MICREL SY87700L Datasheet
3.3V 32-175Mbps AnyRate™
CLOCK AND DATA RECOVERY
DESCRIPTIONFEATURES
SY87700L
■ Industrial temperature range (–40°C to +85°C)
■ 3.3V power supply
■ SONET/SDH/ATM compatible
■ Clock and data recovery from 32Mbps up to
175Mbps NRZ data stream
■ Two on-chip PLLs: one for clock generation and
another for clock recovery
■ Selectable reference frequencies
■ Differential PECL high-speed serial I/O
■ Line receiver input: no external buffering needed
■ Link Fault indication
■ 100K ECL compatible I/O
■ Complies with Bellcore, ITU/CCITT and ANSI
specifications for applications such as OC-1 and
OC-3
■ Available in 28-pin SOIC and 32-pin EP-TQFP
packages
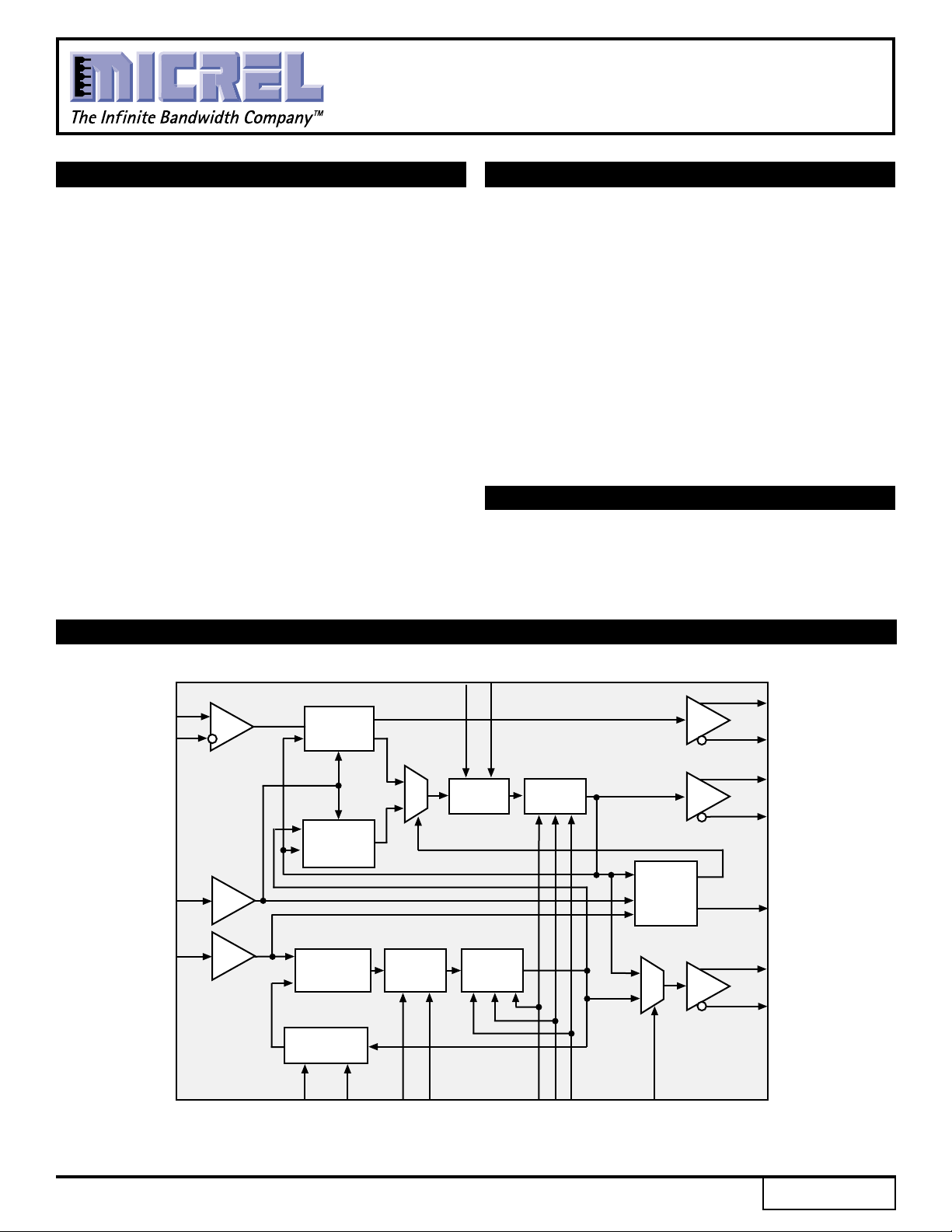
BLOCK DIAGRAM
The SY87700L is a complete Clock Recovery and Data
Retiming integrated circuit for data rates from 32Mbps
up to 175Mbps NRZ. The device is ideally suited for
SONET/SDH/ATM applications and other high-speed data
transmission systems.
Clock recovery and data retiming is performed by
synchronizing the on-chip VCO directly to the incoming
data stream. The VCO center frequency is controlled by
the reference clock frequency and the selected divide
ratio. On-chip clock generation is performed through the
use of a frequency multiplier PLL with a byte rate source
as reference.
The SY87700L also includes a link fault detection
circuit.
APPLICATIONS
■ SONET/SDH/ATM OC-1 and OC-3
■ Fast Ethernet
■ Proprietary architecture up to 175Mbps
RDINP
(PECL)
RDINN
CD
(PECL)
REFCLK
(TTL)
PHASE
DETECTOR
PHASE/
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
PHASE/
FREQUENCY
DETECTOR
DIVIDER
BY 8, 10, 16, 20
DIVSEL 1/2
(TTL)
0
1
CHARGE
PUMP
PLLS P/N
PLLR P/N
CHARGE
PUMP
VCO
SY87700L
VCO
FREQSEL 1/2/3
(TTL)
LINK
FAULT
DETECTOR
1
0
CLKSEL
(TTL)
RDOUTP
(PECL)
RDOUTN
RCLKP
(PECL)
RCLKN
LFIN
(TTL)
TCLKP
(PECL)
TCLKN
V
CC
V
CCA
V
CCO
GND
AnyRate™ is a trademark of Micrel, Inc.
Rev.: B Amendment: /0
1
Issue Date:
September 2000
Micrel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
NC
RDINP
RDINN
FREQSEL1
REFCLK
FREQSEL2
FREQSEL3
NC
RDOUTP
RDOUTN
VCCO
RCLKP
RCLKN
VCCO
TCLKP
TCLKN
9
10
11 12 13 14 15 16
CLKSEL
PLLRP
PLLRN
GND
GND
GNDA
PLLSN
PLLSP
32
31
30 29 28 27 26 25
DIVSEL2
CD
VCC
VCC
VCCA
VCCA
LFIN
DIVSEL1
Top Vie w
EP-TQFP
H32-1
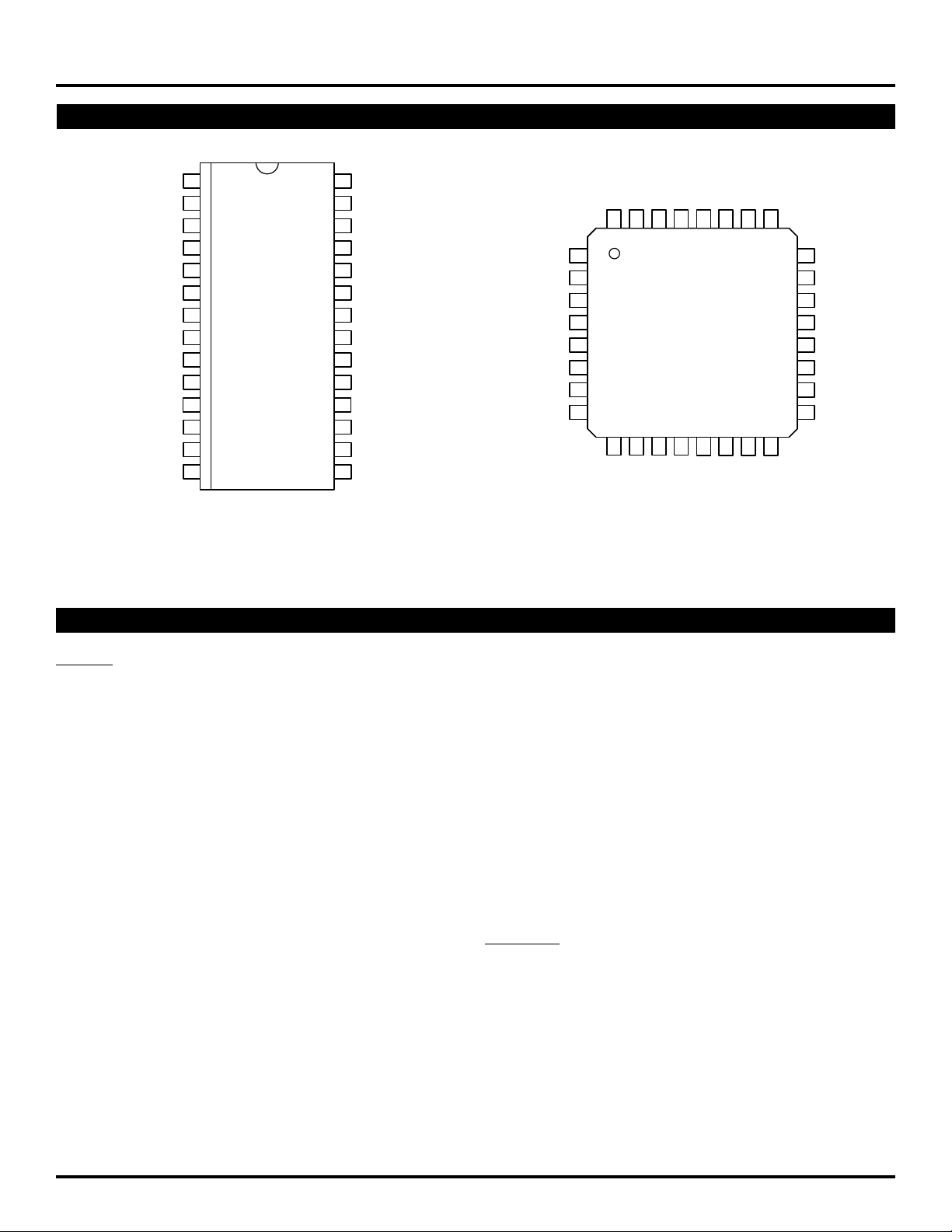
PIN CONFIGURATION
SY87700L
1VCCA
LFIN
2
DIVSEL1
FREQSEL1
REFCLK
FREQSEL2
FREQSEL3
RDINP
RDINN
N/C
10
PLLSP TCLKN1811
PLLSN CLKSEL1712
GND PLLRP1613
GND PLLRN1514
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Top Vie w
SOIC
Z28-1
28 VCC
CD
27
DIVSEL2
26
RDOUTP
25
RDOUTN
24
VCCO
23
RCLKP
22
RCLKN
21
VCCO
20
TCLKP
19
INPUTS
RDINP, RDINN [Serial Data Input] Differential PECL
These built-in line receiver inputs are connected to the
differential receive serial data stream. An internal receive
PLL recovers the embedded clock (RCLK) and data
(RDOUT) information. The incoming data rate can be within
one of five frequency ranges depending on the state of the
FREQSEL pins. See “Frequency Selection” Table.
REFCLK [Reference Clock] TTL inputs
This input is used as the reference for the internal
frequency synthesizer and the "training" frequency for the
receiver PLL to keep it centered in the absence of data
coming in on the RDIN inputs.
CD [Carrier Detect] PECL Input
This input controls the recovery function of the Receive
PLL and can be driven by the carrier detect output of optical
modules or from external transition detection circuitry. When
this input is HIGH the input data stream (RDIN) is recovered
normally by the Receive PLL. When this input is LOW the
data on the inputs RDIN will be internally forced to a constant
LOW, the data outputs RDOUT will remain LOW, the Link
Fault Indicator output LFIN forced LOW and the clock
recovery PLL forced to look onto the clock frequency
generated from REFCLK.
FREQSEL1, ..., FREQSEL3 [Frequency Select]
TTL Inputs
These inputs select the output clock frequency range as
shown in the “Frequency Selection” Table.
DIVSEL1, DIVSEL2 [Divider Select] TTL Inputs
These inputs select the ratio between the output clock
frequency (RCLK/TCLK) and the REFCLK input frequency
as shown in the “Reference Frequency Selection” Table.
CLKSEL [Clock Select] TTL Inputs
This input is used to select either the recovered clock of
the receiver PLL (CLKSEL =HIGH) or the clock of the
frequency synthesizer (CLKSEL = LOW) to the TCLK
outputs.
OUTPUTS
LFIN [Link Fault Indicator] TTL Output
This output indicates the status of the input data stream
RDIN. Active HIGH signal is indicating when the internal
clock recovery PLL has locked onto the incoming data
stream. LFIN will go HIGH if CD is HIGH and RDIN is within
the frequency range of the Receive PLL (1000ppm). LFIN
is an asynchronous output.
2
Micrel
SY87700L
RDOUTP, RDOUTN [Receive Data Output] Differential
PECL
These ECL 100K outputs represent the recovered data
from the input data stream (RDIN). This recovered data is
specified against the rising edge of RCLK.
RCLKP, RCLKN [Clock Output] Differential PECL
These ECL 100K outputs represent the recovered clock
used to sample the recovered data (RDOUT).
TCLKP, TCLKN [Clock Output] Differential PECL
These ECL 100K outputs represent either the recovered
clock (CLKSEL = HIGH) used to sample the recovered data
(RDOUT) or the transmit clock of the frequency synthesizer
(CLKSEL = LOW).
PLLSP, PLLSN [Clock Synthesis PLL Loop Filter]
External loop filter pins for the clock synthesis PLL.
PLLRP, PLLRN [Clock Recovery PLL Loop Filter]
External loop filter pins for the receiver PLL.
POWER & GROUND
VCC Supply Voltage
VCCA Analog Supply Voltage
VCCO Output Supply Voltage
GND Ground
N/C No Connect
NOTE:
1. VCC, VCCA, VCCO must be the same value.
(1)
(1)
(1)
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Clock Recovery
Clock Recovery, as shown in the block diagram generates
a clock that is at the same frequency as the incoming data
bit rate at the Serial Data input. The clock is phase aligned
by a PLL so that it samples the data in the center of the
data eye pattern.
The phase relationship between the edge transitions of
the data and those of the generated clock are compared by
a phase/frequency detector. Output pulses from the detector
indicate the required direction of phase correction. These
pulses are smoothed by an integral loop filter. The output of
the loop filter controls the frequency of the Voltage Controlled
Oscillator (VCO), which generates the recovered clock.
Frequency stability without incoming data is guaranteed
by an alternate reference input (REFCLK) that the PLL locks
onto when data is lost. If the Frequency of the incoming
signal varies by greater than approximately 1000ppm with
respect to the synthesizer frequency, the PLL will be declared
out of lock, and the PLL will lock to the reference clock.
The loop filter transfer function is optimized to enable the
PLL to track the jitter, yet tolerate the minimum transition
density expected in a received SONET data signal. This
transfer function yields a 30µs data stream of continuous
1's or 0's for random incoming NRZ data.
The total loop dynamics of the clock recovery PLL
provides jitter tolerance which is better than the specified
tolerance in GR-253-CORE.
Lock Detect
The SY87700L contains a link fault indication circuit which
monitors the integrity of the serial data inputs. If the received
serial data fails the frequency test, the PLL will be forced to
lock to the local reference clock. This will maintain the correct
frequency of the recovered clock output under loss of signal
or loss of lock conditions. If the recovered clock frequency
deviates from the local reference clock frequency by more
than approximately 1000ppm, the PLL will be declared out
of lock. The lock detect circuit will pull the input data stream
in an attempt to reacquire lock to data. If the recovered
clock frequency is determined to be within approximately
1000ppm, the PLL will be declared in lock and the lock
detect output will go active.
3
Micrel
y
CHARACTERISTICS
SY87700L
Performance
The SY87700L PLL complies with the jitter specifications
proposed for SONET/SDH equipment defined by the Bellcore
Specifications: GR-253-CORE, Issue 2, December 1995 and
ITU-T Recommendations: G.958 document, when used with
differential inputs and outputs.
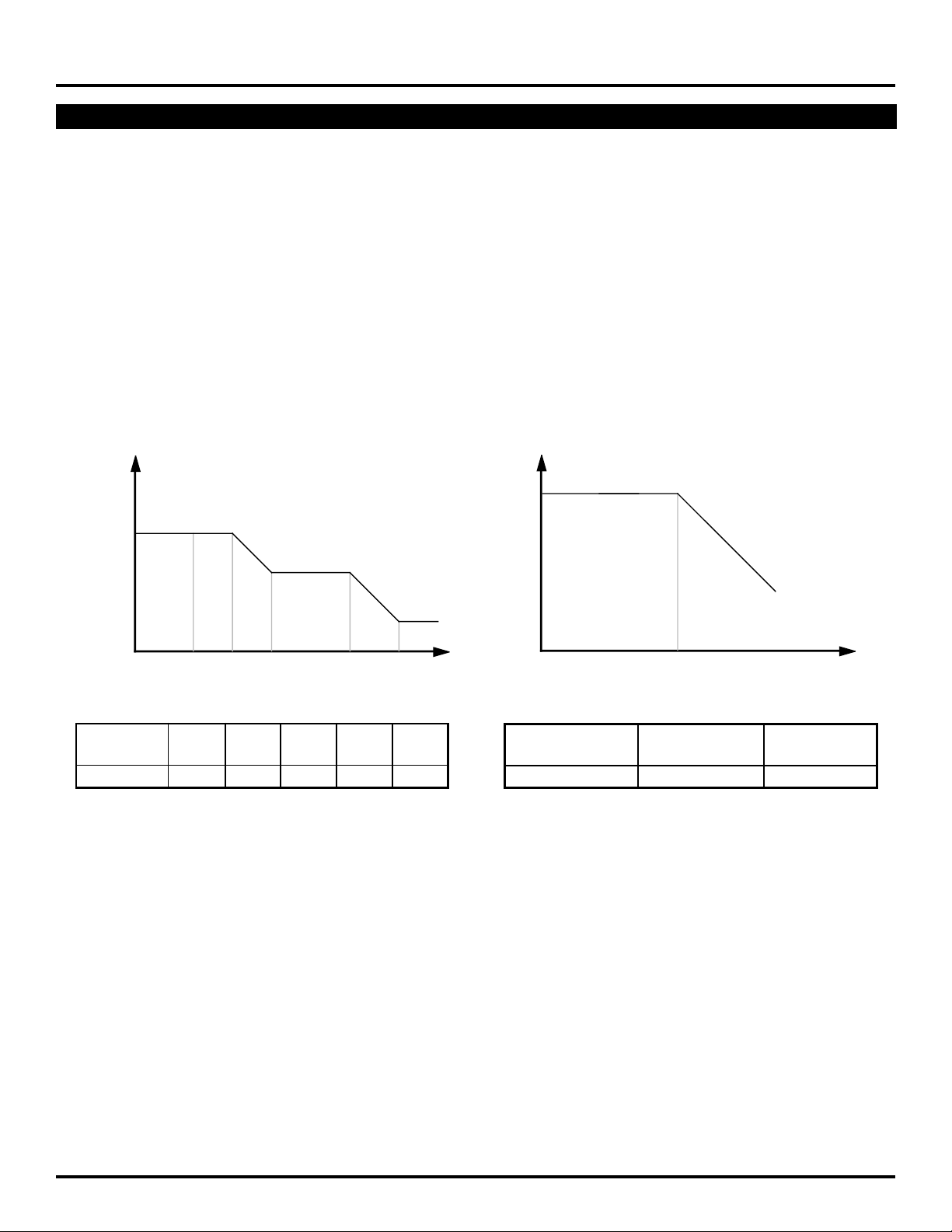
Input Jitter Tolerance
Input jitter tolerance is defined as the peak-to-peak
amplitude of sinusoidal jitter applied on the input signal that
causes an equivalent 1dB optical/electrical power penalty.
SONET input jitter tolerance requirement condition is the
input jitter amplitude which causes an equivalent of 1dB
power penalty.
A
15
1.5
(UI p-p)
Sinusoidal Input
Jitter Amplitude
0.40
-20dB/decade
-20dB/decade
Jitter Transfer
Jitter transfer function is defined as the ratio of jitter on
the output OC-N/STS-N signal to the jitter applied on the
input OC-N/STS-N signal versus frequency. Jitter transfer
requirements are shown in Figure 2.
Jitter Generation
The jitter of the serial clock and serial data outputs shall
not exceed .01 U.I. rms when a serial data input with no
jitter is presented to the serial data inputs.
Jitter Transfer (dB)
0.1
-20dB/decade
-20
Acceptable
Range
f0 f1 f2 f4 ft
Frequency
OC/STS-N f0 f1 f2 f3 ft
Level (Hz) (Hz) (Hz) (kHz) (kHz)
3 10 30 300 6.5 65
Figure 1. Input Jitter Tolerance
fc
Frequenc
OC/STS-N fc P
Level (kHz) (dB)
3 130 0.1
Figure 2. Jitter Transfer
4
 Loading...
Loading...