Page 1

W 650-100
W 650-125
en Original instructions 5
pl Instrukcja oryginalna 11
PRC 使用说明 31
ru Оригинальное руководство по
эксплуатации 17
uk Оригінальна інструкція з експлуатації 24
www.metabo.com
Page 2

345
2
1
6
7
1
7
10
11
8
9
1
8X
8Y
8Z
A
W 650-100
B
C
2
Page 3

13.
Ø mm (in)
t
max1
t
max3
mm (in)
mm (in)
M / l - / mm (in)
n min
P
1
P
2
m kg (lbs)
a
/
h,SG
K
h,SG
a
h,DS
K
h,DS
LpA/K
LWA/K
pA
WA
m/s
/
m/s
dB(A)
dB(A)
-1
W
W
(rpm)
2
2
*1) 03600..
W 650-100
*1) 03602..
W 650-125
)5( 521)4( 001
7,1 (9/
7,1 (9/
32
32
9
( 1,7)
/32)
9
( 1,7)
/32)
M 10 / 19 (3/4)M 14 / 19 (3/4)
0001100011
056056
083083
)7.3( 7,1)5.3( 6,1
5,1/5,95,1/5,9
5,1 / 55,1 / 5
3 / 983 / 98
3 / 893 / 89
3
Page 4
(7)
(1)
(8) (9)
B
630327000
A
CLICK
D
= 100 mm (4“) 630346000
max
= 125 mm (5“) 630352000
D
max
C
4
(M 14) 630706000
(M 10) 34110205
Page 5

Original instructions
1. Specified Conditions of Use
The angle grinders, when fitted with original Metabo
accessories, are suitable for grinding, sanding,
separating and wire brushing metal, concrete,
stone and similar materials without the use of water.
The user bears sole responsibility for any damage
caused by inappropriate use.
Generally accepted accident prevention
regulations and the enclosed safety information
must be observed.
2. General Safety Information
For your own protection and for the
protection of your power tool, pay
attention to all parts of the text that are
marked with this symbol!
WARNING – Read the operating
instructions to reduce the risk of injury.
WARNING Read all safety warnings and
instructions. Failure to follow all safety
warnings and instructions may result in electric
shock, fire and/or serious injury.
Keep all safety instructions and information for
future reference.
Always include these documents when passing on
your power tool.
3. Special Safety Instructions
3.1General Safety Recommendations for
Grinding, Sanding, Wire Brushing or
Abrasive Cutting:
Use
a) This power tool is intended to function as a
grinder, sander, wire brush or cut-off tool. Read
all safety warnings, instructions, illustrations
and specifications provided with this power
tool. Failure to follow all instructions listed below
may result in electric shock, fire and/or serious
injury.
b) Operations such as polishing are not
recommended to be performed with this power
tool. Operations for which the power tool was not
designed may create a hazard and cause personal
injury.
c) Do not use accessories which are not
specifically designed and recommended by the
tool manufacturer. Even if an accessory can be
attached to your power tool, this does not ensure
safe operation.
d) The rated speed of the accessory must be at
least equal to the maximum speed marked on
the power tool. Accessories running faster than
their rated speed can break and fly apart.
e) The external diameter and thickness of your
accessory must be within the capacity rating of
ENGLISH en
your power tool. Incorrectly sized accessories
cannot be adequately guarded or controlled.
f) The threaded mounting of accessories must
match the grinder spindle thread. For
accessories mounted by flanges, the arbour
hole of the accessory must fit the locating
diameter of the flange. Accessories that do not
match the mounting hardware of the power tool will
run out of balance, vibrate excessively and may
result in a loss of control.
g) Do not use damaged accessories. Inspect
accessories such as grinding discs before
each use for chips and cracks and inspect
backing pads for cracks, tear or excess wear
and wire brushes for loose or cracked wires. If
a power tool or accessory is dropped, inspect
for damage or install an undamaged
accessory. After inspecting and installing an
accessory, position yourself and bystanders
away from the plane of the rotating accessory
and run the power tool at the maximum no-load
speed for one minute. Damaged accessories will
normally break apart during this test time.
h) Wear personal protective equipment. Use a
face shield, safety goggles or safety goggles
depending on the application. If necessary,
wear a dust mask, hearing protectors, gloves
and a workshop apron capable of stopping
small abrasive or workpiece fragments. Eye
protection must be capable of stopping flying debris
generated by various operations. A dust mask or
respirator must be capable of filtering particles
generated by your operation. Prolonged exposure
to high intensity noise may cause hearing loss.
i) Keep bystanders a safe distance away from
the work area. Anyone entering the work area
must wear personal protective equipment.
Fragments of a workpiece or broken accessory may
fly off and result in injury beyond the immediate area
of operation.
j) Only hold the cordless tool by its insulated
grip areas while completing work where the
tool may come into contact with hidden power
lines or its own power cable. Cutting accessory
contacting a "live" wire may make exposed metal
parts of the power tool "live" and could give the
operator an electric shock.
k) Position the cord clear of the rotating
accessory. If you lose control, the cord may be cut
or snagged and your hand or arm may be pulled into
the rotating accessory.
I) Never lay the power tool down until the
accessory has come to a complete stop. The
rotating accessory may grab the surface and pull
the power tool out of your control.
m) Do not run the power tool while carrying it at
your side. Accidental contact with a rotating
accessory could snag your clothing, pulling the
accessory into your body.
n) Regularly clean the power tool’s air vents.
The motor’s fan will draw the dust inside the housing
5
Page 6

ENGLISHen
and an excessive accumulation of powdered metal
may cause electrical hazards.
o) Do not operate the power tool near
flammable materials. Sparks could ignite these
materials.
p) Do not use accessories that require liquid
coolants. Using water or other liquid coolants may
result in electrocution or shock.
3.2Kickback and related warnings
Kickback is a sudden reaction to a pinched or
snagged sanding wheel, backing pad, brush or any
other accessory. Pinching or snagging causes the
rotating accessory to stall rapidly, This in turn
causes the uncontrolled power tool to be forced in
the opposite direction from which the accessory is
rotating at the pinched or snagged point.
For example, if an abrasive wheel is snagged or
pinched by the workpiece, the edge of the wheel
entering the pinch point can dig into the surface of
the material causing the wheel to climb out or kick
out. The abrasive wheel may either jump toward or
away from the operator, depending on direction the
disc is moving at the pinch point. Abrasive wheels
may also break under these conditions.
Kickback is the result of power tool misuse and/or
incorrect operating procedures or conditions and
can be avoided if suitable precautionary measures
are taken as described below.
a) Maintain a firm grip on the power tool and
position your body and arm so that you can
resist kickback forces. Always use the
additional handle, if provided, for maximum
control over kickback or a torque reaction
during start-up. The operator can control torque
reactions or kickback forces if proper precautions
are taken.
b) Never place your hand near a rotating
accessory. The accessory may kickback over your
hand.
c) Do not position your body in the area
where the power tool will move if kickback
occurs. Kickback
will propel the tool in the direction opposite to the
grinding wheel’s movement at the pinch or snag
point.
d) Use special care when working corners,
sharp edges etc. Avoid bouncing and snagging
the accessory. Corners, sharp edges or bouncing
have a tendency to snag the rotating accessory and
cause loss of control or kickback.
e) Do not attach a saw chain, woodcarving
blade or toothed saw blade. Such blades create
frequent kickback and can cause you to lose
control.
3.3Safety Warnings Specific for Grinding
and Cut-Off Grinding:
a) Use only wheel types that are recommended
for your power tool and the specific guard
designed for the selected wheel. Wheels for
which the power tool was not designed cannot be
adequately guarded and are unsafe.
6
b) The grinding surface of the centre depressed
wheels must be mounted below the plane of
the guard lip. An improperly mounted grinding
wheel that projects through the plane of the guard
lip cannot be adequately guarded.
c) The guard must be securely attached to the
power tool and positioned for maximum safety
so that the least amount of wheel is exposed
towards the operator. The guard helps to protect
operator from broken wheel fragments and
accidental contact with the wheel and sparks which
could ignite clothing.
d) Grinding media must be used only for
recommended applications.
For example: do not grind with the side of the
cutting disc. Cutting discs are intended for
grinding using the edge of the disc. Applying force
to the sides of these discs may cause them to
shatter.
e) Always use undamaged wheel flanges that
are the correct size and shape for your selected
grinding wheel. Proper wheel flanges support the
grinding wheel, reducing the possibility of
breakage. Flanges for cutting discs may be different
from grinding wheel flanges.
f) Do not use worn down grinding wheels from
larger power tools. Grinding wheels intended for
larger power tools are not suitable for the higher
speed of a smaller tool and may break.
3.4Additional Safety Warnings Specific for
Cut-Off Grinding:
a) Do not “jam” the cutting disc or apply
excessive pressure. Do not attempt to make an
excessively deep cut. Overstressing the cutting
disc increases the load and makes the disc more
susceptible to twisting or bending in the cut and
more likely to kick back and break.
b) Do not position your body in line with or
behind the rotating cutting disc. When the
cutting disc is moving away from your body at the
point of operation, any kickback can propel the
spinning disc and the power tool directly towards
you.
c) If the cutting disc is stuck or when
interrupting a cut for any reason, switch off the
power tool and hold the power tool motionless
until the disc comes to a complete stop. Never
attempt to remove the cutting disc from the cut
while the disc is in motion; otherwise kickback
may occur. Investigate and take corrective action
to eliminate the cause if a disc becomes stuck.
d) Do not restart the cutting operation in the
workpiece. Let the cutting disc reach full speed
and carefully re-enter the cut. The wheel may
bind, walk up or kickback if the power tool is
restarted in the workpiece.
e) Support panels or any oversized workpiece
to minimize the risk of cutting disc pinching
and kickback. Large workpieces tend to sag under
their own weight. Supports must be placed under
the workpiece near the line of the cut and near the
edge of the workpiece on both sides of the wheel.
Page 7
f) Use extra caution when making "pocket cuts"
into existing walls or other blind areas. The
protruding cutting disc may cause kickback when
cutting gas or water pipes, electrical wiring or other
objects.
3.5Safety Warnings Specific for Sanding
Operations:
a) Do not use excessively large sanding disc
paper. Follow the manufacturers
recommendations when selecting sandpaper.
Larger sandpaper that extends beyond the sanding
pad presents a laceration hazard and may cause
snagging or kickback, or may cause the disc to tear
off.
3.6Safety Warnings Specific for Wire
Brushing Operations:
a) Be aware that wire bristles are thrown by the
brush even during ordinary operation. Do not
overstress the wires by applying excessive
load to the brush. Wire bristles can easily
penetrate light clothing and/or skin.
b) If a guard is recommended for wire brushing,
do not allow the wire wheel or brush to come
into contact with the guard. The wire wheel or
brush may expand in diameter due to the work load
and centrifugal forces.
3.7Additional Safety Instructions:
WARNING – Always wear protective
goggles.
Use elastic cushioning layers if they have been
supplied with the grinding media and if required.
Observe the specifications of the tool or accessory
manufacturer! Protect discs from grease or impact!
Grinding wheels must be stored and handled with
care in accordance with the manufacturer's
instructions.
Never use cut-off wheels for roughing work! Do not
apply pressure to the side of cut-off wheels.
The workpiece must lay flat and be secured against
slipping, e.g. using clamps. Large workpieces must
be sufficiently supported.
If accessories with threaded inserts are used, the
end of the spindle may not touch the base of the
hole on the sanding tool. Make sure that the thread
in the accessory is long enough to accommodate
the full length of the spindle. The thread in the
accessory must match the thread on the spindle.
See page 3 and the 12. Technical Specifications
chapter for more information on the spindle length
and thread.
It is recommended to use a stationary extraction
system and to place a ground fault circuit interrupter
(GFCI) downstream. If the angle grinder is shut
down via the GFCI, it must be checked and cleaned.
See the 8. Cleaning chapter for more information on
cleaning the motor.
Damaged, eccentric or vibrating tools must not be
used.
ENGLISH en
Avoid damage to gas or water pipes, electrical
cables and load-bearing walls (building structure).
Pull the plug out of the socket before making any
adjustments, converting or servicing the machine.
A damaged or cracked additional handle must be
replaced. Never operate the machine with a
defective additional handle.
A damaged or cracked safety guard must be
replaced. Never operate a machine with a defective
safety guard.
This power tool is not suitable for polishing work.
Improper use of the machine will void the warranty!
The motor may overheat and damage the electric
power tool. We recommend using our angle
polisher for polishing work.
Secure small workpieces, for example by clamping
them in a vice.
Reducing dust exposure:
WARNING
sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other
construction activities contains chemicals known to
cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive
harm. Some examples of these chemicals are:
-Lead from lead-based paints,
-Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and
other masonry products, and
-Arsenic and chromium from chemically treated
lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending
on how often you do this type of work. To reduce
your exposure to these chemicals: work in a wellventilated area, and work with approved safety
equipment, such as those dust masks that are
specially designed to filter out microscopic
particles.
This also applies to dust from other materials such
as some timber types (like oak or beech dust),
metals, asbestos. Other known diseases are e.g.
allergic reactions, respiratory diseases. Do not let
dust enter the body.
Observe the relevant guidelines and national
regulations for your material, staff, application and
place of application (e.g. occupational health and
safety regulations, disposal).
Collect the particles generated at the source, avoid
deposits in the surrounding area.
Use suitable accessories for special work. In this
way, fewer particles enter the environment in an
uncontrolled manner.
Use a suitable extraction unit.
Reduce dust exposure with the following measures:
-do not direct the escaping particles and the
exhaust air stream towards yourself or nearby
persons or towards dust deposits,
-use an extraction unit and/or air purifiers,
-ensure good ventilation of the workplace and keep
it clean using a vacuum cleaner. Sweeping or
blowing stirs up dust.
-Vacuum or wash protective clothing. Do not blow,
beat or brush protective gear.
- Some dust created by power
7
Page 8
ENGLISHen
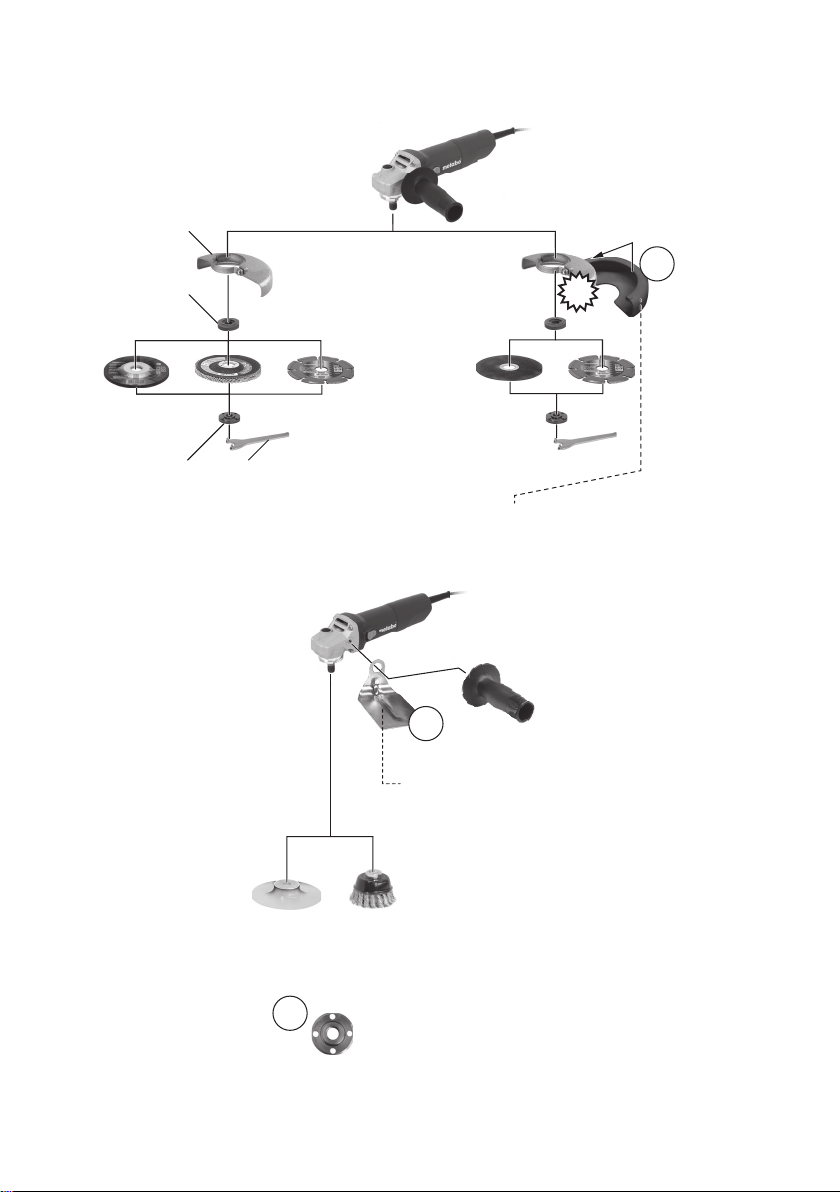
4. Overview
See page 2.
1Support flange
2Spindle
3 Spindle locking button
4 Sliding on/off switch
5Handle
6 Side handle
7Safety cover
8Two-hole nut
9two-hole spanner
10 Clamp screw
11 Clamping ring
* depending on model / not in scope of delivery
5. Initial Operation
Before commissioning, check that the rated
mains voltage and mains frequency stated on
the type plate match your power supply.
Always install an RCD with a maximum trip
current of 30 mA upstream.
5.1 Attaching the additional handle
Always work with the additional handle (6)
attached! Attach the additional handle on the
left or right of the machine and secure.
5.2 Attach the safety guard
For safety reasons, always use the safety
guard provided for the respective wheel! See
also chapter 9. Accessories!
Safety guard for grinding
Designed for work with roughing wheels, flap
sanding pads, diamond cutting discs.
See illustration C on page 2.
- Loosen the clamping screw (10) until the clamping
ring (11) on the safety guard expands sufficiently.
- Place the safety guard (7) in the position
indicated.
- Turn the safety guard until the closed section is
facing the operator.
- Tighten the clamping screw (10) firmly. Make sure
that the guard is seated securely - you should not
be able to turn the safety guard (7).
Use only accessories that
are covered by at least 3.4
mm by the safety guard.
6. Attaching the grinding wheel
Prior to any conversion work: pull the mains
plug out of the socket. The machine must be
switched off and the spindle at a standstill.
For reasons of safety, attach the cut-off
grinding guard before performing cut-off
grinding work (see Chapter 9. Accessories).
8
6.1 Locking the spindle
- Press in the spindle locking button (3) and
turn the spindle (2) by hand until the spindle
locking button engages.
6.2 Placing the grinding wheel in position
See illustration A on page 2.
- Fit the support flange (1) on the spindle. The
flange should not turn on the spindle when
properly attached.
Only W 650-100: Screw support flange with twohole spanner onto spindle so that the small collar
(with diameter 16 mm) is facing upwards.
- Place the grinding wheel on the support flange (1).
The grinding wheel must lay flat on the supporting
flange.
6.3 Secure / loosen two hole nut
Securing the 2-hole nut (8):
The 2 sides of the two-hole nut are different.
Screw the two-hole nut onto the spindle as follows:
See illustration B on page 2.
- X) For thin grinding discs:
The edge of the 2-hole nut (8) faces upwards so
that the thin grinding disc can be attached
securely.
Y) For thick grinding discs:
The edge of the two-hole nut (8) faces downwards
so that the two-hole nut can be attached securely
to the spindle.
Z) Only for W 650-100:
The collar of the two-hole nut faces downwards
and/or the flat surface faces upwards.
- Lock the spindle. Turn the two-hole nut (8)
clockwise using the two-hole spanner (9) to
secure.
Releasing the 2-hole nut:
- Lock the spindle (see chapter 6.1). Turn the twohole nut (8) anticlockwise using the two-hole
spanner (9) to unscrew.
7. Use
7.1 Switching on and off
Always guide the machine with both hands.
Switch on first, then guide the accessory
towards the workpiece.
The machine must not be allowed to draw in
additional dust and shavings. When switching
the machine on and off and keep it away from dust
deposits. After switching off the machine, only set it
down when the motor has come to a standstill.
Avoid inadvertent starts: always switch the
tool off when the plug is removed from the
mains socket or if there has been a power cut.
In continuous operation, the machine
continues running if it is forced out of your
hands. Therefore, always hold the machine with
both hands using the handles provided, stand
securely and concentrate.
Page 9
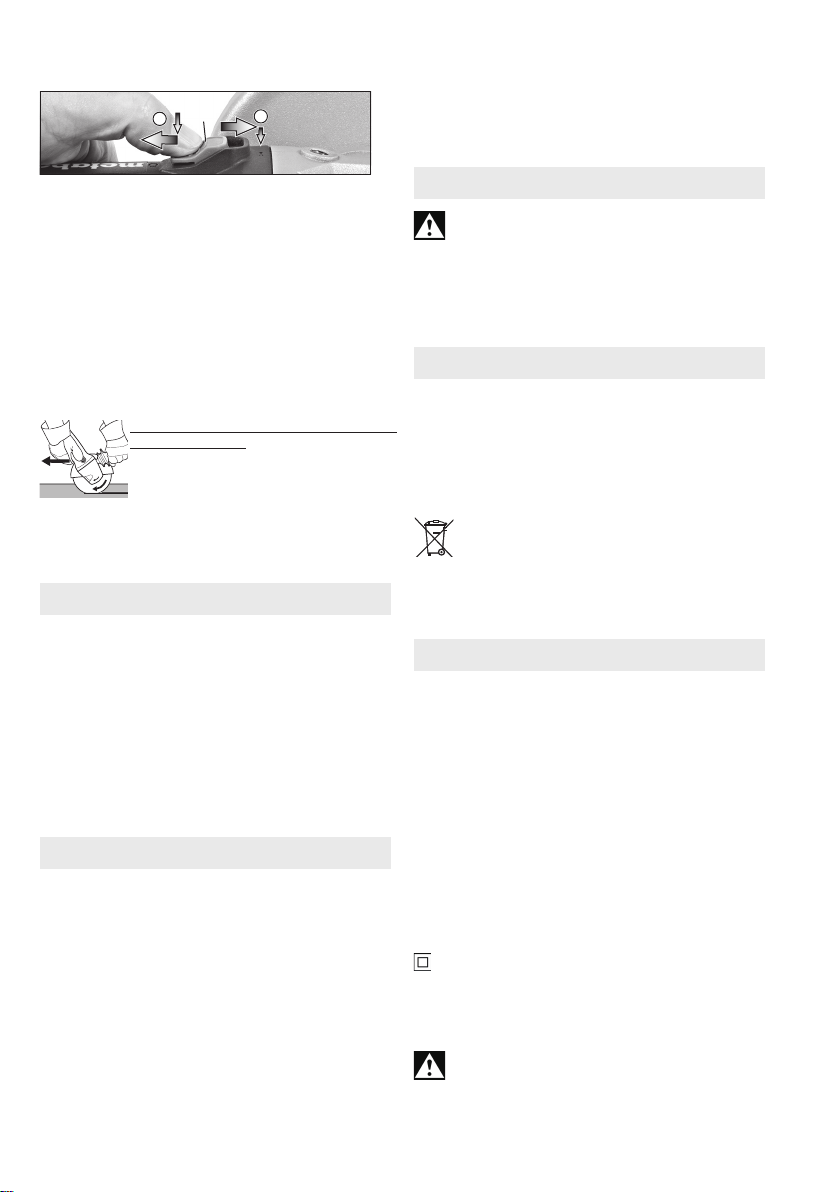
Machines with a slide switch:
4
0
ENGLISH en
Install the hand guard under the additional sidemounted handle.
I
CTwo hole nut (8)
For a complete range of accessories, see
www.metabo.com or the accessories catalogue.
Switching on: push the slide switch (4) forwards.
For continuous operation, tilt it downwards until it
engages.
Switching off: press the rear end of the slide switch
(4) and release it.
7.2Working directions
Grinding and sanding operations:
Press down the machine evenly on the surface and
move it back and forth so that the surface of the
workpiece does not become too hot.
Rough grinding: position the machine at an angle of
30° - 40° for the best working results.
Cut-off grinding:
the material being processed. Do not tilt, apply
excessive force or sway from side to side.
Wire brushing:
Press down the machine evenly.
Always work against the run of the disc
(see illustration). Otherwise the
machine may kick back from the cut in
an out of control manner. Guide the
machine evenly at a speed suitable for
8. Cleaning
Particles may become deposited inside the power
tool during operation. This impairs the cooling of the
power tool. Conductive build-up can impair the
protective insulation of the power tool and create an
electrical hazard.
The power tool should be cleaned regularly, often
and thoroughly through all front and rear air vents
using a vacuum cleaner or by blowing in dry air.
Prior to this operation, separate the power tool from
the power source and wear protective glasses and
dust mask. Ensure appropriate suction is available
when blowing out vents.
9. Accessories
Use only genuine Metabo accessories.
See page 4.
Use only accessories that fulfil the requirements
and specifications listed in these operating
instructions.
ACutting guard clip / guard for cut-off
grinding
Designed for work with cutting disc and diamond
cutting discs. Once the cutting guard clip is fitted,
the safety guard becomes a cutting guard.
BHand protection
Intended for work with backing pads, sanding
plates, wire brushes and support plates, sanding
pads, wire brushes and diamond drill bits for tiles.
10. Repairs
Repairs to electrical tools must ONLY be
carried out by qualified electricians!
Contact your local Metabo representative if you
have Metabo power tools requiring repairs. See
www.metabo.com for addresses.
You can download a list of spare parts from
www.metabo.com.
11. Environmental Protection
The sanding dust generated may contain
hazardous materials: do not dispose of dust with
household waste, but at a special collection point
for hazardous waste.
Observe national regulations on environmentally
compatible disposal and on the recycling of disused
machines, packaging and accessories.
Only for EU countries: never dispose of
power tools in your household waste!
According to European Directive 2012/19/EU
on Waste from Electric and Electronic Equipment
and implementation in national law, used power
tools must be collected separately and recycled in
an environmentally-friendly manner.
12. Technical Specifications
Explanatory notes on the specifications on page 3.
Changes due to technological progress reserved.
Ø=max. diameter of the accessory
=max. permitted thickness of the clamping
t
max,1
t
max,3
M=Spindle thread
l=Length of the sanding spindle
n=No-load speed (maximum speed)
P
P
m=Weight without mains cable
Measured values determined in conformity with
EN 60745.
shank on accessory when using two-hole
nut (8)
=roughing disc/cutting disc:
max. permitted thickness of accessory
=Rated input power
1
=Power output
2
Machine in protection class II
~ AC power
The technical specifications quoted are subject to
tolerances (in compliance with relevant valid
standards).
Emission values
These values make it possible to assess the
emissions from the power tool and to compare
different power tools. The actual load may be higher
or lower depending on operating conditions, the
condition of the power tool or the accessories used.
9
Page 10

ENGLISHen
Please allow for breaks and periods when the load
is lower for assessment purposes. Arrange
protective measures for the user, such as
organisational measures based on the adjusted
estimates.
Total vibration value
determined in accordance with EN 60745:
a
h, SG
a
h, DS
K
h,SG/DS
Typical A-effective perceived sound levels
L
pa
L
WA
K
pA
=Vibration emission value
=Vibration emission value
=Uncertainty (vibration)
=Sound-pressure level
=Acoustic power level
, KWA=Uncertainty
Wear ear protectors!
(vector sum of three directions)
(surface grinding)
(sanding with sanding plate)
:
10
Page 11

Instrukcja oryginalna
1. Użytkowanie zgodne z
przeznaczeniem
Szlifierki kątowe z oryginalnym osprzętem firmy
Metabo są przeznaczone do szlifowania,
szlifowania papierem ściernym, obróbki szczotkami
drucianymi oraz cięcia metalu, betonu, kamienia i
podobnych materiałów bez użycia wody.
Za szkody powstałe w wyniku użytkowania
niezgodnego z przeznaczeniem odpowiedzialność
ponosi wyłącznie użytkownik.
Przestrzegać ogólnie obowiązujących przepisów
BHP oraz dołączonych uwag dotyczących
bezpieczeństwa.
2. Ogólne uwagi dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa
Dla bezpieczeństwa użytkownika oraz w
celu ochrony elektronarzędzia zwracać
szczególną uwagę na miejsca w tekście
oznaczone tym symbolem!
OSTRZEŻENIE – W celu zminimalizowania
ryzyka obrażeń zapoznać się z treścią
instrukcji obsługi.
OSTRZEŻENIE Przeczytać wszystkie
informacje dotyczące bezpieczeństwa i
zalecenia. Nieprzestrzeganie informacji
dotyczących bezpieczeństwa i zaleceń może być
przyczyną porażenia prądem elektrycznym, pożaru
i/lub poważnych obrażeń.
Starannie przechowywać wszystkie informacje
dotyczące bezpieczeństwa i zalecenia, aby
móc z nich skorzystać w przyszłości.
Przekazując elektronarzędzie innym osobom,
należy przekazać również niniejszą dokumentację.
3. Specjalne uwagi dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa
3.1Wspólne uwagi dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa podczas szlifowania,
szlifowania papierem ściernym, obróbki
szczotkami drucianymi oraz cięcia
Zastosowanie
a) Niniejsze elektronarzędzie jest
przeznaczone do użytkowania jako szlifierka,
szlifierka do szlifowania papierem ściernym,
urządzenie do szczotkowania szczotką
drucianą i do przecinania. Należy przestrzegać
wszystkich informacji dotyczących
bezpieczeństwa, instrukcji, ilustracji i danych,
które zostały przekazane wraz z urządzeniem.
W przypadku nieprzestrzegania poniższych
zaleceń może dojść do porażenia prądem, pożaru i/
lub poważnych obrażeń ciała.
b) Niniejsze elektronarzędzie nie nadaje się do
polerowania. Używanie elektronarzędzia do prac,
POLSKI pl
do których nie zostało przewidziane, może
stanowić zagrożenie i być przyczyną obrażeń ciała.
c) Nie stosować osprzętu, którego producent
nie przewidział i nie dopuścił do współpracy z
tym elektronarzędziem. Sama możliwość
zamocowania osprzętu do elektronarzędzia nie
zapewnia jego bezpiecznego użytkowania.
d) Dopuszczalna prędkość obrotowa narzędzia
roboczego musi być co najmniej tak duża, jak
maksymalna prędkość obrotowa podana na
elektronarzędziu. Elementy osprzętu obracające
się z prędkością większą od dopuszczalnej mogą
pęknąć i zostać odrzucone.
e) Średnica zewnętrzna i grubość narzędzia
roboczego muszą odpowiadać wymiarom
podanym dla danego elektronarzędzia.
Narzędzia robocze o nieprawidłowych wymiarach
mogą być niewystarczająco zabezpieczone lub
kontrolowane.
f) Narzędzia robocze z wkładką gwintowaną
muszą dokładnie pasować na wrzeciono
elektronarzędzia. W przypadku narzędzi
roboczych montowanych za pomocą kołnierza
średnica otworu narzędzia roboczego musi
pasować do średnicy gniazda kołnierza.
Narzędzia robocze nieprecyzyjnie zamontowane
na elektronarzędziu obracają się nierównomiernie,
wpadają w mocne wibracje i mogą powodować
utratę kontroli.
g) Nie używać uszkodzonych narzędzi
roboczych. Przed każdym użyciem sprawdzić
narzędzie robocze, np. tarcze szlifierskie pod
kątem odprysków i pęknięć, talerze szlifierskie
pod kątem pęknięć, starcia lub silnego zużycia,
szczotki druciane pod kątem luźnych lub
wyłamanych drutów. Jeśli elektronarzędzie lub
mocowane narzędzie robocze spadnie na
podłogę, należy sprawdzić, czy nie jest
uszkodzone lub użyć nieuszkodzonego
narzędzia roboczego. Po sprawdzeniu i
zamocowaniu narzędzia, należy stanąć
samemu i poprosić osoby znajdujące się w
pobliżu o pozostanie poza płaszczyzną
obrotową wirującego narzędzia oraz
uruchomić zamocowane narzędzie robocze z
maksymalną prędkością obrotową na jedną
minutę. Uszkodzone narzędzia robocze
najczęściej pękają w czasie przeprowadzania tego
testu.
h) Stosować środki ochrony indywidualnej.
Zależnie od rodzaju wykonywanych prac
stosować pełną ochronę twarzy, ochronę oczu
lub okulary ochronne. O ile zachodzi taka
potrzeba, stosować maskę przeciwpyłową,
ochronniki słuchu, rękawice ochronne lub
specjalny fartuch chroniący przed drobnymi
cząstkami ściernicy i szlifowanego materiału.
Chronić oczy przed ciałami obcymi odrzucanymi
podczas wykonywania różnych prac. Maska
przeciwpyłowa i maska ochronna dróg
oddechowych muszą być w stanie odfiltrować pył
powstający podczas pracy. Długotrwałe narażenie
na duży hałas może spowodować utratę słuchu.
11
Page 12

POLSKIpl
i) Należy zwracać uwagę, aby inne osoby
zachowały bezpieczną odległość od strefy
roboczej. Każda osoba, która wchodzi do strefy
roboczej musi nosić środki ochrony
indywidualnej. Odłamki obrabianego elementu
lub pęknięte narzędzia robocze mogą zostać
wyrzucone i spowodować obrażenia również poza
bezpośrednią strefą roboczą.
j) Podczas wykonywania prac, w trakcie
których narzędzie robocze może natrafić na
ukryte przewody elektryczne lub na własny
kabel sieciowy, trzymać elektronarzędzie
wyłącznie za izolowane powierzchnie chwytne.
Kontakt z przewodem znajdującym się pod
napięciem może spowodować przepływ prądu
przez metalowe elementy urządzenia i w efekcie
doprowadzić do porażenia prądem.
k) Kabel sieciowy utrzymywać z dala od
wirujących narzędzi roboczych. W przypadku
utraty kontroli nad urządzeniem może nastąpić
przecięcie albo pochwycenie kabla sieciowego
oraz przedostanie się rąk w zasięg wirującego
narzędzia roboczego.
I) W żadnym wypadku nie odkładać
elektronarzędzia, zanim narzędzie robocze
całkowicie się nie zatrzyma. Obracające się
narzędzie robocze może zetknąć się z
powierzchnią, na którą zostanie odłożone, i w
konsekwencji spowodować utratę kontroli nad
elektronarzędziem.
m) Nie przenosić pracującego
elektronarzędzia. Na skutek przypadkowego
dotknięcia ubranie użytkownika może zostać
pochwycone przez wirujące narzędzie robocze,
które może wwiercić się w ciało.
n) W regularnych odstępach czasu czyścić
szczeliny wentylacyjne elektronarzędzia.
Wentylator silnika wciąga pył do obudowy, a duże
nagromadzenie pyłu metalowego może
spowodować zagrożenia związane z prądem
elektrycznym.
o) Nie używać elektronarzędzia w pobliżu
materiałów palnych. Iskry mogą spowodować
zapłon tych materiałów.
p) Nie używać narzędzi roboczych
wymagających stosowania chłodziw ciekłych.
Stosowanie wody lub innych chłodziw ciekłych
może spowodować porażenie prądem
elektrycznym.
3.2Odrzut i odpowiednie uwagi dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa
Odrzut jest gwałtowną reakcją spowodowaną
zahaczeniem lub zablokowaniem wirującego
narzędzia roboczego, takiego jak tarcza szlifierska,
talerz szlifierski, szczotka druciana itp. Zahaczenie
lub zablokowanie powoduje nagłe zatrzymanie się
wirującego narzędzia roboczego. Wskutek tego
niekontrolowane elektronarzędzie uzyskuje
przyspieszenie w kierunku przeciwnym do kierunku
obrotów zablokowanego narzędzia roboczego.
Jeśli np. tarcza szlifierska ulegnie zakleszczeniu lub
zablokowaniu w elemencie, to zablokowana
krawędź tarczy zagłębiona w elemencie może
12
spowodować wyłamanie tarczy lub odrzut. Tarcza
szlifierska przemieszcza się wtedy w kierunku
operatora albo przeciwnym, zależnie od kierunku
obrotów zablokowanej tarczy. W takim przypadku
tarcze szlifierskie mogą również pękać.
Odrzut jest konsekwencją niewłaściwego lub
niezgodnego z przeznaczeniem użytkowania
elektronarzędzia. Podjęcie odpowiednich,
opisanych poniżej środków ostrożności pozwala
zapobiec temu zjawisku.
a) Mocno trzymać elektronarzędzie oraz
utrzymywać ciało i ramiona w pozycji, która
pozwoli zamortyzować siłę odrzutu. Zawsze
używać dodatkowej rękojeści, aby mieć jak
najlepszą kontrolę nad siłami odrzutu lub
momentami reakcyjnymi podczas rozruchu.
Stosując odpowiednie środki ostrożności operator
może zapanować nad siłą odrzutu i cofnięcia.
b) W żadnym wypadku nie zbliżać rąk do
wirujących narzędzi roboczych. W przypadku
odrzutu narzędzie robocze może osunąć się po
ręce.
c) Utrzymywać ciało poza strefą
ruchu elektronarzędzia podczas odrzutu.
Odrzut
napędza elektronarzędzie w kierunku przeciwnym
do kierunku ruchu
tarczy szlifierskiej w miejscu zablokowania.
d) Szczególną ostrożność zachować podczas
pracy w strefie narożników, ostrych krawędzi
itp. Unikać sytuacji, w których narzędzia
robocze odskakują od elementu obrabianego
lub ulegają zakleszczeniu. W narożnikach, na
ostrych krawędziach lub w przypadku uderzenia
wirujące narzędzie robocze łatwo zakleszcza się w
obrabianym elemencie. Powoduje to utratę kontroli
lub odrzut.
e) Nie stosować łańcuchowych ani zębatych pił
tarczowych. Takie narzędzia robocze często
powodują odrzut lub utratę kontroli nad
elektronarzędziem.
3.3Specjalne zasady bezpieczeństwa
dotyczące szlifowania i przecinania
tarczą:
a) Stosować wyłącznie ściernice dopuszczone
dla danego elektronarzędzia i osłonę
przewidzianą dla tej ściernicy. Ściernice, które
nie są przewidziane dla danego elektronarzędzia
mogą być niedostatecznie osłonięte i nie
gwarantują należytego bezpieczeństwa.
b) Wypukłe tarcze szlifierskie należy mocować
w taki sposób, aby powierzchnia szlifująca nie
wystawała ponad płaszczyznę krawędzi
osłony. Nieprawidłowo zamocowanej tarczy
szlifierskiej, która wystaje poza krawędź osłony, nie
można odpowiednio osłonić.
b) Osłona musi być bezpiecznie zamocowana
na elektronarzędziu i ustawiona w taki sposób,
aby zapewniony był najwyższy stopień
bezpieczeństwa, tzn. w stronę użytkownika
skierowana jest możliwie najmniejsza część
nieosłoniętej ściernicy. Zadaniem osłony jest
ochrona użytkownika przed odłamkami,
Page 13

przypadkowym dotknięciem ściernicy, jak również
przed iskrami, które mogą spowodować zapalenie
odzieży.
d) Ściernic wolno używać tylko do zalecanych
zastosowań.
Np. nigdy nie wolno szlifować powierzchnią
boczną tarczy tnącej. Tarcze tnące są
przeznaczone do usuwania materiału za pomocą
krawędzi tarczy. Boczny nacisk na tarczę może
spowodować jej pęknięcie.
e) Stosować wyłącznie nieuszkodzone
kołnierze mocujące o wielkości i kształcie
odpowiednim dla wybranej ściernicy.
Prawidłowo dobrany kołnierz stanowi oparcie dla
tarczy szlifierskiej, a tym samym zmniejsza ryzyko
jej pęknięcia. Kołnierze do tarcz tnących mogą się
różnić od kołnierzy do innych tarcz szlifierskich.
f) Nie stosować używanych tarcz szlifierskich
przeznaczonych do większych elektronarzędzi.
Tarcze szlifierskie przeznaczone do większych
elektronarzędzi nie są przystosowane do wysokich
prędkości obrotowych mniejszych elektronarzędzi i
mogą pękać.
3.4Dodatkowe specjalne uwagi dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa podczas cięcia:
a) Unikać blokowania tarczy tnącej i zbyt
dużego docisku. Nie wykonywać nadmiernie
głębokich cięć. Przeciążenie tarczy tnącej
zwiększa jej naprężenia i podatność na
zakleszczenie lub zablokowanie, a tym samym
możliwość odrzutu lub pęknięcia tarczy.
b) Unikać strefy przed i za wirującą tarczą
tnącą. W przypadku przemieszczania tarczy tnącej
w obrabianym elemencie od siebie, w razie odrzutu
elektronarzędzie z wirującą tarczą zostaje
wyrzucone bezpośrednio w kierunku użytkownika.
c) W przypadku zakleszczenia tarczy tnącej lub
przerwania pracy należy wyłączyć urządzenie i
przytrzymać je spokojnie, aż tarcza całkowicie
się zatrzyma. Nie wolno wyciągać obracającej
się jeszcze tarczy tnącej z nacięcia, gdyż może
to spowodować odrzut. Zlokalizować i usunąć
przyczynę zakleszczenia.
d) Nie włączać elektronarzędzia dopóki
znajduje się ono w obrabianym elemencie.
Cięcie można ostrożnie kontynuować, dopiero
kiedy tarcza tnąca osiągnie maksymalną
prędkość obrotową. W przeciwnym razie tarcza
może się zakleszczyć, wyskoczyć z obrabianego
detalu lub spowodować odrzut.
e) Aby zmniejszyć ryzyko odrzutu na skutek
zakleszczenia się tarczy tnącej, obrabiane
płyty i większe elementy należy podpierać.
Duże elementy poddawane obróbce mogą się
wyginać pod własnym ciężarem. Element
obrabiany musi być podparty po obu stronach
tarczy, zarówno w pobliżu linii cięcia, jak i przy
krawędzi.
f) Szczególną ostrożność zachować przy
„cięciach wgłębnych” w istniejące ściany lub
inne nieznane obszary. Tarcza tnąca zagłębiona
w ścianie może natrafić na przewody gazowe,
POLSKI pl
wodne, elektryczne lub inne obiekty i spowodować
odrzut.
3.5Specjalne zasady bezpieczeństwa
dotyczące szlifowania papierem
ściernym:
a) Nie używać zbyt dużych arkuszy papieru
ściernego. Przestrzegać informacji producenta
dotyczących wielkości arkuszy. Arkusz
szlifierski wystający poza talerz szlifierski może
spowodować obrażenia, a także zablokowanie,
zerwanie arkusza lub odrzut.
3.6Specjalne uwagi dotyczące
bezpieczeństwa podczas prac z użyciem
szczotek drucianych:
a) Pamiętać, że szczotka druciana traci druty
również w trakcie zwykłego użytkowania. Nie
przeciążać drutów zbyt mocnym dociskiem.
Odrzucone kawałki drutu mogą bardzo łatwo
przebić cienką odzież i/lub skórę.
b) Jeżeli zalecane jest używanie osłony
zabezpieczającej, wyeliminować możliwość
dotykania osłony przez szczotkę drucianą.
Wskutek docisku i działania siły odśrodkowej
szczotki talerzowe i garnkowe mogą zwiększać
swoją średnicę.
3.7Dalsze uwagi dotyczące bezpieczeństwa:
OSTRZEŻENIE – Zawsze nosić okulary
ochronne.
Używać elastycznych podkładek, jeżeli zostały
dostarczone w komplecie z materiałami szlifierskimi
i są wymagane.
Przestrzegać informacji producenta narzędzia i
osprzętu! Chronić tarcze przed smarem i
uderzeniami!
Tarcze szlifierskie przechowywać i stosować
zgodnie z zaleceniami producenta.
W żadnym wypadku nie stosować ściernic tnących
do szlifowania zdzierającego! Nie wolno poddawać
tarcz tnących naciskom bocznym.
Obrabiany element musi być mocno oparty i
zabezpieczony przed przesunięciem, np. za
pomocą urządzeń mocujących. Duże elementy
poddawane obróbce muszą być odpowiednio
podparte.
W przypadku narzędzi roboczych z wkładką
gwintowaną końcówka wrzeciona nie może stykać
się ze spodem otworu narzędzia szlifierskiego.
Zapewnić taką długość gwintu narzędzia
roboczego, aby pomieścił długość wrzeciona.
Gwint w narzędziu roboczym musi pasować do
gwintu na wrzecionie. Długość wrzeciona i gwint
wrzeciona – patrz strona 3 i rozdział 12. Dane
techniczne.
Zalecane jest stosowanie stacjonarnej instalacji
odsysającej i wyposażenie instalacji elektrycznej w
różnicowoprądowy wyłącznik ochronny (FI). W
przypadku wyłączenia szlifierki kątowej przez
wyłącznik różnicowoprądowy sprawdzić i oczyścić
13
Page 14

POLSKIpl
urządzenie. Czyszczenie silnika patrz rozdział 8.
czyszczenie.
Nie wolno używać uszkodzonych, nieokrągłych ani
wibrujących narzędzi roboczych.
Unikać uszkodzenia przewodów gazowych,
wodociągowych, elektrycznych i ścian nośnych
(statyka).
Przed przystąpieniem do regulacji ustawień,
przezbrajania lub konserwacji wyciągnąć wtyczkę z
gniazda sieciowego.
Uszkodzoną lub pękniętą rękojeść pomocniczą
należy wymienić. Nie używać maszyny z
uszkodzoną rękojeścią pomocniczą.
Uszkodzoną lub pękniętą osłonę wymienić. Nie
używać maszyny z uszkodzoną osłoną.
Opisywane elektronarzędzie nie jest przewidziane
do polerowania. W przypadku użycia niezgodnego
z przeznaczeniem traci się uprawnienia z tytułu
gwarancji! Silnik może się przegrzać, a
elektronarzędzie ulec uszkodzeniu. Do prac
polerskich polecamy stosowanie polerki kątowej
naszej firmy.
Małe elementy poddawane obróbce należy
odpowiednio zamocować. Można je zamocować na
przykład w imadle.
Redukcja zapylenia:
OSTRZEŻENIE – Niektóre rodzaje pyłów,
które powstają podczas szlifowania papierem
ściernym, cięcia, szlifowania, wiercenia i innych
prac, zawierają substancje chemiczne, o których
wiadomo, że wywołują raka, wady wrodzone lub
zaburzają zdolność rozrodczą. Takie chemikalia to
na przykład:
-Ołów z jastrychów na bazie ołowiu,
-pył mineralny z cegieł, cement i inne wyroby
murarskie oraz
-Arsen i chrom zawarty w drewnie poddawanym
obróbce chemicznej.
Ryzyko narażenia zależy od częstotliwości
wykonywania takich prac. Aby zmniejszyć
zagrożenie ze strony substancji chemicznych:
pracować w obszarze o dobrej wentylacji i
stosować atestowane środki ochronne, np. maski
przeciwpyłowe zaprojektowane do filtrowania
cząstek mikroskopijnej wielkości.
Powyższe informacje odnoszą się również do
pyłów powstających przy obróbce innych
materiałów, np. niektórych rodzajów drewna
(drewno dębowe lub bukowe), metali, azbestu. Inne
znane schorzenia, to np. reakcje alergiczne i
choroby układu oddechowego. Zapobiegać
przedostawaniu się cząstek pyłu do organizmu.
Przestrzegać wytycznych dotyczących
obrabianego materiału, pracowników, rodzaju i
miejsca zastosowania oraz przepisów krajowych
(np. przepisów dotyczących ochrony pracy,
utylizacji).
Eliminować szkodliwe cząstki z powietrza w
miejscu ich emisji i zapobiegać ich odkładaniu się w
otoczeniu.
Do prac specjalnych używać odpowiedniego
osprzętu. Pozwoli to ograniczyć ilość cząstek
14
przenikających w niekontrolowany sposób do
otoczenia.
Stosować odpowiedni układ odsysania pyłu.
W celu zminimalizowania zagrożenia pyłem:
-Nie kierować uwalnianych cząstek i strumienia
powietrza wylotowego z maszyny w stronę
samego siebie, w kierunku innych osób
znajdujących się w pobliżu ani na osiadły pył.
-Używać systemów odpylania i/albo oczyszczaczy
powietrza.
-Zapewnić dobrą wentylację miejsca pracy oraz
jego czystość dzięki stosowaniu wyciągu
powietrza. Zamiatanie i nadmuch powodują
wzbijanie pyłu.
-Odzież ochronną odkurzać lub prać. Nie
przedmuchiwać, nie trzepać, nie czyścić
szczotką.
4. Elementy urządzenia
Patrz strona 2.
1Kołnierz podporowy
2Wrzeciono
3Przycisk blokady wrzeciona
4Włącznik/wyłącznik suwakowy
5Rękojeść
6Rękojeść pomocnicza
7Osłona
8Nakrętka z dwoma otworami
9Klucz dwutrzpieniowy
10 Śruba mocująca
11 Pierścień mocujący
* zależnie od modelu / nieujęte w zakresie dostawy
5. Uruchomienie
Przed uruchomieniem urządzenia sprawdzić,
czy napięcie zasilania i częstotliwość sieci
podane na tabliczce znamionowej są zgodne z
parametrami zasilania sieciowego w miejscu pracy.
Na zasilaniu elektrycznym zainstalować
wyłącznik różnicowoprądowy (RCD) o maks.
prądzie wyzwalającym 30mA.
5.1Mocowanie rękojeści pomocniczej
Zawsze pracować z zamocowaną rękojeścią
pomocniczą (6)! Rękojeść pomocniczą
przykręcić mocno z lewej lub z prawej strony
maszyny.
5.2Montaż osłony
Ze względów bezpieczeństwa stosować
wyłącznie osłonę przewidzianą dla danej
ściernicy! Patrz także rozdział 9. Osprzęt!
Osłona do szlifowania
Przeznaczona do prac z użyciem ściernic do
obróbki zgrubnej, ściernic lamelkowych i
diamentowych tarcz tnących.
Patrz strona 2, rysunek C.
-Poluzować śrubę mocującą (10), aby
odpowiednio rozprężyć pierścień mocujący (11)
osłony.
Page 15

-Nasadzić osłonę (7) w pokazanej pozycji.
-Obrócić osłonę w taki sposób, aby zamknięta
strefa była skierowana w stronę użytkownika.
-Mocno dociągnąć śrubę mocującą (10).
Sprawdzić bezpieczne zamocowanie – osłona (7)
nie może dać się obracać.
Stosować wyłącznie
narzędzia robocze, ponad
które osłona wystaje o co
najmniej 3,4 mm.
6. Mocowanie tarczy szlifierskiej
Przed rozpoczęciem prac związanych z
przezbrajaniem wyciągnąć wtyczkę sieciową
z gniazda. Urządzenie musi być wyłączone, a
wrzeciono nieruchome.
Ze względów bezpieczeństwa do prac z
tarczami tnącymi stosować osłonę do
przecinania (patrz rozdział 9. Osprzęt).
6.1Blokowanie wrzeciona
-Wcisnąć przycisk blokady wrzeciona (3) i
obracać wrzeciono ręką (2) aż do wyraźnego
zatrzaśnięcia się przycisku.
6.2Zakładanie tarczy szlifierskiej
Patrz strona 2, rysunek A.
-Nałożyć kołnierz podporowy (1) na wrzeciono.
Kołnierz jest zamontowany prawidłowo, jeżeli nie
da się go obracać na wrzecionie.
Dotyczy tylko W 650-100: za pomocą klucza
dwutrzpieniowego przykręcić kołnierz podporowy
do wrzeciona w taki sposób, aby mały pierścień (o
średnicy 16 mm) był skierowany do góry.
-Założyć tarczę szlifierską na kołnierz podporowy
(1). Tarcza szlifierska musi równomiernie
przylegać do kołnierza podporowego.
6.3Mocowanie/odkręcanie nakrętki z
dwoma otworami
Mocowanie nakrętki z dwoma otworami (8):
Dwie strony nakrętki z dwoma otworami różnią się
od siebie. Nakręcić nakrętkę z dwoma otworami na
wrzeciono w następujący sposób:
Patrz strona 2, rysunek B.
- X) W przypadku cienkich tarcz szlifierskich:
Pierścień oporowy nakrętki z dwoma otworami (8)
jest skierowany do góry, aby cienka tarcza
szlifierska mogła zostać bezpiecznie
zamocowana.
X) W przypadku grubych tarcz szlifierskich:
Pierścień oporowy nakrętki z dwoma otworami (8)
jest skierowany w dół, aby można było
bezpiecznie zamocować nakrętkę z dwoma
otworami na wrzecionie.
Z) Tylko model W 650-100:
Pierścień oporowy nakrętki z dwoma otworami
skierowany jest w dół względnie płaska
powierzchnia jest skierowana do góry.
-Zablokować wrzeciono. Przykręcić nakrętkę z
dwoma otworami (8) za pomocą klucza
POLSKI pl
dwutrzpieniowego (9) w kierunku ruchu
wskazówek zegara.
Odkręcanie nakrętki z dwoma otworami:
-Zablokować wrzeciono (patrz rozdział 6.1).
Odkręcić nakrętkę z dwoma otworami (8) za
pomocą klucza dwutrzpieniowego (9) w kierunku
przeciwnym do ruchu wskazówek zegara.
7. Użytkowanie
7.1Włączanie i wyłączanie
Maszynę zawsze prowadzić obiema rękami.
Najpierw włączyć maszynę, a dopiero potem
przyłożyć narzędzie robocze do obrabianego
elementu.
Zapobiegać zasysaniu przez maszynę
dodatkowego pyłu i wiórów. Maszynę włączać
i wyłączać z dala od nagromadzonego pyłu. Po
wyłączeniu urządzenie wolno odkładać dopiero po
całkowitym zatrzymaniu silnika.
Unikać niezamierzonego uruchomienia:
zawsze wyłączać maszynę po wyciągnięciu
wtyczki z gniazda wtykowego lub w przypadku
przerwy w dopływie prądu.
Po włączeniu trybu pracy ciągłej maszyna
będzie pracować nadal, nawet jeżeli
wypadnie z ręki. Z tego względu maszynę zawsze
trzymać oburącz za przewidziane do tego celu
rękojeści, przyjąć bezpieczną postawę i
skoncentrować uwagę na wykonywanej pracy.
Maszyny z przełącznikiem suwakowym:
4
0
Włączanie: przesunąć przełącznik suwakowy (4)
do przodu. Następnie w celu włączenia trybu pracy
ciągłej wcisnąć przełącznik w dół do zablokowania.
Wyłączanie: nacisnąć na tylną końcówkę
przełącznika suwakowego (4) i zwolnić przełącznik.
7.2Wskazówki dotyczące pracy z
urządzeniem
Szlifowanie i szlifowanie papierem ściernym:
Umiarkowanie dociskać urządzenie i przesuwać po
powierzchni zmieniając kierunek, aby nie dopuścić
do nadmiernego rozgrzania powierzchni
obrabianego elementu.
Szlifowanie zdzierające: dobry efekt uzyskuje się
przy pracy pod kątem 30°-40°.
Przecinanie:
przecinanego elementu. Pracować z
umiarkowanym posuwem dostosowanym do
Podczas przecinania zawsze
pracować przeciwbieżnie (patrz
ilustracja). W przeciwnym wypadku
istnieje ryzyko, że maszyna w sposób
niekontrolowany wyskoczy z
I
15
Page 16

POLSKIpl
obrabianego materiału. Nie ustawiać pod skosem,
nie naciskać, nie kołysać.
Praca z użyciem szczotek drucianych:
Umiarkowanie dociskać urządzenie.
8. Czyszczenie
Podczas obróbki drobiny zanieczyszczeń mogą się
osadzać wewnątrz elektronarzędzia. Ma to
negatywny wpływ na chłodzenie elektronarzędzia.
Przewodzące prąd osady mogą zaburzyć izolację
ochronną elektronarzędzia i nieść ze sobą ryzyko
porażenia prądem.
Należy regularnie, często i dokładnie odsysać z
elektronarzędzia zanieczyszczenia przez wszystkie
otwory wentylacyjne z przodu i z tyłu urządzenia lub
przedmuchać suchym powietrzem. Na czas
czyszczenia odłączyć elektronarzędzie od zasilania
i nosić okulary ochronne oraz maskę
przeciwpyłową. Podczas przedmuchiwania
zapewnić sprawność układu odsysania pyłu.
9. Osprzęt
Używać wyłącznie oryginalnego osprzętu Metabo.
Patrz strona 4.
Stosować wyłącznie osprzęt, który spełnia
wymagania i parametry określone w niniejszej
instrukcji obsługi.
AOsłona zatrzaskowa do tarcz / osłona do
przecinania
Przeznaczona do prac z użyciem tarcz tnących,
diamentowych tarcz tnących. Z zamontowanym
zaciskiem osłonę można stosować jako pokrywę
ochronną tarczy tnącej.
BOsłona ręki
Przeznaczona do prac z użyciem talerza
podporowego, talerza szlifierskiego, szczotek
drucianych i diamentowych wierteł koronowych do
glazury.
Przymocować osłonę ręki pod bocznym uchwytem
dodatkowym.
CNakrętka z dwoma otworami (8)
Pełną ofertę osprzętu można znaleźć na stronie
www.metabo.com lub w katalogu osprzętu.
10. Naprawy
Wszelkie naprawy elektronarzędzi wolno
wykonywać wyłącznie elektrykom!
W sprawie naprawy elektronarzędzia zwracać się
do przedstawiciela Metabo. Adresy można znaleźć
na stronie www.metabo.com.
Wykazy części zamiennych można pobrać pod
adresem www.metabo.com.
11. Ochrona środowiska
Pył powstający podczas szlifowania może zawierać
substancje szkodliwe: Nie usuwać z odpadami
komunalnymi, przekazać do punktu odbioru
odpadów specjalnych.
16
Przestrzegać lokalnych przepisów dotyczących
ekologicznej utylizacji i recyklingu zużytych
maszyn, opakowań i osprzętu.
Dotyczy tylko państw UE: nie wyrzucać elektronarzędzi wraz z odpadami komunalnymi!
Zgodnie z dyrektywą europejską 2012/19/UE
o zużytych urządzeniach elektrycznych i elektronicznych oraz jej implementacją w prawodawstwie
krajowym zużyte elektronarzędzia trzeba segregować i poddawać odzyskowi surowców wtórnych
zgodnie z przepisami o ochronie środowiska.
12.Dane techniczne
Wyjaśnienia do informacji podanych na stronie 3.
Prawo do zmian związanych z postępem
technicznym zastrzeżone.
Ø=maks. średnica narzędzia roboczego
=maks. dopuszczalna grubość narzędzia
t
max,1
t
max,3
M=gwint wrzeciona
l=długość wrzeciona szlifierskiego
n=prędkość obrotowa na biegu jałowym
P
P
m=ciężar bez kabla sieciowego
roboczego w zakresie mocowania za
pomocą nakrętki z dwoma otworami (8)
=tarcza zdzierająca / tarcza tnąca:
maks. dopuszczalna grubość narzędzia
roboczego
(maksymalna prędkość obrotowa)
=nominalny pobór mocy
1
=moc oddawana
2
Wartości pomiarów ustalone zgodnie z normą
EN 60745.
Maszyna w klasie ochronności II
~ prąd przemienny
Zamieszczone dane techniczne podlegają
tolerancji (odpowiednio do obowiązujących
standardów).
Wartości emisji
Wartości te umożliwiają oszacowanie emisji
elektronarzędzia i porównanie różnych
elektronarzędzi. W zależności od warunków
użytkowania, stanu elektronarzędzia lub narzędzi
roboczych rzeczywiste obciążenie może być
większe lub mniejsze. Podczas dokonywania oceny
uwzględnić przerwy w pracy i fazy mniejszego
obciążenia. Na podstawie odpowiednio
dopasowanych wartości szacunkowych określić
środki ochrony dla użytkownika, np. środki
organizacyjne.
Łączna wartość wibracji
trzech kierunków) określona zgodnie z normą
EN 60745:
a
h, SG
a
h, DS
K
h,SG/DS
=wartość emisji drgań
(szlifowanie powierzchni)
=wartość emisji drgań
(szlifowanie talerzem szlifierskim)
=niepewność wyznaczenia (drgania)
Typowe poziomy hałasu w ocenie akustycznej
L
pA
L
WA
K
pA
=poziom ciśnienia akustycznego
=poziom mocy akustycznej
, KWA= niepewność pomiarowa
Nosić ochronniki słuchu!
(suma wektorowa dla
:
Page 17

РУССКИЙ ru
Оригинальное руководство по эксплуатации
1. Использование по
назначению
Угловые шлифмашины, оснащенные
оригинальными принадлежностями Metabo,
предназначены для шлифования, шлифования
наждачной бумагой, обработки кардощетками
и абразивной резки металла, бетона, камня и
схожих с ними материалов без использования
воды.
За ущерб, возникший в результате
использования не по назначению,
ответственность несет только пользователь.
Необходимо соблюдать общепринятые правила
предотвращения несчастных случаев, а также
указания по технике безопасности,
приведенные в данном руководстве.
2. Общие указания по технике
безопасности
Для вашей собственной безопасности
и защиты электроинструмента от
повреждений необходимо соблюдать
данным символом!
безопасности. Несоблюдение инструкций и
указаний по технике безопасности может
привести к поражению электрическим током,
возникновению пожара и/или к получению
тяжелых травм.
Необходимо сохранять все инструкции и
указания по технике безопасности для
использования в будущем.
Передавать электроинструмент следующему
владельцу можно только вместе с этими
документами.
указания, отмеченные в тексте
ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ! В целях снижения
риска травмы следует прочесть данное
руководство по эксплуатации.
ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ! Следует прочесть
все инструкции и указания по технике
3. Особые указания по технике
безопасности
3.1Общие указания по технике
безопасности при шлифовании,
шлифовании наждачной бумагой,
обработке кардощетками и
абразивной резке:
Применение
а) Данный электроинструмент следует
использовать в качестве шлифмашины,
шлифователя с наждачной бумагой,
проволочной щетки и шлифовальноотрезной машины. Необходимо соблюдать
все указания по технике безопасности,
инструкции, изображения и данные,
полученные вместе с прибором.
Несоблюдение следующих инструкций может
привести к поражению электрическим током,
пожару и/или серьезным травмам.
б) Данный электроинструмент не
предназначен для полирования.
Использование электроинструмента не по
назначению может привести к возникновению
опасной ситуации и получению травм.
в) Не использовать принадлежности, не
предусмотренные и не рекомендованные
производителем для данного
электроинструмента. Одно лишь надежное
крепление принадлежности в
электроинструменте не гарантирует его
надежной эксплуатации.
г) Допустимая частота вращения рабочего
инструмента не должна превышать
максимальную частоту вращения,
указанную на электроинструменте.
Принадлежности, скорость вращения которых
превышает допустимое значение, могут
сломаться и отлететь в сторону.
д) Наружный диаметр и толщина рабочего
инструмента должны соответствовать
размерным данным электроинструмента.
Невозможно обеспечить экранирование и
контроль рабочих инструментов с неверно
рассчитанными параметрами.
е) Рабочие инструменты с резьбовой
вставкой должны точно подходить к
шлифовальному шпинделю
электроинструмента. У рабочих
инструментов, закрепленных с помощью
фланцев, крепежное отверстие должно
точно подходить к форме фланца. Рабочие
инструменты, размеры которых не
соответствуют зажимному приспособлению,
вращаются неравномерно, очень сильно
вибрируют и могут привести к потере контроля
над электроинструментом.
ж) Не использовать поврежденные рабочие
инструменты. Перед каждым
использованием осматривать рабочие
инструменты: шлифовальные круги не
должны иметь сколов и трещин,
шлифовальные тарелки — трещин, следов
износа или сильного истирания, в
проволочных щетках не должно быть
выпавших или обломившихся проволочных
прядей. В случае падения
электроинструмента или рабочего
инструмента проверить его исправность и
использовать только неповрежденный
рабочий инструмент. После проверки и
установки рабочего инструмента
убедиться, что никто не находится в зоне
вращающегося рабочего инструмента, и на
одну минуту запустить инструмент с
максимальной частотой вращения.
Поврежденные рабочие инструменты обычно
ломаются в ходе такой проверки.
17
Page 18

РУССКИЙru
з) Использовать средства индивидуальной
защиты. В зависимости от вида
выполняемой работы использовать маску
для полной защиты лица, средства для
защиты глаз или защитные очки. Для
защиты от мелких частиц шлифовального
инструмента и материала надевать
респиратор, защитные наушники,
защитные перчатки или специальный
фартук. Защищать глаза от отлетающих
посторонних предметов при выполнении
различных работ. Респираторы и защитные
маски должны отфильтровывать пыль,
возникающую во время работы. Длительное
воздействие громкого шума может привести к
потере слуха.
и) Следить за тем, чтобы другие люди
находились на безопасном расстоянии от
вашего рабочего места. Каждый человек,
входящий в рабочую зону, обязан надевать
средства индивидуальной защиты.
Отлетающие осколки заготовки или обломки
рабочих инструментов могут нанести травму
даже за пределами рабочей зоны.
й) При выполнении работ вблизи скрытой
электропроводки или сетевого кабеля
самого инструмента держать
электроинструмент только за
изолированные поверхности. При контакте с
находящимися под напряжением проводами
возможна передача напряжения на
металлические части прибора и удар
электрическим током.
к) Сетевой кабель должен находиться
вдали от вращающихся рабочих
инструментов. В случае потери контроля над
инструментом он может перерезать или
затянуть сетевой кабель, при этом руки могут
попасть в зону вращения рабочего
инструмента.
л) Никогда не класть электроинструмент до
полной остановки рабочего инструмента.
Вращающийся рабочий инструмент может
коснуться поверхности, в результате чего
возможна потеря контроля над
электроинструментом.
м) Не включать электроинструмент во
время его переноски. Возможно попадание
одежды во вращающийся рабочий инструмент,
в результате чего можно получить травму.
н) Регулярно очищать вентиляционные
щели электроинструмента. Вентилятор
двигателя затягивает пыль в корпус, а большое
скопление металлической пыли сопряжено с
опасностью поражения электрическим током.
o) Не использовать электроинструмент
вблизи легковоспламеняющихся
материалов. Искры могут вызвать
воспламенение этих материалов.
п) Не использовать рабочие инструменты,
для которых требуется использование
охлаждающей жидкости. Использование
воды или иной охлаждающей жидкости может
привести к поражению электрическим током.
18
3.2Отдача и соответствующие указания
по технике безопасности
Отдача представляет собой внезапную
реакцию в результате зацепления или
заклинивания вращающегося рабочего
инструмента, например, шлифовального круга,
шлифовальной тарелки, проволочной щетки и
т. д. Зацепление или заклинивание ведет к
внезапной остановке вращающегося рабочего
инструмента. В результате происходит
неконтролируемое движение
электроинструмента в направлении,
противоположном направлению вращения
рабочего инструмента в месте блокировки.
Если, например, шлифовальный круг цепляется
или заедает в заготовке, кромка круга
застревает, в результате чего круг может
обломиться или вызвать отдачу. Вследствие
этого шлифовальный круг движется на
оператора или в противоположном
направлении, в зависимости от направления
вращения круга в месте заклинивания. При
этом шлифовальный круг может разломиться.
Отдача является следствием неправильной или
неумелой эксплуатации электроинструмента.
Ее можно избежать при соблюдении описанных
ниже мер предосторожности.
a) Крепко держать электроинструмент в
руках и занимать такую позицию, чтобы
суметь противодействовать силе отдачи.
При наличии дополнительной рукоятки
всегда использовать ее, чтобы
максимально контролировать силу отдачи
и реактивный момент при запуске. При
соблюдении мер предосторожности можно
управлять отдачей и реактивными силами.
б) Никогда не держать руку вблизи
вращающихся рабочих инструментов. При
отдаче возможен контакт рабочего
инструмента с рукой.
в) Избегать нахождения в зоне,
в которую электроинструмент смещается
во время отдачи. При отдаче
электроинструмент смещается в направлении,
обратном направлению движения
шлифовального круга в месте блокировки.
г) Особенно осторожно работать в области
углов, острых кромок и т.п. Не допускать
отскакивания или заклинивания рабочих
инструментов в заготовке. Вращающийся
рабочий инструмент склонен к заклиниванию
при работе в области углов, острых кромок или
при отскакивании. Это вызывает потерю
контроля или отдачу.
д) Не использовать цепное или зубчатое
пильное полотно. Подобные рабочие
инструменты часто вызывают отдачу или
потерю контроля над электроинструментом.
3.3Особые указания по технике
безопасности при шлифовании и
абразивной резке:
а) Использовать только подходящий для
соответствующего электроинструмента
Page 19

шлифовальный инструмент и
предназначенный для него защитный
кожух. Шлифовальные инструменты, не
предназначенные для данного
электроинструмента, в достаточной степени не
защищены экраном и не являются
безопасными.
б) Выпуклые шлифовальные круги должны
быть размещены таким образом, чтобы их
рабочая поверхность находилась ниже
кромки защитного кожуха. Неправильно
размещенный шлифовальный круг,
выступающий за кромку защитного кожуха, не
может быть защищен должным образом.
в) Защитный кожух должен быть надежно
закреплен на электроинструменте и в целях
максимальной безопасности
отрегулирован таким образом, чтобы
открытой оставалась лишь самая малая
часть шлифовального инструмента.
Защитный кожух служит для защиты оператора
от осколков и случайного соприкосновения с
шлифовальным инструментом, а также от искр,
от которых может воспламениться одежда.
г) Шлифовальные инструменты должны
использоваться строго по назначению.
Например, нельзя проводить шлифование
боковой поверхностью отрезного круга.
Отрезные круги предназначены для снятия
материала кромкой круга. Боковое силовое
воздействие на отрезной круг может
разрушить его.
д) Всегда использовать исправный
зажимной фланец, его размер и форма
должны соответствовать выбранному
шлифовальному кругу. Подходящие фланцы
представляют собой опору для шлифовального
круга и тем самым снижают опасность его
разлома. Фланцы для отрезных кругов могут
отличаться от фланцев для других
шлифовальных кругов.
е) Не использовать изношенные
шлифовальные круги от
электроинструментов большего размера.
Шлифовальные круги для
электроинструментов большего размера не
рассчитаны на повышенную частоту вращения
электроинструментов меньшего размера и
могут разломиться.
3.4 Дополнительные особые указания по
технике безопасности при абразивной
резке:
а) Избегать заклинивания отрезного круга
или слишком большого давления прижима.
Не выполнять слишком глубокие пропилы.
Перегрузка отрезного круга приводит к его
перенапряжению и перекосам или
заклиниванию, что увеличивает вероятность
отдачи или поломки шлифовального
инструмента.
б) Не стоять в зоне перед вращающимся
отрезным кругом и за ним. Если начать
двигать отрезной круг с заготовкой от себя, то в
случае отдачи электроинструмент с
РУССКИЙ ru
вращающимся кругом будет отброшен прямо на
пользователя.
в) В случае зажима отрезного круга или при
перерыве в работе отключить инструмент и
подержать его в руке до полной остановки
вращающегося круга. Никогда не пытаться
извлечь движущийся отрезной круг из
пропила, так как это может вызвать отдачу.
Определить и устранить причину
заклинивания.
г) Не включать электроинструмент, если он
находится в заготовке. Сначала дать
отрезному кругу набрать полную частоту
вращения, только после этого осторожно
продолжить резку. В противном случае круг
может заклинить, отскочить из заготовки или
вызвать отдачу.
д) Для снижения риска отдачи в результате
заклинивания отрезного круга при
обработке плит и заготовок большого
размера использовать опору. Заготовки
большого размера могут прогнуться под
собственным весом. Под заготовку следует
подвести опоры с двух сторон, а именно вблизи
реза и кромки.
е) Следует проявить особую осторожность
при выполнении погружных пропилов в
имеющихся стенах или других
непросматриваемых зонах. Погружаемый
отрезной круг может вызвать отдачу при
разрезании газо- и водопроводов,
электрических проводов или иных объектов.
3.5Особые указания по технике
безопасности при шлифовании
наждачной бумагой:
a) Не использовать шлифовальные листы
слишком большого размера, соблюдать
указанные производителем размеры.
Шлифовальные листы, выступающие за края
шлифовальных тарелок, могут стать причиной
травм, разорваться, а также привести к
заклиниванию или к отдаче.
3.6Особые указания по технике
безопасности при обработке
проволочными щетками:
а) Помнить о том, что из щетки выпадают
кусочки проволоки даже при обычной
эксплуатации. Не перегружать проволоку
слишком высоким давлением прижима.
Отлетающие кусочки проволоки могут легко
проникнуть сквозь тонкую одежду и/или кожу.
б) Если рекомендовано применение
защитного кожуха, не допускать
соприкосновения кожуха и проволочной
щетки. Диаметр тарельчатых и чашечных
щеток может увеличиваться под воздействием
давления прижима и центробежных сил.
3.7Дополнительные указания по технике
безопасности:
ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ! Всегда носить
защитные очки.
19
Page 20

РУССКИЙru
При необходимости использовать эластичные
прокладки, если они поставляются вместе с
инструментом.
Соблюдать указания производителей рабочих
инструментов или принадлежностей! Беречь
круги от ударов и контакта с жирами и
смазками!
Бережно хранить шлифовальные круги и
применять их в соответствии с предписаниями
производителя.
Никогда не использовать круги для
абразивного отрезания для обдирочных работ!
Отрезные круги нельзя подвергать боковому
давлению.
Заготовку нужно прочно закрепить и
зафиксировать от сдвига, например, с помощью
зажимных приспособлений. Крупные заготовки
должны иметь достаточную опору.
При использовании рабочих инструментов с
резьбовой вставкой конец шпинделя не должен
касаться основания отверстия шлифовального
инструмента. Следить за тем, чтобы резьба
рабочего инструмента имела достаточную
длину для шпинделя. Резьба рабочего
инструмента должна совпадать с резьбой
шпинделя. Длина шпинделя и резьба шпинделя
указаны на стр.3 и в главе 12. «Технические
характеристики».
Компания рекомендует использовать
стационарную установку для удаления пыли и
предварительно включать автомат защиты от
тока утечки (FI). В случае отключения угловой
шлифмашины автоматом защиты от тока утечки
инструмент следует проверить и очистить.
Очистка двигателя описана в главе 8.
«Очистка».
Использование поврежденных,
деформированных или вибрирующих
инструментов запрещено.
Не допускать повреждений газо- или
водопроводов, линий электропитания и
несущих стен (статика).
Перед проведением каких-либо настроек,
переоснащения или работ по техобслуживанию
извлекайте сетевую вилку из розетки.
Поврежденная или потрескавшаяся
дополнительная рукоятка подлежит замене. Не
использовать электроинструмент с дефектной
дополнительной рукояткой.
Поврежденный или потрескавшийся защитный
кожух подлежит замене. Не использовать
инструмент с дефектным защитным кожухом.
Данный электроинструмент не предназначен
для полирования. Претензии по гарантии не
принимаются при использовании не по
назначению! Возможен перегрев двигателя и
повреждение электроинструмента. Для
проведения полировальных работ мы
рекомендуем угловую полировальную машину.
Небольшие заготовки следует закреплять,
например, зажимать их в тисках.
20
Снижение пылевой нагрузки:
ПРЕДУПРЕЖДЕНИЕ — Пыль,
образовавшаяся в результате шлифовки
наждачной бумагой, распиливания, шлифовки,
сверления и других видов работ, может
содержать химические вещества, о которых
известно, что они вызывают рак, врожденные
дефекты или другие повреждения
репродуктивной системы. Примеры таких
химических веществ:
-свинец в краске с содержанием свинца,
-минеральная пыль от строительного кирпича,
цемента и других веществ кирпичной кладки,
а также
-мышьяк и хром из химически обработанной
древесины.
Степень риска зависит от того, как часто вы
выполняете этот вид работ. Чтобы уменьшить
воздействие химических веществ: работайте в
помещениях с достаточной вентиляцией и с
использованием разрешенных средств
индивидуальной защиты, например, с
респираторами, разработанными специально
для фильтрации микроскопических частиц.
Это также касается пыли от других материалов,
например, некоторых видов древесины
(древесная пыль дуба или бука), металла,
асбеста. Другие известные заболевания — это,
например, аллергические реакции,
заболевания дыхательных путей. Не
допускайте попадания пыли внутрь организма.
Необходимо соблюдать директивы,
действующие в отношении материалов,
персонала, вариантов применения и мест
проведения работ, а также национальные
предписания (например, положения об охране
труда, правила утилизации).
Обеспечьте удаление образующихся частиц, не
допускайте образования отложений в
окружающем пространстве.
Для специальных работ используйте
подходящую оснастку. Это позволит сократить
количество частиц, неконтролируемо
выбрасываемых в окружающую среду.
Используйте подходящее устройство удаления
пыли.
Для уменьшения пылевой нагрузки:
-не направляйте выбрасываемые из
электроинструмента частицы и отработанный
воздух на себя, находящихся рядом людей
или на скопления пыли,
-используйте вытяжное устройство и/или
воздухоочиститель,
-хорошо проветривайте рабочее место и
содержите его в чистоте с помощью пылесоса.
Подметание или продувка только поднимают
пыль в воздух.
-Защитную одежду следует обрабатывать
пылесосом или стирать. Не продувать одежду
воздухом, не выбивать и не сметать с нее
пыль.
Page 21

РУССКИЙ ru
4. Обзор
См. стр. 2.
1Опорный фланец
2Шпиндель
3Кнопка фиксатора шпинделя
4Переключатель для включения/выключения
5Рукоятка
6Дополнительная рукоятка
7Защитный кожух
8Гайка с двумя торцевыми отверстиями
9Ключ под два отверстия
10 Зажимной винт
11 Зажимное кольцо
* в зависимости от модели / не входит в объем
поставки
5. Ввод в эксплуатацию
Перед вводом в эксплуатацию проверить,
совпадают ли указанные на заводской
табличке значения напряжения и частоты сети
с параметрами электросети.
Перед инструментом всегда подключать
устройство защиты от тока утечки (УЗО) с
макс. током отключения 30мА.
5.1Установка дополнительной рукоятки
Работать только с установленной
дополнительной рукояткой (6)! Прочно
привинтить дополнительную рукоятку с левой
или с правой сторон инструмента.
5.2Установка защитного кожуха
Из соображений безопасности
использовать только такой защитный
кожух, который предусмотрен для
соответствующего шлифовального
инструмента! См. также главу 9.
«Принадлежности»!
Защитный кожух для шлифования
Предназначен для работ с шлифовальными
кругами, ламельными шлифовальными
тарелками, алмазными отрезными кругами.
См. рисунок C на стр. 2.
-Ослабить зажимной винт (10) так, чтобы
зажимное кольцо (11) защитного кожуха
расширилось в достаточной степени.
-Установить защитный кожух (7) в показанное
положение.
-Повернуть защитный кожух таким образом,
чтобы его закрытая зона была обращена к
вам.
- Прочно затянуть зажимной винт (10).
Проверить прочность посадки — защитный
кожух (7) не должен проворачиваться.
Использовать только те
рабочие инструменты,
которые выступают из-под
защитного кожуха не
более чем на 3,4 мм.
6. Установка шлифовального
круга
Перед любой переналадкой: извлечь
сетевую вилку из розетки. Инструмент
должен находиться в выключенном состоянии,
а шпиндель должен быть неподвижным.
Для работ с отрезными кругами в целях
безопасности использовать специальные
защитные кожухи для абразивного отрезания
(см. главу 9.«Принадлежности»).
6.1Фиксация шпинделя
-Нажать кнопку фиксатора шпинделя (3) и
крутить шпиндель (2) от руки до тех пор, пока
кнопка фиксатора шпинделя не
зафиксируется.
6.2Установка шлифовального круга
См. рисунок A на стр. 2.
-Установить опорный фланец (1) на шпиндель.
Фланец установлен правильно, если он не
проворачивается на шпинделе.
Только для W 650-100: навернуть
поддерживающий фланец двухштифтовым
ключом на шпиндель таким образом, чтобы
небольшой буртик (диаметром 16 мм) был
обращен наверх.
-Уложить шлифовальный круг на опорный
фланец (1). Шлифовальный круг должен
равномерно прилегать к опорному фланцу.
6.3Крепление/отвинчивание гайки с
двумя торцевыми отверстиями
Крепление гайки с двумя торцевыми
отверстиями (8):
Две стороны гайки с двумя торцевыми
отверстиями отличаются друг от друга.
Навинтить гайку с двумя торцевыми
отверстиями на шпиндель следующим образом:
См. рисунок B на стр. 2.
- X) Для тонких шлифовальных кругов:
буртик гайки с двумя торцевыми отверстиями
(8) обращен наверх для надежного зажима
шлифовального круга.
Y) Для толстых шлифовальных кругов:
Буртик гайки с двумя торцевыми отверстиями
обращен вниз для надежной фиксации гайки
на шпинделе (8).
Z) Только для W 650-100:
буртик гайки с двумя торцевыми отверстиями
обращен вниз, а ровная поверхность гайки —
наверх.
-Зафиксировать шпиндель. Затянуть гайку с
двумя торцевыми отверстиями (8) с помощью
ключа под два отверстия (9) по часовой
стрелке.
Отвинчивание гайки с двумя торцевыми
отверстиями:
-Зафиксировать шпиндель (см. главу 6.1).
Отвинтите гайку с двумя торцевыми
21
Page 22

РУССКИЙru
отверстиями (8) с помощью ключа (9) против
часовой стрелки.
7. Эксплуатация
7.1Включение/выключение
Инструмент необходимо всегда держать
обеими руками.
Подводить инструмент к заготовке только
во включенном состоянии.
Следить за тем, чтобы инструмент не
втягивал излишнюю пыль и опилки. При
включении и выключении держать его
подальше от скопившейся пыли. Не класть
инструмент до полной остановки двигателя.
Не допускать непреднамеренного запуска:
всегда выключать инструмент, если вилка
была извлечена из розетки, или если
произошел сбой в подаче электроэнергии.
В режиме непрерывной работы
инструмент продолжает вращаться, даже
если он вырвется из руки. Поэтому всегда
следует крепко держать инструмент двумя
руками за рукоятки, занимать устойчивое
положение и полностью концентрироваться на
выполняемой работе.
Инструменты с переключателем:
4
0
Включение: сдвинуть переключатель (4)
вперед. Для непрерывной работы нажать
переключатель вниз до фиксации.
Выключение: Нажмите на задний конец
переключателя (4), а затем отпустите его.
7.2Рабочие указания
Стандартное шлифование и шлифование
наждачной бумагой:
Прижимать инструмент с умеренным усилием и
перемещать его по поверхности назад и вперед,
чтобы поверхность заготовки не
перегревалась.
Черновое шлифование: для получения
хорошего результата работать с установочным
углом 30°–40°.
Абразивное отрезание:
работать с умеренной подачей,
соответствующей обрабатываемому
материалу. Не допускать перекоса, не
нажимать и не раскачивать инструмент.
Обработка проволочными щетками:
Умеренно прижимать инструмент.
22
При абразивном отрезании всегда
работать во встречном
направлении (см. рисунок). Иначе
инструмент может неожиданно
выскочить из пропила. Следует
I
8. Очистка
При работе возможно скопление частиц
обрабатываемого материала внутри
электроинструмента. Это ухудшает
охлаждение электроинструмента.
Токопроводящие скопления могут нарушить
защитную изоляцию электроинструмента, что
сопряжено с опасностью поражения
электрическим током.
Через небольшие равные промежутки времени
тщательно удалять загрязнения из передних и
задних вентиляционных щелей
электроинструмента или продувать их сухим
воздухом. Перед этим отсоедините
электроинструмент от источника питания и
носите при этом защитные очки и респиратор.
При продувке должна быть обеспечена
достаточная вытяжная вентиляция.
9. Принадлежности
Используйте только оригинальные
принадлежности Metabo.
См. стр. 4.
Используйте только такие принадлежности,
которые отвечают требованиям и параметрам,
перечисленным в данном руководстве по
эксплуатации.
AЗажим защитного кожуха для отрезных
работ/ защитный кожух для абразивной
резки
Предназначен для работы с отрезными
кругами, алмазными отрезными кругами. При
установленном зажиме защитного кожуха для
отрезных работ защитный кожух можно
использовать для абразивной резки.
BЗащитный элемент для рук
Предназначен для работ с опорными
тарелками, шлифовальными тарелками,
кардощетками и алмазными сверлильными
коронками для керамической плитки.
Защитный элемент для рук устанавливается
под боковую дополнительную рукоятку.
CГайка с двумя торцевыми отверстиями
(8)
Полный ассортимент принадлежностей см. на
сайте www.metabo.com или в каталоге
принадлежностей.
10.Ремонт
Ремонт электроинструментов должен
осуществляться только
квалифицированными специалистамиэлектриками!
Для ремонта электроинструмента Metabo
обращайтесь в региональное
представительство Metabo. Адрес см. на сайте
www.metabo.com.
Списки запасных частей можно скачать с сайта
www.metabo.com.
Page 23
11. Защита окружающей среды
Утилизацию шлифовальной пыли выполнять
отдельно от бытовых отходов на
соответствующей площадке для спецотходов,
т. к. в составе пыли могут быть вредные
вещества.
Соблюдайте национальные предписания по
экологически безопасной утилизации и
переработке отслуживших машин, упаковки и
принадлежностей.
Только для стран ЕС: не утилизировать
электроинструменты вместе с бытовыми
отходами! Согласно европейской директиве 2012/19/ЕС по отходам электрического и
электронного оборудования и соответствующим национальным нормам отработавшие
электроинструменты подлежат сбору с целью
их последующей экологически безопасной
переработки.
12. Технические
характеристики
Пояснения к данным, приведенным на стр. 3.
Оставляем за собой право на изменения,
обусловленные техническим прогрессом.
Ø=макс. диаметр рабочего инструмента
=макс. допустимая толщина рабочего
t
max,1
t
max,3
M=резьба шпинделя
l=длина шлифовального шпинделя
n=частота вращения без нагрузки
P
P
m=вес без сетевого кабеля
Результаты измерений получены в
соответствии со стандартом EN60745.
~
Указанные технические характеристики имеют
допуски (предусмотренные действующими
стандартами).
сравнивать эмиссию шума различных
электроинструментов. В зависимости от
условий эксплуатации, состояния
электроинструмента или используемых
рабочих инструментов фактическая нагрузка
может быть выше или ниже. Для оценки
примерного уровня эмиссии следует учитывать
перерывы в работе и фазы работы с
пониженной шумовой нагрузкой. Определить
перечень мер, например, организационных
мероприятий, по защите пользователя с учетом
тех или иных значений эмиссии шума.
инструмента в области зажима при
использовании гайки с двумя
торцевыми отверстиями (8)
=обдирочный круг / отрезной круг:
макс. допустимая толщина рабочего
инструмента
(максимальная частота вращения)
=номинальная потребляемая мощность
1
=отдаваемая мощность
2
Инструмент класса защиты II
переменный ток
Значения эмиссии шума
Эти значения позволяют оценивать и
РУССКИЙ ru
Общее значение вибрации
трех направлений), расчет согласно EN 60745:
a
h, SG
a
h, DS
K
h,SG/DS
Типичный амплитудно-взвешенный уровень
L
pA
L
WA
KpA, KWA=коэффициент погрешности
=значение вибрации
(шлифование поверхности)
=значение вибрации
(шлифование шлифовальной
тарелкой)
= коэффициент погрешности
(вибрация)
звукового давления:
=уровень звукового давления
=уровень звуковой мощности
Используйте защитные наушники!
Информация для покупателя:
Сертификат соответствия:
Сертификат соответствия: № ТС RU C-
DE.БЛ08.В.01717, срок действия с 26.09.2018
по 25.09.2023 г., выдан органом по
сертификации продукции «ИВАНОВОСЕРТИФИКАТ» ООО «Ивановский Фонд
Сертификации»; Адрес(юр. и факт.): 153032,
Российская Федерация, Ивановская обл., г.
Иваново, ул. Станкостроителей, д. 1; тел.
(4932)77-34-67; E-mail: info@i-f-s.ru; Аттестат
аккредитации № RA.RU.11БЛ08 от 24.03.16 г.
Страна изготовления: Китай
Производитель: "Metabowerke GmbH",
Metaboallee 1, D-72622 Nuertingen, Германия
Импортер в России:
ООО "Метабо Евразия"
Россия, 127273, Москва
ул. Березовая аллея, д 5 а, стр 7, офис 106
тел.: +7 495 980 78 41
Дата производства зашифрована в 10-значном
серийном номере инструмента, указанном на
его шильдике. 1 я цифра обозначает год,
например «4» обозначает, что изделие
произведено в 2014 году. 2 я и 3 я цифры
обозначают номер месяца в году производства,
например «05» - май
Срок службы изделия составляет 7 лет. Не
рекомендуется к эксплуатации по истечении 5
лет хранения с даты изготовления без
предварительной проверки (дату изготовления
см. На этикетке).
(векторная сумма
23
Page 24

УКРАЇНСЬКАuk
Оригінальна інструкція з експлуатації
1. Використання за
призначенням
Кутова шліфмашина з оригінальним приладдям
Metabo призначена для шліфування,
шліфування наждачним папером, обробки
дротяними щітками та відрізання абразивним
диском металу, бетону, каменю та аналогічних
матеріалів без використання води.
За пошкодження, викликані експлуатацією не
за призначенням, несе відповідальність
виключно користувач.
Необхідно дотримуватись загальноприйнятих
правил запобігання нещасним випадкам, а
також правил техніки безпеки, наведених в цій
інструкції.
2. Загальні правила техніки
безпеки
Задля вашої власної безпеки та
захисту електроінструмента від
ушкоджень слід дотримуватись
вказівок, позначених цим символом!
ПОПЕРЕДЖЕННЯ — З метою зниження
ризику отримання тілесних ушкоджень
прочитайте цю інструкцію з експлуатації.
ПОПЕРЕДЖЕННЯ — Ознайомтеся з
усіма правилами та вказівками з
техніки безпеки. Недотримання правил та
вказівок з техніки безпеки може призвести до
ураження електричним струмом, пожежі та/або
тяжких тілесних ушкоджень.
Зберігайте правила та вказівки з техніки
безпеки для майбутнього використання.
Передавайте ваш електроінструмент тільки
разом з цими документами.
3. Спеціальні вказівки з
техніки безпеки
3.1Загальні вказівки з техніки безпеки
під час стандартного шліфування та
шліфування наждачним папером,
обробки дротяними щітками та
відрізання абразивними дисками:
Застосування
a) Цей електроінструмент призначений для
стандартного шліфування та шліфування
наждачним папером, обробки дротяними
щітками та відрізання абразивними
дисками. Приймайте до уваги усі вказівки та
рекомендації щодо техніки безпеки,
зображення та дані, які ви отримали разом
з цим пристроєм. Недотримання наступних
вказівок може призвести до удару електричним
струмом, пожежі та/або тяжких тілесних
ушкоджень.
24
b) Цей електроінструмент не призначений
для полірування. Використання, до якого
електроінструмент не призначений, може
призвести до пошкоджень та травм.
c) Не використовуйте приладдя, яке не було
передбачене та рекомендоване
виробником для відповідного
електроінструменту. Тільки те, що приладдя
підходить до вашого електроінструменту, не
гарантує безпечне використання.
d) Допустима кількість обертів
інструментальної насадки не повинна бути
менше вказаної на електроінструменті
максимальної кількості обертів. Приладдя,
яке обертається швидше допустимої швидкості,
може зламатися та розлетітися по сторонам.
e) Зовнішній діаметр та товщина
інструментальної насадки повинні
відповідати даним вашого
електроінструменту. Для інструментальних
насадок, габарити яких не відповідають
електроінструменту, не забезпечені достатній
захист та контроль.
f) Інструментальні насадки з різьбовою
вставкою повинні точно співпадати з
наріззю шліфувального шпинделя. Для
інструментальних насадок, які
встановлюють за допомогою фланця,
діаметр отвору інструментальної насадки
має відповідати монтажному діаметру
фланця. Інструментальні насадки, які не точно
прикріплені до електроінструменту,
обертаються нерівномірно, сильно вібрують та
можуть призвести до втрати контролю.
g) Не використовуйте пошкоджені
інструментальні насадки. Перед кожним
використанням перевіряйте
інструментальні насадки: шліфувальні
диски на наявність відколів та тріщин;
тарілчасті шліфувальні круги на наявність
відколів, зносу та спрацьовування; дротяні
щітки на наявність слабо закріпленого або
пошкодженого дроту. У разі падіння
електроінструменту або інструментальної
насадки переконайтеся, що немає
пошкоджень, або візьміть непошкоджену
насадку. Після перевірки та встановлення
інструментальної насадки увімкніть
пристрій на хвилину на максимальні оберти,
в цей час користувач та інші люди повинні
триматися поза зоною обертання
інструментальної насадки. Пошкоджені
інструментальні насадки як правило ламаються
на цьому етапі тестування.
h) Використовуйте особисті засоби захисту.
Залежно від сфери використання обирайте
захисний щіток для обличчя, захист для
очей або захисні окуляри. Якщо потрібно,
використовуйте респіратор, засоби захисту
органів слуху, захисні рукавички або
спеціальний фартух, які захистять вас від
невеликих шліфувальних та сировинних
часточок. Очі повинні бути захищені від
Page 25

часточок, що розлітаються під час проведення
різних робіт. Респіратор або фільтрувальна
захисна маска повинні бути розраховані на пил,
що утворюється під час робіт. Якщо ви довгий
час зазнаєте впливу шуму, може статися
зниження слуху.
i) Слідкуйте за тим, щоб інші люди
знаходились на безпечній відстані від вашої
робочої зони. Кожен, хто наближається до
робочої зони, повинен використовувати
засоби захисту. Відламки заготовки або
інструментальної насадки можуть відлетіти та
завдати шкоди навіть за межами робочої зони.
j) Тримайте електроінструмент тільки за
ізольовані поверхні під час роботи, якщо є
ризик зіткнення інструментальної насадки з
прихованим електродротом або кабелем
самого інструменту. Контакт з
електропроводкою під напругою може
призвести до передачі напруги також на
металеві частини пристрою та спричинити
ураження електричним струмом.
k) Тримайте кабель живлення в стороні від
інструментальної насадки, що обертається.
Якщо ви втратите контроль над приладом,
можливе перерізання або захоплення
мережевого кабелю, що може призвести до
потрапляння вашої руки в зону обертання
інструментальної насадки.
I) Ніколи не відкладайте електроінструмент,
доки інструментальна насадка повністю не
зупиниться. Можливий контакт
інструментальної насадки, що обертається, з
поверхнею, що може призвести до втрати
контролю над електроінструментом.
m) Під час перенесення електроінструмент
не повинен працювати. Є ризик випадкового
захоплення вашого одягу та поранення тіла
інструментальною насадкою, що обертається.
n) Регулярно очищуйте вентиляційні отвори
вашого електроінструменту. Вентилятор
двигуна затягує пил усередину корпусу,
внаслідок чого велике скупчення металевого
пилу викликає ризик ураження електричним
струмом.
o) Не використовуйте електроінструмент
поблизу займистих матеріалів. Іскри можуть
викликати займання цих матеріалів.
p) Не використовуйте інструментальні
насадки, які потребують рідких
охолоджувальних засобів. Використання
води або інших рідких охолоджувальних засобів
може призвести до удару електричним
струмом.
3.2Віддача та відповідні правила безпеки
Віддача - це раптова реакція в результаті
застрягання або блокування інструментальної
насадки, щ о обертається: шліфувального диска,
тарілчастого шліфувального круга, дротяної
щітки та ін. - що веде до різкої зупинки
інструментальної насадки. Це викликає
неконтрольований рух електроінструменту в
УКРАЇНСЬКА uk
місті блокування у напрямку, протилежному
напрямку обертання інструментальної насадки.
Якщо, наприклад, шліфувальний диск
заблокований або застряг в заготовці, кромка
шліфувального диска, що занурена у заготовку,
викликає пошкодження диска та віддачу.
Шліфувальний диск рухається у напрямку
користувача або від нього, залежно від
напрямку обертання диска в момент
блокування. При цьому шліфувальні диски
також можуть ламатися.
Віддача є наслідком невірного або помилкового
використання електроінструменту. Запобігти
з'явленню віддачі допоможуть відповідні
заходи, які описані нижче.
a) Міцно тримайте електроінструмент, ваші
тіло та руки повинні перебувати в
положенні, яке гарантує можливість
протистояти віддачі. Завжди
використовуйте додаткову рукоятку, якщо
вона є, для максимального контролю над
віддачею та реактивними моментами під
час розгону. За умови вживання відповідних
заходів безпеки користувач здатний
контролювати сили віддачі та реакції.
b) Не тримайте руки поблизу
інструментальної насадки, що обертається.
Інструментальна насадка може в момент віддачі
травмувати вашу руку.
c) Уникайте знаходження в зоні,
в яку електроінструмент потрапить при
віддачі. При віддачі
електроінструмент рухається в напрямку,
протилежному напрямку обертання
шліфувального диска в момент блокування.
d) Працюйте особливо уважно біля кутів,
гострих кромок тощо. Не допускайте
рикошету інструментальної насадки від
заготовки та її заклинювання.
Інструментальна насадка, що обертається,
може заклинитися біля кутів, гострих кромок та
при рикошеті. Наслідком є втрата контролю або
віддача.
e) Не використовуйте зубчасті пилкові
диски або диски для ланцюгової пилки. Такі
інструментальні насадки часто викликають
віддачу або втрату контролю над
електроінструментом.
3.3Особливі вказівки з техніки безпеки
під час шліфування та абразивного
відрізання:
a) Використовуйте тільки ті абразивні
інструменти, що рекомендовані для вашого
електроінструменту, і захисний кожух, що
передбачений для цих абразивних
інструментів. Для абразивних інструментів, що
не передбачені для вашого електроінструменту,
не гарантований достатній захист, отже немає
гарантії безпеки.
b) Шліфувальні диски вигнутого профілю
мають бути встановлені таким
шліфувальна поверхня не виступала над
площиною захисного краю. Неправильно
ч ином, щоб їх
25
Page 26

УКРАЇНСЬКАuk
встановлений шліфувальний круг, який
виходить за межі захисного краю, не може бути
затемнений належним чином.
c) Захисний кожух треба надійно
встановити на електроінструмент і для
максимальної безпеки налаштувати таким
чином, щоб відкритою залишалася лише
найменша частина абразивного
інструменту. Захисний кожух допомагає
захистити користувача від уламків,
випадкового контакту з абразивним
інструментом та іскор, від яких може зайнятися
одяг.
d) Абразивні інструменти повинні
використовуватися тільки за
призначенням.
Наприклад: забороняється виконувати
шліфування бічною поверхнею відрізного
круга. Відрізні диски призначені для зняття
матеріалу кромкою круга. Сили, що впливають
на круг з бічної сторони, можуть стати причиною
його руйнування.
e) Для установки шліфувального диска
завжди використовуйте справний
затискний фланець потрібного розміру і
форми. Відповідні за формою і розміром фланці
фіксують шліфувальний диск і знижують ризик
його розлому. Затискні фланці для відрізних
кругів можуть відрізнятися від затискних
фланців для інших шліфувальних дисків.
f) Не використовуйте зношені шліфувальні
диски від електроінструментів більшого
розміру. Шліфувальні диски, виготовлені для
електроінструментів більшого розміру, не
розраховані на високу частоту обертання
малогабаритних електроінструментів і тому
можуть зруйнуватися.
3.4Додаткові вказівки з техніки безпеки
при відрізанні абразивними дисками:
a) Уникайте блокування відрізного круга та
занадто високого притискного зусилля. Не
виконуйте занадто глибокі розрізи.
Перевантаження відрізного круга прискорює
його знос і збільшує схильність до перекосу або
блокування, а як наслідок - можливість віддачі
або руйнування.
b) Уникайте знаходження в зоні перед
відрізним кругом, що обертається, і позаду
нього. При зміщенні відрізного круга в
оброблюваній деталі в напрямі від себе
електроінструмент у випадку віддачі може
відскочити прямо на вас разом з диском, що
обертається.
c) У разі заклинювання відрізного круга або
переривання роботи вимкніть інструмент і
дочекайтеся, поки круг повністю
зупиниться. Ніколи не намагайтеся
витягнути відрізний круг, що обертається, з
розрізу - можлива віддача. Встановіть і
усуньте причину заклинювання.
d) Не вмикайте інструмент знову, якщо він
все ще знаходиться в оброблюваній деталі.
Перед продовженням роботи дочекайтеся,
26
поки інструмент досягне робочої частоти
обертання. Інакше можливе заїдання круга,
його вискакування з оброблюваної деталі або
поява віддачі.
e) Підпирайте плити або заготовки великого
розміру, щоб знизити ризик у випадку
заїдання відрізного круга. Великі заготовки
можуть прогинатися під власною вагою.
Оброблювану деталь слід підпирати з двох
сторін: близько місця виконання розрізу та
уздовж її кромки.
f) Будьте особливо обережні при виконанні
заглибних розрізів в стінах та інших зонах,
що не проглядаються. При заглибленні диска
під час різання можливий контакт з газо- і
водопроводами, електричною проводкою та
іншими об'єктами, що викликає віддачу.
3.5Особливі вказівки з техніки безпеки
при шліфуванні наждачним папером:
a) Не використовуйте наждачний папір
занадто великого розміру, дотримуйтесь
інструкцій виробника паперу щодо його
розмірів. Наждачний папір, що виступає за
межі тарілчастого шліфувального круга, може
стати причиною травм, блокування, розриву
наждачного паперу та віддачі.
3.6Особливі вказівки з техніки безпеки
при виконанні робіт з дротяними
щітками:
a) Приміть до уваги, що дротяні щітки
втрачають шматочки дроту також при
звичайному використанні. Не прикладайте
занадто високе притискне зусилля.
Відлітаючі шматочки дроту можуть легко
проходити скрізь тонку тканину одягу та/або
проникати в шкіру.
b) При використанні захисного кожуха не
допускайте його контакту з дротяною
щіткою. Тарілчасті і чашкові щітки під дією
притискного зусилля і відцентрових сил можуть
збільшувати свій діаметр.
3.7 Додаткові вказівки з техніки безпеки:
ПОПЕРЕДЖЕННЯ – Завжди надягайте
захисні окуляри.
Використовуйте еластичні вкладки, якщо вони
входять до комплекту абразивних інструментів і
виробник наполягає на їх використанні.
Дотримуйтесь рекомендацій виробника
інструменту та приладдя! Захищайте диски від
потрапляння мастила та ударів!
Зберігайте шліфувальні диски та поводьтеся з
ними відповідно до вказівок виробника.
Ніколи не використовуйте відрізні шліфувальні
диски для обдирних робіт! Треба уникати
бічного тиску на відрізний шліфувальний диск.
Заготовка повинна надійно прилягати до
поверхні та бути закріплена від зісковзування,
наприклад, за допомогою затискних пристроїв.
Для великих заготовок треба передбачити
достатню опору.
Page 27

При використанні інструментальних насадок з
різьбовою вставкою кінець шпинделя не
повинен торкатися перфорованої основи
абразивного інструменту. Переконайтеся, що
різьба інструментальної насадки має достатню
довжину для кріплення до шпинделя. Різьба
інструментальної насадки повинна співпадати з
різьбою шпинделя. Дані щодо довжини та
різьби шпинделя див. на стор. 3 та в розділі 12.
Технічні характеристики.
Рекомендується використовувати стаціонарну
витяжну установку і підключати пристрій
захисного відключення (ПЗВ). Після
відключення кутової шліфмашини пристроєм
захисного відключення треба перевірити та
почистити машину. Про чищення двигуна див. у
розділі 8. Чищення.
Не використовуйте пошкоджені, ексцентричні
та вібруючі інструментальні насадки.
Уникайте пошкодження газових та
водопровідних труб, електричної проводки та
несучих стін (статика).
Перед проведенням робіт з налаштування,
переоснащення або обслуговування витягніть
вилку з розетки.
Пошкоджену або потріскану додаткову
рукоятку слід замінити. Не експлуатуйте
машину з пошкодженою рукояткою.
Пошкоджений або потрісканий захисний кожух
слід замінити. Не експлуатуйте машину з
пошкодженим захисним кожухом.
Цей електроінструмент не призначений для
полірування. Гарантійні претензії не
приймаються при використанні не за
призначенням! У разі перегріву двигуна
електроінструмент може отримати
ушкодження. Для полірувальних робіт ми
рекомендуємо нашу кутову полірувальну
машину.
Закріплюйте малі заготовки. Використовуйте,
наприклад, лещата.
Зниження впливу пилу
ПОПЕРЕДЖЕННЯ — пил, що утворився
внаслідок шліфування наждачним
папером, розпилювання, шліфування,
свердління та інших видів робіт, містить хімічні
речовини, що спричиняють рак, вроджені
дефекти або інші ушкодження репродуктивної
системи. Приклади таких хімічних речовин:
-свинець у фарбі з вмістом свинцю
-мінеральний пил з будівельної цегли, цементу
та інших речовин цегляної кладки, а також
-миш’як та хром з хімічно обробленої деревини.
Ступінь ризику залежить від того, як часто ви
виконуєте цей вид робіт. Щоб зменшити вплив
від хімічних речовин: працюйте в приміщеннях з
достатньою вентиляцією та з затвердженим
особистим захисним спорядженням, як-от
респіратор, розроблений спеціально для
фільтрації мікроскопічних частинок.
Це також стосується пилу від інших матеріалів,
наприклад деяких видів дерева (деревинний
пил дуба або бука), металу, азбесту. Інші відомі
УКРАЇНСЬКА uk
захворювання — це, наприклад, алергічні
реакції, захворювання дихальних шляхів.
Уникайте потрапляння пилу усередину тіла.
Дотримуйтесь правил та приписів стосовно
вашого матеріалу, персоналу, сфери та місця
використання (наприклад, положення про
охорону праці, утилізацію тощо).
Забезпечуйте вловлювання пилу в місці
утворення, не допускайте його відкладення на
поверхнях.
Для спеціальних робіт використовуйте
відповідне приладдя. Це дозволить зменшити
кількість часток, що неконтрольовано
потрапляють у довкілля.
Використовуйте відповідні засоби уловлювання
пилу.
Для зменшення впливу пилу:
-не направляйте потік повітря, що виходить з
інструмента, на себе, людей, які знаходяться
поблизу, та на скупчення пилу;
-використовуйте витяжний пристрій та/або
очищувач повітря;
-добре провітрюйте робоче місце та
забезпечуйте чистоту за допомогою пилососа.
Підмітання та видування підіймає пил у
повітря.
-Захисний одяг треба пилососити або прати.
Не можна його продувати, вибивати або
чистити щіткою.
4. Огляд
Див. стор. 2.
1Опорний фланець
2Шпиндель
3Кнопка фіксації шпинделя
4Перемикач для включення/виключення
5Рукоятка
6Додаткова рукоятка
7Захисний кожух
8Гайка з двома отворами
9Ключ під два отвори
10 Затискний гвинт
11 Затискне кільце
* залежно від моделі / не входить у комплект
постачання
5. Введення в експлуатацію
Перед початком роботи переконайтеся,
що вказані на технічній табличці приладу
напруга та частота в мережі співпадають з
даними вашої електромережі.
Завжди підключайте пристрій захисного
відключення (ПЗВ) з максимальним
струмом витоку 30мА.
5.1Встановлення додаткової рукоятки
При виконанні будь-яких робіт завжди має
бути встановлена додаткова рукоятка (6)!
Додаткова рукоятка кріпиться з лівого або
правого боку машини.
27
Page 28

УКРАЇНСЬКАuk
5.2 Встановлення захисного кожуха
З причин безпеки використовуйте
захисний кожух, призначений для
відповідних абразивних інструментів! Див.
також розділ 9. Приладдя!
Захисний кожух для шліфування
Призначений для роботи з обдирними дисками,
ламельними шліфувальними кругами,
алмазними відрізними дисками.
див. стор. 2, мал. С.
-Відкрутіть затискний гвинт (10) для
забезпечення достатньої ширини затискного
кільця (11) захисного кожуха.
-Встановіть захисний кожух (7) на вказане
місце.
-Поверніть кожух закритою стороною до
користувача.
-Міцно затягніть (10) затискний гвинт.
Перевірте надійність кріплення: захисний
кожух (7) не повинен повертатися.
Використовуйте
інструментальні насадки,
які захисний кожух
перекриває не менше, ніж
на 3,4 мм.
6. Встановлення
шліфувального диска
Перед будь-якими роботами з
переоснащення завжди витягайте вилку з
розетки. Машина повинна бути вимкнена,
шпиндель повинен зупинитися.
При роботі з відрізними дисками з метою
безпеки користуйтеся захисним кожухом
для відрізання абразивними дисками (див.
розділ 9. Приладдя).
6.1Фіксація шпинделя
-Натисніть кнопку фіксації шпинделя (3) та
поверніть
шпиндель (2) рукою, доки кнопка не
зафіксується.
6.2 Встановлення шліфувального диска
див. стор. 2, мал. А.
-Встановіть опорний фланець (1) на шпиндель.
Фланець встановлений правильно, якщо він не
обертається на шпинделі.
Тільки для W 650-100: накрутіть опорний
фланець ключем під два отвори на шпиндель
так, щоб невеликий буртик (діаметром 16 мм)
був обернений догори.
-Покладіть шліфувальний диск на опорний
фланець (1). Шліфувальний диск повинен
рівномірно прилягати до фланця.
6.3Затягнення/відкручування гайки з
двома отворами
Затягнення гайки з двома отворами (8):
Гайка з двома отворами має дві різні сторони.
Накрутіть гайку з двома отворами на шпиндель,
як показано на малюнку:
див. стор. 2, мал. В.
- X) Для тонких шліфувальних дисків:
Буртик гайки з двома отворами (8) повернутий
догори, що забезпечує надійний затиск тонких
дисків.
Y) Для товстих шліфувальних дисків:
Буртик гайки з двома отворами (8) повернутий
донизу, що забезпечує надійне розташування
гайки на шпинделі.
Z) Тільки для W 650-100:
Буртик гайки з двома отворами повернутий
донизу, а рівна поверхня - догори.
-Зафіксуйте шпиндель. Затягніть гайку з двома
отворами (8) відповідним ключем (9) за
годинниковою стрілкою.
Відкручування гайки з двома отворами:
-Зафіксуйте шпиндель (див. розділ 6.1).
Відкрутіть гайку з двома отворами (8)
відповідним ключем (9) проти годинникової
стрілки.
7. Експлуатація
7.1Увімкнення/вимкнення
Інструмент завжди треба тримати обома
руками.
Підводьте до заготовки тільки увімкнений
інструмент.
Стежте за тим, щоб інструмент не втягував
зайвий пил і тирсу. При увімкненні та
вимкненні тримайте його подалі від скупчень
пилу. Не кладіть вимкнений електроінструмент
до повної зупинки двигуна.
Не допускайте неумисного запуску:
завжди вимикайте інструмент, якщо вилка
була витягнута з розетки або якщо стався збій в
подачі електроенергії.
У режимі безперервної роботи інструмент
продовжує працювати, навіть якщо він
вирветься з рук. Тому завжди міцно тримайте
інструмент двома руками за рукоятку, займіть
стійке положення і повністю сконцентруйтеся
на виконуваній роботі.
Інструменти з перемикачем:
4
0
Увімкнення: пересуньте перемикач (4) уперед.
Для роботи у безперервному режимі
пересуньте перемикач назад до фіксації.
Вимкнення: натисніть на задній кінець
перемикача (4) і відпустіть.
I
28
Page 29

7.2Робочі вказівки
Стандартне шліфування і шліфування
наждачним папером:
Притискуйте інструмент з помірним зусиллям і
переміщуйте його по поверхні назад і вперед,
щоб поверхня заготовки не перегрівалася.
Обдирні роботи: для отримання доброго
результату працюйте з кутом нахилу 30°- 40°.
Відрізання абразивними дисками:
Працюйте з помірною подачею, відповідно до
оброблюваного матеріалу. Не допускайте
перекосу, не натискайте і не розгойдуйте
інструмент.
Обробка дротяними щітками:
помірно притискуйте інструмент.
При відрізанні абразивними
дисками завжди працюйте в
зустрічному напрямі (див.
малюнок). Інакше інструмент може
несподівано вискочити з пропилу.
8. Очищення
При роботі можливе скупчення часток
оброблюваного матеріалу усередині
електроінструменту. Це погіршує охолодження
електроінструменту. Струмопровідні скупчення
можуть погіршити захисну ізоляцію
електроінструменту, що викликає ризик
ураження електричним струмом.
Через невеликі рівні проміжки часу ретельно
очищуйте передні і задні вентиляційні щілини
електроінструменту або продувайте їх сухим
повітрям. Перед цим від'єднайте
електроінструмент від джерела живлення і
надіньте захисні окуляри і респіратор.
Звертайте увагу на технічно правильну витяжку
при видуванні.
9. Приладдя
Використовуйте тільки оригінальне приладдя
Metabo.
Див. стор. 4.
Використовуйте тільки те приладдя, яке
відповідає вимогам і параметрам цієї інструкції з
експлуатації.
AЗатиск захисного к ожуха для відрізання
/ захисний кожух для абразивного
відрізання
Призначений для роботи з відрізними кругами,
алмазними відрізними кругами. Зі
встановленим затиском захисного кожуха для
відрізання інструмент можна використовувати
для абразивного відрізання.
BЗахист рук
Призначений для робіт з опорною тарілкою,
шліфувальною тарілкою, дротяними щітками й
алмазними кільцевими свердлами для плитки.
Захисний елемент установлюється під бічну
додаткову рукоятку.
CГайка з двома отворами (8)
УКРАЇНСЬКА uk
Повний асортимент приладдя див. на сайті
www.metabo.com або в каталозі.
10. Ремонт
Ремонт електроінструмента повинен
здійснюватися тільки кваліфікованими
фахівцями-електриками!
Для ремонту електроінструмента Metabo
звертайтесь до регіонального представництва
Metabo. Адреси див. на сайті www.metabo.com.
Списки запасних частин можна завантажити на
сайті www.metabo.com.
11. Захист довкілля
Пил, що утворюється при шліфуванні, може
містити шкідливі речовини, тому його слід
утилізувати належним чином окремо від
побутових відходів, в призначених для цього
місцях.
Дотримуйтеся національних правил безпечної
утилізації і переробки використаних
інструментів, пакувальних матеріалів і
приладдя.
Тільки для країн ЄС: не утилізуйте
електроінструменти разом з побутовими
відходами! Згідно з директивою ЄС 2012/
19/ЄС про електричні та електронні пристрої та
відповідними національними нормами
відпрацьовані електроінструменти підлягають
роздільній утилізації з метою їх подальшої
екологічно безпечної переробки.
12. Технічні характеристики
Пояснення до даних, наведених на стор. 3.
Залишаємо за собою право на технічні зміни.
Ø=макс. діаметр інструментальної
t
max,1
t
max,3
M=різьба шпинделя
l=довжина шліфувального шпинделя
n=частота обертання на холостому ході
P
P
m=вага без кабелю
Результати вимірювань отримані згідно зі
стандартом EN 60745.
~
На вказані технічні характеристики
поширюються допуски, передбачені чинними
стандартами.
насадки
=макс. допустима товщина
інструментальної насадки в області
затиску при використанні гайки з
двома отворами (8)
=обдирний/відрізний диск:
макс. допустима товщина
інструментальної насадки
(максимальна)
=номінальна споживана потужність
1
=віддавана потужність
2
Інструмент класу захисту ІІ
Змінний струм
Значення емісії шуму
29
Page 30

УКРАЇНСЬКАuk
Ці значення дозволяють оцінювати і
порівнювати емісію шуму різних
електроінструментів. Залежно від умов
експлуатації, стану електроінструмента або
робочих інструментів фактичне навантаження
може бути вище або нижче. Для оцінки
зразкового рівня емісії враховуйте перерви в
роботі та фази роботи зі зниженим (шумовим)
навантаженням. Визначте перелік
організаційних заходів щодо захисту
користувача з урахуванням тих чи інших
значень емісії шуму.
Сумарне значення вібрації
напрямів) розраховується у відповідності зі
стандартом EN 60745:
a
h, SG
a
h, DS
K
h,SG/DS
Рівень звукового тиску за типом А
L
pA
L
WA
K
pA
=значення вібрації
(шліфування поверхонь)
=значення вібрації
(шліфування шліфувальною
тарілкою)
= коефіцієнт похибки (вібрація)
=рівень звукового тиску
=рівень звукової потужності
, KWA= коефіцієнт похибки
Використовуйте захисні навушники!
( векторна сума трьох
:
30
Page 31

使用说明
1. 特定使用条件
安装有麦太保原厂配件的角磨机,适用于干式研
磨、砂光、切断、钢丝刷磨金属、混凝土、石材以
及类似材料。
用户自行承担因使用不当造成的任何损坏的责任。
必须遵守通用事故预防规章和随附的安全资料。
2. 一般安全说明
为了您自身的安全及保护您的电动工具,
请特别注意标有此符号的所有文本!
警告 – 仔细阅读使用说明可降低受伤风险。
警告 – 请仔细阅读所有安全警告和说明。
果未遵守这些安全警告和说明,可能导致电
击、火灾和/或人员重伤。
保存好所有警告和说明以备查阅。
转交电动工具时,请一并转交这些文件。
3. 特殊安全说明
3.1 砂磨、砂光、钢丝砂光、抛光或砂磨切割操
作的通用安全警告
a) 该电动工具是用于实现砂轮机、砂光机、钢丝
刷、抛光机或切断工具功能的。阅读随该电动工
具提供的所有安全警告、说明、图解和规定。不
了解以下所列所有说明将导致电击、着火和/或严
重伤害。
b) 该电动工具不适用于抛光等作业。若强行用该
工具进行不适当操作,则可能会造成危险和人身
伤害。
c) 不使用非工具制造商推荐和专门设计的附件。
否则该附件可能被装到你的电动工具上,而它不
能保证安全操作。
d) 附件的额定速度必须至少等于电动工具上标出
的最大速度。附件以比其额定速度大的速度运转
会发生爆裂和飞溅。
e) 附件的外径和厚度必须在电动工具额定能力范
围之内。不正确的附件尺寸不能得到充分防护或
控制。
如
简体中文 PRC
f) 砂轮、法兰盘、靠背垫或任何其他附件的轴孔
尺寸 必须适合于安装到电动工具的主轴上。带轴
孔的、与电动工具安装件不配的附件将会失稳、
过度振动并会引起失控。
g) 不要使用损坏的附件。在每次使用前要检查附
件,例如砂轮是否有碎片和裂缝,靠背垫是否有
的裂缝、撕裂或过度磨损,钢丝刷是否松动或金
属丝是否断裂。如果电动工具或附件跌落了,检
查是否有损坏或安装没有损坏的附件。检查和安
装附件后,让自己和旁观者的位置远离旋转附件的
平面,并以电动工具最大空载速度运行 1 分钟。
损坏的附件通常在该试验时会碎裂。
h) 戴上防护用品。根据适用情况,使用面罩、
安全护目镜或安全眼镜。适用时,戴上防尘面
具、听力保护器、手套和能挡小磨料或工件碎片
的工作围裙。眼防护罩必须挡住各种操作产生的
飞屑。防尘面具或口罩必须能过滤操作产生的颗
粒。长期暴露在高强度噪声中会引起失聪。
i) 让旁观者与工作区域保持一定安全距离。任何
进入工作区域的人必须戴上防护用品。工件或破
损附件的碎片可能会飞出并引起紧靠着操作区域
的旁观者的伤害。
j) 当在切割附件有可能切割到暗线或自身电线的
场所进行操作时,只能通过绝缘握持面来握住电动
工具。切割附件碰到一根带电导线可能会使电动工
具的外露金属零件带电并使操作者发生电击危险。
k) 使软线远离旋转的附件。如果控制不当,软线
可能被切断或缠绕,并使得你的手或手臂可能被
卷入旋转附件中。
I) 直到附件完全停止运动才放下电动工具。旋转
的附件可能会抓住表面并拉动电动工具而让你失
去对工具的控制。
m) 当携带电动工具时不要开动它。意外地触及旋
转附件可能会缠绕你的衣服而使附件伤害身体。
n) 经常清理电动工具的通风口。电动机风扇会将
灰尘吸进机壳,过多的金属粉末沉积会导致电气
危险。
o) 不要在易燃材料附件操作电动工具。火花可能
会点燃这些材料。
p) 不要使用需用冷却液的附件。用水或其他冷却
液可能会导致电腐蚀或电击。
31
Page 32

PRC 简体中文
3.2 反弹和相关警告
反弹是因卡住或缠绕住的旋转砂轮、靠背垫、钢
丝刷或其他附件而产生的突然反作用力。卡住或
缠绕会引起旋转附件的迅速堵转,随之使失控的
电动工具在卡住点产生与附件旋转方向相反的
运动。
例如,如果砂轮被工件缠绕或卡住,伸入卡住点
的砂轮边缘可能会进入材料表面而引起砂轮爬出
或反弹。砂轮可能飞向或飞离操作者,这取决于
砂轮在卡住点的运动方向。在此条件下砂轮也可
能碎裂。
反弹是电动工具误用和/或不正确操作工序或条件
的结果,可以通过采取以下给出的适当预防措施
得以避免。
a) 保持紧握电动工具,使你的身体和手臂处于正
确状态以抵抗反弹力。如有辅助手柄,则要一直
使用,以便最大限度控制住起动时的反弹力或反
力矩。如采取合适的预防措施,操作者就可以控
制反力矩或反弹力。
b) 绝不能将手靠近旋转附件。附件可能会反弹碰
到手。
c) 不要站在发生反弹时电动工具可能移动到的
地方。反弹将在缠绕点驱使工具逆砂轮运动方向
运动。
d) 当在尖角、锐边等处作业时要特别小心。避免
附件的弹跳和缠绕。尖角、锐边和弹跳具有缠绕
旋转附件的趋势并引起反弹的失控。
e) 不要附装上锯链、木雕刀片或带齿锯片。这些
锯片会产生频繁的反弹和失控。
3.3 对磨削和砂磨切割操作的专用安全警告
a) 只使用所推荐的砂轮型号和为选用砂轮专门设
计的护罩。不是为电动工具设计的砂轮不能充分
得到防护,是不安全的。
b) 护罩必须牢固地装在电动工具上,且放置得最
具安全性,只有最小的砂轮部分暴露在操作人面
前。护罩帮助保护操作者免于受到爆裂砂轮碎片
和偶然触及砂轮的危险。
c) 砂轮只用作推荐的角途。例如:不要用切割砂
轮的侧面进行磨削。施加到砂轮侧面的力可能会
使其碎裂。
d) 始终为所选砂轮选用未损坏的、有恰当规格和
形状的砂轮法兰盘。合适的砂轮法兰盘支承砂轮
可以减小砂轮破裂的可能性。切割砂轮的法兰盘
可以不同于砂轮法兰盘。
e) 不要使用从大规格电动工具上用剩的磨损砂
轮。用于大规格电动工具上的砂轮不适于较小规
格工具的高速工况并可能会爆裂。
3.4 对砂轮切割操作的附加专用安全警告
a) 不要“夹”住切割砂轮或施加过大的压力。不
要试图做过深的切割。给砂轮施加过应力增加了
砂轮在切割时的负载,容易缠绕或卡住,增加了
反弹或砂轮爆裂的可能性。
b) 身体不要对着旋转砂轮,也不要站在其后。当
把砂轮从操作者身边的操作点移开时,可能的反
弹会使旋转砂轮和电动工具朝你推来。
c) 当砂轮被卡住或无论任何原因而中断切割时,
关掉电动工具并握住工具不要动,直到砂轮完全
停止。决不要试图当砂轮仍然运转时使切割砂轮
脱离切割,否则会发生反弹。调查并采取校正措
施以消除砂轮卡住的原因。
d) 不能在工件上重新起动切割操作。让砂轮达到
全速后再小心地重新进入切割。如果电动工具在工
件上重新起动,砂轮可能会卡住、爬出或反弹。
e) 支撑住板材或超大工件可使得砂轮卡住和反弹
的危险降到最低限度。大工件凭借自重而下垂。
必须在工件靠近切割线处和砂轮两侧近工件边缘
处放置支承。
f) 当进行“盲切割”进入墙体或其他盲区时要格
外小心。伸出的砂轮可能会割到煤气管或水管,
电线或由此引起反弹的物体。
3.5 砂光操作的专用安全警告
a) 当砂光时,不要使用超大砂盘纸。选用砂盘纸
时应按照制造商的推荐。超出砂光垫盘的大砂盘
纸有撕裂的危险并且会引起缠绕、砂盘的撕裂或
反弹。
3.6 钢丝刷操作的专用安全警告
a) 要意识到即使正常操作时钢丝线也会随刷子甩
出。不要对钢丝刷施加过大的负荷而使得钢丝线
承受过应力。钢丝线可能会轻易刺入薄的衣服和/
或皮肤内。
32
Page 33

b) 如果建议钢丝刷使用护罩,则不允许该护罩对
钢丝轮或钢丝刷有任何干扰。钢丝轮或钢丝刷在
工作负荷和离心力作用下直径会变大。
3.7 附加安全说明:
警告 – 务必始终佩戴护目镜。
如果制造商为研磨件配备了研磨介质,请在必要
时使用。
请遵循工具或配件制造商的规格说明!保护研磨
盘免受油脂侵蚀或冲撞损坏!
遵照制造商说明,细心存放并使用磨轮。
切勿使用切断砂轮进行粗加工作业!不得在切断
砂轮侧面施加压力。
工件必须平放并加以固定从而防止滑动,例如,
使用夹具固定。大型工件必须加以充分支承。
如果使用附带螺纹插入件的配件,则主轴末端不
得触及砂磨工具孔底。应确保配件螺纹长度足以
容纳主轴总长度。配件螺纹必须与主轴螺纹吻
合。请参见第 3 页和第 14 章“技术规格”,了解
主轴长度和螺纹的详细信息。
建议使用固定除尘系统,并在下游安装一个接地
故障断路器 (GFCI)。如果通过 GFCI 关闭角磨机,
则必须对其进行检查和清洁。请参见第 9 章“清
洁”,了解关于清洁电机的详细信息。
切勿使用损坏的、偏心的或振荡的工具。
避免损坏燃气管道或水管、电线和承重墙(建筑
结构)。
在调试、更换或维修工具前,请将主电源拔下。
必须更换损坏或破裂的附加手柄。切勿使用存在
问题的附加手柄操纵工具。
必须更换损坏或破裂的护罩。切勿使用存在问题
的护罩操纵工具。
该电动工具不适合抛光作业。工具使用不当会使
保修失效!电机可能会过热并损坏电动工具。我
们建议使用角抛光机进行抛光作业。
固定小工件,例如使用老虎钳固定。
减少粉尘暴露:
警告 - 使用此电动工具进行砂光、切割、研
磨、钻孔及其他施工作业时产生的部分粉尘
简体中文 PRC
可能包含已知可导致癌症、先天缺陷或其他生殖危
害的化学物质。此类化学物质的一些示例包括:
- 含铅油漆中的铅,
- 砖块、水泥及其他石材产品的结晶二氧化硅,
以及
- 经化学处理的木材中的砷和铬。
暴露于此类物质所带来的风险取决于操作人员进
行此类工作的频率。为降低对这些化学物质的暴
露程度:在通风良好的区域作业,并穿戴经认可
的防护装备,例如专为过滤微小颗粒而设计的防
尘面罩等。
这同样适用于其他材料的粉尘,如木材(橡木或
榉木粉尘)、金属、石棉。已知可导致的其他疾
病包括过敏反应、呼吸系统疾病等。切勿吸入这
些粉尘。
遵守物料、员工、应用和应用地点的相关准则和
国家规定(例如,职业卫生与安全法规、废物处
理规范等)。
从源头收集产生的颗粒,避免在周围环境中沉积。
对于特殊作业,使用适当的配件。这样一来,肆
意侵入环境的微粒将减少。
使用适当的除尘装置。
通过以下措施降低粉尘暴露程度:
- 请勿将颗粒和废气流朝向自己或附近人员逃逸
或排放,也不要将其朝向沉积的粉尘。
- 使用除尘装置和/或空气净化器。
- 确保工作区域通风良好,使用真空吸尘器保证
工作区域的清洁。吹扫会使粉尘飞散。
- 使用吸尘器或水清洁防护服。请勿吹、打或刷
防护服。
4. 概述
请参见第 2 页。
1 支承法兰
2 主轴
3 主轴锁定按钮
4 滑动开关
5 手柄
6 侧向手柄
7 安全罩
33
Page 34

PRC 简体中文
8 2 孔螺母
9 2 孔扳手
10 夹紧螺钉
11 夹紧环
* 取决于具体型号/不在交付范围内
5. 首次运行
调试前,请查看额定电源电压及频率(标在
铭牌上)是否与现有的电源相同。
务必在上游安装一个最大脱扣电流为 30 mA
的 RCD。
5.1 安装附加手柄
作业中务必始终使用加装的手柄 (6)!将手柄
加装在工具左侧或右侧并固定到位。
5.2 安装护罩
出于安全原因,请务必一直使用为各个砂轮相
应配备的护罩。另请参见第 10 章“配件”!
研磨护罩
专为粗砂轮、翼片砂光垫、金刚石切割片作业设计。
请参见第 2 页中的插图 C。
- 旋松夹紧螺钉 (10),直至护罩上的夹紧环 (11)
完全松开。
- 将护罩 (7) 置于图示的位置。
- 转动护罩,直至闭合的防护部分面向操作者。
- 牢牢拧紧夹紧螺钉 (10)。确保护罩已固定到位 -
护罩 (7) 应无法转动。
务必让护罩罩住配件至少
3.4 mm。
6. 安装磨轮
在更换任何配件之前:请将主电源线从插座
上拔出。工具必须切断,主轴必须静止。
出于安全考虑,请在进行研磨切断作业之前安
装研磨切断护罩(请参见第 10 章“配件”)。
6.1 锁定主轴
- 按下主轴锁定按钮 (3),手动转动主轴 (2),直至
主轴锁定按钮已卡合到位。
34
6.2 放置磨轮到位
请参见第 2 页中的插图 A。
- 在主轴上安装支承法兰 (1)。一旦正确安装完毕,
法兰将无法在主轴上转动。
仅适用于 W 650-100:使用 2 孔扳手将支承法兰
拧到主轴上,使小套管(直径 16 mm)朝上。
- 将磨轮置于支承法兰 (1) 之上。磨轮在支承法兰
上必须摆平。
6.3 拧紧/松开 2 孔螺母
拧紧 2 孔螺母 (8):
2 孔螺母的两个侧面并不相同。按照以下步骤将
2 孔螺母旋拧到主轴上:
请参见第 2 页中的插图 B。
- X) 对于薄研磨盘:
2 孔螺母 (8) 的边沿朝上,从而可安装固定薄研
磨盘。
Y) 对于厚研磨盘:
2 孔螺母 (8) 的边沿朝下,从而可将 2 孔螺母安
装固定在主轴上。
Z) 仅适用于 W 650-100:
2 孔螺母的套管朝上/朝下。
- 锁定主轴。使用 2 孔扳手 (8) 顺时针拧紧 2 孔螺
母 (9)。
松开 2 孔螺母:
- 锁定主轴(参见章节 7.1)。使用 2 孔扳手 (8)
逆时针松开 2 孔螺母 (9)。
7. 使用
7.1 接通和切断
务必始终双手操纵工具。
首先接通工具,然后将配件移向工件。
不得让工具吸入多余的粉尘和削屑。接通与
切断时,工具应远离沉积的粉尘。一旦接通
工具,只有在电机停止后才能放下工具。
避免意外启动:从主插座拔下插头或停电
时,务必关闭工具。
连续工作期间,如过电动工具脱手,它会继
续运转。因此,双手必须始终握住工具的手
柄,站稳,专心工作。
Page 35

配备滑动开关的工具:
4
0
I
接通:向前推移滑动开关 (4)。如需持续运行,则
向下斜压,直至其卡合到位。
切断:按下滑动开关 (4) 后端,然后松开。
7.2 工作方向
研磨和砂光操作:
平稳均匀地压低工具并前后移动,以使工件表面
不至于过热。
粗研磨:将工具置于 30° - 40°角的位置,以确保实
现最佳作业效果。
研磨切断:
切断作业方向应始终与砂轮转动方向
相反(如图)。否则工具将失控并从
切口处反弹。以适于工件的速度平稳
均匀地移动工具。切勿倾斜、用力过
猛或左右摇摆。
钢丝刷磨:
平稳均匀地压低工具。
8. 清洁
在操作过程中,微粒可能会在电动工具内部堆
积。这会对电动工具降温造成不利影响。导电粉
尘的堆积会破坏电动工具的绝缘保护并引发电气
危险。
应使用真空吸尘器或通过吹送干燥空气的方式,定
期彻底清洁电动工具的所有前后通风口。进行该操
作之前,请切断电动工具的电源并佩戴护目镜和防
尘面罩。吹出通风口时,确保有适当的吸力。
9. 配件
只能使用麦太保原厂配件。
请参见第 4 页。
仅可使用符合使用说明中所列要求及规格的配件。
A 用于研磨切断作业的切割防护夹/护罩
专为切割片和金刚石切割片而设计。安装切割防
护夹后,护罩即为切割护罩。
简体中文 PRC
B 手部防护
专为背垫、砂磨板、钢丝刷以及用于瓷砖的托
板、砂光垫、钢丝刷和金刚石钻头而设计。
在侧装的附加手柄下安装护手。
C 2 孔螺母 (8)
如需了解全部配件,请访问 www.metabo.com 或
参见配件目录。
10. 维修
只能由合格的电工修理电动工具!
如果需要维修麦太保电动工具,请联系您当地的
麦太保代表。有关具体地址,请参见
www.metabo.com。
您可以从 www.metabo.com 下载配件列表。
11. 环境保护
产生的砂光粉尘包含危险物质:请勿随生活垃圾一
同处置,而应在危险废物的特定收集点进行处置。
有关废弃的工具、包装和配件的环保性处置及回
收,请遵循国家相关规定。
仅适用于欧盟国家/地区:不得将电动工具
与生活垃圾一同处置!根据欧盟关于废旧电
子和电气设备的指令 2012/19/EU 及其在国
家法律系统中的实施方案,废旧的电动工具必须
单独收集并以环保的方式回收。
12. 技术规格
对规格的解释性说明请见第 3 页。保留因技术发展
而进行变更的权利。
Ø = 配件最大直径
t
= 使用 2 孔螺母 (8) 时配件夹柄的最大允许
max,1
t
max,3
M = 主轴螺纹
l = 砂磨主轴长度
n
P
P
厚度
= 粗加工盘/切割盘:
配件的最大允许厚度
= 空载转速(最大转速)
= 额定输入功率
1
= 输出功率
2
35
Page 36

PRC 简体中文
m = 不含电源电缆的重量
测量值依照 EN 60745 确定。
工具的防护等级为 II 级
~ 交流电
引用的技术资料皆含有公差值在内(依照相关有
效标准)。
排放值
这些值可用来评估电动工具的排放量,以及
比较不同的电动工具。根据操作条件、使用的电
动工具及配件的情况,实际载荷可能会更高或更
低。当载荷较低,无法进行评估时,请让工具休
息一下。根据调整后的估计值,为使用者安排保
护措施,例如组织措施。
振动总值(三个方向的矢量和)依据 EN 60745
确定:
a
= 振动排放值
h, SG
a
h, DS
K
h, SG/DS
典型 A 荷重声音等级:
LpA = 声压等级
LWA = 声压功率等级
K
pA, KWA
(表面研磨)
= 振动排放值
(使用砂磨板砂光)
= 不确定性(振动)
= 不确定性
佩戴护耳器!
36
Page 37

Page 38

Page 39

Page 40

170 27 6270 - 0119
Metabowerke GmbH
Metabo-Allee 1
72622 Nuertingen
Germany
www.metabo.com
 Loading...
Loading...