Page 1
DISCLAIMER
Information in this manual is designed for user purposes only and is not
intended to supersede information contained in customer regulations, technical
manuals/documents, positional handbooks, or other official publications. The
copy of this manual provided to the customer will not be updated to reflect
current data.
Customers using this manual should report errors or omissions,
recommendations for improvements, or other comments to MFJ Enterprises, 300
Industrial Park Road, Starkville, MS 39759. Phone: (662) 323-5869; FAX: (662)
323-6551. Business hours: M-F 8-4:30 CST.
Page 2
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TOPIC
PAGE
TABLE OF CONTENTS ii
LIST OF FIGURES ii
LIST OF TABLES ii
RF HAZARD PRECAUTIONS 1
INTRODUCTION & SYSTEM FEATURES 7
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION 10
LOOP THEORY 12
SYSTEM SETUP 14
LOOP CONSTRUCTION 15
SYSTEM OPERATION 17
FAST START INSTRUCTIONS 20
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE 23
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum 2
Figure 2 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
Figure 3 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
Figure 4 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
Figure 5 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
Figure 6 Typical MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
8
TM
w/ MFJ-57B PVC Cross Loop Kit Installed 9
TM
Front Panel Controls & Indicators 10
TM
Rear Panel Connectors 11
TM
Setup Configuration 14
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1 Indoor & Outdoor Operating Environments at 100 Watts 5
Table 2 Indoor & Outdoor Operating Environments at 150 Watts 6
Table 3 MFJ-935B Most Efficient Single-band Loop Lengths 15
Table 4 MFJ-935B Convenient Multi-band Loop Lengths 15
- ii -
Page 3
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
RF HAZARD BACKGROUND INFORMATION
The following WARNING is labeled on the MFJ-935B LOOP TUNERTM Rear
Panel:
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
RF HAZARD PRECAUTIONS
WARNING
DO NOT touch or come into contact with Loop
Connectors or Loop Antenna while transmitting
YOU CAN BE SERIOUSLY INJURED
Using the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
voltages and HIGH CURRENTS during normal operation. The Hi-Q circuit
produced by resonating the wire loop connected to the tuner, and matching it to
the 50-Ohm coax supplying power creates this unique operating environment.
TM
can, and in fact does, produce LETHAL
!!!
NOTICE
It is imperative that the operator specifically follows operating instructions and
complies with all CAUTIONS, WARNINGS, and FCC Guidelines for Human
Exposure to Radio frequency (RF) Electromagnetic Fields
Radio frequency (RF) Radiation
Radio frequency (RF) energy is one type of electromagnetic energy.
Electromagnetic waves and associated phenomena can be discussed in terms of
energy, radiation or fields. Electromagnetic "radiation" is defined as waves of
electric and magnetic energy moving together (i.e., radiating) through space.
The movement of electrical charges generates these waves. For example, the
movement of charge in a radio station antenna (the alternating current) creates
electromagnetic waves radiating away from the antenna and intercepted by
receiving antennas. Electromagnetic "field" refers to the electric and magnetic
environment existing at some location due to a radiating source such as an
antenna.
- 1 -
Page 4
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
RF HAZARD PRECAUTIONS
An electromagnetic wave is characterized by its wavelength and frequency. The
wavelength is the distance covered by one complete wave cycle. The frequency
is the number of waves passing a point in a second. For example, a typical radio
wave transmitted by a 2-meter VHF station has a wavelength of about 2 meters
and a frequency of about 145 million cycles per second (145 million Hertz): one
cycle/second = one Hertz, abbreviated Hz.
Electromagnetic waves travel through space at the speed of light. Wavelength
and frequency are inversely related by a simple equation: (frequency) times
(wavelength) = the speed of light. Since the speed of light is a constant quantity,
High Frequency (HF) electromagnetic waves have short wavelengths, and LowFrequency (LF) waves have long wavelengths. Frequency bands used for
amateur radio transmissions are usually characterized by their approximate
corresponding wavelengths, e.g., 12, 15, 17, 20 meters, etc.
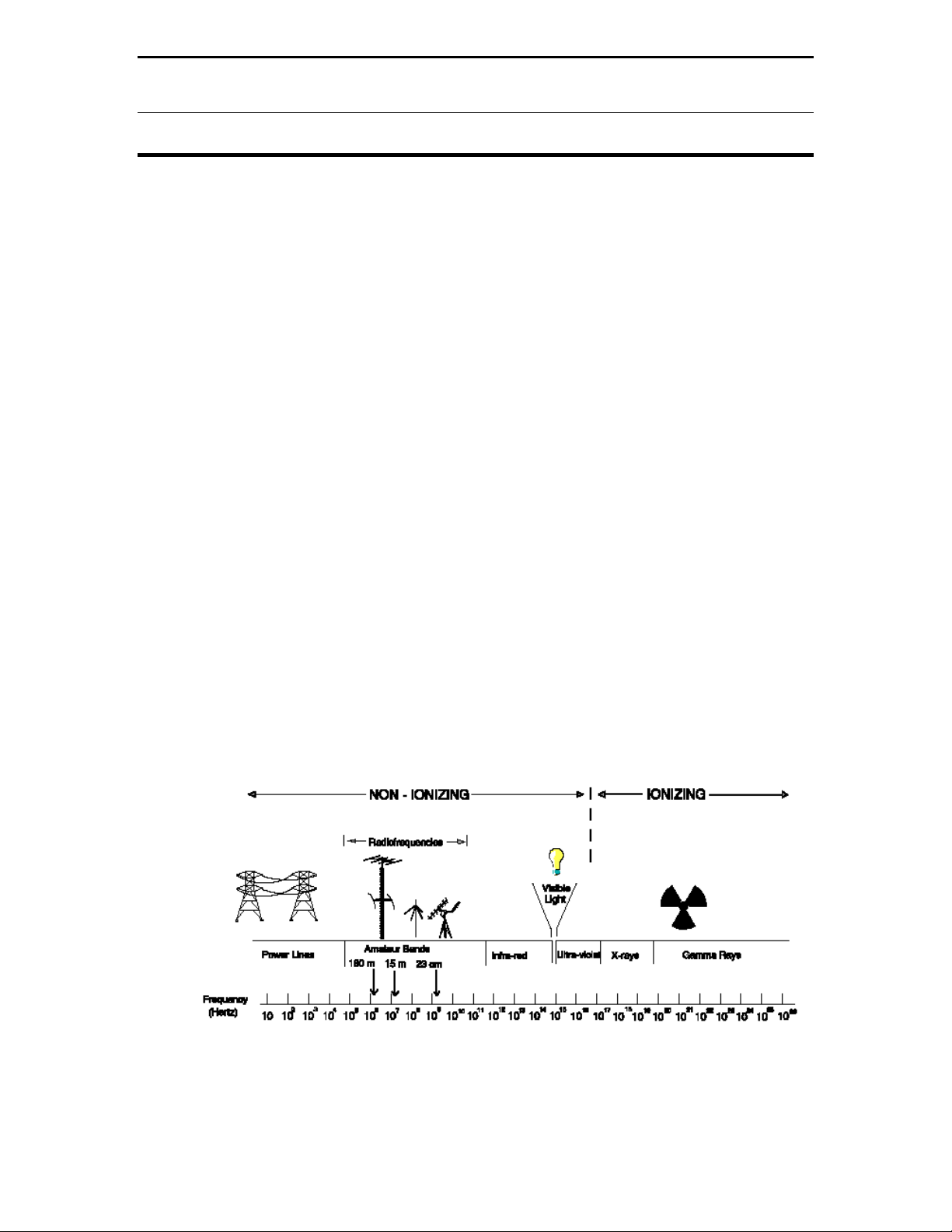
The electromagnetic "spectrum" includes all of the various forms of
electromagnetic energy ranging from extremely low frequency (ELF) energy (with
very long wavelengths) to all the way up to X-rays and gamma rays, which have
very high frequencies and correspondingly short wavelengths. In between these
extremes lie radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light and
ultraviolet radiation, respectively. The RF part of the electromagnetic spectrum
can generally be defined as that part of the spectrum where electromagnetic
waves have frequencies that range from about 3 kilohertz (kHz) to 300 gigahertz
(GHz). Figure 1 illustrates the electromagnetic spectrum.
Figure 1 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- 2 -
Page 5

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
RF HAZARD PRECAUTIONS
FCC OET Bulletin 65, Supplement B, Evaluating Compliance with FCC
Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio frequency Electromagnetic
Fields.
The FCC Office of Engineering Technology (OET) Bulletin 65, Supplement B,
Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio
frequency Electromagnetic Fields impacts directly the use and operation of the
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
. It establishes safe operating distances from the loop
antenna and associated power levels in order to permit the operator and persons
that may be impacted by operation to exist in a safe, RF radiation hazard-free
environment. Guidelines for Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) are defined
in Supplement B of the bulletin.
IMPORTANT NOTE
Use Supplement B in connection with FCC OET Bulletin 65,
Version 97-01. The information in the supplement provides
additional detailed information used for evaluating compliance of
amateur radio stations with FCC guidelines for exposure to radio
frequency electromagnetic fields. However, Supplement B users
should also consult Bulletin 65 for complete information on FCC
policies, guidelines and compliance-related issues. Definitions of
terms used in this supplement appear in Bulletin 65. Bulletin 65
can be viewed and downloaded from the FCC’s Office of
Engineering and Technology’s World Wide Web Internet Site:
http://www.fcc.gov/oet/rfsafety
OPERATING ENVIRONMENTS
Under some circumstances, such as an antenna located unusually near humans,
an indoor antenna in a living space, or a balcony-mounted antenna a foot or so
away from a neighbor’s balcony, the FCC could require a station evaluation or
take other action. Computer models of small HF loops, for example, yield RF
fields very near the antenna that are much higher than the standard amateur
radio station outdoor antenna installation yields. Therefore, when you use the
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
one such as a hotel/motel room care must be taken not to exceed established
MPE to yourself and others who may encounter the RF field associated with your
operation.
TM
in your Ham Shack, at a portable location (outdoors), or
- 3 -
Page 6

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
RF HAZARD PRECAUTIONS
RF RADIATION EXPOSURE CONCERNS
Controlled population exposure limits apply to amateur licensees and members
of their immediate household (but not their neighbors - see next paragraph). In
general, a controlled environment is one for which access is controlled or
restricted.
In the case of a fixed or portable amateur station, the licensee or grantee is the
person responsible for controlling access and providing the necessary
information and training as described in FCC OET Bulletin 65, Supplement B.
General population/uncontrolled exposure limits apply to situations in which the
general public may be exposed, or in which persons who are exposed as a
consequence of their employment, such as hotel/motel employees or overnight
residents, may not be made fully aware of the potential for exposure or cannot
exercise control over their exposure. Therefore, members of the general public
always fall under this category when exposure is not employment-related, as in
the case of residents in an area near a broadcast tower. Neighbors of amateurs
and other non-household members would normally be subject to the general
population/uncontrolled exposure limits.
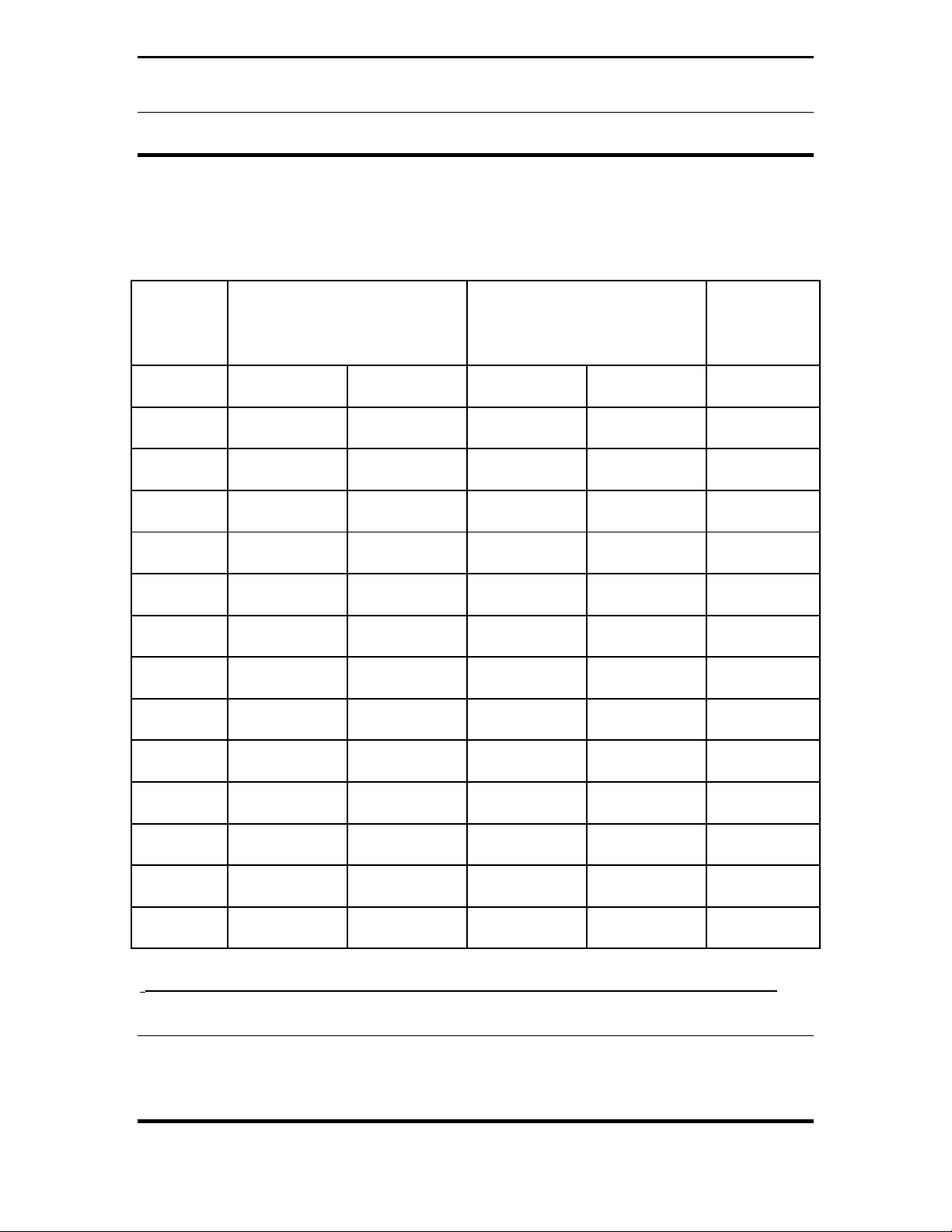
OPERATING ENVIRONMENTS & GUIDELINES
Table 1 and Table 2 lists MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
operating environments,
average power level, and safe distances that should provide compliance with the
FCC’s MPE recommendations/standards for controlled and uncontrolled
populations. Distance data listed is a result of computer-modeling a circular loop,
which is the most efficient radiator configuration. Parameters used include those
listed below:
• Loop perimeter or circumference (75% of a quarter wave loop in length for
each band)
• Diameter of loop conductor (approximately 4mm/10 gauge)
• Height of lowest section of loop above ground (1 and 3 meters feed-point
heights)
• Operating frequencies (7.175, 10.1, 14.2, 18.1, 21.2, 24.95, & 28.5 MHz)
• Output power in watts (100 Watts average for Table 1 and 150 Watts
average for Table 2)
- 4 -
Page 7
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
Table 1 Indoor & Outdoor Operating Environments at 100 Watts
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
RF HAZARD PRECAUTIONS
Freq
(MHz)
7.0
1
Controlled Population
Exposure
(Distance in feet/meters)
1.2 0.36 2.0 0.51 100
Uncontrolled Population
Exposure
(Distance in feet/meters)
Output
Power
(Watts)
7.02 1.2 0.38 2.1 0.75 100
10.01 1.9 0.57 3. 0 0.75 100
10.02 2.3 0.69 3.6 0.92 100
14.01 2.4 0.72 3.8 0.96 100
14.02 2.5 0.77 4.6 0.96 100
18.01 2.8 0.85 5.1 1.06 100
18.02 2.9 0.87 5.2 1.08 100
21.01 3.0 0.92 5.9 1.23 100
21.02 3.1 0.93 6.0 1.50 100
24.01 3.2 0.98 6.6 1.66 100
24.02 3.3 1.02 6.6 1.67 100
28.01 3.4 1.05 7.2 1.83 100
28.02 3.4 1.05 7.3 1.83 100
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
1
TM
located at one meter in height above ground level.
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
2
TM
located at three meters in height above ground level.
- 5 -
Page 8
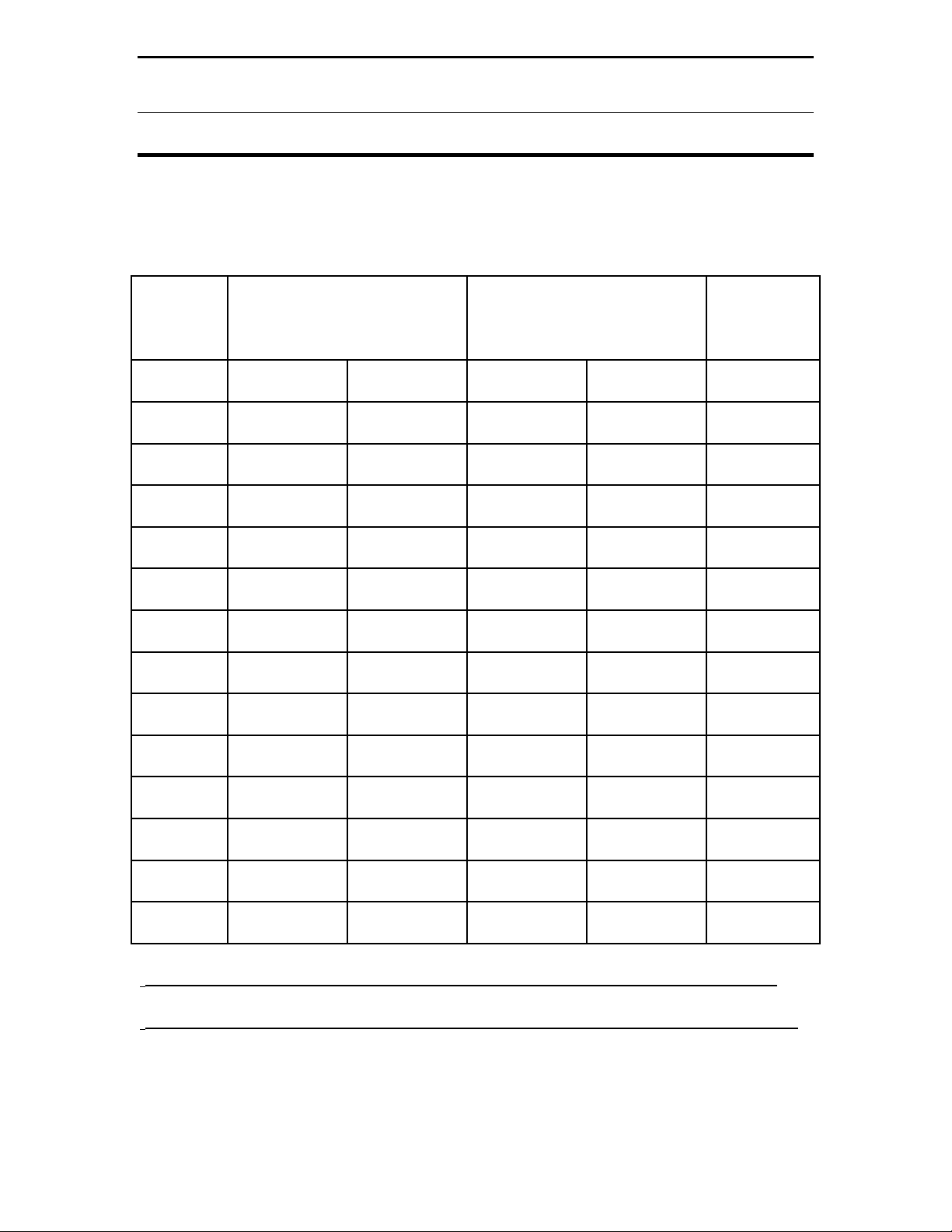
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
Table 2 Indoor & Outdoor Operating Environments at 150 Watts
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
RF HAZARD PRECAUTIONS
Freq
(MHz)
7.0
1
Controlled Population
Exposure
(Distance in feet/meters)
1.4 0.44 2.0 0.62 150
Uncontrolled Population
Exposure
(Distance in feet/meters)
Output
Power
(Watts)
7.02 1.5 0.46 2.1 0.91 150
10.01 2.3 0.69 3. 0 0.91 150
10.02 2.7 0.84 3.6 1.11 150
14.01 2.8 0.87 3.8 1.16 150
14.02 3.0 0.93 4.6 1.40 150
18.01 3.4 1.03 5.1 1.56 150
18.02 3.4 1.05 5.2 1.59 150
21.01 3.7 1.12 5.9 1.80 150
21.02 3.7 1.13 6.0 1.82 150
24.01 3.9 1.19 6.6 2.01 150
24.02 4.1 1.24 6.6 2.02 150
28.01 4.2 1.27 7.2 2.22 150
28.02 4.2 1.27 7.3 2.22 150
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
1
TM
located at one meter in height above ground level.
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
2
TM
located at three meters in height above ground level.
- 6 -
Page 9

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
INTRODUCTION & FEATURES
MFJ-935B LOOP TUNER
TM
INTRODUCTION
The MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
is a small, versatile, high-efficiency device that
turns any wire loop into a high-efficiency multi-band transmitting loop antenna
system designed for 50-ohm use at 150 Watts maximum input (all modes). It
consists of two functional units:
• MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
• Wire Loop(s) (not included)
One function of the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
tunes/resonates various lengths of
wire into a very Hi-Q tuned-circuit used as a transmitting loop antenna. It uses
an MFJ low-loss Butterfly capacitor with no rotating contacts (available
separately) in this circuit. The second function is a matching network that serves
to match the Hi-Q transmitting loop circuit to any length of 50-Ohm coaxial cable.
No ground, radials, or counterpoise system is required or needed. The MFJ935B Loop Tuner
TM
tunes any shape loop: circle, square, rectangle or any odd
shape. However, a wire approaching a quarter wavelength shaped as a circle is
the most efficient configuration.
The MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
uses fixed wire lengths, which cover about 1.5 to 1
frequency ranges (i.e. 28 – 18 or 10 – 7 MHz, etc.). Exact frequency coverage
depends on each individual installation configuration involving choice of wire
length and diameter, shape of loop, Loop Tuner
and operating environment. Figure 2 illustrates the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
height above ground level,
TM
.
TM
The MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
mounts an assembled PVC Cross provided in the
MFJ-57B Loop Antenna Kit by inserting the cross into a PVC receptacle mounted
on the top of the unit’s cover. This kit provides a means to operate 20 and 30
meters using an insulated 10-gauge flexible wire loop fitted with direct contact
low-resistance lugs and strung on the PVC after assembly.
Assembly takes less than five minutes from packaged kit to ready for operation.
Figure 3 illustrates the PVC Cross mounted on the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
in a
typical outdoor operation environment. Care should be taken, however, to
secure the loop if wind becomes a factor in the operating environment.
- 7 -
Page 10

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
INTRODUCTION & FEATURES
Figure 2 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
MFJ-935B LOOP TUNERTM FEATURES:
• Powerless: No power supply required.
• Maximum Input Power: 150 Watts (all modes)
• Easy-to-Read Loop RF Current Indicator: 0 to 100 scale with adjustable
sensitivity.
• Easy-Carry Handle: Permits easy handling to/from portable location(s)
• Small Physical Profile: 6 ¼” W, 9 ½” D, 5 ¼” H
• Low Radiation Angle: Rivals full size dipoles.
• Quiet Reception: Extremely quiet receiving antenna. Hi-Q rejects out-of-
band interference, reduces overloading, and rejects harmonics.
• Indoor Use: Perfect for apartments & hotel/motel rooms, antenna
restricted, and portable locations.
- 8 -
Page 11

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
INTRODUCTION & FEATURES
Figure 3 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
with MFJ-57B PVC Cross Loop Antenna
Kit Installed
- 9 -
Page 12

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
TM
MFJ-935B LOOP TUNER
The MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
CONTROLS & INDICATORS
TM
Front Panel controls and indicators function to
permit resonating the wire loop at the output, and matching the coaxial line
impedance at the input of the tuner. Refer to Figure 4 and the numbered
component locations.
5
3
6
2
TM
Figure 4 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
• A Tuning control (1) permits adjustment of the Butterfly capacitor to
peak/resonate the wire loop.
• A Matching control (2) matches the tuned loop circuit to a 50-Ohm coaxial
cable.
• An Antenna Current Meter (3) indicates antenna current on a scale of 0-
100, and is controlled by a Meter Sensitivity Control (4) located beneath
the Tuning knob.
• A PVC Mount (5) located on the enclosure top permits mounting of the
PVC Cross Assembly.
• An easy-to-carry Handle (6) permits easy handling to/from portable
locations.
Front Panel Controls and Indicators
1
4
- 10 -
Page 13

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Rear Panel connections function to permit
connecting the wire loop at the output, and connecting the coaxial line at the
input of the tuner. Refer to Figure 5 and the labeled component locations.
1
2
Figure 5 MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
The loop antenna connects to the Loop Connectors (1) with the two wing nuts
provided on the Loop Connector standoff rods. Care must be taken not to
disturb the wires leading from the lugs on the Loop Connector stand-off rods and
entering through the back of the tuner. These two Loop Connector connection
points must be kept clean at all times. To minimize contact resistance, the loop
wire is in direct contact with the low resistance soldered lug.
When not in use for periods of time, always clean the connectors before reattaching loop antennas of any kind. This unit is not intended for outdoor
installation except during portable operation and must be protected from the
elements.
Coaxial line connects to the SO-239 connector labeled Transmitter (2) providing
RF power input to the tuner. The WARNING label must be obeyed!
TM
Rear Panel Connections
- 11 -
Page 14

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
LOOP THEORY
LOOP ANTENNA BACKROUND INFORMATION
A small loop antenna is one that is characterized by low-noise reception, works
well even when mounted at ground level, and has a conductor length or
circumference of less than 1/3 wavelength. The ideal small transmitting antenna
would have performance equal to a large antenna, and a small loop antenna
approaches that performance. Bandwidth is quite narrow due to the extreme hiQ of the tuned-circuit configuration when paired with a capacitor.
The components in a resonated transmitting loop are subjected to high currents
and voltages because of the large circulating currents found in the high-Q tuned
circuit formed by the antenna. It is very important that capacitors used in this
antenna have a high RF current rating. Even a 100-W transmitter develops
currents in the tens of amperes, and voltages across the tuning capacitor in
excess of 10,000 V. This consideration also applies to any conductors used to
connect the loop to the capacitor. A piece of #14 wire may have more resistance
than the entire loop conductor! The best electrical connections possible, are
those using soldered or welded joints.
The heart of the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
is the “Butterfly” loop-tuning capacitor,
which has no rotating contacts. When coupled to a low-resistance loop
conductor, such as a copper strap, it provides a high efficiency-transmitting loop.
As the loop antenna is elevated, its efficiency improves accordingly. When
traveling, a room at some elevation above ground level makes for a better
portable operation experience with the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
. At very low
heights, close coupling to the ground causes detuning and losses due to current
induced into a mirror image of the loop below the surface with resistance of the
image loop proportional to soil resistance. Another loss component is due to
current flowing in the soil via capacitance between the loop and soil surface.
An operational height equal to 1/2 diameter of the loop antenna is recommended
to prevent detuning and excess ground losses when using the MFJ-935B Loop
TM
Tuner
loop antenna system. This means the tuner should be at that
recommended height, since it is connected to the bottom (ends) of the loop,
whatever the loop antenna configuration: Circle, Square, Hexagonal, etc.
For operation on the 14 MHz band and higher, ground losses are a minimum
near ground, so it is fine to operate on the ground floor. For the 7 MHz band and
lower, ground losses become significant on the ground floor. To reduce ground
losses, operate on a second or third floor.
- 12 -
Page 15

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
LOOP THEORY
For minimum ground loss when operating near ground, the loop should be
mounted vertically. For higher elevations (relative to the wavelength), horizontal
mounting will also give low ground losses.
Using freeware-modeling programs, it is possible to improve the efficiency of the
loop antenna system by varying the parameters until you optimize your particular
operational configuration, even while portable. One source example for free
programs is G4FPQ’s Web site: http://www.btinternet.com/~g4fgq.regp/.
- 13 -
Page 16

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
SYSTEM SETUP
SYSTEM SETUP CONFIGURATION
The MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
setup configuration is simple and consists of the
following components:
• RF Generator (Transmitter/Transceiver; ~5 Watts minimum)
• SWR/Wattmeter
TM
• MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
• Coaxial cable(s)
• #10 gauge (or larger) stranded wire cut to approximately 75% of a ¼
wavelength at the chosen resonant frequency
Figure 6 is a block diagram of the typical MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
setup
configuration.
Transmitter/
Transceiver
SWR/
Wattmeter
Matching
Network
RF Current
Meter
Loop
MFJ – 935B Loop Tuner
TM
Figure 6 Typical MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
Configuration
- 14 -
Page 17

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
LOOP CONSTRUCTION
LOOP CONSTRUCTION
Loop construction for the MFJ – 935B Loop Tuner is reasonably simple, and
Table 3 lists the maximum tunable length for the most efficient operation for the
upper frequency limit of each band. Each length can be tuned lower in
frequency. Exact frequency coverage depends on each individual installation
configuration involving choice of wire length and diameter, shape of loop, Loop
Tuner
TM
height above ground level, and operating environment.
Table 3: MFJ – 935B Most Efficient Single-Band Loop Lengths
Band (meters) Most Efficient Single-Band
Loop Lengths (feet)
80 63.0
40 28.0
30 20.0
20 13.0
17 9.0
15 7.0
12 5.5
10 4.0
Table 4 lists the loop lengths for the most convenient band coverage. These
lengths will allow the most frequency coverage for each loop.
Table 4: MFJ – 935B Convenient Multi-Band Loop Lengths
Band (meters) Convenient Multi-Band Loop
Lengths (feet)
40, 30 20.0
30, 20 13.0
30, 20, 17 9.0
20,15 7.0
17,15,10 4.0
The loop can be constructed from wire, tubing, sheet, and an especially good
material is 1” wide PC board. However, finding a piece of PC board long enough
to form into a circular loop for 7.175 MHz may prove to be difficult! This leads us
to the unique opportunity to EXPERIMENT while using the MFJ-935B Loop
TunerTM to resonate the loop antenna you design.
- 15 -
Page 18

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
The applications and parameters can be adjusted easily with the help of the
Freeware programs previously mentioned, and you may choose to design a
totally new and unique loop antenna for on-air experimentation. Designing an
outdoor loop for a band such as 7 MHz could be a challenge and result in a very
good radiator and especially good receiving antenna for DX-ing and/or ragchewing. We, at MFJ, think the experimental aspects of the Loop Tuner
TM
are
exciting, and can provide hours of quality operating, even at QRP levels.
- 16 -
Page 19

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
SYSTEM OPERATION
TM
MFJ-935B LOOP TUNER
OPERATION
The most important aspect of using the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
is it opens-up
opportunity for Hams to once again experiment while enjoying operating at the
same time. Imagine how exciting it can be to establish contact with a distant
station using an antenna that you designed for the first time. Even more so, what
if you are just using a few watts, and the antenna is just a few feet away from
your operating position inside your home!
Operation is simple, but must follow specific steps in a specific order. Moreover,
you must have first consulted the RF Hazards section of this manual to ensure
compliance with established standards for Minimum Permissible Exposure (MPE)
to certain levels of RF radiation.
WARNING
DO NOT touch or come into contact with Loop
Connectors or Loop Antenna while transmitting
YOU CAN BE SERIOUSLY INJURED
Step 1
Place the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
connect the loop antenna to the wing nut terminals on the rear panel.
Step 2
Using a pre-cut prepared wire and fasteners (non-conductive plastic clothespins
for example) form a loop to enclose as much area as possible (for example,
clothespin a wire loop to a curtain around a window frame). A circle encloses the
maximum area. Otherwise, drape it across bookcases or similar objects to
fashion a loop of sorts to use. If the loop antenna is rigid, then place the Loop
TM
Tuner
in a position to accommodate its particular shape and size.
Step 3
Complete the typical MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
in Figure 6 of this manual.
TM
at the chosen place of operation, and
TM
setup configuration as illustrated
!!!
- 17 -
Page 20

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
SYSTEM OPERATION
Step 4
Make the following preliminary settings on the controls of the Loop Tuner:
• TUNING control to position “0, Low Freq”.
• MATCHING control to position “10, Min C”.
• METER SENSITIVITY control to fully clockwise position.
Step 5
Tune the transceiver or receiver to the band and frequency of interest and “Earball” tune the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner controls for maximum noise and S-Meter
reading. “Ear-balling”, like “Ball-parking” is a term often used to describe the
listening process as used to hear a “peak” in reception before actually applying a
transmit signal to the tuner. The tuner will produce a peak when the proper
positions for the controls are achieved. The normal process consists of the
following suggested instructions:
• Slowly rotate TUNING control clockwise while listening for a peak until you
reach position “5, High Freq.”
• If no peak is found, re-position TUNING control to “0, Low Freq.”
• Rotate MATCHING control counter-clockwise one position to “9”.
• Slowly rotate TUNING control clockwise while listening for a peak until you
reach position “5, High Freq.”
• If no peak is found, re-position TUNING control to “0, Low Freq.”
• Rotate MATCHING control counter-clockwise one more position to “8”.
• Slowly rotate TUNING control clockwise while listening for a peak until you
reach position “5, High Freq.”
• Repeat this sequence until the MATCHING control reaches position “0”.
• If no peak is found, the loop length is incorrect for the frequency of
interest. (See Table 3 for the Most Efficient Loop Length for the frequency
of interest.)
• Once a peak is found, alternately adjust TUNING and MATCHING
controls until the peak is maximized.
Step 6
Apply 10 to 20 Watts of power to the MFJ – 935B Loop Tuner and adjust the
TUNING control for maximum RF antenna current. Adjust the MATCHING
control for minimum SWR on your external SWR/Wattmeter. Re-adjust the
- 18 -
Page 21

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
TUNING control for maximum RF antenna current. Repeat this sequence until
you see no further improvement in minimum SWR and maximum antenna
current. Always adjust for maximum RF antenna current as the final adjustment.
Be sure to adjust the RF Antenna Current Meter using the METER SENSITIVITY
control for center scale reading as you make adjustments.
Step 7
Once you are satisfied that the adjustments and settings are correct for minimum
SWR, you can advance the power to 150 Watts if desired. Be sure that MPE
distance standard as defined in Supplement B of the FCC OET Bulletin 65,
version 97-01 is met. Should any arcing be detected, stop transmitting and
check connections and proximity to objects that may be suspect. If arcing seems
to be inside of the MFJ – 935B, Loop Tuner, lower output power and re-check for
arcing.
As a courtesy to our fellow hams, for safety and to keep within FCC regulations
you should use the minimum power needed for communications. Power levels of
20 to 50 Watts often provide very reliable communications. The difference
between 50 and 100 Watts is less than ½ S-Unit and is not noticeable on the
receiving end.
Step 8
You can now enjoy operating in your favorite mode. However, if you change
frequency more than about 5 KHz, you may find you’ll need to re-adjust the
TUNING controls for minimum SWR. Rotate TUNING clockwise for higher
frequencies and counter clockwise for lower frequencies. Even greater
frequency excursions can cause the MATCHING control to also require
adjustment.
This concludes the MFJ – 935B Loop Tuner System Operation instructions.
MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
System Accessories
TM
Two Kits are available for use with the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
, and each
enables the operator expanded operational capabilities, and use of premade/fabricated wires and equipment. These kits are:
• MFJ-57B, which contains a PVC Cross device for mounting a precut and
lugged wire loop to the top cover of the tuner. This flexible 10-gauge wire
loop covers 20 and 30 meters, and the ends have low-resistance lugs.
• MFJ-58B, which contains all of the MFJ-57 items, plus a 40-meter, 15 - 20
meter and 10 - 17meter wire loops, with clips to hang loops as needed.
- 19 -
Page 22

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
FAST START OPTION
Although careful and complete reading of the technical manual is certainly
foremost when receiving new equipment, MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
be achieved with minimum time and effort as long as certain and specific
instructions are followed. Strict adherence to WARNINGS and CAUTIONS
associated with personal safety, coupled with following specific procedural steps
can lead to a unique operating experience in a very short time.
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
FAST-START INSTRUCTIONS
TM
operation can
WARNING
DO NOT touch or come into contact with Loop
Connectors or Loop Antenna while transmitting
YOU CAN BE SERIOUSLY INJURED
!!!
NOTICE
It is imperative that the operator specifically follows operating instructions and
complies with all CAUTIONS, WARNINGS, and FCC Guidelines for Human
Exposure to Radiofrequency (RF) Electromagnetic Fields
Step 1
Place the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
the PVC Cross and connect the precut loop antenna found in the MFJ-57B
Accessory Kit to the wing nut terminals on the rear panel. Using the pre-cut loop
antenna, form a loop around the PVC Cross to enclose as much area as
possible. A circle encloses the maximum area.
Step 2
Complete the typical MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
in Figure 6 of this manual.
TM
at the chosen place of operation, assemble
TM
setup configuration as illustrated
- 20 -
Page 23

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
FAST-START INSTRUCTIONS
Step 3
Pre-set the MFJ – 935B Loop Tuner controls to the following settings for the 14.2
MHz operation (settings are approximate, but should be reasonable):
• TUNING control to position “3”.
• MATCHING control to position “9”.
• METER SENSITIVITY control to fully clockwise position.
Step 4
Tune the transceiver or receiver to the 20 meter band and frequency of interest
and “Ear-ball” fine-tune the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
controls for maximum
noise and S-Meter reading. “Ear-balling,” like “Ball-parking” is a term often to
describe the listening process as used to hear a “peak” in reception before
actually applying a transmit signal to the tuner. The tuner will produce a peak
when the exact position for the controls and switches is found.
Step 5
Apply 10 to 20 Watts of power to the MFJ – 935B Loop Tuner and adjust the
TUNING control for maximum RF antenna current. Adjust the MATCHING
control for minimum SWR on your external SWR/Wattmeter. Re-adjust the
TUNING control for maximum RF antenna current. Repeat this sequence until
you see no further improvement in minimum SWR and maximum antenna
current. Always adjust for maximum RF antenna current as the final adjustment.
Be sure to adjust the RF Antenna Current Meter using the METER SENSITIVITY
control for center scale reading as you make adjustments.
Step 6
Once you are satisfied that the adjustments and settings are correct for minimum
SWR and maximum antenna current, you can advance the power to 150 Watts if
desired. Be sure that MPE distance standard is met. Should any arcing be
detected, stop transmitting and check connections and proximity to objects that
may be suspect. If arcing seems to be inside of the MFJ – 935B, Loop Tuner,
lower output power and re-check for arcing.
As a courtesy to our fellow hams, for safety and to keep within FCC regulations
you should use the minimum power needed for communications. 20 to 50 watts
often provides very reliable communications. The difference between 50 and
100 watts is less than ½ S-unit and is not noticeable on the receiving end.
- 21 -
Page 24

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
FAST-START INSTRUCTIONS
Step 7
You can now enjoy operating in your favorite mode. However, if you change
frequency more than about 5 KHz, you may find you’ll need to re-adjust the
TUNING controls for minimum SWR. Rotate TUNING clockwise for higher
frequencies and counter clockwise for lower frequencies. Even greater
frequency excursions can cause the MATCHING control to also require
adjustment.
This concludes the MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Fast Start Operation instructions.
- 22 -
Page 25

MFJ-935B Loop Tuner
TM
Instruction & Technical Manual
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
If you have any problem with this unit first check the appropriate section of this
manual. If the manual does not reference your problem or reading the manual
does not solve your problem, you may call MFJ Technical Service at 662-323-
0549 or the MFJ Factory at 662-323-5869. You will be best helped if you have
your unit, manual and all information on your station handy so you can answer
any questions the technicians may ask.
You can also send questions by mail to MFJ Enterprises, Inc., 300 Industrial Park
Road, Starkville, MS 39759; by Facsimile (FAX) to 662-323-6551; or by email to
techinfo@mfjenterprises.com. Send a complete description of your problem, an
explanation of exactly how you are using your unit, and a complete description of
your station.
NOTES
- 23 -
 Loading...
Loading...