Page 1

Operating Instructions
UPA-P Series
UPA-1P and UPA-2P
Self-Powered Loudspeakers
(Serial Numbers 981000 and above)
UPA-1P
Copyright © 1997
Meyer Sound Laboratories, Inc.
All rights reserved
Part #: 05.054.017.01 Rev B
Keep these important operating instructions.
Page 2
Contents
Introduction .................................................. 3
AC Power .................................................... 4
The Modular Rear Panel .................................. 5
Amplification, Limiting, and Cooling System ........ 6
Rigging ......................................................... 7
Full-Range Systems ........................................ 7
Verifying Driver Polarity ................................ 9
Troubleshooting ......................................... 10
Safety Summary ........................................ 12
Rear Panel and Input Modules Drawings ......... 13
Dimensions ............................................... 14
Notes ...................................................... 15
Symbols Used
These symbols indicate important safety or operating features in this booklet and on the chassis.
Dangerous voltages:
risk of electric shock
Pour indiquer les risques
résultant de tensions
dangereuses
Zu die gefahren von
gefährliche spanning zeigen
Para indicar azares provengo
de peligroso voltajes
Important operating
instructions
Pour indequer important
instructions
Zu wichtige betriebs-
anweisung und unter-
haltsanweisung zeigen
Para indicar importante
funcionar y mantenimiento
instrucciones
Declaration of Conformity According to ISO/IEC Guide and EN 45014
The Manufacturer:
Name: Meyer Sound Laboratories, Inc.
Address: 2832 San Pablo Avenue
Berkeley, California 94702-2204, USA
Conforms to the following Product Specifications:
Safety: EN60065: 1994
EMC: EN55103-1 emmission
EN55103-2 immunity
The product herewith complies with the requirements
of the Low Voltage Directive 73 / 23 / EEC and
the EMC Directive 89 / 336 / EEC.
Office of Quality Manager
Berkeley, California USA
October 1, 1994
Frame or chassis
Masse, châssis
Rahmen oder chassis
Armadura o chassis Tierra proteccionista
Protective earth ground
Terre de protection
Die schutzerde
Declares that the product:
Product Name: UPA-1P, UPA-2P
Product Options: All
Environmental Specifications for
Meyer Sound Electronics Products:
Operating temperature: 0
o
to + 45
o
Nonoperating temperature:< -40o C or > +75o C
Humidity: to 95% at 35
Operating Altitude: to 4600 m (15,000 ft)
Nonoperating Altitude: to 6300 m (25,000 ft)
Shock: 30g 11 msec half-sine
on each of 6 sides
Vibration: 10 Hz to 55 Hz (0.010m
peak-to-peak excursion)
The following Meyer Sound patents apply to the UPA-P:
Des. 271,967 (U.S.A.)
4,152,552 (U.S.A)
2,379,220 (France)
1,591,480 (U.K.)
Other patents pending
Made by Meyer Sound Laboratories
Berkeley, California USA
European Office:
Meyer Sound Lab. GmbH
Carl Zeiss Strasse 13
56751 Polch, Germany
Page 3

Introduction
The Integrated Design
The Meyer UPA-P Series (UPA-1P, UPA-2P) self-pow-
ered loudspeakers are comprised of:
• one 12-inch cone driver and one 3-inch diaphragm
compression driver;
• phase-corrected, optimized control electronics;
• a two-channel amplifier (350 Wrms/ch).
The drivers, control electronics, and amplifier are integrated into a compact, trapezoidal enclosure. The UPA-P
Series is ideally suited for compact, high-powered PA applications, such as main PA, churches, surround systems,
and theatres. In addition the UPA-P is an excellent solution for use under-balcony, ordown-fill, or front fill and
even as a musical instrument speaker.
The UPA-P Series, more than a powered version of the
Meyer UPA-C Series (UPA-1C, UPA-2C), implements these
significant design improvements:
• The gain structure between the control electronics
and amplifier is perfectly matched.
• The amplifier is optimized for the system, providing
substantial power without endangering the drivers.
• The integrated design simplifies setup and installation, eliminates amp racks, and extends the durability and reliability of the loudspeaker.
The UPA-P produces flat acoustical phase and amplitude
response, full-range bandwidth, precise imaging, and
exceptional system impulse response. The UPA-P supplies a maximum SPL of 132.5 dB at 1 m with excellent
intelligibility, without the distortion or coloration commonly
exhibited by small PA speakers.
NOTE: In the past, beamwidth was often used to describe
the angle at which the sound pressure decreased 10 dB
from its on-axis amplitude because many listeners perceive -10 dB as a halving in pressure. Meyer Sound
defines beamwidth as the angle at which sound pressure
decreases 6 dB. -6 dB represents the actual halving of
sound pressure. When reading a beamwidth specification, it is essential to determine whether it refers to the 6
or 10 dB points. As the two standards produce very
different results: the 10 dB points yield a wider angle.
Previous technologies produced horns whose beamwidth
varied over the operating frequency range. These horns
also displayed nonuniform frequency response within,
and significant side lobe energy outside their beamwidth.
Both undesirable characteristics, particularly prevalent
for horns with a wide beamwidth, make array design
extremely problematic.
The UPA-P was developed in Meyer Sound’s anechoic chamber
by measuring coverage patterns using angular and frequency resolutions of 1° and 1/36 octave, respectively.
The UPA-P horns exhibit constant-Q: the beamwidth remains consistent across the horn’s operating frequency
range in both the vertical and horizontal planes. The
UPA-2P horn’s narrow beamwidth (45°H x 45°V) permits precise coverage with minimal interaction between
neighboring array elements. The UPA-1P horn’s wide
horizontal beamwidth (100°H x 40°V) addresses a larger
coverage area with fewer speakers.
Both speakers share the following remarkable attributes:
• uniform frequency response within the beamwidth
• rapid and uniform amplitude attenuation for all
frequencies outside the beam width
• minimal side lobes
The UPA-P Horns: Constant-Q
As a part of its research and development efforts, Meyer
Sound has solved the most difficult problems associated
with horn design. In order to appreciate the significance
of this work, it is necessary to define an often misunderstood term: the beamwidth of a horn is the angle at
which the sound pressure at a given frequency decreases
to half (–6 dB) its on-axis amplitude. Specifying beamwidth using the –6 dB points has been proposed as the
audio industry standard and Meyer Sound adheres to
this definition.
!
Page 4
AC Power
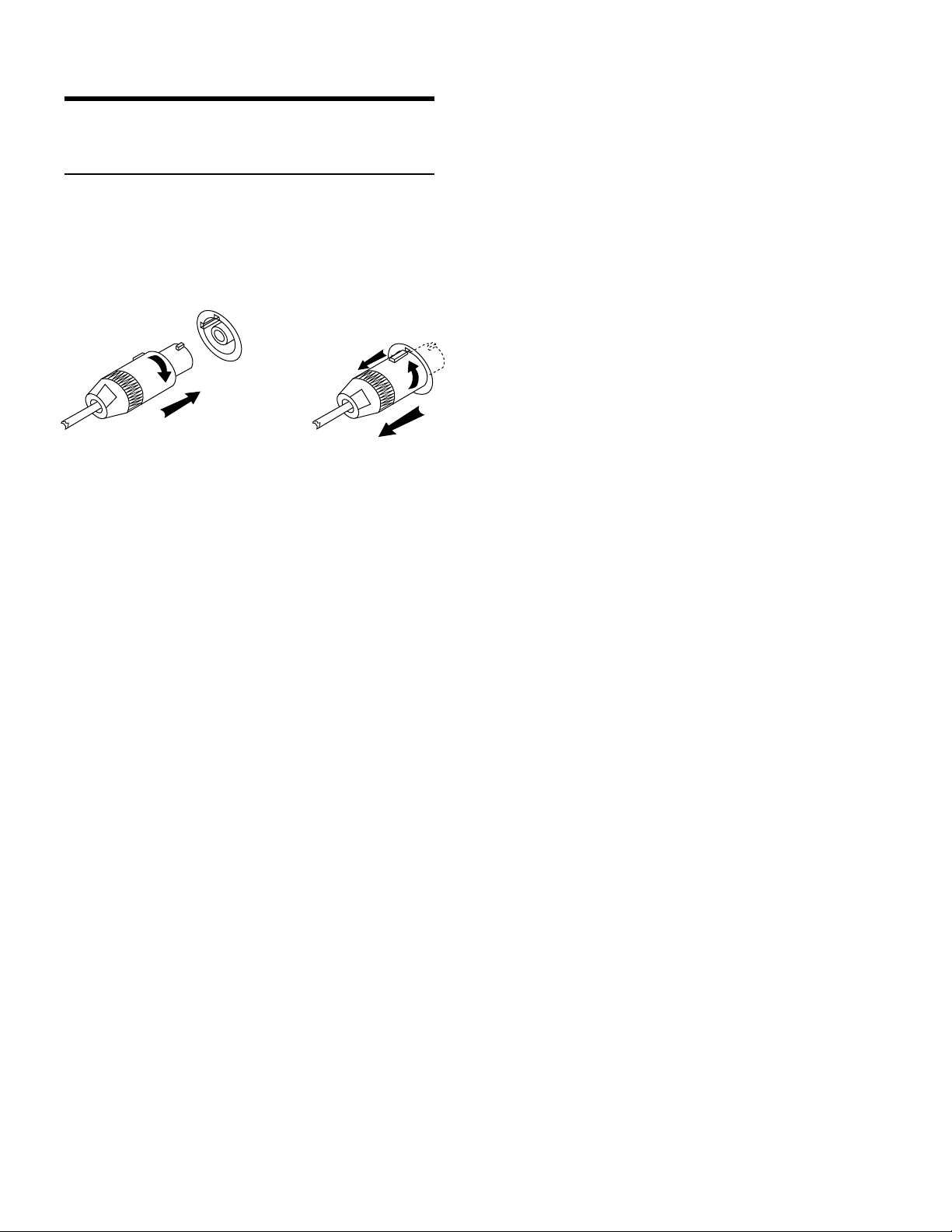
The UPA-P uses a PowerCon locking 3-pole AC mains
connector that prevents inadvertent disconnection. The
unit must have the correct power plug for the AC power
in the area in which it will be used.
Engagement
Separation
length of time the unit will continue to function during
brownout depends on the operating level and how low
the voltage drops. The unit turns off if the voltage does
not increase above 88V for 1 to 5 seconds. If the UPA-P
shuts down due to brownout, the power supply automatically turns on if the voltage returns to the normal
operating range. If the UPA-P does not turn back on after
ten seconds, consult the Troubleshooting section.
NOTE: We recommend that the supply be operated at
least a few volts away from the upper and lower bounds
of the operating range to avoid possible shutdown.
1
2
1
When AC power is applied to the UPA-P, the Intelligent
ACtm supply automatically selects the correct operating
voltage, allowing the UPA-P to be used internationally
without manually setting voltage switches. The Intelligent
AC supply performs the following protective functions
to compensate for hostile conditions on the AC mains:
• suppresses high voltage transients up to several
kilovolts
• filters EMI (radio frequencies and noise present on
the AC line)
• sustains operation during low-voltage periods,
which minimizes audio discontinuity
• provides soft-start power-up, which eliminates high
inrush current
The UPA-P can withstand continuous voltages up to
264V and allows any combination of voltage to GND (i.e.
Neutral-Hot-GND, Hot-Hot-GND). Continuous voltages higher than 264V may damage the unit.
2
3
Voltage Requirements
Current Requirements
Each UPA-P requires approximately 3 Arms @115V
(1.5 Arms@230V) for proper operation, allowing up to
five UPA-Ps to be powered from one 15 A circuit. However, we recommend powering no more than three UPA-Ps
per 15 A branch to allow a 30% margin for peak voltages.
The UPA-P presents a dynamic load to the AC mains
which causes the amount of current to fluctuate between
quiet and loud operating levels. This affects the number
of UPA-Ps that can be used for a given breaker type. Since
different types of cables and circuit breakers heat up and
trip at varying rates, it is essential to understand the
types of current ratings and how they correspond to
circuit breaker and cable specifications.
The maximum continuous RMS current is the maximum
RMS current over a duration of at least 10 seconds. It is
used to calculate the temperature increase in cables, which
is used to select cables that conform to electrical code
standards. It is also used to select the rating for slowreacting thermal breakers.
The maximum burst RMS current is the maximum RMS
current over a one second duration. It is used to select the
rating for most magnetic breakers.
The maximum instantaneous peak current during burst
is used to select the rating for fast-reacting magnetic
breakers and to calculate the peak voltage drop in long
AC cables according to the formula
The UPA-P operates safely and without audio discontinuity if the AC voltage stays within the range 88–264V,
47–63 Hz. After applying AC power, the system is muted
while the circuitry charges up and stabilizes. After two
seconds, the On/Temp. LED on the user panel illumi-
nates green, the system unmutes and is ready to pass
audio signals. If the On/Temp. LED does not illuminate
or the system does not respond to audio input after ten
seconds, consult the Troubleshooting section.
The UPA-P’s power supply uses stored energy to continue
functioning for about 10 AC cycles if the voltage decreases
below 88V (a condition known as brownout). The precise
"
Vpk
= Ipk x Rtotal cable
drop
Page 5
Use the table below as a guide to select cables and circuit
breakers with appropriate ratings for your operating voltage.
UPA-P Current Ratings
V511V032V001
SMReldIA52.0
SMRsuounitnoC.xaMA8.2
SMRtsruB.xaMA2.3
tsruBgniruDkaeP.xaMA0.5
SMR
SMR
SMR
SMR
A31.0
A4.1
SMR
A6.1
SMR
A5.2
SMR
A3.0
SMR
SMR
A2.3
SMR
A7.3
SMR
A8.5
SMR
To determine the minimum total service power required
by a system of UPA-P, or other Meyer self-powered speakers, add their maximum continuous RMS currents together. We recommend allowing an additional 30% above
the minimum amperage to prevent peak voltage drops at
the service entry and nuisance tripping.
Power Connector Wiring
Use the following AC cable wiring diagram to create
international or special-purpose power connectors:
Keep all liquids away from the UPA-P to avoid hazards
from electrical shock.
Do not operate the unit with worn or frayed cables;
replace them immediately.
If the UPA-P will be installed outdoors contact Meyer
Sound for information about the rain hood and weather
protection for the drivers and electronics
The Modular Rear Panel
The rear panel of the UPA-P has two slots for processor
modules. The top slot contains the Audio Input and
Control Module; the bottom slot contains the optional
Remote Monitoring System™ (RMS) Module. A blank
plate covers the bottom slot if RMS is not installed. For
drawings of the modules refer to page 13.
Audio Input
There are three, interchangeable Audio Input and Control
Modules with optimized connectors and controls for different applications. Each module has a 24V Fan connector to power an optional fan (see page 7).
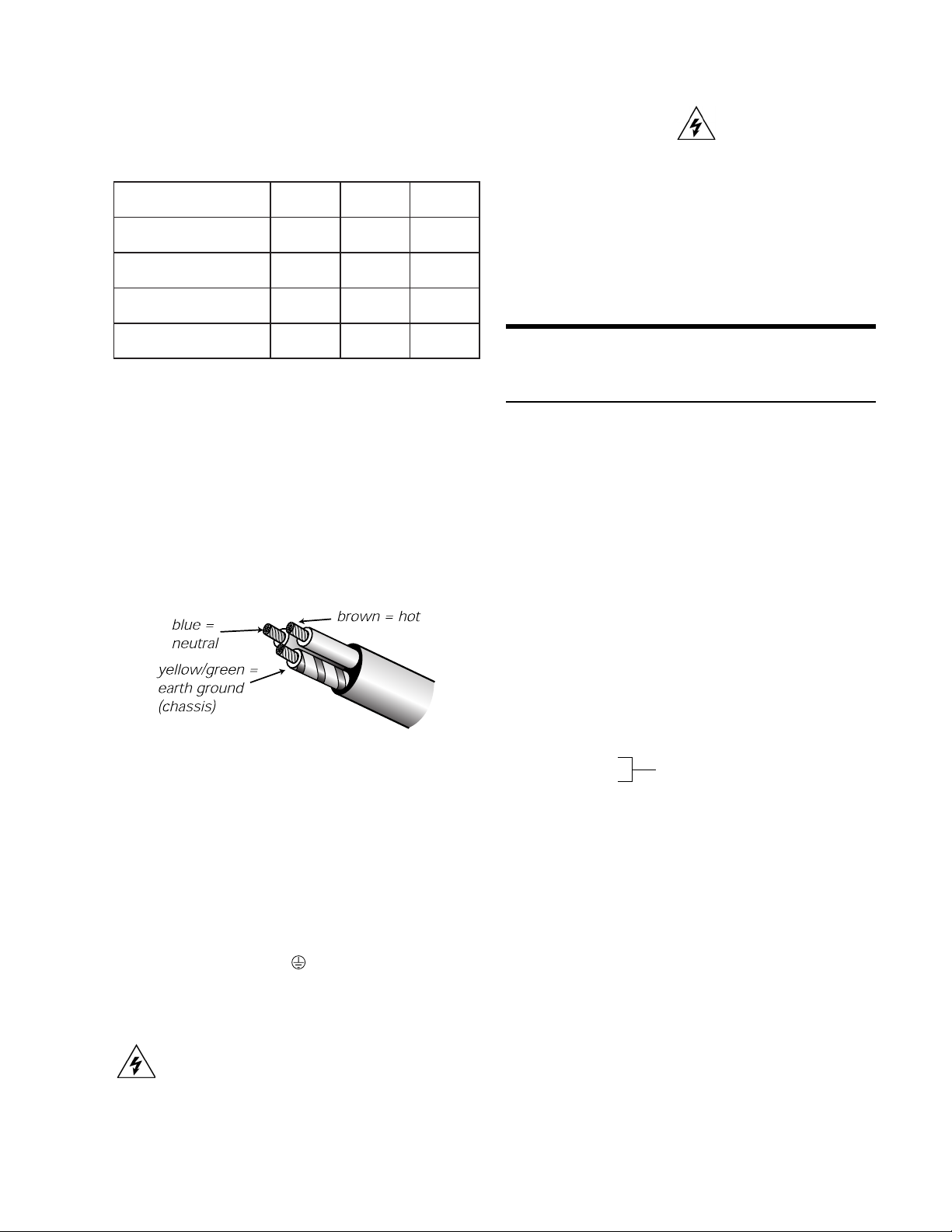
AC cable color code
If the colors referred to in the diagram don't correspond to
the terminals in your plug, use the following guidelines:
• Connect the blue wire to the terminal marked with
an N or colored black.
• Connect the brown wire to the terminal marked
with an L or colored red.
• Connect the green and yellow wire to the terminal
marked with an E (or ) or colored green (or green
and yellow).
Safety Issues
Do not use a ground-lifting adapter or cut the AC
cable ground pin.
Each module uses a three-pin, female XLR audio input
connector with a 10 kΩ balanced input impedance wired
with the following convention:
Pin 1 — 220 kΩ to chassis and earth ground (ESD clamped)
Pin 2 — Signal
Pin 3 — Signal
Case — Earth (AC) ground and chassis
Differential Inputs
Pins 2 and 3 carry the input as a differential signal. Use
standard audio cables with XLR connectors for balanced
signal sources. A single audio source can drive multiple
UPA-Ps with a paralleled input loop, creating an unbuffered hardwired loop connection, with negligible loss in
signal level. For example, since the input impedance of
one UPA-P is 10 kΩ, looping 20 UPA-Ps produces a balanced input impedance of 500Ω. With a 150Ω audio source,
the 500Ω load results in only a 2.28 dB loss.
#
Page 6

Looping Audio Input Module
This standard module uses a balanced, female XLR connector for audio input and a male XLR loop connector to
interconnect multiple speakers. The audio input connector is hardwired with pin 2 hot to comply with audio
industry standards. The loop connector, wired in parallel
to the audio input, transmits the input signal if the UPAP is turned off for any reason.
Summing Audio Input Module
This module has two balanced female XLR connectors.
The second female XLR connector functions as a summing
input. Applying a signal to one of the inputs results in a
normal signal level. Utilizing both summing inputs creates a correctly summed mono signal with each input 6
dB below the level of a single input. This is an effective
method for distributing both sides of a stereo signal to a
single UPA-P without requiring external level control.
Amplification, Limiting, and
Cooling System
Amplification and Limiting
Each driver in the UPA-P is powered by one channel of a
proprietary Meyer Sound amplifier utilizing complementary power MOSFET output stages (class AB, bridged,
350 Wrms/ch). Each channel has a limiter that prevents
driver over-excursion and regulates the temperature of
the voice coil. The limiters protect the drivers without the
glaring compression effects imposed by typical limiters,
allowing high SPLs across each driver’s entire frequency
range. Limiter activity for the high and low channels is
indicated by two yellow Limit LEDs on the rear panel
(the High Limit LED is above the Low Limit LED).
Looping, Polarity, and Attenuating Audio
Input Module
This module has a balanced, female XLR audio input
connector, a male XLR loop connector, an input polarity
switch, and a level attenuator knob. The input polarity
switch offers a convenient method of reversing the phase
of the speaker. When the input polarity switch is in the
up (+) position, pin 2 is hot relative to pin 3, resulting
in a positive pressure wave when a positive signal is
applied to pin 2. When the switch is down (-), pin 3 is hot
relative to pin 2, resulting in a positive pressure wave
when a positive signal is applied to pin 3. The level
attenuator knob operates between 0 dB (no level attenuation) in a fully clockwise position to –12 dB in a fully
counterclockwise position.
Remote Monitoring System
The UPA-P can be equipped to operate with the Remote
Monitoring System (RMS) network and software appli-
cation. RMS displays signal and power levels, driver
and cooling fan status, limiter activity, the state of the
polarity switch, attenuator level, and amplifier temperature for all speakers in the network on a Windows-based
PC. RMS can also be configured to enable speaker muting. RMS is an excellent field-diagnostic tool that removes the guesswork from troubleshooting during a performance. All Meyer loudspeakers with RMS can be integrated on the same network. Installing an RMS module
requires only a Phillips screwdriver. Contact Meyer
Sound for more information about RMS.
The UPA-P performs within its acoustical specifications
and operates at a normal temperature if the Limit LEDs
are on for no longer than two seconds, and off for at least
one second. If either LED remains on for longer than three
seconds, that channel incurs these consequences:
• Increasing the input level will not increase the
volume.
• The system distorts due to clipping and nonlinear
driver operation.
• Unequal limiting between the low and high frequency drivers alters the frequency response.
While the UPA-P limiters fully protect the system under
overload conditions and exhibit smooth sonic characteristics; we recommend that you do not intentionally
drive the UPA-P into continuous limiting to attain compression effects.
For applications where large amounts of compression
are required, we recommend using an outboard compressor/limiter for greater control of limit and compressor
effects.
Amplifier Natural Convection Cooling System
The UPA-P’s amplifier employs a natural convection cooling system that is cooled by the air flowing over the
heatsink. Allow for proper ventilation of fresh air when
using the speaker in tightly packed conditions.
If the temperature of the heatsink reaches 85°C (185°F),
the On/Temp. LED on the rear panel turns from green
(On) to red (Temp.) and the limiter threshold is lowered to
$
Page 7
a safe level to prevent the system from overheating. Under
high temperature conditions the output level is reduced
6 dB. When the heatsink temperature decreases to 75°C
(167°F), the On/Temp. LED changes from red to green
and the limiter threshold returns to normal.
The heatsink reaches temperatures up to 185°F
(85°C) during normal operation. Use extreme
caution when approaching the rear of the cabinet.
Fan Assembly Kit
While convection cooling is adequate for most applications, in situations where the UPA-P is driven into continuous limiting under severe temperature conditions,
or where ventilation is restricted, we recommend the installation of an optional fan kit to maintain a safe operating temperature.
The easy-to-install fan, powered through the 24V Fan
connector on the rear panel, blows air directly onto the
heatsink. The fan speed increases as the heatsink temperature rises, which maintains a safe operating temperature with minimal fan noise. Contact Meyer Sound
to order the fan kit.
Power Supply Fan
The power supply is cooled by a single small internal fan
that turns on low when the unit is first powered up. The
fan doubles its speed as the system is driven with audio.
Since the fan draws air in from, and exhausts it at the
back of the cabinet, there must be at least six inches
clearance behind the cabinet, and adequate air flow.
Rigging load ratings assume a straight tensile pull and
that the cabinet is in new condition with aircraft pan
fittings. If these conditions are not met, the load ratings
can be reduced significantly. Load ratings can also be
reduced by age, wear, and damage. It is important to
inspect the rigging hardware regularly and replace worn
or damaged components immediately.
NOTE: All Meyer Sound products must be used in accordance with local, state, federal, and industry regulations.
It is the owner’s and/or user’s responsibility to evaluate
the reliability of any rigging method for their application.
Rigging should be done only by experienced professionals.
Full-Range Systems
Introductory Concepts
The UPA-P is not a full range speaker. It is optimized to be
used with the Meyer USW-1P and UMS-1P self-powered
subwoofers. It can also be used with the Meyer 650-P and
PSW-2 self-powered subwoofers. For information on integrating the UPA-P with speakers other than the USW-1P
contact Meyer Sound Technical Support.
Using the UPA-P in a full-range system is straightforward
but the following concepts are important to consider before installing a system.
Polarity
Rigging
The UPA-P weighs 77.5 lb (35.2 kg). The maximum recommended load for an UPA-P with aircraft pan fittings
is 420 lb (191 kg). This working load is based on a 5:1
safety factor. The UPA-P has four rigging brackets (two
on top, two on bottom of the cabinet); each bracket is
capable of supporting the full working load of the cabinet.
There are four types of interchangeable rigging brackets,
each fastened by six Phillips screws:
• aircraft pan fittings (ring and stud)
•3/8”-16 nut plates
• M-10 x 1.5 metric nut plates
• blank plates (if no rigging brackets are requested)
NOTE: Units with nut plates are rated for the weight of one
cabinet only.
With the UPA-P in close-proximity to, and coplanar with,
the USW-1P, 650-P, or PSW-2, both speakers should be set
to the same polarity. Separating the UPA-P from the
subwoofer by more than 5 feet may require polarity reversal or a delay line to compensate for the propagation
delay between the speakers and the measurement position.
Array Design
Creating an effective array with the UPA-P requires a
precise understanding of how to combine the coverage
area and SPL of the individual speaker with those of
adjacent speakers. Array design is a trade-off between
increasing on-axis power and creating smooth transitions
between the coverage areas of adjacent speakers.
As the splay angle (the angle between adjacent cabinet
faces) decreases below the coverage angle of the indi-
%
Page 8

vidual speaker, the power at the center of the array increases, but the coverage overlap between adjacent speakers
causes comb filtering and other frequency response variations.
As the splay angle increases toward the coverage angle,
the power at the center of the array decreases, but the
variations in frequency response diminish. As the splay
angle increases beyond the coverage angle, noticeable
gaps begin to form in the array’s coverage area.
Measurement and Correction Tools
It is recommended that even the most carefully assembled
sound systems be analyzed with precise measurement
tools. We recommend using the Meyer SIM® System II
Sound Analyzer and CP-10 Parametric Equalizer to
• choose, place, and array speakers;
• measure propagation delays between speakers to
set the correct polarity and delay times;
• measure and equalize variations in frequency response caused by the acoustical environment and
the placement and interaction of speakers.
UPA-P with the USW-1P
UPA-P Frequency Range: 60 Hz – 18 kHz
USW-1P Frequency Range: 32 Hz – 150 Hz
Two UPA-Ps placed on top of, and coplanar to, one halfspace loaded USW-1P were designed to produce a flat
system frequency response (32 Hz – 18 kHz) when the
same full-range signal is sent to all speakers. It is important to emphasize that the UPA-P and USW-1P are in
phase in the region in which their responses overlap (60
– 120 Hz).
These documents are also available on the Meyer Sound
website: http://www.meyersound.com.
A single UPA-1P paired with a USW-1P provides < 134 dB
SPL across 100° of horizontal coverage.
For a system that requires a wider horizontal coverage
area, we recommend using two UPA-1Ps splayed at 85°
with a single USW-1P. The array pictured below provides < 136 dB SPL across 180° of horizontal coverage.
All Meyer self-powered subwoofers have internal crossovers which enable them to receive full-range signals.
UPA-Ps and USW-1Ps can be configured in a wide variety of array configurations to suit specific application
needs. The following section shows four recommended
configurations.
For additional system design ideas, contact Meyer Sound
for the following TechNotes on UPA-P array design:
• Two UPA-1Ps @ 70° Horizontal Splay
(Doc #: 01.990.101.90 A)
• Two UPA-1Ps @ 85° Horizontal Splay
(Doc #: 01.990.101.91 A)
• Two UPA-2Ps Tightpack (Doc #: 01.990.101.92 A).
• Three UPA-2Ps Tightpack (Doc #: 01.990.101.93 A).
&
Page 9

For a high power, compact system, we recommend using
two UPA-2Ps and two USW-1Ps. This array provides
< 143 dB SPL across 60° of horizontal coverage
Loading
As a general rule, if subwoofers are located in half-space
(single boundary, like a floor), then they have 6 dB more
gain than in free-field conditions.
Verifying Driver Polarity
Incorrect driver polarity impairs system performance and
may damage the drivers. All Meyer loudspeakers are
shipped with the drivers in correct alignment.
If the driver or circuit wiring has been removed or disassembled it is essential to check the polarity between drivers and between adjacent loudspeakers.
Polarity In Adjacent Loudspeakers
Use the following test procedure to verify the polarity
between two adjacent loudspeakers of the same type:
1. Position two loudspeakers adjacent to each other.
2. Place a measurement microphone 3 ft from the speakers on the axis to the center of the array.
This increase in low frequency energy is ideal for many
musical styles and venues but in some circumstances,
where a flatter response is desired we offer the following
solutions:
The VX-1:
The VX-1 is an ideal control option for a UPA-P and
USW-1P system. The VX-1 is a stereo virtual crossover
which allows the user to adjust the gain, switch between
stereo and mono distribution of two inputs and make
shelving EQ adjustments to the left and right sides of the
system.
Separate Feeds:
One simple method of attenuating the USW-1P is to feed
sperate signals to the USW-1P(s) and to the UPA-P(s).
With independent control of the main outputs and sub
levels, their relative proportions can be adjusted.
The Looping, Polarity, and Attenuating
Audio Input Module:
This optional module, described on page 6 of this user
guide allows for level control on the user panel of the
UPA.
3. Connect a signal source to one speaker and note the
frequency response and overall level.
4. Apply the same signal to the second speaker with
the first speaker still connected.
The polarity is correct if the frequency response remains
constant with a 5-6 dB SPL increase in amplitude. Broadband cancellation (decreased overall level) indicates polarity reversal.
Since polarity reversal causes excessive driver
excursion at high source levels, use moderate
levels when conducting these tests.
'
Page 10

Polarity within a UPA-P
Use the following test procedure to verify polarity between drivers in the same loudspeaker:
1. Place a measurement microphone 1 meter from
the front of the loudspeaker at the midway point between
the low and high frequency drivers.
2. Connect a full range signal to the loudspeaker
andnote the frequency response.
The polarity is correct if the frequency response is smooth
through the crossover region (800 Hz to 1.5 kHz). Cancellation of 6dB or more in this region indicates polarity
reversal.
Troubleshooting
This section suggests several possible solutions to some
common problems encountered by UPA-P users and is
not intended to be a thorough troubleshooting guide.
Qualified electronics technicians with access to a test
bench can request the following documents from Meyer
Sound: Troubleshooting Guide, The Low Frequency Driver
Replacement Procedure, and The High Frequency Driver Replacement Procedure for the UPA-1P/2P.
The On/Temp. LED does not illuminate, there
is no audio, and the power supply fan is
off.
1. Make sure the AC power cable is the correct type for
the regional voltage and that it is securely connected
to the AC inlet then unplug and reconnect the AC
cable.
2. Use an AC voltmeter to verify that the AC voltage is
within the ranges 88–264V, 47–63 Hz.
3. Call Meyer Sound Technical Support.
The On/Temp. LED is illuminated but there
is no sound.
1. Verify that the audio source (mixer, EQ, delay) is
sending a valid signal.
2. Make sure the XLR cable is securely fastened to the
XLR audio input connector.
3. Verify that the XLR cable is functioning by substituting another cable or by using the cable in question in a working system.
4. Send the audio signal to another speaker to insure
signal presence and that the level is within the proper
range. Turn the source level down before reconnecting the audio input and increase the level slowly to
avoid a sudden blast of sound.
5. If possible, monitor the audio source with headphones.
Hum or noise is produced by the speaker.
1. Disconnect the audio input. If the noise persists, the
problem is within the UPA-P. In this case return the
unit to the factory or nearest authorized service center. If the hum ceases, the noise originates somewhere earlier in the signal path.
2. Make sure the XLR cable is securely fastened to the
XLR audio input connector.
3. Send the audio signal to another speaker to insure
signal presence and that the level is within the proper
range. Turn the source level down before reconnecting the audio input and increase the level slowly to
avoid a sudden blast of sound.
5. Hum or noise can be produced by a ground loop.
Since the UPA-P is effectively ground-lifted, the loop
must be broken elsewhere in the system.
The audio produced by the speaker is
distorted or compressed but the limit light
is not illuminated.
1. Make sure the XLR cable is securely fastened to the
XLR audio input connector.
2. Send the audio signal to another speaker to insure
that the level is within the proper range. Turn the
source level down before reconnecting the audio
input and increase the level slowly to avoid a sudden blast of sound.
3. Monitor the audio source with headphones.
Page 11

The audio produced by the speaker is
highly compressed and the limit light is
constantly yellow.
There is no sound, the On/Temp. LED is
dim or off, and the power supply fan is on
high speed.
1. Turn down the level of the input signal to the
speaker system.
Only the high or low driver seems to produce sound.
1. Make sure the audio signal is full-range and has not
been filtered in a previous stage of the signal chain.
If possible, monitor the audio source with highquality headphones.
2. Send the audio signal to another speaker to insure
that the signal is full-range. Turn the source level
down before reconnecting the audio input and increase the level slowly to avoid a sudden blast of
sound.
3. Use a sine wave and/or pink noise generator to
send a variety of frequencies to the speaker.
There is sound but it is does not seem to
be at full power and the On/Temp. LED is
red.
This occurs in conditions where the heatsink temperature reaches 85°C (185°F), indicating that the amplifier is
thermally overloaded. The limiter threshold has dropped
to a safe level, so the audio level is reduced.
This extremely rare event occurs when the power supply
overheats, causing a 1-2 minute interruption in operation.
The unit turns on again when the power supply has
cooled sufficiently.
1. Make sure there is at least six inches clearance behind the unit.
2. Make sure there is sufficient air flow around the
unit.
See the section Amplification, Limiting, and Cooling System
on page 6 for a more information about the power supply’s
internal fan and cooling system.
1. Make sure there is enough clearance above, below,
and behind the unit.
2. Make sure there is sufficient air flow around the
unit.
3. Avoid exposing the heatsink to direct sunlight if the
ambient temperature is high.
4. If the ambient temperature is greater than 30°C and
this condition occurs frequently, contact Meyer
Sound to order the optional Fan Kit.
See the section Amplification, Limiting, and Cooling System
on page 6 for a complete discussion about the cooling
system.
Page 12

Safety Summary
English Français
• To reduce the risk of electric shock, disconnect the loudspeaker
from the AC mains before installing audio cable. Reconnect the
power cord only after making all signal connections.
• Connect the loudspeaker to a two-pole, three wire grounding mains
receptacle. The receptacle must be connected to a fuse or circuit
breaker. Connection to any other type of receptacle poses a
shock hazard and may violate local electrical codes.
• Do not install the loudspeaker in wet or humid locations
without using weather protection equipment from Meyer Sound.
• Do not allow water or any foreign object to get inside the
loudspeaker. Do not put objects containing liquid on, or near,
the unit.
• To reduce the risk of overheating the loudspeaker, avoid exposing it to direct sunlight. Do not install the unit near heat emitting
appliances, such as a room heater or stove.
• This loudspeaker contains potentially hazardous voltages. Do
not attempt to disassemble the unit. The unit contains no user
serviceable parts. Repairs should be performed only by factory
trained service personnel.
• Pour réduire le risque d’électrocution, débrancher la prise
principale de l’haut-parleur, avant d’installer le câble d’interface
allant à l’audio. Ne rebrancher le bloc d’alimentation qu’après
avoir effectué toutes les connections.
• Branchez l’haut-parleur dans une prise de courant à 3 dérivations
(deux pôles et la terre). Cette prise doit être munie d’une
protection adéquate (fusible ou coupe-circuit). L e branchement
dans tout autre genre de prise pourrait entraîner un risque
d’électrocution et peut constituer une infraction à la
réglementation locale concernant les installations électriques.
• Ne pas installer l’haut-parleur dans un endroit où il y a de l’eau
ou une humidité excessive.
• Ne pas laisser de l’eau ou tout objet pénétrer dans l’hautparleur. Ne pas placer de r´cipients contenant un liquide sur cet
appareil, ni à proximité de celui-ci.
• Pour éviter une surchauffe de l’haut-parleur, conserver-la à
l’abri du soleil. Ne pas installer à proximité d’appareils dégageant
de la chaleur tels que radiateurs ou appareils de chauffage.
• Ce haut-parleur contient des circuits haute tension présentant
un danger. Ne jamais essayer de le démonter. Il n’y a aucun
composant qui puisse être réparé par l’utilisateur. Toutes les
réparations doivent être effectuées par du personnel qualifié et
agréé par le constructeur.
Deutsch
• Um die Gefahr eines elektrischen Schlages auf ein Minimum zu
reduzieren, den Lautsprecher vom Stromnetz trennen, bevor
ggf. ein Audio-Schnittstellensignalkabel angeschlossen wird.
Das Netzkabel erst nach Herstellung aller Signalverbindungen
wieder einstecken.
• Der Lautsprecher an eine geerdete zweipolige DreiphasenNetzsteckdose anschließen. Die Steckdose muß mit einem
geeigneten Abzweigschutz (Sicherung oder Leistungsschalter)
verbunden sein. Der Anschluß der unterbrechungsfreien
Stromversorgung an einen anderen Steckdosentyp kann zu
Stromschlägen führen und gegen die örtlichen Vorschriften
verstoßen.
• Der Lautsprecher nicht an einem Ort aufstellen, an dem sie mit
Wasser oder übermäßig hoher Luftfeuchtigkeit in Berührung
kommen könnte.
• Darauf achten, daß weder Wasser noch Fremdkörper in das
Innere den Lautsprecher eindringen. Keine Objekte, die
Flüssigkeit enthalten, auf oder neben die unterbrechungsfreie
Stromversorgung stellen.
• Um ein Überhitzen dem Lautsprecher zu verhindern, das Gerät
vor direkter Sonneneinstrahlung fernhalten und nicht in der
Nähe von wärmeabstrahlenden Haushaltsgeräten (z.B. Heizgerät
oder Herd) aufstellen.
• Im Inneren diesem Lautsprecher herrschen potentiell gefährliche
Spannungen. Nicht versuchen, das Gerät zu öffnen. Es enthält
keine vom Benutzer reparierbaren Teile. Reparaturen dürfen
nur von ausgebildetem Kundenienstpersonal durchgeführt
werden.
Español
• Para reducir el riesgo de descarga eléctrica, desconecte de la red
el altoparlante antes de instalar el cable de señalización de
interfaz de la segnale. Vuelva a conectar el conductor flexible
de alimentación solamente una vez efectuadas todas las
interconexiones de señalizatción.
• Conecte el altoparlante a un tomacorriente bipolar y trifilar con
neutro de puesta a tierra. El tomacorriente debe estar conectado
a la protección de derivación apropiada (ya sea un fusible o un
disyuntor). La conexión a cualquier otro tipo de tomacorriente
puede constituir peligro de descarga eléctrica y violar los
códigos eléctricos locales.
• No instale el altoparlante en lugares donde haya agua o humedad
excesiva.
• No deje que en el altoparlante entre agua ni ningún objeto
extraño. No ponga objetos con líquidos encima de la unidad ni
cerca de ella.
• Para reducir el riesgo de sobrecalentamiento, no exponga la
unidad a los rayos directos del sol ni la instale cerca de
artefactos que emiten calor, como estufas o cocinas.
• Este altoparlante contiene niveles de voltaje peligrosos en
potencia. No intente desarmar la unidad, pues no contiene
piezas que puedan ser repardas por el usuario. Las reparaciones
deben efectuarse únicamente por parte del personal de
mantenimiento capacitado en la fábrica.
Page 13

Rear Panel and Optional Modules
The user panel and optional modules are described on page 5 of this guide.
User Panel with RMS option and Standard Looping Audio Input Module.
Looping, Polarity, and Attenuating Input Module
Summing Audio Input Module
!
Page 14

14.3
12.8
7.25
7.7
C
L
14.5
30
Dimensions
(in inches)
2.6
7.5
UPA-P Top
10.85
UPA-1P Side
7.4
UPA-P Back
7.25
10.85
UPA-2P Side
"
22.4
UPA-1P Front UPA-2P Front
Center of gravity
represented by
22.4
Page 15

Notes
#
Page 16

$
Contact Information
Meyer Sound Laboratories, Inc.
2832 San Pablo Avenue
Berkeley, California 94702
Telephone: 510 - 486 - 1166
FAX: 510 - 486 - 8356
E-mail: techsupport@meyersound.com
http://www.meyersound.com
 Loading...
Loading...