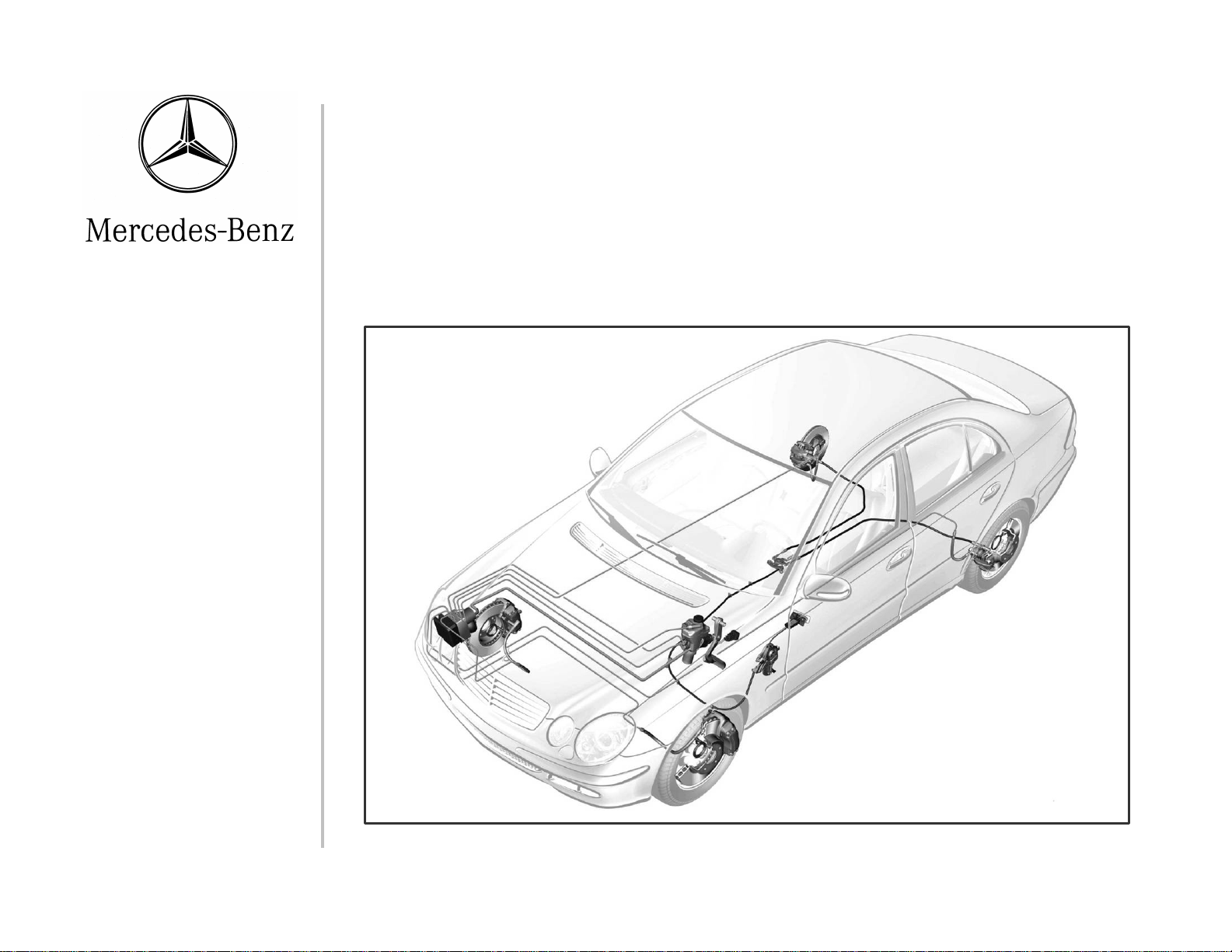
Sensotronic Brake Control
(SBC)
327 HO 09 SBC (WJB) 03 -05-04
1
R230 and W211: Starting MY2003

Objectives
At the end of this presentation, you should be able to:
1. Explain the function of and purpose for SBC
2. Describe the customer interface with SBC
3. List the hydraulic and electronic components used for SBC
4. Describe how the “normal” feel of the brake pedal is maintained
5. Explain emergency operation of the SBC braking system
6. Describe “temperature compensation”
7. Explain “Deactivation” and describe when it is necessary to do it
8. “Activate” the SBC system
9. Locate tools and the proper procedure for bleeding brakes
These technical training materials are current as of the date noted on the materials, and may be revised or updated without notice. Always check for revised or updated information.
To help avoid personal injury to you or others, and to avoid dam age to the vehicle on which you are working, you must always refer to the latest Mercedes-Benz Technical Publication and follow all
pertinent instructions when testing, diagnosing or making repair.
Illustrations and descriptions in this training reference are based on preliminary information and may not correspond to the final US version vehicles. Refer to the official introduction manual and WIS
when available. Copyright Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC, 2004
WIS document numbers shown apply to WIS Version USA/CDN at date of writing.
Reproduction by any means or by any information storage and retr ieval system or translation in whole or part is not permitted without written authorization from Mercedes -Benz USA, LLC or it's
successors. Published by Mercedes-Benz USA, LLC Printed in U. S.A.
2

Contents
Advantages of SBC 5
Driving with SBC 8
SBC components 13
Brake operating unit (BOU) 17
Traction system hydraulic unit 27
Three pressure stages 32
Temperature Compensation 38
Deactivation 39
System activation 42
Bleeding the system 49
3

SBC Incorporates these Functions:
ABS (Anti lock Brakes 1984)
+ ASR (Automatic Slip Regulation 1991)
+ ETS (Electronic Traction System 1995)
+ ESP (Electronic Stability Program 1996)
+ BAS (Brake Assist System 1998)
4

Advantages of SBC
• Improves metering of required brake pressure
– each wheel can be precisely controlled
• Improved BAS function
– monitors release of accelerator pedal and application of
brake
– maximum pressure available immediately
– pre-filling of system (overcoming play)
– when the BAS function is anticipated, slight pressure is
applied
5

Advantages of SBC
• Electronic Brake Proportioning: EBP
– allows brake proportioning front to back and side to side
• No pedal vibration during ABS operation
– eliminates “distraction” to the driver during critical moments
– indicator light in instrument cluster signals traction loss
• Improved driving dynamics: ABS, ASR, and ESP
– faster response to brake request inputs
6

Advantages of SBC
• Pressure reduction at standstill
– reduces stress on components
• Dry braking function
– wiper input via CAN
– ~every 7 to 14 minutes
– brake actuation changes
time interval
7

Driving with SBC - Wake -Up
SBC is functional as soon as it is “wakened” by:
• opening a door (via CAN)
• operating the central locking system (via CAN)
• depressing the brake pedal
• turning key to position 1
• operating parking brake
•The Wake-Up may be followed by a Pre-Drive self
Check performed by SBC
8
Driving with SBC – Pre-Drive Check (PDC)
When SBC performs a PDC after a "wake-up", the following are
checked:
Warning! Pressure is applied to brake calipers (~60 bar)
• reservoir pressure (if low, it will be corrected by running the
high pressure charge pump in the hydraulic unit)
• pressure sensors
• control valves
• leak tests
• operational checks
Note: self-tests are constantly conducted during driving (~ once every 16
brake applications)
9

Driving with SBC – Delayed Off Function
Time that SBC remains operational after use:
• with vehicle stationary and was locked = 20 seconds
• with vehicle stationary and ignition in “0”,
brake pedal not operated = 2 minutes
• with vehicle stationary, ignition in “0”,
brake pedal operated in delayed off phase and
released again = 4 minutes
10

Warning Display
Complete ESP control module failure -
Instrument cluster will scroll through failure displays
11

Warning Display
SBC control module failure
Certain faults will trigger audible signal
12

SBC Components
• Brake Operating Unit (BOU)
• Wheel speed sensors
• Traction System Hydraulic
Unit (A7/3)
13
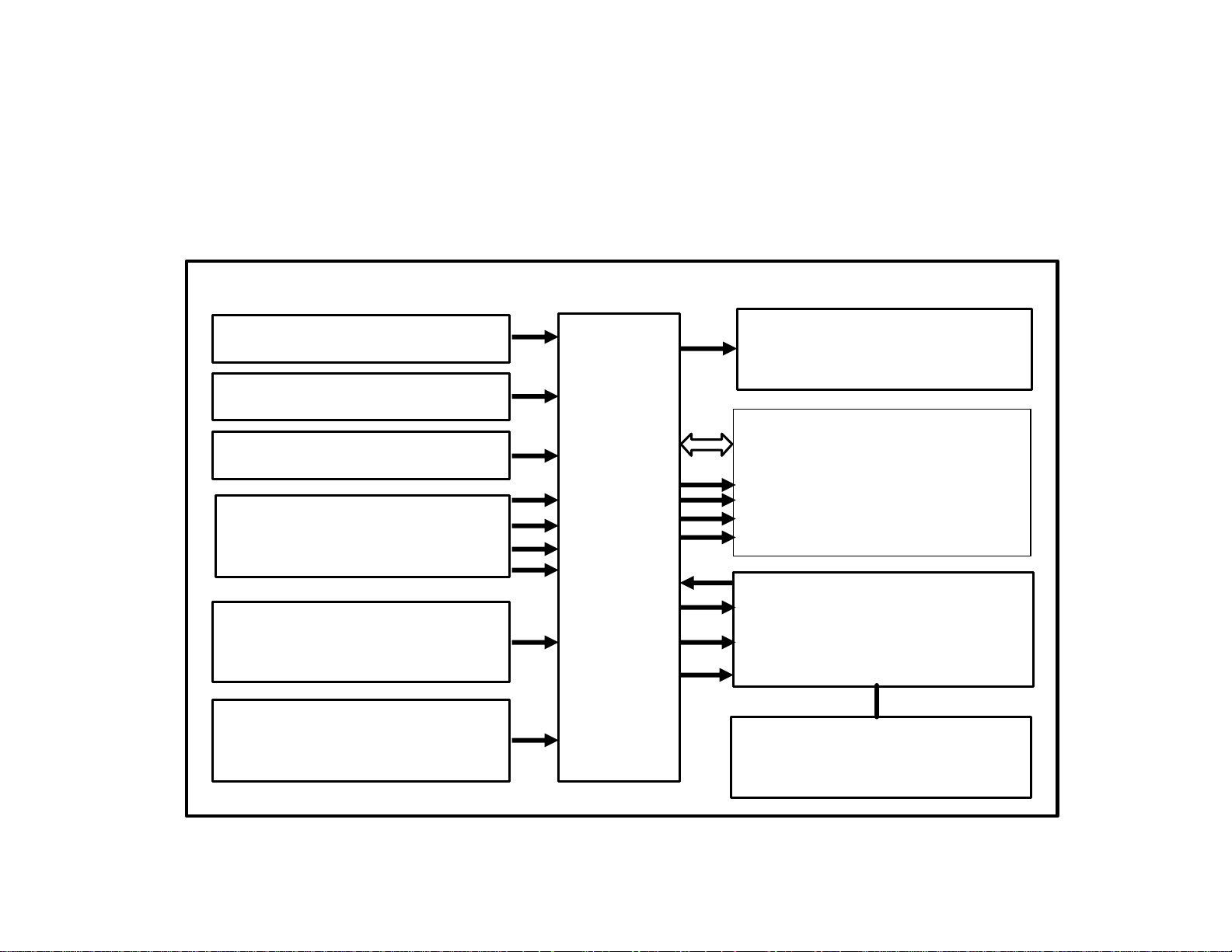
W211 System Overview
Circuit 30
Circuit 87
Circuit 31
Wheel speed sensors
L6/1, L6/2, L6/3, L6/4
Stop lamp switch
(S9/1)
SBC pedal travel
sensor (B37/1)
SBC
control
module
(A7/3n1)
SBC
CAN
Brake lights
Rear SAM
(N10/2)
ESP control
Wheel
speeds
Wake up
Brake lights
Speed status
Diagnostics
module (N47/5)
Front
SAM
(N10/1)
Diagnostic connector
(X11/4)
14
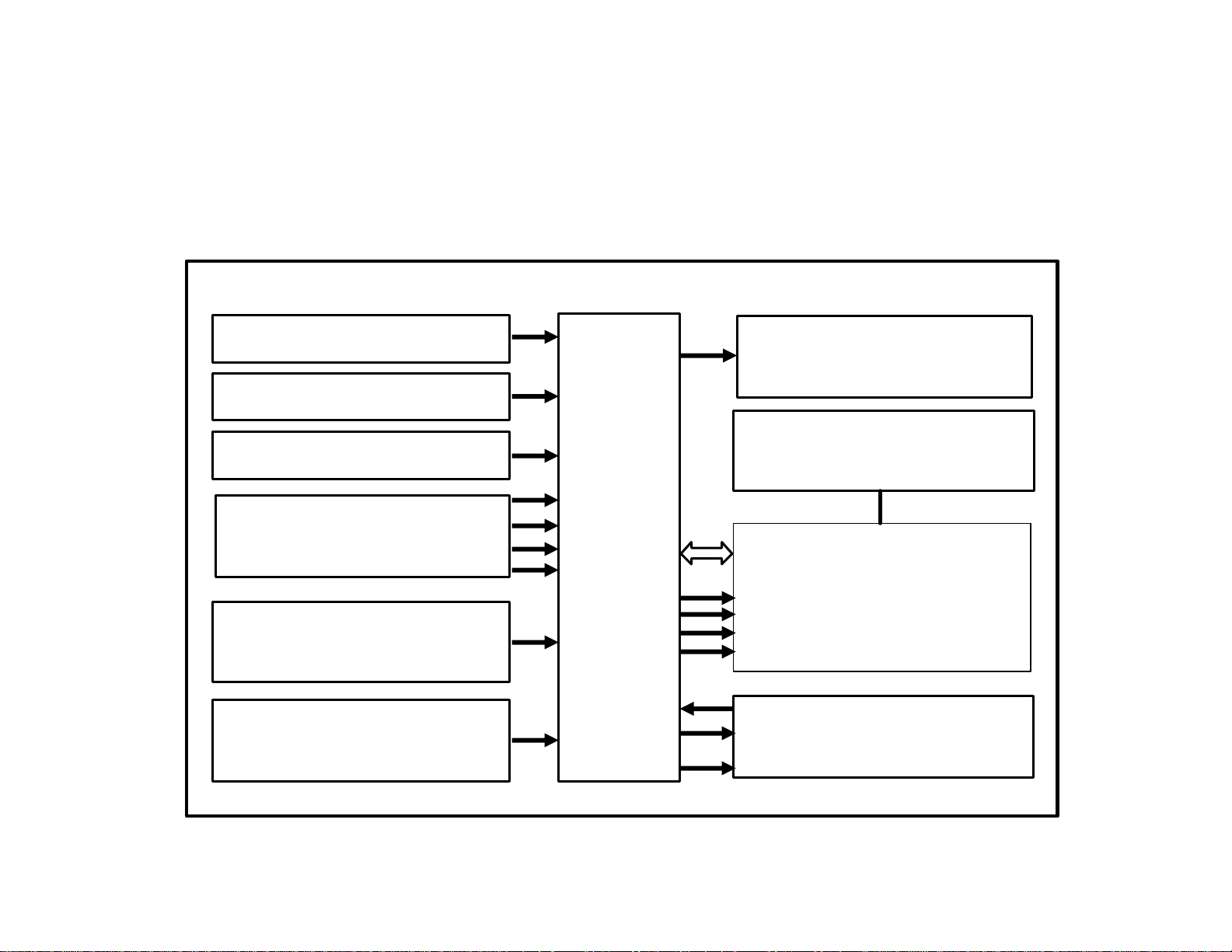
R230 System Overview
Circuit 30
Circuit 87
Circuit 31
Wheel speed sensors
L6/1, L6/2, L6/3, L6/4
Stop lamp switch
(S9/1)
SBC pedal travel
sensor (B37/1)
SBC
control
module
(A7/3n1)
SBC
CAN
Brake lights
Rear SAM
(N10/8)
Diagnostic connector
(X11/4)
ESP control
Wheel
speeds
Wake up
Brake lights
Speed status
module (N47/5)
Passenger side
SAM (N10/11)
15
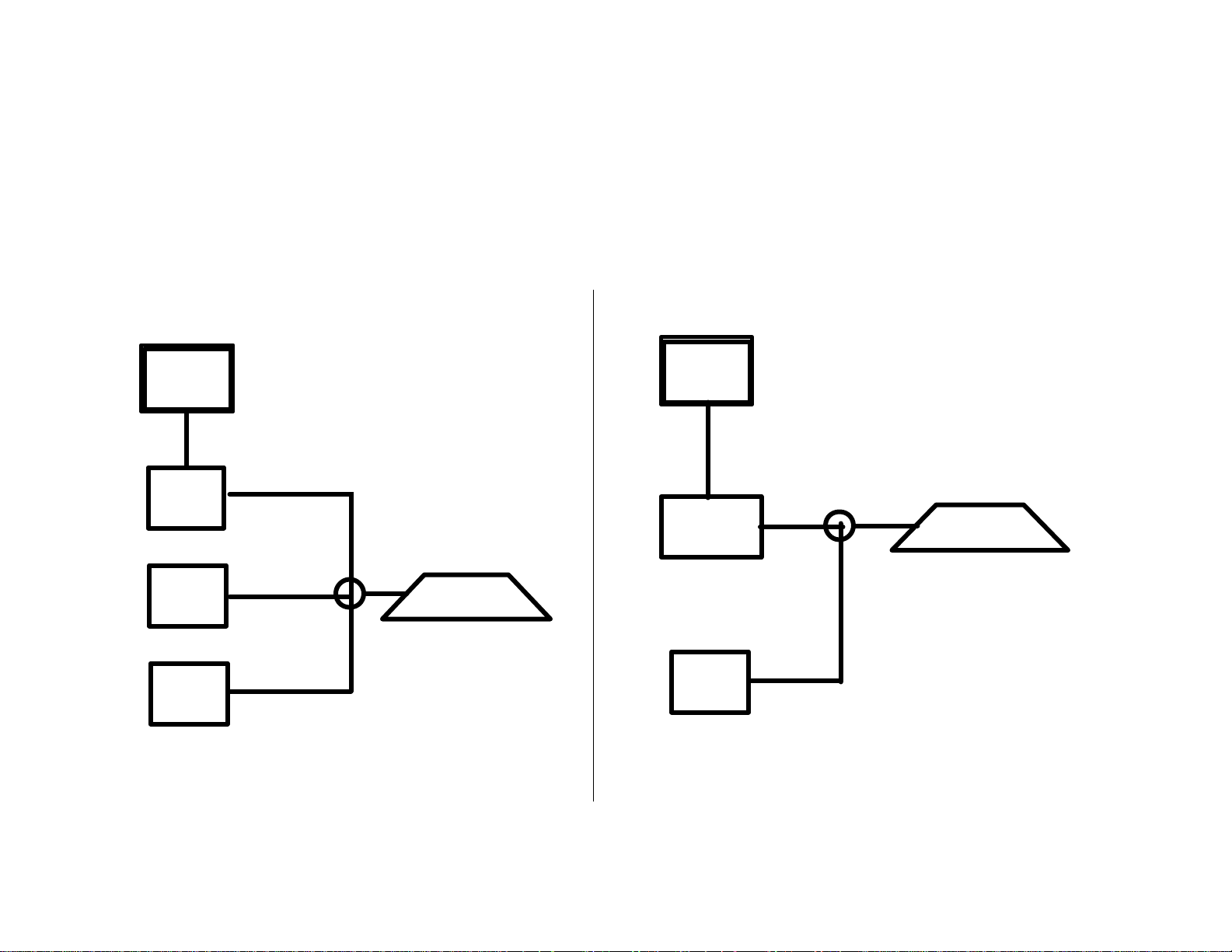
X11/4 Diagnosis Connection
A7/3n1
SBC
N47/5
ESP
N15/5
ESM
N51/2
ABC
Z6/33
R230
X11/4
Pin 9
W211
A7/3n1
SBC
X11/4
N10/1
L.F.SAM
Z70/4
Pin 9
N47/5
ESP
16
 Loading...
Loading...