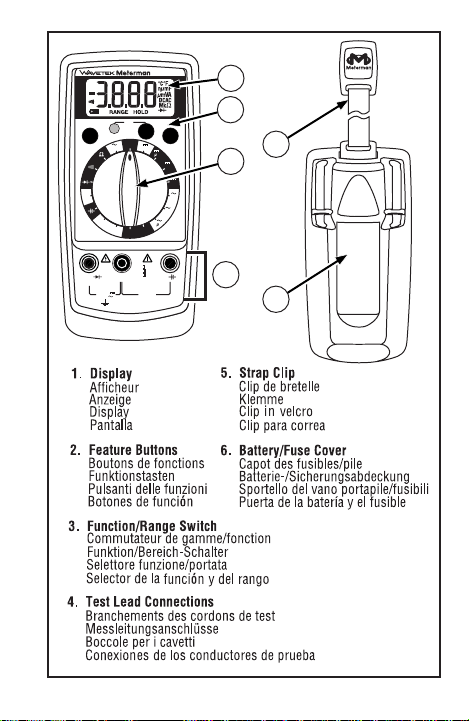
Page 1

Compact
Digital
Multimeter
Users Manual
• Manual de uso
• Mode d'emploi
• Bedienungshandbuch
• Manuale d'Uso
®
®
5XP
15XP
35XP
Page 2
RANGE
HZ
Ω
Hz Temp
35XP
1
NON
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
400
˚C
V
MAX
1000V
750V
mA
A
1000
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
2
5
3
2A
2A
2A
4
6
35XP
Page 3
XP Series Digital Multimeters
Contents
Safety Information.......................................................................................... 2
Symbols Used in this Manual....................................................................... 3
Making Measurements.................................................................................... 3
Verify Instrument Operation......................................................................... 3
Range Selection........................................................................................... 3
Correcting an Overload (0o or
Measuring DC Voltage .................................. See Figure -1- ........................3
Measuring AC Voltage .................................. See Figure -2-........................ 4
Preparing for Current Measurements............................................................ 4
Measuring DC Current .................................. See Figure -3-........................ 4
Measuring AC .............................................. See Figure -4- ........................4
Measuring Resistance .................................. See Figure -5- ........................5
Testing for Continuity ...................................See Figure -6-........................ 5
Testing Diodes.............................................. See Figure -7- ........................5
Measuring Capacitance (35XP only) ..............See Figure -8-........................ 5
Measuring Temperature (35XP only) .............See Figure -9- ........................6
Measuring Frequency (35XP only)................. See Figure -10-...................... 6
Measuring NCV (Non-Contact Voltage).......... See Figure -11- ......................6
Testing Battery Voltage (5XP only)................ See Figure -12- ......................6
Testing Logic Levels (15XP only) .................. See Figure -13-...................... 7
Additional Features .........................................................................................7
Input Test Lead Warning.............................................................................. 7
MIN MAX Measurements (Model 5XP only).................................................. 7
Auto Power Off (Models 15XP and 35XP only) .............................................7
HOLD Measurements................................................................................... 7
Product Maintenance...................................................................................... 8
Cleaning...................................................................................................... 8
Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................8
Battery and Fuse Replacement ...................... See Figure -14- ......................8
WARRANTY ...................................................................................................8
Repair............................................................................................................ 9
Specifications............................................................................................... 10
-0o
) Indication W......................................... 3
English
1
Page 4
5XP
15XP
15XP5XP 35XP
35XP
NON
MIN MAX
V
20M
2M
200k
Ω
BATT 9V
• The XP Series Digital Multimeters conform to EN61010-1, Rev-2; CAT I 1000 V,
CAT II 600 V, CAT III 300 V, class 2 and pollution deg.2; CSA 22.2 -1010-1. It is
recommended for use with local level power distribution, appliances, portable
equipment, etc., where only smaller transient overvoltages may occur, and not
for primary supply lines, overhead lines, and cable systems.
• Do not exceed the maximum overload limits per function (see specifications)
nor the limits marked on the instrument itself. Never apply more than
1000 V dc/750 V ac rms between the test lead and earth ground.
• Inspect the DMM, test leads and accessories before every use. Do not use any
damaged part.
• Never ground yourself when taking measurements. Do not touch exposed
circuit elements or test probe tips.
• Do not operate the instrument in an explosive atmosphere.
• Exercise extreme caution when: measuring voltage >20 V // current >10 mA //
AC power line with inductive loads // AC power line during electrical storms //
current, when the fuse blows in a circuit with open circuit voltage >1000 V //
servicing CRT equipment.
• Always measure current in series with the load – NEVER ACROSS a voltage
source. Check fuse first. Never replace a fuse with one of a different rating.
• Remove test leads before opening the case.
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
1000750
200200
2020
V
22
200
m
V
200
m
200
2m
20m
200
m
200m
20k
20m
2k
2m
200
1.5V
200
9V
BATT
A
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
mA
COM
BATT 1.5V
MAX
1000V
200mA MAX
750V
FUSED
Safety Information
NON
RANGE
V
Ω
LOGIC
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
A
mA
A
A
mA
V
OFF
V
MAX
A
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
1000V
2A MAX
750V
FUSED
NON
RANGE
HZ
Ω
Hz Temp
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
A
A
mA
400
A
˚C
1000
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
V
A
COM
MAX
1000V
2A MAX
750V
FUSED
2
Page 5
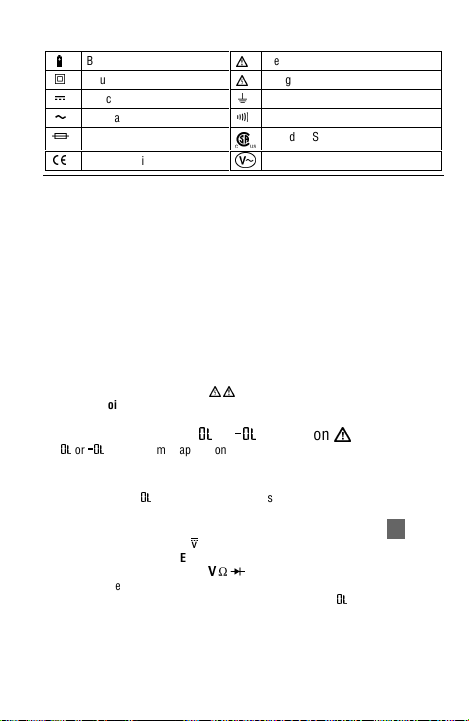
Symbols Used in this Manual
B
Battery
T
Double insulated
F
Direct Current
B
Alternating Current
I
Fuse
Complies with EU directives
P
W
Refer to the manual
X
Dangerous Voltage
J
Earth Ground
R
Audible tone
Canadian Standards Association
)
z
Non-contact Voltage
Making Measurements
Verify Instrument Operation
Before attempting to make a measurement, verify that the instrument is operational
and the battery is good. If the instrument is not operational, have it repaired before
attempting to make a measurement.
Range Selection
In addition to autoranging (Models 15XP and 35XP only) you can manually select
and lock a range by pressing the RANGE button. RANGE appears on the display to
indicate that manual ranging is active and the range is locked. When appropriate,
each subsequent press of the range button steps the meter to the next higher
range. When the highest range is reached the next press returns the meter to the
lowest range. To return to autoranging press the RANGE button. If RANGE still
shows on the display, autoranging is not available for the selected function. Use
autorange for all initial measurements. Then, when appropriate, use the RANGE
button to select and lock a range.
To avoid electrical shock while manual ranging, use the display
annunciators to identify the actual range selected.
Correcting an Overload (0o or
An 0o or
-0o
indication may appear on the display to indicate that an overload
condition exists. For voltage and current measurements, an overload should be
immediately corrected by selecting a higher range. If the highest range setting does
not eliminate the overload, interrupt the measurement until the problem is identified
and eliminated. The 0o indication is normal for some functions; for example,
resistance, continuity, and diode test.
Measuring DC Voltage See Figure -1-
1. Set the Function Switch to v.
2. Select the desired RANGE (5XP only).
3. Connect the test leads: Red to E, Black to COM.
4. Connect the test probes to the circuit test points.
5. Read the display, and, if necessary, correct any overload (0o) conditions.
XW
Warning
-0o
) Indication
W
3
Page 6

Measuring AC Voltage See Figure -2-
1. Set the Function Switch to V.
2. Select the desired RANGE (5XP only).
3. Connect the test leads: Red to E, Black to COM.
4. Connect the test probes to the circuit test points.
5. Read the display, and, if necessary, correct any overload (0o) conditions.
Preparing for Current Measurements
• Turn off circuit power before connecting the test probes.
• Allow the meter to cool between measurements, if current measurements
approach or exceeds 2 amps.
• A warning tone sounds if you connect a test lead to a current input while a
current function is not selected.
• Open circuit voltage at the measurement point must not exceed 1000 V.
• Always measure current in series with the load. Never measure current across a
voltage source.
Measuring DC Current See Figure -3-
1. Set the Function Switch to a current function, µA, mA, or A.
2. Select the desired RANGE (5XP only).
3. Connect the test leads: Red to mA or A, Black to COM.
4. Turn off power to the circuit being measured.
5. Open the test circuit (X) to establish measurement points.
6. Connect the test probes in series with the load (to the measurement points).
7. Turn on power to the circuit being measured.
8. Read the display, and, if necessary, correct any overload (0o or
-0o
) conditions.
Measuring AC Current See Figure -4-
1. Set the Function Switch to a current function and range, µA, mA, or A.
2. Select the desired RANGE (5XP only).
3. Connect the test leads: Red to mA or A, Black to COM.
4. Turn off power to the circuit being measured.
5. Open the test circuit (X) to establish measurement points.
6. Connect the test probes in series with the load (to the measurement points).
7. Turn on power to the circuit being measured.
8. Read the display, and, if necessary, correct any overload (0o) conditions.
4
Page 7
Measuring Resistance See Figure -5-
1. Set the Function Switch to Ω.
2. Select the desired RANGE (5XP only).
3. Connect the test leads: Red to E, Black to COM.
4. Turn off power to the circuit being measured. Never measure resistance across
a voltage source or on a powered circuit.
5. Discharge any capacitors that may influence the reading.
6. Connect the test probes across the resistance.
7. Read the display. If 0o appears on the highest range, the resistance is too large
to be measured or the circuit is an open circuit.
Testing for Continuity See Figure -6-
1. Set the Function Switch to R.
2. Connect the test leads: Red to E, Black to COM.
3. Turn off power to the circuit being measured.
4. Discharge any capacitors that may influence the reading.
5. Connect the test probes across the resistance.
6. Listen for the tone that indicates continuity (< 40 Ω).
Testing Diodes See Figure -7-
1. Set the Function Switch to G.
2. Connect the test leads: Red to E, Black to COM.
3. Turn off power to the circuit being measured.
4. Free at least one end of the diode from the circuit.
5. Connect the test probes across the diode.
6. Read the display. A good diode has a forward voltage drop of about 0.6 V. An
open or reverse biased diode will read 0o.
Measuring Capacitance (35XP only) See Figure -8-
1. Set the Function Switch to the P function.
2. Connect the test leads: Red to
4. Turn off power to the circuit being measured.
5. Discharge the capacitor using a 100 kΩ resistor.
6. Free at least one end of the capacitor from the circuit.
7. Connect the test probes across the capacitor.
8. Read the display.
h
Black to COM.
,
5
Page 8

Measuring Temperature (35XP only) See Figure -9-
1. Set the function Switch to appropriate °C or °F range.
2. Connect the K-type thermocouple to a TEMP adapter (XR-TA).
Match the polarity of the adapter to the polarity of the thermocouple.
3. Connect the TEMP adapter to the
Note: The 35XP is compatible with all K-type thermocouples. The K-type bead
thermocouple supplied with the meter is not intended for contact with liquids or electrical
circuits.
4. Expose the thermocouple to the temperature to be measured.
5. Read the display.
Measuring Frequency (35XP only) See Figure -10-
1. Set the Function Switch to Hz.
2. Connect the test leads: Red to Hz, Black to COM.
3. Connect the test probes to the signal source.
4. Read the display.
E
and COM inputs.
Measuring NCV (Non-Contact Voltage) See Figure -11-
1. Range switch may be set to OFF or any function/range.
2. Test leads are not used for the NCV test.
3. Press the NCV button. The display goes blank, a tone sounds and the green LED
next to the NCV button on the front panel lights up to verify that the instrument
is operational. While pressing the button, hold the top-center of the meter
(sensor location) close to the conductor/circuit in question.
4. If a voltage in the range of 70 to 600 V ac is present, a tone sounds and the
green LED next to the NCV button on the front panel lights up.
Testing Battery Voltage (5XP only) See Figure -12-
1. Set the Function Switch to the appropriate BATT setting, 1.5V or 9V.
2. Connect the test leads: Red to BATT 1.5V or BATT 9V, Black to COM.
3. Connect the test probes across the battery. The meter applies an appropriate
load to the battery.
4. Read the display. A good 1.5 volt battery should measure >1.2 V, and a good
9 volt battery should measure > 7.2 V.
z
6
Page 9

Testing Logic Levels (15XP only) See Figure -13-
The 15XP tests logic levels for TTL logic. The meter displays 0o plus a ∧ for a
high-level (true) condition. The meter beeps and displays an
low-level (false) condition. See
limits. Out-of-limits indications are displayed as 0o only, no ∧, ∨ or beep occur.
1. Set the Function Switch to LOGIC.
2. Connect the test leads: Red to E, Black to COM .
3. Connect the black lead to logic common.
4. Connect the red lead to the logic test point.
5. Read the display.
Specifications
for the logic 1 and logic 0 voltage
0o
and a ∨ for a
Additional Features
Input Test Lead Warning
The meter emits a continuous tone when a test lead is placed in the mA or A input
jack and the Function/Range Switch is not set to a correct current position. (If the
meter is connected to a voltage source with leads connected for current, very high
current could result). All current ranges are protected by fast acting fuses.
MIN MAX Measurements (Model 5XP only)
The MIN MAX feature reads and updates the display to show the maximum,
minimum, or average value measured after you press the MIN MAX button.
Pressing the MIN MAX button for less than 1 second will put the meter into a mode
of displaying the maximum or minimum readings. Each time the button is pressed,
the meter will cycle to the next display mode. Press the MIN MAX button for more
than 1 second to disable this feature.
Auto Power Off (Models 15XP and 35XP only)
Auto Power Off is a battery saving feature that puts the meter into a sleep mode if
the Function/Range Switch has not changed position in the last 6 minutes (15XP)
or 10 minutes (35XP). To wake the meter turn the Function/Range Switch to
another position.
The Auto Power Off feature can be disabled to keep the meter from going to sleep.
To disable the Auto Power Off feature use the following procedure:
1. Set the Function Switch to OFF.
2. Press and hold the Range button while turning the Function Switch from OFF
to the desired function.
3. Release the Range button. The Auto Power Off feature will remain disabled until
the meter is turned off and then on.
HOLD Measurements
The HOLD button causes the meter to capture and continuously display a
measurement reading. To use the HOLD feature make a measurement, and then,
after the reading has stabilized, momentarily press the HOLD button. You can
remove the test leads and the reading will remain on the display. Pressing the
HOLD button again releases the display.
7
Page 10

Product Maintenance
Cleaning
To clean the meter, use a soft cloth moistened with water. To avoid damage to the
plastic components do not use benzene, alcohol, acetone, ether, paint thinner,
lacquer thinner, ketone or other solvents to clean the meter.
Troubleshooting
If the meter appears to operate improperly, check the following items first.
1. Review the operating instructions to ensure the meter is being used properly.
2. Inspect and test the continuity of the test leads.
3. Make sure the battery is in good condition. The low battery symbol
appears when the battery falls below the level where accuracy is guaranteed.
Replace a low-battery immediately.
4. Check the condition of the fuses if the current ranges operate incorrectly.
Battery and Fuse Replacement See Figure -14-
To avoid electrical, shock remove the test leads from both the
meter and the test circuit before accessing the battery or the
fuses.
To replace the fuse:
1. Remove the 2 rear-case screws.
2. Separate the case.
3. Remove and replace the 2 A fuse (15XP or 35XP) or 0.315 fuse (5XP).
4. Reassemble the meter.
Fuse:
Fast Blow 2 A/1000 V, minimum interrupt rating 30 kA (6 x 32 mm)
(Meterman FP200).
Fast Blow 0.315 A/1000V minimum interrupt rating 30 kA (6.3 x 32 mm)
(Meterman FP300)
WARRANTY
The XP Series of Digital Multimeters are warranted against any defects of material
or workmanship within a period of one (1) year following the date of purchase of
the multimeter by the original purchaser or original user. Any multimeter claimed to
be defective during the warranty period should be returned with proof of purchase
to an authorized Meterman Test Tools Service Center or to the local Meterman Test
Tools dealer or distributor where your multimeter was purchased. See Repair
section for details. Any implied warranties arising out of the sale of a Meterman
Test Tools multimeter, including but not limited to implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, are limited in duration to the
above stated one (1) year period. Meterman Test Tools shall not be liable for loss of
use of the multimeter or other incidental or consequential damages, expenses, or
economical loss or for any claim or claims for such damage, expenses or
economical loss. Some states do not allow limitations on how long implied
warranties last or the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential
damages, so the above limitations or exclusions may not apply to you. This
warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights which
vary from state to state.
XW
WARNING
M
8
Page 11

Repair
All test tools returned for warranty or non-warranty repair or for calibration should
be accompanied by the following: your name, company’s name, address, telephone
number, and proof of purchase. Additionally, please include a brief description of
the problem or the service requested and include the test leads with the meter.
Non-warranty repair or replacement charges should be remitted in the form of a
check, a money order, credit card with expiration date, or a purchase order made
payable to Meterman Test Tools.
In-Warranty Repairs and Replacement – All Countries
Please read the warranty statement that follows, and check your batteries and fuses
before requesting repair. During the warranty period any defective test tool can be
returned to your Meterman Test Tools distributor for an exchange for the same or
like product. Please check the “Where to Buy” section on
www.metermantesttools.com for a list of distributors near you. Additionally, in the
United States and Canada In-Warranty repair and replacement units can also be
sent to a Meterman Test Tools Service Center (see below for address).
Non-Warranty Repairs and Replacement – US and Canada
Non-warranty repairs in the United States and Canada should be sent to a
Meterman Test Tools Service Center. Call Meterman Test Tools or inquire at your
point of purchase for current repair and replacement rates.
In USA In Canada
Meterman Test Tools Meterman Test Tools
1420 75th Street SW 400 Britannia Rd. E. Unit #1
Everett, WA 98203 Mississauga, ON L4Z 1X9
Tel: 800-993-5853 Tel: 905-890-7600
Fax: 425-446-6390 Fax: 905-890-6866
Non-Warranty Repairs and Replacement – Europe
European non-warranty units can be replaced by your Meterman Test Tools
distributor for a nominal charge. Please check the “Where to Buy” section on
www.metermantesttools.com for a list of distributors near you.
European Correspondence Address*
Meterman Test Tools Europe
P.O. Box 1186
5602 BD Eindhoven
The Netherlands
*(Correspondence only – no repair or replacement available from this address.
European customers please contact your distributor.)
9
Page 12

Specifications
Display:
5XP and 15XP: 3 ½ digit liquid crystal
display (LCD) with a maximum reading of
1999.
35XP: 3 ¾ digit liquid crystal display
(LCD) with a maximum reading of 3999.
Polarity: Automatic, positive implied,
negative polarity indication.
Overrange: 0o or
Low battery indication: The
symbol is displayed when the battery
voltage drops below the operating level.
Operating environment: 0 °C to 50 °C
at <70 % R.H.
Power: Single standard 9 V battery,
NEDA 1604, JIS 006P, IEC 6F22.
Dimensions: 155 mm (H) ×72 mm (W)
×32 mm (D)
Weight: Approximately 210 g including
battery.
Overload protection: 1000 V dc or
750 V ac
Accessories: One pair test leads TL245,
9 V battery (installed),holster, magnet
strap, Users Manual.
Altitude: 6561.7 Feet (2000 M)
-0o
is displayed.
M
Safety: Conforms to EN61010-1, Rev-2;
CAT I 1000V, CAT II 600V, CAT III 300V,
class 2 and pollution deg.2;
CSA 22.2 -1010-1.
EMC: Conforms to EN61326-1. This
product complies with requirements of the
following European Community Directives:
89/ 336/ EEC (Electromagnetic
Compatibility) and 73/ 23/ EEC (Low
Voltage) as amended by 93/ 68/ EEC (CE
Marking). However, electrical noise or
intense electromagnetic fields in the vicinity
of the equipment may disturb the
measurement circuit. Measuring
instruments will also respond to unwanted
signals that may be present within the
measurement circuit. Users should exercise
care and take appropriate precautions to
avoid misleading results when making
measurements in the presence of electronic
interference.
Replacement Parts
TL36 Test Lead Set
TL245 Test Lead Set
FP200 Fuse – 2 A / 1000 V (15XP and
35XP)
FP300 Fuse – 0.315A / 1000V (5XP)
H2-XR Magne-Grip
XR-TA Input Adapter for K-type
TP255 K type thermocouple
See www.metermantesttools.com for
detailed specifications of the Meterman
XP digital multimeters.
5XP Electrical Specifications
(at 23°C ± 5°C, < 75% R.H.)
DC VOLTS
Ranges: 200 mV, 2 V, 20 V, 200 V, 1000 V
Accuracy: ± (1.0% rdg + 1 dgt)
AC VOLTS (45 Hz to 500 Hz)
Ranges: 200 mV, 2V, 20 V, 200 V, 750 V
Accuracy: ± (1.5% rdg + 5 dgts)
DC CURRENT
Ranges: 200 µA, 2 mA, 20 mA, 200 mA,
± (1.5% rdg + 1 dgt)
AC CURRENT (45 Hz to 500 Hz)
Ranges: 200 µA, 2 mA, 20 mA, 200 mA,
± (2.0% rdg + 5 dgts)
RESISTANCE
Ranges: 200 Ω, 2 kΩ, 20 kΩ, 200 kΩ,
2 MΩ, 20 MΩ
Accuracy: ± (1.0% rdg + 4 dgts) on 200 to
200 kΩ ranges ± (1.5% rdg + 4 dgts) on
2 MΩ range ± (3.0% rdg + 5 dgts) on
20 MΩ range
CONTINUITY
Audible indication: 75 ± 25 Ω
DIODE TEST
Test current: 1.0 mA (approximate)
Accuracy: ± (1.5% rdg + 3 dgts)
Open circuit volts: 3.0 dc typical
and strap
thermocouple
®
Holster, clip, magnet,
10
Page 13

BATTERY TEST
Ranges: 1.5 V, 9 V
Accuracy: ± (3.5% rdg + 2 dgts)
NON-CONTACT VOLTAGE INDICATOR
Sense voltage 70 V to 600 VAC (50 Hz to
60 Hz) beeper chirps and bright green LED
comes on, works when meter dial is on any
range.
OVERLOAD PROTECTION:
Voltage, Resistance, Diode, Continuity:
1000 VDC or 750 VAC rms
200 mV Range: 1000 VDC / 750 VAC rms
(3 minutes)
Current: 0.315 A / 1000 V fast blow ceramic
fuse 6.3 × 32 mm
mA JACK: Input warning detects wrong
switch/input jack configuration
AUXILIARY FEATURES
DATA HOLD: Freeze the latest reading on
the display.
MIN/MAX: Record the maximum and
minimum reading in a measurement.
15XP Electrical Specifications
(at 23°C ± 5°C, < 75% R.H.)
DC VOLTS
Ranges: 200 mV, 2 V, 20 V, 200 V, 1000 V
Accuracy: ±(0.5% rdg + 1 dgt)
AC VOLTS (45 Hz to 500 Hz)
Ranges: 200 mV, 2 V, 20 V, 200 V, 750 V
Accuracy: ±(1.5% rdg + 5 dgts) 45 Hz to
100 Hz on 200 mV range ±(1.5% rdg
+ 5 dgts) on 2 V to 750 V ranges
DC CURRENT
Ranges: 200 µA, 2000 µA, 20 mA, 200 mA,
2 A
Accuracy: ±(1.0% rdg + 2 dgts) on 200 µA
to 200 mA ranges ±(2.0% rdg + 3 dgts) on
2 A range
AC CURRENT (45 Hz to 500 Hz)
Ranges: 200 µA, 2000 µA, 20 mA, 200 mA,
2 A
Accuracy: ±(1.5% rdg + 5 dgts) on 200 µA
to 200 mA ranges ±(2.5% rdg + 5 dgts) on
2 A range
RESISTANCE
Ranges: 200 Ω, 2 kΩ, 20 kΩ, 200 kΩ,
2 MΩ, 20 MΩ
Accuracy: ± (1.0% rdg + 4 dgts) on 200 to
2 MΩ ranges ± (3.0% rdg + 5 dgts) on
20 MΩ range
CONTINUITY
Audible indication: Less than 25 Ω
DIODE TEST
Test current: 1.2 mA (approximate)
Accuracy: ±(1.5% rdg + 3 dgts)
Open circuit volts: 3.0 dc typical
LOGIC TEST
Thresholds Logic 1 (Hi): 2.8 V ± 0.8 V
Thresholds Logic o (Lo): 0.8 V ± 0.5 V
Test voltage: TTL 5 VDC
NON-CONTACT VOLTAGE INDICATOR
Sense voltage 70 V to
60 Hz) beeper chirps and bright green LED
comes on, works when meter dial is on any
range.
OVERLOAD PROTECTION:
Voltage, Resistance, Diode, Continuity,
Logic: 1000 VDC or 750 VAC rms
Current: 2 A / 1000 V fast blow ceramic
fuse 6.3 × 32 mm
A JACK: Input warning detects wrong
switch / input jack configuration
AUXILIARY FEATURES
DATA HOLD: Freeze the latest reading on
the display.
RANGE: Execute manual range mode.
AUTO Power off: After auto power off,
press (RANGE) button to restart the meter,
and the last reading of measurement will be
returned to the display.
600 VAC (50 Hz to
11
Page 14

35XP Electrical Specifications
(at 23°C ± 5°C, < 75% R.H.)
DC VOLTS
Ranges: 400 mV, 4 V, 40 V, 400 V, 1000 V
Accuracy: ± (0.5% rdg + 1 dgt)
AC VOLTS (45 Hz to 500 Hz)
Ranges:400 mV, 4 V, 40 V, 400 V, 750 V
Accuracy: ± (1.5% rdg + 5 dgts) 45 Hz to
100 Hz on 400 mV range ± (1.5% rdg
+ 5 dgts) on 4 V to 750 V ranges
DC CURRENT
Ranges: 400 µA, 4000 µA, 40 mA, 400 mA,
2 A
Accuracy: ± (1.0% rdg + 2 dgts) on 400 µA
to 400 mA ranges ± (2.0% rdg + 3 dgts) on
2 A range
AC CURRENT (45 Hz to 500 Hz)
Ranges: 400 µA, 4000 µA, 40 mA, 400 mA,
2 A
Accuracy: ± (1.5% rdg + 5 dgts) on 400 µA
to 400 mA ranges ± (2.5% rdg + 5dgts) on
2 A range
RESISTANCE
Ranges: 400 Ω, 4 kΩ, 40 kΩ, 400 kΩ,
4 MΩ, 40 MΩ
Accuracy: ± (1.0% rdg + 4 dgts) on 400 to
4 MΩ ranges ± (3.0% rdg + 5 dgts) on
40 MΩ range
CONTINUITY
Audible indication: Less than 25 Ω
DIODE TEST
Test current: 1.2 mA (approximate)
Accuracy: ±(1.5% rdg + 3 dgts)
Open circuit volts: 3.0 dc typical
CAPACITANCE
Ranges: 4 nF, 40 nF, 400 nF, 4 µF, 40 µF,
400 µF, 4 mF
Accuracy: ± (5.0% rdg + 30 dgts) on 4 nF
ranges ± (5.0% rdg + 5 dgts) on 40 nF and
400 µF ranges ± (5.0% rdg + 15 dgts) on
4 mF range
TEMPERATURE
Ranges: -20°C to 1000°C, -4°F to 1832°F
Accuracy: ± (2.0% rdg +4°C) -20°C to 10°C
± (1.0% rdg + 3°C)10°C to 200°C
± (3.0% rdg + 2°C) 200°C to 1000°C
± (2.0% rdg + 8°F) -4°F to 50°F
± (1.0% rdg + 6°F) 50°F to 400°F
± (3.0% rdg + 4°F) 400°F to1832°F
FREQUENCY
Ranges: 4 k, 40 k, 400 k, 4 M, 20 MHz
Accuracy: ± (0.1% rdg + 3 dgts)
Sensitivity:
10 Hz to 4 MHz: >1.5V rms; 4 MHz to
20 MHz: >2 V rms, <5 V rms
NON-CONTACT VOLTAGE INDICATOR
Sense voltage 70 V to 600 VAC (50 Hz to
60 Hz) beeper chirps and bright green LED
comes on, works when meter dial is on any
range.
OVERLOAD PROTECTION:
Voltage, Resistance, Diode, Continuity,
Frequency, Temperature: 1000 VDC or
750 VAC rms
Current, Capacitance: 2 A / 1000 V fast
blow ceramic fuse 6.3 × 32 mm
A JACK: Input warning detects wrong
switch/input jack configuration
AUXILIARY FEATURES
DATA HOLD: Freeze the latest reading on
the display.
RANGE: Execute manual range mode.
AUTO Power off: After auto power off,
press (RANGE) button to restart the meter,
and the last reading of measurement will be
returned to the display.
12
Page 15

1
V
5
35XP
4
2
NON
RANGE
Ω
Hz Temp
HZ
400
V
MAX
1000V
750V
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
A
1
A
mA
A
˚C
1000
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
3
2
V
5
35XP
4
2
NON
RANGE
Ω
Hz Temp
HZ
400
V
MAX
1000V
750V
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
A
1
A
mA
A
˚C
1000
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
3
13
Page 16

3
RANGE
Ω
Hz Temp
A
8
35XP
NON
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
HZ
400
˚C
1000
V
MAX
1000V
750V
A
A
mA
A
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
4
2
7
5
1
6
3
4
A
8
4
2
7
5
1
3
6
RANGE
Ω
Hz Temp
35XP
NON
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
HZ
400
˚C
1000
V
MAX
1000V
750V
A
A
mA
A
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
14
Page 17

5
7
35XP
4
5
2
NON
RANGE
Ω
Hz Temp
HZ
400
˚C
V
MAX
1000V
750V
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
A
1000
400
1832
˚F
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
mA
mA
mA
auto-off
A
1
2A
A
A
6
3
6
35XP
NON
RANGE
Ω
Hz Temp
HZ
400
˚C
V
MAX
1000V
750V
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
A
A
1
mA
A
1000
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
3
2
4
6
5
15
Page 18

7
35XP
NON
RANGE
Ω
Hz Temp
HZ
400
V
MAX
1000V
750V
HOLD
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
A
A
mA
A
˚C
400
1000
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
3
6
4
1
5
2
8
NON
RANGE
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
V
V
A
A
HZ
400
Ω
V
Hz Temp
MAX
1000V
750V
A
˚C
400
1000
1832
˚F
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
COM
2A MAX
FUSED
HOLD
auto-off
A
7
35XP
1
mA
mA
2A
A
A
mA
2
6
3
4
5
16
Page 19

9
4
5
1
10
2
3
4
1
2
K
3
17
Page 20

11
NCV
35XP
3
RANGE HOLD
HZ
Ω
V
Hz Temp
12
MIN MAX
V
200
m
20M
2M
200k
20k
Ω
V
BATT 9V
V
400
˚C
1000
COM
MAX
1000V
750V
BATT
2k
200
1.5V
COM
MAX
1000V
750V
OFF
V
A
A
mA
mA
2A
mA
A
400
1832
˚F
auto-off
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
A
2A MAX
FUSED
1
35XP
A
A
2
RANGE HOLD
V
OFF
V
A
A
HZ
mA
mA
2A
2A
400
2A
˚C
1000
mA
1832
400
A
˚F
auto-off
Ω
V
Hz Temp
CAT 1000V
COM
CAT 600V
MAX
CAT 300V
1000V
750V
A
2A MAX
FUSED
4
4
5XP
NON
CONTACT
VOLTAGE
OFF
1000750
200200
2020
20m
2m
200
9V
BATT
CAT 1000V
CAT 600V
CAT 300V
200mA MAX
FUSED
1
HOLD
V
22
200
m
200
2m
20m
200
m
200m
A
2
mA
BATT 1.5V
3
18
Page 21

19
Page 22

®
®
U.S. Service Center
Meterman Test Tools
1420 75th Street SW
Everett, WA 98203
Tel: 888-993-5853
Fax: 425-446-6390
Canadian Service Center
Meterman Test Tools
400 Britannia Rd. E. Unit #1
Mississauga, ON L4Z 1X9
Tel: 905-890-7600
Fax: 905-89-6866
European Correspondence Address*
Meterman Test Tools Europe
P.O. Box 1186
5602 BD Eindhoven
The Netherlands
*Correspondence only - no repair or replacement
available from this address. European customers
please contact your distributor.
Visit www.metermantesttools.com for
• Catalog
• Application notes
• Product specifications
• Product manuals
5XP
15XP
35XP
PN 2095408
October 2003
© Wavetek Meterman Test Tools.
All rights reserved. Printed in Taiwan.
Please Recycle
 Loading...
Loading...