Page 1
Not recommended for new designs –
Please use 25AA160A/B or 25LC160A/B.
25AA160/25LC160/25C160
16K SPI™ Bus Serial EEPROM
Device Selection Table
Part
Number
25AA160 1.8-5.5V 1 MHz I
25LC160 2.5-5.5V 2 MHz I
25C160 4.5-5.5V 3 MHz I,E
VCC
Range
Max Clock
Frequency
Temp
Ranges
Features:
• Low-power CMOS technology:
- Write current: 3 mA maximum
- Read current: 500 µA typical
- Standby current: 500 nA typical
• 2048 x 8-bit organization
• 16 byte page
• Write cycle time: 5 ms max.
• Self-timed erase and write cycles
• Block write protection:
- Protect none, 1/4, 1/2 or all of array
• Built-in write protection:
- Power on/off data protection circuitry
- Write enable latch
- Write-protect pin
• Sequential read
• High reliability:
- Endurance: 1 M cycles
- Data retention: > 200 years
- ESD protection: > 4000V
• 8-pin PDIP and SOIC packages
• Temperature ranges supported:
- Industrial (I): -40°Cto +85°C
- Automotive (E) (25C160): -40°C to +125°C
Description:
The Microchip Technology Inc. 25AA160/25LC160/
25C160 (25XX160
Erasable PROMs. The memory is accessed via a
simple Serial Peripheral Interface™ (SPI™) compatible serial bus. The bus signals required are a clock
input (SCK) plus separate data in (SI) and data out
(SO) lines. Access to the device is co ntrolled throu gh a
Chip Select (CS
Communication to the device can be paused via the
hold pin (HOLD
tions on its inputs will be ignored, with the exception of
chip select, allowing the host to service higher priority
interrupts.
*
) are 16 Kbit Serial Electrically
) input.
). While the device is paused, transi-
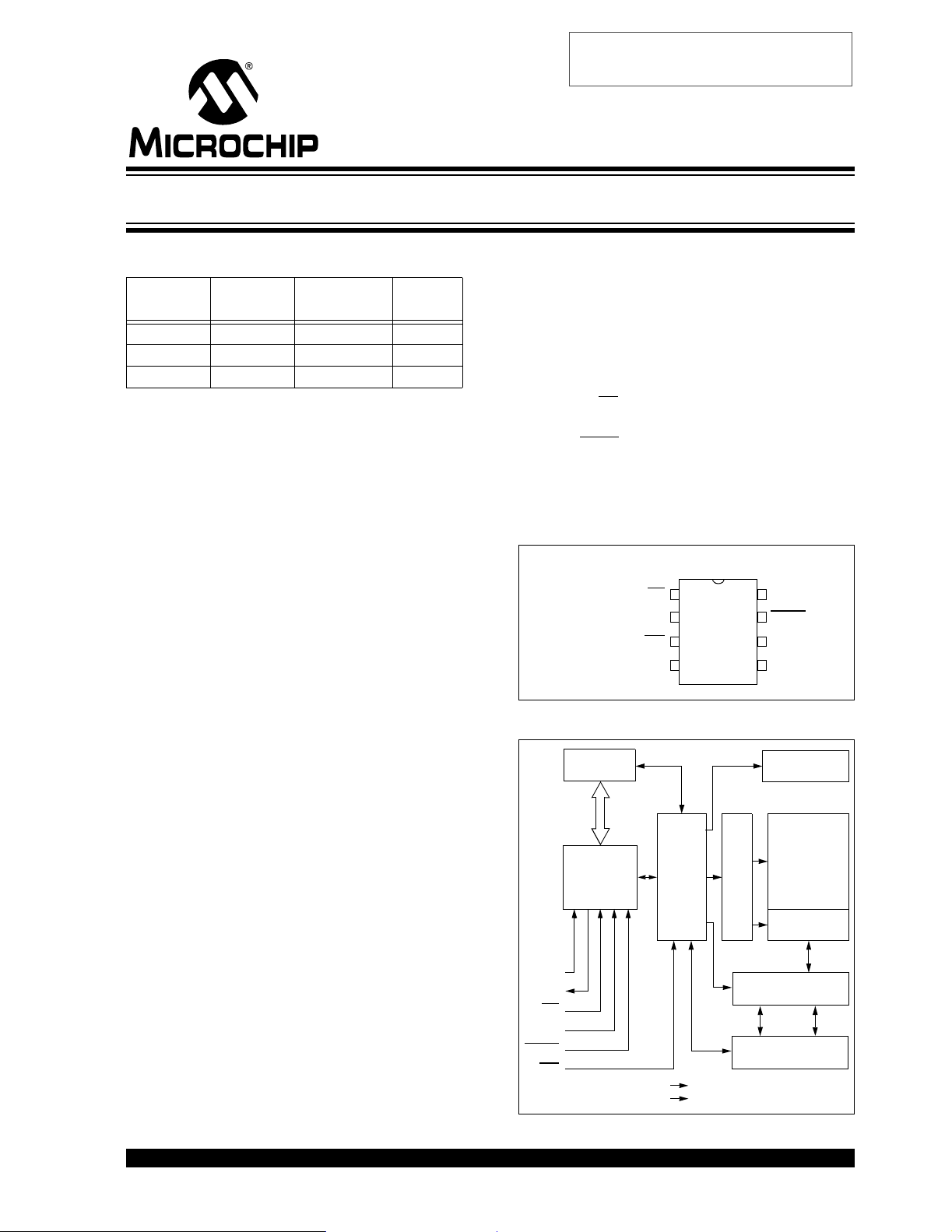
Package Types
PDIP/SOIC
V
CS
SO
WP
VSS
1
25XX160
2
3
4
CC
8
HOLD
7
SCK
6
SI
5
Block Diagram
Status
Register
I/O Control
Logic
Memory
Control
Logic
X
Dec
HV Generato r
EEPROM
Array
Page Latches
SI
SO
CS
SCK
HOLD
WP
*25XX160 is used in this document as a generic part number
for the 25AA160/25LC160/25C160 devices
SPI™ is a trademark of Motorola Inc.
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 1
.
VCC
VSS
Y Decoder
Sense Amp.
R/W Control
Page 2
25AA160/25LC160/25C160
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
(†)
VCC.............................................................................................................................................................................7.0V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. V
SS ........................................................................................................ -0.6V to VCC + 1.0V
Storage temperature .................................................................................................................................-65°C to 150°C
Ambient temperature under bias...............................................................................................................-40°C to 125°C
Soldering temperature of leads (10 seconds).......................................................................................................+300°C
ESD protection on all pins.........................................................................................................................................4KV
† NOTICE: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This
is a stress rating only a nd fu nc tional operation of the device at tho se or an y other conditions above those indi cated in
the operational listings of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for an extended
period of t i me may affect device reliability.
1.1 DC Characteristics
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Param.
No.
D1 V
D2 VIH2 0.7 VCC VCC+1 V VCC< 2.7V (Note)
Sym. Characteristics Min. Max. Units Conditions
IH1 High-level input
voltage
D3 VIL1 Low-level input
D4 V
IL2 -0.3 0.3 VCC VVCC < 2.7V (Note)
voltage
D5 VOL Low -level output
D6 VOL —0.2VIOL = 1.0 mA, VCC < 2.5V
D7 V
OH High-level output
voltage
Industrial (I): T
Automotive (E): T
2.0 VCC+1 V VCC ≥ 2.7V (Note)
-0.3 0.8 V VCC ≥ 2.7V (Note)
—0.4VIOL = 2.1 mA
VCC -0.5 — V IOH = -400 µA
voltage
D8 I
D9 ILO Output leakage
LI Input leakage current -10 10 µACS = VCC, VIN = VSS TO VCC
-10 10 µACS = VCC, VOUT = VSS TO VCC
current
D10 CINT Internal Capacitanc e
—7pFTA = 25°C, CLK = 1.0 MHz,
(all inputs and
outputs)
D11 I
D12 I
CC Read
Operating Current
CC Write —
—
—
—
D13 ICCS Standby Current —
—
Note: This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
A = -40°C to +85°C VCC = 1.8V to 5.5V
A = -40°C to +125°C VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V (25C160 only )
V
CC = 5.0V (Note)
1
500
mAµAVCC = 5.5V; FCLK = 3.0MHz;
SO = Open
VCC = 2.5V; FCLK = 2.0MHz;
SO = Open
5
3
5
1
mAmAVCC = 5.5V
CC = 2.5V
V
µAµACS = VCC = 5.5V, Inputs tied to VCC or
V
SS
CS = VCC = 2.5V, Inputs tied to VCC or
SS
V
DS21231D-page 2 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 3
1.2 AC Characteristics
25AA160/25LC160/25C160
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Param.
No.
1F
2T
3T
4T
5T
6T
7T
8T
9T
10 T
11 T
12 T
13 T
Sym. Characteristic Min. Max. Units Conditions
CLK Clock Frequency —
CSS CS Setup Time 100
CSH CS Hold Time 150
CSD CS Disable Time 500 — ns —
SU Data Setup Time 30
HD Data Hold Time 50
R CLK Rise Time — 2 µs (Note 1)
F CLK Fall Time — 2 µs (Note 1)
HI Clock High Time 150
LO Clock Low Time 150
CLD Clock Delay Time 50 — ns —
CLE Clock Enable Time 50 — ns —
V Output Valid from Cloc k
Low
14 T
15 T
16 T
17 T
18 T
HO Output Hold Time 0 — ns (Note 1)
DIS Output Disable Time —
HS HOLD Setup Time 100
HH HOLD Hold Time 100
HZ HOLD Low to Output High-
Z
19 T
20 T
HV HOLD High to Output Valid 100
WC Internal Write Cycle Time — 5 ms —
Industrial (I): T
Automotive (E): T
—
—
250
500
250
475
50
50
100
100
230
475
230
475
—
—
—
—
—
100
200
100
200
100
150
200
150
200
A = -40°C to +85°C VCC = 1.8V to 5.5V
A = -40°C to +125°C VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V (25C160 only)
3
2
1
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
150
230
475
200
250
500
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
MHz
MHz
MHz
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
ns
21 — Endurance 1 M — E/W
Cycles
Note 1: This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
2: This parameter is not tested but ensured by characterization. For endurance estimates in a specific application, please
consult the Total Endurance
™
Model which can be obtained from Microchip’s web site at: www.microchip.com.
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
CC = 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
CC = 4.5V to 5.5V (Note1)
V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V (Note1)
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V (Note1)
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
V
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V (Note1)
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V (Note1)
V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V (Note1)
VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V
CC = 2.5V to 4.5V
V
V
CC = 1.8V to 2.5V
(Note 2)
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 3
Page 4
25AA160/25LC160/25C160
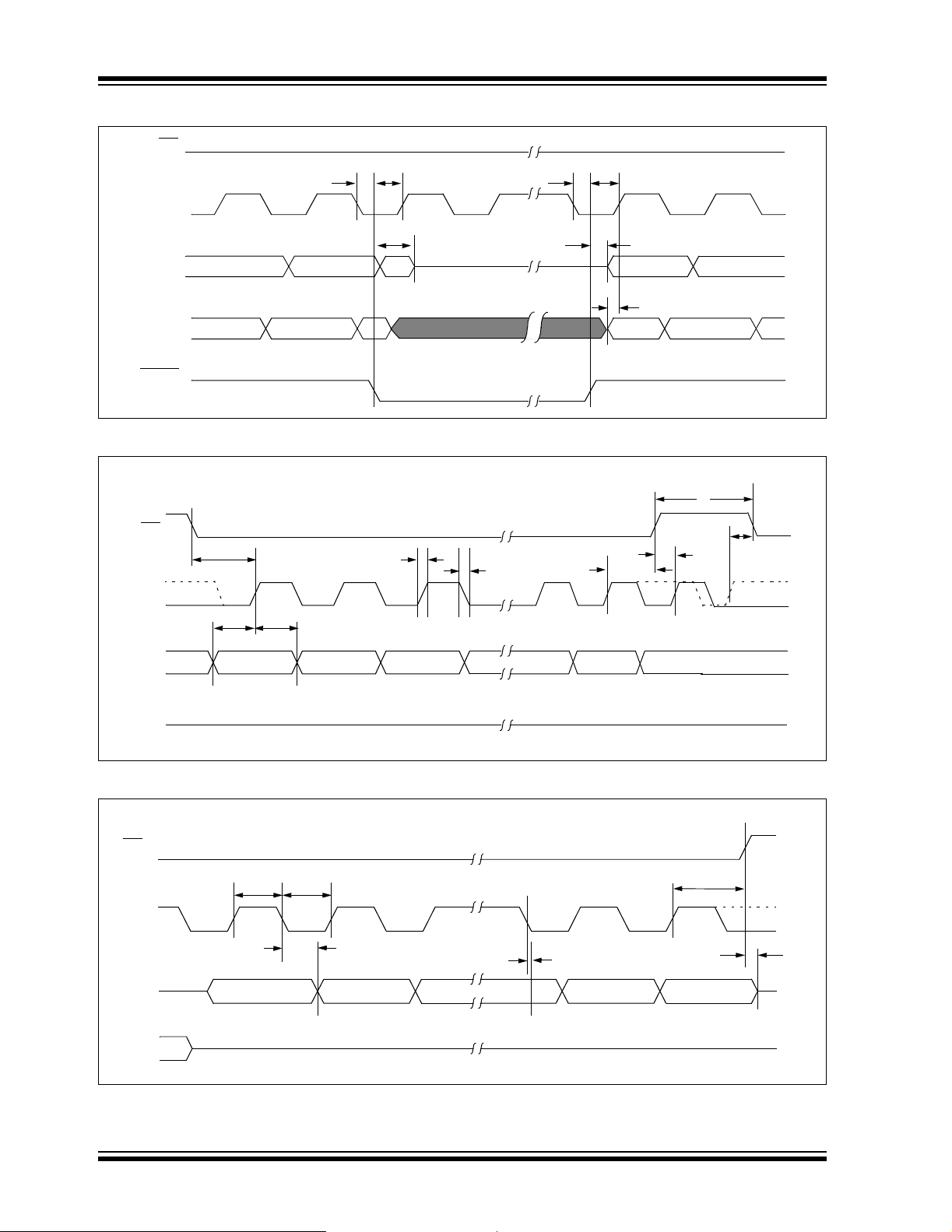
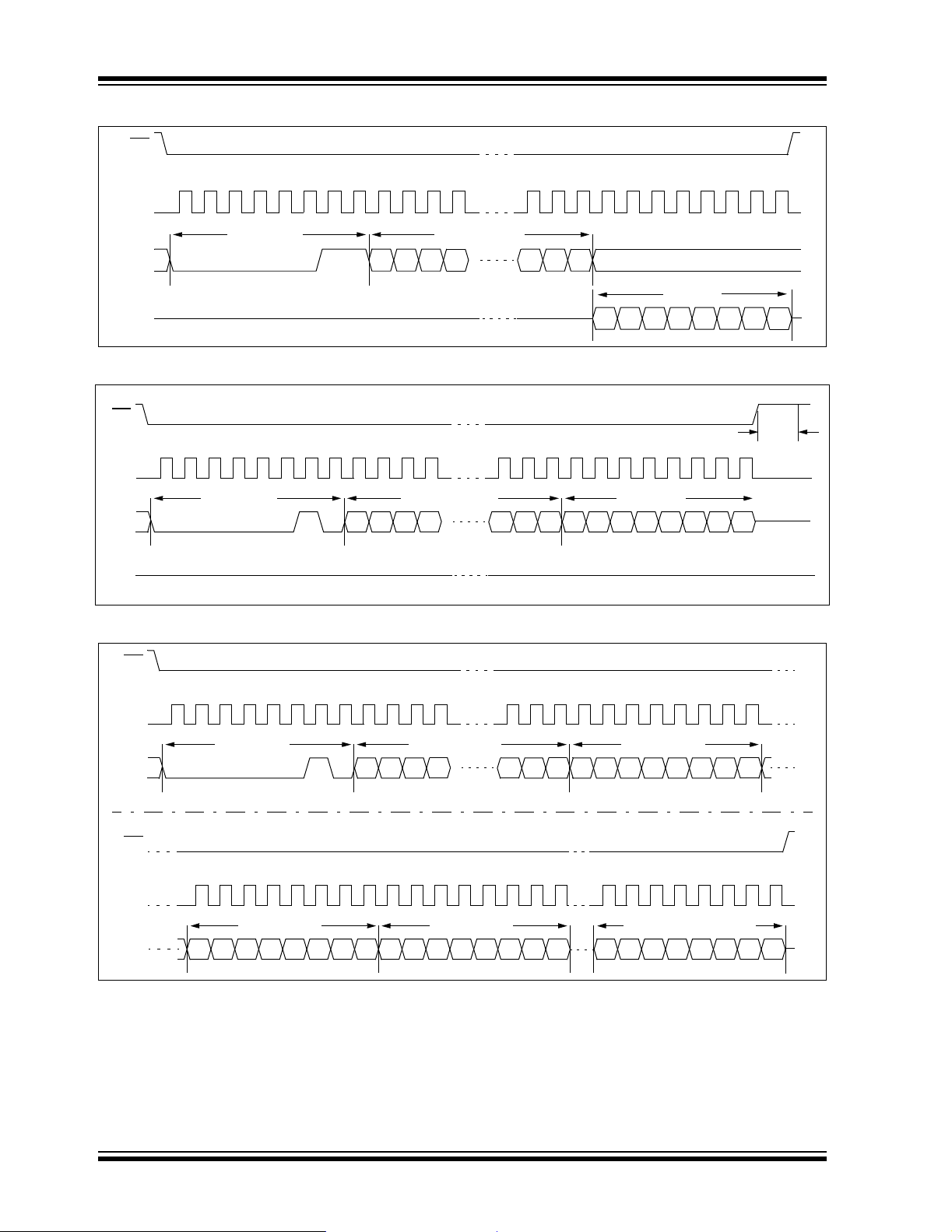
FIGURE 1-1: HOLD TIMING
CS
17
High-impedance
SCK
SO
16 16 17
n+2 n+1 n n-1
1918
n
SI
HOLD
n+2 n+1 n
FIGURE 1-2: SERIAL INPUT TIMING
CS
SCK
SI
SO
2
Mode 1,1
Mode 0,0
65
MSB in
High-impedance
7
don’t care
8
3
LSB in
5
n
n-1
4
12
11
FIGURE 1-3: SERIAL OUTPUT TIMING
CS
9
10
SCK
13
SO
SI
DS21231D-page 4 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
MSB out
don’t care
14
3
Mode 1,1
Mode 0,0
15
ISB out
Page 5
25AA160/25LC160/25C160
1.3 AC Test Conditions
AC Waveform:
VLO = 0.2V —
HI = VCC - 0.2V (Note 1)
V
VHI = 4.0V (Note 2)
Timing Measurement Reference Lev el
Input 0.5 V
Output 0.5 VCC
Note 1: For VCC ≤ 4.0V
2: For V
CC > 4.0V
CC
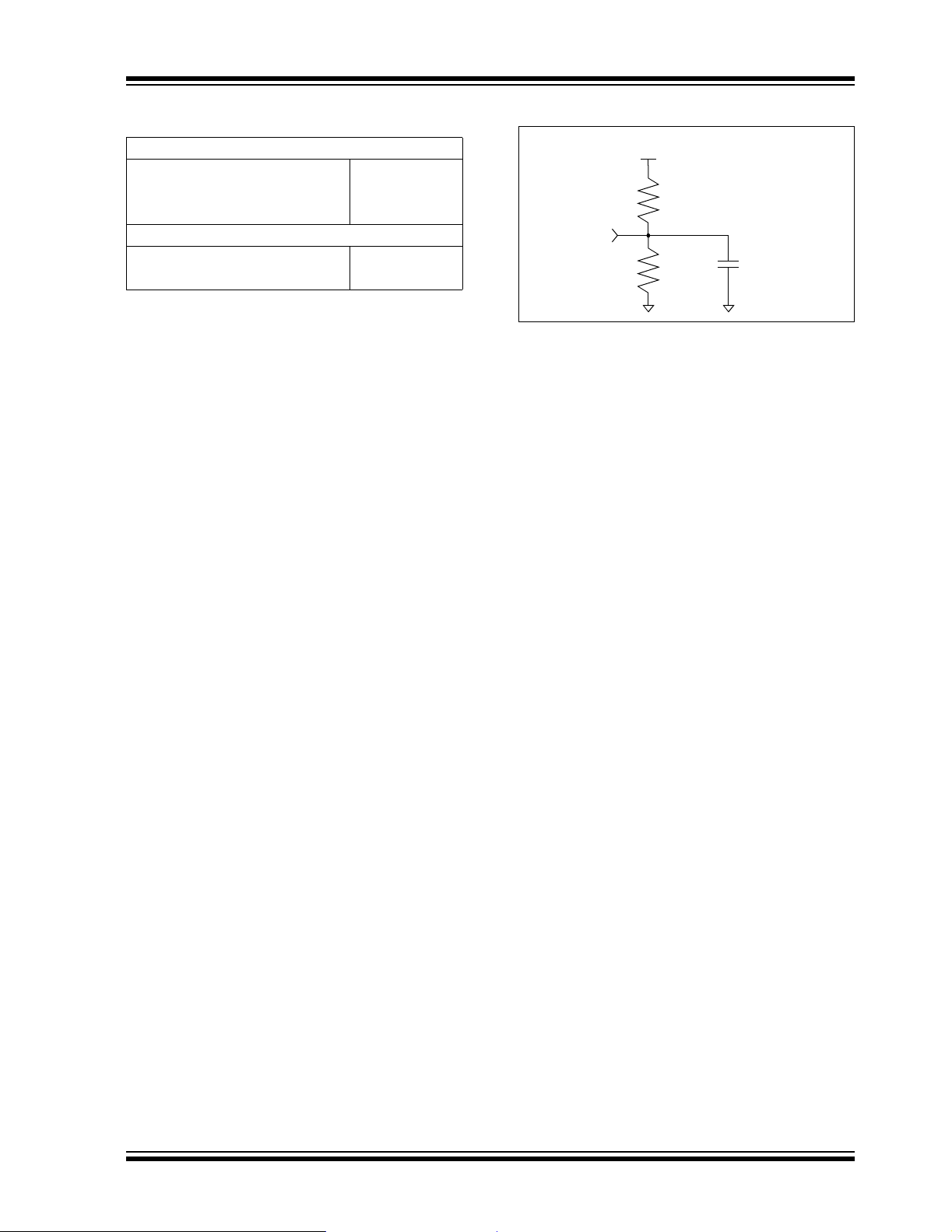
FIGURE 1-4: AC TEST CIRCUIT
VCC
2.25 KΩ
SO
1.8 KΩ
100 pF
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 5
Page 6

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
2.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
The descriptions of the pins are listed in Table 2-1.
TABLE 2-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Name PDIP SOIC Description
CS
SO 2 2 Serial Data Output
WP
SS 4 4 Ground
V
SI 5 5 Serial Data Input
SCK 6 6 Serial Clock Input
HOLD
Vcc 8 8 Supply Voltage
11
3 3 Write- Protect Pi n
7 7 Hold Input
2.1 Chip Select (CS)
A low level on this pin selects the device. A high level
deselects the device and forces it into Standby mode.
However, a programming cycle which is already initiated or in progres s will be co mplet ed, reg ardl ess of th e
CS input signal. If CS is brought high duri ng a progra m
cycle, the device will go into Standby mode as soon as
the programming cyc le is comp lete. When the device is
deselected, SO goes to the high-impedance state,
allowing multiple parts to share the same SPI bus. A
low-to-high transition on CS
sequence initiates an internal write cycle. After powerup, a low level on CS is r equ ired p r ior to any sequence
being initiated.
Chip Select Input
after a valid write
2.4 Serial Input (SI)
The SI pin is used to transfer data into the device. It
receives instructions, addresses and data. Data is
latched on the rising edge of the serial clock.
2.5 Serial Clock (SCK)
The SCK is used to synchronize the communication
between a master and the 25XX160. Instructions,
addresses, or data present on the SI pin are latched on
the rising edge of t he c lo ck input, while data on the SO
pin is updated after the falling edge of the clock input.
2.6 Hold (HOLD)
The HOLD pin is used to suspend transmission to the
25XX160 while in the middle of a serial sequence
without having to retra nsmit the e ntire sequ ence agai n.
It must be held hi gh an y tim e this f unct ion is not be ing
used. Once the device is selected and a serial
sequence is underway, the HOLD
low to pause further serial communication without
resetting the serial sequence. The HOLD pin must be
brought low while SCK is low, otherwise the HOLD
function will not be invoked until the next SCK high-tolow transition. The 25XX160 must remain selected
during this sequenc e. The SI, SC K, an d SO p ins a re i n
a high-impedance state during the time the device is
paused and transitions on these p ins will be ignored. To
resume serial communication, HOLD
high while the SCK p in is lo w, otherwise seria l com munication will not resum e. Lowering the HOLD lin e at any
time will tri-state the SO line.
pin may be pulled
must be brought
2.2 Serial Output (SO)
The SO pin is used to transfer data out of the 25XX160.
During a read cycle, data is shifted out on this pin after
the falling edge of the serial clock.
2.3 Write-Protec t (WP)
This pin is used in conjunction with the WPEN bit in the
Status register to prohibit writes to the nonvolatile bits
in the Status register. When WP is low and WPEN is
high, writing to the no nvolatil e bits in the Status register
is disabled. All other operations function normally.
When WP
nonvolatile bits in the Status register operate normally.
If the WPEN bit is set, WP
write sequence will disable writing to the Status
register. If an internal write cycle has already begun,
WP
The WP
the Status register is low. This allows the user to install
the 25XX160 in a system with WP pin grounded and
still be able to write to the Status register. The WP
functions will be enabled when the WPEN bit is set
high.
is high, all functions, including writes to the
low during a Status register
going low will have no effect on the write.
pin function is blocked when the WPEN bit in
pin
DS21231D-page 6 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 7

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
3.0 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
3.1 Principles of Operation
The 25XX160 are 2048 byte Serial EEPROMs
designed to interf ace di rec tly with the Serial Peripheral
Interface (SPI) port of many of today’s popular microcontroller families, including Microchip’s PIC16C6X/7X
microcontrollers. It may also interface with microcontrollers that do not have a built-i n SPI port by usin g discrete I/O lines progra mmed prop erly with th e softwar e.
The 25XX160 conta ins an 8-bit instr uction regi ster . The
device is accessed via the SI pin, with data being
clocked in on the rising edge of SCK. The CS
be low and the HOLD
operation. The WP
writing to the memory array.
Table 3-1 contains a list of the possible instruction
bytes and format for device operation. All instructions,
addresses, and data are transferred MSB first, LSB
last.
Data is sampled on the fir st rising edge of SCK after CS
goes low. If the clock line is shared with other peripheral devices on the SPI bus, the user can assert the
HOLD input and pl ace the 25X X160 in ‘HO LD’ mode.
After releasing the HOLD
from the point when the HOLD
pin must be high fo r the entire
pin must be held high to allow
pin, operation will resume
was asserted.
3.2 Read Sequence
The device is selected by pulling CS low. The 8-bit
READ instruction is transmitted to the 25XX160
followed by the 16-bit address, with the five MSBs of
the address being "don’t care" bits. After the correct
READ instruction and addre ss are sen t, th e da ta stored
in the memory at the select ed addres s is shifte d out on
the SO pin. T h e da ta st or ed i n t h e me mo r y a t t he n ex t
address can be read sequentially by continuing to
provide clock pulses. The internal address pointer is
automatical ly increment ed to the next h igher address
after each byte of data is shifted out. When the hig hes t
address is reached (07FFh), the address counter rolls
over to address 0000h allowing the read cycle to be
continued indefi nitely. The read operat ion is te rminated
by raising the CS
pin (Figure 3-1).
pin must
3.3 Write Sequence
Prior to any attempt to write data to the 25XX160, the
write enable latch must be set by issuing the WREN
instruction (Figure3-4). This is done by setting CS
and then clocking out the proper instruction into the
25XX160. After all eight bi ts of the in struction are transmitted, the CS
enable latch. If the write operation is initiated immediately after the WREN instruction without CS being
brought high, the data will not be written to the array
because the write enable latch will not have been
properly set.
Once the write enable latch is set, the user may
proceed by setting the C S
tion, followed by the 16 -bit add ress, wit h the fiv e MSB s
of the address be ing "don’t care" bit s, and then the data
to be written. Up to 16 bytes of data can be sent to the
25XX160 before a write cycle is necessary. The only
restriction is that all of the bytes must reside in the
same page. A pa ge ad dress b egins with
0000 and ends with xxxx xxxx xxxx 1111.
xxxx
If the internal address counter reaches
xxxx
1111 and the clock continues, the counter will
roll back to the first address of the page and overwrite
any data in the page that may have been written.
For the data to be actually written to the array, the CS
must be brought high after the Leas t Significant bit (D0)
of the n
brought high at any other time, the write operation will
not be completed. Refer to Figure 3-2 and Figure 3-3
for more detailed illustrations on the byte write
sequence and the page write sequence respectively.
While the write is in progress, the Status register may
be read to check the status of the WPEN, WIP, WEL,
BP1, and BP0 bits (Figure 3-6). A read attempt of a
memory array location will not be possible during a
write cycle. When the write cycle is completed, the
write enable latch is reset.
must be brought high to set the write
low, issuing a WRITE instruc-
xxxx xxxx
xxxx xxxx
th
data byte has been clocked in. If CS is
low
TABLE 3-1: INSTRUCTION SET
Instruction Name Instruction Format Description
READ 0000 0011 Read data from memory array beginning at selected address
WRITE 0000 0010 Write data to memory array beginning at selected address
WRDI 0000 0100 Reset the write enable latch (disable write operations)
WREN 0000 0110 Set the write enable latch (enable write operations)
RDSR 0000 0101 Read Status register
WRSR 0000 0001 Write Status register
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 7
Page 8
25AA160/25LC160/25C160
FIGURE 3-1: READ SEQUENCE
CS
0 234567891011 21222324252627282930311
SCK
instruction 16-bit address
SI
0100000115 14 13 12 210
High-impedance
SO
FIGURE 3-2: BYTE WRITE SEQUENCE
CS
8
91011 2122232425262728293031
SCK
SI
SO
0 2345671
instruction 16-bit address data byte
0000000115 14 13 12
High-impedance
FIGURE 3-3: PAGE WRITE SEQUENCE
CS
0 23456718
SCK
9 1011 2122232425262728293031
data out
76543210
Twc
21076543210
instruction 16-bit add ress data byte 1
SI
CS
32 34 35 36 37 38 3933
SCK
data byte 2
SI
DS21231D-page 8 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
76543210
0000000115 14 13 12
41 42 43 46 47
40
data byte 3
76543210
21076543210
44 45
data byte n (16 max)
76543210
Page 9

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
3.4 Write Enable (WREN) and Write
Disable (WRDI)
The 25XX160 contains a write enable latch. See
Table 3-3 for the Write-Protect Functionality Matrix.
This latch must be set before any write operation w ill be
completed internally. The WREN instruction will set the
latch, and the WRDI will reset the latch.
FIGURE 3-4: WRITE ENABLE SEQUENCE
CS
0 2345671
SCK
SI
SO
010000 01
High-impedance
The following is a list of conditions under which the
write enable latch will be reset:
• Power-up
• WRDI instruction successfully executed
• WRSR instruction successfully executed
• WRITE instruction successfully executed
FIGURE 3-5: WRITE DISABLE SEQUENCE
CS
0 2345671
SCK
SI
SO
010000 01
High-impedance
0
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 9
Page 10

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
3.5 Read Status Register (RDSR)
The Read Status Register (RDSR) instruction provides
access to the Status register. The Status register may
be read at any time, even during a write cycle. The
Status register is formatted as follows:
7 654 3 2 1 0
WPEN X X X BP1 BP0 WEL WIP
The Write-In-Process (WIP) bit indicates whether the
25XX160 is busy with a write operation. When set to a
1’, a write is in progress, when set to a ‘0’, no write is
‘
in progress. This bit is read-only.
The Wri te Enable Lat ch (WEL) bit indicat es the st atus
of the write enable latch. When set to a ‘1’, the latch
allows writes to the array, when set to a ‘
prohibits writes to the array. The state of this bit can
always be updated via the WREN or WRDI comma nds
regardless of the state of write protection on the Status
register. This bit is read-only.
The Block Protection (BP0 and BP1) bits indicate
which blocks are currently write-protected. These bits
are set by the user issuing the WRSR instruction. These
bits are nonvolatile.
See Figure 3-6 for the RDSR timing sequence.
FIGURE 3-6: READ STATUS REGISTER TIMING SEQUENCE
CS
8
0 2345671
SCK
instruction
9101112131415
0’, the latch
SI
High-impedance
SO
11000000
3.6 Write Status Register (WRSR)
The Write Status register (WRSR) instruction allows the
user to select one of four levels of protection for the
array by writing to the appropriate bits in the Status
register. The array is divided up into four segments.
The user has the ability to write-protect none, one, two
or all four of the segment s of the array. The partitioning
is controlled as shown in Table 3-2.
The Write-Protect Enable (WPEN) bit is a nonvolatile
bit that is available as an enable bi t for the WP
Write-Protect (WP
(WPEN) bit in the Status register control the programmable hardware write-protect feature. Hardware write
protection is enabled when WP
WPEN bit is high. Hardw are write protec tion is disa bled
when either the WP pin is high or the WPEN bit is low.
When the chip is hardware write-protected, only writes
to nonvolatile bits in the Status register are disabled.
See T a ble 3-3 for a matrix of functionality on the WPEN
bit.
See Figure 3-7 for the WRSR timing sequence.
) pin and the Write-Protect Enable
pin is low and the
pin. The
data from Status register
7654 210
3
TABLE 3-2: ARRAY PROTECTION
BP1 BP0
0 0 none
0 1 upper 1/4
1 0 upper 1/2
11 all
Array Addresses
Write-Protected
(0600h - 07FFh)
(0400h - 07FFh)
(0000h - 07FFh)
DS21231D-page 10 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 11

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
FIGURE 3-7: WRITE STATUS REGISTER TIMING SEQUENCE
CS
0 23456718
SCK
instruction data to Status register
SI
SO
01000000
High-impedance
3.7 Data Protection
The following protection has been implemented to
prevent inadvertent writes to the array:
• The write enable latch is reset on power-up
•A WRITE ENABLE instruction must be issued to
set the write enable latch
• After a byte write, page write, or Status register
write, the write enable latch is reset
must be set high after the proper number of
•CS
clock cycles to start an internal write cycle
• Access to the array during an internal write cycle
is ignored and programming is continued
9101112131415
7654 210
3
3.8 Power On State
The 25XX160 powers on in the following state:
• The device is in lo w powe r Standby mode (CS
• The write enable latch is reset
• SO is in high-impedance state
• A low level on CS
is required to enter active state
=1)
TABLE 3-3: WRITE-PROTECT FUNCTIONALITY MATRIX
WPEN WP WEL Protected Blocks Unprotected Blocks Status Register
XX0
0X1
1
X
Low
High
1
1
Protected Protected Protected
Protected Writable Writable
Protected Writable Protected
Protected Writable Writable
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 11
Page 12

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
4.0 PACKAGING INFORMATION
4.1 Package Marking Information
8-Lead PDIP (300 mil)
XXXXXXXX
XXXXXNNN
YYWW
8-Lead SOIC (150 mil)
XXXXXXXX
XXXXYYWW
NNN
Example:
25LC160
I/PNNN
YYWW
Example:
25C160
I/SNYYWW
NNN
Legend: XX...X Customer specific information*
YYear code (last digit of calendar year)
YYYear code (last 2 digits of calendar year)
WWWeek code (week of January 1 is week ‘01’)
NNNAlphanume ric trac ea bil ity code
Note: In the event the full Mic r ochip part number cannot be ma rke d on one line, it
will be carried over to the next line thus limiting the number of available
characters for customer specific information.
* Standard PICmicro device marking consists of Microchip part number, year code, week code, and
traceability code. For PICmicro device marking beyond this, certain price adders apply. Please check with
your Microchip Sales Office. For QTP devices, any special marking adders are included in QTP price.
DS21231D-page 12 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 13

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
8-Lead Plastic Dual In-line (P) – 300 mil (PDIP)
E1
D
2
n
E
β
eB
Number of Pins
Pitch
Top to Seating Plane A .140 .155 .170 3.56 3.94 4.32
Molded Package Thickness A2 .115 .130 .145 2.92 3.30 3.68
Base to Seating Plane A1 .015 0.38
Shoulder to Shoulder Width E .300 .313 .325 7.62 7.94 8.26
Molded Package Width E1 .240 .250 .260 6.10 6.35 6.60
Overall Length D .360 .373 .385 9.14 9.46 9.78
Tip to Seating Plane L .125 .130 .135 3.18 3.30 3.43
Lead Thickness
Upper Lead Width B1 .045 .058 .070 1.14 1.46 1.78
Lower Lead Width B .014 .018 .022 0.36 0.46 0.56
Overall Row Spacing § eB .310 .370 .430 7.87 9.40 10.92
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-001
Drawing No. C04-018
Dimension Limits MIN NOM MAX MIN NOM MAX
1
α
A
c
Units INCHES* MILLIMETERS
n
p
c
α
β
.008 .012 .015 0.20 0.29 0.38
A1
B1
B
88
.100 2.54
51015 51015
51015 51015
A2
L
p
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 13
Page 14

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
8-Lead Plastic Small Outline (SN) – Narrow, 150 mil (SOIC)
E
E1
p
D
2
B
Number of Pins
Pitch
Foot Angle
Lead Thickness
Mold Draft Angle Top
Mold Draft Angle Bottom
* Controlling Parameter
§ Significant Characteristic
Notes:
Dimensions D and E1 do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed
.010” (0.254mm) per side.
JEDEC Equivalent: MS-012
Drawing No. C04-057
n
45°
c
β
n
p
φ
c
α
β
1
h
A
φ
L
048048
A1
MILLIMETERSINCHES*Units
1.27.050
α
A2
MAXNOMMINMAXNOMMINDimension Limits
88
1.751.551.35.069.061.053AOverall Height
1.551.421.32.061.056.052A2M old ed Packag e Thickness
0.250.180.10.010.007.004A1Standoff §
6.206.025.79.244.237.228EOverall Width
3.993.913.71.157.154.146E1Molded Package Width
5.004.904.80.197.193.189DOverall Length
0.510.380.25.020.015.010hChamfer Distance
0.760.620.48.030.025.019LFoot Length
0.250.230.20.010.009.008
0.510.420.33.020.017.013BLead Width
1512015120
1512015120
DS21231D-page 14 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 15

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
APPENDIX A: REVISION HISTORY
Revision D
Added note to page 1 header (Not recommended for
new designs).
Updated document format.
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 15
Page 16

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
NOTES:
DS21231D-page 16 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 17

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
ON-LINE SUPPORT
Microchip provides on-line support on the Microchip
World Wide Web site.
The web site is used b y Mic rochip as a me ans to m ake
files and information easily available to customers. To
view the site, the use r must have access to the Intern et
and a web browser, such as Netscape
Internet Explorer. Files are also available for FTP
download from our FTP site.
Connecting to the Microchip Internet
Web Site
The Microchip web site is available at the following
URL:
www.microchip.com
The file transfer site is available by using an FTP
service to connect to:
ftp://ftp.microchip.com
The web site and file transfer site provide a variety of
services. Users may download files for the latest
Development Tools, Data Sheets, Application Notes,
User's Guides, Articles and Sample Programs. A variety of Micr ochip specific bu siness informatio n is also
available, including listings of Microchip sales offices,
distributors and factory representatives. Other data
available for consideration is:
• Latest Microchip Press Releases
• Technical Support Section with Frequently Asked
Questions
• Design Tips
• Device Errata
• Job Postings
• Microchip Consultant Program Member Listing
• Links to other useful web sites related to
Microchip Products
• Conferences for p roducts, D evelopment Systems,
technical information and more
• Listing of seminars and events
®
or Microsoft
SYSTEMS INFORMATION AND UPGRADE HOT LINE
The Systems Information and Upgrade Line provides
system users a listing of the latest versions of all of
Microchip's development systems software products.
®
Plus, this line provides information on how customers
can receive the most c urrent upgrade kit s. The Hot Line
Numbers are:
1-800-755-2345 for U.S. and most of Canada, and
1-480-792-7302 for the rest of the world.
042003
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 17
Page 18

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
READER RESPONSE
It is our intentio n to pro vi de you with the best documentation possible to ens ure suc c es sfu l u se of y ou r M ic roc hip product. If you wish to provid e your c omment s on org anizatio n, clarity, subject matter , and ways in w hich o ur document atio n
can better serve you, please FAX your comments to the Technical Publications Manager at (480) 792-4150.
Please list the following information, and use this outline to provide us with your comments about this document.
To:
RE: Reader Response
From:
Application (optional):
Would you like a reply? Y N
Device: Literature Number:
Questions:
1. What are the best features of this document?
2. How does this document meet your hardware and software development needs?
3. Do you find the organization of this document easy to follow? If not, why?
Technical Publications Manager
Name
Company
Address
City / State / ZIP / Country
Telephone: (_______) _________ - _________
Total Pages Sent ________
FAX: (______) _________ - _________
DS21231D25AA160/25LC160/25C160
4. What additions to the document do you think would enhance the structure and subject?
5. What deletions from the document could be made without affecting the overall usefulness?
6. Is there any incorrect or misleading information (what and where)?
7. How would you improve this document?
DS21231D-page 18 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 19

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION SYSTEM
To order or obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, refer to the factory or the listed sales office.
PART NO. X /XX XXX
Device
Device 25AA160: 16 Kbit 1.8V SPI Serial EEPROM
Temperature Range I = -40°C to +85°C
Range
25AA160T: 16 Kbit 1.8V SPI Serial EEPROM (Tape and Reel)
25LC160: 16 Kbit 2.5V SPI Serial EEPROM
25LC160T: 16 Kbit 2.5V SPI Serial EEPROM (Tape and Reel)
25C160: 16 Kbit 5.0V SPI Serial EEPROM
25C160T: 16 Kbit 5.0V SPI Serial EEPROM (Tape and Reel)
E= -40°C to +125°C
PatternPackageTemperature
Examples:
a) 25AA160-I/P: Industrial Temp.,
PDIP package
b) 25AA160-I/SN: Industrial Temp.,
SOIC package
c) 25LC160-I/SN: Industrial Temp.,
SOIC package
d) 25LC160T-I/SN: Tape and Reel,
Industrial Temp., SOIC package
e) 25C160-E/P: Extended Temp.,
PDIP package
f) 25C160-E/SN: Extended Temp.,
SOIC package
Package P = Plastic DIP (300 mil body), 8-lead
SN = Plastic SOIC (150 mil body), 8-lead
Sales and Support
Data Sheets
Products supported by a preliminary Data Sheet may have an errata sheet describing minor operational differences and
recommended workarounds. To determine if an errata sheet exists for a particular device, please contact one of the following:
1. Your local Microchip sales office
2. The Microchip Corporate Literature Center U.S. FAX: (480) 792-7277
3. The Microchip Worldwide Site (www.microchip.com)
Please specify which device, revision of silicon and Data Sheet (include Literature #) you are using.
New Customer Notification System
Register on our web site (www.microchip.com/cn) to receive the most current information on our products.
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 19
Page 20

25AA160/25LC160/25C160
NOTES:
DS21231D-page 20 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
Page 21

Note the following details of the code protection feature on Microchip devices:
• Microchip products meet the specification contained in their particular Microchip Data Sheet.
• Microchip believes that its family of products is one of the most secure families of its kind on the market today, when used in the
intended manner and under normal conditions.
• There are dishonest and possibly illegal methods used to breach the code protection feature. All of these methods, to our
knowledge, require using the Microchip products in a manner outside the operating specifications contained in Microchip’s Data
Sheets. Most likely, the person doing so is engaged in theft of intellectual property.
• Microchip is willing to work with the customer who is concerned about the integrity of their code.
• Neither Microchip nor any other semiconductor manufacturer can guarantee the security of their code. Code protection does not
mean that we are guaranteeing the product as “unbreakable.”
Code protection is constantly evolving. We at Microchip are com mitted to continuously improving the code protect ion f eatures of our
products. Attempts to break Microchip’s code protection feature may be a violation of the Digit al Mill ennium Copyright Act. If such acts
allow unauthorized access to your software or other copyrighted work, you may have a right to sue for relief under that Act.
Information contained in this publication regarding device
applications and the like is intended through suggestion only
and may be superseded by updates. It is your responsibility to
ensure that your application meets with your specifications.
No representation or warranty is given and no liability is
assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect
to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement of
patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such
use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical
components in life support systems is not authorized except
with express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are
conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual
property rights.
Trademarks
The Microchip name and logo, the Microchip logo, Accuron,
dsPIC, K
EELOQ, microID, MPLAB, PIC, PICmicro, PICSTART,
PRO MATE, PowerSmart, rfPIC, and SmartShunt are
registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated
in the U.S.A. and other countries.
AmpLab, FilterLab, MXDEV, MXLAB, PICMASTER, SEEVAL,
SmartSensor and The Embedded Control Solutions Company
are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology
Incorporated in the U.S.A.
Analog-for-the-Digital Age, Application Maestro, dsPICDEM,
dsPICDEM.net, dsPICworks, ECAN, ECONOMONITOR,
FanSense, FlexROM, fuzzyLAB, In-Circuit Serial
Programming, ICSP, ICEPIC, Migratable Memory, MPASM,
MPLIB, MPLINK, MPSIM, PICkit, PICDEM, PICDEM.net,
PICLAB, PICtail, PowerCal, PowerInfo, PowerMate,
PowerTool, rfLAB, rfPICDEM, Select Mode, Smart Serial,
SmartTel and Total Endurance are trademarks of Microchip
Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries.
SQTP is a service mark of Microchip T echnology Incorporated
in the U.S.A.
All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their
respective companies.
© 2004, Microchip Technology Incorporated, Printed in the
U.S.A., All Rights Reserved.
Printed on recycled paper.
Microchip received ISO/TS-16949:2002 quality system certification for
its worldwide headquarters, design and wafer fabrication facilities in
Chandler and Tempe, Arizona and Mountain View, California in
October 2003. The Company’s quality system processes and
procedures are for its PICmicro
devices, Serial EEPROMs, microperipherals, nonvolatile memory and
analog products. In addition, Microchip’s quality system for the design
and manufacture of development systems is ISO 9001:2000 certified.
®
8-bit MCUs, KEELOQ
®
code hopping
2004 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21231D-page 21
Page 22

WORLDWIDE SALES AND SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 480-792-72 00
Fax: 480-792-7277
Technical Support: 480-792-7627
Web Address: www.microchip.com
Atlanta
3780 Mansell Road, Suite 130
Alpharetta, GA 30022
Tel: 770-640- 003 4
Fax: 770-640-0307
Boston
2 Lan Drive, Suite 120
Westford, MA 01886
Tel: 978-692- 384 8
Fax: 978-692-3821
Chicago
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 630-285- 007 1
Fax: 630-285-0075
Dallas
16200 Addison Road, Suite 255
Addison Plaza
Addison, TX 75001
Tel: 972-818- 742 3
Fax: 972-818-2924
Detroit
Tri-Atria Office Building
32255 Northwestern Highway, Suite 190
Farmington Hills, MI 48334
Tel: 248-538- 225 0
Fax: 248-538-2260
Kokomo
2767 S. Albright Road
Kokomo, IN 46902
Tel: 765-864- 836 0
Fax: 765-864-8387
Los Angeles
25950 Acero St., Suite 200
Mission Viejo, CA 92691
Tel: 949-462- 952 3
Fax: 949-462-9608
San Jose
1300 Terra Bella Avenue
Mountain View, CA 94043
Tel: 650-215- 144 4
Fax: 650-961-0286
Toronto
6285 Northam Drive, Suite 108
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1X5, Cana da
Tel: 905-673- 069 9
Fax: 905-673-6509
ASIA/PACIFIC
Australia
Microchip Technology Australia Pty Ltd
Unit 32 41 Rawson Street
Epping 2121, NSW
Sydney, Australia
Tel: 61-2-986 8-6 73 3
Fax: 61-2-9868-6755
China - Beijing
Unit 706B
Wan Tai Bei Hai Bldg.
No. 6 Chaoyangmen Bei Str.
Beijing, 100027, China
Tel: 86-10-85 282 10 0
Fax: 86-10-85282104
China - Chengdu
Rm. 2401-2402, 24th Floor,
Ming Xing Financial Tower
No. 88 TIDU Street
Chengdu 610016, China
Tel: 86-28-86 766 20 0
Fax: 86-28-86766599
China - Fuzhou
Unit 28F, World Trade Plaza
No. 71 Wusi Road
Fuzhou 350001, China
Tel: 86-591-7 503 50 6
Fax: 86-591-7503521
China - Hong Kong SAR
Unit 901-6, Tower 2, Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T., Hong Kong
Tel: 852-2401 -12 00
Fax: 852-2401-3431
China - Shanghai
Room 701, Bldg. B
Far East International Plaza
No. 317 Xian Xia Road
Shanghai, 200051
Tel: 86-21-62 75- 57 00
Fax: 86-21-6275-5060
China - Shenzhen
Rm. 1812, 18/F, Building A, United Plaza
No. 5022 Binhe Road, Futian District
Shenzhen 518033, China
Tel: 86-755-8 290 13 80
Fax: 86-755-8295-1393
China - Shunde
Room 401, Hongjian Building, No. 2
Fengxiangnan Road, Ronggui Town, Shunde
District, Foshan City, Guangdong 528303, China
Tel: 86-757-28395507 Fax: 86-757-28395571
China - Qingdao
Rm. B505A, Fullhope Plaza,
No. 12 Hong Kong Central Rd.
Qingdao 266071, China
Tel: 86-532-5027355 Fax: 86-532-5027205
India
Divyasree Chambers
1 Floor, Wing A (A3/A4)
No. 11, O’Shaugnessey Road
Bangalore, 560 025, India
Tel: 91-80-22 290 06 1 Fax: 91- 80 -22 29 006 2
Japan
Yusen Shin Yokohama Building 10F
3-17-2, Shin Yokohama, Kohoku-ku,
Yokohama, Kanagawa, 222-0033, Japan
Tel: 81-45-47 1- 616 6 Fax: 81-4 5-4 71 -6122
Korea
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku
Seoul, Korea 135-882
Tel: 82-2-554-7200 Fax: 82-2-558-5932 or
82-2-558-5934
Singapore
200 Middle Road
#07-02 Prime Centre
Singapore, 188980
Tel: 65-6334-8870 Fax: 65-6334-8850
Taiwan
Kaohsiung Branch
30F - 1 No. 8
Min Chuan 2nd Road
Kaohsiung 806, Taiwan
Tel: 886-7-536-4816
Fax: 886-7-536-4817
Taiwan
Taiwan Branch
11F-3, No. 207
Tung Hua North Road
Taipei, 105, Taiwan
Tel: 886-2-2717-7175 Fax: 886-2-2545-0139
Taiwan
Taiwan Branch
13F-3, No. 295, Sec. 2, Kung Fu Road
Hsinchu City 300, Taiwan
Tel: 886-3-572-9526
Fax: 886-3-572-6459
EUROPE
Austria
Durisolstrasse 2
A-4600 Wels
Austria
Tel: 43-7242-2244-399
Fax: 43-7242-2244-393
Denmark
Regus Business Centre
Lautrup hoj 1-3
Ballerup DK-2750 Denmark
Tel: 45-4420-9895 Fax: 45-4420-9910
France
Parc d’Activite du Moulin de Massy
43 Rue du Saule Trapu
Batiment A - ler Etage
91300 Massy, France
Tel: 33-1-69-53-63-20
Fax: 33-1-69-30-90-79
Germany
Steinheilstrasse 10
D-85737 Ismaning, Germany
Tel: 49-89-627-144-0
Fax: 49-89-627-144-44
Italy
Via Salvatore Quasimodo, 12
20025 Legnano (MI)
Milan, Italy
Tel: 39-0331-742611
Fax: 39-0331-466781
Netherlands
Waegenburghtplein 4
NL-5152 JR, Drunen, Netherlands
Tel: 31-416-690399
Fax: 31-416-690340
United Kingdom
505 Eskdale Road
Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham
Berkshir e, England RG41 5T U
Tel: 44-118-921-5869
Fax: 44-118-921-5820
07/12/04
DS21231D-page 22 2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...