Page 1

MICOM-H
HF-SSB Transceiver
Amateur Mobile/Base Radio
Owner’s Guide
Draft – October 2000
68MB000023
Mobat Communications Ltd. 2000
All rights reserved
Page 2

Table of Contents
Acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . v
Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
General
Options
Accessories
Transmitter
Receiver
Military and Industrial Standards
FCC Information
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .viii
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .x
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xi
Information for Safe, Efficient Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xiii
Exposure to Radio Frequency Energy
Guidelines and Warnings
Restrictions
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .xiv
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiv
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . xiii
Before You Begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
The MICOM-H HF-SSB Radio
Options and Accessories
Transmission
Reception
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Frequency Sources
Power Sources
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
CW Keying Operation
Radio Programming
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide i
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Page 3

Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
The Front Panel
LED Indicators
Radio Display
Icon Indicators
The Rear Panel
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Beeps
Basic Radio Operations
Function Keys
Predetermined Numeric Value Mode
Toggle Mode
Up/Down Scroll Keys
Scanning Wheel
Transmission/Reception Quality Aids
Conventions in this Manual
Procedures
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Display Representation
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Radio Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Basic Radio Procedures
PTT Types
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Bandwidth Filters
Channel Mode
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Channel Mode Options
Frequency Mode
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
VFO Operation
Frequency Mode Options
Storing Frequencies
Scan Mode
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Scan Mode Options
Using the BITE (Built-In Test Equipment)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Locking the Radio
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide ii
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Page 4

Display Brightness
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Programming Mode
Display Language
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Radio Programming. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Programming Channels
Copying Channel Parameters
Erasing a Channel
Transmission Power Level
Channel Frequency
Band Types
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Operating Modes
Automatic Gain Control (AGC)
Bandwidths
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Radio Parameters
Baud Rate
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Data Power
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Microphone Side Tone
Accessory Side Tone
PTT Release Beep
Keyboard Beep
Tone Level
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Alternate Display Time-out
Attenuator
CW Operation
Receive Level
Display Mode
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Setting the Radio Options
Tuner
Accessory Settings
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide iii
Page 5

Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Preventative Maintenance
System Integrity
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Periodic Calibration
Using BITE
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Maintenance Error Messages
Troubleshooting
Service
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
General
Base Station Installation
Mobile Installation
Installation Procedures
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Inspection
Planning the Installation of your Radio
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Mobile Mounting Kit
DC Power Connection
Microphone Clip
Final Connections
External Speaker Installation
Operational Checks
Connectors
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Microphone Connector J1
Antenna Connector J2
Accessory Connector J3
DC Connector J4
Reduction of Vehicular Noise
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
List of Procedures. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . lxiii
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide iv
Page 6

Acronyms
AGC
AME
ARQ
BITE
CW
DSP
DTCXO
FEC
FSK
GND
HF
HSM
LED
LSB
LSM
MCW
Automatic Gain Control
Amplitude Modulation Equivalent
Automatic Repeat Request
Built-In Test Equipment
Continuous Wave
Digital Signal Processing
Digitally Temperature Controlled Crystal Oscillator
Forward Error Correction
Frequency Shift Keying
Ground
High Frequency
High Speed Modem
Light Emitting Diode
Lower Side Band
Low Speed Modem
Modulated Continuous Wave
OCXO
PEP
PLL
PTT
RGC
RSS
RTTY
SINAD
SSB
ULQ
USB
VFO
VSWR
XMIT
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide v
Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator
Peak Envelope Power
Phase Lock Loop
Push To Talk
Receiver Gain Control
Radio Service Software
Radio Telex Teletype
Signal to Signal Noise Distortion Ratio
Single Side Band
Update Link Quality
Upper Side Band
Variation Frequency Offset
Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
Tra nsm it
Page 7

Acronyms
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide vi
Page 8

Technical Specifications
General
The general technical specifications of the MICOM-H are:
Model Number M82AMN0KV5-K
Frequency range Receiver: 100 kHz-30.000 MHz
Tra nsm it :1.800-1.999999 MHz
3.500-3.999999 MHz
7.000-7.300 MHz, 10.100-10.150 MHz
14.000-14.350 MHz, 18.068-18.168 MHz
21.000-21.450 MHz, 24.890-24.990 MHz
28.000-29.700 MHz
Number of channels
Scanning
Frequency stability
Frequency drift (aging)
Synthesizer lock time
Frequency resolution
Audio bandwidths @ -6dB
200; user programmable; simplex or half duplex
5 groups with up to 100 channels per group
0.6 PPM (0.1 PPM optional)
1 PPM per year
10 msec max.
10 Hz
Voice & Data: 350-2100 Hz, 350-2700 Hz,
350-3000 Hz, 350-3300 Hz
CW: 775-1025 Hz, 650-1150 Hz, 500-1300 Hz
Low speed data: 1450 to 1950 Hz
Operating temperature
range
Humidity
Operating voltage
VFO
Current drain @ 13.8 VDC: Receive Transmit
Key down
Dimensions and weight Height Width Depth Weight
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide vii
-30°C to +60°C
95% @ 50°C
13.8 V DC ± 20% Neg. Ground
VFO operation
Squelch Full Audio Voice 2 Tone 1 Tone
1.7A 2.5A 14A 23A 28A
mm/inch mm/inch mm/inch Kg/Lb.
92/3.7 302/11.9 270/10.7 5.7/12.5
Page 9

Technical Specifications
Options
The following operational options can be added to the MICOM-H:
High stability oscillator
Noise Blanker
Remote control
Accessory Stop Scan
RS232 remote control interface
Linear amplifier interface
Phone patch interface
Data/Fax modem interface
MicomNet-internet gateway
Interlink interface
Enables frequency stability of 0.1 PPM.
(Hardware option).
Helps to eliminate noise resulting from motor
interference.
Connection of the radio to a remote PC with radio
controlled software.
Enables stopping and resuming normal scanning
from the accessory connector.
–
–
–
–
–
–
Accessories
24 VDC operation
–
The following accessories can be added to the MICOM-H
CW key and headphones
Phone patch
Interlink (FM-HF repeater)
Automatic Antenna Tuner
Continuous duty kit
AC power supply
Antennas and grounding kit
Data/fax modem
Mobile mounting kit
Desk Microhone
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide viii
Page 10

Technical Specifications
Transmi tter
The MICOM-H transmits signals in accordance witht the following specifications:
Output power
Reduced power levels
Audio bandwidth ripple
Intermodulation
Harmonic emissions
Spurious emissions
Carrier suppression
Undesired sideband
suppression
Audio distortion
1/2 power microphone
sensitivity
Hum & ripple
125W P.E.P. and average
25W, 62W, 100W (RSS programmable)
3 dB
-31 dB/P.E.P (-35 dB/P.E.P Typical*)
-64 dB/P.E.P (-70 dB/P.E.P Typical*)
-64 dB/P.E.P (-70 dB/P.E.P Typical*)
-50 dB/P.E.P
-55 dB/P.E.P
2.5%
25 to 125 mV (RMS)/600 Ohms
-50 dB
Inband noise
Tx/Rx switching time
*. Values noted as “Typical” are valid over 90% or more of the frequency
range.
-60 dB (30 Hz BW)
10 msec
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide ix
Page 11

Technical Specifications
Receiver
The MICOM-H receives signals in accordance witht the following specifications:
Sensitivity (SINAD) SSB
(voice)
1/2 rated power sensitivity
Selectivity
Image rejection
IF rejection
Undesired sideband rejection
Spurious rejection
Cross modulation rejection
Desensitization
Reciprocal mixing
Audio power @ speaker
RGC range
RGC time constants
Voi c e
CW/Data
Squelch
0.5 mV for 10 dB SINAD (0.35 mV Typical)
0.1 - 1.6 MHz reduced performance
1 mV for 2.5W audio @ speaker
-6 dB @ 350 to 2700 Hz
-60 dB @ -1 kHz; +4 kHz
-80 dB
-85 dB
-55 dB @ -1 kHz
-80 dB
-100 dB @ 100 kHz
-100 dB @ 100 kHz
-100 dB @ 100 kHz
5W @ 2.5% distortion
5mV-1V (2 dB change in output level)
Attack time 10 msec
Release time 1500 msec
Attack time 10 msec
Release time 10 msec
Constant SINAD (digital)
*
RIT variable range (Clarifier)
Preselector sections
Maximum antenna input
*. Values noted as “Typical” are valid over 90% or more of the frequency
range.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide x
200 Hz in 10 Hz steps
±
Sub-octave (1.6 MHz to 30 MHz range)
20 kV maximum transient, 100V RMS for 2
minutes
Page 12

Technical Specifications
Military and
Industrial
Standards
FCC Information
The MICOM-H meets the following US military and industrial standard requirement
for adverse environmental conditions (without the need of external shock mounts)
Environmental
Condition
Vibration
Shock
Rain
Dust
Salt Fog
US Military
STD 810C
Method 514.2 Method 514.3 Method 514.4
516.2 516.3 516.4
506.1 506.2 506.3
510.1 510.2 510.3
509.1 509.2 509.3
US Military
STD 810D
US Military
STD 810E
The MICOM-H also meets the EIA-RS152B for shock, vibration and applicable test
procedures, US FCC for channel occupancy, spurious, interference and frequency
tolerance. It is manufactured according to the demanding standards of ISO 9000 and
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility).
The following FCC information is applicable for theMICOM-H:
Emissions
FCC applicable parts of rules
J3E, R3E, H3E, J2A, J2B
15, 18, 90
FCC type acceptance number
With high stability option
ABZ9QCC1635
ABZ9QCC1634
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide xi
Page 13

Technical Specifications
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide xii
Page 14

Information for Safe, Efficient Operation
Exposure to
Radio Frequency
Energy
In August 1996, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) adopted updated
RF energy exposure guidelines for wireless products regulated by the FCC. These
guidelines are consistent with the safety standards previously set by both U.S. and
international standards bodies. The design of your Motorola radio complies with the
FCC guidelines and these standards:
■
American National Standards Institute (C95.1-1992)
■
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements
NCRP-1986)
■
International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection
(ICNRP-1986).
To assure optimal radio performance and to ensure that exposure to RF energy is
within the guidelines in the above standards, install antennas correctly, following
recommended installation procedures.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide xiii
Page 15
Information for Safe, Efficient Operation
Guidelines and
Warnin gs
Restrictions
Symbols
The Warning symbol denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure
!
Warning
!
Important
Note
Because this radio contains a transmitter, federal law prohibits unauthorized, nonlicensed personnel from adjusting or maintaining it. If any operational difficulties
should arise while using this product, report them to authorized service personnel as
soon as possible.
or practice that could result in personal injury, damage to the radio or
loss of programmed information, if not performed correctly.
The Important symbol denotes a procedure or practice to which a
particular attention should be paid.
The Note symbol calls your attention to additional information.
!
Warning
Do not attempt any unauthorized modification to the radio.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide xiv
Page 16

Before You Begin
This manual is designed to acquaint you with the features, care, and installation of
your radio, to better serve your communication needs.
The manual includes general descriptions as well as step-by-step procedures.
Before you begin using the radio, we recommend that you read the following
chapters:
■
Overview
■
Getting Started
■
Operating Instructions
Theoretical explanations are included in Overview, and later sections of this manual
assume familiarity with these functions.
Basic aspects of radio use, for instance keypad functionality, are covered in detail in
Getting Started. Later sections of this manual assume familiarity with such
functions, and do not repeat instructions for common actions.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 1
Page 17

Before You Begin
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 2
Page 18

Overview
Overview
Welcome to the Motorola HF-SSB radio family! Your choice of a MICOM-H radio
means that you have selected the highest of standards in design, quality, and
performance.
The compact sized MICOM-H is an advanced ruggedized Digital Signal Processing
(DSP) HF all-band transceiver intended for very wide area radio communications. It
combines sophisticated voice, data, fax and e-mail solutions with a high signal
quality and reliability, while remaining very simple to operate.
The MICOM-H
HF-SSB Radio
Your radio includes the following features:
■
Scanning wheel
■
Ruggedized mobile/fixed
transceiver
■
High MBTF
■
Va r i abl e b an dw id th fo r op ti ma l
signal processing
■
Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
■
Selectable front-end attenuator
■
Excellent frequency stability
■
Small size, light weight
■
Sub-octave pre-selector
■
RF power indicator
■
Programmable channel scan
■
VFO operation
■
Adaptable internal configuration
options
■
Security access code
■
Multi-language Liquid Crystal
Display (LCD)
■
Built-In Test Equipment (BITE)
■
Enhanced voice quality
■
Selectable power output
■
Va r i abl e n ot ch fi lt er
■
Front panel programming
■
Voice-activated digital squelch
■
Priority and guard channels
■
Automatic IF shift
■
Excellent transmitter and receiver
performance
■
Conforms to MIL-STD 810 and EIA
specifications
■
Meets FCC and EMC standards
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 3
■
Digital noise blanking and clarifier
■
200-channel capacity, simplex or
half-duplex
■
Complies with ISO 9001
requirements
Page 19

Overview
Options and
Accessories
Transmission
You can add the following operational options and/or accessories to your radio:
■
High frequency stability option
■
Linear amplifier interface
■
Data/fax modem interface
■
RSS for PC
■
Phone patch
■
Automatic antenna tuners
■
AC power supply
■
Antennas and grounding
■
CW key and headphones
■
RS232 remote control interface
■
Phone patch interface
■
Interlink interface
■
High (0.1 PPM) frequency stability
■
Interlink
■
Continuous duty data trans. kit
■
1 KW amplifier
■
Data/fax modems
■
24V Operation kit
The maximum output power of the transmitter is 125W PEP (Peak Envelope Power),
with an average transmission duty cycle of 1 to 4, thus enabling even the CW
(Continues Wave) signal to be transmitted at the maximum available power. Output
power can be preprogrammed to one of four possible levels: 25W, 62W, 100W and
125W. Accurate sensors are used to keep the output power within the nominal value.
Reception
The radio includes mismatch protection. If the VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio)
rises to more than 2:1, the transmitter is inhibited in order to avoid any damage and a
relevant message is displayed.
The transmitter is thermally protected. If the transmitter internal temperature
exceeds the maximum permitted temperature, the output power is automatically
reduced to avoid any fault due to excessive heat.
The radio utilizes Digital Signal Processing (DSP) to implement reception functions
such as demodulation, narrow filtering, automatic gain control, noise blanking and
squelch.
The automatic digital noise blanker is activated whenever repetitive noise (e.g.
ignition spikes) is encountered in the received signal. The digital syllabic (speech
identifier) squelch is activated whenever speech is identified, thus opening the audio
path. However, if speech is not received, the audio path is muted, thus preventing
background noise from disturbing the operator.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 4
Page 20

Overview
Frequency Sources
Power Sources
CW Keying
Operation
Two types of frequency sources are available for the MICOM-H radio. The standard
0.6 PPM DTCXO frequency source which assures a frequency stability of better than
±18Hz. For frequencies lower than 10 MHz, it assures a frequency stability of better
than ±6 Hz.
When higher frequency stability is required, the G478 0.1 PPM OCXO frequency
source can be ordered. It will assure a frequency stability of better than ±3 Hz at
30 MHz.
The radio is designed for 13.8 V±20% negative-ground operation and may be
connected to a standard 12 V battery, or with the optional kit to a power supply of
24V±25%.
When the CW key is pressed, the radio transmits a continuous wave (at the full
programmed power) and stops transmission when the key is released.
CW keying operation is enabled by connecting the Morse key between CW (pin #10)
and ground (pin #18) at the accessory connector. If you wish to operate CW keying
with external headphones, use the CW cable supplied with the radio. This will enable
a standard PL55 headphone and standard PL99 Morse key to be connected to the
accessories connector.
Radio Programming
The following radio features can be programmed:
■
Up to 200 simplex/half duplex channels at SSB (J3E), AME (H3E), or Pilot (R3E)
modes of transmission.
■
Up to four levels of output power (up to 125W PEP and average).
■
Five scanning groups of up to 200 channels, each with a guard channel.
Most radio functions can be programmed directly from the front panel of the radio as
described in the
Radio Programming
chapter.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 5
Page 21

Overview
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 6
Page 22
Getting Started
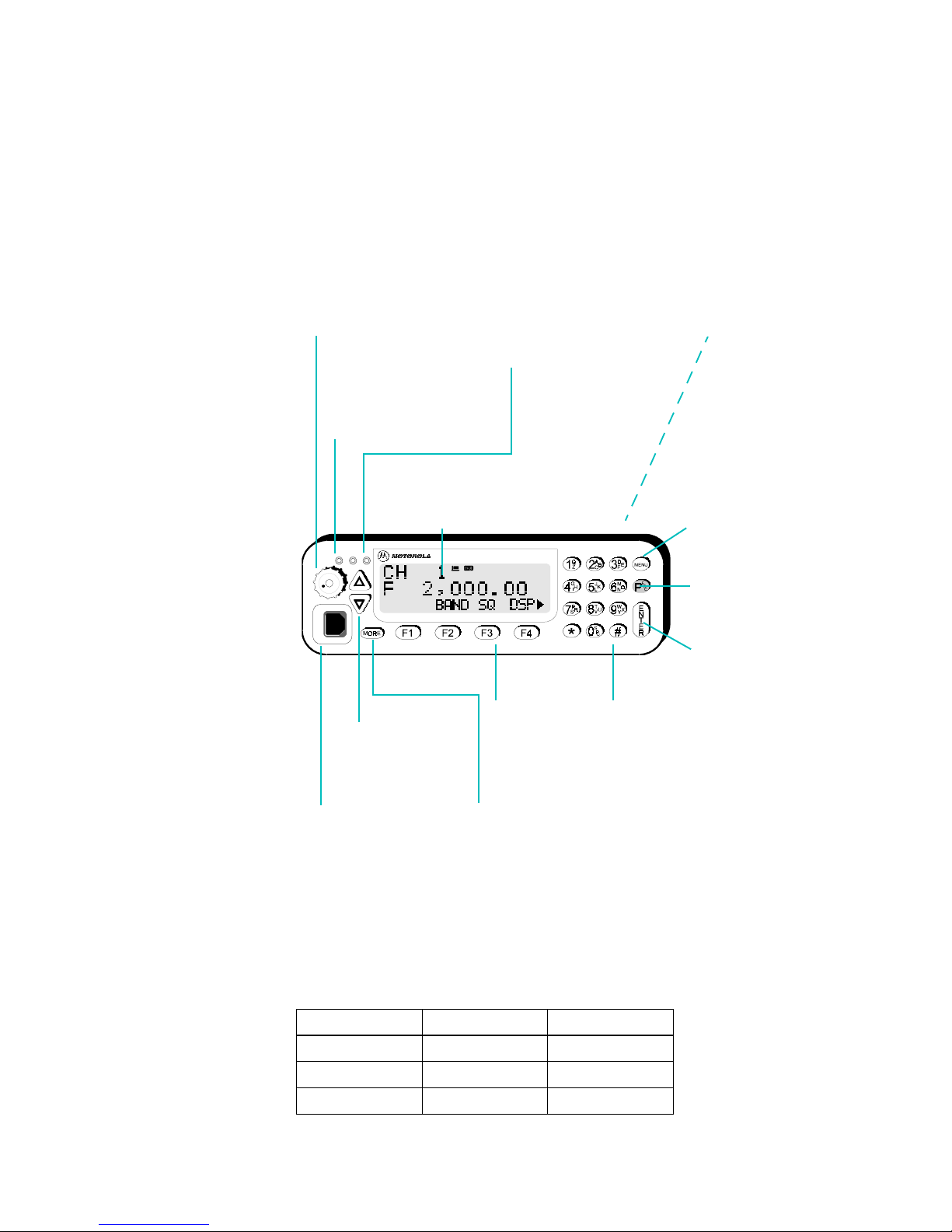
The Front Panel
The MICOM-H includes a 5W external speaker and a scanning wheel, as well as the
following controls:
ON/OFF Volume Knob
Turns radio on and off and
controls the speaker volume.
Keyboard Lock Indicator
Lights up when radio
is controlled from a
remote PC.
Display
Three-line LCD display
showing alphanumeric data,
and icons.
Tx Indicator
Lights up when
radio is transmitting.
External 5W
Speaker
Mode function keys
MENU
Displays the main menu.
ESC
Cancels the last action
and reverts to the
previous screen.
ENTER
Saves the selection
and/or value.
LED Indicators
Keypa d
A set of keys
used to enter data.
Up/Down Keys
Used to scroll
values
Microphone Connector
Connector for a PTT
microphone
Function Keys
Activate different
functions as
displayed above
More Key
Displays additional menu
options when an arrow appears
at the bottom right of the display.
Figure 1: Radio Front Panel
The LEDs, located on the left hand-side of the control head, indicate radio operating
conditions (from left to right):
Color LED Indicates
Yellow Remote control Keyboard lock
Orange (not used)
Red Tx Transmission
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 7
Page 23
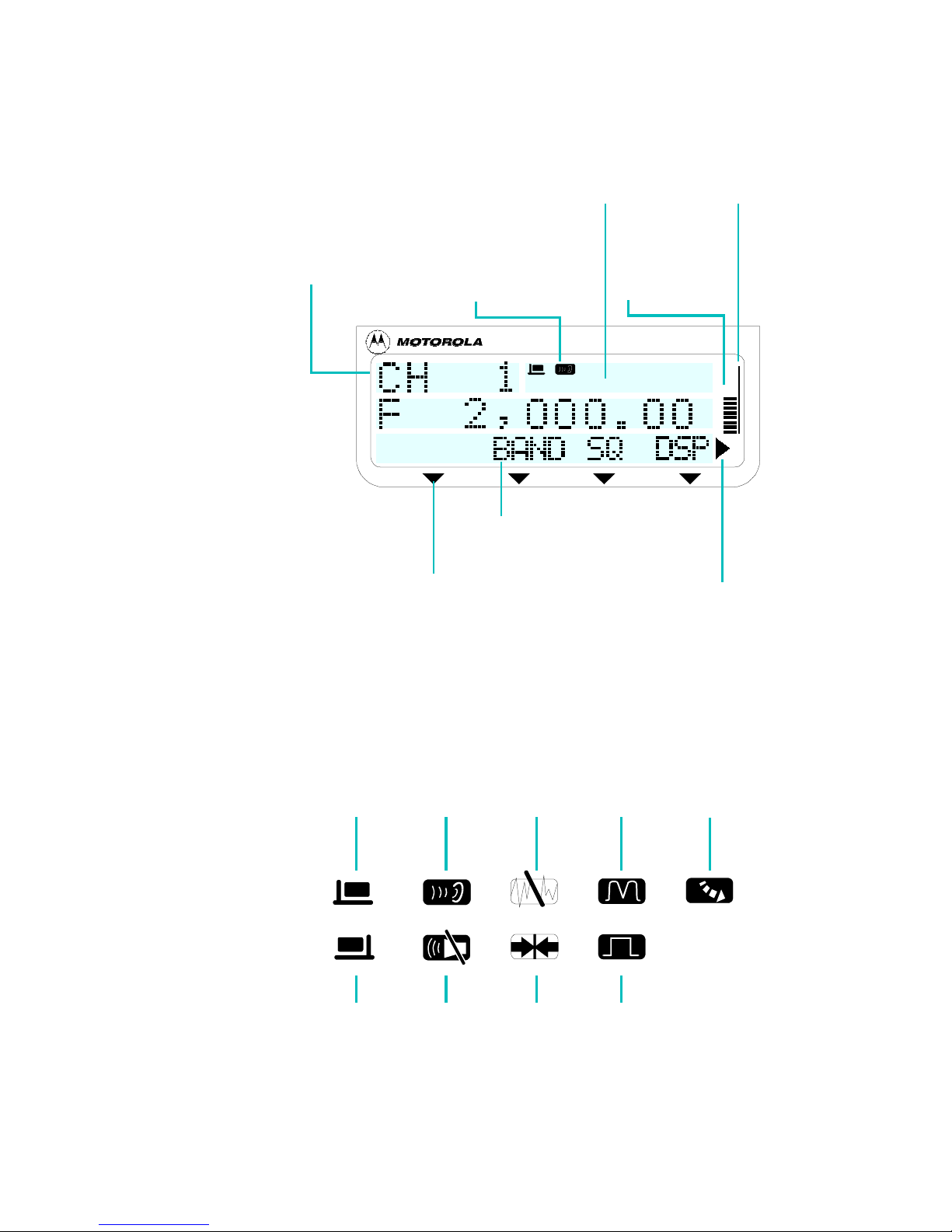
Radio Display
Line 2: Information Field
Provides information on the
current action or mode and
displays various messages.
Getting Started
Tx/Rx Bar
Indicates that the
radio is transmitting
or receiving.
Line 1: Mode/Status
Shows the current mode
or radio status.
Funct ion Key Indicator
These arrows indicate the
available function keys (F1,
F2, F3, or F4), located below
the arrows .
Icon Indicators
Indicate active options
for reception/
transmission.
Line 3: Function Key Names
A list of options available
in the current mode.
The option is selected by
pressing the relevant function
key (F1, F2, F3, F4).
Rx/Tx Level
Displays the
output/received
power level.
More Indicator
Indicates that the menu
includes additional
functions. Press the MORE
key to display the next four
function keys.
Icon Indicators
There are nine icons that can appear in the upper right area of the display.
The icons appear in the following order:
Upper Side
Band
Lower Side
Band
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 8
Squelch
active
Monitoring
off
Noise Blanker
active
Clarifier
in use
Notch Filter
active
Non-standard
Bandwidth
Fil ter
Automatic Gain
Control –
Fast or Off
Page 24
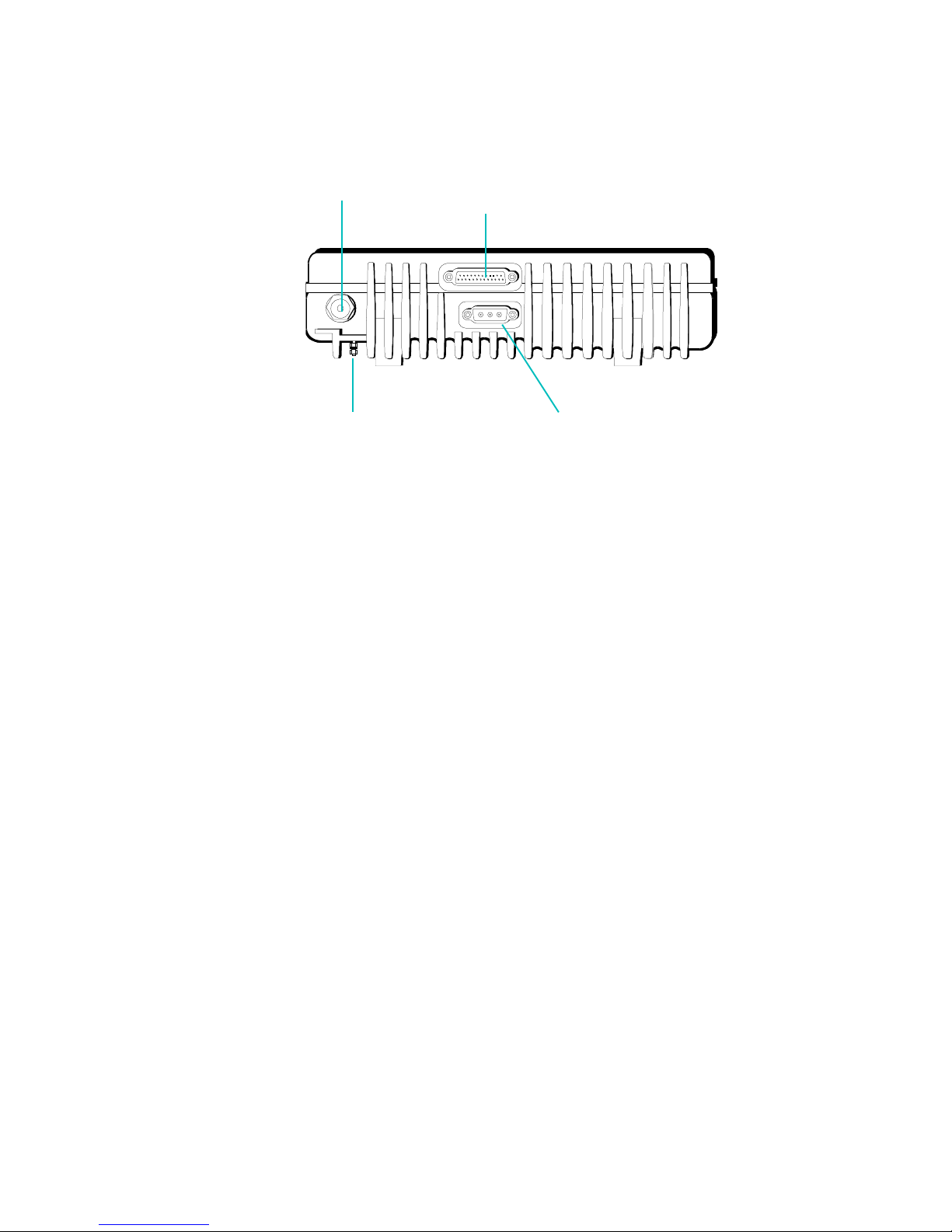
Getting Started
The Rear Panel
Beeps
The rear panel of the MICOM-H includes the following connectors:
Accessory Connector (J3)
Antenna
Socket
Ground Screw
Used to ground the radio
to the vehicle in a mobile
installation.
25-pin connector for external
accessories such as PC’s, modems,
Morse key devices, etc.
DC Connector (J4)
Power input connector.
The MICOM-H can be set to beep when the keys on the front panel are pressed,
indicating that the key press has been registered. A different beep can be heard when
the PTT button of the remote radio is released, indicating that the other party to the
call has completed transmission and that you can now transmit.
You can enable or disable these beeps, and can set their volume (PTBP and KBBP
functions in Radio Programming).
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 9
Page 25

Basic Radio
Operations
Getting Started
Function Keys
Predetermined
Numeric Value Mode
Tog g le M od e
The function keys (F1, F2, F3, F4) are used to select a wide variety of options, which
depend on the current radio mode. An acronym or abbreviation denoting the current
function is displayed in the bottom line of the display, above the relevant key.
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
F1 F2 F3 F4
If a certain function key is not available (for instance if the radio is locked), the space
above the key will remain blank, and the key will not function.
When there is a parameter for which there are
predetermined values, F1 enters the lowest possible value
(minimum or OFF); F4 enters the highest possible value and
PROG
ADT - 3 SEC
1 10
F2 and F3 increment or decrement the value.
You can not use the keypad to enter the value for this type of parameter.
When the function being set is a yes/no toggle, one function
key will be
YES
and another NO.
PROG
TUNER - NO
YES NO
Up/Down Scroll Keys
Scanning Wheel
The UP/
DOWN
scroll keys are used to scroll between values that are already
programmed into the radio.
For example, in Channel mode you can view the programmed channels:
A single keypress on the
UP/DOWN
scroll keys displays the next or previous channel
respectively; pressing either key continuously browses among the channels, four
channels per second.
In Frequency mode the
When programming, you can use the
UP/DOWN
scroll keys are used to change the frequency.
UP/DOWN
scroll keys to scroll between the
different programmable parameters.
The scanning wheel is used to scan the available frequencies. It can also be used
instead of the
UP/DOWN
scroll keys to scroll between values that are already
programmed into the radio.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 10
Page 26

Getting Started
Transmission/
Reception
Quality Aids
The MICOM-H offers you a variety of aids which can be used in different
circumstances to improve the quality of transmission/reception. When these options
are activated, the appropriate icon appears in the icon display.
Squelch
When Squelch is activated, the radio switches the speaker on only when it identifies
speech, silencing reception noise at all other times.
Noise Blanker
Reduces repetitive cyclic noise such as motor interference when the radio is working
in a vehicle.
Clarifier
When there is a deviation in the frequency of the broadcasting radio, the receive
frequency can be modified using the clarifier.
Notch Filter
When an undesired continuous tone is evident in reception, the Notch Filter can
eliminate that specific tone, retaining all other tones.
Non-Standard Bandwidth Filter
Adapts the reception/transmission bandwidth in accordance with the type of signal
received/transmitted.
Automatic Gain Control Fast/Off
The Fast AGC function can be used for receiving certain types of data in order to
prevent data distortion. When receiving a voice message, the AGC should be set to
slow (icon not displayed).
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 11
Page 27

Conventions in
this Manual
Getting Started
Procedures
Display
Representation
Procedures are step-by-step instructions that tell you how to operate specific aspects
of the radio. Procedures in this manual have a bold-face heading beginning with the
To...
word “
”.
Steps are accompanied by a representation of the radio’s display, to the right of the
step. These representations always reflect the state of the radio display
after
the
relevant step has been made.
When front panel keys are to be pressed to execute a step, the keys are highlighted in
this manner:
on the screen, is highlighted, in this manner:
ENTER
. When function keys are used, the function itself, as displayed
CHAN
(F1).
When you can perform a step in more than one way, you will see the word “or” on its
own line, and then an alternate method of performing the step.
When a procedure begins with a series of steps common to all procedures in that
section, the series of steps is represented in an abbreviated manner, with a > sign
indicating the next step.
For instance, the following string represents five key presses:
>
MENU
The display is presented in schematic form. The icons are
enlarged in order to facilitate easy identification, so that they
do not represent the actual position of the icon on the radio
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
CHAN
(F1).
CH 1
BW 2.7
2.1 2.7 3.0 3.3
display.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 12
Page 28

Radio Operation
This chapter provides instructions on operation of the MICOM-H, and includes
subjects such as turning the radio on, transmitting and receiving, channel mode,
frequency mode, scan mode, built in test equipment, radio locking, display language
and display brightness.
Basic Radio
Procedures
To turn the radio on:
Tur n t he ON/
OFF/VOLUME
knob clockwise until
it clicks.
The words SELF TEST are displayed for about three seconds.
When the self-test procedure is completed, the display enters
the last operating mode used: CH, SCAN, or FREQ.
If the self-test procedure fails, the first line indicates the
error number. The second line blinks, with a short
description of the error (see page 48 for a list of error
messages).
Use the
UP/DOWN
keys to scroll to additional messages, if any.
SELF TEST
CH 1
F 2,000.00
BAND SQ DSP
ERR01
DSP FAIL
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 13
Page 29

Radio Operation
To Tr an sm it :
Before transmitting, ensure that the RF output of the radio is
connected to a tuned antenna or to a dummy load.
Note
To transmit, press and hold down the Push-To-Talk (PTT) button on the side of the
handset and speak slowly and clearly. This method of transmission is used regardless
of the type of transmission (voice, data or Morse), and regardless of whether you are
in Channel, Frequency or Scan mode.
The Tx LED will remain lit until the PTT button is released to indicate that you are
transmitting.
When you press the PTT button, the RF power and Tx bar are displayed.
Tx bar
max
forward
power
PTT Types
reverse
power
min
To R ece iv e:
The default radio mode is Receive mode.
You can program the radio to display an Rx bar similar to the Tx bar, see “Receive
Level” (page 44).
The radio can receive and transmit four different types of PTT:
Data PTT, Voice PTT, CW PTT or MIC PTT.
The radio automatically identifies the transmitted PTT type according to the type of
device connected to the accessory port, and identifies MIC if a microphone is
connected to the front panel.
When using CW PTT, the squelch should be set to OFF.
Note
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 14
Page 30

Radio Operation
Bandwidth Filters
Unless a particular filter is set for the current channel, the radio retains the
previously used filter. When a new type of call is received or sent, the bandwidth filter
changes automatically, depending on the PTT source (voice, data or CW), and the
programmed bandwidth for the channel being used.
Bandwidth set to: Filter changes after:
LSM (data modem) first data PTT
2.1 K (voice + data) microphone or voice PTT
2.7 K (voice + data) microphone or voice PTT
3.0 K (voice + data) microphone or voice PTT
3.3 K (voice + data) microphone or voice PTT
CW (Morse) first CW PTT
When the bandwidth filter is set to CW, the following CW bandwidths can be set in
the radio’s Programming mode, see “CW Operation” (page 44):
■
0.25 K
■
0.5 K
■
0.8 K
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 15
Page 31

Radio Operation
Channel Mode
Channel mode is used to select a channel which is already programmed in the radio,
in order to transmit/receive calls on that channel.
You can also operate a variety of functions and options to facilitate good
transmission and reception.
To choose a channel:
In order to choose the priority channel, you must be in Channel mode. To enter
Note
channel mode, press
MENU
>
To access the priority channel preprogrammed by the RSS, press
(F1) and confirm by pressing
CHAN
ESC
ENTER
.
momentarily.
1.
If you are not in Channel mode, press
the menu screen, and press
CHAN
(F1).
The last active channel number is displayed, blinking.
2.
If you wish to use the displayed channel, press
MENU
to display
ENTER
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
CH 1
.
OR
Select a channel by pressing the
UP/DOWN
keys unt il you
CH 2
reach the required channel, or use the keypad to enter the
channel number.
BACK CLR
The channel number blinks, indicating that the selection has not yet been
confirmed.
If you enter a channel that is not programmed, a “NOT PROG”
message appears. To program a new channel, see
Note
3.
When the desired channel is displayed, press
“Programming Channels” (page 32), or use the RSS software.
to confirm your choice.
ENTER
To transmit in Channel mode:
1.
If you are not in Channel mode, press
the menu screen, and press
2.
Choose a channel (see above).
3.
To initiate transmission, press the PTT button.
CHAN
(F1).
MENU
to display
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 16
Page 32

Radio Operation
Channel Mode
Options
In Channel mode, you can operate functions and options to eliminate noise and
assist reception and/or transmission. The icon display reflects the options selected.
The change of channel options is temporary. When you next change the
currently used channel, all current parameters will be lost.
Note
(F1) enables you to view and listen to the channel
TXM
transmit frequency (visible for duplex and Tx only channels).
(F2) toggles between upper side band (USB) and
BAND
lower side band (LSB).
(F3) toggles the squelch
SQ
(on/off).
(F4) accesses the Digital Signal Processing menu,
DSP
which includes:
•
CLAR
(F1) clarifier
(off/less/more)
* not available for Tx Only channels
•
(F2) notch filter
NF
(off/less/more)
*
not available for CW or Tx Only channels
CH 1
BAND LSB
TXM BAND SQ DSP
CH 1
SQUELCH ON
TXM BAND SQ DSP
CH 1
DSP PARAM
CLAR NF CLIP NB
CH 1
CLAR +100
OFF
CH 1
NF –– ––
OFF
•
(F3) clipper
CLIP
(on/off)
•
(F4) noise blanker
NB
(on/off)
*
optional, to be purchased separately
•
(MORE, F2) attenuator
ATT N
(on/off).
(MORE, F1) power level selection
PWR
(low, med, high or max).
(MORE, F2) operation mode selection
MODE
(SSB, AME or PLT).
(MORE, F3) automatic gain control
AGC
(fast/slow/off).
(MORE, F4) bandwidth selection
BW
(2.1 K, 2.7 K, 3.0 K, 3.3 K, LSM or CW;
CW includes bandwidths 0.25 K, 0.5 K and 0.8 K,
see “CW Operation” (page 44)).
(MORE, MORE, F1) displays the reception level
RCLV
when F1 is pressed.
*
If the reception is programmed as OFF, this option does
not appear, see “Receive Level” (page 44)
.
CH 1
–
CLIP
OFF
CLAR NF CLIP NB
CH 1
–
NB
CLAR NF CLIP NB
CH 1
ATTEN – OF F
CH 1
POWER LOW
LOW MED HIGH MAX
CH 1
MODE SSB
SSB AME PLT
CH 1
AGC FAST
PWR MODE AGC B W
CH 1
BW 3.3
2.1 2.7 3.0 3.3
CH 1
F 10,000.00
RCLV
ON
ATTN
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 17
Page 33

Radio Operation
Frequency Mode
Frequency mode is used to receive and transmit on a specific frequency. You can
select the frequency type, change the frequency being used, and operate a variety of
functions and options to facilitate good transmission and reception. You can also
store the frequency in a channel of your choice.
– Frequency mode is accessible only if the radio is not locked.
key on the keypad as a
*
Notes
– When setting a new frequency, use the
decimal point.
There are four frequency types:
■
SMPX (Simplex Frequency)
– the same frequency is used for transmission and
reception. The frequency can not be zero.
■
DPLX (Duplex Frequency)
– transmits on one frequency and receives on a
different frequency. The frequencies can not be zero.
■
RXO (Receiving Only Frequency)
■
TXO (Transmitting Only Frequency)
– defines a frequency for reception only.
– defines a frequency for transmission only.
The available frequency ranges are:
Recept ion
: 100 kHz-30.000 MHz
Tr a n s m i s i o n
: 1.800-1.999999 MHz
3.500-3.999999 MHz
7.000-7.300 MHz, 10.100-10.150 MHz
14.000-14.350 MHz, 18.068-18.168 MHz
21.000-21.450 MHz, 24.890-24.990 MHz
28.000-29.700 MHz
To en te r f re qu en cy m od e:
1.
Press
2.
Press
the frequency type is displayed in the top line.
to display the Menu screen.
MENU
(F2). The last active frequency blinks, and
FREQ
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
SMPX
F 10,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
The letter preceding the frequency in the second line of the display indicates
whether the frequency is Transmission (T), Reception (R) or both transmission
and reception (F).
3.
If you wish to use the displayed frequency and frequency type, press
ENTER
OR
.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 18
Change the frequency type and the frequency as required (see “To change the
current frequency/frequencies” (page 19)).
Page 34

To change the current frequency/frequencies:
1.
If you are not in frequency mode, press
the menu screen, and press
FREQ
(F2).
MENU
to access
The last active frequency blinks, and the frequency type
is displayed in the top line.
OR
If you are already in frequency mode, press
MORE
the T/R function appears above the F1 function key, and
press
T/R
(F1).
until
Radio Operation
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
SMPX
F 10,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
FREQ
R 15,000.00
T/R BAND SQ DSP
The current frequency type is displayed in the top line,
and the used frequencies are displayed.
2.
If necessary, change the frequency type by pressing the
DPLX
R 15,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
relevant function key:
SMPX
(F1),
DPLX
(F2),
RXO
(F3) or
TXO
(F4).
Different frequency types may have default frequency setting which
will appear automatically when that frequency type is selected.
Note
3.
If you are using SMPX, RXO or TXO frequency type, and you wish to use the
displayed frequency, press
OR
use the scanning wheel, keypad or UP/
ENTER
The frequency number blinks, indicating that the
selection has not yet been confirmed.
ENTER
Press
4.
If you are using DPLX frequency type, the frequency
to confirm your choice.
displayed first is the Rx frequency. If you want to use the
displayed frequency, press
OR
use the scanning wheel, keypad or UP/
ENTER
The frequency number blinks, indicating that the
selection has not yet been confirmed
Press
ENTER
to confirm your choice.
.
keys to enter a new frequency.
DOWN
SMPX
F 12,345.67
DPLX
R 15,000.00
.
keys to enter a new frequency.
DOWN
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
DPLX
R 3,568.20
BACK C LR
BACK C LR
5.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 19
After confirm ation of the Rx frequency, the display blinks
with the Tx frequency. If you want to use the displayed Tx
frequency, press
OR
use the scanning wheel, keypad or UP/
ENTER
.
keys to enter a new frequency.
DOWN
The frequency number blinks, indicating that the
selection has not yet been confirmed.
Press
Press
ENTER
ENTER
to confirm your choice.
to confirm the frequency type and the
frequencies you have set.
DPLX
T 14,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
DPLX
T 21,468.13
BACK C LR
FREQ
R 30,000.00
T/R BAND SQ DSP
Page 35

Radio Operation
VFO Operation
VFO (Variation Frequency Offset) is available in Simplex mode, and enables you to
operate simultaneously on two different channels (A and B).
Using the A/B function, you can “freeze” the frequency of channel A, switch to
channel B and return to channel A again.
Using the A=B option, you can copy the frequency in the current channel to the
alternate channel.
1.
If you are not in frequency mode, press
the menu screen, and press
FREQ
(F2).
The last active frequency blinks, and the frequency type
is displayed in the top line.
MENU
to access
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
SMPX
F 10,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
OR
If you are already in frequency mode, press
the T/R function appears above the F1 function key, and
press
T/R
(F1).
The current frequency type is displayed in the top line,
and the used frequencies are displayed.
2.
If necessary, change the frequency type to Simplex
by pressing
SMPX
(F1).
MORE
until
FREQ
R 15,000.00
T/R BAND SQ DSP
DPLX
R 15,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
3.
If you wish to use the displayed frequency, press
OR
use the scanning wheel, keypad or UP/
DOWN
enter a new frequency.
ENTER
keys to
.
SMPX
F 12,345.67
The frequency number blinks, indicating that the
selection has not yet been confirmed.
When the desired frequency is displayed,
press
ENTER
4.
Press
MORE
above the F1 and F2 function keys.
Press
A/B
Press
A=B
channel to the alternate channel.
Press
<--
to confirm your choice.
until the A/B and A=B functions appear
(F1) to alternate between the two channels.
(F2) to copy the frequency of the current
(F3) and
(F4) to move the cursor backwards
-->
FRQ-A
F 7,000.00
T/R BAND SQ DSP
FRQ-A
F 7,000.00
A/B A=B
and forwards.
When these arrows are used in conjunction with the scaning wheel or the
scroll keys, the frequency scrolls according to the location of the cursor,
DOWN
enabling you to change the frequency with greater ease.
For instance, if the frequency is 7,500.54 and the cursor is
at the hundreds location (7,_00.54), pressing the scaning
wheel or the
UP/DOWN
scroll keys will scroll the
FREQ
R 7,_00.54
A/B A=B
hundreds values to 7,400.54; 7,600.54; 7,700.54 and so on.
BACK C LR
UP
/
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 20
Page 36

Radio Operation
Frequency Mode
Options
In Frequency mode, you can operate functions and options to eliminate noise and
assist reception and/or transmission. The icon display reflects the options selected.
(F1) sets the transmit and receive frequencies and
T/R
frequency type.
(F2) toggles between upper side band (USB) and
BAND
lower side band (LSB).
(F3) toggles the squelch
SQ
(on/off).
(F4) accesses the Digital Signal Processing menu,
DSP
which includes:
•
CLAR
(F1) clarifier
(off/less/more)
*
not available for Tx Only channels
•
(F2) notch filter
NF
(off/less/more)
*
not available for CW or Tx Only channels
•
(F3) clipper
CLIP
(on/off)
•
(F4) noise blanker
NB
(on/off)
*
optional, to be purchased separately
FREQ
R 15,000.00
T/R BAND SQ DSP
FREQ
BAND LSB
T/R BAND SQ DSP
FREQ
SQUELCH ON
TXM BAND SQ DSP
FREQ
DSP PARAM
CLAR NF CLIP NB
FREQ
CLAR +100
OFF
FREQ
NF –– ––
OFF
FREQ
–
CLIP
ON
CLAR NF CLIP NB
FREQ
–
NB
CLAR NF CLIP NB
ON
•
(MORE, F2) attenuator
ATT N
(on/off).
(MORE, F1) power level selection
PWR
(low, med, high or max).
(MORE, F2) operation mode selection
MODE
(SSB, AME or PLT).
(MORE, F3) automatic gain control
AGC
(fast/slow/off).
BW (MORE, F4) bandwidth selection
(2.1 K, 2.7 K, 3.0 K, 3.3 K, LSM or CW;
CW includes bandwidths 0.25 K, 0.5 K and 0.8 K,
see “CW Operation” (page 44)).
(MORE, MORE, F1) displays the reception level
RCLV
when F1 is pressed.
*If the reception is programmed as
not appear,
STOR
see “Receive Level” (page 44).
(MORE, MORE, F2) stores the frequency
, this option does
OFF
parameters in the selected channel.
FREQ
ATTEN – OF F
ATTN
FREQ
POWER HIGH
LOW MED HIGH MAX
FREQ
MODE PILOT
SSB AME PLT
FREQ
AGC FAST
PWR MODE AGC B W
FREQ
BW 3.0
2.1 2.7 3.0 3.3
FREQ
F 10,000.00
RCLV STOR
FREQ
R 15,000
RCLV STOR
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 21
Page 37

Radio Operation
Storing Frequencies
You can store specific frequencies and frequency parameters in channels which you
have programmed (see “Programming Channels” (page 32)).
To store a frequency in a channel:
1.
If you are not in Frequency mode, press
MENU
to display
MENU
the Menu screen.
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
2.
Press
The last active frequency blinks, and the frequency type
is displayed in the top line.
3.
If you wish to use the displayed frequency and frequency type, press
the Frequency type is Duplex, press
FREQ
(F2).
ENTER
SMPX
F 10,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
ENTER
. If
twice to accept both transmission
and reception frequencies.
OR
Change the frequency type and the frequency as required (see “To change the
current frequency/frequencies” (page 19)).
4.
If necessary, set other parameters, using the
key and pressing the
MORE
required function keys (see “Frequency Mode Options” (page 21)).
5.
Press
6.
Select a channel using the scanning wheel, keypad or
UP/DOWN
use the keypad to enter the channel number.
twice, and press
MORE
STOR
(F2).
keys until you reach the required channel, or
FREQ
R 15,000.00
RCLV STOR
FREQ
STORE CH 5
BACK C LR
7.
When the desired channel is displayed, press
confirm your choice.
The frequency parameters are stored in the selected
channel.
ENTER
to
FREQ
STORING
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 22
Page 38

Radio Operation
Scan Mode
In Scan mode, the radio scans the programmed scan channels. Up to five scan groups
(A to E) can be created via the RSS, each containing up to 200 channels. When a
guard channel is selected, it is monitored after every other scanned channel.
To use scan mode:
1.
Press
2.
Press
The last active group blinks (A).
to display the menu screen.
MENU
(F3).
SCAN
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
SCAN
GROUP A
BCDE
If there are no defined groups, the message “NO GROUPS”
appears in the display.
Note
3.
If you want to use the currently displayed scan group, press
ENTER
OR
Press the function key beneath the group you want to choose and press
ENTER
to
confirm your choice.
1.
In scan mode, one of the five groups is always selected, and
the other four groups are displayed over the function keys.
Notes
2.
If the selected group is not programmed, the message
“GRP X EMPTY” appears in the display (X being the
selected group).
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 23
Page 39

Radio Operation
Scan Mode Options
In Scan mode various parameters and options can be set, using the function keys.
The change of options is temporary. When you resume
scanning, all changed parameters will be lost.
Note
To select scan mode options:
(F1) stops scanning.
STOP
(F2) decreases the scan speed.
SLOW
(F3) increases the scan speed.
FAST
The scan speed can be: 1 to 5 seconds, 1 second per
step; or 150 to 950 milliseconds, 50 milliseconds
Note
GRP
per step.
(F4) enables selection of a scan group.
STOP
GROUP A 59
SCAN BAND SQ GRP
SCAN
RATE 4 sec
STOP SLOW FAST GRP
SCAN
RATE 900 ms
STOP SLOW FAST GRP
SCAN
GROUP A
BCDE
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 24
Page 40

When scanning has been stopped, you can use the following options:
(F1) activates scanning.
SCAN
(F2) toggles between upper side band (USB) and
BAND
lower side band (LSB).
(F3) toggles the squelch
SQ
(on/off).
(F4) accesses the Digital Signal Processing menu,
DSP
which includes:
•
CLAR
(F1) clarifier
(off/less/more)
*
not available for Tx Only channels
•
(F2) notch filter
NF
(off/less/more)
*
not available for CW or Tx Only channels
SCAN
GROUP A 4
STOP SLOW FAST GRP
STOP
BAND LSB
SCAN BAND SQ DSP
STOP
SQUELCH ON
SCAN BAND SQ DSP
STOP
DSP PARAM
CLAR NF CLIP NB
STOP
CLAR +100
OFF
STOP
NF –– ––
OFF
Radio Operation
•
(F3) clipper
CLIP
(on/off)
•
(F4) noise blanker
NB
(on/off)
*
optional, to be purchased separately
•
(MORE, F2) attenuator
ATT N
(on/off)
(MORE, F1) power level selection
PWR
(low, med, high or max)
(MORE, F2) operation mode selection
MODE
(SSB, AME or PLT)
(MORE, F3) automatic gain control
AGC
(fast/slow/off)
(MORE, F4) bandwidth selection
BW
(2.1 K, 2.7 K, 3.0 K, 3.3 K, LSM or CW;
CW includes bandwidths 0.25 K, 0.5 K and 0.8 K,
see “CW Operation” (page 44)
).
STOP
–
CLIP
ON
CLAR NF CLIP NB
STOP
–
NB
CLAR NF CLIP NB
STOP
ATTEN – OF F
STOP
POWER HIGH
LOW MED HIGH MAX
STOP
MODE PLT
SSB AME PLT
STOP
AGC FAST
PWR MODE AGC B W
STOP
BW 3.3
2.1 2.7 3.0 3.3
ON
ATTN
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 25
Page 41

Radio Operation
Using the BITE
(Built-In Test
Equipment)
BITE is a testing tool used for radio maintenance and troubleshooting.
To ru n B IT E:
1.
Press
2.
Press
In BITE mode, you can run the following tests:
•
FULL
•
CHAN
•
3.
(F3) low RF; tests the low RF path.
L.RF
While BITE is in progress, the message “IN TEST...” is
displayed. The number of periods indicates the
to display the menu screen.
MENU
(F4).
BIT
(F1) runs a full test of the hardware device
(F2) tests the device on the current channel frequencies
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
BITE
FULL CHAN L.RF
BITE
IN TEST...
progress of the test.
4.
If the test passes successfully, the name of the test and
the word PASS are displayed.
5.
If BITE detects a malfunction, the error number is
displayed in the first line of the display and a short
description of the error appears in the second line.
BITE
–
L.RF
FULL CHAN L.RF
ERR23
PRESELECTOR
EXIT
See page 48.
PASS
6.
Press the UP/
7.
Press
scroll keys to see if there are additional error messages.
DOWN
(F1) to exit Error mode.
EXIT
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 26
Page 42

Radio Operation
Locking the Radio
Lock mode enables you to lock the radio using a password, so that programming and
frequency modes are not accessible.
The lock password is a number of up to six digits. The default factory-defined
password is 123456. See “To change the password” (page 28) for details on defining a
new password.
If you enter the wrong password, the error message “WRONG PSW!” is
displayed.
Note
To l oc k t he ra di o:
1.
Press
2.
Press
3.
Press
4.
Enter the password to lock the radio.
5.
Press
to display the menu screen.
MENU
to scroll to the second menu screen.
MORE
(F1).
LOCK
(F1) or press the
O.K.
ENTER
key to confirm.
MENU
CHAN FREQ SCAN BIT
MENU
LOCK PROG PSW DIM
LOCK
:
PSW
LOCK
:
PSW
******
O.K. CLR
LOCK
LOCKED
To u nl ock th e ra di o:
1.
Press
to display the menu screen.
MENU
When the radio is locked, not all functions are available. For instance,
the F2 key, which is usually used to access
Note
2.
Press
3.
Press
4.
Enter the password number to unlock the radio.
5.
Press
to scroll to the second menu screen.
MORE
(F1).
OPEN
(F1) or press the
O.K.
ENTER
key to confirm.
MENU
CHAN SCAN BIT
, is blank.
FREQ
MENU
OPEN PSW DIM
UNLCK
:
PSW
UNLCK
:
PSW
******
O.K. CLR
UNLCK
UNLOCKED
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 27
Page 43

Radio Operation
To c ha nge th e pa ss wo rd :
For security reasons, you may want to change your password, used to lock the radio.
1.
Press
2.
Press
3.
Press
4.
Enter the old password, using the keypad.
to display the menu screen.
MENU
to scroll to the second menu screen.
MORE
(F3).
PSW
MENU
CHAN FR EQ SCAN BIT
MENU
LOCK PROG PSW DIM
PSW
:
OLD
PSW
:
OLD
******
O.K. CLR
– If you have not yet set a password, the radio has a factory-defined
password which is 123456.
Notes
– When you enter the correct password, you are prompted to enter
your new password.
5.
Enter the new password, using the keypad.
6.
Press
ENTER
to confirm.
PSW
:
NEW
******
O.K. CLR
PSW
PSW SAVED
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 28
Page 44

Radio Operation
Display
Brightness
The DIM function can control the brightness of the display. There are four levels of
brightness, ranging from 0 (dimmest) to 3 (brightest).
You can only change the display brightness if the display is
Note
programmed to
“Display Mode” (page 45)), the display is normally turned off, and
. If the display is programmed as
DIM
ALT
(see
automatically turns on at a predetermined level when the radio
detects any type of activity (scanning wheel, keypad, PTT, incoming
call, etc.).
To change the display brightness level:
1.
Press
2.
Press
3.
Press
brightness level.
to display the menu screen.
MENU
to scroll to the second menu screen.
MORE
(F4) repeatedly until you reach the desired
DIM
MENU
CHAN FR EQ SCAN BIT
MENU
LOCK PROG PSW DIM
MENU
DIM LEVEL 3
LOCK PROG PSW DIM
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 29
Page 45

Radio Operation
Programming
Mode
Display Language
Most programmable parameters are accessible through programming mode.
In programming mode you can set radio programmable parameters (see “Radio
Programming” (page 31)) and the display language.
The radio display can be in the following languages:
■
English
■
French
■
Spanish
To change the radio language:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Press
Press
Press
Press
to display the menu screen.
MENU
to scroll to the second menu screen.
MORE
(F2) to enter Program mode.
PROG
(F3) to display the Language screen.
LANG
MENU
CHAN FR EQ SCAN BIT
MENU
LOCK PROG PSW DIM
PROG
RAD LANG
LANG
ENGLISH
FRNC SPAN
5.
6.
Press
Press
Press
Press
(F1) for English.
ENG
(F2) for French.
FRNC
(F3) for Spanish.
SPAN
ENTER
to confirm.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 30
Page 46

Radio Programming
The MICOM-H is already configured for use at the time of purchase. However, you
may wish to change the configuration to suit your own needs or to reflect changes in
the environment or networks. The radio can be programmed through the front panel
(if the radio is not locked), or using the appropriate RSS (Radio Service Software).
If the message “NOT PROGRAM” is displayed after the self test, you cannot
!
Important
The following sections relate to programming of radio parameters using the front
panel.
After locating the required radio parameter in the programming menu, you can
change it by pressing the function key under the parameter name
OR
enter programming mode, and the radio must be programmed through the
RSS.
you can press the UP/
DOWN
keys to scroll through the parameters.
To enter Radio Programming mode:
1.
Press
2.
Press
3.
Press
4.
Press
In this menu, you can program:
■
channels
■
radio parameters
■
radio options
to display the menu screen.
MENU
to scroll to the second menu screen.
MORE
(F2) to enter Program mode.
PROG
(F1) to enter Radio Programming mode.
RAD
MENU
CHAN FR EQ BIT
MENU
LOCK PROG PSW DIM
PROG
RAD LANG
RADIO
PROGRAMMING
CHAN PRMT OPTS
The following sections explain the programming procedures in detail.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 31
Page 47

Radio Programming
Programming
Channels
When programming channels, you can use the following options:
■
GET – Retrieve preprogrammed channel parameters
■
STOR – Store channel parameters
■
ERAS – Erase programmed channel
■
PWR – Tx power level
■
FREQ – Frequency
■
BAND – Band type
■
MODE – Mode of operation
■
AGC – Automatic Gain Control
■
BW – Bandwidth
The use of each option is explained in the following sections.
When you enter Channel programming, the channel parameters have the following
default values:
■
Rx Frequency – 15,000.00 kHz
■
Tx Frequency – 15,000.00 kHz
■
Band – USB
■
Bandwidth – 2.7
■
Tx Power – Max
■
AGC Type – Slow
■
Mode – SSB
When programming a new channel, you do not need to define all parameters
change only those for which the default values are not suitable.
–
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 32
Page 48

Radio Programming
Copying Channel
Parameters
GET
and
are used to copy all channel parameters
STOR
To c op y c han ne l pa ra me te rs :
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
2.
MENU
Press
>
GET
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
CHAN
(F1) to retrieve all parameters from an
existing channel.
The last active channel number is displayed, blinking.
3.
With the keypad, enter the number of the channel
whose parameters you want to copy.
OR
Use the scanning wheel or the UP/
scroll keys to select the channel whose
DOWN
parameters you want to copy.
4.
5.
Press
Press
ENTER
STOR
to confirm.
(F2) to store the retrieved channel
parameters in a different channel.
The last active channel number is displayed, blinking.
from one channel to another
CHAN
(F1).
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
PROG
GET CHAN 1
PROG
GET CHAN 13
BACK C LR
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
PROG
STORE CH 1
.
6.
With the keypad, enter the number of the channel into which you wish to save
the copied parameters.
OR
Use the scanning wheel or the UP/
scroll keys to select the channel into
DOWN
which you wish to save the copied parameters.
7.
Press
ENTER
to confirm.
PROG
STORING
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 33
Page 49

Radio Programming
Erasing a Channel
ERAS is used to delete a channel from the radio.
To erase a channel:
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
2.
MENU
Press
>
ERAS
MORE
(F3).
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
CHAN
The last active channel number is displayed, blinking.
3.
With the keypad, enter the channel number you want to
delete.
OR
Use the scanning wheel or the UP/
scroll keys to select the channel you wish
DOWN
to delete.
4.
Press
Notes
ENTER
to confirm.
• If the channel is not programmed, you will receive a “NOT
PROG” message.
In all these cases, the erase request is rejected by the radio.
(F1).
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
PROG
ERASE CH 1
PROG
ERASE CH 31
BACK C LR
PROG
ERASING
Transmission Power
Level
You can set one of four transmission power levels for a programmed channel:
•LOW– 25W
•MED– 62.5W (medium)
• HIGH – 100W
• MAX – 125W (maximum)
To set the channel’s transmission power level:
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
PWR
3.
Press the function key that appears below the power level of your choice:
(F1),
LOW
4.
Press
ENTER
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
CHAN
(F4) to access the power level options.
MED
(F2),
HIGH
(F3) or
MAX
(F4).
to confirm.
(F1).
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
PROG
POWER LOW
LOW MED HIGH MAX
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 34
Page 50

Radio Programming
Channel Frequency
The Channel Frequency setting enables you to determine the specific frequency for
each channel, and the frequency type:
Simplex Frequency (SMPX)
Duplex Frequency (DPLX)
– transmits and receives on the same frequency.
– transmits on one frequency and receives on a different
frequency.
Receiving Only Frequency (RXO)
Transmitting Only Frequency (TXO)
– restricts a frequency for reception only.
– restricts a frequency for transmission only.
To set a channel’s frequency:
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
2.
3.
MENU
Press
Press
>
MORE
FREQ
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
to scroll to the second menu screen.
(F1) to access the frequency options.
RAD
(F1) >
CHAN
(F1).
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
CHAN
PARAMETERS
FREQ BAND MODE AGC
SMPX
F 10,000.00
SMPX DPLX RXO TXO
4.
Press the function key below the frequency type of your choice:
SMPX
(F1),
DPLX
(F2),
RXO
(F3) or
TXO
(F4).
When the DPLX function is selected, the F2 key toggles between Rx
and Tx frequencies.
Note
5.
Use the keypad to enter the frequency of your choice.
Use the * key as a decimal point if you need to program the 100 Hz and
10 Hz digits after the decimal point.
Note
6.
Press
ENTER
twice
to confirm.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 35
Page 51

Radio Programming
Band Types
Operating Modes
MICOM-H has two band types:
■
USB – upper side band
■
LSB – lower side band.
To set the channel band type:
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
MORE
3.
Press
BAND
4.
Press the function key below the option of your choice
(
or
USB
5.
Press
ENTER
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the second menu screen.
(F2) to access band type options.
).
LSB
to confirm.
CHAN
The MICOM-H offers three operating mode options:
(F1).
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
CHAN
PARAMETERS
FREQ BAND MODE AGC
PROG
BAND – LSB
USB LSB
■
SSB – single side band
■
AME – amplitude modification equivalent
■
PLT – pilot mode.
To set the operating mode:
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
MORE
3.
Press
MODE
4.
Press the function key below the operation mode of your choice:
(F1),
SSB
5.
Press
ENTER
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the second menu screen.
(F3) to access operation mode options.
AME
(F2) or
PLT
(F3).
to confirm.
CHAN
(F1).
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
CHAN
PARAMETERS
FREQ BAND MODE AGC
PROG
MODE SSB
SSB AME PLT
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 36
Page 52

Radio Programming
Automatic Gain
Control (AGC)
The MICOM-H supports two AGC speeds: slow and fast, or the AGC can be turned
off.
To set the AGC speed:
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
MORE
3.
Press
AGC
4.
Press the function key below the AGC speed of your choice:
(F1),
SLOW
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the second menu screen.
(F4) to access AGC speed settings.
FAST
(F2) or
OFF
(F3).
CHAN
If you choos e FAST, the AGC FAST icon w ill be
visible.
Note
5.
Press
ENTER
to confirm.
(F1).
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
CHAN
PARAMETERS
FREQ BAND MODE AGC
PROG
AGC – SLOW
SLOW FAS T OFF
PROG
AGC – FAST
SLOW FAS T OFF
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 37
Page 53

Radio Programming
Bandwidths
The MICOM-H offers the following bandwidths:
■
2.1 K
■
2.7 K
■
3.0 K
■
3.3 K
■
LSM – Low Speed Modem
■
CW – Continuous Wave, including:
– 0.25 K
– 0.5 K
– 0.8 K
To set the channel bandwidth:
1.
Access the Channel Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
MORE
3.
Press BW (F1) to access the bandwidth options.
MORE
twice
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the third menu screen.
CHAN
(F1).
CHAN
PARAMETERS
GET STOR ERAS PWR
CHAN
CHAN
PARAMETERS
PARAMETERS
BW
BW
PROG
BW – 2.7
2.1 2.7 3.0 3.3
4.
Press the function key below the bandwidth of your choice:
(F1),
2.1
5.
If you want to set the radio to
MORE
Select
6.
Press
(F2),
2.7
key.
(F1) or CW (F2).
LSW
ENTER
to confirm.
3.0
(F3) or
(F4).
3.3
or CW, press the
LSM
The standard bandwidth is 2. If you
choose any other bandwidth, the Non-
Note
Standard bandwidth icon will be
visible.
PROG
BW – 2.7
LSM CW
PROG
BW – 3.3
2.1 2.7 3.0 3 .3
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 38
Page 54

Radio Programming
Radio Parameters
Baud Rate
You can program the following radio parameters:
■
BAUD – Baud rate
■
DPWR – Data power
■
MST – Microphone Side Tone
■
AST – Accessory Side Tone
■
PTBP – PTT Release Beep
■
KBBP – Keyboard Beep
■
TONE – Tone level
■
ADT – Alternate Display Time-out
■
AT TN – At te nu at or
■
CW – Continuous Wave
■
RCLV – Receive Level
■
DIM – Dimming Mode
The definition of each of the parameters is explained in the following sections.
The MICOM-H provides four baud rates:
■
1200 bps
■
2400 bps
■
4800 bps
■
9600 bps.
These baud rates are used when the radio is to communicate with external devices
such as: RSS, E-mail and remote control.
To set the baud rate:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
BAUD
3.
Press the function key below the baud rate of your
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
(F1) to access baud rate options.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
PROG
BAUD – 2400
1.2 2.4 4.8 9.6
choice:
(F1) - 1200 bps
1.2
(F2) - 2400 bps
2.4
(F3) - 4800 bps
4.8
(F4) - 9600 bps
9.6
4.
Press
ENTER
to confirm.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 39
The message “WAIT...” appears on the display for a few
seconds.
PROG
WAIT . . .
1.2 2.4 4.8 9.6
Page 55

Radio Programming
Data Power
The MICOM-H provides four data power levels:
■
LOW – 25W
■
MED – 62.5W (medium)
■
HIGH – 100W
■
MAX – 125W (maximum).
When data PTT is used, the radio sets the transmitter power level to the minimum
possible value between the determined data power value and the power level of the
currently used channel.
To set the data power level:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
DPWR
3.
Press the function key below the power level of your choice:
(F1),
LOW
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
(F2) to access the data power options.
MED
(F2),
HIGH
(F3) or
MAX
(F4).
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
PROG
DT PWR – LOW
LOW MED HIGH MAX
Microphone Side
To ne
4.
Press
ENTER
to confirm.
You can enable or disable the microphone side tone, which echoes the transmitted
voice from the MIC PTT to the speaker.
To enable/disable the Microphone Side Tone (MST):
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
MENU
Press
>
MST
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
(F3) to access the Microphone Side Tone
options.
3.
4.
Press
Press
(F1) to enable or NO (F2) to disable the microphone sidetone.
YES
ENTER
to confirm.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
PROG
MIC ST-NO
YES NO
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 40
Page 56

Radio Programming
Accessory Side Tone
PTT Release Beep
You can enable or disable the accessory side tone, which echoes the transmitted voice
from the accessory entry to the speaker.
To enable/disable the Accessory Side Tone (AST):
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
MENU
Press
>
AST
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
(F4) to access the Accessory Side Tone
options.
3.
4.
Press
Press
(F1) to enable or NO (F2) to disable the accessory sidetone.
YES
ENTER
to confirm.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
PROG
ACC ST-NO
YES NO
You can enable or disable the transmission of a beep when the push-to-talk (PTT)
button is released. The PTT release beep function is used to indicate to the remote
station that the local radio has returned to receive mode, (i.e. that it can begin
transmitting).
To enable/disable the PTT Release Beep (PTBP):
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
3.
MENU
Press
Press
>
MORE
PTBP
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
for the second menu screen.
(F1) to access the PTT Beep Release
options.
4.
5.
Press
Press
(F1) to enable or NO (F2) to disable the beep.
YES
ENTER
to confirm.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
PTBP KBBP TONE ADT
PROG
PTT BP-NO
YES NO
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 41
Page 57

Radio Programming
Keyboard Beep
Tone Level
You can enable or disable the keypad beep, which beeps every time a valid key is
pressed.
To enable/disable the Keyboard Beep (KBBP):
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
3.
4.
5.
MENU
Press
Press
Press
Press
>
MORE
KBBP
YES
ENTER
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
for the second menu screen.
(F2) to access the Keyboard Beep options.
(F1) to enable or NO (F2) to disable the keypad beep.
to confirm.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
PTBP KBBP TONE ADT
PROG
KYB BP-NO
YES NO
You can set the tone level (volume) to high or low.
To set the tone level:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
3.
4.
5.
MENU
Press
Press
Press
Press
>
MORE
TONE
LOW
ENTER
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
for the second menu screen.
(F3) to access the Tone options.
(F1) to set to low volume or
to confirm.
HIGH
RADIO
PRMT
(F2).
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
PTBP KBBP TONE ADT
PROG
TONE – HIGH
LOW HIGH
(F2) to set to high volume.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 42
Page 58

Radio Programming
Alternate Display
Time-out
Attenuator
You can define the number of seconds that elapse before the menu display returns to
the previous screen.
To set the display time-out:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
3.
4.
5.
>
MENU
Press
MORE
Press
ADT
Press
<--
Press
-->
Press
(F1) to quick-set the value to 1.
1
Press
Press
(F4) to quick-set the value to 10.
10
ENTER
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the second menu screen.
(F4) to access the time-out setting display.
(F2) to decrement the displayed value by 1.
(F3) to increment the displayed value by 1.
to confirm.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
PTBP KBBP TONE ADT
PROG
ADT – 5 SEC
1 10
You can enable or disable the attenuator.
To enable/disable the attenuator:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
3.
4.
5.
MENU
Press
Press
Press
Press
>
MORE
ATTN
YES
ENTER
MORE
twice
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the third menu screen.
(F1) to access the attenuator options.
(F1) to enable or NO (F2) to disable the attenuator.
to confirm.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
ATTN CW RCLV DIM
PROG
ATTEN – NO
YES NO
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 43
Page 59

Radio Programming
CW Operation
Receive Level
You can select one of three CW frequency filters: 0.25 K, 0.5 K or 0.8 K.
To select a CW frequency filter:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
MORE
3.
Press CW (F2) to access the CW filters.
4.
Press
0.25
5.
Press
ENTER
MORE
twice
(F1),
to confirm.
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the third menu screen.
(F2) or
0.5
(F3) as required.
0.8
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
ATTN CW RCLV DIM
PROG
CW – 0.8
0.25 0.5 0.8
You can enable or disable the Receive Level (Rx) bar.
To enable/disable the receive level bar:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
3.
MENU
Press
Press
>
MORE
RCLV
MORE
twice
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the third menu screen.
(F3) to change the Rx bar status.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
ATTN CW RCLV DIM
PROG
Rx LEVEL – NO
YES NO
4.
5.
Press
Press
(F1) to enable or NO (F2) to disable the Rx bar.
YES
ENTER
to confirm.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 44
Page 60

Radio Programming
Display Mode
You can select one of two display modes:
Dimming mode
Alternate mode
In
enables you to select one of four constant display light levels.
the display is normally turned off, and automatically turns on at
a predetermined level when the radio detects any type of activity (scanning wheel,
keypad, PTT, incoming call, etc.).
To select the Dimming or Fixed display modes:
1.
Access the Radio Parameters Programming menu:
2.
3.
4.
5.
MENU
Press
Press
Press
Press
>
MORE
DIM
YES
ENTER
MORE
twice
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
to scroll to the third menu screen.
(F4) to select the display mode.
(F1) for Alternate mode or NO (F2) for Dimming mode.
to confirm.
PRMT
(F2).
RADIO
PARAMETERS
BAUD DPWR MS T AST
RADIO
PARAMETERS
ATTN CW RCLV DIM
PROG
DISPLAY – ALT
YES NO
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 45
Page 61

Radio Programming
Setting the Radio
Options
Tuner
Accessory Settings
The MICOM-H offers the following programmable radio options:
■
TUNE – Tuner
■
ACC – Accessory
The radio can be set to work with or without a tuner. If you are using a tuner, you
must set this option to YES.
To set the tuner on or off:
1.
Access the Radio Options Programming menu:
2.
3.
4.
MENU
Press
Press
Press
>
TUNE
YES
ENTER
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) to access the tuner options.
(F1) to set the tuner option on or NO (F2) to set the tuner option off.
to confirm.
(F1) >
OPTS
(F3).
RADIO
OPTIONS
TUNE ACC
PROG
TUNER – NO
YES NO
The radio can be set to work with or without a 400W/1KW amplifier.
To set the amplifier option on or off:
1.
Access the Radio Options Programming menu:
>
MENU
2.
Press
ACC
3.
Press the function key below the option of your choice:
(F1),
AMP
Press
NON
MORE
>
PROG
(F2) >
RAD
(F1) >
OPTS
(F2) to access the accessory options.
ACC1
(F2),
ACC2
(F3).
(F4) if there is no accessory being used.
ACC1
(F2) and
ACC2
(F3) are for future use.
Selecting these options will have no effect.
Note
4.
Press
ENTER
to confirm.
(F3).
RADIO
OPTIONS
TUNE ACC
PROG
ACC – NONE
AMP ACC1 ACC2 NON
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 46
Page 62

Maintenance
Preventative
Maintenance
This section provides maintenance information for the MICOM-H. Correct
installation and maintenance will ensure on-going operation of your radio set.
If an internal problem is suspected, the BITE (Built In Test Equipment) will assist you
in locating the source of the problem and in informing your service representative.
System Integrity
Periodic Calibration
Using BITE
Periodically check the integrity of your system, by examining the power source,
cables, coaxes, connectors, antenna tuner (if used) and antenna. Carefully check that
no damage has been caused to your cables, pay extra attention to runway through
holes and bent cables.
To maintain the frequency accuracy of your radio, the internal frequency source must
be calibrated after 3, 6 and 12 months of operation in the first year, and once a year
thereafter. Please ensure that your radio is calibrated on time.
Every time the radio is turned on, a self-test procedure is activated. If an internal
malfunction is found, an error message will be displayed. Please contact your service
representative and report the indicated malfunction or error. A list of possible error
messages is given on page 48.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 47
Page 63

Maintenance Error Messages
No. Description
00 O.K. - no errors
01 DSP boot checksum fail (download)
02 DSP PLL unlock
03 DSP external RAM memory
04 (Not applicable)
05 DSP internal RAM memory
06 (Not applicable)
07 (Not applicable)
08 HC16 flash memory checksum
09 HC16 RAM memory
10 No 16.8 MHz clock
11 Battery low
12 Control head wake-up
13 Control head is not responding
14 Radio not programmed
15 Database fail
16 VCO 1 first injection
17 VCO 2 first injection
18 VCO 3 first injection
19 VCO second injection
20 Synthesizer unlock
21 Receiver failure
22 Preselector range 1
23 Preselector range 2
24 Preselector range 3
25 Preselector range 4
26 Preselector range 5
27 Preselector range 6
28 Preselector range 7
29 Preselector range 8
30 Exiter test
31 Antenna mismatch
32 Harmonic filter range 1
33 Harmonic filter range 2
34 Harmonic filter range 3
35 Harmonic filter range 4
36 Harmonic filter range 5
37 Harmonic filter range 6
38 Harmonic filter range 7
39 Power amplifier fail
Maintenance
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 48
Page 64

Maintenance
Troubleshooting
If the radio is malfunctioning, try to solve the problem as follows:
Problem Troubleshooting
Blank Display
Display present
but weak or no
receive signal or
noise
Engine noise
picked up by the
antenna
Check whether:
• DC power cable is connected properly to the radio and
battery.
• A 7.5A fuse is installed in the fuse holder located on the
green wire of the DC power cable.
Check whether:
• Connection of antenna to antenna tuner and antenna tuner
to radio cables (loose or broken connections).
• Correct programming of operating channel (frequency,
mode of operation, etc.).
Determine by observing difference in the reception by turning
the Engine ON/OFF.
Ve ri fy th at :
• The ground leads are properly connected, all power wires
and ground leads are as short as possible
• The Noise Blanker (if installed) is enabled.
Poor or no
transmission
If the problem persists:
• Install noise reduction Kit TLN8845.
Check whether:
• A 30A fuse is installed in the fuse holder located on the red
wire of the power cable.
• Proper grounding cables are connected from the radio and
from the antenna tuner to the vehicle chassis.
• While speaking, check RF power bars for activity.
The resulting RF power output is displayed in approximately
15 W increments (bars) being added from the bottom of the
display upwards.
• Three or more bars disappear from the RF power bar display.
There may be a problem in the antenna system. If the
antenna cabling or the antenna mast rigging position has
changed since the antenna was last tuned, the antenna tuner
will not be adjusted automatically. To retune the antenna
tuner, press the ENTER key. If transmission is still poor,
inspect the tuner, antenna and ground plane for loose
connections or misplaced parts. If no loose connections are
found, call your service representative for assistance.
• There are no bars at the RF power bar graph. Indicates low
transmitter power, which can be caused by a faulty
microphone, faulty transmitter, overheating, or defective
antenna system.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 49
Page 65

Maintenance
In case of a failure during operation, one of the following messages may appear on
the display:
Message Troubleshooting
NO CLOCK
SYN FAIL
PW LATCH
OVER TMP
CU-LIMIT
NOT PROG
(This message appears
if three is a failure in the
DC power to the radio
during RSS programming)
Check whether:
• A 30A fuse is installed in the fuse holder on the red wire
of the power cable.
Perform a built-in test (BITE) for more information.
Perform a built-in test (BITE) for more information.
Check whether:
• There is any fan obstruction
• Perform a built-in test (BITE) for more information.
Check whether:
• The radio is programmed to TUNER OFF if
your antenna system is not equipped with an ATU
• A short circuit occurred in the antenna’s coax
• The ATU is in working condition.
Check whether:
• The radio is not programmed and the baud rate is 1200
bit/sec. If necessary, program the radio parameters
(from RSS).
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 50
Page 66

Maintenance
Service
Proper repair and maintenance procedures will ensure efficient operation and long
life for this product. A Motorola maintenance agreement will provide expert service
to keep this and all other communication equipment in perfect operating condition.
Through its maintenance and installation program, Motorola makes available the
finest service to those desiring reliable, continuous communications on a contract
basis.
Motorola's Customer Service Division is the largest service organization specializing
in mobile communications. It includes over 900 authorized or company-owned
stations. In addition, our products are serviced throughout the world by a wide
network of company or authorized independent distributor service organizations.
For a contract service agreement, please contact your nearest Motorola service
representative, or Motorola sales representative. If you suspect a radio problem, check
the following items before requesting service.
Phone line support:
Motorola Radio Support Center
3761 S. Central Avenue
Rockford, IL 61102
USA
Phone:
International: 847-725-4830
Domestic USA: 1-800-227-6772
For customers of the US Federal Market, phone line support is available at:
Motorola USFG Depot
7940 Penn Randall Place
Upper Marlboro, MD 20772
USA
Phone:
International: 301-736-4300 (Fax: 301-735-7414)
Domestic USA: 1-800-969-6680 (Fax: 800-784-4133)
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 51
Page 67

Maintenance
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 52
Page 68

Installation
General
Inspection
Planning the
Installation of your
Radio
This section describes the installation of the radio.
Carefully inspect the radio immediately upon receipt, and notify the shipper of any
damage incurred in transit.
Before installing the radio, familiarize yourself with the installation procedure
detailed.
Select the mounting location taking into account convenience of access to electrical
connections and maintenance. The selected location should be clean, dry and well
ventilated. Do not mount the unit in close proximity to strong electrical fields
produced by brush motors and generators, welders, etc.
The antenna, antenna tuner and associated cable kits are provided separately, and
these should be installed before the radio itself is installed. Follow the instructions
included with the units and kits.
The radio may be placed on any sturdy, flat surface. An accessory mounting tray
(included in the Mobile Mounting Kit, FLN2272) allows the radio to be mounted in
any position.
No preliminary internal wiring connections are required before installing the radio.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 53
Page 69

Installation
Base Station
Installation
You can use either an AC power supply or a 12 V battery as the radio power supply .
(It is possible to connect a backup battery to the battery terminals on the power
supply). Power Supply model F2369 for 220 V AC, 50 Hz, field programmable for 110
VAC, 60 Hz should be used for this purpose.
RED
POWER SUPPLY
POWER SUPPLY
F2369
F2369
GRN
BAT+
GND-BLK
GND-
- +
12-V BACKUP
12-V BACK UP
BATTERY
BATTERY
RADIO
FKN5865
Figure 2: Power Supply
This power supply also serves as a charger for the external backup 12V battery, if
connected. When AC power failure occurs, the battery functions as the main power
source. When AC power is again available, the power supply charges the battery.
The cable and connector supplied with the power supply enable connecting the
supply directly to DC connector J4 at the radio rear panel. (The DC Power Cable
supplied with the radio is not used in this installation).
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 54
Page 70

Installation
Mobile
Installation
Figure 3 illustrates the installation procedure, and shows the location of the installed
components inside a vehicle.
Installation
Procedures
Radio
ATU
Antenna cable
DC Power
cable
BAT
Figure 3: Front Model Installation
The radio is installed on the dashboard of the vehicle inside the passenger
compartment. The other components connect to the power source, the battery, and
to the antenna, which enables the radio to transmit and receive. If the battery is
located in the rear section of the vehicle, the power cable extends to the battery
location in the rear.
Follow these procedures to install the radio in the desired location. If the accessory
mounting tray is not used, ignore the steps pertaining to it.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 55
Page 71

Mobile Mounting Kit
1.
Mount the accessory mounting tray in the desired location. Use the tray as a
template if holes must be drilled.
11.8” (300mm )
8.74” (222mm )
Figure 4: Accessory Mounting Tray
Installation
2.
Use the four supplied screws to fasten the mounting tray bracket to the bottom
of the radio housing.
3.
Drill an additional hole for the grounding bolt.
4.
If a mounting tray is used, slide the radio with the bracket into the tray and
fasten the bracket to the tray with the supplied screw.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 56
Page 72

Installation
DC Power
Connection
To connect a 12V negative-ground vehicular battery.
1.
Lead the power connector on the DC Power Cable to the DC connector on the
radio, but do not attach it. Lead the three heavy wires (red, green and black) to the
12V battery, threading them through the access holes as required.
The wires must be as short as possible. Cut off any excess wire.
2.
Thread the red and green wires from the power connector through the two fuse
holder caps; separate the fuse clips and solder or crimp them to the wires.
3.
Install the 30A fuse in the fuse holder on the red wire, and the 7.5A fuse in the
fuse holder on the green wire.
4.
Crimp or solder the supplied lugs to the red, green, and black wires.
5.
Connect the lugs on both red and green cables to the battery’s positive terminal.
Then connect the lug on the black wire to the battery’s negative terminal.
FUSE
30 A
FUSE
7.5 A
RED (# 8)
GRN (# 12)
-
BATTERY
12V
+
RADIO
* MO BIL E C H A SS IS
J3
POWER
BLK (# 12)
Figure 5: DC Power Connection
– Connect the grounding (black wire) to the vehicle chassis, as close as
possible to the radio.
Note
– In front installation, add one ferrite (supplied with the installation radio
kit) on the DC cable as close as possible to the radio.
– In trunk mount installation, add one ferrite (supplied with installation
kit) on the DC cable as close as possible to the radio and one ferrite on the
control cable, halfway between the control head and the radio.
No.14 X 3/4” self-tapping screw
3/16’ (187”) diameter hole
.
1/4” lockwasher
Figure 6: Wire Attachment to Chassis
Chassis cable and lug
F
l
o
o
s
r
u
r
f
a
c
e
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 57
Page 73

Installation
Microphone Clip
Final Connections
The microphone cable enables placing the microphone clip in any convenient
location up to five feet from the radio. To install the clip, use it as a template to drill
two holes to receive self-threading sheet-metal screws. Mount the clip using the
supplied screws.
Figure 7: Microphone Clip
Ensure that the radio is off before making these connections.
!
Warning
1.
Connect the power cable to DC connector J4 and connect the antenna RF cable to
antenna connector J2.
If an antenna tuner is used, connect the antenna to the tuner, connect the tuner RF
cable to connector J2, located on the radio rear panel.
2.
If a mounting tray is used, slide the radio with the bracket into the tray and
fasten the bracket to the tray with the supplied screw.
3.
Use the tie straps included with the Cable Kit to tie loose cables out of the way.
4.
Connect a ground lead from the GND screw on the radio rear panel to the chassis
of the vehicle.
Special attention should be given to locating an appropriate vehicle
!
Important
ground. Optimum radio performance can only be achieved with a ground
connection having a very low resistance.
The vehicle frame makes the best ground, but body structural
reinforcement members are also suitable for grounding purposes. The
ground lead should be as short as possible.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 58
Page 74

Installation
External Speaker
Installation
Operational Checks
Connectors
Microphone
Connector J1
An external speaker can be connected to the radio. Any speaker with an impedance
greater than 8
Ω
can be used, and is connected through the accessory connector (pin
1,3).
When installation is complete, carefully check all operating functions (refer to the
Operation section). In case of malfunctioning, refer to the sections on
Troubleshooting and Tuning the Antenna in this manual.
The microphone connector is located on the lower part of the radio front panel. Table
1 lists the functions of the microphone connector pins.
Table 1. Connector J1, Pin Connections
No. Pin Name Description
SWA+
1
RXD
2
Microphone Power
Serial communication
Antenna
Connector J2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TXD
GND
MIC AUDIO
PTT MIC
MONITOR
AUDIO OUT
Serial communication
Ground line
Input audio signals generated by the microphone (600ΩΩΩΩ
impedance, 100 mV 1 KHz tone is required for full output
power)
Activates transmission by short to ground
Mutes the speaker before transmission is enabled (short
momentary to ground to open speaker)
Receive audio 600ΩΩΩΩ (300 mVRMS)
The “N type” antenna connector is located on the rear panel of the transceiver and is
used to connect the antenna.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 59
Page 75

Installation
Accessory
Connector J3
Accessory connector J3 is a 25-pin D-type plug located on the rear panel of the radio.
It is used with external accessories such as a modem, a linear amplifier, a phone
patch, etc.
If you wish to connect Morse key and headphones using their standard connectors,
use interface cable FKN4403.
To connect up to four devices simultaneously, use FLN2271.
Table 2 lists the pin connections of Connector J3.
Table 2. Connector J3, Pin Connections
No. Pin Name Description
SPKR
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
-
(Do not connect to GND)
OPTION
SPKR+
RX AUDIO+
RX AUDIO-
(Do not connect to GND)
TX AUDIO+
TX AUDIO-
(Do not connect to GND)
PTT IN VOICE
PTT IN DATA
PTT IN CW
SWA+
KW C C
KW ON/OFF
AGC FAST/SLOW
RXD
TXD
RESET
GND
KW PTT
EXT ALARM
VPP
KW ALC
SQ GATE
FAN ON/OFF
KW TUNE
Differential output to the external 8Ω, 5W speaker
Option dependent
Differential output to the external 8Ω, 5W speaker
Differential output received audio signals (0 dBm;
600Ω; not controlled by volume)
Differential output received audio signals (0 dBm;
600Ω; not controlled by volume)
Differential input received audio signals (600Ω input
impedance, 0 dBm is required for full power)
Differential input received audio signals (600Ω input
impedance, 0 dBm required for full power)
Xmit command (by short to ground) for voice signals
Xmit command (by short to ground) for data signals
Xmit command (by short to ground) for CW (Morse)
13.8V (nominal) current limited
KW option channel change
KW option power ON/OFF
AGC fast or slow release
Point to point communication line to HOST/HLC
Point to point communication line to HOST/HLC
External RESET
Ground
KW PTT
External Alarm Operation (open collector –pulled to
ground when external alarm is activated)
Flash programming voltage
KW ALC
Squelch Indication
FAN ON/OF F
KW tune
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 60
Page 76

Installation
DC Connector J4
Reduction of
Vehicular Noise
DC connector J4 is mounted on the rear panel of the radio. It is used to feed the radio
with the required power from an AC to 13.8V power supply or from the battery. The
following table lists the function of the DC connector lines.
Table 3. Connector J4, Pin Connections
No. Pin Name Description
TX Power Used to deliver high currents (up to 28 Amp) to the
1
radio, mainly for the transmitter circuitry
Ground Used as return line for receive and transmit lines
2
RX Power Used to deliver relatively low currents (up to 3 Amp)
3
to the radio, mainly for the receiver circuitry
Most vehicles are subject to several noise sources which greatly disturb a received
signal. The most noisy sources are the high voltage ignition sparks that are produced
at the vehicle's plugs. Alternator activity also generates significant noise.
By following these insulation guidelines, and if necessary by adding certain damping
components, it is usually possible to reduce vehicular noise:
1.
Keep your antenna tuner and antenna as far as possible from the engine
compartment.
2.
Connect the primary power lead of the radio directly to the battery instead of the
starter relay. The battery acts as a large capacitor (about one farad for 50 A-H
capacity batteries) by passing the noise to ground.
3.
If necessary, connect 0.01 - 0.1 mF capacitors across the primary leads of the
coil and across the alternator output.
4.
Keep your DC and RF cables as short as possible.
5.
If your vehicle does not have a resistive ignition wire, it is recommended to
replace it with such a wire.
6.
The MOTOROLA RF noise reduction kit for alternator equipped vehicles
(TLN8845) includes some useful accessories for noise reduction, including a
resistive ignition coil suppressor cable. In severe noise conditions, you may find
this kit helpful.
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 61
Page 77

Installation
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide 62
Page 78

List of Procedures
To turn the radio on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
To Transmit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
To Receive Calls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
To choose a channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
To transmit in Channel mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
To enter frequency mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
To change the current frequency/frequencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
To store a frequency in a channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
To use scan mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
To select scan mode options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
To run BITE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
To lock the radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
To unlock the radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
To change the password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
To change the display brightness level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
To change the radio language . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
To enter Radio Programming mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
To copy channel parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
To erase a channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
To set the channel’s transmission power level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
To set a channel’s frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
To set the channel band type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
To set the operating mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
To set the AGC speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
To set the channel bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
To set the baud rate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
To set the data power level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
To enable/disable the Microphone Side Tone (MST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
To enable/disable the Accessory Side Tone (AST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
To enable/disable the PTT Release Beep (PTBP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
To enable/disable the Keyboard Beep (KBBP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
To set the tone level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
To set the display time-out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
To enable/disable the attenuator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
To select a CW frequency filter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
To enable/disable the receive level bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
To select the Dimming or Fixed display modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
To set the tuner on or off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
To set the amplifier option on or off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
To connect a 12V negative-ground vehicular battery. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
MICOM-H Owner’s Guide lxiii
Page 79

MICOM-H Owner’s Guide lxiv
 Loading...
Loading...