查询27C128供应商
27C128
128K (16K x 8) CMOS EPROM
FEATURES
• High speed performance
- 120 ns access time available
• CMOS Technology for low power consumption
- 20 mA Active current
- 100 µ A Standby current
• Factory programming available
• Auto-insertion-compatible plastic packages
• Auto ID aids automated programming
• Separate chip enable and output enable controls
• High speed “express” programming algorithm
• Organized 16K x 8: JEDEC standard pinouts
- 28-pin Dual-in-line package
- 32-pin PLCC Package
- 28-pin SOIC package
- Tape and reel
• Available for the following temperature ranges:
- Commercial: 0˚C to +70˚C
- Industrial: -40˚C to +85˚C
- Automotive: -40˚C to +125˚C
DESCRIPTION
The Microchip Technology Inc. 27C128 is a CMOS
128K bit (electrically) Programmable Read Only Memory. The device is organized as 16K words by 8 bits
(16K bytes). Accessing individual bytes from an
address transition or from power-up (chip enable pin
going low) is accomplished in less than 120 ns. CMOS
design and processing enables this part to be used in
systems where reduced power consumption and high
reliability are requirements.A complete family of packages is offered to provide the most flexibility in applications. For surface mount applications, PLCC, SOIC, or
TSOP packaging is available. Tape and reel packaging
is also available for PLCC or SOIC packages. UV erasable versions are also available.
A complete family of packages is offered to provide the
most flexibility in applications. For surface mount applications, PLCC or SOIC packaging is available. Tape
and reel packaging is also available for PLCC or SOIC
packages.
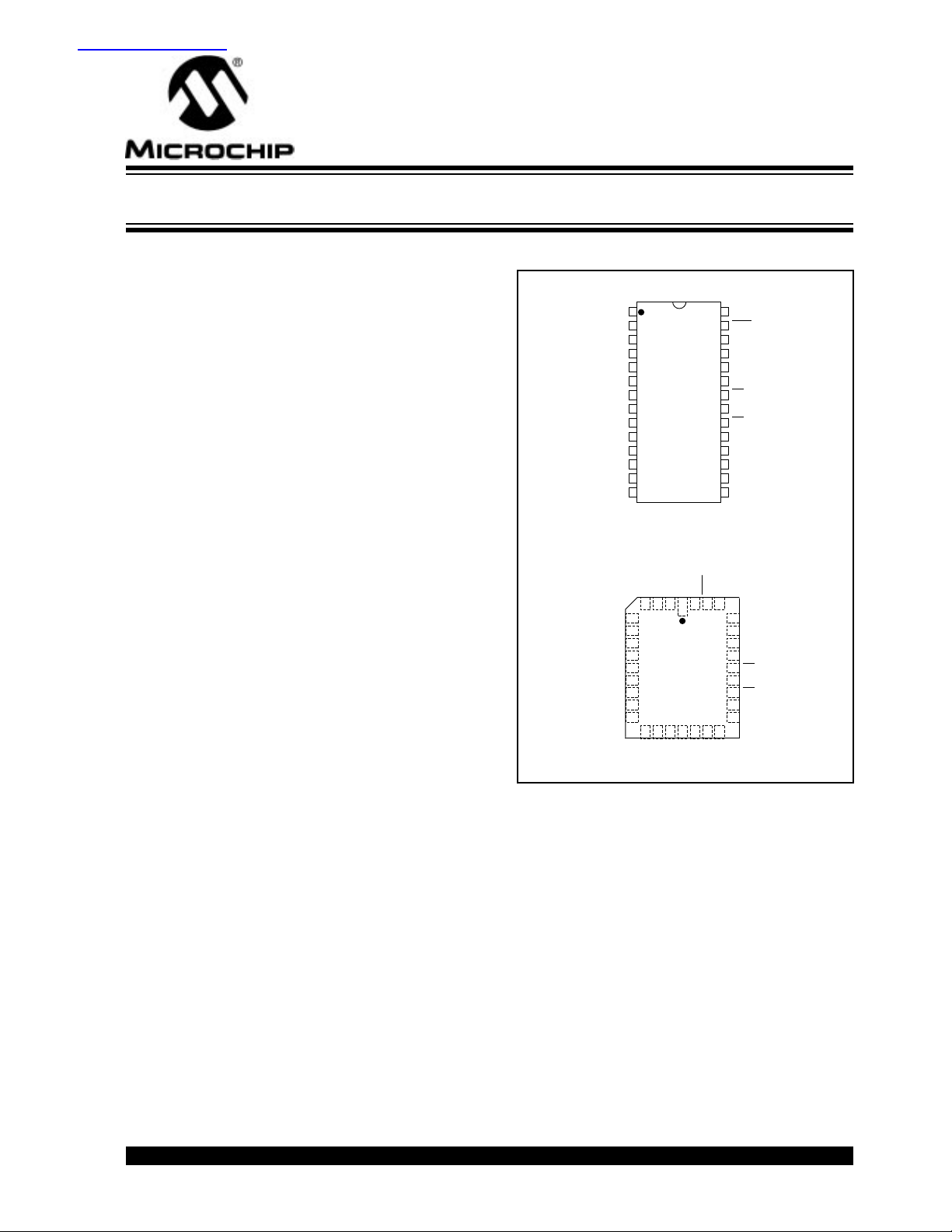
PACKAGE TYPES
DIP/SOIC
• 1
V
PP
A12
2
A7
3
A6
4
A5
5
A4
6
A3
7
A2
8
A1
9
A0
10
O0
11
O1
12
O2
13
V
14
SS
PLCC
A7
A12
432
5
A6
6
A5
7
A4
8
A3
9
A2
10
A1
11
A0
12
NC
13
O0
14151617181920
O1
O2
28
27
26
25
24
27C128
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
PP
V NUVcc
1
323130
27C128
SS
O3O4O5
NU
V
PGM
A13
V
CC
PGM
A13
A8
A9
A11
OE
A10
CE
O7
O6
O5
O4
O3
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
A8
A9
A11
NC
OE
A10
CE
O7
O6
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS11003K-page 1

27C128
µ
µ
µ
±
µ
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARA CTERISTICS
1.1 Maxim
CC
V
and input voltages w.r.t. V
voltage w.r.t. V
PP
V
um Ratings*
during
SS
SS
........-0.6V to +7.25V
TABLE 1-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
A0-A13 Address Inputs
programming..........................................-0.6V to +14V
Voltage on A9 w.r.t. V
Output voltage w.r.t. V
......................-0.6V to +13.5V
SS
SS
............... -0.6V to V
CC
+1.0V
Storage temperature ..........................-65˚C to +150˚C
Ambient temp. with power applied .....-65˚C to +125˚C
*Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum Ratings”
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operation listings of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
O0 - O7 Data Output
TABLE 1-2: READ OPERATION DC CHARACTERISTICS
CC
V
= +5V ( ± 10%)
Commercial: Tamb = 0˚C to +70˚C
Industrial: Tamb = -40˚C to +85˚C
Extended (Automotive): Tamb = -40 ° C to +125 ° C
Name Function
CE
OE
PGM
PP
V
V
CC
V
SS
Chip Enable
Output Enable
Program Enable
Programming Voltage
+5V Power Supply
Ground
NC No Connection; No Internal Connec-
tions
NU Not Used; No External Connection Is
Allowed
Parameter Part* Status Symbol Min. Max. Units Conditions
Input Voltages all Logic "1"
Logic "0"
Input Leakage all — I
Output Voltages all Logic "1"
Logic "0"
Output Leakage all — I
Input Capacitance all — C
V
IH
IL
V
LI
V
OH
OL
V
LO
IN
2.0
V
+1
CC
-0.5
0.8
-10 10
V
V
AV
2.4
0.45VV
-10 10
AV
— 6 pF V
IN
= 0 to V
I
= -400 µ A
OH
I
OL
= 2.1 mA
OUT
= 0V; Tamb = 25 ° C;
IN
CC
= 0V to V
CC
f = 1 MHz
Output Capacitance all — C
OUT
—12pFV
OUT
= 0V; Tamb = 25 ° C;
f = 1 MHz
Power Supply Current,
Active
C
I,E
TTL input
TTL input
CC1
I
CC2
I
—
—
2025mAmAV
CC
= 5.5V; V
f = 1 MHz;
OE
= CE = V
I
= 0 mA;
OUT
V
IL
= -0.1 to 0.8V;
IH
V
= 2.0 to V
IL
PP
CC
;
= V
;
CC
Note 1
CC
Power Supply Current,
Standby
I
Read Current
PP
V
Read Voltage
PP
* Parts: C=Commercial Temperature Range; I, E=Industrial and Extended Temperature Ranges
C
I, E
all
all
all
TTL input
TTL input
CMOS input
Read Mode
Read Mode
S
I
(
)—
I
PP
V
PP
—
—
V
CC
-0.7
2
3
100
100
V
CC
mA
mA
ACE
AVV
= V
= 5.5V
PP
CC
0.2V
Note 1: Typical active current increases .75 mA per MHz up to operating frequency for all temperature ranges.
DS11003K-page 2
1996 Microchip Technology Inc.
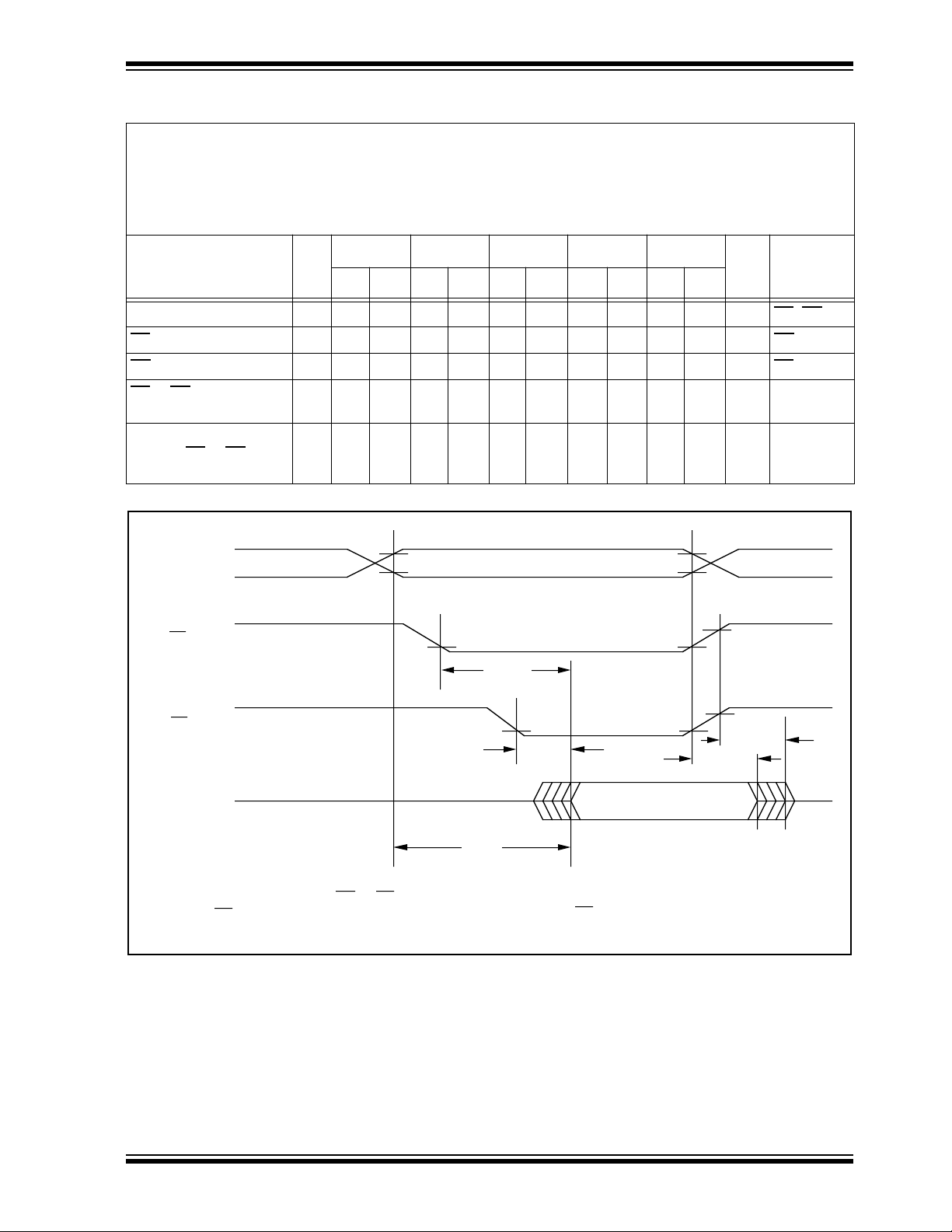
TABLE 1-3: READ OPERATION AC CHARACTERISTICS
27C128
AC Testing Waveform: V
Output Load: 1 TTL Load + 100 pF
Input Rise and Fall Times: 10 ns
Ambient Temperature: Commercial: Tamb = 0˚C to +70˚C
27C128-12 27C128-15 27C128-17 27C128-20 27C128-25
Parameter Sym
Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max Min Max
Address to Output Delay t
CE
to Output Delay t
OE to Output Delay t
or OE to O/P High
CE
— 120 — 150 — 170 — 200 — 250 ns CE
ACC
— 120 — 150 — 170 — 200 — 250 ns OE
CE
OE
— 65 — 70 — 70 — 75 — 100 ns CE=V
t
OFF
050050050055060ns
Impedance
Output Hold from
Address CE
or OE,
OH
0—0—0—0—0—ns
t
whichever occurs first
FIGURE 1-1: READ WAVEFORMS
IH
Address
V
VIL
IH
= 2.4V and V
IL
= 0.45V; V
OH
= 2.0V V
OL
= 0.8V
Industrial: Tamb = -40˚C to +85˚C
Extended (Automotive): Tamb = -40 ° C to +125 ° C
Units Conditions
Address Valid
=OE=V
=V
IL
IL
IL
CE
OE
Outputs
O0 - O7
Notes:
VIH
VIL
tCE(2)
VIH
VIL
OH
V
High Z
VOL
tACC
(1) tOFF is specified for OE or CE, whichever occurs first
(2) OE may be delayed up to t
CE - tOE after the falling edge of CE without impact on tCE
(3) This parameter is sampled and is not 100% tested.
tOE(2)
Valid Output
tOFF(1,3)
tOH
High Z
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS11003K-page 3
27C128
TABLE 1-4: PROGRAMMING DC CHARACTERISTICS
Ambient Temperature: Tamb = 25 ° C ± 5 ° C
CC
V
= 6.5V ± 0.25V, V
Parameter Status Symbol Min Max. Units Conditions
PP
= 13.0V ± 0.25V
µ
Input Voltages Logic”1”
Logic”0”
Input Leakage — I
Output Voltages Logic”1”
Logic”0”
V
Current, program & verify — I
CC
V
PP
Current, program — I
A9 Product Identification — V
Note 1: V
CC
must be applied simultaneously or before V
V
V
V
V
CC2
PP2
IH
LI
OH
OL
2.0
V
CC
+1
V
IL
-0.1
-10 10
2.4
0.8
0.45
V
AV
IN
VVI
OH
I
OL
= 0V to V
= -400 µ A
= 2.1 mA
CC
— 20 mA Note 1
— 25 mA Note 1
H
11.5 12.5 V
PP
and removed simultaneously or after V
PP
TABLE 1-5: PROGRAMMING AC CHARACTERISTICS
for Program, Program Verify AC Testing Waveform: V
and Program Inhibit Modes Ambient Temperature: Tamb=25°C± 5°C
V
CC= 6.5V ± 0.25V, VPP = VH = 13.0V ± 0.25V
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units Remarks
Address Set-Up Time t
Data Set-Up Time t
Data Hold Time t
Address Hold Time t
Float Delay (2) t
CC Set-Up Time tVCS 2—µs
V
Program Pulse Width (1) t
Set-Up Time tCES 2—µs
CE
Set-Up Time tOES 2—µs
OE
PP Set-Up Time tVPS 2—µs
V
Data Valid from OE
Note 1: For express algorithm, initial programming width tolerance is 100 µs ±5%.
2: This parameter is only sampled and not 100% tested. Output float is defined as the point where data is no
longer driven (see timing diagram).
=2.4V and V
IH
AS 2—µs
DS 2—µs
DH 2—µs
AH 0—µs
DF 0 130 ns
PW 95 105 µs 100 µs typical
=0.45V; V
IL
=2.0V; V
OH
OL=0.8V
tOE — 100 ns
DS11003K-page 4
1996 Microchip Technology Inc.

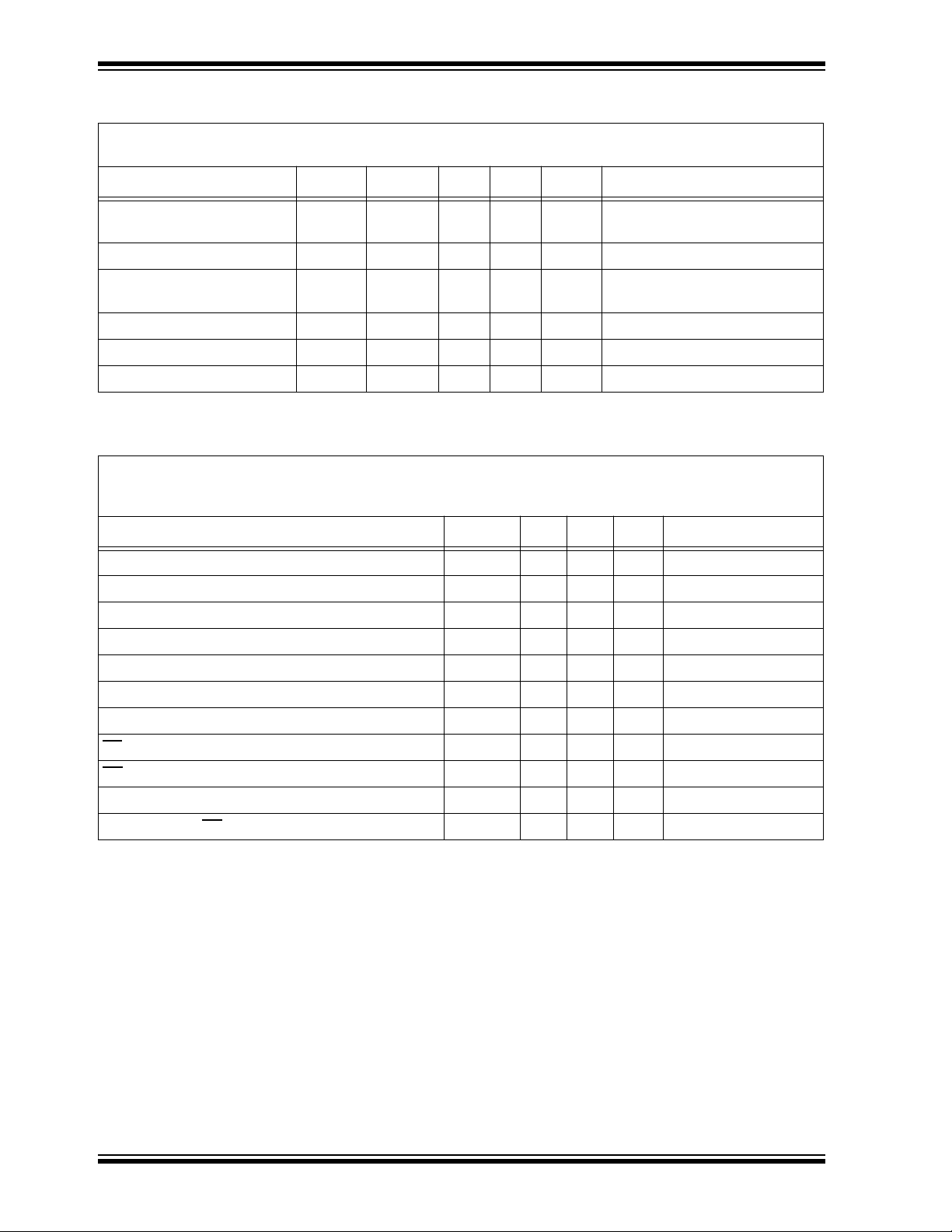
FIGURE 1-2: PROGRAMMING WAVEFORMS (1)
27C128
Address
Data
V
PP
VCC
CE
PGM
OE
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
13.0 V (3)
5.0 V
6.5 V (3)
5.0 V
IH
V
VIL
VIH
VIL
VIH
VIL
Program
Address Stable
tAS
tOES
High Z
tOE
(2)
Data In Stable Data Out Valid
tDS
tVPS
tVCS
tCES
tPW
tOPW
tDH
Verify
t
tDF
(2)
AH
Notes: (1)
The input timing reference is 0.8V for VIL and 2.0V for VIH.
(2)
t
DF and tOE are characteristics of the device but must be accommodated by the programmer.
(3)
Vcc = 6.5V ±0.25V, V
PP = VH = 13.0V ±0.25V for Express algorithm.
TABLE 1-6: MODES
Operation Mode CE OE PGM VPP A9 O0 - O7
Read V
Program VIL VIH VIL VH XDIN
Program Verify VIL VIL VIH VH XDOUT
Program Inhibit VIH XXVH X High Z
Standby V
Output Disable V
Identity V
X = Don’t Care
1.2 Read Mode
(See Timing Diagrams and AC Characteristics)
Read Mode is accessed when
a) the CE
b) the OE
pin is low to power up (enable) the chip
pin is low to gate the data to the output
pins
IL VIL VIH VCC XDOUT
IH XXVCC X High Z
IL VIH VIH VCC X High Z
IL VIL VIH VCC VH Identity Code
For Read operations, if the addresses are stable, the
address access time (t
CE
to output (tCE). Data is transferred to the output
after a delay from the falling edge of OE
ACC) is equal to the delay from
(tOE).
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS11003K-page 5

27C128
1.3 Standby Mode
The standby mode is defined when the CE pin is high
(VIH) and a program mode is not defined.
When these conditions are met, the supply current will
drop from 20 mA to 100 µA.
1.4 Output Enable
This feature eliminates bus contention in microprocessor-based systems in which multiple devices may drive
the bus. The outputs go into a high impedance state
when the following condition is true:
• The OE
and PGM pins are both high.
1.5 Erase Mode (U.V. Windowed Versions)
Windowed products offer the capability to erase the
memory array. The memory matrix is erased to the all
1’s state when exposed to ultraviolet light. To ensure
complete erasure, a dose of 15 watt-second/cm
required. This means that the device window must be
placed within one inch and directly underneath an ultraviolet lamp with a wavelength of 2537 Angstroms,
intensity of 12,000µW/cm
utes.
2
for approximately 20 min-
2
is
1.6 Programming Mode
The Express Algorithm has been developed to improve
the programming throughput times in a production
environment. Up to ten 100-microsecond pulses are
applied until the byte is verified. No overprogramming
is required. A flowchart of the express algorithm is
shown in Figure 1-3.
Programming takes place when:
a) V
CC is brought to the proper voltage,
b) V
PP is brought to the proper VH level,
c) the CE
d) the OE
e) the PGM
Since the erased state is “1” in the array, programming
of “0” is required. The address to be programmed is set
via pins A0-A13 and the data to be programmed is presented to pins O0-O7. When data and address are stable, OE
PGM
pin is low,
pin is high, and
pin is low.
is high, CE is low and a low-going pulse on the
line programs that location.
1.7 Verify
After the array has been programmed it must be verified to ensure all the bits have been correctly programmed. This mode is entered when all the following
conditions are met:
a) V
CC is at the proper level,
b) V
PP is at the proper VH level,
c) the CE
d) the PGM
e) the OE
line is low,
line is high, and
line is low.
1.8 Inhibit
When programming multiple devices in parallel with different data, only CE
control to each device. By pulsing the CE
low on a particular device in conjunction with the PGM
or CE line low, that device will be programmed; all other
devices with CE
grammed with the data, although address and data will
be available on their input pins (i.e., when a high level
is present on CE
from programming.
or PGM need be under separate
or PGM line
or PGM held high will not be pro-
or PGM); and the device is inhibited
1.9 Identity Mode
In this mode specific data is output which identifies the
manufacturer as Microchip Technology Inc. and device
type. This mode is entered when Pin A9 is taken to V
(11.5V to 12.5V). The CE and OE lines must be at VIL.
A0 is used to access any of the two non-erasable bytes
whose data appears on O0 through O7.
Pin Input Output
Identity
Manufacturer
Device Type*
* Code subject to change
A0
V
VIH
IL
07O6O5O4O3O2O1O
010010001000011129
H
e
0
x
83
H
DS11003K-page 6 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.

FIGURE 1-3: PROGRAMMING EXPRESS ALGORITHM
Conditions:
T
amb = 25˚C ±5˚C
V
CC = 6.5 ±0.25V
V
PP = 13.0 ±0.25V
ADDR = First Location
Program one 100 µs pulse
Start
V
CC = 6.5V
V
PP = 13.0V
X = 0
Increment X
27C128
Verify
Byte
Fail
No Yes
X = 10 ?
Last
Address?
No
Increment Address
CC = VPP = 4.5V, 5.5V
V
Pass
Yes
Device
Failed
Device
Passed
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS11003K-page 7
Yes No
All
bytes
= original
data?
Device
Failed

27C128
NOTES:
DS11003K-page 8 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.

NOTES:
27C128
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS11003K-page 9

27C128
NOTES:
DS11003K-page 10 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.

27C128
27C128 Product Identification System
To order or to obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, please use the listed part numbers, and refer to the factory or the listed
sales offices.
27C128 –25 I /P
Package: L = Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier (PLCC)
P = Plastic DIP (600 Mil)
SO = Plastic SOIC (300 Mil)
Temperature Blank = 0˚C to +70˚C
Range: I = -40˚C to +85˚C
E = -40˚C to +125˚C
Access 12 = 120 ns
Time: 15 = 150 ns
17 = 170 ns
20 = 200 ns
25 = 250 ns
Device: 27C128 128K (16K x 8) CMOS EPROM
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS11003K-page 11

WORLDWIDE SALES & SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
Microchip Technology Inc.
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 602 786-7200 Fax: 602 786-7277
Technical Support:
Web:
http://www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Microchip Technology Inc.
500 Sugar Mill Road, Suite 200B
Atlanta, GA 30350
Tel: 770 640-0034 Fax: 770 640-0307
Boston
Microchip Technology Inc.
5 Mount Royal Avenue
Marlborough, MA 01752
Tel: 508 480-9990 Fax: 508 480-8575
Chicago
Microchip Technology Inc.
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 708 285-0071 Fax: 708 285-0075
Dallas
Microchip Technology Inc.
14651 Dallas Parkway, Suite 816
Dallas, TX 75240-8809
Tel: 972 991-7177 Fax: 972 991-8588
Dayton
Microchip Technology Inc.
Suite 150
Two Prestige Place
Miamisburg, OH 45342
Tel: 513 291-1654 Fax: 513 291-9175
Los Angeles
Microchip Technology Inc.
18201 Von Karman, Suite 1090
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 714 263-1888 Fax: 714 263-1338
New Y ork
Microchip Technmgy Inc.
150 Motor Parkway, Suite 416
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Tel: 516 273-5305 Fax: 516 273-5335
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First Street, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408 436-7950 Fax: 408 436-7955
Toronto
Microchip Technology Inc.
5925 Airport Road, Suite 200
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1W1, Canada
Tel: 905 405-6279 Fax: 905 405-6253
602 786-7627
ASIA/PACIFIC
China
Microchip Technology
Unit 406 of Shanghai Golden Bridge Bldg.
2077 Yan’an Road West, Hongiao District
Shanghai, Peoples Republic of China
Tel: 86 21 6275 5700
Fax: 011 86 21 6275 5060
Hong Kong
Microchip Technology
RM 3801B, Tower Two
Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T. Hong Kong
Tel: 852 2 401 1200 Fax: 852 2 401 3431
India
Microchip Technology
No. 6, Legacy, Convent Road
Bangalore 560 025 India
Tel: 91 80 526 3148 Fax: 91 80 559 9840
Korea
Microchip Technology
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku,
Seoul, Korea
Tel: 82 2 554 7200 Fax: 82 2 558 5934
Singapore
Microchip Technology
200 Middle Road
#10-03 Prime Centre
Singapore 188980
Tel: 65 334 8870 Fax: 65 334 8850
Taiwan, R.O.C
Microchip Technology
10F-1C 207
Tung Hua North Road
Taipei, Taiwan, ROC
Tel: 886 2 717 7175 Fax: 886 2 545 0139
EUROPE
United Kingdom
Arizona Microchip Technology Ltd.
Unit 6, The Courtyard
Meadow Bank, Furlong Road
Bourne End, Buckinghamshire SL8 5AJ
Tel: 44 1628 850303 Fax: 44 1628 850178
France
Arizona Microchip Technology SARL
Zone Industrielle de la Bonde
2 Rue du Buisson aux Fraises
91300 Massy - France
Tel: 33 1 69 53 63 20 Fax: 33 1 69 30 90 79
Germany
Arizona Microchip Technology GmbH
Gustav-Heinemann-Ring 125
D-81739 Muenchen, Germany
Tel: 49 89 627 144 0 Fax: 49 89 627 144 44
Italy
Arizona Microchip Technology SRL
Centro Direzionale Colleone Pas Taurus 1
Viale Colleoni 1
20041 Agrate Brianza
Milan Italy
Tel: 39 39 6899939 Fax: 39 39 689 9883
JAPAN
Microchip Technology Intl. Inc.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shin Yokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Y okohama
Kanagawa 222 Japan
Tel: 81 45 471 6166 Fax: 81 45 471 6122
9/3/96
All rights reserved. 1996, Microchip Technology Incorporated, USA. 9/96
Printed on recycled paper.
Information contained in this publication regarding device applications and the like is intended through suggestion only and may be superseded by updates. No representation or warranty is given and no liability is assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement
of patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical components in life support systems is not authorized except with express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual property rights. The Microchip logo and
name are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. All rights reserved. All other trademarks mentioned herein are the property of their respective companies.
DS11003K-page 12 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...