Micrel MIC2185 User Manual
MIC2185 Micrel
MIC2185
Low Voltage Synchronous Boost PWM Control IC
Final Information
General Description
Micrel’s MIC2185 is a high efficiency synchronous boost
PWM control IC. With its wide input voltage range of 2.9V to
14V, the MIC2185 can be used to efficiently boost voltages in
1- or 2-cell Li Ion battery powered applications, as well as
fixed 3.3V and 5V systems. Its powerful 5Ω output drivers
allow the MIC2185 to supply large output currents with the
selection of the proper external MOSFETs.
With it’s fixed frequency PWM architecture, and easily synchronized drive, the MIC2185 is ideal for noise-sensitive
telecommunications applications. The nominal 400kHz operating frequency of the MIC2185 can be divided by two,
allowing the device to be externally synchronized to frequencies below 400kHz.
The MIC2185 also features a low current shutdown mode and
a programmable undervoltage lockout. A skipped pulse mode
of operation can be manually set to achieve higher efficiencies at light load conditions.
The MIC2185 is available in a 16 pin SOIC package and 16
pin QSOP package with an ambient temperature operating
range from –40°C to 85°C.
Ordering Information
Part Number Frequency Voltage Junction Temp. Range Package
MIC2185BM 200/400kHz Adj –40°C to +125°C 16-lead SOP
MIC2185BQS 200/400kHz Adj –40°C to +125°C 16-lead QSOP
Features
• Input voltage range: 2.9V to 14V
• 95% efficiency
• Oscillator frequency of 200kHz/400kHz
• Frequency sync to 600kHz
• 0.5µA shutdown current
• Two 5Ω output drivers
• Front edge blanking
• PWM Current Mode Control
• Cycle-by-Cycle current limiting
• Frequency foldback protection
• Adjustable under-voltage lockout
• Precision 1.245V reference output
• 16 pin SOIC narrow body package
Applications
• 3.3V to 5V conversion in telecom systems
• Satellite Phones
• Cable Modems
• 1-and 2-cell Li Ion battery operated equipment
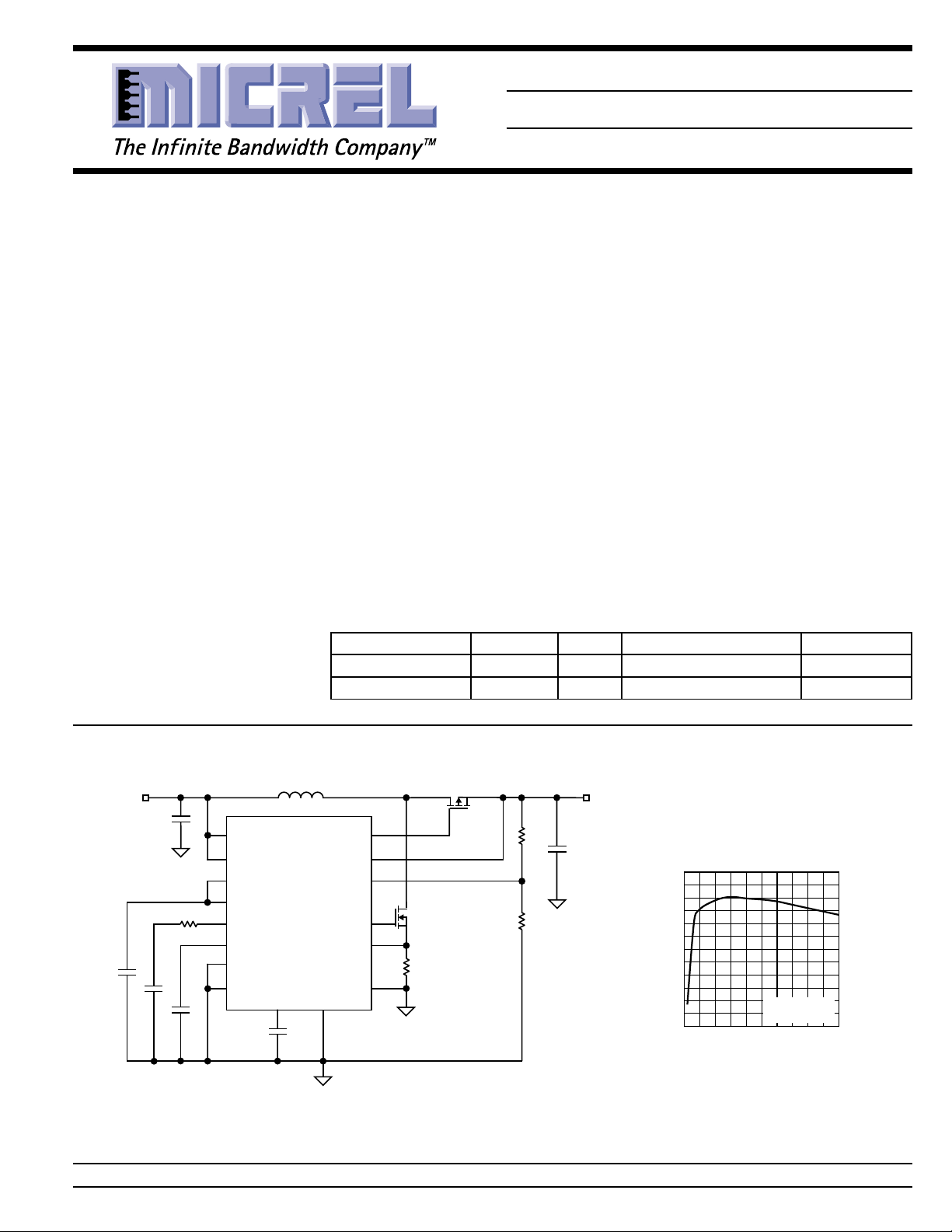
T ypical Application
VIN = 3.3V
C
IN
1
VINA
7
EN/UVLO
15
FREQ/2
10
VDD
4
COMP
8
VREF
11
SYNC
2
SKIP
2.4µH
MIC2185
SS
3
SGND
5
OUTP
VINP
FB
OUTN
CSH
PGND
14
16
6
13
9
12
Si9803DY (x2)
Si4884DY (x2)
8mΩ
Adjustable Output Synchronous Boost Converter
Micrel, Inc. • 1849 Fortune Drive • San Jose, CA 95131 • USA • tel + 1 (408) 944-0800 • fax + 1 (408) 944-0970 • http://www.micrel.com
December 2002 1 MIC2185
V
= 5V
OUT
C
OUT
5V Output Efficiency
100
95
90
85
80
EFFICIENCY (%)
75
70
012345
OUTPUT CURRENT (A)
VIN = 3.3V
200kHz PWM
MIC2185 Micrel
Pin Configuration
SKIP
COMP
SGND
EN/UVLO
VREF
16-pin Narrow Body SOP (M)
Pin Description
Pin Number Pin Name Pin Function
1 VINA Input voltage to control circuitry (2.9V to 14V).
2 SKIP Skip (Input): Regulator operates in PWM mode (no pulse skipping) when pin
3 SS Soft Start (External Component) : Reduces the inrush current and delays
4 COMP Compensation (Output): Internal error amplifier output. Connect to a
5 SGND Small Signal Ground (Return) : Must be routed separately from other
6 FB Feedback (Input) : Regulates FB to 1.245V.
7 EN/UVLO Enable/Undervoltaqe Lockout (Input): A low level on this pin will power down
8 VREF Voltage Reference (Output) : The 1.245V reference is available on this pin.
9 CSH Current Sense (Input) : The (+) input to the current limit comparator. A built
10 VDD 3V Internal Linear-Regulator (Output) : VDD is also the supply voltage bus
11 SYNC Frequency Synchronization (Input): Connect an external clock signal to
12 PGND MOSFET Driver Power Ground (Return) : Connects bottom of current sense
13 OUTN N-Channel Drive (Output) : High current drive for n-channel MOSFET.
14 OUTP P-Channel Drive (Output) : High current drive for the synchronous p-channel
15 FREQ/2 Frequency Divider (Input) : When this pin is low, the oscillator frequency is
16 VINP Gate Drive Voltage (Input) : This is the power input to the gate drive circuitry
SS
FB
1VINA
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
16 VINP
FREQ/2
15
OUTP
14
OUTN
13
PGND
12
SYNC
11
VDD
10
CSH
9
16-pin QSOP (QS)
is pulled low, and skip mode when raised to VDD. There is no automatic
switching between PWM and skip mode available on this device.
and slows the output voltage rise time. A 5µA current source will charge the
capacitor up to VDD.
capacitor or series RC network to compensate the regulator’s control loop.
grounds to the (–) terminal of C
the device, reducing the quiescent current to under 0.5µA. This pin has two
separate thresholds, below 1.5V (typical) the output switching is disabled,
and below 0.9V (typical) the device is forced into a complete micropower
shutdown. The 1.5V threshold functions as an accurate undervoltage lockout
(UVLO) with 140mV hysteresis.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected form this pin to SGnd.
in offset of 100mV (typical) between CSH and SGnd in conjunction with the
current sense resistor sets the current limit threshold level. This is also the
(+) input to the current amplifier.
for the chip. Bypass to SGND with 1µF. Maximum source current is 0.5mA.
synchronize the oscillator. Leading edge of signal above 1.4V (typical) starts
switching cycle. Connect to SGND if not used.
resistor and the (–) terminal of CIN.
Voltage swing is from ground to VINP. On-resistance is typically 5Ω.
MOSFET. Voltage swing is from ground to VINP. On-resistance is typically
5Ω.
400KHz. When this pin is raised to VDD, the oscillator frequency is 200KHz.
(2.9V to 14V). This pin is typically connected to the output voltage to
enhance gate drive.
OUT
.
MIC2185 2 December 2002
MIC2185 Micrel
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
Supply Voltage (VINA, VINP) .........................................15V
Digital Supply Voltage (V
Skip Pin Voltage (V
SKIP
Comp Pin Voltage (V
Feedback Pin Voltage (V
Enable Pin Voltage (V
Current Sense Voltage (V
Sync Pin Voltage (V
SYNC
Freq/2 Pin Voltage (V
) ...........................................7V
DD
) .................................. –0.3V to 7V
).............................. –0.3V to 3V
COMP
) ............................ –0.3V to 3V
FB
EN/UVLO
) ..................... –0.3V to 15V
)......................... –0.3V to 1V
CSH
) ................................ –0.3V to 7V
) ........................... –0.3V to 7V
FREQ/2
Operating Ratings (Note 2)
Supply Voltage (V
Operating Ambient Temperature.........–40°C ≤ T
Junction Temperature ....................... –40°C ≤ T
PackageThermal Resistance
16-lead SOP ...............................................100°C/W
θ
JA
θJA 16-lead QSOP.............................................163°C/W
ESD Rating, Note 3
A, VINP) ........................ +2.9V to +14V
IN
≤ +85°C
A
≤ +125°C
J
Power Dissipation (PD)
16 lead SOP..................................400mW @ TA = 85°C
16 lead QSOP ................................ 245mW@ TA = 85°C
Ambient Storage Temp ............................–65°C to +150°C
Electrical Characteristics
VINA= 5V, VinP= V
indicate –40°C < TJ < +125°C.
Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Units
Regulation
Feedback Voltage Reference (±1%) 1.233 1.245 1.258 V
Feedback Bias Current 50 nA
Output Voltage Line Regulation 3V ≤ VINA ≤ 9V +0.08 % / V
Output Voltage Load Regulation 0mV ≤ CSH ≤ 75mV –1.2 %
Input & VDD Supply
VINA Input Current, PWM mode V
VINP Input Current, PWM mode V
VINA Input Current, SKIP mode V
Shutdown Quiescent Current V
Digital Supply Voltage (VDD) IL = 0 2.8 3.0 3.2 V
Digital Supply Load Regulation IL = 0 to 0.5mA 0.03 V
Undervoltage Lockout VDD upper threshold (turn on threshold) 2.9 2.75 V
Reference Output (V
Reference Voltage (±1.5%) 1.226 1.245 1.264 V
Reference Voltage Line 5V < VinA < 9V 2 mV
Regulation
Reference Voltage Load 0 < I
Regulation
Enable/UVLO
Enable Input Threshold 0.6 0.9 1.2 V
UVLO Threshold 1.4 1.5 1.6 V
UVLO Hysteresis 140 mV
Enable Input Current V
OUT
=12V, V
)
REF
EN/UVLO
= 5V, V
(±2%) 1.220 1.270 V
3V ≤ VINA ≤ 9V; 0mV ≤ CSH ≤ 75mV; (±3%) 1.208 1.245 1.282 V
= 0V 0.8 mA
SKIP
= 0V (excluding external MOSFET gate current) 3.8 mA
SKIP
= 5V 0.6 mA
SKIP
EN/UVLO
VDD lower threshold (turn off threshold) 2.65 V
(±2.5%) 1.213 1.276 V
REF
EN/UVLO
= 0V, V
SKIP
= 0V; (I
< 100µA1mV
= 5V 0.2 5 µA
VINA
+ I
= 0V, V
FREQ/2
) 0.5 µA
VINP
= 0V, TJ = 25°C, unless otherwise specified. Bold values
CSH
December 2002 3 MIC2185
MIC2185 Micrel
Parameter Condition Min Typ Max Unit
Soft Start
Soft Start Current 5 µA
Current Limit
Current Limit Threshold Voltage Voltage on CSH to trip current limit 100 mV
Error Amplifier
Error Amplifier Gain 20 V/V
Current Amplifier
Current Amplifier Gain 3.7 V/V
SKIP Input
SKIP Threshold 0.6 1.4 2.2 V
SKIP Input Current V
Oscillator Section
Oscillator Frequency (fS) 360 400 440 kHz
Maximum Duty Cycle VFB = 1.0V 85 %
Minimum On Time VFB = 1.5V 180 ns
FREQ/2 frequency (fS)V
Frequency Foldback Threshold Measured at FB pin 0.3 V
Frequency Foldback Frequency V
SYNC Threshold Level 0.6 1.4 2.2 V
SYNC Input Current 0.1 5 µA
SYNC Minimum Pulse Width 200 ns
SYNC Capture Range Note 4 fO+15 % 600 kHz
Gate Drivers (OUTN and OUTP)
Rise/Fall Time CL = 3300pF 50 ns
Driver Non-overlap Time VINP = 12V 70 ns
Output Driver Impedance Source; VINP = 12V 4 8 Ω
= 3V 0.1 5 µA
SKIP
=3V 170 200 230
FREQ/2
=0V 90 kHz
FREQ/2
VINP = 5V 90 ns
Sink; VINP = 12V 3 7 Ω
Source; VINP = 5V 5 11 Ω
Sink; VINP = 5V 5 11 Ω
Note 1. Absolute maximum ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the component December occur. Electrical specifications do not apply
Note 2. The device is not guaranteed to function outside its operating rating.
Note 3. Devices are ESD sensitive. Handling precautions recommended.
Note 4. See application information for limitations on maximum operating frequency.
when operating the device outside of its operating ratings. The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of the maximum junction
temperature, T
, the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, θJA, and the ambient temperature, TA.
J(max)
MIC2185 4 December 2002
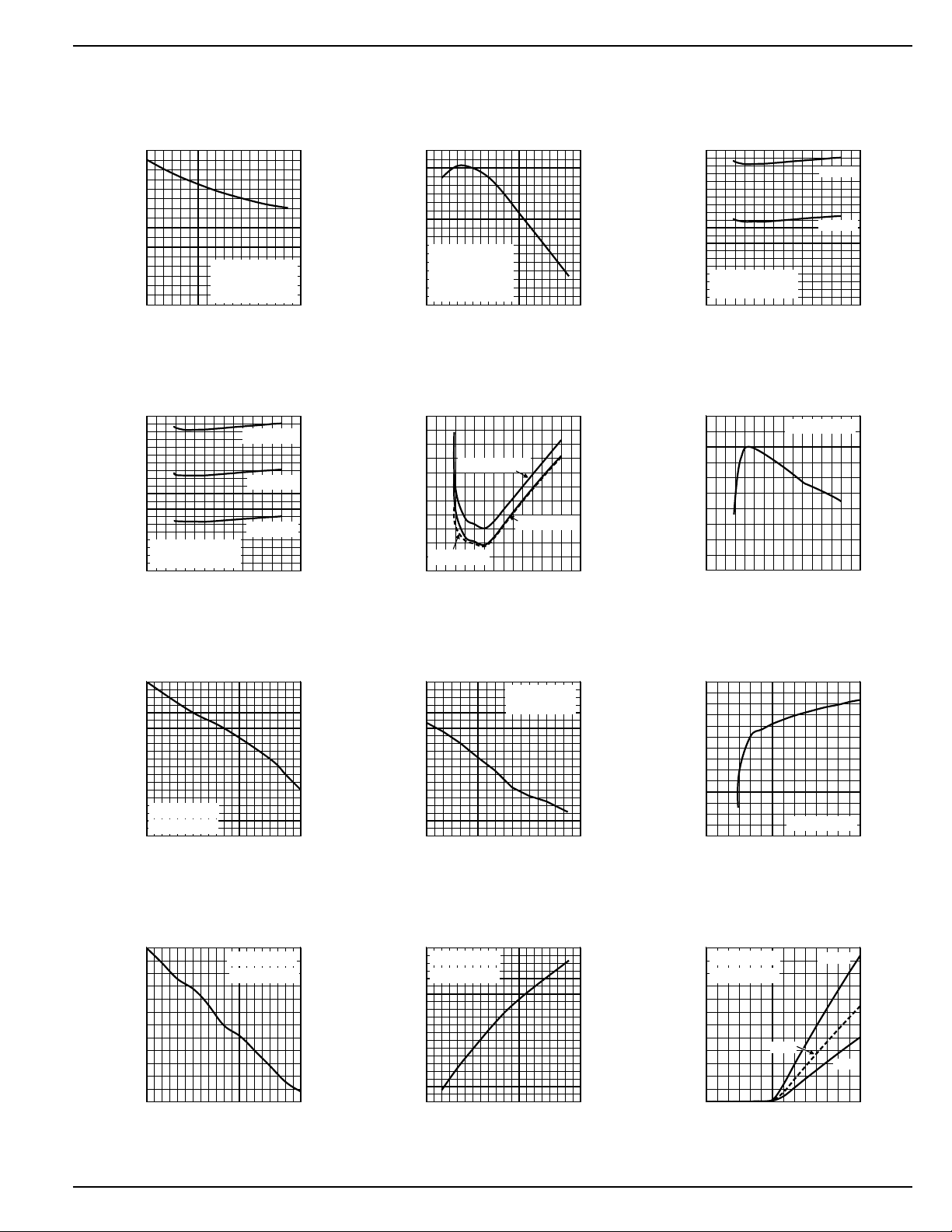
MIC2185 Micrel
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
I
Q
(mA)
INPUT VOLTAGE (V
INA
)
Quiescent Current vs.
Input Voltage(PWM Mode)
400kHz
200kHz
VINP =12V
DC
IQ = I
QVINA+IQVINP
g
g
1.245
1.2455
1.246
1.2465
1.247
1.2475
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
REFERENCE VOLTAGE (V)
INPUT VOLTAGE (V
INA
)
Reference Voltage
vs. Input Voltage
VINP = 12V
DC
2.80
2.85
2.90
2.95
3.00
3.05
3.10
3.15
02468101214
VDD (V)
INPUT VOLTAGE (V
INA
)
VDD vs.
Input Voltage
VINP = 12V
DC
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
02468101214
I
ENABLE
(µA)
V
ENABLE
(V)
I
ENABLE
vs. V
ENABLE
VINP = 12V
DC
VINA = 5V
DC
85°C
–40°C
20°C
Typical Characteristics
Quiescent Current vs.
Temperature (SKIP Mode)
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
(mA)
0.4
0.3
Q(SKIP)
I
0.2
0.1
0
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100120140
Quiescent Current vs.
Input Volta
VINA = 5V
DC
VINP = 12V
IQ = I
QVINA+IQVINP
TEMPERATURE (°C)
e (PWM Mode)
DC
5
4.5
VINP = 12V
4
3.5
3
(mA)
2.5
2
Q(PWM)
I
1.5
1
IQ = I
0.5
fS = 400kHz
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
+ I
QVINA
INPUT VOLTAGE (V
VINP = 9V
VINP = 5V
QVINP
INA
Quiescent Current vs.
Temperature (PWM Mode)
4.75
4.70
4.65
4.60
4.55
(mA)
4.50
VINA = 5V
Q(PWM)
I
4.45
4.40
4.35
4.30
Input Volta
DC
VINP = 12V
fS = 400kHz
IQ = I
-60
DC
QVINA+IQVINP
0
204060
-40
-20
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Quiescent Current vs.
e (SKIP Mode)
80
100
120
140
0.8
0.75
VINP = 12V
DC
0.7
(mA)
Q
I
0.65
VINP = 9V
DC
0.6
VINP = 5V
0.55
)
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
DC
INPUT VOLTAGE (V
INA
)
1.2470
1.2469
1.2468
1.2467
1.2466
1.2465
1.2464
1.2463
1.2462
1.2461
REFERENCE VOLTAGE (V)
1.2460
3.040
3.035
3.030
3.025
VDD (V)
3.020
3.015
3.010
December 2002 5 MIC2185
Reference Voltage
vs. Reference Current
VINP = 12V
VINA = 5V
0 102030405060708090100
0 0.10.20.30.40.50.60.70.80.91.0
DC
DC
REFERENCE CURRENT (µA)
VDD vs.
Load Current
VINP = 12V
VINA = 5V
I
(mA)
VDD
DC
DC
Reference Voltage
1.257
1.255
1.253
vs. Temperature
VINP = 12V
VINA = 5V
1.251
1.249
1.247
1.245
1.243
1.241
1.239
REFERENCE VOLTAGE (V)
1.237
-40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100120140
TEMPERATURE (°C)
VDD vs.
3.08
3.07
3.06
Temperature
VINP = 12V
VINA = 5V
DC
DC
3.05
3.04
3.03
3.02
VDD (V)
3.01
3.00
2.99
2.98
0
-60
204060
-40
-20
TEMPERATURE (°C)
DC
DC
80
100
120
140
 Loading...
Loading...