.
When the value in PTMR<14:0> matches the value in
PTPER<14:0>, the time base will either reset to ‘0’, or
reverse the count direction on the next occurring clock
cycle. The action taken depends on the operating
mode of the time base.
Note: If the Period register is set to 0x0000, the
timer will stop counting, and the interrupt
and the special event trigger will not be
generated, even if the special event value
is also 0x0000. The module will not update
the Period register if it is already at
0x0000; therefore, the user must disable
the module in order to update the Period
register.
The PWM time base can be configured for four different
modes of operation:
• Free-Running mode
• Single-Shot mode
• Continuous Up/Down Count mode
• Continuous Up/Down Count mode with interrupts
for double updates
These four modes are selected by the PTMOD<1:0>
bits in the PTCON SFR. The Up/Down Counting modes
support center-aligned PWM generation. The SingleShot mode allows the PWM module to support pulse
control of certain Electronically Commutative Motors
(ECMs).
The interrupt signals generated by the PWM time base
depend on the mode selection bits (PTMOD<1:0>) and
the postscaler bits (PTOPS<3:0>) in the PTCON SFR.
15.1.1 FREE-RUNNING MODE
In the Free-Running mode, the PWM time base counts
upwards until the value in the Time Base Period register (PTPER) is matched. The PTMR register is reset on
the following input clock edge and the time base will
continue to count upwards as long as the PTEN bit
remains set.
When the PWM time base is in the Free-Running mode
(PTMOD<1:0> = 00), an interrupt event is generated
each time a match with the PTPER register occurs and
the PTMR register is reset to zero. The postscaler
selection bits may be used in this mode of the timer to
reduce the frequency of the interrupt events.
15.1.2 SINGLE-SHOT MODE
In the Single-Shot Counting mode, the PWM time base
begins counting upwards when the PTEN bit is set.
When the value in the PTMR register matches the
PTPER register, the PTMR register will be reset on the
following input clock edge and the PTEN bit will be
cleared by the hardware to halt the time base.
When the PWM time base is in the Single-Shot mode
(PTMOD<1:0> = 01), an interrupt event is generated
when a match with the PTPER register occurs, the
PTMR register is reset to zero on the following input
clock edge, and the PTEN bit is cleared. The postscaler
selection bits have no effect in this mode of the timer.
15.1.3 CONTINUOUS UP/DOWN COUNTING MODES
In the Continuous Up/Down Counting modes, the PWM
time base counts upwards until the value in the PTPER
register is matched. The timer will begin counting
downwards on the following input clock edge. The
PTDIR bit in the PTCON SFR is read-only and indicates the counting direction. The PTDIR bit is set when
the timer counts downwards.
In the Up/Down Counting mode (PTMOD<1:0> = 10),
an interrupt event is generated each time the value of
the PTMR register becomes zero and the PWM time
base begins to count upwards. The postscaler selection bits may be used in this mode of the timer to reduce
the frequency of the interrupt events.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 95
Page 98

dsPIC30F5015/5016
15.1.4 DOUBLE UPDATE MODE
In the Double Update mode (PTMOD<1:0> = 11), an
interrupt event is generated each time the PTMR register is equal to zero, as well as each time a period match
occurs. The postscaler selection bits have no effect in
this mode of the timer.
The Double Update mode provides two additional functions to the user. First, the control loop bandwidth is
doubled because the PWM duty cycles can be
updated, twice per period. Second, asymmetrical
center-aligned PWM waveforms can be generated,
which are useful for minimizing output waveform
distortion in certain motor control applications.
Note: Programming a value of 0x0001 in the
Period register could generate a continuous interrupt pulse and hence, must be
avoided.
15.1.5 PWM TIME BASE PRESCALER
The input clock to PTMR (FOSC/4), has prescaler
options of 1:1, 1:4, 1:16, or 1:64, selected by control
bits PTCKPS<1:0> in the PTCON SFR. The prescaler
counter is cleared when any of the following occurs:
• a write to the PTMR register
• a write to the PTCON register
• any device Reset
The PTMR register is not cleared when PTCON is
written.
15.1.6 PWM TIME BASE POSTSCALER
The match output of PTMR can optionally be postscaled through a 4-bit postscaler (which gives a 1:1 to
1:16 scaling).
The postscaler counter is cleared when any of the
following occurs:
• a write to the PTMR register
• a write to the PTCON register
• any device Reset
The PTMR register is not cleared when PTCON is written.
The PWM period can be determined using
Equation 15-1:
EQUATION 15-1: PWM PERIOD
T
TPWM =
(PTMR Prescale Value)
If the PWM time base is configured for one of the Up/
Down Count modes, the PWM period will be twice the
value provided by Equation 15-1.
The maximum resolution (in bits) for a given device
oscillator and PWM frequency can be determined using
Equation 15-2:
CY • (PTPER + 1)
EQUATION 15-2: PWM RESOLUTION
• TPWM/TCY)
Resolution =
log (2)
log (2
15.3 Edge-Aligned PWM
Edge-aligned PWM signals are produced by the module
when the PWM time base is in the Free-Running or
Single-Shot mode. For edge-aligned PWM outputs, the
output has a period specified by the value in PTPER
and a duty cycle specified by the appropriate Duty Cycle
register (see Figure 15-2). The PWM output is driven
active at the beginning of the period (PTMR = 0) and is
driven inactive when the value in the Duty Cycle register
matches PTMR.
If the value in a particular Duty Cycle register is zero,
then the output on the corresponding PWM pin will be
inactive for the entire PWM period. In addition, the output on the PWM pin will be active for the entire PWM
period if the value in the Duty Cycle register is greater
than the value held in the PTPER register.
FIGURE 15-2: EDGE-ALIGNED PWM
New Duty Cycle Latched
15.2 PWM Period
PTPER is a 15-bit register and is used to set the counting
period for the PWM time base. PTPER is a doublebuffered register. The PTPER buffer contents are loaded
into the PTPER register at the following instants:
• Free-Running and Single-Shot modes:
PTMR register is reset to zero after a match with
the PTPER register.
• Up/Down Counting modes: When the PTMR
register is zero.
The value held in the PTPER buffer is automatically
loaded into the PTPER register when the PWM time
base is disabled (PTEN = 0).
DS70149A-page 96 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
When the
PTPER
PTMR
Value
0
Duty Cycle
Period
Page 99

dsPIC30F5015/5016
15.4 Center-Aligned PWM
Center-aligned PWM signals are produced by the
module when the PWM time base is configured in an
Up/Down Counting mode (see Figure 15-3).
The PWM compare output is driven to the active state
when the value of the Duty Cycle register matches the
value of PTMR and the PWM time base is counting
downwards (PTDIR = 1). The PWM compare output is
driven to the inactive state when the PWM time base is
counting upwards (PTDIR = 0) and the value in the
PTMR register matches the duty cycle value.
If the value in a particular Duty Cycle register is zero,
then the output on the corresponding PWM pin will be
inactive for the entire PWM period. In addition, the output on the PWM pin will be active for the entire PWM
period if the value in the Duty Cycle register is equal to
the value held in the PTPER register.
FIGURE 15-3: CENTER-ALIGNED PWM
Period/2
PTPER
Duty
Cycle
0
PTMR
Value
15.5.1 DUTY CYCLE REGISTER BUFFERS
The four PWM Duty Cycle registers are double-buffered
to allow glitchless updates of the PWM outputs. For each
duty cycle, there is a Duty Cycle register that is accessible by the user and a second Duty Cycle register that
holds the actual compare value used in the present
PWM period.
For edge-aligned PWM output, a new duty cycle value
will be updated whenever a match with the PTPER register occurs and PTMR is reset. The contents of the
duty cycle buffers are automatically loaded into the
Duty Cycle registers when the PWM time base is disabled (PTEN = 0) and the UDIS bit is cleared in
PWMCON2.
When the PWM time base is in the Up/Down Counting
mode, new duty cycle values are updated when the
value of the PTMR register is zero and the PWM time
base begins to count upwards. The contents of the duty
cycle buffers are automatically loaded into the Duty
Cycle registers when the PWM time base is disabled
(PTEN = 0).
When the PWM time base is in the Up/Down Counting
mode with double updates, new duty cycle values are
updated when the value of the PTMR register is zero,
and when the value of the PTMR register matches the
value in the PTPER register. The contents of the duty
cycle buffers are automatically loaded into the Duty
Cycle registers when the PWM time base is disabled
(PTEN = 0).
Period
15.5 PWM Duty Cycle Comparison Units
There are four 16-bit Special Function Registers
(PDC1, PDC2, PDC3 and PDC4) used to specify duty
cycle values for the PWM module.
The value in each Duty Cycle register determines the
amount of time that the PWM output is in the active
state. The Duty Cycle registers are 16 bits wide. The
LSb of a Duty Cycle register determines whether the
PWM edge occurs in the beginning. Thus, the PWM
resolution is effectively doubled.
15.5.2 DUTY CYCLE IMMEDIATE UPDATES
When the Immediate Update Enable bit is set (IUE = 1),
any write to the Duty Cycle registers updates the new
duty cycle value immediately. This feature gives the
option to the user to allow immediate updates of the
active PWM Duty Cycle registers instead of waiting for
the end of the current time base period. System stability is improved in closed-loop servo applications by
reducing the delay between system observation and
the issuance of system corrective commands when
immediate updates are enabled.
If the PWM output is active at the time the new duty
cycle is written, and the new duty cycle is less than the
current time base value, the PWM pulse width is
shortened.
If the PWM output is active at the time the new duty
cycle is written, and the new duty cycle is greater than
the current time base value, the PWM pulse width is
lengthened.
If the PWM output is inactive at the time the new duty
cycle is written, and the new duty cycle is greater than
the current time base value, the PWM output becomes
active immediately and remains active for the new
written duty cycle value.
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS70149A-page 97
Page 100

dsPIC30F5015/5016
15.6 Complementary PWM Operation
In the Complementary mode of operation, each pair of
PWM outputs is obtained by a complementary PWM
signal. A dead time may be optionally inserted during
device switching, when both outputs are inactive for a
short period (Refer to Section 15.7 “Dead-Time
Generators”).
In Complementary mode, the duty cycle comparison
units are assigned to the PWM outputs as follows:
• PDC1 register controls PWM1H/PWM1L outputs
• PDC2 register controls PWM2H/PWM2L outputs
• PDC3 register controls PWM3H/PWM3L outputs
• PDC4 register controls PWM4H/PWM4L outputs
The Complementary mode is selected for each PWM
I/O pin pair by clearing the appropriate PMODx bit in the
PWMCON1 SFR. The PWM I/O pins are set to
Complementary mode by default upon a device Reset.
15.7 Dead-Time Generators
Dead-time generation may be provided when any of the
PWM I/O pin pairs are operating in the Complementary
Output mode. The PWM outputs use Push-Pull drive circuits. Due to the inability of the power output devices to
switch instantaneously, some amount of time must be
provided between the turn off event of one PWM output
in a complementary pair and the turn on event of the
other transistor.
The PWM module allows two different dead times to be
programmed. These two dead times may be used in
one of two methods described below to increase user
flexibility:
• The PWM output signals can be optimized for
different turn off times in the high side and low
side transistors in a complementary pair of transistors. The first dead time is inserted between
the turn off event of the lower transistor of the
complementary pair and the turn on event of the
upper transistor. The second dead time is inserted
between the turn off event of the upper transistor
and the turn on event of the lower transistor.
• The two dead times can be assigned to individual
PWM I/O pin pairs. This operating mode allows
the PWM module to drive different transistor/load
combinations with each complementary PWM I/O
pin pair.
15.7.1 DEAD-TIME GENERATORS
Each complementary output pair for the PWM module
has a 6-bit down counter that is used to produce the
dead-time insertion. As shown in Figure 15-4, each
dead-time unit has a rising and falling edge detector
connected to the duty cycle comparison output.
15.7.2 DEAD-TIME ASSIGNMENT
The DTCON2 SFR contains control bits that allow the
dead times to be assigned to each of the complementary outputs. Table 15-1 summarizes the function of
each dead-time selection control bit.
TABLE 15-1: DEAD-TIME SELECTION BITS
Bit Function
DTS1A Selects PWM1L/PWM1H active edge dead time.
DTS1I Selects PWM1L/PWM1H inactive edge
dead time.
DTS2A Selects PWM2L/PWM2H active edge dead time.
DTS2I Selects PWM2L/PWM2H inactive edge
DTS3A Selects PWM3L/PWM3H active edge dead time.
DTS3I Selects PWM3L/PWM3H inactive edge
DTS4A Selects PWM4L/PWM4H active edge dead time.
DTS4I Selects PWM4L/PWM4H inactive edge
dead time.
dead time.
dead time.
15.7.3 DEAD-TIME RANGES
The amount of dead time provided by each dead-time
unit is selected by specifying the input clock prescaler
value and a 6-bit unsigned value. The amount of dead
time provided by each unit may be set independently.
Four input clock prescaler selections have been provided to allow a suitable range of dead times, based on
the device operating frequency. The clock prescaler
option may be selected independently for each of the
two dead-time values. The dead-time clock prescaler
values are selected using the DTAPS<1:0> and
DTBPS<1:0> control bits in the DTCON1 SFR. One of
four clock prescaler options (T
may be selected for each of the dead-time values.
After the prescaler values are selected, the dead time
for each unit is adjusted by loading two 6-bit unsigned
values into the DTCON1 SFR.
The dead-time unit prescalers are cleared on the
following events:
• On a load of the down timer due to a duty cycle
comparison edge event.
• On a write to the DTCON1 or DTCON2 registers.
• On any device Reset.
Note: The user should not modify the DTCON1
or DTCON2 values while the PWM module is operating (PTEN = 1). Unexpected
results may occur.
CY, 2 TCY, 4 TCY or 8 TCY)
DS70149A-page 98 Preliminary © 2005 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...