Page 1

SAM D21G17D
SAM D21G17D Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit User's Guide
Preface
The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit (DM320119) is a hardware platform to evaluate the SAMD21G17D
microcontroller (MCU), and it is supported by the MPLAB® X Integrated Development Environment (IDE). The
evaluation kit provides an easy access to the features of the SAMD21G17D to integrate the device into a custom
design. The Curiosity Nano series of evaluation kits include an On-Board Nano Debugger, hence no external tools
are necessary to program the SAMD21G17D device. The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano Evaluation Kit is shown
below.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 1
Page 2

SAM D21G17D
Table of Contents
Preface........................................................................................................................................................... 1
1. Introduction............................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1. Features....................................................................................................................................... 3
2. Getting Started........................................................................................................................................ 4
2.1. Curiosity Nano Quick Start........................................................................................................... 4
3. Curiosity Nano.........................................................................................................................................5
3.1. On-Board Nano Debugger........................................................................................................... 5
3.2. Curiosity Nano Standard Pinout................................................................................................... 6
3.3. Power Supply............................................................................................................................... 7
3.4. Disconnecting the On-Board Nano Debugger..............................................................................9
3.5. Current Measurement................................................................................................................ 10
4. Hardware...............................................................................................................................................11
4.1. Connectors................................................................................................................................. 11
4.2. Peripherals................................................................................................................................. 11
4.3. On-Board Nano Debugger Implementation................................................................................12
5. Hardware Revision History....................................................................................................................13
5.1. Identifying Product ID and Revision........................................................................................... 13
6. Schematics............................................................................................................................................14
7. Document Revision History...................................................................................................................17
The Microchip Website.................................................................................................................................18
Product Change Notification Service............................................................................................................18
Customer Support........................................................................................................................................ 18
Product Identification System.......................................................................................................................19
Microchip Devices Code Protection Feature................................................................................................ 19
Legal Notice................................................................................................................................................. 19
Trademarks.................................................................................................................................................. 20
Quality Management System....................................................................................................................... 20
Worldwide Sales and Service.......................................................................................................................21
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 2
Page 3
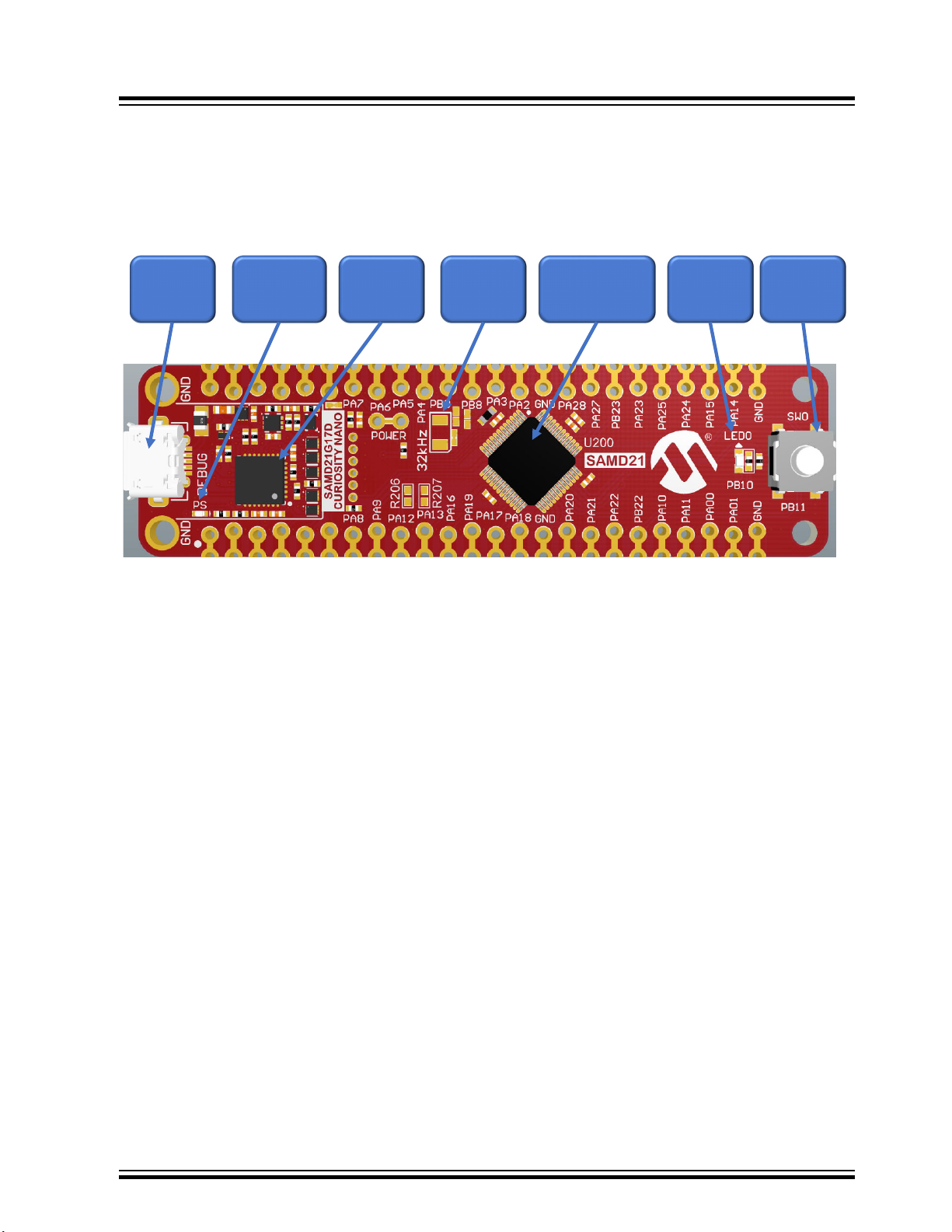
1. Introduction
Micro‐USB
Connector
Power/Status
LED
Nano
Debugger
ATS AMD21 G17D
MCU
UserLED
(LED0)
UserSwitch
(SW0)
32.768kHz
Crystal
(DNP)
Kit Overview
The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano evaluation kit is a hardware platform used to evaluate the SAMD21G17D.
Figure 1-1. Kit Overview
SAM D21G17D
Introduction
1.1 Features
The following are features of the SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano evaluation kit:
• SAMD21G17D microcontroller
• One yellow user LED
• One mechanical user switch
• On-Board Nano Debugger
– Board identification in MPLAB X IDE
– One green power/status LED
– Programing and debugging
– Virtual COM port (CDC)
– One logic analyzer (DGI GPIO)
• USB powered
• Adjustable target voltage
– MIC5353 LDO regulator controlled by the On-Board Nano Debugger
– 1.7V to 3.6V output voltage
– 500 mA maximum output current (limited by ambient temperature and output voltage)
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 3
Page 4

2. Getting Started
2.1 Curiosity Nano Quick Start
Follow these steps to explore the Curiosity Nano platform:
1. Download MPLAB X IDE.
2. Launch MPLAB X IDE.
3. Connect a USB cable (Standard-A to Micro-B or Micro-AB) between the PC and the debug USB port on the
kit.
When the Curiosity Nano kit is connected to the computer for the first time, the operating system will perform a driver
software installation. The driver file supports both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Microsoft® Windows® XP, Windows
Vista®, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10. The drivers for the kit are included with MPLAB X IDE.
After the Curiosity Nano board is powered, the green status LED will be lit and MPLAB X IDE will auto-detect which
Curiosity Nano board is connected. MPLAB X IDE will populate relevant information like data sheets and kit
documentation in the kit window. The SAMD21G17D device is programmed and debugged by the On-Board Nano
Debugger, hence no external programmer or debugger tool is required.
SAM D21G17D
Getting Started
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 4
Page 5

3. Curiosity Nano
Curiosity Nano is an evaluation platform that provides a set of small boards with access to most of the microcontroller
I/Os. The platform consists of a series of low pin-count microcontroller (MCU) boards, which are integrated with
MPLAB X IDE to present relevant user guides, application notes, data sheets, and example codes. The platform
features a Virtual COM port (CDC) for serial communication to a host PC and a Data Gateway Interface (DGI) GPIO.
3.1 On-Board Nano Debugger
The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano contains an On-Board Nano Debugger for programming and debugging. The OnBoard Nano Debugger is a complex USB device consists of several interfaces, such as a debugger, a mass storage
device, a data gateway, and a Virtual COM port (CDC). Together with MPLAB X IDE, the On-Board Nano Debugger
interface can program and debug the SAMD21G17D. An DGI is available for use with the logic analyzer channels for
code instrumentation to visualize program flow. DGI GPIOs can be graphed using the Data Visualizer. The Virtual
COM port is connected to a UART on the SAMD21G17D and it provides an easy way to communicate with the target
application through terminal software. The On-Board Nano Debugger controls one Power/Status LED (marked PS)
on the SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano board. The following table describes how the LED is controlled in different
operation modes.
Table 3-1. On-Board Nano Debugger LED Control
Operation Mode Status LED
SAM D21G17D
Curiosity Nano
Boot Loader mode LED blink at 1 Hz during power up.
Power-up LED is lit, constant.
Normal operation LED is lit, constant.
Programming Activity indicator, the LED flashes slowly during programming or debugging.
Fault The LED flashes fast if a power fault is detected.
Sleep/Off LED is OFF. The On-Board Nano Debugger is either in Sleep mode or Power-Down mode. This
3.1.1 Virtual COM Port
A general-purpose USB serial bridge between a host PC and a target device.
3.1.1.1 Overview
The debugger implements a complex USB device that includes a standard Communications Device Class (CDC)
interface, which appears on the host as a Virtual COM Port. The CDC can be used to stream arbitrary data in both
directions between the host and the target. Characters sent from the host will appear in UART form on the CDC TX
pin, and UART characters sent into the CDC RX pin will be sent back to the host. On Windows machines, the CDC
will enumerate as the Curiosity Virtual COM Port and appear in the ports section of the device manager. The COM
port number is usually shown here.
Note: On the older version of Windows systems a USB driver is required for CDC. This driver is included in Atmel
Studio and MPLAB X IDE installations. On Linux machines, the CDC will enumerate and appear as /dev/ttyACM#.
On MAC machines, the CDC will enumerate and appear as /dev/tty.usbmodem#. Depending on which terminal
program is used, it will appear in the available list of modems as usbmodem#.
will occur only if the kit is externally powered
®
3.1.1.2 Limitations
Not all UART features are implemented in the debugger CDC, and the constraints are outlined below:
• Baud rate: Must be in the range of 1200 bps to 500 kbps. Values outside this range will be capped to these
values, without warning. Baud rate can be changed on-the-fly.
• Character format: Only 8-bit characters are supported.
• Parity: Can be odd, even, or none.
• Hardware flow control: Not supported.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 5
Page 6
• Stop bits: One or two bits are supported.
3.1.1.3 Signaling
During USB enumeration, the host OS will start both communication and data pipes of the CDC interface. At this
point, it is possible to set and read baud rate and other UART parameters of the CDC, but data sending and receiving
will not be enabled. When a terminal connects on the host, it must assert the DTR signal. This is a virtual control
signal that is implemented on the USB interface but not in hardware on the debugger. Asserting DTR from the host
will indicate to the debugger that a CDC session is active, and it will enable its level shifters (if available), and start
the CDC data send and receive mechanisms. Deasserting the DTR signal will not disable the level shifters, but it will
disable the receiver, hence no further data will be streamed to the host. Data packets that are already queued up for
sending to the target will continue to be sent out, but no further data will be accepted.
3.1.1.4 Advanced Use
When the CDC Override mode is in normal operation, the On-Board Nano Debugger is a true UART bridge between
the host and the device. However, under certain use cases, the debugger can override the Basic Operating mode
and use the CDC pins for other purposes. Dropping a text file (with extension .txt) into the debugger’s mass
storage drive can be used to send characters out of the CDC TX pin. The text file must start with the characters:
CMD:SEND_UART=. The maximum message length is 50 characters, and all remaining data in the frame is ignored.
The default baud rate used in this mode is 9600 bps, but if the CDC is already active or has been configured, the
recently used baud rate still applies.
USB-Level Framing Considerations
Sending data from the host to the CDC can be done byte-wise or in blocks, which will be chunked into 64-byte USB
frames. Each frame will be queued up for sending to the CDC TX pin. Sending a small amount of data per frame can
be inefficient, particularly at low-baud rates, because the debugger buffers frames, not bytes. A maximum of 4 x 64byte frames can be active at any time, the debugger will throttle the incoming frames accordingly. Sending full 64byte frames containing data is the most efficient. When receiving data from the target, the debugger will queue up
incoming bytes into 64-byte frames, which are sent to the USB queue for transmission to the host when they are full.
Incomplete frames are also pushed to the USB queue at approximately 100 ms intervals, triggered by USB start-offrame tokens. Up to 8 x 64-byte frames can be active at any time. If the host or software running on it, fails to receive
data fast enough, an overrun will occur. When this happens the last-filled buffer frame will be recycled instead of
being sent to the USB queue, and a full frame of data will be lost. To prevent this occurrence, the user must ensure
that the CDC data pipe is being read continuously, or the incoming data rate must be reduced.
Note: Mass storage disk is not supported during this release.
SAM D21G17D
Curiosity Nano
3.1.2 Mass Storage Disk
Not supported at this time.
3.2 Curiosity Nano Standard Pinout
The twelve edge connections closest to the USB connector on Curiosity Nano kits have a standardized pinout. The
program and debug pins have different functions depending on the target programming interface as shown in the
following table and figure.
Table 3-2. Curiosity Nano Standard Pinout
Debugger Signal ICSP Target Description
NC - No connect.
ID - ID line for extensions.
CDC RX UART TX USB CDC RX line.
CDC TX UART RX USB CDC TX line.
DBG1 SWCLK Debug clock line
DBG2 GPIO DGI GPIO
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 6
Page 7

...........continued
Debugger Signal ICSP Target Description
VTG - Target voltage
GND - Common ground.
DBG0 SWDATA Debug data line.
DBG3 nRESET Reset line
VOFF - Voltage Off input.
VBUS - VBUS voltage for external use.
Figure 3-1. Curiosity Nano Standard Pinout
SAM D21G17D
Curiosity Nano
3.3 Power Supply
The evaluation kit is powered through the USB port and contains two regulators for generating 3.3V for the debugger
and an adjustable regulator for the target. The voltage from the USB connector can vary between 4.4V-5.25V
(according to the USB specification) and will limit the maximum voltage to the target. The following figure shows the
entire power supply system on the SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano.
Figure 3-2. Power Supply Block Diagram
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 7
Page 8

3.3.1 Target Voltage Regulator
WARNING
WARNING
The target voltage regulator is a MIC5353 variable output LDO. The On-Board Nano Debugger can adjust the voltage
output that is supplied to the kit target section by manipulating the MIC5353's feedback voltage. The hardware
implementation is limited to an approximate voltage range from 1.7V-5.1V. Additional output voltage limits are
configured in the debugger firmware to ensure that the output voltage never exceeds the hardware limits of the
SAMD21G17D microcontroller. The voltage limits configured in the On-Board Nano Debugger on the SAMD21G17D
Curiosity Nano are 1.7V-3.6 V. The target voltage is set to 3.3V in production and can be changed through Atmel
Studio. Any change to the target voltage done in Atmel Studio is persistent, even through a power toggle. The
MIC5353 supports a maximum current load of 500 mA. It is an LDO regulator in a small package, placed on a small
PCB, and the thermal shutdown condition can be reached at lower loads than 500 mA. The maximum current load
depends on the input voltage, set output voltage, and the ambient temperature. The following figure shows the safe
operation area for the regulator with an input voltage of 5.1V and an ambient temperature of 23°C.
Figure 3-3. Target Regulator Safe Operation Area
SAM D21G17D
Curiosity Nano
3.3.2 External Supply
The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano evaluation kit can be powered by an external voltage instead of the on-board
target regulator. When the Voltage Off (VOFF) pin is shorted to ground (GND), the On-Board Nano Debugger
firmware disables the target regulator and it is safe to apply an external voltage to the VTG pin.
Programming, debugging, and data streaming are still possible while using the external power. The debugger and
signal level shifters will be powered from the USB cable. Both regulators, the debugger, and the level shifters are
powered down when the USB cable is removed.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
Applying an external voltage to the VTG pin without shorting VOFF to GND may cause permanent damage
to the kit.
Absolute maximum external voltage is 5.5V for the level shifters on board. Applying a higher voltage may
cause permanent damage to the kit.
DS70005409A-page 8
Page 9

3.4 Disconnecting the On-Board Nano Debugger
The following block diagram shows connections between the debugger and the SAMD21G17D microcontroller. The
round boxes represent connections to the board edge on the SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano. The signal names are
shown in Figure 3-1 and printed in silkscreen on the bottom side of the board.
Figure 3-4. On-Board Nano Debugger Connections
SAM D21G17D
Curiosity Nano
By cutting the GPIO straps with a sharp tool, as shown in the following figure, all I/Os connected between the
debugger and the SAMD21G17D can be disconnected. To disconnect the target regulator, cut the VTG strap.
Note:
1. Cutting the connections to the debugger will disable programming, debugging, data streaming, and the target
power supply. The signals will also be disconnected from the board edge next to the On-Board Nano
Debugger section.
2. Solder in 0Ω resistors across the footprints or short-circuit them with tin solder to reconnect any cut signals.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 9
Page 10

3.5 Current Measurement
The power to the SAMD21G17D is connected from the on-board power supply to the target voltage supply (VTG)
with a cut strap as shown in Disconnecting the On-Board Debugger. To measure the power consumption of the
SAMD21G17D and other peripherals connected to the board, cut the strap and connect an ammeter over the strap.
The ammeter can be connected between the target VTG pad edge connector and an external power supply for easy
measurement. Alternatively, an external power supply can be used as described in External Supply.
SAM D21G17D
Curiosity Nano
Tip: The on-board level shifters will draw a small amount of current even when they are not in use.
Disconnect the On-Board Nano Debugger and level shifters as described in Disconnecting the On-Board
Debugger to prevent any current leakage.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 10
Page 11

4. Hardware
USB
Debugger(nEDBG)
SAMD21
UserButton&
UserLED
Edgepinout
SAMD21
4.1 Connectors
4.1.1 SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano Pinout
All of the SAMD21G17D I/O pins are accessible at the edge connectors on the SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano, except
the button and LED (PB10, PB11). The following figure shows the evaluation kit pinout. RA30 and RA31 are only
available at the edge connector in the debugger section as long as the cut straps on the bottom are not cut.
Figure 4-1.
SAM D21G17D
Hardware
4.2 Peripherals
4.2.1 LED
One yellow user LED is available on the SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano evaluation kit which can be controlled either
with a GPIO or PWM. The LED can be activated by driving the connected I/O line to the GND.
Table 4-1. LED Connection
SAMD21G17D Function Shared Functionality
PB10 Yellow LED0 None
4.2.2 Mechanical Switch
The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano has one mechanical switch, a generic user configurable switch. When this switch
is pressed, it will drive the I/O line to ground (GND).
Note: No pull-up resistor is connected to the generic user switch. Ensure that the internal pull-up is enabled in the
SAMD21G17D to use the switch.
Table 4-2. Mechanical Switch
SAMD21G17D Function Shared Functionality
PB11 User switch SW0 DBG2 and Edge connector
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 11
Page 12

4.2.3 Crystal
The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano board has the option for a 32.768 kHz crystal, and by default this crystal is not
connected to the SAMD21G17D, as GPIOs are routed out to the edge connector. To use the crystal, some hardware
modifications are required. The two I/O lines routed to the edge connector must be disconnected to reduce the
chance of contention to the crystal, and to remove excessive capacitance on the lines.
Table 4-3. Crystal Connections
SAMD21G17D pin Function Shared Functionality
PA00 XIN32 Edge connector
PA01 XOUT32 Edge connector
4.3 On-Board Nano Debugger Implementation
The SAMD21G17D Curiosity Nano features an On-Board Nano Debugger that can be used to program and debug
the SAMD21G17D using a Serial wire debug (SWD). The On-Board Nano Debugger also includes a Virtual Com port
interface over UART and DGI GPIO. MPLAB X IDE can be used as a front-end for the On-Board Nano Debugger for
programming and debugging. Data Visualizer can be used as a front-end for the CDC and DGI GPIO.
4.3.1 On-Board Nano Debugger Connections
The following table provides the connection details between the target and the debugger section. All connections
between the target and the debugger are tri-stated as long as the debugger is not actively using the interface,
therefore little contamination of the signals and the pins can be configured to the application requirements. For
additional information on how to use the capabilities of the On-Board Nano Debugger, see Curiosity Nano.
Table 4-4. Connection Details between the Target and Debugger Section
SAM D21G17D
Hardware
SAMD21G17D pin Debugger pin Function Shared Functionality
PB03 CDC TX UART TX (SAMD21G17D RX line) Edge Connector
PB02 CDC RX UART RX (SAMD21G17D TX line Edge Connector
PA31 DBG0 SWDATA Edge Connector
PA30 DBG1 SWCLK Edge Connector
PB11 DBG2 GPIO Edge Connector and SW0
nRESET DBG3 nRESET Edge Connector
VCC_TARGET VCC_LEVEL 1.7V-3.6V supply voltage Edge Connector
GND GND Common ground Edge Connector
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 12
Page 13

5. Hardware Revision History
This user guide provides the latest available revision of the kit. This chapter contains information about known issues,
a revision history of older revisions, and how older revisions differ from the latest revision.
5.1 Identifying Product ID and Revision
The revision and product identifier of Curiosity Nano boards can be found in two ways; either through the MPLAB X
IDE or by looking at the sticker on the bottom of the PCB. By connecting a Curiosity Nano board to a computer with
MPLAB X IDE running, an information window will pop up. The first six digits of the serial number, which is listed
under kit details, contain the product identifier and revision. The same information can be found on the sticker on the
bottom of the PCB. Most kits will print the identifier and revision in plain text as A09-nnnn\rr, where nnnn is the
identifier and rr is the revision. Boards with limited space have a sticker with only a QR-code, which contains a serial
number string. The serial number string has the following format:
“nnnnrrssssssssss"
n = product identifier
r = revision
s = serial number
SAM D21G17D
Hardware Revision History
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 13
Page 14

6. Schematics
CDC_UART
DBG0
DBG2
DBG1
DBG3
VOFF
ID_SYS
U_SAMD21_Curiosity_Nano_Debugger R3
SAMD21_Curiosity_Nano_Debugger R3.SchDoc
DBG0
CDC_UART
DBG1
DBG3
DBG2
VOFF
ID_SYS
U_SAMD21_Curiosity_Nano_Target_MCU R3
SAMD21_Curiosity_Nano_Target_MCU R3.SchDoc
Figure 6-1. Target Microcontroller (SAMD21G17D)
SAM D21G17D
Schematics
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 14
Page 15

GNDVCC_TARGET
100n
C201
32.768kHz
Kyocera Corporation
ST3215SB32768C0HPWBB
XC200
DNP
C203
10pF
DNP
13pF
C204
DNP
GND
GND
VCC_TARGET
100n
C202
VCC_TARGET
100n
C207
GND
32.768kHz
Kyocera Corporatio
n
S
T3215SB32768C0HPWB
B
XC20
0
DNPNDNP
DNP
C203
10p
F
D
13p
F
C204
DN
GND
GND
32kHz Crystal
USER LED
VCC_TARGET
nRESET
GND
USER BUTTON
1k1
R202
YELLOW LED
SML-D12Y1WT86
21
D200
TS604VM1-035CR
1 3
42
SW0
GND
VCC_EDGE
GNDGND
GND GND
J203
J205
J201 J202
J204
J206
J209
BLM18PG471SN1
L200
SAMD21
2.2uF
C205
VCC_EDGE
GND
DBG0
CDC_UART
TX
RX
UART
CDC_TX
CDC_RX
DBG2
DBG1
DBG3
DBG2
DEBUGGER CONNECTIONS
DBG1
DBG3
DBG0
CDC_
UART
_
T
RX
U
ART
D
BG1
DBG3
DBG2
DBG0
VOFF
ID_SYS
ID_SYS
VOFF
2.2
uF
C205
V
CC_EDGE
GND
TARGET BULK
PROG/DEBUG Pull
47k47k
R204
47k
4
7k
R205
DBG0
DBG1
100k
R200
VCC_TARGET
1
R
V
CC_TARGET
nRESET Pull
VBUS
PA10_UART2_TX
PA09_UART0_RX
PA11_UART2_RX
PA08_UART0_TX
PA13_I2C4_SCL
PA12_I2C4_SDA
PA17_SPI_SCK
PA16_SPI_MOSI
PA14
PA15
PA00_XIN32
PA01_XOUT32
PA23
PA24
PA25
PA30_SWCLK
PA18_SPI_SS
PA19_SPI_MISO
PA07_ADC7
PA06_ADC6
PA05_ADC5
PA04_PWM4
PB09_PWM3
PB08_ADC2
PA03_ADC1
PA02_ADC0
PA21_UART3_RX
PA20_UART3_TX
PB23
PA27
PA28
PB10_LED
PB11_BUTTON
PA31_SWDIO
GND
VCC_TARGET
100n
C206
1uC208
GND
(Target Device)
1.8k
R206
DNP 1.8k
R207
DNP
VCC_TARGET
VCC_TARGET
PA00_XIN32
PA01_XOUT32
PB10_LED
PB11_BUTTON
PA30_SWCLK
PB11_BUTTON
PA31_SWDIO
nRESET
PA08_UART0_TX
PA09_UART0_RX
PA12_I2C4_SDA
PA13_I2C4_SCL
PA16_SPI_MOSI
PA19_SPI_MISO
PA17_SPI_SCK
PA18_SPI_SS PA02_ADC0
PA03_ADC1
PB08_ADC2
PB09_PWM3
PA04_PWM4
PA05_ADC5
PA06_ADC6
PA07_ADC7
PA20_UART3_TX
PA21_UART3_RX
PA00_XIN32
PA01_XOUT32 PA14
PA15
PA24
PA25
PA23
PB23
PA27
PA28
PA10_UART2_TX
PA11_UART2_RX
PA12_I2C4_SDA
PA13_I2C4_SCL
110R
R203
CDC RX
3
CDC TX
4
DBG1
5
DBG2
6
0 TX
7
1 RX
8
2 SDA
9
3 SCL
10
4 MOSI
11
5 MISO
12
6 SCK
13
7 SS
14
GND
15
0 (TX)
16
1 (RX)
17
2
18
3
19
0
20
GND
24
DBG3
46
DBG0
45
GND
44
VCC
43
PWM 3
38
ADC 2
37
ADC 1
36
ADC 0
35
GND
34
4
30
4
26
GND
25
ADC 7
42
ADC 6
41
ADC 5
40
PWM 4
39
DEBUGGER
TARGET
ID2VOFF
47
1
21
2
22
3
23
5
27
6
28
7
29
5
31
6
32
7
33
RESERVED1VBUS
48
CNANO48-pin edge connector
J200
PA00
1
PA01
2
PA02
3
PA03
4
GNDANA
5
VDDANA
6
PB08
7
PB09
8
PA04
9
PA05
10
PA06
11
PA07
12
PA0813PA0914PA1015PA1116VDDIO17GND18PB1019PB1120PA1221PA1322PA1423PA15
24
PA16
25
PA17
26
PA18
27
PA19
28
PA20
29
PA21
30
PA22
31
USB_SOF/PA23
32
USB_DM/PA24
33
USB_DP/PA25
34
GND
35
VDDIO
36
PB2237PB2338PA27
39
RESETN
40
PA28
41
GND
42
VDDCORE
43
VDDIN
44
SWDCLK/PA30
45
SWDIO/PA31
46
PB0247PB03
48
SAMD21G17D-AUT
U200
PA22_CDC5_TX
PB22_CDC5_RX
PB03
PB02
PA22_CDC5_TX
PB22_CDC5_RX
PB03
PB02
Crystal datasheet:
Ccrystal = 7pF
max ESR = 70kOhm
Accuracy ±20ppm
SAMD21 datasheet:
Cxin = 5.5pF
Cxout = 5.5pF
Cl ≈ 1/( (1/5.5pF)+ (1/5.5pF) ) ≈ 2.75pF
Maximum Load = 12.5pF
Maximum ESR = 80kOhm
Estimated Cpcb = 0.5pF
Estimated load
C = 2 (Ccrystal- Cpara - Cpcb)
C = 2 (7pF - 2.75pF - 0.5pF)
C = 7.5pF
Selected in design after verification
C= 10/13pF
N
OTE on UART/CDC:
RX/TX on the header denotes the
input/output direction of the signal
respective to it's source.
CDC TX is output from the DEBUGGER.
CDC RX is input to the DEBUGGER.
TX is output from the TARGET device.
RX is input to the TARGET device.
N
OTE on CDC:
TX and RX cross here.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
Figure 6-2. Debuggerrotatethispage90
DS70005409A-page 15
SAM D21G17D
Schematics
Page 16

100n
C107
100n
C108
RX
TX
UART
CDC_UART
SRST
STATUS_LED
VCC_P3V3
GND
TP100
Testpoint Array
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
TCK
TDO
TMS
Vsup
TDI GND
TRST
SRST
VTref
GND
J102
DBG0
DBG0
PAD
33
PAD
PA00
1
PA01
2
PA02
3
PA03
4
GND10VDDANA
9
PA04
5
PA05
6
PA06
7
PA07
8
PA0811PA0912PA1013PA1114PA1415PA15
16
PA16
17
PA17
18
PA18
19
PA19
20
PA22
21
USB_SOF/PA23
22
USB_DM/PA24
23
USB_DP/PA25
24
PA27
25
RESETN
26
PA28
27
GND
28
VDDCORE
29
VDDIN
30
SWDCLK/PA30
31
SWDIO/PA31
32
SAMD21E18A-MUT
U100
USBD_P
USBD_N
GND
1u
C106
VCC_MCU_CORE
VCC_P3V3
VCC_P3V3
74LVC1T45FW4-7
VCCA
1
VCCB
6
A
3
GND
2
DIR
5
B
4
U103
VCC_P3V3
GND
74LVC1T45FW4-7
VCCA
1
VCCB
6
A
3
GND
2
DIR
5
B
4
U104
VCC_P3V3
GND
74LVC1T45FW4-7
VCCA
1
VCCB
6
A
3
GND
2
DIR
5
B
4
U105
VCC_P3V3
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
74LVC1T45FW4-7
VCCA
1
VCCB
6
A
3
GND
2
DIR
5
B
4
U107
VCC_P3V3
GND
DBG2
DBG3_CTRL
S1_0_TX
S1_1_RX
S0_2_TX
DAC
VTG_ADC
RESERVED
S0_3_CLK
DBG0_CTRL
CDC_TX_CTRL
BOOT
EN
1
BYP
6
VOUT
4
GND
2
VIN
3
NC/ADJ
5
GND
7
MIC5353U102
VCC_VBUS
100n
C102
GND
GND
47k
R101
27k
R104
GND
33k
R106
G
ND
EN
6
V
OUT
4
GND
VIN
3
NC/ADJ
5
GND
MIC535
3
U102
V
CC_VBUS
1
00n
C102
G
ND
GND
R1
1
1
G
ND
33
k
R1
06
2.2uF
C103
GND
1k
R108
J100
VCC_LEVELVCC_REGULATOR
74LVC1T45FW4-7
VCCA
1
VCCB
6
A
3
GND
2
DIR
5
B
4
U106
VCC_P3V3
GND
DBG1
CDC_RX
CDC_TX
DBG3
DBG1_CTRL
REG_ENABLE
REG_ENABLE
47k
R103
VCC_LEVEL
VCC_LEVEL
VCC_LEVEL
VCC_LEVEL
VCC_LEVEL
47k
R102
47k
R105
SWCLK
GND
47k
R100
GND
DBG2
S0_0_RX
DBG1_CTRL
DBG0_CTRL
GND
DBG3 OPEN DRAIN
TARGET ADJUSTABLE REGULATOR
SRST
SRS
T
VCC_
P3V3
G
ND
Testpoint Arra
y
356
7
8910
TCK
TD
O
TM
S
V
sup
TDIGND
TRST
SRS
T
V
Tre
f
GNDJ102
SWC
LK
DEBUGGER TESTPOINT
DBG2_CTRL
VOFF
CDC_RX_CTRL
47k
R109
DBG1
CDC_TX_CTRL
CDC_RX_CTRL
SWCLK
REG_ADJUST
DBG2_GPIO
DBG3_CTRL
DBG2_CTRL
nRESET
Signal
DBG0
DBG1
DBG2
DBG3
SWD
Interface
SWDAT
SWCLK
GPIO
DBG3
CDC TX
CDC RX
UART RX
UART TX
TARGET
1k
1k
R110
VBUS_ADC
1
2 3
DMN65D8LFB
Q101
VCC 3.3V
VOFF
VTG_ADC
DAC
MIC94163
VIN
B2
VOUT
A1
VIN
A2
EN
C2
GND
C1
VOUT
B1
U108
GND
ID_SYS
VTG_EN
VTG_EN
VBUS_ADC
SWDIO
TP101
GND
SWDIO
VOFF
47k
R111
GND
DEBUGGER USB MICRO-B CONNECTOR
GND
USBD_P
USBD_N
1k
R107
VCC_P3V3
SHIELD
VBUS
GND
4.7uF
C100
21
GREEN LED
SML-P12MTT86R
D100
VBUS
1
D-
2
D+
3
GND
5
SHIELD1
6
SHIELD2
7
ID
4
SHIELD3
8
SHIELD4
9
MU-MB0142AB2-269
J105
VOUT
1
VOUT
2
GND
3
EN
4
VIN
6
NC
5
EP
7
MIC5528-3.3YMTU101VCC_VBUS VCC_P3V3
GND
G
ND
4
.7u
F
C100
V
OUT
V
OUT
N
6
N
C
5
MIC5528-3.3YMT
U101
V
CC_VBUS
V
CC_P3V3
G
ND
2.2uF
C101
GND
DEBUGGER POWER/STATUS LED
1k
R10
7
V
CC_P3V3
G
REEN LE
D
S
ML-P12MTT86R
D1
00
DEBUGGER REGULATOR
ID_SYS
1k
R112
VCC_P3V3
ID_
SYS
_
1
R11
V
CC_P3V3
ID_SYS
ID PIN
MC36213
F100
VCC_VBUS
VCC_EDGE
J101
VCC_TARGET
GND
10k
R113
BLM15PD800SN1
L100
Programming connector
for factory programming o
f
Debugger.
MIC5353:
Vin: 2.6V to 6V
Vout: 1.25V to 5.1V
Imax: 500mA
Dropout (typical): 50mV@150mA, 160mV @ 500mA
Accuracy: 2% initial
Thermal shutdown and current limit
Maximum output voltage is limited by the input voltage and the dropout voltage in the regulator.
(Vmax = Vin - dropout)
J100:
- Cut-strap used for full separation of target power from the level shifters and on-board regulators.
- For current measurements using the on-board power supply, this strap must be cut and an
ammeter connected across.
- For current measurements using an external power supply, this strap could be cut for more
accurate measurements. Leakage back through the switch is in the micro ampere range.
Adjustable output and limitations:
- The debugger can adjust the output voltage of the regulator between 1.25V and 5.1V to the target.
- The level shifters have a minimal voltage level of 1.65V and will limit the minimum operating voltage allowed for the
target to still allow communication.
- The output switch has a minimal volatege level of 1.70V and will limit the minimum voltage delivered to the target.
- Firmware configuration will limit the voltage range to be within the the target specification.
- Firmware feedback loop will adjust the output voltage accuracy to within 0.5%.
MIC5528:
Vin: 2.5V to 5.5V
Vout: Fixed 3.3V
Imax: 500mA
Dro
p
out: 260mV @ 500mA
PTC Resettable fuse:
Hold current: 500mA
Tri
p
current: 1000mA
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
Figure 6-3. Debuggerrotatethispage90
DS70005409A-page 16
SAM D21G17D
Schematics
Page 17

7. Document Revision History
Rev A - 12/2019
This is the initial released version of this document.
SAM D21G17D
Document Revision History
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 17
Page 18

SAM D21G17D
The Microchip Website
Microchip provides online support via our website at http://www.microchip.com/. This website is used to make files
and information easily available to customers. Some of the content available includes:
• Product Support – Data sheets and errata, application notes and sample programs, design resources, user’s
guides and hardware support documents, latest software releases and archived software
• General Technical Support – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs), technical support requests, online
discussion groups, Microchip design partner program member listing
• Business of Microchip – Product selector and ordering guides, latest Microchip press releases, listing of
seminars and events, listings of Microchip sales offices, distributors and factory representatives
Product Change Notification Service
Microchip’s product change notification service helps keep customers current on Microchip products. Subscribers will
receive email notification whenever there are changes, updates, revisions or errata related to a specified product
family or development tool of interest.
To register, go to http://www.microchip.com/pcn and follow the registration instructions.
Customer Support
Users of Microchip products can receive assistance through several channels:
• Distributor or Representative
• Local Sales Office
• Embedded Solutions Engineer (ESE)
• Technical Support
Customers should contact their distributor, representative or ESE for support. Local sales offices are also available to
help customers. A listing of sales offices and locations is included in this document.
Technical support is available through the website at: http://www.microchip.com/support
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 18
Page 19

PART NO.
–X
/XX
Package
[X]
(1)
Tape
and Reel
Device Temperature
Range
SAM D21G17D
Product Identification System
To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office.
Device: Device A, Feature A, (Package A) Device B, Feature B, (Package B)
Tape & Reel Option: Blank = Tube
T = Tape & Reel
Temperature Range: I = -40°C to +85°C (Industrial)
E = -40°C to +125°C (Extended)
Package: AA = Package AA
BB = Package BB
Examples:
• MCPXXXXXAT-E/AA: Tape and Reel, Extended temperature, XAA package
• MCPXXXXXBT-E/BB: Tape and Reel Extended temperature, XBB package
Note:
1. Tape and Reel identifier only appears in the catalog part number description. This identifier is used for ordering
purposes and is not printed on the device package. Check with your Microchip Sales Office for package
availability with the Tape and Reel option.
2. Small form-factor packaging options may be available. Please check http://www.microchip.com/packaging for
small-form factor package availability, or contact your local Sales Office.
Microchip Devices Code Protection Feature
Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today,
when used in the intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these
methods, to our knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating
specifications contained in Microchip’s Data Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of
intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code
protection does not mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are committed to continuously improving the code protection
features of our products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digital
Millennium Copyright Act. If such acts allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you
may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Legal Notice
Information contained in this publication regarding device applications and the like is provided only for your
convenience and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to ensure that your application meets with
your specifications. MICROCHIP MAKES NO REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND WHETHER
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 19
Page 20

SAM D21G17D
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WRITTEN OR ORAL, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, RELATED TO THE INFORMATION,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ITS CONDITION, QUALITY, PERFORMANCE, MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR PURPOSE. Microchip disclaims all liability arising from this information and its use. Use of Microchip
devices in life support and/or safety applications is entirely at the buyer’s risk, and the buyer agrees to defend,
indemnify and hold harmless Microchip from any and all damages, claims, suits, or expenses resulting from such
use. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any Microchip intellectual property rights unless
otherwise stated.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Adaptec, AnyRate, AVR, AVR logo, AVR Freaks, BesTime,
BitCloud, chipKIT, chipKIT logo, CryptoMemory, CryptoRF, dsPIC, FlashFlex, flexPWR, HELDO, IGLOO, JukeBlox,
KeeLoq, Kleer, LANCheck, LinkMD, maXStylus, maXTouch, MediaLB, megaAVR, Microsemi, Microsemi logo, MOST,
MOST logo, MPLAB, OptoLyzer, PackeTime, PIC, picoPower, PICSTART, PIC32 logo, PolarFire, Prochip Designer,
QTouch, SAM-BA, SenGenuity, SpyNIC, SST, SST Logo, SuperFlash, Symmetricom, SyncServer, Tachyon,
TempTrackr, TimeSource, tinyAVR, UNI/O, Vectron, and XMEGA are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
APT, ClockWorks, The Embedded Control Solutions Company, EtherSynch, FlashTec, Hyper Speed Control,
HyperLight Load, IntelliMOS, Libero, motorBench, mTouch, Powermite 3, Precision Edge, ProASIC, ProASIC Plus,
ProASIC Plus logo, Quiet-Wire, SmartFusion, SyncWorld, Temux, TimeCesium, TimeHub, TimePictra, TimeProvider,
Vite, WinPath, and ZL are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Adjacent Key Suppression, AKS, Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Any Capacitor, AnyIn, AnyOut, BlueSky, BodyCom,
CodeGuard, CryptoAuthentication, CryptoAutomotive, CryptoCompanion, CryptoController, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, Dynamic Average Matching, DAM, ECAN, EtherGREEN, In-Circuit Serial Programming, ICSP,
INICnet, Inter-Chip Connectivity, JitterBlocker, KleerNet, KleerNet logo, memBrain, Mindi, MiWi, MPASM, MPF,
MPLAB Certified logo, MPLIB, MPLINK, MultiTRAK, NetDetach, Omniscient Code Generation, PICDEM,
PICDEM.net, PICkit, PICtail, PowerSmart, PureSilicon, QMatrix, REAL ICE, Ripple Blocker, SAM-ICE, Serial Quad
I/O, SMART-I.S., SQI, SuperSwitcher, SuperSwitcher II, Total Endurance, TSHARC, USBCheck, VariSense,
ViewSpan, WiperLock, Wireless DNA, and ZENA are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A.
The Adaptec logo, Frequency on Demand, Silicon Storage Technology, and Symmcom are registered trademarks of
Microchip Technology Inc. in other countries.
GestIC is a registered trademark of Microchip Technology Germany II GmbH & Co. KG, a subsidiary of Microchip
Technology Inc., in other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies.
©
2019, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
ISBN: 978-1-5224-5413-7
Quality Management System
For information regarding Microchip’s Quality Management Systems, please visit http://www.microchip.com/quality.
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 20
Page 21

Worldwide Sales and Service
AMERICAS ASIA/PACIFIC ASIA/PACIFIC EUROPE
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-7200
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support:
http://www.microchip.com/support
Web Address:
http://www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Duluth, GA
Tel: 678-957-9614
Fax: 678-957-1455
Austin, TX
Tel: 512-257-3370
Boston
Westborough, MA
Tel: 774-760-0087
Fax: 774-760-0088
Chicago
Itasca, IL
Tel: 630-285-0071
Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
Addison, TX
Tel: 972-818-7423
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Novi, MI
Tel: 248-848-4000
Houston, TX
Tel: 281-894-5983
Indianapolis
Noblesville, IN
Tel: 317-773-8323
Fax: 317-773-5453
Tel: 317-536-2380
Los Angeles
Mission Viejo, CA
Tel: 949-462-9523
Fax: 949-462-9608
Tel: 951-273-7800
Raleigh, NC
Tel: 919-844-7510
New York, NY
Tel: 631-435-6000
San Jose, CA
Tel: 408-735-9110
Tel: 408-436-4270
Canada - Toronto
Tel: 905-695-1980
Fax: 905-695-2078
Australia - Sydney
Tel: 61-2-9868-6733
China - Beijing
Tel: 86-10-8569-7000
China - Chengdu
Tel: 86-28-8665-5511
China - Chongqing
Tel: 86-23-8980-9588
China - Dongguan
Tel: 86-769-8702-9880
China - Guangzhou
Tel: 86-20-8755-8029
China - Hangzhou
Tel: 86-571-8792-8115
China - Hong Kong SAR
Tel: 852-2943-5100
China - Nanjing
Tel: 86-25-8473-2460
China - Qingdao
Tel: 86-532-8502-7355
China - Shanghai
Tel: 86-21-3326-8000
China - Shenyang
Tel: 86-24-2334-2829
China - Shenzhen
Tel: 86-755-8864-2200
China - Suzhou
Tel: 86-186-6233-1526
China - Wuhan
Tel: 86-27-5980-5300
China - Xian
Tel: 86-29-8833-7252
China - Xiamen
Tel: 86-592-2388138
China - Zhuhai
Tel: 86-756-3210040
India - Bangalore
Tel: 91-80-3090-4444
India - New Delhi
Tel: 91-11-4160-8631
India - Pune
Tel: 91-20-4121-0141
Japan - Osaka
Tel: 81-6-6152-7160
Japan - Tokyo
Tel: 81-3-6880- 3770
Korea - Daegu
Tel: 82-53-744-4301
Korea - Seoul
Tel: 82-2-554-7200
Malaysia - Kuala Lumpur
Tel: 60-3-7651-7906
Malaysia - Penang
Tel: 60-4-227-8870
Philippines - Manila
Tel: 63-2-634-9065
Singapore
Tel: 65-6334-8870
Taiwan - Hsin Chu
Tel: 886-3-577-8366
Taiwan - Kaohsiung
Tel: 886-7-213-7830
Taiwan - Taipei
Tel: 886-2-2508-8600
Thailand - Bangkok
Tel: 66-2-694-1351
Vietnam - Ho Chi Minh
Tel: 84-28-5448-2100
Austria - Wels
Tel: 43-7242-2244-39
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark - Copenhagen
Tel: 45-4450-2828
Fax: 45-4485-2829
Finland - Espoo
Tel: 358-9-4520-820
France - Paris
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany - Garching
Tel: 49-8931-9700
Germany - Haan
Tel: 49-2129-3766400
Germany - Heilbronn
Tel: 49-7131-72400
Germany - Karlsruhe
Tel: 49-721-625370
Germany - Munich
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Germany - Rosenheim
Tel: 49-8031-354-560
Israel - Ra’anana
Tel: 972-9-744-7705
Italy - Milan
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Italy - Padova
Tel: 39-049-7625286
Netherlands - Drunen
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
Norway - Trondheim
Tel: 47-72884388
Poland - Warsaw
Tel: 48-22-3325737
Romania - Bucharest
Tel: 40-21-407-87-50
Spain - Madrid
Tel: 34-91-708-08-90
Fax: 34-91-708-08-91
Sweden - Gothenberg
Tel: 46-31-704-60-40
Sweden - Stockholm
Tel: 46-8-5090-4654
UK - Wokingham
Tel: 44-118-921-5800
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
© 2019 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS70005409A-page 21
 Loading...
Loading...