Micrel KSZ8842-16, KSZ8842-32 User Manual
查询KSZ8842-16供应商
KSZ8842-16/32
MQL/MVL/MVLI
General Description
The KSZ8842-series of 2-port switches includes PCI and
non-PCI CPU interfaces, and are available in 8/16-bit
and 32-bit bus designs (see
This datasheet describes the KSZ8842M-series of nonPCI CPU interface chips. For information on the
KSZ8842 PCI CPU interface switches, refer to the
KSZ8842P datasheet.
The KSZ8842M is the industry’s first fully managed, 2port switch with a non-PCI CPU interface. It is based on
a proven, 4th generation, integrated Layer-2 switch,
compliant with IEEE 802.3u standards. Also an industrial
temperature grade version of the KSZ8842, the
KSZ8842MQLI, can be ordered (see
Information).
The KSZ8842M can be configured as a switch or as a
low-latency (≤ 310 nanoseconds) repeater in latencycritical, embedded or industrial Ethernet applications.
For industrial applications, the KSZ8842M can run in
half-duplex mode regardless of the application.
Ordering Information).
Ordering
2-Port Ethernet Switch with Non-PCI Interface
Data Sheet Rev 1.4
The KSZ8842M offers an extensive feature set that
includes tag/port-based VLAN, quality of service (QoS)
priority management, management information base
(MIB) counters, and CPU control/data interfaces to
effectively address Fast Ethernet applications.
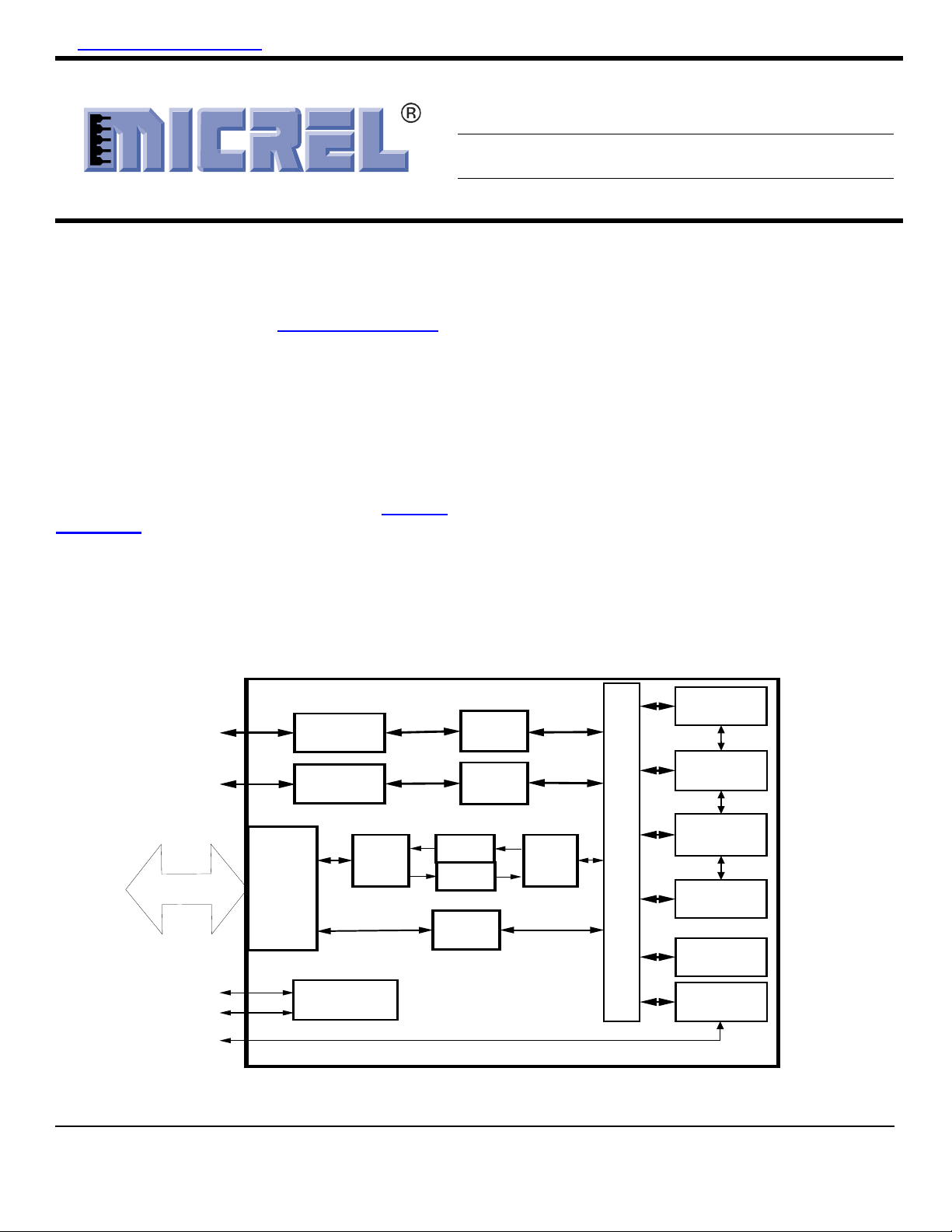
The KSZ8842M contains: Two 10/100 transceivers with
patented, mixed-signal, low-power technology, two
media access control (MAC) units, a direct memory
access (DMA) channel, a high-speed, non-blocking,
switch fabric, a dedicated 1K entry forwarding table, and
an on-chip frame buffer memory.
Functional Diagram
P1 HP Auto
MDI/MDI-X
P2 HP Auto
MDI/MDI-X
d
e
d
d
e
m
b
E
s
o
s
c
e
r
o
P
8,16, or 32-bit
Generic Host
Inte rfac e
P1 LED [3:0]
P2 LED [3:0]
EEPROM I/F
c
e
a
r
f
e
t
n
I
r
Non-PCI
CPU
Bus
Int erfa ce
Unit
10/100 Base-
T/TX
PHY 1
10/100 Base-
T/TX
PHY 2
Channel
LED
Drivers
QMU
DMA
10/100
MAC 1
10/100
MAC 2
RXQ
4KB
TXQ
4KB
Control
Registers
Switch
Host
MAC
1K look-up
Engine
FIFO, Flow Control, VLAN Tagging ,Priority
Scheduling
Managem ent
Buffer
Managem ent
Fram e
B uffe rs
MIB
Counters
EEPROM
Inte rfac e
Figure 1. KSZ8842M Functional Diagram
November 2005 1 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Features
Switch Management
• Non-blocking switch fabric assures fast packet
delivery by utilizing a 1K entry forwarding table
• Fully compliant with IEEE 802.3u standards
• Full-duplex IEEE 802.3x flow control (Pause) with
force mode option
• Half-duplex back pressure flow control
Advanced Switch Management
• IEEE 802.1Q VLAN support for up to 16 groups (full
range of VLAN IDs)
• VLAN ID tag/untag options, on a per port basis
• IEEE 802.1p/Q tag insertion or removal on a per port
basis (egress)
• Programmable rate limiting at the ingress and egress
ports
• Broadcast storm protection
• IEEE 802.1d spanning tree protocol support
• MAC filtering function to filter or forward unknown
unicast packets
• Direct forwarding mode enabling the processor to
identify the ingress port and to specify the egress port
• Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) v1/v2
snooping support for multicast packet filtering
• IPV6 Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) snooping
support
Ordering Information)
(see
• Available in 128-pin PQFP
(optional package: 128-pin LQFP)
• Available in –16 version for 8/16-bit bus support and –
32 version for 32-bit bus support (see
Ordering
Information).
Additional Features
In addition to offering all of the features of an integrated
Layer-2 managed switch, the KSZ8842M offers:
• Repeater mode capabilities to allow for cut through in
latency critical industrial Ethernet or embedded
Ethernet applications
• Dynamic buffer memory scheme
– Essential for applications such as Video over IP
where image jitter is unacceptable
• 2-port switch with a flexible 8, 16, or 32-bit generic
host processor interfaces
™
cable diagnostics to determine cable
• Micrel LinkMD
length, diagnose faulty cables, and determine
distance-to-fault
• Hewlett Packard (HP) Auto-MDIX crossover with
disable and enable options
• Four priority queues to handle voice, video, data, and
control packets
• Ability to transmit and receive jumbo frame sizes up to
1916 bytes
Monitoring
• Port mirroring/monitoring/sniffing: ingress and/or
egress traffic to any port
• MIB counters for fully compliant statistics gathering –
34 MIB counters per port
• Loopback modes for remote failure diagnostics
Comprehensive Register Access
• Control registers configurable on-the-fly (port-priority,
802.1p/d/Q)
QoS/CoS Packets Prioritization Support
• Per port, 802.1p and DiffServ-based
• Remapping of 802.1p priority field on a per port basis
Applications
• Video Distribution Systems
• High-end Cable, Satellite, and IP set-top boxes
• Video over IP
• Voice over IP (VoIP) and Analog Telephone Adapters
(ATA)
• Industrial Control in Latency Critical Applications
• Motion Control
• Industrial Control Sensor Devices (Temperature,
Pressure, Levels, and Valves)
• Security and Surveillance Cameras
Power Modes, Packaging, and Power Supplies
• Full-chip hardware power-down (register configuration
not saved) allows low power dissipation
• Per port-based, software power-save on PHY (idle
link detection, register configuration preserved)
• Single power supply: 3.3V
• Commercial Temperature Range: 0oC to +70oC
• Industrial Temperature Range: –40oC to +85oC
Markets
• Fast Ethernet
• Embedded Ethernet
• Industrial Ethernet
LinkMD is a trademark of Micrel, Inc.
Product names used in this datasheet are for identification purposes only and may be
trademarks of their respective companies.
November 2005 2 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Ordering Information
Part Number Temperature Range Package
KSZ8842-16MQL 0oC to 70oC 128-Pin PQFP
KSZ8842-32MQL 0oC to 70oC 128-Pin PQFP
KSZ8842-16MVL 0oC to 70oC 128-Pin LQFP (Available Q4 Samples)
KSZ8842-32MVL 0oC to 70oC 128-Pin LQFP (Available Q4 Samples)
KSZ8842-16MVLI –40oC to +85oC 128-Pin LQFP (Available Q4 Samples)
KSZ8842-16MQL-Eval Evaluation Board for the KSZ8842-16MQL
Contacts
Location Address
City, State/Province,
Telephone Fax
Country
Corporate HQ 2180 Fortune Drive San Jose, CA 95131 USA +1 (408) 944-0800 +1 (408) 474-1000
Eastern USA 93 Branch Street Medford, NJ 08055 USA +1 (609) 654-0078 +1 (609) 546-0989
Central USA 2425 N.Central Expressway, Suite 351 Richardson, TX 75080 USA +1 (972) 393-2533
Western USA 2180 Fortune Drive San Jose, CA 95131 USA +1 (408) 944-0800 +1 (408) 914-7878
China Room 712, Block B, Intl. Chamber of
Korea 8F AnnJay Tower Bldg
Taiwan 4F, No. 18, Lane 321, Yang-Guang Street,
Singapore 300 Beach Road, #10-07 The Concourse Singapore 199555 +65-6291-1318 +65-6291-1332
Japan 2-3-1 Minato Mirai, Queen’s Tower A 14F,
UK/EMEIA 1st Floor, 3 Lockside Place, Mill Lane Newbury, Berks RG14 5QS UK +44 1635 524455 +44 1635 524466
France/Southern
Europe
New Zealand Office 2, CML Building
Commerce Bldg., Fuhua Rd 1, Futian
718-2 Yeoksam-dong, Kangnam-ku
Nei-Hu Chu
Nishi-ku
10, avenue du Quebec, Villebon BP116 Courtaboeuf Cedex 91944 France +33 (0) 1-6092-4190 +33 (0) 1-6092-4189
2 Perry Street
Shenzhen, PR China 518026 +86 (755) 8302-
Seoul 135-080 Korea +82 (2) 538-2380 +82 (2) 538-2381
Taipei, 11468 Taiwan, R.O.C. +886 (2) 8751-0600 +886 (2) 8751-0746
Yokohama, Kanagawa 220-8543
Japan
Masterton
New Zealand
7618
+81-45-224-6616 +81-45-224-6716
+ 64-6-378-9799 + 64-6-378-9599
+1 (972) 393-2370
+86 (755) 83027637
Revision History
Revision Date Summary of Changes
1.0 06/30/05 First released Preliminary Information
1.1 07/19/05 Updated General Description, Functional Diagram, Pin Description and Features.
Added this Revision History Table, Repeater mode and Loopback support sections.
1.2 08/08/05 Updated Tables, timing and body text.
1.3 10/04/05 Updated Power Saving bit description in P1/2PHYCTRL and P1/2SCSLMD registers
1.4 11/01/05
Updated Figure 16/17/18 Asynchronous Timing and Table 24/25/26 parameters, PQFP
package information
November 2005 3 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Content
General Description.................................................................................................................1
Functional Diagram .................................................................................................................1
Features....................................................................................................................................2
Applications .............................................................................................................................2
Markets .....................................................................................................................................2
Ordering Information...............................................................................................................3
Contacts....................................................................................................................................3
Revision History.......................................................................................................................3
Content .....................................................................................................................................4
List of Figures..........................................................................................................................8
List of Tables............................................................................................................................9
Pin Configuration for KSZ8842-16 Switches (8/16-Bit).......................................................10
Pin Description for KSZ8842-16 Switches (8/16-Bit)...........................................................11
Pin Configuration for KSZ8842-32 Switches (32-Bit)..........................................................16
Pin Description for KSZ8842-32 Switches (32-Bit)..............................................................17
Functional Description..........................................................................................................22
Functional Overview: Physical Layer Transceiver..............................................................22
100BASE-TX Transmit......................................................................................................................................................22
100BASE-TX Receive.......................................................................................................................................................22
Scrambler/De-scrambler (100BASE-TX Only)..................................................................................................................22
10BASE-T Transmit..........................................................................................................................................................22
10BASE-T Receive...........................................................................................................................................................22
Power Management..........................................................................................................................................................23
MDI/MDI-X Auto Crossover ..............................................................................................................................................23
Straight Cable.................................................................................................................................................................23
Crossover Cable.............................................................................................................................................................24
Auto Negotiation ...............................................................................................................................................................24
LinkMD Cable Diagnostics................................................................................................................................................25
Access............................................................................................................................................................................25
Usage.............................................................................................................................................................................26
Functional Overview: MAC and Switch................................................................................ 26
Address Lookup................................................................................................................................................................26
Learning............................................................................................................................................................................26
Migration...........................................................................................................................................................................26
Aging.................................................................................................................................................................................26
Forwarding........................................................................................................................................................................27
Switching Engine..............................................................................................................................................................29
MAC Operation.................................................................................................................................................................29
Inter Packet Gap (IPG) .....................................................................................................................................................29
Back-Off Algorithm............................................................................................................................................................ 29
Late Collision ....................................................................................................................................................................29
legal Packet Size ..............................................................................................................................................................29
Flow Control......................................................................................................................................................................29
Half-Duplex Backpressure................................................................................................................................................29
Broadcast Storm Protection..............................................................................................................................................30
Repeater Mode.................................................................................................................................................................30
Clock Generator................................................................................................................................................................30
November 2005 4 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Bus Interface Unit (BIU).........................................................................................................30
Asynchronous Interface....................................................................................................................................................32
Synchronous Interface......................................................................................................................................................33
Summary ..........................................................................................................................................................................33
BIU Implementation Principles..........................................................................................................................................34
Queue Management Unit (QMU)........................................................................................... 35
Transmit Queue (TXQ) Frame Format..............................................................................................................................35
Receive Queue (RXQ) Frame Format ..............................................................................................................................36
Advanced Switch Functions.................................................................................................38
Spanning Tree Support.....................................................................................................................................................38
IGMP Support...................................................................................................................................................................39
“IGMP” Snooping............................................................................................................................................................39
“Multicast Address Insertion” in the Static MAC Table....................................................................................................39
IPv6 MLD Snooping..........................................................................................................................................................39
Port Mirroring Support.......................................................................................................................................................39
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Support.............................................................................................................................................40
QoS Priority Support.........................................................................................................................................................40
Port-Based Priority............................................................................................................................................................40
802.1p-Based Priority .......................................................................................................................................................40
DiffServ based Priority......................................................................................................................................................41
Rate Limiting Support .......................................................................................................................................................41
MAC Filtering Function .....................................................................................................................................................42
Configuration Interface......................................................................................................................................................42
EEPROM Interface ...........................................................................................................................................................42
Loopback Support.............................................................................................................................................................43
Far-end Loopback ..........................................................................................................................................................43
Near-end (Remote) Loopback........................................................................................................................................43
CPU Interface I/O Registers ..................................................................................................45
I/O Registers.....................................................................................................................................................................45
Internal I/O Space Mapping..............................................................................................................................................46
Register Map: Switch & MAC/PHY........................................................................................ 54
Bit Type Definition .............................................................................................................................................................54
Bank 0-63 Bank Select Register (0x0E): BSR (same location in all Banks)......................................................................54
Bank 0 Base Address Register (0x00): BAR.....................................................................................................................54
Bank 0 Bus Error Status Register (0x06): BESR ..............................................................................................................55
Bank 0 Bus Burst Length Register (0x08): BBLR .............................................................................................................55
Bank 1: Reserved .............................................................................................................................................................55
Bank 2 Host MAC Address Register Low (0x00): MARL ..................................................................................................55
Bank 2 Host MAC Address Register Middle (0x02): MARM .............................................................................................56
Bank 2 Host MAC Address Register High (0x04): MARH.................................................................................................56
Bank 3 On-Chip Bus Control Register (0x00): OBCR.......................................................................................................56
Bank 3 EEPROM Control Register (0x02): EEPCR..........................................................................................................57
Bank 3 Memory BIST INFO Register (0x04): MBIR..........................................................................................................57
Bank 3 Global Reset Register (0x06): GRR......................................................................................................................57
Bank 3 Bus Configuration Register (0x08): BCFG............................................................................................................58
Banks 4—15: Reserved....................................................................................................................................................58
Bank 16 Transmit Control Register (0x00): TXCR............................................................................................................58
Bank 16 Transmit Status Register (0x02): TXSR..............................................................................................................58
Bank 16 Receive Control Register (0x04): RXCR.............................................................................................................59
Bank 16 TXQ Memory Information Register (0x08): TXMIR.............................................................................................59
Bank 16 RXQ Memory Information Register (0x0A): RXMIR............................................................................................60
Bank 17 TXQ Command Register (0x00): TXQCR...........................................................................................................60
Bank 17 RXQ Command Register (0x02): RXQCR..........................................................................................................60
Bank 17 TX Frame Data Pointer Register (0x04): TXFDPR.............................................................................................60
Bank 17 RX Frame Data Pointer Register (0x06): RXFDPR ............................................................................................61
Bank 17 QMU Data Register Low (0x08): QDRL..............................................................................................................61
Bank 17 QMU Data Register High (0x0A): QDRH............................................................................................................61
Bank 18 Interrupt Enable Register (0x00): IER.................................................................................................................62
Bank 18 Interrupt Status Register (0x02): ISR..................................................................................................................63
Bank 18 Receive Status Register (0x04): RXSR..............................................................................................................64
November 2005 5 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Bank 18 Receive Byte Counter Register (0x06): RXBC....................................................................................................64
Bank 19 Multicast Table Register 0 (0x00): MTR0............................................................................................................65
Bank 19 Multicast Table Register 1 (0x02): MTR1............................................................................................................65
Bank 19 Multicast Table Register 2 (0x04): MTR2............................................................................................................65
Bank 19 Multicast Table Register 3 (0x06): MTR3............................................................................................................65
Banks 20 – 31: Reserved..................................................................................................................................................65
Bank 32 Switch ID and Enable Register (0x00): SIDER...................................................................................................66
Bank 32 Switch Global Control Register 1 (0x02): SGCR1...............................................................................................66
Bank 32 Switch Global Control Register 2 (0x04): SGCR2...............................................................................................67
Bank 32 Switch Global Control Register 3 (0x06): SGCR3...............................................................................................68
Bank 32 Switch Global Control Register 4 (0x08): SGCR4...............................................................................................69
Bank 32 Switch Global Control Register 5 (0x0A): SGCR5..............................................................................................69
Bank 33 Switch Global Control Register 6 (0x00): SGCR6...............................................................................................70
Bank 33 Switch Global Control Register 7 (0x02): SGCR7...............................................................................................70
Banks 34 – 38: Reserved..................................................................................................................................................70
Bank 39 MAC Address Register 1 (0x00): MACAR1 ........................................................................................................71
Bank 39 MAC Address Register 2 (0x02): MACAR2 ........................................................................................................71
Bank 39 MAC Address Register 3 (0x04): MACAR3 ........................................................................................................71
Bank 40 TOS Priority Control Register 1 (0x00): TOSR1 .................................................................................................71
Bank 40 TOS Priority Control Register 2 (0x02): TOSR2 .................................................................................................72
Bank 40 TOS Priority Control Register 3 (0x04): TOSR3 .................................................................................................72
Bank 40 TOS Priority Control Register 4 (0x06): TOSR4 .................................................................................................73
Bank 40 TOS Priority Control Register 5 (0x08): TOSR5 .................................................................................................73
Bank 40 TOS Priority Control Register 6 (0x0A): TOSR6.................................................................................................74
Bank 41 TOS Priority Control Register 7 (0x00): TOSR7 .................................................................................................74
Bank 41 TOS Priority Control Register 8 (0x02): TOSR8 .................................................................................................75
Bank 42 Indirect Access Control Register (0x00): IACR...................................................................................................75
Bank 42 Indirect Access Data Register 1 (0x02): IADR1..................................................................................................75
Bank 42 Indirect Access Data Register 2 (0x04): IADR2..................................................................................................76
Bank 42 Indirect Access Data Register 3 (0x06): IADR3..................................................................................................76
Bank 42 Indirect Access Data Register 4 (0x08): IADR4..................................................................................................76
Bank 42 Indirect Access Data Register 5 (0x0A): IADR5..................................................................................................76
Bank 43: Reserved ...........................................................................................................................................................76
Bank 44 Digital Testing Status Register (0x00): DTSR....................................................................................................76
Bank 44 Analog Testing Status Register (0x02): ATSR...................................................................................................76
Bank 44 Digital Testing Control Register (0x04): DTCR..................................................................................................77
Bank 44 Analog Testing Control Register 0 (0x06): ATCR0.............................................................................................77
Bank 44 Analog Testing Control Register 1 (0x08): ATCR1.............................................................................................77
Bank 44 Analog Testing Control Register 2 (0x0A): ATCR2.............................................................................................77
Bank 45 PHY 1 MII-Register Basic Control Register (0x00): P1MBCR ............................................................................77
Bank 45 PHY 1 MII-Register Basic Status Register (0x02): P1MBSR..............................................................................78
Bank 45 PHY 1 PHYID Low Register (0x04): PHY1ILR....................................................................................................79
Bank 45 PHY 1 PHYID High Register (0x06): PHY1IHR..................................................................................................79
Bank 45 PHY 1 Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register (0x08): P1ANAR....................................................................79
Bank 45 PHY 1 Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register (0x0A): P1ANLPR...........................................................80
Bank 46 PHY 2 MII-Register Basic Control Register (0x00): P2MBCR ............................................................................80
Bank 46 PHY 2 MII-Register Basic Status Register (0x02): P2MBSR..............................................................................81
Bank 46 PHY 2 PHYID Low Register (0x04): PHY2ILR....................................................................................................82
Bank 46 PHY 2 PHYID High Register (0x06): PHY2IHR..................................................................................................82
Bank 46 PHY 2 Auto-Negotiation Advertisement Register (0x08): P2ANAR....................................................................83
Bank 46 PHY 2 Auto-Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register (0x0A): P2ANLPR...........................................................83
Bank 47 PHY1 LinkMD Control/Status (0x00): P1VCT.....................................................................................................84
Bank 47 PHY1 Special Control/Status Register (0x02): P1PHYCTRL..............................................................................84
Bank 47 PHY2 LinkMD Control/Status (0x04): P2VCT.....................................................................................................85
Bank 47 PHY2 Special Control/Status Register (0x06): P2PHYCTRL..............................................................................85
Bank 48 Port 1 Control Register 1 (0x00): P1CR1............................................................................................................86
Bank 48 Port 1 Control Register 2 (0x02): P1CR2............................................................................................................87
Bank 48 Port 1 VID Control Register (0x04): P1VIDCR....................................................................................................88
Bank 48 Port 1 Control Register 3 (0x06): P1CR3............................................................................................................88
Bank 48 Port 1 Ingress Rate Control Register (0x08): P1IRCR........................................................................................89
Bank 48 Port 1 Egress Rate Control Register (0x0A): P1ERCR.......................................................................................91
Bank 49 Port 1 PHY Special Control/Status, LinkMD (0x00): P1SCSLMD.......................................................................93
Bank 49 Port 1 Control Register 4 (0x02): P1CR4............................................................................................................94
November 2005 6 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Bank 49 Port 1 Status Register (0x04): P1SR..................................................................................................................95
Bank 50 Port 2 Control Register 1 (0x00): P2CR1............................................................................................................96
Bank 50 Port 2 Control Register 2 (0x02): P2CR2............................................................................................................96
Bank 50 Port 2 VID Control Register (0x04): P2VIDCR....................................................................................................96
Bank 50 Port 2 Control Register 3 (0x06): P2CR3............................................................................................................96
Bank 50 Port 2 Ingress Rate Control Register (0x08): P2IRCR........................................................................................96
Bank 50 Port 2 Egress Rate Control Register (0x0A): P2ERCR.......................................................................................96
Bank 51 Port 2 PHY Special Control/Status, LinkMD (0x00): P2SCSLMD.......................................................................97
Bank 51 Port 2 Control Register 4 (0x02): P2CR4............................................................................................................98
Bank 51 Port 2 Status Register (0x04): P2SR..................................................................................................................99
Bank 52 Host Port Control Register 1 (0x00): P3CR1 ....................................................................................................100
Bank 52 Host Port Control Register 2 (0x02): P3CR2 ....................................................................................................100
Bank 52 Host Port VID Control Register (0x04): P3VIDCR ............................................................................................101
Bank 52 Host Port Control Register 3 (0x06): P3CR3 ....................................................................................................101
Bank 52 Host Port Ingress Rate Control Register (0x08): P3IRCR ................................................................................101
Bank 52 Host Port Egress Rate Control Register (0x0A): P3ERCR ...............................................................................101
Banks 53 – 63: Reserved................................................................................................................................................101
MIB (Management Information Base) Counters................................................................ 102
Format of “All Port Dropped Packet” MIB Counters........................................................................................................103
Additional MIB Information..............................................................................................................................................104
Static MAC Address Table ..................................................................................................105
Static MAC Table Lookup Examples:..............................................................................................................................105
Dynamic MAC Address Table............................................................................................. 106
Dynamic MAC Address Lookup Example:......................................................................................................................106
VLAN Table...........................................................................................................................107
VLAN Table Lookup Examples:......................................................................................................................................107
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Operating Ratings
(1)
.............................................................................................................108
Electrical Characteristics
(1)
.............................................................................................108
(1)
.................................................................................................109
Timing Specifications..........................................................................................................110
Asynchronous Timing without using Address Strobe (ADSN = 0)...................................................................................110
Asynchronous Timing using Address Strobe (ADSN).....................................................................................................111
Asynchronous Timing using DATACSN..........................................................................................................................112
Address Latching Timing for All Modes...........................................................................................................................113
Synchronous Timing in Burst Write (VLBUSN = 1).........................................................................................................114
Synchronous Timing in Burst Read (VLBUSN = 1).........................................................................................................115
Synchronous Write Timing (VLBUSN = 0)......................................................................................................................116
Synchronous Read Timing (VLBUSN = 0)......................................................................................................................117
EEPROM Timing.............................................................................................................................................................118
Auto Negotiation Timing..................................................................................................................................................119
Reset Timing...................................................................................................................................................................120
Selection of Isolation Transformers...................................................................................121
Selection of Reference Crystal...........................................................................................121
Package Information............................................................................................................122
Acronyms and Glossary...................................................................................................... 124
November 2005 7 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
List of Figures
Figure 1. KSZ8842M Functional Diagram ..................................................................................................................................... 1
Figure 2. Standard – KSZ8842-16 MQL 128-Pin PQFP (Top View)............................................................................................ 10
Figure 3. Option – KSZ8842-16 MVL 128-Pin LQFP (Top View) ................................................................................................ 10
Figure 4. Standard – KSZ8842-32 MQL 128-Pin PQFP (Top View)............................................................................................ 16
Figure 5. Option – KSZ8842-32 MVL 128-Pin LQFP (Top View) ................................................................................................ 16
Figure 6. Typical Straight Cable Connection............................................................................................................................... 23
Figure 7. Typical Crossover Cable Connection........................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 8. Auto Negotiation and Parallel Operation ...................................................................................................................... 25
Figure 9. Destination Address Lookup Flow Chart in Stage One ................................................................................................ 27
Figure 10. Destination Address Resolution Flow Chart in Stage Two ......................................................................................... 28
Figure 11. Mapping from ISA-like, EISA-like, and VLBus-like transactions to the KSZ8842M Bus............................................. 34
Figure 12. KSZ8842M 8-Bit, 16-Bit, and 32-Bit Data Bus Connections....................................................................................... 34
Figure 13. 802.1p Priority Field Format....................................................................................................................................... 41
Figure 14. Port 2 Far-End Loopback Path................................................................................................................................... 44
Figure 15. Port 1 and port 2 Near-End (Remote) Loopback Path................................................................................................ 44
Figure 16. Asynchronous Cycle – ADSN = 0............................................................................................................................. 110
Figure 17. Asynchronous Cycle – Using ADSN......................................................................................................................... 111
Figure 18. Asynchronous Cycle – Using DATACSN ................................................................................................................. 112
Figure 19. Address Latching Cycle for All Modes...................................................................................................................... 113
Figure 20. Synchronous Burst Write Cycles – VLBUSN = 1...................................................................................................... 114
Figure 21. Synchronous Burst Read Cycles – VLBUSN = 1 ..................................................................................................... 115
Figure 22. Synchronous Write Cycle – VLBUSN = 0................................................................................................................. 116
Figure 23. Synchronous Read Cycle – VLBUSN = 0................................................................................................................. 117
Figure 24. EEPROM Read Cycle Timing Diagram.................................................................................................................... 118
Figure 25. Auto-Negotiation Timing........................................................................................................................................... 119
Figure 26. Reset Timing............................................................................................................................................................ 120
Figure 27. 128-Pin PQFP Package ........................................................................................................................................... 122
Figure 28. Optional 128-Pin LQFP Package ............................................................................................................................. 123
November 2005 8 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
List of Tables
Table 1. MDI/MDI-X Pin Definitions............................................................................................................................................. 23
Table 2. Bus Interface Unit Signal Grouping ............................................................................................................................... 32
Table 3: Transmit Queue Frame Format..................................................................................................................................... 35
Table 4. Transmit Control Word Bit Fields...................................................................................................................................36
Table 5. Transmit Byte Count Format ......................................................................................................................................... 36
Table 6: Receive Queue Frame Format...................................................................................................................................... 36
Table 7. FRXQ Packet Receive Status........................................................................................................................................ 37
Table 8. FRXQ RX Byte Count Field........................................................................................................................................... 37
Table 9: Spanning Tree States....................................................................................................................................................38
Table 10. FID+DA Lookup in VLAN Mode................................................................................................................................... 40
Table 11. FID+SA Lookup in VLAN Mode................................................................................................................................... 40
Table 12. EEPROM Format......................................................................................................................................................... 42
Table 13. ConfigParam Word in EEPROM Format ..................................................................................................................... 43
Table 14. Format of Per Port MIB Counters.............................................................................................................................. 102
Table 15. Port 1 MIB Counters Indirect Memory Offset............................................................................................................. 103
Table 16. “All Port Dropped Packet” MIB Counters Format ....................................................................................................... 103
Table 17. “All Port Dropped Packet” MIB Counters Indirect Memory Offsets............................................................................ 103
Table 18. Static MAC Table Format .......................................................................................................................................... 105
Table 19. Dynamic MAC Address Table Format....................................................................................................................... 106
Table 20. VLAN Table Format...................................................................................................................................................107
Table 21. Maximum Ratings......................................................................................................................................................108
Table 22. Operating Ratings...................................................................................................................................................... 108
Table 23. Electrical Characteristics ........................................................................................................................................... 109
Table 24. Asynchronous Cycle – ADSN = 0 Timing Parameters............................................................................................... 110
Table 25. Asynchronous Cycle – ADSN Timing Parameters..................................................................................................... 111
Table 26. Asynchronous – DATACSN Timing Parameters........................................................................................................ 112
Table 27. Address Latching Timing Parameters........................................................................................................................ 113
Table 28. Synchronous Burst Write Timing Parameters............................................................................................................ 114
Table 29. Synchronous Burst Read Timing Parameters............................................................................................................ 115
Table 30. Synchronous Write Timing Parameters..................................................................................................................... 116
Table 31. Synchronous Read Timing Parameters.....................................................................................................................117
Table 32. EEPROM Timing Parameters .................................................................................................................................... 118
Table 33. Auto Negotiation Timing Parameters.........................................................................................................................119
Table 34. Reset Timing Parameters.......................................................................................................................................... 120
Table 35. Transformer Selection Criteria................................................................................................................................... 121
Table 36. Qualified Single Port Magnetic .................................................................................................................................. 121
Table 37. Typical Reference Crystal Characteristics................................................................................................................. 121
November 2005 9 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
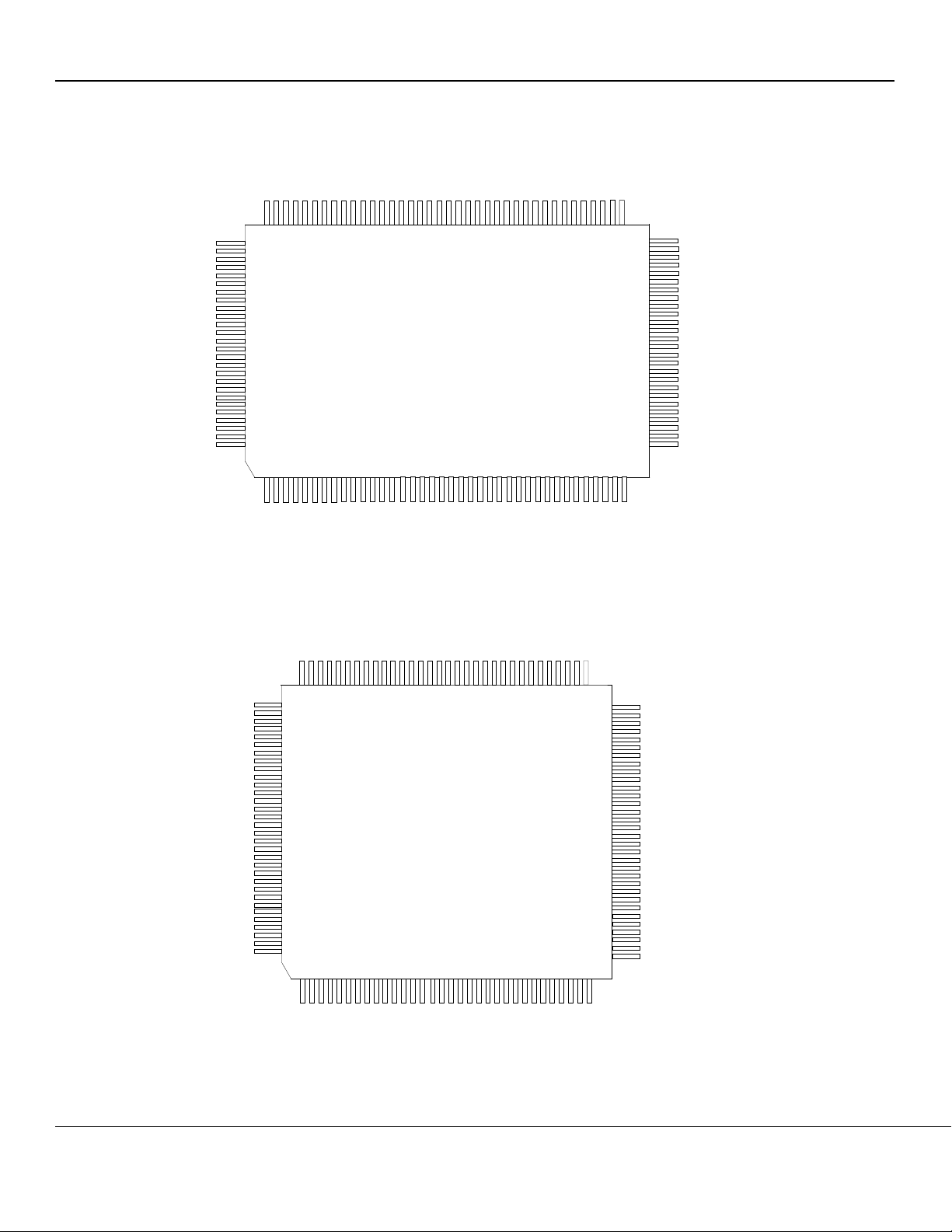
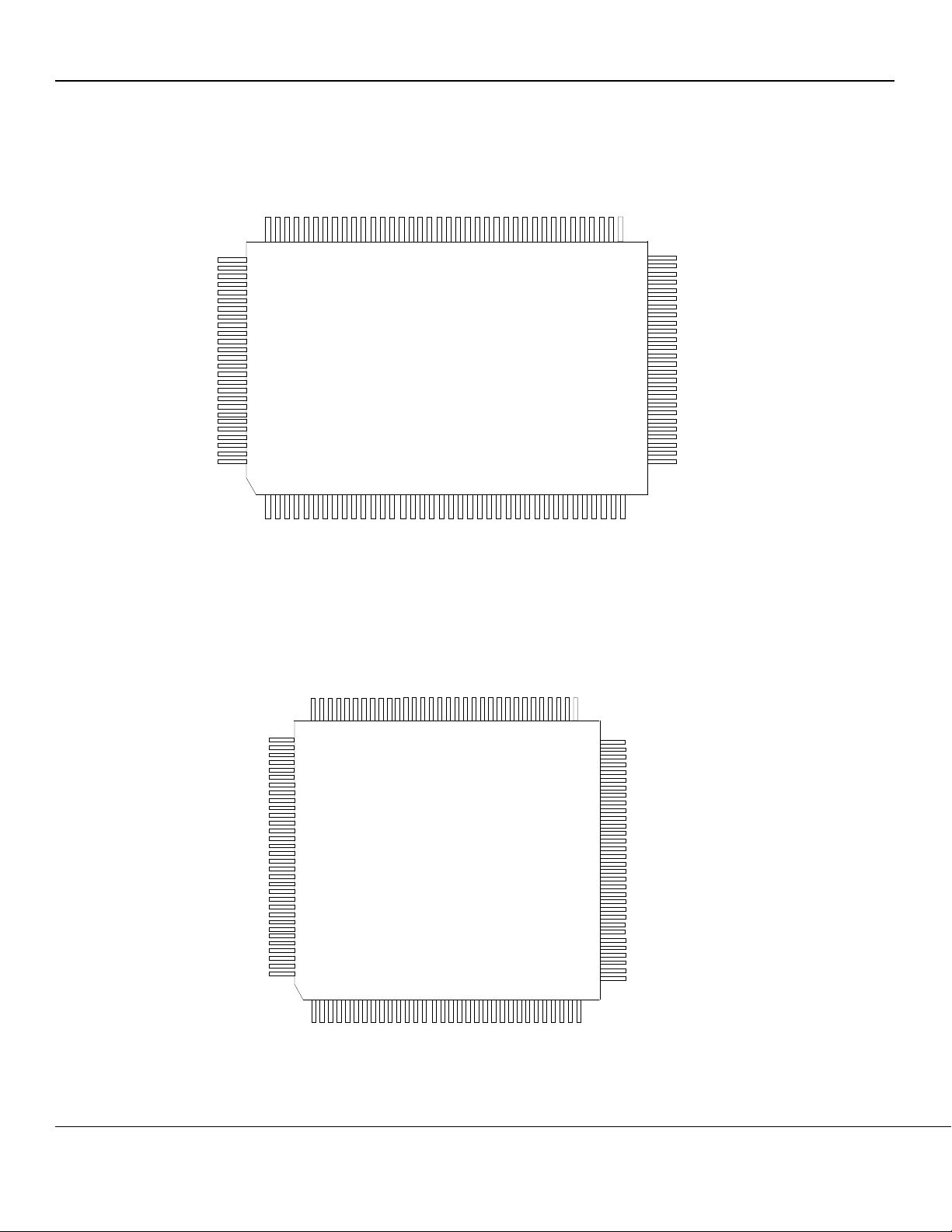
Pin Configuration for KSZ8842-16 Switches (8/16-Bit)
DGND
VDDIO
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
DGND
DGND
VDDIO
VDDIO
NCNCNCNCNC
NCNCNC
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877767574737271706968676665
101
102
100
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
123456789
P1LED2
TESTEN
SCANEN
KSZ8842-16
MQL
P1LED1
P2LED1
P1LED0
P2LED2
VDDC
NC
NC
1011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738
BCLK
DGND
VDDIO
P2LED0
RDYRTNN
NC
BE1N
A1
NCA2A3
DGNDNCBE0N
(Top View)
NC
NC
RDN
EECS
INTRN
LDEVN
SRDYN
ARDY
A4
A6
VDDIO
DGND
VDDCO
A8
DGNDA7A9
EEEN
EEDO
P1LED3
VLBUSN
A10
EESK
A5
P2LED3
CYCLEN
A15
RSTN
AEN
A13
WRN
X2
X1
A14
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
ADSN
VDDA
AGND
DGND
PWRDN
AGND
VDDAP
AGND
ISE T
NC
NC
AGND
VDDA
TXP2
TXM2
AGND
RXP2
RXM2
VDDARX
VDDATX
TXM1
TXP1
AGND
RXM1
RXP1
NC
VDDA
AGND
NC
NC
AGND
A11
A12
SWR
EEDI
Figure 2. Standard – KSZ8842-16 MQL 128-Pin PQFP (Top View)
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
DGND
VDDIO
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D5
D4
D3
DGND
DGND
VDDIO
VDDIO
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
D9
D8
D7
D6
D2
D1
D0
96959493929190898887868584838281807978777675747372717069686766
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
KSZ8842-16
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
MVL
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
123456789
P1LED1
P1LED2
P1LED0
TESTEN
SCANEN
NC
A1
A4
A6
VDDC
DGNDNCBE0N
BE1N
NCA2A3
(Top View)
1011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132
NC
NC
BCLK
DGND
VDDIO
P2LED1
P2LED2
P2LED0
INTRN
SRDYN
RDYRTNN
A5
LDEVN
VDDIO
RDN
A8
DGNDA7A9
EECS
ARDY
P2LED3
CYCLEN
DGND
A11
A10
VDDCO
A12
VLBUSN
A13
EEEN
A15
RSTN
X2
X1
A14
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
AEN
EEDI
SWR
EESK
EEDO
P1LED3
Figure 3. Option – KSZ8842-16 MVL 128-Pin LQFP (Top View)
AGND
VDDAP
AGND
ISET
NC
NC
AGND
VDDA
TXP2
TXM2
AGND
RXP2
RXM2
VDDARX
VDDATX
TXM1
TXP1
AGND
RXM1
RXP1
NC
VDDA
AGND
NC
NC
AGND
VDDA
AGND
PWRDN
ADSN
DGND
WRN
November 2005 10 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin Description for KSZ8842-16 Switches (8/16-Bit)
Pin
Number
1 TEST_EN I
2 SCAN_EN I
3 P1LED2 Opu
4
5 P1LED0 Opu
6 P2LED2 Opu
7 P2LED1 Opu
8 P2LED0 Opu
9 DGND Gnd
10 VDDIO P
11 RDYRTNN Ipd
Pin Name Type Pin Function
Test Enable
For normal operation, pull-down this pin to ground.
Scan Test Scan Mux Enable
For normal operation, pull-down this pin to ground.
Port 1 and Port 2 LED indicators
P1LED1 Opu
[0,0] Default [0,1]
P1LED32 /P2LED3 — —
P1LED2/P2LED2 Link/Act 100Link/Act
P1LED1/P2LED1 Full duplex/Col 10Link/Act
P1LED0/P2LED0 Speed Full duplex
Reg. SGCR5 bit [15,9]
[1,0] [1,1]
P1LED32 /P2LED3 Act —
P1LED2/P2LED2 Link —
P1LED1/P2LED1 Full duplex/Col —
P1LED0/P2LED0 Speed —
Notes:
1. Link = On; Activity = Blink; Link/Act = On/Blink; Full Dup/Col = On/Blink;
Full Duplex = On (Full duplex); Off (Half duplex)
Speed = On (100BASE-T); Off (10BASE-T)
2. P1LED3 is pin 27. P2LED3 is pin 22.
Port 1 and Port 2 LED indicators
[0,0] Default [0,1] [1,0] [1,1]
P1LED3, P2LED3 RPT_COL, RPT_ACT —
P1LED2, P2LED2 RPT_Link3/RX, RPT_ERR3 —
P1LED1, P2LED1 RPT_Link2/RX, RPT_ERR2 —
P1LED0, P2LED0 RPT_Link1/RX, RPT_ERR1 —
Note 3: RPT_COL = Blink; RPT_Link3/RX (Host port) = On/Blink;
RPT_Link2/RX (Port 2) = On/Blink; RPT_Link1/RX (Port 1) = On/Blink;
RPT_ACT = on if any activity, RPT_ERR3/2/1 = RX error on port 3, 2, or 1.
Digital ground
3.3V digital V
Ready Return Not:
For VLBus-like mode: Asserted by the host to complete synchronous read cycles. If
the host doesn’t connect to this pin, assert this pin.
For burst mode (32-bit interface only): Host drives this pin low to signal waiting
states.
1
defined as follows:
Switch Global Control Register 5:
SGCR5 bit [15,9]
3
for Repeater mode defined as follows:
Switch Global Control Register 5: SGCR5 bit
[15,9]
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
November 2005 11 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
12 BCLK Ipd
13 NC Ipu No connect.
14 NC Opu No connect.
15 SRDYN Opu Synchronous Ready Not
16 INTRN Opd Interrupt
17 LDEVN Opd Local Device Not
18 RDN Ipd Read Strobe Not
19 EECS Opu EEPROM Chip Select
20 ARDY Opd Asynchronous Ready
21 CYCLEN Ipd Cycle Not
22 P2LED3 Opd Port 2 LED indicator
23 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
24 VDDCO P 1.2V digital core voltage output (internal 1.2V LDO power supply output), this 1.2V
25 VLBUSN Ipd VLBus-like Mode
26 EEEN Ipd EEPROM Enable
27 P1LED3 Opd Port 1 LED indicator
Pin Name Type Pin Function
Bus Interface Clock
Local bus clock for synchronous bus systems. Maximum frequency is 50MHz.
This pin should be tied Low or unconnected if it is in asynchronous mode.
Ready signal to interface with synchronous bus for both EISA-like and VLBus-like
extend accesses.
For VLBus-like mode, the falling edge of this signal indicates ready. This signal is
synchronous to the bus clock signal BCLK.
For burst mode (32-bit interface only), the KSZ8842M drives this pin low to signal
wait states.
Active Low signal to host CPU to indicate an interrupt status bit is set, this pin need
an external 4.7K pull-up resistor.
Active Low output signal, asserted when AEN is Low and A15-A4 decode to the
KSZ8842M address programmed into the high byte of the base address register.
LDEVN is a combinational decode of the Address and AEN signal.
Asynchronous read strobe, active Low.
ARDY may be used when interfacing asynchronous buses to extend bus access
cycles. It is asynchronous to the host CPU or bus clock.
For VLBus-like mode cycle signal; this pin follows the addressing cycle to signal the
command cycle.
For burst mode (32-bit interface only), this pin stays High for read cycles and Low for
write cycles.
See the description in pins 6, 7, and 8.
output pin provides power to VDDC, VDDA and VDDAP pins.
Note: Internally generated power voltage. Do not connect an external power supply to
this pin. This pin is used for connecting external filter (Ferrite bead and capacitors).
Pull-down or float: Bus interface is configured for synchronous mode.
Pull-up: Bus interface is configured for 8-bit or 16-bit asynchronous mode or EISA-
like burst mode.
EEPROM is enabled and connected when this pin is pull-up.
EEPROM is disabled when this pin is pull-down or no connect.
See the description in pins 3, 4, and 5.
November 2005 12 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
28 EEDO Opd EEPROM Data Out
29 EESK Opd EEPROM Serial Clock
30 EEDI Ipd EEPROM Data In
31 SWR Ipd Synchronous Write/Read
32 AEN Ipd Address Enable
33 WRN Ipd Write Strobe Not
34 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
35 ADSN Ipd Address Strobe Not
36 PWRDN I Full-chip power-down. Active Low (Low = Power down; High = Normal operation).
37 AGND Gnd Analog ground
38 VDDA P
39 AGND Gnd Analog ground
40 NC — No connect
41 NC — No connect
42 AGND Gnd Analog ground
43 VDDA P
44 NC — No connect
45 RXP1 I/O Port 1 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
46 RXM1 I/O Port 1 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (– differential)
47 AGND Gnd Analog ground
48 TXP1 I/O Port 1 physical transmit (MDI) or receive (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
49 TXM1 I/O Port 1 physical transmit (MDI) or receive (MDIX) signal (– differential)
50 VDDATX P 3.3V analog V
51 VDDARX P 3.3V analog V
52 RXM2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (- differential)
53 RXP2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI)or transmit (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
54 AGND Gnd Analog ground
55 TXM2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (- differential)
56 TXP2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
57 VDDA P
Pin Name Type Pin Function
This pin is connected to DI input of the serial EEPROM.
A 4
µs serial output clock to load configuration data from the serial EEPROM.
This pin is connected to DO output of the serial EEPROM when EEEN is pull-up.
This pin can be pull-down for 8-bit bus mode, pull-up for 16-bus mode or don’t care
for 32-bus mode when EEEN is pull-down (without EEPROM).
Write/Read signal for synchronous bus accesses. Write cycles when high and Read
cycles when low.
Address qualifier for the address decoding, active Low.
Asynchronous write strobe, active Low.
For systems that require address latching, the rising edge of ADSN indicates the
latching moment of A15-A1 and AEN.
1.2V analog V
bead and capacitor.
1.2V analog V
bead and capacitor.
1.2 analog V
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external Ferrite
DD
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external Ferrite
DD
input power supply with well decoupling capacitors.
DD
input power supply with well decoupling capacitors.
DD
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external Ferrite
DD
November 2005 13 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
58 AGND Gnd Analog ground
59 NC Ipu No connect
60 NC Ipu No connect
61 ISET O Set physical transmits output current.
62 AGND Gnd Analog ground
63 VDDAP P
64 AGND Gnd Analog ground
65 X1 I
66 X2 O
67 RSTN Ipu
68 A15 I Address 15
69 A14 I Address 14
70 A13 I Address 13
71 A12 I Address 12
72 A11 I Address 11
73 A10 I Address 10
74 A9 I Address 9
75 A8 I Address 8
76 A7 I Address 7
77 A6 I Address 6
78 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
79 VDDIO P 3.3V digital V
80 A5 I Address 5
81 A4 I Address 4
82 A3 I Address 3
83 A2 I Address 2
84 A1 I Address 1
85 NC I No Connect
86 NC I No Connect
87 BE1N I Byte Enable 1 Not, Active low for Data byte 1 enable (don’t care in 8-bit bus mode).
88 BE0N I
89 NC I No Connect
90 DGND Gnd Digital core ground
91 VDDC P
92 VDDIO P 3.3V digital V
93 NC I No Connect
Pin Name Type Pin Function
bead and capacitor.
Pull-down this pin with a 3.01K 1% resistor to ground.
1.2V analog V
Ferrite bead and capacitor.
25MHz crystal or oscillator clock connection.
Pins (X1, X2) connect to a crystal. If an oscillator is used, X1 connects to a 3.3V
tolerant oscillator and X2 is a no connect.
Note: Clock requirement is ± 50ppm for either crystal or oscillator.
Hardware reset pin (active Low). This reset input is required minimum of 10ms low
after stable supply voltage 3.3V.
Byte Enable 0 Not, Active low for Data byte 0 enable (there is an internal inverter
enabled and connected to the BE1N for 8-bit bus mode).
1.2V digital core V
Ferrite bead and capacitor.
for PLL input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external
DD
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external
DD
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
November 2005 14 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
94 NC I No Connect
95 NC I No Connect
96 NC I No Connect
97 NC I No Connect
98 NC I No Connect
99 NC I No Connect
100 NC I No Connect
101 NC I No Connect
102 NC I No Connect
103 NC I No Connect
104 NC I No Connect
105 NC I No Connect
106 NC I No Connect
107 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
108 VDDIO P
109 NC I No Connect
110 D15 I/O Data 15
111 D14 I/O Data 14
112 D13 I/O Data 13
113 D12 I/O Data 12
114 D11 I/O Data 11
115 D10 I/O Data 10
116 D9 I/O Data 9
117 D8 I/O Data 8
118 D7 I/O Data 7
119 D6 I/O Data 6
120 D5 I/O Data 5
121 D4 I/O Data 4
122 D3 I/O Data 3
123 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
124 DGND Gnd Digital core ground
125 VDDIO P 3.3V digital V
126 D2 I/O Data 2
127 D1 I/O Data 1
128 D0 I/O Data 0
Pin Name Type Pin Function
3.3V digital V
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
Legend:
P = Power supply Gnd = Ground.
I/O = Bi-directional I = Input O = Output.
Ipd = Input with internal pull-down.
Ipu = Input with internal pull-up.
Opd = Output with internal pull-down.
Opu = Output with internal pull-up.
November 2005 15 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
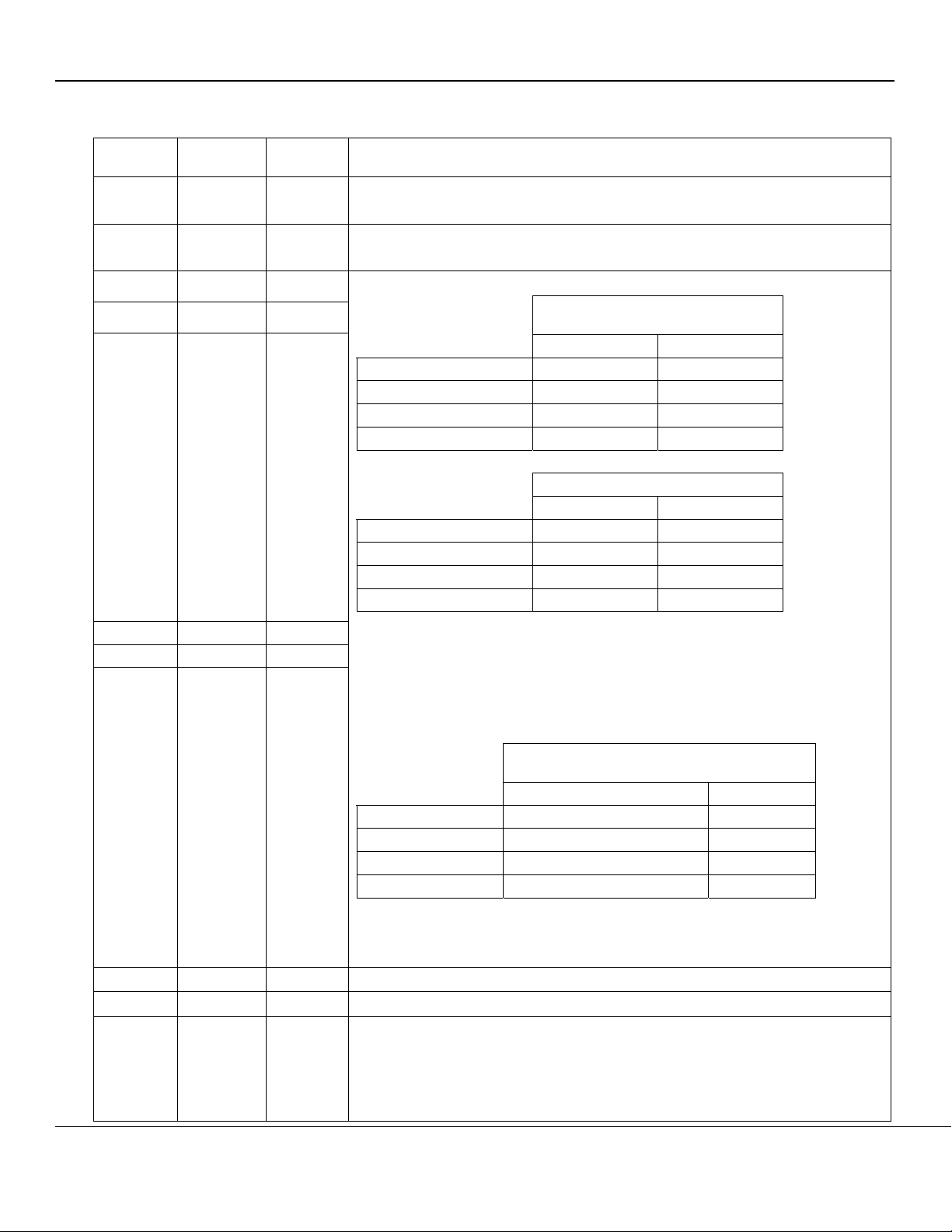
Pin Configuration for KSZ8842-32 Switches (32-Bit)
BE2N
A1
A4
A6
D20
D19
D18
D17
DGND
VDDIO
D16
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
DGND
DGND
VDDIO
VDDC
DGND
D31
BE0N
BE1N
D22
D24
D25
D21
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
D9
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
123456789
D26
D23
9998979695949392919089888786858483828180797877767574737271706968676665
101
100
KSZ8842-32
MQL
VDDIO
D28
D27
D29
D30
1011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738
BE3NA2A3
(Top View)
A5
A8
VDDIO
DGND
A7
A9
A10
A15
RSTN
A11
A12
X2
A13
X1
A14
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
AGND
VDDAP
AGND
ISET
NC
NC
AGND
VDDA
TXP2
TXM2
AGND
RXP2
RXM2
VDDARX
VDDATX
TXM1
TXP1
AGND
RXM1
RXP1
NC
VDDA
AGND
NC
NC
AGND
TESTEN
P1LED2
SCANEN
NC
SRDYN
RDN
EECS
ARDY
INTRN
LDEVN
CYCLEN
EEEN
DGND
VDDCO
P2LED3
VLBUSN
P1LED3
BCLK
DGND
P1LED1
P1LED0
VDDIO
P2LED1
P2LED2
P2LED0
RDYRTNN
DATACSN
EEDO
EESK
EEDI
AEN
SWR
WRN
ADSN
VDDA
AGND
DGND
PWRDN
Figure 4. Standard – KSZ8842-32 MQL 128-Pin PQFP (Top View)
VDDIO
D28
D27
D29
D26
D25
D24
D23
D22
D21
D20
D19
D18
D17
DGND
VDDIO
D16
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D5
D4
D3
DGND
DGND
VDDIO
D30
96959493929190898887868584838281807978777675747372717069686766
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
KSZ8842-32
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
D9
D8
D7
D6
D2
D1
D0
MVL
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
123456789
BE2N
A1
A4
A6
VDDC
DGND
D31
BE0N
BE1N
BE3NA2A3
(Top View)
1011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132
A5
VDDIO
A8
DGNDA7A9
A15
RSTN
A11
A10
X2
A13
A12
X1
A14
65
64
AGND
63
VDDAP
62
AGND
61
ISET
60
NC
59
NC
58
AGND
57
VDDA
56
TXP2
55
TXM2
54
AGND
53
RXP2
52
RXM2
51
VDDARX
50
VDDATX
49
TXM1
48
TXP1
47
AGND
46
RXM1
45
RXP1
44
NC
43
VDDA
42
AGND
41
NC
40
NC
AGND
39
VDDA
38
AGND
37
36
PWRDN
35
ADSN
DGND
34
33
WRN
NC
DATACSN
RDN
EECS
ARDY
INTRN
LDEVN
SRDYN
EEEN
DGND
VDDCO
P2LED3
VLBUSN
CYCLEN
BCLK
DGND
P1LED1
P1LED2
TESTEN
SCANEN
VDDIO
P2LED1
P1LED0
P2LED2
P2LED0
RDYRTNN
AEN
EEDI
SWR
EESK
EEDO
P1LED3
Figure 5. Option – KSZ8842-32 MVL 128-Pin LQFP (Top View)
November 2005 16 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin Description for KSZ8842-32 Switches (32-Bit)
Pin
Number
1 TEST_EN I
2 SCAN_EN I
3 P1LED2 Opu
4 P1LED1 Opu
5 P1LED0 Opu
6 P2LED2 Opu
7 P2LED1 Opu
8 P2LED0 Opu
9 DGND Gnd
10 VDDIO P
11 RDYRTNN Ipd
Pin Name Type Pin Function
Test Enable
For normal operation, pull-down this pin to ground.
Scan Test Scan Mux Enable
For normal operation, pull-down this pin to ground.
Port 1 and Port 2 LED indicators
[0,0] Default [0,1]
P1LED32 /P2LED3 — —
P1LED2/P2LED2 Link/Act 100Link/Act
P1LED1/P2LED1 Full duplex/Col 10Link/Act
P1LED0/P2LED0 Speed Full duplex
Reg. SGCR5 bit [15,9]
[1,0] [1,1]
P1LED32 /P2LED3 Act —
P1LED2/P2LED2 Link —
P1LED1/P2LED1 Full duplex/Col —
P1LED0/P2LED0 Speed —
Notes:
1. Link = On; Activity = Blink; Link/Act = On/Blink; Full Dup/Col = On/Blink;
Full Duplex = On (Full duplex); Off (Half duplex)
Speed = On (100BASE-T); Off (10BASE-T)
2. P1LED3 is pin 27. P2LED3 is pin 22.
Port 1 and Port 2 LED indicators
[0,0] Default [0,1] [1,0] [1,1]
P1LED3; P2LED3 RPT_COL; RPT_ACT —
P1LED2; P2LED2 RPT_Link3/RX; RPT_ERR3 —
P1LED1; P2LED1 RPT_Link2/RX; RPT_ERR2 —
P1LED0; P2LED0 RPT_Link1/RX; RPT_ERR1 —
Note 3: RPT_COL = Blink; RPT_Link3/RX (Host port) = On/Blink;
RPT_Link2/RX (Port 2) = On/Blink; RPT_Link1/RX (Port 1) = On/Blink;
RPT_ACT = on if any activity, RPT_ERR3/2/1 = RX error on port 3, 2, or 1.
Digital ground
3.3V digital V
Ready Return Not
For VLBus-like mode: Asserted by the host to complete synchronous read cycles. If
the host doesn’t connect to this pin, assert this pin.
For burst mode (32-bit interface only): Host drives this pin low to signal waiting
states.
1
defined as follows:
Switch Global Control Register 5:
SGCR5 bit [15,9]
3
for Repeater mode defined as follows:
Switch Global Control Register 5: SGCR5 bit
[15,9]
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
November 2005 17 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
12 BCLK Ipd Bus Interface Clock
13 DATACSN Ipu DATA Chip Select Not (F or KSZ8842-32 Mode only)
14 NC Opu
15 SRDYN Opu
16 INTRN Opd
17 LDEVN Opd
18 RDN Ipd
19 EECS Opu
20 ARDY Opd
21 CYCLEN Ipd
22 P2LED3 Opd
23 DGND Gnd
24 VDDCO P
25 VLBUSN Ipd
26 EEEN Ipd
Pin Name Type Pin Function
Local bus clock for synchronous bus systems. Maximum frequency is 50MHz.
This pin should be tied Low or unconnected if it is in asynchronous mode.
Chip select signal for QMU data register (QDRH, QDRL), active Low.
When DATACSN is Low, the data path can be accessed regardless of the value of
AEN, A15-A1, and the content of the BANK select register.
No connect.
Synchronous Ready Not
Ready signal to interface with synchronous bus for both EISA-like and VLBus-like
extend accesses.
For VLBus-like mode, the falling edge of this signal indicates ready. This signal is
synchronous to the bus clock signal BCLK.
For burst mode (32-bit interface only), the KSZ8842M drives this pin low to signal
wait states.
Interrupt
Active Low signal to host CPU to indicate an interrupt status bit is set, this pin need
an external 4.7K pull-up resistor.
Local Device Not
Active Low output signal, asserted when AEN is Low and A15-A4 decode to the
KSZ8842M address programmed into the high byte of the base address register.
LDEVN is a combinational decode of the Address and AEN signal.
Read Strobe Not
Asynchronous read strobe, active Low.
EEPROM Chip Select
Asynchronous Ready
ARDY may be used when interfacing asynchronous buses to extend bus access
cycles. It is asynchronous to the host CPU or bus clock.
Cycle Not
For VLBus-like mode cycle signal; this pin follows the addressing cycle to signal the
command cycle.
For burst mode (32-bit interface only), this pin stays High for read cycles and Low for
write cycles.
Port 2 LED indicator.
See the description in pins 6, 7, and 8.
Digital IO ground
1.2V digital core voltage output (internal 1.2V LDO power supply output), this 1.2V
output pin provides power to VDDC, VDDA and VDDAP pins.
Note: Internally generated power voltage. Do not connect an external power supply to
this pin. This pin is used for connecting external filter (Ferrite Bead and capacitors).
VLBus-like Mode
Pull-down or float: Bus interface is configured for synchronous mode.
Pull-up: Bus interface is configured for 32-bit asynchronous mode or EISA-like burst
mode.
EEPROM Enable
EEPROM is enabled and connected when this pin is pull-up.
EEPROM is disabled when this pin is pull-down or no connect.
November 2005 18 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
27 P1LED3 Opd Port 1 LED indicator
28 EEDO Opd EEPROM Data Out
29 EESK Opd EEPROM Serial Clock
30 EEDI Ipd EEPROM Data In
31 SWR Ipd Synchronous Write/Read
32 AEN Ipd Address Enable
33 WRN Ipd Write Strobe Not
34 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
35 ADSN Ipd Address Strobe Not
36 PWRDN I Full-chip power-down. Active Low (Low = Power down; High = Normal operation).
37 AGND Gnd Analog ground
38 VDDA P
39 AGND Gnd Analog ground
40 NC — No connect
41 NC — No connect
42 AGND Gnd Analog ground
43 VDDA P
44 NC — No connect
45 RXP1 I/O Port 1 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
46 RXM1 I/O Port 1 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (– differential)
47 AGND Gnd Analog ground
48 TXP1 I/O Port 1 physical transmit (MDI) or receive (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
49 TXM1 I/O Port 1 physical transmit (MDI) or receive (MDIX) signal (– differential)
50 VDDATX P 3.3V analog V
51 VDDARX P 3.3V analog VDD
52 RXM2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (- differential)
53 RXP2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
54 AGND Gnd Analog ground
55 TXM2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (- differential)
Pin Name Type Pin Function
See the description in pins 3, 4, and 5.
This pin is connected to DI input of the serial EEPROM.
µs serial output clock to load configuration data from the serial EEPROM.
A 4
This pin is connected to DO output of the serial EEPROM when EEEN is pull-up.
This pin can be pull-down for 8-bit bus mode, pull-up for 16-bus mode or don’t care
for 32-bus mode when EEEN is pull-down (without EEPROM).
Write/Read signal for synchronous bus accesses. Write cycles when high and Read
cycles when low.
Address qualifier for the address decoding, active Low.
Asynchronous write strobe, active Low.
For systems that require address latching, the rising edge of ADSN indicates the
latching moment of A15-A1 and AEN.
1.2V analog V
bead and capacitor.
1.2V analog V
bead and capacitor.
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external Ferrite
DD
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external Ferrite
DD
input power supply with well decoupling capacitors.
DD
November 2005 19 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
56 TXP2 I/O Port 2 physical receive (MDI) or transmit (MDIX) signal (+ differential)
57 VDDA P
58 AGND Gnd Analog ground
59 NC Ipu No connect
60 NC Ipu No connect
61 ISET O Set physical transmits output current.
62 AGND Gnd Analog ground
63 VDDAP P
64 AGND Gnd Analog ground
65 X1 I 25MHz crystal or oscillator clock connection.
66 X2 O
67 RSTN Ipu
68 A15 I Address 15
69 A14 I Address 14
70 A13 I Address 13
71 A12 I Address 12
72 A11 I Address 11
73 A10 I Address 10
74 A9 I Address 9
75 A8 I Address 8
76 A7 I Address 7
77 A6 I Address 6
78 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
79 VDDIO P 3.3V digital V
80 A5 I Address 5
81 A4 I Address 4
82 A3 I Address 3
83 A2 I Address 2
84 A1 I Address 1
85 BE3N I Byte Enable 3 Not, Active low for Data byte 3 enable.
86 BE2N I Byte Enable 2 Not, Active low for Data byte 2 enable.
87 BE1N I Byte Enable 1 Not, Active low for Data byte 1 enable.
88 BE0N I Byte Enable 0 Not, Active low for Data byte 0 enable.
89 D31 I/O Data 31
90 DGND Gnd Digital core ground
91 VDDC P
92 VDDIO P 3.3V digital V
November 2005 20 Rev. 1.4
Pin Name Type Pin Function
1.2 analog V
bead and capacitor.
Pull-down this pin with a 3.01K 1% resistor to ground.
1.2V analog V
Ferrite bead and capacitor.
Pins (X1, X2) connect to a crystal. If an oscillator is used, X1 connects to a 3.3V
tolerant oscillator and X2 is a no connect.
Note: Clock is ± 50ppm for either crystal or oscillator.
Hardware reset pin (active Low). This reset input is required minimum of 10ms low
after stable supply voltage 3.3V.
1.2V digital core V
Ferrite bead and capacitor.
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external Ferrite
DD
for PLL input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external
DD
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
input power supply from VDDCO (pin24) through external
DD
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Pin
Number
93 D30 I/O Data 30
94 D29 I/O Data 29
95 D28 I/O Data 28
96 D27 I/O Data 27
97 D26 I/O Data 26
98 D25 I/O Data 25
99 D24 I/O Data 24
100 D23 I/O Data 23
101 D22 I/O Data 22
102 D21 I/O Data 21
103 D20 I/O Data 20
104 D19 I/O Data 19
105 D18 I/O Data 18
106 D17 I/O Data 17
107 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
108 VDDIO P
109 D16 I/O Data 16
110 D15 I/O Data 15
111 D14 I/O Data 14
112 D13 I/O Data 13
113 D12 I/O Data 12
114 D11 I/O Data 11
115 D10 I/O Data 10
116 D9 I/O Data 9
117 D8 I/O Data 8
118 D7 I/O Data 7
119 D6 I/O Data 6
120 D5 I/O Data 5
121 D4 I/O Data 4
122 D3 I/O Data 3
123 DGND Gnd Digital IO ground
124 DGND Gnd Digital core ground
125 VDDIO P 3.3V digital V
126 D2 I/O Data 2
127 D1 I/O Data 1
128 D0 I/O Data 0
Pin Name Type Pin Function
3.3V digital V
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
input power supply for IO with well decoupling capacitors.
DDIO
Legend:
P = Power supply Gnd = Ground.
I/O = Bi-directional I = Input O = Output.
Ipd = Input with internal pull-down.
Ipu = Input with internal pull-up.
Opd = Output with internal pull-down.
Opu = Output with internal pull-up.
November 2005 21 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Functional Description
The KSZ8842M contains two 10/100 physical layer transceivers (PHYs), two MAC units, and a DMA channel
integrated with a Layer-2 switch.
The KSZ8842M contains a bus interface unit (BIU), which controls the KSZ8842M via an 8, 16, or 32-bit host
interface.
Physical signal transmission and reception are enhanced through the use of analog circuits in the PHY that make
the design more efficient and allow for low power consumption.
Functional Overview: Physical Layer Transceiver
100BASE-TX Transmit
The 100BASE-TX transmit function performs parallel to serial conversion, 4B/5B coding, scrambling, NRZ-to-NRZI
conversion, and MLT3 encoding and transmission.
The circuitry starts with a parallel-to-serial conversion, which converts the MII data from the MAC into a 125MHz
serial bit stream. The data and control stream is then converted into 4B/5B coding, followed by a scrambler. The
serialized data is further converted from NRZ-to-NRZI format, and then transmitted in MLT3 current output. The
output current is set by an external1% 3.01KΩ resistor for the 1:1 transformer ratio.
The output signal has a typical rise/fall time of 4ns and complies with the ANSI TP-PMD standard regarding
amplitude balance, overshoot, and timing jitter. The wave-shaped 10BASE-T output is also incorporated into the
100BASE-TX transmitter.
100BASE-TX Receive
The 100BASE-TX receiver function performs adaptive equalization, DC restoration, MLT3-to-NRZI conversion,
data and clock recovery, NRZI-to-NRZ conversion, de-scrambling, 4B/5B decoding, and serial to parallel
conversion.
The receiving side starts with the equalization filter to compensate for inter-symbol interference (ISI) over the
twisted pair cable. Since the amplitude loss and phase distortion is a function of the cable length, the equalizer
must adjust its characteristics to optimize performance. In this design, the variable equalizer makes an initial
estimation based on comparisons of incoming signal strength against some known cable characteristics, and then
tunes itself for optimization. This is an ongoing process and self-adjusts against environmental changes such as
temperature variations.
Next, the equalized signal goes through a DC restoration and data conversion block. The DC restoration circuit is
used to compensate for the effect of baseline wander and to improve the dynamic range. The differential data
conversion circuit converts the MLT3 format back to NRZI. The slicing threshold is also adaptive.
The clock recovery circuit extracts the 125MHz clock from the edges of the NRZI signal. This recovered clock is
then used to convert the NRZI signal into the NRZ format. This signal is sent through the de-scrambler followed by
the 4B/5B decoder. Finally, the NRZ serial data is converted to the MII format and provided as the input data to the
MAC.
Scrambler/De-scrambler (100BASE-TX only)
The purpose of the scrambler is to spread the power spectrum of the signal to reduce electromagnetic interference
(EMI) and baseline wander. Transmitted data is scrambled through the use of an 11-bit wide linear feedback shift
register (LFSR). The scrambler generates a 2047-bit non-repetitive sequence, and the receiver then de-scrambles
the incoming data stream using the same sequence as at the transmitter.
10BASE-T Transmit
The 10BASE-T driver is incorporated with the 100BASE-TX driver to allow for transmission using the same
magnetic. They are internally wave-shaped and pre-emphasized into outputs with a typical 2.3V amplitude. The
harmonic contents are at least 27dB below the fundamental frequency when driven by an all-ones Manchesterencoded signal.
10BASE-T Receive
On the receive side, input buffers and level detecting squelch circuits are employed. A differential input receiver
November 2005 22 Rev. 1.4
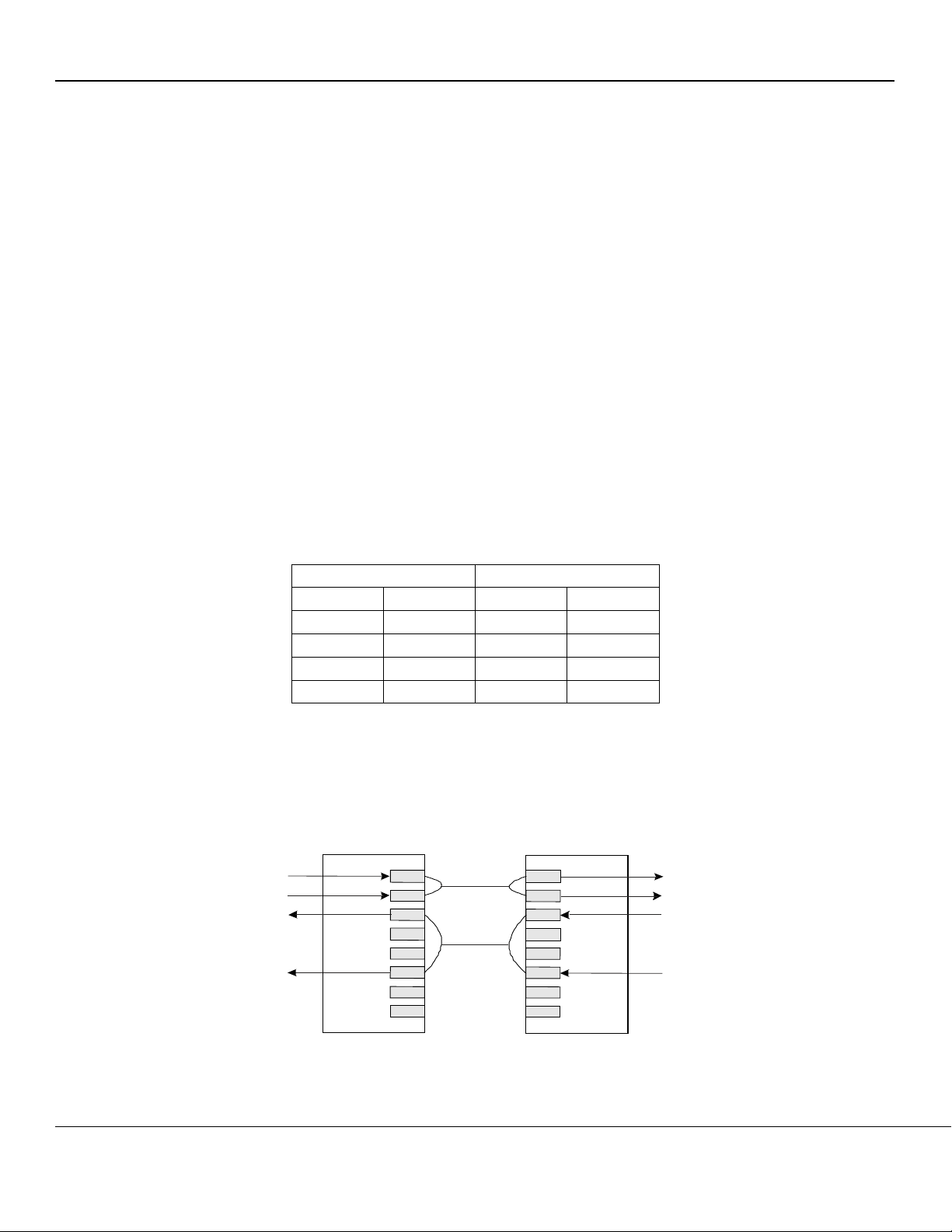
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
circuit and a phase-locked loop (PLL) perform the decoding function. The Manchester-encoded data stream is
separated into clock signal and NRZ data. A squelch circuit rejects signals with levels less than 400mV or with
short pulse widths to prevent noise at the RXP-or-RXM input from falsely triggering the decoder. When the input
exceeds the squelch limit, the PLL locks onto the incoming signal and the KSZ8842M decodes a data frame. The
receiver clock is maintained active during idle periods in between data reception.
Power Management
The KSZ8842M features per port power-down mode. To save power, the user can power-down the port that is not in use
by setting bit 11 in either P1CR4 or P1MBCR register for port 1 and setting bit 11 in either P2CR4 or P2MBCR register for
port 2. To bring the port back up, reset bit 11 in these registers.
In addition, there is a full switch power-down mode. This mode shuts the entire switch down, when the PWRDN (pin 36) is
pulled down to low.
MDI/MDI-X Auto Crossover
To eliminate the need for crossover cables between similar devices, the KSZ8842M supports HP-Auto MDI/MDI-X and
IEEE 802.3u standard MDI/MDI-X auto crossover. HP-Auto MDI/MDI-X is the default.
The auto-sense function detects remote transmit and receive pairs and correctly assigns the transmit and receive pairs for
the KSZ8842M device. This feature is extremely useful when end users are unaware of cable types in addition to saving
on an additional uplink configuration connection. The auto-crossover feature can be disabled through the port control
registers.
The IEEE 802.3u standard MDI and MDI-X definitions are:
MDI MDI-X
RJ45 Pins Signals RJ45 Pins Signals
1 TD+ 1 RD+
2 TD- 2 RD3 RD+ 3 TD+
6 RD- 6 TD-
Table 1. MDI/MDI-X Pin Definitions
Straight Cable
A straight cable connects an MDI device to an MDI-X device or an MDI-X device to an MDI device. The following diagram
shows a typical straight cable connection between a network interface card (NIC) (MDI) and a switch, or hub (MDI-X).
r
e
h
0
t
E
0
1
/
0
h
0
t
E
0
1
/
0
1
M
i
d
e
a
D
n
a
r
T
m
s
e
R
i
e
c
t
e
n
r
e
t
n
e
d
n
e
p
e
i
a
t
P
a
e
v
P
e
c
a
f
r
e
t
n
I
1
i
r
2
3
4
i
r
5
6
7
8
r
t
h
i
t
g
a
S
l
e
b
a
C
1
d
M
e
i
a
e
D
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
t
e
n
t
n
e
d
n
e
p
f
e
c
r
a
e
I
t
n
e
i
v
e
c
e
R
i
r
a
P
m
s
n
a
r
T
i
i
r
a
t
P
M
e
n
n
o
r
C
l
a
u
d
o
t
r
o
c
)
5
4
-
J
R
(
N
I
C
M
u
d
o
e
n
n
o
l
r
C
a
r
t
c
o
-
J
R
(
)
5
4
U
B
H
t
a
e
e
p
R
e
(
)
h
c
i
w
t
r
S
r
o
Figure 6. Typical Straight Cable Connection
November 2005 23 Rev. 1.4
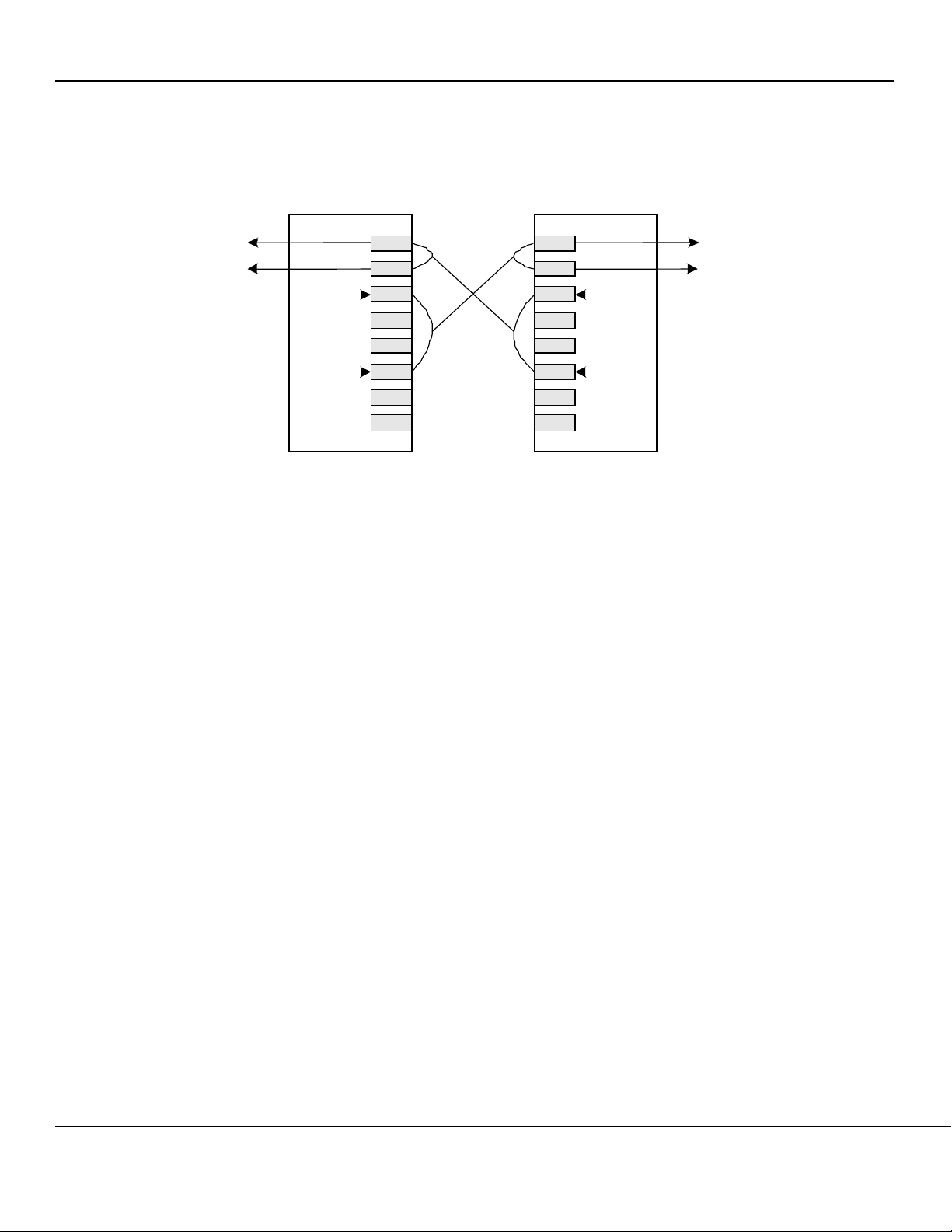
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Crossover Cable
A crossover cable connects an MDI device to another MDI device, or an MDI-X device to another MDI-X device. The
following diagram shows a typical crossover cable connection between two switches or hubs (two MDI-X devices).
1 0 / 1 0 0 E t h e r n et
M
e d i a D e p e n d e n t I n
R e ce i v e P a i r
T
r a n sm i t P a i r
M
o d u l a r C o n n e ct o r
H
U B
( R e p e a t e r o r S
terface
(RJ-45)
tch)
w i
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Crossover
Cable
10/100Ethernet
Media Dependent Interface
1
ReceivePair
2
3
4
Transmit Pair
5
6
7
8
ModularConnector(RJ-45)
HUB
(Repeateror Switch)
Figure 7. Typical Crossover Cable Connection
Auto Negotiation
The KSZ8842M conforms to the auto negotiation protocol as described by the 802.3 committee to allow the channel to
operate at 10Base-T or 100Base-TX.
Auto negotiation allows unshielded twisted pair (UTP) link partners to select the best common mode of operation. In auto
negotiation, the link partners advertise capabilities across the link to each other. If auto negotiation is not supported or the
link partner to the KSZ8842M is forced to bypass auto negotiation, the mode is set by observing the signal at the receiver.
This is known as parallel mode because while the transmitter is sending auto negotiation advertisements, the receiver is
listening for advertisements or a fixed signal protocol.
The link setup is shown in the following flow diagram (Figure 8).
November 2005 24 Rev. 1.4
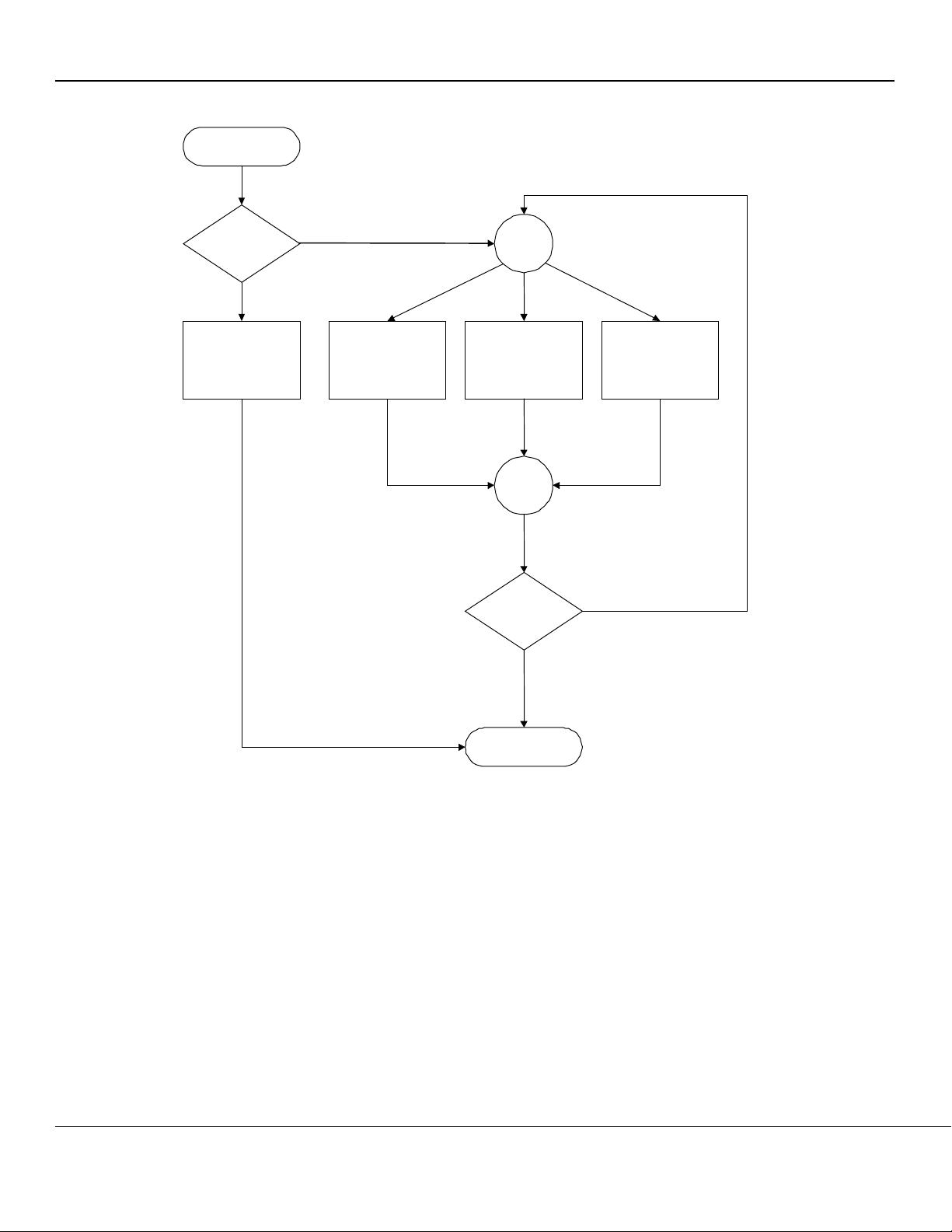
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
A
Start Auto Negotiation
NO
Force Link Setting
YES
Parallel
Operation
Bypass Auto Negotiation
and Set Link Mode
ttempt Auto
Negotiation
Listen for 100BASE-TX
Idles
Join
Flow
Link Mode Set ?
YES
Link Mode Set
Listen for 10BASE-T Link
Pulses
NO
Figure 8. Auto Negotiation and Parallel Operation
LinkMD Cable Diagnostics
The KSZ8842M LinkMD uses time domain reflectometry (TDR) to analyze the cabling plant for common cabling problems
such as open circuits, short circuits, and impedance mismatches.
LinkMD works by sending a pulse of known amplitude and duration down the MDI and MDI-X pairs and then analyzes the
shape of the reflected signal. Timing the pulse duration gives an indication of the distance to the cabling fault with a
maximum distance of 200m and an accuracy of +/–2m. Internal circuitry displays the TDR information in a user-readable
digital format in registers P1VCT[8:0] or P2VCT[8:0].
Note: cable diagnostics are only valid for copper connections –fiber-optic operation is not supported.
Access
LinkMD is initiated by accessing register P1VCT/P2VCT, the LinkMD Control/Status register, in conjunction with register
P1CR4/P2CR4, the 100BASE-TX PHY Controller register.
November 2005 25 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Usage
LinkMD can be run at any time by making sure Auto MDIX has been disabled. To disable Auto-MDIX, write a ‘1’ to
P1CR4[10] for port 1 or P2CR4[10] for port 2 to enable manual control over the pair used to transmit the LinkMD pulse.
The self-clearing cable diagnostic test enable bit, P1VCT[15] for port 1 or P2VCT[15] for port 2 , is set to ‘1’ to start the
test on this pair.
When bit P1VCT[15] or P2VCT[15] returns to ‘0’, the test is complete. The test result is returned in bits P1VCT[14:13] or
P2VCT[14:13] and the distance is returned in bits P1VCT[8:0] or P2VCT[8:0]. The cable diagnostic test results are as
follows:
00 = Valid test, normal condition
01 = Valid test, open circuit in cable
10 = Valid test, short circuit in cable
11 = Invalid test, LinkMD failed
If P1VCT[14:13]=11 or P2VCT[14:13]=11, this indicates an invalid test, and occurs when the KSZ8842M is unable to shut
down the link partner. In this instance, the test is not run, as it is not possible for the KSZ8842M to determine if the
detected signal is a reflection of the signal generated or a signal from another source.
Cable distance can be approximated by the following formula:
P1VCT[8:0] X 0.4m for port 1 cable distance
P2VCT[8:0] X 0.4m for port 2 cable distance
This constant may be calibrated for different cabling conditions, including cables with a velocity of propagation that varies
significantly from the norm.
Functional Overview: MAC and Switch
Address Lookup
The internal lookup table stores MAC addresses and their associated information. It contains a 1K entry unicast address
learning table plus switching information.
The KSZ8842M is guaranteed to learn 1K addresses and distinguishes itself from hash-based lookup tables, which
depending on the operating environment and probabilities, may not guarantee the absolute number of addresses it can
learn.
Learning
The internal lookup engine updates its table with a new entry if the following conditions are met:
1. The received packet's Source Address (SA) does not exist in the lookup table.
2. The received packet is good without receiving errors; the packet size is legal length.
The lookup engine inserts the qualified SA into the table, along with the port number and time stamp. If the table is full, the
last entry of the table is deleted to make room for the new entry.
Migration
The internal lookup engine also monitors whether a station has moved. If a station has moved, it updates the table
accordingly. Migration happens when the following conditions are met:
1. The received packet's SA is in the table but the associated source port information is different.
2. The received packet is good without receiving errors; the packet size is legal length.
The lookup engine updates the existing record in the table with the new source port information.
Aging
The lookup engine updates the time stamp information of a record whenever the corresponding SA appears. The time
stamp is used in the aging process. If a record is not updated for a period of time, the lookup engine removes the record
from the table. The lookup engine constantly performs the aging process and continuously removes aging records. The
aging period is about 200 seconds. This feature can be enabled or disabled through Global Register SGCR1[10].
November 2005 26 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Forwarding
The KSZ8842M forwards packets using the algorithm that is depicted in the following flowcharts. Figure 9 shows stage
one of the forwarding algorithm where the search engine looks up the VLAN ID, static table, and dynamic table for the
destination address, and comes up with “port to forward 1” (PTF1). PTF1 is then further modified by spanning tree, IGMP
snooping, port mirroring, and port VLAN processes to come up with “port to forward 2” (PTF2), as shown in Figure 10.
The packet is sent to PTF2.
Start
PTF1 = NULL
NO
VLAN ID
valid?
- Search VLAN table
- Ingress VLAN filtering
- Discard NPVID check
YES
Search complete.
Get PTF1 from
Static MAC Table
FOUND
Search Static
Table
This search is based on
DA or DA+FID
NOT
FOUND
Search complete.
Get PTF1 from
Dynamic MAC Table
FOUND
Dynamic Table
Search
This search is based on
DA+FID
NOT
FOUND
Search complete.
Get PTF1 from
VLAN table
PTF1
Figure 9. Destination Address Lookup Flow Chart in Stage One
November 2005 27 Rev. 1.4
Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
p
PTF1
- Check receiving port's receive enable bit
Spanning Tree
Process
IG M P Process
Port Mirror
Process
- Check destination port 's transmit enable bit
- Check whet her pa cket s ar e spec ial (BPDU )
or s
ecified
- Applied t o MAC #1 an d MA C #2
- IGMP will be forwarded to the h ost port
- RX Mirror
- TX Mirror
- RX or TX Mirror
- RX and TX Mirror
Port VLAN
Membership
Check
PTF2
Figure 10. Destination Address Resolution Flow Chart in Stage Two
The KSZ8842M will not forward the following packets:
1. Error packets.
These include framing errors, Frame Check Sequence (FCS) errors, alignment errors, and illegal size packet errors.
2. 802.3x pause frames.
The KSZ8842M intercepts these packets and performs the flow control.
3. "Local" packets.
Based on destination address (DA) lookup. If the destination port from the lookup table matches the port from which
the packet originated, the packet is defined as "local."
November 2005 28 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
Switching Engine
The KSZ8842M features a high-performance switching engine to move data to and from the MAC’s packet buffers. It
operates in store and forward mode, while the efficient switching mechanism reduces overall latency.
The switching engine has a 32KB internal frame buffer. This resource is shared between all the ports. There are a total of
256 buffers available. Each buffer is sized at 128B.
MAC Operation
The KSZ8842M strictly abides by IEEE 802.3 standards to maximize compatibility. Additionally, there is an added MAC
filtering function to filter Unicast packets. The MAC filtering function is useful in applications such as VoIP where
restricting certain packets reduces congestion and thus improves performance.
Inter Packet Gap (IPG)
If a frame is successfully transmitted, the minimum 96-bit time for IPG is measured between two consecutive packets. If
the current packet is experiencing collisions, the minimum 96-bit time for IPG is measured from carrier sense (CRS) to the
next transmit packet.
Back-Off Algorithm
The KSZ8842M implements the IEEE standard 802.3 binary exponential back-off algorithm in half-duplex mode, and
optional "aggressive mode" back-off. After 16 collisions, the packet is optionally dropped depending on the switch
configuration in SGCR1[8].
Late Collision
If a transmit packet experiences collisions after 512 bit times of the transmission, the packet is dropped.
legal Packet Size
The KSZ8842M discards packets less than 64 bytes and can be programmed to accept packet size up to 1536 bytes in
SGCR2[1]. The KSZ8842M can also be programmed for special applications to accept packet size up to 1916 bytes in
SGCR2[2].
Flow Control
The KSZ8842M supports standard 802.3x flow control frames on both transmit and receive sides.
On the receive side, if the KSZ8842M receives a pause control frame, the KSZ8842M will not transmit the next normal
frame until the timer, specified in the pause control frame, expires. If another pause frame is received before the current
timer expires, the timer will be updated with the new value in the second pause frame. During this period (while it is flow
controlled), only flow control packets from the KSZ8842M are transmitted.
On the transmit side, the KSZ8842M has intelligent and efficient ways to determine when to invoke flow control. The flow
control is based on availability of the system resources, including available buffers, available transmit queues, and
available receive queues.
The KSZ8842M will flow control a port that has just received a packet if the destination port resource is busy. The
KSZ8842M issues a flow control frame (Xoff), containing the maximum pause time defined in IEEE standard 802.3x. Once
the resource is freed up, the KSZ8842M sends out the other flow control frame (Xon) with zero pause time to turn off the
flow control (turn on transmission to the port). A hysteresis feature is provided to prevent the flow control mechanism from
being constantly activated and deactivated.
The KSZ8842M flow controls all ports if the receive queue becomes full.
Half-Duplex Backpressure
A half-duplex backpressure option (not in IEEE 802.3 standards) is also provided. The activation and deactivation
conditions are the same in full-duplex mode. If backpressure is required, the KSZ8842M sends preambles to defer the
other stations' transmission (carrier sense deference).
November 2005 29 Rev. 1.4

Micrel Confidential KSZ8842-16/32 MQL/MVL
To avoid jabber and excessive deference (as defined in the 802.3 standard), after a certain time, the KSZ8842M
discontinues the carrier sense and then raises it again quickly. This short silent time (no carrier sense) prevents other
stations from sending out packets thus keeping other stations in a carrier sense deferred state. If the port has packets to
send during a backpressure situation, the carrier sense type backpressure is interrupted and those packets are
transmitted instead. If there are no additional packets to send, carrier sense type backpressure is reactivated again until
switch resources free up. If a collision occurs, the binary exponential back-off algorithm is skipped and carrier sense is
generated immediately, thus reducing the chance of further collisions and carrier sense is maintained to prevent packet
reception.
To ensure no packet loss in 10 BASE-T or 100 BASE-TX half-duplex modes, the user must enable the following:
1. Aggressive back off (bit 8 in SGCR1)
2. No excessive collision drop (bit 3 in SGCR2)
Note: These bits are not set in default, since this is not the IEEE standard.
Broadcast Storm Protection
The KSZ8842M has an intelligent option to protect the switch system from receiving too many broadcast packets. As the
broadcast packets are forwarded to all ports except the source port, an excessive number of switch resources (bandwidth
and available space in transmit queues) may be utilized. The KSZ8842M has the option to include “multicast packets” for
storm control. The broadcast storm rate parameters are programmed globally, and can be enabled or disabled on a per
port basis in P1CR1[7] and P2CR1[7]. The rate is based on a 67ms interval for 100BT and a 670ms interval for 10BT. At
the beginning of each interval, the counter is cleared to zero and the rate limit mechanism starts to count the number of
bytes during the interval. The rate definition is described in SGCR3[15:8]. The default setting is 0x63 (99 decimal). This is
equal to a rate of 1%, calculated as follows:
148,800 frames/sec X 67 ms/interval X 1% = 99 frames/interval (approx.) = 0x63
Note: 148,800 frames/sec is based on 64-byte block of packets in 100BASE-T with 12 bytes of IPG and 8 bytes of
preamble between two packets.
Repeater Mode
When the KSZ8842M is set to repeater mode (SGCR3[7] = 1), it only works on 100BT half-duplex mode. In repeater
enabled mode, all ingress packets will be broadcast to the other two ports without MAC address checking and learning.
Before setting to the repeater mode, the user has to set bit 13 (100Mbps), bit 12 (auto-negotiation disabled) and bit 8 (half
duplex) in both P1MBCR and P2MBCR registers as well as set bit 6 (host half duplex) in SGCR3 register for the repeater
mode.
The latency in repeater mode is defined from the 1st bit of DA into the ingress port 1 to the 1st bit of DA out of the egress
port 2. The minimum is 270 ns and the maximum is 310 ns (one clock skew of 25 MHz between TX and RX).
Clock Generator
The X1 and X2 pins are connected to a 25 MHz crystal. X1 can also serve as the connector to a 3.3V, 25 MHz oscillator
(as described in the pin description).
The bus interface unit (BIU) uses BCLK (Bus Clock) for synchronous accesses. The maximum host port frequency is 50
MHz for VLBus-like and burst mode (32-bit interface only).
Bus Interface Unit (BIU)
The host interface of the BIU is designed to communicate with embedded processors. The host interface of the
KSZ8842M is a generic bus interface. Some glue logic may be required when the interface talks to various buses and
processors.
In terms of transfer type, the BIU can support two transfers: asynchronous transfer and synchronous transfer. To support
these transfers (asynchronous and synchronous), the BIU provides three groups of signals:
1. Synchronous signals
2. Asynchronous signals
3. Common signals are used for both synchronous and asynchronous transfers.
Since both synchronous and asynchronous signals are independent of each other, synchronous burst transfer and
asynchronous transfer can be mixed or interleaved but cannot be overlapped (due to the sharing of the common signals).
In terms of physical data bus size, the KSZ8842M supports 8, 16, and 32 bit host/industrial standard data bus sizes.
November 2005 30 Rev. 1.4
 Loading...
Loading...