C
查询24AA32供应商
24AA32
2
32K 1.8V I
C
Smart Serial EEPROM
FEATURES
• Voltage operating range: 1.8V to 6.0V
- Peak write current 3 mA at 6.0V
- Maximum read current 150 µ A at 6.0V
- Standby current 1 µ A typical
• Industry standard two-wire bus protocol, I
compatible
- Including 100 kHz (1.8V) and 400 kHz (5V)
modes
• Self-timed ERASE and WRITE cycles
• Power on/off data protection circuitry
• Endurance:
- 10,000,000 Erase/Write (E/W) cycles guaran-
teed for High Endurance Block
- 1,000,000 E/W cycles guaranteed for Stan-
dard Endurance Block
• 8 byte page, or byte modes available
• 1 page x 8 line input cache (64 bytes) for fast write
loads
• Schmitt trigger, filtered inputs for noise suppression
• Output slope control to eliminate ground bounce
• 2 ms typical write cycle time, byte or page
• Factory programming (QTP) available
• Up to 8 devices may be connected to the same
bus for up to 256K bits total memory
• Electrostatic discharge protection > 4000V
• Data retention > 200 years
• 8-pin PDIP/SOIC packages
• Temperature ranges
- Commercial (C): 0 ° C to +70 ° C
2
DESCRIPTION
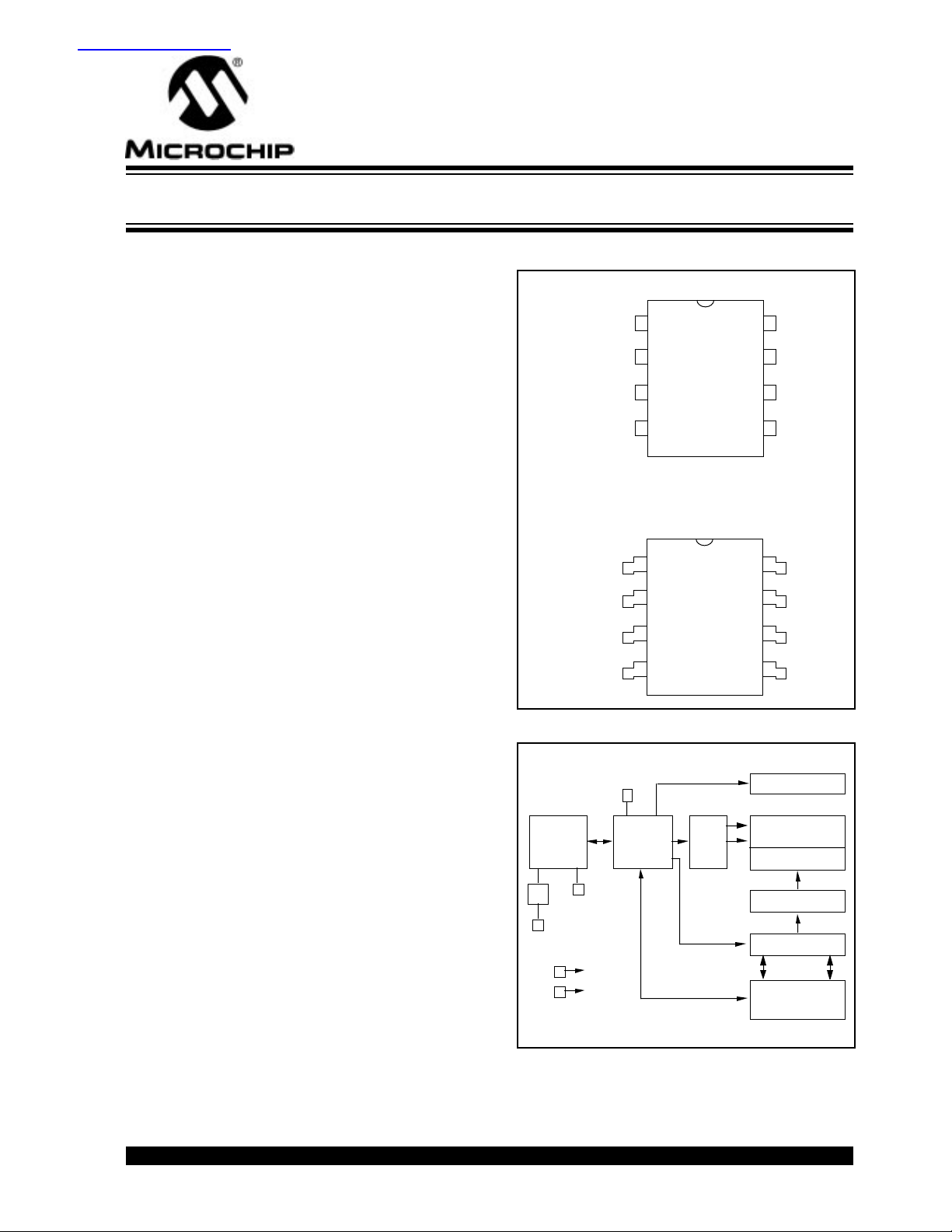
P ACKA GE TYPES
PDIP
A0
1
A1
2
A2
3
V
4
SS
SOIC
A0
A1
A2
V
SS
1
2
3
4
BLOCK DIAGRAM
A0..A2
24AA32
24AA32
8
VCC
7
NC
6
SCL
5
SDA
8
V
CC
7
NC
6
SCL
5
SDA
HV GENERATOR
The Microchip T echnology Inc. 24AA32 is a 4K x 8 (32K
bit) Serial Electrically Erasable PROM capable of operation across a broad voltage range (1.8V to 6.0V). This
device has been developed for advanced, low power
applications such as personal communications or data
acquisition. The 24AA32 features an input cache for
fast write loads with a capacity of eight 8-byte pages, or
64 bytes. It also features a fixed 4K-bit block of ultrahigh endurance memory for data that changes frequently. The 24AA32 is capable of both random and
sequential reads up to the 32K boundary. Functional
address lines allow up to 8 - 24AA32 devices on the
same bus, for up to 256K bits address space. Advanced
CMOS technology and broad voltage range make this
device ideal for low-power/low voltage, nonvolatile code
2
I
C is a trademark of Philips Corporation.
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21124C-page 1
I/O
CONTROL
LOGIC
I/O
SCL
SDA
CC
V
VSS
and data applications. The 24AA32 is available in the
standard 8-pin plastic DIP and 8-pin surface mount
SOIC package.
MEMORY
CONTROL
LOGIC
XDEC
EEPROM ARRAY
PAGE LATCHES
Cache
YDEC
SENSE AMP
R/W CONTROL
24AA32
µ
µ
µ
1.0 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1.1 Maxim
V
CC
..................................................................................7.0V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. V
Storage temperature..................................... -65˚C to +150˚C
Ambient temp. with power applied................ -65˚C to +125˚C
Soldering temperature of leads (10 seconds)............. +300˚C
ESD protection on all pins ..................................................≥ 4 kV
*Notice: Stresses above those listed under “Maximum Ratings”
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at those or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational listings
of this specification is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
TABLE 1-2: DC CHARACTERISTICS
A0, A1, A2, SCL and SDA pins:
um Ratings*
SS
...............-0.6V to V
Parameter Symbol Min Max Units Conditions
CC
+1.0V
TABLE 1-1: PIN FUNCTION TABLE
Name Function
A0..A2 User Configurable Chip Selects
V
SS
SDA Serial Address/Data I/O
SCL Serial Clock
V
CC
NC
CC
V
= +1.8V to 6.0V
Commercial (C): Tamb = 0˚C to +70˚C
Industrial (I): Tamb = -40˚C to +85˚C
Ground
+1.8V to 6.0V Power Supply
No Internal Connection
High level input voltage V
Low level input voltage V
Hysteresis of Schmitt Trigger inputs V
Low level output voltage V
Input leakage current I
Output leakage current I
Pin capacitance
(all inputs/outputs)
Operating current I
Standby current I
Note: This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.
I
CC
CC
IH
IL
HYS
OL
LI
LO
C
IN
C
OUT
Write
Read
CCS
.7 V
CC
— .3 Vcc V
CC
.05 V
— .40 V I
-10 10
-10 10
,
—10pFV
—
—
—5
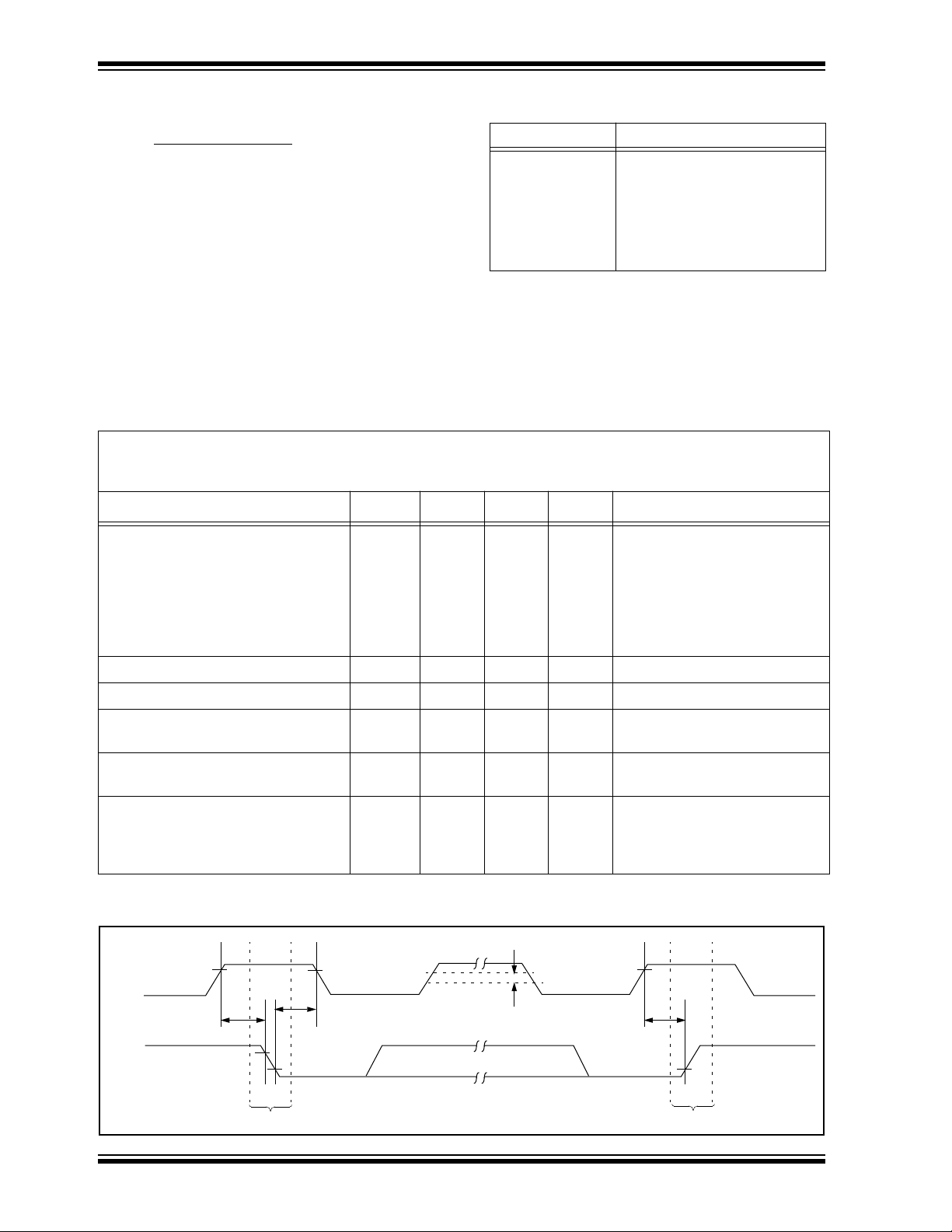
FIGURE 1-1: BUS TIMING START/STOP
SCL
TSU:STA
THD:STA
—V
— V (Note)
OL
IN
AV
OUT
AV
CC
Tamb = 25˚C, Fclk = 1 MHz
3
150
mA
µ
CC
V
CC
A
V
CC
A
V
(Note)
2
µ
A
V
CC
(Note)
VHYS
TSU:STO
= 3.0 mA
= .1V to V
= .1V to V
CC
CC
= 5.0V Note 1
= 6.0V, SCL = 400 kHz
= 6.0V, SCL = 400 kHz
= 5.0V, SCL = SDA = V
= 1.8V, SCL = SDA = V
CC
CC
SDA
DS21124C-page 2
START STOP
1996 Microchip Technology Inc.
24AA32
TABLE 1-3: AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
CC
= 1.8V-6.0V
Parameter Symbol
STD. MODE
Min Max Min Max
Clock frequency F
Clock high time T
Clock low time T
SDA and SCL rise time T
SDA and SCL fall time T
START condition hold time T
START condition setup time T
Data input hold time T
Data input setup time T
STOP condition setup time T
Output valid from clock T
Bus free time T
Output fall time from V
IL
max
V
IH
min to
Input filter spike suppression
HIGH
HD
SU
HD
SU
SU
T
T
CLK
LOW
R
F
:
STA
:
STA
:
DAT
:
DAT
:
STO
AA
BUF
OF
SP
— 100 — 400 kHz
4000 — 600 — ns
4700 — 1300 — ns
— 1000 — 300 ns (Note 1)
— 300 — 300 ns (Note1)
4000 — 600 — ns After this period the first
4700 — 600 — ns Only relevant for repeated
0—0—ns
250 — 100 — ns
4000 — 600 — ns
— 3500 — 900 ns (Note 2)
4700 — 1300 — ns Time the bus must be free
— 250 20 +0.1
— 50 — 50 ns (Note 3)
(SDA and SCL pins)
Write cycle time T
WR
— 5 — 5 ms/page (Note 4)
Endurance
High Endurance Block
Rest of Array
Note 1: Not 100% tested. C
—
—
B
= total capacitance of one bus line in pF.
10M
1M
—
—
2: As a transmitter, the device must provide an internal minimum delay time to bridge the undefined region
(minimum 300 ns) of the falling edge of SCL to avoid unintended generation of START or STOP conditions.
3: The combined T
and V
SP
specifications are due to new Schmitt trigger inputs which provide improved
HYS
noise and spike suppression. This eliminates the need for a Ti specification for standard operation.
4: The times shown are for a single page of 8 bytes. Multiply by the number of pages loaded into the write
cache for total time.
5: This parameter is not tested but guaranteed by characterization. For endurance estimates in a specific appli-
cation, please consult the Total Endurance Model which can be obtained on our BBS or website.
CC
V
= 4.5 - 6.0V
FAST MODE
B
C
10M
1M
Units Remarks
clock pulse is generated
START condition
before a new transmission
can start
250 ns (Note 1), C
—
cycles 25
—
C, Vcc = 5.0V, Block
Cycle Mode (Note 5)
B
≤
100 pF
°
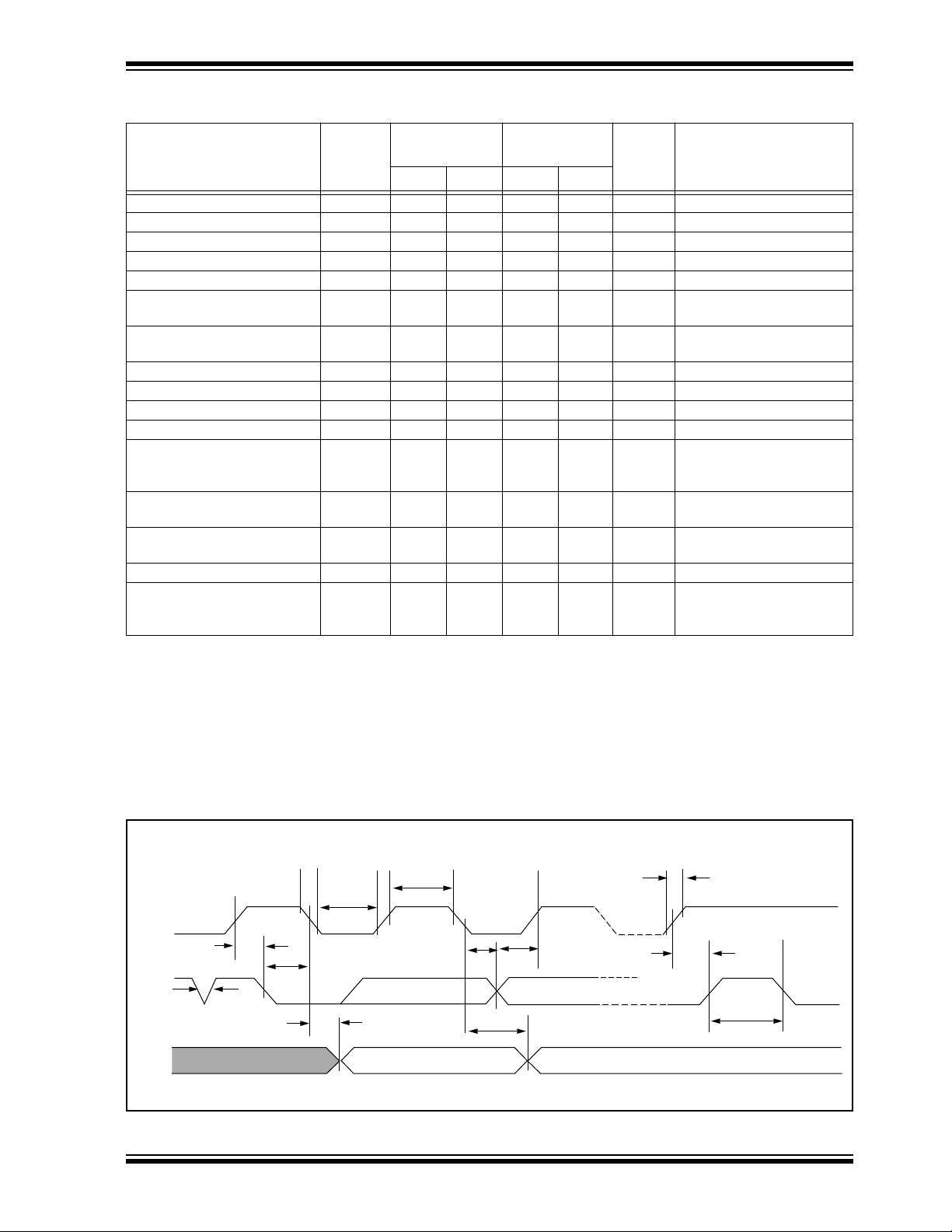
FIGURE 1-2: BUS TIMING DATA
TF
TLOW
SCL
TSU:STA
THD:STA
SDA
IN
SDA
OUT
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21124C-page 3
TSP
TAA
THIGH
THD:DAT
TAA
TSU:DAT
TSU:STO
TR
TBUF
24AA32
2.0 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The 24AA32 supports a bidirectional two-wire bus and
data transmission protocol. A device that sends data
onto the bus is defined as transmitter, and a device
receiving data as receiver. The bus must be controlled
by a master device which generates the serial clock
(SCL), controls the bus access, and generates the
START and STOP conditions, while the 24AA32 works
as slave. Both master and slave can operate as transmitter or receiver but the master device determines
which mode is activated.
3.0 BUS CHARACTERISTICS
The following bus protocol has been defined:
• Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is
not busy.
• During data transfer, the data line must remain
stable whenever the clock line is HIGH. Changes
in the data line while the clock line is HIGH will be
interpreted as a START or STOP condition.
Accordingly, the following bus conditions have been
defined (Figure 3-1).
3.1 Bus not Busy (A)
Both data and clock lines remain HIGH.
3.2 Start Data Transfer (B)
A HIGH to LOW transition of the SDA line while the
clock (SCL) is HIGH determines a STAR T condition. All
commands must be preceded by a START condition.
3.3 Stop Data Transfer (C)
3.4 Data Valid (D)
The state of the data line represents valid data when,
after a START condition, the data line is stable for the
duration of the HIGH period of the clock signal.
The data on the line must be changed during the LOW
period of the clock signal. There is one clock pulse per
bit of data.
Each data transfer is initiated with a START condition
and terminated with a STOP condition. The number of
the data bytes transferred between the START and
STOP conditions is determined by the master device.
3.5 Acknowledge
Each receiving device, when addressed, is obliged to
generate an acknowledge signal after the reception of
each byte. The master device must generate an extra
clock pulse which is associated with this acknowledge
bit.
Note: The 24AA32 does not generate any
acknowledge bits if an internal programming cycle is in progress.
A device that acknowledges must pull down the SDA
line during the acknowledge clock pulse in such a way
that the SDA line is stable LOW during the HIGH period
of the acknowledge related clock pulse. Of course,
setup and hold times must be taken into account. During reads, a master must signal an end of data to the
slave by NOT generating an acknowledge bit on the last
byte that has been clocked out of the slave. In this
case, the slave (24AA32) will leave the data line HIGH
to enable the master to generate the STOP condition.
A LOW to HIGH transition of the SDA line while the
clock (SCL) is HIGH determines a STOP condition. All
operations must be ended with a STOP condition.
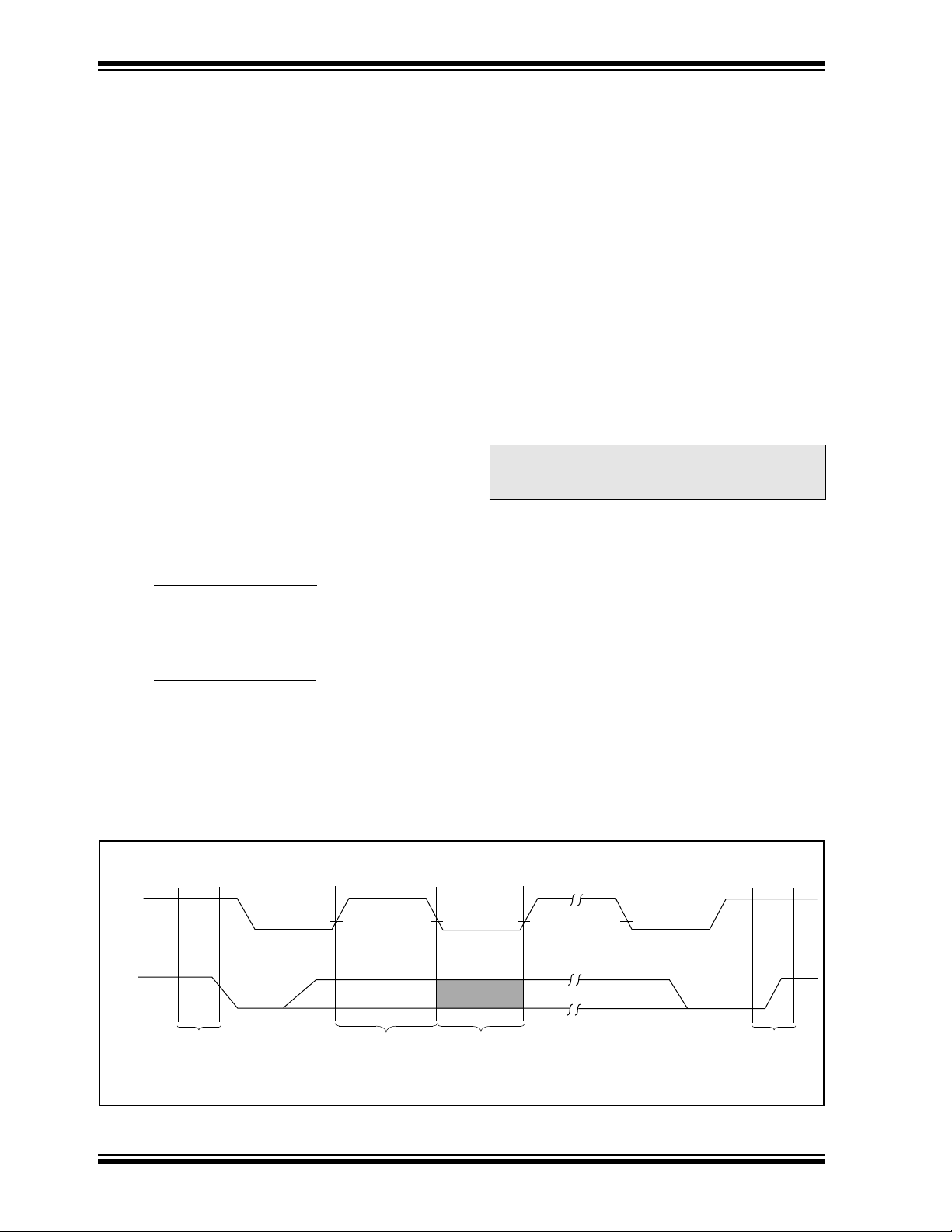
FIGURE 3-1: DATA TRANSFER SEQUENCE ON THE SERIAL BUS
(A) (B) (D) (D) (A)(C)
SCL
SDA
START
CONDITION
ADDRESS OR
ACKNOWLEDGE
VALID
DATA
ALLOWED
TO CHANGE
STOP
CONDITION
DS21124C-page 4
1996 Microchip Technology Inc.

24AA32
3.6 De
A control byte is the first byte received following the
start condition from the master device. The control byte
consists of a four bit control code; for the 24AA32 this
is set as 1010 binary for read and write operations. The
next three bits of the control byte are the device select
bits (A2, A1, A0). They are used by the master device
to select which of the eight devices are to be accessed.
These bits are in effect the three most significant bits of
the word address. The last bit of the control byte defines
the operation to be performed. When set to a one a
read operation is selected, and when set to a zero a
write operation is selected. The next two bytes received
define the address of the first data byte (Figure 3-3).
Because only A11...A0 are used, the upper four
address bits must be zeros. The most significant bit of
the most significant byte of the address is transferred
first.
Following the start condition, the 24AA32 monitors the
SDA bus checking the device type identifier being
transmitted. Upon receiving a 1010 code and appropriate device select bits, the slave device outputs an
acknowledge signal on the SDA line. Depending on the
state of the R/W
write operation.
vice Addressing
bit, the 24AA32 will select a read or
FIGURE 3-2: CONTROL BYTE
ALLOCATION
STAR T READ/WRITE
SLAVE ADDRESS
1010A2A1A0
Operation
Read 1010 Device Address 1
Write 1010 Device Address 0
Control
Code
Device Select R/W
R/W A
FIGURE 3-3: ADDRESS SEQUENCE BIT ASSIGNMENTS
CONTROL BYTE
1010
SLAVE
ADDRESS
A2A1A
0
DEVICE
SELECT
BUS
R/W
ADDRESS BYTE 1
0000
A11A10A
ADDRESS BYTE 0
A
9
8
A
•• ••••
7
A
0
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21124C-page 5

24AA32
4.0 WRITE OPERATION
4.1 Split Endurance
The 24AA32 is organized as a continuous 32K block of
memory. However, the first 4K, starting at address 000,
is rated at 10,000,000 E/W cycles guaranteed. The
remainder of the array, 28K bits, is rated at 100,000 E/
W cycles guaranteed. This feature is helpful in applications in which some data change frequently, while a
majority of the data change infrequently. One example
would be a cellular telephone in which last-number
redial and microcontroller scratch pad require a highendurance block, while speed dials and lookup tables
change infrequently and so require only a standard
endurance rating.
4.2 Byte Write
Following the start condition from the master, the control code (four bits), the device select (three bits), and
the R/W
by the master transmitter. This indicates to the
addressed slave receiver that a byte with a word
address will follow after it has generated an acknowledge bit during the ninth clock cycle. Therefore the next
byte transmitted by the master is the high-order byte of
the word address and will be written into the address
pointer of the 24AA32. The next byte is the least significant address byte. After receiving another acknowledge signal from the 24AA32 the master device will
transmit the data word to be written into the addressed
memory location.
bit which is a logic low are clocked onto the bus
The 24AA32 acknowledges again and the master generates a stop condition. This initiates the internal write
cycle, and during this time the 24AA32 will not generate
acknowledge signals (Figure 4-1).
4.3 Page Write
The write control byte, word address and the first data
byte are transmitted to the 24AA32 in the same way as
in a byte write. But instead of generating a stop condition, the master transmits up to eight pages of eight
data bytes each (64 bytes total) which are temporarily
stored in the on-chip page cache of the 24AA32. They
will be written from cache into the EEPROM array after
the master has transmitted a stop condition. After the
receipt of each word, the six lower order address
pointer bits are internally incremented by one. The
higher order seven bits of the word address remain constant. If the master should transmit more than eight
bytes prior to generating the stop condition (writing
across a page boundary), the address counter (lower
three bits) will roll over and the pointer will be incremented to point to the next line in the cache. This can
continue to occur up to eight times or until the cache is
full, at which time a stop condition should be generated
by the master. If a stop condition is not received, the
cache pointer will roll over to the first line (byte 0) of the
cache, and any further data received will overwrite previously captured data. The stop condition can be sent
at any time during the transfer. As with the byte write
operation, once a stop condition is received, an internal
write cycle will begin. The 64-byte cache will continue
to capture data until a stop condition occurs or the operation is aborted (Figure 4-2).
FIGURE 4-1: BYTE WRITE
Bus Activity:
Master
SDA Line
Bus Activity
S
t
a
Control
r
Byte
t
0000
A
C
K
Word
Address (1)
A
C
K
Word
Address (0)
Data
A
C
K
S
t
o
p
A
C
K
FIGURE 4-2: PAGE WRITE (FOR CACHE WRITE, SEE FIGURE 7-1)
S
t
a
Bus Activity:
Master
SDA Line
Bus Activity
DS21124C-page 6 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.
rtControl
Byte
0000
A
C
K
Word
Address (1)
A
C
K
Word
Address (0)
Data n Data n + 15
A
C
K
A
C
K
7
S
t
o
p
A
C
K

24AA32
5.0 ACKNOWLEDGE POLLING
Since the device will not acknowledge during a write
cycle, this can be used to determine when the cycle is
complete (this feature can be used to maximize bus
throughput). Once the stop condition for a write command has been issued from the master, the device initiates the internally timed write cycle. ACK polling can
be initiated immediately. This involves the master sending a start condition followed by the control byte for a
write command (R/W
the write cycle, then no ACK will be returned. If the
cycle is complete, then the device will return the ACK
and the master can then proceed with the next read or
write command. See Figure 5-1 for flow diagram.
FIGURE 5-1: ACKNOWLEDGE POLLING
= 0). If the device is still busy with
FLOW
Send
Write Command
Send Stop
Condition to
Initiate Write Cycle
Send Start
Send Control Byte
with R/W = 0
Did Device
Acknowledge
(ACK = 0)?
No
6.0 READ OPERATION
Read operations are initiated in the same way as write
operations with the exception that the R/W
slave address is set to one. There are three basic types
of read operations: current address read, random read,
and sequential read.
6.1 Current Address Read
The 24AA32 contains an address counter that maintains the address of the last word accessed, internally
incremented by one. Therefore, if the previous access
(either a read or write operation) was to address n (n is
any legal address), the next current address read operation would access data from address n + 1. Upon
receipt of the slave address with R/W
24AA32 issues an acknowledge and transmits the eight
bit data word. The master will not acknowledge the
transfer but does generate a stop condition and the
24AA32 discontinues transmission (Figure 6-1).
6.2 Random Read
Random read operations allow the master to access
any memory location in a random manner. To perform
this type of read operation, first the word address must
be set. This is done by sending the word address to the
24AA32 as part of a write operation (R/W
After the word address is sent, the master generates a
start condition following the acknowledge. This terminates the write operation, but not before the internal
address pointer is set. Then the master issues the control byte again but with the R/W
24AA32 will then issue an acknowledge and transmit
the eight bit data word. The master will not acknowledge the transfer but does generate a stop condition
which causes the 24AA32 to discontinue transmission
(Figure 6-2).
bit set to a one. The
bit of the
bit set to one, the
bit set to 0).
Yes
Next
Operation
FIGURE 6-1: CURRENT ADDRESS READ
S
t
a
Bus Activity:
Master
SDA Line
Bus Activity
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21124C-page 7
Control
r
Byte
t
Data n
A
C
K
S
t
o
p
N
O
A
C
K

24AA32
6.3 Contiguous Addressing Across
Multiple Devices
The device select bits A2, A1, A0 can be used to
expand the contiguous address space for up to 256K
bits by adding up to eight 24AA32's on the same bus.
In this case, software can use A0 of the control byte
as
address bit A12, A1 as address bit A13, and A2 as
address bit A14.
6.4 Sequential Read
Sequential reads are initiated in the same way as a random read except that after the 24AA32 transmits the
first data byte, the master issues an acknowledge as
opposed to the stop condition used in a random read.
This acknowledge directs the 24AA32 to transmit the
next sequentially addressed 8 bit word (Figure 6-3).
Following the final byte transmitted to the master, the
master will NOT generate an acknowledge but will generate a stop condition.
FIGURE 6-2: RANDOM READ
S
T
A
R
T
CONTROL
BYTE
WORD
ADDRESS (1)
To provide sequential reads the 24AA32 contains an
internal address pointer which is incremented by one at
the completion of each operation. This address pointer
allows the entire memory contents to be serially read
during one operation. The address pointer, however,
will not roll over from address 07FF to address 0000. It
will roll from 07FF to unused memory space.
6.5 Noise Protection
The SCL and SDA inputs have filter circuits which suppress noise spikes to ensure proper device operation
even on a noisy bus. All I/O lines incorporate Schmitt
triggers for 400 kHz (Fast Mode) compatibility.
WORD
ADDRESS (0)
S
T
A
R
T
CONTROL
BYTE
DATA n
S
T
O
P
000
SDA LINE
BUS
ACTIVITY:
A
C
K
0
FIGURE 6-3: SEQUENTIAL READ
Bus Activity:
Master
SDA Line
Bus Activity
Control
Byte
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
N
O
A
C
K
S
t
Data n + 2
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
Data n + XData n + 1Data n
o
p
N
O
A
C
K
DS21124C-page 8 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.

24AA32
6.6 PAGE CACHE AND ARRAY MAPPING
The cache is a 64 byte (8 pages x 8 bytes) FIFO buffer.
The cache allows the loading of up to 64 bytes of data
before the write cycle is actually begun, effectively providing a 64-byte burst write at the maximum bus rate.
Whenever a write command is initiated, the cache
starts loading and will continue to load until a stop bit is
received to start the internal write cycle. The total length
of the write cycle will depend on how many pages are
loaded into the cache before the stop bit is given. Maximum cycle time for each page is 5 ms. Even if a page
is only partially loaded, it will still require the same cycle
time as a full page. If more than 64 bytes of data are
loaded before the stop bit is given, the address pointer
will 'wrap around' to the beginning of cache page 0 and
existing bytes in the cache will be overwritten. The
device will not respond to any commands while the
write cycle is in progress.
6.7 Cache Write Starting at a Page
Boundary
If a write command begins at a page boundary
(address bits A2, A1 and A0 are zero), then all data
loaded into the cache will be written to the array in
sequential addresses. This includes writing across a 4K
block boundary. In the example shown below,
(Figure 4-2) a write command is initiated starting at
byte 0 of page 3 with a fully loaded cache (64 bytes).
The first byte in the cache is written to byte 0 of page 3
(of the array), with the remaining pages in the cache
written to sequential pages in the array. A write cycle is
executed after each page is written. Since the write
begins at page 3 and 8 pages are loaded into the
cache, the last 3 pages of the cache are written to the
next row in the array.
6.8 Cache Write Starting at a Non-Page
Boundary
When a write command is initiated that does not begin
at a page boundary (i.e., address bits A2, A1 and A0
are not all zero), it is important to note how the data is
loaded into the cache, and how the data in the cache is
written to the array. When a write command begins, the
first byte loaded into the cache is always loaded into
page 0. The byte within page 0 of the cache where the
load begins is determined by the three least significant
address bits (A2, A1, A0) that were sent as part of the
write command. If the write command does not start at
byte 0 of a page and the cache is fully loaded, then the
last byte(s) loaded into the cache will roll around to
page 0 of the cache and fill the remaining empty bytes.
If more than 64 bytes of data are loaded into the cache,
data already loaded will be overwritten. In the example
shown in Figure 7-2, a write command has been initiated starting at byte 2 of page 3 in the array with a fully
loaded cache of 64 bytes. Since the cache started loading at byte 2, the last two bytes loaded into the cache
will'roll over' and be loaded into the first two bytes of
page 0 (of the cache). When the stop bit is sent, page
0 of the cache is written to page 3 of the array. The
remaining pages in the cache are then loaded sequentially to the array. A write cycle is executed after each
page is written. If a partially loaded page in the cache
remains when the STOP bit is sent, only the bytes that
have been loaded will be written to the array.
6.9 Power Management
This design incorporates a power standby mode when
the device is not in use and automatically powers off
after the normal termination of any operation when a
stop bit is received and all internal functions are complete. This includes any error conditions, ie. not receiving an acknowledge or stop condition per the two-wire
bus specification. The device also incorporates V
monitor circuitry to prevent inadvertent writes (data corruption) during low-voltage conditions. The V
tor circuitry is powered off when the device is in standby
mode in order to further reduce power consumption.
DD
DD moni-
7.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
7.1 A0, A1, A2 Chip Address Inputs
The A0..A2 inputs are used by the 24AA32 for multiple
device operation and conform to the two-wire bus standard. The levels applied to these pins define the
address block occupied by the device in the address
map. A particular device is selected by transmitting the
corresponding bits (A2, A1, A0) in the control byte
(Figure 3-3).
7.2 SDA Serial Address/Data Input/Output
This is a bidirectional pin used to transfer addresses
and data into and data out of the device. It is an open
drain terminal, therefore the SDA bus requires a pullup
resistor to V
kHz)
For normal data transfer SDA is allowed to change only
during SCL low. Changes during SCL high are
reserved for indicating the START and STOP conditions.
7.3 SCL Serial Clock
This input is used to synchronize the data transfer from
and to the device.
CC (typical 10KΩ for 100 kHz, 1KΩ for 400
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21124C-page 9

24AA32
FIGURE 7-1: CACHE WRITE TO THE ARRAY STARTING AT A PAGE BOUNDARY
1
Write command initiated at byte 0 of page 3 in the array;
First data byte is loaded into the cache byte 0.
cache page 0
2 64 bytes of data are loaded into cache.
cache
byte 0
3
Write from cache into array initiated by STOP bit.
Page 0 of cache written to page 3 of array.
Write cycle is executed after every page is written.
page 0
page 0 page 1 page 2
cache
byte 1
• • •
cache
byte 7
cache page 1
bytes 8-15
cache page 2
bytes 16-23
4 Remaining pages in cache are written
to sequential pages in array.
page 1 page 2 • • • byte 7 • • •
byte 0 byte 1 page 4 page 7
page 4 • • • page 7page 3
5
Last page in cache written to page 2 in next row.
• • •
cache page 7
bytes 56-63
array row n
array row n + 1
FIGURE 7-2: CACHE WRITE TO THE ARRAY STARTING AT A NON-PAGE BOUNDARY
Last 2 bytes
loaded into
page 0 of cache.
3
cache
byte 0
1 Write command initiated; 64 bytes of data
loaded into cache starting at byte 2 of page 0.
cache
byte 1
cache
byte 2
4 Write from cache into array initiated by STOP bit.
Page 0 of cache written to page 3 of array.
Write cycle is executed after every page is written.
• • •
cache
byte 7
cache page 1
bytes 8-15
2 Last 2 bytes loaded 'roll over'
to beginning.
cache page 2
bytes 16-23
• • •
5
Remaining bytes in cache are
written sequentially to array.
cache page 7
bytes 56-63
page 0
page 0
6
page 1 page 2 • • • • • •
page 1 page 2
Last 3 pages in cache written to next row in array.
byte 0 byte 2byte 1
page 4 page 7
byte 7byte 3 byte 4
page 4 • • • page 7page 3
array
row n
array
row
n + 1
DS21124C-page 10 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.

24AA32
24AA32 Product Identification System
To order or to obtain information, e.g., on pricing or delivery, please use the listed part numbers, and refer to the factory or the listed
sales offices.
24AA32 -/P
Package: P = Plastic DIP (300 mil Body), 8-lead
Temperature Blank = 0˚C to +70˚C
Range:
Device: 24AA32 16K I
SN = Plastic SOIC (150 mil Body), 8-lead
2
C Serial EEPROM
2
24AA32T 16K I
C Serial EEPROM (Tape and Reel)
1996 Microchip Technology Inc. DS21124C-page 11

WORLDWIDE SALES & SERVICE
AMERICAS
Corporate Office
Microchip Technology Inc.
2355 West Chandler Blvd.
Chandler, AZ 85224-6199
Tel: 602 786-7200 Fax: 602 786-7277
Technical Support:
Web:
http://www.microchip.com
Atlanta
Microchip Technology Inc.
500 Sugar Mill Road, Suite 200B
Atlanta, GA 30350
Tel: 770 640-0034 Fax: 770 640-0307
Boston
Microchip Technology Inc.
5 Mount Royal Avenue
Marlborough, MA 01752
Tel: 508 480-9990 Fax: 508 480-8575
Chicago
Microchip Technology Inc.
333 Pierce Road, Suite 180
Itasca, IL 60143
Tel: 708 285-0071 Fax: 708 285-0075
Dallas
Microchip Technology Inc.
14651 Dallas Parkway, Suite 816
Dallas, TX 75240-8809
Tel: 972 991-7177 Fax: 972 991-8588
Dayton
Microchip Technology Inc.
Suite 150
Two Prestige Place
Miamisburg, OH 45342
Tel: 513 291-1654 Fax: 513 291-9175
Los Angeles
Microchip Technology Inc.
18201 Von Karman, Suite 1090
Irvine, CA 92612
Tel: 714 263-1888 Fax: 714 263-1338
New Y ork
Microchip Technmgy Inc.
150 Motor Parkway, Suite 416
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Tel: 516 273-5305 Fax: 516 273-5335
San Jose
Microchip Technology Inc.
2107 North First Street, Suite 590
San Jose, CA 95131
Tel: 408 436-7950 Fax: 408 436-7955
Toronto
Microchip Technology Inc.
5925 Airport Road, Suite 200
Mississauga, Ontario L4V 1W1, Canada
Tel: 905 405-6279 Fax: 905 405-6253
602 786-7627
ASIA/PACIFIC
China
Microchip Technology
Unit 406 of Shanghai Golden Bridge Bldg.
2077 Yan’an Road West, Hongiao District
Shanghai, Peoples Republic of China
Tel: 86 21 6275 5700
Fax: 011 86 21 6275 5060
Hong Kong
Microchip Technology
RM 3801B, Tower Two
Metroplaza
223 Hing Fong Road
Kwai Fong, N.T. Hong Kong
Tel: 852 2 401 1200 Fax: 852 2 401 3431
India
Microchip Technology
No. 6, Legacy, Convent Road
Bangalore 560 025 India
Tel: 91 80 526 3148 Fax: 91 80 559 9840
Korea
Microchip Technology
168-1, Youngbo Bldg. 3 Floor
Samsung-Dong, Kangnam-Ku,
Seoul, Korea
Tel: 82 2 554 7200 Fax: 82 2 558 5934
Singapore
Microchip Technology
200 Middle Road
#10-03 Prime Centre
Singapore 188980
Tel: 65 334 8870 Fax: 65 334 8850
Taiwan, R.O.C
Microchip Technology
10F-1C 207
Tung Hua North Road
Taipei, Taiwan, ROC
Tel: 886 2 717 7175 Fax: 886 2 545 0139
EUROPE
United Kingdom
Arizona Microchip Technology Ltd.
Unit 6, The Courtyard
Meadow Bank, Furlong Road
Bourne End, Buckinghamshire SL8 5AJ
Tel: 44 1628 850303 Fax: 44 1628 850178
France
Arizona Microchip Technology SARL
Zone Industrielle de la Bonde
2 Rue du Buisson aux Fraises
91300 Massy - France
Tel: 33 1 69 53 63 20 Fax: 33 1 69 30 90 79
Germany
Arizona Microchip Technology GmbH
Gustav-Heinemann-Ring 125
D-81739 Muenchen, Germany
Tel: 49 89 627 144 0 Fax: 49 89 627 144 44
Italy
Arizona Microchip Technology SRL
Centro Direzionale Colleone Pas Taurus 1
Viale Colleoni 1
20041 Agrate Brianza
Milan Italy
Tel: 39 39 6899939 Fax: 39 39 689 9883
JAPAN
Microchip Technology Intl. Inc.
Benex S-1 6F
3-18-20, Shin Yokohama
Kohoku-Ku, Y okohama
Kanagawa 222 Japan
Tel: 81 45 471 6166 Fax: 81 45 471 6122
9/3/96
All rights reserved. 1996, Microchip Technology Incorporated, USA. 9/96
Printed on recycled paper.
Information contained in this publication regarding device applications and the like is intended through suggestion only and may be superseded by updates. No representation or warranty is given and no liability is assumed by Microchip Technology Incorporated with respect to the accuracy or use of such information, or infringement
of patents or other intellectual property rights arising from such use or otherwise. Use of Microchip’s products as critical components in life support systems is not authorized except with express written approval by Microchip. No licenses are conveyed, implicitly or otherwise, under any intellectual property rights. The Microchip logo and
name are registered trademarks of Microchip Technology Inc. All rights reserved. All other trademarks mentioned herein are the property of their respective companies.
DS21124C-page 12 1996 Microchip Technology Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...