Page 1

Galaxy PW™
100 to 225 kVA
User’s Manual
www.mgeups.com
Page 2

Page 3

Galaxy PW™
User ’s Manual
For service call
1-800-438-7373
86-133060-00 X1 08/02
Copyright © 2002 MGE UPS Systems, Inc..
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
MGE UPS Systems
1660 Scenic Avenue
Costa Mesa, CA 92626
(714) 557-1636
www.mgeups.com
800/523-0142
Page 4

ii Chapter name
Galaxy PW 100 to 225 kVA User’s Manual
This page intentionally left blank
Page 5
iiiImportant Safety Instructions
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS — This manual contains important instructions for EPS 6000
inverters that must be followed during installation, operation and maintenance of the equipment.
WARNING
Opening enclosures expose hazardous voltages. Always refer service to qualified personnel only.
ATTENTION
L'ouverture des cabinets expose des tensions dangereuses. Assurez-vous toujours que le service ne
soit fait que par des personnes qualifiees.
WARNUNG!
Offene Raeume entladen gefaehrliche Stromspannungen. Bitte wenden sie sich an qualifiziertes Dienstpersonal.
WARNING
To reduce the risk of fire or electric shock, install in a temperature and humidity controlled indoor area
free of conductive contaminants.
ATTENTION
Pour réduire le riske d'inccendie ou d'électrocution, installer dans une enciente intérieure contrôlée en
température et humidité et sans contaminants conducteurs.
WARNUNG!
Um die Gefahr von Feuer und elektrischem Schock zu reduzieren, muss das Geraet in einem temperatur und feuchtigkeitskontrolliertem Raum, frei von leitungsfaehigen Verunreinigungen, installiert werden.
WARNING
As standards, specifications, and designs are subject to change, please ask for confirmation of the
information given in this publication.
ATTENTION
Comme les normes, spécifications et produits peuvent changer, veuillez demander confirmation
des informations contenues dans cette publication.
WARNUNG!
Normen, Spezifizierungen und Plaene unterliegen Aenderungen. Bitte beantragen Sie schriftliche
Bestaetigung ueber Informationen die in dieser Herausgabe gemacht wurden.
NOTE
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area
is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct
the interference at his own expense.
Page 6

This page intentionally left blank
iv
Page 7

vWarranty
Galaxy PW™
User ’s Manual
Warranty
Seller warrants to the Ultimate Purchaser (the purchaser who buys for use, and not for resale) that all products furnished under this order and which are manufactured by Seller will conform to final specifications, drawings, samples and other written descriptions approved in writing by Seller, and will be free from defects in
materials and workmanship. These warranties shall remain in effect for period of twelve (12) months after delivery to the Ultimate Purchaser. But if the Seller installs
the equipment or supplies technical direction of installation by contract, said one year shall run from the completion of installation, provided installation is not unreasonably delayed by Ultimate Purchaser. Parts replaced or repaired in the warrant period shall carry the unexpired portion of the original warranty. Aunit placed with
the Purchaser on consignment and then later purchased will be warranted for twelve (12) months from the time the Seller receives notification of the Purchaser’s
intent to purchase said consigned item. The foregoing in its entirety is subject to the provision that in no case will the total warranty period extend beyond 18 months
from date Seller ships equipment from point of manufacture.
The liability of Seller hereunder is limited to replacing or repairing at Seller’s factory or on the job site at Seller’s option, any part or parts which have been returned to
the Seller and which are defective or do not conform to such specifications, drawings or other written descriptions; provided that such part or parts are returned by
the Ultimate Purchaser within ninety (90) days after such defect is discovered. The Seller shall have the sole right to determine if the parts are to be repaired at the
job site or whether they are to be returned to the factory for repair or replacement. All items returned to Seller for repair or replacement must be sent freight prepaid
to its factory. Purchaser must obtain Seller’s Return Goods Authorization prior to returning items. The above conditions must be met if warranty is to be valid. Seller
will not be liable for any damage done by unauthorized repair work, unauthorized replacement parts, from any misapplication of the item, or for damage due to accident, abuse, or Act of God.
In no event shall the Seller be liable for loss, damage, or expense directly or indirectly arising from the use of the units, or from any other cause, except as expressly
stated in this warranty. Seller makes no warranties, express or implied, including any warranty as to merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose or use. Seller is
not liable for and Purchaser waives any right of action it has or may have against Seller for any consequential or special damages arising out of any breach of warranty, and for any damages Purchaser may claim for damage to any property or injury or death to any person arising out of its purchase of the use, operation or
maintenance of the product. Seller will not be liable for any labor subcontracted or performed by Purchaser for preparation of warranted item for return to Seller’s factory or for preparation work for field repair or replacement. Invoicing of Seller for labor either performed or subcontracted by Purchaser will not be considered as a liability by the Seller.
This warranty shall be exclusive of any and all other warranties express or implied and may be modified only by a writing signed by an officer of the Seller. This warranty shall extend to the Ultimate Purchaser but to no one else. Accessories supplied by Seller, but manufactured by others, carry any warranty the manufacturers
have made to Seller and which can be passed on to Ultimate Purchaser.
Seller makes no warranty with respect to whether the products sold hereunder infringe any patent, U.S. or foreign, and Buyer represents that any specially ordered
products do not infringe any patent. Buyer agrees to indemnify and hold Seller harmless from any liability by virtue of any patent claims where Buyer has ordered a
product conforming to Buyer’s specifications, or conforming to Buyer’s specific design.
Buyer has not relied and shall not rely on any oral representation regarding the Product sold hereunder and any oral representation shall not bind Seller and shall not
be part of any warranty.
There are no warranties which extend beyond the description on the face hereof. In no event shall MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. be responsible for consequential damages or for any damages except as expressly stated herein.
Service and Factory Repair - Call 1 - 800 - 438 - 7373
Direct questions about the operation, repair, or servicing of this equipment to MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. Customer Support Services. Include the part number,
assembly number, and serial number of the unit in any correspondence. Should you require factory service for your equipment, contact MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
Customer Support Services and obtain a Return Goods Authorization (RGA) prior to shipping your unit. Never ship equipment to MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc. without
first obtaining an RGA.
Proprietary Rights Statement
The information in this manual is the property of MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc., and represents a proprietary article in which MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc., retains any and
all patent rights, including exclusive rights of use and/or manufacture and/or sale. Possession of this information does not convey any permission to reproduce, print,
or manufacture the article or articles shown herein. Such permission may be granted only by specific written authorization, signed by an officer of MGE UPS SYSTEMS, Inc.
IBM, PC-AT, ES/9000, and AS/400 are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation. MGE and MGE UPS SYSTEMS are trademarks of MGE UPS
SYSTEMS, Inc. Other trademarks that may be used herein are owned by their respective companies and are referred to in an editorial fashion only.
Revision History
Galaxy PW™ User's Manual
86-133060-00
Copyright © 2002 MGE UPS SYSTEMS. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
Revision: X1 08/02
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA user’s manual
Page 8

This page intentionally left blank
vi
Page 9

1Contents
contents
safety instructions ......................................................................................................iii
warranty .....................................................................................................................v
how to use this manual .............................................................................................2
introduction
general characteristics of Galaxy PW™ UPS ..........................................................3
system description ..................................................................................................4
different types of Galaxy PW™ systems ..................................................................5
isolation and protection devices ..............................................................................5
operation in on-line mode ........................................................................................6
inverter shutdown or overload ..................................................................................8
operation with an engine generator set......................................................................9
output voltage quality and continuity ........................................................................9
description of Galaxy PW™ cabinets
UPS ........................................................................................................................10
battery ......................................................................................................................10
control panel
general ....................................................................................................................11
indications ................................................................................................................11
start-up
system start-up ........................................................................................................13
start-up of a module ..............................................................................................13
shutdown
shutdown of the inverter ..........................................................................................14
shutdown of a rectifier/charger ..............................................................................14
control-panel display
general organization ................................................................................................15
display of messages ................................................................................................15
measurement system ..............................................................................................19
voltage measurements ............................................................................................19
current measurements ............................................................................................19
power and frequency measurements ....................................................................19
battery measurements ..........................................................................................20
selections and settings ..........................................................................................20
alarms
general ....................................................................................................................22
maintenance bypass ..............................................................................................22
environment information
signal reception ......................................................................................................23
signal transmission ................................................................................................23
logging and time-stamping
presentation of event time-stamping by Galaxy PW™............................................24
utilization via the Galaxy PW™ display ..................................................................24
utilization via Teleservice ........................................................................................27
maintenance
maintenance configuration........................................................................................28
battery maintenance ................................................................................................30
visual check..............................................................................................................30
functional check ......................................................................................................30
options
galvanic and voltage matching transformers
maintenance bypass ................................................................................................31
electrical supervision ..............................................................................................31
Page 10
2 How to Use this Manual
This manual is designed for ease of use and easy location of information.
To quickly find the meaning of terms used within the text, look in the Glossary.
This manual uses Noteboxes to convey important information. Noteboxes come in four varieties:
A WARNING notebox
indicates information
provided to protect the
user and service
personnel against safety
hazards and/or possible
equipment damage
WARNING
A CAUTION notebox
indicates information
provided to protect the
user and service
personnel against
possible equipment
damage.
CAUTION
An IMPORTANT notebox
indicates information
provided as an operating
instruction, or as an
operating tip.
IMPORTANT
A NOTE notebox
indicates information
provided as an
operating tip or an
equipment feature.
NOTE
All products in the Galaxy PW™ range are protected by patents. They implement original technology not available to competitors of MGE UPS SYSTEMS.
To take into account evolving standards and technology, equipment may be modified
without notice. Indications concerning technical characteristics and dimensions are not
binding unless confirmed by MGE UPS SYSTEMS.
This document may be copied only with the written consent of MGE UPS SYSTEMS.
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
how to use this manual
Page 11
3
introduction
Introduction
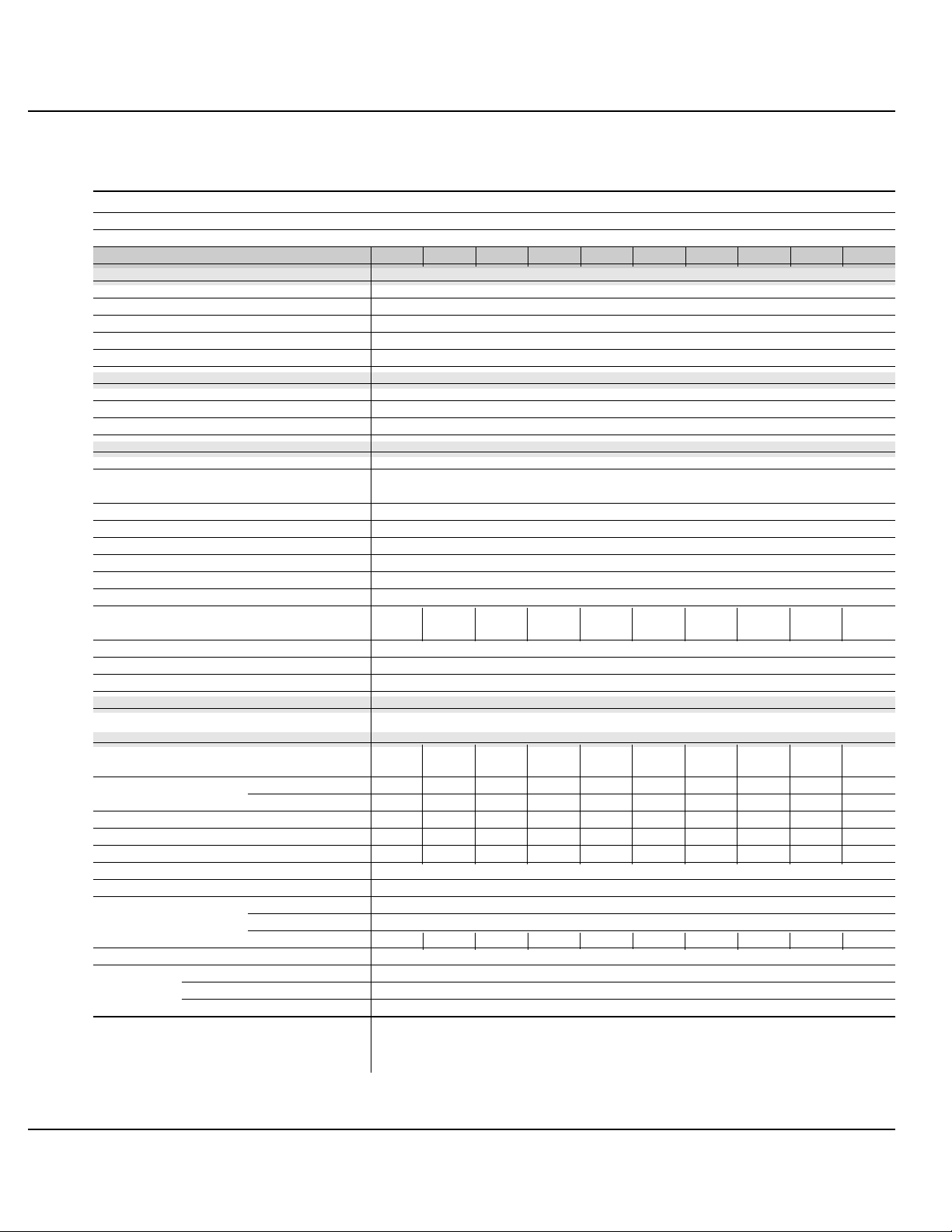
general characteristics of Galaxy PW™ UPS
UPS power rating in kVA 100 130 150 180 200 225
Normal AC input
number of conductors 3 phases
rated voltage and tolerances 480 V ± 10% (adjustable to ± 15%)
rated frequency and tolerances 60 Hz / ± 10%
THDI < 14% < 11% < 10% < 8% < 7.6% < 7.5%
power factor up to 0,9
Bypass AC input
number of conductors 3 phases 3 phases + neutral
rated voltage and tolerances 480 V / ± 10%
rated frequency and tolerances 60 Hz / ± 10%
Load
number of conductors 3 phases 3 phases + neutral
Ph/Ph voltages 480 V
Ph/N voltages 277 V
voltage fluctuations ± 1%
adjustable frequency and tolerances
(on battery power) 60 Hz ± 0,05 Hz
synchronization with bypass ± 0.5 Hz (adjustable from ± 0.25 Hz to ± 2 Hz)
voltage variation for 0 to 100% load step change ± 2% (with battery)
permissible overloads 150% for 1 minute, 125% for 10 minutes
Isc Ph/Ph (% of I rated) 4.7 3.6 3.2 2.6 2.4 2.1
Isc Ph/N (% of I rated) 7.4 5.7 5 4.1 3.7 3.3
THDU Ph/Ph and Ph/N for linear load < 1,5% Ph/Ph, < 2% Ph/N
THDU Ph/Ph and Ph/N for non-linear load < 2% Ph/Ph, < 3% Ph/N
(at 80% of Pn)
Battery
standard battery type gas-recombination sealed lead-acid battery
UPS characteristics
active power (kW) 100 130 150 180 200 225
efficiency at 50% load (%) 90.5 91 92 92.5 92.5 93
(values ± 1%)
efficiency at 100% load (%) 92.5 93 93 93 93.5 93.5
(values ± 1%)
heat losses (1) in KW 8.1 9.8 11.3 13.5 13.9 14.1
in cal./s 1940 2350 2700 3240 3340 3380
storage temperature range -25 °C to +70 °C
operating temperature range 0 °C to 35 °C (40 °C for 8 hours)
relative humidity 95% maximum
maximum operating altitude without derating < 1000 meters
noise level (dBA) 62 63 64 65 67 68
dimensions (mm) width 1215
depth 840
height 1900 ± 10
weight (lbs/kg) 3050/1388
standards design NFPA/ NEC / NEMA / OSMA
product and safety UL 1778 - ULC
electromagnetic compatibility FCC Part 15, Subport J, Class A - IEEE587 / ANSI 62.41
(1): The losses indicated are those produced at full rated load with the battery float charging. They must be taken into account when sizing the ventilation system.
User’s Manual
Page 12

4
system description
(see figure 1)
■ a rectifier/charger module (A) converts
3-phase AC power from the normal AC
source supply (1) into DC power for the
normal inverter input and float charges or
recharges the battery;
■ a battery unit (D) provides backup
power for the inverter in the event of a
voltage drop or a normal AC source failure;
■ an inverter module (B) converts the DC
power supplied by the rectifier/charger
module or the battery unit into 3-phase AC
power for the load;
■ a static bypass module (C) ensures the
instantaneous transfer of the load to the
bypass AC source input in the event of an
inverter shutdown (initiated by the user or
by a protective device) or a sudden overload;
■ a maintenance bypass isolates the UPS
for maintenance and transfers the load to
bypass AC source input without interrupting the supply of power. The maintenance
bypass is made up of three manual
switches (Q3BP, Q4S and Q5N).
Note
■ the normal AC input and the bypass AC
input have different functions and,
depending on the installation, may be protected differently upstream and/or come
from different sources.
■ when increased power is required, sev-
eral Galaxy PW™ units may be connected in parallel (up to four). In this configuration, an "isolation" function is added for
the UPS system as a whole for maintenance purposes, without interrupting the
supply of power to the load.
The system may also include:
■ Isolation or auto transformers on both
input and output.
■ 2 CB or 3 CB maintenance bypass
■ different remote control, indication and
display systems.
Introduction
Fig. 1 *The Fuse is to protect against catastrophic rectifier/inverter
semiconductor failure.
Schematic diagram of the Galaxy PW™ system
maintenance bypass:
Q3BP
inverter (B):
DC to AC
power
isolation:
Q4S
isolation and
protection:
Q5N
rectifier/
charger (A):
AC to DC
power
QF1: isolation
and protection
normal
AC input
load
battery (D):
backup power
static bypass (C):
bypass
AC input
Q1
isolation
and
protection
(1)
(2)
harmonic
fliter
*FUSE
*FUSE
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 13
5
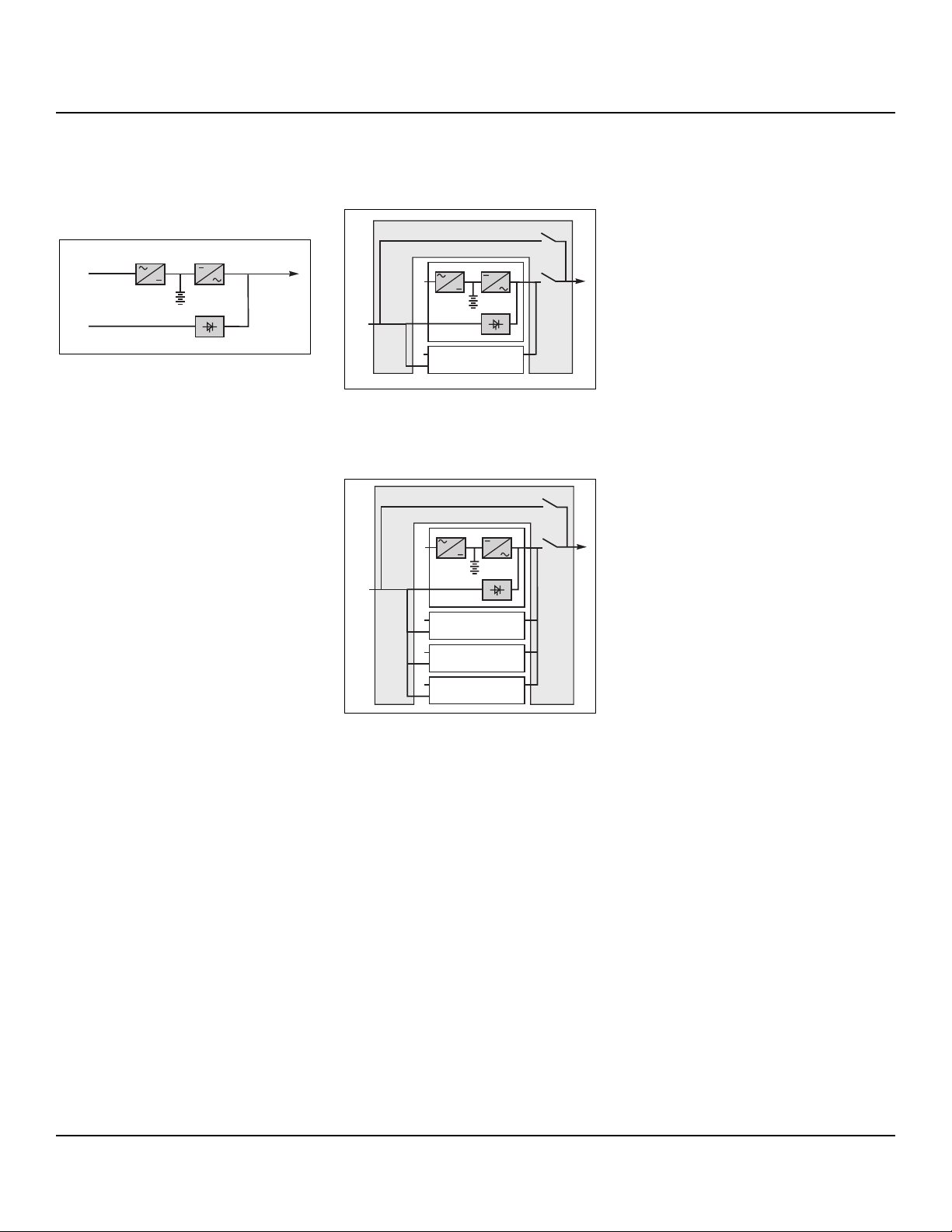
different types of Galaxy
PW™ systems
single-UPS unit
Fig. 2
parallel UPS system
See figure 3 showing two parallel-connected (redundant) UPS units.
Fig. 3
When increased power is required (two to
four parallel units), an external bypass
must be added (see figure 4).
Fig. 4
isolation and protection
devices
(See figure 1 on previous page):
■ Q1 (Molded circuit breaker NA):
❏ isolation of the rectifier/charger (A) from
the normal AC source (1);
❏ rectifier/charger (A) start-up;
■ QF1 (circuit breaker):
❏ battery (D) protection and isolation;
■ Q5N (switch):
❏ isolation of the UPS (B) from the load;
■ Q4S (switch):
❏ isolation of the static bypass (C) from
the bypass AC source (2);
■ Q3BP (switch):
❏ bypass switch for maintenance;
■ FUE (fuses):
❏ protection of the rectifier/charger (A)
from the normal AC source;
■ FUS (fuses):
❏ protection of the inverter (B) from the
load.
Note:
■ switch Q3BP is lock on open position on
parallel UPS systems constituted to
increase available power.
external bypass for parallel
UPSs and the hot-swap
option
See figure 4.
■ Q5N: isolation of the inverters of all the
parallel UPS systems from the load;
■ Q3BP: bypass for maintenance.
2
1
Q3BP
Galaxy 1
Galaxy 2
2
1
Galaxy 3
2
1
Galaxy 4
2
2
Q5N
1
2
1
Q3BP
S
Galaxy 1
Galaxy 2
2
2
Q5N
1
1
2
AB
C
D
User’s Manual
Introduction
Page 14
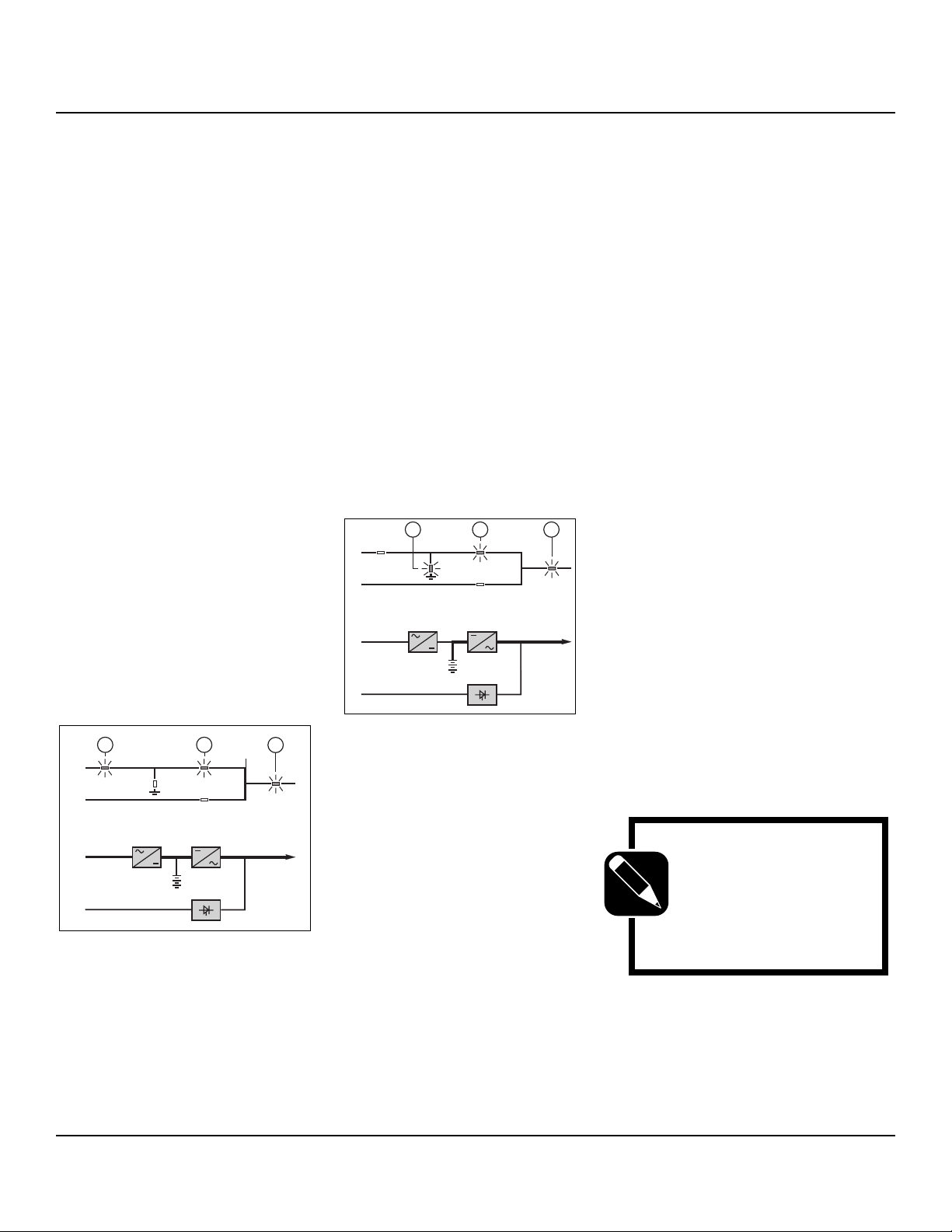
6 Introduction
operation in on-line
mode
normal operation
Normal AC source power is available (see
figure 5).
■ lights 1 , 4 and 5 shine green on
the control panel;
■ the power necessary for the load is pro-
vided by the normal AC source (1) through
the rectifier/charger (A) and the inverter
(B);
■ the rectifier/charger (A) also supplies
the power to float charge and recharge the
battery if any.
The rectifier/charger output voltage (DC) is
regulated to supply:
❏ the float-charging or the recharging volt-
age for vented lead-acid or Ni/Cd batteries,
❏ a single charge voltage for sealed lead-
acid batteries.
The voltages depend on the number of
battery cells and the battery manufacturer.
Factory set, they may also be adjusted by
after-sales support technicians.
An electronic board continuously measures the battery temperature and automatically adjusts the voltages.
Note:
In parallel Galaxy PW™ systems, the
power drawn by the load is equally shared
between the different units.
Fig. 5
operation with the normal AC
source down
See figure 6.
In the event of a normal AC source failure
or voltage outside specified tolerances of
±10% in amplitude (±15% optionally), the
rectifier/charger (A) stops and the battery
(D) supplies the necessary backup power
to the load via the inverter (B). The battery, float-connected between the rectifier/charger and the inverter, discharges
during this operating mode.
Lights 2 , 4 and 5 shine green.
The user is warned of battery operation by
the slow beeping of the buzzer 6 (see
figure 16) and the message "LOAD PROTECTED, BATTERY DISCHARGING", followed by the remaining backup time and
the percent load.
This information is also available via voltfree changeover contacts for remote control devices.
Fig. 6
battery time
The available battery time during a normal
AC source outage depends on the:
■ rated capacity of the battery;
■ power consumed by the load;
■ temperature of the battery;
■ age of the battery.
The specified battery time corresponds to
a minimum duration at full rated load.
The actual backup time can therefore be
greater if the system operates below its
full rated load during the normal AC
source outage. Operation on battery
power can be extended beyond the specified time by reducing the load power consumption (by disconnecting non-critical
loads).
A "low battery" warning signal is sent via
volt-free changeover contacts for remote
control devices when the battery voltage
reaches a level slightly above the minimum level. This signal warns the user of
the imminent end of battery power. On the
device itself, the buzzer beeps rapidly.
The message "LOW-BATTERY SHUTDOWN WARNING" is displayed, followed
by the remaining backup time and the percent load. Light 2 turns red and flashes.
Battery power stops when the voltage
supplied by the battery reaches the minimum threshold. This results in inverter
shutdown and transfer of the load without
interruption to the bypass AC source. Light
2 shines red (not flashing). The message "LOAD NOT PROTECTED, ONLINE MODE" is displayed and the buzzer
sounds continuously.
If the bypass AC source also fails, the
load is no longer supplied. The inverter
automatically shuts down when the time
on battery power exceeds three times the
specified backup time.
NOTE
The "low battery shutdown" warning signal can
be sent with an adjustable
time delay prior to the
effective end of battery
power.
1
2
AB
C
D
2
1
4
5
1
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
4 52
1
2
AB
1
D
C
2
Page 15

7Introduction
operation with the normal AC
source restored
See figure 7.
When normal AC source power (1) is
restored or its voltage returns to within
specified tolerances, the system automatically returns to its normal operating mode
described above (on the condition it did
not reach the end of battery power). If the
end of battery power was reached (with
the resulting inverter shutdown), the rectifier/charger (A) restarts automatically, but
the inverter (B) must be restarted manually.
The rectifier/charger recharges the battery
(D) which was discharged during the
mains outage. During battery charging,
light 2 flashes green.
The message "BATTERY CHARGING" is
displayed, together with the value of the
recharging current and battery voltage.
The battery charge cycle takes place in
two steps (see figure 8):
■ step 1: the battery is recharged at a
constant current limited to 0.1C10 (i.e.
1/10th of the battery capacity specified for
a 10 hour discharge). The DC voltage
increases with the battery charge until the
charge level is reached;
■ step 2: the battery is recharged at con-
stant voltage equal to the charge level.
The charging current gradually decreases
until reaching a specified low value (floating current).
For vented lead-acid batteries, the rectifier/charger supplies the charging voltage
for 0 to 255 hours (parameter defined by
the after-sales support department) and
then the floating voltage. For sealed leadacid batteries, the charging and floating
voltages are the same.
Battery charge cycle
Fig. 8
NOTE
If the normal AC source
failure is shorter than 0 to
255 seconds (default value
= 30 seconds) (parameter
defined by after-sales support department), the
charger automatically supplies the floating voltage
given the low battery discharge.
1
2
AB
C
D
2
1
4 521
U/I
current
limiting
0,1 C10
constant voltage
decreasing current
voltage
current
t
U charge/floating
(sealed batteries)
U "floating"
(vented batteries)
Fig. 7
User’s Manual
Page 16

8 Introduction
inverter shutdown or
overload
See figure 9 for devices or installations
operating in on-line mode with a bypass
AC source.
Fig. 9
single-UPS unit (on-line mode)
■ in the event of a UPS shutdown (initiat-
ed by the user or by an internal protective
device), the load is automatically transferred to the bypass AC source. If transfer
conditions are satisfied, transfer takes
place instantly, without interruption to the
load;
Note: transfer conditions are not satisfied
when bypass AC source characteristics
are outside tolerances (voltage: ±10%; frequency as per personalization; phase sync
with inverter ±3°);
■ in the event of a major transient over-
load (greater than 1.65 In), immediate
transfer takes place as above, without
interruption to the load.
The return to the inverter is automatic
when the overload disappears if the number of possible returns has not been
reached (0 to 255, programmable by personalization). If this number has been
reached, the load continues to be supplied
by the bypass AC source. This operating
mode allows start-up of load devices
causing high inrush currents.
This system requires satisfied transfer
conditions.
If the conditions are not satisfied, the
inverter will current limit to 165% of its
rated current for 1 second before stopping;
■ in the event of a small but extended
overload (i.e. a continuous level of power
exceeding the full rated load), the inverter
will continue to supply power for a period
depending on the magnitude of the overload (10 minutes for a 125% overload, 1
minute for a 150% overload). See the
overload curve in figure 10;
■ in all three of the above cases, inverter
shutdown and supply of the load via the
bypass AC source results in the following
on the control panel:
❏ light 4 goes off,
❏ activation of the buzzer (continuous
beep),
❏ light 3 shines green,
❏ the message "LOAD NOT PROTECT-
ED, ON-LINE MODE" is displayed.
parallel UPSs without redundancy
The shutdown of one inverter results in
overload on the other inverters in operation. Two cases may then arise:
■ if the overload on each remaining invert-
er is >
than 1.65 ln, the load is immediate-
ly transferred to the bypass AC source;
■ if the overload is less than 1.65 ln, the
remaining inverters support the overload
(see curve in figure 14), and the load is
transferred to the bypass AC source;
■ after this transfer:
❏ the light 4 goes off,
❏ the buzzer is activated and sounds con-
tinuously,
❏ the light 3 goes on and turns green,
❏ the message "LOAD NOT PROTECT-
ED, PARALLELON-LINE MODE" is displayed.
Fig. 10
parallel UPSs with redundancy
■ the shutdown of one UPS unit is of no
consequence for the load. The others
each take up an equal amount of load
power and the load continues to be supplied normally;
Unit shutdown results in the following on
the control panel:
❏ lights 4 and 5 go off,
❏ activation of the buzzer (continuous
beep),
❏ the message "LOAD NOT PROTECT-
ED, PARALLELON-LINE MODE" is displayed;
■ in the event of an overload, the system
only loses its redundancy as long as the
overload is less than the total rated power
of the functioning units. If the overload is
greater, the operating mode is that previously described for systems without
redundancy.
2
1
1
2
AB
C
D
3 5
I
12345678910
(min)
1,5 In
1,35 In
1,25 In
1,15 In
1,10 In
1,05 In
In
t
30 120
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 17

9Introduction
operation with an engine
generator set
See figure 11 below.
If a stand-by generator is included in the
installation, it is generally started automatically in the event of a normal AC source
failure and connected to the main low voltage switchboard. It is disconnected when
normal AC source power is restored.
With such a system, the required battery
time may be reduced to the time necessary for starting and bringing on line the
stand-by generator. The battery (D) sup-
plies power to the inverter (B) during the
transfers:
■ normal AC source to the generator;
■ generator to the normal AC source.
The transfer sequences described above
(normal AC source ➜ battery, battery ➜
generator, generator ➜ battery, and battery ➜ normal AC source) are fully automatic. They in no way affect the load and
require no manual operation by the user.
output voltage quality
and continuity
The output voltage is stable in amplitude
and frequency and is free of interruptions or
transients outside specified tolerances, irrespective of normal AC source or load disturbances (outages, load step changes, etc.).
steady state voltage
regulation
For stable or slowly varying load conditions, the inverter output voltage is regulated to within ±0.5% in amplitude.
The frequency of the output voltage can
theoretically be regulated to within 0.1% of
the rated value, however the output frequency range may be intentionally extended to a maximum of ±2 Hz so that the
inverter can remain synchronized with the
bypass AC source and its inherent frequency fluctuations, thus enabling transfer
of the load to the bypass line at any time.
When the bypass AC source frequency
returns to within the specified tolerances,
the inverter is gradually re-synchronized to
the bypass line at a rate of 0.5 Hz to 2
Hz/s (as per the value personalized by the
after-sales support department), thus
avoiding exposing the load to sudden frequency variations.
transient voltage regulation
The inverter output voltage is not notably
affected by instantaneous major variations
in load characteristics.
This is made possible by the PWM (Pulse
Width Modulation) chopping technique
and the microprocessor-based regulation
system that instantly compensates for any
variation. In particular, the inverter output
voltage remains within +/- 2% of the rated
voltage for load step changes of 0 to
100% or of 100 to 0%.
NOTE
The output frequency
range can be personalized
and if necessary modified
on the customer site by a
qualified MGE UPS SYSTEMS support technician
from ±0.25 Hz to ±2 Hz in
0.25 HZ steps.
When the bypass AC
source voltage moves outside this frequency range,
the inverter is desynchronised and operates in
"free running" mode, with
the output frequency regulated to a high level of
accuracy by a quartz
oscillator.
NOTE
To avoid load surges on
the generator, the rectifier/charger is started with
a 10 second maximum
current consumption
walk-in (lasting 3 to 10
seconds, depending on
the percent load).
To avoid overloading an
undersized engine generator set, it is possible to
set a maximum power
level drawn by the normal AC input. Any additional power required is
supplied by the battery.
This modification can be
made on site by an MGE
UPS SYSTEMS field
engineer.
Example of an installation with an engine generator set
Fig. 11
HV system
Mains 2
Mains 1
Galaxy PW
G
A
B
D
C
generator
main LV switchboard
User’s Manual
Page 18

10 Description of Galaxy PWTMCabinets
Description of Galaxy
PW™ Cabinets
UPS cabinet
See figure 12 for the layout of the various
cabinet components.
Legend for figure 12:
1 - rectifier/charger module,
2 - inverter module,
3 - static-bypass module,
4 - card case for electronic control boards,
5 - rectifier/charger input fuses "FUE",
6 - inverter output fuses "FUS",
7 - normal AC input circuit breaker Q1,
8 - bypass AC input switch Q4S,
9 - maintenance bypass switch Q3BP
(locked in open position on parallel UPSs
for greater capacity),
10 - output switch Q5N,
11 - display board,
12 - Media Contacts 11 remote indications
board,
13 - backfeed protection.
battery cabinet
Figure 13 shows an example of component layout in a battery cabinet or a battery circuit-breaker enclosure.
Legend for figure 13:
1 - battery isolation and protection circuit
breaker QF1,
2 - battery cells.
Fig. 13
Example only and may not represent actual units shipped
Fig. 12
11
12
1 2 2 2 3
3
4
8
9
10
5 6
13
GND
N
7
2
2
2
2
1
1
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
description of
galaxy PW™ cabinets
Page 19

11Control Panel
general
The control panel on Galaxy PW™ UPSs
comprises the basic controls and indications required to check the general status
of the system (see figure 14).
Located in the upper right part of the cabinet front, the control panel is designed to
provide an easy and rapid overview of
system status (see figure 14).
Interpretation of symbols is very simple
and requires no particular training. The
information concerns only the cabinet on
which the panel is located.
The panel indicates:
■ normal operation (load protected);
■ operation with load on battery power;
■ abnormal situations (operating problem);
■ dangerous situations (load not protect-
ed).
indications
See figure 14.
"Rectifier/charger" light
1
■ light off: rectifier/charger OFF;
■ light shines green: rectifier/charger ON;
■ light shines red: rectifier/charger fault,
the stored alarm indicates one or several
of the following faults:
❏ input circuit breaker Q1 open,
❏ protection fuse at the rectifier/charger
input (FUE) blown,
❏ abnormally high internal rectifier/charger
temperature,
❏ abnormally high battery charge current,
❏ abnormally high battery voltage,
❏ fault, non-calibration or non-personaliza-
tion of the electronic control board for the
rectifier/charger,
❏ fault on the electronic power-supply
board,
❏ abnormally high temperature in the har-
monic filter inductor.
"Battery light"
2
■ light off: battery float charging;
■ light flashing green: battery recharging;
■ light shines green: load on battery
power;
■ light flashing red: low-battery shutdown
warning;
■ light shines red: battery at end of back-
up time and circuit breaker QF1 open, or
battery fault.
"Static-bypass" light
3
■ light off: bypass AC source within speci-
fied tolerances and static bypass open;
■ light shines green: static bypass closed;
■ light shines red: the stored alarm indi-
cates one or several of the following
faults:
❏ bypass AC source voltage or frequency
outside specified tolerances,
❏ static-bypass fault,
❏ abnormally high internal static-bypass
temperature,
❏ static-bypass ventilation fault,
❏ power-supply fault for the static-bypass
control function,
❏ fault on the electronic board controlling
the transfer function,
❏ non-calibration or non-personalization of
the electronic control board for the inverter,
❏ fault on the electronic power-supply
board,
❏ fault on monitoring the "inverter ready"
response channels (parallel UPS system).
"Inverter" light
4
■ light off: inverter OFF;
■ light flashing green: inverter starting,
inverter ON but not connected to the load;
■ light shines green: normal inverter oper-
ation;
■ light shines red: inverter fault, the stored
alarm indicates one or several of the following faults:
❏ inverter shutdown due to inverter output
voltage outside specified tolerances,
❏ protection fuse at the inverter output
(FUS) blown,
❏ abnormally high inverter-output trans-
former temperature,
❏ abnormally high inverter temperature,
❏ output-voltage fault (amplitude or phase)
(parallel UPSs),
❏ fault, non-calibration or non-personaliza-
tion of the electronic control board for the
inverter,
❏ fault on the electronic power-supply
board.
Fig. 14
1
2
V A W.Hz
fault
18
17
8
7
643 521
22
2119 20
16
9 10 11 12 13 1514 15
User’s Manual
control panel
Page 20

12
"Load" light
5
■ light off: load not supplied;
■ light shines green: load supplied via the
inverter or the bypass AC source (via the
static bypass).
Buzzer
6
The buzzer sounds in the following situations:
■ load supplied by the bypass AC source;
■ load on battery;
■ operating problems.
It sounds slowly and discontinuously for a
minor problem or when the inverter is on
battery power.
When the alarm "LOW BATTERY SHUTDOWN" is activated, the buzzer sounds
more rapidly. Finally, if the inverter shuts
down, the beep is loud and continuous.
The buzzer may be reset by pressing a
button. If the buzzer is reset, a higher
level alarm will set it off again.
"Inverter ON" button
7
This button is used to start the inverter
locally.
"Inverter OFF" button
8
This button turns the inverter off locally.
Keys 9 and 10
These keys are used to select commands
in the main menu and access the secondary messages.
Key 11
This key is used to validate the user’s
choice.
Key 12
This key is used to access the main
menu: display language, display-contrast
setting, sound level of the buzzer, lamp
test, date and time settings, inverse-video
and event log.
"V" key 13
This key is used to access voltage measurements:
■ normal AC source phase-to-phase volt-
ages;
■ bypass AC source phase-to-phase and
phase-to-neutral voltages;
■ load phase-to-phase and phase-to-neu-
tral voltages.
"A" key 14
This key is used to access current measurements:
■ normal AC source, bypass AC source
and load currents;
■ percent load;
■ load crest factor.
"W.Hz" key 15
This key is used to access other measurements:
■ normal AC source, bypass AC source
and inverter frequencies;
■ level of active and apparent power
drawn by the load;
■ load power factor;
■ inverter load level (percent).
"Anomaly" indicator light 16
This indicator light indicates the presence
of anomalies.
key 17
This key is used to access the primary
messages.
"Battery" key 18
This key is used to access battery measurements:
■ battery voltage (or the DC voltage on
frequency converters without a battery);
■ battery current (charge or discharge);
■ battery temperature;
■ available battery backup time;
■ inverter load level (percent).
"Forced-transfer" key 19
This key is used to voluntarily transfer the
load to the inverter or from the inverter to
the static bypass (return transfer). Transfer
and return transfer are carried out only following confirmation requested by the system display and a warning as to the risk of
an interruption in the supply of power to
the load.
"Alarm reset" key 20
This key is used to reset stored alarms.
The system accepts resetting only when
alarms have been cleared.
"Buzzer reset" key 21
This key is used to stop the buzzer.
However, new alarms set the buzzer off
again.
Display 22
The display continuously indicates the
system operating status.
Control Panel
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 21

13
system start-up
single-UPS unit or redundant
parallel UPS
See figure 15.
Proceed in the following order:
■ close the upstream switches supplying
normal and bypass AC source power (on
the LV switchboard);
■ close normal AC input switch Q1. The
system powers up:
❏ the rectifier/charger automatically starts,
❏ green light 1 on the control panel goes
on,
❏ light 2 turns red;
■ close bypass AC input switch Q4S:
❏ green lights 3 and 5 on the control
panel go on;
■ close inverter output switch Q5N;
■ close battery circuit breaker QF1;
❏ light 2 goes off;
■ open maintenance bypass switch
Q3BP;
■ press the "inverter on" button 7 on the
control panel:
❏ the green "inverter" light 4 flashes,
❏ the inverter starts, then, if the bypass AC
source transfer conditions are satisfied,
the load is transferred to the inverter if the
on-line mode is selected.
❏ the green "static-bypass" light 3 goes
off,
❏ the green "inverter" light 4 shines for
on-line mode.
parallel UPS unit for
increased output
See figure 16.
Proceed in the following order:
■ check that all load devices are off or
that the load is disconnected;
■ close the upstream switch supplying
normal AC source power (on the LV
switchboard);
■ close the normal AC input circuit break-
ers Q1 on the UPS units. The system
powers up:
❏ the rectifier/chargers automatically start,
❏ the green "rectifier/charger" lights 1 in
the control panels go on,
❏ lights 2 turn red;
■ close the battery circuit breakers QF1;
❏ lights 2 go off;
❏ green lights 3 and 5 on the control
panels go on;
■ close output switches Q5N for the
inverters and in the external bypass unit;
■ open maintenance bypass switch Q3BP
in the external bypass unit;
■ press the "inverter on" button 7 on
each control panel:
❏ the green "inverter" lights 4 flash;
■ when a sufficient number of inverters
are ready, the inverter-output contactors
close:
❏ the green "inverter" lights 4 shine per-
manently green;
❏ the "static-bypass" lights 3 go off.
start-up of a module
start-up of a rectifier/charger
■ rectifier/charger start-up is automatic
when the normal AC input circuit breaker
Q1 is closed:
❏ the green "rectifier/charger" light 1 on
the control panel goes on;
■ close battery circuit breaker QF1.
start-up of an inverter
When the rectifier/charger is on:
■ press the "inverter ON" button 7 on the
control panel;
❏ the green "inverter" light 4 flashes.
Single-UPS unit
■ the inverter starts, then, if the bypass
AC source transfer conditions are satisfied, the load is transferred to the inverter
if the on-line mode is selected. For online mode:
❏ the green "inverter" light 4 remains on,
❏ the "static-bypass" light 3 goes off.
Parallel UPS unit
■ the inverter starts and awaits the start of
the other inverters;
■ when they are all on or enough have
been started to supply the rated load
power, the output switch for each running
inverter closes and the load is supplied
with power:
❏ the green "static-bypass" light 3 goes
off,
❏ the green "inverter" light 4 on the con-
trol panels of the running inverters goes
on.
WARNING
Rectifier/charger start-up
is automatic when normal
AC input circuit breaker
Q1 is closed. DC voltage
is present in the DC bus.
start-up
Start-up
Fig. 16Fig. 15
Q5NQ1 Q4S
QF1
0
I
3
1
2
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Q3BP
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
5
4
6
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
3
1
2
1
0
1
0
4
Q5NQ1
Q5NQ1
QF1
0
I
1
0
1
0
User’s Manual
Page 22

14
shutdown of the inverter
■ press the "inverter OFF" button 8 on
the control panel for three seconds (see
figure 19).
single-UPS unit
■ the green "inverter" light 4 on the con-
trol panel goes off;
■ the green "static-bypass" light 3 goes
on;
■ the inverter stops;
■ if bypass AC source (Mains 2) transfer
conditions are satisfied, the inverter shuts
down and the load is transferred to the
bypass AC source;
■ if bypass AC source (Mains 2) transfer
conditions are not satisfied, the inverter
does not shut down. The message
"MAINS 2 OUTSIDE TOLERANCES,
TRANSFER DISABLED" is displayed.
parallel UPS unit
■ if the system is redundant, i.e. the other
parallel-connected inverters can supply
the load on their own, the inverter shuts
down and the green "inverter" light 4
goes off.
The load is not affected in that the other
inverters continue to supply it normally;
■ if the system is not redundant, the other
inverters go to overload status.
If overload conditions are overrun, the
load is transferred to the bypass AC
source:
❏ the green lights 3 turn green,
❏ the green "inverter" light 4 goes off.
shutdown of a
rectifier/charger
It is recommended not to stop the rectifier/charger because the battery will no
longer be charged. Except in the case of a
test of the inverter on battery power, the
rectifier/charger should be shutdown after
the inverter to avoid unnecessary battery
discharge.
Proceed in the following order:
■ open battery circuit breaker QF1;
■ open normal AC input circuit breaker
Q1:
❏ the rectifier/charger shuts down,
❏ the green "rectifier/charger" light 1
goes off.
Shutdown
shutdown
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 23

15
control-panel display
general organization
The display is structured around primary
and secondary messages, measuring
tables and setting screens. As a rule, the
message displayed on the screen is
always a primary one. The secondary
messages, if any, are accessed by pressing keys 9 ▼ and 10 ▼ (see figure 16).
The presence of secondary messages is
indicated by the arrow ↓↓at the end of the
primary message. Return to the primary
messages is automatic if the keypad is not
used for 2 minutes, or direct by pressing
key 17 (see figure 14). The display
screen lights up when a key is pressed,
and goes off if no key is pressed for 5
minutes.
display of messages
In addition to keypad operations, the
graphical display brings up a window giving the overall device status. The message displayed is then said to be primary
(see list in the paragraph below). Aprimary message can be used to access the
measuring tables using keys 13 , 14 , 15
and 18 on the keypad (see figure 17 in
the general appendix). The configuration
screens can be accessed by pressing key
12 .
A flashing arrow appears at the end of a
primary message if there is a problem or
an alarm; secondary messages can be
accessed by pressing key 9 on the keypad (see the list of secondary messages).
The presence of another message is indicated by the arrows ↓↓and ↑↑at the end
of the secondary message. They can be
accessed by pressing keys 9 and 10
on the keypad.
The return to the primary message is
automatic after a 2 minute time delay or
by pressing key 17 on the keypad.
IMPORTANT
Select English U. S. as
the display language to
match the displays as
presented in this manual.
NOTE
Most functions may be
directly accessed. For
example, when voltage
measurements are currently displayed, it is possible to directly access
current measurements by
pressing the "A" button.
Control-panel Display
Fig. 18
(ALARM MESSAGE N° 2)
(LAST ALARM MESSAGE)
primary message
main screen
(ALARM MESSAGE N° 1)
Display of alarms
Fig. 17
1
2
V A W.Hz
fault
18
17
8
7
643 521
22
2119 20
16
9 10 11 12 13 1514 15
User’s Manual
Page 24

16
list of primary messages
LOAD PROTECTED
ON-LINE MODE
This is the normal display when there are
no alarms or problems and the load is correctly supplied by the inverter, in on-line
mode.
LOAD PROTECTED
PARALLELON-LINE MODE
This is the normal display when there are
no alarms or problems and the load is correctly supplied by the inverter in a parallel
UPS system, in on-line mode.
LOAD NOT PROTECTED
ON-LINE MODE
↓↓
This display indicates that the load is not
supplied by the inverter, or that there is no
battery backup. The arrow ↓↓indicates
the presence of one or more problems
specified in secondary messages.
The buzzer sounds continuously.
LOAD NOT PROTECTED
PARALLELON-LINE MODE
↓↓
Situation identical to that in the previous
screen, but for parallel UPS systems.
LOAD PROTECTED
BATTERY DISCHARGING
Remaining battery time (min) = XX
% kW used = XXX
The load is supplied by the inverter, but
the normal AC source is down or outside
tolerances and power is supplied by the
battery.
This message indicates the remaining battery time in minutes prior to inverter shutdown and the percent load. The battery
time calculation takes into account:
■ the percentage of full rated load power
currently being drawn;
■ the type of battery;
■ battery temperature;
■ battery age.
The buzzer sounds slowly and discontinuously.
LOAD PROTECTED,
LOW-BATTERY SHUTDOWN
WARNING,
Remaining battery time (min) = XX
% kW used = XXX
This message replaces the preceding if
the power outage persists and the warning
level has been reached.
The user is warned that the battery is
about to shut down.
The buzzer sounds rapidly and discontinuously.
LOAD PROTECTED
ECO MODE
This is the normal display when there are
no problems: the load is supplied by the
inverter or the bypass AC source, and battery backup is available.
LOAD NOT PROTECTED
ECO MODE
↓↓
This display indicates that the load is supplied but has no battery backup. The
arrow ↓↓indicates the presence of one or
more problems specified in secondary
messages.
The buzzer sounds continuously.
LOAD FORCED TO INVERTER
ECO MODE
The load has been transferred to the
inverter following a specific request by the
user.
Control-panel Display
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 25

17
list of secondary messages
LOAD ON MAINS 2
The load has been transferred to the
bypass AC source (M2) and is no longer
protected (only in on-line mode). The
buzzer sounds continuously.
MAINS 2 OUTSIDE TOLERANCES
TRANSFER DISABLED
CHECK MAINS 2
The bypass AC source (M2) frequency or
voltage is outside tolerances and the
inverter is unable to synchronize.
Transfer of the load from the inverter to
the bypass AC source (M2) or vice-versa
will result in an interruption of the supply
of power to the load. The buzzer sounds
slowly and discontinuously.
BATTERY OVERTEMPERATURE,
CHECK VENTILATION
The battery temperature is outside tolerances. The buzzer sounds slowly and discontinuously.
BATTERY ROOM VENTILATION
FAULT, CHECK VENTILATION
A fault requiring servicing has occurred in
the battery room ventilation system. The
rectifier/charger shuts down after a 30second time delay.
The user must take steps to re-establish
correct operation of the ventilation system.
This message also signals an abnormally
high temperature in the filter inductor.
The buzzer sounds slowly and discontinuously.
MAINS 1 OUTSIDE TOLERANCES,
CHECK MAINS 1
The normal AC source (M1) frequency or
voltage is outside specified tolerances and
the rectifier/charger has shut down. The
inverter is on battery power.
MAINS 1 INPUT SWITCH Q1
IS OPEN
The normal AC input (M1) switch Q1 is
open. It must be closed for rectifier/charger start-up. The buzzer sounds slowly and
discontinuously.
INTERNAL UPS FAULT,
LOAD TRANSFER FAULT,
CALL MAINTENANCE
A fault has occurred in the static switch
that transfers the load between the inverter and the bypass AC source (M2).
Servicing by the after-sales support
department is required. The buzzer
sounds continuously.
OVERLOAD
RATED CURRENT PER PHASE =
XXX A
CHECK LOAD LEVEL
This display informs the user that load current is greater than rated current, and
gives the value. The buzzer sounds continuously.
UPS SHUTDOWN DUE TO AN
OVERLOAD,
CHECK LOAD LEVEL
This message follows the preceding when
the overload persists. The UPS has shut
down and the buzzer sounds continuously.
INVERTER NOT IN PHASE WITH
MAINS 2.
TRANSFER DISABLED,
CHECK MAINS 2
The phase difference between the inverter
and the bypass AC source (M2) is outside
tolerances. Transfer of the load between
the inverter and the bypass AC source
(M2) will result in an interruption in the supply of power to the load.
For parallel UPSs, this message should be
interpreted as meaning the phase difference between the inverter for which the
message is displayed and the other inverters is outside tolerances.
UPS SHUTDOWN
BY AN EXTERNAL COMMAND
The inverter has received a command to
shut down. The command is in the form of
a signal from received the remote-indications relay board which has been set for
this function.
n the inverter is started again.
MAINS 2 INPUT SWITCH Q4S IS
OPEN
The bypass AC source (M2) input switch
Q4S is open, i.e. backup power for the
load via the bypass AC source (M2) is not
available.
INVERTER OUTPUT SWITCH Q5N
IS OPEN
Inverter output switch Q5N is open, i.e.
the load cannot be supplied via the inverter.
Control-panel Display
User’s Manual
Page 26
18
BYPASS SWITCH Q3BP
IS CLOSED
Maintenance bypass switch Q3BP is
closed. The system is in maintenance
configuration and the load is supplied by
the bypass AC source.
STATIC SWITCH (M2) OFF
DUE TO AN OVERLOAD
The load is no longer supplied by the
bypass AC source (M2), due to an extended overload. The buzzer sounds continuously.
BATTERY CHARGING
I BAT. = XXX A U BAT. = XXX V
The battery is currently being recharged.
BATTERY AT END OF SERVICE
LIFE CALL MAINTENANCE
The battery is nearing the end of its estimated service life. This information is
based on average service-life calculations
since its initial installation. The buzzer
sounds slowly and discontinuously.
EMERGENCY OFF
This message is displayed when the
external emergency-off pushbutton is
pressed. The result is:
■ shutdown of the inverter;
■ shutdown of the rectifier/charger;
■ opening of the battery circuit breaker;
■ blocking of the static bypass;
■ opening of the backfeed protection con-
tactor (M2),
■ opening of the Q1 circuit breaker (M1),
■ activation of a relay contact on the
remote-indications relay board.
Servicing by the after-sales support
department is required.
The buzzer sounds discontinuously.
THE BATTERY C.B. QF1 IS OPEN,
CHECK THE INSTALLATION
Battery circuit breaker QF1 is open. The
load is no longer protected because battery power is no longer available in the
event of a normal AC source outage. The
buzzer sounds continuously.
LOW BATTERY SHUTDOWN
The inverter has shut down at the end of
battery power. The buzzer sounds continuously.
INTERNAL UPS FAULT,
INVERTER FAULT,
CALL MAINTENANCE
A fault has occurred in the inverter.
Servicing by the after-sales support
department is required. The buzzer
sounds continuously.
INTERNAL UPS FAULT,
CHARGER FAULT,
CALL MAINTENANCE
A fault has occurred in the rectifier/charger. Servicing by the after-sales support
department is required.
The buzzer sounds slowly and discontinuously.
FORCED TRANSFER TO
INVERTER REQUESTED, POWER
TO LOAD MAY BE INTERRUPTED,
CONFIRM YOUR REQUEST WITH
KEY
↵↵
The requested transfer to the inverter may
provoke an interruption in the supply of
power to the load if Mains 2 characteristics are not within the specified tolerances.
THE NUMBER OF UPS READY IS
INSUFFICIENT,
LOAD TRANSFER IN STAND BY
This message may be displayed in nonredundant, parallel UPS systems, when
the number of ready inverters in not sufficient to supply the load.
INVERTER NOT CONNECTED
This message may be displayed in parallel
UPS systems, when the inverter is not
connected to the load.
PARALLELUPS,
FORCED TRANSFER INHIBITED
This message is displayed when forced
connection is requested on a parallel UPS
system for a power extension.
INTERNAL UPS FAULT,
SELF-TEST FAULT
Communication between the system and
the display is faulty. The buzzer sounds
slowly and discontinuously.
FORCED TRANSFER TO M2
REQUESTED,
POWER TO LOAD MAY BE INTERRUPTED
CONFIRM YOUR REQUEST WITH
KEY
↵↵
This message is displayed following
pressing of the "forced-transfer" key 20,
when the load is supplied via the inverter.
UPS SUPPLIED BY A GENERATOR
SET
This message informs the user that the
UPS has received the order to limit the
current drawn by the rectifier/charger. It is
displayed when the corresponding signal
is transmitted by the remote indications
board which must be configured for this
function.
VENTILATION FAULT
This message is displayed when a fault
occurs on a fan.
Control-panel Display
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 27

19
measurement system
The display may be used to read a number of input and output measurements
made at different points in the system.
See figure 18 .
■ normal AC source 1
❏ phase-to-phase voltages,
❏ currents of the three phases,
❏ frequency;
■ bypass AC source 2
❏ phase-to-neutral voltage,
❏ phase-to-phase voltages,
❏ frequency,
❏ currents of the three phases;
voltage measurements
These measurements may be accessed
by pressing the "V" key 13 . The following
data is displayed.
Note:
M1: normal AC source
M2: bypass AC source
current measurements
These measurements may be accessed
by pressing the "A" key 14 . The following
data is displayed.
Note:
CF: crest factor
power and frequency
measurements
These measurements may be accessed
by pressing the "W.HZ" key 16 . The following data is displayed.
Note:
PF: power factor
■ battery 3
❏ voltage;
❏ charge or discharge current;
❏ remaining battery time (for the UPS unit
concerned);
❏ battery temperature;
■ inverter output 4
❏ frequency;
■ total load 6
❏ phase-to-neutral voltage,
❏ phase-to-phase voltages,
❏ currents of the three phases,
❏ frequency,
❏ active and apparent power.
Control-panel Display
1
2
Q1
Q5N
QF1
U - V - I - F
U - I - F
U - I
F
U - V - I - F - P
AB
C
D
Q4S
6431
2
Fig. 19
LOAD KW KVA PL/PN = --- % FREQ.HZ
P1 ---- ---- M1 --.P2 ---- ---- M2 --.P3 ---- ---- FP.LOAD = -.- INV --.-
RMS M1 M2 LOAD FC-LOAD I-LOAD/I-NOM
I1 ---- ---- ---- -.-- ---- %
I2 ---- ---- ---- -.-- ---- %
I3 ---- ---- ---- -.-- ---- %
RMS M1 M2 LOAD RMS M2 LOAD
U12 ---- ---- ---- V1 ---- ---U23 ---- ---- ---- V2 ---- ---U31 ---- ---- ---- V3 ---- ----
User’s Manual
Page 28

20
battery measurements
These measurements may be accessed
by pressing the "battery" key 18 . The
following data is displayed.
selections and settings
These selections and settings may be
accessed by pressing the "contrast" key
12 . The following menu is displayed.
■ selecting the language:
■ adjusting the display contrast:
■ adjusting the buzzer volume:
■ lamp test:
When this function is selected, all the
lights shine orange for three seconds.
■ set date and time:
Use the "▲▼" keys to enter the data and
confirm using the "↵↵" key.
Control-panel Display
DA TE AND TIME SETUP
YEAR ---- MONTH -DA Y -- HOURS -MINUTES -- SECONDS --
BUZZER VOLUME SETUP
CHOOSE WITH KEYS
▼ OR ▼
VALIDATE WITH KEY
↵↵
DISPLAY CONTRAST SETUP
CHOOSE WITH KEYS
▼ OR ▼
VALIDATE WITH KEY
↵↵
FRENCH SPANISH
ENGLISH DUTCH
GERMAN SWEDISH
ITALIAN PORTUGUESE
CHOOSE LANGUAGE DATE AND TIME
CONTRAST SETUP INVERSE VIDEO
BUZZER SETUP PAST EVENTS
LAMP TEST BATTERY TEST
BATTERY
U = ---- V REMAINING TIME = ---- MIN
I = ---- A PL / PN = ---- %
T° = ---- °C
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 29

21
■ inverse video:
When this function is selected, the text and
background colours are reversed (white
text on black or black text on white).
■ past events:
See section "logging and time-stamping".
■ battery test:
❏ the screen opposite is displayed when a
battery test is requested. It indicates the
battery charge status and the remaining
service life. Amanual or automatic test
may be requested,
❏ the screen opposite is displayed during
a battery test, whether manual or automatic,
❏ the screen opposite is displayed follow-
ing a positive, manual battery test,
❏ the screen opposite is displayed follow-
ing a negative, manual battery test,
❏ the screen opposite is displayed follow-
ing a positive, automatic battery test. It
indicates the time since the last test and
provides access to test settings,
❏ the screen opposite is displayed follow-
ing a negative, automatic battery test. It
indicates the time since the last test and
provides access to test settings,
❏ the screen opposite is displayed when
the user requests access to the automatic
test settings. It is possible to modify the
interval between two automatic tests,
❏ the screen opposite is displayed when
the battery test cannot be completed.
Control-panel Display
SELECT TIME OF NEXT TEST WITH KEYS ▼▼
CHANGE UNITS WITH
↵↵
WEEK -- DAY -- HOUR -confirm with key
TIME SINCE LAST TEST
WEEK -- DAY -- HOUR -LAST BATTERY TEST RESULT NOT OK
NEW PARAMETERS YES = ▼ NO = ▼
TIME SINCE LAST TEST
WEEK -- DAY -- HOUR -LAST BATTERY TEST RESULT OK
NEW PARAMETERS YES = ▼ NO = ▼
BATTERY TEST RESULT NOT OK
BATTERY TEST RESULT OK
TESTING BATTERY
U BATTERY = --- V
CHARGE LEVEL = -- %
REMAINING SERVICE LIFE = -- MONTH
■ MANUAL TEST press key
↵↵
■ AUTO TEST press key
↵↵
TEST INTERRUPTED
CHECK PRESENCE OF THE BATTERY
CHECK ALARMS
User’s Manual
Page 30

22
general
The auto diagnostic system considers any
system status other than normal as a
problem.
Before taking any action, note down the
messages displayed on the control panel.
Certain problems may prevent the control
panel from functioning.
In this case, it is strongly recommended to call the MGE UPS SYSTEMS aftersales support department.
■ If the load is still correctly supplied with
power, it has probably been transferred to
the bypass AC source (static bypass) and
is therefore no longer protected (if the system is in on-line mode);
■ if the load is no longer supplied with
power, transfer it manually to the maintenance bypass (see section below).
maintenance bypass
This operation is possible only if the system includes a bypass AC source. It
results in the load being directly supplied
by the bypass AC source via maintenance
bypass switch Q3BP, thus ensuring a
higher level of security in the event of a
malfunction.
Switching procedures are explained on
drawings next to each switch in the UPS
cabinet and the external bypass unit. See
section "maintenance configuration".
Alarms
alarms
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 31

23
environment information
Terminals XR2, XR3, XR4 and XR5 on the
"Media Contacts 11" board of each type of
unit can be used to receive signals from
the operating environment and to transmit
signals concerning the operating status of
the UPS (see figure 16 for the position of
the board, item 12).
signal reception
The signals should be provided by voltfree contacts.
■ emergency off:
An NC contact causes shutdown of the
inverter and the rectifier/charger, opening
of the battery circuit breaker, blocking of
the static bypass and activation of a relay
contact on the "Media Contacts 11" board;
■ battery room ventilation fault:
An NO contact causes shutdown of the
rectifier/charger;
■ battery circuit breaker QF1 closed:
An NO contact prevents inverter start-up if
the circuit breaker is open;
■ battery temperature:
A PC-board, placed near the battery, supplies information on the battery temperature, thus enabling the rectifier/charger to
regulate the battery voltage;
■ "auxiliary" signals:
Depending on the selected settings, these
signals may be used to provoke:
❏ forced shutdown of the inverter (whatev-
er the status of the bypass AC source),
❏ protected shutdown of the inverter (load
transfer to the bypass AC source).
❏ limiting of the current drawn by the recti-
fier/charger (programmable value) when
supplied by an engine generator set with
an insufficient power rating. The additional
power required by the inverter is supplied
by the battery which discharges,
❏ limiting of the battery charge current
(programmable value) if the normal AC
source is replaced by an engine generator
set with an insufficient power rating.
signal transmission
■ an auxiliary 24 V power supply, isolat-
ed and backed up, is used to supply:
❏ the undervoltage release of the battery
circuit breaker(s) QF1,
❏ the board that measures the tempera-
ture in the battery room;
■ "low battery" warning signal (volt-free
changeover contact) indicating that battery
time is about to run out. The warning
threshold may be personalized;
■ "load on UPS" signal (volt-free
changeover contact) indicating that the
load is supplied by the inverter. For a single-UPS unit, one volt-free changeover
contact may be used to indicate that the
load is supplied by the bypass AC source;
■ "load on battery power" signal (volt-
free changeover contact) indicating that
the inverter is supplied by the battery in
the following cases:
❏ normal AC source outage or voltage
drop,
❏ rectifier/charger shutdown,
❏ rectifier/charger current limiting.
This signal, which may be used to initiate
process saving and shutdown procedures,
is time-delayed 30 seconds to avoid
unnecessary operations following microbreaks;
■ "maintenance position" signal (volt-
free changeover contact) indicating that:
❏ maintenance bypass switch Q3BP is
closed,
❏ bypass AC source input switch Q4S is
open,
❏ inverter output switch Q5N is open,
❏ battery circuit breaker QF1 is open;
■ signal to open battery circuit break-
er(s) QF1 in the event the "emergency off"
button is pressed or to avoid an excessive
battery discharge (lasting more than three
times the rated backup time plus two
hours);
■ repo contact (volt-free changeover con-
tact) used to trip switching devices in the
event of an emergency shutdown.
■ "general alarm" information (volt-free
changeover contact) which includes:
❏ internal faults,
❏ information on temperatures outside tol-
erances in the battery room (optional),
❏ overload information (> In),
❏ static-switch ventilation and power-sup-
ply faults.
NOTE
The maximum breaking
capacity of the
changeover contacts is
5A at 250V.
Environment Information
User’s Manual
Page 32

24
presentation of event
time-stamping by Galaxy
PW™
Time-stamping of events by Galaxy PW™
makes it possible to:
■ log the events;
■ consult the last 500 events that occurred
on the Galaxy PW™ UPS;
■ consult general statistical data on UPS
operation;
utilization via the Galaxy
PW™ display
main menu
The time and date can be set for the UPS
via the main menu on the display (see
below), using the DATE AND TIME command. The time-stamping information, statistics and measurement records are also
available via the same menu, using the
PAST EVENTS command.
Simply select the desired command with
the ">" sign that can be moved using the
▼ and ▼keys. The selected command
can be confirmed by pressing the ↵↵key.
general instructions for using
most screens
You can display the desired information
and enter commands using the
▼, ▼
and ↵↵keys.
Press the key to exit the time-stamping consultation mode and return to the
main menu. If no commands are entered
for five minutes, the system automatically
returns to the normal display mode.
You can scroll through the screens displaying information. Press the
▼ and ▼
keys to scroll up and down through the
screens.
■ consult measurement records for a
number of physical values concerning system operation.
The time-stamping information may be
accessed via the Galaxy PW™ keypad
and display (standard equipment). This
information may also be forwarded for the
Teleservice function using the JBUS
RS232/485 communications board.
For time-stamped events, the display
begins with the last event logged. To
access older events, press the
▼ key. If
during consultation, you wish to review
more recent events, press the
▼ key.
setting the date and time for
the UPS
When the DATE AND TIME command is
selected, the screen presented opposite is
displayed:
■ the current values are automatically dis-
played;
■ you can modify any of the displayed val-
ues;
■ position the ">" sign opposite the value
to be modified. Then press the ↵↵key;
■ use the ▼ and ▼ keys to modify the
value;
■ the ▼key increments the value by one;
■ the ▼key decrements the value by
one;
■ the selected value can be confirmed by
pressing the ↵↵key. A second value may
then be selected for modification, again
using the
▼ and ▼keys;
■ modifications are made and confirmed
value by value;
■ press the key at any time to exit the
DATE AND TIME function.
Logging and time-stamping
DATE AND TIME SETUP
> YEAR 1997 MONTH 9
DAY 8 HOURS 8
MINUTES 11 SECONDS 42 ▼▼
logging and time-stamping
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 33

25
That is the only means to leave the function.
If no modifications to values are confirmed, exiting the function corresponds to
cancelling the request.
consulting logged (timestamped) events
When the PAST EVENTS command is
selected, the system displays a screen
indicating the last event logged. Log
screens are very similar to those displayed for current events. However, log
screens include a line indicating the corresponding date and time with the mention
"Appearance of" or "Disappearance of",
followed by the standard text for the event
(see example opposite). Consult the user
manual for indications on the meaning of
events.
The complete log may comprise up to 500
events. If over 500 events have occurred,
only the last 500 may be consulted:
■ press the ▼ key to display the event
that occurred just before the displayed
event. If the displayed event is the oldest
in the list, the display is not modified;
■ press the ▼ key to display the event
that occurred just after the displayed
event. If the displayed event is the most
recent in the list, the display is not modified.
consulting statistics
See the screen opposite.
■ total backup time (h): this is the total
time of operation on battery power since
initial startup of the UPS. It is expressed in
hours;
■ total time on static switch (h): this is
the total time of operation on the static
switch since initial startup of the UPS. It is
expressed in hours;
■ total time on UPS (d): this is the total
time that the load has been supplied by
the UPS since initial startup. It is
expressed in days;
Logging and time-stamping
Note: numerical values are never indicated in screens for time-stamped events.
For example:
Example:
FIGURES SINCE COMMISSIONING
total backup time (h): 0
total time on static switch (h): 0
total time on UPS (d): 3627
total time with Tbatt >25°C (h): 1
FIGURES SINCE RESET
last reset: 05/09/1997
elapsed backup time (min): 0
03/09/1997 15:30:23 Disappearance:
OVERLOAD
RATED CURRENT PER PHASE
= _ _ _ A
CHECK LOAD LEVEL
02/09/1997 07:25:03 Appearance:
MAINS 2 INPUT SWITCH Q4S IS OPEN
DATE AND TIME SETUP
> YEAR 1997 MONTH 9
DAY 8 HOURS 8
MINUTES 11 SECONDS 42 ▼▼
User’s Manual
Page 34

26
■ total time with Tbatt > 25° C (h): this
is the total time of operation with the battery temperature greater than 25° C since
initial startup of the UPS. It is expressed in
hours;
■ last reset: this is the date that the infor-
mation was last set to zero by the
Teleservice function;
■ elapsed backup time (min): this is the
total time of operation on battery power
since the last reset. It is expressed in minutes.
■ nb of backups: this is the number of
times the load was supplied by the UPS
from battery power since the last reset;
■ nb of backups < 1 min: this is the
number of times the load was supplied by
the UPS from battery power for less than
one minute, since the last reset;
■ 1 min < nb of backups < 3 min: this is
the number of times the load was supplied
by the UPS from battery power for more
than one minute and less than three minutes, since the last reset;
consulting recorded
measurements
Recorded measurements are presented in
the same manner (see opposite):
■ the lists indicate the last 30 measure-
ments recorded for the given parameter.
The chronological order of the measurements is indicated in the figure opposite;
■ the most recent measurement is pre-
sented first, in the upper left-hand corner
of the list. The following measurement is
listed just below, and so on until the 30th
value listed in the bottom right-hand corner of the list;
■ the period T between two successive
measurements is 30 days. The displayed
measurements are instantaneous values.
■ nb of backups > 3 min: this is the
number of times the load was supplied by
the UPS from battery power for more than
three minutes, since the last reset;
■ nb of overloads < 5 s: this is the num-
ber of times the UPS was overloaded (output current greater than In) for less than
five seconds, since the last reset;
■ nb of overloads > 5 s: this is the num-
ber of times the UPS was overloaded (output current greater than In) for more than
five seconds, since the last reset;
■ nb of times TBatt. > 25° C: this is the
number of times the battery temperature
was measured at over 25° C, since the
last reset.
NOTE
when this screen is
selected, approximately
ten seconds are required
to call up and display the
information.
If the number of measurements is greater than
30, only the last 30 (the
most recent) are displayed
Logging and time-stamping
FIGURES SINCE RESET
nb of backups: 0
nb of backups < 1 min: 0
1 min < nb of backups < 3 min: 0
nb of backups > 3 min: 0
nb of overloads < 5 s: 0
nb of overloads > 5 s: 0
nb of times TBatt. > 25°C: 0
Use the ▼ and ▼ keys to shift between the beginning and the end of the display.
PARAMETER NAME (units) T=30 days
▼ last read: 05/09/1997
M(t+29T)|M(t+23T) |M(t+17T)|M(t+11T)|M(t+05T)
||||
M(t+28T)|M(t+22T) |M(t+16T)|M(t+10T)|M(t+04T)
||||
M(t+27T)|M(t+21T) |M(t+15T)|M(t+09T)|M(t+03T)
||||
M(t+26T)|M(t+20T) |M(t+14T)|M(t+08T)|M(t+02T)
||||
M(t+25T)|M(t+19T) |M(t+13T)|M(t+07T)| M(t+T)
||||
M(t+24T)|M(t+18T) |M(t+12T)|M(t+06T)| M(t)
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 35

27
The battery capacity is the value mea-
sured by the UPS microprocessor. It is
expressed in Ampere-hours. This value
changes over time depending on the parameters of the battery itself and its environment. This measurement is used to check
that the battery is capable of supplying the
rated power in the event of a mains outage.
The backup time is the value calculated
by the UPS microprocessor on the basis
of measurements carried out on the battery. It is expressed in minutes. The calculation uses the percent load and the battery charge status at the time of the measurement.
The load level is the ratio between the
power supplied by the UPS to the load at
the time of the measurement and the
rated output of the UPS. It is expressed as
a percentage.
utilization via Teleservice
When the optional JBUS RS232/485 communications board is installed, the timestamped information can be sent to the
Teleservice center.
The center can remotely consult the same
information and carry out the same modifications as the user locally on the display.
Note that only the Teleservice centre can
reset the counters for the statistical data.
Logging and time-stamping
BATTERY CAPACITY (Ah) T=30 days
▼ last read: 05/09/1997
97|0|0|0|0
96|0|0|0|0
95|0|0|0|0
94|0|0|0|0
0| 0| 0| 0| 0
0| 0| 0| 0| 0
OUTPUT LOAD LEVEL(%) T=30 days
▼ last read: 05/09/1997
63|0|0|0|0
52|0|0|0|0
63|0|0|0|0
63|0|0|0|0
0| 0| 0| 0| 0
0| 0| 0| 0| 0
BACKUP (min) T=30 days
▼ last read: 05/09/1997
120|0|0|0|0
115|0|0|0|0
110|0|0|0|0
105|0|0|0|0
0| 0| 0| 0| 0
0| 0| 0| 0| 0
User’s Manual
Page 36
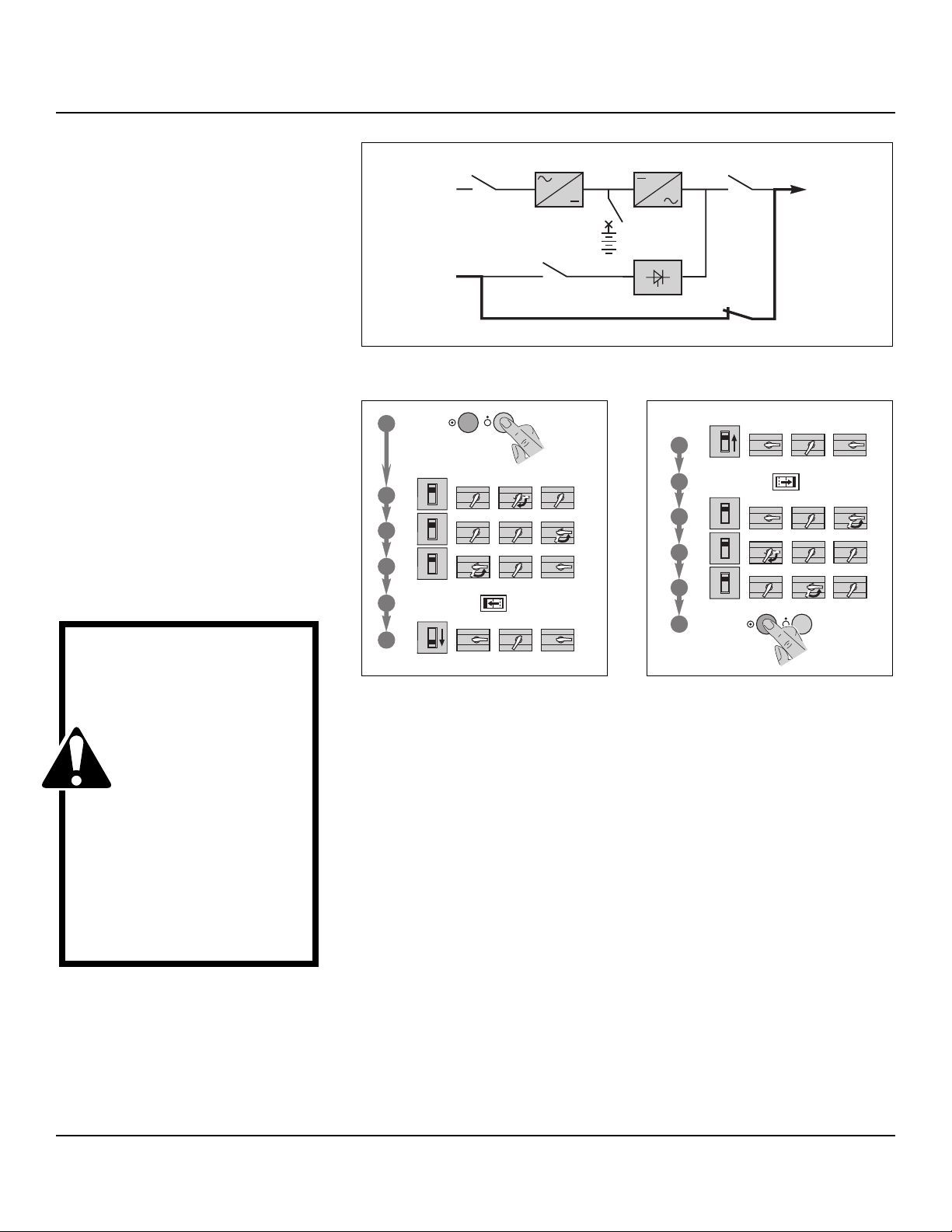
28
maintenance
configuration
single-UPS unit
See figure 19. During maintenance, the
UPS must be isolated from the normal and
bypass AC source, the battery and the
load.
■ UPS isolation
Proceed in the following order (see figure
20):
❏ shut down the inverter (press the "invert-
er OFF" button 8 for three seconds),
❏ close bypass switch Q3BP,
❏ open isolating switches Q5N, Q4S, QF1
and Q1.
The UPS is powered down once the
capacitors have discharged (a few minutes);
■ start-up
Following servicing, proceed in the following order (see figure 21):
❏ close switch Q1, then after approximate-
ly ten seconds, switches QF1, Q5N and
Q4S,
❏ open bypass switch Q3BP,
❏ start the inverter (press the "inverter ON"
button 7 ).
CAUTION
■ work should be car-
ried out in accordance
with applicable safety
regulations;
■ to avoid interrupting
the load, the various
switching operations
must be carried out in the
correct order. Operations
are explained in diagrams placed next to the
switches;
■ the system cabinet is
only partially powered
down. The load is still
supplied via the bypass
AC source and switch
Q3BP.
Maintenance
Fig. 21Fig. 20
Fig. 19
Q1
Q5N
QF1
Q3BP
Q4S
AB
C
D
1
2
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Q5NQ1 Q4S
3
1
2
1
0
Q3BP
1
0
1
0
5
4
6
QF1
0
I
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
OFFOFF
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Q5NQ1 Q4S
3
1
2
Q3BP
1
0
5
4
6
1
0
1
0
1
0
OFF
1
0
QF1
0
I
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
maintenance
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 37

29
parallel UPS redundant and
for increased output
See figure 22.
■ isolate all UPSs
Proceed in the following order (see figure
23):
❏ shut down the inverters (press the
"inverter OFF" buttons 8 for three seconds),
❏ close switch Q3BP and open switch
Q5N in the external bypass unit,
❏ open switches Q1, QF1 and Q5N on the
UPS units.
■ start-up
Following servicing, proceed in the following order (see figure 24):
❏ close switches Q5N on the UPS units,
❏ close switch in the external bypass unit,
❏ open switch Q3BP in the parallel-con-
nection unit,
❏ close switches Q1 and QF1 on the UPS
units,
❏ start the inverters (press the "inverter
ON" buttons 7 ).
NOTE
We recommend that you
call on the after-sales
support department to
carry out these operations.
Note that for parallel
UPSs for increased output, the entire installation
must be bypassed
because it is not possible
to isolate just one UPS
unit.
Maintenance
Fig. 24
Fig. 23
Fig. 22
2 3 4 5
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Q5N
Q3BP
Q5NQ1 Q4S
QF1
0
I
external bypass
7
5
6
1
Galaxy PW
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
2 3 4 5
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
Q5N
Q3BP
Q5NQ1 Q4S
QF1
0
I
external bypass
7
5
6
1
Galaxy PW
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
2
1
Q3BP
Galaxy 1
Galaxy 2
2
1
Galaxy 3
2
1
Galaxy 4
2
Q5N
1
2
Q1
QF1
Q5N
Q4S
User’s Manual
Page 38

30
battery maintenance
Consult the instructions supplied by the
battery manufacturer. Below are a few
general indications:
■ sealed lead-acid batteries: these bat-
teries require no maintenance, but check
the terminals of each cell from time to time
and clean if necessary;
■ vented lead-acid batteries:
❏ check the electrolyte level regularly and
add water if necessary,
❏ check the voltage of each cell to deter-
mine if it is necessary to equalize the battery,
❏ check the terminals of each cell and
clean if necessary.
visual check
■ Power down the system prior to any
maintenance operations.
Note: in redundant parallel UPS systems
the check may be carried out successively
on each UPS unit without interrupting the
load. In other configurations, the load
must be supplied via the maintenance
bypass (see "maintenance bypass" in the
"Alarm" section);
■ clean the system regularly, particularly
the air filter inlet and outlet grills. Check
that the air circulates freely in the cabinets. Use a vacuum cleaner if necessary;
■ check that nothing hinders the ventila-
tion at the top and at the back of the system.
functional check
■ Check that lights 1 , 2 and 3 on the
control panel are not red, to avoid an
interruption in the supply of power to the
load due to incorrect transfer conditions or
a battery problem;
■ press the "inverter OFF" button and
check that the buzzer and control panel
lights function correctly (see the section
on operating modes in the introduction);
■ press the "inverter ON" button and
check again that the control panel lights
function correctly;
■ run a transfer to battery test. With the
inverter on, open input circuit breaker Q1.
The orange "battery" light on the control
panel should light. After two minutes on
battery power, close input circuit breaker
Q1. The rectifier/charger should automatically restart and the orange "battery" light
on the control panel should go off;
■ in parallel systems, run these tests on
each UPS unit.
CAUTION
Battery maintenance is
undertaken with the system
powered up. Operations must
be carried out in accordance
with applicable safety regulations by qualified personnel
using insulated tools, gloves
and safety goggles.
Batteries contain dangerous substances that will harm
the environment if thrown
away. If you change the batteries yourself, call on qualified organizations for battery
recovery and recycling.
Maintenance
Pb
Pb
Galaxy PWTM100 to 225 kVA
Page 39

31
Galvanic isolation and
voltage matching
transformers
The UPS can be equipped with an isolation or auto transformer on both the input
and output to provide galvanic isolation or
voltage step-up or step-down as required.
Maintenance bypass
Maintenance bypass option provides a
direct bypass AC input source (mains 2)
that can be used to supply the critical load
while the UPS is being serviced.
electrical supervision
"Teleservice"
"Teleservice" is a contract offering continuous remote supervision and maintenance
of UPS systems via a modem. Real-time
communication is established with our
"Teleservice" centre for communication of
all alarms and events occurring in the
installation.
GTC board
This electronic board provides user
access to the J-Bus communications protocol. Using the data and address tables
provided, the user can customize his
installation.
GTC + software
The user has access to the J-Bus protocol
and, in addition, the associated software
acquires system parameters (measurements, status conditions) and transforms
them into diagrams, alarm messages and
tables. With the click of a mouse, the user
can locally or remotely supervise the UPS
system (comprising one or many UPS
units).
management of computer
networks
Integrated SNMP agent
This electronic board, installed in the UPS
system, enables direct connection to all
Ethernet networks using TCP/IP.
The UPSs may then be supervised via the
computer network. Furthermore, they can
be used to close system files without having to add an external SNMP agent.
This board is fully compatible with
"Solution PacTM" software.
The RJ45 connector of the communications option delivers information using the
SNMP protocol. The sticker located on the
board indicates the UPS MAC address.
■ your MAC address is written in the fol-
lowing way : 0080C8 ZZ XX YY ;
■ your default IP address is 168.8.xx.yy
(xx and yy are
decimal values of XX and YY).
For example, MAC address 00 80 C8 AB
AA 01 is related to IP address
168.8.170.1.
Please refer to the "userman.doc" user
manual contained in the directory
"emb/galaxy/snmp/release3.xx" of the
Solution-Pac CD-ROM in order to discov-
er the management capabilities of your
SNMP Galaxy PW™ UPS.
Please contact your sales representative
for more detailed
information.
Two-channel network board
This electronic board comprises two ports,
each of which may be user set, either for
the U-Talk protocol or as a relay contact.
U-Talk is the protocol required to establish
contact with the communications software.
Relay contacts may be used for specific
network applications (IBM AS400, Novell,
etc.).
Options
options
User’s Manual
0080C8ABAA01
Page 40

This page intentionally left blank
32
Page 41

33
Reorder form
to order additional copies of this document, or to report any errors,
omissions, or other problems you have experienced.
NAME
COMPANY
STREET ADDRESS
CITY ___________________________________ STATE ___________ ZIP ______________
I would like to order ________ (quantity @ $50.00 each) additional copies of the:
Galaxy PW™
100 to 225 kVA
User’s Manual
86-133060-00 X1
I would like to report the following problems with this document:
Use this form
1660 Scenic Avenue
Costa Mesa, CA 92626
Page 42

34
Page 43

35
Page 44

1660 Scenic Avenue, Costa Mesa, California 92626 • (714) 557-1636
www.mgeups.com
 Loading...
Loading...