Page 1

Easergy MiCOM P634
Transformer Differential Protection Device
P634/EN M/R-42-A
Version P634 -311 -410/411 -653
Technical Manual
Page 2

Page 3
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
NOTICE: Read these instructions carefully, and look at the equipment to become familiar
with the device before trying to install, operate, or maintain it. The following
special messages may appear throughout this documentation or on the equipment
to warn of potential hazards or to call attention to information that clarifies or
simplifies a procedure.
The addition of this symbol to a Danger or Warning safety label indicates that an
electrical hazard exists, which will result in death or serious injury if the
instructions are not followed.
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to a potential personal injury
hazard. Obey all safety messages that follow this symbol to avoid possible injury or
death.
DANGER
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
can result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
can result in minor or moderate injury.
NOTICE
NOTICE, used without safety alert symbol, indicates a potentially hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, can result in equipment damage.
Page 4

WARNING
When electrical equipment is in operation dangerous voltage will be present in certain parts of the
equipment. Failure to observe warning notices, incorrect use or improper use may endanger personnel
and equipment and cause personal injury or physical damage.
Before working in the terminal strip area, the P634 must be isolated. Where stranded conductors are
used, insulated crimped wire end ferrules must be employed.
The signals MAIN: Blocked/faulty and SFMON: Warning (LED) (permanently assigned to the
LEDs labeled OUT OF SERVICE and ALARM) can be assigned to output relays to indicate the health of
the P634. Schneider Electric strongly recommends that these output relays are hardwired into the
substation's automation system, for alarm purposes.
Any modifications to this P634 must be in accordance with the manual. If any other modification is
made without the express permission of Schneider Electric, it will invalidate the warranty, and may
render the product unsafe.
Proper and safe operation of this P634 depends on appropriate shipping and handling, proper storage,
installation and commissioning, and on careful operation, maintenance and servicing.
For this reason only qualified personnel may work on or operate this P634.
The User should be familiar with the warnings in the Safety Guide (SFTY/4LM/J11 or later version), with
the warnings in Chapter 5, (p. 5-1), Chapter 10, (p. 10-1), Chapter 11, (p. 11-1) and
Chapter 12, (p. 12-1) and with the content of Chapter 14, (p. 14-1), before working on the
equipment. If the warnings are disregarded, it will invalidate the warranty, and may render the
product unsafe.
Installation of the DHMI:
A protective conductor (ground/earth) of at least 1.5 mm² (US: AWG14 or thicker) must be connected
to the DHMI protective conductor terminal to link the DHMI and the main relay case; these must be
located within the same substation.
To avoid the risk of electric shock the DHMI communication cable must not be in contact with
hazardous live parts.
The DHMI communication cable must not be routed or placed alongside high-voltage cables or
connections. Currents can be induced in the cable which may result in electromagnetic interference.
PLEASE NOTE:
Electrical equipment should be installed, operated, serviced, and maintained only by qualified
personnel. No responsibility is assumed by Schneider Electric for any consequences arising out of the
use of this material. A qualified person is one who has skills and knowledge related to the construction
and operation of electrical equipment and the installation, and has received safety training to
recognize and avoid the hazards involved.
Page 5

Qualified Personnel
are individuals who
are familiar with the installation, commissioning and operation of the P634 and of the system to
●
which it is being connected;
are able to perform switching operations in accordance with safety engineering standards and
●
are authorized to energize and de-energize equipment and to isolate, ground and label it;
are trained in the care and use of safety apparatus in accordance with safety engineering
●
standards;
are trained in emergency procedures (first aid).
●
Note
This operating manual gives instructions for installation, commissioning and operation of the P634.
However, the manual cannot cover all conceivable circumstances or include detailed information on all
topics. In the event of questions or specific problems, do not take any action without proper
authorization. Contact the appropriate technical sales office of Schneider Electric and request the
necessary information.
Any agreements, commitments, and legal relationships and any obligations on the part of Schneider
Electric, including settlement of warranties, result solely from the applicable purchase contract, which
is not affected by the contents of the operating manual.
Page 6

Page 7

Changes after going to press
Page 8

Page 9

P634
Table of Contents
1 Application and Scope ........................................................................................ 1-1
1.1 Overview - P634 ..........................................................................................................1-1
1.1.1 Design ........................................................................................................................................................... 1-2
1.2 Including Function Groups in the Configuration ..........................................................1-3
1.3 Overview of Function Groups - Part 1 ......................................................................... 1-4
1.4 Overview of Function Groups - Part 2 ......................................................................... 1-6
1.5 Configurable Function Keys ........................................................................................ 1-8
1.6 Inputs and Outputs ..................................................................................................... 1-9
1.7 Control and Display ...................................................................................................1-10
1.8 Information Interfaces ...............................................................................................1-11
2 Technical Data ....................................................................................................2-1
2.1 Conformity ..................................................................................................................2-1
2.2 General Data ...............................................................................................................2-2
2.2.1 General Device Data ..................................................................................................................................... 2-2
2.3 Tests ...........................................................................................................................2-4
2.3.1 Type Tests .....................................................................................................................................................2-4
2.3.2 Routine Tests .................................................................................................................................................2-7
2.4 Environmental Conditions ...........................................................................................2-9
2.5 Inputs and Outputs ................................................................................................... 2-10
2.5.1 Measuring Inputs .........................................................................................................................................2-10
2.5.2 Binary Signal Inputs .....................................................................................................................................2-11
2.5.3 IRIG‑B Interface ........................................................................................................................................... 2-12
2.5.4 Direct Current Input .....................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.5 Resistance Thermometer ............................................................................................................................ 2-12
2.5.6 Direct Current Output ..................................................................................................................................2-12
2.5.7 Output Relays ..............................................................................................................................................2-13
2.5.8 BCD Measured Data Output ........................................................................................................................ 2-13
2.6 Interfaces ..................................................................................................................2-14
2.6.1 Local Control Panel ......................................................................................................................................2-14
2.6.2 PC Interface .................................................................................................................................................2-14
2.6.3 Serial Communication Interface .................................................................................................................. 2-14
2.6.4 IEC Communication Interface ......................................................................................................................2-15
2.6.5 IRIG‑B Interface ........................................................................................................................................... 2-15
2.7 Information Output ................................................................................................... 2-16
2.8 Settings – Typical Characteristic Data .......................................................................2-17
2.8.1 Main Function ..............................................................................................................................................2-17
2.8.2 Differential Protection ..................................................................................................................................2-17
2.8.3 Definite-Time and Inverse-Time Overcurrent Protection ............................................................................. 2-17
2.8.4 Time-Voltage Protection ..............................................................................................................................2-17
2.8.5 Overfluxing Protection .................................................................................................................................2-17
2.9 Deviations .................................................................................................................2-18
2.9.1 Deviations of the Operate Values ................................................................................................................2-18
2.9.2 Deviations of the Timer Stages ................................................................................................................... 2-20
2.9.3 Deviations of Measured Data Acquisition ....................................................................................................2-20
2.10 Resolution of the Fault Data Acquisition ...................................................................2-21
2.10.1 Time Resolution ...........................................................................................................................................2-21
2.10.2 Currents .......................................................................................................................................................2-21
2.10.3 Voltage ........................................................................................................................................................2-21
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 1
Page 10

P634
Table of Contents
2.11 Recording Functions ................................................................................................. 2-22
2.11.1 Organization of the Recording Memories .................................................................................................... 2-22
2.12 Power Supply ............................................................................................................ 2-24
2.13 Current Transformer Specifications .......................................................................... 2-25
2.13.1 Symbols .......................................................................................................................................................2-25
2.13.2 General Equations .......................................................................................................................................2-26
2.13.3 Transformer Differential Protection .............................................................................................................2-27
3 Operation ............................................................................................................3-1
3.1 Modular Structure .......................................................................................................3-1
3.2 Operator-Machine Communication ............................................................................. 3-3
3.3 Configuration of the Measured Value Panels (Function Group LOC) ........................... 3-4
3.3.1 Operation Panel .............................................................................................................................................3-5
3.3.2 Fault Panel .....................................................................................................................................................3-6
3.3.3 Overload Panel ..............................................................................................................................................3-7
3.3.4 Configurable Clear Key ..................................................................................................................................3-7
3.4 Communication Interfaces ..........................................................................................3-8
3.4.1 PC Interface (Function Group PC) .................................................................................................................. 3-9
3.4.2 Communication Interface 1 (Function Group COMM1) ................................................................................ 3-10
3.4.3 Communication Interface 2 (Function Group COMM2) ................................................................................ 3-19
3.4.4 Communication Interface IEC 61850 (Function Groups IEC and GOOSE) .................................................... 3-21
3.4.5 Redundant Ethernet Board ..........................................................................................................................3-31
3.5 IRIG-B Clock Synchronization (Function Group IRIGB) ...............................................3-34
3.6 Configurable Function Keys (Function Group F_KEY) ................................................ 3-35
3.7 Configuration and Operating Mode of the Binary Inputs (Function Group INP) .........3-37
3.8 Measured Data Input (Function Group MEASI) ..........................................................3-39
3.8.1 Direct Current Input on the Analog (I/O) Module Y ...................................................................................... 3-40
3.8.2 Input for Connection of a Resistance Thermometer .................................................................................... 3-43
3.9 Configuration, Operating Mode, and Blocking of the Output Relays (Function Group
OUTP) ........................................................................................................................3-45
3.9.1 Configuration of the Output Relays ............................................................................................................. 3-45
3.9.2 Operating Mode of the Output Relays ......................................................................................................... 3-45
3.9.3 Blocking the Output Relays ......................................................................................................................... 3-46
3.9.4 Testing the Output Relays ...........................................................................................................................3-47
3.10 Measured Data Output (Function Group MEASO) ......................................................3-48
3.10.1 General Settings ..........................................................................................................................................3-48
3.10.2 BCD Measured Data Output ........................................................................................................................ 3-50
3.10.3 Analog Measured Data Output .................................................................................................................... 3-53
3.10.4 Output of “External” Measured Data ...........................................................................................................3-59
3.11 Configuration and Operating Mode of the LED Indicators (Function Group LED) ...... 3-60
3.11.1 Configuring the LED Indicators ....................................................................................................................3-60
3.11.2 Layout of the LED Indicators ........................................................................................................................3-60
3.11.3 Operating Mode of the LED Indicators .........................................................................................................3-61
3.12 Main Functions of the P634 (Function Group MAIN) ..................................................3-63
3.12.1 Conditioning of the Measured Values ..........................................................................................................3-63
3.12.2 Phase Reversal Function ..............................................................................................................................3-67
3.12.3 Disconnecting Transformer Ends .................................................................................................................3-68
3.12.4 Selection of the Residual Current to be Monitored ......................................................................................3-72
3.12.5 Forming a Virtual Transformer End ..............................................................................................................3-72
3.12.6 Operating Data Measurement ..................................................................................................................... 3-75
3.12.7 Configuring and Enabling the Device Functions .......................................................................................... 3-86
3.12.8 Activation of “Dynamic Parameters” ...........................................................................................................3-88
2 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 11

Table of Contents
3.12.9 Multiple Blocking ......................................................................................................................................... 3-89
3.12.10 Multiple Signaling of the Measuring Circuit Monitoring Function .................................................................3-90
3.12.11 Multiple Signaling ........................................................................................................................................3-90
3.12.12 Blocked/Faulty .............................................................................................................................................3-91
3.12.13 Starting Signals and Tripping Logic .............................................................................................................3-91
3.12.14 Time Tagging and Clock Synchronization ....................................................................................................3-95
3.12.15 Resetting Actions .........................................................................................................................................3-96
3.12.16 Assigning Communications Interfaces to Physical Communications Channels ............................................3-98
3.12.17 Test Mode ....................................................................................................................................................3-99
3.13 Parameter Subset Selection (Function Group PSS) ................................................. 3-100
3.14 Self-Monitoring (Function Group SFMON) ................................................................3-102
3.14.1 Tests During Start-up ................................................................................................................................ 3-102
3.14.2 Cyclic Tests ................................................................................................................................................3-102
3.14.3 Signals .......................................................................................................................................................3-102
3.14.4 Device Response .......................................................................................................................................3-103
3.14.5 Monitoring Signal Memory .........................................................................................................................3-104
3.14.6 Monitoring Signal Memory Time Tag .........................................................................................................3-104
3.15 Operating Data Recording (Function Group OP_RC) ............................................... 3-105
3.16 Monitoring Signal Recording (Function Group MT_RC) ............................................3-106
3.17 Overload Data Acquisition (Function Group OL_DA) ............................................... 3-107
3.17.1 Overload Duration .....................................................................................................................................3-107
3.17.2 Acquiring Measured Overload Data from the Thermal Overload Protection ..............................................3-108
3.18 Overload Recording (Function Group OL_RC) ..........................................................3-109
3.18.1 Start of Overload Recording ......................................................................................................................3-109
3.18.2 Counting Overload Events .........................................................................................................................3-109
3.18.3 Time Tagging .............................................................................................................................................3-109
3.18.4 Overload Logging ...................................................................................................................................... 3-110
3.19 Fault Data Acquisition (Function Group FT_DA) ...................................................... 3-111
3.19.1 Running Time and Fault Duration ..............................................................................................................3-112
3.19.2 Fault Data Acquisition Time .......................................................................................................................3-113
3.19.3 Acquisition of the Fault Currents ............................................................................................................... 3-114
3.19.4 Acquisition of the Differential and Restraining Currents ............................................................................3-115
3.19.5 Fault Data Reset ........................................................................................................................................3-117
3.20 Fault Recording (Function Group FT_RC) ................................................................ 3-118
3.20.1 Start of Fault Recording .............................................................................................................................3-118
3.20.2 Fault Counting ...........................................................................................................................................3-119
3.20.3 Time Tagging .............................................................................................................................................3-119
3.20.4 Fault Recordings ........................................................................................................................................3-120
3.20.5 Fault Value Recording ............................................................................................................................... 3-121
3.21 Differential Protection (Function Group DIFF) ......................................................... 3-123
3.21.1 Enabling or Disabling Differential Protection .............................................................................................3-123
3.21.2 Amplitude Matching ...................................................................................................................................3-124
3.21.3 Vector Group Matching ..............................................................................................................................3-128
3.21.4 Zero-sequence Current Filtering ................................................................................................................3-128
3.21.5 Tripping Characteristics .............................................................................................................................3-132
3.21.6 Rapid (high-set) Differential Protection ..................................................................................................... 3-134
3.21.7 Inrush Stabilization (2nd Harmonic Restraint) ...........................................................................................3-136
3.21.8 Overfluxing Stabilization (5th Harmonic Restraint) ................................................................................... 3-138
3.21.9 Saturation Discriminator ............................................................................................................................3-139
3.21.10 Measured Operating Data of Differential Protection ..................................................................................3-139
3.22 Ground Differential Protection (Function Groups REF_1 to REF_3) ..........................3-141
3.22.1 Enabling or Disabling Ground Differential Protection ................................................................................ 3-141
3.22.2 Blocking ground differential protection ..................................................................................................... 3-141
3.22.3 Amplitude Matching ...................................................................................................................................3-142
P634
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3
Page 12

P634
3.22.4 Operating Modes .......................................................................................................................................3-144
3.22.5 Idiff>>> Threshold ....................................................................................................................................3-148
3.22.6 Applying Current Transformer Supervision ................................................................................................3-148
3.22.7 Measured Operating Data of Ground Differential Protection .....................................................................3-148
3.22.8 Protection of Autotransformers ................................................................................................................. 3-149
Table of Contents
3.23 Definite-Time Overcurrent Protection (Function Groups DTOC1 to DTOC4) ............3-152
3.23.1 Enabling or Disabling DTOC Protection ......................................................................................................3-152
3.23.2 Phase Current Stages ................................................................................................................................3-154
3.23.3 Negative-Sequence Current Stages ...........................................................................................................3-156
3.23.4 Residual Current Stages ............................................................................................................................3-157
3.23.5 General Starting ........................................................................................................................................3-159
3.23.6 General Trip Signal ....................................................................................................................................3-159
3.23.7 Counters of the DTOC Protection Function ................................................................................................3-160
3.24 Inverse-time Overcurrent Protection (Function Groups IDMT1 to IDMT3) ............... 3-161
3.24.1 Enabling or Disabling IDMT Protection .......................................................................................................3-161
3.24.2 Time-Dependent Characteristics ............................................................................................................... 3-163
3.24.3 Phase Current Stage ..................................................................................................................................3-167
3.24.4 Negative-Sequence Current Stage ............................................................................................................ 3-168
3.24.5 Residual Current Stage ..............................................................................................................................3-170
3.24.6 Hold Time ..................................................................................................................................................3-171
3.24.7 General Starting ........................................................................................................................................3-172
3.24.8 Counters of the IDMT Protection Function .................................................................................................3-173
3.25 Thermal Overload Protection (Function Groups THRM1 and THRM2) ......................3-174
3.25.1 Enabling or Disabling Thermal Overload Protection .................................................................................. 3-174
3.25.2 Readiness of Thermal Overload Protection ................................................................................................3-174
3.25.3 Selection of Current ...................................................................................................................................3-176
3.25.4 Tripping Characteristics .............................................................................................................................3-177
3.25.5 Coolant Temperature Acquisition .............................................................................................................. 3-178
3.25.6 Warning Signal .......................................................................................................................................... 3-180
3.26 Time-Voltage Protection (Function Group V<>) ..................................................... 3-182
3.26.1 Disabling and Enabling V<> Protection .....................................................................................................3-182
3.26.2 V<> Protection Readiness .........................................................................................................................3-182
3.26.3 Voltage Monitoring .................................................................................................................................... 3-182
3.27 Over-/Underfrequency Protection (Function Group f<>) ........................................ 3-185
3.27.1 Disabling or Enabling Over‑/Underfrequency Protection ............................................................................3-185
3.27.2 Undervoltage Blocking and Evaluation Time .............................................................................................3-186
3.27.3 Operating Modes of Over-/Underfrequency Protection ..............................................................................3-186
3.27.4 Frequency Monitoring ................................................................................................................................3-186
3.27.5 Frequency Monitoring Combined with Differential Frequency Gradient Monitoring (df/dt) ........................3-186
3.27.6 Frequency Monitoring Combined with Mean Frequency Gradient Monitoring (Δf/Δt) ................................ 3-187
3.27.7 f
Measurement ...............................................................................................................................3-189
min/fmax
3.28 Overfluxing Protection (Function Group V/f) ........................................................... 3-190
3.28.1 Enabling or Disabling Overfluxing Protection ............................................................................................ 3-190
3.28.2 Conditioning the Measured Value ..............................................................................................................3-190
3.28.3 Fixed-time Warning Stage .........................................................................................................................3-191
3.28.4 Fixed-time Tripping Stage ......................................................................................................................... 3-191
3.28.5 Variable-time Tripping Stage .....................................................................................................................3-191
3.29 Current Transformer Supervision (Function Group CTS) .........................................3-196
3.29.1 Enabling or Disabling the CTS Function .....................................................................................................3-196
3.29.2 Blocking CTS ..............................................................................................................................................3-196
3.29.3 Monitoring Condition ................................................................................................................................. 3-197
3.29.4 Signaling and Indication ............................................................................................................................3-199
3.29.5 Reset .........................................................................................................................................................3-200
3.29.6 Multiple Signaling from the CTS Function ..................................................................................................3-200
4 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 13

Table of Contents
3.30 Measuring-Circuit Monitoring (Function Groups MCM_1 to MCM_4) ........................ 3-202
3.30.1 Enabling or Disabling Measuring-Circuit Monitoring ..................................................................................3-202
3.30.2 Measuring-Circuit Monitoring .....................................................................................................................3-202
3.30.3 Multiple Signaling from the Measuring-Circuit Monitoring Function .......................................................... 3-203
3.31 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection (Function Groups CBF_1 to CBF_4) .................... 3-204
3.31.1 Assigning Transformer Ends ......................................................................................................................3-204
3.31.2 Assigning Circuit Breakers .........................................................................................................................3-204
3.31.3 Assigning the Trip Command .....................................................................................................................3-204
3.31.4 Enabling or Disabling the CBF Function .....................................................................................................3-204
3.31.5 Readiness of Circuit Breaker Protection .................................................................................................... 3-205
3.31.6 Detecting a CB Tripping .............................................................................................................................3-206
3.31.7 Current flow monitoring .............................................................................................................................3-206
3.31.8 Evaluation of CB Status Signals .................................................................................................................3-207
3.31.9 Startup Criteria ..........................................................................................................................................3-208
3.31.10 Trip Commands ......................................................................................................................................... 3-210
3.31.11 Starting Trigger ......................................................................................................................................... 3-211
3.31.12 Fault Behind CB Protection ........................................................................................................................3-211
3.31.13 CB Synchronization Supervision ................................................................................................................3-212
3.32 Limit Value Monitoring (Function Group LIMIT) .......................................................3-213
3.32.1 Enabling or Disabling the Limit Value Monitoring Function ....................................................................... 3-213
3.32.2 Monitoring the Linearized Measured DC Values ........................................................................................ 3-213
3.32.3 Monitoring the Measured Temperature Value ........................................................................................... 3-214
3.33 Limit Value Monitoring (Function Groups LIM_1 to LIM_3) .......................................3-216
3.33.1 Monitoring Minimum and Maximum Phase Currents ................................................................................. 3-216
3.34 Transformer Monitoring (Function Group TRMON) ..................................................3-218
3.35 Programmable Logic (Function Groups LOGIC and LOG_2) .....................................3-219
3.36 Binary Counts (Function Group COUNT) ..................................................................3-227
3.36.1 Enable/Disable the Counting Function .......................................................................................................3-227
3.36.2 Debouncing ............................................................................................................................................... 3-227
3.36.3 Counting Function ..................................................................................................................................... 3-227
3.36.4 Transmitting the Counter Values via Communications Interface ...............................................................3-227
3.36.5 Counter Values Reset ................................................................................................................................3-228
P634
4 Design .................................................................................................................4-1
4.1 Designs .......................................................................................................................4-2
4.2 Dimensional Drawings ................................................................................................ 4-4
4.2.1 Dimensional Drawings for the 84 TE Case .....................................................................................................4-4
4.2.2 Detachable HMI .............................................................................................................................................4-5
4.3 Hardware Modules ......................................................................................................4-7
5 Installation and Connection ................................................................................ 5-1
5.1 Unpacking and Packing ...............................................................................................5-3
5.2 Checking Nominal Data and Design Type ...................................................................5-4
5.3 Location Requirements ...............................................................................................5-5
5.3.1 Environmental Conditions ..............................................................................................................................5-5
5.3.2 Mechanical Conditions ...................................................................................................................................5-5
5.3.3 Electrical Conditions for Auxiliary Voltage of the Power Supply .................................................................... 5-5
5.3.4 Electromagnetic Conditions ...........................................................................................................................5-5
5.4 Installation ..................................................................................................................5-6
5.5 Protective and Operational Grounding ......................................................................5-12
5.6 Connection ................................................................................................................5-13
5.6.1 Connecting Measuring and Auxiliary Circuits .............................................................................................. 5-13
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 5
Page 14

P634
5.6.2 Connecting the IRIG‑B Interface .................................................................................................................. 5-17
5.6.3 Connecting the Serial Interfaces ................................................................................................................. 5-17
Table of Contents
5.7 Location and Connection Diagrams .......................................................................... 5-22
5.7.1 Location Diagrams P634‑410/411 ................................................................................................................5-22
5.7.2 Terminal Connection Diagrams P634‑410/411 ............................................................................................ 5-22
6 Local Control (HMI) ............................................................................................. 6-1
6.1 Local Control Panel (HMI) ............................................................................................6-1
6.2 Display and Keypad .................................................................................................... 6-2
6.2.1 Text Display ...................................................................................................................................................6-2
6.2.2 Display Illumination .......................................................................................................................................6-2
6.2.3 Contrast of the Display ..................................................................................................................................6-2
6.2.4 Short Description of Keys .............................................................................................................................. 6-3
6.3 Display Levels .............................................................................................................6-5
6.4 Display Panels .............................................................................................................6-6
6.5 Menu Tree and Data Points .........................................................................................6-7
6.6 List Data Points ...........................................................................................................6-8
6.7 Note Concerning the Step-by-Step Descriptions .........................................................6-9
6.8 Configurable Function Keys ...................................................................................... 6-10
6.8.1 Configuration of the Function Keys F1 to Fx ................................................................................................6-11
6.9 Changing Between Display Levels ............................................................................ 6-14
6.10 Control at Panel Level ...............................................................................................6-15
6.11 Control at the Menu Tree Level .................................................................................6-16
6.11.1 Navigation in the Menu Tree ....................................................................................................................... 6-16
6.11.2 Switching Between Address Mode and Plain Text Mode ..............................................................................6-17
6.11.3 Change-Enabling Function ...........................................................................................................................6-18
6.11.4 Changing Parameters ..................................................................................................................................6-21
6.11.5 List Parameters ........................................................................................................................................... 6-22
6.11.6 Memory Readout .........................................................................................................................................6-25
6.11.7 Resetting .....................................................................................................................................................6-28
6.11.8 Password-Protected Control Actions ............................................................................................................6-29
6.11.9 Changing the Password ...............................................................................................................................6-31
7 Settings ...............................................................................................................7-1
7.1 Parameters .............................................................................................................. 7-1
7.1.1 Device Identification ............................................................................................................................. 7-3
7.1.2 Configuration Parameters .................................................................................................................. 7-12
7.1.3 Function Parameters ............................................................................................................................7-74
8 Information and Control Functions ......................................................................8-1
8.1 Operation ................................................................................................................. 8-1
8.1.1 Cyclic Values ............................................................................................................................................ 8-2
8.1.2 Control and Testing ............................................................................................................................8-151
8.1.3 Operating Data Recording ................................................................................................................8-160
8.2 Events ...................................................................................................................8-161
8.2.1 Event Counters .................................................................................................................................... 8-161
8.2.2 Measured Event Data .........................................................................................................................8-163
8.2.3 Event Recording .................................................................................................................................. 8-169
9 IEC 61850 Settings via IED Configurator .............................................................9-1
9.1 Manage IED .................................................................................................................9-2
9.2 IED Details .................................................................................................................. 9-3
6 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 15

Table of Contents
9.3 Communications .........................................................................................................9-4
9.4 SNTP ........................................................................................................................... 9-5
9.4.1 General Config ...............................................................................................................................................9-5
9.4.2 External Server 1 ...........................................................................................................................................9-5
9.4.3 External Server 2 ...........................................................................................................................................9-5
9.5 Dataset Definitions ..................................................................................................... 9-6
9.6 GOOSE Publishing .......................................................................................................9-7
9.6.1 System/LLN0 ................................................................................................................................................. 9-7
9.7 GOOSE Subscribing .....................................................................................................9-9
9.7.1 Mapped Inputs ...............................................................................................................................................9-9
9.8 Report Control Blocks ............................................................................................... 9-12
9.8.1 System/LLN0 ............................................................................................................................................... 9-12
9.9 Controls .....................................................................................................................9-13
9.9.1 Control Objects ............................................................................................................................................9-13
9.9.2 Uniqueness of Control ................................................................................................................................. 9-13
9.10 Measurements .......................................................................................................... 9-15
9.11 Configurable Data Attributes .................................................................................... 9-16
9.11.1 System/LLN0 ............................................................................................................................................... 9-16
P634
10 Commissioning ................................................................................................. 10-1
10.1 Safety Instructions ....................................................................................................10-1
10.2 Commissioning Tests ................................................................................................10-4
10.2.1 Preparation ..................................................................................................................................................10-4
10.2.2 Testing .........................................................................................................................................................10-6
10.2.3 Checking the Binary Signal Inputs ...............................................................................................................10-6
10.2.4 Checking the Output Relays ........................................................................................................................10-6
10.2.5 Checking the Protection Function ................................................................................................................10-7
10.2.6 Completing Commissioning .......................................................................................................................10-10
11 Troubleshooting ................................................................................................11-1
12 Maintenance .....................................................................................................12-1
12.1 Maintenance Procedures in the Power Supply Area ..................................................12-2
12.2 Routine Functional Testing ....................................................................................... 12-4
12.3 Analog Input Circuits .................................................................................................12-5
12.4 Binary Opto Inputs ....................................................................................................12-6
12.5 Binary Outputs ..........................................................................................................12-7
12.6 Serial Interfaces ........................................................................................................12-8
13 Storage .............................................................................................................13-1
14 Accessories and Spare Parts .............................................................................14-1
15 Order Information .............................................................................................15-1
A1 Function Groups ............................................................................................... A1-1
A2 Internal Signals .................................................................................................A2-1
A3 Glossary ............................................................................................................A3-1
Modules ......................................................................................................................................A3-1
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 7
Page 16

P634 Table of Contents
Symbols ......................................................................................................................................A3-1
Examples of Signal Names ......................................................................................................... A3-7
Symbols Used .............................................................................................................................A3-8
A4 Telecontrol Interfaces .......................................................................................A4-1
A4.1 Telecontrol Interface per EN 60870-5-101 or IEC 870-5-101 (Companion Standard)
.................................................................................................................................. A4-1
A4.1.1 Interoperability ............................................................................................................................................A4-1
A4.2 Communication Interface per IEC 60870-5-103 ........................................................A4-9
A4.2.1 Interoperability ............................................................................................................................................A4-9
A5 P634 Version History ........................................................................................A5-1
8 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 17

1 Application and Scope
1.1 Overview - P634
The P634 differential protection device is intended for the fast and selective
short-circuit protection of transformers, motors, generators and other
installations with 4 windings.
P634
Fig. 1-1: P634 in 84 TE case.
The P634 provides high-speed three-system differential protection using a tripleslope characteristic and two high-set differential elements in combination with
transformer inrush restraint, overfluxing restraint and through-stabilization.
Amplitude and vector group matching is done just by entering the nominal values
of transformer windings and associated current transformers. An (optional)
overreaching current measuring circuit monitoring function will prevent
unwanted tripping by differential protection for faults in the CT's secondary
circuit.
For ring bus and breaker-and-a-half applications a virtual winding can be defined
for which the current measuring inputs are based on the vector sum of currents
from two or three freely selectable windings.
Phase swapping allows motor / generator protection applications with enlarged
protection zones.
In addition many supplementary protective functions are incorporated in the
devices. These can be individually configured and cancelled.
The relevant protection parameters can be stored in four independent parameter
subsets in order to adapt the protection device to different operating and power
system management conditions.
The powerful programmable logic provided by the protection device also makes
it possible to accommodate special applications.
For a list of all available function groups see the Appendix.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 1-1
Page 18
24
V/f
27/59
V<>
81
f<>
I
Y,b
I
Y,a
I
Y,c
V
I
P,a
I
P,b
I
P,c
I
P,d
I
virtual
87
DIFF
49
THRM1
49
THRM2
51
IDMT1
51
IDMT2
51
IDMT3
50
DTOC2
50
DTOC3
87G
REF_1
87G
REF_3
Metering
LIM_1
Overload rec.
Self Monitoring
LIM_2LIM_3
Fault rec.
Communication
to SCADA / substation control / RTU / modem ...
via RS485 or Fiber optics
using IEC 60870-5-101, -103, Modbus, DNP3, Courier
resp.
via RJ45 or Fiber optics using IEC 61850
16S
COMM1
16S
COMM2
16E
IEC
CLK
IRIGB
CMD_1SIG_1
26
MEASI MEASO
Transformer Differential Protection
P634
Always availableOptional
LIMIT
50
DTOC1
87G
REF_2
50/62BF
CBF_2
50/62BF
CBF_1
50/62BF
CBF_3
50/62BF
CBF_4
MCM_4MCM_3MCM_2MCM_1
CTS
Recording and
Data Acquisition
∑ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑Φ ∑
LGC
LOGIC / LOG2
TRMON
P634
1 Application and Scope
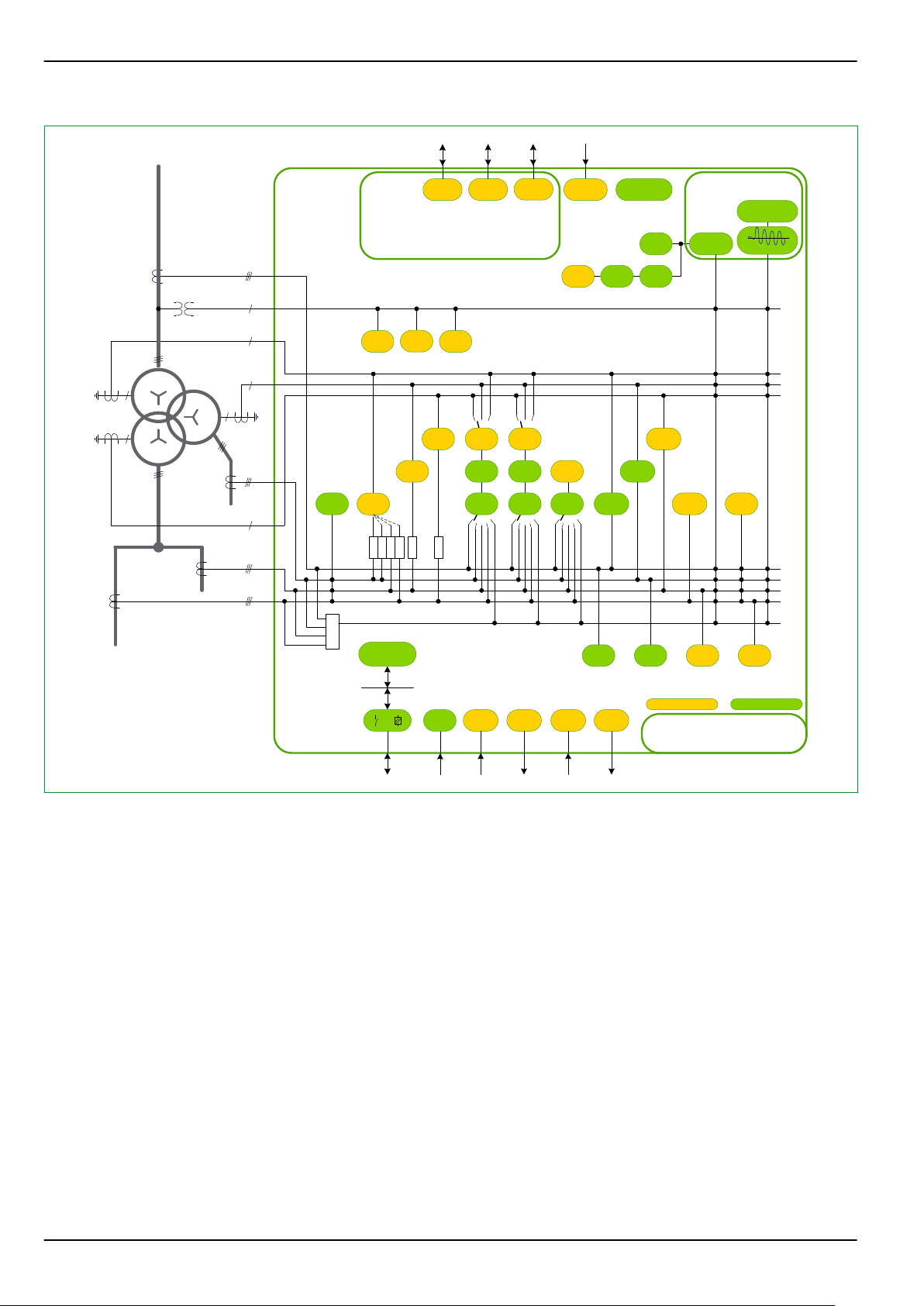
Fig. 1-2: Function diagram.
1.1.1 Design
The P634 is modular in design. The plug-in modules are housed in a robust
aluminum case and electrically interconnected via one analog p/c board and one
digital p/c board.
1-2 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 19

1 Application and Scope P634
1.2 Including Function Groups in the Configuration
Functions listed in the tables in Section 1.3, (p. 1-4) are self-contained
function groups and can be individually configured or de-configured according to
the specific application requirements by using the MiCOM S1 operating program.
Unused or cancelled function groups are hidden to the user, thus simplifying the
menu of the MiCOM S1.
This concept provides a large choice of functions and makes wide-ranging
application of the protection device possible, with just one model version. On the
other hand, simple and clear parameter settings can be made.
In this way the protection and control functions can be included in or excluded
from the configuration.
Example
For example, the current transformer supervision (function group CTS)
can be included in the configuration by setting
●
CTS: Function group CTS to With
can be excluded from the configuration by setting
●
CTS: Function group CTS to Without
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 1-3
Page 20

P634 1 Application and Scope
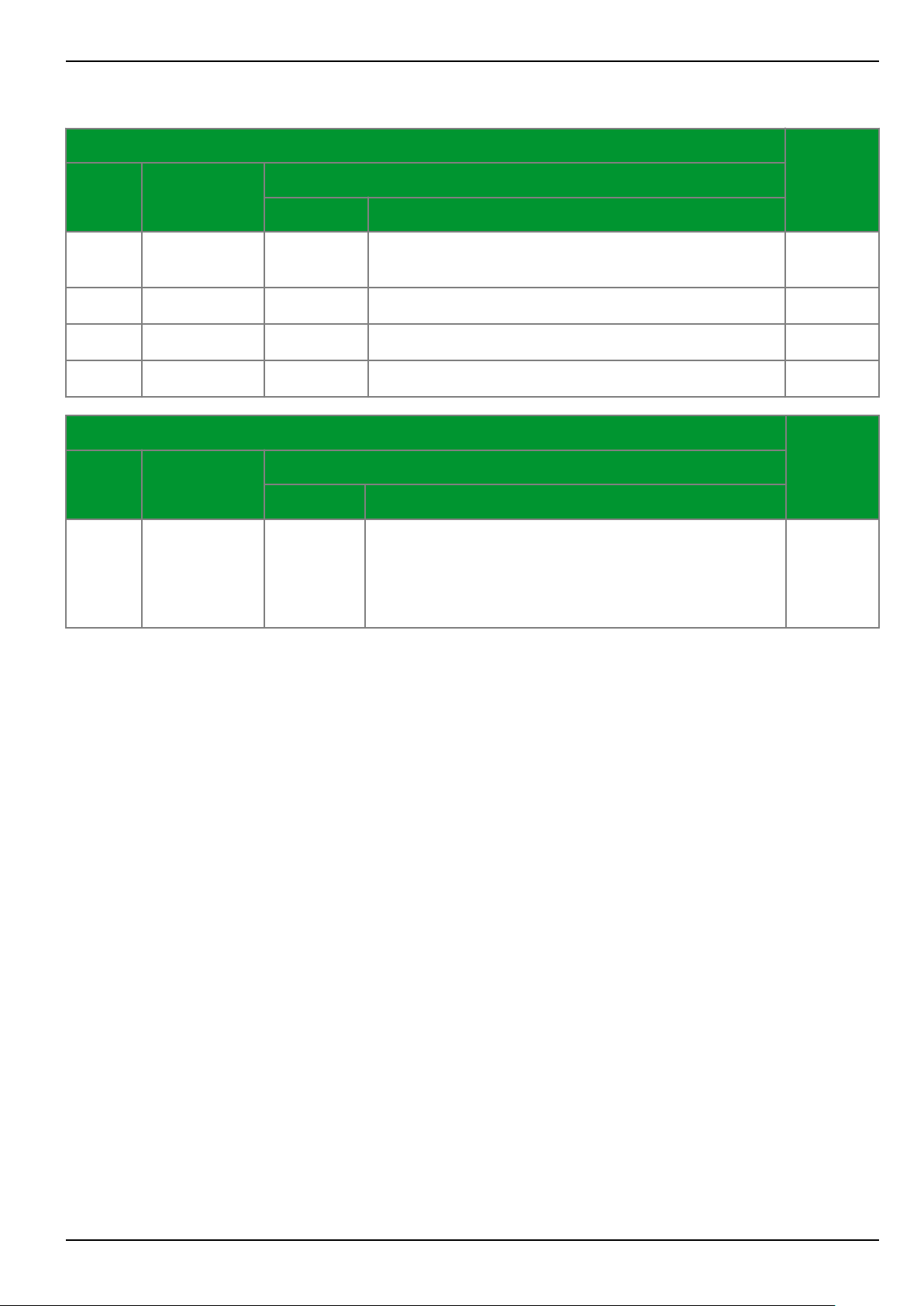
1.3 Overview of Function Groups - Part 1
The following tables list the function groups that can be included in or excluded
from the configuration of the P634.
✓ = Standard; (✓) = Ordering option.
Protection functions
P634ANSI IEC 61850 Function group
Abbrev. Description
87T PhsPDIF1 DIFF Differential protection, phase selective 4 wind.
PHAR1 Inrush stabilization (functionality that is part of the
DIFF function group)
87N
50TD
P/ Q/ N
DtpPhs- /
DtpEft- /
DtpNgsPTCO
REF_x Restricted earth-fault protection 3
DTOCx Definite-time overcurrent protection, 3 stages,
phase-, negative-sequence-, residual/starpoint-
overcurrent
x
51 P/
Q/ N
ItpPhs- /
ItpEft- /
ItpNgsPTCOx
IDMTx Inverse-time overcurrent protection, one stage,
phase-, negative-sequence-, residual/starpoint-
overcurrent
49 ThmPTTR1 THRMx Thermal overload protection 2
27/ 59
P/ Q/ N
VtpPhs- /
VtpNgs- /
V<> Time-voltage Protection 1
VtpPss- /
VtpRefPTyVx
81 FrqPTyFx f<> Over / Underfrequency protection 1
24
V/f Overfluxing protection 1
✓
3
3
50 BF RBRFx CBF_x Circuit breaker failure protection 4
CTS Current transformer supervision 1
30/ 74 AlmGGIO1 MCM_x Measuring-circuit monitoring 4
LIMIT
Limit value monitoring 3
LIM_x
LGC PloGGIOx LOGIC /
TRMON Transformer monitoring ✓
Programmable logic ✓
LOG_2
1-4 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 21
1 Application and Scope P634
Communication functions
P634ANSI IEC 61850 Function group
Abbrev. Description
16S
CLK
16E
COMM1,
COMM2
2 communication interfaces serial, RS 422 / 485 or
fiber optic
(✓)
IRIGB Time synchronization IRIG-B (✓)
IEC Communication interface Ethernet (✓)
16E GosGGIOx GOOSE IEC 61850 (✓)
Measured value functions
P634ANSI IEC 61850 Function group
Abbrev. Description
26 RtdGGIO1
IdcGGIO1
MEASI
MEASO
Analog inputs and outputs
RTD input
●
1× Measuring data input 20 mA
●
2× Measuring data output 20 mA
●
(✓)
(✓)
(✓)
(✓)
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 1-5
Page 22
P634 1 Application and Scope
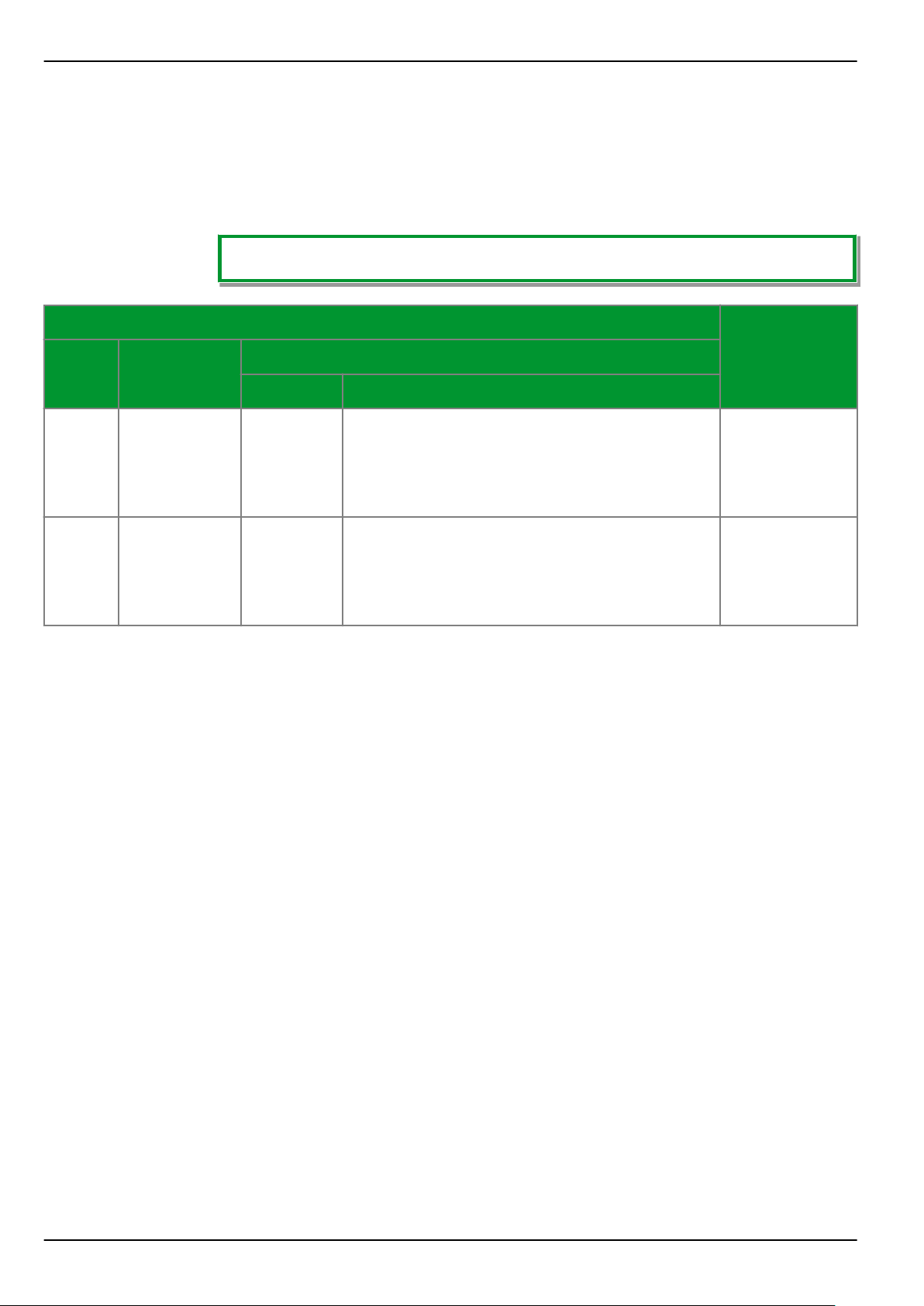
1.4 Overview of Function Groups - Part 2
The following tables list the function groups that are generally available for the
P634, and which cannot be excluded from the configuration.
✓ = Standard; (✓) = Ordering option.
Inputs and outputs
P634ANSI IEC 61850 Function group
Abbrev. Description
Measuring inputs
Phase currents
●
Residual current or star-point current
●
Voltage
●
INP
●
INP
●
OUTP
●
Binary inputs and outputs
Optical coupler inputs
●
Add. optical coupler inputs
●
Output relays
●
4×3
●
3
●
1
●
4 (… 10)
●
24
●
8 (… 22)
●
1-6 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 23
1 Application and Scope P634
General functions
P634ANSI IEC 61850 Function group
Abbrev. Description
DVICE Device ✓
LOC Local control panel ✓
PC PC link ✓
F_KEY 6 configurable function keys ✓
LED LED indicators ✓
MAIN Main function ✓
LLN0.SGCB PSS Parameter subset selection ✓
SFMON Comprehensive self-monitoring ✓
OP_RC Operating data recording (time-tagged event
logging)
MT_RC Monitoring Signal Recording ✓
OL_DA Overload Data Acquisition ✓
OL_RC Overload recording (time-tagged event logging) ✓
✓
PTRCx /
RDRE1
FT_DA Fault data acquisition for a particular, settable point
in time during a fault
FT_RC Fault recording (time-tagged event logging together
with fault value recording of the phase and residual
currents as well as the voltage)
✓
✓
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 1-7
Page 24

P634 1 Application and Scope
1.5 Configurable Function Keys
To the right of the text display, there are six freely configurable function keys
available. These may be used for easy control operation access.
1-8 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 25

1 Application and Scope P634
1.6 Inputs and Outputs
The nominal current and voltage values of the measuring inputs on the P634 can
be set with the function parameters.
The nominal voltage range of the optical coupler inputs is 24 to 250 V DC. As an
option binary signal input modules with a higher operate threshold are available.
The auxiliary voltage input for the power supply is also designed for an extended
range. The nominal voltage ranges are 60 to 250 V DC and 100 to 230 V AC. A 24
to 60 V DC version is also available.
All output relays can be utilized for signaling and command purposes.
The optional PT 100 input is lead-compensated, balanced and linearized for
PT 100 resistance thermometers as per IEC 751 / DIN EN 60751.
The optional 0 to 20 mA input provides open-circuit and overload monitoring,
zero suppression defined by a setting, plus the option of linearizing the input
variable via 20 adjustable interpolation points.
Two selectable measured values (cyclically updated measured operating data
and stored measured fault data) can be output as a burden-independent direct
current via the two optional 0 to 20 mA outputs. The characteristics are defined
via 3 adjustable interpolation points allowing a minimum output current (4 mA,
for example) for slave-side open-circuit monitoring, knee-point definition for fine
scaling, and a limitation to lower nominal currents (10 mA, for example). Where
sufficient output relays are available, a selectable measured value can be output
in BCD-coded form by contacts.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 1-9
Page 26

P634 1 Application and Scope
1.7 Control and Display
Local control panel with an LC display containing 4 × 20 alphanumeric
●
characters.
23 LED indicators, 18 of which allow freely configurable function
●
assignment for the colors red and green. Furthermore there are various
operating modes and flashing functions available.
PC interface.
●
One or two communication interface(s) for connection to a substation
●
control system (optional).
1-10 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 27

1 Application and Scope P634
1.8 Information Interfaces
Information is exchanged through the local control panel, the PC interface, or two
optional communication interfaces (channel 1 and channel 2).
Using the first channel of the communication interfaces (COMM1), the P634 can
be wired either to the substation control system or to a telecontrol system. This
channel is optionally available with a switchable protocol (per IEC 60870‑5‑103,
IEC 870‑5‑101, DNP 3.0, MODBUS or Courier).
The second communication interface (COMM2, communication protocol per
IEC 60870‑5‑103 only) is designed for remote control.
As an order option, there is an Ethernet interface for communication per
IEC 61850 available instead of channel 1.
External clock synchronization can be accomplished via one of the
communication protocols or by using the optional IRIG‑B input.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 1-11
Page 28

P634 1 Application and Scope
1-12 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 29

2 Technical Data
2.1 Conformity
Notice
Applicable to P634, version -311 -410/411 -653.
Declaration of Conformity
The product designated “P634 Transformer Differential Protection Device” has
been designed and manufactured in conformance with the European standards
EN 60255‑26 and EN 60255‑27 and with the “EMC Directive” and the “Low
Voltage Directive” issued by the Council of the European Community.
P634
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-1
Page 30

P634
2.2 General Data
2.2.1 General Device Data
Design
Surface-mounted case suitable for wall installation, or
●
Flush-mounted case for 19″ cabinets and for control panels.
●
Installation Position
Vertical ± 30°.
●
Degree of Protection
Per DIN VDE 0470 and EN 60529 or IEC 529.
IP 52 for the front panel.
●
Flush-mounted case:
●
o
IP 50 for the case (excluding the rear connection area)
o
IP 20 for the rear connection area, pin-terminal connection
o
IP 10 for the rear connection area, ring-terminal connection
Surface-mounted case:
●
o
IP 50 for the case
o
IP 50 for the fully enclosed connection area with the supplied rubber
grommets fitted
2 Technical Data
Weight
●
●
Dimensions and Connections
See dimensional drawings (Section 4.2, (p. 4-4)), and the location and
terminal connection diagrams (Section 5.7, (p. 5-22)).
Terminals
PC interface (X6)
●
Communication interfaces COMM1, COMM2
●
●
●
40 TE case: Approx. 7 kg
84 TE case: Approx. 11 kg
EIA RS232 (DIN 41652) connector, type D-Sub, 9-pin
Fiber (X7, X8)
o
F-SMA optical fiber connection per IEC 60874‑2 (for plastic fibers), or
o
optical fiber connection BFOC-ST® connector 2.5 per IEC 60874‑10‑1 (for
glass fibers).
(ST® is a registered trademark of AT&T Lightguide Cable Connectors.)
Wire leads (X9, X10)
o
M2 threaded terminal ends for wire cross-sections up to 1.5 mm² (US:
AWG16).
IRIG-B Interface (X11)
o
BNC plug
2-2 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 31

2 Technical Data P634
Communication interface IEC 61850
Fiber (X7, X8)
●
o
optical fiber connection BFOC-ST® connector 2.5 per IEC 60874‑10 (for
glass fibers).
(ST® is a registered trademark of AT&T Lightguide Cable Connectors.)
Fiber (X13)
●
o
SC connector per IEC 60874‑14‑4 (for glass fibers)
Wire leads (X12)
●
o
RJ45 connector per ISO/IEC 8877.
Current measuring inputs (conventional inputs)
Threaded terminal ends, pin-type cable lugs: M5, self-centering with cage
●
clamp to protect conductor cross-sections ≤ 4 mm² (US: AWG12), or
Threaded terminal, ring-terminal connection: M4.
●
Other inputs and outputs
Threaded terminal ends, pin-type cable lugs: M3, self-centering with cage
●
clamp to protect conductor cross-sections 0.2 to 2.5 mm² (US: AWG25 to
AWG14), or
Threaded terminal ends, ring-type cable lugs: M4.
●
Creepage Distances and Clearances
Per EN 60255-27.
●
Pollution degree 3, working voltage 250 V,
●
overvoltage category III, impulse test voltage 5 kV.
●
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-3
Page 32

P634
2.3 Tests
2.3.1 Type Tests
Type Tests
All tests per EN 60255-26.
2.3.1.1 Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Interference Suppression
Per EN 55022 or IEC CISPR 22, Class A.
1 MHz Burst Disturbance Test
Per EN 60255-22-1, Class III.
Common-mode test voltage: 2.5 kV.
●
Differential test voltage: 1.0 kV.
●
Test duration: > 2 s.
●
Source impedance: 200 Ω.
●
2 Technical Data
Immunity to Electrostatic Discharge
Per EN 60255-22-2 and IEC 60255-22-2, severity level 4.
Contact discharge
Single discharges: > 10.
●
Holding time: > 5 s.
●
Test voltage: 8 kV.
●
Test generator: 50 to 100 MΩ, 150 pF / 330 Ω.
●
Immunity to Radiated Electromagnetic Energy
Per EN 61000‑4‑3 and ENV 50204, severity level 3.
Antenna distance to tested device: > 1 m on all sides.
●
Test field strength, frequency band 80 to 1000 MHz: 10 V / m.
●
Test using AM: 1 kHz / 80 %.
●
Single test at 900 MHz: AM 200 Hz / 100%.
●
Electrical Fast Transient or Burst Requirements
Per EN 61000-4‑4 and IEC 60255‑22‑4, severity levels 3 and 4.
Rise time of one pulse: 5 ns.
●
Impulse duration (50% value): 50 ns.
●
Amplitude: 2 kV / 1 kV or 4 kV / 2 kV.
●
Burst duration:15 ms.
●
Burst period: 300 ms.
●
Burst frequency: 5 kHz.
●
Source impedance: 50 Ω.
●
Power Frequency Immunity
Per IEC 60255‑22‑7, Class A:
2-4 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 33

2 Technical Data
Phase-to-phase
RMS value 150 V.
●
Coupling resistance 100 Ω.
●
Coupling capacitor 0.1 μF, for 10 s.
●
Phase-to-ground
RMS value 300 V.
●
Coupling resistance 220 Ω.
●
Coupling capacitor 0.47 μF, for 10 s.
●
To comply with this standard, it is suggested to set the parameter (010 220)
INP: Filter to 6 [steps].
Current/Voltage Surge Immunity Test
Per EN 61000-4‑5 and EN 60255-22‑5, insulation class 4.
Testing of circuits for power supply and asymmetrical or symmetrical
lines.
Open-circuit voltage, front time / time to half-value: 1.2 / 50 µs.
●
Short-circuit current, front time / time to half-value: 8 / 20 µs.
●
Amplitude: 4 / 2 kV.
●
Pulse frequency: > 5 / min.
●
Source impedance: 12 / 42 Ω.
●
P634
Immunity to Conducted Disturbances Induced by Radio Frequency Fields
Per EN 61000-4-6 and EN 60255-22‑6, severity level 3.
Test voltage: 10 V.
●
Power Frequency Magnetic Field Immunity
Per EN 61000-4-8 or IEC 61000-4-8, severity level 4.
Test frequency: 50 Hz
●
Test field strength: 30 A / m.
●
Alternating Component (Ripple) in DC Auxiliary Energizing Quantity
Per EN 60255-11.
12 %.
●
2.3.1.2 Insulation
Voltage Test
Per EN 60255-27.
2 kV AC, 60 s
●
Only direct voltage (2.8 kV DC) must be used for the voltage test on the power
supply inputs. The PC interface must not be subjected to the voltage test.
Impulse Voltage Withstand Test
Per EN 60255-27.
Front time: 1.2 µs
●
Time to half-value: 50 µs
●
Peak value: 5 kV
●
Source impedance: 500 Ω
●
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-5
Page 34

P634
2.3.1.3 Environmental tests
Temperature Stability Test
Per IEC 60068-2-1
-25°C (-13°F) storage (96 hours)
●
-40°C (-40°F) operation (96 hours)
●
Per IEC 60068-2-2
+85°C (185°F) storage (96 hours)
●
+85°C (185°F) operation (96 hours)
●
Per IEC 60068-2-14
Change of temperature, 5 cycles, 1°C / min rate of change
●
Ambient Humidity Range Test
Per IEC 60068-2-3
56 days at ≤ 93% relative humidity and 40°C (104°F)
●
Per IEC 60068-2-30
Damp heat, cyclic (12 + 12 hours)
●
93 % relative humidity, +25°C … +55°C (77°F … 131°F)
2 Technical Data
Corrosive Environment Tests
Per IEC 60068-2-60: 1995, Part 2, Test Ke, Method (class) 3
Industrial corrosive environment/ poor environmental control, mixed gas flow
test.
21 days at 75% relative humidity and 30°C (86°F) with exposure to
●
elevated concentrations of H2S, NO2, Cl2 and SO2.
2.3.1.4 Mechanical Robustness 1
Applicable to the following case variants:
Flush mounted case, flush-mounting method 1 (without angle brackets and
●
frame)
Vibration Test
Per EN 60255‑21-1 or IEC 60255‑21-1, test severity class 1.
Frequency range in operation
10 to 60 Hz, 0.035 mm, and
●
60 to 150 Hz, 0.5 g
●
Frequency range during transport
10 to 150 Hz, 1 g
●
Shock Response and Withstand Test, Bump Test
Per EN 60255-21-2 or IEC 60255-21-2.
Acceleration and pulse duration:
Shock Response tests are carried out to verify full operability (during
●
operation), test severity class 1:
5 g for 11 ms.
Shock Withstand tests are carried out to verify the endurance (during
●
transport), test severity class 1:
15 g for 11 ms.
2-6 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 35

2 Technical Data
Seismic Test
Per EN 60255‑21‑3 or IEC 60255‑21‑3, test procedure A, class 1.
Frequency range
5 to 8 Hz, 3.5 mm / 1.5 mm, 8 to 35 Hz, 10 / 5 m/s², 3 x 1 cycle.
●
2.3.1.5 Mechanical Robustness 2
Applicable to the following case variants:
Flush mounted case, flush-mounting method 2 (with angle brackets and
●
frame)
Surface-mounted case
●
Vibration Test
Per EN 60255‑21-1 or IEC 60255‑21-1, test severity class 2.
Frequency range in operation
10 to 60 Hz, 0.075 mm, and
●
60 to 150 Hz, 1.0 g
●
P634
Frequency range during transport
10 to 150 Hz, 2 g
●
Shock Response and Withstand Test, Bump Test
Per EN 60255-21-2 or IEC 60255-21-2.
Acceleration and pulse duration:
Shock Response tests are carried out to verify full operability (during
●
operation), test severity class 2:
10 g for 11 ms.
Shock Withstand tests are carried out to verify the endurance (during
●
transport), test severity class 1:
15 g for 11 ms.
Shock bump tests are carried out to verify permanent shock (during
●
transport), test severity class 1:
10 g for 16 ms.
Seismic Test
Per EN 60255‑21‑3 or IEC 60255‑21‑3, test procedure A, class 2.
Frequency range
5 to 8 Hz, 7.5 mm / 3.5 mm, 8 to 35 Hz, 20 / 10 m/s², 3 x 1 cycle.
●
2.3.2 Routine Tests
All tests per EN 60255-1.
Voltage Test
Per EN 60255-27.
2.2 kV AC, 1 s
●
Only direct voltage (2.8 kV DC) must be used for the voltage test on the power
supply inputs.
The PC interface must not be subjected to the voltage test.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-7
Page 36

P634 2 Technical Data
Additional Thermal Test
100% controlled thermal endurance test, inputs loaded.
●
2-8 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 37

2 Technical Data P634
2.4 Environmental Conditions
Temperatures
Recommended temperature range
-5°C to +55°C [+23°F to +131°F].
●
Limit temperature range
Operation: -25°C to +55°C [-13°F to +131°F].
●
Storage and transport: -25°C to +70°C [-13°F to +158°F].
●
Ambient Humidity Range
≤ 75 % relative humidity (annual mean).
●
56 days at ≤ 95 % relative humidity and 40°C [104°F].
●
Condensation not permitted.
●
Solar Radiation
Direct solar radiation on the front of the device must be avoided.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-9
Page 38

P634 2 Technical Data
2.5 Inputs and Outputs
2.5.1 Measuring Inputs
Current Measuring Inputs
Voltage Measuring Inputs
Nominal current I
●
Nominal consumption per phase: < 0.1 VA at I
●
Load rating:
●
o
continuous: 20 A,
o
for 10 s: 150 A,
o
for 1 s: 500 A.
Nominal surge current: 1250 A.
●
Nominal voltage V
●
Nominal consumption per phase: < 0.3 VA at V
●
Load rating:
●
o
continuous: 150 V AC
o
for 10 s: 300 V AC
: 1 and 5 A AC (adjustable).
nom
: 50 to 130 V AC (adjustable).
nom
.
nom
= 130 V AC.
nom
Frequency
Nominal frequency f
●
Operating range: 0.95 to 1.05 f
●
Frequency protection: 40 to 70 Hz.
●
: 50 Hz and 60 Hz (adjustable).
nom
nom
.
2-10 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 39

2 Technical Data P634
2.5.2 Binary Signal Inputs
Threshold pickup and drop-off points as per ordering option
18 V standard variant (V
●
o
Switching threshold in the range 14 V to 19 V.
Special variants with switching thresholds from 58% to 72% of the nominal input
voltage (i.e. definitively “low” for VA < 58% of the nominal supply voltage,
definitively “high” for VA > 72% of the nominal supply voltage).
Special variant 72 V: Nominal supply voltage 110 V DC.
●
Special variant 83 V: Nominal supply voltage 127 V DC.
●
Special variant 143 V: Nominal supply voltage 220 V DC.
●
Special variant 163 V: Nominal supply voltage 250 V DC.
●
Power consumption per input
18 V standard variant:
●
VA = 19 to 110 V DC : 0.5 W ± 30%,
VA > 110 V DC: VA ·5 mA ± 30%.
Special variants:
●
VA > switching threshold: VA ·5 mA ± 30%.
: = 24 to 250 V DC):
A,nom
The standard variant of binary signal inputs (opto couplers) is recommended in
most applications, as these inputs operate with any voltage from 19 V. Special
versions with higher pick-up/drop-off thresholds are provided for applications where
a higher switching threshold is expressly required.
The maximum voltage permitted for all binary signal inputs is 300 V DC.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-11
Page 40

P634 2 Technical Data
2.5.3 IRIG‑B Interface
Minimum / maximum input voltage level (peak-peak): 100 mVpp / 20 Vpp
●
Input impedance: 33 kΩ at 1 kHz
●
Electrical isolation: 2 kV
●
2.5.4 Direct Current Input
Input current: 0 to 26 mA
●
Value range: 0.00 to 1.20 I
●
Maximum continuous input current permitted: 50 mA
●
Maximum input voltage permitted: 17 V DC
●
Input load: 100 Ω
●
Open-circuit monitoring: 0 to 10 mA (adjustable)
●
Overload monitoring: > 24.8 mA
●
Zero suppression: 0.000 to 0.200 I
●
DC,nom
(I
DC,nom
DC,nom
= 20 mA)
(adjustable).
2.5.5 Resistance Thermometer
Only PT 100 permitted for analog (I/O) module, mapping curve per IEC 75.1.
PT 100, Ni 100 or Ni 120 permitted for temperature p/c board (the RTD module).
Value range: ‑40.0°C to +215.0°C (‑40°F to +419°F).
●
3-wire configuration: max. 20 Ω per conductor.
●
Open and short-circuited input permitted.
●
Open-circuit monitoring: Θ > +215°C and Θ < -40°C (Θ > +419°F and
●
Θ < -40°F).
2.5.6 Direct Current Output
Output current: 0 to 20 mA
●
Maximum permissible load: 500 Ω
●
Maximum output voltage: 15 V
●
2-12 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 41

2 Technical Data P634
2.5.7 Output Relays
Binary I/O Module X(4H)
with high-break contacts, applicable to
DC circuits only.
All other modules
Rated voltage: 250 V DC 250 V DC, 250 V AC.
Continuous
10 A 5 A
current:
250 A for 0.03 s,
Short-duration
current:
●
30 A for 3 s
●
30 A for 0.5 s.
Making capacity: 30 A 1000 W (VA) at
L/R = 40 ms.
Breaking capacity:
7500 W resistive or 30 A at
●
250 V DC,
Maximum values: 30 A and
0.2 A at 220 V DC and L/
●
R = 40 ms,
4 A at 230 V AC and cos φ = 0.4.
●
300 V DC.
2500 W inductive (L/R = 40 ms) or
●
10 A at 250 V DC,
Maximum values: 10 A and
300 V DC.
Operating time: less than 0.2 ms less than 5 ms
Reset time: less than 8 ms less than 5 ms
2.5.8 BCD Measured Data Output
Maximum numerical value that can be displayed: 399
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-13
Page 42

P634
2.6 Interfaces
2.6.1 Local Control Panel
Input or output
With 13 keys and a 4 ×20 character liquid crystal display (LCD).
●
State and fault signals
23 LED indicators (5 permanently assigned, 18 freely configurable).
●
2.6.2 PC Interface
Transmission rate: 300 to 115,200 baud (adjustable)
●
2.6.3 Serial Communication Interface
The communication module can be provided with up to two communication
channels, depending on the module variant. Channel 1 may either be equipped
to connect wire leads or optical fibers and channel 2 is only available to connect
wire leads.
For communication interface 1, communication protocols based on
IEC 870-5‑103, IEC 60870‑5‑101, MODBUS, DNP 3.0, or Courier can be set.
Transmission rate: 300 to 64000 baud (adjustable).
●
Communication interface 2 can only be operated with the interface protocol
based on IEC 60870-5-103.
Transmission rate: 300 or 57600 baud (adjustable).
●
2 Technical Data
Wire Leads
Per RS 485 or RS 422, 2 kV isolation
●
Distance to be bridged
●
o
Point-to-point connection: max. 1200 m
o
Multipoint connection: max. 100 m
Plastic Fiber Connection
Optical wavelength: typically 660 nm
●
Optical output: min. -7.5 dBm
●
Optical sensitivity: min. -20 dBm
●
Optical input: max. -5 dBm
●
Distance to be bridged: max. 45 m
●
(Distance to be bridged given for identical optical outputs and inputs at
both ends, a system reserve of 3 dB, and typical fiber attenuation)
Glass Fiber Connection G 50/125
Optical wavelength: typically 820 nm
●
Optical output: min. -19.8 dBm
●
Optical sensitivity: min. -24 dBm
●
Optical input: max. -10 dBm
●
Distance to be bridged: max. 400 m
●
(Distance to be bridged given for identical optical outputs and inputs at
both ends, a system reserve of 3 dB, and typical fiber attenuation)
2-14 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 43

2 Technical Data
Glass Fiber Connection G 62.5/125
Optical wavelength: typically 820 nm
●
Optical output: min. -16 dBm
●
Optical sensitivity: min. -24 dBm
●
Optical input: max. -10 dBm
●
Distance to be bridged: max. 1,400 m
●
(Distance to be bridged given for identical optical outputs and inputs at
both ends, a system reserve of 3 dB, and typical fiber attenuation)
2.6.4 IEC Communication Interface
Ethernet-based communications per IEC 61850:
Wire Leads
RJ45, 1.5 kV isolation
●
Transmission rate: 100 Mbit/s
●
Distance to be bridged: max. 100 m
●
P634
Optical Fiber (100 Mbit/s)
Optical wavelength: typically 1300 nm
●
ST connector
●
Glass fiber G50/125:
●
o
Optical output: min. −18.85 dBm
o
Optical sensitivity: min. −32.5 dBm
o
Optical input: max. −12 dBm
Glass fiber G62.5/125:
●
o
Optical output: min. −15 dBm
o
Optical sensitivity: min. −32.5 dBm
o
Optical input: max. −12 dBm
SC connector
●
Glass fiber G50/125:
●
o
Optical output: min. −23.5 dBm
o
Optical sensitivity: min. −31 dBm
o
Optical input: max. −14 dBm
Glass fiber G62.5/125:
●
o
Optical output: min. −20 dBm
o
Optical sensitivity: min. −31 dBm
o
Optical input: max. −14 dBm
2.6.5 IRIG‑B Interface
B122 format
●
Amplitude modulated signal
●
Carrier frequency: 1 kHz
●
BCD- coded variable data (daily)
●
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-15
Page 44

P634 2 Technical Data
2.7 Information Output
Counters, measured data, and indications: see chapter “Information and Control
Functions”.
2-16 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 45

2 Technical Data P634
2.8 Settings – Typical Characteristic Data
2.8.1 Main Function
Minimum output pulse for trip command: 0.1 to 10 s (adjustable)
●
Minimum output pulse for close command: 0.1 to 10 s (adjustable)
●
2.8.2 Differential Protection
Operate time including output relay:
●
o
≤ 16 ms without inrush stabilization or operation of I
o
≤ 32 ms with inrush stabilization
Reset time (measured variable from fault infeed to 0): ≤ 30 ms, approx.
●
25 ms
2.8.3 Definite-Time and Inverse-Time Overcurrent Protection
Operate time including output relay (measured variable from 0 to 2-fold
●
operate value): ≤ 40 ms, approx. 30 ms
Reset time (measured variable from 2-fold operate value to 0): ≤ 40 ms,
●
approx. 30 ms
Starting resetting ratio: approx. 0.95
●
diff>>
, I
diff>>>
2.8.4 Time-Voltage Protection
Operate time including output relay (measured variable from nominal value
●
to 1.2-fold operate value or measured variable from nominal value to 0.8fold operate value):
o
≤ 40 ms, approx. 30 ms
Reset time (measured variable from 1.2-fold operate value to nominal
●
value or measured variable from 0.8-fold operate value to nominal value):
o
≤ 45 ms, approx. 30 ms
Resetting ratio for V<>:
●
o
1% to 10% (adjustable)
2.8.5 Overfluxing Protection
Starting resetting ratio: approx. 0.95
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-17
Page 46

P634 2 Technical Data
2.9 Deviations
2.9.1 Deviations of the Operate Values
2.9.1.1 Definitions Reference Conditions
Quasi-stationary sinusoidal signals at nominal frequency f
●
protection excepted), total harmonic distortion ≤ 2 %, ambient
temperature 20°C (68°F), and nominal auxiliary voltage V
Deviation
Deviation relative to the setting under reference conditions.
●
2.9.1.2 Differential Protection Measuring system with default value 1 for the amplitude matching
factors (DIFF: Matching fact. kam,x = 1, x=a, b, c, d):
at I
at I
< 0.2·I
diff
>= 0.2·I
diff
●
●
: ± 10%
ref
: ± 5%
ref
(frequency
nom
.
A,nom
2-18 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 47

2 Technical Data
Inrush Stabilization (2nd harmonic)
Deviation: ± 10%
●
Overflux Blocking (5th harmonic)
Deviation: +0/–20%
●
2.9.1.3 Restricted Earth-Fault Protection Measuring system with default value for the amplitude matching
factors = 1:
at Id = 0.2·I
●
: ± 5%
ref
2.9.1.4 Overcurrent-Time Protection Operate values
Deviation: ± 5%
●
2.9.1.5 Thermal Overload Protection Operate value Θ
Deviation: ± 5% of the setting or ± 1% of the nominal value
●
P634
2.9.1.6 Time-Voltage Protection Operate values
V<>: ± 1% (in the range 0.6 to 1.4 Vnom)
●
2.9.1.7 Frequency Protection Operate values f<>
± 5 mHz
●
Operate values df/dt
± 100 mHz/s
●
2.9.1.8 Overexcitation Protection
Operate values: ± 3%
●
2.9.1.9 Direct Current Input
Deviation: ± 1 %
●
2.9.1.10 Resistance Thermometer
Deviation: ± 2°C (in the range −40°C ... 120°C)
●
2.9.1.11 Analog Measured Data Output
Deviation: ± 1 %
●
Output residual ripple with max. load: ± 1 %
●
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-19
Page 48

P634
2.9.2 Deviations of the Timer Stages
2.9.2.1 Definitions Reference conditions
Sinusoidal signals at nominal frequency f
●
≤ 2 %, ambient temperature 20°C (68°F), and nominal auxiliary voltage
V
Deviation
Deviation relative to the setting under reference conditions.
●
2.9.2.2 Definite-time stages
Deviation: ± 1% + 20 ms to 40 ms
●
2.9.2.3 Inverse-time stages
A,nom
.
2 Technical Data
, total harmonic distortion
nom
Deviation when I ≥ 2 I
●
For “extremely inverse” IEC characteristics and for thermal overload
●
: ± 5% + 10 to 25 ms
ref
characteristics: ± 7.5% + 10 to 20 ms
2.9.3 Deviations of Measured Data Acquisition
2.9.3.1 Definitions Reference conditions
Sinusoidal signals at nominal frequency fnom, total harmonic distortion ≤
●
2%, ambient temperature 20°C (68°F), and nominal auxiliary voltage
V
Deviation
Deviation relative to the setting under reference conditions.
●
2.9.3.2 Operating Data Measurement
Currents (measuring inputs): ± 1%
●
Voltages (measuring input): ± 0.5%
●
Currents (internally calculated): ± 2%
●
Voltages (internally calculated): ± 2%
●
Frequency: ± 10 mHz
●
A,nom
.
2.9.3.3 Fault Data Short-circuit, differential and restraining currents
Deviation: ± 3%
●
2.9.3.4 Internal Clock With free running internal clock
Deviation: < 1 min/month
●
With external synchronization (with a synchronization interval ≤ 1 min)
Deviation: < 10 ms
●
With synchronization via IRIG-B interface
± 1 ms
●
2-20 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 49

2 Technical Data P634
2.10 Resolution of the Fault Data Acquisition
2.10.1 Time Resolution
20 sampled values per period
●
2.10.2 Currents
Dynamic range
33·I
●
Amplitude resolution
●
●
2.10.3 Voltage
●
●
nom
at I
at I
= 1 A: 2.0 mA
nom
= 5 A: 10.1 mA
nom
rms
rms
Dynamic range: 150 V
Amplitude resolution: 9.2 mV
rms
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-21
Page 50

P634
2.11 Recording Functions
2.11.1 Organization of the Recording Memories
Operating Data Memory
Scope for signals
All signals relating to normal operation; from a total of 1024 different logic
●
state signals.
Depth for signals
The 1000 most recent signals.
●
Monitoring Signal Memory
Scope for signals
All signals relevant for self-monitoring from a total of 1024 different logic
●
state signals.
2 Technical Data
Overload Memory
Ground Fault Memory
Depth for signals
Up to 30 signals.
●
Number
The 8 most recent overload events
●
Scope for signals
All signals relevant for an overload event from a total of 1024 different logic
●
state signals.
Depth for signals
200 entries per overload event.
●
Number
The 8 most recent ground fault events
●
Scope for signals
All signals relevant for a ground fault event from a total of 1024 different
●
logic state signals.
Depth for signals
200 entries per ground fault event.
●
Fault Memory
Number
The 8 most recent faults.
●
Scope for signals and fault values
All fault-relevant signals from a total of 1024 different logic state signals.
●
Sampled values for all measured currents and voltages
●
2-22 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 51

2 Technical Data P634
Depth for signals and fault values
200 entries per fault event
●
max. number of cycles per fault can be set by user;
●
820 periods in total for all faults, that is 16.4 s (for fnom = 50 Hz) or 13.7 s
(for fnom = 60 Hz).
Resolution of the Recorded Data
As per Section 2.10, (p. 2-21), with maximum current dynamic ranges
●
(100 I
nom
/ 16 I
N,nom
)
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-23
Page 52

P634 2 Technical Data
2.12 Power Supply
Nominal auxiliary voltage V
24 to 60 V DC or 60 to 250 V DC and 100 to 230 V AC (ordering option).
●
A,nom
Operating range for direct voltage
0.8 to 1.1 V
●
with a residual ripple of up to 12 % V
A,nom
A,nom
.
Operating range for alternating voltage
0.9 to 1.1 V
●
A,nom
.
Nominal burden
… where VA = 220 V DC and with maximum module configuration
●
o
84 TE case, relays de-energized/energized): approx. 14.5 W / 42.3 W
Start-up peak current
< 3 A for duration of 0.25 ms
●
Stored energy time
≥ 50 ms for interruption of VA ≥ 220 V DC (upper range supply)
●
≥ 50 ms for interruption of VA ≥ 60 V DC (lower range supply)
●
2-24 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 53

2 Technical Data P634
2.13 Current Transformer Specifications
2.13.1 Symbols
The following symbols are used in accordance with IEC 61869 standards:
IpnRated primary current (nominal primary current) of the CT
IsnRated secondary current (nominal secondary current) of the CT
I
Rated primary (symmetrical) short-circuit current
psc
K
Rated symmetrical short-circuit current factor:
ssc
I
=
psc
I
pn
K
ssc
I
Reference current of IDMT protection element
ref
RbnRated resistive burden (secondary connected) of the CT
PbnEquivalent power over the rated resistive burden of the CT for rated
secondary current:
Pbn= Rbn·I
2
sn
RbActual resistive burden (secondary connected) of the CT
PbEquivalent power over the actual resistive burden of the CT for rated
secondary current:
Pb= Rb·I
2
sn
RctSecondary winding resistance of the CT
PctEquivalent power over the secondary winding resistance of the CT for
secondary rated current:
Pct= Rct·I
V
Secondary accuracy limiting voltage (e.m.f.) of the CT
sal
2
sn
VkRated knee point voltage (e.m.f.) of the CT
nnRated accuracy limit factor of the CT
nbActual accuracy limit factor of the CT:
nb= nn·
Rct+ R
Rct+ R
bn
b
= nn·
Pct+ P
Pct+ P
bn
b
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-25
Page 54

P634
R
One-way lead resistance from CT to relay
l
R
Resistive burden of relay’s CT input
rel
T
Primary time constant (primary system time constant)
p
ω (System) angular frequency
Xp/Rp Primary impedance ratio (system impedance ratio):
X
p
= ω ·T
R
p
K
Dimensioning factor for the CT
d
K
Relay specific, empirically determined dimensioning factor for the CT
emp
p
2.13.2 General Equations
The current transformer can be dimensioned
either for the minimum required secondary accuracy limiting voltage acc.
●
to IEC 61869, 3.4.209:
V
≥ Kd· K
sal
or for the minimum required rated accuracy limit factor acc. to IEC 61869,
●
3.4.208, as follows:
nn≥ Kd· K
The relation between both methods is given as follows:
P
V
= nn·(
sal
ssc
bn
+ Isn·Rct)
I
sn
ssc·Isn
Rct+ R
·
Rct+ R
·(Rct+ Rb)
b
= Kd· K
bn
ssc
Pct+ P
·
Pct+ P
2 Technical Data
b
bn
The actual secondary connected burden Rb is given as follows:
For phase-to-ground faults: Rb= 2 ·Rl+ R
●
For phase-to-phase faults: Rb= Rl+ R
●
rel
rel
The wire lead burden is calculated as:
Rl= ρ ⋅
l
A
ρ = specific conductor resistance
●
(e.g. for copper 0.021 Ω mm²/m = 2.1⋅10-8 Ω m, at 75°C)
l = wire length
●
A = wire cross section
●
For devices out of the platform Easergy MiCOM 30, the input CT burden R
rel
is
less than 20 mΩ, independent of the set nominal current (1 A or 5 A). Usually this
relay burden can be neglected.
The rated knee point voltage Vk according to IEC 61869, 3.4.217 is lower than
the secondary accuracy limiting voltage V
not possible to give a general relation between Vk and V
according to IEC 61869, 3.4.209. It is
sal
, but for standard core
sal
material the following relations applies:
VK≈0.85⋅V
●
VK≈0.75⋅V
●
for class 5P CTs, and
sal
for class 10P CTs, respectively.
sal
Theoretically, the specifications of the current transformer could be calculated to
avoid saturation by inserting its maximum value, instead of the required overdimensioning factor Kd:
2-26 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 55

0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
4.5
5.0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
K
emp
Xp/pR
0.5
1.5
2.5
3.5
2 Technical Data
X
Kd= K
max
≈ 1 +
p
= 1 + ω ·T
R
p
p
However, this is not necessary. Instead, it is sufficient to consider an empirically
determined dimensioning factor Kd=K
such that the appropriate operation of
emp
the protection function is ensured under the given conditions. This factor
depends on application and relay type, as outlined in the following.
2.13.3 Transformer Differential Protection
For Transformer Differential Protection Devices the empirical dimensioning factor
Kd = K
flowing currents) can be taken from the following diagram:
for the CTs considering external faults (assuming maximum through-
emp
P634
This CT dimensioning assures through fault stability of the differential element.
Due to the inbuilt saturation discriminator the CT requirement is independent of
the current sensitivity given by the set basic threshold of the tripping
characteristic.
The empirical dimensioning factor K
(shown in the diagram above) has been
emp
determined by investigations using 3-shot auto-reclosing sequences with 450 ms
of fault current feed (starting at worst case point on wave) for each shot and
300 ms dead time between shots. In most practical cases faults would be cleared
in 100 to 200 ms for external protection operation and the dead time between
auto-reclose shots would be longer than 300 ms. This would reduce the flux
build-up in the core. Therefore the above shown empirical dimensioning factor
K
can be considered as being based on a conservative approach.
emp
For internal fault steady-state saturation is permissible with maximum fault
currents up to 4 times the steady-state accuracy limit current of the CT. This
corresponds to a dimensioning factor of Kd = 0.25 for internal faults.
It is recommended to use CTs of accuracy class 5P (or equivalent).
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 2-27
Page 56

P634 2 Technical Data
2-28 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 57

3 Operation
3.1 Modular Structure
The P634 is a numerical device out of Schneider Electric's family of devices
named “Easergy MiCOM 30”. The device types included in this family are built
from identical uniform hardware modules. The figure below shows the basic
hardware structure of the P634.
P634
Communication
interface(s)
B
Analog bus module
Digital bus module
Analog bus module
P
L
Processor module
PC interface
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
F6
Local control module
A A
μP
T X Y V
Transformer module
Voltages Currents
Binary I/O module
Signals
Commands
Commands
Signals
Analog I/O module
Signals
Commands
Measured data
Power supply module
Signals
Commands
Commands
Signals
Auxiliary voltage
Fig. 3-1: Basic hardware structure.
External analog quantities and binary quantities – electrically isolated – are
converted to the internal processing levels by the peripheral modules T, Y, and X.
The optional binary I/O modules X are equipped with optical couplers for binary
signal input as well as output relays for the output of signals and commands or
combinations of these.
The external auxiliary voltage is applied to the power supply module V, which
supplies the auxiliary voltages that are required internally.
Analog data is transferred from the transformer module T via the analog bus
module B to the processor module P. The processor module contains all the
elements necessary for the conversion of measured analog variables, including
multiplexers and analog/digital converters. The analog data conditioned by the
analog I/O module Y is transferred to the processor module P via the digital bus
module.
The processor handles the processing of digitized analog variables and of binary
signals, generates the protective trip and signals, and transfers them to the
binary I/O modules X via the digital bus module. The processor module also
handles overall device communication.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-1
Page 58

P634 3 Operation
The optional communication modules provide one or two serial communication
interfaces for the integration of the protection and control unit into a substation
control system.
The local control module L is located behind the front panel and connected to the
processor module via a ribbon cable. It encompasses all control and display
elements as well as a PC interface for running the operating program S1.
3-2 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 59

3 Operation
3.2 Operator-Machine Communication
The following interfaces are available for the exchange of information between
the user and the P634:
Integrated user interface (LOC: local control panel)
●
PC interface
●
Communication interface
●
All settings and signals as well as all measurements and control functions are
arranged within the branches of the menu tree following a scheme that is
uniform throughout the device family. The main branches are:
“Parameters” Branch
All settings are contained in this branch. This branch carries all settings,
including the identification data of the P634, the configuration parameters for
adapting the P634 interfaces to the system, and the function parameters for
adapting the device functions to the process. All values in this group are stored
in non-volatile memory, which means that the values will be preserved even if
the power supply fails.
P634
“Operation” Branch
This branch includes all information relevant for operation such as measured
operating data and binary signal states. This information is updated periodically
and consequently is not stored. In addition, various controls are grouped here,
for example those for resetting counters, memories and displays.
“Events” Branch
The third branch is reserved for the recording of events. All information in this
group is therefore stored. In particular, the start/end signals during a fault, the
measured fault data, and the sampled fault waveforms are stored here and can
be read out when required.
Display of Settings and Signals
Settings and signals are displayed either in plain text or as addresses, in
accordance with the user’s choice. All settings and signals of the P634 are
documented in a separate collection of documents, the so-called
“DataModelExplorer”. The “Addresses” document (being part of the
“DataModelExplorer”) is complete in the sense that it contains all settings,
signals and measured variables that are relevant for the user of the P634.
The configuration of the local control panel also permits the installation of
Measured Value “Panels” on the LCD display. Different Panels are automatically
displayed for specific system operating conditions. Priority increases from normal
operation to operation under overload conditions and finally to operation
following a short circuit in the system. Thus the P634 provides the measured
data relevant for the prevailing conditions.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-3
Page 60

P634 3 Operation
3.3 Configuration of the Measured Value Panels (Function Group LOC)
The P634 offers Measured Value Panels, which display the measured values
relevant at a given time.
During normal power system operation, the Operation Panel is displayed. If the
Operation Panel is activated as an event occurs, the display switches to the
appropriate Event Panel – provided that measured values have been selected for
the Event Panels. In the event of overload or ground fault events, the display will
automatically switch to the Operation Panel at the end of the event. In the event
of a fault, the Fault Panel remains active until the LED indicators or the fault
memories are reset.
3-4 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 61

3 Operation P634
3.3.1 Operation Panel
The Operation Panel is displayed after the set return time has elapsed, provided
that at least one measured value has been configured.
The user can select which of the measured operating values will be displayed on
the Operation Panel by means of an “m out of n” parameter. When more
measured operating values are selected for display than the LC display can
accommodate, then the display will either switch to the next set of measured
operating values at intervals defined by the setting for LOC: Hold-time for
Panels or when the appropriate key on the local control panel is pressed.
LOC:
Fct. Operation Panel
[ 053 007 ]
Measured value 1
Measured value 2
Measured value 3
Measured value N
FT_RC:
Record. in progress
[ 035 000 ]
OL_RC:
Record. in progress
[ 035 003 ]
m out of n
Selected meas. val.
S1 1
R1
≥1
Autom. return time
[ 003 014 ]
Hold-time for Panels
[ 031 075 ]
C
Operation Panel
LOC:
LOC:
LOC:
Autom. return time
LOC:
Hold-time for Panels
MAIN:
General reset USER
[ 003 002 ]
1: execute
MAIN:
General reset EXT
[ 005 255 ]
FT_RC:
Reset record. USER
[ 003 006 ]
1: execute
FT_RC:
Reset record. EXT
[ 005 243 ]
MAIN:
Reset LED
306 020
Fig. 3-2: Operation Panel.
≥1
63Z80CXA
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-5
Page 62

P634 3 Operation
3.3.2 Fault Panel
The Fault Panel is displayed in place of another data panel when there is a fault,
provided that at least one measured value has been configured. The Fault Panel
remains on display until the LED indicators or the fault memories are cleared.
The user can select the measured fault values that will be displayed on the Fault
Panel by setting an “m out of n” parameter. When more measured fault values
are selected for display than the LC display can accommodate, then the display
will either switch to the next set of measured fault values at intervals defined by
the setting for LOC: Hold-time for Panels or when the appropriate key on the
local control panel is pressed.
LOC:
Fct. Fault Panel
[ 053 003 ]
Measured value 1
Measured value 2
Measured value 3
Measured value N
LOC:
Hold-time for Panels
[ 031 075 ]
MAIN:
General reset USER
[ 003 002 ]
1: execute
MAIN:
General reset EXT
[ 005 255 ]
FT_RC:
Reset record. USER
[ 003 006 ]
1: execute
FT_RC:
Reset record. EXT
[ 005 243 ]
MAIN:
Reset LED
306 020
Fig. 3-3: Fault panel.
m out of n
Selected meas. val.
≥1
R
Fault Panel
50Z01EJA
3-6 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 63

3 Operation P634
3.3.3 Overload Panel
The Overload Panel is automatically displayed in place of another data panel
when there is an overload, provided that at least one measured value has been
configured. The Overload Panel remains on display until the overload ends,
unless a fault occurs. In this case the display switches to the Fault Panel.
The user can select the measured values that will be displayed on the Overload
Panel by setting a “m out of n” parameter. When more measured fault values are
selected for display than the LC display can accommodate, then the display will
either switch to the next set of measured fault values at intervals defined by the
setting for LOC: Hold-time for Panels or when the appropriate key on the
local control panel is pressed.
LOC:
Fct. Overload Panel
[ 053 005 ]
Measured value 1
Measured value 2
Measured value 3
Measured value n
LOC:
Hold-time for Panels
[ 031 075 ]
MAIN:
General reset USER
[ 003 002 ]
1: execute
MAIN:
General reset EXT
[ 005 255 ]
OL_RC:
Reset record. USER
[ 100 003 ]
1: execute
OL_RC:
Reset record. EXT
[ 005 241 ]
MAIN:
Reset LED
306 020
Fig. 3-4: Overload Panel.
m out of n
Select. meas. values
≥1
R
Overload Panel
50Z0140A
3.3.4 Configurable Clear Key
The P634 has a Clear key –
assigned by selecting the required functions at LOC: Fct. reset key. Details on
the functions' resetting features are given in Section 3.12.15, (p. 3-96).
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-7
–, to which one or more reset functions can be
Page 64

P634 3 Operation
3.4 Communication Interfaces
The P634 has a PC interface as a standard component. Communication module A
is optional and can be provided with one or two communication channels –
depending on the design version. Communication between the P634 and the
control station’s computer is through the communication module A. Setting and
interrogation is possible through all the P634's interfaces.
If the communication module A with two communication channels is installed,
settings for two communication interfaces will be available. The setting of
communication interface 1 (COMM1) may be assigned to the physical
communication channels 1 or 2 (see Section 3.12.16, (p. 3-98)). If the COMM1
settings have been assigned to communication channel 2, then the settings of
communication interface 2 (COMM2) will automatically be active for
communication channel 1.
COMM2 can only be used to transmit data to and from the P634 if its PC interface
has been de-activated. As soon as the PC interface is used to transmit data,
COMM2 becomes “dead”. It will only be enabled again when the “time-out”
period for the PC interface has elapsed.
If tests are run on the P634, the user is advised to activate the test mode. In this
way the PC or the control system will recognize all incoming test signals
accordingly (see Section 3.12.17, (p. 3-99)).
3-8 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 65

3 Operation
3.4.1 PC Interface (Function Group PC)
Communication between the P634 and a PC is through the PC interface. In order
for data transfer between the P634 and the PC to function, several settings must
be made in the P634.
There is support software available as an accessory for P634 control.
PC:
Sig./meas.val.block.
[ 003 086 ]
0
1
0: No
1: Yes
MAIN:
Prot. ext. disabled
[ 038 046 ]
PC:
Command blocking
[ 003 182 ]
0
1
0: No
1: Yes
PC:
Bay address
[ 003 068 ]
PC:
Device address
[ 003 069 ]
PC:
Baud rate
[ 003 081 ]
PC:
Parity bit
[ 003 181 ]
PC:
Spontan. sig. enable
[ 003 187 ]
PC:
Select. spontan.sig.
[ 003 189 ]
PC:
Transm.enab.cycl.dat
[ 003 084 ]
PC:
Cycl. data ILS tel.
[ 003 185 ]
PC:
Delta V
[ 003 055 ]
PC:
Delta I
[ 003 056 ]
PC:
Delta f
[ 003 057 ]
PC:
Delta meas.v.ILS tel
[ 003 155 ]
PC:
Delta t
[ 003 058 ]
PC:
Time-out
[ 003 188 ]
PC interface
P634
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
64Z51ECA
Fig. 3-5: PC interface settings.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-9
Page 66

P634 3 Operation
3.4.2 Communication Interface 1 (Function Group COMM1)
There are several different interface protocols available at the communication
interface 1. The following user-selected interface protocols are available for use
with the P634:
IEC 60870‑5‑103, "Transmission protocols - Companion standard for the
●
informative interface of protection equipment, first edition, 1997-12
(corresponds to VDEW / ZVEI Recommendation, "Protection communication
companion standard 1, compatibility level 2", February 1995 edition) with
additions covering control and monitoring
IEC 870‑5‑101, "Telecontrol equipment and systems ‑ Part 5: Transmission
●
protocols ‑ Section 101 Companion standard for basic telecontrol tasks,"
first edition 1995‑11
ILS‑C, proprietary protocol of Schneider Electric
●
MODBUS
●
DNP 3.0
●
COURIER
●
In order for data transfer to function properly, several settings must be made in
the P634.
Communication interface 1 can be blocked through a binary signal input. In
addition, a signal or measured-data block can also be imposed through a binary
signal input.
3-10 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 67

3 Operation
COMM1:
Command block. EXT
[ 003 173 ]
COMM1:
Command block. USER
[ 003 172 ]
0: No
1: Yes
COMM1:
Basic IEC870-5 enabl
[ 003 215 ]
0: No
1: Yes
COMM1:
Addit. -101 enable
[ 003 216 ]
0: No
1: Yes
P634
0
1
COMM1:
Command blocking
[ 003 174 ]
COMM1:
Communicat. protocol
0
1
0
1
[ 003 167 ]
Selected protocol
COMM1:
Selected protocol
304 415
0: No
1: Yes
0: No
1: Yes
0: No
1: Yes
0: No
1: Yes
COMM1:
Addit. ILS enable
[ 003 217 ]
COMM1:
MODBUS enable
[ 003 220 ]
COMM1:
DNP3 enable
[ 003 231 ]
COMM1:
COURIER enable
[ 103 040 ]
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
64Z51FEA
Fig. 3-6: Communication interface 1, selecting the interface protocol.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-11
Page 68

P634
3 Operation
COMM1:
Selected protocol
304 415
COMM1:
IEC 870-5-103
[ 003 219 ]
COMM1:
Command blocking
[ 003 174 ]
General enable USER
0: No
1: Yes
COMM1:
[ 003 170 ]
COMM1:
-103 prot. variant
[ 003 178 ]
COMM1:
Line idle state
[ 003 165 ]
COMM1:
Baud rate
[ 003 071 ]
COMM1:
Parity bit
[ 003 171 ]
COMM1:
Dead time monitoring
[ 003 176 ]
COMM1:
Mon. time polling
[ 003 202 ]
COMM1:
Octet comm. address
[ 003 072 ]
COMM1:
Test monitor on
[ 003 166 ]
COMM1:
Name of manufacturer
[ 003 161 ]
COMM1:
Octet address ASDU
[ 003 073 ]
0
1
C
C
C
COMM1:
Spontan. sig. enable
[ 003 177 ]
COMM1:
Select. spontan.sig.
[ 003 179 ]
COMM1:
Transm.enab.cycl.dat
[ 003 074 ]
COMM1:
Cycl. data ILS tel.
[ 003 175 ]
COMM1:
Delta V
[ 003 050 ]
COMM1:
Delta I
[ 003 051 ]
COMM1:
Delta f
[ 003 052 ]
COMM1:
Delta meas.v.ILS tel
[ 003 150 ]
COMM1:
Delta t
[ 003 053 ]
COMM1:
Contin. general scan
[ 003 077 ]
C
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
COMM1:
Sig./meas. block EXT
[ 037 074 ]
MAIN:
Prot. ext. disabled
[ 038 046 ]
Sig./meas.block.USER
0: No
1: Yes
COMM1:
[ 003 076 ]
0
1
Commun. interface
Fig. 3-7: Communication interface 1, settings for the IEC 60870‑5-103 interface protocol.
COMM1:
Sig./meas.val.block.
[ 037 075 ]
64Z70FFA
3-12 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 69

3 Operation
P634
COMM1:
Selected protocol
304 415
COMM1:
IEC 870-5-101
[ 003 218 ]
COMM1:
Command blocking
[ 003 174 ]
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
General enable USER
0: No
1: Yes
Sig./meas.block.USER
COMM1:
[ 003 170 ]
COMM1:
[ 003 076 ]
COMM1:
Line idle state
[ 003 165 ]
COMM1:
Baud rate
[ 003 071 ]
COMM1:
Parity bit
[ 003 171 ]
COMM1:
Dead time monitoring
[ 003 176 ]
COMM1:
Mon. time polling
[ 003 202 ]
COMM1:
Octet comm. address
[ 003 072 ]
COMM1:
Test monitor on
[ 003 166 ]
COMM1:
Name of manufacturer
[ 003 161 ]
COMM1:
Octet address ASDU
[ 003 073 ]
COMM1:
Spontan. sig. enable
[ 003 177 ]
COMM1:
Select. spontan.sig.
[ 003 179 ]
COMM1:
Transm.enab.cycl.dat
[ 003 074 ]
COMM1:
Cycl. data ILS tel.
[ 003 175 ]
COMM1:
Delta V
[ 003 050 ]
COMM1:
Delta I
[ 003 051 ]
COMM1:
Delta f
[ 003 052 ]
COMM1:
Delta meas.v.ILS tel
0
1
[ 003 150 ]
COMM1:
Delta t
[ 003 053 ]
COMM1:
Contin. general scan
[ 003 077 ]
COMM1:
Comm. address length
[ 003 201 ]
COMM1:
Octet 2 comm. addr.
[ 003 200 ]
COMM1:
Cause transm. length
[ 003 192 ]
COMM1:
Address length ASDU
[ 003 193 ]
COMM1:
Octet 2 addr. ASDU
[ 003 194 ]
COMM1:
Addr.length inf.obj.
[ 003 196 ]
COMM1:
Oct.3 addr. inf.obj.
[ 003 197 ]
COMM1:
Inf.No.<->funct.type
[ 003 195 ]
COMM1:
Time tag length
[ 003 198 ]
COMM1:
ASDU1 / ASDU20 conv.
[ 003 190 ]
COMM1:
ASDU2 conversion
[ 003 191 ]
COMM1:
Initializ. signal
[ 003 199 ]
COMM1:
Balanced operation
[ 003 226 ]
COMM1:
Direction bit
[ 003 227 ]
COMM1:
Time-out interval
[ 003 228 ]
COMM1:
Sig./meas. block EXT
[ 037 074 ]
MAIN:
Prot. ext. disabled
[ 038 046 ]
0
1
0: No
1: Yes
Commun. interface
COMM1:
Sig./meas.val.block.
[ 037 075 ]
64Z51FGA
Fig. 3-8: Communication interface 1, settings for the IEC 870-5-101 interface protocol.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-13
Page 70

P634
3 Operation
COMM1:
Selected protocol
304 415
COMM1:
IEC 870-5,ILS
[ 003 221 ]
COMM1:
Command blocking
[ 003 174 ]
General enable USER
0: No
1: Yes
COMM1:
[ 003 170 ]
COMM1:
Line idle state
[ 003 165 ]
COMM1:
Baud rate
[ 003 071 ]
COMM1:
Parity bit
[ 003 171 ]
COMM1:
Dead time monitoring
[ 003 176 ]
COMM1:
Mon. time polling
[ 003 202 ]
COMM1:
Octet comm. address
[ 003 072 ]
COMM1:
Test monitor on
[ 003 166 ]
COMM1:
Name of manufacturer
[ 003 161 ]
COMM1:
Octet address ASDU
[ 003 073 ]
0
1
COMM1:
Spontan. sig. enable
[ 003 177 ]
COMM1:
Select. spontan.sig.
[ 003 179 ]
COMM1:
Transm.enab.cycl.dat
[ 003 074 ]
COMM1:
Cycl. data ILS tel.
[ 003 175 ]
COMM1:
Delta V
[ 003 050 ]
COMM1:
Delta I
[ 003 051 ]
COMM1:
Delta f
[ 003 052 ]
COMM1:
Delta meas.v.ILS tel
[ 003 150 ]
COMM1:
Delta t
[ 003 053 ]
COMM1:
Contin. general scan
[ 003 077 ]
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
COMM1:
Sig./meas. block EXT
[ 037 074 ]
MAIN:
Prot. ext. disabled
[ 038 046 ]
Sig./meas.block.USER
0: No
1: Yes
COMM1:
[ 003 076 ]
0
1
Commun. interface
Fig. 3-9: Communication interface 1, settings for the ILS-C interface protocol.
COMM1:
Sig./meas.val.block.
[ 037 075 ]
64Z51FHA
3-14 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 71

3 Operation P634
COMM1:
Selected protocol
304 415
COMM1:
MODBUS
[ 003 223 ]
COMM1:
General enable USER
[ 003 170 ]
1: Yes
COMM1:
Command blocking
[ 003 174 ]
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
COMM1:
MODBUS prot. variant
[ 003 214 ]
COMM1:
Line idle state
[ 003 165 ]
COMM1:
Baud rate
[ 003 071 ]
COMM1:
Parity bit
[ 003 171 ]
COMM1:
Dead time monitoring
[ 003 176 ]
COMM1:
Mon. time polling
[ 003 202 ]
COMM1:
Octet comm. address
[ 003 072 ]
Commun. interface
COMM1:
Test monitor on
[ 003 166 ]
COMM1:
Reg.asg. selec. cmds
[ 003 210 ]
COMM1:
Reg.asg. selec. sig.
[ 003 211 ]
COMM1:
Reg.asg. sel. m.val.
[ 003 212 ]
COMM1:
Reg.asg. sel. param.
[ 003 213 ]
COMM1:
Delta t (MODBUS)
[ 003 152 ]
COMM1:
Autom.event confirm.
[ 003 249 ]
COMM1:
Communication error
304 422
Fig. 3-10: Communication interface 1, settings for the MODBUS protocol.
19Z50FJB
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-15
Page 72

P634 3 Operation
COMM1:
Selected protocol
304 415
COMM1:
DNP3
[ 003 230 ]
COMM1:
General enable USER
[ 003 170 ]
1: Yes
COMM1:
Line idle state
[ 003 165 ]
COMM1:
Baud rate
[ 003 071 ]
COMM1:
Parity bit
[ 003 171 ]
COMM1:
Dead time monitoring
[ 003 176 ]
COMM1:
Mon. time polling
[ 003 202 ]
COMM1:
Octet comm. address
[ 003 072 ]
COMM1:
Oct.2 comm.addr.DNP3
[ 003 240 ]
COMM1:
Test monitor on
[ 003 166 ]
COMM1:
Phys. Charact. Delay
[ 003 241 ]
COMM1:
Phys. Char. Timeout
[ 003 242 ]
COMM1:
Link Confirm. Mode
[ 003 243 ]
COMM1:
Link Confirm.Timeout
[ 003 244 ]
COMM1:
Link Max. Retries
[ 003 245 ]
COMM1:
Appl.Confirm.Timeout
[ 003 246 ]
COMM1:
Appl. Need Time Del.
[ 003 247 ]
COMM1:
Ind./cl. bin. inputs
[ 003 232 ]
COMM1:
Ind./cl. bin.outputs
[ 003 233 ]
COMM1:
Ind./cl. analog inp.
[ 003 235 ]
COMM1:
Ind./cl. analog outp
[ 003 236 ]
COMM1:
Delta meas.v. (DNP3)
[ 003 250 ]
COMM1:
Delta t (DNP3)
[ 003 248 ]
COMM1:
Command blocking
[ 003 174 ]
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
Commun. interface
Fig. 3-11: Communication interface 1, settings for the DNP 3.0 protocol.
64Z50AZA
3-16 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 73

3 Operation P634
COMM1:
Line idle state
[ 003 165 ]
COMM1:
Baud rate
[ 003 071 ]
COMM1:
COMM1:
Selected protocol
304 415
COMM1:
COURIER
[ 103 041 ]
COMM1:
Command blocking
[ 003 174 ]
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
COMM1:
General enable USER
[ 003 170 ]
0: No
1: Yes
0
1
Parity bit
[ 003 171 ]
COMM1:
Dead time monitoring
[ 003 176 ]
COMM1:
Mon. time polling
[ 003 202 ]
COMM1:
Octet comm. address
[ 003 072 ]
Commun. interface
Fig. 3-12: Communication interface 1, settings for the COURIER protocol.
COMM1:
Test monitor on
[ 003 166 ]
COMM1:
Command selection
[ 103 042 ]
COMM1:
Signal selection
[ 103 043 ]
COMM1:
Meas. val. selection
[ 103 044 ]
COMM1:
Parameter selection
[ 103 045 ]
COMM1:
Delta t (COURIER)
[ 103 046 ]
COMM1:
Communication error
304 422
19Z51BAA
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-17
Page 74

P634 3 Operation
3.4.2.1 COMM1 – Checking Spontaneous Signals
For interface protocols based on IEC 60870‑5‑103, IEC 870‑5‑101, or ILS-C it is
possible to select a signal for test purposes. The transmission of this signal to the
control station as ‘sig. start‘ or ‘sig. end‘ can then be triggered using setting
parameters.
COMM1:
Sel.spontan.sig.test
[ 003 180 ]
Signal 1
Signal 2
Signal 3
Signal n
Selected signals
COMM1:
Test spont.sig.start
[ 003 184 ]
0
1
0: don't execute
1: execute
COMM1:
Spontan. sig. start
[ --- --- ]
COMM1:
Test spont.sig. end
[ 003 186 ]
0
0: don't execute
1: execute
1
Fig. 3-13: COMM1 – Checking spontaneous signals.
COMM1:
Spontan. sig. end
[ --- --- ]
48Z50FKA
3-18 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 75

3 Operation
3.4.3 Communication Interface 2 (Function Group COMM2)
Communication interface 2 supports the IEC 60870‑5‑103 interface protocol.
In order for data transfer to function properly, several settings must be made in
the P634.
COMM2:
Line idle state
[ 103 165 ]
COMM2:
Baud rate
[ 103 071 ]
COMM2:
Parity bit
[ 103 171 ]
COMM2:
Dead time monitoring
[ 103 176 ]
COMM2:
Mon. time polling
[ 103 202 ]
COMM2:
Octet comm. address
[ 103 072 ]
COMM2:
Name of manufacturer
[ 103 161]
COMM2:
Octet address ASDU
[ 103 073 ]
COMM2:
Spontan. sig. enable
[ 103 177 ]
COMM2:
Select. spontan.sig.
[ 103 179 ]
COMM2:
Transm.enab.cycl.dat
[ 103 074 ]
COMM2:
Cycl. data ILS tel.
[ 103 175 ]
COMM2:
Delta V
[ 103 050 ]
COMM2:
Delta I
[ 103 051 ]
COMM2:
Delta f
[ 103 052 ]
COMM2:
Delta meas.v.ILS tel
[ 103 150 ]
COMM2:
Delta t
[ 103 053 ]
MAIN:
Prot. ext. disabled
[ 038 046 ]
COMM2:
General enable USER
[ 103 170 ]
0: No
1: Yes
COMM2:
Sig./meas.block.USER
[ 103 076 ]
0: No
1: Yes
0
1
0
1
P634
COMM2:
Command block. USER
[ 103 172 ]
0
1
0: No
MAIN:
Test mode
[ 037 071 ]
1: Yes
Commun. interface
64Z5189A
Fig. 3-14: Settings for communication interface 2.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-19
Page 76

P634 3 Operation
3.4.3.1 COMM2 – Checking Spontaneous Signals
It is possible to select a signal for test purposes. The transmission of this signal to
the control station as ‘sig. start‘ or ‘sig. end‘ can then be triggered via the local
control panel.
COMM2:
Sel.spontan.sig.test
[ 103 180 ]
Signal 1
Signal 2
Signal 3
Signal n
Selected signals
COMM2:
Test spont.sig.start
[ 103 184 ]
0
1
0: don't execute
1: execute
COMM2:
Spontan. sig. start
[ --- --- ]
COMM2:
Test spont.sig. end
[ 103 186 ]
0
0: don't execute
1: execute
1
Fig. 3-15: COMM2 – Checking spontaneous signals.
COMM2:
Spontan. sig. end
[ --- --- ]
48Z50FLA
3-20 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 77

3 Operation
3.4.4 Communication Interface IEC 61850 (Function Groups IEC and GOOSE)
The IEC 61850 communication protocol is implemented by these function groups
and the Ethernet module.
Function group IEC is only available as an alternative to function group COMM1
(hardware ordering option!).
3.4.4.1 Communication Interface IEC 61850 (Function Group IEC)
The P634 offers as an ordering option a communication protocol according to the
Ethernet based IEC 61850 protocol.
3.4.4.1.1 IEC 61850 IEC 61850 was created jointly by users and manufacturers as an international
standard. The main target of IEC 61850 is interoperability of devices. This
includes the capability of two or more intelligent electronic devices (IED),
manufactured by the same company or different companies, to exchange data
for combined operation.
This communication standard IEC 61850 has now created an open and common
basis for communication from the process control level down to the network
control level, for the exchange of signals, data, measured values and commands.
For a standardized description of all information and services available in a field
device a data model, which lists all visible functions, is created. Such a data
model, specifically created for each device, is used as a basis for an exchange of
data between the devices and all process control installations interested in such
information. In order to facilitate engineering at the process control level a
standardized description file of the device, based on XML, is created with the
help of the data model. This file can be imported and processed further by the
relevant configuration program used by the process control device. This makes
possible an automated creation of process variables, substations and signal
images.
Available is the following documentation providing the description of the
IEC 61850 data model which is used with the P634:
ICD file based on XML in the SCL (Substation Configuration Description
●
Language) with a description of data, properties and services, available
from the P634, that are to be imported into the configuration tool “IED
Configurator” or into a system configurator.
PICS_MICS_ADL file with the following contents:
●
o
PICS (Protocol Implementation Conformance Statement) with an
overview of available services.
o
MICS (Model Implementation Conformance Statement) with an overview
of available object types.
o
ADL (Address Assignment List) with an overview of the assignment of
parameter addresses (signals, measuring values, commands, etc.) used
by the P634 with the device data model as per IEC 61850.
P634
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-21
Page 78

P634 3 Operation
3.4.4.1.2 Ethernet Module The optional Ethernet module provides an RJ45 connection and a fiber optic
interface where an Ethernet network can be connected. The selection which of
the two interfaces is to be used to connect to the Ethernet network is made by
setting the parameter [IC]: Media.
Setting parameters identified by “[IC]:…” in the IEC function group are set with the
“IED Configurator”. They cannot be modified from the local control panel (HMI) or
with the operating program.
There are two ordering variants available for the fiber-optic interface: the ST
connector and the SC connector both for 100 Mbit/s and 1300 nm. The RJ45
connector supports 10 Mbit/s and 100 Mbit/s.
The optional Ethernet module additionally provides an RS485 interface for
remote access with the MiCOM S1 support software (function group COMM2).
The P634 may be equipped with the optional Ethernet module only as an
alternative to the standard optional communication module. Therefore the
Ethernet-based communication protocol IEC 61850 is available only as an
alternative to function group COMM1.
3.4.4.1.3 Configuration and Enabling The IEC function group can be included in the configuration by setting the
parameter IEC: Function group IEC. This parameter is only visible if the
optional Ethernet communication module is fitted to the P634. After activation of
IEC, all data points associated with this function group (setting parameters,
binary state signals etc.) become visible.
The function can then be enabled or disabled by setting IEC: General enable
USER.
The setting parameters from the IEC function group as well as the related GOOSE
function group are not automatically active in the P634. The P634 features two
memory “banks” one of which includes the active setting parameters. The other
memory bank is used with the configuration procedure for parameters from the
IED Configurator and the operating system. Specific project-related extensions of
the IEC 61850 parameters from the IED Configurator are loaded into the P634 by
downloading a .MCL file. The inactive communication parameters are activated
by executing the command IEC: Switch Config. Bank. This command may
also be issued from the IED Configurator.
3-22 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 79

3 Operation P634
System configurator
PACiS SCE
.iid
.scd
.icd
IED Configurator
IED Configurator
.mcl
Fig. 3-16: Configuration according to IEC 61850-6.
Operating program
.x3v
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
P634
F6
12Z7001A
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-23
Page 80

P634
3 Operation
IEC 61850 parameters separate from protection device parameters!
Control PC
Operating program
IED
Configurator
Processor module
Device
parameters
Parameter download
Parameter upload
IEC 61850
parameter
Bank 1
Bank switching to enable the
device parameters
New approach to IED parameter management
IED
Parameter
switch
Ethernet module
IEC 61850
parameter
Bank 2
19Z7002B
Fig. 3-17: Saving configuration parameters.
3.4.4.1.4 Client Log-on Communication in Ethernet no longer occurs in a restrictive master slave system,
as is common with other protocols. Instead, server or client functionalities, as
defined in the “Abstract Communication Service Interface” (ACSI, IEC 61870‑7‑2),
are assigned to the devices. A “server” is always that device which provides
information to other devices. A client may log on to this server in order to receive
information, for instance “reports”. In its function as server the P634 can supply
up to 16 clients, linked into the network, with spontaneous or cyclic information.
3.4.4.1.5 Clock Synchronization With IEC 61850 clock synchronization is effected via the SNTP protocol, defined
as standard for Ethernet. Here the P634 functions as an SNTP client.
For clock synchronization one can choose between the operating modes Anycast
from SNTP Server or Request from Server. With the first operating mode
synchronization occurs by a broadcast message sent from the SNTP server to all
devices in the network, and in the second operating mode the P634 requests a
device-specific time signal during a settable cycle.
Two SNTP servers may be set. In this case, clock synchronization is preferably
performed by the first server. The second server is only reverted to if no signal is
received from the first server.
When looking at the source priority for clock synchronization, which is set at the
MAIN function then, by selecting COMM1/IEC, synchronization per IEC 61850 is
automatically active but only if this communication protocol is applied.
3-24 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 81

3 Operation
3.4.4.1.6 Generating Datasets, Reporting The specific project related feature of the P634’s communications behavior is
determined by the configuration of datasets, reports and high priority
transmission methods. A piece of information must be included in a dataset so as
to be transmitted as a signal. A dataset is a list to transmit certain data objects.
The selection of data objects and the resulting length of the dataset is
determined by the application; merely the GOOSE capacity, i.e. the maximum
size of a dataset to be transmitted by GOOSE, is limited to 1500 bytes.
It is not possible to read the IEC configuration back from the P634 if the “Dataset”
sizes exceed the GOOSE size limit significantly. Therefore it is recommended to
limit the “Dataset” size(s) to 100% of the GOOSE capacity. Too large a dataset can
spoil IEC 61850 communication. Hence, the dataset size limit of 100% of the
GOOSE capacity should not be exceeded, neither for GOOSE nor for reports.
Data objects provided by the P634 are available for selection with a structure as
specified by IEC 61850. Within the quality descriptor for each piece of
information the invalid bit and the test bit are served according to the P634’s
state; the other attributes are not set. Any number of datasets may be created
with the IED Configurator. Saving datasets at System\LLN0 is compulsory. The
knowledge of dataset content is imperative for decoding and evaluating received
signals. Configuration files possess a listing of all datasets with a description of
all data objects included.
Next to their use with high priority transmission methods (see Section 3.4.4.1.10,
(p. 3-27)) datasets are used mainly for reporting. The P634 provides up to
sixteen unbuffered reports and eight buffered reports independent of the number
of clients logged-on. Management is arranged into sixteen Unbuffered Report
Control Blocks (urcbA to urcbP) and eight Buffered Report Control Blocks (brcbA
to brcbH). Whereas with unbuffered reporting pieces of information may be lost
during a communications failure, the buffered report control blocks support a
buffered transmission which is required for the uninterrupted writing of events. A
pre-defined dataset may be assigned to each report which will then determine
which data object will be transmitted with the relevant report. Assigning datasets
is not limited; the same dataset may be referenced in various reports or even in
GOOSEs.
The P634 can serve up to sixteen clients. Each client can log-on to any number of
available reports. One unbuffered report can be allocated to max. 8 clients, and
one buffered report can be allocated to max. 4 clients. A client is then able to
activate the wanted report for himself and to set the transmission behavior to his
requirements. The system concept with intended clients must be taken into
account when datasets are assigned to the reports.
Reports are not received by the P634.
P634
3.4.4.1.7 Transmitting Modeled Signals Not Provided by the IEC 61850 Data Model In addition to the information included in the IEC 61850 data model an optional
number of up to 16 signals can be selected from all the signals available in the
P634 to be transmitted via reporting. A selection of state signals (shuttling to
communications) is made by setting IEC: SigGGIO1 selection. The data
object indexes defined for SigGGIO1 must follow the sequence given for the ‘m
out of n’ selection for the state signals. The indexes SigGGIO1.ST.ind1 to
SigGGIO1.ST.ind16 may then be included in the datasets just as the other data
objects.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-25
Page 82

P634 3 Operation
3.4.4.1.8 Single Commands Single commands (e.g. short command, long command, persistent command)
are configured with the operating program. Sending commands to the P634 can
be carried out from all clients that have previously logged-on to the P634. But
only one command at a time is carried out. The operating mode Direct control
with normal security is provided for single commands.
3-26 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 83

3 Operation P634
3.4.4.1.9 Fault Transmission Including fault transmission for the IEC 61850 in the configuration is only possible
with the IED Configurator.
Transmission of fault files is supported per “File Transfer”. COMTRADE fault files
in the P634 are transmitted uniformly either as ASCII or binary formatted files.
Fault transmission can be cancelled from the configuration.
3.4.4.1.10 High Priority Transmission of Information Whereas normal server-client services are transmitted at the MMS and TCP/IP
level the high priority transmission of information is carried out directly at
Ethernet level. Furthermore messages in such a particular form can be received
by all participants in the relevant sub-network, independent of their server or
client function. They are deployed in instances where high speed transmission of
information is wanted between two or more devices. Applications, for example,
are reverse interlocking, transfer trip or decentralized substation interlock.
The standard IEC 61850 provides the Generic Object Oriented Substation Event
(GOOSE) for high priority transmission of information. The GOOSE enables
transmission of all data formats available in the data model, such as binary
information, integer values, two-pole contact position signals or analog measured
values. The P634 supports receipt and evaluation of GOOSE including binary
information and two-pole contact position signals from external devices.
3.4.4.1.11 Communication with the MiCOM S1 Support Software via the Ethernet Interface Direct access by the MiCOM S1 support software via the Ethernet interface on
the P634 may occur through the “tunneling principle”. Transmission is carried
out by an Ethernet Standard Protocol, but this is only supported by the
associated MiCOM S1 support software (specific manufacturer solution). Such
transmission is accomplished over the same hardware for the network, which is
used for server-client communication. Available are all the familiar functions
offered by the MiCOM S1 support software such as reading/writing of setting
parameters or retrieving stored data.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-27
Page 84

P634
3 Operation
3.4.4.2 Generic Object Oriented Substation Event (Function Group GOOSE)
For high priority exchange of information between individual devices (IEDs) in a
local network, the P634 provides the function group GOOSE as defined in the
standard IEC 61850. GOOSE features high-speed and secure transmission of
information for reverse interlocking, decentralized substation interlock, trip
commands, blocking, enabling, contact position signals and other signals.
GOOSE Messages are only transmitted by switches but not by routers. GOOSE
messages therefore remain in the local network to which the P634 is connected.
3.4.4.2.1 Configuration and Enabling Function group GOOSE can be configured by setting the parameter
GOOSE: Function group GOOSE This parameter is only visible if the optional
Ethernet communication module is fitted to the P634. After having configured the
GOOSE all parameters associated to this function group are then visible and
ready to be configured.
Further setting parameters from function group GOOSE are set with the
IED Configurator, but they cannot be modified from the local control panel (MMI)
or with the operating program.
The function can then be enabled or disabled by setting GOOSE: General
enable USER.
»
Device A
IEC 61850
Mapping
IED Configurator
System/LLN0/Dataset
IED Configurator
System/LLN0/gcb01 ... 08
S1 Studio System/GosGGIO2
GOOSE: Output 1 ... 32
System/GosGGIO2.ST.ind1 ... 32
x
Fig. 3-18: GOOSE configuration.
3.4.4.2.2 Sending GOOSE The GOOSE can send up to eight different GOOSE messages which are managed
in eight GOOSE Control Blocks (gcb01 to gcb08). Information content depends on
the respective dataset assigned to GOOSE. The maximum size of a dataset to be
sent by GOOSE is limited to 1500 bytes. A control display is shown by the IED
Configurator to check this limit.
MCL
»
Device B
S1 Studio
GOOSE: Input 1 ... 128 (SPS)
Ext. Dev 1 ... 128 (DPS)
IED Configurator
Pos1.stVal ... Pos128.stVal
System/GosGGIO1
19Z8203B
3-28 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 85

3 Operation
P634
It is not possible to read the IEC configuration back from the P634 if the “Dataset”
sizes exceed the GOOSE size limit significantly. Therefore it is recommended to
limit the “Dataset” size(s) to 100% of the GOOSE capacity. Too large a dataset can
spoil IEC 61850 communication. Hence, the dataset size limit of 100% of the
GOOSE capacity should not be exceeded, neither for GOOSE nor for reports.
When defining the datasets for GOOSE it is advised to select the individual data
attributes and not the overlapping data objects. By this the amount of data is
kept within a limit and decoding is guaranteed on the receiving end.
In addition to the information included in the IEC 61850 data model an optional
number of up to 32 signals can be selected from all the signals available in the
P634 to be transmitted via GOOSE, as it is also possible with reporting.
Selection of binary state signals (shuttling to communications) is made by setting
GOOSE: Output 1 fct.assig.. (or Output 2, ..., Output 32). The data object
indexes defined for SigGGIO1 must follow the function assignments for the
GOOSE outputs. The indexes GosGGIO2.ST.ind1 to GosGGIO2.ST.ind32 may then
be included in the datasets just as the other data objects.
When a state change occurs with a selected state signal or a measured value
changes which is greater than the dead band set for the relevant data point then
the complete GOOSE is sent. There will be multiple send repetitions at ascending
time periods. The first send repetition occurs at the given cycle time set with the
parameter [IC]: Minimum Cycle Time. The cycles for the following send
repetitions result from a conditional equation with the increment set with the
parameter [IC]: Increment. Should no further state changes occur up to the
time when the maximum cycle time has elapsed [IC]: Maximum Cycle Time,
then GOOSE will be sent cyclically at intervals as set for the maximum cycle
time.
In order to have unambiguous identification of a GOOSE sent, characteristics
such as [IC]: Multicast MAC Address, [IC]: Application ID (hex),
[IC]: VLAN Identifier (hex), [IC]: VLAN Priority and
[IC]: GOOSE Identifier must be entered in the IED Configurator settings.
Further characteristics are [IC]: Dataset Reference and
[IC]: Configuration Revision.
Each GOOSE is given the state change index and the number of send repetitions.
3.4.4.2.3 Receiving GOOSE With GOOSE up to 128 logic binary state signals as well as 128 two-pole contact
position signals from external devices (Ext.Devxx) can be received. For each
state signal or contact position signal to be received a specific GOOSE message
is to be selected, which will contain the information wanted, by setting
[IC]: Multicast MAC Address, [IC]: Application ID (hex),
[IC]: Source Path, [IC]: GOOSE Identifier and [IC]: DataSet Reference.
With the further setting of [IC]: Data Obj Index / Type, which corresponds to
the GOOSE position index and the information structure of the sending device,
the required information from the chosen GOOSE will be selected. The
identification features "VLAN identifier" and [IC]: Configuration Revision
that are also included in the GOOSE received will not be evaluated.
These parameters characterizing the information may be taken either from
device or project planning documentation of the sending device or from a
configuration file which is conform to IEC 61850. The IED Configurator will
support the import of .IID, .SCD and .MCL files when the "browse function"
(virtual key) is applied. The selection and acceptance of parameters from an
existing project planning is distinguished by a simplified and very reliable data
input.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-29
Page 86

P634
Each GOOSE includes time information on the duration of validity of its
information. This corresponds to the double time period to the next GOOSE
repetition. If the duration of validity has elapsed without having received this
GOOSE again (i.e. because of a fault in communications), the signals received
will automatically be set to their respective default value
[IC]: Default Input Value. Which of the possible state values will set the
wanted security grade is dependent on the relevant application.
The following configuration (shuttling to the device functions) of the logic state
signals received from the logic node GosGGIO1 (GOOSE: Input 1 fct.assig.
(or Input 2, …, Input 128)) is made on the basis of the selection table of the
binary signal inputs (opto‑coupler inputs).
The virtual key "Unmap" may be used to remove the link of a binary signal input
to an external data point. In such a case all entries for this binary signal input are
deleted.
3.4.4.2.4 Uniqueness of Control within a System
3 Operation
»
Device A
IED Configurator
Control/LLN0.ST.OrdRun.stVal
IED Configurator
System/LLN0/Datasetx
IED Configurator
System/LLN0/gcb01 ... 08
Fig. 3-19: Uniqueness of Control.
S1 Studio
If with a system application it must be ensured that only one control command at
a time is being processed system wide (“uniqueness”) then interlocking of
secondary devices among themselves is setup with GOOSE. The P634 sets the
status information Control/LLN0.ST.OrdRun.stVal. when it has received a control
command. This information – stored in a dataset – is distributed in the system by
GOOSE and is therefore available to all other devices as an interlocking
condition. The state information is reset and accordingly signaled after
termination of the command sequence.
The P634 is capable to monitor the command status of up to 32 further devices.
With the IED Configurator OrdRunGGIO1.ind1.stVal to OrdRunGGIO1.ind32.stVal
are configured in a similar way to the other GOOSE inputs. A shuttling to the
interlocking equations is not necessary as their consideration within command
checking is automatically enabled when the first binary signal input is configured.
During a signaling receipt phase command effecting will be rejected.
MCL
»
Device B
IED Configurator
Ind1.stVal ... Ind32.stVal
System/OrdRunGGIO1
19Z7004B
3-30 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 87

3 Operation
3.4.5 Redundant Ethernet Board
The P634 Transformer Differential Protection Device can be (optionally) fitted
with a special communication module named Redundant Ethernet Board, as an
alternative to the single Ethernet board. (See Chapter 15, (p. 15-1) for the
exact order information and Section 5.7, (p. 5-22) for the location and
connection diagrams.)
The Redundant Ethernet Board assures redundancy at IED level, which allows an
alternative path to be always available, thus providing bumpless redundancy.
Industrial or substation control network failure can be disastrous. Redundancy
provides increased safety and reliability, but also devices can be added to or
removed from the network without network downtime.
3.4.5.1 Hardware Modules
P30 devices (i. e. devices from the device family Easergy MiCOM 30) are
constructed from standard hardware modules. The following table lists the item
numbers of the Redundant Ethernet board variants:
Type Item number Description Width
P634
A 9651 531 KE Dual Ethernet SHP + RS 485 + IRIG-B 4 TE
A 9651 532 KE Dual Ethernet RSTP + RS 485 + IRIG-B 4 TE
A 9651 533 KE Dual Ethernet DualHoming + RS 485 + IRIG-B 4 TE
A 9652 036 KE Dual Ethernet PRP + RS 485 + IRIG-B 4 TE
Tab. 3-1: Redundant Ethernet board variants.
All of these boards have 1300 nm multi mode 100BaseFx fiber-optic Ethernet
ports (ST® connector) and modulated IRIG-B input and furthermore connections
for a watchdog relay and an RS485 link (COMM2 interface, see Section 3.4.3,
(p. 3-19)).
The Redundant Ethernet board is fitted into Slot 2 of the P634. Each board has
two MAC addresses, one for the managed embedded switch and one for the
P634.
3.4.5.2 Redundancy Protocols
The following list shows Schneider Electric’s implementation of Ethernet
redundancy, which has four variants with embedded IEC 61850, plus SHP, RSTP,
DHP and PRP redundancy protocols.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-31
Page 88

P634
Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP IEC 62439‑3 (2012))
The PRP uses two independent Ethernet networks that operate in parallel.
●
The PRP is a “redundancy in the devices” method that provides bumpless
switchover in case of failure or reintegration. Furthermore, it provides the
shortest Ethernet network reconfiguration time as network reconfiguration
is seamless.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP IEEE 802.1D‑2004)
This board offers compatibility with any RSTP device. RSTP is a standard
●
used to quickly reconnect a network fault by finding an alternative path,
allowing loop-free network topology. Although RSTP can recover network
faults quickly, the fault recovery time depends on the number of devices
and the topology.
This board offers compatibility with any RSTP device, and in particular with
C264 (with the “SWS2x2” Switch Unit fitted).
Self Healing Protocol (SHP)
Self healing is applied to double ring network topologies and allows a
●
complete network reconfiguration time of less than 1 s.
When a fiber is broken, both end stations detect the break. Using both the
primary and redundant networks the ring is automatically reclosed.
This board offers compatibility with C264 (with the “SWR2x2” Switch
Redundant Unit fitted) and MiCOM H35x multi-mode switches. Self Healing
Protocol is a Schneider Electric proprietary solution providing extremely
fast recovery time.
3 Operation
Dual Homing Protocol (DHP)
Dual home is applied to double star architectures and provides bumpless
●
redundancy (0 ms change over time).
If the optical fiber connection between two devices is broken, the network
continues to operate correctly. The dual homing mechanism handles
topologies where a device is connected to two independent networks. One
is the main link, the other is the backup. Both are active at the same time.
This board offers compatibility with C264 (with the “SWD2x2” Switch Unit
fitted) and MiCOM H36x multi-mode switches. Dual Homing Protocol is a
Schneider Electric proprietary solution providing bumpless redundancy to
the P634.
3.4.5.3 Generic Functions for All Redundant Ethernet Boards
The following apply to all four redundant Ethernet protocols (SHP, RSTP, DHP and
PRP).
Ethernet 100Base Fx
The fiber optic ports are full duplex 100 Mbps ST connectors.
Forwarding
The devices from the families Easergy MiCOM 30, 40, the C264 and the MiCOM H
switches support store and forward mode. The MiCOM switch forwards messages
with known addresses to the appropriate port. The messages with unknown
addresses, the broadcast messages and the multicast messages are forwarded
out to all ports except the source port. MiCOM switches do not forward error
packets, 802.3x pause frames or local packets.
3-32 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 89

3 Operation P634
Priority Tagging
802.1p priority is enabled on all ports.
Simple Network Management Protocol – SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the network protocol developed
to manage devices in an IP network. SNMP relies on a Management Information
Base (MIB) that contains information about parameters to supervise. The MIB
format is a tree structure, with each node in the tree identified by a numerical
Object IDentifier (OID). Each OID identifies a variable that can be read or set
using SNMP with the appropriate software. The information in the MIBs is
standardized.
Various SNMP client software tools can be used with the Series 30, 40, C264 and
Hx5x range. Schneider Electric recommends using an SNMP MIB browser which
can perform the basic SNMP operations such as GET, GETNEXT, RESPONSE. To
access the network using SNMP, use the IP address of the embedded switch in
the Redundant Ethernet board.
Simple Network Time Protocol – SNTP
Simple Network Time Protocol is supported by both the P634 and the Redundant
Ethernet switch. SNTP is used to synchronize the clocks of computer systems
over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. A jitter buffer is used to
reduce the effects of variable latency introduced by queuing in packet switched
networks, ensuring a continuous data stream over the network.
The P634 receives the synchronization from the SNTP server. This is done using
the IP address of the SNTP server entered into the P634 from the IED
Configurator software.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-33
Page 90

P634 3 Operation
3.5 IRIG-B Clock Synchronization (Function Group IRIGB)
If, for example, a GPS receiver with IRIG-B connection is available, the internal
clock of the P634 can be synchronized to run on GPS time using the optional
IRIG-B interface. It should be noted that the IRIG-B signal holds information on
the day only (day of the current year). Using this information and the year set at
the P634, the P634 calculates the current date (DD.MM.YY).
Disabling and Enabling the IRIG-B Interface
The IRIG‑B interface can be disabled or enabled using a setting parameter.
Synchronization Readiness
If the IRIG-B interface is enabled and receiving a signal, the P634 checks the
received signal for plausibility. Implausible signals are rejected by the P634. If
the P634 does not receive a correct signal in the long run, synchronization will
not be ready any longer.
Fig. 3-20: IRIG‑B interface.
IRIGB:
General enable USER
[ 023 200 ]
IRIGB:
Enabled
[ 023 201 ]
IRIGB:
Synchron. ready
[ 023 202 ]
47Z02BAA
3-34 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 91

3 Operation
3.6 Configurable Function Keys (Function Group F_KEY)
The P634 provides six freely configurable function keys. A password may be
configured for each function key (e.g. for F1 at F_KEY: Password funct.key
1), and if a password has been configured then the respective function key will
only be enabled when the configured password is entered.
As an example the operation of function key F1 is shown in Fig. 3-21, (p. 3-36).
After the password has been entered the function key will remain active for the
time period set at F_KEY: Return time fct.keys. Thereafter, the function key
is disabled until the password is entered again. The same is valid for function
keys F2 to F6. Exception: If a function key is configured as a control key a
password request is only issued when the function “Local/Remote switching” has
been assigned to this function key.
Configuration of function keys with a single function
One function may be assigned to each function key (e.g. for F1) at F_KEY: Fct.
assignm. F1 or by selecting a logic state signal (except LOC: Trig. menu
jmp 1 EXT and LOC: Trig. menu jmp 2 EXT). The assigned function is
triggered by pressing the respective function key on the P634.
P634
Configuration of function keys with menu jump lists
Instead of a single function each function key may have one of the two menu
jump lists assigned (e.g. for F1) at F_KEY: Fct. assignm. F1 by selecting the
listing at LOC: Trig. menu jmp 1 EXT or LOC: Trig. menu jmp 2 EXT. The
functions of the selected menu jump list are triggered in sequence by repeated
pressing of the assigned function key.
Both menu jump lists are assembled at LOC: Fct. menu jmp list 1 or
LOC: Fct. menu jmp list 2. Up to 16 functions such as setting parameters,
event counters and/or event logs may be selected.
LED indicators including the six positioned directly next to the function keys are
configured independently and in this respect there is no relationship to the
respective function key configuration.
Configuration of the READ key
As with LOC: Fct. menu jmp list 1 or LOC: Fct. menu jmp list 2 up to 16
functions may also be selected from the same menu jump list at LOC: Fct.
read key. They are triggered in sequence by repeated pressing of the “READ”
key.
Operating mode of the function keys
For each function key the operating mode may be selected (e.g. for F1) at
F_KEY: Operating mode F1. Here it is possible to select whether the function
key operates as a key or as a switch. In the Key operating mode the selected
function is active while the function key is pressed. In the Switch operating mode
the selected function is switched on or off every time the function key is pressed.
The state of the function keys can be displayed.
Handling keys
If backlighting for the LC display is switched off it will automatically light up when
a function key or the “READ” key is pressed. The assigned function will only be
triggered when the respective key is pressed a second time. This is also valid for
the other keys.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-35
Page 92

P634 3 Operation
F_KEY:
Fct. assignm. F1
[ 080 112 ]
Function 1 EXT
Function 2 EXT
Function 3 EXT
Function n EXT
Selected function
F_KEY:
Operating mode F1
[ 080 132 ]
&
Activate function
1: Key
2: Switch
1
2
1)
Keys, local control1)
&
S1
1
&
&
0
R1
&
1
F_KEY:
State F1
[ 080 122 ]
40Z5003A
Fig. 3-21: Configuration and operating mode of function keys. The assigned function is either a single function or a
menu jump list.
3-36 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 93

3 Operation P634
3.7 Configuration and Operating Mode of the Binary Inputs (Function Group INP)
The P634 has opto coupler inputs for processing binary signals from the
substation. The functions that will be activated in the P634 by triggering these
binary signal inputs are defined by the configuration of the binary signal inputs.
In order to ensure that during normal operation the P634 will recognize an input
signal, it must persist for at least 20 ms. With the occurrence of a general
starting this time period may have to be increased to 40 ms under unfavorable
conditions.
Configuring the Binary Inputs
One function can be assigned to each binary signal input by configuration. The
same function can be assigned to several signal inputs. Thus one function can be
activated from several control points having different signal voltages.
It should be noted that time-critical applications such as time synchronization
commands should not be mapped to the binary signal inputs of the analog I/O
module as these have an increased reaction time due to internal processing.
In this technical manual, it is assumed that the required functions (marked “EXT”
in the address description) have been assigned to binary signal inputs by
configuration.
Operating Mode of the Binary Inputs
The operating mode for each binary signal input can be defined. The user can
specify whether the presence (Active "high" mode) or absence (Active "low"
mode) of a voltage shall be interpreted as the logic ‘1’ signal. The display of the
state of a binary signal input – "low" or "high" – is independent of the setting for
the operating mode of the signal input.
Filter Function
An additional filter function may be enabled in order to suppress transient
interference peaks at the logic signal inputs (operating modes Active "high", filt.
or Active "low", filt.). With this function enabled a status change at the binary
logic input is only signaled when the input signal remains at a steady signal level
during a set number of sampling steps (sampling step size = period / 20). The
number of sampling steps is set at parameter INP: Filter.
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-37
Page 94

P634 3 Operation
INP:
Fct. assignm. U xxx
[ XXX XXX ]
Function 1 EXT
Function 2 EXT
Function 3 EXT
Function n EXT
Activate function
INP:
State U xxx
[ ZZZ ZZZ ]
Input signal
-Uxxx
Selected function
INP:
Oper. mode U xxx
[ YYY XXX ]
0: Active "low"
1: Active "high"
2: Active "low", filt.
3: Active "high", filt.
INP:
Filter
[ 010 220 ]
&
0
1
2
3
&
&
&
&
&
&
Fig. 3-22: Configuration and operating mode of the binary signal inputs.
12Z6213A
3-38 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 95

3 Operation P634
3.8 Measured Data Input (Function Group MEASI)
When the P634 is equipped with the analog (I/O) module Y it has two analog
inputs available for measured data input. Direct current is fed to the P634
through the 20 mA analog input (input channel 1). The other input is designed for
connection of a PT 100 resistance thermometer.
The input current IDC present at the analog (I/O) module Y is displayed as a
measured operating value. The current that is conditioned for monitoring
purposes (I
monitored by the Limit Value Monitoring function to detect whether it exceeds or
falls below set thresholds (see Section 3.32, (p. 3-213)).
The measured temperature is also displayed as measured operating value and
monitored by the Limit Value Monitoring function to determine whether it
exceeds or falls below set threshold (see Section 3.32, (p. 3-213)).
All measured variables are also forwarded to the Thermal Overload Protection
function. With this protection it is possible to set whether the PT 100 resistance
thermometer or the 20 mA analog input is to be used for the thermal replica (see
Section 3.25.1, (p. 3-174)).
) is also displayed as a measured operating value. In addition, it is
DC,lin
Disabling or Enabling the Measured Data Input Function
The Measured Data Input function can be disabled or enabled via setting
parameters.
MEASI:
General enable USER
[ 011 100 ]
0: No
1: Yes
Fig. 3-23: Disabling or enabling the measured data input function.
0
1
MEASI:
Enabled
[ 035 008 ]
S8Z52H1A
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-39
Page 96

P634
3.8.1 Direct Current Input on the Analog (I/O) Module Y
External measuring transducers normally supply an output current of 0 to 20 mA
that is directly proportional to the physical quantity being measured – the
temperature, for example.
If the output current of the measuring transducer is directly proportional to the
measured quantity only in certain ranges, linearization can be arranged,
provided that the measured data input is set accordingly. Furthermore, for
certain applications it may be necessary to limit the range being monitored or to
monitor certain parts of the range with a higher or lower sensitivity.
By setting the value pair MEASI: IDC 1 and MEASI: IDC,lin 1, the user
specifies which input current IDC will correspond to the current that is monitored
by the Limit Value Monitoring function, i.e. I
refer to value pair number 1; setting parameters for value pairs 2 to 20 are
available, too.)
The resulting points, called “interpolation points”, are connected by straight lines
in an IDC‑I
diagram. In order to implement a simple characteristic, it is
DC,lin
sufficient to specify two interpolation points, which are also used as limiting
values (see Fig. 3-24, (p. 3-40)). Up to 20 interpolation points are available to
implement a complex characteristic.
When setting the characteristic the user must remember that only a rising/rising
or falling/falling curve sense is allowed (no peak or vee-shapes). If the setting
differs, the signal SFMON: Invalid scaling IDC will be generated.
. (These two setting parameters
DC,lin
3 Operation
/ I
I
DC,lin DC,nom
1.2
1.1
I
DC,lin20
I
DC,lin1
1
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5 0.6
/ I
I
DC DC,nom
I
DC1
Fig. 3-24: Example of the conversion of 4 to 10 mA input current to 0 to 20 mA monitored current, IDC,lin.
3-40 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
I
DC20
19Z5266A_EN
Page 97

3 Operation P634
IDC,lin / IDC,nom
0.8
Interpolation points
IDC,lin20
IDC,lin4
IDC,lin3
IDC,lin2
IDC,lin1
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 1.1 1.2
IDC1
Enable IDC p.u.
IDC2 IDC3 IDC4 IDC20
IDC / IDC,nom
D5Z52KEC_EN
Fig. 3-25: Example of a characteristic with five interpolation points (characteristic with zero suppression setting of
0.1 I
is shown as a broken line).
DC,nom
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-41
Page 98

P634
3 Operation
MEASI:
Enabled
[ 035 008 ]
MEASI:
IDC 1
[ 037 150 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 1
[037 151 ]
MEASI:
IDC 2
[ 037 152 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 2
[ 037 153 ]
MEASI:
IDC 3
[ 037 154 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 3
[ 037 155 ]
MEASI:
IDC 4
[ 037 156 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 4
[ 037 157 ]
MEASI:
IDC 5
[ 037 158 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 5
[ 037 159 ]
MEASI:
IDC 6
[ 037 160 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 6
[ 037 161 ]
MEASI:
IDC 7
[ 037 162 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 7
[ 037 163 ]
MEASI:
IDC 8
[ 037 164 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 8
[037 165 ]
MEASI:
IDC 9
[ 037 166 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 9
[ 037 167 ]
MEASI:
IDC 10
[ 037 168 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 10
[ 037 169 ]
MEASI:
IDC 11
[ 037 170 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 11
[ 037 171 ]
MEASI:
IDC 12
[ 037 172 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 12
[ 037 173 ]
MEASI:
IDC 13
[ 037 174 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 13
[ 037 175 ]
MEASI:
IDC 14
[ 037 176 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 14
[ 037 177 ]
MEASI:
IDC 15
[ 037 178 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 15
[037 179 ]
MEASI:
IDC 16
[ 037 180 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 16
[ 037 181 ]
MEASI:
IDC 17
[ 037 182 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 17
[ 037 183 ]
MEASI:
IDC 18
[ 037 184 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 18
[ 037 185 ]
MEASI:
IDC 19
[ 037 186 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 19
[ 037 187 ]
MEASI:
IDC 20
[ 037 188 ]
MEASI:
IDC,lin 20
[ 037 189 ]
MEASI:
Enable IDC p.u.
[ 037 190 ]
MEASI:
IDC< open circuit
[ 037 191 ]
Input channel 1(I-1)
Fig. 3-26: Analog direct current input.
Beyond the linearization described above, the user has the option of scaling the
linearized values. Thereby negative values, for example, can be displayed as well
and are available for further processing by protection functions.
SFMON:
Invalid scaling IDC
[ 093 116 ]
MEASI:
Overload 20mA input
[ 040 191 ]
SFMON:
Overload 20 mA input
[ 098 025 ]
MEASI:
Open circ. 20mA inp.
[ 040 192 ]
SFMON:
Open circ. 20mA inp.
[ 098 026 ]
MEASI:
Curr. IDC,lin. p.u.
[ 004 136 ]
MEASI:
Current IDC p.u.
[ 004 135 ]
MEASI:
Current IDC
[ 004 134 ]
S8Z52H2A
3-42 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
Page 99

3 Operation
MEASI:
Scaled val. IDC,lin1
[ 037 192 ]
MEASI:
Scaled val.IDC,lin20
[ 037 193 ]
P634
MEASI:
Curr. IDC,lin. p.u.
[ 004 136 ]
Fig. 3-27: Scaling of the linearized measured value.
3.8.1.1 Zero Suppression
Zero suppression is defined by setting MEASI: Enable IDC p.u. If the direct
current does not exceed the set threshold, the per-unit input current I
the current I
will be displayed as having a value of “0”.
DC,lin
3.8.1.2 Open-Circuit and Overload Monitoring
The P634 is equipped with an open-circuit monitoring function. If current IDC falls
below the set threshold MEASI: IDC< open circuit, the signal MEASI: Open
circ. 20mA inp. is issued.
The input current is monitored in order to protect the 20 mA analog input against
overloading. If it exceeds the set threshold of 24.8 mA, the signal
MEASI: Overload 20mA input is issued.
MEASI:
Scaled value IDC,lin
[ 004 180 ]
DC p.u.
Q9Z5029A
and
3.8.2 Input for Connection of a Resistance Thermometer
This input is designed to connect a PT 100 resistance thermometer. The mapping
curve, R = f(T), of PT 100 resistance thermometers is defined in the IEC 751
standard. If the PT 100 resistance thermometer is connected using the 3-wire
method, then no further calibration is required.
Open-Circuit Monitoring
If there is an open measuring circuit due to a broken wire, the signal
SFMON: PT100 open circuit is issued.
Maximum Temperature Value Since the Last Reset
The result of a temperature measurement cannot only be read out as a direct
measured value (temperature T) or as a normalized value (temperature norm. T),
but also as the maximum value since the last reset (temperature Tmax).
For this the following menu points are available:
MEASI: Temperature Tmax (maximum temperature value)
●
MEASI: Reset Tmax EXT (reset via a binary signal)
●
MEASI: Reset Tmax USER (manual reset)
●
P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653 3-43
Page 100

P634 3 Operation
MEASI:
Enabled
[ 035 008 ]
Measur. input PT100
+
-
C
Fig. 3-28: Temperature measurement with a resistance thermometer
MEASI:
PT100 faulty
[ 040 190 ]
SFMON:
PT100 open circuit
[ 098 024 ]
MEASI:
Temperature
[ 004 133 ]
MEASI:
Temperature p.u.
[ 004 221 ]
MEASI:
Temperature Tmax
[ 004 233 ]
64Z70H3A
3-44 P634/EN M/R-42-A // P634‑311‑653
 Loading...
Loading...