Page 1
Fault Code Manual
for
Mercedes-Benz
Analog Systems 1988-1997
Digital Systems 1993-2000
©Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. February 1, 2001
Page 2

Table of Contents
The Diagnostic Process
Information Gathering .................................................................... 4
Diagnostic Codes & Adaptation
Diagnostic Code Readout ................................................................. 6
About Stored, Registered and Current Faults ................................................... 6
Fault Code Types ....................................................................... 7
Check Engine Light (MIL) Diagnosis ......................................................... 7
Mixture Adaptation ....................................................................... 8
Resetting and Reactivating BOSCH Engine Control Module Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Using the Data Stream.................................................................... 9
Equipment Connections
Connection Table....................................................................... 10
Connector Layout of Vehicle Diagnostic Connector ............................................. 11
8-pole Diagnostic Connector ......................................................... 11
16-pole Diagnostic Connector......................................................... 11
38-pin Diagnostic Connector ......................................................... 12
9-pole Diagnostic Connector (1980-94) ................................................. 13
Mercedes Model Identifier ............................................................... 100
Fault Codes
Engine Control
Electronic Diesel Idle Speed Control (ELR) .................................................... 14
Electronic Diesel System (EDS) ............................................................. 14
Continuous Fuel Injection System (CFI) ....................................................... 15
Continuous Fuel Injection System (MAS Controller) .............................................. 16
LH Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System - Analog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
LH Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System - Digital . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
HFM Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System - Analog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
HFM Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System - Digital . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
PMS (PEC) Fuel Injection System .......................................................... 25
ME Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System ................................................. 26
Diagnostic Module (DM) - Analog ........................................................... 41
Diagnostic Module (DM) - Digital LH (104, 119, 120) ............................................. 43
Diagnostic Module (DM) - Digital HFM (104, 111) ............................................... 45
Base Module (BM) - LH-SFI ............................................................... 47
Distributor Ignition (DI) - LH-SFI ............................................................ 48
Cruise Control/idle Speed Control (CC/ISC) w/o ASR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Electronic Accelerator / Cruise Control / Idle Speed Control (EA/CC/ISC) w/ASR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Chassis Control
Electronic Automatic Transmission Control (ETC) CFI (722.5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Electronic Automatic Transmission Control (ETC) 1990-95 (722.5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Automatic-engaged Four-wheel Drive (4MATIC) ................................................ 52
Electronic Automatic Transmission Control (ETC) 1996-2000 (722.6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Adaptive Damping System (ADS) ........................................................... 54
Automatic Locking Differential (ASD) ......................................................... 55
Anti-lock Brake System (ABS) .............................................................. 55
Anti-lock Brake system (ABS w/ASR) ........................................................ 56
Electronic Traction Systems (ASR, ETS) ...................................................... 57
Speed Sensitive Power Steering (SPS) ....................................................... 58
2
Page 3

Electronic Traction Systems (ABS, ASR, ETS, SPS) Digital . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Body Control
Cabriolet Soft Top (CST) ................................................................. 61
Roll Bar (RB) for CST .................................................................... 61
Roadster Soft Top (RST) ................................................................62, 63
Roll Bar (RB) for RST .................................................................... 63
Infrared Remote Control For Central Locking (IRCL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64, 65
Pneumatic Systems Equipment (PSE) ........................................................ 65
Anti-theft Alarm System( ATA) .............................................................. 66
Cellular Telephone (CT)................................................................... 66
Convenience Features (CF)................................................................ 67
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) ....................................................... 68
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) BAE, ZAE System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) with Side Airbags . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Body Control Systems (SRS, IRCL, PSE, ATA. RST, MSC, CF) Digital . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Climate Control
Tempmatic A/C ......................................................................... 73
Automatic A/C .......................................................................... 74
A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS
TAU 2.1........................................................................... 75
129 Chassis 1990-95................................................................. 77
129 Chassis 1996-99................................................................. 79
140 Chassis 1992-95................................................................. 81
140 Chassis 1996-99................................................................. 86
202 Chassis 1995 ................................................................... 89
202 Chassis 1996-99................................................................. 93
210 Chassis 1996-99................................................................. 94
Mercedes Technical Acronyms ........................................................... 97
Mercedes Model Identifier ............................................................... 100
Mercedes Diagnostic Manuals .......................................................... 106
Technical Support Contact Information ................................................. 107
DISCLAIMER: All information contained in this document is correct to the best of our knowledge. Errors may occur
therefore Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. makes no warrantee, guarantee or assurance that damage may not occur from the
use of this information. The user takes all responsibility for its use.
Mercedes Benz is a registered trademark of Daimler Chrysler AG.
All rights reserved. Any reproduction in whole or in part without perm ission is strictly prohibited.
Copyright © 1998-2001 BAUM TOOLS UNLIMITED INC.
3
Page 4

This book is designed to help you in the basic diagnostic procedures for Mercedes Benz.
It is intended to be a starting point in the diagnostic process and is not intended to be a complete
resource.
THE DIAGNOSTIC PROCESS
The diagnostic process divides itself into several levels; Information Gathering, Analysis of Codes, Testing and then
Repair. We will cover Information Gathering and Analysis of codes in this book.
For those experienced in diagnostics jump to page
INFORMATION GATHERING
The information gathering stage always starts with the Customer.
Step 1
The Customer Interview
This is truly an art.
It consists of getting the Customer to tell you what the complaint is and under what conditions it occurs.
The customer of course is, as always, the “MOST HELPFUL” source of information. Their concise insight into the
problem is a valuable step in getting the problem solved and the car back on the road. Also it’s the most fun part of
the diagnostic process. Watching the customer use body gestures, make funny faces and funny sounds in an attempt
to imitate vehicle noises can really brighten your day.
Actually the process of getting the information out of the customer can be relatively painless if you ask the correct
questions.
Here are some suggestions:
1) What is the problem/symptom(s)?
2) When did it start?
3) Under what conditions did the problem/symptom occur (if intermittent)? Wet, dry, hot, cold or changing weather,
rough road,...etc.
4) Has there been any work done on the car recently? New radio, shocks, tires...etc?
5) Any jump starts or hard starts with long crank times.
6) Did you run out of gas recently?
7) Are you sure this hasn’t happened before, even for a short time?
Next the exact nature of the complaint must be addressed.
Step 2
The Test Drive
Go on a test drive with the Customer so you can/cannot experience the problem/symptom. This ensures that the
malfunction you try to diagnose and fix is the one with that the customer is concerned about and that it is a real
malfunction and not just a lack of understanding of normal vehicle operation.
Few things are more frustrating for you and the customer than repairing a suspension noise in the front of the car
(even if it did need new shocks, thrust bushings, brakes and a set of tires) when it was an engine noise that the
customer wanted fixed.
It is also a good idea to let the customer drive on the outbound leg so you can watch the customers driving technique.
The customer is more likely to be able to make the car “do it” then you will.
Sometimes a customer can mistake normal vehicle operation for a problem. An example of this is a customer whose
vehicle has an Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS), and is concerned because of a pulsating brake pedal when braking
hard. Since many people are unaware of this characteristic of normal ABS operation, they mistake this for a
malfunction.
Also if you start diagnosing a vehicle for a problem when the vehicle is operating normally, you can be in for a long
frustrating day.
4
Page 5

Step 3
Visually Inspect the Vehicle
Don’t leave out this step. You can save lots of time with this.
Engine - Look under the hood. Check for missing covers, oil and water splash, burn marks, nesting
materials, mis-routed wiring and anything else that looks out of place.
ABS/ASC/DSC/ASR - Lift hood and inspect the fluid level. Raise the car and inspect the brakes/wheels for
excess dust and corrosion. Check that all static charge grounding straps are in place.
Transmission - Look for beverage spillage on the center console area. Look for problems in the operation of
the instrument cluster and on-board computer. These systems share data with the engine, transmission and
traction systems. Inspect the transmission housing and connection cables.
SRS/Airbag - Has the car been in a collision, jumped a curb, been to the body shop (welded) or jump started.
Any or all of these can be signs of something amiss.
Remember you’re gathering information at this point so don;’t ignore anything at this step.
Step 4
Check the Battery
Visually inspect the battery for corroded cables and terminals. Also old batteries are pure trouble in a late model car.
If you see any problem clean it up and grab your DMM (Fluke 88, Vantage, or whatever volt meter you use) and ...
Check voltage Key Off Engine Off, KOEO and KOER.
Key Off Engine Off >11.4Volts
KOEO >11.4Volts
KOER >13.2 but not higher than 14.2volts
Step 5
Recall Fault Codes
Even without a “Check this or that Light” illuminated, pull the codes from all systems, not just the suspect system.
Late model cars have highly integrated controls and faults can cascade from one system to another. Simple things like
and wrong size tire can turn on the Transmission Failure message, yet not turn on the ABS or ASR light. Both
systems, though, may register codes.
Record and then Clear the codes.
Write them down. Write them down. W rite them down.
There is nothing more fun then the call to tech support that starts.
Technician: “I got this code. Something about the O2 sensor. I replaced it but the code came back the next day.
Why?”
Tech Support: “What is the type and year of the car and what was the fault code number?”
Technician: “It was a ‘94 C220, but I don’t remember the code number. It came in last week.”
Tech Support: (Knocking back another bottle of Mallox) “Could it have been a Lambda Control code?”
Technician: “Ya! I think that was it. Why’d the new plugs make it go away and not the new O2 sensor?”
Test drive the car then pull the codes again. For some codes you will need to perform 2 test drives to get a code.
5
Page 6

Diagnostic Codes & Adaptation
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Readout:
The engine control module (N3/4) for the LH-SFI, HFM-SFI and ME-S FI sys tems are equipped with diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) memory. Malfunctions are recognized and stored as trouble codes and are distinguished as follows:
u Malfunctions which are constantly present,
u Malfunctions which occur longer than a pre determined number of seconds,
u Intermittent contact malfunctions which have occurred 5x during a trip.
The DTC memory remains active even if the vehicle's battery is disconnected.
Malfunctions which are no longer present, are automatically erased again after a maximum of 19 trips.
Under HFM-SFI a TRIP has occurred if:
u Engine running more than 5 minutes
u Vehicle speed >4 km/h (2.5 mph),
u Engine speed >700 rpm,
u Engine shut off for 30 seconds.
Under ME-SFI a TRIP is
u Engine running for more than 20 minutes,
u Engine temperature is greater than -7 degrees C,
u Engine speed is greater than 500 RPM,
The stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) can be read at the 16 (124 E-class) or 38 pin data link connector (X11/4) with
the ignition switched "ON" or with the "engine running".
Diagnosis via an on-off ratio readout has been eliminated in all models.
About Stored, Registered and Current Faults
Stored or Permanent Faults - These faults generally turn on the MIL (malfunction indicator lamp previously known as
the Check Engine Light) and are recorded in the permanent memory of the cars system controller. Clearing these codes
most often will extinguish the MIL. (See Registered Faults below.)
Registered or Pending Faults - These faults can keep the MIL on. These faults are recorded in the temporary memory
of the of the cars system controller. This temporary memory records the number of times a component fails. When a
certain number of failures has occurred the fault is moved to permanent storage and the Check Engine Light (MIL) will
be illuminated. On cars equipped with Fault Registers the Check Engine Light may stay on after the Stored or Permanent
Fault has been erased if another occurrence of the fault has happened since the original Permanent Fault was stored.
To ensure the MIL is extinguished, erase the Stored and Registered faults.
Current or Actual Faults - These faults are detected while the car is running at idle or speed. They represent components
currently failing or, in the case of HFM and LH systems, components not present. These codes cannot be erased, and
are only meaningful with the ignition on and the engine running. Codes found in this system with the KOEO have no
meaning. Components not present on the vehicle may be flagged as failing by the cars internal diagnostics due to the
generic nature of the cars software. This is particularly true in C-Class (202) cars.
6
Page 7

Fault Code Types
There are basically 2 code types. Component failure codes and System Malfunction or Logic codes.
Component Failure Codes are just that. The ECU specifically targets a “component” as failing. These codes make it easy
to spot the problem.
Some of these components are:
Oxygen Sensor
MAP
MAF
TPS
Vehicle Speed Sensor
Coolant Temperature Sensor
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
Camshaft Position Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Exhaust Temperature Sensor
Injectors
Ignition (coils)
Idle Air Valve
Pressure Regulator (optional)
EGR Valve
EVAP Purge Valve
Secondary Air Valve
Secondary Air Pump...etc.
System Failure or Logic Codes indicate that, when the “system” operated it did not produce the desire result.
Examples of these codes are;
Fuel Trim, O2 Control at Limit (Lambda control)
Possible cause: Fuel tank ran empty, Incorrect Fuel Pressure, Injector valve defective or coked, Engine
Temperature Sensor defective, EGR valve leak, Secondary air leak, EVAP control system defective, Air Mass
Meter defective, O2 sensor aging (slow response) or inactive, Combustion disturbed by mechanical failure
(Spark plugs, compression, intake/exhaust valves, ...etc.)
Ignition Feedback Fault
Possible cause: Coils, Sparkplug Wires, Sparkplugs, ECU, Low or high battery voltage.
ASR CAN Signal to Another Controller Lost.
Possible cause: ABS/ASR Control Unit Fault, ABS/ASR Component Fault, CAN Bus Communications Fault,
Faulty Electronic Accelerator (EA) controller, Faulty EA Actuator, Low or high battery voltage.
Electronic Accelerator Fuel Cutoff Signal to Engine Control
Possible cause: Faulty EA Actuator System, Faulty EA Actuator, Low or high battery voltage
ECU Faults
Internal Control M odule, internal communication fault
Internal Control Module, Keep Alive Memory (CMOS)
Internal Control Module, Memory check sum (ROM/RAM)
Internal Control Module, RAM
Internal Control Module, EEPROM.
Load Calculation Cross Check, Range/Perf....etc.
These types of codes are more difficult to diagnose, but generally there will be other conditions that can give you a clue.
Other fault codes will be present, physical engine condition (wear and tear), nature of the complaint itself, and information
from the datastream can help refine your analysis.
7
Page 8
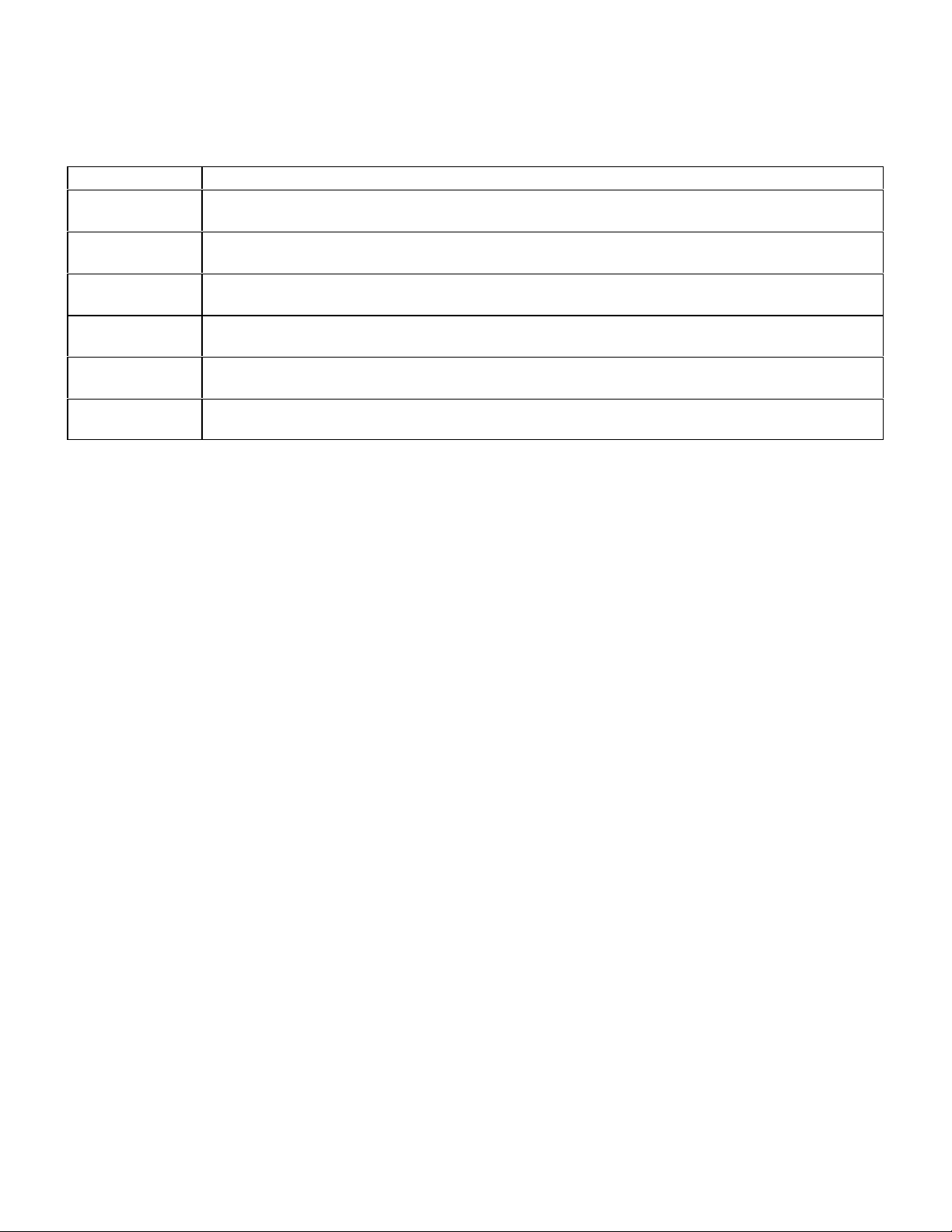
Check Engine Light (MIL) Diagnosis
Mercedes S(140), SL(129), E(124, 210) and C(202) class have multiple systems which can turn on an Check Engine Light.
All related systems must be tested for codes and repaired before the light will extinguish.
Injection System Diagnostic Socket Pin and CS1000 System to Use
129 LH
(1992-95)
140 LH
(1992-95)
124 HFM
(1993-95)
140 HFM
(1993-96)
202 HFM
(1995-96)
210 HFM
(1996-97)
LH (pin 4 & 5), EA/CC/ISC (pin 7), BM (pin 8), DI (pin 17 & 18) and DM (pin 19 check stored and
registered codes only)
LH (pin 4), EA/CC/ISC (pin 7), BM (pin 8), DI (pin 17) and DM (pin 19 check stored and
registered codes only)
HFM (pin 8), EA/CC/ISC (pin 14), and DM (pin 3 check stored and registered codes only)
HFM (pin 4), EA/CC/ISC (pin 7) and DM (pin 19 check stored and registered codes only)
HFM (pin 4), EA/CC/ISC (pin 7) (except C220) and DM (pin 19 check stored and registered
codes only)
HFM (pin 4), EA/CC/ISC (pin 7) and DM (pin 19 check stored and registered codes only)
Note: ME-SFI injected vehicles integrate Injection, Ignition, Electronic Accelerator,
Diagnostic Module and Base module into the ME controller module.
Mixture Adaptation:
The Lambda control system precisely determines fuel injection duration so that the fuel/air ratio is consistently kept at
Lambda equal 1 (Lambda=1 is 14.7 kg air per 1 kg fuel) under all operating conditions.
Should a malfunction occur in the form of:
u Intake air leaks
u Injector defects or carbon build-up,
u Air Flow Sensor defects
u Pressure regulator defects, such as a blown diaphragm.
u Fuel tank purge control valve defects or EVAP system leaks.]
u EGR defects
u Vacuum leaks of any kind.
u Mechanical engine wear, such as, chipped valves or leaking rings.
The engine control module automatically performs a mixture adjustment. The degree of correction is calculated constantly
and stored in KAM (Keep Alive Memory) RAM. The self-adaptation is performed at idle and under partial load. Maximum
correction towards rich or lean is 25%. After repair work is performed, the engine control module will automatically adapt
itself again after approx. 10 trips. After eliminating a malfunction or after trial installation of an engine control module from
another vehicle, the self-adaptation feature must be reset to its mean value.
8
Page 9

"Resetting and Reactivating for BOSCH Engine Control Module Memory"
For LH & HFM systems only.
To reset and reactivate the module :
1. Read and clear all fault codes
2. After display of 1 (No faults present) short the diagnostic plug (pin 8 for 16 pin diagnostic socket, pin
4 for 38 pin diagnostic socket) to ground for 6 to 8 seconds
3. Switch ignition off and wait at least 5 seconds
4. Turn ignition on, wait minimum of 10 seconds then restart engine.
Long Term Adaptation (Additive) - Engine at idle.
Short Term Adaptation (Multiplicative) - Engine at partial load
The correction towards rich or lean is + - 1.0 msec (Injection Duration) at idle and the factor of 0.68-1.32 at partial load.
After repair work is performed the engine control will automatically adapt itself again (ME injection) over the course of 10
TRIPS.
Codes Present in the Absent of Trouble Light
Not all control systems will trigger codes or turn on malfunction lights when codes are stored.
INJECTION/IGNITION system problems will trigger trouble codes, but may not turn on the MIL unless the fault results
in a change in the exhaust gases or can damage the engine in the short term. Also some mechanical problems in
earlier cars (pre 1988-96) can cause poor drivability without ever tripping a code or turning on the light. On later
models that is much less likely.
BRAKING/TRACTION systems will only turn on their check light when the system has become inactive. It does not
mean there isn’t a problem and codes haven’t been stored.
TRANSMISSION systems will turn on the “Check Engine” light if any shared system is detected as failing test.
AIRBAG and RESTRAINT SYSTEMS will turn on the light and record codes if incorrectly coded for the car. A good
example is the 1995 C280 and the 1995 S320. The same controller is used in both vehicles, however the S-class has
more features in the Airbag system such as side bags and baby seat detection. The coding of the controller for the
C280 masks the features not present so the controller doesn’t register a code. The controllers generally come off the
parts dept. shelf coded for maximum features.
In All Systems low or high battery voltages can trigger invalid or multiple codes without real failures of the indicated
components. Always check the battery condition before starting analysis.
Using the Data Stream to Diagnose/Confirm Faults
The Serial Data Information Stream of the ECU is a “window” into the operation of the system under test. By looking at
the values of the suspect components in operation and the computed values of the ECU, we can build a picture of the
operation of the system and what is causing the fault. The interpretation of the Data Stream is beyond the scope of
this book. Please refer to the Diagnostic Manuals from Mercedes Benz for complete discussion of the topic.
The nominal values for all Mercedes vehicles 1990-2000 can be found in the Mercedes Engine Diagnostic Manual
Volume 1 Section A.
A listing of these manuals can be found at the end of this document.
Multiple system and component faults can almost always be traced to faulty wiring
harnesses or water damage.
9
Page 10

Connection Table
Test Lead of Cable Connection source
Red Power -To power supply socket or vehicle battery
Black Ground - To socket 1
Yellow To diagnostic test socket
Power supply (B+) socket on the vehicle Diagnostic Connectors
8-pole connector Use with the battery extension cable to the vehicle battery
16-pole connector Socket 16 (circuit 15 - ignition ON)*
Not present in some models. Use battery +.
38-pole connector Socket 3 (circuit 30 - Battery+)
*Must be performed with the ignition ON to power up the scanner
Ground (-) socket on the vehicle Diagnostic Connectors
8-pole connector socket 1
16-pole connector socket 1
38-pole connector socket 1
10
Page 11
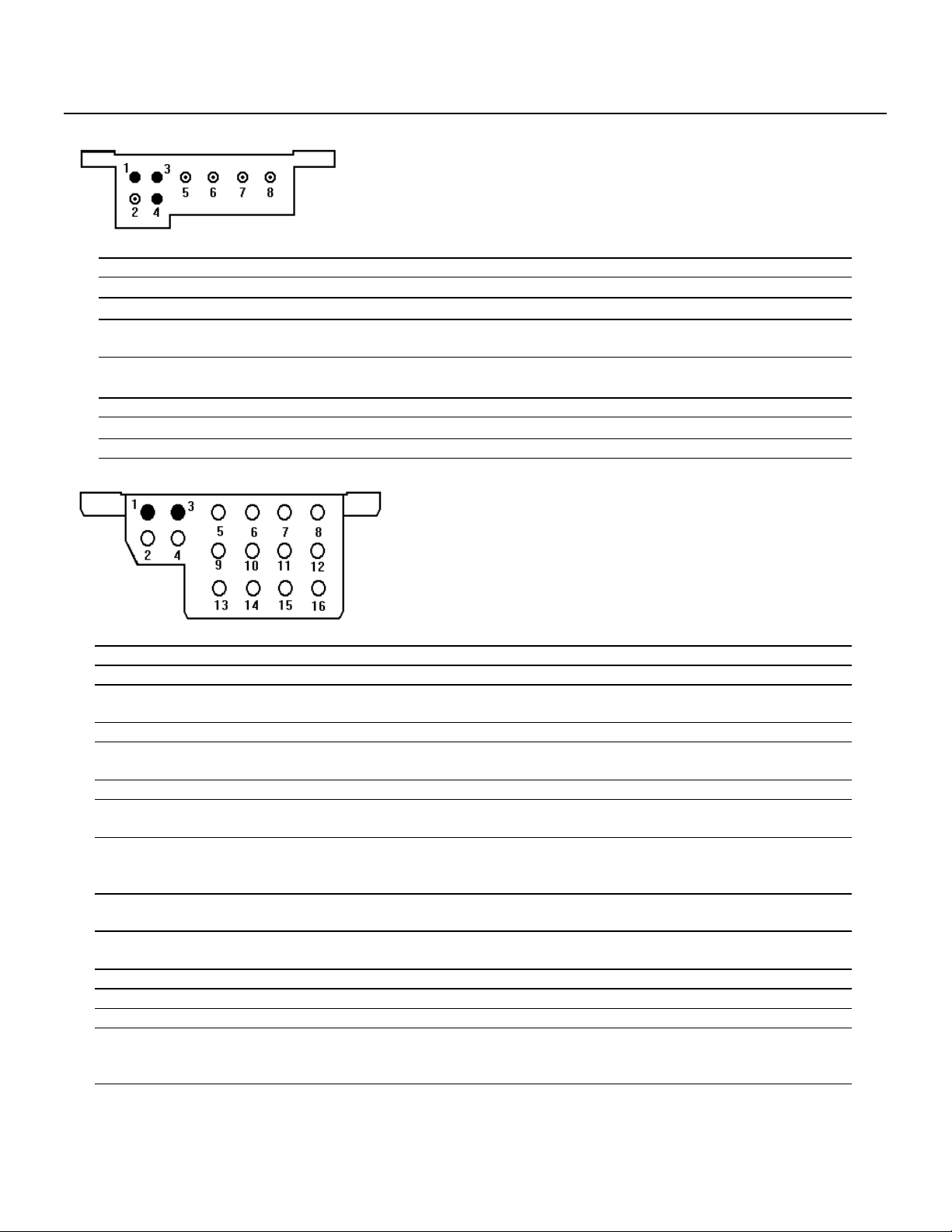
Connector Layout of Vehicle Diagnostic Connector
8-pole Diagnostic Connector
Models 201, 124, 126
1 Ground
2 Not used
3 CIS-E Continuous fuel injection system (CFI)
4 ELR
EDS
5 ASD
4MATIC
6 SRS Supplemental Restraint System
7 A/C Air Conditioning
8 Not used
Diesel injection system - Electronic idle speed control system
Electronic diesel system
Automatic locking differential
Automatic-engaged four wheel drive (124 only)
16-pole Diagnostic Connector
Models 124, 129
1 Ground
2 OBD Push-button for On Board Diagnostic (California only)
3 CIS-E
DM
4 EDS Electronic diesel system
5 ASD
4MATIC
6 SRS / AB Supplemental Restraint System / Air Bag
7 A/C
RB
8DI
HFM-SFI
PEC
9 ADS
RB
10 RST Roadster Soft Top (Model 129)
11 ATA Anti Theft Alarm system
12 IRCL Infrared Remote Central Locking
13 ETC Electronic automatic Transmission Control
14 EA
CC / ISC
ESCM
Continuous Fuel injection system (CFI)
Diagnostic Module - LED (California only)
Automatic locking differential
Automatic-engaged four wheel drive
Air Conditioning (Model 124)
Roll Bar (Model 129)
Distributor ignition
HFM Sequential multi-port Fuel Injection/Ignition system
Pressurized engine control
Adaptive Damping System
Roll Bar (Model 124)
TN-signal (Gasoline)
Electronic Accelerator (Model 124)
Cruise Control / Idle Speed Control (Model 124)
Engine System Control Module (MAS), (Model 129)
11
Page 12

15 Not used
16 Voltage, Ignition ON (Circuit 15) (Not equipped on all models.)
38-Pin Diagnostic Connector
Models 124.034/036, 129.058/063/067/076, 140, 170, 202, 208,
210, 215, 220
The Mercedes Diagnostic “Mushroom” #140-1463 available from
Baum Tools Unltd. is recommended to allow easy access to the
diagnostic connector. Call 800-848-6657 or 941-927-1414
for more information.
Pin System Description
1 Ground (Terminal 31) W12 (Chassis Ground), W15 (Electronics Ground)
2 Voltage, terminal 87 Ignition Switch 12volts +
3 Voltage, terminal 30 Battery 12volts +
4 EDS Electronic Diesel System
IFI In-line Fuel Injection
DFI Electronic Distributor-type Fuel Injection (Diesel)
HFM-SFI Hot-Film Engine Management Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection/ignition
LH-SFI LH Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection System
Engines 104, 119
Engine 120 Right Bank
ME-SFI Motor Electronics with Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection/ignition System
Engine 119
Engine 120, Right Bank
5 LH-SFI LH Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection, Engine 120 Left Bank
ME-SFI Motor Electronics with Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection/ignition System
Engine 120 Left Bank
6 ABS Anti-lock Brake System
ETS Electronic Traction System
ASR Acceleration Slip Regulation
ESP Electronic Stability Program
7 EA Electronic Accelerator+
ISC Idle Speed Control
CC Cruise Control/idle Speed Control
8 BM Base Module
BAS Brake Assist
9 ASD Automatic Locking Differential, Models 124, 129, 140
10 EATC Electronic Automatic Transmission Control (5-speed AT) (722.6)
ETC Electronic Transmission Control (722.6)
11 ADS Adaptive Damping System
12 SPS Speed-sensitive Power Steering
13 TD Speed Signal (Time Division) (Di) (Diesel) Models 202, 210
12
Page 13
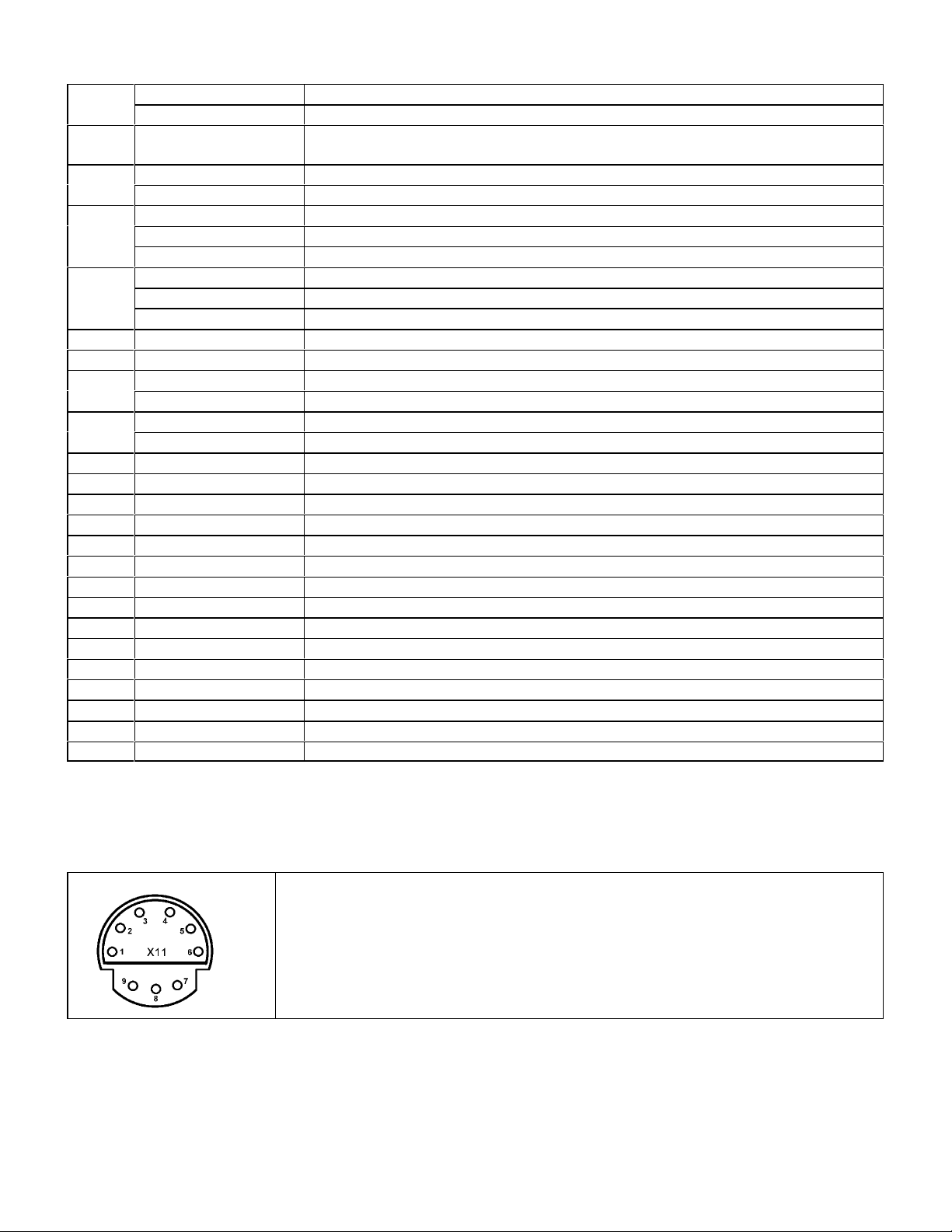
TNA Signal (Gasoline) on LH-SFI
TN Speed Signal (DI/KSS) (Gasoline) on HFM-SFI, ME-SFI
14 Lambda on/off ratio LH-SFI Engine 119,
LH-SFI Engine 120 LH-SFI, Right Bank
15 Lambda on/off ratio LH-SFI Engine 120 Left Bank
IC Instrument Cluster
16 HEAT Automatic Heater
TA/C Air Conditioning (Tempmatic)
AA/C Air Conditioning (Automatic)
17 DI Distributor Ignition, Engines 104, 119, Engine 120, Right
TD Speed Signal (Time Division) (Di) (Diesel) Model 140
TN Speed Signal (DI/KSS) (Gasoline) on LH-SFI / model 202 HFM-SFI
18 DI Distributor Ignition, Engine 120, Left
19 DM Diagnostic Module
20 PSE Pneumatic System Equipment, Model 140
MFCM Multi-function Control Module, Model 210
21 CF Convenience Feature, Model 140
RST Roadster Soft Top, Model 129
22 RB Roll Bar, Model 129
23 ATA Anti-theft Alarm
24-25 -
26 ASD Automatic Locking Differential, Model 202
27 28 PTS Parktronic System, Model 140
29 30 AB Airbag/emergency Tensioning Retractor
31 RCL Remote Central Locking
32-33 -
34 CNS Communication and Navigation System
35 36 STH Stationary Heater
36 ZUH Heater Booster
37-38 -
The following connector is not for use with the CS1000 or CS2000 scanners
9-Pole Diagnostic Connector (1980-94)
The 9-pole Diagnostic Connector is used on earlier model vehicles. It can display on-off
ratio fault codes (1986-1992), RPM and Lambda sensor values. Various on-off ratio
Meters are available that provide access to this type of diagnostic connector. Call Baum
Tools at 800-848-6657 or 941-927-1414 for more information on these meters.
13
Page 14
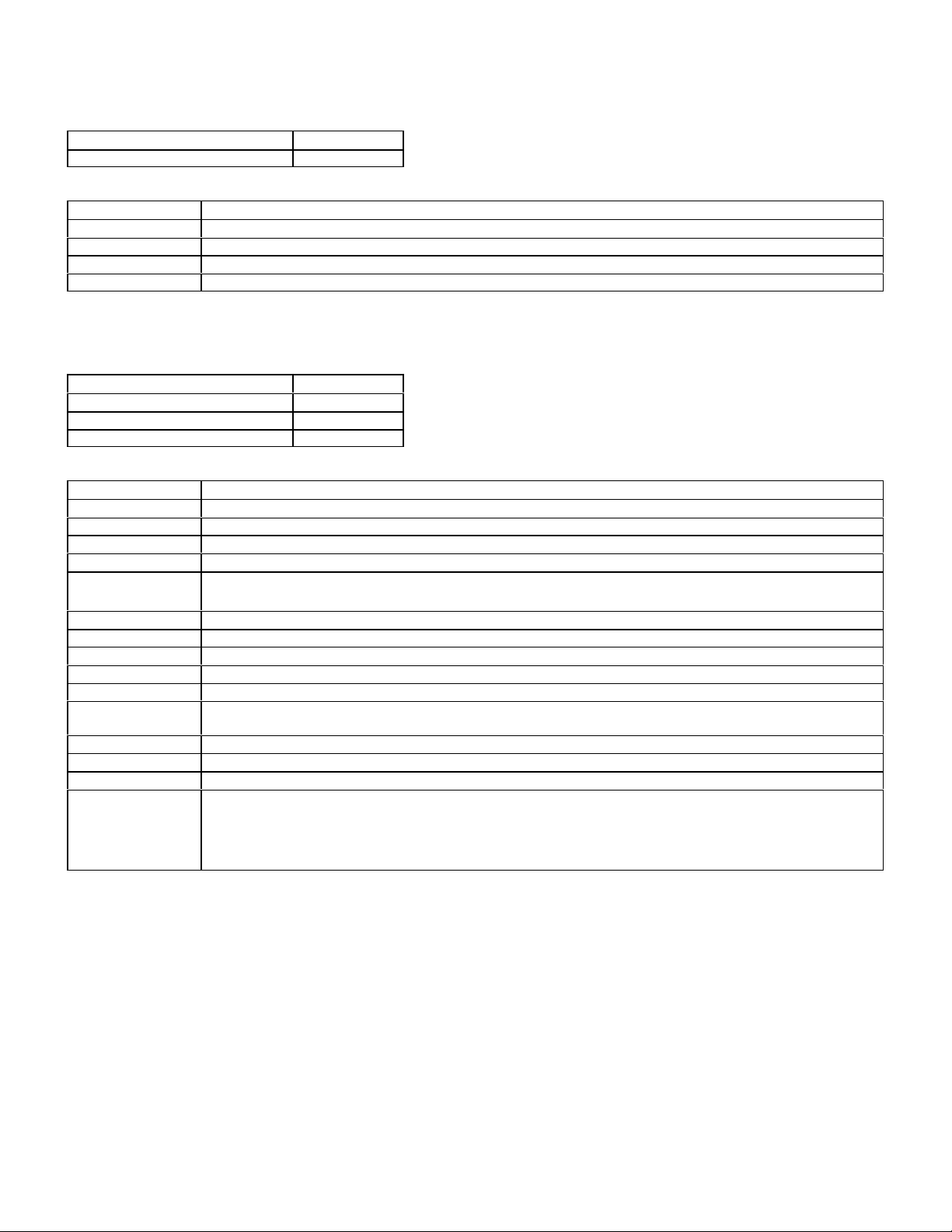
ELECTRONIC IDLE SPEED CONTROL (ELR)
Model Model Year
201.126 1989
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Speed sensor signal
3 Coolant temperature sensor signal
4 ELR control unit or Idle speed control (ISC) system
ELECTRONIC DIESEL SYSTEM (EDS)
Model Model Year
124.128 1990-93
126.134 126.135 1990-91
140.134 1992-93
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Fuel rack position sensor (L7)
3 Air flow sensor signal (B2/1)
4 Electronic diesel system (EDS) control unit (N39) or atmospheric pressure sensor
5 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve vacuum transducer (Y31/1) or fault in exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR) control circuit
6 Electronic diesel system (EDS) control unit (N39), internal voltage supply
7 Starter ring gear speed sensor (L3)
8 Engine coolant temperature sensor (B11/4)
9 Intake air temperature sensor (B2/1a)
10 Voltage supply insufficient
11 Electronic idle speed control actuator (Y22) or exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve vacuum transducer
(Y31/1) or Boost pressure cut-out switchover valve
12 Not used
13 Electronic diesel system control unit (N39), faulty (internal fault memory)
14 Electronic diesel system pressure sensor (B5/1), defective
15 Boost pressure control/ pressure control flap vacuum transducer (Y31/5) , or defect in Boost pressure
control circuit.
Or
Intake manifold air pressure control valve vacuum transducer (Y31/2), wastage vacuum transducer
(Y31/3), or malfunction Intake manifold air pressure circuit
14
Page 15
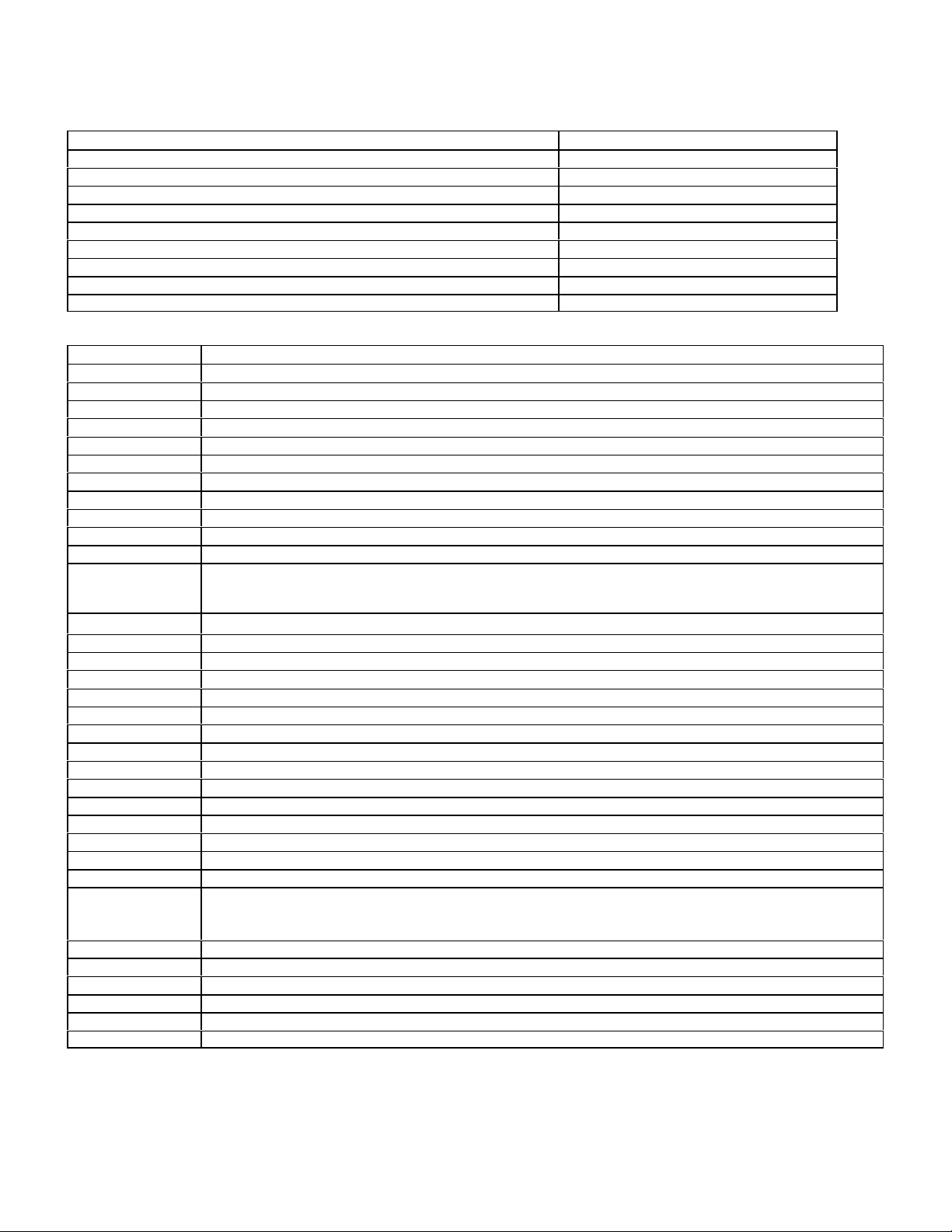
CONTINUOUS FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM (CFI)
Models Model Years
107.048 1988-91 (California version only)
124.026 124.030 124.050 124.090 1988-89 (California version only)
126.024 126.025 1988-89 (California version only)
126.035 126.039 126.045 1988-91 (California version only)
201.028 (1988-93) 201.029 1988-89 (California version only)
124.026 124.030 124.051 124.090 124.230 124.290 1990-93
126.024 126.025 1990-93
129.061 129.066 1990-92
201.029 1990-93
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Throttle position switch - wide open throttle (WOT), signal faulty
3 Engine coolant temperature sensor faulty
4 Air flow sensor position potentiometer voltage illogical
5 Oxygen sensor signal illogical
6 Not used
7 TNA/TD signal (RPM) read by CFI control module
8 Altitude pressure signal from ignition control module illogical
9 Electronic hydraulic actuator (EHA) current faulty.
10 Throttle position switch - closed throttle position fault (idle)
11 Air injection system, open or short circuit
12 Absolute pressure values from EZL ignition control module are illogical
or
Exhaust gas recirculation temperature sensor
13 Intake air temperature reading is illogical
14 Vehicle speed signal read by CFI control module is illogical
15 Not used
16 Exhaust gas recirculation switchover valve, open or short circuit
17 Oxygen sensor is shorted to positive or ground
18 Current to idle control valve is illogical
19 Not used
20 Not used
21 Not used
22 Oxygen sensor heater voltage illogical
23 Short circuit to positive in purge switchover valve circuit
24 Not used
25 Short circuit to positive in start valve circuit
26 Short circuit to positive in upshift delay solenoid valve circuit
27 Data exchange between CFI control module and ignition control module interrupted
28 Intermittent contact in engine coolant temperature sensor circuit
29 CFI and ignition control module reading different engine coolant temperatures - Faulty sensor or wires
30 Not used
31 Intermittent contact in engine coolant temperature sensor circuit
32 Not used
33 Not used
34 Engine coolant temperature read from ignition control module illogical
15
Page 16

Continuous Fuel Injection System (MAS Controller)
Models Model Years
124.026 124.030 124.090 124.230 124.290 129.066 201.029 1990-92
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Fuel pump relay (circuit 87) not functioning
3 TN/TD signal (RPM) interrupted
4 Output for oxygen sensor heater control defective
5 Output for air injection pump control defective
6 Output for kickdown switch control defective
7 Not used
8 Engine coolant temperature sensor signal out of range
9 Circuit 50 failure
10 Output failure of the start valve
11 A/C compressor engagement signal missing (87Z)
12 Output for A/C compressor control defective
13 Excessive A/C compressor clutch slippage
14 Vehicle speed signal illogical
15 Short circuit detected in fuel primp circuit
16
Page 17
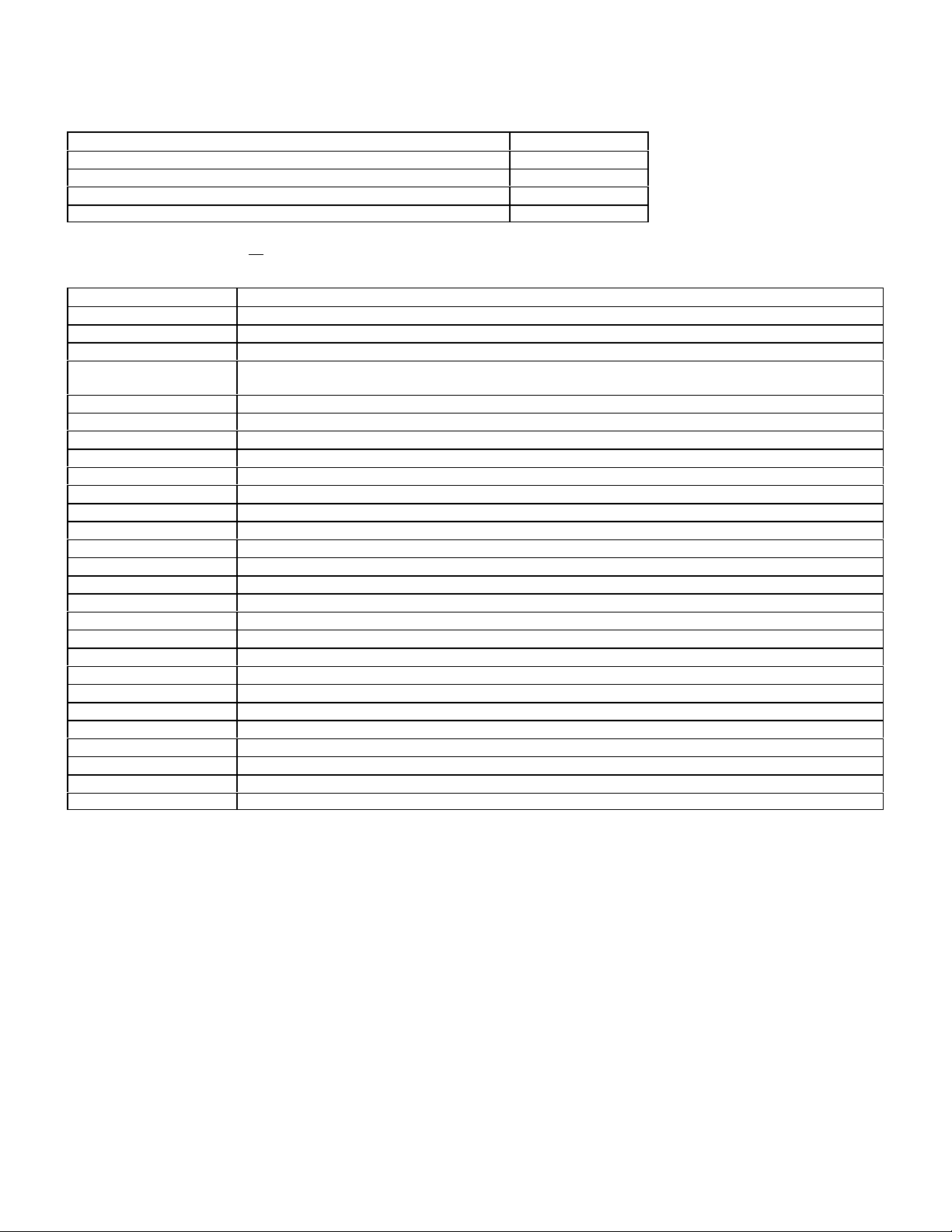
LH Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection - Analog
Models Model Years
140.032 140.057 140.076 1992-93
124.034 124.036 1992-93
129.067 1992-93
140.042 140.043 140.051 1992-93
See digital LH injection page 18 for models 3/93 and later.
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Engine coolant temperature sensor circuit 1, open or short circuit.
3 Engine coolant temperature sensor circuit 2, open or short circuit.
4 Voltage at mass air sensor (MAF) with hot wire circuit insufficient or too high. Open or short circuit in
ground wire.
5 Not used
6 Not used
7 TNA-signal (rpm signal ) incorrect or open or short circuit.
8 Camshaft position sensor signal. Open or short circuit.
9 Starter signal (circuit 50) missing, open or short circuit.
10 Closed throttle position recognition from electronic accelerator control unit, short circuit.
11 Secondary air injection system, open or short circuit.
12 Burn-off control for mass air sensor with hot-wire, open or short circuit.
13 Intake air temperature sensor, open or short circuit.
14 Not used
15 Not used
16 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) switchover valve, open or short circuit.
17 CAN data: Electronic accelerator control module - no data transmission
18 CAN data: Ignition control module - no data transmission from DI module
19 Left LH-SFI control module no data transmission to right LH-SFI control module
20 LH-SFI control module - no data transmission
21 Oxygen sensor open circuit.
22 Oxygen sensor heater, open or short circuit.
23 Purge switchover valve, open or short circuit.
24 Left adjustable camshaft timing solenoid (Y49/1), open or short circuit
25 Adjustable camshaft timing solenoid, open or short circuit.
27 Injectors, open or short circuit.
29 I GR Start relay module (K29/1), open or short circuit
17
Page 18
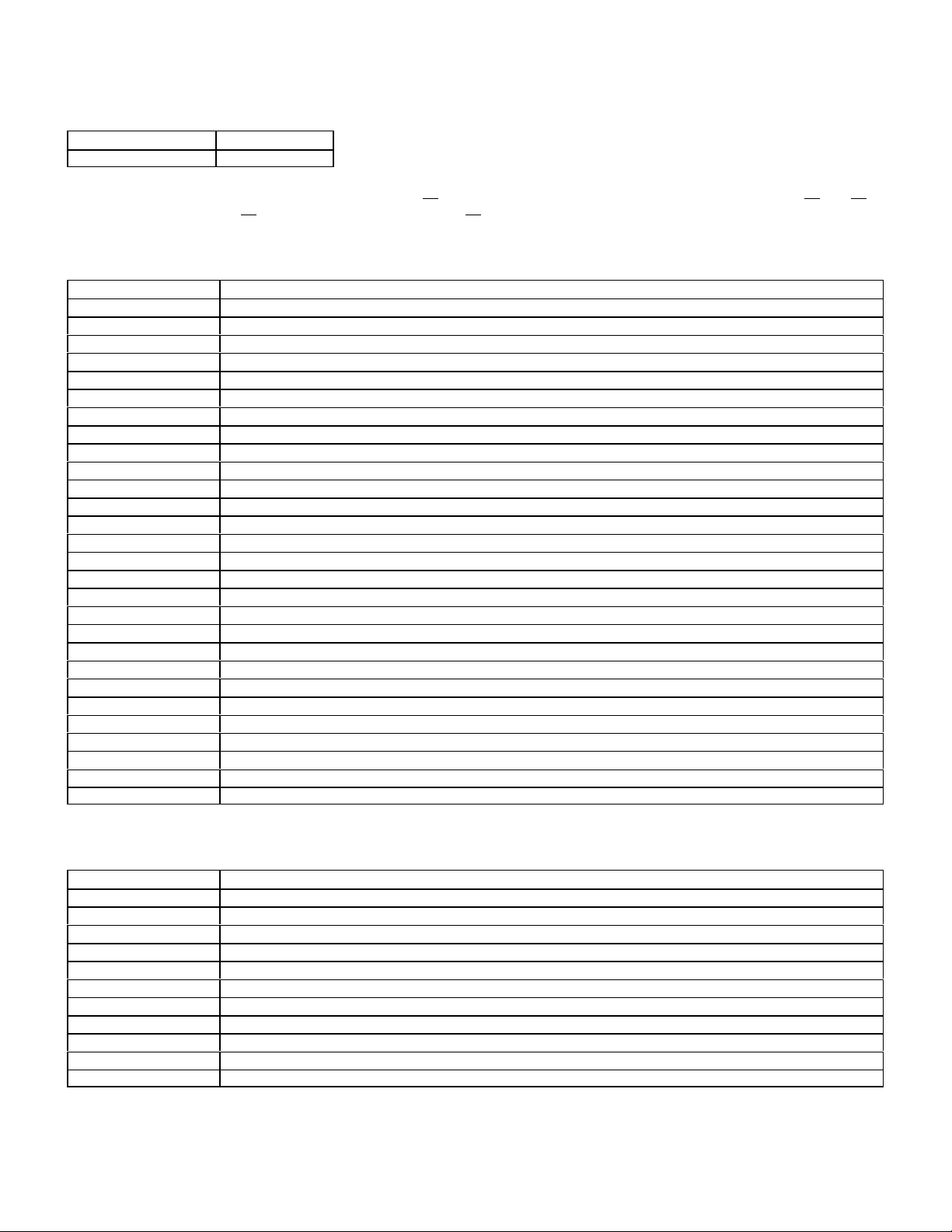
LH Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection - Digital
Engines Model Years
104 119 120 1992-1995
Also check for codes in the Diagnostic Module (DM page 43), Electronic Accelerator/Cruise Control (EA/CC/ISC pages 50 and 49),
Distributor Ignition (DI page 48) and the Base Module (BM page 47).
(These fault codes numbers are only for the CS1000 Code Scanner. They are different from those found in the Mercedes Benz
original Diagnostic Manual fault code tables.)
LH-SFI “Stored” Fault Codes
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
002 Engine coolant temperature sensor circuit 1, short or open circuit
003 Engine coolant temperature sensor circuit 2, short or open circuit
004 Voltage of Hot Wire MAF sensor too low or too high or ground wire has open circuit.
005 Not used.
006 Japan only Exhaust temperature sensor, circuit short or open
007 TNA-signal (rpm signal ) incorrect or open or short circuit.
008 Camshaft position sensor signal. Open or short circuit.
009 Starter signal (circuit 50) missing, open or short circuit.
010 Closed throttle position recognition from electronic accelerator control unit, short circuit.
011 Secondary air injection system, open or short circuit.
012 Burn-off control for mass air sensor with hot-wire, open or short circuit.
013 Intake air temperature sensor, open or short circuit.
014 Not used.
015 Not used.
016 EGR switchover valve, circuit open or short
017 CAN data: Electronic accelerator control module - no data transmission
018 CAN data: Ignition control module - no data transmission from DI module
019 Left LH-SFI control module no data transmission to right LH-SFI control module
020 LH-SFI control module - no data transmission (Left or Right)
021 Oxygen sensor open circuit.
022 Oxygen sensor heater, open or short circuit.
023 Purge switchover valve, open or short circuit.
024 Left adjustable camshaft timing solenoid (Y49/1), open or short circuit (119 only)
025 Adjustable camshaft timing solenoid, open or short circuit.
026 Upshift Delay Switchover Valve, open or short circuit
027 Injectors, open or short circuit.
028 LH Control Module incorrectly coded or open circuit.
029 1GR Start relay module (K29/1), open or short circuit
These codes require special scanners to access.
LH-SFI “Current” Fault Codes
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
001 Injector, cylinder 1 circuit short to positive
002 Injector, cylinder 5 circuit short to positive
003 Injector, cylinder 4 circuit short to positive
004 Injector, cylinder 8 circuit short to positive
005 Injector, cylinder 6 circuit short to positive
006 Injector, cylinder 3 circuit short to positive
007 Injector, cylinder 7 circuit short to positive
008 Injector, cylinder 2 circuit short to positive
009 Injector, cylinder 1 open circuit or short to ground
010 Injector, cylinder 5 open circuit or short to ground
011 Injector, cylinder 4 open circuit or short to ground
18
Page 19
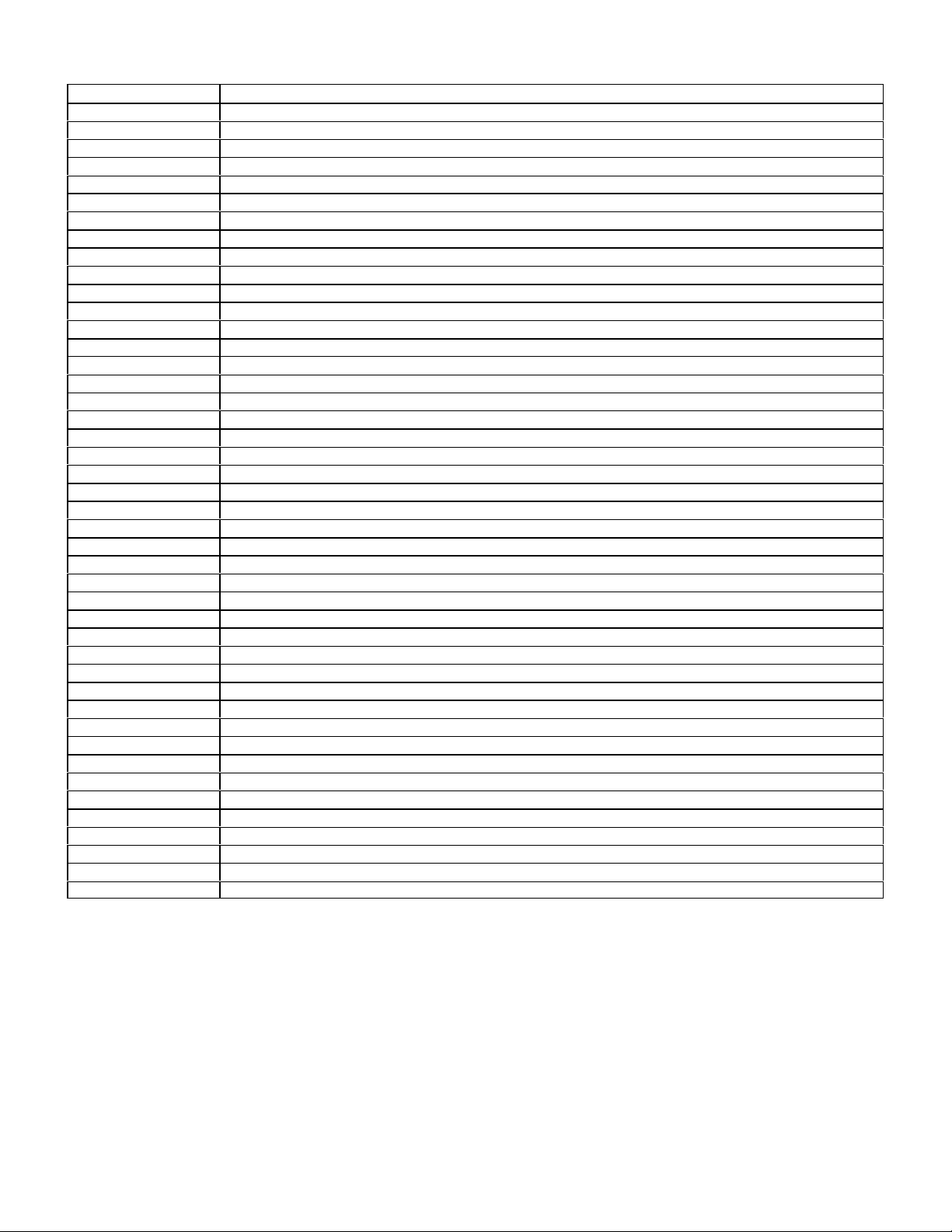
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
012 Injector, cylinder 8 open circuit or short to ground
013 Injector, cylinder 6 open circuit or short to ground
014 Injector, cylinder 3 open circuit or short to ground
015 Injector, cylinder 7 open circuit or short to ground
016 Injector, cylinder 2 open circuit or short to ground
017 HFM sensor Voltage too high or too low, may open circuit
018 Engine coolant temperature sensor short or open circuit
019 Engine coolant temperature sensor short or open circuit
020 Engine coolant temperature sensor signal questionable
021 Intake air temperature sensor short or open circuit
022 Exhaust temperature sensor short or open circuit (Japan version only)
023 CO potentiometer open circuit (non KAT)
024 LH-SFI control unit coding plug open circuit (not USA version)
025 Starter signal missing (circuit 50), may short or open circuit
026 Idle speed recognition from Cruise control/Electronic accelerator (CC/EA), circuit short to ground
027 Not used
028 O2S 1 signal, short or open circuit
029-030 Not used
031 O2S 2 signal, short or open circuit
032 Not used
033 CAN communication problem, No communication from LH control unit
034 CAN communication problem, No communication from ASR control unit
035 CAN communication problem, No communication from LH control unit
036 CAN communication problem, No communication from LH control unit
037 CAN communication problem, No communication from EZL/AKR ignition control unit
038 CAN communication problem, No communication from EZL/AKR ignition control unit
038 CAN communication problem, No communication from Cruise control/Electronic accelerator
040 Not used
041 Air injection system short or open circuit
042 Fuel purge switchover valve open or short circuit
043 Transmission switchover valve, circuit open or short
044 EGR switchover valve, circuit open or short
045 Camshaft timing adjust solenoid, circuit open or short
046 Camshaft timing adjust solenoid, circuit open or short
047 First gear start relay, circuit open or short
048 Not used
049 Air injection system circuit short or open
050 Fuel purge switchover valve circuit short or open
051 Transmission switchover valve relay or solenoid, circuit short or open
052 EGR switchover valve circuit short or open
053 camshaft timing Adjust solenoid circuit short or open
054 camshaft timing Adjust solenoid circuit short or open
055 First gear start relay circuit short or open
056 Not used
19
Page 20
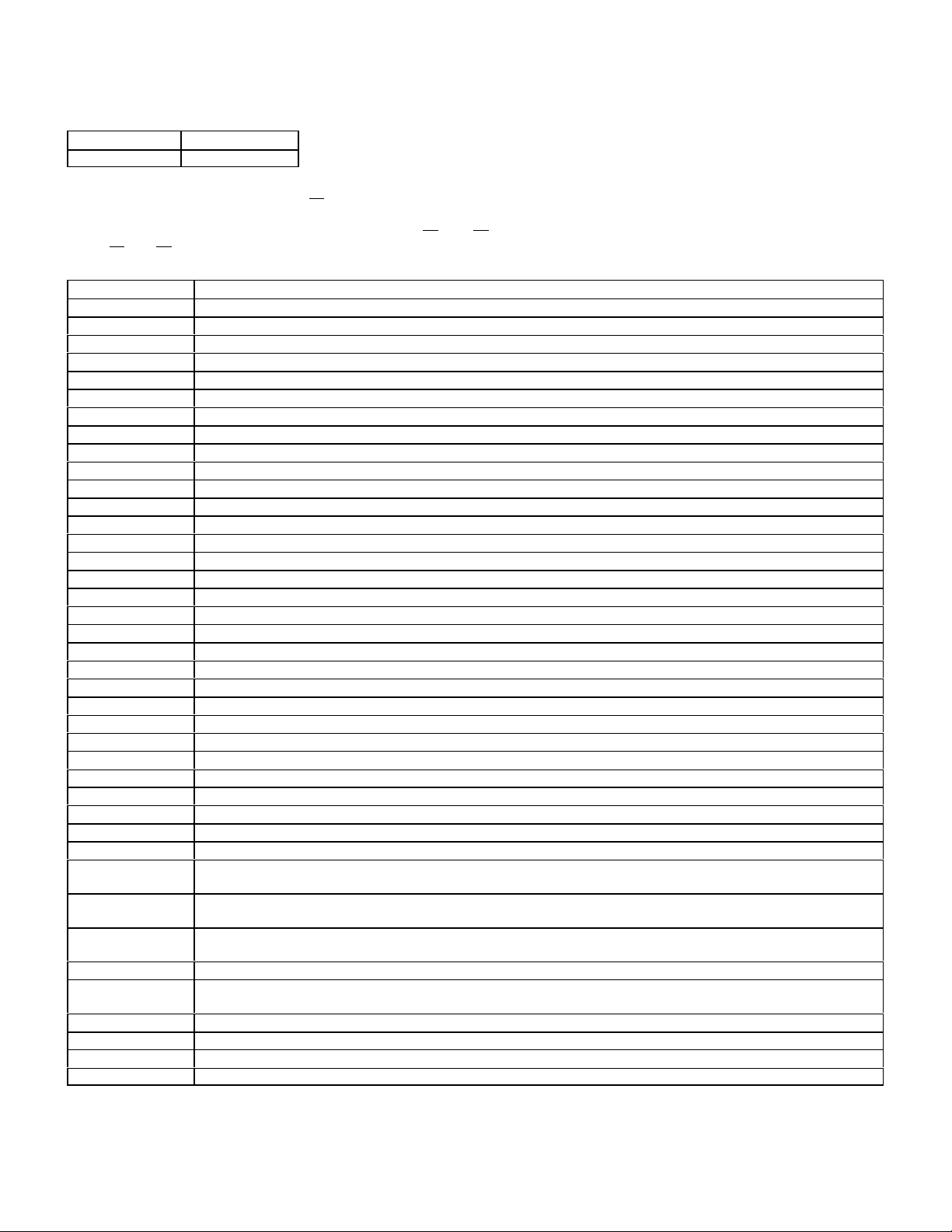
HFM Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection - Analog
Engines Model Year
104 111 1993
See digital HFM injection section page 22 for models 3/93 and later.
Also check for codes in the Diagnostic Module (DM page 41 and 43) and the Electronic Accelerator/Cruise Control (EA/CC/ISC
pages 50 and 49).
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Engine Coolant temperature sensor
3 Intake air temperature sensor
4 Hot film mass air flow sensor
5 CTP switch
6-7 Not used
8 Idle speed control (ISC) system at upper or lower control stop or CC or EA indicates "limp home" mode.
9 O2S 1 (before TWC) - voltage too high, circuit open or voltage implausible
10 O2S 2 (after TWC)voltage too high, circuit open or voltage implausible
11 O2S 1 heater (before TWC) - Current too high/low or short circuit.
12 O2S 2 heater (after TWC) - Current too high/low or short circuit.
13 O2S (Lambda) control system operating at rich or lean limit
14 Injector, cylinder 1
15 Injector, cylinder 2
16 Injector, cylinder 3
17 Injector, cylinder 4
18 Injector, cylinder 5
19 Injector, cylinder 6
20 Self-adaptation at idle speed or upper/lower partial load at rich or lean limit
21 Ignition output 3 or ignition coil for cylinder 1 and 6
22 Ignition output 1 or ignition coil for cylinder 2 and 5 (Engine 111, cylinder 1 and 4)
23 Ignition output 2 or ignition coil for cylinder 3 and 4 (Engine 111, cylinder 2 and 3)
24 CKP sensor or magnet for position sensor not recognized
25 CMP sensor not recognized or implausible
26 Not used
27 TN-signal (rpm signal ) - open or short to ground
28 VSS - open circuit
29 Not used
30 Fuel pump relay module - open or short circuit
31 Not used
32 Knock sensors 1 and /or 2
33 Maximum retard setting on at least one cylinder has been reached or the ignition angle deviation between the
individual cylinders is greater than 6 degrees crankshaft angle
34 Knock control-output switch in engine control module faulty Momentary fault in self-adaptation closed throttle
speed/partial load
35 Model 124,129 and 140 AIR pump switchover valve and/or electromagnetic AIR pump clutch.
Model 202 AIR pump switchover valve and/or AIR relay module
36 Purge control valve - open/short to ground or B+
37 Transmission Upshift delay switchover valve (Y3/3) without function (Logic Chain) - Check vacuum and
adjust Bowden cable.
38 Adjustable camshaft timing solenoid - open/short to ground or B+
39 Exhaust gas recirculation switchover valve - open/short to ground or B+
40 Transmission overload protection switch - open/short to ground or B+ or open or closed or implausible
41 CAN communication from engine control module faulty
20
Page 21

DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
42 CAN communication from ASR, EA/CC/ISC module or diagnostic module (OBD II) faulty
43 Starter signal (circuit 50) not present
44 Not used
45 Fuel safety shut-off of electronic accelerator or cruise control active
46 Resonance intake manifold switchover valve - open/short to ground or B+
48 O2S 2 (after TWC) heating circuit relay module - open/short to ground or B+
49 Voltage supply at engine control module implausible/low volts.
50 Engine control module faulty or not coded.
21
Page 22
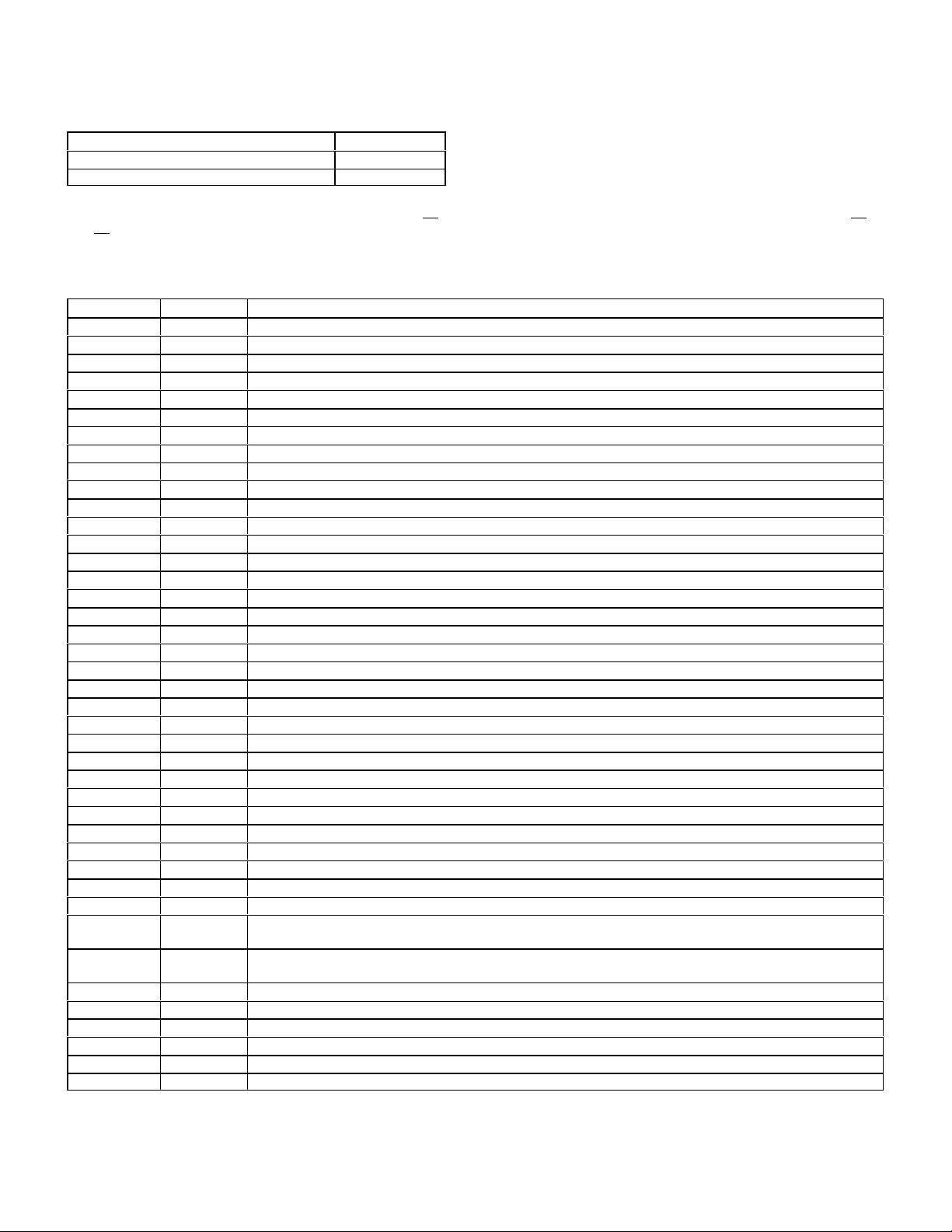
HFM Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection - Digital
Engines Model Years
111 (4 cylinder, 2.2/2.3L engine) 1994-97
104 (6 cylinder, 2.8/3.2L engine) 1994-97
Also check for codes in the Diagnostic Module (DM page 43) and the Electronic Accelerator/Cruise Control (EA/CC/ISC pages 50
and 49).
HFM-SFI Stored Fault Codes
Only Stored Fault Codes illuminate the Check Engine Light. (Code Scanner will display the fault code numbers listed under OB15,
Mercedes factory numbers are listed under MB for referral to factory literature.)
OB15 MB Description
0 No Fault Found
1 (002) Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor - Short Circuit
2 (003) Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor - Open Circuit
3 (004) Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor - Signal Incorrect
(005) Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor - Intermittent Contact
4 (006) Intake Air Temperature Sensor, Short Circuit
5 (007) Intake Air Temperature Sensor, Open Circuit
(008) Intake Air Temperature Sensor - Intermittent Contact
6 (009) Hot Film Air Mass Sensor - Signal Too High
7 (010) Hot Film Air Mass Sensor - Open Circuit
8 (011) Engine idle speed contact Throttle valve position too large
9 Not used
10 (012) Engine idle speed contact air mass too large
11 (113) HFM-SFI control unit not coded
12 (014) Throttle valve potentiometer actual value too high.
13 (015) Throttle valve potentiometer actual value too low.
14 (017) Throttle valve potentiometer drive value implausibly high.
15 (018) Throttle valve potentiometer drive value implausibly low.
16 (020) ISC (Idle speed control) at lower control stop area, malfunction.
17 (021) ISC (Idle speed control) at upper control stop area, malfunction.
18 (022) CC,EFP actuator signals in limp home mode (emergency mode).
19 (023) O2 sensor (before/upstream of Cat. Conv.), voltage too large.
20 (024) O2 sensor (before/upstream of Cat. Conv.), open circuit
21 (025) O2 sensor (before/upstream of Cat. Conv.), signal incorrect
22 (026) O2 sensor (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), voltage too large
23 (027) O2 sensor (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), open circuit
24 (028) O2 sensor (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), signal incorrect
25 (029) O2 sensor heater (before/upstream of Cat. Conv.), heater current (amp) too small
26 (030) O2 sensor heater (before/upstream of Cat. Conv.), heater current (amp) too large
27 (031) O2 sensor heater (before/upstream of Cat. Conv.), heater current, short circuit
28 (032) O2 sensor heater (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), heating current (amp) too small
29 (033) O2 sensor heater (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), heating current (amp) too large
30 (034) O2 sensor heater (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), heating current, short circuit
31 (035) Fuel adaptation (lambda) control, mixture too lean (rich stop)
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator)
32 (036) Fuel adaptation (lambda) control, mixture too rich (lean stop)
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator)
33 (037) Injection valve cylinder 1, short to positive
34 (038) Injection valve cylinder 1, open circuit or short to ground
35 (039) Injection valve cylinder 2, short to positive
36 (040) Injection valve cylinder 2, open circuit or short to ground
37 (041) Injection valve cylinder 3, short to positive
38 (042) Injection valve cylinder 3, open circuit or short to ground
22
Page 23
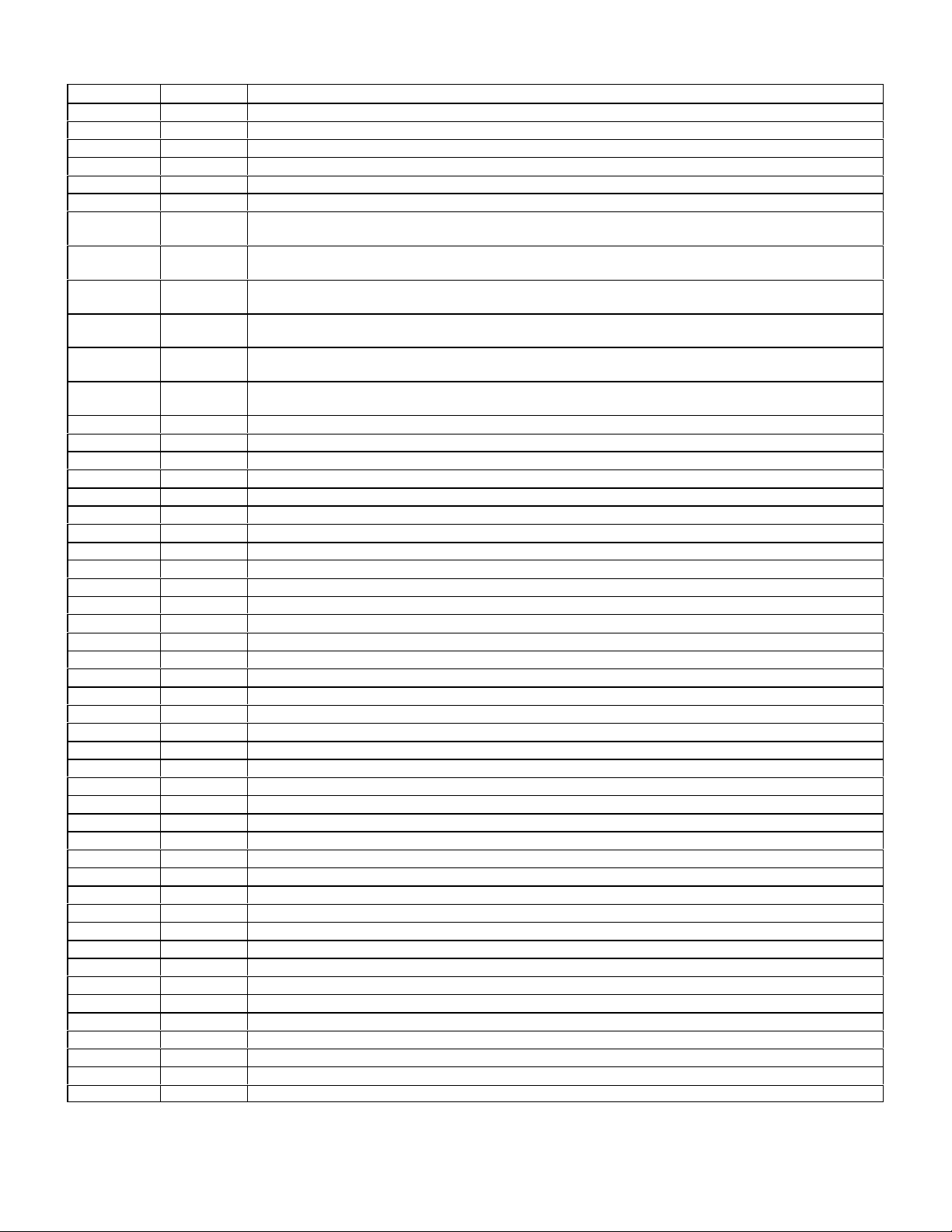
OB15 MB Description
39 (043) Injection valve cylinder 4, short to positive
40 (044) Injection valve cylinder 4, open circuit or short to ground
41 (045) Injection valve cylinder 5, short to positive
42 (046) Injection valve cylinder 5, open circuit or short to ground
43 (047) Injection valve cylinder 6, short to positive
44 (048) Injection valve cylinder 6, open circuit or short to ground
45 (049) Self-adjustment too rich at Idle
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
46 (050) Self-adjustment too lean at Idle
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
47 (051) Self-adjustment too rich at Lower part load
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
48 (052) Self-adjustment too lean at Lower part load
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
49 (053) Self-adjustment too rich at Upper part load
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
50 (054) Self-adjustment too lean at Upper part load
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
51 (061) Ignition system output stage 3, Cylinder 1 misfires
52 (062) Ignition system output stage 3, Cylinder 6 misfires
53 (063) Ignition system output stage 3, Current value not reached
54 (055) Ignition system output stage 1, Cylinder 2 misfires
55 (056) Ignition system output stage 1, Cylinder 5 misfires
56 (057) Ignition system output stage 1, Current value not reached
57 (058) Ignition system output stage 2, Cylinder 3 misfires
58 (059) Ignition system output stage 2, Cylinder 4 misfires
59 (060) Ignition system output stage 2, Current value not reached
60 (064) Crankshaft signal incorrect
61 (065) Crankshaft signal Magnet missing or Number of teeth incorrect
62 (066) Crankshaft signal Speed incorrect, too high
63 (067) Camshaft signal incorrect/not recognized
64 (068) HFM circuit/trimming plug short to ground
65 (069) HFM circuit/trimming plug open circuit or short to positive
66 (070) TN speed signal (rpm) Output short to ground
67 (071) TN speed signal (rpm) Output short to positive
68 (072) Vehicle speed signal not recognized, short circuit
69 (073) Vehicle speed signal implausibly high, short circuit
70 (074) PSV relay K3/1 circuit short to positive
71 Not used
72 (076) Fuel pump relay open circuit or short circuit
73 Not used
74 (077) CO potentiometer Input short to positive
75 (079) Knock sensor 1 signal open circuit
76 (080) Knock sensor 2 signal open circuit
77 (081) Ignition timing max retardation reached at least one cylinder
78 (082) Ignition angle deviation between the individual cylinders too high
79 (083) Knock control analysis, HFM control unit defective
80 (084) Short-term self-adjustment Idle/Part-load fault
81 (085) Air pump relay-module/switch-valve output, open circuit or short circuit
82-83 Not used
84 (086) Fuel purge switch-valve, open circuit/short circuit
85 (087) Fuel purge switch-valve, short to positive
86 (088) Transmission Upshift delay switchover valve (Y3/3) without function (Logic Chain)
87-88 Not used
89 (089) Camshaft timing adjust actuator circuit short to positive
90 (090) Camshaft timing adjust actuator open circuit or short to ground
23
Page 24
OB15 MB Description
91 (091) EGR switch-valve short to positive
92 (092) EGR switch-valve open circuit or short to ground
93 (093) Transmission overload protection switch short to ground
94 (094) Transmission overload protection switch, circuit short or open
95 (095) Transmission overload protection switch, circuit short or open
96 (096) Transmission overload protection switch signal implausible
97 (097) CAN problem Transmission communication from HFM control system faulty
98 (098) CAN problem No data reception from ASR
99 (116) CAN problem No data reception from IRCL. ( if equip with IRCL) Voltage supply at Circuit 87M, low
voltage or implausible (Starting 06/93)
100 Not used
101 (099) CAN problem No data reception from EFP,TPM
102 (100) CAN problem No data reception from Diagnosis Module
103 Not used
104 (117) Attempt to start with IRCL locked
105 (101) No starter signal (Terminal 50), open or short circuit
106 (102) Thermocouple CAT B16/6 Temperature too high
107 (103) Thermocouple CAT B16/6 Temperature too low
108 (104) Fuel safety cut-off settled
109 Not used
110 (105) Resonance intake manifold switchover valve, short to positive
111 (106) Resonance intake manifold switchover valve, open circuit/short to ground
112 (107) Ignition dwell angle control output stage, short to ground
113 (114) HFM control unit identification illogical
114 (108) Oxygen sensor heater (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), short to positive
115 (109) Oxygen sensor heater (after/downstream of Cat. Conv.), open circuit or short to ground
116 (115) HFM-SFI control unit N3/4 coding bytes illogical
117 Not used
118 (110) Voltage supply to HFM-SFI control unit, incorrect
119 (111) Voltage supply at HFM-SFI control unit, voltage too low
120 (112) HFM control unit faulty
121 (005) Coolant temperature sensor, Loose contact
122 (008) Intake air temperature sensor, Loose contact
123 (013) Idle speed contact, Loose contact
124 (016) Potentiometer throttle valve, Loose contact
125 (019) Potentiometer throttle valve drive, Loose contact
126 (078) CO potentiometer R33 Loose contact
127-128 Not used
24
Page 25
PMS (PEC) Fuel Injection - Digital
Engines Model Years
111 (4 cylinders, 1.8/2.0L engine) 1994-97
PMS Stored Fault Codes
Only Stored Fault Codes illuminate the Check Engine Light.(Code Scanner will display the fault code numbers listed under OB15,
Mercedes factory numbers are listed under MB.)
OB15 MB Description
001 (002) Coolant temperature sensor, short circuit
002 (003) Coolant temperature sensor, open circuit
003 (004) Coolant temperature sensor, incorrect
004 (006) Intake air temperature sensor, short circuit
005 (007) Intake air temperature sensor, open circuit
006 (009) PMS Control unit, Intake manifold pressure implausible
007 (010) PMS Control unit, No Intake manifold pressure
008 (011) Idle speed contact closed signal incorrect
009 (068) Idle speed contact open circuit
010-011 Not used
012 (013) Potentiometer throttle valve, value too high
013 (014) Potentiometer throttle valve, value too low
014 (016) Potentiometer throttle valve drive value too high/incorrect
015 (017) Potentiometer throttle valve drive value too low/incorrect
016 (019) Idle speed control at lower control stop area, malfunction
017 (020) Idle speed control at upper control stop area, malfunction
018 (021) Idle speed control in limp home-mode (emergency operation)
019 (022) O2 sensor voltage too large
020 (023) O2 sensor, open circuit
021 (024) O2 sensor signal illogical
022 (069) Exhaust flap short to positive
023 (070) Exhaust flap open circuit or short to ground
024 Not used
025 (025) O2 sensor heater current (amps) too small
026 (026) O2 sensor heater current (amps) too large
027 (027) O2 sensor heater, short circuit
028-030 Not used
031 (028) Fuel adaptation (lambda) control mixture too lean (Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm
pressure regulator)
032 (029) Fuel adaptation (lambda) control mixture too rich (Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm
pressure regulator)
033 (030) Injection valve cylinder 1/4 short to positive
034 (031) Injection valve cylinder 1/4 open circuit or short to ground
035 (032) Injection valve cylinder 2/3 short to positive
036 (033) Injection valve cylinder 2/3 open circuit or short to ground
037 (064) Input signal from IFZ, open circuit or short to positive
038 (065) Input signal from IFZ, short to ground
039 (066) IFZ system unresponsive
040 (067) Input signal from IFZ incorrect
041-044 Not used
045 (034) Self-adjustment too rich at Idle
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
046 (035) Self-adjustment too lean at Idle
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
047 (036) Self-adjustment too rich at Part load (Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure
regulator, wear engine)
25
Page 26
OB15 MB Description
048 (037) Self-adjustment too lean at Part load
(Intake air leak, fuel injectors, diaphragm pressure regulator, wear engine)
049-050 Not used
051 (038) Ignition system output stage 1, short to positive
052 (039) Ignition system output stage 1, Cylinder 1/4 misfires
053 (040) Ignition system output stage 1, Amperage not achieved
054 (041) Ignition system output stage 2, short to positive
055 (042) Ignition system output stage 2, Cylinder 2/3 misfires
056 (043) Ignition system output stage 2, Amperage not achieved
057-059 Not used
060 (044) Crankshaft signal incorrect
061 (045) Crankshaft signal Magnet missing or Numbers of teeth incorrect
062 (046) Crankshaft signal Speed incorrect, too high
063 Not used
064 (047) PMS circuit/trimming plug short to ground
065 (048) PMS circuit/trimming plug open circuit or short to positive
066 (049) TN speed signal (rpm) Output short to ground
067 (050) TN speed signal (rpm) Output short to positive
068 (051) Vehicle speed signal not recognized, short circuit
069 (052) Vehicle speed signal too high, short circuit
070 (053) PSV relay open circuit or short to positive
071 (054) PSV relay short to ground
072 (055) Fuel pump relay open circuit or short to positive
073 (056) Fuel pump relay short to ground
074 (057) CO potentiometer Input circuit short to positive
075 ~079 Not used
080 (061) Short-term self-adjustment faulty at idle speed or part load
081 (071) Rear axle ratio was changed
082 (072) Rear axle ratio signal incorrect
083 Not used
084 (059) Fuel purge switch-valve open circuit or short to positive
085 (060) Fuel purge switch-valve short to ground
086 (062) Transmission shifting delay/smooth switch-valve, open circuit or short circuit
087 ~092 Not used
093 (073) Transmission protection short to ground or active too long
094-095 Not used
096 (074) Transmission protection open circuit or short to positive
097 ~ 118 Not used
119 (063) PMS control unit voltage supply too low
120 Not used
121 (005) Coolant temperature sensor, Loose contact
122 (008) Intake air temperature sensor, Loose contact
123 (012) Idle speed contact, Loose contact
124 (015) Potentiometer throttle valve, Loose contact
125 (018) potentiometer throttle valve drive value, Loose contact
126 (058) CO potentiometer circuit, Loose contact
127-128 Not used
26
Page 27
ME Sequential Multiport Fuel Injection (ME-SFI)
Engines Model Years
104 (6 cylinders, 2.8/3.2L engine) 8/96111 (4 cylinder 2.0, 2.2, 2.3L) 8/96112 (V6 engine, 2.4/2.8/3.2L) 8/97113 (V8 engine, 4.3, 5.0L) 8/98119 (V8 engine 4.2/5.0L) 8/95-1998
120 (12 cylinder engine) 8/95-2000
ME-SFI ME Injection incorporates EA/CC/ISC, DM, DI and BM codes.
MB ME Code Description
P00XX Fuel and Air Metering and Auxiliary Emission Controls
P0010 A Camshaft Position Actuator Circuit (Bank 1)
P0011 A Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1)
P0012 A Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Retarded (Bank 1)
P0013 B Camshaft Position - Actuator Circuit (Bank 1)
P0014 B Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 1)
P0015 B Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Retarded (Bank 1)
P0020 A Camshaft Position Actuator Circuit (Bank 2)
P0021 A Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 2)
P0022 A Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Retarded (Bank 2)
P0023 B Camshaft Position - Actuator Circuit (Bank 2)
P0024 B Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Advanced or System Performance (Bank 2)
P0025 B Camshaft Position - Timing Over-Retarded (Bank 2)
P0030 H02S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1) Sensor 1)
P0031 H02S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0032 H02S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0033 Turbo Charger Bypass Valve Control Circuit
P0034 Turbo Charger Bypass Valve Control Circuit Low
P0035 Turbo Charger Bypass Valve Control Circuit High
P0036 H02S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0037 H02S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0038 H02S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0042 H02S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0043 H02S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0044 H02S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0050 H02S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0051 H02S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0052 H02S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0056 H02S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0057 H02S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0058 H02S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0062 H02S Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0063 H02S Heater Control Circuit Low (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0064 H02S Heater Control Circuit High (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0065 Air Assisted Injector Control Range/Performance
P0066 Air Assisted Injector Control Circuit or Circuit Low
P0067 Air Assisted Injector Control Circuit High
P0070 Ambient Air Temperature Sensor Circuit
P0071 Ambient Air Temperature Sensor Range/Performance
P0072 Ambient Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0073 Ambient Air Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
P0074 Ambient Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0075 Intake Valve Control Solenoid Circuit (Bank 1)
27
Page 28
MB ME Code Description
P0076 Intake Valve Control Solenoid Circuit Low (Bank 1)
P0077 Intake Valve Control Solenoid Circuit High (Bank 1)
P0078 Exhaust Valve Control Solenoid Circuit (Bank 1)
P0079 Exhaust Valve Control Solenoid Circuit Low (Bank 1)
P0080 Exhaust Valve Control Solenoid Circuit High (Bank 1)
P0081 Intake valve Control Solenoid Circuit (Bank 2)
P0082 Intake Valve Control Solenoid Circuit Low (Bank 2)
P0083 Intake Valve Control Solenoid Circuit High (Bank 2)
P0084 Exhaust Valve Control Solenoid Circuit (Bank 2)
P0085 Exhaust Valve Control Solenoid Circuit Low (Bank 2)
P0086 Exhaust Valve Control Solenoid Circuit High (Bank 2)
P01XX Fuel and Air Metering
P0100 Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit
P0101 Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Range/Performance Problem
P0102 Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Low Input
P0103 Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit High Input
P0104 Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit Intermittent
P0105 Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit
P0106 Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Range/Performance Problem
P0107 Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Low Input
P0108 Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit High Input
P0109 Manifold Absolute Pressure/Barometric Pressure Circuit Intermittent
P0110 Intake Air Temperature Circuit
P0111 Intake Air Temperature Circuit Range/Performance Problem
P0112 Intake Air Temperature Circuit Low Input
P0113 Intake Air Temperature Circuit High Input
P0114 Intake Air Temperature Circuit Intermittent
P0115 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit
P0116 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Range/Performance Problem
P0117 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Low Input
P0118 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit High Input
P0119 Engine Coolant Temperature Circuit Intermittent
P0120 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit, EA/CC/ISC Actuator
P0121 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit Range/Performance Problem
P0122 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit Low Input
P0123 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit High Input
P0124 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch A Circuit Intermittent
P0125 Insufficient Coolant Temperature for Closed Loop Fuel Control
P0126 Insufficient Coolant Temperature for Stable Operation
P0127 Intake Air Temperature Too High
P0128 Coolant Thermostat (Coolant Temperature Below Thermostat Regulating Temperature)
P0130 02 Sensor Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0131 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0132 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0133 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0134 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0135 02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
P0136 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0137 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0138 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0139 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0140 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0141 02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
P0142 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0143 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
28
Page 29
MB ME Code Description
P0144 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0145 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0146 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0147 02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 3)
P0148 Fuel Delivery Error
P0149 Fuel Timing Error
P0150 02 Sensor Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0151 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0152 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0153 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0154 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0155 02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
P0156 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0157 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0158 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0159 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0160 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0161 02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
P0162 02 Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0163 02 Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0164 02 Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0165 02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0166 02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0167 02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 3)
P0168 Fuel Temperature Too High
P0169 Incorrect Fuel Composition
P0170 Fuel Trim (Bank 1)
P0171 System too Lean (Bank 1)
P0172 System too Rich (Bank 1)
P0173 Fuel Trim Malfunction (Bank 2)
P0174 System too Lean (Bank 2)
P0175 System too Rich (Bank 2)
P0176 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit
P0177 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0178 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0179 Fuel Composition Sensor Circuit High Input
P0180 Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit
P0181 Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance
P0182 Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Low Input
P0183 Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit High Input
P0184 Fuel Temperature Sensor A Circuit Intermittent
P0185 Fuel Temperature Sensor B Circuit
P0186 Fuel Temperature Sensor B Circuit Range/Performance
P0187 Fuel Temperature Sensor B Circuit Low Input
P0188 Fuel Temperature Sensor B Circuit High Input
P0189 Fuel Temperature Sensor B Circuit Intermittent
P0190 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit
P0191 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0192 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0193 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit High Input
P0194 Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0195 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor
P0196 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Range/Performance
P0197 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Low
P0198 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor High
29
Page 30
MB ME Code Description
P0199 Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Intermittent
P02XX Fuel and Air Metering
P0200 Injector Circuit
P0201 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 1
P0202 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 2
P0203 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 3
P0204 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 4
P0205 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 5
P0206 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 6
P0207 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 7
P0208 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 8
P0209 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 9
P0210 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 10
P0211 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 11
P0212 Injector Circuit - Cylinder 12
P0213 Cold Start Injector 1
P0214 Cold Start Injector 2
P0215 Engine Shutoff Solenoid
P0216 Injector/Injection Timing Control Circuit
P0217 Engine Coolant Over Temperature Condition
P0218 Transmission Fluid Over Temperature Condition
P0219 Engine Overspeed Condition
P0220 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit
P0221 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit Range/Performance Problem
P0222 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit Low Input
P0223 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit High Input
P0224 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit Intermittent
P0225 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "C" Circuit
P0226 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "C" Circuit Range/Performance Problem
P0227 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "C" Circuit Low Input
P0228 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "C" Circuit High Input
P0229 Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch "C" Circuit Intermittent
P0230 Fuel Pump Primary Circuit
P0231 Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit Low
P0232 Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit High
P0233 Fuel Pump Secondary Circuit Intermittent
P0234 Turbo/Super Charger Overboost Condition
P0235 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "A" Circuit
P0236 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "A" Circuit Range/Performance
P0237 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "A" Circuit Low
P0238 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "A" Circuit High
P0239 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "B" Circuit
P0240 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "B" Circuit Range/Performance
P0241 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "B" Circuit Low
P0242 Turbo/Super Charger Boost Sensor "B" Circuit High
P0243 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "A"
P0244 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "A" Range/Performance
P0245 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "A" Low
P0246 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "A" High
P0247 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "B"
P0248 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "B" Range/Performance
P0249 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "B" Low
P0250 Turbo/Super Charger Wastegate Solenoid "B" High
P0251 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "A" (Cam/Rotor/injector)
P0252 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "A" Range/Performance (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
30
Page 31

MB ME Code Description
P0253 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "A" Low (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0254 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "A" High (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0255 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "A" Intermittent (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0256 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "B" (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0257 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "B" Range/Performance (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0258 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "B" Low (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0259 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "B" High (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0260 Injection Pump Fuel Metering Control "B" Intermittent (Cam/Rotor/Injector)
P0261 Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit Low
P0262 Cylinder 1 Injector Circuit High
P0263 Cylinder 1 Contribution/Balance
P0264 Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit Low
P0265 Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit High
P0266 Cylinder 2 Contribution/Balance
P0267 Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit Low
P0268 Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit High
P0269 Cylinder 3 Contribution/Balance
P0270 Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit Low
P0271 Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit High
P0272 Cylinder 4 Contribution/Balance
P0273 Cylinder 5 Injector Circuit Low
P0274 Cylinder 5 Injector Circuit High
P0275 Cylinder 5 Contribution/Balance
P0276 Cylinder 6 Injector Circuit Low
P0277 Cylinder 6 Injector Circuit High
P0278 Cylinder 6 Contribution/Balance
P0279 Cylinder 7 Injector Circuit Low
P0280 Cylinder 7 Injector Circuit High
P0281 Cylinder 7 Contribution/Balance
P0282 Cylinder 8 Injector Circuit Low
P0283 Cylinder 8 Injector Circuit High
P0284 Cylinder 8 Contribution/Balance
P0285 Cylinder 9 Injector Circuit Low
P0286 Cylinder 9 Injector Circuit High
P0287 Cylinder 9 Contribution/Balance
P0288 Cylinder 10 Injector Circuit Low
P0289 Cylinder 10 Injector Circuit High
P0290 Cylinder 10 Contribution/Balance
P0291 Cylinder 11 Injector Circuit Low
P0292 Cylinder 11 Injector Circuit High
P0293 Cylinder 11 Contribution/Balance
P0294 Cylinder 12 Injector Circuit Low
P0295 Cylinder 12 Injector Circuit High
P0296 Cylinder 12 Contribution/Balance
P0298 Engine Oil Over Temperature
P03XX Ignition System or Misfire
P0300 Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected - Mechanical, Ignition or Injection Malfunction
P0301 Cylinder 1 Misfire Detected
P0302 Cylinder 2 Misfire Detected
P0303 Cylinder 3 Misfire Detected
P0304 Cylinder 4 Misfire Detected
P0305 Cylinder 5 Misfire Detected
P0306 Cylinder 6 Misfire Detected
P0307 Cylinder 7 Misfire Detected
P0308 Cylinder 8 Misfire Detected
31
Page 32

MB ME Code Description
P0309 Cylinder 9 Misfire Detected
P0310 Cylinder 10 Misfire Detected
P0311 Cylinder 11 Misfire Detected
P0312 Cylinder 12 Misfire Detected
P0313 Misfire Detected with Low Fuel
P0314 Single Cylinder Misfire (Cylinder not Specified)
P0320 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input Circuit
P0321 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input Circuit Range/Performance
P0322 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input Circuit No Signal
P0323 Ignition/Distributor Engine Speed Input Circuit Intermittent
P0324 Knock Control System Error
P0325 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0326 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Range/Performance (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0327 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0328 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit High Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0329 Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Input Intermittent (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0330 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit (Bank 2)
P0331 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Range/Performance (Bank 2)
P0332 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Low Input (Bank 2)
P0333 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit High Input (Bank 2)
P0334 Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Input Intermittent (Bank 2)
P0335 Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit
P0336 Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Range/Performance
P0337 Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Low Input
P0338 Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit High Input
P0339 Crankshaft Position Sensor A Circuit Intermittent
P0340 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
P0341 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Range/Performance (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0342 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Low Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0343 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit High Input (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
P0344 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Intermittent (Bank 1 or Single Sensor
P0345 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit (Bank 2)
P0346 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Range/Performance (Bank 2)
P0347 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Low Input (Bank 2)
P0348 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit High Input (Bank 2)
P0349 Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Intermittent (Bank 2)
P0350 Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0351 Ignition Coil "A" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0352 Ignition Coil "B" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0353 Ignition Coil "C" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0354 Ignition Coil "D" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0355 Ignition Coil "E" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0356 Ignition Coil “F" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0357 Ignition Coil "G" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0358 Ignition Coil "H" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0359 Ignition Coil "I" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0360 Ignition Coil "J" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0361 Ignition Coil "K" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0362 Ignition Coil "L" Primary/Secondary Circuit
P0365 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit (Bank 1)
P0366 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Range/Performance (Bank 1)
P0367 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Low Input (Bank 1)
P0368 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit High Input (Bank 1)
P0369 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Intermittent (Bank 1)
P0370 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "A" (Camshaft to Crankshaft Angle)
32
Page 33

MB ME Code Description
P0371 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "A" Too Many Pulses
P0372 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "A" Too Few Pulses
P0373 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "A" Intermittent/Erratic Pulses
P0374 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "A" No Pulse
P0375 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "B"
P0376 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "B" Too Many Pulses
P0377 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "B" Too Few Pulses
P0378 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "B" Intermittent/Erratic Pulses
P0379 Timing Reference High Resolution Signal "B" No Pulses
P0380 Glow Plug/Heater Circuit "A"
P0381 Glow Plug/Heater Indicator Circuit
P0382 Glow Plug/Heater Circuit "B"
P0385 Crankshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit
P0386 Crankshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Range/Performance
P0387 Crankshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Low Input
P0388 Crankshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit High Input
P0389 Crankshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Intermittent
P0390 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit (Bank 2)
P0391 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Range/Performance (Bank 2)
P0392 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Low Input (Bank 2)
P0393 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit High Input (Bank 2)
P0394 Camshaft Position Sensor "B" Circuit Intermittent (Bank 2)
P04XX Auxiliary Emission Controls
P0400 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow
P0401 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Insufficient Detected
P0402 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Flow Excessive Detected
P0403 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Control Circuit
P0404 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Control Circuit Range/Performance
P0405 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor "A" Circuit Low
P0406 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor "A" Circuit High
P0407 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor "B" Circuit Low
P0408 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor "B" Circuit High
P0409 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor "A" Circuit
P0410 Secondary Air Injection System
P0411 Secondary Air Injection System Incorrect Flow Detected
P0412 Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve "A" Circuit
P0413 Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve "A" Circuit Open
P0414 Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve "A" Circuit Shorted
P0415 Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve "B" Circuit
P0416 Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve "B" Circuit Open
P0417 Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve "B" Circuit Shorted
P0418 Secondary Air Injection System Relay "A" Circuit
P0419 Secondary Air Injection System Relay "B" Circuit
P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
P0421 Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
P0422 Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
P0423 Heated Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
P0424 Heated Catalyst Temperature Below Threshold (Bank 1)
P0425 Catalyst Temperature Sensor (Bank 1)
P0426 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Range/Performance (Bank 1)
P0427 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Low Input (Bank 1)
P0428 Catalyst Temperature Sensor High Input (Bank 1)
P0429 Catalyst Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1)
P0430 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
P0431 Warm Up Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
33
Page 34

MB ME Code Description
P0432 Main Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
P0433 Heated Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
P0434 Heated Catalyst Temperature Below Threshold (Bank 2)
P0435 Catalyst Temperature Sensor (Bank 2)
P0436 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Range/Performance (Bank 2)
P0437 Catalyst Temperature Sensor Low Input (Bank 2)
P0438 Catalyst Temperature Sensor High Input (Bank 2)
P0439 Catalyst Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2)
P0440 Evaporative Emission Control System
P0441 Evaporative Emission Control System Incorrect Purge Flow
P0442 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (small leak)
P0443 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit
P0444 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit Open
P0445 Evaporative Emission Control System Purge Control Valve Circuit Shorted
P0446 Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Control Circuit
P0447 Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Control Circuit Open
P0448 Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Control Circuit Shorted
P0449 Evaporative Emission Control System Vent Valve/Solenoid Circuit
P0450 Evaporative Emission Control System Pressure Sensor
P0451 Evaporative Emission Control System Pressure Sensor Range/Performance
P0452 Evaporative Emission Control System Pressure Sensor Low Input
P0453 Evaporative Emission Control System Pressure Sensor High Input
P0454 Evaporative Emission Control System Pressure Sensor Intermittent
P0455 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (gross leak)
P0456 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (very small leak)
P0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (fuel cap loose/off)
P0460 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit
P0461 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0462 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0463 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit High Input
P0464 Fuel Level Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0465 EVAP Purge Flow Sensor Circuit
P0466 EVAP Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0467 EVAP Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0468 EVAP Purge Flow Sensor Circuit High Input
P0469 EVAP Purge Flow Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0470 Exhaust Pressure Sensor
P0471 Exhaust Pressure Sensor Range/Performance
P0472 Exhaust Pressure Sensor Low
P0473 Exhaust Pressure Sensor High
P0474 Exhaust Pressure Sensor Intermittent
P0475 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve
P0476 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve Range/Performance
P0477 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve Low
P0478 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve High
P0479 Exhaust Pressure Control Valve Intermittent
P0480 Cooling Fan 1 Control Circuit
P0481 Cooling Fan 2 Control Circuit
P0482 Cooling Fan 3 Control Circuit
P0483 Cooling Fan Rationality Check
P0484 Cooling Fan Circuit Over Current
P0485 Cooling Fan Power/Ground Circuit
P0486 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Sensor "B" Circuit
P0487 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Throttle Position Control Circuit
P0488 Exhaust Gas Recirculation Throttle Position Control Range/Performance
34
Page 35

MB ME Code Description
P0491 Secondary Air Injection System (Bank 1)
P0492 Secondary Air Injection System (Bank 2)
P05XX Vehicle Speed, Idle Control, and Auxiliary Inputs
P0500 Vehicle Speed Sensor
P0501 Vehicle Speed Sensor Range/Performance
P0502 Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0503 Vehicle Speed Sensor Intermittent/Erratic/High
P0505 Idle Control System
P0506 Idle Control System RPM Lower Than Expected
P0507 Idle Control System RPM Higher Than Expected
P0508 Idle Control System Circuit Low
P0509 Idle Control System Circuit High
P0510 Closed Throttle Position Switch
P0512 Starter Request Circuit
P0513 Incorrect Immobilizer Key ("Immobilizer" pending SAE J1930 approval) See P1570
P0515 Battery Temperature Sensor Circuit
P0516 Battery Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
P0517 Battery Temperature Sensor Circuit High
P0520 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Circuit
P0521 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Range/Performance
P0522 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch Low Voltage
P0523 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor/Switch High Voltage
P0524 Engine Oil Pressure Too Low
P0530 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit
P0531 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0532 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0533 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Circuit High Input
P0534 Air Conditioner Refrigerant Charge Loss
P0540 Intake Air Heater Circuit
P0541 Intake Air Heater Circuit Low
P0542 Intake Air Heater Circuit High
P0544 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit (Bank 1)
P0545 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit Low (Bank 1)
P0546 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit High (Bank 1)
P0547 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit (Bank 2)
P0548 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit Low (Bank 2)
P0549 Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor Circuit High (Bank 2)
P0550 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit
P0551 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0552 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0553 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit High Input
P0554 Power Steering Pressure Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0560 System Voltage
P0561 System Voltage Unstable
P0562 System Voltage Low
P0563 System Voltage High
P0564 Cruise Control Multi-Function Input Signal
P0565 Cruise Control On Signal
P0566 Cruise Control Off Signal
P0567 Cruise Control Resume Signal
P0568 Cruise Control Set Signal
P0569 Cruise Control Coast Signal
P0570 Cruise Control Acceleration Signal
P0571 Cruise Control/Brake Switch A Circuit
P0572 Cruise Control/Brake Switch A Circuit Low
35
Page 36

MB ME Code Description
P0573 Cruise Control/Brake Switch A Circuit High
P0574 Cruise Control System - Vehicle Speed Too High
P0575 Cruise Control Input Circuit
P0576 Cruise Control Input Circuit Low
P0577 Cruise Control Input Circuit High
P0578 through P0580 Reserved for Future Cruise Control Codes
P06XX Computer and Auxiliary Outputs
P0600 Serial Communication Link - General
P0601 Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
P0602 Control Module Programming Error
P0603 Internal Control Module Keep Alive Memory (KAM) Error
P0604 Internal Control Module Random Access Memory (RAM) Error
P0605 Internal Control Module Read Only Memory (ROM) Error
P0606 ECM/PCM Processor
P0607 Control Module Performance
P0608 Control Module VSS Output "A"
P0609 Control Module VSS Output "B"
P0610 Control Module Vehicle Options Error
P0615 Starter Relay Circuit
P0616 Starter Relay Circuit Low
P0617 Starter Relay Circuit High
P0618 Alternative Fuel Control Module KAM Error
P0619 Alternative Fuel Control Module RAM/ROM Error
P0620 Generator Control Circuit
P0621 Generator Lamp "L" Terminal Control Circuit
P0622 Generator Field "F" Terminal Control Circuit
P0623 Generator Lamp Control Circuit
P0624 Fuel Cap Lamp Control Circuit
P0630 VIN Not Programmed or Mismatch - ECM/PCM
P0631 VIN Not Programmed or Mismatch - TCM
P0635 Power Steering Control Circuit
P0636 Power Steering Control Circuit Low
P0637 Power Steering Control Circuit High
P0638 Throttle Actuator Control Range/Performance (Bank 1)
P0639 Throttle Actuator Control Range/Performance (Bank 2)
P0640 Intake Air Heater Control Circuit
P0645 A/C Clutch Relay Control Circuit
P0646 A/C Clutch Relay Control Circuit Low
P0647 A/C Clutch Relay Control Circuit High
P0648 Immobilizer Lamp Control Circuit ("Immobilizer" pending SAE J1930 approval)
P0649 Speed Control Lamp Control Circuit
P0650 Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Control Circuit
P0654 Engine RPM Output Circuit
P0655 Engine Hot Lamp Output Control Circuit
P0656 Fuel Level Output Circuit
P0660 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve Control Circuit (Bank 1)
P0661 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve Control Circuit Low (Bank 1)
P0662 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve Control Circuit High (Bank 1)
P0663 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve Control Circuit (Bank 2)
P0664 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve Control Circuit Low (Bank 2)
P0665 Intake Manifold Tuning Valve Control Circuit High (Bank 2)
P07XX Transmission
P0700 Transmission Control System (MIL Request)
P0701 Transmission Control System Range/Performance
P0702 Transmission Control System Electrical
36
Page 37

MB ME Code Description
P0703 Torque Converter/Brake Switch B Circuit
P0704 Clutch Switch Input Circuit Malfunction
P0705 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Malfunction (PRNDL Input)
P0706 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0707 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0708 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit High Input
P0709 Transmission Range Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0710 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit
P0711 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Low Input
P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit High Input
P0714 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0715 Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit
P0716 Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0717 Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal
P0718 Input/Turbine Speed Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0719 Torque Converter/Brake Switch B Circuit Low
P0720 Output Speed Sensor Circuit
P0721 Output Speed Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0722 Output Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal
P0723 Output Speed Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0724 Torque Converter/Brake Switch B Circuit High
P0725 Engine Speed Input Circuit
P0726 Engine Speed Input Circuit Range/Performance
P0727 Engine Speed Input Circuit No Signal
P0728 Engine Speed Input Circuit Intermittent
P0730 Incorrect Gear Ratio
P0731 Gear 1 Incorrect Ratio
P0732 Gear 2 Incorrect Ratio
P0733 Gear 3 Incorrect Ratio
P0734 Gear 4 Incorrect Ratio
P0735 Gear 5 Incorrect Ratio
P0736 Reverse Incorrect Ratio
P0737 TCM Engine Speed Output Circuit
P0739 TCM Engine Speed Output Circuit Low
P0739 TCM Engine Speed Output Circuit High
P0740 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit
P0741 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Performance or Stuck Off
P0742 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Stuck On
P0743 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Electrical
P0744 Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Intermittent
P0745 Pressure Control Solenoid "A"
P0746 Pressure Control Solenoid "A" Performance or Stuck Off
P0747 Pressure Control Solenoid "A" Stuck On
P0748 Pressure Control Solenoid "A" Electrical
P0749 Pressure Control Solenoid "A" Intermittent
P0750 Shift Solenoid "A"
P0751 Shift Solenoid "A" Performance or Stuck Off
P0752 Shift Solenoid "A" Stuck On
P0753 Shift Solenoid "A" Electrical
P0754 Shift Solenoid "A" Intermittent
P0755 Shift Solenoid "B"
P0756 Shift Solenoid "B" Performance or Stuck Off
P0757 Shift Solenoid "B" Stuck On
P0758 Shift Solenoid "B" Electrical
37
Page 38

MB ME Code Description
P0759 Shift Solenoid "B" Intermittent
P0760 Shift Solenoid "C"
P0761 Shift Solenoid "C" Performance or Stuck Off
P0762 Shift Solenoid "C" Stuck On
P0763 Shift Solenoid "C" Electrical
P0764 Shift Solenoid "C" Intermittent
P0765 Shift Solenoid "D"
P0766 Shift Solenoid "D" Performance or Stuck Off
P0767 Shift Solenoid "D" Stuck On
P0768 Shift Solenoid "D" Electrical
P0769 Shift Solenoid "D" Intermittent
P0770 Shift Solenoid "E"
P0771 Shift Solenoid "E" Performance or Stuck Off
P0772 Shift Solenoid "E" Stuck On
P0773 Shift Solenoid "E" Electrical
P0774 Shift Solenoid "E" Intermittent
P0775 Pressure Control Solenoid "B"
P0776 Pressure Control Solenoid "B" Performance or Stuck off
P0777 Pressure Control Solenoid "B" Stuck On
P0778 Pressure Control Solenoid "B" Electrical
P0779 Pressure Control Solenoid "B" Intermittent
P0780 Shift
P0781 1-2 Shift
P0782 2-3 Shift
P0783 3-4 Shift
P0784 4-5 Shift
P0785 Shift/Timing Solenoid
P0786 Shift/Timing Solenoid Range/Performance
P0787 Shift/Timing Solenoid Low
P0788 Shift/Timing Solenoid High
P0789 Shift/Timing Solenoid Intermittent
P0790 Normal/Performance Switch Circuit
P0791 Intermediate Shaft Speed Sensor Circuit
P0792 Intermediate Shaft Speed Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0793 Intermediate Shaft Speed Sensor Circuit No Signal
P0794 Intermediate Shaft Speed Sensor Circuit Intermittent
P0795 Pressure Control Solenoid "C"
P0796 Pressure Control Solenoid "C" Performance or Stuck off
P0797 Pressure Control Solenoid "C" Stuck On
P0798 Pressure Control Solenoid "C" Electrical
P0799 Pressure Control Solenoid "C" Intermittent
P08XX Transmission
P0801
P0802 Resonance Intake Manifold Switchover Valve Circuit
P0803 1-4 Upshift (Skip Shift) Solenoid Control Circuit
P0804 1-4 Upshift (Skip Shift) Lamp Control Circuit
P0805 Clutch Position Sensor Circuit
P0805 Air-flap recirculation signal output stage incorrect
P0806 Clutch Position Sensor Circuit Range/Performance
P0806 A/C compressor output stage, magnetic combination
P0807 Clutch Position Sensor Circuit Low
P0808 Clutch Position Sensor Circuit High
P0809
P0809 Variation in angle of camshaft to crankshaft incorrect
Reverse Inhibit Control Circuit/Electric-Suction type fan (engine AAC) connector M4/3.
Clutch Position Sensor Circuit Intermittent/Angular deviation between cam and crankshaft
38
Page 39

MB ME Code Description
P0810 Clutch Position Control Error
P0811 Excessive Clutch Slippage
P0811 CAN problem - No reception from EZS (Ignition Lock)
P0812 Reverse Input Circuit
P0813 Reverse Output Circuit
P0814 Transmission Range Display Circuit
P0815 Upshift Switch Circuit
P0816 Downshift Switch Circuit
P0816 Oil pressure sensor open circuit or short circuit, malfunction
P0817 Starter Disable Circuit
P0818 Driveline Disconnect Switch Input Circuit
P0820 Gear Lever X-Y Position Sensor Circuit
P0821 Gear Lever X Position Circuit
P0822 Gear Lever Y Position Circuit
P0823 Gear Lever X Position Circuit Intermittent
P0824 Gear Lever Y Position Circuit Intermittent
P0825 Gear Lever Push-Pull Switch (Shift Anticipate)
P0830 Clutch Pedal Switch "A" Circuit
P0831 Clutch Pedal Switch "A" Circuit Low
P0832 Clutch Pedal Switch "A" Circuit High
P0833 Clutch Pedal Switch "B" Circuit
P0834 Clutch Pedal Switch "B" Circuit Low
P0835 Clutch Pedal Switch "B" Circuit High
P0836 Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Switch Circuit
P0837 Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Switch Circuit Range/Performance
P0838 Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Switch Circuit Low
P0839 Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Switch Circuit High
P0840 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "A" Circuit
P0841 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "A" Circuit Range/Performance
P0842 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "A" Circuit Low
P0843 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "A" Circuit High
P0844 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "A" Circuit Intermittent
P0845 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit
P0846 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit Range/Performance
P0847 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit Low
P0848 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit High
P0849 Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor/Switch "B" Circuit Intermittent
P09XX Transmission
None defined at this time.
P1XXX Mercedes Benz Manufacturer Specific Codes
P10XX Fuel and Air Metering and Auxiliary Emission Controls
P1031 O2 sensor (G3/3 and G3/4) connections reversed
P11XX Fuel and Air Metering
P1146 Mass air flow circuit malfunction - Bank 2 (left)
P1147 ECT circuit malfunction - Bank 2 (left)
P1148 IAT circuit malfunction - Bank 2 (left)
P1149 MAP circuit malfunction - Bank 2 (left)
P1162 Throttle position sensor circuit failure - Bank 2 (left)
P1163 Oil level switch.
P1176 Oil pressure sensor open circuit or short circuit, malfunction.
P1177 Oil sensor, temperature incorrect.
P1178 Oil sensor, engine oil level incorrect.
P1179 Oil sensor, engine oil quality incorrect.
39
Page 40

MB ME Code Description
P1180 Oil sensor, engine oil temperature too high
P1181 Engine electric-fan /Air conditioning malfunction
P1182 Starting system relay in fuse and relay module box
P1183 Right cylinders bank cut-off output stage malfunction
P1184 Left cylinders bank cut-off output stage malfunction
P1185 Water in engine oil, Oil sensor
P1186 Fuel safety shut-off recognized.
P12XX Fuel and Air Metering
P1225 Resonance intake manifold switchover valve circuit
P1233 Throttle Valve Actuator - Mechanically jammed
P1235 Air-flap recirculated signal output stage faulty
P1236 A/C compressor output stage, magnetic combination incorrect
P13XX Ignition System or Misfire
P1300 CKP sensor circuit failure - Bank 2 (left)
P1384 Knock sensor circuit malfunction - Left front.
P1385 Knock sensor circuit malfunction - Left rear.
P1386 Knock sensor control from electronic control module - at limit
P1397 CMP sensor circuit range/performance - Bank 2 (left)
P14XX Auxiliary Emission Controls
P1400 EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) output stage faulty
P1420 Air-pump switchover valve circuit
P1443 EVAP system malfunction - Bank 2 (left)
P1453 Air-pump relay, relay module, fuse or circuit
P1463 Left AIR system malfunction
P1490 EVAP system purge control valve circuit malfunction - Bank 2 (left)
P1491 A/C system refrigerant pressure too high
P1492 Exhaust-flap faulty
P15XX Vehicle Speed, Idle Control, and Auxiliary Inputs
P1519 Right or sole adjustable camshaft timing solenoid mechanically faulty.
P1522 Left adjustable camshaft timing solenoid mechanically faulty.
P1525 Right or sole adjustable camshaft timing solenoid electrically faulty
P1533 Left adjustable camshaft timing solenoid electrically faulty
P1542 Pedal position sensor signal
P1570 CAN bus signal from DAS to the ME-SFI control unit - DAS locked, signal interrupted, mismatched ECMs.
P1580 Right or sole EA/CC/ISC Actuator circuit faulty
P1581 Left EA/CC/ISC Actuator circuit faulty
P1584 Stop lamp switch/Brake switch signal
P1587 Left engine control module voltage supply faulty.
P1588 CAN bus signal from the RCL controller to the Left engine controller faulty.
P1589 Knock sensor control from the left engine controller at limit.
P16XX Computer and Auxiliary Outputs
P1603 CAN bus problem. No data reception from EIS
P1605 CAN fault. ABS speed sensor error vs. VSS (RPM)
P1632 Left engine control module faulty.
P1641 Right of left CTP signal to the engine control module faulty or CAN bus communication by the left engine control
has been interrupted.
P1642 Engine control module incorrect coding (MT coded has AT)
P1643 Engine control module incorrect coding or CAN signal from Transmission system faulty.
P1644 Transmission control module, voltage too low. Transmission control system version cannot be checked.
P17XX Transmission
P1747 CAN signal from ETC. CAN signal failure from ETC or instrument cluster faulty.
40
Page 41

Diagnostic Module (DM) - Analog
Models Model Years
124.034 124.036 1992-1993
124.028 124.032 124.052 124.092 1994-95
119.067 1992-1994
140.032 140.042 140.043 140.051 1992-1994
140.057 140.076 1992-1995
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Oxygen sensor faulty - Bank 1 Sensor 1
3 Lambda control out of range - Bank 1 - Air, fuel metering or ignition problem.
4 Air injection faulty - Bank 1
5 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) of control module faulty - Bank 1
6 Idle speed control faulty
7 Ignition system faulty - Bank 1
8 Engine coolant temperature sensor, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 1
9 Intake air temperature sensor, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 1
10 Voltage at mass air sensor too high/low - Bank 1
11 Tn-signal (rpm signal ) at control module faulty - Bank 1
12 Oxygen sensor heater, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 1
13 Camshaft position sensor signal ignition control module faulty - Bank 1
14 Intake manifold pressure at startup too low or too high - Bank 1
15 Wide open throttle (WOT) position information faulty
16 Closed throttle position (CTP) information faulty
17 Data exchange (CAN) fault between engine control module, ignition control module or electronic
accelerator/cruise control module. Bank 1
18 Adjustable camshaft timing solenoid circuit open or circuit short - Bank 1
19 Injector circuit open or circuit short or emission control system adaptation at limit - Bank 1
20 Vehicle speed signal missing
21 Purge switchover valve, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 1
22 Camshaft position sensor signal faulty - Bank 1
23 Intake manifold pressure with engine running, too low/high - Bank 1
24 Starter ring gear segments faulty or crankshaft position sensor faulty - Bank 1
25 Knock sensors or ignition control module faulty - Bank 1
26 Upshift delay switchover valve, circuit open or circuit short
27 Engine coolant temperature sensor deviation between circuit 1, and sensor circuit 2 - Bank 1
28 Engine coolant temperature sensor (engine coolant temperature change monitor) - Bank 1
34 Oxygen sensor faulty - Bank 2 Sensor 1
35 Lambda control out of range - Bank 2 - Air, fuel metering or ignition problem.
36 Air injection faulty - Bank 2
37 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) of control module faulty - Bank 2
38 Not used
39 Ignition system faulty - Bank 2
40 Engine coolant temperature sensor, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 2
41 Intake air temperature sensor, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 2
42 Voltage at mass air sensor too high/low - Bank 2
43 Tn-signal (rpm signal ) at control module faulty - Bank 2
44 Oxygen sensor heater, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 2
45 Camshaft position sensor signal ignition control module faulty - Bank 2 or Fuel safety shut-off electronic
accelerator or cruise control active (HFM only)
46 Intake manifold pressure at startup too low or too high - Bank 2 or Resonance intake manifold switchover
valve (HFM only)
41
Page 42

DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
47-48 Not used
49 Data exchange (CAN) fault between engine control module, ignition control module or electronic
accelerator/cruise control module. - Bank 2 or Voltage supply at engine control module <8V (HFM only)
50 Adjustable camshaft timing solenoid circuit open or circuit short - Bank 2 or Engine control module (HFM
only)
51 Injector circuit open or circuit short or emission control system adaptation at limit - Bank 2
52 Not used
53 Purge switchover valve, circuit open or circuit short - Bank 2
54 Camshaft position sensor signal faulty - Bank 2
55 Intake manifold pressure with engine running, too low/high - Bank 2
56 Starter ring gear segments faulty or crankshaft position sensor faulty - Bank 2
57 Knock sensors or ignition control module faulty - Bnak 2
58 Not used
59 Engine coolant temperature sensor deviation between circuit 1, and sensor circuit 2 - Bank 2
60 Engine coolant temperature sensor (engine coolant temperature change monitor) - Bank 2
42
Page 43

Diagnostic Module (DM) - Digital LH
SEE ME-SFI INJECTION FOR ALL DIAGNOSTIC CODES FROM 8/96 PRODUCTION AND LATER FOR ALL MODELS.
Engines Model Years
104 (LH-SFI) 1992
104 (124 only) 1992-95
119 120 1991-96
Stored Codes turn on the Check Engine Light (MIL)
Registered or Pending Codes will keep the light on.
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
0 No fault found
2 Oxygen sensor. No signal (right bank in 120)
3 Fuel adaptation (lambda control), inoperative. Engine control module (right bank in 120)
4 Air injection defective, fault from Fuel control system (right bank in 120)
5 EGR exhaust gas recirculation incorrect, fault. Engine control module (right bank in 120)
6 Idle speed control incorrect, fault from EA/CC/ISC
7 Ignition system defective, fault from Fuel/Ignition control system (right bank in 120)
8 Coolant temperature sensor signal. Open or short circuit (right bank in 120)
9 Intake air temperature sensor signal. Open or short circuit (right bank in 120)
10 Air mass sensor voltage signal too high /low. (right bank in 120)
11 Engine speed signal TN (RPM) or Engine control module (right bank in 120) defective
12 Oxygen sensor heater circuit. Open or short circuit (right bank in 120)
13 Camshaft position sensor (CMP) signal, fault from Fuel/Ignition control system (right bank in 120)
14 Intake manifold pressure value at start too high/low, fault from Fuel/Ignition control system (right bank in 120)
15 Wide open throttle (WOT) signal incorrect/implausible.
16 Closed throttle position (CTP) sensor signal incorrect/implausible.
17 CAN communication faulty in between control units (right bank in 120).
18 Camshaft timing adjust solenoid, open or short circuit (right bank in 120)
19 Fuel injector circuit, open or short circuit or self adaptation at limit. (right bank in 120)
20 Speed signal missing
21 Fuel purge control valve, open or short circuit (right bank in 120)
22 Camshaft position sensor (CMP) signal defective (right bank in 120)
23 Intake manifold pressure sensor signal incorrect, too high/low. (right bank in 120)
24 Crankshaft position sensor (CKP) signal incorrect or starter ring gear segment damaged.
25 Knock sensors circuit or Ignition control module defective (right bank in 120)
26 Transmission Upshift delay switchover valve (Y3/3) without function (Logic Chain)
27 Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensors circuit 1 and 2 have difference values. (right bank in 120)
28 Engine coolant sensor/Operating temperature error. (right bank in 120)
34 Oxygen sensor. No signal (left bank in 120)
35 Fuel adaptation (lambda control), inoperative. Engine control module (left bank in 120)
36 Air injection defective, fault from Fuel control system (left bank in 120)
37 EGR exhaust gas recirculation incorrect, fault. Engine control module (left bank in 120)
38 Not used
39 Ignition system defective, fault from Fuel/Ignition control system (left bank in 120)
40 Coolant temperature sensor signal. Open or short circuit (left bank in 120)
41 Intake air temperature sensor signal. Open or short circuit (left bank in 120)
42 Air mass sensor voltage signal too high /low. (left bank in 120)
43 Engine speed signal TN (RPM) or Engine control module (left bank in 120) defective
44 Oxygen sensor heater circuit. Open or short circuit (left bank in 120)
45 Camshaft position sensor (CMP) signal, fault from Fuel/Ignition control system (left bank in 120)
46 Intake manifold pressure value at start too high/low, fault from Fuel/Ignition control system (left bank in 120)
47-48 Not used.
49 CAN communication faulty in between control units (left bank in 120).
43
Page 44

DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
50 Camshaft timing adjust solenoid, open or short circuit (left bank in 120)
51 Fuel injector circuit, open or short circuit or self adaptation at limit. (left bank in 120)
52 Not used.
53 Fuel purge control valve, open or short circuit (left bank in 120)
54 Camshaft position sensor (CMP) signal defective (left bank in 120)
55 Intake manifold pressure sensor signal incorrect, too high/low. (left bank in 120)
56 Crankshaft position sensor (CKP) signal incorrect or starter ring gear segment damaged.
57 Knock sensors circuit or Ignition control module defective (left bank in 120)
58 Not used.
59 Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensors circuit 1 and 2 have difference values. (left bank in 120)
60 Engine coolant sensor/Operating temperature error. (left bank in 120)
63 Anomalous Code (Battery Jump most likely Caused)
65 EVAP Purge Valve
Be sure to reset adaptation once the codes have been cleared from the
Diagnostic Module (see page 8).
44
Page 45

Diagnostic Module (DM) - Digital HFM
SEE ME-SFI INJECTION FOR ALL DIAGNOSTIC CODES FROM 8/96 PRODUCTION AND LATER FOR ALL MODELS.
Engines Model Years
104, 111 (HFM) 1994-96
Stored Codes turn on the Check Engine Light (MIL).
Registered or Pending Codes will keep the light on.
Fault Code Table
OB15 MB/SAE ME Code Description
002 P0132 Oxygen sensor (G3/2) circuit high voltage
003 P0134 Oxygen sensor (G3/2) circuit no activity detected
004 P0131 Oxygen sensor (G3/2) circuit low voltage
005 P1131 Oxygen sensor (G3/2) circuit short circuit
006 P0133 Oxygen sensor (G3/2) circuit slow response
007 P0135 Oxygen sensor (G3/2) heater circuit malfunction
008 P1132 Oxygen sensor (G3/2) circuit "rich" stop
009 P0138 Oxygen sensor (G3/1) circuit high voltage
010 P0412 Secondary air injection (AIR) system switching valve/circuit malfunction
Model 202: AIR pump switchover valve (Y32) and AIR relay module (K17)
Models 129, 140: AIR pump switchover valve (Y32) and electromagnetic AIR
pump clutch (Y33)
011 P0141 Oxygen sensor (G3/1) heater circuit malfunction
012 P1137 Oxygen sensor (G3/1) circuit short circuit
013 P1138 Oxygen sensor (G3/1) operating condition
015 P0411 Secondary air injection system incorrect flow detected
016 P1400 Electrical activation of the EGR switchover valve (Y27)
017 P0400 Exhaust gas recirculation flow malfunction
018 P0507 Idle control system RPM higher than expected
019 P0505 Idle control system malfunction
020 P030X Cylinder X misfire detected
021 P1342 Electrical activation of adjustable camshaft timing solenoid (Y49)
021 P0300 Random misfire detected
022 P030X Cylinder X misfire detected
023 P0300 Random misfire detected
024 P030X Cylinder X misfire detected
025 P0300 Random misfire detected
026 P0420 Catalyst system efficiency below threshold
028 P1341 Adjustable camshaft timing solenoid (Y49) without function (Logic chain)
029 P0200 Injector circuit malfunction
030 P1170 Short term fuel trim (self-adaptation of fuel mixture)
031 P0170 Fuel trim malfunction
032 P0443 Evaporative emission control system (EVAP) purge control valve circuit
malfunction (Purge switchover valve [Y58/1 ])
032 P1701 Electrical activation of upshift delay switchover valve (Y3/3)
034 P1700 Transmission upshift delay switchover valve (Y3/3) without function (Logic chain)
035 P030X Cylinder X misfire detected
036 P0300 Random misfire detected
037 P030X Cylinder X misfire detected
038 P0300 Random misfire detected
039 P030X Cylinder X misfire detected
040 P0300 Random misfire detected
042 P1340 Camshaft position sensor monitoring signal from engine control module (N3/4)
043 P1335 Engine speed signal TNA to diagnostic module (OBD II) not received
044 P1711 Engine 104 only: Electrical activation of resonance intake manifold switchover valve (Y22/6)
45
Page 46

OB15 MB/SAE ME Code Description
045 P0116 Engine coolant temperature circuit range/performance problem
(Engine coolant temperature sensor [B11/3])
046 P0125 Insufficient coolant temperature for closed loop fuel control
047 P0111 Intake air temperature circuit range/performance problem
(Intake air temperature sensor [B17])
048 P0101 Mass or volume air flow circuit range/performance problem
(Hot film mass air flow sensor [B2/5])
049 P0335 Crankshaft position sensor circuit malfunction
050 P1336 Crankshaft sensor signal: Magnet coding on segment
051 P0501 Vehicle speed sensor range/performance
051 P1337 Engine speed signal TNA transmitted from engine control module
052 P1740 Full load information: Load implausible
053 P1741 Full load information: Throttle valve position implausible
054 P0510 Closed throttle position switch malfunction
055 P0600 Serial communication link malfunction (CAN)
056 P0500 Vehicle speed sensor malfunction
058 P0341 Camshaft position sensor circuit range/performance
(Camshaft position sensor [L5/1])
059 P0105 Manifold absolute pressure/barometric pressure circuit malfunction
060 P0327 Knock sensor 1 circuit low input
061 P0326 Knock sensor 1 circuit range/performance
062 P0325 Knock sensor 1 circuit malfunction
063 P1750 Battery voltage too low
064 P1443 Electrical activation of purge flow switchover valve (Y27/6)
065 P0441 EVAP incorrect purge flow
066 P1444 Pressure switchover without function (Logic chain)
Be sure to reset adaptation once the codes have been cleared from the
Diagnostic Module (see page 8).
46
Page 47

Base Module (BM)
Models Model Years
124.034 124.036 1992-93
129.067 1992-95
140.032 140.042 140.043 140.051 140.057 140.076 1992-95
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2, 3, 4 Not used
5 Maximum permissible temperature in module box exceeded
6 Electromagnetic a/c compressor clutch blocked
7 Poly v-belt slipping
8 Voltage supply for LH-SFI control module interrupted
9 Voltage supply for LH-SFI control module interrupted
10 Voltage supply for LH-SFI control module interrupted
Voltage supply for fuel injectors interrupted
11 Voltage supply for accessory equipment control module interrupted
12 Voltage supply for ABS control module, ABS/ASR control module or ASD control module interrupted
13, 14 Not used
15 Voltage supply for kickdown valve interrupted
16 Voltage supply for electromagnetic a/c compressor clutch interrupted
17 Voltage supply for module box blower motor interrupted
47
Page 48

Distributor Ignition (DI)
Model Model Years
124.051 1990-1995
124.034 124.036 1992-1995
129.061 129.066 1990-1995
129.067 129.076 1992-1995
140.032 1992-1993
140.042 140.043 140.051 140.057 140.070 140.076 1992-1995
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Maximum retard setting on at least one cylinder has been reached
3 Engine coolant temperature sensor faulty
4 Load sensor in EAL/AKR control module faulty
5 Knock sensors 1 and/or 2 faulty
6 Camshaft position sensor faulty
7 Knock output switch in EAL/AKR ignition control module faulty
8 Transmission overload switch does not close
9 Transmission overload switch does not open
10 Data exchange from EAL/AKR engine control module to CFI control module faulty.
11 Preference resistor faulty
12 Tn-signal is outside the tolerance range
13 Full load contact does not open.
14 Idle speed contact does not open.
15 Ignition coil 1 output from EAL/AKR ignition control module faulty
16 Ignition coil 2 output from EAL/AKR ignition control module faulty
17 Crankshaft position sensor faulty
18 Magnets for crankshaft position sensor (CKP) not recognized.
19 Ground, coding from left EZL/AKR ignition control module not present.
20 Ignition control module DTC memory faulty.
21 Load sensor in control module faulty. (Recognized with engine running)
22 -25 Not used
26 Ignition control module data exchange fault
27 LH-SFI control module data exchange fault
28 Electronic accelerator control module/idle speed control data exchange fault
34 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 1 (104) / cylinder 1 (119)
35 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 5 (104) / cylinder 5 (119)
36 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 3 (104) / cylinder 4 (119)
37 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 6 (104) / cylinder 8 (119)
38 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 2 (104) / cylinder 6 (119)
39 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 4 (104) / cylinder 3 (119)
40 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 7 (119)
41 Ignition misfire detected at cylinder 2 (119)
48
Page 49

Cruise Control/Idle Speed Control (CC/ISC) w/o ASR
Models Model Years
124 129 140 202 1992-97
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Cruise control/idle speed control module
3 Cruise control/idle speed control actuator
4 Cruise control switch
5 Stop lamp switch
6 Starter lock-out/backup lamp switch
7 Data bus (CAN)
8 Left front axle vehicle speed sensor
9 Left rear axle vehicle speed sensor or Hall-effect speed sensor
Rear axle vehicle speed sensor from ABS control module
Rear axle vehicle speed sensor from ETS/SPS control module
Incorrect CC/ISC control module installed ETS signal
10 Engine speed (RPM) signal (TNA)
11 Fuel safety shut-off to LH-SFI control module
12 Cruise control/idle speed control voltage supply
49
Page 50

Electronic Accelerator / Cruise Control / Idle Speed Control
(EA/CC/ISC) w/ASR
Models Model Year
124 129 140 202 1992-96
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 EA/CC/ISC control module (N4/1) or
Safety contact switch (M16/1s1) or
Stop lamp switch or
Cruise control switch or
Actual value potentiometer or
Starter lock-out/back-up lamp switch or
Engine speed signal or
Vehicle speed signal or
Closed throttle position switch or
Safety relay in EA/CC/ISC control module
3 Right EA/CC/ISC actuator (left cylinder bank) (M16/1)
4 Cruise control switch (S40)
5 Stop lamp switch (S9/1)
6 Starter lock-out/backup lamp switch
7 CAN data bus signal from EA/CC/ISC, ABS/ASR, HFM-SFI or LH-SFI (right or left) control module
faulty.
8 Left front axle vehicle speed sensor from ABS/ASR control module
9 Left rear axle vehicle speed sensor from ABS/ASR control module or in 124 chassis Hall-effect speed
sensor.
10 Engine speed signal (TN) from base module (LH-SFI) or engine control module (HFM-SFI)
11 Closed throttle recognition signal to engine control module (HFM-SFI or Left LH-SFI)
Fuel safety shut-off to engine control module (HFM-SFI or left or right LH-SFI)
12 EA/CC/ISC control module voltage supply
13 Left EA/CC/ISC actuator (right cylinder bank) or actual value potentiometer (M16/4r1 or M16/4r2) or
actuator motor (M16/4m1)or magnetic clutch (M16/4k1).
14 Closed throttle position contact switch
15 CAN data exchange with ABS/ASR control module illogical
50
Page 51

Electronic Automatic Transmission Control (ETC) with CFI (722.5)
Models Model Years
129 1990-1993
See 4matic and digital transmission control diagnosis beginning on page ?.
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Not used
3 Engine load signal interrupted
4 Throttle valve switch (potentiometer) interrupted
5 Engine speed (RPM) signal interrupted
6 Vehicle speed signal interrupted
7 Output fault in 5-speed automatic transmission control module or fault in control valve.
8 5-speed automatic transmission control module
9 Control valve
10 Control valve short circuit
Electronic Transmission Control 5-speed (722.5)
Models Model Years
129, 140 1990-1996
Fault Code Table
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Engine control module (N3/4) does not match TCM
3 Transmission overload protection switch 4th/5th gear defective
4 CAN data line from EA/CC/ISC control module (N4/1) signal distorted
5 CAN data line from DI control module (N1/3) or HFM control module signal distorted
6 CAN data line signal distorted, Short or open circuit
7 Control valve block (Y3/1y2), open circuit or TCM (N15/1) defective
8 Automatic Transmission Control Module (TCM) (N15/1) defective
9 Control valve block (Y3/1y2)
10 Control valve block (Y3/1y2), short circuit
51
Page 52

Automatic-Engaged Four-wheel Drive (4MATIC)
Models Model Years
124.230 124.290 1990-1993
NOTE: Engine must be at idle to read and clear 4MATIC fault codes.
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 4MATIC control module
3 Brake light switch
4 Left front axle vehicle speed sensor
5 Right front axle vehicle speed sensor
6 Rear speed sensor signal
7 All 3 vehicle speed sensors
8 Over volts protection relay, front axle train valve
9 Over volts protection relay, central differential lock valve
10 Over volts protection relay, stop lamp switch, Rear axle differential lock valve
11 Steering angle sensor signal
The following faults cannot be detected by the 4MATIC controller:
< 4MATIC function indicator lamp defective.
< 4MATIC MIL defective.
< Oil Pressure Switch defective.
52
Page 53

Electronic Transmission Control (ETC) for ME-SFI
5-speed (722.6)
Models Engines Model Years
129 140 163 170 202 208 210 104 111 112 113 119 120 606 1995-99
Fault Code Table
DTC Readout Possible cause of Failure
1 No fault stored
2 1-2/4-5 shift solenoid valve circuit fault (Y3/6y3)
3 2-3 shift solenoid valve circuit fault (Y3/6y5)
4 3-4 shift solenoid valve circuit fault (Y3/6y4)
5 PWM solenoid valve (torque converter lock-up) circuit fault (Y3/6y6)
6 Pressure regulating solenoid valve circuit fault (Y3/6y1)
7 Shift pressure regulating solenoid valve circuit fault (Y3/6y2)
8 R/P lock solenoid, function defective (Y66/1)
9 Cable to starter lock-out relay module, function defective (K38/3)
10 Voltage supply to solenoid valves
11 Voltage supply to RPM sensors
12 RPM sensor 2 (Y3/6n2), signal defective
13 RPM sensor 3 (Y3/6n3), signal defective
16 Transmission output sensor (B49) defective
17 Transmission selector lever coding invalid
18 Selector lever signal incorrect (This code can be ignored.) or between ranges
19 Transmission fluid temperature sensor (Y3/6b1) signal defective
20 Starter lock-out contact (Y3/6s1) not functioning
20 Transmission oil temperature sensor defective/Starter lock-out contact not functioning
21 Supply voltage (terminal 87) too low or overvoltage.
22 CAN data: Right rear wheel speed (VSS) from traction system incorrect/implausible
23 CAN data: Left rear wheel speed (VSS) from traction system incorrect/implausible
24 CAN data: Pedal value from ME-SFI controller incorrect/implausible
24 CAN data: Right front wheel speed (VSS) from traction system incorrect/implausible
25 CAN data: Engine RPM from ME-SFI controller system incorrect/implausible
25 CAN data: Left front wheel speed (VSS) from traction system incorrect/implausible
26 CAN data: Right engine torque from ME-SFI controller system incorrect/implausible
26 CAN data: Pedal value from ME-SFI controller incorrect/implausible
27 CAN data: Altitude adjustment factor from the ME-SFI controller incorrect/implausible (This fault code can
be ignored if no relative faults stored in the ME-SFI
27 CAN data: Adjusted engine torque incorrect/implausible
28 CAN data: Left engine torque from ME-SFI controller system incorrect/implausible
28 CAN data: Engine RPM from ME-SFI controller system incorrect/implausible
29 CAN data: Right engine torque from ME-SFI controller system incorrect/implausible
30 CAN data: Communication with traction system faulty
30 CAN data: Altitude adjustment factor from the ME-SFI controller incorrect/implausible (This fault code can
be ignored if no relative faults stored in the ME-SFI
31 CAN data: Communication to the ME-SFI controller is faulty
31 CAN data: Maximum induced engine torque from ME-SFI controller incorrect/implausible
32 CAN data: Communication to/from the ME-SFI controller is faulty
32 CAN data: Left engine torque from ME-SFI controller system incorrect/implausible
33 CAN data: Communication to/from the ME-SFI controller is faulty
33 CAN data: Throttle valve actuator actual value from ME-SFI incorrect/implausible
34 CAN data: Communication to/from the ME-SFI controller is faulty
35 CAN data: Communication to/from the ME-SFI controller is faulty
36 CAN data: Communication to/from the ME-SFI controller is faulty or the engine temperature is implausible.
53
Page 54

DTC Readout Possible cause of Failure
37 CAN data: All communications are faulty
38 CAN data: Communication to/from the Traction system controller is faulty
39 CAN data: Communication to/from the ME-SFI controller is faulty
40 CAN data: Communication to/from the Instrument Cluster is faulty
50 Speed sensor n3 or clutch K1 are faulty
51 Gear implausible or transmission slips.
52 Command valve (6, 14, or 25) sticking under pressure.
52 Unauthorized locking of Torque Converter lock-up clutch. Replace Torque Converter.
53 Torque converter lock-up clutch, not functioning. Replace Torque Converter.
53 Torque converter lock-up clutch, input (RPM) too high. Replace Torque Converter.
54 No feedback signal from transmission overload protection.
55 Gear comparison incorrect or target gear selection not achieved.
56-65 Transmission control unit (N15/3) faulty .
98-155 These codes are intermittent. To establish their meaning, subtract 96 from the code number given
and look in the table above for the definition of the intermittent fault.
Adaptive Damping System (ADS)
Models Model Years
129.061 129.066 129.067 129.076 1991-1995
140.032 140.042 140.051 140.057 140.070 140.076 140.134 1991-1994
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Faults
1 No fault found
2 Adaptive damping system control module
3 Body acceleration sensor
4 Wheel acceleration sensor
5 Steering angle sensor
6 Front axle solenoid valves 1
7 Front axle solenoid valves 2
8 Rear axle solenoid valves 1
9 Rear axle solenoid valves 2
12 Right front axle vehicle speed signal
or
ABS Signal
13 Oil level switch (ADS)
14 Steering angle sensor not activated/initialized
15 Comfort or sport switch (ADS) short circuit
17 Vehicle load sensor
18 Adaptive damping system warning lamp
19 Volts supply too low
20 Steering angle sensor
21 Volts supply too high
22 Comfort or sport switch (ADS)
54
Page 55

Automatic Locking Differential (ASD)
Models Model Years
124.128 1991-1995
126.134 126.135 1991
129.061 1991-1995
140.134 1991-1995
201.028 1991-1993
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible cause of faults
1 No fault found
2 Adaptive damping system control module
3 Stop lamp switch
4 Left front axle vehicle speed sensor signal
5 Right front axle vehicle speed sensor signal
6 Rear speed sensor signal
7 No speed signal from any sensor, missing ground
8 Adaptive damping system valve or stop lamp switch
Anti-lock Brake System (ABS)
Models Model Years
140.032 140.042 140.043 140.134 1992-1993
202 1994-1995
210 1995
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Faults
1 No faults found
2 Left front axle vehicle speed sensor, open circuit
3 Right front axle vehicle speed sensor, open circuit
4 Rear axle speed sensor signal
6 Solenoid valve, Left front axle
7 Solenoid valve, Right front axle
8 Solenoid valve, Rear axle
10 Return/pressure pump motor or return/pressure pump relay
11 Solenoid valves relay
12 Master cylinder switchover valve
13 Stop lamp switch
14 ABS Lateral acceleration sensor
15 ABS control module
16 Vehicle speed sensors incorrect, dirty or damaged toothed rotor
17 Low voltage at solenoid valves relay
25 Left front vehicle speed sensors signal Illogical
26 Right front vehicle speed sensors signal Illogical
27 Rear axle vehicle speed sensors signal Illogical
55
Page 56

Anti-lock Brake System (ABS & ABS w/ASR)
Models Model Years
124.034 124.036 1992-1995
129 1994-95
140 1994-95
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Faults
1 No fault found
2 Left front axle vehicle speed sensor, open circuit
3 Right front axle vehicle speed sensor, open circuit
4 Left rear axle vehicle speed sensor signal or Rear axle speed sensor, open circuit
5 Right rear axle vehicle speed sensor signal
6 Left front axle solenoid valve
7 Right front axle solenoid valve
8 Left rear axle solenoid valve or rear axle solenoid valve
9 Right rear axle solenoid valve
10 Return/pressure pump motor or return/pressure pump relay
11 Solenoid valves relay
12 Master cylinder switchover valve - Models 140.04/05
13 Brake lamp switch (ASD/ASR)
14 Lateral acceleration sensor - Models 140.04/05
15 ABS/ASR control module
16 Vehicle speed sensors incorrect, dirty or damaged toothed rotor
17 Low volts at solenoid valves relay
20 Switchover or solenoid valve
21 Pressure switch charge
22 Pressure switch charge
23 Pressure switch hydraulic system
24 ASR charging pump
25 Left front vehicle speed sensors signal, Illogical
26 Right front vehicle speed sensors signal, Illogical
27 Rear axle vehicle speed sensors signal, Illogical
29 Lateral acceleration sensor signal, Illogical - Models140.04/05
30 CAN data line to electronic accelerator/cruise control/idle speed control module
31 CAN data line to LH-SFI control module left LH-SFI control module Right LH-SFI control module
32 CAN data line to left ignition control module right ignition control module Ignition control module, LH-SFI
33 CAN data line, short or open circuit
56
Page 57

Electronic Traction Systems (ASR, ETS)
Models Model Years
129 140 202 1995
210 1995-96
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Faults
1 No fault found
2 ASR/SPS or ETS/SPS control module
3 Left front axle VSS sensor, open circuit
4 Right front axle VSS sensor, open circuit
5 Left rear axle VSS sensor, open circuit
6 Right rear axle VSS sensor, open circuit
7 Left front axle VSS valves, illogical
8 Right front axle VSS valves illogical
9 Left rear axle VSS valve illogical
10 Right rear axle VSS valve illogical
11 VSS signal illogical
12 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, solenoid valves relay
13 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, Left front axle solenoid valves(hold)
14 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, Left front axle solenoid valve(hold)
15 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, right front axle solenoid valve (release)
16 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, right front axle solenoid valve (release)
17 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, left rear axle solenoid valve(hold)
18 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, left rear axle solenoid valve (release)
19 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, right rear axle solenoid valve(hold)
20 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, right rear axle solenoid valve (release)
21 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, switchover/solenoid valve
22 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, inlet solenoid valve
23 ASR only: ASR system pressure too low
24 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, high-pressure/return pump relay
27 Stop lamp switch
28 Battery voltage too low, circuit 87
29 ETS only Circuit 30, volts supply
30 ASR only CAN date bus to EA/CC/ISC control module, interrupted
31 ASR only CAN communication with LH-SFI control module Left LH-SFI control module right LH-SFI
control module faulty CAN communication with engine control module faulty
32 ASR only CAN communication with DI or left and right DI control module, faulty
33 ASR only CAN communication faulty in general
34 ETS only Brakes overheated
35 Model 129.076,140.04/05/07 Master brake cylinder switchover valve
36 Model 129.076,140.04/05/07 ASR lateral acceleration sensor, open circuit
37 Model 129.076,140.04/05/07 ASR lateral acceleration sensor, illogical
38 ETS only EST/SPS control module not identify the software (not coded)
39 Model 140/210 ETS/SPS or ASR/SPS control module
40 Model 140 SPS P-valve
41 Model 140/210 ASR/SPS or ETS/SPS control module
57
Page 58

Speed Sensitive Power Steering (SPS)
Models Model Years
140.032 140.042 140.051 140.057 140.070 140.076 140.134 1992-5/93
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Speed sensitive power steering control module
3 Left/center rear axle speed sensor signal
4 Right rear axle vehicle speed sensor signal
5 Diffident vehicle speed signals from right and left rear axle sensor
6 No vehicle speed sensor signal
7 Inductive speed sensor, transmission faulty
8 Short circuit between positive connection of speed sensitive power steering valve and ground (-)
9 Short circuit at speed sensitive power steering valve
10 Open circuit at speed sensitive power steering valve
11 Volts supply at speed sensitive power steering control module
Speed Sensitive Power Steering (SPS)
Model Model Years
140 6/93-8/95
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Speed sensitive power steering control module
3 Comparison of axle vehicle speed signal attars/left front axle vehicle speed signal faulty
4 Axle vehicle speed signal status missing
5 Speed-sensitive power steering control module
6 Speed-sensitive power steering P-valve; short circuit
7 Speed-sensitive power steering P-valve; open circuit
8 Short circuit between speed sensitive power steering P-valve (+) and ground (-)
58
Page 59

Electronic Traction Systems (ABS, ASR, ETS, SPS)
Model Model Years
129, 140, 202 9/95-2000
210 6/96-2000
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
C1000 ESP/SPS/Traction control module (N47-5)
C1010 Battery voltage too low, circuit 87
C1011 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit solenoid valve voltage supply, open/short circuit, Voltage supply
C1012 Battery voltage too high, circuit 87
C1020 CAN communication faulty, general.
C1021 CAN communication with EA/CC/ISC control module, interrupted.
C1022 CAN communication with engine control module (right)(ME-SFI, N3/12), interrupted.
C1023 CAN communication with engine control module (left)(ME-SFI, N3/11), interrupted.
C1024 CAN communication with transmission control module (N15/3), interrupted
C1100 Left front axle VSS sensor (L6/1), open circuit, loose contact or signal out of range
C1101 Right front axle VSS sensor (L6/2), open circuit, loose contact or signal out of range
C1102 Left rear axle VSS sensor (ETS/EPS/SPS/ASR L6/3, ABS L6), open circuit, loose contact or signal out of
range
C1103 Right rear axle VSS sensor (L6/4), open circuit, loose contact or signal out of range
C1104 Left front axle VSS sensor (L6/1), signal out of range.
C1105 Right front axle VSS sensor (L6/2), signal out of range.
C1106 Left rear or rear axle VSS sensor (ETS/ASR L6/3, ABS L6), signal out of range.
C1107 Right rear axle VSS sensor (L6/4), signal out of range.
C1120 ESP yaw sensor (N64) signal wire or reference wire, open/short circuit
C1140 Steering angle sensor (N49), open/short circuit or initialization not performed.
C1141 ESP brake pressure sensor (B34)
C1142 ABS lateral acceleration sensor (B24/2), open/short circuit
C1143 ABS lateral acceleration sensor (B24/2), signal out of range.
C1200 Stop lamp switch (S9/1), open/short circuit or Stop lamp switch (S9/1), signal out of range.
C1300 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, left front axle solenoid valve (hold) (A7/3y6), short/open sircuit.
C1301 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, left front axle solenoid valve (release) (A7/3y7), short/open sircuit.
C1302 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, right front axle solenoid valve (hold) (A7/3y8), short/open sircuit.
C1303 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, right front axle solenoid valve (release) (A7/3y9), short/open sircuit.
C1304 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, left rear axle solenoid valve (hold) (A7/3y10), short/open sircuit.
C1305 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, left rear axle solenoid valve (release) (A7/3y11), short/open sircuit.
C1306 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, right rear axle solenoid valve (hold) (A7/3y12), short/open sircuit.
C1307 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, right rear axle solenoid valve (release) (A7/3y13), short/open sircuit.
C1308 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, front axle precharge solenoid valve (A7/3y16), short/open sircuit.
C1309 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, rear axle precharge solenoid valve (A7/3y17), short/open sircuit.
C1310 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, front axle switchover valve (A7/3y18), short/open sircuit.
C1311 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, rear axle switchover valve (A7/3y19) or ASR/ETS Switchover solenoid (A7/3y5),
short/open sircuit.
C1312 Master brake cylinder switchover valve (Y61).
C1313 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, solenoid valve relay (A7/3k1).
C1314 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, solenoid valve relay (A7/3k1), voltage supply.
C1315 ASR/ETS hydraulic unit, inlet solenoid valve (A7/3y15), voltage supply.
C1400 ASR/ESP charging pump (M15), open/short circuit.
59
Page 60

DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
C1401 ASR/ETS/ESP hydraulic unit, high-pressure/return pump (A7/3m1), open/short circuit or does not turn off.
C1500 Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) (L6/1, L6/2, L6/3, L6/4) signal out of range.
C1501 SPS P-valve (Y10)
C1503 Pressure transfer piston unit. - Check condition of rear brake pads and Pressure transfer piston unit.
C1504 System turned off, Steering angle sensor (N49) not initialized or Low voltage to ESP yaw rate sensor (N64)
C1511 ETS/SPS control module (N47-2), not version coded
C1512 Brakes overheated - Brakes were momentarily overloaded, erase DTC.
C1513 ASR/SPS (N47-1) or ME-SFI (N3/10) engine control module, version coding incorrect.
C1514 SPS P-valve (Y10) adjustment data
C1515 Version coding SPS
C1600 Temperature after engine turned off, too high.
60
Page 61

Cabriolet Soft Top (CST)
Model Model Years
124.066 1993-95
Connect wires of Scanner as follows
Scanner Data Link Connector
Yellow Power Soft top test connection (4 pole) at Socket 2. The connection is located at the right front passenger
footwell. To avoid the need for an extension cable, connect the black lead of code scanner to any good ground
and red lead to a battery + source inside vehicle.
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Volts low
3 Normal operating time exceeded
4 Limit switch signals Illogical
5 Soft top compartment cover "locked", limit switch,
6 Soft top compartment cover "closed", limit switch,
7 Soft top compartment cover "open", limit switch
8 Soft top fabric bow "locked", limit switch
9 Soft top fabric bow "down", limit switch
10 Soft top fabric bow "raised", limit switch
11 Left front soft top "locked", limit switch
12 Right front soft top "locked", limit switch
13 Soft top "open" switch (soft top in storage compartment), limit switch ,
14 Soft top "overhead", limit switch
15 Soft top "retracted", limit switch
16 Roll bar "extended", limit switch,
17 Automatic deployment of roll bar has occurred
18 Power soft top switch
19 Vehicle speed signal
20 Circuit in power soft top control module, solenoid valve, roll bar retracted
21 Circuit hydraulic unit, circuit solenoid valve, roll bar retracted
22 Circuit in power soft top control module, solenoid valve, roll bar extended
23 Circuit solenoid valve, roll bar extended
24 Circuit in power soft top control module, Power windows
Roll Bar (RB) for CST
Model Model Year
124.066 1993-95
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No faults found
2 Roll bar control module
3 Roll bar control module volts supply
6 Roll bar deployment solenoid, open circuit, short circuit to Battery + or ground (-).
7 Rear axle switch, short circuit to Battery + or ground (-).
8 Roll bar indicator lamp faulty
61
Page 62

Roadster Soft Top (RST)
Models Model Years
129.061 129.066 129.067 129.076 1990-12/93
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No faults stored
2 Limit switch, left locked, soft top storage compartment cover
3 Limit switch, right locked, soft top storage compartment cover
4 Limit switch, left closed, soft top storage compartment cover
5 Limit switch, right closed, soft top storage compartment cover
6 Limit switch, left locked, soft top fabric bow
7 Limit switch, right locked, soft top fabric bow
8 Limit switch, left closed, soft top fabric bow
9 Limit switch, right closed, soft top fabric bow
10 Limit switch, left front locked, soft top
11 Limit switch, right front locked, soft top
12 Limit switch soft top storage compartment cover open
13 Limit switch soft top fabric bow raised
14 Limit switch soft top down (in storage compartment)
15 Limit switch soft top up (secondary closing speed )
16 Limit switch roll bar retracted
17 Limit switch left side window down Circuit in power soft top control module, solenoid valve, roll bar
retracted
18 Limit switch right side window down Circuit hydraulic unit, circuit solenoid valve, roll bar retracted
19 Axle vehicle speed signal illogical Circuit in power soft top control module, solenoid valve, roll bar
extended
20 Hardtop installed recognition Circuit solenoid valve, roll bar extended
21 Power soft top switch Circuit in power soft top control module, Power windows
22 Roll bar switch
23 Roll bar control module
24 Roll bar crash deployment
25 Limit switch signals illogical
26 Operation time exceeded
27 Insufficient volts
28 No speedometer signal
29 No axle vehicle wheel speed sensor signal
30 Soft top operation blocked
62
Page 63

Roadster Soft Top (RST)
Model Model Years
129 1/94-6/96
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No faults stored
2 Low voltage
3 RST/RB hydraulic unit locked up.
4 Vehicle speed sensor fault
5 RST/RB hydraulic unit
6 Right or left power window activation
7 Right or left front soft top “locked” switch fault, Soft top open/closed switch, Fabric bow locked switch,
8 Power soft top control module defective
9 Roll bar crash deployment has occurred
10 Power soft top switch or Roll bar switch.
11 Power soft top switch indicator lamp or Roll bar switch indicator lamp or Warning buzzer.
Roll Bar (RB) for RST
Models Model Years
129.061 129.066 129.067 129.076 1990-12/93
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No faults found
2 Roll bar control module
3 Volts supply
4 Driver seat belt lock relay open circuit or short circuit to Battery + or ground (-).
5 Passenger seat belt lock relay open circuit or short circuit to Battery + or ground (-).
6 Roll bar deployment solenoid, open circuit or short circuit to Battery + or ground (-).
7 Left and/or right axle switch, roll bar, short circuit to 30 or 31
8 Roll bar warning lamp
9 SRS warning lamp and/or code scanner button held to erase faulty
10 SRS control unit
63
Page 64

Infrared Remote Control for Central Locking (IRCL)
Models Model Years
129.061 129.066 129.067 129.076 1990-1993
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Infrared remote control module
3 Supply pump, central locking system short to ground
4 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Red indicator lamps, short to
ground
5 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Green indicator lamps, short
to ground
6 Supply pump, central locking system, short to circuit 30
7 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Red indicator lamps, short to
circuit 30 or open circuit
8 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Green indicator lamps, in
receiver have short to short to circuit 30 or open circuit
9 Driver door switch group wiring, short to circuit 30 ATA/convenience microswitch wiring short to circuit
30 ATA/convenience microswitch wiring short to circuit 30
10 Ignition/starter switch-position recognition switch, open circuit
11 Ignition/starter switch-position recognition switch, open circuit 31
12 Left front door actuator, open circuit
13 Right door actuator, open circuit
14 Trunk lid lock actuator, open circuit
Infrared Remote Control for Central Locking (IRCL)
Model Model Years
140 1992-96
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Left front door actuator, open circuit
3 Warning buzzer -open circuit
4 Warning buzzer -open circuit to ground
5 Red indicator lamps, short to ground
6 Green indicator lamps, short to ground
7 Short to positive, lock circuit 1
8 Short to positive, lock circuit 2
9 Red indicator lamps, short to positive
10 Green indicator lamps, short to positive
11 Infrared remote control module faulty
12 Immobilization output, short to circuit 30 (Battery +)
64
Page 65

Infrared Remote Control for Central Locking (IRCL)
Model Model Years
129 1993-96
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 IRCL control module
3 Supply pump, central locking system short to ground
4 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Red indicator lamps, short to
ground
5 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Green indicator lamps, short
to ground
6 Supply pump, central locking system, short to B (+)
7 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Red indicator lamps , short to
B (+) or open circuit
8 Infrared remote control receiver, Left front door/Right front door/Trunk lid Green indicator lamps, short
to B (+) or open circuit
9 Driver door switch group wiring, short to B (+) ATA/CF microswitch wiring short to B (+) ATA/CF
microswitch wiring short to B (+)
10 Ignition/starter switch-position recognition switch, open circuit
11 Ignition/starter switch-position recognition switch, open circuit 31
12 Left front door actuator, open circuit
13 Right door actuator, open circuit
14 Trunk lid lock actuator, open circuit
15 Immobilization output, short to B (+)
Pneumatic Systems Equipment (PSE)
Models Model Years
129 140 1992-94
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Central locking system, air demand too high, leakage
3 Retractable trunk lid grip, air demand too high, leakage
4 Backup assist, air demand too high, leakage
5 Orthopedic backrest pressure, air demand too high, leakage
6 Manifold vacuum assist, air demand too high, leakage
7 Short to positive, lock circuit 1
8 Short to positive, lock circuit 2
9 Signal fault, Rear head restraint retraction
10 Signal fault, Central locking interior control switch
11 Signal fault, Front door
12 Signal from lock circuit 1 is present for longer than 2 minutes
13 Signal from lock circuit 2 is present for longer than 2 minutes,
14 Central locking interior control switch signal is present for longer than 2 minutes
15 Rear head restraint retraction signal is present for longer than 2 minutes
16 Not used
65
Page 66

17 Pneumatic control module faulty
Anti-theft Alarm System(ATA)
Models Model Years
129.061 129.066 129.067 129.076 1990-93
140.032 140.042 140.051 140.057 140.070 140.076 140.134 1990-93
129 140 202 1994-96
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Alarm activated, trunk sensor circuit
3 Alarm activated, engine hood circuit
4 Alarm triggered, glove compartment
5 Alarm activated, rear door circuit Console compartment circuit
6 Alarm activated, front door circuit
10 Alarm activated, radio circuit
12 Alarm activated, ignition circuit
14 Alarm activated, brake circuit
19 AT Control module faulty
20 Left front door actuator, No ground connection
21 ATA disarmed, Starter lock-out relay module. short to circuit 30
23 ATA armed, Open to circuit 30
Cellular Telephone (CT)
Models Model Years
129.061 129.066 129.067 129.076 1992-95
140.032 140.042 140.051 140.057 140.070 140.076 140.134 1992-95
If a fault code is set, the code is shown on the in-car telephones display and the phone goes off-line.
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 TR memory defect (ROM)
2 TR memory defect (RAM)
3 NAM defect
4 ESN defect
5 TR memory defect (EE PROM)
6 TR output power defect
7 IDCM defect
8 TR output power control defect
66
Page 67

Convenience Features (CF)
Model Model Year
140 1992-96
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 Control module, Close circuit for left front power window motor
3 Control module, Open circuit for left front power window motor
4 Control module, Close circuit for right front power window motor
5 Control module, Open circuit for right front power window motor
6 Control module, Close circuit for left rear power window motor
7 Control module, Open circuit for left rear front power window motor
8 Control module, Close circuit for right rear power window motor
9 Control module, Open circuit for right rear power window motor
10 Switch for left front power window Closing time exceeded
11 Switch for left front power window Opening time exceeded
12 Switch for right front power window Closing time exceeded
13 Switch for right front power window Opening time exceeded
14 Left rear power window circuit and left rear power window switch front console closing time exceeded
15 Left rear power window circuit and left rear power window switch front console opening time exceeded
16 Right rear power window circuit and right rear power window switch front console closing time exceeded
17 Right rear power window circuit and right rear power window switch front console opening time exceeded
18 Circuit for left front lock switch, right front, trunk lid lock switch closing time exceeded, lock switch circuit 2
19 Circuit for left front lock switch, right front, trunk lid lock switch opening time exceeded, lock switch circuit 1
20 Left front power window switch short to ground or wires reversed
21 Right front power window switch short to ground or wires reversed
22 Left rear window circuit and left rear power window switch front console short to ground or wires reversed
23 Right rear power window circuit and right rear power window switch front console short to ground or wires reversed
24 Left front power window motor , wiring or speed sensor
25 Right front power window motor, wiring or speed sensor
26 Left rear power window motor, wiring or speed sensor
27 Right rear power window motor, wiring or speed sensor
28 Left front power window motor, sensor wiring reversed
29 Right front power window motor, sensor wiring reversed
30 Left rear power window motor, sensor wiring reversed
31 Right rear power window motor, sensor wiring reversed
32 Left front power window motor, Speed sensor signal faulty
33 Right front power window motor, Speed sensor signal faulty
34 Left rear power window motor, Speed sensor signal faulty
35 Right rear power window motor, Speed sensor signal faulty
36 Convenience control module faulty
37 Volts too low(9V), circuit 30E fuse F4-11
38 Sliding/pop-up roof switch circuit short, check wiring harness
39 Volts supply circuit 30 A, control module
40 Volts supply circuit 30 B, control module
67
Page 68

Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - Analog-
Models Model Years
107 124 126 129 201 140 1988-1993
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 SRS Control unit self test failure
3 Driver Airbag squib (Firing charge circuit)
4 Front passenger Airbag squib
5 Driver seat beat buckle switch (ETR,)
6 Front passenger seat belt buckle switch (ETR)
7 Front passenger Airbag resistor
8 Voltage supply interrupted (Circuit 15R)
9 SRS Warning Lamp (with flashing SRS warning lamp Impulse counter scan tool button held too little
time to read out the DTC memory or too long to erase DTC codes. Reread codes.)
10 SRS Control unit activated - Replace (1990 and later switch to next circuit if used 3 times replace)
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) BAE, ZAE - Digital
Models Model Years
129 140 124 1994-95
202 210 From beginning of manufacture -1995
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 SRS Control unit
2 SRS Driver air bag squib
3 Left front ETR squib
4 Right front ETR squib
5 Model 140R12/8Front passenger airbag squib 1
17 Low volts, Voltage supply circuit 15R
19 SRS indicator lamp. failure
20 Front passenger seat occupation signal (currently not used)
24 Driver seat belt buckle switch (Airbag/ETR)
25 Front passenger seat belt buckle switch (ETR)
73 Squib short circuit
68
Page 69

Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) w/Side Airbags - Digital
Models Model Years
129 (R) 140 (S) 202 (C) 210 (E) 1996-99
FAULT CODE TABLE
000
DTC 1
1 1 SRS control module failed self test (N2/2) 2.0
2 4 Driver Airbag ignitor (R12/3) 3.0, 4.0
3 5 Left front seat belt ignitor (ETR) (R12/1) 5.0, 6.0
4 6 Right front seat belt ignitor (ETR) (12/2) 7.0, 8.0
5 7 Front passenger Airbag ignitor (R12/8) 9. 0, 10. 0
8 8 Left side door Airbag ignitor (R12/9) 15.0, 16.0
9 9 Right side door Airbag ignitor (R12/10) 17.0, 18.0
10 4-9, 16, 17,
17 3 Voltage supply (low voltage) Circuit 15R 1.0
19 2 SRS indicator lamp circuit failure (A1e15) 11.0
20 25 Front passenger seat occupied recognition sensor (B41/1) or
10 26 Programming does not comply with vehicle version 31.0, verify vehicle version, repeat
24 (USA) 16 Left front seat belt buckle micro-switch 12.0
25 (USA) 17 Right front seat belt buckle micro-switch 13.0
73 Ignitors are short circuited to each other. 14.0
001
DTC 2
26, 29, 34
18 Left side Airbag harness fault. (A53) 16.0
19 Left side Airbag sensor defective. (A53) Replace sensor
20 Left side Airbag sensor defective. (A53) Replace sensor
21 Right side Airbag harness fault. (A54) 18.0
22 Right side Airbag sensor defective. (A54) Replace sensor
23 Right side Airbag sensor defective. (A54) Replace sensor
27 Front passenger seat occupied recognition with automatic
28 Front passenger seat occupied recognition with automatic
31 Front passenger seat occupied recognition with automatic
32 Left side Airbag communication interference (A53) Electromagnetic interference, check
33 Right side Airbag communication interference (A54) Electromagnetic interference, check
34 Digital crash output, harness fault (ARTHUR - Model 170)
35 Analog crash output, harness fault (Model 170 Kompressor)
Possible cause Test step/Remedy
(See Diag Man. B&A V5.1)
Programming does not comply with vehicle version 31.0, verify vehicle version, repeat
programming.
19.0
(B48)
programming.
20.0
child seat recognition (ACSR), communication. (B48)
Position child seat properly or replace,
child seat recognition (ACSR)
Improperly positioned child seat or faulty.
Connection between passenger seat and child seat faulty.
Metallic objects on passenger seat or child seat.
Short term electromagnetic interference in immediate area
such as electronic transmitters, telephones etc. (B48).
child seat recognition (ACSR) (B48)
Replace B48
Replace B48
harness routing if accessories installed.
harness routing if accessories installed.
69
Page 70

BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS (SRS, IRCL, PSE, ATA. RST, MSC, CF)
Models Model Years
129 140 124 1996-2000
202 210 1997-2000
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
B1000 Control module faulty, fails self test.
B1001 Left/right front ESA control module (N32/1, N32/2) (with memory)
B1001 Switch illumination, circuit 58d, wiring (short circuit)
B1010 Low supply voltage, less than 9/10 Volts
B1011 High supply voltage, greater than 15.5 Volts
B1013 Circuit 15R voltage supply missing at circuit 15.
B1014 Circuit 49 travel direction, has no voltage at circuit 15.
B1015 Circuit 30C, fuse F4-7
B1017 Circuit 31B
B1021 CAN data line, communication with PSE control module (A37) interrupted.
B1022 Driver's seat does not communicate via CAN data line.
B1023 Passenger's seat does not communicate via CAN data line.
B1024 CAN data line LOW or Combination Control Module (N10-1 or N10-3), open circuit or short to B+ or ground.
B1025 CAN data line HIGH or Combination Control Module (N10-1 or N10-3), open circuit or short to B+ or ground.
B1054 CAN LOW (CAN-L) communications fault with front door module.
B1055 CAN HIGH (CAN-H) communications fault with front door module.
B1100 Lock Switch circuit SN1/SN2 from RCL control module (N54) to CCVM (N10-1 or N10-3), open circuit or short
to B+ or ground.
B1100 Control line deactivation, (PSE/CL, CF, ATA), short to B+ or Ground
B1101 Control line for Lock nut 2/Panic alarm from RCL control module (N54) to CCM (N10)
B1101 Control line activation, (PSE/CL, CF, ATA), short to B+ or Ground
B1102 Left Front Door IR receiver or Drive Authorization System (DAS) control line, short to B+ or Ground
B1103 Right Front door IR receiver or Red indicator lamp, short to B+ or Ground
B1104 Green indicator lamp, short to B+ or Ground
B1111 Backrest switch harness or Short to ground.
B1112 Front head restraint adjustment and height adjustment harness or Short to ground.
B1113 Rear fore/aft adjustment and height adjustment harness or Short to ground.
B1114 Steering column up/down switch (S91/2s11) or Steering column in/out switch (S91/2s12) stuck/binding, or
wiring fl (short circuit)
B1115 Rear window defroster switch > 25 s, f l +
B1116 RHR unlock switch (S6/1s3), signal greater than 25 sec.
B1117 Interior switch (CL) (S6/1s2), signal greater than 25 sec.
B1119 Outside rearview mirror vertical/horizontal/left/right adjustment (S21 s6/s7/s8) > 25 seconds.
B1124 Remote trunk release switch (S15), signal > 25 sec., short to ground.
B1132 Alarm triggered via glove box.
B1148 Circuit 50 output, open circuit or short to B+ or ground.
B1156 Left front seatback release microswitch (S91/3) or Left front hibernation microswitch (S91/1s2), circuit short
B1157 ESC Control Module (N26/5), open circuit or short to B+ or ground.
B1200 Hall-sensor for fore/aft motor (M27m1)
B1201 Hall-sensor for front raise/lower motor (M27m3)
B1202 Hall-sensor for rear raise/lower motor (M27m2)
B1203 Left front ESA motor group (with memory), head restraint raise/lower motor (M27m4) (Hall sensor defective) or
open circuit.
B1204 Left front ESA motor group (with memory), backrest fore/aft motor (M27m5) (Hall sensor defective) or open
70
Page 71

circuit.
B1213 Electrically adjustable and heated driver-side outside rearview mirror (with memory) (M21/4) >25 seconds
B1214 Electrically adjustable and heated driver-side outside rearview mirror (with memory) (M21/4) >2 seconds.
B1217 Non-USA vehicles only, continue to next test step.
B1220 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1221 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1276 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1277 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1278 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1279 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1310 Left side airbag sensor (A53/1)
B1311 Right side airbag sensor (A54/1)
B1315 Front passenger seat occupied recognition with automatic child seat recognition (ACSR (B48))
B1321 Left front seat belt buckle switch (AB/ETR) (S68/3)
B1322 Right front seat belt buckle switch (AB/ETR) (S68/4)
B1406 Dome lamp control wire short to B+ from combination control module. (N10-1 or N10-3).
B1407 Entrance/exit lamp wiring short to B+ or combination control module (N10-1) I
B1407 Faulty signal from mirror postion memory (M21/7n1) (up/down) to right outside rearview mirror (M21/7)
B1407 Faulty signal from mirror postion memory (M21/7n1) (right/left) to right outside rearview mirror (M21/7)
B1408 Verticle adjustment motor (M21/5m1) (up/down) or Horizontal adjustment motor (M21/5m2) (in/out).
B1409 Verticle adjustment motor (M21/4m1) (up/down) or Horizontal adjustment motor (M21/4m2) (in/out).
B1410 Combination control module (N10-1) does not switch
B1411 Combination control module (N10-1) does not switch
B1435 Short circuit to ATA tow sensor.
B1436 Central locking - Pneumatic demand too high or CL pneumatic system leak. Door or Fuel Door.
B1437 Retractable head restraint - Pneumatic demand too high.
B1438 Multi-contour seat, air pressure or safety time - Pneumatic demand too high.
B1439 Manifold vacuum assist, Time > maximum - Pneumatic demand too high.
B1440 Remote trunk lid release (RTR), Time > maximum - Pneumatic demand too high.
B1470
B1471
B1476 SRS MIL (Lamp) (A1e15)
B1497 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1507 CAN - Communication fault with Roof Control Module (N70)
B1508 CAN - Communication fault with Signal pick-up and activation module (SAM) (N10/1).
B1510 Left front ESA control module (N32/1)
B1521 Mirror-Horizontal adjustment motor (M21/7m2) (short circuit wiring or motor)
B1521 Mirror-Vertical adjustment motor (M21/7m1) (short circuit wiring or motor)
B1521 Mirror-adjustment motor (M21/7m1, M21/7m2) (short circuit wiring or motor)
B1521 Mirror heater (M21/7r1) (short circuit) or Front passenger-side door control module (N69/2)
B1701 Incorrect authorization code, right cylinder bank, (4 or 6 cylinder) (CAN)
B1702 Incorrect authorization code, left cylinder bank, (8 or 12 cylinder) (CAN)
B1703 Attempt was made to start vehicle locked via RCL or invalid transponder code.
B1704 Coil for transponder (coil will not saturate), faulty coil.
B1705 Activation of locking confirmation relay module (K54), turn signal system, short to B+ or Ground.
B1706 Activation of locking confirmation relay module (K54) or combination relay module or turn signal system, short
to B+ or Ground.
B1707 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1708 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1709 Alarm siren with auxilliary battery (H3/1) not installed, not version coded or defective.
71
Page 72

B1710 Alarm (ATA) triggered via trunk lamp switch (S17/8)
B1711 Alarm (ATA) triggered via engine hood switch (S62)
B1712 Alarm (ATA) triggered via left front door switch (S17/3)
B1713 Alarm (ATA) triggered via right front door switch (S17/4)
B1714 Alarm (ATA) triggered via left rear door switch (S17/5) I
B1715 Alarm (ATA) triggered via right rear door switch (S17/6)
B1716 Reserve Alarm Input.
B1718 Alarm (ATA) triggered via radio (running change during M. Y. 1996)
B1719 Alarm (ATA) triggered via telephone
B1720 Alarm (ATA) triggered via FAX equipment
B1721 Alarm (ATA) triggered via ignition system
B1722 Alarm (ATA) triggered via stop lamp switch (S9/1)
B1723 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1724 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1725 Alarm (ATA) triggered via anti-tow protection.
B1726 Circuit 30 interupted while in armed state
B1727 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1728 Not applicable for U.S. A. vehicles.
B1729 PSE Control Module combined functions, (A37)
B1748
B1755 Serial interface from K2 control module interupted.
B1850 Left front ESA control module (N32/1) does not communicate with front driverside door control module (N69/1)
B1851 Left front ESA control module (N32/1) does not communicate with front driverside door control module (N69/1)
B1852 Left front ESA control module (N32/1) does not communicate with electronic ignition lock control module (N73)
B1853 Left front ESA control module (N32/1) does not communicate with PSE control module (A37)
B1854 Left front ESA control module (N32/1) does not communicate with electronic ignition lock control module (N73)
B1859 Driver airbag squib (R12/3)
B1861 Front passenger AB squib (R12/8)
B1863 Driver ETR squib (R12/1)
B1864 Front passenger ETR squib (R12/2)
B1865 LR ETR squib (R12/6)
B1866 RR ETR squib (R12/7)
B1867 Left front side airbag squib (R12/20)
B1868 Left rear windowbag squib (R12/22)
B1869 RR side airbag squib (R12/12)
B1871 Right front side airbag squib (R12/21)
B1872 Right rear side airbag squib (R12/23)
B1873 RR side airbag squib (R12/12)
B1875 Digital crash output
B1876 Analoge crash output
B1878 Automatic child seat recognition warning lamp (N72e1) (AIRBAG OFF)
72
Page 73

Tempmatic A/C
Models Model Year
201.028 201.029 201.034 201.126 201.128 1988-93
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 In car temperature sensor, short circuit
3 In car temperature sensor, open circuit
4 Outside temperature sensor, short circuit
5 Outside temperature sensor, open circuit
6 Evaporator temperature sensor, short circuit
7 Evaporator temperature sensor, open circuit
12 Coolant temperature gauge sensor, short circuit
13 Coolant temperature gauge sensor, open circuit
14 Feedback potentiometer, short circuit
15 Feedback potentiometer, open circuit
30 Coolant pump, short circuit
33 A/C compressor control module, short circuit
34 Auxiliary fan relay short circuit
50 Switchover valve unit (5 connections) between pins 5 and 4 faulty
51 Switchover valve unit (5 connections) between pins 5 and 6 faulty
52 Switchover valve unit (5 connections) between pins 5 and 2 faulty
54 Switchover valve unit (5 connections) between pins 5 and 3 faulty
55 Switchover valve unit (4 connections) between pins 5 and 1 faulty
56 Switchover valve unit (4 connections) between pins 5 and 2 faulty
57 Switchover valve unit (4 connections) between pins 5 and 1 faulty
58 Switchover valve blend air flaps (warm) short circuit
59 Switchover valve blend air flaps (cold) short circuit
60 Switchover valve blend air flaps (closes) short circuit
61 Blower switch, low speed faulty
62 Blower switch, high speed faulty
73
Page 74

Automatic A/C
Models Model Years
124.026 124.030 124.034 124.036 124.050 124.090 124.051 124.230 124.290 1988-95
126.024 126.025 126.035 126.039 126.045 126.134 126.135 1988-91
FAULT CODE TABLE
DTC Readout Possible Cause of Failure
1 No fault found
2 In car temperature sensor - Short circuit
3 In car temperature sensor - Open circuit
4 Outside temperature sensor - Short circuit
5 Outside temperature sensor - Open circuit
6 Evaporator temperature sensor - Short circuit
7 Evaporator temperature sensor - Open circuit
8 Left heat exchanger temperature sensor - Short circuit
or Heater core temperature sensor - Short circuit
9 Left heat exchanger sensor - Open circuit
or
Heater core sensor - Open circuit
10 Right heat exchanger temperature sensor - Short circuit
11 Right heat exchanger temperature sensor - Open circuit
12 Engine coolant temperature sensor - Short circuit
13 Engine coolant temperature sensor - Open circuit
30 Coolant circulation pump - Short or open circuit
31/32 Duo valve - Short or open circuit
33 A/C compressor cut-out control module - Short or open circuit
34 Auxiliary fan 2nd stage (actuation) - Short circuit
50 Switchover valve unit, faulty at between pins 5 and 8 (7 connections)
51 Switchover valve unit, faulty between pins 8 and 7 (7 connections)
52 Switchover valve unit, faulty between pins 8 and 3 (7 connections)
54 Switchover valve unit, faulty between pins 8 and 4 (7 connections)
55 Switchover valve unit, faulty between pins 8 and 6 (7 connections)
56 Switchover valve fresh air/recirculated air flaps, long stroke - Short circuit
or
Switchover valve unit, faulty between pins 8 and 2 (7 connections)
57 Switchover valve fresh air/recalculated air flaps, long stroke - Short circuit
or
Switchover valve unit, faulty between pins 8 and 1 (7 connections)
74
Page 75

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
TAU 2.1
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. Remove the operating console from the TAU
2. At the upper side of the operating consol there is a display.
3. Ignition ON : Position 1
4. The fan speed selector NOT on position 1
5. The display alternates between the sensor/component number and the value of that sensor/component. Example: "OP E" :
Open circuit or "CL O" : Closed circuit.
COMPONENT UNDER TEST
Number Component
02 Interior Temperature Sensor
04 Exterior Temperature Sensor
06 Evaporator Temperature Sensor
08 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor
10 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor
12 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECT)
14 Left Temperature Selector Wheel Setting (Degree C)
16 Right Temperature Selector Wheel Setting (Degree C)
18 Vehicle Speed Signal(km/h)
20 Soft Top OPEN : "U", Soft Top CLOSED : "O"
22 Power Supply Voltage
83 OFF/ON (Not Used)
84 Blower Motor Voltage "050" (0.5v) - "600" (6.0v)
TAU 2.1
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1 Turn temperature selector wheel into the white area.
2 Place the air speed selector at position 0 and the air direction to "DOWN"
3 IGNITION = ON : Position 1
4 Within the next 10 sec., press the "RECIRCULATE AIR" and "REST" button simultaneously for 3 sec.
5 Press the AUTO button until all error numbers are read and recorded.
FAULT CODES - TAU 2.1
DTC Readout Description Cause
1 No DTC's Stored in System Memory. No faults
2 In-Car Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Short Circuit
3 In-Car Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Open Circuit
4 Outside Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short Circuit
5 Outside Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Open Circuit
6 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short Circuit
7 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Open Circuit
8 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)) Short Circuit
9 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1) Open Circuit
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
75
Page 76

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - TAU 2.1
DTC Readout Description Cause
10 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (Right) Short Circuit
11 Heater Core Temperature Sensor(Right) Open Circuit
12 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Short Circuit
13 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Open Circuit
16 Center Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r2) Short Circuit
17 Center Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r2) Open Circuit
18 Center Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/3) Short Circuit
19 Center Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/3) Open Circuit
20 Left Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r1) Short Circuit
21 Left Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r1) Open Circuit
22 Left Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/1) Short Circuit
23 Left Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/1) Open Circuit
24 Right Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r3) Short Circuit
25 Right Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r3) Open Circuit
26 Right Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/2) Short Circuit
27 Right Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/2) Open Circuit
30 Auxiliary Coolant Pump Short Circuit
31 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Left) Short Circuit
32 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Right) Short Circuit
33 A/C Compressor Signal Short Circuit
34 Auxiliary Fan Signal 2 Stage Short Circuit
35 Auxiliary Fan Signal 1 Stage Short Circuit
50 Switchover Valve Block Signal Short Circuit
70 Auxiliary Coolant Pump Open Circuit
71 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Left) Open Circuit
72 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Right) Open Circuit
73 A/C Compressor Signal Open Circuit
74 Auxiliary Fan Signal 2nd Stage Open Circuit
75 Auxiliary Fan Signal 1st Stage Open Circuit
76
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 77

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
129 Chassis to 8/95
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. IGNITION ON : Position 1
2. Press the REST button and within 1 second press blower speed button 4.
3. The temperature window (upper left) will alternately display the test step number (ex. "02" In-car Temp) or "0P E" for Open
Circuit or "Cl 0" for Closed Circuit.
4. Press "F" button to go to higher test.
5. Press "C" button to go to a lower test.
6. To end this test mode turn IGNITION OFF : Position 0 for longer then 5 seconds.
COMPONENT UNDER TEST
Number Component
02 In-Car Temperature Sensor
04 Outside Temperature Sensor
06 Evaporator Temperature Sensor
08 Heater Core Temperature Sensor
12 Engine Coolant Temperature (ETC) Sensor
14 Temperature Selector Wheel Setting
18 Vehicle Speed Signal(km/h)
20 Soft Top OPEN : "U" ; Soft Top CLOSED : "O"
22 Power Supply Voltage
83 OFF/ON (Not Used)
84 Blower motor voltage "050" (0,5V) - "600" (6,0V)
129 Chassis to 8/95
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1. Turn temperature selector wheel into the white area.
2. IGNITION ON : Position 1
3. Within the next 10 sec., press the "F", "RECIRCULATE AIR" and "REST" buttons simultaneously for 2 to 4 seconds.
4. The display will show the permanent DTC's stored. press the "RECIRCULATE AIR" button after each is displayed until the
display reads "END"
5. Press "RECIRCULATE AIR" button again and the intermittent DTC's will be shown. A SQUARE is shown after each DTC to
indicate that it is intermittent. Press the "RECIRCULATE AIR" button again to see the next DTC. Until "END" is shown.
6. To erase the DTC's : IGNITION ON : Position 1 Press the "RECIRCULATE AIR", "REST" and "UP" buttons simultaneously until
--- is displayed in the window.
FAULT CODES - 129 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause
1 No DTC's Stored in System Memory. No Faults
2 In-Car Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Short Circuit
3 In-Car Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Open Circuit
4 Outside Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short Circuit
5 Outside Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Open Circuit
6 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short Circuit
7 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Open Circuit
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
77
Page 78

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 129 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause
8 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)(Left) Short Circuit
9 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)(Left) Open Circuit
10 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (Right) Short Circuit
11 Heater Core Temperature Sensor(Right) Open Circuit
12 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Short Circuit
13 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Open Circuit
16 Center Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r2) Short Circuit
17 Center Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r2) Open Circuit
18 Center Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/3) Short Circuit
19 Center Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/3) Open Circuit
20 Left Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r1) Short Circuit
21 Left Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r1) Open Circuit
22 Left Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/1) Short Circuit
23 Left Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/1) Open Circuit
24 Right Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r3) Short Circuit
25 Right Air Vent Control Module (N18/2r3) Open Circuit
26 Right Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/2) Short Circuit
27 Right Air Vent Feedback Potentiometer (R23/2) Open Circuit
30 Auxiliary Coolant Pump (M13) Short Circuit
31 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Y19) Short Circuit
32 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Right) Short Circuit
33 A/C Compressor Signal Short Circuit
34 Auxiliary Fan Signal, 2nd Stage Short Circuit
35 Auxiliary Fan Signal, 1st Stage Short Circuit
50 Switchover Valve Block Signal (Y11) Short Circuit
70 Auxiliary Coolant Pump (M13) Open Circuit
71 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Y19) Open Circuit
72 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Right) Open Circuit
73 A/C Compressor Signal Open Circuit
74 Auxiliary Fan Signal, 2nd Stage Open Circuit
75 Auxiliary Fan Signal, 1st Stage Open Circuit
78
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 79

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
129 Chassis from 9/95
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Set temperature selector to 72 degrees F.
3. Press the REST button for more than 6 seconds.
4. The left display will alternately show the number "01" and the in-car temperature.
5. Press the FAN button and the next component number and its value will be displayed.
6. Press the REST button to end the test program.
COMPONENT UNDER TEST
Number Component
01 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4)
02 Outside Temperature Sensor (B14)
03 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2)
05 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
06 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECT) (B11/4)
07 Refrigerant Pressure in Bar
08 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
09 Not Used
10 Blower Control Voltage
20 Control Current for Auxiliary Fan exp. : 7 = 7 mA
21 Engine RPM. example 00..99 (x100) = 9900
22 Vehicle Speed
23 PIN 58D exp. 99.0 = 99% of Battery Voltage
24 Battery Voltage : 12.8 = 12,8 Volt
40 A/C Controller Software Version Coding
41 A/C Controller Hardware Version
42 Variant code 1
43 Variant code 2
50 Not Used
51 Not Used
52 Not Used
54 ON/OFF A/C Compressor emergency off signal from engine control module.
60 Roof "OPE" = OPEN, "CLO" = CLOSED
61 Left Air Outlet, Potentiometer Voltage
62 Vacuum Actuator 46, Feedback Potentiometer Voltage
63 Center Air Outlet, Potentiometer Voltage
64 Vacuum Actuator 47, Feedback Potentiometer Voltage
65 Right Air Outlet, Potentiometer Voltage
66 Vacuum Actuator 47, Feedback Potentiometer Voltage
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
79
Page 80

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
129 Chassis from 9/95
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Temperature selector wheel : "LO"
3. Within 20 seconds press the REST and DEFROST buttons simultaneously for more than 5 seconds.
4. The LED in the RECIRCULATE button flashes and "dI A" appears on the display.
5. Press the AUTO button until all DTC's are displayed and recorded.
6. The current faults are displayed first, then the intermittent faults. "END'" is displayed when all codes have been displayed.
7. To erase codes press AUTO again, "dEL" will be displayed. Press v and ^ simultaneously for more than 5 seconds. The display
will then show "---". Press AUTO to cancel the erase.
8. IGNITION : OFF to end the test program.
FAULT CODES - 129 Chassis from 9/95
DTC Readout Description
026 CAN Bus Communication
226 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4)
227 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B14)
228 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2)
230 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
231 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B11/4)
232 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12)
233 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
241 Refrigerant Level
416 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1)
417 Automatic A/C Monovalve (Y19)
419 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1)
420 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase
421 Auxiliary Fan Control Module (N65/1)
422 Serial Interface Connection (K1) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
423 Switchover Valve Block (15 connection multiplex) (Y11)
459 Serial Interface Connection (K2) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
80
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 81

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
140 Chassis to 8/95
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. Turn temperature selector wheel into the white area.
2. IGNITION = ON : Position 1
3. Press the left and right "AUTO" buttons.
4. Within 20 seconds press the "REST" button for more than 5 sec.
5. LEFT DISPLAY = Component Number
RIGHT DISPLAY = Actual Component Value or "HI" for a short circuit or "LO" for an open circuit
6. Press the left "AUTO" button to monitor the next component.
7. Press the "REST" button to end the test mode.
COMPONENTS UNDER TEST
Number Component
01 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4)
02 Outside Temperature Sensor (B10/5)
03 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2)
04 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/3)
05 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
06 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor (A/C) (B10/8)
07 Refrigerant Pressure in Bar : Ex. 06'4 = 6.4 Bar
08 Blower Control Voltage from 8(min) - 60(max)
09 Software Status, A/C Pushbutton Control Module(N22) Mfg.
10 Left rear heater core temperature sensor (B10/9)
11 Right rear heater core temperature sensor (B10/10)
12 Rear Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/11)
13 Software Status, Rear A/C Pushbutton Control Module(N22) Mfg.
16 Control Module Applicable for Charcoal Filter : "A"=YES "0 "=NO
140 Chassis to 8/95
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1. Turn the left selector wheel into the red area.
2. Turn the right selector wheel into the blue area.
3. IGNITION = ON : Position 1.
4. Press the "AUTO" button.
5. Within 20 seconds, press the "REST" and "O" button for more than 2 seconds.
6. The display will show the permanent DTC's stored. Left window "E0" or "E1", right window "01", "02"...etc. Record each DTC
and press the right "AUTO" button to display the next code. Continue until "END" is displayed.
7. To erase the DTC's : Turn IGNITION OFF, Then turn IGNITION ON : Position 1. Press the left "AUTO" button. A "d" (delete) is
displayed in the left window. By pressing the right "AUTO" button the DTC will be deleted. Alternate left and right "AUTO"
buttons until all DTCs are erased and "E0 00" is displayed.
Go to next page for Fault Codes
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
81
Page 82

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 140 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause Fault Type
001 No DTC's Stored in System Memory.
002 A/C Pushbutton Control Module (N22)
003 Rear A/C Pushbutton Control Module (N22/3)
006 Connection to the Switchover Valve Block (Y11)
007 Data Exchange (CAN B) Short Circuit.
008 Data Exchange (CAN A) Short Circuit.
009 Data Exchange (CAN A and CAN B) Short Circuit.
010 Make the Diagnosis Again.
011 Data Exchange (CAN B) Open Circuit.
012 Data Exchange (CAN A) Open Circuit.
013 Connection with the Rear A/C Pushbutton Control Module
014 Data Exchange (CAN B) : Rear A/C Control Module Open Circuit.
015 Data Exchange (CAN A) : Rear A/C Control Module Open Circuit.
016 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Short Circuit Continuous
017 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Short Circuit Intermittent
018 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
019 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
024 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2) Short Circuit Continuous
025 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2) Short Circuit Intermittent
026 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
027 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
028 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/3) Short Circuit Continuous
029 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/3) Short Circuit Intermittent
030 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/3) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
031 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/3) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
032 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short Circuit Continuous
033 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short Circuit Intermittent
034 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
035 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
036 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short Circuit Continuous
037 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short Circuit Intermittent
038 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
039 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
040 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Short Circuit Continuous
041 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Short Circuit Intermittent
042 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
82
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 83

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 140 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause Fault Type
043 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
044 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short Circuit Continuous
045 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short Circuit Intermittent
046 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
047 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
048 Left Temperature Wheel Short Circuit Continuous
049 Left Temperature Wheel Short Circuit Intermittent
050 Left Temperature Wheel Short or Open Circuit Continuous
051 Left Temperature Wheel Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
052 Right Temperature Wheel Short Circuit Continuous
053 Right Temperature Wheel Short Circuit Intermittent
054 Right Temperature Wheel Short or Open Circuit Continuous
055 Right Temperature Wheel Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
072 Heater Supply Unit Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1) Short Circuit Continuous
073 Heater Supply Unit Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1) Short Circuit Intermittent
074 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
075 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
076 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1) Overload Continuous
077 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1) Overload Intermittent
080 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y1) Short Circuit Continuous
081 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y1) Short Circuit Intermittent
082 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y1) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
083 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y1) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
084 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y2) Short Circuit Continuous
085 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y2) Short Circuit Intermittent
086 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y2) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
087 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31y2) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
088 A/C Compressor Ground Activation Continuous
089 A/C Compressor Ground Activation Intermittent
090 A/C Compressor Ground Activation Short or Open Circuit Continuous
091 A/C Compressor Ground Activation Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
096 Auxiliary Fan, 1ST Stage Activation Short Circuit Continuous
097 Auxiliary Fan, 1ST Stage Activation Short Circuit Intermittent
098 Auxiliary Fan, 1ST Stage Activation Short or Open Circuit Continuous
099 Auxiliary Fan, 1ST Stage Activation Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
100 Auxiliary Fan, 2ND Stage Activation Short Circuit Continuous
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
83
Page 84

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 140 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause Fault Type
101 Auxiliary Fan, 2ND Stage Activation Short Circuit Intermittent
102 Auxiliary Fan, 2ND Stage Activation Short or Open Circuit Continuous
103 Auxiliary Fan, 2ND Stage Activation Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
104 Auxiliary Fan, 3RD Stage Activation Short Circuit Continuous
105 Auxiliary Fan, 3RD Stage Activation Short Circuit Intermittent
106 Auxiliary Fan, 3RD Stage Activation Short or Open Circuit Continuous
107 Auxiliary Fan, 3RD Stage Activation Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
108 Auxiliary Coolant Pump Control Relay Module (K30), Power
Supply
109 Auxiliary Coolant Pump Control Relay Module (K30), Power
Supply
110 Auxiliary Coolant Pump Control Relay Module (K30), Power
Supply
111 Auxiliary Coolant Pump Control Relay Module (K30), Power
Supply
112 Engine RPM Increase Diode Matrix (V2) Short Circuit Continuous
113 Engine RPM Increase Diode Matrix (V2) Short Circuit Intermittent
114 Engine RPM Increase Diode Matrix (V2) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
115 Engine RPM Increase Diode Matrix (V2) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
116 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (OPEN) Short Circuit Continuous
117 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (OPEN) Short Circuit Intermittent
118 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (OPEN) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
119 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (OPEN) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
120 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (CLOSED) Short Circuit Continuous
121 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (CLOSED) Short Circuit Intermittent
122 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (CLOSED) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
123 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : (CLOSED) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
128 Left Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/9) Short Circuit Continuous
129 Left Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/9) Short Circuit Intermittent
130 Left Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/9) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
131 Left Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/9) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
132 Right Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/10) Short Circuit Continuous
133 Right Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/10) Short Circuit Intermittent
134 Right Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/10) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
135 Right Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/10) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
136 Left Temperature Selector wheel Short Circuit Continuous
137 Left Temperature Selector wheel Short Circuit Intermittent
138 Left Temperature Selector wheel Short or Open Circuit Continuous
Short Circuit Continuous
Short Circuit Intermittent
Short or Open Circuit Continuous
Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
84
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 85

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 140 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause Fault Type
139 Left Temperature Selector wheel Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
140 Right Temperature Selector wheel Short Circuit Continuous
141 Right Temperature Selector wheel Short Circuit Intermittent
142 Right Temperature Selector wheel Short or Open Circuit Continuous
143 Right Temperature Selector wheel Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
144 Rear Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/11) Short Circuit Continuous
145 Rear Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/11) Short Circuit Intermittent
146 Rear Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/11) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
147 Rear Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/11) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
148 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31/1m1) Short Circuit Continuous
149 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31/1m1) Short Circuit Intermittent
150 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31/1m1) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
151 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31/1m1) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
152 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31/1m1) Overload Continuous
153 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31/1m1) Overload Intermittent
156 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y1) Short Circuit Continuous
157 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y1) Short Circuit Intermittent
158 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y1) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
159 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y1) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
160 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y2) Short Circuit Continuous
161 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y2) Short Circuit Intermittent
162 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y2) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
163 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (A31/1y2) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
164 Rear Refrigerant Shut-Off Valve (Y67) Short Circuit Continuous
165 Rear Refrigerant Shut-Off Valve (Y67) Short Circuit Intermittent
166 Rear Refrigerant Shut-Off Valve (Y67) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
167 Rear Refrigerant Shut-Off Valve (Y67) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
168 Rear Tunnel Flap Vacuum Valve (Y67/1) Short Circuit Continuous
169 Rear Tunnel Flap Vacuum Valve (Y67/1) Short Circuit Intermittent
170 Rear Tunnel Flap Vacuum Valve (Y67/1) Short or Open Circuit Continuous
171 Rear Tunnel Flap Vacuum Valve (Y67/1) Short or Open Circuit Intermittent
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
85
Page 86

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
140 Chassis from 9/95
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Press the AUTO button
3. Set both temperature selectors to 72 degrees F.
4. Press the REST button for more than 5 seconds.
5. The left display will alternately show the number "1" and the in-car temperature.
6. Press the AUTO button and the next component number and its value will be displayed.
7. Press the REST button to end the test program.
COMPONENT UNDER TEST
Number Component
01 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4)
02 Outside Temperature Sensor (B10/5) 1996, (B14) as of 1997
03 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2)
04 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/3)
05 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
06 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor (A/C) (B11/4)
07 Refrigerant Pressure in Bar
08 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
10 Blower Control Voltage
11 Emissions (Refrigerant Leak) Sensor (B31)
12 Sun (Excessive Heat) Sensor (B32)
20 Control Current for Auxiliary Fan example : 7 = 7 mA
21 Engine RPM. example 00..99 (x100) = 9900
22 Vehicle Speed
23 PIN 58D example. 99.0 = 99% of Battery Voltage
24 Battery Voltage : 12.8 = 12,8 Volt
30 Left Rear Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/9)
31 Right Rear Heater Core Temperature sensor (B10/10)
32 Rear Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/11)
33 Rear Blower Control Voltage
34 Left Rear Temperature Sensor version
35 Right Rear Temperature Sensor
38 Rear A/C Controller Software Version Coding
39 Rear A/C Controller Hardware Version
40 Front A/C Controller Software Version Coding
41 Front A/C Controller Hardware Version
42 Variant code 1
43 Variant code 2
86
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 87

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
140 Chassis from 9/95
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Left Temperature selector wheel : HI
Right Temperature selector wheel : LO
3. Within 20 seconds press the REST and EC buttons simultaneously for more than 5 seconds.
4. The LED in the RECIRCULATE button flashes and "OFF" appears on the display.
5. Press the right AUTO button until all DTC's are displayed and recorded.
6. To erase all codes must be read out. Press both AUTO buttons simultaneously for more than 2 seconds. "d" will be displayed on
the left and "FF" is displayed on the right. The erase can be canceled by pressing the AUTO button.
7. Reset temperature selector to normal setting.
8. IGNITION : OFF to end the test program.
FAULT CODES - 140 Chassis from 9/95
DTC Readout Description
026 CAN Bus Communication
226 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4)
227 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) to 1996, (B14) as of 1997
228 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/2)
229 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/3)
230 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
231 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B11/4)
or
DFI or IFI models Right Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B11/10) to 1996
232 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12)
233 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
234 Sun Sensor (B32)
235 Emissions (Refrigerant Leak) Sensor (B31)
241 Refrigerant Level
416 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1)
417 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21y1)
418 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21y2)
419 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1)
420 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase
421 Pulse Module (N65)
422 Serial Interface Connection (K1) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
423 Switchover Valve Block (Y11)
424 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : OPEN
425 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : CLOSE
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
87
Page 88

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 140 Chassis from 9/95
DTC Readout Description
432 Maximum Heat
459 Serial Interface Connection (K2) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
460 LED - Center Air Outlet "Warm"
461 LED - Center Air Outlet "Cold"
462 Wide Open Throttle (WOT) Position Signal - Diesel Engine Only
88
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 89

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
202 Chassis to 8/95
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. IGNITION : Position 2 (ON)
2. Set temperature selection to 72 degrees F (Press v and ^ simultaneously).
3. Press the AUTO button.
4. Press the REST button for more than 5 seconds.
5. The display will alternately show the number "01" and the in-car temperature or "LO" if there is an open circuit or "HI" if there is
a short circuit.
6. Press the "Top Air Outlet" button to increase the component tested and the "Bottom Air Outlet" button to decrease the
component number tested.
7. Press the REST button to end the test program.
COMPONENT UNDER TEST
Number Component
01 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4)
02 Outside Temperature Sensor (B10/5)
03 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)
05 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
06 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor (A/C) (B10/8)
07 Refrigerant Pressure in Bar
08 Blower Control Voltage
09 Software Status of A/C Pushbutton Control Module
15 Selected In-Car Temperature
20 Version Code
21 Engine Speed in RPM
22 A/C Compressor Speed in RPM
23 Vehicle Speed in km/h
50 Not Used
51 Number of Current Poly-V Belt Slip Recognitions
52 Number of Stored Poly-V Belt Slip Recognitions
202 Chassis to 8/95
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1 IGNITION : Position 2 (ON)
2 Press the V button until "LO" appears on the display.
3 Within 20 seconds press the REST and DEFROST buttons simultaneously for more then 2 seconds.
4 The LED in the RECIRCULATE button flashes and "dI R" appears on the display
5 Press the AUTO button until all DTC's are displayed and recorded. Continuous faults are displayed first. if no faults are stored,
"En d" is displayed. Press AUTO again to retrieve intermittent faults. If no intermittent faults are stored, "En d" is displayed.
6 Press the AUTO button until "dE L" is displayed. To erase codes press both V and ^ simultaneously for at least 5 seconds. The
display will show "---"
7 IGNITION : OFF to end the test program.
Go to next page for Fault Codes.
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
89
Page 90

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 202 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause Fault Type
01 No ERROR Stored No Faults
02 A/C Pushbutton Control Module (N22). Power failure or damaged
computer
03 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4) Short circuit Continuous
04 In Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4) Short circuit Intermittent
05 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4) Short or Open circuit Continuous
06 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
07 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short circuit Continuous
08 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short circuit Intermittent
09 Outside air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short or Open circuit Continuous
10 Outside air Temperature Sensor (B10/5) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
11 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1) Short circuit Continuous
12 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1) Short circuit Intermittent
13 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1) Short or Open circuit Continuous
14 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
19 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short circuit Continuous
20 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short circuit Intermittent
21 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short or Open circuit Continuous
22 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
23 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ETC) (B10/8) Short circuit Continuous
24 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ETC) (B10/8) Short circuit Intermittent
25 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ETC) (B10/8) Short or Open circuit Continuous
26 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ETC) (B10/8) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
27 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short circuit Continuous
28 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short circuit Intermittent
29 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short or Open circuit Continuous
30 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
31 A/C Compressor RPM Sensor (A9l1) Bad Sensor
32 Poly-V Belt Slip Recognition Slipping Belt
47 Auxiliary Coolant Pump (M13) Unknown
48 Auxiliary Coolant Pump (M13) Short circuit Intermittent
49 Auxiliary Coolant Pump (M13) Short or Open circuit Continuous
50 Auxiliary Coolant Pump (M13) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
51 Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21) Short circuit Continuous
52 Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21) Short circuit Intermittent
53 Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21) Short or Open circuit Continuous
54 Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
90
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 91

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 202 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause Fault Type
59 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1) Short circuit Continuous
60 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1) Short circuit Intermittent
61 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1) Short or Open circuit Continuous
62 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
63 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 1 Short circuit Continuous
64 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 1 Short circuit Intermittent
65 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 1 Short or Open circuit Continuous
66 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 1 Short or Open circuit Intermittent
67 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 2 Short circuit Continuous
68 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 2 Short circuit Intermittent
69 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 2 Short or Open circuit Continuous
70 Activation of Auxiliary Fan Stage 2 Short or Open circuit Intermittent
71 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase Short or Open circuit Continuous
72 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase Short or Open circuit Intermittent
73 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase Short circuit Continuous
74 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase Short circuit Intermittent
75 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Diverter Flap Continuous
76 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Diverter Flap Intermittent
77 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Diverter Flap Short or Open circuit Continuous
78 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Diverter Flap Short or Open circuit Intermittent
79 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Tempering Flap Continuous
80 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Tempering Flap Intermittent
81 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Tempering Flap Short or Open circuit Continuous
82 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Tempering Flap Short or Open circuit Intermittent
83 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap
Long Stroke (80%)
84 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap
Long Stroke (80%)
85 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap
Long Stroke (80%)
86 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap Short or Open circuit Intermittent
87 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap
Short Stroke (20%)
88 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap
Short Stroke (20%)
89 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap
Short Stroke (20%)
90 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Fresh/Recirculating Air Flap
Short Stroke (20%)
Short or Open circuit Continuous
Short or Open circuit Continuous
Short or Open circuit Intermittent
Continuous
Intermittent
Continuous
Intermittent
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
91
Page 92

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
FAULT CODES - 202 Chassis to 8/95
DTC Readout Description Cause Fault Type
91 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Long Stroke
(80%)
92 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Long Stroke
(80%)
93 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Long Stroke
(80%)
94 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Long Stroke
(80%)
95 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
96 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
97 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
98 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Defroster Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
99 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Long Stroke (80%) Continuous
100 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Long Stroke (80%) Intermittent
101 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Long Stroke (80%) Short or Open circuit Continuous
102 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Long Stroke (80%) Short or Open circuit Intermittent
103 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
104 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
105 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
106 Switchover Valve Block (Y11/3), Footwell Flap Short Stroke
(20%)
Short or Open circuit Continuous
Short or Open circuit Intermittent
Short or Open circuit Continuous
Short or Open circuit Intermittent
Short or Open circuit Continuous
Short or Open circuit Intermittent
Continuous
Intermittent
Continuous
Intermittent
Continuous
Intermittent
92
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 93

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
202 Chassis from 9/95
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Set temperature selector to 72 degrees F.
3. Press the REST button for more than 6 seconds.
4. The left display will alternately show the number "01" and the in-car temperature.
5. Press the FAN button and the next component number and its value will be displayed.
6. Press the REST button to end the test program.
COMPONENT UNDER TEST
Number Component
01 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4)
02 Outside Temperature Sensor (B14)
03 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)
05 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
06 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECT) (B11/4)
07 Refrigerant Pressure in Bar
08 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
09 Not Used
10 Blower Control Voltage
20 Control Current for Auxiliary Fan exp. : 7 = 7 mA
21 Engine RPM. example 00..99 (x100) = 9900
22 Vehicle Speed
23 PIN 58D exp. 99.0 = 99% of Battery Voltage
24 Battery Voltage : 12.8 = 12,8 Volt
40 A/C Controller Software Version Coding
41 A/C Controller Hardware Version
42 Variant code 1
43 Variant code 2
50 Not Used
51 Not Used
52 Not Used
54 ON/OFF A/C Compressor emergency off signal from engine control module.
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
93
Page 94

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
202 Chassis from 9/95
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Temperature selector wheel : "LO"
3. Within 20 seconds press the REST and DEFROST buttons simultaneously for more than 5 seconds.
4. The LED in the RECIRCULATE button flashes and "dI A" appears on the display.
5. Press the AUTO button until all DTC's are displayed and recorded.
6. The current faults are displayed first, then the intermittent faults. "END'" is displayed when all codes have been displayed.
7. To erase codes press v and ^ simultaneously for more than 5 seconds. The display will then show "---". Press AUTO to cancel
the erase.
8. IGNITION : OFF to end the test program.
FAULT CODES - 202 Chassis from 9/95
DTC Readout Description
026 CAN Bus Communication
226 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4)
227 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B14)
228 Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)
230 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
231 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B11/4)
232 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12)
233 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
241 Refrigerant Level
416 Coolant Circulation Pump (A31m1)
417 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21y1)
418 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21y2)
419 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1)
420 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase
421 Pulse Module (N65)
422 Serial Interface Connection (K1) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
451 Diverter Flap (Y11/3)
452 Blend Air Flap (Y11/3)
453 Fresh/Recirculated Air Flap (Y11/3) Long Stroke
454 Fresh/Recirculated Air Flap (Y11/3) Short Stroke
455 Defroster Outlet Flap (Y11/3) Long Stroke
456 Defroster Outlet Flap (Y11/3) Short Stroke
457 Footwell Flap (Y11/3) Long Stroke
458 Footwell Flap (Y11/3) Short Stroke
459 Serial Interface Connection (K2) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
462 Wide Open Throttle (WOT) Position Signal - Diesel Engine Only
94
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 95

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
210 Chassis from 9/95
READING ACTUAL VALUES
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Press the AUTO button
3. Set both temperature selectors to 72 degrees F.
4. Press the REST button for more than 5 seconds.
5. The left display will alternately show the number "1" and the in-car temperature.
6. Press the AUTO button and the next component number and its value will be displayed.
7. Press the REST button to end the test program.
COMPONENT UNDER TEST
Number Component
01 In-Car Temperature Sensor with Aspirator Blower (B10/4)
02 Outside Temperature Sensor (B14)
03 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)
04 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)
05 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
06 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor (A/C) (B1/4)
07 Refrigerant Pressure in Bar
08 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
10 Blower Control Voltage
11 Emissions (Refrigerant Leak) Sensor (B31)
12 Sun (Excessive Heat) Sensor (B32)
20 Control Current for Auxiliary Fan exp. : 7 = 7 mA
21 Engine RPM. example 00..99 (x100) = 9900
22 Vehicle Speed
23 PIN 58D exp. 99.0 = 99% of Battery Voltage
24 Battery Voltage : 12.8 = 12,8 Volt
40 Software Version Encoded
41 Hardware Version
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
95
Page 96

A/C SELF DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEMS - 1990-97
210 Chassis from 9/95
FAULT DIAGNOSIS
1. IGNITION : Position 1
2. Left Temperature selector wheel : HI
Right Temperature selector wheel : LO
3. Within 20 seconds press the REST and EC buttons simultaneously for more than 5 seconds.
4. The LED in the RECIRCULATE button flashes and "dI R" appears on the display
5. Press the right AUTO button until all DTC's are displayed and recorded.
6. To erase, all codes must be read out. Press both AUTO buttons simultaneously for more than 2 seconds. "d" will be displayed
on the left and "FF" is displayed on the right. The erase can be canceled by pressing the AUTO.
7. Reset temperature selector to normal setting.
8. IGNITION : OFF to end the test program.
FAULT CODES - 210 Chassis from 9/95
DTC Readout Description
026 CAN - Communication
226 In-Car Air Temperature Sensor (B10/4)
227 Outside Air Temperature Sensor (B14)
228 Left Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)
229 Right Heater Core Temperature Sensor (B10/1)
230 Evaporator Temperature Sensor (B10/6)
231 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (B10/8)
232 Refrigerant Pressure Sensor (B12)
233 Refrigerant Temperature Sensor (B12/1)
234 Sun Sensor (B32)
235 Emissions (Refrigerant Leak) Sensor (B31)
241 Refrigerant Level
416 Coolant Circulation Pump (M13)
417 Left Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21y1)
418 Right Duovalve (Water Valve) (Y21y2)
419 A/C Compressor Electromagnetic Clutch (A9k1)
420 Closed (Idle) Throttle Speed Increase
421 Pulse Module
422 Serial Interface Connection (K1) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
423 Switchover Valve Block (Y11)
424 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : OPEN
425 Activated Charcoal Filter Actuator (A32m2) : CLOSE
432 Maximum Heat
459 Serial Interface Connection (K2) to Instrument Cluster (IC)
462 Wide Open Throttle (WOT) Position Signal - Diesel Engine Only
96
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 97

MERCEDES-BENZ ACRONYMS
ACRONYM DESCRIPTION
4MATIC 4 Wheel Drive Transmission Control
A/C (Automatic)* Air Conditioning (Automatic)
A/C (Tempmatic)* Air Conditioning (Tempmatic)
AAC Automatic Air Conditioning
AAM All Activity Module
AB Supplemental Restraint System (Airbag)
ABS Anti-lock Brake System
ACSR Automatic Child Seat Recognition
ADM Automatic Dimming Inside Rearview Mirror
ADS Automatic Damping System (Suspension)
AIR Secondary Air Injection
AKR Anti-Knock Regulation
AP Accelerator Pedal
APS Auto Pilot System
AS Antenna System
ASD Automatic Locking Differential
ASR Acceleration Slip Regulation
AT Automatic Transmission
ATA* Anti-theft Alarm System
BA Backup Assist
BARO Barometric Pressure
BCAPC Barometric Pressure-charge Air Pressure Compensation
BDC Bottom Dead Center
BM* Base Module (Master Ecu Controller)
BPC Barometric Pressure Compensation
CA Closing Assist
CAN Controller Area Network
CC* Cruise Control (Tempomat)
CCM Combination Control Module
CDC Cd Changer
CF Convenience Feature
CFI Continuous Fuel Injection
CKA Crank Angle
CKP Crankshaft Position
CL Central Locking
CLUS Instrument Cluster
CMP Camshaft Position
CNS Communication and Navigation System
CST* Cabriolet Soft Top
CTEL Cellular Telephone
CTP Closed Throttle Position (Idle)
CTU Central Triggering Unit
DAS Driver Authorization System
DFI* Electronic Distributor-type Fuel Injection
DI* Distributor Ignition System
DM (USA) Diagnostic Module (Emissions)
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code
EA* Electronic Accelerator
EAG Electronic Automatic Transmission Control
EATC* Electronic Automatic Transmission Control
EBR Engine Brake Regulation
ECL Engine Coolant Level
ECT Engine Coolant Temperature
EDC Electronic Diesel Control
EDR Electronic Diesel Regulation
EDS Electronic Diesel System
EDW* Anti-theft Alarm System
EFP* Electronic Accelerator
EGR Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGS Electronic Transmission Control
EI Electronic Ignition (distributorless)
EIFI Electronic In-line Fuel Injection
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
97
Page 98

MERCEDES-BENZ ACRONYMS
EL Exterior Lighting
EMSC Electric Mirror, Steering Column Adjustment, Heated Mirrors
EPC Electronic Power Control
ERE* Electronic In-line Fuel System
ESA Electric Seat Adjustment
ESC Electric Steering Column Adjustment
ESCM Engine System Control Module
ESP Electronic Stability Program
ETC Electronic Transmission Control
ETR Emergency Tensioning Retractor
ETS Electronic Traction System
EVAP Evaporative Emission Control System
EVE Electronic Distributor-type Fuel Injection
EZL Distributor Ignition System
FAN Fanfare Horns
FFS Frame Floor System
FOM Folding Outside Mirrors
FP Fuel Pump
GIM Governor Impulse Method
GM Base Module (Master Ecu Controller)
HAU Automatic Heater
HCS Headlamp Cleaning System
HEAT Automatic Heater
HFM Hot Film Engine Management
HFS Hands Free System
HHT Hand Held Tester
HM Heated Mirrors
HORN Horn Signal System
HS Heated Seats
IAT Intake Air Temperature
IC Instrument Cluster
IDC In Dash Controller
IFI* Electronic In-line Fuel System(diesel)
IFZ Infrared Remote Central Locking
IL Interior Lighting
IR Infrared
IRCL* Infrared Remote Central Locking
IRM Inside Rearview Mirror
ISC* Idle Speed Control
KE Continuous Injection System (Cis)
KFB Convenience Feature
KI Instrument Cluster
KLA Air Conditioning
KS Knock Sensor
KSS Knock Sensor System
LH LH Sequential Fuel Management Bank 1 (1-6 or 1-8 Cylinders)
LH2 LH Sequential Fuel Management Bank 2 (7-12 Cylinders)
LHS Left Hand Steering
LLR Cruise Control
LOC Low Compression
LS Loudspeaker System
MAF Mass Air Flow
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure
ME Motor Electronics
MIL Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine)
MSC Mirror, Steering Column Adjustment, Heated Mirrors
MT Manual Transmission
MVA Manifold Vacuum Assist
MWH Main Wiring Harness
NS Network System (CAN)
O2S Oxygen (O2) Sensor
OBD On-board Diagnostics
OC Oxidation Catalytic Convertor
98
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
Page 99

MERCEDES-BENZ ACRONYMS
OCP Over-head Control Panel
ORM Outside Rearview Mirror
OSB Orthopedic Seat Backrest
PL Power Lock
PML Speed-sensitive Power Steering
PMP Partial Intake Manifold Preheater
PNP Park/neutral Position
PS Power Steering
PSE Pneumatic System Equipment
PTS Parktronic System
PW Power Windows
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
RB* Roll Bar Control
RCL Remote Central Locking
RD Radio
REST Residual Engine Heat Utilization
RHR Retractable Rear Head Restraints
RHS Rear Heated Seats
RPM Revolutions Per Minute (Engine Speed)
RST* Roadster Soft Top
RTG Retractable Trunk Lid Grip
RTR Remote Trunk Release
RV Roadster Soft Top
RWD Rear Window Defroster
SBE Seat Belt Extender
SLO Starter Lock-out
SMS Service Microfiche System
SOR Seat Occupied recognition
SPS Speed-sensitive Power Steering
SR Sliding/Pop-up Roof
SRS Supplemental Restraint System (Airbag)
STH Stationary Heater
TB Throttle Body
TC Turbo Charger
TCM Transmission Control Module
TD Speed Signal (Time Division) (EZL)
TDC Top Dead Center
TIC Transistorized Ignition Control
TN Speed Signal (EZL/AKR)
TPC Tire Pressure Control
TRAP Trap Oxidizer
TS Towing Sensor
TVV Tank Ventilation Valve
TWC Three Way Catalytic Convertor
ÜRB Roll Bar Control
VAF Volume Air Flow
VSS Vehicle Speed Signal
WOT Wide Open Throttle (Full Load)
WS Wiper System
* USA Acronym only.
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. 941-927-1414 / Technical Support 800-804-1002 or tech@baumtools.com
99
Page 100

MERCEDES BENZ - USA MODEL IDENTIFIER
MODEL YEARS CHASSIS ENGINE TRANSMISSION STEERING
190C 1961-65 110 121.924 GA190C LO 1
190D 2.2 1984-85 201.122 601.921 717.4/722.4 LO75Z/68
190D 2.5 1986-89 201.126 602.911 717.4/722.4 LS68
190D 2.5 TURBO 1987- 201.128 602.961 722.4 LS68
190DC 1961-65 110 621.912 GA190DC LO 1
190E 2.3 1982-86 201.024 102.961 K 717.4/722.4 LS68
190E 2.3 1982-86 201.024 102.985 KE 717.4/722.4 LS68
190E 2.3 1987-93 201.028 102.985 KE 717.413/722.408 765.903
190E 2.3-16v 1984-87 201.034 102.983 KE 717.4/722.4 765.9
190E 2.5-16v 1988-93 201E25 102.983 KE 717.4/722.4 765.9
190E 2.6 1986-93 201.029 103.942 KE 717.432/722.409 765.903
200 1965-68 110 121.940 GA190C LO 1
200CE 1990-93 124.021 102 KE 717.4/722.400 765.905
200D 1965-68 110 621.918 GA190DC LO 1
200E 1993 124.021 102.963 KE 717.4/722.400 765.905
200TE 1988-92 124.021 102. KE 717.4/722.400 765.905
220 1967-72 115.010 115.920 722.1 L1Z/LS75/765.706
220B 1959-65 111 180.940 GA220B LO 1
220D 1967-72 115.110 615.912 722.2 L1Z/LS75/765.706
220SB 1959-65 111 180.941 GA220SB LO 1
220SE Cabriolet 1951-65 111.023 127.984 GA220SEB LO 1
220SE Coupe 1959-65 111.021 127.984 GA220SEB LO 1
220SEB 1959-65 111 127.982 GA220SEB LO 1
220SEB/C 1951-65 111 127.984 GA220SEB LO 1
230 123.023 115.954 722.1 765.706
230 1965-66 110 180.945 GA230 LO 1
230 1967-72 114.015 180.954 722.2 L1Z/LS75/765.706
230 1973-78 115.017 115.951 716/722.1 L1Z/765.706
230S 1965-68 111 180.945 GA220B,SB LO 1
230SL 1963-68 113.042 127.981 GA230SL LO 1
240D 1973-75 115.117 616.916 716/722.1 L1Z
240D 1976-85 123.123 616.912 716.0,.2/722.1 L1Z/765.706
250 1967-69 114.010 114.920 722.2 L1Z/LS75/765.706
250 1970-75 114.011 130.923 722.2 L1Z/LS75/765.706
250C 1969-75 114.023 130.923 722.2 L1Z/ LS75/ 765.706
250D 1986-93 124.125 602.912 722.414 765.904
250S 1963-68 108 108.920 GA230SL LO 1
250SE 1965-68 108 129.980 GA230SL LO 1
250SE Cabriolet 1965-68 111.023 129.980 GA230SL LO 1
250SE Coupe 1965-68 111.021 129.980 GA230SL LO 1
100
Baum Tools Unlimited Inc. Toll Free 1-800-848-6657
 Loading...
Loading...