MERKLE PU 300 K Operation Manual

Operation Manual
Synergic Pulse Welding Unit
Model PU 300 K
MERKLE
Schweissanlagen-Technik GmbH
Industriestrasse 3
D-89359 Koetz,
Germany
Tel.: ++49-8221-915-0
Fax: ++49-8221-915-40
www.merkle.de

.

Content page
1 Security indications before introduction 3
2 Accident prevention regulations 3
2.1 Safety instructions 3
3 Duty cycle 5
4 Instructions to avoid interferences due to electromagnetic influences EMC 5
5 Technical Data 7
5.1 Synergic Pulse Welding Unit Model PU 300 K 7
5.2 Accessories, water cooling unit, model WK 230 9
6 Start Up 9
6.1 Installation of the Machine 9
6.2 Main Supply 9
6.3 Welding Torch 10
6.4 Gas Connection 10
6.5 Wire Installation 10
6.6 Earth Lead (Work Cable) 10
7 Portable Pulse-Arc Welding Unit Model PU 300 K 10
8 Generalities of the welding unit 11
8.1 Cooling of the power modul 11
8.2 Electronics 11
8.3 TEDAC-System 11
9 Control Panel PU 300 K 13
10 Operation of the Unit PU 300 K 14
10.1 Selection of the welding process 14
10.2 MIG-MAG welding 14
10.3 PULSE welding 14
10.4 INTERPULSE welding 14
10.5 STICK ELECTRODE welding 14
10.6 Setting of the welding energy 14
10.7 Setting of the operation mode 15
10.8 TIG (DC) welding 15
10.9 Adjusting of 'start current', 'down slope' time, 'final current' and 'wire burn back correction' 16
10.10 Safety cut off 17
1

11 Activation of the fixed TEDAC programs 17
11.1 Generating your own TEDAC program 17
12 TIG (DC) operation 18
13 MMA stick electrode –welding 19
14 Maintenance and Accident Prevention 19
15 Cleaning 19
16 Aluminium Welding 20
17 MIG-Brazing 22
18 Trouble Shooting 23
18.1 Machine does not operate after switching on 23
18.2 Machine does not react on the torch switch 23
18.3 Machine has no or too low welding current 23
18.4 Welding Quality is not good 23
18.5 Problems with wire feeding and wire contacting 23
18.6 Burning of the wire core 23
19 Stored programs 24
20 Wire feeder system model DV-25/4 25
21 Torch - and Spare parts 28
22 Wiring diagram and list of machine spares 32
22.1 List of machine spares PU 300 K 32
22.2 Wiring diagram PU 300 K 33
22.3 Spare part list WK 230/300 39
22.4 Wiring diagram WK 230/300 39
23 Conformity Attestation PU 300 K 41
24 Conformity Attestation WK 230/300 42
2

1 Security indications before introduction
The unit device is built after the recognized standards. Safe works are nevertheless only
possible if you read the operating instructions and the safety regulations contained in it
entirely and obey strictly. Install yourselves by trained staff of our establishments or
appointed dealers.
2 Accident prevention regulations
The following accident prevention regulation is applied for pulse arc welding unit, model
PU 300 K
BGV D1 (earlier VBG 15) * Welding, cutting and allied processes.
A copy of this regulation should be readily accessible in every welding shop. The stipulations
of this regulation are to be observed in the interests of safe and correct welding operation.
* Available from the trade association responsible or
Carl Heymanns-Verlag, Luxemburger Strasse 449, 50939 Cologne.
2.1 Safety instructions
This unit is manufactured according to the requirements and stipulations of EN 60974.1 /
VDE 0544 part 1. BGV D1 (earlier VBG 15) of the trade association for precision
engineering and electrical engineering are as well valid.
1) In case of an accident, the cutting unit must be disconnected from the mains
immediately.
2) If electrical contact voltages arise, switch off the unit immediately, disconnect it from
the mains and proceed to inspection by a qualified electrician or by our Service
Department.
3) Before opening the unit, disconnect it from the mains supply.
4) Repair work may only be carried out by a skilled electrician or by our Service
Department.
5) Before the unit is put to operation, check it visually, as well as the torch and all cables
and connectors regarding possible external damages.
6) Personal protective equipment in accordance with DIN EN 175, DIN EN 379 and
DIN EN 169.
During the work, the welder’s body must be completely protected against radiation
and burns by means of protective clothing and face protection. Long gloves, aprons
and welding shields with welding filters conforming to DIN EN 470-1 and BGR 189
must be worn.
Synthetic clothing are excluded. Shoes must be closed, not opened (due to spatters). If
necessary, protective headwear must be worn (e.g. for overhead welding). If cover
glasses are used, these must be in accordance with the norms specified above.
As additional protection for the eyes against UV radiation, safety goggles with side
shields and corresponding face protection in accordance with BGR 192 and BGI 553
must be worn.
Accident prevention regulation BGV D1 § 27 stipulates that it is the responsibility of
the employer to provide suitable personal protective equipment, while § 28 stipulates
that it is the responsibility of the insured to wear suitable clothing.
3

7) Protection when welding under increased electrical risks
Welding rectifiers and welding power sources which can optionally be used for either
direct or alternating current must be marked "S" in accordance with EN 60974-1 and
BGI 534.
Use insulating materials to protect you against contact with electrically conductive
parts and damp floors. Wear dry, undamaged work clothing, long gloves and footwear
with rubber soles. Ventilate rooms, install extraction systems if required, and wear
respiratory protective equipment if necessary (see Procedural instructions BGV D1
§ 27 and BGI 533, Section 5).
8) In order to prevent stray currents and the effects thereof (e.g. destruction of electrical
protective ground conductors), the welding return cable (workpiece cable) must be
connected directly to the workpiece to be welded or to the table (e.g. welding table,
grid-type welding table, workbench) supporting the workpiece (see BGV D1 § 20).
When installing the ground connection, assure that there is a good electrical contact
(remove rust, paint, etc.).
9) During welding pauses, the welding torch is to be laid down on an insulated surface or
hung up in such a way that it is not in contact with the workpiece and its support
connected to the welding power source (see § 20 BGV D1).
In the case of longer work pauses, the welding unit must be switched off and the gas
cylinder valve must be closed.
10) The shielding gas cylinder must always be protected against tumbling downing using a
safety chain.
11) Under no circumstances the unit may be put into operation while it is opened
(e.g. for repair work). Apart from the safety regulations, sufficient cooling of the
electrical components provided by the fan cannot be guaranteed.
12) In accordance with BGV D1 § 5, people in the vicinity of the arc must also be
informed of the hazards and protected against them. Safety partitions (“welding safety
curtains”) must be erected in accordance with DIN EN 1598.
14) N
o welding work may be carried out on containers in which gases, fuels, mineral oils
or similar substances have been stored Öeven if they have been empty for a long
timeÕ (risk of explosion). See § 31 of accident prevention regulation BGV D1.
15) Welds which will be subjected to high loads and which need to meet specific safety
requirements may only be carried out by specially trained and qualified welders.
15) Never bring the torch close to your face.
16) In areas at particularly high risk of fire, the welder must obtain a welding permit and
have this on his person throughout the duration of the welding work. On completion of
welding, a fire-guard must be delegated to ensure fire protection.
17) Ventilation measures must be applied in accordance with BGI 553, Section 9.
18) The hazard to eyesight must be indicated by means of a sign at the work site
"CAUTION! Do not look into the arc!".
4

3 Duty cycle
The duty cylce measurings have been carried out in accordance with
EN 60974-1 / VDE 0544 part 1 (10 min working period).
60% duty cycle means:
After a 6 min. welding period a 4 min welding pause must be respected. The electrical
components are thermally protected against overheating.
4 Instructions to avoid interferences due to electromagnetic influences
EMC
The welding unit has been manufactured in accordance with the requirements of guideline
EN 60974-10 / VDE 0544-part 10 regarding electromagnetic compatibility. It is nonetheless
the responsibility of the user to ensure that the welding equipment is installed and operated in
accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. If electromagnetic interference is detected, it
is the responsibility of the user of the welding equipment to find a solution with the technical
assistance of the manufacturer. In some cases, it may be sufficient simply to ground the
welding current circuit. In other cases, it may be necessary to build a complete shield for the
welding power source and workpiece using the input filters. In all cases, electromagnetic
interference must be reduced to avoid any possible malfunctions.
Note:
For safety reasons, the welding current circuit may or may not be grounded. No
modifications may be made to the grounding without the approval of an expert who is able to
determine whether the changes might increase the risk of accidents, e.g. by allowing parallel
welding current return paths which could destroy the ground conductors of other equipment.
Further instructions are contained in TEC 974-XX "Arc welding equipment – installation and
use".
a) Evaluation of the installation site
Before installing the welding equipment, the user must evaluate potential
electromagnetic problems in the vicinity. The following must be taken into
consideration:
a. Other power cables, control cables, signal and telecommunication cables above, below
and next to the welding equipment
¾ Radio and television transmitters and receivers
¾ Computers and other control devices
¾ The health of people in the vicinity, e.g. use of heart pacemaker and hearing aids
¾ Calibration and measuring equipment
¾ Interference immunity of other devices in the vicinity. The user must ensure the
electromagnetic compatibility of other devices used in the vicinity. This may require
additional safety measures.
b) Procedures to reduce emitted interference
1) Mains supply
Welding equipment is to be connected to the mains in compliance with the
recommendations of the manufacturer. If interference occurs, it may be necessary to
take additional precautions, e.g. filters for the mains connection. Make sure that the
power cable of welding equipment is installed in a fixed position shielded by means of
a metal conduit or similar. The entire length of the shield must be electrically
connected. The shield must be connected to the welding power source in the way to
obtain a good electrical contact between the metal conduit and the housing of the
welding unit.
5

2) Maintenance of the welding equipment
Welding equipment must be maintained regularly in accordance with the
recommendations of the manufacturer. All access and service doors and covers must
be closed and fastened securely when the welding equipment is in operation. No
modifications whatsoever may be made to welding equipment with the exception of
modifications and adjustments specified in the manufacturer’s operating instructions.
3) Welding cables
Welding cables should be kept as short as possible and routed close together on or
near the floor.
4) Equipotential bonding
It is advisable to interconnect all metallic parts in and next to the welding equipment.
Metallic parts connected to the workpiece can, however, increase the risk of the
welder receiving an electric shock by touching these metallic parts and the electrode
simultaneously. The welder must be electrically insulated against all these connected
metallic parts.
5) Grounding the workpiece
If the workpiece is not connected to the ground for electrical safety reasons, or due to
the size and position of the workpiece, e.g. steel structure or outer wall of a ship,
grounding the workpiece may in some cases, but not all, reduce emitted interference. It
must be ensured that grounding the workpiece will not increase the risk of accidents
for the user and cannot cause the destruction of other electrical equipment. If
necessary, the grounding of the workpiece must be carried out by means of a direct
connection to the workpiece. In countries where a direct connection is prohibited, the
connection must be made by means of suitable reactors, selected in accordance with
national regulations.
6) Shielding
Selective shielding of other cables and devices in the vicinity can reduce interference
problems. For special applications, it may be worth considering shielding the entire
welding system.
6

5 Technical Data
5.1 Synergic Pulse Welding Unit Model PU 300 K
Primary:
Power supply: 3 x 380-440 V (3 x 200-240 V)
Frequency: 50/60 Hz
cos phi: 0.99
Synergic pulse / MIG-MAG operation:
Open circuit voltage: 57 V
Welding voltage: 15-29 V
Welding current: 20-300 A
Duty cycle 60 %: 300 A (25°C)
Duty cycle 100 %: 250 A (40°C)
Prim. contin. power: 10.0 kVA
Prim. contin. current: 14 A
Prim. max. current: 19 A
TIG operation:
Open circuit voltage: 57 V
Welding voltage: 10-22V
Welding current: 10-300A
Duty cycle 60 %: 300 A (10 min, 25°C)
Duty cycle 100 %: 260 A (40°C)
Prim. contin. power: 7 kVA
Prim. contin. current: 10 A
Prim. max. current: 14.5 A
MMA/stick electrode operation:
Open circuit voltage: 57 V
Welding voltage: 20-32 V
Welding current: 10-300 A
Duty cycle 60 %: 300 A (10 min, 25°C)
Duty cycle 100 %: 250 A (40°C)
Prim. contin. power: 11.5 kVA
Prim. contin. current: 16.5 A
Prim. max. current: 21 A
Protection class: IP 23
Insulation class: H
Cooling: AF
Main switch: 3-phase
Frequency: 20-500 Hz
Pulse shape: 144 pulse shapes programmable
Ignition process: 13 parameters programmable
Arc length: automatic energy control
Program capacity: 144 Programme
Programs: MIG/MAG, Pulse-Arc, Interpuls,
MMA/stick elektrode, TIG-DC (Lift
Arc), gasless cored wire
7

and MIG brazing, programs for
mild steel, aluminium, alloys,
stainless steel, special program
Program selection: selector 5-step: Pulse/MIG-MAG/
Interpulse/MMA/Stick electode/TIG
selector 6-step: wire diameter
selector 12-step: material
Wire diameter: 0.8/1.0/1.2/1.6 mm + special
Down slope: in 4-stroke mode (latch)
Current program: 4-stroke with start current,
down slope and final current
Energy control: continuous control for energy
and voltage trim, synergic contr.
Operation modes: selector: 2-/4-stroke/4-stroke welding
start current/stitch/spot welding
Gas check: button with hold function
and automatic switch off
Digital display: current and voltage with hold
function and pre-display for
current, voltage, wire feed speed
and material thickness
Energy adjustment: selection by 3-step switch:
potentiometer on the machine,
cont. setting by the TEDAC torch,
10 programs at the TEDAC torch
TIG operation: adjustable down slope time,
adjustable gas post flow time,
second welding current adjustable
at the torch, TIG pulsation
LEDs: mains, failure, temp. protection,
hold function, TIG operation
Button: wire feed
Automated functions: wire burn back (int. adjustable)
soft start (programmable)
Motor controller: 2 Q controller
Power source: inverter
Norm: EN 60974-1 "S" / CE
Torch cooling: gas (option: water)
Connection: 6 pol. for water cooler
Weight: 33 kg
Dimensions l x w x h: 600 x 300 x 565 mm
Sockets 50 mm²: earth lead and electrode cable
Mains supply cable: 4 x 2.5 mm², 5 m long
Gas hose: 2 m
Handle: on top of the machine
Wire feeder: compact mounted
Model DV-25
Supply voltage: 26 V-DC
Wire feed: 4-roller drive system DV-25
0.5 - 25 m/min.
8

Reel hub assembly: D 300/15 DIN 8559
for 5 kg and 15 kg wire spools
Torch connection: EURO connector
Standard wire equipm: steel 1.0 mm
Standard accessories:
Regulator argon/CO2, single stage 012.0.0300
Earth lead 50 mm², 4 m long 022.1.0402
with plug and earth clamp
5.2 Accessories, water cooling unit, model WK 230
Technical data:
Power supply: 1 x 400 V / 230 V
Frequency: 50 Hz (60 Hz)
Mains current: 1 A / 1.6 A
Water pump: high efficient pump 230 V
Water prussure: 3.5 bar
Water capacity: 3 l
Transformer: 400 / 230 V
Water pressure switch: integrated
Functions: automatic switch of fan
and water pump
Electr. connection: cable with 6-pole plug
water connection: 2 quick couplings
Weight: 18 kg
Dimensions L x W x H: 530 x 230 x 215 mm
6 Start Up
6.1 Installation of the Machine
If the unit is brought from cold ambient temperatures into a tempered room, for example due
to transportation or from unheated storage depots, it must be adapted before being put to
operation a certain time according to the temperature difference onto the ambient temperature.
Place the machine at least 0.80 m from a wall etc. to guarantee the cooling air can go
through the unit. The room temperature should not exceed 40°C.
The room were the unit is placed should have a low degree of humidity
(max. 50 % at 40°C, max. 90 % at 20° C).
The unit has passed the quality control in accordance with IP 23.
The air in the surroundings must be free from extreme quantities of dust, free from acides and
corrosive gases etc. Otherwise use air filters.
6.2 Main Supply
The main supply must be connected by a trained person. The main supply voltage is displayed
on the front or rear panel of the machine. A connection to ground (GND) must be done.
9

6.3 Welding Torch
Connect the torch to the Euro-connector.
6.4 Gas Connection
Place the gas bottle on the gas bottle holder and secure it with the safty chain. Remove
the cap and open the bottle momentarily to purge the valve. Install the regulator on the
bottle valve. Connect the gas hose from the machine to the pressure reducer. Slowly open
gas valve and set the gas flow.
6.5
Wire Installation
Place the wire spool over the wire drive. Loosen the end and cut off the bent end section.
Hold the wire to prevent unwinding of the spool. Open the lightning lever and lift the
pressure finger. Feed the wire into the wire feed guide. Push the wire forward onto the
wire drive roller grooves. Close the lightning lever and switch on the machine.
Check the wire feeding: Place your hand 10 cm in front of the contact tip. Let the wire run
into your hand. If the wire is running, the pressure of the drive rollers is o.k.
6.6 Earth Lead (Work Cable)
The earth lead must have an excellent ground. The clamp should be attached to a clean, paint
and rust free area on the work piece or on the welding table.
7 Portable Pulse-Arc Welding Unit Model PU 300 K
The universal welding unit:
This unit disposes of six different welding processes. According to the welding task, the
material and the location, the following welding processes can be realized:
1. MIG/MAG welding
2. Pulse-Arc welding
3. TIG (DC) welding
4. Stick electrode welding
5. Welding of self-shield, cored wires without shield gas (Open Arc)
6. MIG brazing
This unit comes to operation in metal-working medium size companies, workshops,
locksmith's shops, installation companies and on building sites.
Easiest adjusting and a maximum of functions in MIG/MAG and Pulse-Arc welding:
• Continuous one button adjusting.
• Setting and indication of the energy on the TEDAC-welding torch (see rear).
10

• 2-stroke/4-stroke/spot welding/continuous interval switching.
• 4-roller drive wire feeding system.
• Reproducible welding results due to a save microprocessor control
• Proven welding programs for steel, stainless steel, aluminium and its alloys
• Interpulse welding as a standard.
• Recently developped welding arc ignition process.
• Digital read-out for welding current, welding voltage, wire feed speed and material
thickness with pre-indication and HOLD-function.
• Approved for operation in confined areas. S-symbol.
• Option: socket for remote control and push-pull torch.
• As a standard precise 4-roller drive flansh gear with wire insertion automatic. Suitable
for 5 kg or 15 kg wire spools.
• EURO-connection for MIG and TIG welding torches. Fittings for earth lead and
electrode welding cable mounted on the rear. Quick polarity change, welding cored
wire without shield gas, by using different plugs mounted on the rear.
8 Generalities of the welding unit
The welding unit PU 300 K is based on inverter technique, and suitable for MIG/MAG,
Pulse-Arc and MMA/stick electrode welding. Continuous setting of the welding current up to
300 A.
The unit can be characterized by numerous features:
¾ inverter power source with continuous setting of the current 10 - 300 A
¾ socket for remote control
¾ digital read out with pre-display and hold-function
8.1 Cooling of the power modul
The fans which are cooling the power modul are switched on automatically as soon as the arc
is enlighted.
8.2 Electronics
The electronic is divided in to 3 sections:
¾ Display, selection of the logic and the operation mode
¾ Adjusting and program parameters
¾ Supervision of the temperature, fan control
8.3 TEDAC-System
The TEDAC-System offers the possibility to adjust the energy from min. to max. by means of
a slide switch. The poti „energy“ is limiting the range of the welding current.
The multi-coloured LED at the handle inside shows the actual setting of the welding current.
red - max. energy
green - min. energy
11
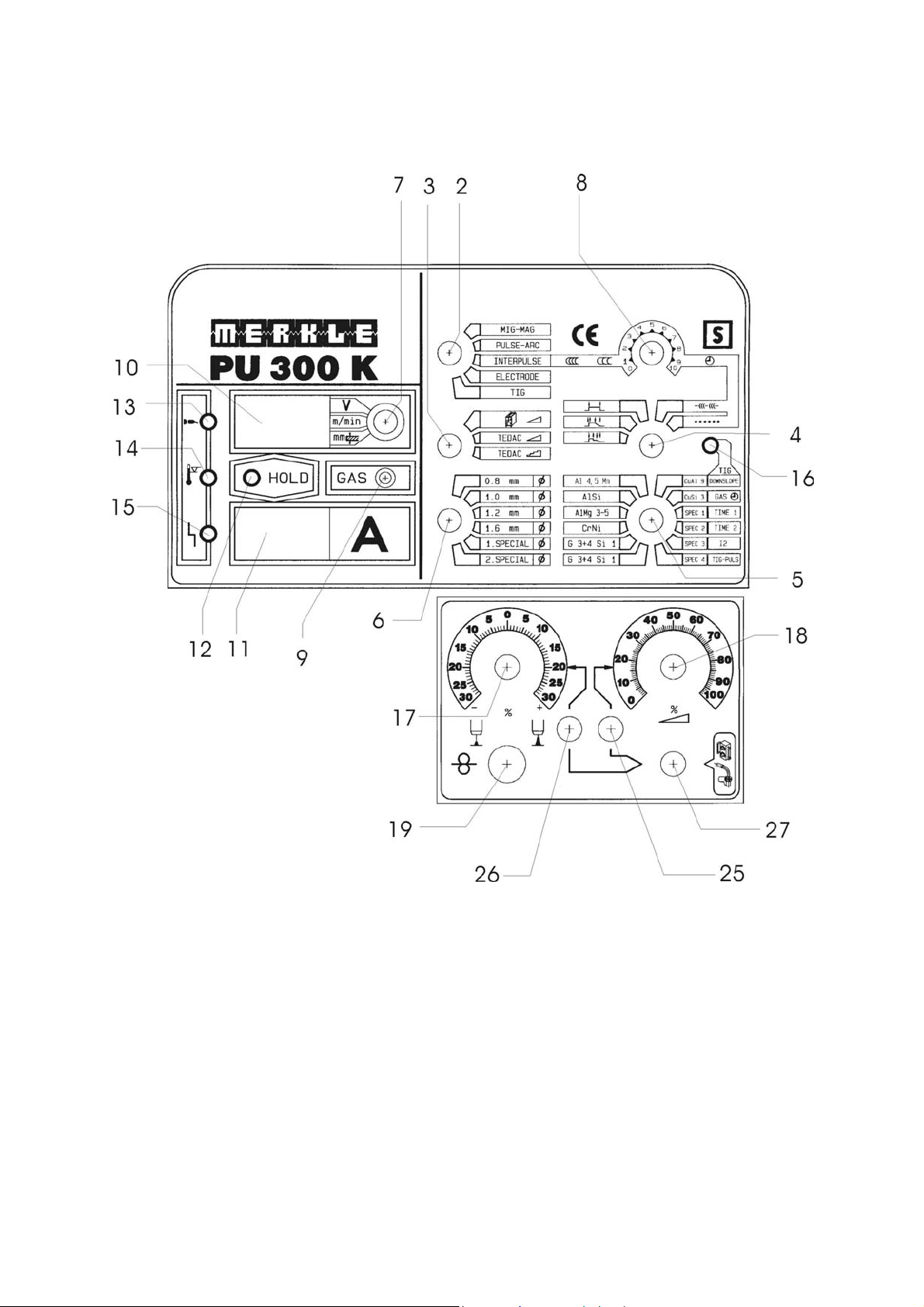
Control Panel PU 300 K
12
 Loading...
Loading...