
USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
1 of 228
RRC-1258 MkII(s)
Yaesu Twin, Elecraft K3-Twin etc.
User Manual

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
2 of 228
Table of contents
Statement of Conditions .............................................................................. 7
General Description ..................................................................................... 8
Detachable control panel ................................................................................. 9
PC-based control .......................................................................................... 10
Step by step system setup ........................................................................ 11
Hardware .................................................................................................. 13
Front .......................................................................................................... 13
Back ........................................................................................................... 17
Strapping and jumpers ................................................................................. 21
Configuration with Microbit Setup Manager .............................................. 26
FW/HW version ............................................................................................ 27
FW update ................................................................................................... 27
Setup ......................................................................................................... 29
Net info....................................................................................................... 30
WiFi and Serial Port tabs ............................................................................... 30
Initial IP setup .......................................................................................... 31
Configuration with WEB-interface ............................................................. 34
Info ............................................................................................................ 35
Status ......................................................................................................... 36
Profiles ....................................................................................................... 38
IP Settings .................................................................................................. 40
Radio Settings ............................................................................................. 43
Serial Settings ............................................................................................. 49
Advanced settings ........................................................................................ 56
Dynamic DNS setting (only Radio-RRC) ........................................................... 60
Remoterig dynamic dns service ...................................................................... 60
DynDNS dynamic dns service ........................................................................ 63
Keyer Settings (Control-RRC) ........................................................................ 65
Keyer Settings (Radio-RRC) ........................................................................... 67
IO Settings .................................................................................................. 69
Ping settings (only Radio-RRC) ...................................................................... 73
Wi-Fi settings .............................................................................................. 74
Export settings (HTML) ................................................................................. 75
Export settings (bin) ..................................................................................... 75
Import settings (bin) .................................................................................... 76
Application firmware upgrade ........................................................................ 77
Bootloader firmware upgrade ......................................................................... 78
Restart device .............................................................................................. 78
Configuration with terminal-interface ....................................................... 79
WiFi ........................................................................................................... 80
General ....................................................................................................... 80

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
3 of 228
Connecting to a Wifi network ......................................................................... 81
CW-Keyer .................................................................................................. 87
General ....................................................................................................... 87
Settings ...................................................................................................... 87
Connections................................................................................................. 88
RTTY Keying .............................................................................................. 90
General ....................................................................................................... 90
RTTY with MMTTY ......................................................................................... 92
Settings ...................................................................................................... 94
Connections................................................................................................. 95
ICOM CI-V ................................................................................................. 96
General ....................................................................................................... 96
Hardware configuration ................................................................................. 96
Radio settings (example) .............................................................................. 97
Connections................................................................................................. 97
ICOM IC-7100 ......................................................................................... 101
General ..................................................................................................... 101
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 101
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 102
Connections............................................................................................... 102
Power supply ............................................................................................. 103
ICOM IC-703, IC-706............................................................................... 104
General ..................................................................................................... 104
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 104
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 105
Connections............................................................................................... 105
Power supply ............................................................................................. 106
Prepare the separation cable to IC-703 and IC-706 ........................................ 108
ICOM IC-R2500 ....................................................................................... 112
General ..................................................................................................... 112
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 112
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 112
Connections............................................................................................... 113
Power supply ............................................................................................. 113
ICOM IC-E2820 ....................................................................................... 116
General ..................................................................................................... 116
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 116
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 116
Connections............................................................................................... 117
Using HM-133 Microphone ........................................................................... 118
Power supply ............................................................................................. 120
ICOM ID-E880 ......................................................................................... 123
General ..................................................................................................... 123
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 123

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
4 of 228
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 123
Connections............................................................................................... 124
HM-133/880 Microphone adapter boards ....................................................... 124
Power supply ............................................................................................. 126
ICOM IC-2725 ......................................................................................... 129
General ..................................................................................................... 129
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 129
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 131
Connections............................................................................................... 131
Power supply ............................................................................................. 131
YAESU TWIN ........................................................................................... 134
General ..................................................................................................... 134
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 135
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 136
Connections............................................................................................... 137
Logging or computer control, RTTY etc. ......................................................... 139
YAESU FT-857 ......................................................................................... 145
General ..................................................................................................... 145
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 145
Connections............................................................................................... 147
Power supply ............................................................................................. 147
YAESU FTM-350 ....................................................................................... 150
General ..................................................................................................... 150
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 150
Connections............................................................................................... 152
Power supply ............................................................................................. 152
YAESU FT-7800/8800/8900 .................................................................... 155
General ..................................................................................................... 155
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 155
Connections............................................................................................... 157
Power supply ............................................................................................. 157
YAESU FT-897, FT-1000 etc. .................................................................... 159
General ..................................................................................................... 159
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 159
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 160
Connections............................................................................................... 160
YAESU in General (FT-2000) ................................................................... 165
General ..................................................................................................... 165
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 165
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 165
Connections............................................................................................... 166
KENWOOD in General .............................................................................. 170
General ..................................................................................................... 170
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 170

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
5 of 228
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 171
Connections............................................................................................... 171
KENWOOD TS-480 ................................................................................... 175
General ..................................................................................................... 175
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 175
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 176
Connections............................................................................................... 176
Power supply ............................................................................................. 177
KENWOOD TM-D710 ................................................................................ 180
General ..................................................................................................... 180
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 180
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 181
Power supply ............................................................................................. 181
KENWOOD TM-D700 ................................................................................ 184
General ..................................................................................................... 184
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 184
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 185
Power supply ............................................................................................. 185
KENWOOD TS-2000 ................................................................................. 188
General ..................................................................................................... 188
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 188
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 189
Connections............................................................................................... 189
ELECRAFT K3-Twin .................................................................................. 193
General ..................................................................................................... 193
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 193
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 194
Connections............................................................................................... 195
Connections............................................................................................... 195
Logging or computer control, RTTY etc. ......................................................... 198
ELECRAFT ................................................................................................ 203
General ..................................................................................................... 203
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 203
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 204
Connections............................................................................................... 204
ALINCO DX-SR8 and DX-R8 ..................................................................... 208
General ..................................................................................................... 208
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 209
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 209
Connections............................................................................................... 209
Power supply ............................................................................................. 210
RRC-1258MkII with 2-wire or 4-wire interfaces ..................................... 211
General ..................................................................................................... 211
Hardware configuration ............................................................................... 211

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
6 of 228
Radio settings (example) ............................................................................ 212
Connections............................................................................................... 212
Power supply ............................................................................................. 212
Schematics I/O and PAD interface ......................................................... 213
MIC/AUX Interface Control-RRC MkII ............................................................ 214
Speaker output interface Control-RRC MkIIs .................................................. 215
Speaker input interface Radio-RRC MkIIs ...................................................... 215
MIC/AUX Interface Radio-RRC ...................................................................... 216
Networks and Firewalls ........................................................................... 217
DMZ ......................................................................................................... 218
Portforwarding ........................................................................................... 219
SIP ALG .................................................................................................... 220
Mobile Network Routers .............................................................................. 221
Appendix B - COM-port Keyer interface ................................................... 223
Appendix D - Technical Data ................................................................... 224
Appendix E - Safety and Regulatory Information .................................... 225
FCC Statement .......................................................................................... 225
Safety Notice ............................................................................................. 225
Disclaimer ................................................................................................. 226
FCC / CE - Declaration of conformity............................................................. 227

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
7 of 228
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improving internal design, operational function, and/or reliability, Microbit
2.0 AB reserves the right to make changes to the product described in this document without
notice. Microbit does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of
the product(s) or circuit layout(s) described herein.
All parts of the software are property of Microbit 2.0 AB. The hardware design, schematics
PCB layout, concept, graphics, user manual, etc. are property of Microbit 2.0 AB. The device
may not be disassembled, copied or reversed engineered.
Copyright © 2010,2011,2012,2013,2014
Microbit 2.0 AB
All rights reserved.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
8 of 228
General Description
The Remoterig RRC-1258MkII (RRC) is developed especially for remote control of Amateur
radio stations via the Internet in a user-friendly and cost-effective way. The RRC units are
used in pairs, one is connected to the radio (Radio-RRC) and the other is connected to the
control equipment (Control-RRC). The system is unique in the way that no PC is needed for
the voice and data communication it’s handled by the two RRC. There are two versions
available RRC1258MkII and RRC1258MkIIs, the difference is that the (s) versions handles two
audio channels from the radio which is useful together with dual receiver equipment. The
Remoterig system can be configured to work together with most Amateur radio stations
available on the market from ICOM, Kenwood, Yaesu, Elecraft, Alinco and Tentec. The
Remoterig system fits very well in the following situations:
You are not allowed to put up antennas at your home.
The noise level is too high to make Amateur radio activity possible.
You want to build so big antennas that can’t be done in urban areas.
You do not want to be dependent of PC:s for the remote control.
Etc.
The Remoterig system itself will not introduce any latency and the latencies introduced by
Internet and buffering will rarely be any noticeable problem. The Remoterig system also
includes a unique solution for operating CW over Internet and it also includes a CW-keyer.
The Remoterig system is connected to the Internet primarily via 10 or 100 Mbit Ethernet and
fixed connections like DSL, cable and WLAN. 3G based mobile solutions will also work but
sometimes with reduced performance. The system is portable and you can use it from almost
any network connection in the world. Session control, audio (VoIP) and data is transferred
using standardized protocols like SIP, RTP etc. where you can select different audio qualities
depending on available bandwidth. The RRC-1258MkII is easily configured via modern USB
and WEB based user interfaces.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
9 of 228
Detachable control panel
You will get the ultimate function of the Remoterig system together with radio stations with
detachable control panels like Kenwood TS-480, Kenwood TM-D710, Kenwood TS-2000,
Yaesu FT-857, ICOM IC-7100, IC-703, ICOM IC-706, IC-2820 and Alinco DX-SR8. You simply
replace the cable between the control panel and the radio with the Remoterig system. You will
get the same feeling and functionality as with the original setup.
TWIN
The twin solution for Elecraft K3 and Yaesus is the high end solution for the DX-er or
contester who do not want to compromise in the selection of radio. The Twin solution is based
on the idea that one local radio controls the remote radio and you get the feeling that you
have the radio at your control site. For the Elecraft K3-Twin solution there is also a special K3
called K3/0 available which is specially designed to use as control as it has no RF-parts.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
10 of 228
PC-based control
The system also works very well for more traditional remote control from PC-based control
software’s like HamRadioDeLuxe. The Remoterig system solves the voice and data
transmission but you need a PC for the Control software itself in this setup.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
11 of 228
Step by step system setup
Below follows a recommendation about how to proceed when setting up the system.
1. Spend some time to read thru this user manual to get familiar with the product.
2. Apply 12V DC (good stabilized power) to both units.
3. Connect both units with CAT5 patch cables to the same Ethernet switch or router as
your PC which you will use to setup the system is connected.
4. Download the Microbit Setup Manager and the latest firmware from
http://www.remoterig.com to your PC. Follow the instructions about how to install the
Microbit Setup Manager (see chapter Configuration with Microbit Setup Manager).
5. Find out how your network is configured and configure the RRC to fit into your network
(see chapter Initial IP Setup) with the Microbit Setup Manager. This has to be done
with both units.
6. Check the installed firmware version. If the one you downloaded from Remoterig is
newer, update the units with the new firmware. Always update both units to the same
version (see chapter FW/HW about how to update).
7. When you have configured the units to fit into your network, Start your Web browser
and connect to the units one by one by entering their resp. IP-address. If you get in
contact with their internal web server everything is OK.
8. Disconnect all cables from the units and open the housings (see chapter Strappings
and jumpers) and make the hardware strapping according to the instruction which is
provided in the chapter for your radio in the end of this Users manual. Check the red
jumpers with a ohm meter to verify that they are not broken before assembling the
housings again.
9. Make the basic software configuration for your system which is described in the
chapter for your radio in the end of this Users manual.
10. Prepare the cables needed for your radio station and/or PC according to the cable
drawings provided in the chapter for your radio in the end of this Users manual.
Double check your home made cables with an ohm meter before connecting them to
the RRC and the radio to prevent harm of any equipment. Microbit do not take any
responsibility of damaged RRC-units or radio equipment.
11. After preparing the cables connect them to the RRC-units and the radio equipment.
Connect the power to all equipment. Check with your web browser again that you are
in contact with both RRC-units.
12. Now try to establish the connection between the Control-RRC and the Radio-RRC. If
you use a radio with a detached control panel it’s done when you press the ordinary
power on button. If you are using a PC-at the control end you need to browse to the
status page in the Control-RRC and connect by clicking on the “Connect” button on.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
12 of 228
13. When the connection is established, test the functionality. Check that you can hear the
receiver audio, check that PTT is working and microphone level is OK to be sure that
the strappings are OK.
14. When this basic functionality are OK you can go further connecting cables for CW,
rotor control, PA-control etc. Prepare all functions that you need and test them before
moving the RRC:s apart to different locations, everything gets much more complicated
to test when travelling is needed.
15. When it’s time to move the RRC:s apart you need to gather some information about
how the network at the remote site is configured. The first thing is to determine if your
Internet Service Provider (ISP) are providing you with a fixed or dynamic IP-address.
Fixed IP:s are rare so you probably have a dynamic IP-address if you are not paying
extra for a fixed one. A dynamic IP is no problem but you need to use a dynamic DNS
service. You can use Remoterigs free dynamic DNS service or a DynDNS account. New
DynDNS account is no longer free. For detailed information about Dynamic DNS
services see the Dynamic DNS chapters under Configuration with WEB-Interface.
16. After moving the RRC-apart you need to connect a PC to the local network at the
remote site where the Radio-RRC should be connected and find out how the network is
configured (see chapter Initial IP Setup). You have to set up the new IP, Netmask and
Gateway. When it’s done use your web browser to connect to the Radio-RRC:s internal
web server and configure the DNS IP.
17. Configure the Radio-RRC:s Dynamic DNS settings (see chapter Dynamic DNS Setting).
18. Now it’s time to configure your remote router. We recommend that you first of enable
the remote configuring of your router, you may need it later. After that’s done
configure DMZ or port forwarding (see chapter Network and Firewalls). When this is
done your remote Radio-RRC should be reachable over the Internet.
19. When back at the Control QTH try to browse to the Dynamic DNS address (Own host
name) you have setup at the Radio-RRC. You should get in contact with the Radio-RRC
internal web server exactly as it was local.
20. The only setting which need to be changed in the Control-RRC is the SIP-contact at the
Radio settings page. The SIP-contact should be changed to the Dynamic DNS “Own
host name” you have setup in the Radio-RRC or to the fixed IP of the Radio QTH if you
have one. Then everything should work remotely.
Enjoy the remote controlling.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
13 of 228
Hardware
Front
PWR LED
Green light is indicating normal status. When the green LED is flashing slow the unit is trying
to connect to the Ethernet, normally it only takes a few seconds. If the LED do not end
flashing it's probably something wrong with the network connection or network setup. A fast
flashing power LED indicate that the unit is powered from USB (see USB below).
USB
The USB-interface is used to initially set up the IP parameters. It can also be used for
downloading new software (can also be done via the WEB-interface). At the Control-RRC it
can also be used for CAT control, PTT, RTTY or CW control via the RTS and DTR signals in the
virtual COM-port delivered by the RRC USB device. From Version 6 the RRC can be powered
via the USB to make it easier to update the Firmware. Note that the RRC need to be
connected to 12V DC for normal operation. When the unit is powered from the USB the green
power LED will flash fast.
COM1
COM1 can in special cases be used to set parameters and check statuses if USB or WEB
cannot be used. The COM1 port can also be used for ex. rotator control as it can be
configured as transparent serial port between the RRC:s.
RS-232
Pin no
RS-232 Interface (9-pol D-sub female)
1 2
TXD (Out)

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
14 of 228
3
RXD (in)
4
5
GND
6 7
CTS (In)
8
RTS (Out)
9
AUX/MIC
The AUC/MIC connector (RJ-45) is used for microphone connection or for connection of the
radio control panel (IC-703/706, DX-SR8). Inside the RRC behind the connector is a set of
straps with can be used to decide how the connector should be configured depending on radio
or microphone. The red and yellow LED:s are indicating SIP-status:
LED
LED Red
LED Yellow
Off
Incoming audio stream OK
SIP disconnected
Flashing
-
SIP connection failed
On
Incoming audio stream fail
SIP connection OK
Pin no
AUX (RJ45)
1
depends on the inside straps
2
depends on the inside straps
3
depends on the inside straps
4
depends on the inside straps
5
depends on the inside straps
6
depends on the inside straps
7
depends on the inside straps
8
depends on the inside straps
TTL Control-RRC
The TTL connector on Control-RRC (RJ-12) is used primary for connection of the radio control
panel (TS-480, RC-2000 and IC-E2820) and in other cases where you need to connect via a
TTL level (5V) port. The connector is configured so a straight cable can be used to a TS-480
and RC-2000 control panel.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
15 of 228
Pin no
AUX (RJ45)
6
AF output, Speaker 2W/8 ohm
5
TDO input, data from panel to radio (TTL)
4
RDO output, data from radio to panel (TTL)
3
GND
2
8V output, always active
1
GND
TTL Radio-RRC
The TTL connector on Radio-RRC (RJ-12) is used for connection of the cable which is normally
connected between the control panel and the radio (TS-480, RC-2000, and IC-2820). It's also
used for CAT control of radios with 5V.s inputs e.g. all ICOM with 3.5mm C-IV connector and
FT-8x7 with the mini DIN-connector. The connector is configured so a straight cable can be
used to a TS-480 control panel and to RC-2000.
Pin no
AUX (RJ45)
6
AF Input (TS-480)
5
TDO input, data to radio (TTL)
4
RDO output, data to radio (TTL)
3
GND
2
8V output, always active
1
GND
SP Control-RRC
At the Control-RRC the connector is used as a speaker output. It's connected in parallel with
the audio output pins in the MIC/AUX and TTL connectors. The connector is a standard 3.5
mm jack for a mini stereo plug and there is no switch in the connector. The speaker output
power is 2W at 8 ohm. In the dual RX (stereo) version there are signals from both the MainRX and Sub-RX available in the SP-connector. There is only a Lf power amplifier on the Main
RX signal so I recommend that you set jumper JMP-4 in the Headset position and use headset

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
16 of 228
or Stereo speakers with built in lf-power amplifier if you use a Dual Receiver system. PC-type
speakers are very well suited for this.
Sub Receiver (*)
Main receiver
GND
(*) Sub receiver, only available in RRC-1258MkIIs version
SP Radio-RRC
At the Radio-RRC the speaker connector is an input for the speaker signals from the radio.
The Dual-Rx version has inputs for both the Main-Rx and Sub-RX. The Main-Rx input is
connected in parallel with the input pins in the MIC/AUX and TTL connector. The inputs has
resistive loads of 50 ohms. The connector is a standard 3.5 mm jack for a mini stereo plug
and there is no switch in the connector.
Sub Receiver (*)
Main receiver
GND
(*) Sub receiver, only available in RRC-1258MkIIs version
CW Control-RRC
The CW knob is used for adjusting the CW-speed of the built in CW-keyer. The CW –Speed
adjustment is also connected to the WinKeyer emulator. There is no knob on the Radio-RRC.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
17 of 228
Back
COM2 Control-RRC
COM2 is used to connect to a PC COM port (RS-232). It has a female connector which makes
it possible to use a straight cable between RRC and PC. The communication parameter is set
via the web interface.
Pin no
RS-232 Interface for PC connection
(9-pol D-sub female)
1
2
RXD (out) to PC RXD
3
TXD (in) from PC TXD
4
5
GND
6 7
RTS - connected to JMP-3
8
CTS - connected to JMP-3
9
COM2 Radio-RRC
COM2 is used to connect to a Radio with RS-232 port. It has a male connector, which makes
it possible to use a straight cable between RRC and the radio. The communication parameter
is set via the web interface.
RS-232
RS-232

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
18 of 228
Pin no
RS-232 Interface for Radio connection
(9-pol D-sub male)
1 2
RXD (in) to pc RXD
3
TXD (out) from pc TXD
4
5
GND
6
7
RTS - connected to JMP-3
(*)
8
CTS - connected to JMP-3
(*)
9
(*)
Both Kenwood and Yaesu transceivers need the RTS and CTS pins to be strapped together.
JMP-3 inside the box can be used to strap them if you want to use a standard fully connected
cable.
PAD Control-RRC
At the Control-RRC the input is used to connect a CW-paddle. The input is for a standard 3.5
mm stereo plug. Normally the left paddle is connected to the tip and the right paddle to the
ring. Common is connected to the inner ring and ground. Note that the CW-Keyer function
must be enabled to activate this function.
PAD Radio-RRC
At the Radio-RRC the output is used to connect the output signal from the CW-keyer to the
radio straight KEY input. The output is for a standard 3.5 mm stereo plug. A standard cable
with 3.5 mm connector in both ends can often be used. Note that the OUT1 mode or OUT2
mode must be set to Keyer to activate this function.
PWR
The RRC is powered via the PWR connector (2.1/5.5 mm) with 10-18 VDC.
Radio
Control-RRC (12 VDC)
Radio-RRC (12 VDC)
IC-706
up to 600mA, depending on
back lighter and audio volume
max 160 mA (110mA 10Mbit)
TS-480
up to 500mA, depending on
audio volume
max 160 mA (110mA 10Mbit)
RS-232
up to 400mA, depending on
audio volume
max 160 mA (110mA 10Mbit)

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
19 of 228
Pin no
PWR
+
+ 10-18 VDC (centre)
-
GND
RESET
A short press on the reset switch will reboot the unit. By pressing and keep the button
pressed for 20 sec the unit reset to factory default settings with the following network
settings:
Control-RRC IP-address: 192.168.0.227
Radio-RRC IP-address: 192.168.0.228
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.0.1
DNS: 192.168.0.1
I/O
In the I/O connector is 3(2) inputs and 3 outputs, 8V and GND available (see below). The
connector is used for transferring signals from one RRC to the other. If the CW-keyer function
is not used the connector can be used for whatever controls signals needed in both directions.
The output transistor can sink max 200mA so install an external relay if it's not strong
enough.
Pin no
I/O (RJ45)
1
IN1, active low (CW-Keyer right-paddle)
2
IN2, active low (CW-Keyer left-paddle)
3
OUT2, open collector (parallell with PAD Tip at Radio-RRC)
4
IN0, active low (only available at Control-RRC)
5
OUT0 open collector
6
OUT1 open collector (parallell with PAD Ring at Radio-RRC)
7
8V OUT (max 100mA)
8
GND
12V DC

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
20 of 228
ETHERNET
The unit can be connected to both 10 and 100 Mbit/s Ethernet based TCP/IP network. The
RRC can be configured for different connection types for Ethernet port, Auto, 10HDX, 10FDX,
100HDX, 100FDX and Auto-with-preferred-10FDX. Default is Auto-with-preferred-10FDX
which works best in most cases.
Pin no
Ethernet (RJ45)
1
Out [+]
2
Out [-]
3
In [+]
4
5
6
In [-]
7
8
LINK
Green LED indicates link OK flashing LED indicates traffic
ACT
Yellow LED indicates speed = 100Mbit/s (off = 10MBits/s)

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
21 of 228
Strapping and jumpers
Before connecting the RRC to your radio you need to put some straps in place depending
on your radio. Down below follows instructions of how to disassembly the RRC and
pictures showing where to find the different straps.
1:
Start with removing the screws holding the D-sub on the rear marked COM2. The tool
should be 5 mm (3/16").
2:
Open the box by pressing the D-sub until you can get your fingers behind the edge of
the lid and can slide the housing apart.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
22 of 228
3:
Behind the AUX/MIC connector there is a strapping area which looks like an IC-socket. There
are two rows with 9 holes. The row next to the AUX/MIC connector is connected to the
connector. The strapping is done by connecting the red strap wires, supplied with the RRC,
between the holes according to the description for the radio (see radio chapter). Normally the
same strapping should be done in both Control-RRC and Radio-RRC. (The picture shows the
strapping for IC-706). Attention! The strapping wires should NOT be soldered. Just
push them into the socket. The mechanical friction is enough to get connection.
5 7 8 6 4 2 1 3
Socket Pin 1
4:
Control-RRC only: JMP-1 is placed behind the TTL connector. With the strap in place a DC
voltage is feed to the microphone element. All ICOM microphones should be DC-feed.
Dynamic microphones like the ones used by Kenwood should not be DC-feed. HEIL
microphones should not be DC-feed either.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
23 of 228
5:
Control-RRC only: JMP-2 is placed near the back of the RRC next to the RESET button. JMP-2
is used to select if the DC-power to the front panels should be 8 or 9 V. With the strap in
place it will be 8V, which fits all ICOM radios. Without the strap the voltage will be 9V, which
fits Kenwood TS-480 and RC-2000 panels that need 9V for the back-lighter.
6:
JMP-3 is placed next to the rear D-sub COM2. JMP-3 is used to connect RTS and CTS together
(pin 7 and 8) in COM2. Most of the Yaesu and Kenwood radios with RS-232 port need to have
them tied together. This is convenient if you want to use a prefabricated fully connected
cable.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
24 of 228
7:
Control-RRC Only: JMP-4 is placed behind the CW-pot, and is available only in the ControlRRC and are only present in the RRC-1258MkIIs up to Hardware version 5. JMP-4 is used to
select between Speaker level or Headset level for the Main-Rx output. The Sub-Rx is always
Headset level. From hardware version 6 it’s always speaker level from both RX.
8:
JMP-5 is placed behind the TLL connector and is only present in the RRC-1258MkIIs from
hardware version 7. JMP-5 is used to decide if pin1 in the TTL connector should be grounded
or not. It should be grounded (in place) for all Radios but Yaesu FT-857 and ICOM ID-E-880

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
25 of 228
9:
When you are done you can slide the lid on the bottom part and put back the screws. Be
careful the threads do not stand to much force.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
26 of 228
Configuration with Microbit Setup Manager
The initial settings of the network parameters are easiest done with the Microbit Setup
Manager. The Setup Manager is a software which runs under Windows on a PC and connects
to the RRC via USB (an USB cable is supplied with the RRC). The Setup Manager can be used
for:
IP Settings and verification
o IP-address
o Netmask
o Gateway
o DNS
o DHCP
Firmware upgrade
o Application
o Bootloader
Changing profile
Scanning for WiFi networks and WiFi setup.
Start with downloading the Microbit Setup Manager from the homepage www.remoterig.com.
Install the Microbit Setup Manager by following the instructions which shows up. If you have
an old version of Windows P where Netframework 2.0 is not installed, you have to install
Netframework from Microsoft before installing the Setup Manager. When you have finished
the installation a new shortcut to the Setup Manager will show up on the desktop. Click on the
icon to start Setup Manager
Connect your RRC to 12V and connect the USB-cable between your computer and the USB
jack on the front of the RRC. Windows will automatically install the necessary drivers. When
it's done the text in the bottom field will change from "RRC not connected" to "RRCconnected" which is an indication that you are in connection with the unit.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
27 of 228
FW/HW version
When you connect the RRC the version of the firmware and Bootloader will show up in the
upper window. The hardware versions is also shown. Go to the page www.remoterig.com and
under downloads you can find the latest firmware. If there is a newer firmware available
download it to your desktop unzip it and change to the "FW-update" tab.
FW update

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
28 of 228
Click on the "Select file" button and browse to the file with the new firmware, it should be
something like “RRC-1258-CRC_v2.42_2011-08-17.bin” depending on the version and release
date. When you have selected the file click on the "Update" button and the update process
will start, the text in the bottom field will change to "Updating firmware". Attention -- Do not
interrupt the update process in any way!
After about a 1 minute the update is finished and the RRC will restart. When the text "RRCconnected" shows up again in the lower field of the Microbit Setup Manager, you can change
to the "FW/HW" tab and check software version.
USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
29 of 228
Setup
The setup tab are used to setup the IP address and/or select the profile (from v2.44). More
info about the IP setup see Initial IP-setup.
A new window wills pop-up with the basic IP settings. Change the settings so they fit into your
local network and press the "Save" button to save the new settings. The RRC will restart
again and when the text "RRC-connected" shows up again in the lower field of the Setup
Manager, you can click on the "Setup" button again to verify the changes.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
30 of 228
Net info
Click on the “Get” button to read the IP setting currently in use by the RRC.
WiFi and Serial Port tabs
The Wifi tab is described in the WiFi Chapter. The Serial port tab is not used for the RRC1258MkII it’s used for other products.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
31 of 228
Initial IP setup
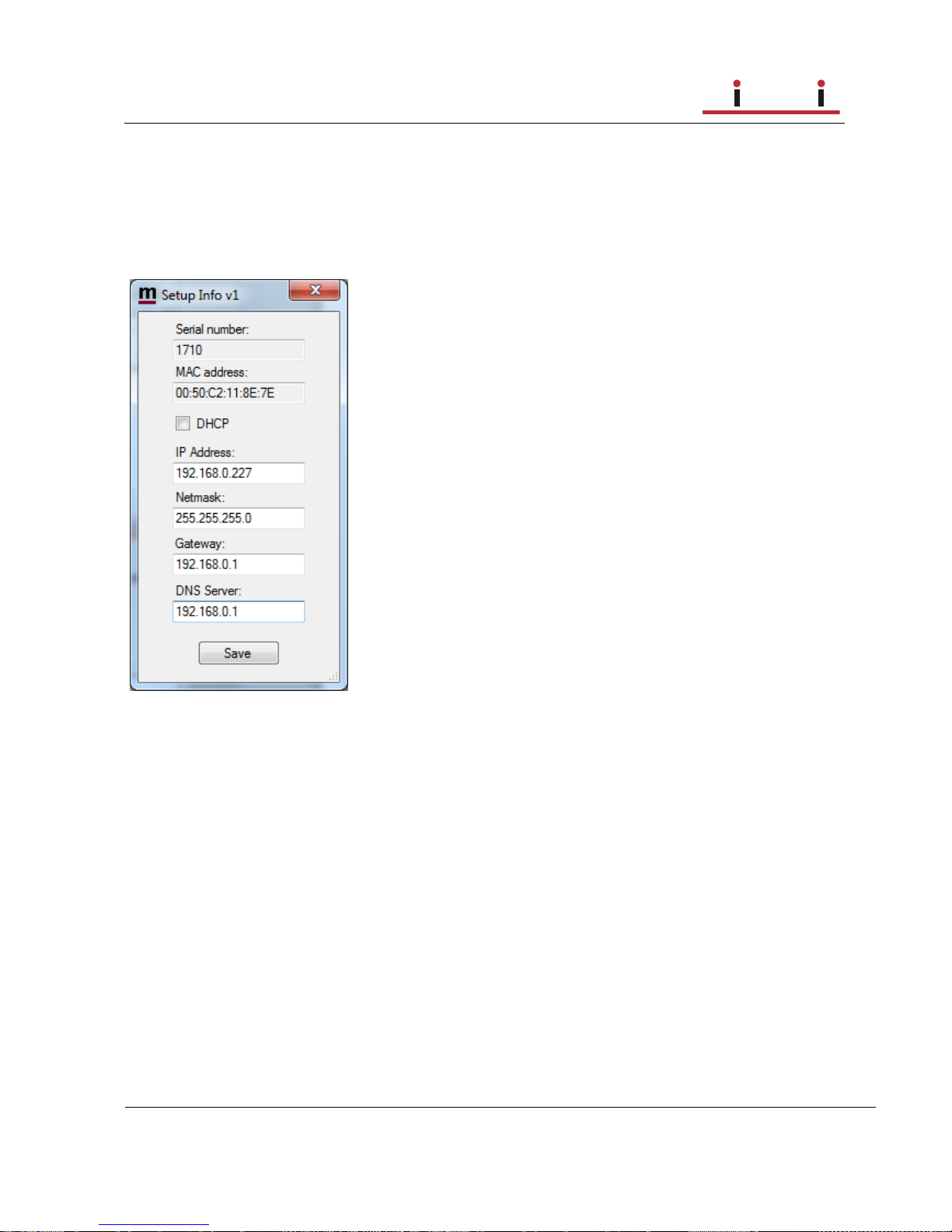
The default Ip settings from the factory is 192.168.0.227 (Control-RRC) and 192.168.0.228
(Radio-RRC). The net mask is 255.255.255.0. and the gateway 192.168.0.1.
To be able to contact the RRC-units via the network you must configure the units to fit into
your home network. You can check your network configuration from your PC.
On the start menu select Run. In the Run dialog box enter cmd.
You will get a DOS-window.
At the DOS-promt enter ipconfig.
Then you will get the needed information:
Your PC IP address in this example is 192.168.0.101 this means that the IP of the RRC:s must
have IP:s in the area 192.168.0.2 to 192.168.0.255.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
32 of 228
The Netmask is 255.255.255.0 the Netmask in the RRC:s should be the same
The Default gateway is 192.168.0.1 the Gateway in the RRC:s should be the same
In this case all the default IP setting will be OK.
In an other network, this is the result of the ipconfig command.
Your PC IP address in this example is 192.168.128.10 this means that the IP of the RRC:s
must have IP:s in the area 192.168.128.2 to 192.168.128.255.
The Netmask is 255.255.128.0 this the Netmask in the RRC:S should be the same
The Default gateway is 192.168.128.1 the Gateway and in the RRC:S should be the same
The DNS should in almost all situation be the same as Default gateway.
In this case you must change the IP:s of the RRC. I recommend to use 192.168.128.227 and
192.168.128.228
Use the Microbit Setup Manager to change the IP settings.
Select the Setup tab click on the “Get Setup” button and enter the IP addresses in the Setup
info dialog box.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
33 of 228

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
34 of 228
Configuration with WEB-interface
Before you can use your RRC-1258MkII you must configure both the hardware (strapping)
and the software settings. The units will have the default IP addresses 192.168.0.227
(Control-RRC) and 192.168.0.228 (Radio-RRC). The net mask is 255.255.255.0. The
configuration is easiest done via the web interface. Be aware of that your PC must be in the
same net e.g. having an IP-number between 192.168.0.2 and 192.168.0.254 and not be the
same as the RRC. If the default IP-addresses of the RRC not fit your network please use the
PC-program Microbit Setup Manager to change the IP-addresses via USB. It's convenient to
use DHCP at the Control-RRC but wait to active DHCP until everything is setup and working.
Select setup page from the links on the left side and edit the parameters. After each setup
pages is finished press Submit to temporary store the new settings. When you do that a new
red Apply changes button appears on the pages. You can now change parameters on other
pages but the new settings will not take effect until you press Apply changes. When you do that
the unit will reboot and start up with the new settings. If you change your mind after clicking
on submit you can click on Restart device on the left to restart the device without changing
any settings.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
35 of 228
Info
The info page shows some static information about the RRC as firmware revision etc. and also
the basic IP-configuration.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
36 of 228
Status
On the status page you can check some parameters which can be useful when debugging etc.
But the most important is that here is the "Connect" and "Disconnect" button used to connect
or disconnect the Internet connection between the two RRC in some modes.
If the system is setup to be used with Control panels or Twins then there is no
Connect/disconnect buttons, the connection is controlled by the power on switch on the
control panel.
In some modes there are a disconnect button on the Radio-RRC status page which in a multi
user system can be used to disconnect a user who have forgot to do it.
When connecting you will see how the SIP-status is changed to "Connected/Transferring" if
everything is OK. Here is also shown how your NAT-router has mapped the ports and the
momentary status of the inputs and outputs and some other things.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
37 of 228

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
38 of 228
Profiles
The profile menu is used to store and load settings profiles. This could be convenient if you
change settings often. But NO settings are needed here if you do not use it, so leave this
page to later if it’s your initial setup of the RRC:s.
You can use up to five profiles and you can give them describing names.
The first time you activate another profile than the default profile the default profile will be
copied to the other profiles.
When you save settings in the normal way with the red “apply settings” button the data will
be saved in the profile which is active for the moment.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
39 of 228
To change profile just select “Active profile” to the profile you want to change to, and press
submit. The new profile will then be loaded but will not be used before restart so you can
check all settings and the restart to make the new profile active.
Profiles can also be changed from the Setup Manager which can be useful if you connected it
to different networks.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
40 of 228
IP Settings
The IP Settings menu is used to setup the initial IP parameters needed for the unit to connect
to the IP network. Down below the settings are described more in details.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
41 of 228
Parameter
Setting
Unit ID (Banner)
Text, whatever you want, that will be shown at the
top of the web-page (within brackets). Used to
identify different RRC.
“empty” (default)
“text”
DHCP
Select between a fixed IP address and DHCP. DHCP
can be practical for the Control-RRC but fixed IP
address is preferred in Radio-RRC.
No (default)
Yes
IP
IP-address (only when fixed IP-address is used)
192.168.0.227 (default Control-RRC)
192.168.0.228 (default Radio-RRC)
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
Netmask
Net mask (only when fixed IP-address is used)
255.255.255.0 (default)
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
Gateway
Gateway (only when fixed IP-address is used)
192.168.0.1 (default)
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
Dns server
DNS-address (only when fixed IP-address is used)
192.168.0.1 (default)
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
Extern IP/Host
Fixed external IP-address of your NAT-router. Should
NOT be used in normal installations.
“empty” (default)
nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
Eth-type
Type of Ethernet connection:
Auto
Auto, prefer 10 Mbit (default)
10HDX*
10FDX*
100HDX*
100FDX*
Auto prefer 10 Mbit is default as more speed is not
needed and the emissions from a 10 Mbit LAN is
much less than from a 100 Mbit LAN
(*) If you use fixed settings you must have a
managed switch where you can set the same
setting.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
42 of 228
IP-interface
Normally the RRC connects via the Ethernet interface
if it’s available, and as second choice via the WiFi. If
you set it to “Ethernet” you can force the RRC not to
connect via WiFi even if the Ethernet is not available
for the moment.
“Auto, prefer Ethernet” (default)
“Ethernet”
Web page user
Enable password protection for the web pages and
also the telnet connection by entering a username
(this field) and a password (next field). If this field is
empty the RRC will not ask for password. Some of
the pages are still accessible but no editing is
possible.
“empty” (default)
“username”
Web page pwd
Password for the web pages and telnet connection.
The password are shown as **** to view it click on
the “show” button”
“empty” (default)
“password”

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
43 of 228
Radio Settings
The Radio settings are used to setup the RRC to act together with different radios. The
settings must be done in both Control-RRC and Radio-RRC and the parameters are partly
different for the both RRC.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
44 of 228

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
45 of 228
Parameter
Setting
Program mode
Select the program mode depending on connected
radio:
0 = Transparent (for repeater links etc.)
1 = ICOM CI-V (generic)
2 = IC706 (with detached control panel)
3 = FT-8x7, FT-1000 (generic)
4 = Kenwood, Yaesu, Elecraft
5 = TS480/TM-D710 (with detached control panel)
6 =
(*1)
7 = IC-R2500/IC-2725(with detached control panel)
8 = TS-2000/TM-D700 (TS-2000 with RC-2000)
9 = IC-2820 (with detached control panel)
10 = Yeasu FT-950/FT-2K/FT-5K/FT-9K- Twin
11 = Transparent, 4-wire (for repeater links etc.)
12 = DX-SR8 (with detached control panel)
13 = ID-E880(with detached control panel)
14 = K3 twin
15 = Yaesu FT-857 (with detached control panel)
16 = Yaesu FT-100 (with detached control panel)
17 = Yaseu FTM-350 (with detached control panel)
(*1)
These selections are only possible in special
editions of the RRC.
Sip password
Protect your remote rig and should be same in both
ends. Normally shown as **** click on the “show”
button to view the password.
(default: no password)
Sip contact
Control-RRC:
Sets the fixed IP address or the Dynamic DNS “own
host name” to the Radio-RRC
Auto connect
Control-RRC:
When enabled the Control-RRC will connect to
Radio-RRC immediately after power up in program
mode 0, 1, 3 and 4.
No (default)
Yes

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
46 of 228
Audio quality
Sets the audio quality depending on available
bandwidth. Sample rate must be same in both RRC
but coding can be different (more information can
be found in appendix-A Audio coding):
0 = A-law 8 kHz
1 = Linear 12 bits 8 kHz
2 = Linear 16 bits 8 kHz (default)
3 = A-law 12 kHz
4 = Linear 12 bits 12 kHz
5 = Linear 16 bits 12 kHz
6 = A-law 16 kHz
7 = Linear 12 bits 16 kHz
8 = Linear 16 bits 16 kHz
9 = A-law 24 kHz
10 = Linear 12 bits 24 kHz
11 = Linear 16 bits 24 kHz
12 = IMA ADPCM 4 bits 8 kHz
12 = IMA ADPCM 4 bits 16 kHz
Audio Dual-RX
Sets if LF from the Sub-RX should be sent as an
separate audio channel. Be aware of that this
doubles the need of Bandwidth. (Only available in
the (s) version.)
Codec out gain
Sets the attenuation for the audio output, in 255
steps and 0.5 dB per step. Should always be set to
255.
255 = no attenuation (default)
254 = -0.5 dB
253 = -1.0 dB
…
0 = max attenuation
Codec inp gain
Sets the gain for the audio input in 63 steps and
0.75 dB per step. Should be 18 at Control-RRC for
high level electret microphones and should always
be 0 at Radio-RRC.
0 = default Radio-RRC
…
18 = default Control-RRC
…
63 = max value

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
47 of 228
Codec inp HPF Hz
Sets the low cut frequency for the audio passband
[Hz]:
82
102
131
163 (default)
204
261
327
408
The upper cut frequency is set automatically
depending on the sampling rate.
Codec inp preamp
Control-RRC:
Enables a +20 dB pre-amplifier for the audio input
at the Control-RRC:
No
Yes (default)
Codec inp attenuation
Radio-RRC:
Enables a -20 dB attenuator to the speaker input at
the Radio-RRC:
No (default)
Yes
COM0 baudrate
Set COM0 baudrate for the radio communication
[bps]:
600
1200
2400
4800
9600 (IC-R2500,IC-2725)
19200 (IC703/706)
38400 (IC2820,DX-SR8,ID-E880)
48000 (FTM-350)
57600 (TS480, TS2000)
64000 (FT-857, FT-100)
COM0 data bits
Set COM0 data bits:
5
6
7
8 (default)
COM0 stop bits
Set COM0 stop bits:
1 (default)
2
COM0 parity
Set COM0 parity:
0 = Off (default)
1 = Odd
2 = Even
3 = Forced-1
4 = Forced-0

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
48 of 228
COM0 Program mode 3
char timeout
The char timeout can be programmed. The default
timeout should be 2 and works for all radios except
FT-1000 in 4800 baud which need it to be set to 60.
2 = default
60 = FT-1000 in 4800 baud
Use USB Com Port as
COM0
COM0 can be connected to the USB interface instead
of the normal serial interface. When installing
Microbit Setup manager a virtual Com port called
“Microbit RRC Virtual Comport (COMX)” is installed.
That’s the one you should connect to when using
HRD or other softwares.
Yes or No (default = No).

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
49 of 228
Serial Settings
The serial ports COM1 and COM2 can be used as a transparent serial channel between
Control-RRC and Radio-RRC over Internet. The COM-ports can be used for CAT control,
rotator control etc. COM1 is always free to be used with the drawback that you cannot use
COM1 for configuration. COM2 is used for the radio control in some of the program modes and
can then not be used as a transparent serial channel. There is also a COM3 which is only
available via USB and only for WinKey and RTTY.
Radio settings /
Program mode
COM1
free channel
COM2
free channel
0 - Transparent
yes
yes
1 - ICOM CI-V
yes
no
2 – IC-7100,IC-706,IC-703
yes
yes
3 – FT-8x7, FT-1000x
yes
no
4 – Yaesu, Kenwood, Elecraft
yes
no
5 – TS480/TM-D710
yes
yes
6 –
(*)
yes
yes
7 – IC-R2500/IC-2725(*1)
yes
yes
8 – TS2000/TM-D700
yes
yes
9 – IC-2820
yes
yes
10 – Yeasu FT-450/FT-950/FT-
2000/FT-5000/FT-9000 Twin
yes
no
11 – Transparent, 2/4-wire(*1)
yes
yes
12 – DX-SR8
yes
yes
13 – ID-E880 (*1)
yes
yes
14 – Elecraft K3-Twin
yes
no
15 – Yaesu FT-857
yes
yes
16 – FT-100
yes
yes
17 – FTM-350
yes
yes
COM1 and COM2 mode can be configured differently depending on what they will be used for.
The same settings must be done in both Control-RRC and Radio-RRC.
(*1) = Need special hardware

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
50 of 228

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
51 of 228
Parameter
Setting
COM1 mode
Select mode for COM1-to-COM1 transparent transfer
of serial data between two opposite RRC. The setting
defines the event that triggers the data transfer over
Internet.
Inactive (default)
Mode 1 = Char-by-char. A data packet is send for
each char, needs lot of bandwidth.
Mode 2 = ICOM CI-V. Used for CI-V control of
IC-703/706 at the same time as you
use the control panel.
Mode 3 = Char-timeout. A data packet is sent
when there is a pre-defined pause
between two received char.
Mode 4 = Kenwood, Yaesu, Elecraft. Used for CAT
control of TS-480 or TS-2000 at the
same time as you use the control panel.
Mode 5 = User-def-terminator. Used if you want
to define the terminator char by your self (see below).
Should be activated together with Mode-7
in Radio-RRC to combine data from COM1
with the other ports described above.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
52 of 228
Mode 6 = CAT to COM2 local (Control-RRC)
makes it possible to connect for example a
logger PC which needs to speak to the
Control radio to COM1 at the Radio-RRC.
The IP-data from radio side COM2 and this
local COM1 will be intelligent
mixed (in sequence) before sent to local
COM2. Data from local COM2 goes to both
local COM1 and to the radio side COM2
via IP. This function is only for the Yaesu
Twin configuration only.
Mode 6 = CAT to COM2 local (Radio-RRC)
makes it possible to connect other hardware
which needs to speak to the radio via COM1
at the Radio-RRC. The IP-data from control
side COM2 and local COM1 will be intelligent
mixed (in sequence) before sent to local
COM2. Data from local COM2 goes to both
local COM1 and to the control side COM2
via IP. Can be used for MicroHam, the Web Switch, Power Amplifier etc. This function is
for Yaesu, Kenwood and Elecraft only.
Mode 7 = CAT to COM2 local & remote (Radio-RRC)
Same function as above but it also com bines data sent from COM1 in Control-RRC
with data from the local COM1 and Control RRC COM2. (Remember that this function
doubles the data amount sent over the
Internet).
Mode 7 = CAT to COM2 remote (Control-RRC)
Is used in combination with mode 7 at the
Radio-RRC.
Mode 8 = The WinKeyer emulator is activated, and
data received from COM1 are sent as CW
from the Radio-RRC in parallel with the
ordinary keyer.
COM1 baudrate
Set COM1 baudrate [bps]:
600
1200
2400
4800
9600 (default)
19200
38400
48000
57600
COM1 databits
Set COM1 data bits:
5
6
7
8 (default)

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
53 of 228
COM1 stop bits
Set COM1 stop bits:
1 (default)
2
COM1 parity
Set COM1 parity:
0 = Off (default)
1 = Odd
2 = Even
3 = Forced-1
4 = Forced-0
COM1 cts/rts
Enable the transfer of CTS input to RTS output of
other RRC.
0 = No (default)
1 = Yes
COM1 terminator
Defines the terminator character used in COM1mode=5 (user-def-terminator). Character should be
in HEX-format.
00 (default)
Use USB Com Port as
COM1
COM1 can be connected to the USB interface instead
of the RS-232 interface if your PC do not have
traditional com ports. When installing Microbit Setup
manager a virtual Com port called “Microbit RRC
Virtual Comport (COMX)” is installed. That’s the one
you should connect to when using HRD or other
softwares.
Yes or No (default = No).

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
54 of 228
COM2 mode
Select mode for COM2-to-COM2 transparent transfer
of serial data between two opposite RRC. The setting
defines the event that triggers the data transfer over
Internet.
Inactive (default)
Logical parallel with COM0. = Is used for level
converting for CI-V and FT-8x7. The
settings from “Radio settings” are used.
Mode 1 = Char-by-char. A data packet is send for
each char, needs lot of bandwidth.
Mode 2 = ICOM CI-V. Used for CI-V control of IC 703/706 at the same time as you use the
control panel.
Mode 3 = Char-timeout. A data packet is sent when
there is a pre-defined pause between two
received char.
Mode 4 = Kenwood, Yaesu, Elecraft. Used for CAT
control of TS-480 or TS-2000 at the same
time as you use the control panel.
Mode 5 = User-def-terminator. Used if you want to
define the terminator char by yourself (see
below).
Mode 8 = The WinKeyer emulator is activated, and
data received from COM1 are sent as CW
from the Radio-RRC in parallel with the
ordinary keyer.
COM2 databits
See COM1
COM2 stop bits
See COM1
COM2 parity
See COM1
COM2 terminator
See COM1
Use USB Com Port as
COM2
COM2 can be connected to the USB interface instead
of the RS-232 interface if your PC do not have
traditional com ports. When installing Microbit Setup
manager a virtual Com port called “Microbit RRC
Virtual Comport (COMX)” is installed. That’s the one
you should connect to when using HRD or other
softwares.
Yes or No (default = No).
COM3 mode
(USB-COMFSK)
Only available in the
Control-RRC
COM3 is available only via USB. It’s shown as
COMFSK in Widows Device manager. In mode-8 the
WinKeyer emulator is activated, and data received
from the USB port are sent as CW from the RadioRRC in parallel with the ordinary keyer. In mode-10
received data from the USB port RTTY are sent by the
Radio-RRC via one of the (selectable) outputs.
“Inactive” (default)
“Mode-8 WinKeyer”
“Mode-10 Baudot RTTY”

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
55 of 228

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
56 of 228
Advanced settings
Under advanced settings it is possible to change the default port numbers used by the RRC. It
can be necessary if there are more than one RRC on your LAN. In earlier versions we used
port 5060 for SIP but it’s often reserved for IP-telephony today so we have changed default
ports. You really need to know what you are doing when you change port numbers especially
on the Radio-RRC so that you don't disconnect yourself. Change web and telnet port number
ONLY if you have to due to other services or more than one RRC on your LAN. If you lose the
connection a car ride might be the next thing you do.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
57 of 228
Parameter
Setting
UDP cmd port
Port number used for the Command channel.
13002 (default)
UDP audio port
Port number used for the audio channel
13001 (default)
SIP port
Port number used for the SIP session.
13000 (default)

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
58 of 228
Web server port
Port number used for the internal http web server.
80 (default)
Telnet server port
Port number used for the internal telnet server.
23 (default)
Rx jitter buffer size
Set the maximum number of audio packets from the
received audio stream that is buffered. Dictates
maximum playback delay. Higher values result in
better tolerance against bad Internet connections.
Note that this value must be larger than the jitter
delay.
4 (default)
Rx jitter delay
Set the number of audio packets received and
buffered from the audio stream before beginning
playback. Dictates minimum playback delay. Small
values gives short delays, higher values result in
better tolerance against bad Internet connections but
the delay will increase. Note that this value must be
less than the jitter buffer size.
3 (default)
Audio packet size (ms)
Sets the max size (length) of the audio packets in ms.
If you have a good Internet connection with lots of
bandwidth or running both RRC:s under the same
LAN/WLAN it's possible to reduce the packet size
down to 1 ms. Smaller packets means decreased
delay but increased bandwidth.
20 (default)
RTP Tx Mode
Control-RRC: If VOX will be used switch on this
function. It means that the audio stream is sent
continuously from the Control-RRC to the Radio-RRC.
This can be a security problem for some user because
the audio from the mic is sent to the Internet all the
time.
Radio-RRC: Some mobile (3G) networks have a delay
before they open up for the audio stream which ends
up in problems when releasing the PTT. This function
often solves this problem. If you use a Squelched
radio you can set “RTP tx mode” to Squelched, the
audio data will then only be sent when the squelch is
open to reduce cost if you pay by Mb for example.
Normal (default)
Continuous
Squelch (Only radio-RRC)
Debug level
Not used, and should not be changed.
Off (default)
Low
Medium
High
Disable Audio tones
(Control-RRC only).
Makes it possible to disable the Busy and Error tones.
No (default)
Yes

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
59 of 228
Audio tones-dB [70-0]
(Control-RRC only)
You can set the level of the different status tones
generated by the RRC
70-0
30 (default)
IP identification
(morse)
(Control-RRC only)
Makes it possible to let the Control-RRC to send it’s IP
number in morse code, can be useful when DHCP is
used.
No (default)
Yes
Full Duplex
(Control-RRC only)
Makes it possible to use full duplex. Eg. the speaker
will not be muted when PTT is pressed. To use the
function “Continuous RTP Tx” must be activated in the
Radio-RRC.
No (default)
Yes
Yaesu pwr-on/off
(Radio-RRC only)
Is used to switch on and off Yaesu FT450/950/2000/5000/9000radios automatically on
connect/disconnect when radiomode 4 or 10 is used.
No (default)
Yes
PTT-off mute delay
(Control-RRC only)
Makes it possible to mute chirps coming from Txmonitor audio when PTT is released.
0-999 (0 = default)
IP Type-of-Service
(dec)
The RTP packets can be tagged for ToS according to
RFC 791 to make it possible to use QoS in networks
which support QoS. The parameter is entered in
decimal.
0 (default)
Elecraft advanced
Not in use
UDP antenna-switch
port (Radio-RRC only)
Sets the port to which the Remoterig 10 x Antenna
switch should connect to, Should match the settings in
the antenna switch.
13010 (default)
UDP cmd min-datasize
In some very rare situations routers/ISP will not
transfer very short UDP messages. In this situations
you can set the min data size of the message. The
message is filled out with dummy data.
0-100
0 (default)

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
60 of 228
Dynamic DNS setting (only Radio-RRC)
The Radio-RRC has a Dynamic DNS client to be used when the Internet Service Provider (ISP)
uses dynamic IP addresses (DHCP) instead of fixed IP address. DHCP is the most common for
private users. The RRC supports our own free Remoterig dynamic DNS service and
DynDNS which is not free for new users anymore. You can choose to use one of them. The
advantage with using a dynamic DNS service is that you do not need to know the IP address
to your remote router, you only need to remember the own host name. The Radio-RRC will
automatically update the DNS server when the IP changes so you don’t need to bother about
it.
Remoterig dynamic dns service
The Remoterig dynamic dns service only support equipment from Remoterig and Microbit like
the RRC-1258 and the WebSwitch 1216H etc.
The Remoterig dynamic dns service do not need any registration it’s automatically generated
based on the serial number on the equipment.
To activate the Remoterig dynamic dns client select “ddns.remoterig.com” from the drop
down on the Dynamic DNS settings page. Also select a DNS check interval, if your IP address
change often you can select a low value, if it goes month between the changes you can select
a higher value. After that click on “Submit” and “Apply changes”, the RRC will restart.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
61 of 228
After the RRC has restarted go back to the Dynamic DNS settings page. You will now see that
the settings Own hostname, Username and Password are automatically generated. The only
important information is the Own hostname, copy the whole row, this is the information you
should put into the SIP contact box in the Control-RRC and the web address you should use
when remote configure the Radio-RRC in the future. No more registration is needed.
Remember that DNS address like this is only for use when you connect over the internet, as
long as you are operating on you own LAN use the IP address. When using ddns it’s important
that the DNS settings are ok as they are needed for the RRC to be able to update the ddns.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
62 of 228
When you have done the setup and restarted the RRC, it will update the Remoterig DDNS.
You can check the status of the update at http://ddns.remoterig.com/status
Enter the hostname from your RRC in this example = hfd3dqw6.
If your RRC has updated the DDNS you will see when and what current public IP the RRC has
reported.
If it’s not updated check the RRC-status page and check the DNS and DDNS status.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
63 of 228
DynDNS dynamic dns service
The Radio-RRC also supports the commercial dynamic DNS service DynDns. Earlier this was a
free service, it’s still free for old users but not for new. If your router has a DynDNS client you
can also use that one, and do not activate more than one DynDNS client at the same LAN
segment. DynDNS do not accept multiple updates from same IP. The DynDNS client checks
what IP address your router has got from the ISP and sends the information to DynDNS:s
DNS server. When using DynDNS you enter "Own host name" instead of an IP address in the
SIP contact setting in the Control-RRC and you don't need to bother if the IP address at the
Radio-RRC changes. You need to register an account at
http://www.dyndns.com/services/dns/dyndns/ and get a domain name. There are other
providers of the same service but RRC-1258MkII only supports DynDNS or Remoterig ddns.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
64 of 228
Parameter
Setting
Dynamic DNS check
interval
Sets how often the external IP address of your
router should be checked, value in minutes:
Off (Dynamic DNS client disabled)
10
20
30
40
50
60
180
600
1440
Dynamic DNS host name
Sets which DNS service you will use
ddns.remoterig.com (our own free service)
members.dyndns.org (commercial service)
Own host name
Domain name registered at DynDNS.com.
Example:
my-radio-site.ham-radio-op.net
Username
Dynamic DNS account username.
Password
Dynamic DNS account password.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
65 of 228
Keyer Settings (Control-RRC)
A very powerful function for remote CW operation is implemented in the RRC-1258MkII. The
system is able to handle delays and jitter caused by Internet in a unique way. This function is
also dependent on the I/O configuration, see IO settings. The Keyer also handles straight key
CW generated from an old fashion straight keyer or a computer. The RRC also emulate a
WinKeyer to be able to send CW from a log program supporting WinKeyer. The WinKeyer
emulator has to be assigned to COM1, COM2 or COM3 (USB) see serial settings.
Parameter
Setting
Enable
Enable the CW-keyer function.
No = CW-keyer is off
Yes = CW-keyer is on (default)

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
66 of 228
Iambic
Set the CW-keyer iambic mode.
Old type, squeeze keyer
Mode-A
Mode-B (default)
Mode-B + auto-char-space
Paddle reverse
Set the reverse mode for the CW-paddle.
No, left paddle dot & right paddle dash (default)
Yes, left paddle dash & right paddle dot
Weight
Time ratio between dash and dot.
25-40 = 2.5-4.0/1
30 = 3.0/1 (default)
Side tone hz
Frequency for the side-tone in Hz.
0,300-1500 = side-tone frequency in Hz
800 = 800 Hz (default)
0 = No local side tone is generated, can be used to test how the CW
sounds if you enable side tone in the radio and send with memory
keyer or PC.
Side tone -dB
Audio level for the side-tone in dB.
50-0 = audio level in –dB
20 = -20 dBm (default)
Lf delay ms
Mute (delay) time for audio from the radio at Control-RRC after a
dot/dash command. Recommendation - start with same value as the
ping time.
0-500 = delay in milliseconds
0 = no delay (default)
Key delay ms
Delay time before the keying of the radio is executed at RRC- radio.
0-250 = delay in milliseconds
50 = 50 ms delay (default)
Speed pot min
wpm[5-99]
Sets the lower limit of the pot range
5-99 = 5-99 wpm
10 = 10 wpm (default)
Speed pot
max wpm[599]
Sets the upper limit of the pot range
5-99 = 5-99 wpm
10 = 40 wpm (default)
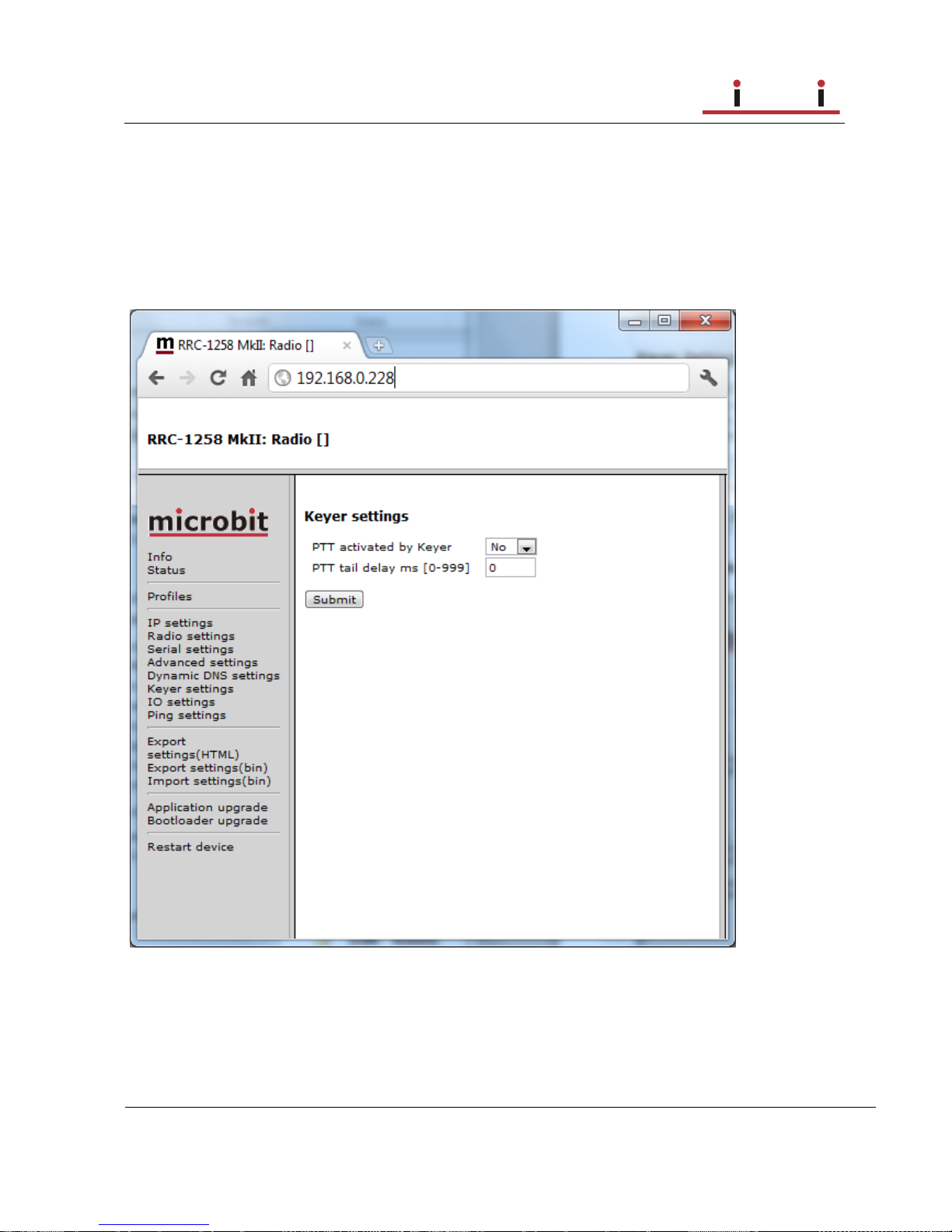
USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
67 of 228
Keyer Settings (Radio-RRC)
In the Radio-RCC only one parameter is available. “PTT-activated by keyer” is a function that
is useful if you want the PTT input of the radio to be activated when using the Remoterig
keying function. The PPT is activated before the “Key delay” meaning that a PA for example
can be activated x ms before the keying signal is activated to prevent hot switching. With the
PTT tail delay you can decide how long the PTT will be kept active after the last CW character
is sent.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
68 of 228
Parameter
Setting
PTT activated by keyer
Enable the PTT function.
No = (default)
Yes = PTT is activated by the keyer
PTT tail delay ms
[999]
Enable the PTT Tail function
0 = No delay (default)
1-999 = delay in ms.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
69 of 228
IO Settings
The inputs and outputs in both the Control-RRC and Radio-RRC are configurable to meet
different needs.
Control-RRC:
Parameter
Setting
IN0 mode
Select the function for Input-0 (IN0) signal in the I/O connector.
0 = I/O, input status is transferred to Radio-RRC (default)
1 = Keyer, straight key or external keyer
2 = PTT, PTT-switch or foot-switch etc.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
70 of 228
OUT0 mode
Output 0 can only be configured for one of two functions.
I/O = Indicating that SIP connection is up.
Keyer = The output follows the Keyer output.
OUT1 mode
OUT1 mode Output 1 can be configured for one of two functions.
I/O = The output follows Input 1 from the Radio-RRC.
Keyer = The output follows the Keyer output.
OUT2 mode
Output 2 can can be configured for one oftwo functions.
I/O = The output follows Input 2 from the Radio-RRC.
Keyer = The output follows the Keyer output.
USB RTS as PTT
Select which of the USB virtual COM ports RTS signal which should be used
as external PTT. Useful when using Logging software, RTTY programs etc.
Disabled = (default)
COM0 = COM0 rts is used as PTT control
COM1 = COM1 rts is used as PTT control
COM2 = COM2 rts is used as PTT control
USB DTR as CW
Select which of the USB virtual COM ports DTR signal which should be
used as CW key input. Useful when using Logging software, RTTY
programs etc.
Disabled = (default)
COM0 = COM0 dtr is used as CW key input
COM1 = COM1 dtr is used as CW key input
COM2 = COM2 dtr is used as CW key input

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
71 of 228
Radio-RRC:

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
72 of 228
Parameter
Setting
OUT0 mode
Select the function for output-0 (OUT0) signal the I/O connector.
0 = I/O, active when IN0 on Control-RRC is active (Control-RRC IN0-mode
setting must be in state I/O). (default)
1 = Keyer, output to the radio straight key input
2 = PTT, used as external PTT
3 = Connect, active when the SIP-connection is active
4 = On/Off, controlled by the ON/OFF button on this side
(*)
5 = Keyer PTT, active when CW is send via the keyer (can be used to key
a PA). If you set “key delay” in the Control-RRC this output will be
activate “key delay” ms before the actual CW-keying is started.
6 = Baudot/45 used as output for RTTY 45.45 baud. RTTY input via USB
virtual com port at Control-RRC. Connect PC software to the virtual
com named FSK COM.
7 = Baudot/45 (inv) same as above but the RTTY key signal is inverted.
OUT1 mode
Select the function for output-1 (OUT1) signal the I/O connector (or tip in
the PAD-jack).
0 = I/O, active when IN0 on Control-RRC is active. (Control-RRC CW Keyer
function must be disabled). (default)
1 = Keyer, output to the radio straight key input
2 = PTT, used as external PTT
3 = Connect, active when the SIP-connection is active
4 = On/Off, controlled by the ON/OFF button on this side
(*)
5 = Keyer PTT, active when CW is send via the keyer (can be used to key
a PA). If you set “key delay” in the Control-RRC this output will be
activate “key delay” ms before the actual CW-keying is started.
6 = Baudot/45 used as output for RTTY 45.45 baud. RTTY input via USB
virtual com port at Control-RRC. Connect PC software to the virtual
com port named FSK COM.
7 = Baudot/45 (inv) same as above but the RTTY key signal is inverted.
OUT2 mode
Select the function for output-2 (OUT2) signal the I/O connector (or ring in
the PAD-jack).
0 = I/O, active when IN0 on Control-RRC is active. (Control-RRC CW Keyer
function must be disabled).
1 = Keyer, output to the radio straight key input. (default)
2 = PTT, used as external PTT
3 = Connect, active when the SIP-connection is active
4 = On/Off, controlled by the ON/OFF button on this side
(*)
5 = Keyer PTT, active when CW is send via the keyer (can be used to key
a PA). If you set “key delay” in the Control-RRC this output will be
activate “key delay” ms before the actual CW-keying is started.
6 = Baudot/45 used as output for RTTY 45.45 baud. RTTY input via USB
virtual com port at Control-RRC. Connect PC software to the virtual
com port named FSK COM.
7 = Baudot/45 (inv) same as above but the RTTY key signal is inverted.
(*)
When the ON/OFF buttons are pushed the output change will be immediate, but will
resume to last saved position after power on. To make the changes permanent use the "apply
changes" button.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
73 of 228
Ping settings (only Radio-RRC)
The Radio-RRC has a Ping Watchdog function which can be used as an extra security. This
function is quite common in network equipments. It can be set to ping an IP address and
when it does not get any answer, it will make a hard reboot of the RRC. The status of the ping
watchdog can be checked at the status page. This function is only available on the Radio-RRC.
Enable ping watchdog
Enables the function.
No = Function is disabled
Yes, test = Function enabled but it will not actually
reboot, can be used for test
Yes, reboot = Function is enabled.
IP address to ping
IP address to ping is entered here, In normal cases
use the Gateway IP.
Ping Interval (seconds)
Interval between the ping is sent.
(1-65535, default 300 s)
Startup delay (seconds)
Delay before the first ping is sent.
( 300-65535), default 300 s.
If Test mode is activated it can be set to 10-65535
Failure count to reboot
Sets how many times the ping is allowed to fail
before reboot is done. (1-255, default 3 )

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
74 of 228
Wi-Fi settings
You can enter SSID and Password direct or check them on the WiFi page. See more in the
WiFi Chapter.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
75 of 228
Export settings (HTML)
This function creates a text file with the actual settings and status of the unit. This file can be
sent via email for support purposes for example.
Export settings (bin)
This function is used to backup your settings to a file in your PC. When clicking on the link a
dialog box will show up where you can decide where to store and the name of your backup
file.
Note! The exported file will only include settings for the active profile.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
76 of 228
Import settings (bin)
This function is used import your backup file from your PC. Click on select file and browse to
your file and then click import.
Note that the imported settings will be stored in the currently selected profile.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
77 of 228
Application firmware upgrade
The application firmware can be updated over the Internet via the web interface when bugs
are fixed and/or new functionality is implemented. You don't have to be where the RRC1258MkII is to do the updates. Download the new firmware from www.remoterig.com and
save the file on your computer (it has a name like RRC1258-CRC_v1.38_2009-09-04.bin).
Connect to the RRC you want to update and select 'Application-upgrade'. Then click on the
'Browse' button and select the file with the new firmware. After that you click on the 'Upgrade'
button and the new firmware will be transferred and saved into the RRC. When the firmware
is updated the RRC will restart. Note -- Do not interrupt the upgrade process in any way.
Wait a minute or two then connect to the RRC again and select 'Info' and verify that the
Software version is updated. If it looks like its not updated empty the web browser cache, to
prevent it from showing an old cached page. The update NEVER fails but the browser is a
common problem.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
78 of 228
Bootloader firmware upgrade
This follows the same steps as the application firmware upgrade procedure above.
Restart device
Restart device can be used if you want to reset and restart the RRC without saving any
changes (before apply changes) or just for ordinary reset.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
79 of 228
Configuration with terminal-interface
All parameters can also be programmed via the serial interface COM1 (RS-232) or Telnet port.
COM1 has the following settings: 38400 baud, 8 bits, No parity, and 1 stop bit. Select the sys
[s] and setup-edit [1] menus to configure the RRC. This method of configuration is not user
friendly and should be avoided.
=========================
a: audio
c: codec
d: debug
e: extio
f: flash
i: sip
l: led
q: audio quality
p: power
r: radio
s: sys
u: usb
=========================
s
sys
=========================
1: setup edit
2: setup view
3: setup clear
4: sntp
5: rtc
6: wdt reset
7: dns query
8: show network info
9: STUN test
0: memory
a: UDP send
b: UDP receive
c: Setup default 1(Control)
d: Setup default 2(Radio)
r: COM1-rts/cts on/off
q: exit

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
80 of 228
WiFi
General
The RRC-1258 can be equipped with a WiFi Interface. A WiFi interface is convenient when you
want to connect the RRC:s to a WiFi network. You do not need any extra cables or boxes. For
the Control-RRC the main reason to use WiFi might be the portability, and for the Radio-RRC
to physically separate the RRC from the telephone/DSL line which is the most common route
for lightning storms to hit the RRC and the Radio.
The WiFi Interface is mounted on the pin header P3 in the RRC-box. Units produced from the
summer 2012 has P3 in place from production. Units produced earlier do not have P3 in place
you have to solder to put it in place, Instruction for how this is done can be found on the
Remoterig website under Support/Mods (hardware).

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
81 of 228
The 2.4 GHz Wifi Interface is compliant to 802.11b/g and single stream 802.11n and supports
WPA2- (AES), WEP (64 and 128 bit) modes of security in infrastructure mode and also TKIP in
SPI mode.
There is no limitations compared to Ethernet, all settings that are used when they are
connected to Ethernet can be used.
The RRC automatically switch between WiFi or Ethernet. IF Ethernet is connected, Ethernet
will be used.
Connecting to a Wifi network
The easiest way to setup the WiFi connection is to do it via the Microbit Setup manager. If you
know the parameters it can be done from the web interface also, but you cannot scan WiFi
Networks that way so we focus on using the Setup manager.
Do not forget to connect 12V power to the RRC, the setup works when the unit is powered
from USB but you can not scan for WiFi networks until you connect 12V.
The RRC can store settings for up to 8 different WiFi networks. The RRC will automatically
connect to the strongest network from the list. You can not force the RRC to connect to a
specific network, if you must do that, you have to remove the unwanted network from the
list.
- Disconnect the Ethernet cable if it’s connected, Connect 12V to the RRC, and connect the
USB cable from your PC to the RRC. Start the Microbit setup manager
- Select the WiFi tab

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
82 of 228
Click on the Get button.
- You will get a empty page when the unit is not programmed, when you later open this
page you will see the stored settings for your WiFi networks. Click Scan.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
83 of 228
- After a 1 second you will see the WiFi networks which are available at your current
location. The networks are sorted in order decided by Signal strength, the strongest on
top. Up to 32 WiFi networks can be shown.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
84 of 228
- Select the network you want to use by clicking on the button beside the SSID.
- Click on the button on the row where you want to store the Network.
- Click on the “use” button.
- Enter the password (Private shared key) if it’s needed.
- Click “Save and close” button.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
85 of 228
- Give The RRC a few seconds to reboot and connect to the WiFi Network.
- Click on the Net info tab.
- Click on the “Get” button. You will now see that the Box has got an IP-adress from the
DHCP- server. If it still shows 000.000.000.000 etc. wait a moment and click on the “Get”
button again

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
86 of 228
- Click on the “Browse unit” button. You will now see the RRC internal web pages(*1).
- Click on “Info” and you will see the WiFi network status
*1 - Your PC has to be connected to the same network as the RRC if it should be possible to
connect to it. If the PC is connected to the same WiFi Network, “wireless isolation” must be
switched off in the Router/access point.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
87 of 228
CW-Keyer
General
The RRC-1258 has a CW-keyer function that makes CW operation possible over Internet even
if there are long latencies and lots of jitter. Note that the CW-keyer is by default disabled.
The CW-keyer side-tone is generated locally at the control RRC. When the dot or dash is
executed the audio from the radio can be muted at the Control-RRC to disable the radio sidetone or annoying clicks and sounds. The time the mute function is active is defined by the lfdelay setting. The value of lf-delay depends on the latency of Internet. A good start value is
the same value as the ping time between control and radio QTH.
Another unique feature is a kind of adjustable jitter buffer at the radio end. If the Internet
connection has varying latencies, you can set a key-delay before the keying of the radio is
executed. This delay makes it possible to reconstruct the transmission on-the-fly and the
system will be much more tolerant against varying latencies (jitter). Longer key-delays give
higher tolerance against jitter but also add delay until the keying is executed at the radio.
Even if you have a good connection you could try with a low value. Remember that when you
increase this value you must also increase the lf-delay value.
Settings
Keyer settings:
Control
Radio
Enable
Yes
Iambic
Mode-A
Paddle reverse
No Weight [25-40]
30 Side tone hz [500-1500]
800
Side tone –dB [50-0]
20 Lf delay [0-500]
0 Key delay [0-250]
0
IO settings:
Control
Radio
IN0 mode
I/O
USB DTR as CW
No
OUT0 mode
I/O
OUT1 mode
I/O
OUT2 mode
Keyer

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
88 of 228
Connections
PAD – Control-RRC:
At the Control-RRC the PAD-jack is used to connect a CW-paddle. The input is for a standard
3.5 mm stereo plug. The left paddle is connected to the tip and the right paddle to the ring.
Common is connected to the inner ring and house. Note - these signals are also available in
the I/O-connector.
Signal
PAD jack
IO setting
left-paddle
tip
-
right-paddle
ring
-
gnd
inner ring
-
PAD – Radio-RRC:
At the Radio-RRC the PAD-jack is used to connect the output signal from the CW-keyer to the
radio straight-KEY input. The output is for a standard 3.5 mm stereo plug. A standard cable
with 3.5 mm connector in both ends can often be used. Note - these signals are also available
in the I/O-connector.
Signal
PAD jack
IO setting
keyer-output
tip
OUT2 mode = Keyer
keyer-output
ring
OUT1 mode = Keyer
gnd
inner ring
-
USB – Control-RRC:
A PC with straight-key functionality can be used to perform the keying, alone or in
combination with a CW-paddle. To activate keying the PC could use the DTR signal in the
virtual USB COM-port delivered by the RRC USB device. The PC control works in parallel with
the CW-paddle so it is possible to shift between PC-keying and the CW-paddle without
changing the configuration.
I/O-connector – Control-RRC:
A PC with straight-key functionality or other external keyer can be used to perform keying,
alone or in combination with a CW-paddle. To activate keying connect pin-4 (IN0) to GND.
The external keyer works in parallel with the CW-paddle so it is possible to shift between
external keying and the CW-paddle without changing the configuration.
Note - The straight-key input (IN0) is a generic input and cannot be connected direct to a PC,
you need an interface, see appendix.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
89 of 228
Signal
I/O connector
IO setting
right-paddle
1 (IN1)
-
left-paddle
2 (IN2)
-
straight-key/PC
4 (IN0)
IN0 mode = Keyer
gnd
8
-
I/O-connector – Radio-RRC:
The output signal from the CW-keyer to the radio straight-KEY input can also be found in the
I/O connector.
Signal
I/O connector
IO setting
keyer-output
5 (OUT0)
OUT0 mode = Keyer
keyer-output
6 (OUT1)
OUT1 mode = Keyer
keyer-output
3 (OUT2)
OUT2 mode = Keyer
gnd
8
-

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
90 of 228
RTTY Keying
General
Most HF-radios have a special FSK/RTTY keying input which is better to use than AFSK (audio
frequency shift keying) since you don’t need to set mic gain and other settings. The RRC-1258
has a separate serial channel for transfer of 45.45 baud RTTY keying data. The RTTY serial
channel is only available via the USB interface.
When installing the Microbit Setup manager a USB-driver called COMFSK is installed
In your RTTY PC-Software you should select the serialport number assigned to the driver by
Windows, in the example above it’s COM4.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
91 of 228
At the Radio-RRC IO-settings page you need to select which output you want to use for the
RTTY keying signal. RTS from the RRC-1258 COMFSK USB port is used to key PTT.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
92 of 228
RTTY with MMTTY
The Remoterig specific settings to use MMTTY for RTTY is shown below.
At the TX tab select the PTT & FSK comport to the same comport as Device Manager showed
to be assigned to RRC-1258 COMFSK port, in this example it’s COM4.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
93 of 228
At the Misc tab e select COM-TxD(FSK) and click on the “USB Port” button.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
94 of 228
In the “USB port option” dialog select “C-limiting speed”. If not limiting speed is selected the
PTT will be released before the whole RTTY string is sent, because the USB communication is
so much faster than a ordinary RS-232 serial port.
Settings
IO settings:
Control
Radio
OUT0 mode
- OUT1 mode
Baudot/45
OUT2 mode
Keyer

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
95 of 228
Connections
PAD – Control-RRC:
Only the USB interface can be used for RTTY as described above.
PAD – Radio-RRC:
At the Radio-RRC the PAD-jack can be used to connect the RTTY signal from the FSK serial
port. The PAD will then be shared with CW key output. The pad jack is for a standard 3.5 mm
stereo plug. Note - these signals are also available in the I/O-connector.
Signal
PAD jack
IO setting
keyer-output
tip - keyer-output
ring
OUT1 mode = Baudot/45
gnd
inner ring
-
USB – Control-RRC:
A PC with a suitable software like MMTTY can be used to perform the RTTY keying. Together
with the RTTY keying signal PTT need to be activated this is done by activating the RTS signal
in the virtual comport (COMFSK). MMTTY does this by default other software may need
manual configuration.
I/O-connector – Radio-RRC:
The output signal for the RTTY keying can also be found in the I/O connector.
Signal
I/O connector
IO setting
RTTY- output
5 (OUT0)
OUT0 mode = Baudot /45
RTTY -output
6 (OUT1)
-
RTTY -output
3 (OUT2)
-
gnd
8
-
The I/O connector can also be used for the PTT signal if the Mic PTT is not used. If you want
this function change one of the free outputs to PTT.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
96 of 228
ICOM CI-V
General
RRC-1258MkII supports the CI-V protocol used by almost every ICOM radio. Then you have to
use a PC-software e.g. HamRadioDeLuxe or similar rig control software at the control site. All
audio and data communication goes true the RRC:s and you don't need a PC at the remote
site. The Connect/Disconnect button on the web status page is used to connect/disconnect
to/from the remote site. It can also be done by the UP-button on the microphone or be set to
always be connected.
Hardware configuration
Normal:

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
97 of 228
SIP-Connect/disconnect via MIC UP button:
Radio settings (example)
Parameter
Control
Radio
Program mode
1 – ICOM CI-V
1 – ICOM CI-V
SIP password
hello
hello
SIP contact
192.168.0.228
Auto connect
No Audio quality
2 – Linear 16 bits 8 kHz
2 – Linear 16 bits 8 kHz
Audio dual-rx (*)
No
Codec out gain
255
255
Codec inp gain
18
0
Codec inp preamp
Yes
Codec inp HPF Hz
163
163
COM0 baudrate
9600
9600
COM0 data bits
8 8 COM0 stop bits
1
1
COM0 parity
0 - Off
0 - Off
(*) Available only in RRC-1258MkIIs, remember that the bandwidth demand is doubled.
Connections
Drawings of the connection cables can be found under appendix B.
Control-RRC:
Connect a Remoterig-I10c cable or a standard RS-232 cable between the PC and the RRC
COM2.

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
98 of 228
The microphone can be connected direct to the RRC AUX/MIC connector if you have a
microphone with RJ-45 connector, like the HM-103. If you have a microphone with a
circular connector like HM-36 you have to use the Remoterig I10a cable, the OPC-589,
from ICOM or make one by yourself (drawing for I10a is provided).
The speaker is connected direct to the RRC SP-jack with a 3.5 mm stereo plug.
Radio-RRC:
From the RRC TTL connector to the radios CI-V jack you can use the Remoterig I11c cable
or make it by your self. The cable should have a 4/6 modular connector in one end and a
3.5 mm stereo plug in the other end. The 3.5 mm plug is connected to the radio CI-V jack.
Between the RRC AUX/MIC connector and the radios microphone jack you can connect a
standard patch cable if the radio have a RJ-45 jack. If the radio have a circular
microphone jack you can use the Remoterig I11a or make the cable by yourself. (drawings
for I11a is provided). Make the cable as short as possible to prevent it from picking up HF.
The speaker signal from the radios external speaker jack to the RRC SP jack is connected
via a standard "off- the-shelf” cable with 3.5 mm stereo plugs in both ends.
I11a,I10a

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
99 of 228
1258 Cable I10 1(1)
Generic ICOM cables
RRC-1258MkII
1:2
m crob t
8-pol RJ 45 Con
Mic Inp
8-pol Circular
male
I10a screened 20 cm
75166
7
5
3
8
3
4
GND
GND
MIC
MIC
MICE
MICE
PTT
PTT
1
2
2
8V
8VUPUP
AF
PC
COM2
RRC-1258MkII
Front panel view
3
7
3
7
1
5
8
5
8
8
2
2
DSUB- 9pol
Female
I10c
DSUB- 9pol
Male
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SPEAKER
3.5 mm stereo plug

USER MANUAL
RRC-1258 MKII
Ba1258B_RemoteRig_MkIIs-A30
Microbit 2.0 AB 2010. All rights reserved
a
User manual
Rev. A30 – 2014 Jan 21
100 of 228
1258 Cable I11 1(1)
Generic ICOM cables
RRC-1258MkII
1:2
m crob t
Front panel view
1
8
TTL 4/6 modular
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
SPEAKER
3.5 mm stereo plug
SPEAKER
3.5 mm stereo plug
CI-V
3.5 mm stereo plug
1
2
5
6
3
4
1
6
GND
TDO
RDO
I11b
I11c
RRC-1258MkII
716
8
5
MICE
AUX/MIC 8-pol RJ 45 Con
1
2
5
6
7
8
3
4
8V
GND
AF
GND
AF
MIC
MIC
MICE
PTT
PTT
2
8V
PWR ON indication
I11a screened 1 m
8-pol Circular
female
 Loading...
Loading...